Author(s): Katherine A. Perry (University of Michigan), RN, BSN 2012
|
|
|
- Terence Harrell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Project: Ghana Emergency Medicine Collaborative Document Title: Infectious Diseases Overview Author(s): Katherine A. Perry (University of Michigan), RN, BSN 2012 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike-3.0 License: We have reviewed this material in accordance with U.S. Copyright Law and have tried to maximize your ability to use, share, and adapt it. These lectures have been modified in the process of making a publicly shareable version. The citation key on the following slide provides information about how you may share and adapt this material. Copyright holders of content included in this material should contact open.michigan@umich.edu with any questions, corrections, or clarification regarding the use of content. For more information about how to cite these materials visit Any medical information in this material is intended to inform and educate and is not a tool for self-diagnosis or a replacement for medical evaluation, advice, diagnosis or treatment by a healthcare professional. Please speak to your physician if you have questions about your medical condition. Viewer discretion is advised: Some medical content is graphic and may not be suitable for all viewers. 1
2 Attribution Key Use + Share + Adapt Make Your Own Assessment for more information see: { Content the copyright holder, author, or law permits you to use, share and adapt. } Public Domain Government: Works that are produced by the U.S. Government. (17 USC 105) Public Domain Expired: Works that are no longer protected due to an expired copyright term. Public Domain Self Dedicated: Works that a copyright holder has dedicated to the public domain. Creative Commons Zero Waiver Creative Commons Attribution License Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike License Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike License GNU Free Documentation License { Content Open.Michigan believes can be used, shared, and adapted because it is ineligible for copyright. } Public Domain Ineligible: Works that are ineligible for copyright protection in the U.S. (17 USC 102(b)) *laws in your jurisdiction may differ { Content Open.Michigan has used under a Fair Use determination. } Fair Use: Use of works that is determined to be Fair consistent with the U.S. Copyright Act. (17 USC 107) *laws in your jurisdiction may differ Our determination DOES NOT mean that all uses of this 3rd-party content are Fair Uses and we DO NOT guarantee that your use of the content is Fair. To use this content you should do your own independent analysis to determine whether or not your use will be Fair. 2
3 Communicable & Infectious Disease Emergencies Katherine A. Perry RN, BSN 3
4 Priorities & Major Goals To properly assess the patient with an infectious disease emergency To properly identify the infectious disease emergency To understand the specific emergency management 4
5 Definitions Communicable disease : an infectious disease transmissible by direct contact with an affected individual or the individual's discharges or by indirect means Infectious Disease : a disease caused by the entrance into the body of organisms as bacteria, protozoans, fungi, or viruses 5
6 Parasitic Infections Parasites enter through the mouth or skin Mouth Drinking Eating Skin Burrowing Bloodstream 6
7 Most Common Parasitic Infections Malaria Helminths (parasitic worm) African Trypanosomiasis ( sleeping sickness ) Cryptosporidiosis Courtesy of WHO 7
8 Malaria Malaria is caused by a parasite called Plasmodium, which is transmitted via the bites of infected female mosquitoes Sub-Saharan Africa 90% of all Malaria cases 1.8 million die each year 1 in 5 childhood deaths Optigan13, Wikimedia Commons 8
9 Clinical Presentation In the early stages, malaria symptoms are sometimes similar to those of many other infections such as Fever Chills Headache Fatigue Nausea & vomiting Sweats Dry (nonproductive) cough. Muscle and/or back pain Enlarged spleen Mikael Häggström, Wikimedia Commons 9
10 Tim Vickers, Wikimedia Commons 10
11 Cerebral Malaria Altered mental status Cognitive difficulties, language and behavior problems Possible seizure Fever, rigor and/or chills Signs of irritability, restlessness or psychotic behavior Risk Factors: Young & Old Pregnancy Poor nutrition HIV 11
12 Different Types of Malaria Plasmodium falciparum- the most severe infections and is responsible for nearly 90% of malaria-related deaths in sub Saharan Africa Obstruction to blood flow Secondary organ dysfunction Pregnancy- adhere to placenta, so maternal anemia & low birth weight Plasmodium malaria- cyclic paroxysms occur every 72 hours, not usually life-threatening 12
13 Different Types of Malaria Plasmodium ovale- can rest in the liver for several months up to 4 years after a person is bitten by an infected mosquito Plasmodium vivax- widest geographic distribution throughout the world 13
14 Cerebral Malaria Develops when infected red blood cells adhere to the cerebral microvasculature, causing blockage of the blood's pathway which stops blood flow, leading to a shortage of oxygen and nutrients to the brain, fatal if untreated Tim Vickers, Wikimedia Commons 14
15 Clinical Presentation Cyclic symptoms Parasites develop, reproduce, and released from red blood cells and liver In severe cases malaria can lead to cerebral malaria, impaired function of the brain or spinal cord, seizures, and/or loss of consciousness 15
16 Diagnosis Depends on the demonstration of parasites in the blood, usually by microscopy Peripheral smear examination Gold-standard in confirming the diagnosis of malaria Quantitative Buffy Coat (QBC) Test fluorescence microscopy-based malaria diagnostic test components of blood (including parasites) separate into distinct layers based on their differing densities Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 16
17 Thin and Thick Blood Smears Deep view of blood Single-layer of RBCs Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 17
18 Diagnosis A clinician who faces these symptoms would need answers to the following questions: Is it malaria? If yes; What is the species? Is it severe? Is it new/ recurrence? Is it active? 18
19 Diagnosis Malaria may be described as simple or uncomplicated when the malaria infection is NOT life threatening and is easily treatable The definition of complicated Malaria is based on clinical presentation A change in behavior, confusion or drowsiness; Impaired consciousness or unarousable coma; Multiple/recurrent convulsion Deep breathing or respiratory distress Pulmonary edema (x-ray) Circulatory collapse or shock Jaundice Bleeding tendency or anemia Prostration- generalized weakness so the patient cannot walk, or sit up without assistance 19
20 As a nurse, what nursing interventions do you expect? 20
21 Blood tests Urine Analysis Your laboratory results would include: Hyperparasitemia Hypoglycemia Metabolic acidosis Severe anemia packed cell volume < 20%, Hgb < 6 Hemoglobinuria Hyperlacticemia Renal impairment, abnormal creatinine and urea levels 21
22 Risk factors for Malaria infection Children between the age of 6 months and 5 years People from non malaria to malaria endemic areas Returnees to highly endemic areas Indigenous pregnant women People with sickle cell disease People of all ages, no matter their location, who have lowered immunity and have exposure to Malaria 22
23 Treatment of Malaria The effectiveness of anti-malarial drugs differs with different species of the parasite and with different stages of the parasite's life cycle To alleviate symptoms: Chloroquine, quinine, artemisinin, artesunate, amodiaquine combinations (Blood schizonticidal drugs) To prevent relapses: Primaquine (tissue schizonticidal drugs) To prevent spread: Primaquine for P. falciparum, Chloroquine for all other 23
24 Treatment General principles: Administer antimalarial drug intravenously for at least 48 h; then administer orally as soon as patient can swallow Administer a loading dose Total duration of therapy depends on sensitivity of parasite, but usually 7 days Type of Infection Treatment P. Vivax Chloroquine 25 mg of salt/kg over hours + Primaquine for 14 days. P. Falciparum Treatment depends on severity and sensitivity Artesunate+Pyrimethamine/sulphadoxine or other ACTs, OR Quinine plus tetracycline as suppressive therapy + Primaquine as gametocytocidal in single dose Mixed (P. Vivax + P. ACT as for P. falciparum + Primaquine as falciparum) for P. vivax 24
25 Educate the patient Apply an insect repellant containing DEET (active ingredient) or any insect repellant to your skin and clothing. Insect repellant containing permethrin (active ingredient) may be applied to clothes, bednets, tents, blankets, and other equipment Infants, who are less than 2 months old, should use repellants with 30 percent DEET or less. Do not use DEET on the hands of young children or on infants who may rub their eyes or mouth. 25
26 Education Continued Sleep under mosquito net, check your bed-net for holes before using it Insecticide-treated mosquito net Mike Blyth, Wikimedia Commons 26
