A Histochemical Study of Epithelial Mucin
|
|
|
- Gervase Harris
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Histochemical Study of Epithelial Mucin in the Chick Chorioallantois JAMES L. CONKLIN Department of Anatomy, The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigun ABSTRACT Histochemical methods demonstrate the accumulation of two types of mucous inclusion in the allantoic epithelial cells of the chick embryo. One type of inclusion contains a sialomucin that is PAS-reactive, unstained by Alcian blue and other anionophilic dyes and is susceptible to digestion by Vibrio choleme neuraminidase. The second inclusion contains an apparent sulfomucin which is Alcianophilic at ph 1.0, unstained by anionophilic dyes after a methylation-demethylation sequence and resistant to testicular hyaluronidase. This sulfomucin exhibits PAS reactivity after desulfation procedures. Both types of mucus occur in individual cells and are normal components of the chorioallantois. Accumulation of the inclusions is enhanced by lowering the ph of the allantoic fluid or as a result of organ transplantation. Microscopic examination of chick chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) revealed the presence of abundant mucus-like material within and on the surface of the allantoic epithelial cells. It was also observed that transplantation of certain organs to the CAM apparently enhanced the accumulation of this mucus. An interest in the morphology and function of the intact and transplant-recipient CAM prompted a more extensive histochemical investigation of the allantoic mucus. The objective was to obtain additional information about the normal CAM as well as to be able to interpret the results of subsequent studies of organ transplantation. MATERIALS AND METHODS The material employed in this study consisted of samples of CAM from white leghorn chick embryos ranging in age from 7-18 days (Hamburger and Hamilton, '51), although day CAM was most extensively used. Samples of CAM were fixed in either 10% neutral-buffered formalin (ph 7.0), Bouin's fluid or 10% formalin containing 0.5 % cetylpyridinium chloride. Following fixation, the samples were washed, dehydrated in graded ethanol and embedded in paraffin. Sectioned samples were stained in the following: (1 ) periodic acid Schiff (PAS) and colloidal iron-pas (Mowry, '58); (2) alde- AM. J. ANAT., 121: hyde fuchsin (Gomori, '50) (prepared with basic fuchsin, ( ), with and without oxidation in Lugol's solution; (3) aldehyde fuchsin and Masson trichrome (Masson, '29) (acid fuchsin, C.I. 4285, Ponceau R, ( , light green SF, C.I ); (4) 0.01% aqueous azure A, cert. no. NAz 17, adjusted to ph 2.0 and 4.2 with hydrochloric acid; (5) 0.1% Alcian blue 8 GX (( ) in 3% acetic acid (ph 2.5) or 0.5% Alcian blue in 0.1 N hydrochloric acid (ph 1.0). Tissues stained with azure A were either rinsed in water and examined both before and after mounting in glycerogel or dehydrated in tertiary butyl alcohol and mounted in HSR. Routinely, all other stained tissues were dehydrated in graded ethanol, cleared in xylene and mounted in HSR. The only exception to the preceding routine was to blot rather than dehydrate some sections after staining in Alcian blue (Lev and Spicer, '64). Prior to the use of certain methods, tissue sections were treated by incubation in acidified methanol (0.3 cm3 concentrated HC1 in 40 cm3 methanol) for four hours at 37 C (mild methylation) or 60 C (strong methylation). After methylation, some sections were subjected to a saponification step involving immersion in 1% 1Research supported by grant HD from the National Institute of Child Health and Development. National Institutes of Health. 74 1
2 ~~ 742 JAMES L. CONKLIN KOH in 80% ethanol at 25 C for 20 minutes (Conklin, 62). To confirm the absence of reactive lipids, sections were additionally extracted with chloroform-methanol (1 : 1) at 60 C for 24 hours. Before staining, for enzymatic digestion, sections were incubated in solutions of either 0.5% a-amylase (Nutritional Biochemicals) in M acetate buffer (ph 5.5) at 37 C for three hours, 0.5% testicular hyaluronidase in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (ph 5.5) at 37 C for four hours, or 100 units of Vibrio cholearae neuraminidase (Behringe Chemical Works) in 0.05 M acetate buffer (ph 5.5) at 37 C for four hours. As a control procedure, other sections were incubated in buffer only solutions for a similar length of time. Since digestion with hyaluronidase did not alter the staining reactions, sections of umbilical cord were incubated in the hyaluronidase solutions (controlled as above) to confirm the activity of this enzyme. Such sections exhibited a marked reduction in staining after enzymatic digestion. As the control procedure confirmed the specificity of the enzymatic digestions, the results to be described include only the effects of digestion upon the staining reaction (table 1). RESULTS The allantoic epithelium is a single layer of approximately cuboidal cells which line the inner surface of the chorioallantoic membrane (CAM). The nuclei of the cells are located basally while the cytoplasm is most abundant at the apical end bordering on the allantoic lumen. The apical surface of the cells exhibits short microvilli (Leeson and Leeson, 63) which are indistinct when viewed with the light microscope. On about the ninth day of development, inclusions appear in the supranuclear cytoplasm of the allantoic epithelial cells. These inciusions increase until, by the eighteenth day, they appear to fill most of the apical cytoplasm (fig. 1-3). Concomitantly, similar material accumulates on the surface of the cells within the allantoic lumen. The inclusions, because of their affinity for certain stains, are subsequently termed TABLE 1 Staining response of allantoic epithelial mucin Procedure Response PAS Colloidal iron Alcian blue Aldehyde fuchsin Azure A, ph 4.2 Azure A, ph Colloidal iron, PAS +,+I Methylation, PAS + Methylation, colloidal iron - Methylation, azure A, ph Methylation, azure A, ph Methylation, aldehyde fuchsin - Methylation, demethylation, PAS +* Methylation. demethylation, colloidal iron - Methylation, demethylation, aldehyde fuchsin - Methylation, demethylation, azure A, ph Methylation, demethylation, azure A, ph Amylase, PAS + Neuraminidase, PAS - Neuraminidase, colloidal iron Neuraminidase, alcian blue + Hyaluronidase, PAS Hyaluronidase, colloidal iron Hyaluronidase, alcian blue + -indicates that no staining occurred; + indicates an affinity for the stain. 1After this sequence some inclusions are PASpositive, while some are stained by colloidal iron. 2 After this sequence, inclusions that were formerly PAS-negative are now PAS-reactive. mucous inclusions. It seems probable that these mucous inclusions correspond to the weakly osmiophilic vacuoles observed by Leeson and Leeson ( 63) in an electron microscopic study of the chorioallantois. As indicated in table 1, the mucous inclusions of the allantoic epithelium are stained by many of the methods commonly employed in carbohydrate histochemistry. They are colored a deep red by the PAS reaction and also stained by colloidal iron, Alcian blue, aldehyde fuchsin and azure A. However, when the inclusions are stained with a colloidal iron-pas sequence, it is apparent that, while most inclusions are stained by colloidal iron, some inclusions are unstained by colloidal iron yet are PAS-reactive. This duality in the staining of the inclusions is most evident in day CAM when fewer inclusions are present. The same duality in staining is exhibited by the mucus covering the surface of the epithelium.
