Esthetic evaluation of periimplant soft tissue of immediate single-implant placement and provisionalization in the anterior maxilla
|
|
|
- Beverly Atkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Esthetic evaluation of periimplant soft tissue of immediate single-implant placement and provisionalization in the anterior maxilla Franck Bonnet, DDS Private Practice, Cannes, Le Cannet, France Director of Formation Implantaire & Dentaire Esthétique (FIDE) Michel Karouni, DDS Private Practice limited to Periodontics and Implantology, Beirut, Lebanon Assistant Professor, St Joseph University, School of Dentistry, Beirut, Lebanon Hadi Antoun, DDS Private Practice limited to Periodontics and Implantology, Paris, France Director, Training Institute of Advanced Implant Surgery, IFCIA Correspondence to: Dr Michel Karouni Dr Karouni Dental Clinic, Credit Commercial Center, Beirut, Lebanon; Tel: ; 378
2 Bonnet et al Abstract Purpose: To investigate periimplant soft tissue response following flapless extraction and immediate implant placement and provisionalization (IIPP) associated with bovine hydroxyapatite bone and connective tissue grafting in the anterior maxilla. The study evaluated the effectiveness of this technique in terms of soft tissue contours in esthetic areas with the use of the pink esthetic score (PES). Materials and methods: In this retrospective study, 39 consecutive patients were treated and followed by two experienced clinicians for single-tooth implant treatment in the esthetic zone. Treatment consisted of flapless extraction, immediate implant placement, inorganic bovine bone filling of the periimplant gap, and connective tissue grafting. A provisional crown was placed at the time of implant placement. The final crown was positioned 5 to 8 months after surgery. To assess the esthetic outcome of the technique, the soft tissue around the tooth to be extracted was scored according to the PES by seven evaluators before the surgery at visit 1 (v1), and at least 1 year after the final prosthesis placement at visit 2 (v2). Results: After a mean follow-up of 4 years, the mean total PES score on a scale from 1 to 10 was 5.64 and 7.07 at v1 and v2, respectively. Statistical analysis revealed a significant difference between the PES scores before surgery and at the follow-up examination of the anterior single implants (P = ). Conclusion: Within the limitations of this study, postextraction with immediate implant loading associated with bovine hydroxyapatite and connective tissue grafting is a predictable technique. The esthetic outcome is that soft tissue seems to be maintained or improved significantly according to PES assessment compared with baseline. (Int J Esthet Dent 2018;13: ) 379
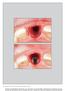
3 Introduction Implant placement in the anterior region has gained in popularity since the technique was first used. 1 Many studies have reported similar implant survival and success rates for implants inserted in the esthetic zone compared with those placed in other jaw segments. 2-5 In the anterior maxilla, osseointegration alone is not sufficient; patient satisfaction is a key factor in the success of implant therapy. 6 The criteria outlined by Albrektsson et al 7 are widely used in clinical studies as a guide for analyzing the success rate of implant surgery. 7 Smith and Zarb 8 extended these criteria by indicating that Fig 1 Preoperative facial view of maxillary central incisors. Fig 2 Preoperative facial view and clinical evaluation to assess the PES at v1. a successful implant must have an adequate esthetic appearance. The esthetic outcome is determined by healthy and stable periimplant tissue as well as the final implant crown. In 2005, Fürhauser et al 9 proposed an index known as the pink esthetic score (PES), which focuses essentially on the soft tissue aspects of an anterior implant restoration. The PES analyzes seven variables: mesial papilla, distal papilla, soft tissue level, soft tissue contour, alveolar process deficiency, soft tissue color, and soft tissue texture. These authors also proposed that the PES was a useful technique for reproducibility, as it evaluates the soft tissue around single-tooth implant crowns that might change over time. It can therefore be a useful tool for monitoring long-term soft tissue alterations. Belser et al 10 modified the previously published PES. These authors added a white esthetic score (WES), and proposed an implant restoration index to analyze single-tooth implants. In contrast to the original PES, their PES/ WES of soft tissue alone comprises five variables: mesial papilla, distal papilla, curvature of the facial mucosa, level of the facial mucosa, and root convexity/ soft tissue color and texture at the facial aspect of the implant site. Nowadays, there is a growing tendency to place implants immediately after extraction, often combined with immediate provisionalization. This is probably a result of evolving societal factors, more demanding patients, and the wish for quick results, among other reasons. Timing of implant placement and provisionalization influences periimplant soft and hard tissue, thus challenging the esthetic and patient-centered outcome
