MMG 301 Lec. 35 Epidemiology and Bioterrorism
|
|
|
- Merilyn Lang
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MMG 301 Lec. 35 Epidemiology and Bioterrorism Questions for Today: (consider Med Micro course) 1. What is epidemiology? 2. How is epidemiology important to public health? 3. What pathogens are important in germ warfare and bioterrorism? Definitions Epidemiology: the study of the occurrence, distribution, and control of diseases. Endemic: the low, constant frequency of a disease in a population. Epidemic: higher than normal frequency of a disease in a population. Pandemic: Significant increase in frequency of a disease on a continent-wide or world-wide scale. Carrier: Individual who may not exhibit symptoms, yet carriers and passes on to others a disease. Reservoir: animate or inanimate sites where the pathogen is maintained in nature between outbreaks.
2 Epidemiologists must collect and analyze data to look for patterns (much like a detective or criminal investigator -- think CSI) Spike due to influenza pandemic. Seasonal incidence of encephalitis due to mosquitoes.
3 Relationships Between Epidemiologists and Public Health Typhoid Mary: Mary Mallon, a cook/housekeeper in NYC. Contracted typhoid in 1901, permanently infected in gallbladder, shed pathogen in feces. Dr. George Soper made connection after 28 cases: identified & arrested. Refused offer to surgically remove gallbladder, jailed 3 yr. Agreed to stay out of food service, but disappeared/changed name. Cook at hotels & hospitals, leaving jobs after each new outbreak. Caught after 5 yr and ~200 cases. Jailed 23 years until death. Cholera in London: Dr. John Snow mapped out cases of cholera in London ( ) versus sources water (2 main distributors). Only 37/100,000 using Lambeth Co. (intake located in Thames above London) vs. 315/10,000 using Southwark & Vauxhall Co. (intake located after raw sewage outlet). Shutting down the latter system resulted in plummet in # cases. AIDS: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDCP) identified a large number of deaths among homosexual males in Los Angeles in This observation stimulated research leading to the discovery of HIV. Emerging Diseases: Constant vigilance is used to detect newly emerging diseases and identify the associated pathogen (e.g., Ebola, SARS)
4 Types of Public Health Measures Reporting: Doctors are required to collect data and report specified information to State Health Depts. and the CDCP (see list in book, p.864, if interested). must be within 24 hr for some diseases. Reservoir controls: an entire herd may be killed after discovering a single infected individual (e.g., cattle with Brucella abortus). large-scale slaughter of animals may occur when some are suspected of carrying a human pathogen (chickens in Japan, cattle/sheep in UK). wild animals are destroyed to prevent infection of domesticated species (bison in Yellowstone, deer with wasting disease ). eliminate rats (plague), mosquitoes, etc. Quarantine: effective approach before antibiotics for scarlet fever, tuberculosis, leprosy. isolation wards are used in hospitals for cholera, plague, typhoid, yellow & relapsing fever. Measures involving food/water: inspection of abattoirs and meat processing plants. pasteurization water treatment (e.g., separate storm/sewage systems) Very Important (damaged by disasters)
5 Vaccination: effective for animals and humans. Diphtheria/tetanus/pertussis (DTP), measles, mumps, rubella, influenza B, polio, chicken pox, hepatitus B, are all common for children/adults. in some cases, new vaccines are available every year for new strains. herd immunity means that not all individuals need to be vaccinated for the vaccine to be effective. can use targeted immunization (Smallpox) booster shots are needed for some types of vaccines to be effective
6 A few more definitions (that I forgot to mention earlier) Fomite: an inanimate object that can transfer a pathogen from an infected host to a new host. Zoonosis (pl. zoonoses): a disease that occurs primarily in animals, but can be transmitted to humans. Acute: a short-term infection that exhibits a dramatic onset and typically a rapid recovery. Incidence: number of individuals exhibiting a disease. Prevalence: proportion or percentage of people having a disease. Agglutination: clumping of particles (e.g., result of adding an Ab). Monoclonal Antibodies: Identical antibodies (exactly the same specificities) that are produced by a clone of B cells (e.g., some autoimmune diseases or created in lab) Polyclonal Ab: Collection of Ab made by different B cell clones, may recognize different epitopes of the same Ag.
7 Bacterial Priority Organisms of Bioterrorism CDCP categorizes biological organisms according to ease of dissemination, mortality rates, and ease of procurement and growth. Category A: Anthrax, Botulism, Plague, Smallpox, Tularemia, Viral Hemorrhagic fever can be easily disseminated or transmitted from person to person. result in high mortality rates and have the potential for major public health impact. might cause public panic and social disruption. require special action for public health preparedness. Bacillus anthracis
8 Bacillus anthracis anthrax: Gram-positive, nonmotile, spore-forming rod Has three virulence factors Routes of human infection (all can lead to death if untreated): Cutaneous (skin), Inhalation (respiratory tract), Gastrointestinal Clostridium botulinum botulism Direct ingestion of toxin, wound infection by bacterium Yersinia pestis bacterium that causes the plague Three forms of infection: Pneumonic plague infection in lungs Bubonic plague infection through skin from flea (bubo is a swelling) Septicemic plague bacteria infect the blood; complication of pneumonic or bubonic Francisella tularensis - tularemia skin ulcers, swollen and painful lymph glands, inflamed eyes, sore throat, oral ulcers, or pneumonia Highly infectious only cells needed for infection F. tularensis occurs widely in nature; easy to isolate Inhaled bacteria can cause severe illness quickly
9 Smallpox variola virus; transmitted by aerosol or direct contact After infection, development of skin rash which progresses to formation of pustules Septic shock and toxemia (toxic substances in the blood) can result in fatality rates of up to 30% Disease has been eradicated in the world (eliminated from US in 1960 by vaccination; WHO begin world-wide effort in 1967 to vaccinate endemic areas, target outbreaks, and quaranteen those infected; last natural disease case in 1976; declared success in 1980); factors that aided eradication: Only human reservoir No asymptomatic carriers Short period of infectivity [Other targets for eradication: polio, leprosy, Chaga s disease, Guinea worm; with syphilis and rabies as candidates] Measures to combat bioterrorism 1972 Biological and Toxic Weapons Convention led to international agreement to forego these weapons. Vaccinations protective suits, lotions, etc.
Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences
 Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Chapter 11. Epidemiology and Public Health Chapter 11 Outline Epidemiology Interactions Among Pathogens, Hosts and the Environment Chain of Infection Reservoirs
Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Chapter 11. Epidemiology and Public Health Chapter 11 Outline Epidemiology Interactions Among Pathogens, Hosts and the Environment Chain of Infection Reservoirs
Disease Transmission Methods
 Disease Transmission Methods In epidemiology, transmission simply means any method by which an infectious agent is spread from one host to another. Knowing the type of pathogen often, but not always, identifies
Disease Transmission Methods In epidemiology, transmission simply means any method by which an infectious agent is spread from one host to another. Knowing the type of pathogen often, but not always, identifies
B-NICE Overview. Types of WMD Agents. Types of WMD Agents. Types of WMD Agents. Job Aid Version 1.0 and 2.0. CDC & Prevention
 B-NICE Overview Types of WMD Agents Biological Nuclear Incendiary Chemical Explosive Types of WMD Agents Job Aid Version 1.0 and 2.0 Chemical Biological Radiological Nuclear Explosive Types of WMD Agents
B-NICE Overview Types of WMD Agents Biological Nuclear Incendiary Chemical Explosive Types of WMD Agents Job Aid Version 1.0 and 2.0 Chemical Biological Radiological Nuclear Explosive Types of WMD Agents
An Overview of Bioterrorism. SAEMS January 30, Charles A. Schable, M.S. Institutional Biosafety Committee University of Arizona
 An Overview of Bioterrorism SAEMS January 30, 2008 Charles A. Schable, M.S. Institutional Biosafety Committee University of Arizona Bioterrorism Intentional or threatened use of viruses, bacteria, fungi,
An Overview of Bioterrorism SAEMS January 30, 2008 Charles A. Schable, M.S. Institutional Biosafety Committee University of Arizona Bioterrorism Intentional or threatened use of viruses, bacteria, fungi,
Advisory on Plague WHAT IS PLAGUE? 19 October 2017
 19 October 2017 Advisory on Plague WHAT IS PLAGUE? Plague is an infectious disease caused by the zoonotic bacteria, Yersinia pestis. This bacteria often infects small rodents (like rats, mice, and squirrels)
19 October 2017 Advisory on Plague WHAT IS PLAGUE? Plague is an infectious disease caused by the zoonotic bacteria, Yersinia pestis. This bacteria often infects small rodents (like rats, mice, and squirrels)
PART A. True/False. Indicate in the space whether each of the following statements are true or false.
 MCB 55 Plagues and Pandemics Midterm I Practice questions Read each question carefully. All the questions can be answered briefly, in the space allotted. PART A. True/False. Indicate in the space whether
MCB 55 Plagues and Pandemics Midterm I Practice questions Read each question carefully. All the questions can be answered briefly, in the space allotted. PART A. True/False. Indicate in the space whether
Scientific and Medical Differences of Category A Pathogens
 Scientific and Medical Differences of Category A Pathogens Richard Gorman, M.D. Chair, Pediatric and Obstetrics Integrated Program Team HHS Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response
Scientific and Medical Differences of Category A Pathogens Richard Gorman, M.D. Chair, Pediatric and Obstetrics Integrated Program Team HHS Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response
Understanding and Confronting Emerging Disease
 Understanding and Confronting Emerging Disease Michael J. Buchmeier, PhD. Professor, Departments of Molecular Biology and Biochemistry, and Div. of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, UCI Deputy
Understanding and Confronting Emerging Disease Michael J. Buchmeier, PhD. Professor, Departments of Molecular Biology and Biochemistry, and Div. of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, UCI Deputy
Bioterrorism. Eric S. Toner, MD. National Governors Association July 22, 2009
 Bioterrorism Eric S. Toner, MD National Governors Association July 22, 2009 Biological Weapons Have a Long History 14th century: Tartars catapulted bodies of plague victims over siege walls in Crimea 1750
Bioterrorism Eric S. Toner, MD National Governors Association July 22, 2009 Biological Weapons Have a Long History 14th century: Tartars catapulted bodies of plague victims over siege walls in Crimea 1750
Understanding and Confronting Emerging Disease
 Understanding and Confronting Emerging Disease Michael J. Buchmeier, PhD. Professor, Departments of Molecular Biology and Biochemistry, and Div. of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, UCI Deputy
Understanding and Confronting Emerging Disease Michael J. Buchmeier, PhD. Professor, Departments of Molecular Biology and Biochemistry, and Div. of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, UCI Deputy
Endemic: rhinovirus, Epidemic: pertussis several years ago Pandemic: H1N1 in was a pandemic just not as severe as originally feared
 1 2 3 Endemic: rhinovirus, Epidemic: pertussis several years ago Pandemic: H1N1 in 2009 10 was a pandemic just not as severe as originally feared 4 5 Endemic, Epidemic 6 Endemic, Epidemic 7 H5N1 H7N9 8
1 2 3 Endemic: rhinovirus, Epidemic: pertussis several years ago Pandemic: H1N1 in 2009 10 was a pandemic just not as severe as originally feared 4 5 Endemic, Epidemic 6 Endemic, Epidemic 7 H5N1 H7N9 8
UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS FIELD MEDICAL TRAINING BATTALION Camp Lejeune, NC
 UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS FIELD MEDICAL TRAINING BATTALION Camp Lejeune, NC 28542-0042 FMST 304 Manage Biological Agent Casualties TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVE 1. Given a casualty and the absence of a
UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS FIELD MEDICAL TRAINING BATTALION Camp Lejeune, NC 28542-0042 FMST 304 Manage Biological Agent Casualties TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVE 1. Given a casualty and the absence of a
Fundamental Principles about Bioterrorism
 Fundamental Principles about Bioterrorism The following discussion provides a useful framework for putting into perspective the enormous volume of information being disseminated regarding health and Bioterrorism.
Fundamental Principles about Bioterrorism The following discussion provides a useful framework for putting into perspective the enormous volume of information being disseminated regarding health and Bioterrorism.
Bio Agents of Concern/Interest
 Bio Agents of Concern/Interest Potential Biological Threats 1. Ricin 2. Botulism toxin (Clostridium botulinum) 3. Anthrax (Bacillus( anthracis) 4. Plague (Yersinia( pestis) 5. Tularemia (Francisella( tularensis)
Bio Agents of Concern/Interest Potential Biological Threats 1. Ricin 2. Botulism toxin (Clostridium botulinum) 3. Anthrax (Bacillus( anthracis) 4. Plague (Yersinia( pestis) 5. Tularemia (Francisella( tularensis)
Below you will find information about diseases, the risk of contagion, and preventive vaccinations.
