Discrete Signal Processing
|
|
|
- Theodora Randall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Discrete Signal Processing C.M. Liu Perceptual Lab, College of Computer Science National Chiao-Tung University ( Office: EC538 (03) cmliu@cs.nctu.edu.tw
2 0. Preface 2 Engineer Modeling Discrete Signals & Systems Examples Definition Historical Perceptive Engineering Discovery Digital Environments Contents Discussed Topics & Textbooks Outline & Time Scheduling
3 0. Preface 3 Related Courses in NCTU Mathematics Signals & Systems Advanced Courses & Applications Requirements Presentation & Discussions Homework Score Decision
4 0.1 Modeling 4 Two distinct engineer modeling Physical systems are modeled by mathematical equations. Physical signals are modeled by mathematical functions. R i(t) C v(t 0 ) y(t) R C v(t 0 ) y zi (t) 1 t y ( t ) Ri ( t ) i ( ) d v ( t ) C 0 t 0 Problem formulation Physical system Solution translation Mathematical models of systems and signals Conceptual Aspects Mathematical Solutions of equations
5 5 0.2 Signals & Systems: Speech Example Speech Signals
6 6 0.2 Signals & Systems: Speech Example (c.1) Speech Modeling Applications Speech Synthesis Compression Systems Pitch period P Voiced DT Impulse Generation White-Noise Generation Unvoiced V U ADC voiced/unvoiced All-Pole Filter Gain estimate 0 ( z ) Parameter excitation Parameter excitation s( n) signal speech Output device Speech Recognition Systems Microphone Template memory
7 0.2 Signals & Systems: Audio Example 7 CD Record & Play Systems 0 t
8 0.2 Signals & Systems: Audio Example (c.1) 8 Psychoacoustic Modeling
9 Ear Functioning: Hearing
10 Structures of the ear The pinnae help collect the sound, but are also somewhat directionally sensitive (much more so in dogs, bats and other animals) The ear canal actually amplifies frequencies of Hz due to resonance. The middle ear is filled with air through the Eustachian tubes which open in the throat. The ossicles of the middle ear amplify the pressure waves through lever action and by concentration (the oval window is 15x smaller than the eardrum. Tiny muscles on these bones reflex-ively contract in response to very high pressures, preventing cochlear damage Page 193 (344)
11 Inner Ear: Vestibule, Canals, Cochlea
12 Equal Loudness Curves Two different 60 decibel sounds will not in general have the same loudness equal intensity is not the same thing as equal loudness. Since the human hearing sensitivity varies with frequency, it is useful to plot equal loudness curves which show that variation for the average human ear.
13 Equal Loudness Curves (with labels) Source: - astr.gsu.edu/hbase/soun d/phon.html#c1 Qual loudness curves are the basis for the measurement of loudness in phons. If a given sound is perceived to be as loud as a 60 db sound at 1000 Hz, then it is said to have a loudness of 60 phons. 60 phons means "as loud as a 60 db, 1000 Hz tone"
14 0.2 Signals & Systems: Audio Example (c.2) 14 Psychoacoustic Modeling (c.1) Masking Just-noticeable Distortion Frequency (khz) 16
15 The Nature of Sound (P. 149) Sound as mechanical wave energy requires a medium such as air or water in which to move. Sound: vibratory energy caused by movement of physical objects Rate of vibration is called frequency What we hear is pitch (high or low) We hear 20-20,000 Hz (cycles/sec) Size (intensity) of vibration is amplitude What we experience is loudness Measured in decibels (db) (too loud too long = hearing loss)
16 Additive synthesis & Fourier analysis As in Fourier analysis of patterns of light, the same method can be used for representing and constructing complex sound wave phenomena. Figure 10.7, page 338 Here (d) is a composite of the fundamental (a) plus its second and third harmonics, (b) and (c).
17 0.2 Signals & Systems: Audio Example (c.3) 17 Spatial Information Applications Audio Compression 3D Sounds Music Synthesis L C R S L S R
18 0.2 Signals & Systems: Visual Example 18 Psychovisual Modeling Eye Structure Color Information Spectral Absorption of Three Types of Cones
19 The Human Eye
20 0.2 Signals & Systems: Visual Example 20 Image blurring Systems
21 A beam of light separated into its Wavelengths Page 157 (38)
22 The Electromagnetic Spectrum Colour is a secondary quality, a relation between light entering eye and brain function, a construct of the mind, not a quality in objects (not a primary quality ) Primary qualities are quantifiable, mathematical, external. Galileo (1623) The book of Nature is written in language of mathematics Newton (1721): For the rays, to speak properly, are not colored.
23 Copyright 2002 Wadsworth Group. Wadsworth is an imprint of the Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning at-man (man) Adapted from The Role of Frequency in Developing Perceptual Sets, by B. R. Bugelski and D. A. Alampay, 1961, Canadian Journal of Psychology, 15, Copyright 1961 by the Canadian Psychological Association. Reprinted with permission.
24 Copyright 2002 Wadsworth Group. Wadsworth is an imprint of the Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning Rat-Man (rat) Adapted from The Role of Frequency in Developing Perceptual Sets, by B. R. Bugelski and D. A. Alampay, 1961, Canadian Journal of Psychology, 15, Copyright 1961 by the Canadian Psychological Association. Reprinted with permission.
25 Copyright 2002 Wadsworth Group. Wadsworth is an imprint of the Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning Rat-Man (middle) Adapted from The Role of Frequency in Developing Perceptual Sets, by B. R. Bugelski and D. A. Alampay, 1961, Canadian Journal of Psychology, 15, Copyright 1961 by the Canadian Psychological Association. Reprinted with permission.
26 Copyright 2002 Wadsworth Group. Wadsworth is an imprint of the Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning at-man (man) Adapted from The Role of Frequency in Developing Perceptual Sets, by B. R. Bugelski and D. A. Alampay, 1961, Canadian Journal of Psychology, 15, Copyright 1961 by the Canadian Psychological Association. Reprinted with permission.