3 ALLANTOZC MUCIN 743 Both types of mucous inclusions are present in most epithelial cells. The presence of both PAS-reactive and colloidal iron-positive inclusions in individual cells as well as the occurrence of mixed reactive material in the lumen of the allantois suggests that the allantoic cells contain at least two kinds of mucus and that this same material is secreted into the allantoic lumen. To obtain additional information about the nature of the reactive groups in the mucous inclusions, control procedures were employed prior to the application of certain staining reactions. While the use of alcohol-dehydrated, paraffin-embedded sections indicated that the PAS-reactive material was not lipid in character, some sections were further treated with hot chloroform-methanol before staining with PAS. Chloroform-methanol extraction did not alter the PAS staining of the inclusions. Also, predigestion with amylase did not alter the the PAS staining of inclusions. In contrast, incubation of the sections in neuraminidase abolished all PAS staining of the inclusions. As anticipated, methylation of the tissue sections did not alter PAS staining. However, after a methylation-demethylation sequence, PAS staining of inclusions was greater than in untreated sections. After either methylation or a methylation-demethylation sequence, the inclusions were not stained by colloidal iron, Alcian blue, aldehyde fuchsin or azure A (fig. 4). Colloidal iron or Alcian blue staining of the inclusions was unaffected by either hyaluronidase or neuraminidase digestion (fig. 5). The preceding results were nearly the same following fixation in either of the three fixatives. In general, staining was less intense following fixation in neutralbuffered formalin. Results after fixation in CPF or Bouin's fixative were comparable. DISCUSSION The methods employed in this study fall into two categories. The first, the PAS reaction, is generally considered specific for reactive vicinal hydroxyl groups, although certain lipids are also capable of reacting (Lillie, '65). The remaining stains are those which exhibit an affinity for tissue anions such as sulfate, phosphate or carboxyl groups (Pearse, '60). The specificity of these anionophilic stains is dependent, to some extent, on the ph at which they are employed. The mucous inclusions of the allantoic epithelial cells are also of two types. There are inclusions which are only PAS-reactive and inclusions which are colloidal ironpositive, PAS-negative, when stained by a sequential stain. The appearance of similar material in the allantoic lumen suggest that at least two types of mucus produced by the allantoic epithelial cells is subsequently secreted into the allantoic fluid, which does contain copious quantities of mucus (Needham, '50). The identification of specific carbohydrates in tissue sections is difficult if not impossible with the methods employed. It is possible, however, to describe the nature of the reactive material in the mucous inclusions. The contents of one type of inclusion are PAS-reactive, unstained by anionophilic methods, resistant to hyaluronidase and amylase and susceptible to neuraminidase digestion. Avoiding the current dispute over the histochemical nomenclature of carbohydrates (Spicer et al., '65; Meyer, '66; Saunders and Rosan, '66), it seems reasonable to consider the contents of this inclusion as a neuraminic acid-containing sialomucin. While the significance of its occurrence remains obscure, its presence is not unexpected. Neuraminidase occurs in the CAM in large quantities (Ada and Lind, '61; Cook and Ada, '63); Bogach et al. ('62) have isolated a sialic acid-containing material, sialoresponsin, from allantoic fluid, following virus innoculation of the CAM. Although the localization of the CAM neuraminidase has not been demonstrated, it seems probable that it would occur in the allantoic epithelium where the sialomucin is found The second, most numerous type of mucous inclusion is intensely stained by procedures which have an affinity for negative groups. While colloidal iron and Alcian blue stain both sulfate and carboxyl groups, they are more specific if the ph of the staining solution is maintained well below the pk of carboxyl groups, (Lev and
4 744 JAMES L. CONKLIN Spicer, '64) which indicates that staining is due to sulfate. (Phosphate groups are also weakly stained but can probably be discounted since they have not been reported in mucus). Staining with azure A, at ph 2.0, and with aldehyde fuchsin, while not specific, is also indicative of sulfate groups. That the anions in the mucous inclusions are sulfate rather than carboxyl groups is further indicated by the lack of staining which is observed after methylation-demethylation treatment of the tissue sections. It is assumed (Lillie, '65) that, after a methylation-demethylation sequence, only carboxyl groups are available for staining. Neuraminidase digestion did not alter the staining with colloidal iron and this reaction was also unaffected by hyaluronidase digestion. Since hyaluronic acid, and chondroitin sulfates A and C are digested by testicular hyaluronidase (Pearse, '60; Lillie, '65), the sulfated mucus (sulfomucin) is probably other than one of these three carbohydrates. The enhancement of PAS reactivity of the mucous inclusions by methylation-demethylation suggests the presence of vicinal hydroxyl groups in the sulfomucin and the occurrence of sulfate in a position which prevents PAS reactivity (Lillie, '65). Desulfation removes the hindrance effect of the sulfate, and the molecule becomes PAS-reactive. For the present, the contents of the second type of mucous inclusion can only be identified as a sulfated mucin which also contains vicinal PAS-reactive groups and is lacking in demonstrable carboxyl groups. Protein is present in both types of epithelial mucus, as evidenced by bromphenol blue staining of the components following electrophoretic separation (unpublished observation). Presently, the significance of the allantoic mucus remains obscure. It has been suggested that it is secreted in response to the accumulation of noxious materials in the allantoic fluid (Needham, '50). This view is supported by the observation that artificial lowering of the ph of the allantoic fluid enhances mucus accumulation. Other factors are also involved, however, since transplantation of certain tissues to the CAM also accelerates mucus accumulation. In any event, the allantoic epithelium should provide an interesting tissue for the study of mucus synthesis and secretion, since the cells are apparently capable of synthesizing two quite different types of mucous material. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS I am grateful for the technical assistance of Mrs. Lana Brock and Mrs. Dorothy Kangas. LITERATURE CITED Ada, G. L., and P. E. Lind 1961 Neuraminidase in the chorioallantois of the chick embryo. Nature, 190: Bogoch, S., R. F. Gilfillan and P. Evans 1962 Sialoresponsin: neuraminic acid-containing substance which accumulates in the chorioallantoid fluid during the first few minutes of virus infection. Nature, 196: Conklin, J. L Staining properties of hyaline cartilage. Am. J. Anat., 112: Cook, B., and G. L. Ada 1963 Neuraminase in tissues of the chick embryo and chick. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 73: Gomori, G Aldehyde fuchsin: a new stain for elastic tissue. Am. J. Clin. Path., 20: Hamburger, V., and H. L. Hamilton 1951 A series of normal stages in the development of the chick embryo. J. Morph., 88: Leeson, T. S., and C. R. Leeson 1963 The chorioallantois of the chick. Light and electron microscopic observations at various times of incubation. J. Anat., 97: Lillie, R. D Histopathologic Technic and Practical Histochemistry. McGraw-Hill, New York. Lev, R., and S. S. Spicer 1964 Specific staining of sulphate groups with alcian blue at low ph. J. Histochem., 12: 309. Masson, P Some histological methods: Trichrome staining and their preliminary technique. J. Techn. Methods, 12: Meyer, K Problems of histochemical identification of carbohydrate-rich tissue components. J. Histochem., 14: Mowry, R. W Improved procedures for the staining of acidic polysaccharides by Muller's colloidal (hydrous) ferric oxide and its combination with the Fuelgen and the periodic acid-schiff reactions. Lab. Invest., 7: Needham, J Biochemistry and Morphogenesis. University Press, Cambridge. Pearse, A. G. E Histochemistry, Theoretical and Applied. Little, Brown, Boston. Saunders, A. M., and R. C. Rosan 1966 Histochemical nomenclature of carbohydrate-rich components. J. Histochem., 14: 869. Spicer, S. S., T. J. Leppi and P. J. Stoward 1965 Suggestions for a histochemical terminology of carbohydrate-rich tissue components. J. Histochem., 13:
5 PLATE
6 PLATE 1 EXPLANATION OF FIGURES 1 A section through the chorioallantoic membrane (CAM). From top to bottom are the ectodermal, mesodermal and entodermal components. The allanloic epithelial cells (arrow) contain copious amounts of mucus. Colloidal iron a:id PAS. X The mucus (arrow) of the allantoic epithelium as it appears after staining with aldehyde fuchsin. x The allantoic epithelium and mucous components. The distinction between the two types of mucous inclusions is not apparent, Note the presence of mucus in the allantoic Iumen (arrow). x A section of CAM after a methylation-demethylation sequence and staining with colloidal iron. Note the absence of stained material in the allantoic epithelium (arrow). X The CAM after treatment with neuraminidase. Only the mucous inclusions that are stained by colloidal iron (arrow) are visible (contrast with fig. 1). Colloidal iron and PAS. x
7 ALLANTOIC MUCIN James L. Conklin PLATE
ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1
 ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1 R. I. Wordinger, 2 J. B. Ramsey, I. F. Dickey and I. R. Hill, Jr. Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1 R. I. Wordinger, 2 J. B. Ramsey, I. F. Dickey and I. R. Hill, Jr. Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
Comparative Histochemical Study of Mucin in Colonic Goblet Cells of Albino Rat, Goat & Dog
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 4 Ver. XIII (Apr. 2016), PP 48-53 www.iosrjournals.org Comparative Histochemical Study of Mucin
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 4 Ver. XIII (Apr. 2016), PP 48-53 www.iosrjournals.org Comparative Histochemical Study of Mucin
Atlas of Stains. Special Stains on Artisan Link Pro
 Atlas of Stains Special Stains on Artisan Link Pro Intended use Routinely processed samples (paraffin-embedded) may be used. The preferred fixative is neutral buffered formalin. The clinical interpretation
Atlas of Stains Special Stains on Artisan Link Pro Intended use Routinely processed samples (paraffin-embedded) may be used. The preferred fixative is neutral buffered formalin. The clinical interpretation
Special Staining (I)
 Special Staining (I) Carbohydrates 1- PERIODIC ACID SCHIFF'S (PAS ) Purpose: Glycogen is present in liver, kidney, skeletal and cardiac muscle. The PAS stain is used to demonstrate neutral polysaccharides
Special Staining (I) Carbohydrates 1- PERIODIC ACID SCHIFF'S (PAS ) Purpose: Glycogen is present in liver, kidney, skeletal and cardiac muscle. The PAS stain is used to demonstrate neutral polysaccharides
Studies of differential staining with acid dyes in the human adenohypophysis
 467 Studies of differential staining with acid dyes in the human adenohypophysis By A. W. F. FISHER and D. BULMER (From the Anatomy Department, University of Manchester) Summary With Mallory techniques
467 Studies of differential staining with acid dyes in the human adenohypophysis By A. W. F. FISHER and D. BULMER (From the Anatomy Department, University of Manchester) Summary With Mallory techniques
Fixation... Questions 1 Answers 16. Processing... Questions 25 Answers 36. Safety... Questions 67 Answers 73
 Table of Contents Fixation... Questions 1 Answers 16 Processing... Questions 25 Answers 36 Instrumentation... Questions 43 Answers 58 Safety... Questions 67 Answers 73 Laboratory Mathematics & Solution
Table of Contents Fixation... Questions 1 Answers 16 Processing... Questions 25 Answers 36 Instrumentation... Questions 43 Answers 58 Safety... Questions 67 Answers 73 Laboratory Mathematics & Solution
Histochemical Studies of Pancreas in Prenatal Goat (Capra hircus)
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 1163-1169 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.144
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 1163-1169 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.144
THE HOLOCRINE CELLS of the epithelium of the rat epididymis and vas
 Holocrine Cells of the Human Epididymis JAN MARTAN, Ph.D.,"' PAULL. RISLEY, Ph.D., and ZDENEK HRUBAN, M.D., Ph.D. t THE HOLOCRINE CELLS of the epithelium of the rat epididymis and vas deferens undergo
Holocrine Cells of the Human Epididymis JAN MARTAN, Ph.D.,"' PAULL. RISLEY, Ph.D., and ZDENEK HRUBAN, M.D., Ph.D. t THE HOLOCRINE CELLS of the epithelium of the rat epididymis and vas deferens undergo
Histology and Histochemical Distribution of Goblet Cells in the Descending Colonic Epithelium of the Swamp Buffalo (Bubalus bubalis)
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 43 : 63-68 (2009) Histology and Histochemical Distribution of Goblet Cells in the Descending Colonic Epithelium of the Swamp Buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) Pakawadee Pongket 1 *, Maleewan
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 43 : 63-68 (2009) Histology and Histochemical Distribution of Goblet Cells in the Descending Colonic Epithelium of the Swamp Buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) Pakawadee Pongket 1 *, Maleewan
Carbohydrates and mucins. Dr Phil Bryant, Wales, UK
 Carbohydrates and mucins Dr Phil Bryant, Wales, UK Carbohydrates Provide cells with energy by converting to glucose Excess glucose stored in liver and muscle as glycogen Residual unstored glycogen is turned
Carbohydrates and mucins Dr Phil Bryant, Wales, UK Carbohydrates Provide cells with energy by converting to glucose Excess glucose stored in liver and muscle as glycogen Residual unstored glycogen is turned
Mucin Histochemistry Study of the Prostate in Normal and Malignant Lesions
 ISSN 2231-4261 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mucin Histochemistry Study of the Prostate in Normal and Malignant Lesions 1* 1 1 1 Manoj P.Ambali, Megha A. Doshi, Pratibha P. Patil, Shweta H. Chavan 1 Department of Anatomy,
ISSN 2231-4261 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mucin Histochemistry Study of the Prostate in Normal and Malignant Lesions 1* 1 1 1 Manoj P.Ambali, Megha A. Doshi, Pratibha P. Patil, Shweta H. Chavan 1 Department of Anatomy,
IN the skin of the mouse we find that the dermal papilla of growing hair
 (240 Cyclic Changes in Polysaccharides of the Papilla of the Hair Follicle By WILLIAM MONTAGNA, HERMAN B. CHASE, JANET D. MALONE, AND HELEN P. MELARAGNO (From Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island,
(240 Cyclic Changes in Polysaccharides of the Papilla of the Hair Follicle By WILLIAM MONTAGNA, HERMAN B. CHASE, JANET D. MALONE, AND HELEN P. MELARAGNO (From Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island,
Yara Saddam. Amr Alkhatib. Ihsan
 1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
-26- MATERIALS AND METHODS
 -26- MATERIALS AND METHODS The pollutant : Sevin (1-naphthyl N-methyl carbamate) was used at a concentrations of 0.5 and 1.0 mg/l. At these concentrations, the insecticide was completely soluble in water.
-26- MATERIALS AND METHODS The pollutant : Sevin (1-naphthyl N-methyl carbamate) was used at a concentrations of 0.5 and 1.0 mg/l. At these concentrations, the insecticide was completely soluble in water.
Preface 1. Fixation and Processing 1
 Contents Preface xi 1. Fixation and Processing 1 Fixation 1 Processing 2 What Should Be Seen in a Well-Fixed, Well-Processed Specimen Stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin 3 Problems Encountered With Fixation
Contents Preface xi 1. Fixation and Processing 1 Fixation 1 Processing 2 What Should Be Seen in a Well-Fixed, Well-Processed Specimen Stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin 3 Problems Encountered With Fixation
by authors and SVSBT.