 Vaccinations Below you will find information about diseases, the risk of contagion, and preventive vaccinations. DTP - Diphtheria Tetanus Polio Yellow fever Hepatitis A Typhoid fever Cerebrospinal meningitis
Vaccinations Below you will find information about diseases, the risk of contagion, and preventive vaccinations. DTP - Diphtheria Tetanus Polio Yellow fever Hepatitis A Typhoid fever Cerebrospinal meningitis
Yersinia pestis. Yersinia and plague. Dr. Hala Al Daghistani
 Yersinia pestis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Yersinia species Short, pleomorphic gram-negative rods that can exhibit bipolar staining. Catalase positive, and microaerophilic or facultatively anaerobic. Animals
Yersinia pestis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Yersinia species Short, pleomorphic gram-negative rods that can exhibit bipolar staining. Catalase positive, and microaerophilic or facultatively anaerobic. Animals
Chapter 17 Disease and Resistance: The Wars Within
 Chapter 17 Disease and Resistance: The Wars Within Objectives: After reading Chapter 17, you should understand The concepts relating to infectious diseases, the difference between disease and infection
Chapter 17 Disease and Resistance: The Wars Within Objectives: After reading Chapter 17, you should understand The concepts relating to infectious diseases, the difference between disease and infection
BODY DEFENCES AGAINST DISEASE AND THE ROLE OF VACCINES
 BODY DEFENCES AGAINST DISEASE AND THE ROLE OF VACCINES Topic 3 This topic links in with MICROBES (from unit 1) 1. What are the 3 types of microbes? 2. Which microbe do antibiotics destroy? 3. What microbe
BODY DEFENCES AGAINST DISEASE AND THE ROLE OF VACCINES Topic 3 This topic links in with MICROBES (from unit 1) 1. What are the 3 types of microbes? 2. Which microbe do antibiotics destroy? 3. What microbe
Multiple Choice Questions
 Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which one of the following is not a viral disease? (a) Dengue (b) AIDS (c) Typhoid (d) Influenza 2. Which one of the following is not a bacterial disease? (a) Cholera (b) Tuberculosis
Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which one of the following is not a viral disease? (a) Dengue (b) AIDS (c) Typhoid (d) Influenza 2. Which one of the following is not a bacterial disease? (a) Cholera (b) Tuberculosis
Bioterrorism Capabilities in Rural Texas Hospitals and Laboratories by
 Bioterrorism Capabilities in Rural Texas Hospitals and Laboratories by Taylor M. Johnson Public Health Internship Program School of Biological Sciences The University of Texas at Austin Mentor: Dr. Grace
Bioterrorism Capabilities in Rural Texas Hospitals and Laboratories by Taylor M. Johnson Public Health Internship Program School of Biological Sciences The University of Texas at Austin Mentor: Dr. Grace
Dr. Alongkone Phengsavanh University of Health Sciences Vientiane, Laos
 Dr. Alongkone Phengsavanh University of Health Sciences Vientiane, Laos Epidemiology: Epi = upon Demos = people Logy = study of Epidemiology is a discipline that describes, quantifies, and postulates causal
Dr. Alongkone Phengsavanh University of Health Sciences Vientiane, Laos Epidemiology: Epi = upon Demos = people Logy = study of Epidemiology is a discipline that describes, quantifies, and postulates causal
Principles of Infectious Disease Lecture #13 Dr. Gary Mumaugh
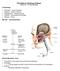 Principles of Infectious Disease Lecture #13 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Terminology Pathology study of disease Etiology cause of disease Pathogenesis disease process Infection colonization by microbes Disease illness
Principles of Infectious Disease Lecture #13 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Terminology Pathology study of disease Etiology cause of disease Pathogenesis disease process Infection colonization by microbes Disease illness
Pathogens: Microorganisms that are capable of causing disease Infection: Results when a pathogen invades and begins growing within the host Disease:
 Infectious Diseases Pathogens: Microorganisms that are capable of causing disease Infection: Results when a pathogen invades and begins growing within the host Disease: Results only if and when normal
Infectious Diseases Pathogens: Microorganisms that are capable of causing disease Infection: Results when a pathogen invades and begins growing within the host Disease: Results only if and when normal
Immune System. Before You Read. Read to Learn
 Immune System 37 section 1 Infectious Diseases Biology/Life Sciences 10.d Students know there are important differences between bacteria and viruses with respect to their requirements for growth and replication,
Immune System 37 section 1 Infectious Diseases Biology/Life Sciences 10.d Students know there are important differences between bacteria and viruses with respect to their requirements for growth and replication,
Bioterrorism. Environmental Encyclopedia, 2011 Updated: August 30, 2017 From Opposing Viewpoints in Context
 Bioterrorism Environmental Encyclopedia, 2011 Updated: August 30, 2017 From Opposing Viewpoints in Context Bioterrorism refers to the use of lethal biological agents to wage terror against a civilian population.
Bioterrorism Environmental Encyclopedia, 2011 Updated: August 30, 2017 From Opposing Viewpoints in Context Bioterrorism refers to the use of lethal biological agents to wage terror against a civilian population.
FINAL. Etiologic Agents & Related Information to Know. Chapter 21: Microbial Diseases of Skin and Eyes Page No. Know term "diphtheroids"...