27 0.2 Signals & Systems: Definition 27 Signals Functions of one or two variables. Typically contain information about the behavior or nature of some phenomenon. Systems Respond to particular signals by producing other signals. Example 1: Electrical Circuits Signals: Voltage and Currents as a function of time in a electrical circuit are examples of signals. Systems: The circuit is a system. Example 2: Automobile Driver Automobile Driver Depresses the Accelerator Pedal Systems: The automobile Input Signals: The pressure on the acceleration pedal. Output Signals: Automobile speed
28 0.3 Historical Perspective 28 17th Century Invention of the Calculus (Newton, ) Model physical phenomena in terms of functions of continuous variables and differential equations. 18th Century Euler ( ) Bernoulli ( ) Lagrange ( ) 19th Century Gauss ( ) Fourier ( )
29 0.3 Historical Perspective (c.1) 29 Digital Computer (1950s) Analog Systems were used for real-time applications The need for sophisticated signal processing Oil prospecting. Digital computers are used to simulate & approximate analog systems. Microelectronics Wafer-scale integration DSP Processors Flexibility and High Computing Speeds High speed fixed point and floating point processor. Personal Computers Storage Computing Power Media Applications
30 0.4 Contents-- Topics & Textbooks 30 Discussed Topics The concepts of signals and systems arise in an extremely wide variety of fields. Although the physical nature of the signals and systems may be drastically different, there are common tools for signal analysis and system design. These common tools are the discussed topics in this course. Objective of the Course Provide the reader with the knowledge necessary for the wide scope of applications for digital signal processing. A foundation for future developments. Text Books A.V. Oppenheim and R.W. Schafer, Discrete-Time Signal Processing, Prentice Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey, 2nd Edition, A.V. Oppenheim and R.W. Schafer, Discrete-Time Signal Processing, Pearson, 3 rd Edition, 2010.
31 Contents-- Outline & Time Scheduling (48 h) Introduction (1) Discrete-Time Signals and Systems (72 pages, 8 hours) Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals (69 pages, 6 hours) The z-transform (53 pages, 4 hours) Transform Analysis of Linear Time-Invariant Systems (88 pages, 5 hours) Structures for Discrete-Time Systems (113 pages, 5 hours) Filter Design Techniques (111 pages, 5 hours) The Discrete Fourier Transform (67 pages, 4 hours) Computation of the Discrete Fourier Transform (81 pages, 3 hours) Fourier Analysis of Signals Using the Discrete Fourier Transform (73 pages, 3 hours) Hilbert Transform Discrete Cosine Transform
32 0.5 Related Courses in NCTU 32 Course Links in Our Departments Mathematics Linear Algebra Discrete Math. Differential Equations Probability CS Courses Electronics & Electrical Circuits Computer Programming and Peripherals Advanced Courses & Applications Image Processing Audio Processing Speech Processing Neural Network...
33 0.6 Requirements 33 Presentation (2h/week) Slices Discussion (1h/week) Homeworks Tests Reviewing Homeworks Problems Score Decision Homeworks (30%) 3 Examinations (70%) Prospects Thoroughly familiar with 80% of the teaching and well acquainted with another 20%. Be able to tackle about the assigned homeworks. Have a reading time at least 5 hours per week.
SUBJECT: Physics TEACHER: Mr. S. Campbell DATE: 15/1/2017 GRADE: DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: The Physics Of Hearing
 SUBJECT: Physics TEACHER: Mr. S. Campbell DATE: 15/1/2017 GRADE: 12-13 DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: The Physics Of Hearing The Physics Of Hearing On completion of this section, you should be able to:
SUBJECT: Physics TEACHER: Mr. S. Campbell DATE: 15/1/2017 GRADE: 12-13 DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: The Physics Of Hearing The Physics Of Hearing On completion of this section, you should be able to:
Hearing. Figure 1. The human ear (from Kessel and Kardon, 1979)
 Hearing The nervous system s cognitive response to sound stimuli is known as psychoacoustics: it is partly acoustics and partly psychology. Hearing is a feature resulting from our physiology that we tend
Hearing The nervous system s cognitive response to sound stimuli is known as psychoacoustics: it is partly acoustics and partly psychology. Hearing is a feature resulting from our physiology that we tend
Hearing Sound. The Human Auditory System. The Outer Ear. Music 170: The Ear
 Hearing Sound Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
Hearing Sound Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
Music 170: The Ear. Tamara Smyth, Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016
 Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 1 Hearing Sound Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 1 Hearing Sound Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
The Ear. The ear can be divided into three major parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear.
 The Ear The ear can be divided into three major parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The Ear There are three components of the outer ear: Pinna: the fleshy outer part of the ear which
The Ear The ear can be divided into three major parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The Ear There are three components of the outer ear: Pinna: the fleshy outer part of the ear which
Hearing. istockphoto/thinkstock
 Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Hearing. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Module 14. Hearing. Hearing
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Hearing Module 14 2 Hearing Hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves The
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Hearing Module 14 2 Hearing Hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves The
Chapter 11: Sound, The Auditory System, and Pitch Perception
 Chapter 11: Sound, The Auditory System, and Pitch Perception Overview of Questions What is it that makes sounds high pitched or low pitched? How do sound vibrations inside the ear lead to the perception
Chapter 11: Sound, The Auditory System, and Pitch Perception Overview of Questions What is it that makes sounds high pitched or low pitched? How do sound vibrations inside the ear lead to the perception
! Can hear whistle? ! Where are we on course map? ! What we did in lab last week. ! Psychoacoustics
 2/14/18 Can hear whistle? Lecture 5 Psychoacoustics Based on slides 2009--2018 DeHon, Koditschek Additional Material 2014 Farmer 1 2 There are sounds we cannot hear Depends on frequency Where are we on
2/14/18 Can hear whistle? Lecture 5 Psychoacoustics Based on slides 2009--2018 DeHon, Koditschek Additional Material 2014 Farmer 1 2 There are sounds we cannot hear Depends on frequency Where are we on
Sound and its characteristics. The decibel scale. Structure and function of the ear. Békésy s theory. Molecular basis of hair cell function.
 Hearing Sound and its characteristics. The decibel scale. Structure and function of the ear. Békésy s theory. Molecular basis of hair cell function. 19/11/2014 Sound A type of longitudinal mass wave that
Hearing Sound and its characteristics. The decibel scale. Structure and function of the ear. Békésy s theory. Molecular basis of hair cell function. 19/11/2014 Sound A type of longitudinal mass wave that
whether or not the fundamental is actually present.
