Diseases That Animals and Humans Share: The Words You Need to Know
|
|
|
- Cassandra Whitehead
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 4H1665 4ZOONOTIC DISEASE VOCABULARY ACTIVITY Diseases That Animals and Humans Share: The Words You Need to Know Skill Level: 4Beginner to advanced Life Skills: 4Communication, critical thinking and disease prevention Setting: 4An indoor space where participants can easily hear as well as lay out several vocabulary cards; seating is optional Time: minutes Materials: Diseases That Animals and Humans Share: The Words You Need to Know vocabulary cards for activity: 412 cards for beginner participants 436 cards for advanced participants (set of 12 also used in beginning) 48 sticky notes 1 permanent marker Scissors Overview: The Diseases That Animals and Humans Share: The Words You Need to Know lesson is designed to give participants a basic understanding of essential vocabulary related to zoonotic diseases that may be unclear or misunderstood. The lesson features a matching game to help give participants an understanding of the vocabulary words as well as the importance of zoonotic awareness. Objective: After completing this activity, participants will be able to: 4Determine the definition of each zoonotic vocabulary word used. 4Match correct terms with definitions. 4Understand each vocabulary word when used in a sentence. PROCEDURE: Before the meeting: 1. Review the lesson and verify that you have all the vocabulary cards necessary for the activity. Study the vocabulary words and the given definitions to be prepared for the activity. Tables 1 and 2 on page 2 list the vocabulary words and give an example of each used in a sentence. When a participant is confused about a word, use the tables to read an example sentence that contains its proper use. Tables 3 and 4 on pages 3 list the vocabulary words and their definitions. Keep these tables handy for yourself for quick reference. 2. Separate beginner cards from advanced cards. Pair each definition up with its appropriate vocabulary word and lay out the pairs for both groups. You will need these pairs for the introductory exercise. 3. If you do not have a prepared set of vocabulary cards, prepare them by the following methods: A. Cut apart the included cards for the beginner and advanced level participants located at the end of this lesson. B. Beginning at 1, write the numbers 1 through 12 on sticky notes (one number per note using the permanent marker). C. Beginning at 1, write the numbers 1 through 36 on sticky notes (one number per note using the permanent marker). D. Place one number on the opposite site of printing for each set of cards (beginner 1-12, advanced 1-36). E. If you re concerned about knowing the correct definition of a term, keep Tables 3 and 4 handy. 4. Make sure that you have enough space for one or two groups to lay out all of their cards. 4-H Animal Science Anywhere Michigan 4-H Youth Development Michigan State University Extension Copyright 2016 Michigan State University Board of Trustees. Michigan State University is an affirmative action/equal opportunity employer. 1
2 4ZOONOTIC DISEASE VOCABULARY ACTIVITY Table 1. Diseases That Animals and Humans Share: The Words You Need to Know Sentence Examples (Beginner) Vocabulary Word Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) disease outbreak epidemiologist pathogen sterilize zoonotic Proper Use in a Sentence The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention worked hard to educate Americans about Ebola during the West African outbreak. In the past few years, there has been a troubling disease outbreak of porcine epidemic diarrhea on swine farms in the United States. Jackie wants to become an epidemiologist and study influenza. The spread of pathogens can be prevented by washing your hands with soap and water. Sterilize laboratory equipment before use to prevent contamination with unwanted germs. Rabies is a serious zoonotic disease that can be transmitted to humans through a bite from an infected animal. Table 2. Diseases That Animals and Humans Share: The Words You Need to Know Sentence Examples (Advanced) Vocabulary Word bacteria blood-borne pathogen Proper Use in a Sentence For bacteria to grow there must be nutrients, moisture, oxygen (in most cases) and an appropriate temperature. Malaria is a blood-borne pathogen that affects people and is spread by mosquitoes. E. Coli The swine became sick from E. Coli after drinking water contaminated with fecal matter. fomite foodborne illness fungi incubation period influenza microorganism quarantine Salmonella state veterinarian symptoms United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) vaccination vector virus withdrawal period You should disinfect fomites, such as boots, in-between farm visits. One of the most common foodborne illnesses in the United States is salmonellosis, caused by germs that are generally found in raw meat or eggs. The yeast used to help bread rise is actually a type of fungi. The incubation period for rabies is around 1 to 3 months from the time of the bite to when symptoms begin to show. H1N1 is a particularly dangerous strain of influenza. Microorganisms are responsible for many illnesses. When a farm is quarantined, there should be no movement of infected animals from that location, and no healthy animals should be introduced to that farm until the quarantine is lifted. It is possible to contract salmonella from eating raw cookie dough due to the germs in the raw eggs. The State Veterinarian s Office investigates the cause of a disease outbreak in animals by employing epidemiologists. A stuffy nose is a symptom of the common cold. The United States Department of Agriculture helps farmers affected by drought, floods, pest infestations and other harmful events. It is extremely important for everyone to stay up to date on vaccinations for their health and the health of those around them. Mosquitos can be vectors for disease, carrying pathogens from one host to the next when they take a blood meal. There are 15 types of avian flu viruses that affect birds. After a dairy cow is treated with antibiotics for a mastitis infection, she must go through a withdrawal period during which her milk is not used for human consumption. 2 4-H Animal Science Anywhere Michigan 4-H Youth Development Michigan State University Extension Copyright 2016 Michigan State University Board of Trustees. Michigan State University is an affirmative action/equal opportunity employer.
3 4ZOONOTIC DISEASE VOCABULARY ACTIVITY Table 3. Diseases That Animals and Humans Share: The Words You Need to Know Vocabulary Words (Beginner) Vocabulary Word zoonotic pathogen epidemiologist disease outbreak Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) sterilize Definition A disease that can spread from animals to people. Something such as a virus or bacterium that causes disease. A specialist in diseases that affect groups of people or animals. When many people or animals in a specific area become ill in greater numbers than normal. Government agency that protects the health, safety and security of Americans from disease threats. To make free from living microorganisms by using physical or chemical agents. Table 4. Diseases That Animals and Humans Share: The Words You Need to Know Vocabulary Words (Advanced) Vocabulary Word microorganism virus influenza Salmonella Definition A microscopic living organism that can be single or multi celled. Small infectious agent that can only reproduce inside the host cell it infects. A highly contagious respiratory disease. Bacteria that often cause food poisoning in humans, commonly found in chicken and egg products. E. Coli (Escherichia coli) Bacteria that often affect the intestinal track (gut) and cause severe diarrhea, and are associated with fecal contamination. foodborne illness vector quarantine bacteria fungi blood-borne pathogen incubation period vaccination United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) symptoms withdrawal period state veterinarian fomite Sickness caused by food contaminated with bacteria, parasites or viruses. A living organism (usually a biting insect) that can transfer a disease from one animal or plant to another. Separation and restriction of the movement of people or animals that may have been exposed to an infectious disease to see if they become sick. Single-celled (Prokaryotic) living microorganisms that can cause disease. Multi-celled (Eukaryotic) organisms such as yeasts, molds and mushrooms. A microorganism in blood that can cause disease, usually transferred by needles or biting insects. The time between being exposed to a pathogen and when symptoms begin. A harmless version of a microorganism that is introduced to humans or animals to help stimulate immunity, making them resistant to infection by that microorganism. A government agency focused on food, agriculture, natural resources, rural development, nutrition and the public policy related to these issues. Physical changes in an animal or person caused by a pathogen that are often non-specific (for example, fever, body aches) that may indicate disease being present. The amount of time it takes for medicine given to a production animal to decrease to a safe, acceptable level so the animal can be milked or harvested for food. The person in charge of receiving notification of reportable animal diseases from all laboratories and veterinarians in the state. An object such as a car, boots or even door knobs, that can help carry pathogens from one location to another. 4-H Animal Science Anywhere Michigan 4-H Youth Development Michigan State University Extension Copyright 2016 Michigan State University Board of Trustees. Michigan State University is an affirmative action/equal opportunity employer. 3
4 During the meeting: 1. Introduce the activity by reading aloud or paraphrasing the following: Often times, the things we cannot see make humans and animals sick. Being able to understand the risks associated with diseases allows us to be better caretakers of ourselves as well as of production and companion animals. Today, we are going to learn about some of the words that describe health and illness for humans and animals. To start, what is a pathogen? 2. Allow participants time to consider the question and then gather answers from volunteers. 3. Read aloud or paraphrase the following: A pathogen is something such as a virus or a bacterium that causes disease. Illnesses caused by pathogens can spread quickly through a herd or flock, or from animal to human or human to animal. Knowing what the words mean can help you to understand veterinarians (doctors who care for animals) as well as prepare yourself for raising and caring for animals. Today, you will be learning key vocabulary words that allow you to better understand the risks posed to you and your animals. 4. Read aloud or paraphrase the following: To get started, we are going to look at five more definitions. You may have heard or read about an agency called the CDC. CDC is an acronym that stands for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, a government agency that protects the health, safety and security of Americans from disease threats. For example, the CDC has helped ill and healthy people when they enter the United States from places in West Africa where there is concern about Ebola virus disease. Ebola is actually a zoonotic disease that can also be spread person to person. Does anyone know what zoonotic means? 5. Allow participants time to consider the question and then gather answers from volunteers. 6. Read aloud or paraphrase the following: 4ZOONOTIC DISEASE VOCABULARY ACTIVITY Zoonotic or zoonosis refers to a disease that can be spread from animals to humans. Because people are around animals so much, we must know the risks and take preventive measures to keep both our animals and ourselves healthy. Epidemiologists help keep everyone healthy. These are scientists who specialize in diseases that affect groups of people or animals. They investigate patterns and causes of disease in humans. They mostly study any sudden increase in the presence of a disease (when many people or animals in a specific area become ill in greater numbers than normal), which is called a disease outbreak. If you are counting, we have already reviewed five words so that leaves one more: sterilize. To sterilize means to remove living microorganisms by using physical or chemical agents. 4 4-H Animal Science Anywhere Michigan 4-H Youth Development Michigan State University Extension Copyright 2016 Michigan State University Board of Trustees. Michigan State University is an affirmative action/equal opportunity employer.