27 Education Continued Do not go outside, especially at night or between dawn (sunrise) and dusk (sunset). Mosquitoes feed most actively during these times. Avoid activities in places where mosquitoes are usually present Wear long-sleeved shirts and long pants to keep your skin covered. Choose clothes that are light-colored because mosquitoes are attracted to dark clothing. 27
28 Discharge Information Keep a current list of your medicines: amounts, and when, how, and why you take them. Take the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency. Use vitamins, herbs, or food supplements only as directed Take your medicine as directed: Contact a healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not working as expected. Tell him about any medicine allergies, and if you want to quit taking or change your medicine 28
29 Discharge Information CONTACT A CAREGIVER IF: You have a fever. Your skin is itchy, swollen, or has a rash If your symptoms do not improve with treatment You have any questions or concerns about your illness medicine, care, or recovery SEEK CARE IMMEDIATELY IF: You become confused, act differently than normal, or it is harder than normal to wake you up You have a bad headache or trouble thinking clearly You have seizures (convulsions) You have trouble breathing all of a sudden Your symptoms are getting worse or coming back 29
30 Summary You have now come to the end of this lecture on severe and complicated Malaria. You have learned that severe and complicated Malaria is a medical emergency and it requires early diagnosis and prompt treatment 30
31 Case Study #2 Akpene Agbo is 30 years old. She is approximately 24 weeks pregnant with her second baby. She comes to the antenatal clinic for her ANC visit complaining of severe headache, fever and dizziness. Akpene and her family moved to the area 6 months ago. She has never suffered from malaria Basic Assessment: 1) What will you include in your initial assessment of Akpene and why? 31
32 Case Study #2 Gather information - onset, duration, and severity of headache, fever, and dizziness, and any medications taken Ask about previous history of headache, dizziness, recent illness, signs of other infection (pain when passing urine, chest pain, painful cough, abdominal pain/tenderness), history of any other danger signs, signs of uncomplicated and severe malaria, and history of the pregnancy (e.g., last menstrual period, symptoms of pregnancy, quickening, presence of contractions, leaking of fluid) This is because every pregnant woman living in malaria-endemic areas who presents with a fever should be suspected of having malaria (other causes of fever in pregnancy should still be considered) Check Akpene's VS: temperature, pulse, blood pressure, and respiratory rate to identify and treat life-threatening illnesses as rapidly as possible 32
33 Case Study #2 What screening procedures and laboratory tests will you include (if available) in your assessment of Akpene and why? 33
34 Case Study #2 Check CBC, metabolic panel, urine analysis for kidney function & protein, X-ray and vital signs Carry out a laboratory test to confirm whether she has malaria or not Blood Smear QBC 34
35 Case Study #2 1. Akpene states she has felt well during this pregnancy, and began having fever and headache yesterday morning. She states that she does not have other symptoms such as cough, difficulty urinating, abdominal pain, or leaking of fluid from the vagina. She has not had convulsions or loss of consciousness. She has not taken any medication 2. Akpene is 60 kg and her temperature is 38.7 C. Her blood pressure is 122/68, pulse rate is 92 bpm, RR 18. Akpene is pale, not jaundiced and well hydrated. Her fundal height is 23 cm (which is compatible with the dates of her last menstrual period) and fetal heart tones are 140 bpm 3. Her Hgb is 10.5 g/dl; the blood film for malaria is positive. 35
36 Case Study #2 Based on these findings, what is Akpene's evaluation, and why? 36
37 Case Study #2 Akpene is 24 weeks pregnant (determined by last menstrual period and uterine size) She has uncomplicated malaria (based on her positive blood film, symptoms, and vital signs) 37
38 Case Study #2 Based on your evaluation, what is your plan of care for Akpene and why? 38
39 Case Study #2 Instruct her to Artesunate 200mg-Amodiaquine 600 mg taken in two divided doses after meals Pt should also take Tylenol (two tablets every 6 hours until her temperature returns to normal) Tell her and her relatives to return to the clinic in 48 hours if she is not feeling better, or immediately if she has signs and symptoms of severe malaria (e.g., convulsions, loss of consciousness) Tell her that she must take all of her medication, and describe the side effects it may cause (tinnitus, skin rashes, stomach upsets, low blood sugar, if she is on quinine) 39
40 TUBERCULOSIS 40
41 Tuberculosis Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (TB) = #1 Cause of Death Worldwide from a Single Infectious Agent TB most common in lungs (85%), but can occur in other parts of the body (extrapulmonary) 41
42 Transmission Infection = Person to Person via Airborne Infectious Aerosol: Coughing Sneezing Talking 42
43 Clinical Presentation Prolonged cough Chest pain Hemoptysis Fever Chills Night sweats Fatigue Loss of appetite Weight loss/failure to gain weight 43
44 Droplet nuclei are inhaled Macrophages and T lymphocytes try to contain the infection In weaker immune systems, the wall loses integrity and the infection spreads to other alveoli/other organs Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 44
45 Children with TB Children have few tubercle bacilli in lungs, therefore, are rarely infectious Children less than 12 years of age usually lack the pulmonary force to produce airborne bacilli For a case of childhood TB infection, it is likely that an adolescent or adult transmitted TB bacilli to the child 45
46 Types of TB Active Tuberculosis: When the immune system of a patient with dormant TB is weakened, the TB can become active (reactivate) and cause infection in the lungs or other parts of the body Latent Tuberculosis: do not feel sick and do not have any symptoms They are infected with M. tuberculosis, but do not have TB disease Only sign of TB infection is a positive reaction to the tuberculin skin test or TB blood test Are NOT infectious and cannot spread TB 46
47 Types of TB Multi drug resistant (MDR TB) is TB that is resistant to at least two of the best anti-tb drugs, isoniazid and rifampicin This can result from poor patient compliance, inappropriate dosing or prescribing of medication, poorly formulated medications, and/or an inadequate supply of medication 47
48 Diagnosis of TB PPD Sputum Culture Chest X-Ray 48
49 Diagnosis PPD Purified Protein Derivative The Tuberculin Skin Test Identifies Individuals infected with Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Injection Site = Intradermally Dorsal Side of Forearm Inflammatory Reaction = Hours Result Test in Hours (If Positive at 6 Days = true Positive) Greg Knobloch, Wikimedia Commons 49
50 Chest X-ray The chest X-ray examination is done and if there are any changes in the lung, a sputum sample will be sent for microscopic examination & culture 50
51 A. Infiltrates in left lung B. Bilateral advanced pulmonary tuberculosis Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 51
52 Sputum Culture Definitive diagnosis of tuberculosis requires the identification of M tuberculosis in a culture of a diagnostic specimen The most frequent sample used from a patient with a persistent and productive cough is sputum Mycobacteria grow slowly, 3 to 6 weeks may be required for detectable growth on solid media. 52
53 Treatment First-line anti-tb agents: isoniazid (INH) rifampin (RIF) ethambutol (EMB) pyrazinamide (PZA) 53
54 Diagnosis TB Infection TB Disease 3 or 4 drugs Treatment INH 9 Months First 2 months INH, RIF, PZA, EMB (add EMB if drug resistance is suspected) Next 4 months 2 most effective sensitive rugs (INH & RIF in pan-sensitive cases) Multidrug resistant TB disease (resistance to at least INH & RIF) Treat with sensitive drugs for at least 18 months 54
55 Prevention BCG (Bacille Calmette Guerin) is a vaccine made from a live weakened bacterium related to tuberculosis (TB) bacteria (Mycobacterium tuberculosis). The BCG vaccine prevents the bacteria from spreading within the body, thus preventing TB from developing If patients plan to travel, they should talk to their health care providers and make sure they have enough medicine to last while away. 55
56 Discharge Instructions Take your medicine as directed Call your primary healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not working Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency You must complete your treatment until you are cured of TB, even if you do not feel sick. It is very important that you take your TB medicines exactly as your caregiver tells you. If you skip or stop your pills, TB germs will not be killed. You will always have TB germs in your body unless you correctly take all your medicines. 56