 The Indian Journal of Veterinary Sciences & Biotechnology (2018) Volume 13, Issue 4, 20-25 ISSN (Print) : 2394-0247 : ISSN (Print and online) : 2395-1176, abbreviated as IJVSBT 10.21887/ijvsbt.v13i4.11553
The Indian Journal of Veterinary Sciences & Biotechnology (2018) Volume 13, Issue 4, 20-25 ISSN (Print) : 2394-0247 : ISSN (Print and online) : 2395-1176, abbreviated as IJVSBT 10.21887/ijvsbt.v13i4.11553
COLLOID DROPLET FORMATION IN DOG THYROID IN VITRO
 COLLOID DROPLET FORMATION IN DOG THYROID IN VITRO Induction by Dibutyryl Cyclic-AMP I. PASTAN and S. HI. WOLLMAN. Froml the National Institute of Arthritis and Metabolic Diseases and the National Cancer
COLLOID DROPLET FORMATION IN DOG THYROID IN VITRO Induction by Dibutyryl Cyclic-AMP I. PASTAN and S. HI. WOLLMAN. Froml the National Institute of Arthritis and Metabolic Diseases and the National Cancer
H,.ereditary macular dystrophy of the
 Histochemistry of corneal macular dystrophy Alec Garner Histochemical investigation of 22 corneal discs removed from patients with hereditary macular dystrophy has revealed two types of lesion. One is
Histochemistry of corneal macular dystrophy Alec Garner Histochemical investigation of 22 corneal discs removed from patients with hereditary macular dystrophy has revealed two types of lesion. One is
Histochemical differentiation of the basement membrane of the mouse seminiferous tubule By A. H. BAILLIE
 3 5 Histochemical differentiation of the basement membrane of the mouse seminiferous tubule By A. H. BAILLIE (From the Department of Anatomy, The University, Glasgow) With 2 plates (figs i and 2) Summary
3 5 Histochemical differentiation of the basement membrane of the mouse seminiferous tubule By A. H. BAILLIE (From the Department of Anatomy, The University, Glasgow) With 2 plates (figs i and 2) Summary
A Histological and Histochemical Study of the Brown and Yellow Adipose Tissue of the Bat, Hipposideros speoris
 369 A Histological and Histochemical Study of the Brown and Yellow Adipose Tissue of the Bat, Hipposideros speoris By J. C. GEORGE and J. EAPEN {From the Laboratories of Animal Physiology and Histochemistry,
369 A Histological and Histochemical Study of the Brown and Yellow Adipose Tissue of the Bat, Hipposideros speoris By J. C. GEORGE and J. EAPEN {From the Laboratories of Animal Physiology and Histochemistry,
Morphogenesis of the residual body of the mouse testis
 93 Morphogenesis of the residual body of the mouse testis By CASIMIR F. FIRLIT and JOSEPH R. DAVIS (From the Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Stritch School of Medicine, and Graduate School,
93 Morphogenesis of the residual body of the mouse testis By CASIMIR F. FIRLIT and JOSEPH R. DAVIS (From the Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Stritch School of Medicine, and Graduate School,
IN a previous publication (Hewitt, 1954) a description was given of the
 i 9 9 Further Observations on the Histochemistry of Fat Absorption in the Small Intestine of the Rat By W. HEWITT, M.B., B.S. (From the Department of Anatomy, St. Thomas' Hospital Medical School, London,
i 9 9 Further Observations on the Histochemistry of Fat Absorption in the Small Intestine of the Rat By W. HEWITT, M.B., B.S. (From the Department of Anatomy, St. Thomas' Hospital Medical School, London,
The Effect of Cortisone on Cell Proliferation and Migration in Peripheral Nerves undergoing Wallerian degeneration
 The Effect of Cortisone on Cell Proliferation and Migration in Peripheral Nerves undergoing Wallerian by G. A. THOMAS 1 From the Department of Anatomy, Guy's Hospital Medical School, London INTRODUCTION
The Effect of Cortisone on Cell Proliferation and Migration in Peripheral Nerves undergoing Wallerian by G. A. THOMAS 1 From the Department of Anatomy, Guy's Hospital Medical School, London INTRODUCTION
Histological and Histochemical Observations on Brunner s Glands of Guinea pig
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 8 Ver. XI (August. 2016), PP 100-106 www.iosrjournals.org Histological and Histochemical Observations
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 8 Ver. XI (August. 2016), PP 100-106 www.iosrjournals.org Histological and Histochemical Observations
Lipid Histochemistry of Surgically Resected Adrenal. Glands in Hyperadrenocorticism
 Lipid Histochemistry of Surgically Resected Adrenal Glands in Hyperadrenocorticism Hideo TSUCHIYAMA Department of Pathology, Nagasaki University School of Medicine, Nagasaki Recently, fresh adrenal tissue
Lipid Histochemistry of Surgically Resected Adrenal Glands in Hyperadrenocorticism Hideo TSUCHIYAMA Department of Pathology, Nagasaki University School of Medicine, Nagasaki Recently, fresh adrenal tissue
Human Saliva as a Convenient Source of Ribonuclease. By S. BRADBURY
 Human Saliva as a Convenient Source of Ribonuclease 323 By S. BRADBURY (From the Cytological Laboratory, Department of Zoology, University Museum, Oxford) SUMMARY Saliva, heated to 80 C for 10 minutes
Human Saliva as a Convenient Source of Ribonuclease 323 By S. BRADBURY (From the Cytological Laboratory, Department of Zoology, University Museum, Oxford) SUMMARY Saliva, heated to 80 C for 10 minutes
Histochemical Study of Mucopolysaccharides in Goblet Cells of the Chicken Oviduct
 J. Fac. Fish. Anim. Husb. Hiroshima Univ. (1965), 6 : 25..._35 Histochemical Study of Mucopolysaccharides in Goblet Cells of the Chicken Oviduct Shunsaku Fum, Tatsudo TAMURA and Hakaru KUNISAKI Department
J. Fac. Fish. Anim. Husb. Hiroshima Univ. (1965), 6 : 25..._35 Histochemical Study of Mucopolysaccharides in Goblet Cells of the Chicken Oviduct Shunsaku Fum, Tatsudo TAMURA and Hakaru KUNISAKI Department
BenchMark Special Stains. Product guide
 BenchMark Special Stains Product guide Quick reference table Product name Ordering code Catalog number Tissue thickness Tests per kit Total vials in kit package *Not all vials in the kit are used at one
BenchMark Special Stains Product guide Quick reference table Product name Ordering code Catalog number Tissue thickness Tests per kit Total vials in kit package *Not all vials in the kit are used at one
Intercellular Matrix in Colonies of Candida
 JouRNAL OF BAcTEROLOGY, Sept. 1975, p. 1139-1143 Vol. 123, No. 3 Copyright 0 1975 American Society for Microbiology Printed in U.S.A. ntercellular Matrix in Colonies of Candida K. R. JOSH, J. B. GAVN,*
JouRNAL OF BAcTEROLOGY, Sept. 1975, p. 1139-1143 Vol. 123, No. 3 Copyright 0 1975 American Society for Microbiology Printed in U.S.A. ntercellular Matrix in Colonies of Candida K. R. JOSH, J. B. GAVN,*
Histochemical comparison of the epithelial mucins
 Journal ofclinical Pathology, 1977, 30, 1063-1067 Histochemical comparison of the epithelial mucins in the ileum in Crohn's disease and in normal controls C. F. A. CULLING, P. E. REID, W. L. DUNN, AND
Journal ofclinical Pathology, 1977, 30, 1063-1067 Histochemical comparison of the epithelial mucins in the ileum in Crohn's disease and in normal controls C. F. A. CULLING, P. E. REID, W. L. DUNN, AND
mstochemical ANALYSIS OF MUCOUS CELLS IN THE EPIDERMIS OF SNAKE EEL PISOODONOPHIS BORO (HAM-BUCH)
 J. mar. biot. Ass. Ma, 1987, 29 (1 & 2): 244-24^ mstochemical ANALYSIS OF MUCOUS CELLS IN THE EPIDERMIS OF SNAKE EEL PISOODONOPHIS BORO (HAM-BUCH) K. JAYALAKSHMI AND A. SUBRAMANIAN Centre of Advanced Study
J. mar. biot. Ass. Ma, 1987, 29 (1 & 2): 244-24^ mstochemical ANALYSIS OF MUCOUS CELLS IN THE EPIDERMIS OF SNAKE EEL PISOODONOPHIS BORO (HAM-BUCH) K. JAYALAKSHMI AND A. SUBRAMANIAN Centre of Advanced Study
PRELIMINARY OBSERVATIONS ON THE HISTOCHEMISTRY OF
 741 PRELIMINARY OBSERVATIONS ON THE HISTOCHEMISTRY OF THE CELL SURFACE OF CARCINOMA OF THE CERVIX S. BRADBURY, G. WIERNIK, E. A. WILLIAMS AND R. H. COW1DELL From the Department of Human Anatomy, Oxford,
741 PRELIMINARY OBSERVATIONS ON THE HISTOCHEMISTRY OF THE CELL SURFACE OF CARCINOMA OF THE CERVIX S. BRADBURY, G. WIERNIK, E. A. WILLIAMS AND R. H. COW1DELL From the Department of Human Anatomy, Oxford,
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 4, 2016,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 4, 2016, 1813 1819 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) HISTOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON MAJOR SALIVARY GLANDS IN PRENATAL BUFFALO (Bubalus
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 4, 2016, 1813 1819 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) HISTOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON MAJOR SALIVARY GLANDS IN PRENATAL BUFFALO (Bubalus
ALAEZI CM 1 *, ADISA JO 2, OKOROCHI EC 3 and OKECHI OO 4
 Global Journal of Scientific Researches Available online at gjsr.blue-ap.org 2014 GJSR Journal. Vol. 2(2), pp. 51-55, 28 February, 2014 E-ISSN: 2311-732X METHYL GREEN PYRONIN: A PROGRESSIVE NUCLEAR STAIN
Global Journal of Scientific Researches Available online at gjsr.blue-ap.org 2014 GJSR Journal. Vol. 2(2), pp. 51-55, 28 February, 2014 E-ISSN: 2311-732X METHYL GREEN PYRONIN: A PROGRESSIVE NUCLEAR STAIN
Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/-
 Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018, 1608 1614 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMPARATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES OF DUEODENUM IN CATTLE SHEEP AND GOATS Thete
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018, 1608 1614 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMPARATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES OF DUEODENUM IN CATTLE SHEEP AND GOATS Thete
AN EXAMINATION OF SKIN FROM PATIENTS WITH COLLAGEN
 AN EXAMINATION OF SKIN FROM PATIENTS WITH COLLAGEN DISEASE UTILIZING THE COMBINED ALCIAN BLUE-PERIODIC ACID SCHIFF STAIN EDWARD P. CAWLEY, M.D.,* J. F. A. McMANTJS, M.D.,t CHARLES H. LTJPTON, JR., M.D.t
AN EXAMINATION OF SKIN FROM PATIENTS WITH COLLAGEN DISEASE UTILIZING THE COMBINED ALCIAN BLUE-PERIODIC ACID SCHIFF STAIN EDWARD P. CAWLEY, M.D.,* J. F. A. McMANTJS, M.D.,t CHARLES H. LTJPTON, JR., M.D.t
(From the Schools of Anatomy and Pathology, University of Virginia, Department of Medicine, Charlottesville, Virginia) With one plate (fig.