4 Bonnet et al According to some studies, implant survival hardly seems to be affected by the timing of implant placement relative to tooth extraction. 12,13 Lang et al 14 evaluated only implant survival and success rates, whereas Lin et al 15 and Cosyn et al 16 observed only soft tissue recession. A systematic review of all identified variables affecting the treatment outcome of immediate implant placement and provisionalization (IIPP) is not available in the literature. The aim of this study was to evaluate the esthetic outcome of the soft tissue around implant-supported single crowns using a five-point scale, and to assess changes after IIPP in the anterior maxilla at least 1 year after final crown placement. Materials and methods Patients and study protocol Thirty-nine patients (12 males; 27 females) with a mean age of 37.6 years (range 23 to 64 years) with single-tooth implants in the anterior maxilla were selected. The patients had root fractures and untreatable caries and were treated in private practice by two different dentists between 2003 and 2012: 15 patients were treated by Dr H. Antoun, and 24 by Dr F. Bonnet. The patients underwent a complete preoperative evaluation comprising a detailed medical history as well as clinical and radiographic examinations. All patients signed a consent form. The following information was recorded during the clinical examination: date of extraction, mesiodistal space, Fig 3 Preoperative CBCT scan image of tooth 21. The buccal plate was recognized. prosthetic space, amplitude of mouth opening, dental and periodontal status, and type of occlusion (Figs 1 and 2). The radiographic examination included a panoramic, periapical digital radiograph, and cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) imaging was performed for all patients to assess the volume of residual bone (Fig 3). Prior to surgery, the patients underwent conventional periodontal treatment. The treatment sites included 25 central incisors and 14 lateral incisors. Patients included in the study had to be at least 20 years of age or older, with acceptable oral hygiene (pink gums that did not bleed when brushing, and clean teeth free of calculus). All patients had an extraction socket with four intact walls or a maximum of 2 mm lost on the buccal plate with the presence of adjacent teeth. Exclusion criteria included patients with uncontrolled diabetes, coagulation disorders, allergies to any of the materials used in the study, acute infection with the presence of suppuration at the surgical site, and heavy smokers (more than 10 cigarettes per day). 381
5 Fig 4 Occlusal view of the bone graft in the gap between the facial bone and the implant. View of connective tissue graft placement. Fig 5 View of donor site after suturing. Pharmacological treatment associated with surgical procedure Antibiotics were administered prophylactically 1 hour prior to surgery (2 g amoxicillin; Amoxicilline Biogaran, GlaxoSmithKline) and then routinely for 7 days. 43 Patients allergic to penicillin were given 600 mg clindamycin (Dalacin 600 mg, Pfizer). Metronidazole was also given 1 h prior to surgery (1000 mg Flagyl, Sanofi-Aventis), and daily for 5 days. A dose of arnica 9CH was given the night before and for 2 days following surgery. Oral bromazepam (3 mg Lexomil, Roche) was given for sedation 1 h before surgery, and patients were asked to rinse with 0.12% chlorhexidine digluconate (Paroex, Sunstar) mouthwash for 1 min immediately before surgery. Patients were instructed to continue rinsing with chlorhexidine thrice daily for 2 weeks postoperatively. Implant surgery was performed under local anesthesia with articaine hydrochloride 4% and an adrenaline 1/100,000 injection (Septanest, Septodont). Surgical protocol All patients underwent extraction with preservation of the buccal plate, followed by IIPP. Teeth were electively sectioned with rotary instruments and extraction was realized using perio tomes in order to minimize trauma on the soft tissue and alveolar bone. Sockets were rinsed with iodine and debrided with hand instruments and burs to remove any residual granulation tissue. A total of 39 implants (NobelReplace/NobelActive, Nobel Biocare) were placed according to the manufacturer s instructions, engaging the palatal wall and the native bone above the alveolus. The platform was positioned 3 to 4 mm apically to the gingival margin Remaining gaps between the implant and the surrounding bone were filled with Bio-Oss (Geistlich) granules. During the initial osteotomy, bone quality was assessed according to resistance while drilling with a 2-mm twist drill. Bone was classified as D1, D2, D3, or D4. Final insertion torque was measured from 30 to 70 Ncm. Implants that did not achieve 382