 10 th Edition Tortora FINAL Microbiology Etiologic Agents & Related Information to Know Chapter 21: Microbial Diseases of Skin and Eyes Know term "diphtheroids"................. 586 Agents of boils and
10 th Edition Tortora FINAL Microbiology Etiologic Agents & Related Information to Know Chapter 21: Microbial Diseases of Skin and Eyes Know term "diphtheroids"................. 586 Agents of boils and
County of Los Angeles-Department of Public Health Acute Communicable Disease Control Program Acute Communicable Disease Control Manual (B73) current
 County of Los Angeles-Department of Public Health Acute Communicable Disease Control Program Acute Communicable Disease Control Manual (B73) PART I: COMMUNICABLE DISEASE CONTROL MEASURES PART II: REGULATIONS
County of Los Angeles-Department of Public Health Acute Communicable Disease Control Program Acute Communicable Disease Control Manual (B73) PART I: COMMUNICABLE DISEASE CONTROL MEASURES PART II: REGULATIONS
Preventing Infectious Diseases. Chapter 28 Lesson 3
 Preventing Infectious Diseases Chapter 28 Lesson 3 Active Immunity One important feature in the body s s immune system is that it remembers the pathogen it meets. This gives the body long term protection-immunity
Preventing Infectious Diseases Chapter 28 Lesson 3 Active Immunity One important feature in the body s s immune system is that it remembers the pathogen it meets. This gives the body long term protection-immunity
Biological Warfare & Terrorism
 Biological Warfare & Terrorism COL Ted Cieslak, MC, USA Director, Clinical Services Division U.S. Army Medical Command Ft Sam Houston TX USAMRIID: A Unique National Resource Page 1 Page 2 USAMRIID 9/15/2011
Biological Warfare & Terrorism COL Ted Cieslak, MC, USA Director, Clinical Services Division U.S. Army Medical Command Ft Sam Houston TX USAMRIID: A Unique National Resource Page 1 Page 2 USAMRIID 9/15/2011
Bacterial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 Bacterial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity 1 st Lecture Introduction Infection and Disease A. Definitions B. Generalized Stages of Infection C. Virulence Factors and Toxins A. Definitions Disease and Infectious
Bacterial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity 1 st Lecture Introduction Infection and Disease A. Definitions B. Generalized Stages of Infection C. Virulence Factors and Toxins A. Definitions Disease and Infectious
COMMUNICATING IN A CRISIS
 NEWS &TERRORISM COMMUNICATING IN A CRISIS A fact sheet from the National Academies and the U.S.Department of Homeland Security BIOLOGICAL ATTACK HUMAN PATHOGENS, BIOTOXINS, AND AGRICULTURAL THREATS Communication
NEWS &TERRORISM COMMUNICATING IN A CRISIS A fact sheet from the National Academies and the U.S.Department of Homeland Security BIOLOGICAL ATTACK HUMAN PATHOGENS, BIOTOXINS, AND AGRICULTURAL THREATS Communication
Health Department MEMORANDUM Office of the Commissioner
 Health Department MEMORANDUM Office of the Commissioner TO: FROM: Halton Robert Physicians M. Nosal, Medical Medical Officer Chiefs of Health of Staff: Joseph Brant Memorial Hospital DATE: October 11,
Health Department MEMORANDUM Office of the Commissioner TO: FROM: Halton Robert Physicians M. Nosal, Medical Medical Officer Chiefs of Health of Staff: Joseph Brant Memorial Hospital DATE: October 11,
Outline. Introduction to Epidemiology. Epidemiology. Epidemiology. History of epidemiology
 Outline Introduction to Epidemiology Joshua Vest Epidemiologist Austin/Travis County Health & Human Services Department Define History Basis of epidemiology Objectives of epidemiology Causal inference
Outline Introduction to Epidemiology Joshua Vest Epidemiologist Austin/Travis County Health & Human Services Department Define History Basis of epidemiology Objectives of epidemiology Causal inference
Infection, Detection, Prevention...
 Infection, Detection, Prevention... A disease is any change that disrupts the normal function of one or more body systems. Non infectious diseases are typically caused by exposure to chemicals or are inherited.
Infection, Detection, Prevention... A disease is any change that disrupts the normal function of one or more body systems. Non infectious diseases are typically caused by exposure to chemicals or are inherited.
Downloaded from
 Class IX: Biology Chapter: Why do we fall ill Chapter Notes Key learnings: 1) Our body s well-being is dependent on the proper functioning of its cells and tissues. 2) All our body parts and activities
Class IX: Biology Chapter: Why do we fall ill Chapter Notes Key learnings: 1) Our body s well-being is dependent on the proper functioning of its cells and tissues. 2) All our body parts and activities
Infectious Diseases Affecting the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
 Infectious Diseases Affecting the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 1 Defenses Cardiovascular system Lymphatic system Protection 2 Cardiovascular system Blood vessels Arteries, capillaries, and veins
Infectious Diseases Affecting the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 1 Defenses Cardiovascular system Lymphatic system Protection 2 Cardiovascular system Blood vessels Arteries, capillaries, and veins
"Wanted Poster" Diseases
 "Wanted Poster" Diseases Part One - Choosing a Disease Listed below are several bacteria and the disease they cause. Pick any one bacteria/disease to research. It is highly recommended that you pick a
"Wanted Poster" Diseases Part One - Choosing a Disease Listed below are several bacteria and the disease they cause. Pick any one bacteria/disease to research. It is highly recommended that you pick a
How to Respond to an Anthrax Threat
 How to Respond to an Anthrax Threat http://www.gsa.gov/mailpolicy Objectives Define - What is anthrax and what do I need to know. - The three forms of anthrax and treatment. Identify - What to look for
How to Respond to an Anthrax Threat http://www.gsa.gov/mailpolicy Objectives Define - What is anthrax and what do I need to know. - The three forms of anthrax and treatment. Identify - What to look for
Biology. Slide 1 of 30. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 30 2 of 30 What causes disease? 3 of 30 Disease A disease is any change, other than an injury, that disrupts the normal functions of the body. Disease-causing agents are called pathogens.
Biology 1 of 30 2 of 30 What causes disease? 3 of 30 Disease A disease is any change, other than an injury, that disrupts the normal functions of the body. Disease-causing agents are called pathogens.
Agents of Bioterrorism: Argument for and Against a List That Needs Cropping
 Agents of Bioterrorism: Argument for and Against a List That Needs Cropping Bioterrorism Preparedness: A Conference for Senior Practitioners and Professionals Dr. Arnold N. Weinberg Professor of Medicine
Agents of Bioterrorism: Argument for and Against a List That Needs Cropping Bioterrorism Preparedness: A Conference for Senior Practitioners and Professionals Dr. Arnold N. Weinberg Professor of Medicine
Infectious Diseases through Viruses. Obj. 3.c. & 3.g.