5 7. Pass out the 12 cards from the beginner portion of the lesson (6 vocabulary words and 6 corresponding definitions). Have participants work as a group to match the individual holding the vocabulary word to the individual holding the correct definition. If you have less than 12 people, use less cards, making sure that the correct definitions and vocabulary words are included in those that are passed out. You may have more cards than you have participants. If so, just make sure each participant has a card. If you have fewer cards than participants or an odd number of participants then they may pair up and have one word or definition for two people. 8. Read aloud or paraphrase the following: Now we are going to apply what we just learned. Twelve of you are going to get a card. Once you have your card, you are to work as a large group to match the individual holding the vocabulary word to the individual holding the correct definition. Once the match is complete, link arms. You have 2 minutes starting now. 9. Once the group has matched each individual holding the vocabulary word to each individual holding the corresponding definition, announce that time is up. Check that participants have matched the correct word with its definition. Use the six Diseases That Animals and Humans Share: The Words You Need to Know Vocabulary Words (Beginner) as your key. If partners are paired incorrectly, allow them to switch to a new partner, but do not give the correct answer. Check pairs again and assist participants as needed. Once all pairs are matched, go around the circle of pairs and have a participant in each pair read the vocabulary word and definition. 10. If you are working with young participants, skip to step 13. If you are working with advanced participants, continue here by reading aloud or paraphrasing the following: Knowing the definition ahead of time makes a matching game much easier. Now let s try a little tougher version. Each of you will get one card and without being told the definition ahead of time, you will be asked to go find your match. Just like before, once you have your cards, individuals holding a vocabulary word will need to match up with the individual holding the corresponding definition. Once the match is complete, link arms. You have 4 minutes starting now. 4ZOONOTIC DISEASE VOCABULARY ACTIVITY 11. Once all individuals holding vocabulary words match up with individuals with corresponding definitions, announce that time is up. Check that participants have matched the correct word with its definition. Use the 36 Diseases That Animals and Humans Share: The Words You Need to Know Vocabulary Words (Advanced) as your key. If any are incorrect, allow them to switch to a new partner, but do not give the correct answer. If participants seem to struggle with the matching, assist them by providing the answer or asking other participants to assist them to make the match correct. Once all pairs are matched, go around the circle of pairs and have a participant in each pair read the vocabulary word and definition. 12. To increase retention, have participants place all of the pairs in a pile and then form a circle. Pass out the cards in random order so that participants most likely get a new card. Announce that you are going to try the same activity again providing 4 minutes for them to find their match. Follow the instructions in step 11 to determine correct answers. Repeating the definitions as a group is optional. 4-H Animal Science Anywhere Michigan 4-H Youth Development Michigan State University Extension Copyright 2016 Michigan State University Board of Trustees. Michigan State University is an affirmative action/equal opportunity employer. 5
6 4ZOONOTIC DISEASE VOCABULARY ACTIVITY 13. Read aloud or paraphrase the following: Building our vocabulary takes time, but all of you are doing great. Next, we are going to try a matching game using the same vocabulary words. On my signal, please number off with every other person being a one or a two. Then the ones will be on my right (We will call them Team 1) and twos on my left (We will call them Team 2). You will work together as a group taking turns to match the correct vocabulary word with its definition. Go ahead and number off and move to your new team. Example of card layout for a beginner game version using a prepared card set. A match has been turned over. Example of card layout for an advanced game version using a prepared card set. 14. While participants are numbering off, place the cards in a random order on a hard surface such as a table or floor in a grid pattern so that the cards are easy to flip over. 15. Read aloud or paraphrase the following: Now time for the game! To play, we will alternate with Team 1 and Team 2 taking turns trying to find matches. When I say go, Team 1 should flip up two cards at a time as a team. (Members can take turns flipping or choose a team captain to do it.) If the team believes they have a definition and its correctly matching vocabulary word, set both cards aside. If it is not a correct pair (that is, two definitions or the wrong vocabulary word for the definition), flip both cards back over and allow Team 2 to try. You will repeat this until we match all of the definitions to the correct vocabulary word. 16. Each time a new vocabulary word is flipped, use both the beginner and advanced versions of Diseases That Animals and Humans Share: The Words You Need to Know Sentence Examples to say the word in a sentence. Repeat words and sentences if desired to assist participants in making matches. If needed, assist participants by telling them it is not the correct answer so that the game keeps moving. 17. Once this portion of the game is complete, consider allowing the beginner participants to add in some of the advanced words. If desired, count off by ones and twos again to create new teams, and repeat the game to increase retention. 18. Read aloud or paraphrase the following: Today we have learned about just some of the terms that professionals in agriculture discuss every day. Being able to understand the terminology allows for you as consumers and producers to make educated decisions. These decisions help you in preventing disease outbreaks and enable you to better understand animal and human health concerns. 6 4-H Animal Science Anywhere Michigan 4-H Youth Development Michigan State University Extension Copyright 2016 Michigan State University Board of Trustees. Michigan State University is an affirmative action/equal opportunity employer.
7 4ZOONOTIC DISEASE VOCABULARY ACTIVITY ADAPTATIONS & EXTENSIONS: 4 To ensure that participants are not memorizing numbers, change the number on the card by writing a new number on a sticky note and placing it on the card. Make notes on your sheet if needed to help serve as the key. 4 Take portions of the lesson and use them at county fairs to increase zoonotic disease literacy of fairgoers and participants. 4 For older or more experienced participants: Have all cards face up so that the vocabulary word and definition are visible. Time each participant to see how quickly and accurately they can pair the word and definition. For a larger audience, adapt steps to number participants into additional teams so that participants are more active. Consider dividing the cards if needed to have smaller matching games if additional volunteers are available to assist with running the game. Form teams and allow each team to work together to match the vocabulary word to the definition and time how long it takes to accurately complete the task. If working with a smaller group, create an additional card and allow participants to play a version of Old Maid. Begin by handing out an equal number of cards to each player. To play, begin with one person and then each player takes turns offering a card to the person on the left. That person selects a card and adds it to his or her cards. This player then sees if the selected card matches the definition of any of his or her original cards. If so, the vocabulary word and definition is discarded face up as well. Other players approve the definition and then the player who just took a card then offers his or her hand to the person to the left and so on. 4 For younger or less experienced participants: Have participants draw pictures as a group or individually of what they believe each of the six beginner vocabulary words would look like. For example, they would draw people to present the CDC staff working to learn more. Compare drawings at the end to help increase understanding. Over time, add in additional cards to the game by selecting cards from the advanced card group to increase vocabulary of participants. To increase readability, take the included terms and definitions in Table 3 and print each out on a separate sheet of paper. Number each sheet 1 through 12 and then place the sheets on the floor so that participants can read the sheets from a distance when playing the matching game. TALKING IT OVER: Ask the group the following questions. 4 What is a zoonotic disease? Why should we continue to learn more about them? 4 How might some of these vocabulary words help you in working with agricultural youth organizations? 4 What are some careers relating to animal and human health? 4 Based on what you learned, what are some things you can do to help keep you and your animals healthy? 4-H Animal Science Anywhere Michigan 4-H Youth Development Michigan State University Extension Copyright 2016 Michigan State University Board of Trustees. Michigan State University is an affirmative action/equal opportunity employer. 7
8 4ZOONOTIC DISEASE VOCABULARY ACTIVITY ALIGNMENT TO SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING PRACTICES: How 4-H Increases Science Literacy Nationally and in Michigan, 4-H has long enjoyed a reputation for engaging young people in positive, experiential (hands-on), and nonformal activities that are inquiry based. The activities in the 4-H Animal Science Anywhere series can be used to enhance classroom science education. The activities are aligned with the eight Scientific and Engineering Practices from A Framework for K 12 Science Education (National Research Council, 2012, p. 42). The activities in 4-H Animal Science Anywhere: Diseases That Animals and Humans Share The Words You Need to Know were evaluated for their alignment with the Science and Engineering practices by Michigan State University (MSU) Extension Educator Tracy D Augustino in Table 5. How This Lesson Aligns With the Science and Engineering Practices (National Research Council, 2012, p. 42) Science & Engineering Practice Action Activity Step 4 Asking questions and defining problems 4 Developing and using models 4 Planning and carrying out investigations Participants brainstorm possible definitions for the words pathogen and zoonotic. 4 Analyzing and interpreting data Participants discuss the need to know the specialized vocabulary of different fields and how this knowledge might help them. Participants apply the knowledge they gain while learning the vocabulary to discuss things they can do to keep themselves and their animals healthy. 4 Using mathematics and computational thinking 4 Constructing explanations and designing solutions 4 Engaging in argument from evidence 4 Obtaining, evaluating, and communicating information Participants obtain information (new vocabulary words), discuss the words and their implications, then communicate this information with each other and with other young people at the fair or other events. 1 2, 4 5 Talking It Over Whole lesson 8 4-H Animal Science Anywhere Michigan 4-H Youth Development Michigan State University Extension Copyright 2016 Michigan State University Board of Trustees. Michigan State University is an affirmative action/equal opportunity employer.
