Endemic: rhinovirus, Epidemic: pertussis several years ago Pandemic: H1N1 in was a pandemic just not as severe as originally feared
|
|
|
- Morris Little
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1
2 2
3 3
4 Endemic: rhinovirus, Epidemic: pertussis several years ago Pandemic: H1N1 in was a pandemic just not as severe as originally feared 4
5 5
6 Endemic, Epidemic 6
7 Endemic, Epidemic 7
8 H5N1 H7N9 8
9 9
10 10
11 11
12 12
13 13
14 Point out that MRC response would be similar in many BT/PHP emergencies 14
15 15
16 16
17 17
18 18
19 Nipah virus causes encephalitis or respiratory inflammation Animal-to-human and human-to-human transmission. Fruit bats are the natural host. First recognized in Pigs are a common source of human disease and outbreaks. 19
20 These are examples of the highest-risk agents for BT according to the CDC. Category A agents are easily disseminated or transmitted, have high mortality and/or potential for considerable social disruption. 20
21 The name Variola is derived from a practice termed "variolation," which was the first effective, preventative method developed to provide protection from an infectious disease. Variolation is the practice of inhaling material from the dried pox scabs or inoculating this material directly beneath the skin. This method was effective, but had the disadvantage of producing smallpox when the material was active and not providing full immunological protection in some recipients. Nevertheless, this practice of variolation was practiced in the 18 th century in China, India, western Asia, and Europe. Smallpox is a highly communicable severe rash illness. There are different strains of the virus: one set causing more severe disease called variola major and other strains causing a more mild illness called variola minor. Historically there were 3 serious and 2 less serious forms of variola major. The most common form, ordinary smallpox, occurred in 90% of cases and had case-fatality rates of 15-45%. Other severe types of variola major were flat-type smallpox aka malignant smallpox and hemorrhagic smallpox. The milder forms of variola major were modified smallpox and variola without eruption. These occurred in persons with some immmunity from past infection or vaccination. Variola minor was less severe, was caused by different strains of variola virus and in the 20 th century was the most prevalent form of smallpox in the USA. 21
22 22
23 After a global 12-year international campaign involving mass vaccination programs combined with surveillance and containment of outbreaks, Smallpox became the first (and only) infectious human disease to be eradicated from the world! Efforts to vaccinate and contain the spread of this disease had been made ever since the 18 th century with variolation techniques. Then came along Jenner, who used the cowpox virus to give the worldís first vaccination against smallpox. This was highly effective, but could cause later neurological sequealae, and so the standard vaccine that was used to eradicate smallpox was the vaccinia virus. Vaccinia virus either had its origins from a recombinational event between the cowpox or variola virus through serial passage or could be the representative of a long-since extinct virus. Now only laboratory workers that handle the variola virus and continue to be vaccinated. 23
24 24
25 These are examples of the highest-risk agents for BT according to the CDC. Category A agents are easily disseminated or transmitted, have high mortality and/or potential for considerable social disruption. 25
26 Bacillus anthracis is a large spore forming aerobic encapsulated bacteria. In an environment rich in nutrients, the spores germinate and form bacteria. When nutrients in the environment are exhausted, the bacteria form spores. Anthrax spores are resistant to drying, heat, ultraviolet light, gamma radiation, and some disinfectants. Spores can persist in soli for years, wheras anthrax bacteria survive poorly outside of mammalian hosts. Anthrax spores are found in soil in many parts of the world, including Bay Area counties with grazing cattle (in 2001, an outbreak of bovine anthrax caused death of 21 beef cattle in Santa Clara county). ANTHRAX: Depending upon the route of exposure Bacillus anthraces can cause: Cutaneous Anthrax, Inhalational Anthrax, gastrointestinal anthrax, anthrax meningitis Cutaneous: initial lesion is small, pruritic papule or vesicle, papule then ulerates with central drying and necrosis. Painless, localized non-pitting edema, black eschar which sloughs off after days. Can have painful lymphadenopathy. Fever and maliase common. Lesions resolve without complications in 80-90% patients. Treatment is aimed at preventing systemic dissemination which occurs in 10-20% of cases. Inhalational:inhaled spores go to aveoli, get phagocytosed and travel to regional lymph 26
27 nodes, then germinate to become bacterial cells, which multiply in the lymphatic system and cause lymphadenitis of the mediastinal and peribronchial lymph nodes. The bacteria cause focal hemorrhagic necrosis in the lungs. Baceria entering the bloodstream lead to septicemia, shock, death. Illness is biphasic, initial phase is flulike, with progression after a few days to acute severe respiratory distress, high fever, shock, death. CXR notable for widened mediastinum. NOT CONTAGIOUS. Anthrax meningitis: can occur as a complication of cutaneous, inhalational or gi anthrax. 26
28 New slide to consider 27
29 28
30 These are examples of the highest-risk agents for BT according to the CDC. Category A agents are easily disseminated or transmitted, have high mortality and/or potential for considerable social disruption. 29
31 Y. pestis can enter Bioterrorism: aerosolized Y. pestis => contagious Pneumonic Plague (without bubonic plague features) Environmental Cycle: Flea (infected) bite => Bubonic Plague => septicemia => Pneumonic Plague => contagious respiratory droplets 30
32 31
33 These are examples of the highest-risk agents for BT according to the CDC. Category A agents are easily disseminated or transmitted, have high mortality and/or potential for considerable social disruption. 32
34 Botulism is an intoxication caused by botulinum toxin, which is produced by Clostridium botulinum and rarely other species. C. Botulinum is a large, strictly anaerobic, spore-forming bacteria commonly isolated from soil and from marine and lake sediments. There are several strains, all of which make toxins. C. botulinum bacteria, are not, in and of themselves, toxic to humans. Disease is caused by exposure to the bacterial toxin. Food borne botulism cased by ingesting of food contaminated with toxin. Dispersion of aerosolized toxin would cause inhalational botulism Wound caused by infection of a contaminated wound with C. botulinum organisms, and subsequent absortpion in the the circulation of locally produced toxin. Most cases related to injection drug use. In California, associated with black tar heroin. Infant is caused by ingestion of C. Botulinum spores. The spores colonize the gi tract, germinate and produce toxin which is absorbed into the circulation. Regardless of exposure, the same neurologic syndrome occurs: WHICH IS NOT CONTAGIOUS 33
35 Symptoms start hours after ingestion/inhalation/contamination profound muscle paralysis respiratory failure (< 24 hrs after onset of sx s) most toxic biological compounds known to man 10, ,000X more toxic than nerve agents 33
36 34
37 These are examples of the highest-risk agents for BT according to the CDC. Category A agents are easily disseminated or transmitted, have high mortality and/or potential for considerable social disruption. 35