 1) Which of the following uses a computer CPU to combine various pure tones to generate interesting sounds or music? 1) _ A) MIDI standard. B) colored-noise generator, C) white-noise generator, D) digital
1) Which of the following uses a computer CPU to combine various pure tones to generate interesting sounds or music? 1) _ A) MIDI standard. B) colored-noise generator, C) white-noise generator, D) digital
COM3502/4502/6502 SPEECH PROCESSING
 COM3502/4502/6502 SPEECH PROCESSING Lecture 4 Hearing COM3502/4502/6502 Speech Processing: Lecture 4, slide 1 The Speech Chain SPEAKER Ear LISTENER Feedback Link Vocal Muscles Ear Sound Waves Taken from:
COM3502/4502/6502 SPEECH PROCESSING Lecture 4 Hearing COM3502/4502/6502 Speech Processing: Lecture 4, slide 1 The Speech Chain SPEAKER Ear LISTENER Feedback Link Vocal Muscles Ear Sound Waves Taken from:
Outline. 4. The Ear and the Perception of Sound (Psychoacoustics) A.1 Outer Ear Amplifies Sound. Introduction
 4. The Ear and the Perception of Sound (Psychoacoustics) 1 Outline A. Structure of the Ear B. Perception of Loudness C. Perception of Pitch D. References Updated May 13, 01 Introduction 3 A. The Structure
4. The Ear and the Perception of Sound (Psychoacoustics) 1 Outline A. Structure of the Ear B. Perception of Loudness C. Perception of Pitch D. References Updated May 13, 01 Introduction 3 A. The Structure
Sound. Audition. Physics of Sound. Properties of sound. Perception of sound works the same way as light.
 Sound Audition Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Sound Audition Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Audition. Sound. Physics of Sound. Perception of sound works the same way as light.
 Audition Sound Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Audition Sound Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Ganglion Cells Blind Spot Cornea Pupil Visual Area of the Bipolar Cells Thalamus Rods and Cones Lens Visual cortex of the occipital lobe
 How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
Intro to Audition & Hearing
 Intro to Audition & Hearing Lecture 16 Chapter 9, part II Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Fall 2017 1 Sine wave: one of the simplest kinds of sounds: sound for which pressure
Intro to Audition & Hearing Lecture 16 Chapter 9, part II Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Fall 2017 1 Sine wave: one of the simplest kinds of sounds: sound for which pressure
17.4 Sound and Hearing
 You can identify sounds without seeing them because sound waves carry information to your ears. People who work in places where sound is very loud need to protect their hearing. Properties of Sound Waves
You can identify sounds without seeing them because sound waves carry information to your ears. People who work in places where sound is very loud need to protect their hearing. Properties of Sound Waves
HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR CLINICAL PROFESSIONALS HEARING.HEALTH.MIL. HCE_ClinicalProvider-Flip_FINAL01.indb 1
 HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR CLINICAL PROFESSIONALS HCE_ClinicalProvider-Flip_FINAL01.indb 1 TEMPORAL MUSCLE TEMPORAL BONE EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL MALLEUS INCUS STAPES SEMICUIRCULAR CANALS COCHLEA VESTIBULAR
HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR CLINICAL PROFESSIONALS HCE_ClinicalProvider-Flip_FINAL01.indb 1 TEMPORAL MUSCLE TEMPORAL BONE EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL MALLEUS INCUS STAPES SEMICUIRCULAR CANALS COCHLEA VESTIBULAR
Perception of Sound. To hear sound, your ear has to do three basic things:
 Perception of Sound Your ears are extraordinary organs. They pick up all the sounds around you and then translate this information into a form your brain can understand. One of the most remarkable things
Perception of Sound Your ears are extraordinary organs. They pick up all the sounds around you and then translate this information into a form your brain can understand. One of the most remarkable things
Digital. hearing instruments have burst on the
 Testing Digital and Analog Hearing Instruments: Processing Time Delays and Phase Measurements A look at potential side effects and ways of measuring them by George J. Frye Digital. hearing instruments
Testing Digital and Analog Hearing Instruments: Processing Time Delays and Phase Measurements A look at potential side effects and ways of measuring them by George J. Frye Digital. hearing instruments
Outline. The ear and perception of sound (Psychoacoustics) A.1 Outer Ear Amplifies Sound. Introduction
 The ear and perception of sound (Psychoacoustics) 1 Outline A. Structure of the Ear B. Perception of Pitch C. Perception of Loudness D. Timbre (quality of sound) E. References Updated 01Aug0 Introduction
The ear and perception of sound (Psychoacoustics) 1 Outline A. Structure of the Ear B. Perception of Pitch C. Perception of Loudness D. Timbre (quality of sound) E. References Updated 01Aug0 Introduction
Consciousness and Blindsight
 Consciousness and Blindsight Blindsight: The ability to respond appropriately to visual inputs while lacking the feeling of having seen them These patients are unable to see, but are able to reach for
Consciousness and Blindsight Blindsight: The ability to respond appropriately to visual inputs while lacking the feeling of having seen them These patients are unable to see, but are able to reach for
SLHS 1301 The Physics and Biology of Spoken Language. Practice Exam 2. b) 2 32
 SLHS 1301 The Physics and Biology of Spoken Language Practice Exam 2 Chapter 9 1. In analog-to-digital conversion, quantization of the signal means that a) small differences in signal amplitude over time
SLHS 1301 The Physics and Biology of Spoken Language Practice Exam 2 Chapter 9 1. In analog-to-digital conversion, quantization of the signal means that a) small differences in signal amplitude over time
Auditory Perception: Sense of Sound /785 Spring 2017
 Auditory Perception: Sense of Sound 85-385/785 Spring 2017 Professor: Laurie Heller Classroom: Baker Hall 342F (sometimes Cluster 332P) Time: Tuesdays and Thursdays 1:30-2:50 Office hour: Thursday 3:00-4:00,
Auditory Perception: Sense of Sound 85-385/785 Spring 2017 Professor: Laurie Heller Classroom: Baker Hall 342F (sometimes Cluster 332P) Time: Tuesdays and Thursdays 1:30-2:50 Office hour: Thursday 3:00-4:00,
Chapter 13 Physics of the Ear and Hearing
 Hearing 100 times greater dynamic range than vision Wide frequency range (20 ~ 20,000 Hz) Sense of hearing Mechanical system that stimulates the hair cells in the cochlea Sensors that produce action potentials
Hearing 100 times greater dynamic range than vision Wide frequency range (20 ~ 20,000 Hz) Sense of hearing Mechanical system that stimulates the hair cells in the cochlea Sensors that produce action potentials
SOLUTIONS Homework #3. Introduction to Engineering in Medicine and Biology ECEN 1001 Due Tues. 9/30/03
 SOLUTIONS Homework #3 Introduction to Engineering in Medicine and Biology ECEN 1001 Due Tues. 9/30/03 Problem 1: a) Where in the cochlea would you say the process of "fourier decomposition" of the incoming
SOLUTIONS Homework #3 Introduction to Engineering in Medicine and Biology ECEN 1001 Due Tues. 9/30/03 Problem 1: a) Where in the cochlea would you say the process of "fourier decomposition" of the incoming
Presentation On SENSATION. Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur
 Presentation On SENSATION Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur INTRODUCTION:- Sensation is a specialty area within Psychology that works at understanding how are senses work and how we perceive stimuli in the environment.