6 Bonnet et al an insertion torque 30 Ncm were excluded from the study (Fig 4). Concerning the donor site of the connective tissue, a single-incision technique was carried out with a palatal horizontal incision along the row of teeth starting from the mesial border of the first molar to the first premolar, 2 mm apical to the gingival margin, 1- to 1.5-mm deep. All the remaining incisions were made below the mucosal surface. Thereafter, the size of the graft was defined by executing two horizontal and two vertical incisions inside the created envelope. These incisions may be extended to the bone and overlap at the intersections (Fig 5). An additional incision could be made above the periosteum by sharp dissection with a scalpel blade. Finally, the connective tissue graft was immediately placed into the recipient site after a tunneling procedure and sutured with 6-0 nonresorbable monofilament sutures (Surgipro, Covidien). Fig 6 Connective tissue graft drawn into prepared envelope with the aid of nonresorbable monofilament sutures. Fig 7 Facial view of the provisional restoration immediately after surgery. Prosthetic protocol Temporary crowns Crowns were constructed over a titanium temporary abutment using photopolymerized injectable composite (Rest Automix, Elsodont) or an autopolymerized acrylic resin (Unifast). Medical-grade Vaseline (Vaseline officinale, Cooper) was applied over the sutures (Fig 6). The occlusion was checked, and care was taken to avoid any tooth contact in static and dynamic occlusion. After complete polymerization, the crown and the temporary abutment (forming a single entity) were removed and placed on the implant replica. Composite or acrylic resin was used to achieve properly sealed margins between the abutment and the crown, and to establish a proper emergence profile (concave on the buccal side, and not compressive). The screw-retained provisional restoration was meticulously polished with acrylic abrasives and was not removed during the healing period to prevent any manipulation that could compromise osseointegration (Fig 7). Patients maintained a liquid diet for 2 days postoperatively followed by a soft diet for 8 weeks. 383
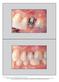
7 Fig 8 Implant site before pickup impression. No signs of inflammation are detectable. Fig 9 View of the custom impression transfer. Final crown The definitive ceramic crown was delivered 5 to 8 months after surgery. Based on restorative preferences, the definitive crown was either cemented or screwretained (Figs 8 and 9). The main types of crown materials used were either ceramic fused to metal or metal-free prostheses such as zirconium crowns. For the screw-retained method, the crown was placed in chlorhexidine mouthwash for 2 min for sanitization, then placed onto the implant and screwed into place with a manual screwdriver. For the cemented crown method, a retraction cord was placed around the abutment. Prior to cementing, the screw access hole of the abutment was occluded with Fermit (3M ESPE). A thin layer of polycarboxylate was applied on the crown, away from the cervical margins. The crown was seated onto the abutment with finger pressure rather than occlusal pressure. Excess cement was eliminated prior to complete polymerization, and the retraction cord removed. Further cleaning of the cement margins was accomplished with an explorer No. 23 (Hu-Friedy) and dental floss. The occlusion was checked, and the complete seating of the crown confirmed with a radiograph. After the adjustment of the contour and the occlusion for screw-retained restorations, a silicon plug was placed into the screw access channel. The remainder of the channel was filled with a temporary filling. Screwing the restoration may cause pressure on the periimplant mucosa, which may result in short-term ischemia of the soft tissue. Outcome measures The patients were recalled at 10 days, 6 months, and 12 months after surgery to assess the periimplant marginal bone level, biologic or prosthetic complications, or implant failure (any mobility or infection that required implant removal). The Albrektsson et al 7 criteria were applied to assess the outcome. Radiographs were taken subsequent to implant insertion, and postoperatively at 6 and 12 months. Each single-tooth implant was photographed with a digital camera (D500, Canon Medical Objective 105 mm, Ôta Corporation). For assessing the anterior tooth replacements, the reference tooth 384