 Histochemical Distribution of 5-Nucleotidase in Snake Tissues: Presence of 5-Nucleotidase and Absence of Alkaline Phosphomonoesterase in Venom Glands of the Rattlesnake By D. E. BRAGDON AND J. F. A. McMANUS
Histochemical Distribution of 5-Nucleotidase in Snake Tissues: Presence of 5-Nucleotidase and Absence of Alkaline Phosphomonoesterase in Venom Glands of the Rattlesnake By D. E. BRAGDON AND J. F. A. McMANUS
FIXATION BY MEANS OF GLUTARALDEHYDE-HYDROGEN PEROXIDE REACTION PRODUCTS
 FIXATION BY MEANS OF GLUTARALDEHYDE-HYDROGEN PEROXIDE REACTION PRODUCTS CAMILLO PERACCHIA and BRANT S. MITTLER. From the Department of Anatomy, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina 27706,
FIXATION BY MEANS OF GLUTARALDEHYDE-HYDROGEN PEROXIDE REACTION PRODUCTS CAMILLO PERACCHIA and BRANT S. MITTLER. From the Department of Anatomy, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina 27706,
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio211 Laboratory 2. Epithelial and Connective Tissues
 Bio211 Laboratory 2 Epithelial and Connective Tissues 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue (p. 79 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Connective Tissue (p. 93 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Muscle/Nervous
Bio211 Laboratory 2 Epithelial and Connective Tissues 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue (p. 79 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Connective Tissue (p. 93 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Muscle/Nervous
MITOSIS IN DEVELOPING CARDIAC MUSCLE. FRANCIS J. MANASEK. From the Department of Anatomy, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts 02115
 Published Online: 1 April, 1968 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.37.1.191 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on June 30, 2018 MITOSIS IN DEVELOPING CARDIAC MUSCLE FRANCIS J. MANASEK. From the Department
Published Online: 1 April, 1968 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.37.1.191 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on June 30, 2018 MITOSIS IN DEVELOPING CARDIAC MUSCLE FRANCIS J. MANASEK. From the Department
ABOUT US WORLDWIDE DISTRIBUTION ICON KEY STAIN LINE PRODUCT LIST
 ABOUT US WORLDWIDE DISTRIBUTION ICON KEY STAIN LINE PRODUCT LIST BQCKit Company is one of the three differentiated business lines of Bioquochem S.L. We are a Spanish biotechnology company specialized
ABOUT US WORLDWIDE DISTRIBUTION ICON KEY STAIN LINE PRODUCT LIST BQCKit Company is one of the three differentiated business lines of Bioquochem S.L. We are a Spanish biotechnology company specialized
ISOLATION OF A SARCOMA VIRUS FROM A SPONTANEOUS CHICKEN TUMOR
 ISOLATION OF A SARCOMA VIRUS FROM A SPONTANEOUS CHICKEN TUMOR Shigeyoshi ITOHARA, Kouichi HIRATA, Makoto INOUE, Masanori Veterinary Pathology, Faculty of Agriculture, Yamaguchi University* HATSUOKA, and
ISOLATION OF A SARCOMA VIRUS FROM A SPONTANEOUS CHICKEN TUMOR Shigeyoshi ITOHARA, Kouichi HIRATA, Makoto INOUE, Masanori Veterinary Pathology, Faculty of Agriculture, Yamaguchi University* HATSUOKA, and
HRP cytochemistry. Division of Radiooncology, Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum, Heidelberg, Germany
 HRP cytochemistry WOLF D. KUHLMANN, M.D. Division of Radiooncology, Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany A range of substrates is available for the cytochemical staining of peroxidase
HRP cytochemistry WOLF D. KUHLMANN, M.D. Division of Radiooncology, Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany A range of substrates is available for the cytochemical staining of peroxidase
Variations in the Appearance of Human Elastic Cartilage
 The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 69, Issue 6 (November, 1969) 1969-11 Variations in the Appearance of
The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 69, Issue 6 (November, 1969) 1969-11 Variations in the Appearance of
STUDIES ON HISTOLOGICAL STRUCTURES OF THE ABDOMEN ON ADULT WORKER BEES (APIS MELLIFERA CARPATHICA)
 STUDIES ON HISTOLOGICAL STRUCTURES OF THE ABDOMEN ON ADULT WORKER BEES (APIS MELLIFERA CARPATHICA) Petruţ T. 1, D. Condur 1, N. Velicu 1, V. Călin 1 1 Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Spiru Haret, 9-11 Energeticienilor
STUDIES ON HISTOLOGICAL STRUCTURES OF THE ABDOMEN ON ADULT WORKER BEES (APIS MELLIFERA CARPATHICA) Petruţ T. 1, D. Condur 1, N. Velicu 1, V. Călin 1 1 Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Spiru Haret, 9-11 Energeticienilor
RECOVERY OF DAMAGES IN THE SKIN OF ARSENIC EXPOSED CLARIAS BATRACHUS (LINN.) FOLLOWING WITHDRAWAL OF THE STRESS
 Iran. J. Environ. Health. Sci. Eng., 2008, Vol. 5, No. 4, pp. 217-224 RECOVERY OF DAMAGES IN THE SKIN OF ARSENIC EXPOSED CLARIAS BATRACHUS (LINN.) FOLLOWING WITHDRAWAL OF THE STRESS A. K. Singh, * T. K.
Iran. J. Environ. Health. Sci. Eng., 2008, Vol. 5, No. 4, pp. 217-224 RECOVERY OF DAMAGES IN THE SKIN OF ARSENIC EXPOSED CLARIAS BATRACHUS (LINN.) FOLLOWING WITHDRAWAL OF THE STRESS A. K. Singh, * T. K.
Histochemical study of asbestos fibre coating in experimental carrageenin granulomas
 British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 1973, 30, 248-252 Histochemical study of asbestos fibre coating in experimental carrageenin granulomas M. GOVERNA and C. ROSANDAVADALA Laboratory of Experimental
British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 1973, 30, 248-252 Histochemical study of asbestos fibre coating in experimental carrageenin granulomas M. GOVERNA and C. ROSANDAVADALA Laboratory of Experimental
abruptly retrogress and remain quiescent throughout the winter. The insecti
 HISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF THE SEMINAL VESICLE SECRETION OF THE INDIAN HEDGEHOG WITH PARTICULAR REFERENCE TO THE CRYSTALLOID BODIES PUSHPAMALA P. BIDWAI and S. R. BAWA Department of Biophysics, Panjab University,
HISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF THE SEMINAL VESICLE SECRETION OF THE INDIAN HEDGEHOG WITH PARTICULAR REFERENCE TO THE CRYSTALLOID BODIES PUSHPAMALA P. BIDWAI and S. R. BAWA Department of Biophysics, Panjab University,
SURGICAL PATHOLOGY - HISTOLOGY STAINING MANUAL - NERVE TISSUE Page: 1 of 3 BODIAN'S METHOD - NERVE FIBERS PURPOSE: For demonstrating nerve fibers.