Presentation On SENSATION Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur INTRODUCTION:- Sensation is a specialty area within Psychology that works at understanding how are senses work and how we perceive stimuli in the environment.
Receptors / physiology
 Hearing: physiology Receptors / physiology Energy transduction First goal of a sensory/perceptual system? Transduce environmental energy into neural energy (or energy that can be interpreted by perceptual
Hearing: physiology Receptors / physiology Energy transduction First goal of a sensory/perceptual system? Transduce environmental energy into neural energy (or energy that can be interpreted by perceptual
HEARING AND PSYCHOACOUSTICS
 CHAPTER 2 HEARING AND PSYCHOACOUSTICS WITH LIDIA LEE I would like to lead off the specific audio discussions with a description of the audio receptor the ear. I believe it is always a good idea to understand
CHAPTER 2 HEARING AND PSYCHOACOUSTICS WITH LIDIA LEE I would like to lead off the specific audio discussions with a description of the audio receptor the ear. I believe it is always a good idea to understand
Speech Generation and Perception
 Speech Generation and Perception 1 Speech Generation and Perception : The study of the anatomy of the organs of speech is required as a background for articulatory and acoustic phonetics. An understanding
Speech Generation and Perception 1 Speech Generation and Perception : The study of the anatomy of the organs of speech is required as a background for articulatory and acoustic phonetics. An understanding
Signals, systems, acoustics and the ear. Week 5. The peripheral auditory system: The ear as a signal processor
 Signals, systems, acoustics and the ear Week 5 The peripheral auditory system: The ear as a signal processor Think of this set of organs 2 as a collection of systems, transforming sounds to be sent to
Signals, systems, acoustics and the ear Week 5 The peripheral auditory system: The ear as a signal processor Think of this set of organs 2 as a collection of systems, transforming sounds to be sent to
L2: Speech production and perception Anatomy of the speech organs Models of speech production Anatomy of the ear Auditory psychophysics
 L2: Speech production and perception Anatomy of the speech organs Models of speech production Anatomy of the ear Auditory psychophysics Introduction to Speech Processing Ricardo Gutierrez-Osuna CSE@TAMU
L2: Speech production and perception Anatomy of the speech organs Models of speech production Anatomy of the ear Auditory psychophysics Introduction to Speech Processing Ricardo Gutierrez-Osuna CSE@TAMU
Glossary For Parents. Atresia: closure of the ear canal or absence of an ear opening.
 Glossary For Parents This is not a complete or comprehensive glossary of audiologic and medical terms. It does include many technical and often unfamiliar terms that parents may hear used in connection
Glossary For Parents This is not a complete or comprehensive glossary of audiologic and medical terms. It does include many technical and often unfamiliar terms that parents may hear used in connection
Vision and Audition. This section concerns the anatomy of two important sensory systems, the visual and the auditory systems.
 Vision and Audition Vision and Audition This section concerns the anatomy of two important sensory systems, the visual and the auditory systems. The description of the organization of each begins with
Vision and Audition Vision and Audition This section concerns the anatomy of two important sensory systems, the visual and the auditory systems. The description of the organization of each begins with
ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear
 ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear Lecturer: Ahmad Nasrul Norali The Ear The Ear Components of hearing mechanism - Outer Ear - Middle Ear - Inner Ear - Central Auditory Nervous System Major Divisions
ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear Lecturer: Ahmad Nasrul Norali The Ear The Ear Components of hearing mechanism - Outer Ear - Middle Ear - Inner Ear - Central Auditory Nervous System Major Divisions
TEAK Bioengineering Artificial Hearing Lesson Plan Page 1 TEAK Traveling Engineering Activity Kits
 TEAK Bioengineering Artificial Hearing Lesson Plan Page 1 TEAK Traveling Engineering Activity Kits Biomedical Engineering Kit: Artificial Sensory Artificial Hearing Activity TEAK Bioengineering Artificial
TEAK Bioengineering Artificial Hearing Lesson Plan Page 1 TEAK Traveling Engineering Activity Kits Biomedical Engineering Kit: Artificial Sensory Artificial Hearing Activity TEAK Bioengineering Artificial
HEARING. Structure and Function
 HEARING Structure and Function Rory Attwood MBChB,FRCS Division of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch Analyse Function of auditory system Discriminate
HEARING Structure and Function Rory Attwood MBChB,FRCS Division of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch Analyse Function of auditory system Discriminate
Hearing: Physiology and Psychoacoustics
 9 Hearing: Physiology and Psychoacoustics Click Chapter to edit 9 Hearing: Master title Physiology style and Psychoacoustics The Function of Hearing What Is Sound? Basic Structure of the Mammalian Auditory
9 Hearing: Physiology and Psychoacoustics Click Chapter to edit 9 Hearing: Master title Physiology style and Psychoacoustics The Function of Hearing What Is Sound? Basic Structure of the Mammalian Auditory
5. Which word refers to making
 Name: Date: WEEK 6 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. How do people hear? Look in a mirror, and you will see that your ears are shaped a little like a funnel. That shape amplifies sounds you
Name: Date: WEEK 6 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. How do people hear? Look in a mirror, and you will see that your ears are shaped a little like a funnel. That shape amplifies sounds you
PHYS 1240 Sound and Music Professor John Price. Cell Phones off Laptops closed Clickers on Transporter energized