9 REFERENCES & RESOURCES: Michigan 4-H Youth Development. (2014). Be a zoonotic disease detective (4H1671; adapted from Georgia 4-H original). East Lansing: Michigan State University, MSU Extension. National Center for Infectious Diseases. (2008). Teachers tools: Educational resources for teachers at k-12 levels. Atlanta, GA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved from United States Department of Agriculture. (2014). Animal health. Washington DC: Author. Retrieved from portal/usda/usdahome?navid=animal_health ACKNOWLEDGMENTS: Author: 4 Hannah Piper, Michigan State University Undergraduate Student, Class of Julie Thelen, 4-H Livestock and Veterinary Science Educator, Michigan State University Extension This bulletin was produced by ANR Communications and Marketing (anrcom.msu.edu) for MSU Extension (msue.anr.msu.edu) 4ZOONOTIC DISEASE VOCABULARY ACTIVITY Diseases That Animals and Humans Share: The Words You Need to Know 2016 by Michigan State University Board of Trustees. 4-H and Cooperative Extension System groups and other nonprofit educational groups may print up to 25 hard copies of this material for noncommercial, educational use, provided that attribution is given to Michigan State University. All other rights reserved. For information, contact 4-H Youth Development, 108 Agriculture Hall, 446 West Circle Drive, East Lansing, MI MSU is an affirmative-action, equal-opportunity employer, committed to achieving excellence through a diverse workforce and inclusive culture that encourages all people to reach their full potential. Michigan State University Extension programs and materials are open to all without regard to race, color, national origin, gender, gender identity, religion, age, height, weight, disability, political beliefs, sexual orientation, marital status, family status or veteran status. Issued in furtherance of MSU Extension work, acts of May 8 and June 30, 1914, in cooperation with the U.S. Department of Agriculture. Jeffrey W. Dwyer, Director, MSU Extension, East Lansing, MI This information is for educational purposes only. Reference to commercial products or trade names does not imply endorsement by MSU Extension or bias against those not mentioned. The 4-H Name and Emblem have special protections from Congress, protected by code 18 USC P 1R Web 09:2017 PA/MR WCAG H Animal Science Anywhere Michigan 4-H Youth Development Michigan State University Extension Copyright 2016 Michigan State University Board of Trustees. Michigan State University is an affirmative action/equal opportunity employer. 9
10 zoonotic pathogen
11 A specialist in diseases that affect groups of people or animals. disease outbreak
12 Government agency that protects the health, safety and security of Americans from disease threats. To make free from living microorganisms by using physical or chemical agents.
13 When many people or animals in a specific area become ill in greater numbers than normal. A disease that can spread from animals to people.
14 sterilize Something such as a virus or bacterium that causes disease.
15 epidemiologist Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
16 A microscopic living organism that can be single or multi celled. Sickness caused by food contaminated with bacteria, parasites or viruses.
17 The time between being exposed to a pathogen and when symptoms begin. The amount of time it takes for medicine given to a production animal to decrease to a safe, acceptable level so the animal can be milked or harvested for food.
18 fomite virus
19 microorganism Small infectious agent that can only reproduce inside the host cell it infects.
20 A highly contagious respiratory disease. Bacteria that often cause food poisoning in humans, commonly found in chicken and egg products.
21 Bacteria that often affect the intestinal track (gut) and cause severe diarrhea, and are associated with fecal contamination. Salmonella
22 A living organism (usually a biting insect) that can transfer a disease from one animal or plant to another. Separation and restriction of the movement of people or animals that may have been exposed to an infectious disease to see if they become sick.
23 blood-borne pathogen fungi
24 A microorganism in blood that can cause disease, usually transferred by needles or biting insects. influenza
25 vaccination A government agency focused on food, agriculture, natural resources, rural development, nutrition and the public policy related to these issues.
26 symptoms E. Coli (Escherichia coli)
27 The person in charge of receiving notification of reportable animal diseases from all laboratories and veterinarians in the state. An object such as a car, boots or even door knobs, that can help carry pathogens from one location to another.
28 foodborne illness vector
29 Multi-celled (Eukaryotic) organisms such as yeasts, molds and mushrooms. quarantine
30 A harmless version of a microorganism that is introduced to humans or animals to help stimulate immunity, making them resistant to infection by that microorganism. Physical changes in an animal or person caused by a pathogen that are often non-specific (for example, fever, body aches) that may indicate disease being present.
31 United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) bacteria
32 Single-celled (Prokaryotic) living microorganisms that can cause disease. incubation period
33 withdrawal period state veterinarian
34
35 BE A ZOONOTIC 1 BE A ZOONOTIC 2
36 BE A ZOONOTIC 3 BE A ZOONOTIC 4
37 BE A ZOONOTIC 5 BE A ZOONOTIC 6
38 BE A ZOONOTIC 7 BE A ZOONOTIC 8
39 BE A ZOONOTIC 9 BE A ZOONOTIC 10
40 BE A ZOONOTIC 11 BE A ZOONOTIC 12
41 BE A ZOONOTIC 13 BE A ZOONOTIC 14
42 BE A ZOONOTIC 15 BE A ZOONOTIC 16
43 BE A ZOONOTIC 17 BE A ZOONOTIC 18
44 BE A ZOONOTIC 19 BE A ZOONOTIC 20
45 BE A ZOONOTIC 21 BE A ZOONOTIC 22
46 BE A ZOONOTIC 23 BE A ZOONOTIC 24
47 BE A ZOONOTIC 25 BE A ZOONOTIC 26
48 BE A ZOONOTIC 27 BE A ZOONOTIC 28
49 BE A ZOONOTIC 29 BE A ZOONOTIC 30
50 BE A ZOONOTIC 31 BE A ZOONOTIC 32
51 BE A ZOONOTIC 33 BE A ZOONOTIC 34
52 BE A ZOONOTIC 35 BE A ZOONOTIC 36
53 BE A ZOONOTIC 37 BE A ZOONOTIC 38
54 BE A ZOONOTIC 39 BE A ZOONOTIC 40
55 BE A ZOONOTIC 41 BE A ZOONOTIC 42
56 BE A ZOONOTIC 43 BE A ZOONOTIC 44
57 BE A ZOONOTIC 45 BE A ZOONOTIC 46
58 BE A ZOONOTIC 47 BE A ZOONOTIC 48
59 BE A ZOONOTIC 49 BE A ZOONOTIC 50
Why care about Zoonotic Diseases?
 Why care about Zoonotic Diseases? Julie Thelen - MSU Extension 4-H Livestock & Veterinary Science Educator Nancy Thelen - MSU Extension Agricultural Literacy Educator MSU is an affirmativeaction, equal-opportunity
Why care about Zoonotic Diseases? Julie Thelen - MSU Extension 4-H Livestock & Veterinary Science Educator Nancy Thelen - MSU Extension Agricultural Literacy Educator MSU is an affirmativeaction, equal-opportunity
Basics of Biosecurity
 4H1661 4BIOSECURITY ACTIVITY Basics of Biosecurity Skill Level: 4Beginner to intermediate Life Skills: 4Communication, critical thinking and disease prevention Setting: 4An outdoor or indoor space where
4H1661 4BIOSECURITY ACTIVITY Basics of Biosecurity Skill Level: 4Beginner to intermediate Life Skills: 4Communication, critical thinking and disease prevention Setting: 4An outdoor or indoor space where
Bridging Human and Animal Health
 4H1690 4CAREERS ACTIVITY Bridging Human and Animal Health Overview: The Careers Bridging Human and Animal Health lesson is designed to encourage participant discussion of careers in human and animal health.