38 Caused by bacteria Francisella tularensis Cultured 1912 in Tulare County (CA) Spread via direct contact with contaminated meat, inhalation and insect vectors Historical illnesses: rabbit fever, deer fly fever, market men s disease Organism of warfare research since
39 60 s Natural disease of Northern Hemisphere North America, Europe, Asia True pneumonia looks same as many pneumonias Not contagious human to human Standard precautions 36
40 Treatment Pre or Post exposure Prophylaxis: ciprofloxacin or doxycycline Live Vaccine Strain (LVS) investigational 37
41 These are examples of the highest-risk agents for BT according to the CDC. Category A agents are easily disseminated or transmitted, have high mortality and/or potential for considerable social disruption. 38
42 These viruses each are characterized by an acute generalized febrile illness that includes malaise, prostration, increased vascular permeability, and abnormalities of circulatory regulation. All agents are highly infectious via the aerosol route, most are stable as respiratory aerosols, and they can be replicated in cell culture. Thus, they possess characteristics ideal for use by terrorists. 4 families of viruses, which include the Arenaviridae (Lassa, Argentine, Bolivian, Brazilian, Venezuelan hemorrhagic fevers), Bunyaviridae (Rift Valley, Crimean Congo, Hantavirus), Filoviridae (Marburg, Ebola hemorrhagic fevers), and Flaviviridae (yellow, dengue, Kyasanur Forest, Omsk hemorrhagic fevers). Filoviridae family 39
43 highly contagious body fluids high mortality Ebola virus Sudan, Zaire, Gabon, Ivory Coast 50 90% mortality Marburg virus Africa, Germany, Yugoslavia African Green Monkey vector 39
44 40
45 41
46 Pose question to participants. Record responses on white board. 42
47 43
48 Something like a virus, bacteria, parasite or fungus can get Someone, usually a susceptible host, which will be discussed in more detail shortly, sick. That Someone however needs to be exposed to that Something Somehow, like through the mouth or broken skin, and lack of basic precautions can cause us to pick up that Something from Somewhere. So if we do not take basic precautions to protect ourselves we may get sick. 44
49 Water contaminated water can cause GI illness and wound infections. Giardia is a parasite that causes gastrointestinal illness and has often been linked with contaminated water. Outbreaks of bacterial illnesses like Salmonella and E. coli and also norovirus have also been associated with fecally contaminated water. A type of bacteria called Vibrio can be present in coastal waters and is capable of causing infection if an open wound is exposed to contaminated water. Air there were over 200 cases of coccidioidomycosis or valley fever after the 1994 northridge earthquake. Coccidioidomycosis is a fungus that exists naturally in the soil and can become airborne when a lot of dust is stirred up. People in dust clouds following the earthquake were at higher risk for infection. Can cause a flu-like illness (~60% asymptomatic). Some people can develop chronic pulmonary infection or widespread disseminated infection. Air can also contain infectious droplets that cause respiratory illnesses (influenza, TB, etc). Food food contaminated with human or animal fecal matter can cause a wide range of GI illnesses. Salmonella, E. coli, Campy, norovirus, etc Soil Clostridium tetani, which causes tetanus is present in soil. Clostridium sp. are 45
50 also capable of causing gangrene when they enter an open wound. Gangrene is characterized by tissue death and can occur when a body part loses its blood supply. This may happen from, for example, injury or infection. People are sources for many respiratory illnesses. Also many vaccine preventable illnesses such as measles, chickenpox, whooping cough etc. Skin infections such as those caused by Staphylococcus may occur due to close contact with infected individuals or sharing personal items like towels. Animals are natural reservoirs for many infectious agents that can cause human illness. Rabies, Salmonella, E. coli, leptospirosis are just a few examples. Vectors transmit diseases to people that are usually from an animal reservoir. Examples would be ticks which can transmit Lyme disease and have a mouse reservoir. Mosquitoes that can transmit WNV, which has a bird reservoir. There usually isn t an immediate risk for increase in vector-borne diseases following a disaster unless, for example, people are suddenly outside a lot more than previously and are therefore much more likely to be bitten (say by mosquitoes during the summer). What you might be more likely to encounter in a shelter setting would be nuisance vectors, such as head lice, mites, and bed bugs. They do not transmit diseases to humans, but they are still a public health concern because they can spread from person to person and cause rashes and discomfort. 45
51 46
52 Direct contact sexual transmission, diarrhea Indirect contact surface contamination Droplets cold, flu, meningitis Airborne dust, droplets, aerosol from medical procedures Vehicle-borne ingestion contaminated food/water, injection drug use Vector-borne WNV/mosquitoes Vertical mother to child at birth 47
53 Nurses will be familiar with these principals of infection control already, but will need to remind patients and the public of the importance of basic sanitation following a disaster. 48
54 49
Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences
 Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Chapter 11. Epidemiology and Public Health Chapter 11 Outline Epidemiology Interactions Among Pathogens, Hosts and the Environment Chain of Infection Reservoirs
Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Chapter 11. Epidemiology and Public Health Chapter 11 Outline Epidemiology Interactions Among Pathogens, Hosts and the Environment Chain of Infection Reservoirs
Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers
 Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers (VHFs) http://www.ncrr.nih.gov/publications/ncrr_reporter/summer-fall2009/images/essential_2.jpg Definition Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) refer to a group of illnesses that are
Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers (VHFs) http://www.ncrr.nih.gov/publications/ncrr_reporter/summer-fall2009/images/essential_2.jpg Definition Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) refer to a group of illnesses that are
Disease Transmission Methods
 Disease Transmission Methods In epidemiology, transmission simply means any method by which an infectious agent is spread from one host to another. Knowing the type of pathogen often, but not always, identifies
Disease Transmission Methods In epidemiology, transmission simply means any method by which an infectious agent is spread from one host to another. Knowing the type of pathogen often, but not always, identifies
An Overview of Bioterrorism. SAEMS January 30, Charles A. Schable, M.S. Institutional Biosafety Committee University of Arizona
 An Overview of Bioterrorism SAEMS January 30, 2008 Charles A. Schable, M.S. Institutional Biosafety Committee University of Arizona Bioterrorism Intentional or threatened use of viruses, bacteria, fungi,
An Overview of Bioterrorism SAEMS January 30, 2008 Charles A. Schable, M.S. Institutional Biosafety Committee University of Arizona Bioterrorism Intentional or threatened use of viruses, bacteria, fungi,