 PHYS 1240 Sound and Music Professor John Price Cell Phones off Laptops closed Clickers on Transporter energized The Ear and Hearing Thanks to Jed Whittaker for many of these slides Ear anatomy substructures
PHYS 1240 Sound and Music Professor John Price Cell Phones off Laptops closed Clickers on Transporter energized The Ear and Hearing Thanks to Jed Whittaker for many of these slides Ear anatomy substructures
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 29. Hearing
 Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
PSY 310: Sensory and Perceptual Processes 1
 Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Multimedia Systems 2011/2012
 Multimedia Systems 2011/2012 Perception Prof. Dr. Paul Müller University of Kaiserslautern Department of Computer Science Integrated Communication Systems ICSY http://www.icsy.de Outline Multimedia and
Multimedia Systems 2011/2012 Perception Prof. Dr. Paul Müller University of Kaiserslautern Department of Computer Science Integrated Communication Systems ICSY http://www.icsy.de Outline Multimedia and
Definition Slides. Sensation. Perception. Bottom-up processing. Selective attention. Top-down processing 11/3/2013
 Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception = the process of organizing and interpreting
Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception = the process of organizing and interpreting
BCS 221: Auditory Perception BCS 521 & PSY 221
 BCS 221: Auditory Perception BCS 521 & PSY 221 Time: MW 10:25 11:40 AM Recitation: F 10:25 11:25 AM Room: Hutchinson 473 Lecturer: Dr. Kevin Davis Office: 303E Meliora Hall Office hours: M 1 3 PM kevin_davis@urmc.rochester.edu
BCS 221: Auditory Perception BCS 521 & PSY 221 Time: MW 10:25 11:40 AM Recitation: F 10:25 11:25 AM Room: Hutchinson 473 Lecturer: Dr. Kevin Davis Office: 303E Meliora Hall Office hours: M 1 3 PM kevin_davis@urmc.rochester.edu
PSY 214 Lecture # (11/9/2011) (Sound, Auditory & Speech Perception) Dr. Achtman PSY 214
 PSY 214 Lecture 16 Topic: Sound, Auditory System & Speech Perception Chapter 11, pages 270-289 Corrections: None Announcements: CD is available outside Dr Achtman s office if you would like to see demonstrations
PSY 214 Lecture 16 Topic: Sound, Auditory System & Speech Perception Chapter 11, pages 270-289 Corrections: None Announcements: CD is available outside Dr Achtman s office if you would like to see demonstrations
Speech (Sound) Processing
 7 Speech (Sound) Processing Acoustic Human communication is achieved when thought is transformed through language into speech. The sounds of speech are initiated by activity in the central nervous system,
7 Speech (Sound) Processing Acoustic Human communication is achieved when thought is transformed through language into speech. The sounds of speech are initiated by activity in the central nervous system,
= add definition here. Definition Slide
 = add definition here Definition Slide Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception
= add definition here Definition Slide Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception
Hearing Aids. Bernycia Askew
 Hearing Aids Bernycia Askew Who they re for Hearing Aids are usually best for people who have a mildmoderate hearing loss. They are often benefit those who have contracted noise induced hearing loss with
Hearing Aids Bernycia Askew Who they re for Hearing Aids are usually best for people who have a mildmoderate hearing loss. They are often benefit those who have contracted noise induced hearing loss with
Chapter 1: Introduction to digital audio
 Chapter 1: Introduction to digital audio Applications: audio players (e.g. MP3), DVD-audio, digital audio broadcast, music synthesizer, digital amplifier and equalizer, 3D sound synthesis 1 Properties
Chapter 1: Introduction to digital audio Applications: audio players (e.g. MP3), DVD-audio, digital audio broadcast, music synthesizer, digital amplifier and equalizer, 3D sound synthesis 1 Properties
Hearing. Juan P Bello
 Hearing Juan P Bello The human ear The human ear Outer Ear The human ear Middle Ear The human ear Inner Ear The cochlea (1) It separates sound into its various components If uncoiled it becomes a tapering
Hearing Juan P Bello The human ear The human ear Outer Ear The human ear Middle Ear The human ear Inner Ear The cochlea (1) It separates sound into its various components If uncoiled it becomes a tapering
College of Medicine Dept. of Medical physics Physics of ear and hearing /CH
 College of Medicine Dept. of Medical physics Physics of ear and hearing /CH 13 2017-2018 ***************************************************************** o Introduction : The ear is the organ that detects
College of Medicine Dept. of Medical physics Physics of ear and hearing /CH 13 2017-2018 ***************************************************************** o Introduction : The ear is the organ that detects
Sound Waves. Sensation and Perception. Sound Waves. Sound Waves. Sound Waves
 Sensation and Perception Part 3 - Hearing Sound comes from pressure waves in a medium (e.g., solid, liquid, gas). Although we usually hear sounds in air, as long as the medium is there to transmit the
Sensation and Perception Part 3 - Hearing Sound comes from pressure waves in a medium (e.g., solid, liquid, gas). Although we usually hear sounds in air, as long as the medium is there to transmit the
The Outer and Middle Ear PERIPHERAL AUDITORY SYSTEM HOW WE HEAR. The Ear in Action AUDITORY NEUROPATHY: A CLOSER LOOK. The 3 parts of the ear
 AUDITORY NEUROPATHY: A CLOSER LOOK HOW WE HEAR The 3 parts of the ear The ear consists of three main parts: 1. The outer ear The part you see, which is called the auricle (ohr-a-kal). 2. The middle ear
AUDITORY NEUROPATHY: A CLOSER LOOK HOW WE HEAR The 3 parts of the ear The ear consists of three main parts: 1. The outer ear The part you see, which is called the auricle (ohr-a-kal). 2. The middle ear
Linguistic Phonetics. Basic Audition. Diagram of the inner ear removed due to copyright restrictions.