57 Discharge Instructions The most important way to keep from spreading TB is to take all your medicines exactly as your caregivers told you Keep all of your follow-up appointments. Your caregivers need to see how you are doing Avoid close contact with others, especially babies and elderly people ALWAYS cover your mouth and nose with a paper tissue when you cough or sneeze. Throw the used tissue away. If possible, flush used tissues down a toilet ALWAYS wash your hands with soap and water after you cough or sneeze. Family members, close friends, and co-workers should have a TB skin test. They may have gotten the TB germ without being sick. To keep from getting TB, these contacts may need to take medicines 57
58 Discharge Instructions CONTACT A CAREGIVER IF: You have any problems that may be caused by the medicines you are taking. Tell your caregiver if you have a skin rash, nausea, vomiting, or your eyes or skin are yellow. Call your caregiver if your urine looks like dark tea or coffee Your TB symptoms do not go away or get worse, even if you are taking your TB medicines. Anyone who spent time near you gets symptoms of TB: - Fever, not wanting to eat, losing weight, night sweats, or cough. These people will need to be tested for TB. 58
59 Discharge Instructions You have a cough that does not go away after 3 or 4 weeks following a cold. You have a fever. You have questions about your condition and your medicines SEEK CARE IMMEDIATELY IF: You have chest pain or cough up blood You have trouble breathing You have a fever, headache, and a stiff neck 59
60 Isolation Precautions 60
61 Standard Precautions Protection of all patients regardless of their diagnosis or presumed infection status Apply to blood (including dried blood), all body fluids, secretions, and excretions (except sweat) Include the following Hand hygiene Personal Protective Equipment Respiratory hygiene/cough etiquette Personal Protective Equipment: Barrier between micro-organisms and the wearer 61
62 Standard Precautions Gloves should be worn when touching or handling: blood, body fluids, secretions, excretions, contaminated items or surfaces Hand hygiene must be performed after removal of gloves. James Heilman, MD, Wikimedia Commons 62
63 Airborne Precautions By dissemination in the air of droplet nuclei containing the infectious agent Diseases include active pulmonary tuberculosis (TB), measles, chicken pox, pneumonic (pulmonary) plague and hemorrhagic fever with pneumonia 63
64 AIRBORNE PRECAUTIONS - Private room with door closed at all times. - Surgical mask upon room entry and surgical mask on patient before transportation and visitors before entering room. - Wear eye protection when performing procedures that may generate aerosols. - Hand hygiene before and after contact with patient and/or anything in room. ** Visitors please check at desk before entering room. 64
65 Droplet Precautions Droplets containing micro-organisms come in contact with mucus membranes Droplet distribution is limited by the force of expulsion and gravity Diseases include influenza, pertussis, mumps and pneumonias 65
66 DROPLET PRECAUTIONS - Private room. Door may remain open. - Surgical mask upon room entry and surgical mask on patient before transportation and visitors before entering room. - Wear eye protection when performing procedures that may generate aerosols. - Hand hygiene before and after contact with patient and/or anything in room. - Wear a gown and gloves when anticipating secretions remove gown and gloves before leaving room. ** Visitors please check at desk before entering room. 66
67 Contact Precautions Direct contact transmission: Direct physical transfer of microorganisms from an infected person to a susceptible host Indirect contact transmission: Contact with a contaminated object such as contaminated equipment or instruments Diseases include multi-resistant organism (MRO) infection, enteric and skin infections 67
68 CONTACT PRECAUTIONS - Private room. Door may remain open. - Put gloves on when you enter the room. Remove gloves before leaving the room and place in trash. Clean your hands. - Put gown on before entering room. Remove gown in ROOM and place in trash. - Hand hygiene before and after contact with patient and/or anything in room. - Dedicated equipment such as stethoscope and blood pressure cuff. ** Visitors please check at desk before entering room. 68
69 As a nurse, what is your nursing role? 69
70 Nurses Role Patients with TB should be monitored regularly to ensure that: No interruptions occur in treatment; Serious side-effects from the treatment are quickly identified; There is improvement in the patient's condition, although this is often very gradual The nurse's role is vital in the control of TB and for the successful completion of the patient's therapy 70
71 Case Study #1 Physical Exam: BP 130/70 HR 90 RR18 T-38.6 Lung: Crackles in the Right Upper lung (RUL) There is Dullness to Percussion in the RUL Heart: Regular Rate Rhythm No Murmurs Pt is having difficulty breathing What nursing interventions do you expect? 71
72 Administer oxygen if ordered and as ordered by a physician Give the TB patients fluids to loosen up secretions for easier expulsion from the lungs Position the patient in a high fowlers position to reduce the work needed to breathe Encourage and provide rest periods so the tuberculosis patient can have energy to breathe. 72
Document Title: Communicable & Infectious Diseases Emergencies. Author(s): Katherine A. Perry (University of Michigan), RN, BSN 2012
 Project: Ghana Emergency Medicine Collaborative Document Title: Communicable & Infectious Diseases Emergencies Author(s): Katherine A. Perry (University of Michigan), RN, BSN 2012 License: Unless otherwise
Project: Ghana Emergency Medicine Collaborative Document Title: Communicable & Infectious Diseases Emergencies Author(s): Katherine A. Perry (University of Michigan), RN, BSN 2012 License: Unless otherwise
Invest in the future, defeat malaria
 Invest in the future, defeat malaria Malaria is caused by parasites from the genus Plasmodium, which are spread to people by infected mosquitoes. There are five species of Plasmodium that can infect humans.
Invest in the future, defeat malaria Malaria is caused by parasites from the genus Plasmodium, which are spread to people by infected mosquitoes. There are five species of Plasmodium that can infect humans.
Tuberculosis Facts. TB is not spread by: Sharing food and drink Shaking someone s hand Touching bed lines or toilet seats
 Tuberculosis Facts Below are frequently asked questions about TB, and their answers. If you have additional questions you may contact the City of Ennis Department of Health Services at 972-875-1234 or
Tuberculosis Facts Below are frequently asked questions about TB, and their answers. If you have additional questions you may contact the City of Ennis Department of Health Services at 972-875-1234 or
Fundamentals of Tuberculosis (TB)
 TB in the United States Fundamentals of Tuberculosis (TB) From 1953 to 1984, reported cases decreased by approximately 5.6% each year From 1985 to 1992, reported cases increased by 20% 25,313 cases reported
TB in the United States Fundamentals of Tuberculosis (TB) From 1953 to 1984, reported cases decreased by approximately 5.6% each year From 1985 to 1992, reported cases increased by 20% 25,313 cases reported
Questions and Answers About
 Questions and Answers About TB 2005 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES TB Elimination Questions and Answers About TB 2005 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Questions and Answers About TB 2005 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES TB Elimination Questions and Answers About TB 2005 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Questions and Answers About
 Questions and Answers About TB 2002 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES n Questions and Answers About TB 2002 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National
Questions and Answers About TB 2002 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES n Questions and Answers About TB 2002 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National
Tuberculosis (TB) Fundamentals for School Nurses
 Tuberculosis (TB) Fundamentals for School Nurses June 9, 2015 Kristin Gall, RN, MSN/Pat Infield, RN-TB Program Manager Marsha Carlson, RN, BSN Two Rivers Public Health Department Nebraska Department of
Tuberculosis (TB) Fundamentals for School Nurses June 9, 2015 Kristin Gall, RN, MSN/Pat Infield, RN-TB Program Manager Marsha Carlson, RN, BSN Two Rivers Public Health Department Nebraska Department of
All you need to know about Tuberculosis
 All you need to know about Tuberculosis What is tuberculosis? Tuberculosis is an infectious disease that usually affects the lungs. Doctors make a distinction between two kinds of tuberculosis infection:
All you need to know about Tuberculosis What is tuberculosis? Tuberculosis is an infectious disease that usually affects the lungs. Doctors make a distinction between two kinds of tuberculosis infection:
Stop TB Poster (laminated copies are available from TB Control: )
 Tuberculosis Prevention and Control Recommendations For Homeless Shelters in Maine Tool Kit What Your Shelter Can Do to Prevent TB Assessing Your Shelter Guests Risk for TB Cough Alert Policy Think TB
Tuberculosis Prevention and Control Recommendations For Homeless Shelters in Maine Tool Kit What Your Shelter Can Do to Prevent TB Assessing Your Shelter Guests Risk for TB Cough Alert Policy Think TB
Tuberculosis 6/7/2018. Objectives. What is Tuberculosis?