 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY - HISTOLOGY Date: STAINING MANUAL - NERVE TISSUE Page: 1 of 3 BODIAN'S METHOD - NERVE FIBERS PURPOSE: For demonstrating nerve fibers. PRINCIPLE: Protargol-S (silver proteinate) is used
SURGICAL PATHOLOGY - HISTOLOGY Date: STAINING MANUAL - NERVE TISSUE Page: 1 of 3 BODIAN'S METHOD - NERVE FIBERS PURPOSE: For demonstrating nerve fibers. PRINCIPLE: Protargol-S (silver proteinate) is used
Freshwater Biological Association. FBA Translation (New Series) No. 132
 Freshwater Biological Association FBA Translation (New Series) No. 132 Title: A contribution to the knowledge of the skin albuminose cells of Torpedo ocellata Raf. Author(s) CELADA M. & DE PAOLI A.M. Reference:
Freshwater Biological Association FBA Translation (New Series) No. 132 Title: A contribution to the knowledge of the skin albuminose cells of Torpedo ocellata Raf. Author(s) CELADA M. & DE PAOLI A.M. Reference:
I-ITSTOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON THE OLFACTORY EPITHELIUM OF SOME HILLSTREAM TELEOSTS
 Journal of the Indian Fisheries Association, 16 & 17, 1986-87, 25-30 I-ITSTOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON THE OLFACTORY EPITHELIUM OF SOME HILLSTREAM TELEOSTS WAZIR SINGH* AND H. R. SINGH Department of Zoology,
Journal of the Indian Fisheries Association, 16 & 17, 1986-87, 25-30 I-ITSTOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON THE OLFACTORY EPITHELIUM OF SOME HILLSTREAM TELEOSTS WAZIR SINGH* AND H. R. SINGH Department of Zoology,
PRACTICAL HISTOPATHOLOGY IN MOUSE MODELS OF HUMAN DISEASE: GUIDES TO PHENOTYPING THE GENETICALLY ALTERED MOUSE
 PRACTICAL HISTOPATHOLOGY IN MOUSE MODELS OF HUMAN DISEASE: GUIDES TO PHENOTYPING THE GENETICALLY ALTERED MOUSE http://mousepheno.ucsd.edu/ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc3693904/ 1. Approval
PRACTICAL HISTOPATHOLOGY IN MOUSE MODELS OF HUMAN DISEASE: GUIDES TO PHENOTYPING THE GENETICALLY ALTERED MOUSE http://mousepheno.ucsd.edu/ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc3693904/ 1. Approval
Mucoprotein-containing histiocytes (muciphages)
 J. clin. Path. (1966), 19, 368 Mucoprotein-containing histiocytes (muciphages) in the rectum J. G. AZZOPARDI AND D. J. EVANS' From the Department of Morbid Anatomy, Postgraduate Medical School, London
J. clin. Path. (1966), 19, 368 Mucoprotein-containing histiocytes (muciphages) in the rectum J. G. AZZOPARDI AND D. J. EVANS' From the Department of Morbid Anatomy, Postgraduate Medical School, London
Histology of the aortic media in dissecting aneurysms
 J. clin. Path. (964), 7, Histology of the aortic media in dissecting aneurysms GERALD MANLEY From the Department of Pathology, The Radcliffe nfirmary, Oxford SYNOPSS Sections of the ascending aorta of
J. clin. Path. (964), 7, Histology of the aortic media in dissecting aneurysms GERALD MANLEY From the Department of Pathology, The Radcliffe nfirmary, Oxford SYNOPSS Sections of the ascending aorta of
Glandular Epithelium. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Glandular epithelia are tissues formed by cells specialized to produce secretion. Secretion: if substances produced
Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Glandular epithelia are tissues formed by cells specialized to produce secretion. Secretion: if substances produced
Bronchial gland histochemistry in lungs removed for cancer
 Thorax, 1980, 35, 546-551 Bronchial gland histochemistry in lungs removed for cancer W DE POITIERS, P W LORD, B BILES, AND W F WHIMSTER From the Department of Morbid Anatomy, King's College Hospital, and
Thorax, 1980, 35, 546-551 Bronchial gland histochemistry in lungs removed for cancer W DE POITIERS, P W LORD, B BILES, AND W F WHIMSTER From the Department of Morbid Anatomy, King's College Hospital, and
MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE GALL BLADDER OF THE CHUKAR PARTRIDGE (ALECTORIS CHUKAR)
 Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine (2012), 15, No 2, 73 78 MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF TH GALL BLADDR OF TH CHUKAR PARTRIDG (ALCTORIS CHUKAR) Summary B. MOBINI Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Islamic Azad
Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine (2012), 15, No 2, 73 78 MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF TH GALL BLADDR OF TH CHUKAR PARTRIDG (ALCTORIS CHUKAR) Summary B. MOBINI Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Islamic Azad
An Evaluation of Xylene-free Processing of Tissues From the Central Nervous System Using the PelorisTM Dual Retort Rapid Tissue Processor
 An Evaluation of Xylene-free Processing of Tissues From the Central Nervous System Using the PelorisTM Dual Retort Rapid Tissue Processor Geoffrey Rolls Leica Microsystems, iosystems Division, Melbourne,
An Evaluation of Xylene-free Processing of Tissues From the Central Nervous System Using the PelorisTM Dual Retort Rapid Tissue Processor Geoffrey Rolls Leica Microsystems, iosystems Division, Melbourne,
FIXATION OF TISSUES MODULE 5.1 INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 5.2 AIMS OF FIXATION 5.3 PRINCIPLE OF FIXATION. Notes
 MODULE Fixation of Tissues 5 FIXATION OF TISSUES 5.1 INTRODUCTION It is a process by which the cells or tissues are fixed in chemical and partly physical state so that they can withstand subsequent treatment
MODULE Fixation of Tissues 5 FIXATION OF TISSUES 5.1 INTRODUCTION It is a process by which the cells or tissues are fixed in chemical and partly physical state so that they can withstand subsequent treatment
Adenoid basal carcinoma of the cervix uteri'
 Adenoid basal carcinoma of the cervix uteri' K. B. SHILKIN From the Department of Pathology, University of Singapore, Singapore J clin. Path., 1972, 13, 301-305 SYNOPSIS This paper describes a case of
Adenoid basal carcinoma of the cervix uteri' K. B. SHILKIN From the Department of Pathology, University of Singapore, Singapore J clin. Path., 1972, 13, 301-305 SYNOPSIS This paper describes a case of
Sheet #9. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 Sheet #9 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Elastic fibers The main function of elastic fibers is to provide elasticity. In other words these fibers are able to restore the original
Sheet #9 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Elastic fibers The main function of elastic fibers is to provide elasticity. In other words these fibers are able to restore the original
Occurrence of Ciliated Vesicle-Containing Reticular Cells in the Mouse Thymus
 Occurrence of Ciliated Vesicle-Containing Reticular Cells in the Mouse Thymus By Takeshi Hoshino Department of Anatomy, Hokkaido University School of Medicine, Sapporo, Japan (Director : Prof. Takashi
Occurrence of Ciliated Vesicle-Containing Reticular Cells in the Mouse Thymus By Takeshi Hoshino Department of Anatomy, Hokkaido University School of Medicine, Sapporo, Japan (Director : Prof. Takashi
Behzad Mobini* Islamic Azad University, Shahrekord Branch, Shahrekord, Iran. Received: 25 October 2010, Accepted: 4 January 2011
 Original Article Veterinary Research Forum Vol: 2, No: 1, March, 2011, 25-29 Histological Studies on Pancreas of Goose (Anser Albifrons) Behzad Mobini* * Department of Anatomical Sciences, Faculty of Veterinary
Original Article Veterinary Research Forum Vol: 2, No: 1, March, 2011, 25-29 Histological Studies on Pancreas of Goose (Anser Albifrons) Behzad Mobini* * Department of Anatomical Sciences, Faculty of Veterinary
QUALITATIVE TESTS OF CARBOHYDRATE
 QUALITATIVE TESTS OF CARBOHYDRATE MACROMOLECULE CARBOHYDRATES Are the key source of energy used by living things. Also serve as extracellular structural elements as in cell wall of bacteria and plant.