Communicable diseases. Gastrointestinal track infection. Sarkhell Araz MSc. Public health/epidemiology
 Communicable diseases Gastrointestinal track infection Sarkhell Araz MSc. Public health/epidemiology Communicable diseases : Refer to diseases that can be transmitted and make people ill. They are caused
Communicable diseases Gastrointestinal track infection Sarkhell Araz MSc. Public health/epidemiology Communicable diseases : Refer to diseases that can be transmitted and make people ill. They are caused
Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers CDC, AFIP
 CDC, AFIP Diverse group of illnesses caused by RNA viruses from 4 families: Arenaviridae, Bunyaviridae, Filoviridae, Flaviridae Differ by geographic occurrence and vector/reservoir Share certain clinical
CDC, AFIP Diverse group of illnesses caused by RNA viruses from 4 families: Arenaviridae, Bunyaviridae, Filoviridae, Flaviridae Differ by geographic occurrence and vector/reservoir Share certain clinical
B-NICE Overview. Types of WMD Agents. Types of WMD Agents. Types of WMD Agents. Job Aid Version 1.0 and 2.0. CDC & Prevention
 B-NICE Overview Types of WMD Agents Biological Nuclear Incendiary Chemical Explosive Types of WMD Agents Job Aid Version 1.0 and 2.0 Chemical Biological Radiological Nuclear Explosive Types of WMD Agents
B-NICE Overview Types of WMD Agents Biological Nuclear Incendiary Chemical Explosive Types of WMD Agents Job Aid Version 1.0 and 2.0 Chemical Biological Radiological Nuclear Explosive Types of WMD Agents
MMG 301 Lec. 35 Epidemiology and Bioterrorism
 MMG 301 Lec. 35 Epidemiology and Bioterrorism Questions for Today: (consider Med Micro course) 1. What is epidemiology? 2. How is epidemiology important to public health? 3. What pathogens are important
MMG 301 Lec. 35 Epidemiology and Bioterrorism Questions for Today: (consider Med Micro course) 1. What is epidemiology? 2. How is epidemiology important to public health? 3. What pathogens are important
UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS FIELD MEDICAL TRAINING BATTALION Camp Lejeune, NC
 UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS FIELD MEDICAL TRAINING BATTALION Camp Lejeune, NC 28542-0042 FMST 304 Manage Biological Agent Casualties TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVE 1. Given a casualty and the absence of a
UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS FIELD MEDICAL TRAINING BATTALION Camp Lejeune, NC 28542-0042 FMST 304 Manage Biological Agent Casualties TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVE 1. Given a casualty and the absence of a
Medical Bacteriology - Lecture 7. Spore- forming Gram Positive Rods. Bacillus
 Medical Bacteriology - Lecture 7 Spore- forming Gram Positive Rods Bacillus 1 Bacillus Characteristics - Gram positive - Large rod. - Arranged in long chain - Spore forming - Aerobic or facultative anaerobic
Medical Bacteriology - Lecture 7 Spore- forming Gram Positive Rods Bacillus 1 Bacillus Characteristics - Gram positive - Large rod. - Arranged in long chain - Spore forming - Aerobic or facultative anaerobic
Immune System. Before You Read. Read to Learn
 Immune System 37 section 1 Infectious Diseases Biology/Life Sciences 10.d Students know there are important differences between bacteria and viruses with respect to their requirements for growth and replication,
Immune System 37 section 1 Infectious Diseases Biology/Life Sciences 10.d Students know there are important differences between bacteria and viruses with respect to their requirements for growth and replication,
Biological Warfare Agents
 Biological Warfare Agents Chapter 29 Biological Warfare Agents The reader is strongly advised to supplement material in this chapter with the following reference: US Army Medical Research Institute of
Biological Warfare Agents Chapter 29 Biological Warfare Agents The reader is strongly advised to supplement material in this chapter with the following reference: US Army Medical Research Institute of
Breaking the Chain of Infection Designated Officer Education Day September 3, 2014 Jodi-Marie Black RN BScN PHN
 Breaking the Chain of Infection Designated Officer Education Day September 3, 2014 Jodi-Marie Black RN BScN PHN Topics Covered in Presentation The Chain of infection and how to break the chain Role of
Breaking the Chain of Infection Designated Officer Education Day September 3, 2014 Jodi-Marie Black RN BScN PHN Topics Covered in Presentation The Chain of infection and how to break the chain Role of
Agents of Bioterrorism: Argument for and Against a List That Needs Cropping
 Agents of Bioterrorism: Argument for and Against a List That Needs Cropping Bioterrorism Preparedness: A Conference for Senior Practitioners and Professionals Dr. Arnold N. Weinberg Professor of Medicine
Agents of Bioterrorism: Argument for and Against a List That Needs Cropping Bioterrorism Preparedness: A Conference for Senior Practitioners and Professionals Dr. Arnold N. Weinberg Professor of Medicine
Infectious Diseases Weekly Report. 23 August 2018 / Number 33. The infectious diseases which all physicians must report
 Infectious Diseases Weekly Report TOKYOIDWR Tokyo Metropolitan Infectious Disease Surveillance Center 23 August / Number 33 Surveillance System in Tokyo, Japan The infectious diseases which all physicians
Infectious Diseases Weekly Report TOKYOIDWR Tokyo Metropolitan Infectious Disease Surveillance Center 23 August / Number 33 Surveillance System in Tokyo, Japan The infectious diseases which all physicians
Infectious Diseases Weekly Report. 8 November 2018 / Number 44. The infectious diseases which all physicians must report
 Infectious Diseases Weekly Report TOKYOIDWR Tokyo Metropolitan Infectious Disease Surveillance Center 8 November / Number 44 Surveillance System in Tokyo, Japan The infectious diseases which all physicians
Infectious Diseases Weekly Report TOKYOIDWR Tokyo Metropolitan Infectious Disease Surveillance Center 8 November / Number 44 Surveillance System in Tokyo, Japan The infectious diseases which all physicians
Infectious Diseases Weekly Report. 15 November 2018 / Number 45. The infectious diseases which all physicians must report
 Infectious Diseases Weekly Report TOKYOIDWR Tokyo Metropolitan Infectious Disease Surveillance Center 15 November / Number 45 Surveillance System in Tokyo, Japan The infectious diseases which all physicians
Infectious Diseases Weekly Report TOKYOIDWR Tokyo Metropolitan Infectious Disease Surveillance Center 15 November / Number 45 Surveillance System in Tokyo, Japan The infectious diseases which all physicians
Infectious Diseases Weekly Report. 14 March 2019 / Number 10. The infectious diseases which all physicians must report
 Infectious Diseases Weekly Report TOKYOIDWR Tokyo Metropolitan Infectious Disease Surveillance Center 14 March / Number 10 Surveillance System in Tokyo, Japan The infectious diseases which all physicians
Infectious Diseases Weekly Report TOKYOIDWR Tokyo Metropolitan Infectious Disease Surveillance Center 14 March / Number 10 Surveillance System in Tokyo, Japan The infectious diseases which all physicians
Infectious Diseases Weekly Report. 22 March 2019 / Number 11. The infectious diseases which all physicians must report
 Infectious Diseases Weekly Report TOKYOIDWR Tokyo Metropolitan Infectious Disease Surveillance Center 22 March / Number 11 Surveillance System in Tokyo, Japan The infectious diseases which all physicians
Infectious Diseases Weekly Report TOKYOIDWR Tokyo Metropolitan Infectious Disease Surveillance Center 22 March / Number 11 Surveillance System in Tokyo, Japan The infectious diseases which all physicians