 Tuberculosis Understanding, Investigating, Eliminating Jeff Maupin, RN Tuberculosis Control Nurse Sedgwick County Division of Health Objectives At the conclusion of this presentation, you will be able
Tuberculosis Understanding, Investigating, Eliminating Jeff Maupin, RN Tuberculosis Control Nurse Sedgwick County Division of Health Objectives At the conclusion of this presentation, you will be able
What Is TB? 388 How TB Is Spread 388 How to Know if a Person Has TB 389 How to Treat TB 389 Resistance to TB medicines 390
 386 Chapter 25 In this chapter: What Is TB? 388 How TB Is Spread 388 How to Know if a Person Has TB 389 How to Treat TB 389 Resistance to TB medicines 390 Preventing TB 391 Working for Change 391 387 (TB)
386 Chapter 25 In this chapter: What Is TB? 388 How TB Is Spread 388 How to Know if a Person Has TB 389 How to Treat TB 389 Resistance to TB medicines 390 Preventing TB 391 Working for Change 391 387 (TB)
Hot Topic: H1N1 Flu (Swine Flu)
 Hot Topic: H1N1 Flu (Swine Flu) For additional information go to: http://www.cdc.gov/ swineflu/general_info.htm Note: The information in this document is based on information from the CDC. The CDC site
Hot Topic: H1N1 Flu (Swine Flu) For additional information go to: http://www.cdc.gov/ swineflu/general_info.htm Note: The information in this document is based on information from the CDC. The CDC site
CHILD HEALTH. There is a list of references at the end where you can find more information. FACT SHEETS
 SOME 18,000 CHILDREN STILL DIE EVERY DAY FROM DISEASES THAT ARE MOSTLY PREVENTABLE. This fact sheet outlines some of the basic information related to the health and wellbeing of children under five years
SOME 18,000 CHILDREN STILL DIE EVERY DAY FROM DISEASES THAT ARE MOSTLY PREVENTABLE. This fact sheet outlines some of the basic information related to the health and wellbeing of children under five years
Malaria prevention and control
 COMMUNITY TOOLS Tool 1 Malaria prevention and control Point to first picture: What do you see in this picture? 1. A small child who looks very sick. The child is sweating and shaking. There are mosquitoes
COMMUNITY TOOLS Tool 1 Malaria prevention and control Point to first picture: What do you see in this picture? 1. A small child who looks very sick. The child is sweating and shaking. There are mosquitoes
Infection Control for Anesthesia Personnel
 Infection Control for Anesthesia Personnel 2017 A leading cause of death and increased morbidity for hospitalized ptns Hospitals, nursing homes, long-term care facilities, home care settings Higher rate
Infection Control for Anesthesia Personnel 2017 A leading cause of death and increased morbidity for hospitalized ptns Hospitals, nursing homes, long-term care facilities, home care settings Higher rate
INFLUENZA (FLU) Cleaning to Prevent the Flu
 INFLUENZA (FLU) Cleaning to Prevent the Flu Cleaning to Prevent the Flu 24 hours How long can the flu virus live on objects, such as doorknobs and tables? The flu virus can live on some surfaces for up
INFLUENZA (FLU) Cleaning to Prevent the Flu Cleaning to Prevent the Flu 24 hours How long can the flu virus live on objects, such as doorknobs and tables? The flu virus can live on some surfaces for up
 Malaria parasites Malaria parasites are micro-organisms that belong to the genus Plasmodium. There are more than 100 species of Plasmodium, which can infect many animal species such as reptiles, birds,
Malaria parasites Malaria parasites are micro-organisms that belong to the genus Plasmodium. There are more than 100 species of Plasmodium, which can infect many animal species such as reptiles, birds,
Etiological Agent: Pulmonary Tuberculosis. Debra Mercer BSN, RN, RRT. Definition
 Pulmonary Tuberculosis Debra Mercer BSN, RN, RRT Definition Tuberculosis is a contagious bacterial infection of the lungs caused by Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (TB) Etiological Agent: Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
Pulmonary Tuberculosis Debra Mercer BSN, RN, RRT Definition Tuberculosis is a contagious bacterial infection of the lungs caused by Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (TB) Etiological Agent: Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
"GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS IN INSTITUTIONAL FACILITIES"
 MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS IN INSTITUTIONAL FACILITIES" Training For THE CDC "TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTION GUIDELINES" "Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today...and Tomorrow"
MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS IN INSTITUTIONAL FACILITIES" Training For THE CDC "TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTION GUIDELINES" "Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today...and Tomorrow"
ATOVAQUONE PROGUANIL INFORMATION FOR THE PATIENT
 ATOVAQUONE PROGUANIL INFORMATION FOR THE PATIENT Please read this information carefully before taking your medication. If you have any questions ask your doctor or pharmacist. What is malaria? Malaria
ATOVAQUONE PROGUANIL INFORMATION FOR THE PATIENT Please read this information carefully before taking your medication. If you have any questions ask your doctor or pharmacist. What is malaria? Malaria
#114 - Tuberculosis Update [1]
![#114 - Tuberculosis Update [1] #114 - Tuberculosis Update [1]](/thumbs/96/128750142.jpg) Published on Excellence In Learning (https://excellenceinlearning.net) Home > #114 - Tuberculosis Update #114 - Tuberculosis Update [1] Please login [2] or register [3] to take this course. $8.00 Course
Published on Excellence In Learning (https://excellenceinlearning.net) Home > #114 - Tuberculosis Update #114 - Tuberculosis Update [1] Please login [2] or register [3] to take this course. $8.00 Course
The Respiratory System
 130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
SOP GEN-2016B. Revision/ Review Log Revision Date Approved by Reviewed by Revision Details/ Proposal Notes 04 October 2016
 Page 1 of 5 SOP GEN-2016B 1.0 Introduction 2.0 3.0 Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment 4.0 Return to Work 5.0 Special Concerns: Zika 5.1 Microcephaly 6.0 Resources Revision/ Review Log Revision Date Approved
Page 1 of 5 SOP GEN-2016B 1.0 Introduction 2.0 3.0 Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment 4.0 Return to Work 5.0 Special Concerns: Zika 5.1 Microcephaly 6.0 Resources Revision/ Review Log Revision Date Approved
"GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS IN HEALTHCARE FACILITIES"
 MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS IN HEALTHCARE FACILITIES" Training For THE CDC "TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTION GUIDELINES" "Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today...and Tomorrow" Outline
MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS IN HEALTHCARE FACILITIES" Training For THE CDC "TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTION GUIDELINES" "Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today...and Tomorrow" Outline
PNEUMONIA. Your Treatment and Recovery
 PNEUMONIA Your Treatment and Recovery Understanding Pneumonia Symptoms of Pneumonia Do you feel feverish and tired, with a cough that won t go away? If so, you may have pneumonia. This is a lung infection
PNEUMONIA Your Treatment and Recovery Understanding Pneumonia Symptoms of Pneumonia Do you feel feverish and tired, with a cough that won t go away? If so, you may have pneumonia. This is a lung infection
Chapter 7 Tuberculosis (TB)
 Chapter 7 Tuberculosis (TB) TB infection vs. TB disease Information about TB TB skin testing Active TB disease TB risk factors Role of Peel Public Health in TB prevention and control Environmental and
Chapter 7 Tuberculosis (TB) TB infection vs. TB disease Information about TB TB skin testing Active TB disease TB risk factors Role of Peel Public Health in TB prevention and control Environmental and
Infection Prevention To navigate, click the Page Up or Page Down keys on your keyboard
 Infection Prevention To navigate, click the Page Up or Page Down keys on your keyboard Welcome to Infection Prevention This course is intended to present a brief overview of various infection control topics.