QUALITATIVE TESTS OF CARBOHYDRATE MACROMOLECULE CARBOHYDRATES Are the key source of energy used by living things. Also serve as extracellular structural elements as in cell wall of bacteria and plant.
Glandular Epithelium. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Gla dular epithelia are tissues for ed y ells spe ialized to produ e se retio. Secretion: if substances produced
Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Gla dular epithelia are tissues for ed y ells spe ialized to produ e se retio. Secretion: if substances produced
Fish (Leiognathus argenteum).
 Cytochemical Studies on Polysaccharide and Protein of Ovarian Egg-Cells of an Osseous Fish (Leiognathus argenteum). By Mono Ihnuma and Tomi Tsukuda (Department of Anatomy, School of Medicine, Keio-Gijuku
Cytochemical Studies on Polysaccharide and Protein of Ovarian Egg-Cells of an Osseous Fish (Leiognathus argenteum). By Mono Ihnuma and Tomi Tsukuda (Department of Anatomy, School of Medicine, Keio-Gijuku
BIOCHEMICAL AND HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES
 Brit. J. Ophthal., 35, 784. BIOCHEMICAL AND HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN DEVELOPING RABBIT EYES* BY B. A. BEMBRIDGE AND ANTOINETTE PIRIE From the Nuffield Laboratory of Ophthalmology. Oxford AN attempt has
Brit. J. Ophthal., 35, 784. BIOCHEMICAL AND HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN DEVELOPING RABBIT EYES* BY B. A. BEMBRIDGE AND ANTOINETTE PIRIE From the Nuffield Laboratory of Ophthalmology. Oxford AN attempt has
Some Observations on the Fine Structure of the Goblet Cells. Special Reference to the Well-Developed Agranular Endoplasmic Reticulum
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 58(4-6) : 583-594, March 1982 Some Observations on the Fine Structure of the Goblet Cells in the Nasal Respiratory Epithelium of the Rat, with Special Reference to the Well-Developed
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 58(4-6) : 583-594, March 1982 Some Observations on the Fine Structure of the Goblet Cells in the Nasal Respiratory Epithelium of the Rat, with Special Reference to the Well-Developed
Non-hematogenous endogenous pigments
 Non-hematogenous endogenous pigments 0 This group contains the following : 1. Melanins. 2. Lipofuscins. 3. Chromaffin. 4. Pseudomelanosis. 5. Dubin-Johnson pigments. 6. Ceroid-type lipofuscins. 7. Hamazaki-Weisenberg
Non-hematogenous endogenous pigments 0 This group contains the following : 1. Melanins. 2. Lipofuscins. 3. Chromaffin. 4. Pseudomelanosis. 5. Dubin-Johnson pigments. 6. Ceroid-type lipofuscins. 7. Hamazaki-Weisenberg
DOCTORAL THESIS (SUMMARY)
 Translation from Romanian UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA THE FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS (SUMMARY) Scientific coordinator Prof. Dr. Laurentiu MOGOANTA PhD student, Dr. Madalin IONILA
Translation from Romanian UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA THE FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS (SUMMARY) Scientific coordinator Prof. Dr. Laurentiu MOGOANTA PhD student, Dr. Madalin IONILA
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio 101 Laboratory 3. Epithelial Tissues and Integument
 Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Tyrosinase Activity in the Pigmented Cells of the Nucleus Substantiae Nigrae. I. Monophenolase and Diphenolase Activity. By C. D.
 4 7 Tyrosinase Activity in the Pigmented Cells of the Nucleus Substantiae Nigrae. I. Monophenolase and Diphenolase Activity By C. D. MARSDEN (From the Department of Anatomy, St. Thomas's Hospital Medical
4 7 Tyrosinase Activity in the Pigmented Cells of the Nucleus Substantiae Nigrae. I. Monophenolase and Diphenolase Activity By C. D. MARSDEN (From the Department of Anatomy, St. Thomas's Hospital Medical
Histochemistry of the colonic epithelial mucins in normal subjects and in patients with ulcerative colitis
 Gut, 1967, 8, 491 Histochemistry of the colonic epithelial mucins in normal subjects and in patients with ulcerative colitis A qualitative and histophotometric investigation V. GRECO, G. LAURO, A. FABBRN,
Gut, 1967, 8, 491 Histochemistry of the colonic epithelial mucins in normal subjects and in patients with ulcerative colitis A qualitative and histophotometric investigation V. GRECO, G. LAURO, A. FABBRN,
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Harvard Medical School Brigham and Women s Hospital VA Boston Healthcare System 2.79J/3.96J/BE.
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Harvard Medical School Brigham and Women s Hospital VA Boston Healthcare System 2.79J/3.96J/BE.441/HST522J TISSUE TYPES M. Spector, Ph.D. and I.V. Yannas, Ph.D. The
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Harvard Medical School Brigham and Women s Hospital VA Boston Healthcare System 2.79J/3.96J/BE.441/HST522J TISSUE TYPES M. Spector, Ph.D. and I.V. Yannas, Ph.D. The
Upper Respiratory Histology
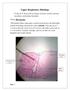 Upper Respiratory Histology - Today we ll discuss the histology of larynx, trachea, primary, secondary, and tertiary bronchus. *First: The Larynx: -The picture below represents a section in the larynx,
Upper Respiratory Histology - Today we ll discuss the histology of larynx, trachea, primary, secondary, and tertiary bronchus. *First: The Larynx: -The picture below represents a section in the larynx,
There is scanty information on the biochemistry
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 24, No.4, April 1973 Printed in U.S.A. ACTIVITY AND LOCALIZATION OF ISOCITRIC DEHYDROGENASE, ASPARTATE AMINOTRANSFERASE, ALANINE
FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 24, No.4, April 1973 Printed in U.S.A. ACTIVITY AND LOCALIZATION OF ISOCITRIC DEHYDROGENASE, ASPARTATE AMINOTRANSFERASE, ALANINE
Properties of Alcohols and Phenols Experiment #3
 Properties of Alcohols and Phenols Experiment #3 Objectives: To observe the solubility of alcohols relative to their chemical structure, to perform chemical tests to distinguish primary, secondary and
Properties of Alcohols and Phenols Experiment #3 Objectives: To observe the solubility of alcohols relative to their chemical structure, to perform chemical tests to distinguish primary, secondary and
A study of the histochemical demonstration of cytochrome oxidase
 497 A study of the histochemical demonstration of cytochrome oxidase By R. G. BUTCHER, J. V. DIENGDOH, and J. CHAYEN (From the Department of Pathology, Royal College of Surgeons of England, Lincoln's Inn
497 A study of the histochemical demonstration of cytochrome oxidase By R. G. BUTCHER, J. V. DIENGDOH, and J. CHAYEN (From the Department of Pathology, Royal College of Surgeons of England, Lincoln's Inn
CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
TISSUES TYPES. CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. HISTOLOGY = the study of tissues
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
Biometrical, Histological and Histochemical Studies on Omasum of Gaddi Sheep
 DOI: 10.30954/2277-940X.2018.00150.20 Journal of Animal Research: v.8 n.1, p. 125-129. February 2018 Biometrical, Histological and Histochemical Studies on Omasum of Gaddi Sheep Shabir Ahmad Malik 1*,
DOI: 10.30954/2277-940X.2018.00150.20 Journal of Animal Research: v.8 n.1, p. 125-129. February 2018 Biometrical, Histological and Histochemical Studies on Omasum of Gaddi Sheep Shabir Ahmad Malik 1*,
FD Rapid MultiStain Kit
 Quality & Excellence since 1996 FD Rapid MultiStain Kit An effective histological staining system with multiple functions designed for easy use in all types of neuroscience laboratories User Manual PK
Quality & Excellence since 1996 FD Rapid MultiStain Kit An effective histological staining system with multiple functions designed for easy use in all types of neuroscience laboratories User Manual PK
SYNTHESIS OF COMPLEX CARBOHYDRATES IN THE GOLGI REGION, AS SHOWN BY RADIOAUTOGRAPHY AFTER INJECTION OF LABELED GLUCOSE
 SYNTHESIS OF COMPLEX CARBOHYDRATES IN THE GOLGI REGION, AS SHOWN BY RADIOAUTOGRAPHY AFTER INJECTION OF LABELED GLUCOSE MARIAN PETERSON and C. P. LEBLOND. From the Department of Anatomy, MeGill University,
SYNTHESIS OF COMPLEX CARBOHYDRATES IN THE GOLGI REGION, AS SHOWN BY RADIOAUTOGRAPHY AFTER INJECTION OF LABELED GLUCOSE MARIAN PETERSON and C. P. LEBLOND. From the Department of Anatomy, MeGill University,
Histology Review Can you identify the Cell Structures? Can you identify the Stain? Can you identify the Cell type?