Infectious Diseases Weekly Report. 28 March 2019 / Number 12. The infectious diseases which all physicians must report
 Infectious Diseases Weekly Report TOKYOIDWR Tokyo Metropolitan Infectious Disease Surveillance Center 28 March / Number 12 Surveillance System in Tokyo, Japan The infectious diseases which all physicians
Infectious Diseases Weekly Report TOKYOIDWR Tokyo Metropolitan Infectious Disease Surveillance Center 28 March / Number 12 Surveillance System in Tokyo, Japan The infectious diseases which all physicians
Infectious Diseases Weekly Report. 4 April 2019 / Number 13. The infectious diseases which all physicians must report
 Infectious Diseases Weekly Report TOKYOIDWR Tokyo Metropolitan Infectious Disease Surveillance Center 4 April / Number 13 Surveillance System in Tokyo, Japan The infectious diseases which all physicians
Infectious Diseases Weekly Report TOKYOIDWR Tokyo Metropolitan Infectious Disease Surveillance Center 4 April / Number 13 Surveillance System in Tokyo, Japan The infectious diseases which all physicians
Infectious Diseases Weekly Report. 11 April 2019 / Number 14. The infectious diseases which all physicians must report
 Infectious Diseases Weekly Report TOKYOIDWR Tokyo Metropolitan Infectious Disease Surveillance Center 11 April / Number 14 Surveillance System in Tokyo, Japan The infectious diseases which all physicians
Infectious Diseases Weekly Report TOKYOIDWR Tokyo Metropolitan Infectious Disease Surveillance Center 11 April / Number 14 Surveillance System in Tokyo, Japan The infectious diseases which all physicians
Bacterial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 Bacterial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity 1 st Lecture Introduction Infection and Disease A. Definitions B. Generalized Stages of Infection C. Virulence Factors and Toxins A. Definitions Disease and Infectious
Bacterial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity 1 st Lecture Introduction Infection and Disease A. Definitions B. Generalized Stages of Infection C. Virulence Factors and Toxins A. Definitions Disease and Infectious
Biological Terrorist Agents: Part 2 Viral Agents
 Biological Terrorist Agents: Part 2 Viral Agents ROBERT BURKE Published: July 2002 Viruses are the simplest type of microorganisms and the smallest of all living things. They are much smaller than bacteria
Biological Terrorist Agents: Part 2 Viral Agents ROBERT BURKE Published: July 2002 Viruses are the simplest type of microorganisms and the smallest of all living things. They are much smaller than bacteria
Infectious Diseases Weekly Report. 14 March 2013 / Number 10
 Infectious Diseases Weekly Report TOKYOIDWR Tokyo Metropolitan Infectious Disease Surveillance Center 14 March / Number 10 Surveillance System in Tokyo, Japan The infectious diseases which all physicians
Infectious Diseases Weekly Report TOKYOIDWR Tokyo Metropolitan Infectious Disease Surveillance Center 14 March / Number 10 Surveillance System in Tokyo, Japan The infectious diseases which all physicians
Infectious Diseases Weekly Report. 12 January 2018 / Number 1. The infectious diseases which all physicians must report
 Infectious Diseases Weekly Report TOKYOIDWR Tokyo Metropolitan Infectious Disease Surveillance Center 12 January / Number 1 Surveillance System in Tokyo, Japan The infectious diseases which all physicians
Infectious Diseases Weekly Report TOKYOIDWR Tokyo Metropolitan Infectious Disease Surveillance Center 12 January / Number 1 Surveillance System in Tokyo, Japan The infectious diseases which all physicians
Bio Agents of Concern/Interest
 Bio Agents of Concern/Interest Potential Biological Threats 1. Ricin 2. Botulism toxin (Clostridium botulinum) 3. Anthrax (Bacillus( anthracis) 4. Plague (Yersinia( pestis) 5. Tularemia (Francisella( tularensis)
Bio Agents of Concern/Interest Potential Biological Threats 1. Ricin 2. Botulism toxin (Clostridium botulinum) 3. Anthrax (Bacillus( anthracis) 4. Plague (Yersinia( pestis) 5. Tularemia (Francisella( tularensis)
Fundamental Principles about Bioterrorism
 Fundamental Principles about Bioterrorism The following discussion provides a useful framework for putting into perspective the enormous volume of information being disseminated regarding health and Bioterrorism.
Fundamental Principles about Bioterrorism The following discussion provides a useful framework for putting into perspective the enormous volume of information being disseminated regarding health and Bioterrorism.
Overview Existing, Emerging, and Re-Emerging Communicable Diseases
 Overview Existing, Emerging, and Re-Emerging Communicable Diseases Many communicable diseases have existed with us since the beginning of time. Communicable diseases, which are infections we catch from
Overview Existing, Emerging, and Re-Emerging Communicable Diseases Many communicable diseases have existed with us since the beginning of time. Communicable diseases, which are infections we catch from
Advisory on Plague WHAT IS PLAGUE? 19 October 2017
 19 October 2017 Advisory on Plague WHAT IS PLAGUE? Plague is an infectious disease caused by the zoonotic bacteria, Yersinia pestis. This bacteria often infects small rodents (like rats, mice, and squirrels)
19 October 2017 Advisory on Plague WHAT IS PLAGUE? Plague is an infectious disease caused by the zoonotic bacteria, Yersinia pestis. This bacteria often infects small rodents (like rats, mice, and squirrels)
Index. Infect Dis Clin N Am 20 (2006) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Infect Dis Clin N Am 20 (2006) 475 483 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abortion storms, 363 Adult intestinal toxemia botulism, 317 Allergen Pharmaceuticals, 315 Alphaviruses
Infect Dis Clin N Am 20 (2006) 475 483 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abortion storms, 363 Adult intestinal toxemia botulism, 317 Allergen Pharmaceuticals, 315 Alphaviruses
SUBJECT: ISOLATION PRECAUTIONS REFERENCE #6003 PAGE: 1 DEPARTMENT: REHABILITATION SERVICES OF: 6 EFFECTIVE:
 PAGE: 1 STANDARD PRECAUTIONS: Precautions which are designed for care of all patients, regardless of diagnosis or presumed infection status to reduce the risk of transmission from both recognized and unrecognized
PAGE: 1 STANDARD PRECAUTIONS: Precautions which are designed for care of all patients, regardless of diagnosis or presumed infection status to reduce the risk of transmission from both recognized and unrecognized
CONTACTS & ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
 CONTACTS & ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Snohomish Health District Communicable Disease Surveillance and Response Analysis and publication: Hollianne Bruce, MPH Program Manager: Amy Blanchard, RN, BSN Communicable
CONTACTS & ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Snohomish Health District Communicable Disease Surveillance and Response Analysis and publication: Hollianne Bruce, MPH Program Manager: Amy Blanchard, RN, BSN Communicable
The Chain of Infection
 The Chain of Infection As healthcare professionals, it is important to understand two facts about infection: 1.The various ways infection can be transmitted. 2. The ways the infection chain can be broken.
The Chain of Infection As healthcare professionals, it is important to understand two facts about infection: 1.The various ways infection can be transmitted. 2. The ways the infection chain can be broken.
Essential Standard. 6.PCH.1 Understand wellness, disease prevention, and recognition of symptoms.