Infection Prevention To navigate, click the Page Up or Page Down keys on your keyboard Welcome to Infection Prevention This course is intended to present a brief overview of various infection control topics.
Pneumonia. Trachea , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. id Last reviewed: 11/11/2017 1
 Pneumonia Introduction Pneumonia is an inflammation and infection of the lungs. Pneumonia causes millions of deaths every year. It can affect anybody, but is more dangerous to older adults, babies and
Pneumonia Introduction Pneumonia is an inflammation and infection of the lungs. Pneumonia causes millions of deaths every year. It can affect anybody, but is more dangerous to older adults, babies and
New Entrant Screening and Latent TB Get screened and find out if you have TB infection before you develop TB disease!
 New Entrant Screening and Latent TB Get screened and find out if you have TB infection before you develop TB disease! Screening and treatment for TB are free. What does this leaflet cover? What is Tuberculosis
New Entrant Screening and Latent TB Get screened and find out if you have TB infection before you develop TB disease! Screening and treatment for TB are free. What does this leaflet cover? What is Tuberculosis
TB and Respiratory Protection
 Slide 1 TB and Respiratory Protection Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease present throughout the United States. Lehigh Valley Health Network is concerned about your health and needs your help to prevent the
Slide 1 TB and Respiratory Protection Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease present throughout the United States. Lehigh Valley Health Network is concerned about your health and needs your help to prevent the
Create the Following Chart in your notebook. Fill in as you go through each one.
 Diseases of Africa Create the Following Chart in your notebook. Fill in as you go through each one. History of disease? Affected Population? How do you catch the disease? Symptoms? Prevention / Treatment?
Diseases of Africa Create the Following Chart in your notebook. Fill in as you go through each one. History of disease? Affected Population? How do you catch the disease? Symptoms? Prevention / Treatment?
AOHS Global Health. Unit 1, Lesson 3. Communicable Disease
 AOHS Global Health Unit 1, Lesson 3 Communicable Disease Copyright 2012 2016 NAF. All rights reserved. A communicable disease is passed from one infected person to another The range of communicable diseases
AOHS Global Health Unit 1, Lesson 3 Communicable Disease Copyright 2012 2016 NAF. All rights reserved. A communicable disease is passed from one infected person to another The range of communicable diseases
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Information About H3N2v
 Information About H3N2v James R. Ginder, MS, NREMT,PI,CHES,NCEE Health Education Specialist Hamilton County Health Department www.hamiltoncounty.in.gov Mary Jo Skinner, RN, BSN, MBA Public Health Nurse
Information About H3N2v James R. Ginder, MS, NREMT,PI,CHES,NCEE Health Education Specialist Hamilton County Health Department www.hamiltoncounty.in.gov Mary Jo Skinner, RN, BSN, MBA Public Health Nurse
What is the most important information I should know about bortezomib? What should I discuss with my healthcare provider before receiving bortezomib?
 1 of 5 6/10/2016 3:46 PM Generic Name: bortezomib (bor TEZ oh mib) Brand Name: Velcade What is bortezomib? Bortezomib interferes with the growth of some cancer cells and keeps them from spreading in your
1 of 5 6/10/2016 3:46 PM Generic Name: bortezomib (bor TEZ oh mib) Brand Name: Velcade What is bortezomib? Bortezomib interferes with the growth of some cancer cells and keeps them from spreading in your
Swine flu - information prescription
 Swine flu - information prescription Introduction Swine flu is a relatively new strain of influenza (flu) that was responsible for a flu pandemic during 2009-2010. It is sometimes known as H1N1 influenza
Swine flu - information prescription Introduction Swine flu is a relatively new strain of influenza (flu) that was responsible for a flu pandemic during 2009-2010. It is sometimes known as H1N1 influenza
Pandemic H1N1 Frequently Asked Questions
 Pandemic H1N1 Frequently Asked Questions What is pandemic H1N1 flu? Pandemic H1N1 influenza (once referred to as swine flu ) is a new flu virus that causes respiratory illness in people. The Centers for
Pandemic H1N1 Frequently Asked Questions What is pandemic H1N1 flu? Pandemic H1N1 influenza (once referred to as swine flu ) is a new flu virus that causes respiratory illness in people. The Centers for
Tuberculosis What you need to know. James Zoretic M.D., M.P.H. Regions 2 and 3 Director
 Tuberculosis What you need to know James Zoretic M.D., M.P.H. Regions 2 and 3 Director What is Tuberculosis? Tuberculosis, (TB) is a communicable disease caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacillus
Tuberculosis What you need to know James Zoretic M.D., M.P.H. Regions 2 and 3 Director What is Tuberculosis? Tuberculosis, (TB) is a communicable disease caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacillus
Chapter 13. Preventing Infectious Diseases. Copyright by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
 Preventing Infectious Diseases Preventing Infectious Diseases Contents Section 1 What Are Infectious Diseases? Section 2 Protecting Yourself from Infectious Diseases Section 3 Common Infectious Diseases
Preventing Infectious Diseases Preventing Infectious Diseases Contents Section 1 What Are Infectious Diseases? Section 2 Protecting Yourself from Infectious Diseases Section 3 Common Infectious Diseases
Tiredness/Fatigue Mild Moderate to severe, especially at onset of symptoms Head and Body Aches and Pains
 What is the difference between a cold COLD FLU and the flu? How it starts Symptoms It s Cold and Flu Season in Snohomish County! Colds and Flu are respiratory illnesses caused by viruses. Our Immune Systems
What is the difference between a cold COLD FLU and the flu? How it starts Symptoms It s Cold and Flu Season in Snohomish County! Colds and Flu are respiratory illnesses caused by viruses. Our Immune Systems
Doctor Discussion Guide
 Doctor Discussion Guide Getting the pain relief you need to stay active is important. Keeping track of your symptoms can help you and your healthcare provider determine if there is a need to adjust your
Doctor Discussion Guide Getting the pain relief you need to stay active is important. Keeping track of your symptoms can help you and your healthcare provider determine if there is a need to adjust your
Swine Influenza (H1N1) precautions being taken in Europe No U.S. military travel advisories issued yet
 News Release EUROPE REGIONAL MEDICAL COMMAND Public Affairs Office CMR 442 APO AE 09042 U.S. Army Hospital Nachrichten Kaserne Postfach 103180 69021 Heidelberg, Germany DSN 371-3317/3049 Tel. 06221-17-3317/3049
News Release EUROPE REGIONAL MEDICAL COMMAND Public Affairs Office CMR 442 APO AE 09042 U.S. Army Hospital Nachrichten Kaserne Postfach 103180 69021 Heidelberg, Germany DSN 371-3317/3049 Tel. 06221-17-3317/3049
EPIDEMIOLOGY AND RISK OF INFECTION IN DENTAL SETTINGS
 Module C EPIDEMIOLOGY AND RISK OF INFECTION IN DENTAL SETTINGS Statewide Program for Infection Control and Epidemiology (SPICE) OBJECTIVES Discuss the infectious process through review of the chain of
Module C EPIDEMIOLOGY AND RISK OF INFECTION IN DENTAL SETTINGS Statewide Program for Infection Control and Epidemiology (SPICE) OBJECTIVES Discuss the infectious process through review of the chain of
Bloodborne Pathogens. Aaron Holmberg, Risk Manager. ARM, MBA, OSHA Authorized Outreach Trainer February 2018
 Bloodborne Pathogens Aaron Holmberg, Risk Manager ARM, MBA, OSHA Authorized Outreach Trainer February 2018 What s This About? Infectious microorganisms (viruses and diseases) found in blood and bodily
Bloodborne Pathogens Aaron Holmberg, Risk Manager ARM, MBA, OSHA Authorized Outreach Trainer February 2018 What s This About? Infectious microorganisms (viruses and diseases) found in blood and bodily
Capecitabine. Other Names: Xeloda. About This Drug. Possible Side Effects. Warnings and Precautions
 Capecitabine Other Names: Xeloda About This Drug Capecitabine is used to treat cancer. It is given orally (by mouth). Possible Side Effects Tired and weakness Loose bowel movements (diarrhea) Nausea and
Capecitabine Other Names: Xeloda About This Drug Capecitabine is used to treat cancer. It is given orally (by mouth). Possible Side Effects Tired and weakness Loose bowel movements (diarrhea) Nausea and
A Guide for Parents. Protect your child. What parents should know. Flu Information The Flu:
 Flu Information The Flu: A Guide for Parents Influenza (also known as flu) is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses that infect the nose, throat, and lungs. Flu is different from
Flu Information The Flu: A Guide for Parents Influenza (also known as flu) is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses that infect the nose, throat, and lungs. Flu is different from
What is tuberculosis? What causes tuberculosis?