4H1690 4CAREERS ACTIVITY Bridging Human and Animal Health Overview: The Careers Bridging Human and Animal Health lesson is designed to encourage participant discussion of careers in human and animal health.
Section One: Background Material
 Section One: Background Material What is the problem? Every day people all over the world get sick from the food they eat. This sickness is called foodborne disease and is caused by dangerous microorganisms
Section One: Background Material What is the problem? Every day people all over the world get sick from the food they eat. This sickness is called foodborne disease and is caused by dangerous microorganisms
The Science of Maryland Agriculture
 Edition 3 (2016) GOAL STATEMENT: Students will gain an understanding of biosecurity and develop a biosecurity plan for a hypothetical livestock production facility. OBJECTIVES: Students will define biosecurity.
Edition 3 (2016) GOAL STATEMENT: Students will gain an understanding of biosecurity and develop a biosecurity plan for a hypothetical livestock production facility. OBJECTIVES: Students will define biosecurity.
MICROORGANISM NORMAL FLORA AND PATHOGENS
 MICROORGANISMS: NORMAL FLORA AND PATHOGENS BELL WORK- GO TO PAGE 468 IN NEW BOOK; READ THE GIVEN DEFINITIONS AND FIRST THREE PARAGRAPHS AND GIVE A BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE FOLLOWING: MICROORGANISM PATHOGENIC
MICROORGANISMS: NORMAL FLORA AND PATHOGENS BELL WORK- GO TO PAGE 468 IN NEW BOOK; READ THE GIVEN DEFINITIONS AND FIRST THREE PARAGRAPHS AND GIVE A BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE FOLLOWING: MICROORGANISM PATHOGENIC
Information About H3N2v
 Information About H3N2v James R. Ginder, MS, NREMT,PI,CHES,NCEE Health Education Specialist Hamilton County Health Department www.hamiltoncounty.in.gov Mary Jo Skinner, RN, BSN, MBA Public Health Nurse
Information About H3N2v James R. Ginder, MS, NREMT,PI,CHES,NCEE Health Education Specialist Hamilton County Health Department www.hamiltoncounty.in.gov Mary Jo Skinner, RN, BSN, MBA Public Health Nurse
Communicable and Noncommunicable. Diseases
 Communicable and Noncommunicable Diseases After this lesson you will be able to: Compare and contrast between noncommunicable and communicable diseases Define the common pathogens that cause communicable
Communicable and Noncommunicable Diseases After this lesson you will be able to: Compare and contrast between noncommunicable and communicable diseases Define the common pathogens that cause communicable
Examining the Milk Production System of Dairy Cows
 4H1666 4MAMMARY GLAND ANATOMY ACTIVITY Examining the Milk Production System of Dairy Cows Alveoli Lobule containing alveoli Connective tissue Major duct Ducts Gland cistern Teat cistern Teat meatus Lobe
4H1666 4MAMMARY GLAND ANATOMY ACTIVITY Examining the Milk Production System of Dairy Cows Alveoli Lobule containing alveoli Connective tissue Major duct Ducts Gland cistern Teat cistern Teat meatus Lobe
Germs. Grade Level: 1-2
 Germs Grade Level: 1-2 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 5 Activity Page pages 6 Practice Page page 7 Homework Page page 8-9 Answer Key page 10 Classroom Procedure: 1. Ask: If you
Germs Grade Level: 1-2 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 5 Activity Page pages 6 Practice Page page 7 Homework Page page 8-9 Answer Key page 10 Classroom Procedure: 1. Ask: If you
Disease Detectives 60-Minute Health & Life Science Lesson Interactive Video Conference Grades: Disease Detectives: An Exercise In Epidemiology
 Disease Detectives 60-Minute Health & Life Science Lesson Interactive Video Conference Grades: 6-12 TEACHER GUIDE Disease Detectives: An Exercise In Epidemiology Description This just in: Nearly half of
Disease Detectives 60-Minute Health & Life Science Lesson Interactive Video Conference Grades: 6-12 TEACHER GUIDE Disease Detectives: An Exercise In Epidemiology Description This just in: Nearly half of
ARTMENT REPUBLIC OF SOUTH AFRICA. Newcastle disease ADRIAAN OLIVIER
 DEPAR ARTMENT TMENT: AGRICULTURE REPUBLIC OF SOUTH AFRICA Newcastle disease ADRIAAN OLIVIER Information provided by Animal Health for Developing Farmers, ARC-Onderstepoort Veterinary Institute, Private
DEPAR ARTMENT TMENT: AGRICULTURE REPUBLIC OF SOUTH AFRICA Newcastle disease ADRIAAN OLIVIER Information provided by Animal Health for Developing Farmers, ARC-Onderstepoort Veterinary Institute, Private
Preparing for a Pandemic: What Parents Need to Know About Seasonal and Pandemic Flu
 Preparing for a Pandemic: What Parents Need to Know About Seasonal and Pandemic Flu A Message from the Health Officer An influenza, or flu, pandemic happens when a new flu virus appears that easily spreads
Preparing for a Pandemic: What Parents Need to Know About Seasonal and Pandemic Flu A Message from the Health Officer An influenza, or flu, pandemic happens when a new flu virus appears that easily spreads
MSU Extension Publication Archive. Scroll down to view the publication.
 MSU Extension Publication Archive Archive copy of publication, do not use for current recommendations. Up-to-date information about many topics can be obtained from your local Extension office. Testing
MSU Extension Publication Archive Archive copy of publication, do not use for current recommendations. Up-to-date information about many topics can be obtained from your local Extension office. Testing
A. No. There are no current reports of avian influenza (bird flu) in birds in the U.S.
 Bird Flu FAQ 2 Frequently Asked Avian Influenza Questions Avian influenza in birds Q. What is avian influenza? A. Avian influenza is an infectious disease of birds caused by type A strains of the influenza
Bird Flu FAQ 2 Frequently Asked Avian Influenza Questions Avian influenza in birds Q. What is avian influenza? A. Avian influenza is an infectious disease of birds caused by type A strains of the influenza
Warm Up. What do you think the difference is between infectious and noninfectious disease?
 Warm Up What do you think the difference is between infectious and noninfectious disease? Infectious Diseases Chapter 14 Lesson 1: Types of Infectious Disease Infectious Diseases An infectious disease
Warm Up What do you think the difference is between infectious and noninfectious disease? Infectious Diseases Chapter 14 Lesson 1: Types of Infectious Disease Infectious Diseases An infectious disease
AOHS Global Health. Unit 1, Lesson 3. Communicable Disease
 AOHS Global Health Unit 1, Lesson 3 Communicable Disease Copyright 2012 2016 NAF. All rights reserved. A communicable disease is passed from one infected person to another The range of communicable diseases
AOHS Global Health Unit 1, Lesson 3 Communicable Disease Copyright 2012 2016 NAF. All rights reserved. A communicable disease is passed from one infected person to another The range of communicable diseases
Infectious Disease. Unit 6 Lesson 1
 Infectious Disease Unit 6 Lesson 1 Reminder Getting Started Pick up your Infectious Disease Notes Objectives Identify five types of infectious agents Describe ways in which infections can spread Explain
Infectious Disease Unit 6 Lesson 1 Reminder Getting Started Pick up your Infectious Disease Notes Objectives Identify five types of infectious agents Describe ways in which infections can spread Explain
Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza:
 United States Department of Agriculture Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service Program Aid No. 1704 Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza: A Threat to U.S. Poultry A Threat to U.S. Poultry Worldwide, there
United States Department of Agriculture Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service Program Aid No. 1704 Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza: A Threat to U.S. Poultry A Threat to U.S. Poultry Worldwide, there
Health & Family Medicare Newsletter Fall 2010
 Health & Family Medicare Newsletter Fall 2010 We are Here to Help You In This Issue We are Here to Help You pg 1 Flu Season is Here! pg 2 HIV Screening pg 3 Spark a New Healthier You! pg 4 Quality of Care
Health & Family Medicare Newsletter Fall 2010 We are Here to Help You In This Issue We are Here to Help You pg 1 Flu Season is Here! pg 2 HIV Screening pg 3 Spark a New Healthier You! pg 4 Quality of Care
Germs! Germs! Everywhere!