 Essential Standard 6.PCH.1 Understand wellness, disease prevention, and recognition of symptoms. Clarifying Standard 6.PCH.1.2 Differentiate between communicable and chronic diseases 6.PCH.1.3 Recall symptoms
Essential Standard 6.PCH.1 Understand wellness, disease prevention, and recognition of symptoms. Clarifying Standard 6.PCH.1.2 Differentiate between communicable and chronic diseases 6.PCH.1.3 Recall symptoms
Yersinia pestis. Yersinia and plague. Dr. Hala Al Daghistani
 Yersinia pestis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Yersinia species Short, pleomorphic gram-negative rods that can exhibit bipolar staining. Catalase positive, and microaerophilic or facultatively anaerobic. Animals
Yersinia pestis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Yersinia species Short, pleomorphic gram-negative rods that can exhibit bipolar staining. Catalase positive, and microaerophilic or facultatively anaerobic. Animals
Smallpox. Houston Academy of Medicine - Texas Medical Center Library. From the SelectedWorks of Richard N Bradley
 Houston Academy of Medicine - Texas Medical Center Library From the SelectedWorks of Richard N Bradley September, 2007 Smallpox Richard N Bradley, The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston
Houston Academy of Medicine - Texas Medical Center Library From the SelectedWorks of Richard N Bradley September, 2007 Smallpox Richard N Bradley, The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston
CE Unit. Viruses and Vaccines
 CE Unit Viruses and Vaccines DO NOT WRITE What is a virus? Have you ever had a virus? What is a vaccine? How is a virus different from bacteria? What are the deadliest viruses? 10. Dengue fever 50 million
CE Unit Viruses and Vaccines DO NOT WRITE What is a virus? Have you ever had a virus? What is a vaccine? How is a virus different from bacteria? What are the deadliest viruses? 10. Dengue fever 50 million
Viruses: Select Agents and Emerging Pathogens. Patricia Bolívar MS., CLS, PHM
 Viruses: Select Agents and Emerging Pathogens Patricia Bolívar MS., CLS, PHM Objectives Review Select Agent Viruses. Key features to recognize Smallpox virus Update on emerging Viruses of possible pandemic
Viruses: Select Agents and Emerging Pathogens Patricia Bolívar MS., CLS, PHM Objectives Review Select Agent Viruses. Key features to recognize Smallpox virus Update on emerging Viruses of possible pandemic
Chapter 38 Viral Infections
 Chapter 38 Viral Infections Primary Objectives of This Chapter Chapter 38 introduces a wide variety of important human viral diseases and serves as an introduction to Medical Virology. It is considered
Chapter 38 Viral Infections Primary Objectives of This Chapter Chapter 38 introduces a wide variety of important human viral diseases and serves as an introduction to Medical Virology. It is considered
Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) By : Assis. Prof Nader Alaridah MD, PhD
 Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) By : Assis. Prof Nader Alaridah MD, PhD Overview Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) are a group of illnesses caused by four families of viruses. Arenaviridae, Bunyaviridae,
Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) By : Assis. Prof Nader Alaridah MD, PhD Overview Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) are a group of illnesses caused by four families of viruses. Arenaviridae, Bunyaviridae,
Transmission (How Germs Spread) Module 1
 Transmission (How Germs Spread) Module 1 Learner outcomes By the end of this module you will be able to: State the goal of infection prevention and control. List the links in the chain of transmission.
Transmission (How Germs Spread) Module 1 Learner outcomes By the end of this module you will be able to: State the goal of infection prevention and control. List the links in the chain of transmission.
SCHEDULE 5 PATHOGENS AND TOXINS VIRUSES
 10/2012 SCHEDULE 5 PATHOGENS AND TOXINS VIRUSES Chikungunya virus Congo- crimean haemorrhagic fever virus Dengue fever virus Dobrava/Belgrade virus Eastern equine encephalitis virus Ebola virus Everglades
10/2012 SCHEDULE 5 PATHOGENS AND TOXINS VIRUSES Chikungunya virus Congo- crimean haemorrhagic fever virus Dengue fever virus Dobrava/Belgrade virus Eastern equine encephalitis virus Ebola virus Everglades
Conference Proceedings
 Conference Proceedings Severe Febrile Respiratory Illnesses As a Cause of Mass Critical Care Christian E Sandrock MD MPH Introduction Importance of Febrile Respiratory Illnesses Febrile Respiratory Illnesses
Conference Proceedings Severe Febrile Respiratory Illnesses As a Cause of Mass Critical Care Christian E Sandrock MD MPH Introduction Importance of Febrile Respiratory Illnesses Febrile Respiratory Illnesses
Bioterrorism. Eric S. Toner, MD. National Governors Association July 22, 2009
 Bioterrorism Eric S. Toner, MD National Governors Association July 22, 2009 Biological Weapons Have a Long History 14th century: Tartars catapulted bodies of plague victims over siege walls in Crimea 1750
Bioterrorism Eric S. Toner, MD National Governors Association July 22, 2009 Biological Weapons Have a Long History 14th century: Tartars catapulted bodies of plague victims over siege walls in Crimea 1750
The Immune System and Pathology
 The Immune System and Pathology The Immune System in Action When a mosquito bites When you breathe When you have allergies When you get a blood transfusion When you die...also called the Lymphatic System
The Immune System and Pathology The Immune System in Action When a mosquito bites When you breathe When you have allergies When you get a blood transfusion When you die...also called the Lymphatic System
Infection, Detection, Prevention...
 Infection, Detection, Prevention... A disease is any change that disrupts the normal function of one or more body systems. Non infectious diseases are typically caused by exposure to chemicals or are inherited.
Infection, Detection, Prevention... A disease is any change that disrupts the normal function of one or more body systems. Non infectious diseases are typically caused by exposure to chemicals or are inherited.
Biological Warfare Agents
 Chapter 29 The reader is strongly advised to supplement material in this chapter with the following reference: US Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases (USAMRIID). Medical Management of
Chapter 29 The reader is strongly advised to supplement material in this chapter with the following reference: US Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases (USAMRIID). Medical Management of
Understanding and Confronting Emerging Disease
 Understanding and Confronting Emerging Disease Michael J. Buchmeier, PhD. Professor, Departments of Molecular Biology and Biochemistry, and Div. of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, UCI Deputy
Understanding and Confronting Emerging Disease Michael J. Buchmeier, PhD. Professor, Departments of Molecular Biology and Biochemistry, and Div. of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, UCI Deputy
Scientific and Medical Differences of Category A Pathogens
 Scientific and Medical Differences of Category A Pathogens Richard Gorman, M.D. Chair, Pediatric and Obstetrics Integrated Program Team HHS Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response
Scientific and Medical Differences of Category A Pathogens Richard Gorman, M.D. Chair, Pediatric and Obstetrics Integrated Program Team HHS Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response
Spore-Forming Gram-Positive Bacilli: Bacillus & Clostridium Species: Introduction