 What is tuberculosis? What causes tuberculosis? Last updated: Thursday 4 September 2014 Tuberculosis Infectious Diseases / Bacteria / Viruses Respiratory / Asthma Some may see Tuberculosis as a historical
What is tuberculosis? What causes tuberculosis? Last updated: Thursday 4 September 2014 Tuberculosis Infectious Diseases / Bacteria / Viruses Respiratory / Asthma Some may see Tuberculosis as a historical
Infection Prevention and Control Annual Education Authored by: Infection Prevention and Control Department
 Infection Prevention and Control Annual Education 2017 Authored by: Infection Prevention and Control Department Objectives After you complete this Computer-Based Learning (CBL) module, you should be able
Infection Prevention and Control Annual Education 2017 Authored by: Infection Prevention and Control Department Objectives After you complete this Computer-Based Learning (CBL) module, you should be able
MEDICATION GUIDE Mefloquine Hydrochloride Tablets, USP
 Important: Your doctor or pharmacist will give you an Information Wallet Card along with this Medication Guide. It has important information about mefloquine and should be carried with you at all times
Important: Your doctor or pharmacist will give you an Information Wallet Card along with this Medication Guide. It has important information about mefloquine and should be carried with you at all times
Sorafenib (Nexavar ) ( sor-af-e-nib )
 Sorafenib (Nexavar ) ( sor-af-e-nib ) How the drug is given: by mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer, liver cancer, and other cancers How to take the drug by mouth Take on
Sorafenib (Nexavar ) ( sor-af-e-nib ) How the drug is given: by mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer, liver cancer, and other cancers How to take the drug by mouth Take on
Advisory on Plague WHAT IS PLAGUE? 19 October 2017
 19 October 2017 Advisory on Plague WHAT IS PLAGUE? Plague is an infectious disease caused by the zoonotic bacteria, Yersinia pestis. This bacteria often infects small rodents (like rats, mice, and squirrels)
19 October 2017 Advisory on Plague WHAT IS PLAGUE? Plague is an infectious disease caused by the zoonotic bacteria, Yersinia pestis. This bacteria often infects small rodents (like rats, mice, and squirrels)
Health advice for travelers
 Health advice for travelers Welcome to Thailand Every year millions of tourists set Thailand as one of their favorite destinations. The information provided here will help you come up with appropriate
Health advice for travelers Welcome to Thailand Every year millions of tourists set Thailand as one of their favorite destinations. The information provided here will help you come up with appropriate
HASPI Medical Biology Lab 03
 Patient 1001 is a 42-year-old female that is experiencing severe heartburn, abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, and vomiting. Ulcers Bleeding sores in the stomach or intestine Gallbladder Disease Gallstones
Patient 1001 is a 42-year-old female that is experiencing severe heartburn, abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, and vomiting. Ulcers Bleeding sores in the stomach or intestine Gallbladder Disease Gallstones
Blood Borne Pathogens. November 2010
 Blood Borne Pathogens November 2010 Objectives Meet requirements of OSHA Standard 29 CFR 1910.1030 OSHA Blood Borne Pathogens Post Test Routes of Transmission Types of Pathogens BSI / PPE Common Diseases
Blood Borne Pathogens November 2010 Objectives Meet requirements of OSHA Standard 29 CFR 1910.1030 OSHA Blood Borne Pathogens Post Test Routes of Transmission Types of Pathogens BSI / PPE Common Diseases
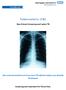
What Drug Treatment Centers Can do to Prevent Tuberculosis
 What Drug Treatment Centers Can do to Prevent Tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is alive and well Learn what you can do to prevent TB among your clients and protect yourself! Transmission TB is spread through
What Drug Treatment Centers Can do to Prevent Tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is alive and well Learn what you can do to prevent TB among your clients and protect yourself! Transmission TB is spread through
Everolimus (Afinitor )
 Everolimus (Afinitor ) ( e-ver-oh-li-mus ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: to slow the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer and other cancers How to take the drug Take with or without food and
Everolimus (Afinitor ) ( e-ver-oh-li-mus ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: to slow the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer and other cancers How to take the drug Take with or without food and
Communicable Diseases. Detection and Prevention
 Communicable Diseases Detection and Prevention Communicable Diseases Communicable Disease an infectious disease transmissible by direct contact (person to person) indirect means (body fluids, objects touched
Communicable Diseases Detection and Prevention Communicable Diseases Communicable Disease an infectious disease transmissible by direct contact (person to person) indirect means (body fluids, objects touched
"GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS AS A FIRST RESPONDER"
 MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS AS A FIRST RESPONDER" Training For THE CDC "TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTION GUIDELINES" "Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today...and Tomorrow" Outline
MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS AS A FIRST RESPONDER" Training For THE CDC "TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTION GUIDELINES" "Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today...and Tomorrow" Outline
Respiratory Tuberculosis (TB)
 Respiratory Tuberculosis (TB) Information Leaflet For Patients and Visitors Please follow this guidance from the Infection Prevention and Control Team What is Respiratory Tuberculosis (TB)? Pulmonary/respiratory
Respiratory Tuberculosis (TB) Information Leaflet For Patients and Visitors Please follow this guidance from the Infection Prevention and Control Team What is Respiratory Tuberculosis (TB)? Pulmonary/respiratory
FACT SHEET. H1N1 Influenza phone
 www.cookcountypublichealth.org 708-492-2000 phone H1N1 Influenza FACT SHEET What is novel H1N1? Novel H1N1 (referred to as swine flu early on) is a new influenza virus causing illness in people. This new
www.cookcountypublichealth.org 708-492-2000 phone H1N1 Influenza FACT SHEET What is novel H1N1? Novel H1N1 (referred to as swine flu early on) is a new influenza virus causing illness in people. This new
Name of Child: Date: The Flu. Seasonal Influenza and H1N1
 The Emily Center The Flu Seasonal Influenza and H1N1 Diagnosis/Disease/Illness Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. Name of Child: Date: The Flu Seasonal
The Emily Center The Flu Seasonal Influenza and H1N1 Diagnosis/Disease/Illness Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. Name of Child: Date: The Flu Seasonal
OBJECTIVES PEOPLE AS RESERVOIRS. Reservoir
 Module C EPIDEMIOLOGY AND RISK OF INFECTION IN OUTPATIENT SETTINGS Statewide Program for Infection Control and Epidemiology (SPICE) UNC School of Medicine OBJECTIVES Discuss the infectious process Review
Module C EPIDEMIOLOGY AND RISK OF INFECTION IN OUTPATIENT SETTINGS Statewide Program for Infection Control and Epidemiology (SPICE) UNC School of Medicine OBJECTIVES Discuss the infectious process Review
What is flu? What are the symptoms of flu? Is flu serious? How does flu spread? How is flu treated? PUBLIC HEALTH FACT SHEET Influenza (Seasonal Flu)
 PUBLIC HEALTH FACT SHEET Influenza (Seasonal Flu) August 2016 Page 1 of 3 What is flu? Flu is a disease of the body s breathing system, including the nose, throat and lungs. Flu is short for influenza.