 24.963 Linguistic Phonetics Basic Audition Diagram of the inner ear removed due to copyright restrictions. 1 Reading: Keating 1985 24.963 also read Flemming 2001 Assignment 1 - basic acoustics. Due 9/22.
24.963 Linguistic Phonetics Basic Audition Diagram of the inner ear removed due to copyright restrictions. 1 Reading: Keating 1985 24.963 also read Flemming 2001 Assignment 1 - basic acoustics. Due 9/22.
ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2003
 ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2003 As always, the Honor Code is in effect and you ll need to write the code and sign it at the end of the exam. Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Although
ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2003 As always, the Honor Code is in effect and you ll need to write the code and sign it at the end of the exam. Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Although
AUDL GS08/GAV1 Signals, systems, acoustics and the ear. Pitch & Binaural listening
 AUDL GS08/GAV1 Signals, systems, acoustics and the ear Pitch & Binaural listening Review 25 20 15 10 5 0-5 100 1000 10000 25 20 15 10 5 0-5 100 1000 10000 Part I: Auditory frequency selectivity Tuning
AUDL GS08/GAV1 Signals, systems, acoustics and the ear Pitch & Binaural listening Review 25 20 15 10 5 0-5 100 1000 10000 25 20 15 10 5 0-5 100 1000 10000 Part I: Auditory frequency selectivity Tuning
Auditory System. Barb Rohrer (SEI )
 Auditory System Barb Rohrer (SEI614 2-5086) Sounds arise from mechanical vibration (creating zones of compression and rarefaction; which ripple outwards) Transmitted through gaseous, aqueous or solid medium
Auditory System Barb Rohrer (SEI614 2-5086) Sounds arise from mechanical vibration (creating zones of compression and rarefaction; which ripple outwards) Transmitted through gaseous, aqueous or solid medium
The Sense Organs 10/13/2016. The Human Eye. 1. Sclera 2. Choroid 3. Retina. The eye is made up of three layers:
 The human body gathers information from the outside world by using the five senses of: The Sense Organs 12.3 Sight Hearing Taste Smell Touch This information is essential in helping the body maintain homeostasis.
The human body gathers information from the outside world by using the five senses of: The Sense Organs 12.3 Sight Hearing Taste Smell Touch This information is essential in helping the body maintain homeostasis.
ID# Final Exam PS325, Fall 1997
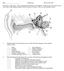 ID# Final Exam PS325, Fall 1997 Good luck on this exam. Answer each question carefully and completely. Keep your eyes foveated on your own exam, as the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect (as always). Have
ID# Final Exam PS325, Fall 1997 Good luck on this exam. Answer each question carefully and completely. Keep your eyes foveated on your own exam, as the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect (as always). Have
Topic 4. Pitch & Frequency
 Topic 4 Pitch & Frequency A musical interlude KOMBU This solo by Kaigal-ool of Huun-Huur-Tu (accompanying himself on doshpuluur) demonstrates perfectly the characteristic sound of the Xorekteer voice An
Topic 4 Pitch & Frequency A musical interlude KOMBU This solo by Kaigal-ool of Huun-Huur-Tu (accompanying himself on doshpuluur) demonstrates perfectly the characteristic sound of the Xorekteer voice An
Linguistic Phonetics Fall 2005
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 24.963 Linguistic Phonetics Fall 2005 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 24.963 Linguistic Phonetics
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 24.963 Linguistic Phonetics Fall 2005 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 24.963 Linguistic Phonetics
Educational Module Tympanometry. Germany D Germering
 Educational Module anometry PATH medical Germany D-82110 Germering Our educational modules 1 are made for providing information on how the hearing organ works and which test procedures are used to test
Educational Module anometry PATH medical Germany D-82110 Germering Our educational modules 1 are made for providing information on how the hearing organ works and which test procedures are used to test
Converting Sound Waves into Neural Signals, Part 1. What happens to initiate neural signals for sound?
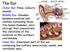 The Ear Outer Ear: Pinna. Collects sounds. Middle Ear: Chamber between eardrum and cochlea containing three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea
The Ear Outer Ear: Pinna. Collects sounds. Middle Ear: Chamber between eardrum and cochlea containing three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea
THE MECHANICS OF HEARING
 CONTENTS The mechanics of hearing Hearing loss and the Noise at Work Regulations Loudness and the A weighting network Octave band analysis Hearing protection calculations Worked examples and self assessed
CONTENTS The mechanics of hearing Hearing loss and the Noise at Work Regulations Loudness and the A weighting network Octave band analysis Hearing protection calculations Worked examples and self assessed
Practice Test Questions
 Practice Test Questions Multiple Choice 1. Which term is most descriptive of the process of sensation? a. transportation c. selection b. interpretation d. transduction 2. Which terms are most descriptive
Practice Test Questions Multiple Choice 1. Which term is most descriptive of the process of sensation? a. transportation c. selection b. interpretation d. transduction 2. Which terms are most descriptive
Hearing Lectures. Acoustics of Speech and Hearing. Subjective/Objective (recap) Loudness Overview. Sinusoids through ear. Facts about Loudness
 Hearing Lectures coustics of Speech and Hearing Week 2-8 Hearing 1: Perception of Intensity 1. Loudness of sinusoids mainly (see Web tutorial for more) 2. Pitch of sinusoids mainly (see Web tutorial for
Hearing Lectures coustics of Speech and Hearing Week 2-8 Hearing 1: Perception of Intensity 1. Loudness of sinusoids mainly (see Web tutorial for more) 2. Pitch of sinusoids mainly (see Web tutorial for
How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz
 The Marvelous Ear How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz 1. How do humans hear sounds? 2. How does human hearing work? Sketch and label the system. 3. Do you know any sensors that detect sound and how they might do
The Marvelous Ear How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz 1. How do humans hear sounds? 2. How does human hearing work? Sketch and label the system. 3. Do you know any sensors that detect sound and how they might do
Chapter 3. Sounds, Signals, and Studio Acoustics
 Chapter 3 Sounds, Signals, and Studio Acoustics Sound Waves Compression/Rarefaction: speaker cone Sound travels 1130 feet per second Sound waves hit receiver Sound waves tend to spread out as they travel
Chapter 3 Sounds, Signals, and Studio Acoustics Sound Waves Compression/Rarefaction: speaker cone Sound travels 1130 feet per second Sound waves hit receiver Sound waves tend to spread out as they travel
Systems Neuroscience Oct. 16, Auditory system. http:
 Systems Neuroscience Oct. 16, 2018 Auditory system http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html The physics of sound Measuring sound intensity We are sensitive to an enormous range of intensities,
Systems Neuroscience Oct. 16, 2018 Auditory system http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html The physics of sound Measuring sound intensity We are sensitive to an enormous range of intensities,
Learning Targets. Module 20. Hearing Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages.