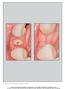
8 Bonnet et al had to be sufficiently visible to ensure comparability. Photographs were taken at, or slightly superior to, the occlusal plane, centered at the contact region. The implant-supported restorations in the region of the incisors were compared to the contralateral tooth. The photographs were magnified and projected as a presentation using Keynote. The implant-supported crowns were marked by arrows. For the PES scoring assessment, seven individuals from various specializations (prosthodontists, periodontists, and oral surgeons) completed a questionnaire. The modified PES (Belser et al 10 ) was used. Each of the five variables (see earlier, and also Fig 10) was assessed with a score, with 2 being the best and 0 being the poorest score. The mesial and distal papillae were evaluated for complete presence, incompleteness, or absence. All other variables were assessed by comparison with a reference tooth, ie, the corresponding tooth (anterior region). The highest possible score reflecting a perfect match of the periimplant soft tissue with that of the reference tooth was 10 (Figs 11 to 13). Fig 10 Guide for using the PES based on virtual presentation of an optimal single-tooth implant restoration. The five variables are: mesial papilla, distal papilla, curvature of the facial mucosa, level of the facial mucosa, and root convexity/soft tissue color and texture. Fig 11 View of the papilla between the maxillary central incisors. Fig 12 Facial view 1 year after crown placement to assess the PES at v2. Fig 13 Postoperative smile view. 385
9 Results Fig 14 Periapical radiograph after 24-month followup. Marginal bone is stable. The PES before the surgery at visit 1 (v1) were evaluated by the same individuals, and for the final study the scores at v1 were compared with those at visit 2 (v2) to assess the difference. Every 12 months, periapical digital radiographs of all the patients were obtained to compare bone changes after loading with the baseline measurements (Fig 14). Statistical analysis Statistical analysis of the data was performed with SPSS for Windows (Version 22). The risk error was set at P The outcome variables of the study were the PES. The measurement reproducibility of the PES between evaluators was assessed using the intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) with a 95% confidence interval (CI). The Kolmogorov- Smirnov test was performed to assess the normality distributions of the scores. The Wilcoxon and Paired Student t tests were used to compare the scores before surgery and at a minimum of 1 year after final implant placement. Of the 39 implants, 11 replaced the right and 14 replaced the left central incisor, while 8 replaced the right and 6 replaced the left lateral incisor. All implants showed osseointegration without complications. The ICC for PES was preoperatively (P < 0.001) and postoperatively (P < 0.001) (Tables 1 and 2). The ICC for each component of PES varied between and (Table 3). The average measurement of each score was obtained for statistical analysis. The mean and standard deviation (SD) of PES and each PES component are shown in Table 4. The mean PES significantly increased (by 25%) after final prosthesis placement (P < 0.001). No significant difference was found after surgery for the score of mesial (P = 0.945) and distal (P = 0.933) papillae. Significant enhancement was found for the level of facial mucosa (P = 0.022), for the curvature of facial mucosa (P < 0.001), and soft tissue color and texture (P < 0.001). Discussion The implant survival rate for the IIPP procedure in this study was 100% after a mean follow-up period of 4 years. Similar success rates (93.5% to 100%) have been reported for short-term studies (1 to 2 years) when single implants were immediately placed in extraction sites and provisionalized in the anterior maxilla. 17,18 Implant success rates have also been reported when single implants placed 386