PUBLIC HEALTH FACT SHEET Influenza (Seasonal Flu) August 2016 Page 1 of 3 What is flu? Flu is a disease of the body s breathing system, including the nose, throat and lungs. Flu is short for influenza.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS SWINE FLU
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS SWINE FLU Updated 5/6/09 ER FAQ What is swine flu? Swine flu is common disease of pigs and is caused by the same category of influenza virus (influenza A) that causes flu in
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS SWINE FLU Updated 5/6/09 ER FAQ What is swine flu? Swine flu is common disease of pigs and is caused by the same category of influenza virus (influenza A) that causes flu in
Infection Prevention Prevention and Contr
 Infection Prevention and Control o What is an infection? An infection is an illness caused by microorganisms A disease producing micro organism is called a pathogen Most microorganisms are classified as:
Infection Prevention and Control o What is an infection? An infection is an illness caused by microorganisms A disease producing micro organism is called a pathogen Most microorganisms are classified as:
FLU VACCINE INFORMATION The FLU JAB
 FLU VACCINE INFORMATION 2018 In the UK the flu vaccine is available each year from late September or early October onwards. It is recommended to get the flu vaccine in the autumn, before outbreaks of flu
FLU VACCINE INFORMATION 2018 In the UK the flu vaccine is available each year from late September or early October onwards. It is recommended to get the flu vaccine in the autumn, before outbreaks of flu
Swine Flu Information Provided by Santa Barbara Human Resources Association
 Swine Flu Information Provided by Santa Barbara Human Resources Association The County Health Department held a briefing on Monday, April 27thto outline the issues surrounding the Swine Flu and its migration
Swine Flu Information Provided by Santa Barbara Human Resources Association The County Health Department held a briefing on Monday, April 27thto outline the issues surrounding the Swine Flu and its migration
Chapter 7 8/23/2016. Asepsis and Infection Control. Asepsis. Asepsis (Cont.) Microorganisms. Infection control and prevention
 Chapter 7 Asepsis and Infection Control All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Asepsis Microorganisms Tiny microscopic entities capable
Chapter 7 Asepsis and Infection Control All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Asepsis Microorganisms Tiny microscopic entities capable
Infection Control Blood Borne Pathogens. Pines Behavioral Health
 Infection Control Blood Borne Pathogens Pines Behavioral Health Definition: Infection control is preventing the spread of germs that cause illness and infection. Infection control starts with understanding
Infection Control Blood Borne Pathogens Pines Behavioral Health Definition: Infection control is preventing the spread of germs that cause illness and infection. Infection control starts with understanding
CHAPTER:1 TUBERCULOSIS. BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY
 CHAPTER:1 TUBERCULOSIS BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY GLOBAL EMERGENCY: * Tuberculosis kills 5,000 people a day! * 2.3 million die each year!
CHAPTER:1 TUBERCULOSIS BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY GLOBAL EMERGENCY: * Tuberculosis kills 5,000 people a day! * 2.3 million die each year!
Tuberculosis (TB) how do we treat it?
 Tuberculosis (TB) how do we treat it? Read this. Here is how you will be cured. You will be cured if you take your medicines every day during the whole treatment. You are not alone, let s do this together!
Tuberculosis (TB) how do we treat it? Read this. Here is how you will be cured. You will be cured if you take your medicines every day during the whole treatment. You are not alone, let s do this together!
In your own words define: Normal flora-what is it and what does it do? Pathogen-what is it and what does it do?
 Bell Work: Based on yesterday s lesson In your own words define: Normal flora-what is it and what does it do? Pathogen-what is it and what does it do? Chain of Infection and Isolation Precautions Standard
Bell Work: Based on yesterday s lesson In your own words define: Normal flora-what is it and what does it do? Pathogen-what is it and what does it do? Chain of Infection and Isolation Precautions Standard
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Kathleen A. Stringer, Pharm. D, 2011 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Kathleen A. Stringer, Pharm. D, 2011 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Standard Precautions & Isolation Precautions. If you have questions about this module, contact the Infection Prevention department at your facility.
 Standard Precautions & If you have questions about this module, contact the Infection Prevention department at your facility. Annual Education 2014 Standard Precautions Standard Precautions should be used
Standard Precautions & If you have questions about this module, contact the Infection Prevention department at your facility. Annual Education 2014 Standard Precautions Standard Precautions should be used
Epidemiology and Risk of Infection in outpatient Settings
 Module C Epidemiology and Risk of Infection in outpatient Settings Statewide Program for Infection Control and Epidemiology (SPICE) UNC School of Medicine Objectives Discuss the infectious process through
Module C Epidemiology and Risk of Infection in outpatient Settings Statewide Program for Infection Control and Epidemiology (SPICE) UNC School of Medicine Objectives Discuss the infectious process through
Epidemiology and Risk of Infection in outpatient Settings
 Module C Epidemiology and Risk of Infection in outpatient Settings Statewide Program for Infection Control and Epidemiology (SPICE) UNC School of Medicine Objectives Discuss the infectious process through
Module C Epidemiology and Risk of Infection in outpatient Settings Statewide Program for Infection Control and Epidemiology (SPICE) UNC School of Medicine Objectives Discuss the infectious process through
Introduction to Global Child Health Elective for Pediatric Residents and Fellows Children s National Medical Center, Washington, DC.
 Introduction to Global Child Health Elective for Pediatric Residents and Fellows Children s National Medical Center, Washington, DC October 11-15, 2010 Pre-Course Test 1. You are preparing for an elective
Introduction to Global Child Health Elective for Pediatric Residents and Fellows Children s National Medical Center, Washington, DC October 11-15, 2010 Pre-Course Test 1. You are preparing for an elective
What to Do When You Have (or Think You Have) the Flu
 V News Release Landstuhl Regional Medical Center Public Affairs Office Phone: DSN 590-7181/8144 Civilian: 06371-9464-7181/8144 Email: 32Tusarmy.landstuhl.medcom-ermc.list.lrmc-public-affairs@mail.mil32T
V News Release Landstuhl Regional Medical Center Public Affairs Office Phone: DSN 590-7181/8144 Civilian: 06371-9464-7181/8144 Email: 32Tusarmy.landstuhl.medcom-ermc.list.lrmc-public-affairs@mail.mil32T
Tuberculosis Procedure ICPr016. Table of Contents
 Tuberculosis Procedure ICPr016 Table of Contents Tuberculosis Procedure ICPr016... 1 What is Tuberculosis?... 2 Any required definitions/explanations... 2 NHFT... 2 Tuberculosis (TB)... 3 Latent TB...
Tuberculosis Procedure ICPr016 Table of Contents Tuberculosis Procedure ICPr016... 1 What is Tuberculosis?... 2 Any required definitions/explanations... 2 NHFT... 2 Tuberculosis (TB)... 3 Latent TB...
HERNOVIR 200 mg tablets
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER HERNOVIR 200 mg tablets ACICLOVIR This leaflet is a copy of the Summary of Product Characteristics and Patient Information Leaflet for a medicine, which outlines
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER HERNOVIR 200 mg tablets ACICLOVIR This leaflet is a copy of the Summary of Product Characteristics and Patient Information Leaflet for a medicine, which outlines
Symptoms of Malaria. Young children, pregnant women, immunosuppressed and elderly travellers are particularly at risk of severe malaria.