 Infectious Diseases through Viruses Obj. 3.c. & 3.g. Diseases Caused By Cells A disease is a condition that stops the body from functioning normally. Non-infectious diseases are not spread from person
Infectious Diseases through Viruses Obj. 3.c. & 3.g. Diseases Caused By Cells A disease is a condition that stops the body from functioning normally. Non-infectious diseases are not spread from person
Communicable diseases. Gastrointestinal track infection. Sarkhell Araz MSc. Public health/epidemiology
 Communicable diseases Gastrointestinal track infection Sarkhell Araz MSc. Public health/epidemiology Communicable diseases : Refer to diseases that can be transmitted and make people ill. They are caused
Communicable diseases Gastrointestinal track infection Sarkhell Araz MSc. Public health/epidemiology Communicable diseases : Refer to diseases that can be transmitted and make people ill. They are caused
DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE AFHSB Reportable Events Monthly Report
 DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE AFHSB Reportable Events Monthly Report July 2016 Report Description Reportable Events among all beneficiaries received from the Services over the past 5 years are used to create ranges
DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE AFHSB Reportable Events Monthly Report July 2016 Report Description Reportable Events among all beneficiaries received from the Services over the past 5 years are used to create ranges
DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE AFHSB Reportable Events Monthly Report
 DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE AFHSB Reportable Events Monthly Report May 2016 Report Description Reportable Events among all beneficiaries received from the Services over the past 5 years are used to create ranges
DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE AFHSB Reportable Events Monthly Report May 2016 Report Description Reportable Events among all beneficiaries received from the Services over the past 5 years are used to create ranges
1/29/2013. Viruses and Bacteria. Infectious Disease. Pathogens cause disease by: Chapters 16 and 17
 Viruses and Bacteria Chapters 16 and 17 Infectious Disease Caused by the invasion of a host by agents whose activities harm the host s tissues Can be transmitted to others Pathogen microorganisms that
Viruses and Bacteria Chapters 16 and 17 Infectious Disease Caused by the invasion of a host by agents whose activities harm the host s tissues Can be transmitted to others Pathogen microorganisms that
Overview Existing, Emerging, and Re-Emerging Communicable Diseases
 Overview Existing, Emerging, and Re-Emerging Communicable Diseases Many communicable diseases have existed with us since the beginning of time. Communicable diseases, which are infections we catch from
Overview Existing, Emerging, and Re-Emerging Communicable Diseases Many communicable diseases have existed with us since the beginning of time. Communicable diseases, which are infections we catch from
BIOSAFETY NEWS 1 st Edition
 Introduction Why have a biosafety newsletter? Well there are a number of reasons why we should have newsletter. It will provide information to researchers and School/Centre managers of any changes to the
Introduction Why have a biosafety newsletter? Well there are a number of reasons why we should have newsletter. It will provide information to researchers and School/Centre managers of any changes to the
INFECTIOUS DISEASES CONTAGIOUS DISEASES COMMUNICABLE DISEASES
 INFECTION it is the entry, development and or multiplication of an infectious agent in body of man or animal. CONTAMINATION it is the presence of infectious agents on the body surface, clothes or articles
INFECTION it is the entry, development and or multiplication of an infectious agent in body of man or animal. CONTAMINATION it is the presence of infectious agents on the body surface, clothes or articles
Biological Agents. What are the biological agents of greatest concern? Anthrax. Pneumonic Plague. Botulism. Smallpox. Brucellosis. Tuleremia.
 Biological Agents Q: What is biological terrorism? A: The Centers for Disease Control (CDC) defines biological terrorism as a planned release of viruses, germs or their toxins in order to harm or kill
Biological Agents Q: What is biological terrorism? A: The Centers for Disease Control (CDC) defines biological terrorism as a planned release of viruses, germs or their toxins in order to harm or kill
Health Questionnaire
 Health Questionnaire The information collected in this document is solely for the purpose of obtaining that which is required under the Ambulance Act of Ontario and is a condition of employment for all
Health Questionnaire The information collected in this document is solely for the purpose of obtaining that which is required under the Ambulance Act of Ontario and is a condition of employment for all
Index. Infect Dis Clin N Am 20 (2006) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Infect Dis Clin N Am 20 (2006) 475 483 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abortion storms, 363 Adult intestinal toxemia botulism, 317 Allergen Pharmaceuticals, 315 Alphaviruses
Infect Dis Clin N Am 20 (2006) 475 483 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abortion storms, 363 Adult intestinal toxemia botulism, 317 Allergen Pharmaceuticals, 315 Alphaviruses
OTHER COMMUNICABLE DISEASES. Sandra Pinzón and Diana Sánchez. Andalusian School of Public Health Gábor Ternák. University of Pécs
 OTHER COMMUNICABLE DISEASES Sandra Pinzón and Diana Sánchez. Andalusian School of Public Health Gábor Ternák. University of Pécs Viral diseases Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis C STI HIV Other viral diseases
OTHER COMMUNICABLE DISEASES Sandra Pinzón and Diana Sánchez. Andalusian School of Public Health Gábor Ternák. University of Pécs Viral diseases Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis C STI HIV Other viral diseases
Viruses: Select Agents and Emerging Pathogens. Patricia Bolívar MS., CLS, PHM
 Viruses: Select Agents and Emerging Pathogens Patricia Bolívar MS., CLS, PHM Objectives Review Select Agent Viruses. Key features to recognize Smallpox virus Update on emerging Viruses of possible pandemic
Viruses: Select Agents and Emerging Pathogens Patricia Bolívar MS., CLS, PHM Objectives Review Select Agent Viruses. Key features to recognize Smallpox virus Update on emerging Viruses of possible pandemic
Infectious Disease Surveillance System in Korea. Byungguk Yang Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
 Infectious Disease Surveillance System in Korea Byungguk Yang Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 1 General information About Korea About KCDC (Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)
Infectious Disease Surveillance System in Korea Byungguk Yang Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 1 General information About Korea About KCDC (Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)
DISEASE PREVENTION & ANTIMICROBIAL USE REDUCTION: IMPACT OF VACCINATION
 DISEASE PREVENTION & ANTIMICROBIAL USE REDUCTION: IMPACT OF VACCINATION Anwar Hoosen Department of Medical microbiology University of Pretoria & Tswane Academic Division, NHLS 1 VACCINE ACHIEVEMENTS At
DISEASE PREVENTION & ANTIMICROBIAL USE REDUCTION: IMPACT OF VACCINATION Anwar Hoosen Department of Medical microbiology University of Pretoria & Tswane Academic Division, NHLS 1 VACCINE ACHIEVEMENTS At
Orientation Program for Infection Control Professionals
 Orientation Program for Infection Control Professionals Module 7: Communicable Diseases Table of Contents Module 7: Communicable Diseases... 1 Objectives... 1 Instructions... 1 Overview... 2 Key Concepts...
Orientation Program for Infection Control Professionals Module 7: Communicable Diseases Table of Contents Module 7: Communicable Diseases... 1 Objectives... 1 Instructions... 1 Overview... 2 Key Concepts...