10 Bonnet et al Table 1 Reproducibility of PES between evaluators at v1 Preoperative Mean PES Standard deviation N ICC with 95% CI E E E [ ] E E E E ICC: intraclass correlation coefficient; CI: confidence interval; E: evaluator Table 2 Reproducibility of PES between evaluators at v2 Postoperative Mean PES SD N ICC with 95% CI E E E [ ] E E E E Table 3 Reproducibility of each PES component between evaluators N ICC with 95% CI Mesial papilla at v [ ] Mesial papilla at v [ ] Distal papilla at v [ ] Distal papilla at v [ ] Level of FM at v [ ] Level of FM at v [ ] Curvature of FM at v [ ] Curvature of FM at v [ ] Color and texture at v [ ] Color and texture at v [ ] PES v [ ] PES v [ ] FM: facial mucosa 387
11 Table 4 Mean PES component within time N Mean Standard deviation P Mesial papilla at v Mesial papilla at v Distal papilla at v Distal papilla at v Level of FM at v Level of FM at v Curvature of FM at v < Curvature of FM at v Color and texture at v < Color and texture at v PES v < PES v FM: facial mucosa in healed sites were either immediately provisionalized (100%) 19,20 or treated with a traditional delayed loading approach (97%). 21,22 It seems that IIPP does not affect implant success when primary stability is achieved during surgery and the provisional restoration is adjusted with non-occlusal contacts. To minimize papillae loss, tooth extraction must be nontraumatic. 23,24 Papillae levels in the anterior single implant are guided by the proximal bone of the adjacent teeth to an appropriate interproximal embrasure form. 25,26 Studies recommend that papilla-saving incisions could decrease interproximal bone loss, thereby decreasing papilla loss. 27,28 In the case of immediate anterior implant placement, a gap is present between the implant and the facial bony wall of the socket. 29,30 It has been demonstrated that, after immediate implant placement in an anterior tooth socket, the facial bony plate undergoes remodeling characterized by bone fill from the inside of the socket, and resorption of the labial bony plate from the outside. 31 Without bone grafting, this results in significant horizontal and vertical facial bone loss and subsequent facial gingival tissue loss To reduce the risk of soft tissue recession, a number of requirements have been described. 36 When immediate implant placement is indicated, a detailed examination before surgery should be carried out to achieve and maintain satisfactory esthetic implant-placement outcomes. Recent studies have focused on the midfacial mucosa level following single-implant treatment, 37,38 with contrasting data: Chen and Buser 39 reported an increased risk of advanced midfacial recession of > 1 mm, whereas other authors 40 reported a limited risk, 388
12 Bonnet et al with midfacial gingival recession varying between 0.55 and 0.75 mm. A study by Cooper et al 41 showed that minor changes in the mesial (0.13 ± 1.61 mm) and distal (0.21 ± 1.61 mm) papillae can occur when there is no connective tissue graft, and after immediate implant placement at the 5-year follow-up. In fact, minor apical movement of the mucosal zenith posi tion was observed from the time of definitive crown placement until the 5-year follow-up (0.05 ± 0.92 mm). At the 3-year follow-up, Cosyn et al 11 showed a mean loss of the mesial papillae of only 0.05 mm from the preoperative status until the end of the study. A similar trend was found for the distal papillae, resulting in a final mean loss of 0.08 mm. From the preoperative status until 3 years, there was a mean recession of 0.34 mm. As suggested by De Rouck et al, 42 it seems that immediate stabilization of the soft tissue after tooth removal by means of immediate implant placement and temporization reveals more soft tissue preservation mid-facially compared to a delayed strategy. In this study, the level of the facial gingival margin had improved, which justifies the advantages of this approach. Results of the present study revealed an improvement of the level, curvature, and color of the facial gingiva. There seems to be a strong correlation between the final aspect of the soft tissue and the starting point: when the starting point is favorable, favorable esthetics may be expected from an implant-based single-tooth replacement, whereas an unfavorable starting point may lead to unsatisfactory results (see Figs 2 and 12). Given the complexity of this aspect on the treatment outcome, a thorough systematic review comparing the risk of advanced midfacial recession between immediate/early and conventional single-implant treatment would be valuable. Few case studies have been published documenting the esthetic characteristics of single-implant crowns using objective parameters. 10,38,42 Most of these studies report that optimal esthetics seem difficult to achieve, regardless of the fact that the patient is selected according to strict criteria and is treated by experienced clinicians. Careful case selection coupled with clinical experience and appropriate surgical and restorative procedures, as well as implant design and surface, are considered to be of crucial importance. Immediate loading of single-tooth implants placed in fresh extraction sockets is suggested only in the case of optimal primary stability (> 30 Ncm). 