 Germs! Germs! Everywhere! Introduction Microorganisms, sometimes called microbes, are tiny living creatures that cannot be seen without a microscope. There are microscopic animals, plants, and fungi, as
Germs! Germs! Everywhere! Introduction Microorganisms, sometimes called microbes, are tiny living creatures that cannot be seen without a microscope. There are microscopic animals, plants, and fungi, as
About the Authors. Table of Contents. Learn more
 Ask A Biologist activity for classroom and home By Julie Dunlap, Esmeralda Manzano, Vanessa Vierkoetter, and Satina Sund Table of Contents Experiment Overview 2 Teaching Tips 4 Tree map 6 Cold and Flu
Ask A Biologist activity for classroom and home By Julie Dunlap, Esmeralda Manzano, Vanessa Vierkoetter, and Satina Sund Table of Contents Experiment Overview 2 Teaching Tips 4 Tree map 6 Cold and Flu
Chapter 2 Keeping Food Safe
 Chapter 2 Keeping Food Safe Copyright 2011 by the National Restaurant Association Educational Foundation (NRAEF) and published by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 2.1 Introduction to Food Safety
Chapter 2 Keeping Food Safe Copyright 2011 by the National Restaurant Association Educational Foundation (NRAEF) and published by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 2.1 Introduction to Food Safety
Grade 2: Historical Lesson Lesson 8: Louis Pasteur, Andrew Taylor Still, and the Digestive System
 Grade 2: Historical Lesson Lesson 8: Louis Pasteur, Andrew Taylor Still, and the Digestive System Objectives: Students will obtain information about the discoveries and contribution made by Louis Pasteur
Grade 2: Historical Lesson Lesson 8: Louis Pasteur, Andrew Taylor Still, and the Digestive System Objectives: Students will obtain information about the discoveries and contribution made by Louis Pasteur
Five Features of Fighting the Flu
 Five Features of Fighting the Flu Public Health Emergency Preparedness Pandemic Influenza Prevention Curriculum Grades 9-12 1 Day One Understand the Flu Virus 2 Five Features of Flu Fighting Code 1: Understand
Five Features of Fighting the Flu Public Health Emergency Preparedness Pandemic Influenza Prevention Curriculum Grades 9-12 1 Day One Understand the Flu Virus 2 Five Features of Flu Fighting Code 1: Understand
2 WHAT do WE KNoW ABoUT flu?
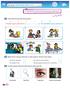 WHAT do WE KNoW ABoUT flu? Joe and Sarah learn about flu. We are going to study flu too. Think about flu and order these pictures. 3 4 5 6 The easiest way to catch the flu The most difficult way to catch
WHAT do WE KNoW ABoUT flu? Joe and Sarah learn about flu. We are going to study flu too. Think about flu and order these pictures. 3 4 5 6 The easiest way to catch the flu The most difficult way to catch
Texas Animal Health Commission (TAHC)
 Texas Animal Health Commission (TAHC) September 7, 2012 Attention Swine Exhibitors: The 2012 Texas fair and rodeo season is right around the corner. The Texas Pork Producers Association, the Texas Animal
Texas Animal Health Commission (TAHC) September 7, 2012 Attention Swine Exhibitors: The 2012 Texas fair and rodeo season is right around the corner. The Texas Pork Producers Association, the Texas Animal
DO NOT TURN THE PAGE UNTIL THE EVENT LEADER TELLS YOU TO!
 DISEASE DETECTIVES DIRECTIONS DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST!! All answers must be written on your response sheet. This test is long. You may wish to divide the test between you. If you take the pages out of
DISEASE DETECTIVES DIRECTIONS DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST!! All answers must be written on your response sheet. This test is long. You may wish to divide the test between you. If you take the pages out of
SEPUP ITEM BANK. Item Banks TR-253. Multiple choice. Circle the best answer.
 Item Banks Name: Teacher: School: Date: SEPUP ITEM BANK UNIT C: CELL BIOLOGY AND DISEASE Multiple choice. Circle the best answer. 1. Which of the following graphs best represents how an infectious disease
Item Banks Name: Teacher: School: Date: SEPUP ITEM BANK UNIT C: CELL BIOLOGY AND DISEASE Multiple choice. Circle the best answer. 1. Which of the following graphs best represents how an infectious disease
Influenza A (H1N1) Fact Sheet
 What is Influenza A (H1N1)? Influenza A (H1N1) (referred to as swine flu early on) is a new influenza virus. This virus is spreading from person- to-person, probably in much the same way that regular seasonal
What is Influenza A (H1N1)? Influenza A (H1N1) (referred to as swine flu early on) is a new influenza virus. This virus is spreading from person- to-person, probably in much the same way that regular seasonal
4-H Market Swine Record Book
 Northwestern Michigan Fair 4-H Market Swine Record Book For ages 12 and Older Name: Age: Address: Street Town Zip Code Name of 4-H Club: Years in the Swine project: Years in 4-H: Animal s Name: Buyer s
Northwestern Michigan Fair 4-H Market Swine Record Book For ages 12 and Older Name: Age: Address: Street Town Zip Code Name of 4-H Club: Years in the Swine project: Years in 4-H: Animal s Name: Buyer s
Communicable diseases. Gastrointestinal track infection. Sarkhell Araz MSc. Public health/epidemiology
 Communicable diseases Gastrointestinal track infection Sarkhell Araz MSc. Public health/epidemiology Communicable diseases : Refer to diseases that can be transmitted and make people ill. They are caused
Communicable diseases Gastrointestinal track infection Sarkhell Araz MSc. Public health/epidemiology Communicable diseases : Refer to diseases that can be transmitted and make people ill. They are caused
Immune System. Before You Read. Read to Learn
 Immune System 37 section 1 Infectious Diseases Biology/Life Sciences 10.d Students know there are important differences between bacteria and viruses with respect to their requirements for growth and replication,
Immune System 37 section 1 Infectious Diseases Biology/Life Sciences 10.d Students know there are important differences between bacteria and viruses with respect to their requirements for growth and replication,
How to Become a Flu Fighter
 How to Become a Flu Fighter Pandemic Influenza Prevention Curriculum Grades 6-8 1 Lesson One Understanding the Flu Virus 2 Five Codes of Flu Fighting Code 1: Understand the flu virus Code 2: Know what
How to Become a Flu Fighter Pandemic Influenza Prevention Curriculum Grades 6-8 1 Lesson One Understanding the Flu Virus 2 Five Codes of Flu Fighting Code 1: Understand the flu virus Code 2: Know what
Biology. Slide 1 of 30. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 30 2 of 30 What causes disease? 3 of 30 Disease A disease is any change, other than an injury, that disrupts the normal functions of the body. Disease-causing agents are called pathogens.
Biology 1 of 30 2 of 30 What causes disease? 3 of 30 Disease A disease is any change, other than an injury, that disrupts the normal functions of the body. Disease-causing agents are called pathogens.
INFECTIOUS DISEASE: Evolving Challenges to Human Health Middle School Virtual Field Trip
 INFECTIOUS DISEASE: Evolving Challenges to Human Health Middle School Virtual Field Trip Overview This activity guides students in an exploration of the online exhibit Infectious Disease: Evolving Challenges
INFECTIOUS DISEASE: Evolving Challenges to Human Health Middle School Virtual Field Trip Overview This activity guides students in an exploration of the online exhibit Infectious Disease: Evolving Challenges
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms
 Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms NC Essential Standard: 1.2.3 Explain how specific cell adaptations help cells survive in particular environments 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms NC Essential Standard: 1.2.3 Explain how specific cell adaptations help cells survive in particular environments 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms
4. Which sentence is a
 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. Your body does a lot of things amazingly well. But as incredible as your body is, it can still be attacked by germs. Germs can invade your body, and until
1 Read the text and then answer the questions. Your body does a lot of things amazingly well. But as incredible as your body is, it can still be attacked by germs. Germs can invade your body, and until
Flu Get the Shot. How Does Flu Spread? How Serious Is Flu?