 Learning Targets Module 20 Hearing 20-1 Describe the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound. 20-2 Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages. 20-3 Discuss how
Learning Targets Module 20 Hearing 20-1 Describe the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound. 20-2 Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages. 20-3 Discuss how
Lecture 3: Perception
 ELEN E4896 MUSIC SIGNAL PROCESSING Lecture 3: Perception 1. Ear Physiology 2. Auditory Psychophysics 3. Pitch Perception 4. Music Perception Dan Ellis Dept. Electrical Engineering, Columbia University
ELEN E4896 MUSIC SIGNAL PROCESSING Lecture 3: Perception 1. Ear Physiology 2. Auditory Psychophysics 3. Pitch Perception 4. Music Perception Dan Ellis Dept. Electrical Engineering, Columbia University
INTRODUCTION TO AUDIOLOGY Hearing Balance Tinnitus - Treatment
 INTRODUCTION TO AUDIOLOGY Hearing Balance Tinnitus - Treatment What is Audiology? Audiology refers to the SCIENCE OF HEARING AND THE STUDY OF THE AUDITORY PROCESS (Katz, 1986) Audiology is a health-care
INTRODUCTION TO AUDIOLOGY Hearing Balance Tinnitus - Treatment What is Audiology? Audiology refers to the SCIENCE OF HEARING AND THE STUDY OF THE AUDITORY PROCESS (Katz, 1986) Audiology is a health-care
Hearing Lectures. Acoustics of Speech and Hearing. Auditory Lighthouse. Facts about Timbre. Analysis of Complex Sounds
 Hearing Lectures Acoustics of Speech and Hearing Week 2-10 Hearing 3: Auditory Filtering 1. Loudness of sinusoids mainly (see Web tutorial for more) 2. Pitch of sinusoids mainly (see Web tutorial for more)
Hearing Lectures Acoustics of Speech and Hearing Week 2-10 Hearing 3: Auditory Filtering 1. Loudness of sinusoids mainly (see Web tutorial for more) 2. Pitch of sinusoids mainly (see Web tutorial for more)
Technical Discussion HUSHCORE Acoustical Products & Systems
 What Is Noise? Noise is unwanted sound which may be hazardous to health, interfere with speech and verbal communications or is otherwise disturbing, irritating or annoying. What Is Sound? Sound is defined
What Is Noise? Noise is unwanted sound which may be hazardous to health, interfere with speech and verbal communications or is otherwise disturbing, irritating or annoying. What Is Sound? Sound is defined
Activity Template. Drexel-SDP GK-12 ACTIVITY
 Drexel-SDP GK-12 ACTIVITY Activity Template Subject Area(s): Sound Associated Unit: None Associated Lesson: None Activity Title: How good is your hearing? Grade Level: 8 (7-9) Activity Dependency: None
Drexel-SDP GK-12 ACTIVITY Activity Template Subject Area(s): Sound Associated Unit: None Associated Lesson: None Activity Title: How good is your hearing? Grade Level: 8 (7-9) Activity Dependency: None
Auditory System & Hearing
 Auditory System & Hearing Chapters 9 part II Lecture 16 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Spring 2019 1 Phase locking: Firing locked to period of a sound wave example of a temporal
Auditory System & Hearing Chapters 9 part II Lecture 16 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Spring 2019 1 Phase locking: Firing locked to period of a sound wave example of a temporal
Adaptive Feedback Cancellation for the RHYTHM R3920 from ON Semiconductor
 Adaptive Feedback Cancellation for the RHYTHM R3920 from ON Semiconductor This information note describes the feedback cancellation feature provided in in the latest digital hearing aid amplifiers for
Adaptive Feedback Cancellation for the RHYTHM R3920 from ON Semiconductor This information note describes the feedback cancellation feature provided in in the latest digital hearing aid amplifiers for
Essential feature. Who are cochlear implants for? People with little or no hearing. substitute for faulty or missing inner hair
 Who are cochlear implants for? Essential feature People with little or no hearing and little conductive component to the loss who receive little or no benefit from a hearing aid. Implants seem to work
Who are cochlear implants for? Essential feature People with little or no hearing and little conductive component to the loss who receive little or no benefit from a hearing aid. Implants seem to work
Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the morphology and function of the following structures:
Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the morphology and function of the following structures:
Loudness. Loudness is not simply sound intensity!
 is not simply sound intensity! Sound loudness is a subjective term describing the strength of the ear's perception of a sound. It is intimately related to sound intensity but can by no means be considered
is not simply sound intensity! Sound loudness is a subjective term describing the strength of the ear's perception of a sound. It is intimately related to sound intensity but can by no means be considered
Hearing the Universal Language: Music and Cochlear Implants
 Hearing the Universal Language: Music and Cochlear Implants Professor Hugh McDermott Deputy Director (Research) The Bionics Institute of Australia, Professorial Fellow The University of Melbourne Overview?
Hearing the Universal Language: Music and Cochlear Implants Professor Hugh McDermott Deputy Director (Research) The Bionics Institute of Australia, Professorial Fellow The University of Melbourne Overview?
PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages
 PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages 189-197 Corrections: NTC 09-1, page 3, the Superior Colliculus is in the midbrain (Mesencephalon). Announcements: Movie next Monday: Case of the frozen
PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages 189-197 Corrections: NTC 09-1, page 3, the Superior Colliculus is in the midbrain (Mesencephalon). Announcements: Movie next Monday: Case of the frozen
Hearing. and other senses
 Hearing and other senses Sound Sound: sensed variations in air pressure Frequency: number of peaks that pass a point per second (Hz) Pitch 2 Some Sound and Hearing Links Useful (and moderately entertaining)
Hearing and other senses Sound Sound: sensed variations in air pressure Frequency: number of peaks that pass a point per second (Hz) Pitch 2 Some Sound and Hearing Links Useful (and moderately entertaining)
Frequency refers to how often something happens. Period refers to the time it takes something to happen.
 Lecture 2 Properties of Waves Frequency and period are distinctly different, yet related, quantities. Frequency refers to how often something happens. Period refers to the time it takes something to happen.
Lecture 2 Properties of Waves Frequency and period are distinctly different, yet related, quantities. Frequency refers to how often something happens. Period refers to the time it takes something to happen.
Auditory System & Hearing
 Auditory System & Hearing Chapters 9 and 10 Lecture 17 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Spring 2015 1 Cochlea: physical device tuned to frequency! place code: tuning of different
Auditory System & Hearing Chapters 9 and 10 Lecture 17 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Spring 2015 1 Cochlea: physical device tuned to frequency! place code: tuning of different
Ear Exam and Hearing Tests
 Ear Exam and Hearing Tests Test Overview A thorough evaluation of a person's hearing requires an ear exam and hearing tests. In children, normal hearing is important for language to develop correctly.
Ear Exam and Hearing Tests Test Overview A thorough evaluation of a person's hearing requires an ear exam and hearing tests. In children, normal hearing is important for language to develop correctly.
Psychoacoustical Models WS 2016/17
 Psychoacoustical Models WS 2016/17 related lectures: Applied and Virtual Acoustics (Winter Term) Advanced Psychoacoustics (Summer Term) Sound Perception 2 Frequency and Level Range of Human Hearing Source:
Psychoacoustical Models WS 2016/17 related lectures: Applied and Virtual Acoustics (Winter Term) Advanced Psychoacoustics (Summer Term) Sound Perception 2 Frequency and Level Range of Human Hearing Source:
Drexel-SDP GK-12 ACTIVITY
 Activity Template Subject Area(s): Sound Associated Unit: None Associated Lesson: None Activity Title: How good is your hearing? Grade Level: 8 (7-9) Activity Dependency: None Time Required: 120 minutes
Activity Template Subject Area(s): Sound Associated Unit: None Associated Lesson: None Activity Title: How good is your hearing? Grade Level: 8 (7-9) Activity Dependency: None Time Required: 120 minutes
Required Slide. Session Objectives
 Auditory Physiology Required Slide Session Objectives Auditory System: At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1. Characterize the range of normal human hearing. 2. Understand the components
Auditory Physiology Required Slide Session Objectives Auditory System: At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1. Characterize the range of normal human hearing. 2. Understand the components
Who are cochlear implants for?
 Who are cochlear implants for? People with little or no hearing and little conductive component to the loss who receive little or no benefit from a hearing aid. Implants seem to work best in adults who
Who are cochlear implants for? People with little or no hearing and little conductive component to the loss who receive little or no benefit from a hearing aid. Implants seem to work best in adults who
THE EAR Dr. Lily V. Hughes, Audiologist
 WHY AM I HERE? HEARING & THE BRAIN THE EAR Dr. Lily V. Hughes, Audiologist Fairbanks Hearing & Balance Center at the ENT Clinic 1 out of every 5 adults has hearing loss. That s more than 48 million people
WHY AM I HERE? HEARING & THE BRAIN THE EAR Dr. Lily V. Hughes, Audiologist Fairbanks Hearing & Balance Center at the ENT Clinic 1 out of every 5 adults has hearing loss. That s more than 48 million people
Binaural Hearing for Robots Introduction to Robot Hearing
 Binaural Hearing for Robots Introduction to Robot Hearing 1Radu Horaud Binaural Hearing for Robots 1. Introduction to Robot Hearing 2. Methodological Foundations 3. Sound-Source Localization 4. Machine
Binaural Hearing for Robots Introduction to Robot Hearing 1Radu Horaud Binaural Hearing for Robots 1. Introduction to Robot Hearing 2. Methodological Foundations 3. Sound-Source Localization 4. Machine
HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours)
 HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will construct a model ear to learn how different materials transmit sound. Topic:
HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will construct a model ear to learn how different materials transmit sound. Topic:
J Jeffress model, 3, 66ff
 Index A Absolute pitch, 102 Afferent projections, inferior colliculus, 131 132 Amplitude modulation, coincidence detector, 152ff inferior colliculus, 152ff inhibition models, 156ff models, 152ff Anatomy,
Index A Absolute pitch, 102 Afferent projections, inferior colliculus, 131 132 Amplitude modulation, coincidence detector, 152ff inferior colliculus, 152ff inhibition models, 156ff models, 152ff Anatomy,
Spectrograms (revisited)
 Spectrograms (revisited) We begin the lecture by reviewing the units of spectrograms, which I had only glossed over when I covered spectrograms at the end of lecture 19. We then relate the blocks of a
Spectrograms (revisited) We begin the lecture by reviewing the units of spectrograms, which I had only glossed over when I covered spectrograms at the end of lecture 19. We then relate the blocks of a
MECHANISM OF HEARING
 MECHANISM OF HEARING Sound: Sound is a vibration that propagates as an audible wave of pressure, through a transmission medium such as gas, liquid or solid. Sound is produced from alternate compression
MECHANISM OF HEARING Sound: Sound is a vibration that propagates as an audible wave of pressure, through a transmission medium such as gas, liquid or solid. Sound is produced from alternate compression
Implementation of Spectral Maxima Sound processing for cochlear. implants by using Bark scale Frequency band partition
 Implementation of Spectral Maxima Sound processing for cochlear implants by using Bark scale Frequency band partition Han xianhua 1 Nie Kaibao 1 1 Department of Information Science and Engineering, Shandong
Implementation of Spectral Maxima Sound processing for cochlear implants by using Bark scale Frequency band partition Han xianhua 1 Nie Kaibao 1 1 Department of Information Science and Engineering, Shandong