 Preventing Malaria 1 Malaria is the world s most prevalent parasitic disease, accounting for an estimated 216 million cases with 655,000 deaths annually. Many people acquire malaria during travel to tropical
Preventing Malaria 1 Malaria is the world s most prevalent parasitic disease, accounting for an estimated 216 million cases with 655,000 deaths annually. Many people acquire malaria during travel to tropical
Symptoms Latent TB Active TB
 1 Tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease that can spread through the air. It is caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It usually affect the lungs. However, it can also affect other
1 Tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease that can spread through the air. It is caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It usually affect the lungs. However, it can also affect other
Recognizing MDR-TB in Children. Ma. Cecilia G. Ama, MD 23 rd PIDSP Annual Convention February 2016
 Recognizing MDR-TB in Children Ma. Cecilia G. Ama, MD 23 rd PIDSP Annual Convention 17-18 February 2016 Objectives Review the definitions and categorization of drugresistant tuberculosis Understand the
Recognizing MDR-TB in Children Ma. Cecilia G. Ama, MD 23 rd PIDSP Annual Convention 17-18 February 2016 Objectives Review the definitions and categorization of drugresistant tuberculosis Understand the
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author: Michael Jibson, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Dexamethasone is used to treat cancer. This drug can be given in the vein (IV), by mouth, or as an eye drop.
 Dexamethasone Other Names: Decadron About This Drug Dexamethasone is used to treat cancer. This drug can be given in the vein (IV), by mouth, or as an eye drop. Possible Side Effects (More Common) Increased
Dexamethasone Other Names: Decadron About This Drug Dexamethasone is used to treat cancer. This drug can be given in the vein (IV), by mouth, or as an eye drop. Possible Side Effects (More Common) Increased
How to Take Care of a Sick Person
 39 How to Take Care of a Sick Person Sickness weakens the body. To gain strength and get well quickly, special care is needed. The care a sick person receives is frequently the most important part of his
39 How to Take Care of a Sick Person Sickness weakens the body. To gain strength and get well quickly, special care is needed. The care a sick person receives is frequently the most important part of his
Breaking the Chain of Infection Designated Officer Education Day September 3, 2014 Jodi-Marie Black RN BScN PHN
 Breaking the Chain of Infection Designated Officer Education Day September 3, 2014 Jodi-Marie Black RN BScN PHN Topics Covered in Presentation The Chain of infection and how to break the chain Role of
Breaking the Chain of Infection Designated Officer Education Day September 3, 2014 Jodi-Marie Black RN BScN PHN Topics Covered in Presentation The Chain of infection and how to break the chain Role of
Lourdes Hospital Infection Prevention and Control
 Lourdes Hospital Infection Prevention and Control Lourdes Infection Prevention Program Ultimate goal: To protect the patient To protect the healthcare workers, visitors and others in the environment To
Lourdes Hospital Infection Prevention and Control Lourdes Infection Prevention Program Ultimate goal: To protect the patient To protect the healthcare workers, visitors and others in the environment To
Vaccine Preventable Respiratory Infections and Tuberculosis
 Vaccine Preventable Respiratory Infections and Tuberculosis Infection Prevention Essentials in Long-Term Care Spring 2019 Teri Hulett, RN, BSN, CIC, FAPIC Leading infection prevention education across
Vaccine Preventable Respiratory Infections and Tuberculosis Infection Prevention Essentials in Long-Term Care Spring 2019 Teri Hulett, RN, BSN, CIC, FAPIC Leading infection prevention education across
Eltrombopag (Promacta )
 Eltrombopag (Promacta ) ( el TROM boe pag ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: to treat aplastic anemia and increase low platelet counts in some conditions How to take this drug 1. Take this medication
Eltrombopag (Promacta ) ( el TROM boe pag ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: to treat aplastic anemia and increase low platelet counts in some conditions How to take this drug 1. Take this medication
H1N1 (Swine) Influenza
 What is H1N1 influenza A? H1N1 (Swine) Influenza The new H1N1 influenza, also called swine flu, is a new influenza virus causing illness in people. This new virus was first detected in 2009. This virus
What is H1N1 influenza A? H1N1 (Swine) Influenza The new H1N1 influenza, also called swine flu, is a new influenza virus causing illness in people. This new virus was first detected in 2009. This virus
Thomas McGee, L.C. 920 Main Street, Suite 1700 Kansas City, MO (816) * Toll Free (800) WEST NILE VIRUS
 Thomas McGee, L.C. 920 Main Street, Suite 1700 Kansas City, MO 64105 (816) 842-4800 * Toll Free (800) 423-9044 www.thomasmcgee.com WEST NILE VIRUS What Is West Nile Virus (WNV)? Potentially serious illness
Thomas McGee, L.C. 920 Main Street, Suite 1700 Kansas City, MO 64105 (816) 842-4800 * Toll Free (800) 423-9044 www.thomasmcgee.com WEST NILE VIRUS What Is West Nile Virus (WNV)? Potentially serious illness
Flu Facts. January 2019
 Flu Facts January 2019 Seasonal influenza is an acute respiratory infection caused by influenza viruses which circulate in all parts of the world. There are 4 types of seasonal influenza viruses, types
Flu Facts January 2019 Seasonal influenza is an acute respiratory infection caused by influenza viruses which circulate in all parts of the world. There are 4 types of seasonal influenza viruses, types
Alberta Health Public Health Notifiable Disease Management Guidelines July 2012
 July 2012 Malaria Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) Case Definition Confirmed Case Laboratory confirmation
July 2012 Malaria Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) Case Definition Confirmed Case Laboratory confirmation
MODULE B. Objectives. Infection Prevention. Infection Prevention. N.C. Nurse Aide I Curriculum
 DHSR/HCPR/CARE NAT I Curriculum - July 2013 1 N.C. Nurse Aide I Curriculum MODULE B Infection Prevention Objectives Relate the chain of infection to the work of a nurse aide in long-term care facilities.
DHSR/HCPR/CARE NAT I Curriculum - July 2013 1 N.C. Nurse Aide I Curriculum MODULE B Infection Prevention Objectives Relate the chain of infection to the work of a nurse aide in long-term care facilities.
PEGCO Inc. 532 N. RIDGEWOOD AVE DAYTONA BEACH, FL Phone: (386) Fax (386)
 PEGCO Inc. 532 N. RIDGEWOOD AVE DAYTONA BEACH, FL. 32114 Phone: (386) 756-4266 Fax (386) 492-7821 WEB SITE: www.volusiacpr.com NURSING HOME #NH 2772 ASSISTED LIVING #ALF 909 HOME HEALTH CARE #HH 1175 PLEASE
PEGCO Inc. 532 N. RIDGEWOOD AVE DAYTONA BEACH, FL. 32114 Phone: (386) 756-4266 Fax (386) 492-7821 WEB SITE: www.volusiacpr.com NURSING HOME #NH 2772 ASSISTED LIVING #ALF 909 HOME HEALTH CARE #HH 1175 PLEASE
Vaccine Information Statement: PEDIATRIC VACCINES (Multiple)
 Vaccine Information Statement: PEDIATRIC VACCINES (Multiple) 1. Your Baby s First Vaccines: What You Need to Know Babies get six vaccines between birth and 6 months of age. These vaccines protect your
Vaccine Information Statement: PEDIATRIC VACCINES (Multiple) 1. Your Baby s First Vaccines: What You Need to Know Babies get six vaccines between birth and 6 months of age. These vaccines protect your
Small living organism Not visible to the naked eye Must be viewed under a microscope Found everywhere in the environment, including on and in the
 Small living organism Not visible to the naked eye Must be viewed under a microscope Found everywhere in the environment, including on and in the human body Many Microorganisms are part of normal flora
Small living organism Not visible to the naked eye Must be viewed under a microscope Found everywhere in the environment, including on and in the human body Many Microorganisms are part of normal flora
Nivolumab. Other Names: Opdivo. About this Drug. Possible Side Effects (More Common) Warnings and Precautions
 Nivolumab Other Names: Opdivo About this Drug Nivolumab is used to treat cancer. It is given in the vein (IV). Possible Side Effects (More Common) Bone marrow depression. This is a decrease in the number
Nivolumab Other Names: Opdivo About this Drug Nivolumab is used to treat cancer. It is given in the vein (IV). Possible Side Effects (More Common) Bone marrow depression. This is a decrease in the number