 Flu Get the Shot Each winter, millions of people suffer from seasonal flu. Flu the short name for influenza is caused by viruses. Viruses are very small germs. Some viruses can spread easily from one person
Flu Get the Shot Each winter, millions of people suffer from seasonal flu. Flu the short name for influenza is caused by viruses. Viruses are very small germs. Some viruses can spread easily from one person
How will you know if you ate contaminated food? Diarrhea Stomach cramps Fever Nausea/Vomiting
 A H E A L T H Y H O U S E You Can Prevent Food Poisoning! The food you eat can make you sick. Many people go to the hospital each year because they get food poisoning. Learn what you can do to prevent
A H E A L T H Y H O U S E You Can Prevent Food Poisoning! The food you eat can make you sick. Many people go to the hospital each year because they get food poisoning. Learn what you can do to prevent
8.L.1 Practice Questions
 Name: Date: 1. Why should antibiotics be given to a person who is ill with a bacterial disease like strep throat, but not to a person who has a viral disease like flu?. ntibiotics kill bacteria but not
Name: Date: 1. Why should antibiotics be given to a person who is ill with a bacterial disease like strep throat, but not to a person who has a viral disease like flu?. ntibiotics kill bacteria but not
Preparing for a Pandemic What Business and Organization Leaders Need to Know
 Preparing for a Pandemic What Business and Organization Leaders Need to Know Information provided by. Introduction An influenza, or flu, pandemic happens when a new flu virus appears that easily spreads
Preparing for a Pandemic What Business and Organization Leaders Need to Know Information provided by. Introduction An influenza, or flu, pandemic happens when a new flu virus appears that easily spreads
COURSE BOOK FOOD SAFETY ON THE GO MODULE 4: FOOD SERVICE WORKERS (STAFF AND VOLUNTEERS) 2012 EDITION
 COURSE BOOK FOOD SAFETY ON THE GO MODULE 4: FOOD SERVICE WORKERS (STAFF AND VOLUNTEERS) 2012 EDITION Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Module 4 - Food service workers (staff and volunteers)... 3 Length...
COURSE BOOK FOOD SAFETY ON THE GO MODULE 4: FOOD SERVICE WORKERS (STAFF AND VOLUNTEERS) 2012 EDITION Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Module 4 - Food service workers (staff and volunteers)... 3 Length...
E. Coli (Escherichia Coli)
 E. Coli (Escherichia Coli) Background: E. Coli is a common kind of bacteria that lives in the intestines of animals and humans and most are harmless. (Mayo Clinic, 2008) The most dangerous strain of E.
E. Coli (Escherichia Coli) Background: E. Coli is a common kind of bacteria that lives in the intestines of animals and humans and most are harmless. (Mayo Clinic, 2008) The most dangerous strain of E.
Concept Attainment Lesson Plan
 Concept Attainment Lesson Plan Course: Foods for Life Unit: Nutrition Lesson: Consumer Agency Practical Problem: How do I gain information on how to select food products for my family? Objectives: 1) Differentiate
Concept Attainment Lesson Plan Course: Foods for Life Unit: Nutrition Lesson: Consumer Agency Practical Problem: How do I gain information on how to select food products for my family? Objectives: 1) Differentiate
INFECTIOUS DISEASE: Evolving Challenges to Human Health Middle School Virtual Field Trip
 INFECTIOUS DISEASE: Evolving Challenges to Human Health Middle School Virtual Field Trip Overview This activity guides students in an exploration of the online exhibit Infectious Disease: Evolving Challenges
INFECTIOUS DISEASE: Evolving Challenges to Human Health Middle School Virtual Field Trip Overview This activity guides students in an exploration of the online exhibit Infectious Disease: Evolving Challenges
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS SWINE FLU
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS SWINE FLU Updated 5/6/09 ER FAQ What is swine flu? Swine flu is common disease of pigs and is caused by the same category of influenza virus (influenza A) that causes flu in
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS SWINE FLU Updated 5/6/09 ER FAQ What is swine flu? Swine flu is common disease of pigs and is caused by the same category of influenza virus (influenza A) that causes flu in
The Animal Control Officer Our First Line of Detection
 The Animal Control Officer Our First Line of Detection West Nile Virus & Exotic Newcastle Disease Presented by: Cynthia Spears Veterinary Public Health-Rabies Control Program 323-730-3723 or 877-747-2243
The Animal Control Officer Our First Line of Detection West Nile Virus & Exotic Newcastle Disease Presented by: Cynthia Spears Veterinary Public Health-Rabies Control Program 323-730-3723 or 877-747-2243
EXPERIMENT. Fomite Transmission. Hands-On Labs, Inc. Version
 EXPERIMENT Fomite Transmission Hands-On Labs, Inc. Version 42-0243-00-02 Review the safety materials and wear goggles when working with chemicals. Read the entire exercise before you begin. Take time to
EXPERIMENT Fomite Transmission Hands-On Labs, Inc. Version 42-0243-00-02 Review the safety materials and wear goggles when working with chemicals. Read the entire exercise before you begin. Take time to
Flu Get the Shot. How Does Flu Spread? How Serious Is Flu?
 National Institute on Aging AgePage Flu Get the Shot Each winter, millions of people suffer from seasonal flu. Flu the short name for influenza is caused by viruses. Viruses are very small germs. Some
National Institute on Aging AgePage Flu Get the Shot Each winter, millions of people suffer from seasonal flu. Flu the short name for influenza is caused by viruses. Viruses are very small germs. Some
H1N1 FLU H1N1 Influenza (Flu) 2009 H1N1 Flu in People. What is 2009 H1N1 flu swine flu? Why is 2009 H1N1 flu sometimes called swine flu?
 2009 H1N1 Influenza (Flu) What is 2009 H1N1 flu swine flu? 2009 H1N1 (also known as swine flu ) is a new flu virus that makes people sick. The 2009 H1N1 flu spreads from person to person like seasonal
2009 H1N1 Influenza (Flu) What is 2009 H1N1 flu swine flu? 2009 H1N1 (also known as swine flu ) is a new flu virus that makes people sick. The 2009 H1N1 flu spreads from person to person like seasonal
Importance and Benefits of Being Prepared
 Importance and Benefits of Being Prepared It is difficult to predict when the next influenza pandemic will occur or how severe it will be. The effects of a pandemic can be lessened if preparations are
Importance and Benefits of Being Prepared It is difficult to predict when the next influenza pandemic will occur or how severe it will be. The effects of a pandemic can be lessened if preparations are
Table of Seasonal Influenza Vaccine Total Doses Distributed
 Table of Seasonal Influenza Vaccine Total Doses Distributed This table reflects the cumulative weekly total number of seasonal influenza vaccine doses distributed in the US as reported to CDC by influenza
Table of Seasonal Influenza Vaccine Total Doses Distributed This table reflects the cumulative weekly total number of seasonal influenza vaccine doses distributed in the US as reported to CDC by influenza
A Guide for Parents. Protect your child. What parents should know. Flu Information The Flu:
 Flu Information The Flu: A Guide for Parents Influenza (also known as flu) is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses that infect the nose, throat, and lungs. Flu is different from
Flu Information The Flu: A Guide for Parents Influenza (also known as flu) is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses that infect the nose, throat, and lungs. Flu is different from
The Food Handler Manual States That Foodborne Illness Can Be Caused By Food Containing
 The Food Handler Manual States That Foodborne Illness Can Be Caused By Food Containing United States. Pathogens can be transferred from one surface or food to another. Some foodborne illnesses are caused
The Food Handler Manual States That Foodborne Illness Can Be Caused By Food Containing United States. Pathogens can be transferred from one surface or food to another. Some foodborne illnesses are caused
How many students at St. Francis Preparatory School in New York City have become ill or been confirmed with swine flu?
 Swine Flu Call Center Script SWINE FLU QUESTIONS What is swine flu? Swine Influenza, also called swine flu, is a respiratory disease of pigs caused by type A influenza viruses. Outbreaks of swine flu happen
Swine Flu Call Center Script SWINE FLU QUESTIONS What is swine flu? Swine Influenza, also called swine flu, is a respiratory disease of pigs caused by type A influenza viruses. Outbreaks of swine flu happen
Employee Health and Personal Hygiene. for SCHOOL NUTRITION STAFF
 Employee Health and Personal Hygiene for SCHOOL NUTRITION STAFF i Institute of Child Nutrition The University of Mississippi The Institute of Child Nutrition was authorized by Congress in 1989 and established
Employee Health and Personal Hygiene for SCHOOL NUTRITION STAFF i Institute of Child Nutrition The University of Mississippi The Institute of Child Nutrition was authorized by Congress in 1989 and established
Lesson Objectives. Core Content Objectives. Language Arts Objectives
 Dr. Wellbody s Heroes 7 Lesson Objectives Core Content Objectives Students will: Explain that germs can cause disease in the body Explain the importance of vaccination in preventing disease Identify Edward
Dr. Wellbody s Heroes 7 Lesson Objectives Core Content Objectives Students will: Explain that germs can cause disease in the body Explain the importance of vaccination in preventing disease Identify Edward
4-H Rabbit Project Record Book
 4-H Rabbit Project Record Book Kent County 4-H Program Place a photo of you and your rabbit here Name: 4-H Age (age on Jan 1 of current year) : # of years in rabbit project: 4-H Club: 4-H Leader: MSU is
4-H Rabbit Project Record Book Kent County 4-H Program Place a photo of you and your rabbit here Name: 4-H Age (age on Jan 1 of current year) : # of years in rabbit project: 4-H Club: 4-H Leader: MSU is
16 HIV/AIDS Infection and Cell Organelles ALTHOUGH MANY OF their characteristics are similar to those of cells, viruses
 16 HIV/AIDS Infection and Cell Organelles ALTHOUGH MANY OF their characteristics are similar to those of cells, viruses are not cells. They contain genetic material and a few proteins, but they do not
16 HIV/AIDS Infection and Cell Organelles ALTHOUGH MANY OF their characteristics are similar to those of cells, viruses are not cells. They contain genetic material and a few proteins, but they do not
Next, your teacher will ask everyone who is infected to raise their hand. How many people were infected?