 Histology Review Can you identify the Cell Structures? Can you identify the Stain? Can you identify the Cell type? 2.01 Border of Epithelia (fluorescence) M A: lamina basalis B: epithelium C: other tissues
Histology Review Can you identify the Cell Structures? Can you identify the Stain? Can you identify the Cell type? 2.01 Border of Epithelia (fluorescence) M A: lamina basalis B: epithelium C: other tissues
Note on the Histochemical Localization of Glycogen and Pentosepolynucleotides in the Visual Cells of the Chick (Gallus gallus)
 Note on the Histochemical Localization of Glycogen and Pentosepolynucleotides in the Visual Cells of the Chick (Gallus gallus) By M. RABINOVITCH, IVAN MOTA, AND S. YONEDA (From the Laboratory of Cell Physiology,
Note on the Histochemical Localization of Glycogen and Pentosepolynucleotides in the Visual Cells of the Chick (Gallus gallus) By M. RABINOVITCH, IVAN MOTA, AND S. YONEDA (From the Laboratory of Cell Physiology,
Periodic Acid-Schiff-Light Green Stain to Detect Glomerular Protein Deposits by Routine Light Microscopy
 Periodic Acid-Schiff-Light Green Stain to Detect Glomerular Protein Deposits by Routine Light Microscopy CHARLES N. GAMBLE, M.D. Department of Pathology, Sutter Memorial Hospital, Sacramento, California
Periodic Acid-Schiff-Light Green Stain to Detect Glomerular Protein Deposits by Routine Light Microscopy CHARLES N. GAMBLE, M.D. Department of Pathology, Sutter Memorial Hospital, Sacramento, California
BCH302 [Practical] 1
![BCH302 [Practical] 1 BCH302 [Practical] 1](/thumbs/81/83984357.jpg) BCH302 [Practical] 1 Carbohydrates are defined as the polyhydroxy aldehydes or polyhydroxy ketones. Most, but not all carbohydrate have a formula (CH 2 O)n (hence the name hydrate of carbon). Sugars ends
BCH302 [Practical] 1 Carbohydrates are defined as the polyhydroxy aldehydes or polyhydroxy ketones. Most, but not all carbohydrate have a formula (CH 2 O)n (hence the name hydrate of carbon). Sugars ends
A Comparative Histological and Histochemical Study of Peritoneal Mast Cells of Albino Rat and Rabbit
 Quest Journals Journal of Medical and Dental Science Research Volume 4~ Issue 1 (2017) pp: 01-05 ISSN(Online) : 2394-076X ISSN (Print):2394-0751 www.questjournals.org Research Paper A Comparative Histological
Quest Journals Journal of Medical and Dental Science Research Volume 4~ Issue 1 (2017) pp: 01-05 ISSN(Online) : 2394-076X ISSN (Print):2394-0751 www.questjournals.org Research Paper A Comparative Histological
1. Arrows A, B, and C in the diagram below represent the processes necessary to make the energy stored in food available for muscle activity.
 1. Arrows A, B, and C in the diagram below represent the processes necessary to make the energy stored in food available for muscle activity. The correct sequence of processes represented by A, B, and
1. Arrows A, B, and C in the diagram below represent the processes necessary to make the energy stored in food available for muscle activity. The correct sequence of processes represented by A, B, and
Histology, Histochemistry and Scanning Electron Microscopy of Tonsil of the Soft Palate of the Young Pigs
 VETERINARY RESEARCH INTERNATIONAL Journal homepage: www.jakraya.com/journal/vri ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histology, Histochemistry and Scanning Electron Microscopy of Tonsil of the Soft Palate of the Young Pigs
VETERINARY RESEARCH INTERNATIONAL Journal homepage: www.jakraya.com/journal/vri ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histology, Histochemistry and Scanning Electron Microscopy of Tonsil of the Soft Palate of the Young Pigs
Epithelium tissue system
 Epithelium tissue system Histology : is the study of the microscopic anatomy (microanatomy) of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is commonly performed by examining cells and tissues under a light
Epithelium tissue system Histology : is the study of the microscopic anatomy (microanatomy) of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is commonly performed by examining cells and tissues under a light
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY. DEFINED Involves the study of function that results from disease processes.
 DEFINED Involves the study of function that results from disease processes. What is pathology? Pathology is the branch of medical sciences that treats the essential nature of disease, especially the changes
DEFINED Involves the study of function that results from disease processes. What is pathology? Pathology is the branch of medical sciences that treats the essential nature of disease, especially the changes
The structure and histochemistry of the oesophageal glands in the crab Menippe rumpmi (Frabricius) (Crustacea : Brachyura)
 Prec. Indian Aead. Sci., Vol. 88 B, Part I, Number 4, August 1979, pp. 27%285, printed in India. The structure and histochemistry of the oesophageal glands in the crab Menippe rumpmi (Frabricius) (Crustacea
Prec. Indian Aead. Sci., Vol. 88 B, Part I, Number 4, August 1979, pp. 27%285, printed in India. The structure and histochemistry of the oesophageal glands in the crab Menippe rumpmi (Frabricius) (Crustacea
Light Microscopical Examination of Glomerular Basement Membrane in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
 ANNALS OF CLINICAL AND LABORATORY SCIENCE, Vol. 8, No. 1 Copyright 1978, Institute for Clinical Science Light Microscopical Examination of Glomerular Basement Membrane in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus J.
ANNALS OF CLINICAL AND LABORATORY SCIENCE, Vol. 8, No. 1 Copyright 1978, Institute for Clinical Science Light Microscopical Examination of Glomerular Basement Membrane in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus J.
(b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food materials 2. Acidification of food (absorption of dietary Fe in small intestine) 3. Partial chemical digest
 (1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
(1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
Quantitation and Identification of Urine Mucopolysaccharides. George Gray MetBioNet Workshop 2008
 Quantitation and Identification of Urine Mucopolysaccharides George Gray MetBioNet Workshop 2008 The Big Questions What are we measuring? Where does it come from? How do we measure it? What are we measuring?
Quantitation and Identification of Urine Mucopolysaccharides George Gray MetBioNet Workshop 2008 The Big Questions What are we measuring? Where does it come from? How do we measure it? What are we measuring?
BLIZARD INSTITUTE CORE PATHOLOGY ATLAS OF TINCTORIAL STAINS
 BLIZARD INSTITUTE CORE PATHOLOGY ATLAS OF TINCTORIAL STAINS Contents Introduction... 3 Background to Tinctorial Stains... 3 Haematoxylin and Eosin Stain (H&E)... 3 Connective Tissue Stains... 4 Nucleic
BLIZARD INSTITUTE CORE PATHOLOGY ATLAS OF TINCTORIAL STAINS Contents Introduction... 3 Background to Tinctorial Stains... 3 Haematoxylin and Eosin Stain (H&E)... 3 Connective Tissue Stains... 4 Nucleic
COMPARATIVE DISTRIBUTION OF CARBOHYDRATES AND LIPID DROPLETS IN THE GOLGI APPARATUS OF INTESTINAL ABSORPTIVE CELLS
 COMPARATIVE DISTRIBUTION OF CARBOHYDRATES AND LIPID DROPLETS IN THE GOLGI APPARATUS OF INTESTINAL ABSORPTIVE CELLS JEAN A. SAGE and RALPH A. JERSILD, JR. Medical Center, Indianapolis, Indiana 46202 From
COMPARATIVE DISTRIBUTION OF CARBOHYDRATES AND LIPID DROPLETS IN THE GOLGI APPARATUS OF INTESTINAL ABSORPTIVE CELLS JEAN A. SAGE and RALPH A. JERSILD, JR. Medical Center, Indianapolis, Indiana 46202 From