 Spore-Forming Gram-Positive Bacilli: Bacillus & Clostridium Species: Introduction The gram-positive spore-forming bacilli are the bacillus and clostridium species. These bacilli are ubiquitous, and because
Spore-Forming Gram-Positive Bacilli: Bacillus & Clostridium Species: Introduction The gram-positive spore-forming bacilli are the bacillus and clostridium species. These bacilli are ubiquitous, and because
OTHER COMMUNICABLE DISEASES. Sandra Pinzón and Diana Sánchez. Andalusian School of Public Health Gábor Ternák. University of Pécs
 OTHER COMMUNICABLE DISEASES Sandra Pinzón and Diana Sánchez. Andalusian School of Public Health Gábor Ternák. University of Pécs Viral diseases Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis C STI HIV Other viral diseases
OTHER COMMUNICABLE DISEASES Sandra Pinzón and Diana Sánchez. Andalusian School of Public Health Gábor Ternák. University of Pécs Viral diseases Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis C STI HIV Other viral diseases
Foundations in Microbiology
 Foundations in Microbiology Fifth Edition Talaro Chapter 13 Microbe Human Interactions: Infection and Disease Chapter 13 2 3 Infection a condition in which pathogenic microbes penetrate host defenses,
Foundations in Microbiology Fifth Edition Talaro Chapter 13 Microbe Human Interactions: Infection and Disease Chapter 13 2 3 Infection a condition in which pathogenic microbes penetrate host defenses,
Understanding and Confronting Emerging Disease
 Understanding and Confronting Emerging Disease Michael J. Buchmeier, PhD. Professor, Departments of Molecular Biology and Biochemistry, and Div. of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, UCI Deputy
Understanding and Confronting Emerging Disease Michael J. Buchmeier, PhD. Professor, Departments of Molecular Biology and Biochemistry, and Div. of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, UCI Deputy
Pathogens: Microorganisms that are capable of causing disease Infection: Results when a pathogen invades and begins growing within the host Disease:
 Infectious Diseases Pathogens: Microorganisms that are capable of causing disease Infection: Results when a pathogen invades and begins growing within the host Disease: Results only if and when normal
Infectious Diseases Pathogens: Microorganisms that are capable of causing disease Infection: Results when a pathogen invades and begins growing within the host Disease: Results only if and when normal
Infection Control Protocol for the Management of Anthrax Cases in Health Care settings
 State of Kuwait Ministry of Health Infection Control Directorate Infection Control Protocol for the Management of Anthrax Cases in Health Care settings 2002 Introduction: Anthrax is a bacterial infectious
State of Kuwait Ministry of Health Infection Control Directorate Infection Control Protocol for the Management of Anthrax Cases in Health Care settings 2002 Introduction: Anthrax is a bacterial infectious
LECTURE topics: 1. Immunology. 2. Emerging Pathogens
 LECTURE 23 2 topics: 1. Immunology 2. Emerging Pathogens Benefits of the Normal Flora: 1. Protect us from colonization by other bacteria and fungi (competitive exclusion). 2. Many synthesize vitamins,
LECTURE 23 2 topics: 1. Immunology 2. Emerging Pathogens Benefits of the Normal Flora: 1. Protect us from colonization by other bacteria and fungi (competitive exclusion). 2. Many synthesize vitamins,
Bioterrorism Capabilities in Rural Texas Hospitals and Laboratories by
 Bioterrorism Capabilities in Rural Texas Hospitals and Laboratories by Taylor M. Johnson Public Health Internship Program School of Biological Sciences The University of Texas at Austin Mentor: Dr. Grace
Bioterrorism Capabilities in Rural Texas Hospitals and Laboratories by Taylor M. Johnson Public Health Internship Program School of Biological Sciences The University of Texas at Austin Mentor: Dr. Grace
Breaking the Chain of Infection DOM Education Day October 27, 2014 Jodi-Marie Black RN BScN PHN
 Breaking the Chain of Infection DOM Education Day October 27, 2014 Jodi-Marie Black RN BScN PHN Topics Covered in Presentation The Chain of infection and how to break the chain Role of the Designated Officer
Breaking the Chain of Infection DOM Education Day October 27, 2014 Jodi-Marie Black RN BScN PHN Topics Covered in Presentation The Chain of infection and how to break the chain Role of the Designated Officer
Diseases Related to Bioterrorism
 Newfoundland and Labrador Disease Control Manual Section 8 Diseases Related to Bioterrorism Bioterrorism Agents...8.1-1 Small Pox, List A...8.2-1 Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers, List A...8.3-1 8.1 Bioterrorism
Newfoundland and Labrador Disease Control Manual Section 8 Diseases Related to Bioterrorism Bioterrorism Agents...8.1-1 Small Pox, List A...8.2-1 Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers, List A...8.3-1 8.1 Bioterrorism
Anthrax: An Epidemiologic Perspective. Denise Dietz Public Health Epidemiologist
 Anthrax: An Epidemiologic Perspective Denise Dietz Public Health Epidemiologist Outline Overview of anthrax Explain different types of anthrax Clinical Why a good weapon Epidemiology Bacillus anthracis
Anthrax: An Epidemiologic Perspective Denise Dietz Public Health Epidemiologist Outline Overview of anthrax Explain different types of anthrax Clinical Why a good weapon Epidemiology Bacillus anthracis
2. According to the information provided by the WHO, there is no justification at this stage for restrictions on travel or trade.
 Outbreak of Plague in Madagascar The following information is being disseminated by both the International Chamber of Shipping and The International Transport Workers Federation to draw attention to the
Outbreak of Plague in Madagascar The following information is being disseminated by both the International Chamber of Shipping and The International Transport Workers Federation to draw attention to the
UPDATE ON INFECTIOUS DISEASES 2015
 UPDATE ON INFECTIOUS DISEASES 2015 William Schaffner, MD Professor of Preventive Medicine, Department of Health Policy Professor of Medicine (Infectious Diseases) Vanderbilt University School of Medicine
UPDATE ON INFECTIOUS DISEASES 2015 William Schaffner, MD Professor of Preventive Medicine, Department of Health Policy Professor of Medicine (Infectious Diseases) Vanderbilt University School of Medicine
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Sandro Cinti, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Sandro Cinti, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Health Department MEMORANDUM Office of the Commissioner
 Health Department MEMORANDUM Office of the Commissioner TO: FROM: Halton Robert Physicians M. Nosal, Medical Medical Officer Chiefs of Health of Staff: Joseph Brant Memorial Hospital DATE: October 11,
Health Department MEMORANDUM Office of the Commissioner TO: FROM: Halton Robert Physicians M. Nosal, Medical Medical Officer Chiefs of Health of Staff: Joseph Brant Memorial Hospital DATE: October 11,
Downloaded from
 Class IX: Biology Chapter: Why do we fall ill Chapter Notes Key learnings: 1) Our body s well-being is dependent on the proper functioning of its cells and tissues. 2) All our body parts and activities
Class IX: Biology Chapter: Why do we fall ill Chapter Notes Key learnings: 1) Our body s well-being is dependent on the proper functioning of its cells and tissues. 2) All our body parts and activities
Below you will find information about diseases, the risk of contagion, and preventive vaccinations.