2. According to the information provided by the WHO, there is no justification at this stage for restrictions on travel or trade.
 Outbreak of Plague in Madagascar The following information is being disseminated by both the International Chamber of Shipping and The International Transport Workers Federation to draw attention to the
Outbreak of Plague in Madagascar The following information is being disseminated by both the International Chamber of Shipping and The International Transport Workers Federation to draw attention to the
Chapter 38 Viral Infections
 Chapter 38 Viral Infections Primary Objectives of This Chapter Chapter 38 introduces a wide variety of important human viral diseases and serves as an introduction to Medical Virology. It is considered
Chapter 38 Viral Infections Primary Objectives of This Chapter Chapter 38 introduces a wide variety of important human viral diseases and serves as an introduction to Medical Virology. It is considered
Yale Environmental Health & Safety Update Form for Request to Use Infectious Agents Status of Protocol
 Yale Environmental Health & Safety Update Form for Request to Use Infectious Agents To update or renew the attached infectious agent registration please review the registration and complete the information
Yale Environmental Health & Safety Update Form for Request to Use Infectious Agents To update or renew the attached infectious agent registration please review the registration and complete the information
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Sandro Cinti, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Sandro Cinti, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Sanofi Pasteur: A partner in eradicating vaccine preventable diseases and improving access to vaccines
 Sanofi Pasteur: A partner in eradicating vaccine preventable diseases and improving access to vaccines 1 Vaccines: the single most effective medical intervention 2 Vaccines save lives Millions of cases
Sanofi Pasteur: A partner in eradicating vaccine preventable diseases and improving access to vaccines 1 Vaccines: the single most effective medical intervention 2 Vaccines save lives Millions of cases
The Immune System: Your Defense Against Disease
 The Immune System: Your Defense Against Disease Terms: Immune System: body s primary defense against disease-causing microorganisms. Immune: condition in which a body is able to permanently fight a disease.
The Immune System: Your Defense Against Disease Terms: Immune System: body s primary defense against disease-causing microorganisms. Immune: condition in which a body is able to permanently fight a disease.
Continuing Education Material: Biological and Chemical Terrorism. ABP, Inc
 Continuing Education Material: Biological and Chemical Terrorism ABP, Inc ABP CONTINUING EDUCATION MATERIAL BIOLOGICAL AND CHEMICAL TERRORISM OBJECTIVES 1. Explain the vulnerability of the U.S. to biological
Continuing Education Material: Biological and Chemical Terrorism ABP, Inc ABP CONTINUING EDUCATION MATERIAL BIOLOGICAL AND CHEMICAL TERRORISM OBJECTIVES 1. Explain the vulnerability of the U.S. to biological
Foundations of Global Health. Communicable Diseases (Part 1): Control & Smallpox Eradication. Communicable Disease Definitions.
 Foundations Global Health Communicable Diseases (Part 1): Control & Smallpox Eradication Learning Objectives Identify components the disease triangle and links in the chain transmission Define prevention,
Foundations Global Health Communicable Diseases (Part 1): Control & Smallpox Eradication Learning Objectives Identify components the disease triangle and links in the chain transmission Define prevention,
The Immune System and Disease
 Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1029 1033) This section describes the causes of disease and explains how infectious diseases are transmitted Introduction
Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1029 1033) This section describes the causes of disease and explains how infectious diseases are transmitted Introduction
Guidelines for Surveillance and Investigation of Infectious Diseases Health Service Region 11 February 2007
 Guidelines for Surveillance and Investigation of Infectious Diseases Health Service Region 11 February 2007 REPORTING The chart below indicates which Texas Department of State Health Services program monitors
Guidelines for Surveillance and Investigation of Infectious Diseases Health Service Region 11 February 2007 REPORTING The chart below indicates which Texas Department of State Health Services program monitors
Wasatch School District Guidelines for Student Exclusion and Readmission
 Wasatch School District Guidelines for Student Exclusion and Readmission Condition Chicken pox (Varicella) Colds, Sore Throat, or a Persistent Cough Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Diarrhea (An increased number
Wasatch School District Guidelines for Student Exclusion and Readmission Condition Chicken pox (Varicella) Colds, Sore Throat, or a Persistent Cough Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Diarrhea (An increased number
Responding to the Threat of Bioterrorism: A Status Report on Vaccine Research in the United States
 Responding to the Threat of Bioterrorism: A Status Report on Vaccine Research in the United States Dixie E. Snider, M.D., M.P.H. Associate Director for Science Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Responding to the Threat of Bioterrorism: A Status Report on Vaccine Research in the United States Dixie E. Snider, M.D., M.P.H. Associate Director for Science Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Unit 4 Student Guided Notes
 Structure of Viruses Discovery of the Virus Unit 4 Student Guided Notes Many human epidemics were well documented and observed in history, but. The following 3 discoveries shaped our knowledge of viruses
Structure of Viruses Discovery of the Virus Unit 4 Student Guided Notes Many human epidemics were well documented and observed in history, but. The following 3 discoveries shaped our knowledge of viruses
Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages )
 Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1031 1035) Key Concepts What causes disease? How are infectious diseases transmitted? Introduction (page 1031) 1. Any change,
Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1031 1035) Key Concepts What causes disease? How are infectious diseases transmitted? Introduction (page 1031) 1. Any change,
Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages )
 Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1031 1035) What causes disease? How are infectious diseases transmitted? Introduction (page 1031) 1 Any change, other than
Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1031 1035) What causes disease? How are infectious diseases transmitted? Introduction (page 1031) 1 Any change, other than
Testing for SSBA (Security Sensitive Biological Agents) Dr Torsten Theis Senior Hospital Scientist RCPA BioSecurity QAP 16 August 2012
 Testing for SSBA (Security Sensitive Biological Agents) Dr Torsten Theis Senior Hospital Scientist RCPA BioSecurity QAP 16 August 2012 Testing for SSBA (Security Sensitive Biological Agents) RCPA BioSecurity