 Some Similarities between the Spread of an Infectious Disease and Population Growth by Jennifer Doherty and Dr. Ingrid Waldron, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania, 2007 1 How Does an Infectious
Some Similarities between the Spread of an Infectious Disease and Population Growth by Jennifer Doherty and Dr. Ingrid Waldron, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania, 2007 1 How Does an Infectious
Lesson Title: Viruses vs. Cells Standards to be Addressed: Acquisition
 Readiness Standards: 4.C: compare the structures of viruses to cells, describe viral reproduction, and describe the role of viruses in causing diseases such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and influenza
Readiness Standards: 4.C: compare the structures of viruses to cells, describe viral reproduction, and describe the role of viruses in causing diseases such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and influenza
AVIAN INFLUENZA. Frequently Asked Questions and Answers
 PENINSULA HEALTH AVIAN INFLUENZA Frequently Asked Questions and Answers Q. What is avian influenza? Answer: Avian influenza is an infectious disease of birds caused by type A strains of the influenza virus.
PENINSULA HEALTH AVIAN INFLUENZA Frequently Asked Questions and Answers Q. What is avian influenza? Answer: Avian influenza is an infectious disease of birds caused by type A strains of the influenza virus.
Learning about HIV. A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum
 Learning about HIV A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering respect and responsibility through age-appropriate sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: By the end of
Learning about HIV A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering respect and responsibility through age-appropriate sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: By the end of
FINLAND S ANIMAL HEALTH SERVICE (FAHS)
 FINLAND S ANIMAL HEALTH SERVICE (FAHS) BIOSECURITY MEASURES IN ANIMAL HUSBANDRY TO PREVENT EPIDEMIC ZOONOSES Veikko Tuovinen DVM, PhD, MS, Diplomate ECVPH Managing Director of FAHS BIOSECURITY - definition
FINLAND S ANIMAL HEALTH SERVICE (FAHS) BIOSECURITY MEASURES IN ANIMAL HUSBANDRY TO PREVENT EPIDEMIC ZOONOSES Veikko Tuovinen DVM, PhD, MS, Diplomate ECVPH Managing Director of FAHS BIOSECURITY - definition
COMMUNITY EMERGENCY RESPONSE TEAM PANDEMIC INFLUENZA INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW
 INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW A pandemic is a global disease outbreak. Pandemics are characterized by the sudden onset of an extremely virulent pathogen with potentially lethal results. Though historically
INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW A pandemic is a global disease outbreak. Pandemics are characterized by the sudden onset of an extremely virulent pathogen with potentially lethal results. Though historically
Coach on Call. Thank you for your interest in Deciding to Get the Flu Vaccine. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful.
 Coach on Call It was great to talk with you. Thank you for your interest in. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful. Please give me a call if you have more questions about this or other topics. As your
Coach on Call It was great to talk with you. Thank you for your interest in. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful. Please give me a call if you have more questions about this or other topics. As your
Indiana State Board of Animal Health
 Indiana State Board of Animal Health Office of the State Veterinarian Marianne Ash, DVM, MVPH, DACVPM Animal Health Division Director BOAH s Charge the prevention, detection, control and eradication of
Indiana State Board of Animal Health Office of the State Veterinarian Marianne Ash, DVM, MVPH, DACVPM Animal Health Division Director BOAH s Charge the prevention, detection, control and eradication of
Communicable Diseases
 Lesson 5.1 Communicable Diseases By Carone Fitness You have probably been in a situation similar to Corry's. The common cold is a communicable disease. 1 Defined Communicable diseases are illnesses that
Lesson 5.1 Communicable Diseases By Carone Fitness You have probably been in a situation similar to Corry's. The common cold is a communicable disease. 1 Defined Communicable diseases are illnesses that
Food Entrepreneurs Series: Science Basics
 Food Entrepreneurs Series: Science Basics How Microorganisms Affect Food Safety and Quality All raw food items contain microorganisms. These microorganisms can eventually lead to food spoilage or even
Food Entrepreneurs Series: Science Basics How Microorganisms Affect Food Safety and Quality All raw food items contain microorganisms. These microorganisms can eventually lead to food spoilage or even
U.S. Human Cases of Swine Flu Infection (As of April 29, 2009, 11:00 AM ET)
 Swine Flu Call Center Script 4/29/2009 3:00 PM SWINE FLU QUESTIONS What is swine flu? Swine Influenza, also called swine flu, is a respiratory disease of pigs caused by type A influenza viruses. Outbreaks
Swine Flu Call Center Script 4/29/2009 3:00 PM SWINE FLU QUESTIONS What is swine flu? Swine Influenza, also called swine flu, is a respiratory disease of pigs caused by type A influenza viruses. Outbreaks
Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences
 Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Chapter 11. Epidemiology and Public Health Chapter 11 Outline Epidemiology Interactions Among Pathogens, Hosts and the Environment Chain of Infection Reservoirs
Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Chapter 11. Epidemiology and Public Health Chapter 11 Outline Epidemiology Interactions Among Pathogens, Hosts and the Environment Chain of Infection Reservoirs
Frequently Asked Questions on Avian Influenza
 Frequently Asked Questions on Avian Influenza What is bird flu (avian influenza) and how does it differ from seasonal flu and pandemic influenza? Avian influenza or bird flu is a disease of birds caused
Frequently Asked Questions on Avian Influenza What is bird flu (avian influenza) and how does it differ from seasonal flu and pandemic influenza? Avian influenza or bird flu is a disease of birds caused
COMMUNITY EMERGENCY RESPONSE TEAM PANDEMIC INFLUENZA INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW
 INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW A pandemic is a global disease outbreak. Pandemics are characterized by the sudden onset of an extremely virulent pathogen with potentially lethal results. Though historically
INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW A pandemic is a global disease outbreak. Pandemics are characterized by the sudden onset of an extremely virulent pathogen with potentially lethal results. Though historically
Disease Transmission Lab
 Disease Transmission Lab Name Introduction and Background: Pathogens are organisms that can cause infectious diseases in humans or other species. There are several means of transmission: Direct contact
Disease Transmission Lab Name Introduction and Background: Pathogens are organisms that can cause infectious diseases in humans or other species. There are several means of transmission: Direct contact
Next, your teacher will ask everyone who is infected to raise their hand. How many people were infected?
 Some Similarities between the Spread of an Infectious Disease and Population Growth by Jennifer Doherty and Dr. Ingrid Waldron, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania, 2007 1 How Does an Infectious
Some Similarities between the Spread of an Infectious Disease and Population Growth by Jennifer Doherty and Dr. Ingrid Waldron, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania, 2007 1 How Does an Infectious
In your own words define: Normal flora-what is it and what does it do? Pathogen-what is it and what does it do?
 Bell Work: Based on yesterday s lesson In your own words define: Normal flora-what is it and what does it do? Pathogen-what is it and what does it do? Chain of Infection and Isolation Precautions Standard
Bell Work: Based on yesterday s lesson In your own words define: Normal flora-what is it and what does it do? Pathogen-what is it and what does it do? Chain of Infection and Isolation Precautions Standard
CAPTAINS EXCHANGE DISEASE DETECTIVES
 SEVEN LAKES HIGH SCHOOL CAPTAINS EXCHANGE DISEASE DETECTIVES 2018-2019 Rules: always show work and keep answers in decimal form, unless otherwise told. /201 points Part 1: General Vocabulary and Knowledge
SEVEN LAKES HIGH SCHOOL CAPTAINS EXCHANGE DISEASE DETECTIVES 2018-2019 Rules: always show work and keep answers in decimal form, unless otherwise told. /201 points Part 1: General Vocabulary and Knowledge
AVIAN FLU BACKGROUND ABOUT THE CAUSE. 2. Is this a form of SARS? No. SARS is caused by a Coronavirus, not an influenza virus.