 Vaccinations Below you will find information about diseases, the risk of contagion, and preventive vaccinations. DTP - Diphtheria Tetanus Polio Yellow fever Hepatitis A Typhoid fever Cerebrospinal meningitis
Vaccinations Below you will find information about diseases, the risk of contagion, and preventive vaccinations. DTP - Diphtheria Tetanus Polio Yellow fever Hepatitis A Typhoid fever Cerebrospinal meningitis
Weapons of Mass Destruction. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012
 Weapons of Mass Destruction Lesson Goal To become familiarize with the concept of weapons of mass destruction (WMD), how these weapons might be used, and the type of treatment that would be appropriate
Weapons of Mass Destruction Lesson Goal To become familiarize with the concept of weapons of mass destruction (WMD), how these weapons might be used, and the type of treatment that would be appropriate
Chapter 17 Disease and Resistance: The Wars Within
 Chapter 17 Disease and Resistance: The Wars Within Objectives: After reading Chapter 17, you should understand The concepts relating to infectious diseases, the difference between disease and infection
Chapter 17 Disease and Resistance: The Wars Within Objectives: After reading Chapter 17, you should understand The concepts relating to infectious diseases, the difference between disease and infection
PUBLIC HEALTH SIGNIFICANCE SEASONAL INFLUENZA AVIAN INFLUENZA SWINE INFLUENZA
 INFLUENZA DEFINITION Influenza is an acute highly infectious viral disease characterized by fever, general and respiratory tract catarrhal manifestations. Influenza has 3 Types Seasonal Influenza Avian
INFLUENZA DEFINITION Influenza is an acute highly infectious viral disease characterized by fever, general and respiratory tract catarrhal manifestations. Influenza has 3 Types Seasonal Influenza Avian
PRINCIPLES OF INFECTIOUS DISEASE EPIDEMIOLOGY MODULE II THE INFECTIOUS DISEASE PROCESS
 PRINCIPLES OF INFECTIOUS DISEASE EPIDEMIOLOGY MODULE II THE INFECTIOUS DISEASE PROCESS This outline is provided as an aid to the student. It contains only the basic content of the module. To view the supporting
PRINCIPLES OF INFECTIOUS DISEASE EPIDEMIOLOGY MODULE II THE INFECTIOUS DISEASE PROCESS This outline is provided as an aid to the student. It contains only the basic content of the module. To view the supporting
DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE AFHSB Reportable Events Monthly Report
 DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE AFHSB Reportable Events Monthly Report July 2016 Report Description Reportable Events among all beneficiaries received from the Services over the past 5 years are used to create ranges
DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE AFHSB Reportable Events Monthly Report July 2016 Report Description Reportable Events among all beneficiaries received from the Services over the past 5 years are used to create ranges
DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE AFHSB Reportable Events Monthly Report
 DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE AFHSB Reportable Events Monthly Report May 2016 Report Description Reportable Events among all beneficiaries received from the Services over the past 5 years are used to create ranges
DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE AFHSB Reportable Events Monthly Report May 2016 Report Description Reportable Events among all beneficiaries received from the Services over the past 5 years are used to create ranges
WASTEWATER WORKERS STAYING HEALTHY ON THE JOB. Protect yourself and your family
 WASTEWATER WORKERS STAYING HEALTHY ON THE JOB Protect yourself and your family LOOK FAMILIAR? WHAT ARE THE RISKS? Exposure to pathogens such as: Biological- Bacteria, Virus, Parasites and Fungi Chemical-
WASTEWATER WORKERS STAYING HEALTHY ON THE JOB Protect yourself and your family LOOK FAMILIAR? WHAT ARE THE RISKS? Exposure to pathogens such as: Biological- Bacteria, Virus, Parasites and Fungi Chemical-
Chapter 13. Topics - Human Host - Progress of an Infection - Epidemiology
 Chapter 13 Topics - Human Host - Progress of an Infection - Epidemiology 1 Human Host Acquire resident flora New born exposure 2 Acquire resident flora The human body supports a wide range of habitats
Chapter 13 Topics - Human Host - Progress of an Infection - Epidemiology 1 Human Host Acquire resident flora New born exposure 2 Acquire resident flora The human body supports a wide range of habitats
Introduction to Public Health and Epidemiology
 Surveillance and Outbreak Investigation Course Introduction to Public Health and Epidemiology King Cholera dispenses contagion: the London Cholera Epidemic of 1866 Learning Objectives Define Epidemiology
Surveillance and Outbreak Investigation Course Introduction to Public Health and Epidemiology King Cholera dispenses contagion: the London Cholera Epidemic of 1866 Learning Objectives Define Epidemiology
Microbiology: A Systems Approach, 2 nd ed. Chapter 20: Infectious Diseases Affecting the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Symptoms
 Microbiology: A Systems Approach, 2 nd ed. Chapter 20: Infectious Diseases Affecting the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Symptoms 20.1 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems and Their Defenses Cardiovascular
Microbiology: A Systems Approach, 2 nd ed. Chapter 20: Infectious Diseases Affecting the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Symptoms 20.1 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems and Their Defenses Cardiovascular
Present State and Measures against Infectious Diseases in Tokyo
 Asian Network of Major Cities 21 Asian Infectious Disease Project Present State and Measures against Infectious Diseases in History of Law on Infectious Diseases Revisions 1897 1999 23 Communicable Disease
Asian Network of Major Cities 21 Asian Infectious Disease Project Present State and Measures against Infectious Diseases in History of Law on Infectious Diseases Revisions 1897 1999 23 Communicable Disease
Disease: any change, other than an injury, that disrupts homeostasis. Pathogen: disease-causing agent such as bacteria, virus, etc.
 The Immune System Disease: any change, other than an injury, that disrupts homeostasis. Pathogen: disease-causing agent such as bacteria, virus, etc. Infectious disease- caused by pathogen Germ theory
The Immune System Disease: any change, other than an injury, that disrupts homeostasis. Pathogen: disease-causing agent such as bacteria, virus, etc. Infectious disease- caused by pathogen Germ theory
Section 6. Communicable Diseases
 Section 6 Communicable Diseases 89 Learning objectives Section 6 Communicable Diseases After completing this section, you will be able to: Describe how communicable diseases spread. Identify some specific
Section 6 Communicable Diseases 89 Learning objectives Section 6 Communicable Diseases After completing this section, you will be able to: Describe how communicable diseases spread. Identify some specific
FINAL. Etiologic Agents & Related Information to Know. Chapter 21: Microbial Diseases of Skin and Eyes Page No. Know term "diphtheroids"...
 10 th Edition Tortora FINAL Microbiology Etiologic Agents & Related Information to Know Chapter 21: Microbial Diseases of Skin and Eyes Know term "diphtheroids"................. 586 Agents of boils and
10 th Edition Tortora FINAL Microbiology Etiologic Agents & Related Information to Know Chapter 21: Microbial Diseases of Skin and Eyes Know term "diphtheroids"................. 586 Agents of boils and
Testing for SSBA (Security Sensitive Biological Agents) Dr Torsten Theis Senior Hospital Scientist RCPA BioSecurity QAP 16 August 2012
 Testing for SSBA (Security Sensitive Biological Agents) Dr Torsten Theis Senior Hospital Scientist RCPA BioSecurity QAP 16 August 2012 Testing for SSBA (Security Sensitive Biological Agents) RCPA BioSecurity
Testing for SSBA (Security Sensitive Biological Agents) Dr Torsten Theis Senior Hospital Scientist RCPA BioSecurity QAP 16 August 2012 Testing for SSBA (Security Sensitive Biological Agents) RCPA BioSecurity
Anthrax. Department of Child Health Medical Faculty University of Sumatera Utara
 Anthrax Malignant pustule, malignant edema, Woolsorters Disease, Ragpickers Disease, Maladi Charbon, Splenic Fever Infectious and Tropical Pediatric Division Department of Child Health Medical Faculty
Anthrax Malignant pustule, malignant edema, Woolsorters Disease, Ragpickers Disease, Maladi Charbon, Splenic Fever Infectious and Tropical Pediatric Division Department of Child Health Medical Faculty
Cholera. Ebola. Symptoms of Ebola include. Fever. Severe headache. Muscle pain. Weakness. Fatigue. Diarrhea. Vomiting. Abdominal (stomach) pain
 Cholera Cholera is caused by a bacterial infection of the intestine. In many cases the infection is mild sometimes producing no symptoms at all. But approximately one in 20 people infected with cholera
Cholera Cholera is caused by a bacterial infection of the intestine. In many cases the infection is mild sometimes producing no symptoms at all. But approximately one in 20 people infected with cholera
Killer Viruses: The Why and The How. Amesh Adalja
 Killer Viruses: The Why and The How Amesh Adalja MD @AmeshAA Disclosures Stockholder: Merck, Luminex, Evolent Bondholder: UPMC Speaker s Bureau: Merck, Roche Consultant: Roche Funding: Open Philanthropy
Killer Viruses: The Why and The How Amesh Adalja MD @AmeshAA Disclosures Stockholder: Merck, Luminex, Evolent Bondholder: UPMC Speaker s Bureau: Merck, Roche Consultant: Roche Funding: Open Philanthropy
LESSON 2.4 WORKBOOK. How can we prove infection causes disease?
 DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Correlation a connection between two factors. Causation when a change in one factor results in a change in another. Vector an organism that transmits a pathogen from reservoir to host.
DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Correlation a connection between two factors. Causation when a change in one factor results in a change in another. Vector an organism that transmits a pathogen from reservoir to host.
INFECTION PREVENTION NEWS & UPDATES
 FEBRUARY 2018 INFECTION PREVENTION NEWS & UPDATES MULTI-COUNTRY OUTBREAK CONTACT + VECTOR NIGERIA, BRAZIL YELLOW FEVER The previously reported outbreak of Yellow Fever in Nigeria has now infected 358 people
FEBRUARY 2018 INFECTION PREVENTION NEWS & UPDATES MULTI-COUNTRY OUTBREAK CONTACT + VECTOR NIGERIA, BRAZIL YELLOW FEVER The previously reported outbreak of Yellow Fever in Nigeria has now infected 358 people
HealthStream Regulatory Script
 HealthStream Regulatory Script [Transmission-Based Precautions: Contact and Droplet] Version: [April 2005] Lesson 1: Introduction Lesson 2: Contact Precautions Lesson 3: Droplet Precautions Lesson 1: Introduction
HealthStream Regulatory Script [Transmission-Based Precautions: Contact and Droplet] Version: [April 2005] Lesson 1: Introduction Lesson 2: Contact Precautions Lesson 3: Droplet Precautions Lesson 1: Introduction
Lil Hirdes RN, BScN Safety Officer
 Presented at the OCA conference 2016 Lil Hirdes RN, BScN Safety Officer Peterborough Regional Health Centre Formerly: Occupational Health Nurse PRHC Emergency Room Nurse PRHC & SJHC ALWAYS: Camp Nurse,
Presented at the OCA conference 2016 Lil Hirdes RN, BScN Safety Officer Peterborough Regional Health Centre Formerly: Occupational Health Nurse PRHC Emergency Room Nurse PRHC & SJHC ALWAYS: Camp Nurse,
Principles of Infectious Disease Lecture #13 Dr. Gary Mumaugh
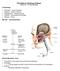 Principles of Infectious Disease Lecture #13 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Terminology Pathology study of disease Etiology cause of disease Pathogenesis disease process Infection colonization by microbes Disease illness
Principles of Infectious Disease Lecture #13 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Terminology Pathology study of disease Etiology cause of disease Pathogenesis disease process Infection colonization by microbes Disease illness
INFECTION PREVENTION NEWS & UPDATES
 CONTACT + DROPLET EBOLA INFECTION While the Ebola outbreak from the Democratic Republic of the Congo from earlier this year is over, a new outbreak of Ebola has been identified that has infected at least
CONTACT + DROPLET EBOLA INFECTION While the Ebola outbreak from the Democratic Republic of the Congo from earlier this year is over, a new outbreak of Ebola has been identified that has infected at least
INFECTIOUS DISEASES CONTAGIOUS DISEASES COMMUNICABLE DISEASES
 INFECTION it is the entry, development and or multiplication of an infectious agent in body of man or animal. CONTAMINATION it is the presence of infectious agents on the body surface, clothes or articles
INFECTION it is the entry, development and or multiplication of an infectious agent in body of man or animal. CONTAMINATION it is the presence of infectious agents on the body surface, clothes or articles
2018 Communicable Disease Annual Report
 2018 Communicable Disease Annual Report Summary of 2018 Events The Licking County Health Department (LCHD) is dedicated to conducting disease surveillance and continues to evaluate investigation protocols
2018 Communicable Disease Annual Report Summary of 2018 Events The Licking County Health Department (LCHD) is dedicated to conducting disease surveillance and continues to evaluate investigation protocols
Wasatch School District Guidelines for Student Exclusion and Readmission
 Wasatch School District Guidelines for Student Exclusion and Readmission Condition Chicken pox (Varicella) Colds, Sore Throat, or a Persistent Cough Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Diarrhea (An increased number
Wasatch School District Guidelines for Student Exclusion and Readmission Condition Chicken pox (Varicella) Colds, Sore Throat, or a Persistent Cough Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Diarrhea (An increased number
CE Unit 7. Viruses and Vaccines
 CE Unit 7 Viruses and Vaccines DO NOT WRITE What is a virus? Have you ever had a virus? What is a vaccine? How is a virus different from bacteria? What are the deadliest viruses? 10. Dengue fever 50 million
CE Unit 7 Viruses and Vaccines DO NOT WRITE What is a virus? Have you ever had a virus? What is a vaccine? How is a virus different from bacteria? What are the deadliest viruses? 10. Dengue fever 50 million
Principles of Disease and Epidemiology
 Principles of Disease and Epidemiology Symbiosis living together An association between two or more species and one species is typically dependent on the other Mutualism - Commensalism - Parasitism - Infection
Principles of Disease and Epidemiology Symbiosis living together An association between two or more species and one species is typically dependent on the other Mutualism - Commensalism - Parasitism - Infection
Isolation Precautions in Clinics
 Purpose Audience General principles Possible Exposures To define isolation precautions in a clinic setting. Clinics Isolation status should be determined primarily by the suspected disease and/or pathogen.
Purpose Audience General principles Possible Exposures To define isolation precautions in a clinic setting. Clinics Isolation status should be determined primarily by the suspected disease and/or pathogen.
Chapter 7 8/23/2016. Asepsis and Infection Control. Asepsis. Asepsis (Cont.) Microorganisms. Infection control and prevention
 Chapter 7 Asepsis and Infection Control All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Asepsis Microorganisms Tiny microscopic entities capable
Chapter 7 Asepsis and Infection Control All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Asepsis Microorganisms Tiny microscopic entities capable
1966 CDC assessment of US Health
 Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, DrPH) Lecture 14 Emerging and New IDs Learning Objectives 1. Describe the threat of emerging and new infectious agents 2. Identify the contributing
Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, DrPH) Lecture 14 Emerging and New IDs Learning Objectives 1. Describe the threat of emerging and new infectious agents 2. Identify the contributing
THE UNIVERSITY OF MISSISSIPPI LABORATORY SERVICES Phone (662) FAX (662)
 THE UNIVERSITY OF MISSISSIPPI LABORATORY SERVICES Phone (662) 915-5433 FAX (662) 915-5480 CONSIGNMENT OF DIAGNOSTIC SPECIMENS The following note was developed by ICAO and issued 20th December 2002. The
THE UNIVERSITY OF MISSISSIPPI LABORATORY SERVICES Phone (662) 915-5433 FAX (662) 915-5480 CONSIGNMENT OF DIAGNOSTIC SPECIMENS The following note was developed by ICAO and issued 20th December 2002. The