Testing for SSBA (Security Sensitive Biological Agents) Dr Torsten Theis Senior Hospital Scientist RCPA BioSecurity QAP 16 August 2012 Testing for SSBA (Security Sensitive Biological Agents) RCPA BioSecurity
Communicable Diseases
 Chapter 23 Communicable Diseases Disease that s spread from one living organism to another or through the environment Infection occurs when pathogens in the body multiply and damage body cells Main Pathogens
Chapter 23 Communicable Diseases Disease that s spread from one living organism to another or through the environment Infection occurs when pathogens in the body multiply and damage body cells Main Pathogens
The Immune System and Pathology
 The Immune System and Pathology The Immune System in Action When a mosquito bites When you breathe When you have allergies When you get a blood transfusion When you die...also called the Lymphatic System
The Immune System and Pathology The Immune System in Action When a mosquito bites When you breathe When you have allergies When you get a blood transfusion When you die...also called the Lymphatic System
Medical Bacteriology - Lecture 7. Spore- forming Gram Positive Rods. Bacillus
 Medical Bacteriology - Lecture 7 Spore- forming Gram Positive Rods Bacillus 1 Bacillus Characteristics - Gram positive - Large rod. - Arranged in long chain - Spore forming - Aerobic or facultative anaerobic
Medical Bacteriology - Lecture 7 Spore- forming Gram Positive Rods Bacillus 1 Bacillus Characteristics - Gram positive - Large rod. - Arranged in long chain - Spore forming - Aerobic or facultative anaerobic
Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C: Occupational Considerations 357 for the Anesthesiologist Stephen H. Jackson and Eddie C. Cheung
 INFECTIOUS DISEASE AND BIOTERRORISM Foreword Lee A. Fleisher xi Preface Samuel C. Hughes and James D. Marks xiii Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C: Occupational Considerations 357 for the Anesthesiologist Stephen
INFECTIOUS DISEASE AND BIOTERRORISM Foreword Lee A. Fleisher xi Preface Samuel C. Hughes and James D. Marks xiii Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C: Occupational Considerations 357 for the Anesthesiologist Stephen
Rapid and progressive necrosis of the tissue underlying epidermis (cellulitis)
 Table 1. Infections of the Skin, Eyes and Ears Folliculitis Furuncles (boils) & Carbuncles Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Scald Skin Syndrome Peeling skin on infants Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Impetigo Lesions
Table 1. Infections of the Skin, Eyes and Ears Folliculitis Furuncles (boils) & Carbuncles Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Scald Skin Syndrome Peeling skin on infants Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Impetigo Lesions
Anthrax is ancient. It's been around since biblical times, and is mentioned by Homer, Virgil & Hippocrates.
 Anthrax I. Introduction & history: Anthrax is ancient. It's been around since biblical times, and is mentioned by Homer, Virgil & Hippocrates. - Some people attribute the sixth plague (in Exodus) to Anthrax.
Anthrax I. Introduction & history: Anthrax is ancient. It's been around since biblical times, and is mentioned by Homer, Virgil & Hippocrates. - Some people attribute the sixth plague (in Exodus) to Anthrax.
Basic Disease Investigation in Colorado Module 1: Communicable Disease Basics
 Basic Disease Investigation in Colorado Module 1: Communicable Disease Basics Introduction This course is designed for non-epidemiologists who work in public health, environmental health, and other healthcare
Basic Disease Investigation in Colorado Module 1: Communicable Disease Basics Introduction This course is designed for non-epidemiologists who work in public health, environmental health, and other healthcare
The Chain of Infection
 The Chain of Infection As healthcare professionals, it is important to understand two facts about infection: 1.The various ways infection can be transmitted. 2. The ways the infection chain can be broken.
The Chain of Infection As healthcare professionals, it is important to understand two facts about infection: 1.The various ways infection can be transmitted. 2. The ways the infection chain can be broken.
Chapter 17. Infectious Diseases
 Chapter 17 Infectious Diseases Lesson 1 What is an infectious disease? Infectious disease Is any disease that is caused by an agent that can be passed from one living thing to another. Disease causing
Chapter 17 Infectious Diseases Lesson 1 What is an infectious disease? Infectious disease Is any disease that is caused by an agent that can be passed from one living thing to another. Disease causing
HEALTH REQUIREMENTS AND SERVICES: FFAD COMMUNICABLE DISEASES (EXHIBIT) REQUIREMENTS FOR EXCLUDING STUDENTS AND REPORTING CONDITIONS
 REQUIREMENTS FOR EXCLUDING STUDENTS AND REPORTING CONDITIONS The information on the chart below has been collected from Department of Health rules at 25 TAC 97.3, 97.6, 97.7, and 97.132 The major criterion
REQUIREMENTS FOR EXCLUDING STUDENTS AND REPORTING CONDITIONS The information on the chart below has been collected from Department of Health rules at 25 TAC 97.3, 97.6, 97.7, and 97.132 The major criterion
Foundations in Microbiology
 Foundations in Microbiology Fifth Edition Talaro Chapter 13 Microbe Human Interactions: Infection and Disease Chapter 13 2 3 Infection a condition in which pathogenic microbes penetrate host defenses,
Foundations in Microbiology Fifth Edition Talaro Chapter 13 Microbe Human Interactions: Infection and Disease Chapter 13 2 3 Infection a condition in which pathogenic microbes penetrate host defenses,
Occupational Health Program Guidance Document for Working with Tier 1 Select Agents and Toxins
 Occupational Health Program Guidance Document for Working with Tier 1 Select Agents and Toxins 7 CFR Part 331, 9 CFR Part 121, 42 CFR Part 73 05 July 2013 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Occupational Health Program Guidance Document for Working with Tier 1 Select Agents and Toxins 7 CFR Part 331, 9 CFR Part 121, 42 CFR Part 73 05 July 2013 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Selected New Jersey Communicable Disease Regulations
 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE OUTBREAK MANUAL New Jersey s Public Health Response Selected New Jersey Communicable Disease Regulations June 2013 Public Health Emergency Response Capability Requirements as stated
COMMUNICABLE DISEASE OUTBREAK MANUAL New Jersey s Public Health Response Selected New Jersey Communicable Disease Regulations June 2013 Public Health Emergency Response Capability Requirements as stated
Ottawa County Health Department James Street, Suite 400 Holland, Mi Phone: Fax:
 Ottawa County Health Department 12251 James Street, Suite 400 Holland, Mi 49424 Phone: 616.393.5757 Fax: 616.494.5546 4th Quarter* MDSS Administrative Report, 2005 Jurisdiction: Ottawa County Health Department
Ottawa County Health Department 12251 James Street, Suite 400 Holland, Mi 49424 Phone: 616.393.5757 Fax: 616.494.5546 4th Quarter* MDSS Administrative Report, 2005 Jurisdiction: Ottawa County Health Department
Introduction to Epidemiology.