 AVIAN FLU BACKGROUND 1. What is Avian Influenza? Is there only one type of avian flu? Avian influenza, or "bird flu", is a contagious disease of animals caused by Type A flu viruses that normally infect
AVIAN FLU BACKGROUND 1. What is Avian Influenza? Is there only one type of avian flu? Avian influenza, or "bird flu", is a contagious disease of animals caused by Type A flu viruses that normally infect
Infectious Disease Learning Packet 3. Infectious Disease: Causes and Prevention
 Name Infectious Disease: Causes and Prevention Objective #3: The students will be able to identify one or more infectious diseases and their cause(s). The students will be able to list at least 3 ways
Name Infectious Disease: Causes and Prevention Objective #3: The students will be able to identify one or more infectious diseases and their cause(s). The students will be able to list at least 3 ways
Food Safety Summary for Food for Learning. Prepared by: Joanna Mestre, BScHE Health Promoter, Environmental Health
 Food Safety Summary for Food for Learning Prepared by: Joanna Mestre, BScHE Health Promoter, Environmental Health Introduction Food safety is about preventing food borne illness. Some people are more vulnerable
Food Safety Summary for Food for Learning Prepared by: Joanna Mestre, BScHE Health Promoter, Environmental Health Introduction Food safety is about preventing food borne illness. Some people are more vulnerable
What Are Communicable Diseases?
 What Are Communicable Diseases? Notes: Welcome to the Health 9 Lesson: What Are Communicable Diseases. Please click the next button to continue. 1.2 Introduction Notes: You've had a cold certainly...well
What Are Communicable Diseases? Notes: Welcome to the Health 9 Lesson: What Are Communicable Diseases. Please click the next button to continue. 1.2 Introduction Notes: You've had a cold certainly...well
Before Statement After
 CHAPTER 17 Immunity and Disease LESSON 1 Diseases What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
CHAPTER 17 Immunity and Disease LESSON 1 Diseases What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
INFLUENZA (FLU) Cleaning to Prevent the Flu
 INFLUENZA (FLU) Cleaning to Prevent the Flu Cleaning to Prevent the Flu 24 hours How long can the flu virus live on objects, such as doorknobs and tables? The flu virus can live on some surfaces for up
INFLUENZA (FLU) Cleaning to Prevent the Flu Cleaning to Prevent the Flu 24 hours How long can the flu virus live on objects, such as doorknobs and tables? The flu virus can live on some surfaces for up
Human Cases of Swine Influenza in California, Kansas, New York City, Ohio, Texas, and Mexico Key Points April 26, 2009
 1 Today, CDC confirmed additional human cases of swine influenza A (H1N1) virus infection in the United States, bringing the total number of U.S. confirmed cases to 21. This includes cases in California,
1 Today, CDC confirmed additional human cases of swine influenza A (H1N1) virus infection in the United States, bringing the total number of U.S. confirmed cases to 21. This includes cases in California,
Microbiology. Bacteria Viruses Fungi Parasites
 Microbiology Bacteria Viruses Fungi Parasites On page C1: What do YOU think? What do you think 8.L.1 means? (look at your section tab) Choose 2 vocabulary words and write a definition and a drawing for
Microbiology Bacteria Viruses Fungi Parasites On page C1: What do YOU think? What do you think 8.L.1 means? (look at your section tab) Choose 2 vocabulary words and write a definition and a drawing for
CRITERIA AND PROCEDURE
 CRITERIA AND PROCEDURE BROAD SUBJECT: SANITATION AND SAFETY NO: SS-06-02 TITLE: Pandemic/Epidemic Flu EFFECTIVE DATE: June 12, 2009 PURPOSE OF THIS CRITERIA/PROCEDURE - Children attending schools in Georgia
CRITERIA AND PROCEDURE BROAD SUBJECT: SANITATION AND SAFETY NO: SS-06-02 TITLE: Pandemic/Epidemic Flu EFFECTIVE DATE: June 12, 2009 PURPOSE OF THIS CRITERIA/PROCEDURE - Children attending schools in Georgia
CHAPTER AT A GLANCE. Science Class (SA-II)- IX
 13 CHAPTER AT A GLANCE Health is a general condition of a preson s mind and body. According to WHO (World Health Organisation) health is a state of physical, metal and social well-being of a person. To
13 CHAPTER AT A GLANCE Health is a general condition of a preson s mind and body. According to WHO (World Health Organisation) health is a state of physical, metal and social well-being of a person. To
Section 6. Communicable Diseases
 Section 6 Communicable Diseases 89 Learning objectives Section 6 Communicable Diseases After completing this section, you will be able to: Describe how communicable diseases spread. Identify some specific
Section 6 Communicable Diseases 89 Learning objectives Section 6 Communicable Diseases After completing this section, you will be able to: Describe how communicable diseases spread. Identify some specific
TECHNICAL REPORT ECDC SCIENTIFIC ADVICE
 TECHNICAL REPORT ECDC SCIENTIFIC ADVICE Health advice for people living in or travelling to countries where the A/H5N1 virus has been detected Version April 2006 www.ecdc.eu.int Health advice for people
TECHNICAL REPORT ECDC SCIENTIFIC ADVICE Health advice for people living in or travelling to countries where the A/H5N1 virus has been detected Version April 2006 www.ecdc.eu.int Health advice for people
Disease dynamics: understanding the spread of diseases
 Disease dynamics: understanding the spread of diseases Image courtesy of Lightspring / shutterstock.com Get to grips with the spread of infectious diseases with these classroom activities highlighting
Disease dynamics: understanding the spread of diseases Image courtesy of Lightspring / shutterstock.com Get to grips with the spread of infectious diseases with these classroom activities highlighting
2011 Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University. All rights reserved.
 2011 Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University. All rights reserved. Traveling Viruses Part I Purpose To generate a discussion of how diseases can be transmitted. Materials For each student: Disposable
2011 Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University. All rights reserved. Traveling Viruses Part I Purpose To generate a discussion of how diseases can be transmitted. Materials For each student: Disposable
Part 1: Direct Transmission Human to Human
 Buzz Buzz Bite! Part 1: Direct Transmission Human to Human Direct human- to- human disease transmission occurs between an infected person and an uninfected person. Examples of diseases spread through direct
Buzz Buzz Bite! Part 1: Direct Transmission Human to Human Direct human- to- human disease transmission occurs between an infected person and an uninfected person. Examples of diseases spread through direct
Breaking the Chain of Infection Designated Officer Education Day September 3, 2014 Jodi-Marie Black RN BScN PHN
 Breaking the Chain of Infection Designated Officer Education Day September 3, 2014 Jodi-Marie Black RN BScN PHN Topics Covered in Presentation The Chain of infection and how to break the chain Role of
Breaking the Chain of Infection Designated Officer Education Day September 3, 2014 Jodi-Marie Black RN BScN PHN Topics Covered in Presentation The Chain of infection and how to break the chain Role of
In the United States, flu season runs from October to May, with most cases occurring between late December and early March.
 Partners in Pediatrics, PC 7110 Forest Ave Suite 105 Richmond, VA 23226 804-377-7100 Influenza (Flu) Influenza, commonly known as "the flu," is a highly contagious viral infection of the respiratory tract.
Partners in Pediatrics, PC 7110 Forest Ave Suite 105 Richmond, VA 23226 804-377-7100 Influenza (Flu) Influenza, commonly known as "the flu," is a highly contagious viral infection of the respiratory tract.
TRAINER: Read this page ahead of time to prepare for teaching the module.
 Module 2 Overview: Employee Illness TRAINER: Read this page ahead of time to prepare for teaching the module. PARTICIPANTS WILL: 1. Describe FOODBORNE ILLNESS symptoms. 2. Explain the difference between
Module 2 Overview: Employee Illness TRAINER: Read this page ahead of time to prepare for teaching the module. PARTICIPANTS WILL: 1. Describe FOODBORNE ILLNESS symptoms. 2. Explain the difference between
Bacteria and Viruses
 CHAPTER 13 LESSON 3 Bacteria and Viruses What are viruses? Key Concepts What are viruses? How do viruses affect human health? What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree
CHAPTER 13 LESSON 3 Bacteria and Viruses What are viruses? Key Concepts What are viruses? How do viruses affect human health? What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree
Infection, Detection, Prevention...
 Infection, Detection, Prevention... A disease is any change that disrupts the normal function of one or more body systems. Non infectious diseases are typically caused by exposure to chemicals or are inherited.
Infection, Detection, Prevention... A disease is any change that disrupts the normal function of one or more body systems. Non infectious diseases are typically caused by exposure to chemicals or are inherited.
Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Science Level 1. Investigate biological ideas relating to interactions between humans and micro-organisms
 Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Science Level 1 This exemplar supports assessment against: Achievement Standard 90950 Investigate biological ideas relating to interactions between humans and
Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Science Level 1 This exemplar supports assessment against: Achievement Standard 90950 Investigate biological ideas relating to interactions between humans and