 Faculty of Medicine Introduction to Community Medicine Course (31505201) Introduction to Epidemiology. By Hatim Jaber MD MPH JBCM PhD 20-11- 2017 1 Introduction to course 31505201 Week 8 Course Content-
Faculty of Medicine Introduction to Community Medicine Course (31505201) Introduction to Epidemiology. By Hatim Jaber MD MPH JBCM PhD 20-11- 2017 1 Introduction to course 31505201 Week 8 Course Content-
Biological Warfare Agents
 Biological Warfare Agents Chapter 29 Biological Warfare Agents The reader is strongly advised to supplement material in this chapter with the following reference: US Army Medical Research Institute of
Biological Warfare Agents Chapter 29 Biological Warfare Agents The reader is strongly advised to supplement material in this chapter with the following reference: US Army Medical Research Institute of
Introduction to Public Health and Epidemiology
 Surveillance and Outbreak Investigation Course Introduction to Public Health and Epidemiology King Cholera dispenses contagion: the London Cholera Epidemic of 1866 Learning Objectives Define Epidemiology
Surveillance and Outbreak Investigation Course Introduction to Public Health and Epidemiology King Cholera dispenses contagion: the London Cholera Epidemic of 1866 Learning Objectives Define Epidemiology
Aerosol Particle Size and Infectivity
 Aerosol Particle Size and Infectivity Today s presentation will describe two important variables and how they interact to cause infections in primary aerosols Particle Size and Agent Concentration Much
Aerosol Particle Size and Infectivity Today s presentation will describe two important variables and how they interact to cause infections in primary aerosols Particle Size and Agent Concentration Much
Infrastructure and Methods to Support Real Time Biosurveillance. Kenneth D. Mandl, MD, MPH Children s Hospital Boston Harvard Medical School
 Infrastructure and Methods to Support Real Time Biosurveillance Kenneth D. Mandl, MD, MPH Children s Hospital Boston Harvard Medical School Category A agents Anthrax (Bacillus anthracis) Botulism (Clostridium
Infrastructure and Methods to Support Real Time Biosurveillance Kenneth D. Mandl, MD, MPH Children s Hospital Boston Harvard Medical School Category A agents Anthrax (Bacillus anthracis) Botulism (Clostridium
CE Unit. Viruses and Vaccines
 CE Unit Viruses and Vaccines DO NOT WRITE What is a virus? Have you ever had a virus? What is a vaccine? How is a virus different from bacteria? What are the deadliest viruses? 10. Dengue fever 50 million
CE Unit Viruses and Vaccines DO NOT WRITE What is a virus? Have you ever had a virus? What is a vaccine? How is a virus different from bacteria? What are the deadliest viruses? 10. Dengue fever 50 million
TEN GERMS THAT SHOOK THE WORLD RICHARD S. NEIMAN, M.D.
 TEN GERMS THAT SHOOK THE WORLD RICHARD S. NEIMAN, M.D. THE GERM A MIGHTY CREATURE IS THE GERM, THO SMALLER THAN A PACHYDERM ITS CUSTOMARY PLACE IS DEEP WITHIN THE HUMAN RACE ITS CHILDISH PRIDE IT OFTEN
TEN GERMS THAT SHOOK THE WORLD RICHARD S. NEIMAN, M.D. THE GERM A MIGHTY CREATURE IS THE GERM, THO SMALLER THAN A PACHYDERM ITS CUSTOMARY PLACE IS DEEP WITHIN THE HUMAN RACE ITS CHILDISH PRIDE IT OFTEN
Bacteria & Viruses. Biology Science Department
 Bacteria & Viruses What do you already know? What are the differences between viruses and bacteria? Are all bacteria harmful? When you get a cold, should you take an antibiotic to help you get better?
Bacteria & Viruses What do you already know? What are the differences between viruses and bacteria? Are all bacteria harmful? When you get a cold, should you take an antibiotic to help you get better?
The prokaryotic domains
 Diversity of Bacteria, Archaea, and Viruses Chapter 19 The prokaryotic domains Bacteria Three types of structure Spherical, rod-shaped, and spiral Archaea Many are extremophilic Prefer to live in very
Diversity of Bacteria, Archaea, and Viruses Chapter 19 The prokaryotic domains Bacteria Three types of structure Spherical, rod-shaped, and spiral Archaea Many are extremophilic Prefer to live in very
Vaccines and other immunological antimicrobial therapy 1
 Vaccines and other immunological antimicrobial therapy 1 Vaccines Vaccine: a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular disease. Vaccine typically contains an agent that
Vaccines and other immunological antimicrobial therapy 1 Vaccines Vaccine: a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular disease. Vaccine typically contains an agent that
Detection of a Simulated Infectious Agent
 The Biotechnology Detection of a Simulated Infectious Agent 166 EDVO-Kit # Storage: Store entire experiment at room temperature. Experiment Objective: The objective of this experiment is to develop an
The Biotechnology Detection of a Simulated Infectious Agent 166 EDVO-Kit # Storage: Store entire experiment at room temperature. Experiment Objective: The objective of this experiment is to develop an
Present State and Measures against Infectious Diseases in Tokyo
 Asian Network of Major Cities 21 Asian Infectious Disease Project Present State and Measures against Infectious Diseases in History of Law on Infectious Diseases Revisions 1897 1999 23 Communicable Disease
Asian Network of Major Cities 21 Asian Infectious Disease Project Present State and Measures against Infectious Diseases in History of Law on Infectious Diseases Revisions 1897 1999 23 Communicable Disease
WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT?
 CHAPTER 7 PRINCIPLES OF DISEASE WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? How diseases are caused (etiology), how they can be characterized, and the concepts of sepsis and shock are important for developing an in-depth understanding
CHAPTER 7 PRINCIPLES OF DISEASE WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? How diseases are caused (etiology), how they can be characterized, and the concepts of sepsis and shock are important for developing an in-depth understanding
Disease: any change, other than an injury, that disrupts homeostasis. Pathogen: disease-causing agent such as bacteria, virus, etc.
 The Immune System Disease: any change, other than an injury, that disrupts homeostasis. Pathogen: disease-causing agent such as bacteria, virus, etc. Infectious disease- caused by pathogen Germ theory
The Immune System Disease: any change, other than an injury, that disrupts homeostasis. Pathogen: disease-causing agent such as bacteria, virus, etc. Infectious disease- caused by pathogen Germ theory