36 In this study, all implants were tapered and inserted with a final torque of > 30 Ncm. All implant sites were characterized by favorable anatomic conditions. Implant surfaces, a flapless technique, and temporary crowns without occlusal contacts are other factors that may help to achieve success with the IIPP protocol. The limitations of this study were the number of implants and the retrospective study design. More prospective studies are needed monitoring soft tissue dynamics over longer time periods and encompassing a larger number of implants. Within the limitations of the present study, results show that early restoration of single-tooth implants placed in fresh extraction sockets in 389
13 periodontically healthy patients may be considered a predictable procedure in terms of implant survival and soft tissue remodeling. Conclusion The results of this study revealed that, from an esthetic point of view, maxillary anterior single-tooth replacement in periodontically healthy patients according to the concept of IIPP seems to be a successful and predictable treatment modality. Prospective clinical trials are needed to further validate and refine this finding. Acknowledgment The authors would like to thank first name? Fistes for her assistance with the images. References 1. Schulte W, Kleineikenscheidt H, Lindner K, Schareyka R. The Tübingen immediate implant in clinical studies [In German]. Dtsch Zahnarztl Z 1978;33: Lindh T, Gunne J, Tillberg A, Molin M. A meta-analysis of implants in partial edentulism. Clin Oral Implants Res 1998;9: Wyatt CC, Zarb GA. Treatment outcomes of patients with implant-supported fixed partial prostheses. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1998;13: Noack N, Willer J, Hoffmann J. Long-term results after placement of dental implants: longitudinal study of 1,964 implants over 16 years. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1999;14: Naert I, Koutsikakis G, Duyck J, Quirynen M, Jacobs R, van Steenberghe D. Biologic outcome of implant-supported restorations in the treatment of partial edentulism. Part I: a longitudinal clinical evaluation. Clin Oral Implants Res 2002 Aug;13: Buser D, Martin W, Belser UC. Optimizing esthetics for implant restorations in the anterior maxilla: anatomic and surgical considerations. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2004;(19 suppl): Albrektsson T, Zarb G, Worthington P, Eriksson AR. The long-term efficacy of currently used dental implants: a review and proposed criteria of success. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1986;1: Smith DE, Zarb GA. Criteria for success of osseointegrated endosseous implants. J Prosthet Dent 1989;62: Fürhauser R, Florescu D, Benesch T, Haas R, Mailath G, Watzek G. Evaluation of soft tissue around singletooth implant crowns: the pink esthetic score. Clin Oral Implants Res 2005;16: Belser UC, Grütter L, Vailati F, Bornstein MM, Weber HP, Buser D. Outcome evaluation of early placed maxillary anterior single-tooth implants using objective esthetic criteria: a cross-sectional, retrospective study in 45 patients with a 2- to 4-year follow-up using pink and white esthetic scores. J Periodontol 2009;80: Cosyn J, Eghbali A, De Bruyn H, Collys K, Cleymaet R, De Rouck T. Immediate single-tooth implants in the anterior maxilla: 3-year results of a case series on hard and soft tissue response and aesthetics. J Clin Periodontol 2011;38: den Hartog L, Slater JJ, Vissink A, Meijer HJ, Raghoebar GM. Treatment outcome of immediate, early and conventional single-tooth implants in the aesthetic zone: a systematic review to survival, bone level, softtissue, aesthetics and patient satisfaction. J Clin Periodontol 2008;35: Esposito M, Grusovin MG, Polyzos IP, Felice P, Worthington HV. Timing of implant placement after tooth extraction: immediate, immediate-delayed or delayed implants? A Cochrane systematic review. Eur J Oral Implantol 2010;3: Lang NP, Pun L, Lau KY, Li KY, Wong MC. A systematic review on survival and success rates of implants placed immediately into fresh extraction sockets after at least 1 year. Clin Oral Implants Res 2012;23(suppl 5): Lin GH, Chan HL, Wang HL. Effects of currently available surgical and restorative interventions on reducing midfacial mucosal recession of immediately placed single-tooth implants: a systematic review. J Periodontol 2014;85:
14 Bonnet et al 16. Cosyn J, Hooghe N, De Bruyn H. A systematic review on the frequency of advanced recession following single immediate implant treatment. J Clin Periodontol 2012;39: Kan JY, Rungcharassaeng K, Sclar A, Lozada JL. Effects of the facial osseous defect morphology on gingival dynamics after immediate tooth replacement and guided bone regeneration: 1-year results. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2007;65(7 suppl 1): Barone A, Rispoli L, Vozza I, Quaranta A, Covani U. Immediate restoration of single implants placed immediately after tooth extraction. J Periodontol 2006;77: Grunder U. Stability of the mucosal topography around single-tooth implants and adjacent teeth: 1-year results. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2000;20: Small PN, Tarnow DP. Gingival recession around implants: a 1-year longitudinal prospective study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2000;15: Romeo E, Chiapasco M, Ghisolfi M, Vogel G. Longterm clinical effectiveness of oral implants in the treatment of partial edentulism. Sevenyear life table analysis of a prospective study with ITI dental implants system used for single-tooth restorations. Clin Oral Implants Res 2002;13: Levin L, Sadet P, Grossmann Y. A retrospective evaluation of 1,387 single-tooth implants: a 6-year followup. J Periodontol 2006;77: Kan JY, Rungcharassaeng K. Site development for anterior single implant esthetics: the dentulous site. Compend Contin Educ Dent 2001;22: , 228, Spear FM. Maintenance of the interdental papilla following anterior tooth removal. Pract Periodontics Aesthetic Dent 1999;11: Kan JYK, Rungcharassaeng K, Umezu K, Kois JC. Dimensions of peri-implant mucosa: an evaluation of maxillary anterior single implants in humans. J Periodontol 2003;74: Choquet V, Hermans M, Adriaenssens P, Daelemans P, Tarnow DP, Malevez C. Clinical and radiographic evaluation of the papilla level adjacent to single-tooth dental implants. A retrospective study in the maxillary anterior region. J Periodontol 2001;72: Gomez-Roman G. Influence of flap design on peri-implant interproximal crestal bone loss around single-tooth implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2001;16: Velvart P, Ebner-Zimmermann U, Ebner JP. Comparison of long-term papilla healing following sulcular full thickness flap and papilla base flap in endodontic surgery. Int Endod J 2004;37: Kan JY, Rungcharassaeng K. Immediate placement and provisionalization of maxillary anterior single implants: a surgical and prosthodontic rationale. Pract Periodontics Aesthetic Dent 2000;12: Kois JC, Kan JY. Predictable peri-implant gingival aesthetics: surgical and prosthodontic rationales. Pract Proced Aesthetic Dent 2001;13: Araújo MG, Lindhe J. Dimensional ridge alterations following tooth extraction. An experimental study in the dog. J Clin Periodontol 2005;32: Araújo MG, Sukekava F, Wennström JL, Lindhe J. Ridge alterations following implant placement in fresh extraction sockets: an experimental study in the dog. J Clin Periodontol 2005;32: Botticelli D, Berglundh T, Lindhe J. Hard-tissue alterations following immediate implant placement in extraction sites. J Clin Periodontol 2004;31: Chen ST, Darby IB, Reynolds EC, Clement JG. Immediate implant placement postextraction without flap elevation. J Periodontol 2009;80: Covani U, Cornelini R, Barone A. Bucco-lingual bone remodeling around implants placed into immediate extraction sockets: a case series. J Periodontol 2003;74: De Rouck T, Collys K, Cosyn J. Single-tooth replacement in the anterior maxilla by means of immediate implantation and provisionalization: a review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2008;23: Chen ST, Darby IB, Reynolds EC. A prospective clinical study of non-submerged immediate implants: clinical outcomes and esthetic results. Clin Oral Implants Res 2007;18: Raes F, Cosyn J, Crommelinck E, Coessens P, De Bruyn H. Immediate and conventional single implant treatment in the anterior maxilla: 1-year results of a case series on hard and soft tissue response and aesthetics. J Clin Periodontol 2011;38: Chen ST, Buser D. Clinical and esthetic outcomes of implants placed in postextraction sites. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2009;(24 suppl):
15 40. Cornelini R, Cangini F, Covani U, Wilson TG Jr. Immediate restoration of implants placed into fresh extraction sockets for single-tooth replacement: a prospective clinical study. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2005;25: Cooper LF, Reside G, Raes F, et al. Immediate provisionalization of dental implants in grafted alveolar ridges in the esthetic zone: a 5-year evaluation. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2014;34: De Rouck T, Collys K, Wyn I, Cosyn J. Instant provisionalization of immediate singletooth implants is essential to optimize esthetic treatment outcome. Clin Oral Implants Res 2009;20: Cooper L, Reside G, Stanford C, et al. A multicenter randomized comparative trial of implants with different abutment interfaces to replace anterior maxillary single teeth. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2015;30:
University of Groningen. Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten
 University of Groningen Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry
 Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Working together as a team, the periodontist
 The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants
 Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
IMPACT OF IMMEDIATE AND NON-IMMEDIATE PROVISIONALIZATION ON THE SOFT TISSUE ESTHETICS OF FINAL RESTORATIONS ON IMMEDIATELY PLACED IMPLANTS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE IMPACT OF IMMEDIATE AND NON-IMMEDIATE PROVISIONALIZATION ON THE SOFT TISSUE ESTHETICS OF FINAL RESTORATIONS ON IMMEDIATELY PLACED IMPLANTS Chong-Hyun Han 1, DDS, PhD, Jeong-Won Paik 2,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE IMPACT OF IMMEDIATE AND NON-IMMEDIATE PROVISIONALIZATION ON THE SOFT TISSUE ESTHETICS OF FINAL RESTORATIONS ON IMMEDIATELY PLACED IMPLANTS Chong-Hyun Han 1, DDS, PhD, Jeong-Won Paik 2,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 2011 BY QUINTESSENCE PUBLISHING CO, INC. PRINTING OF THIS DOCUMENT IS RESTRICTED TO PERSONAL USE ONLY.. 215 Dental Cone Beam Computed Tomography
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 2011 BY QUINTESSENCE PUBLISHING CO, INC. PRINTING OF THIS DOCUMENT IS RESTRICTED TO PERSONAL USE ONLY.. 215 Dental Cone Beam Computed Tomography
Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area
 CLINICAL SCIENCE IJOICR Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area 1 Pedro Peña Martinez, 2 Ramón Palomero Langner, 3 Ramón Palomero
CLINICAL SCIENCE IJOICR Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area 1 Pedro Peña Martinez, 2 Ramón Palomero Langner, 3 Ramón Palomero
Hyun-Jae Cho, Kun-Soo Jang, Ki-Hyun Jeong, Jae-Yun Jeon, Kyung-Gyun Hwang, Chang-Joo Park
 Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
Immediate Implant Placement Along With Guided Bone Regeneration In Mandibular Anterior Region A Case Report.
 IMMEDIATE IMPLANT PLACEMENT ALONG WITH GUIDED BONE REGENERATION IN MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR REGION A CASE REPORT. Dr.C.P.Dhivakar 1, Dr.T.Saravanan 2, Dr.A.Aniz 3 1) Department of Periodontics, Karpaga Vinayaga
IMMEDIATE IMPLANT PLACEMENT ALONG WITH GUIDED BONE REGENERATION IN MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR REGION A CASE REPORT. Dr.C.P.Dhivakar 1, Dr.T.Saravanan 2, Dr.A.Aniz 3 1) Department of Periodontics, Karpaga Vinayaga
Peri-implant Augmentation
 Indication Sheet PIR3 Peri-implant Augmentation Early implantation with simultaneous GBR for contour augmentation using the technique by Prof. Daniel Buser and Prof. Urs Belser, University of Berne, Switzerland
Indication Sheet PIR3 Peri-implant Augmentation Early implantation with simultaneous GBR for contour augmentation using the technique by Prof. Daniel Buser and Prof. Urs Belser, University of Berne, Switzerland
In the esthetic zone, osseointegration
 CASE REPORT A Method for Obtaining Peri-Implant Soft-Tissue Contours by Using Screw- Retained Provisional Restorations as Impression Copings: A Clinical Report Bi-Yuan Tsai, DDS, MS* In the esthetic zone,
CASE REPORT A Method for Obtaining Peri-Implant Soft-Tissue Contours by Using Screw- Retained Provisional Restorations as Impression Copings: A Clinical Report Bi-Yuan Tsai, DDS, MS* In the esthetic zone,
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Evaluation of immediate loading of single dental implants in the maxillary esthetic zone: Clinical and radiographical comparative study
 Evaluation of immediate loading of single dental implants in the maxillary esthetic zone: Clinical and radiographical comparative study Received: 9/6/2013 Accepted: 30/7/2013 Serwan Saeb Al Naqshabandi
Evaluation of immediate loading of single dental implants in the maxillary esthetic zone: Clinical and radiographical comparative study Received: 9/6/2013 Accepted: 30/7/2013 Serwan Saeb Al Naqshabandi
Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants. Agenda. Agenda. Smile line revitalization with implants Priest Prosthodontics, LLC 1
 Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants Board Certified Prosthodontist Hilton Head Island, SC Agenda Implant placement and esthetic potential Single immediate implant placement Soft tissue preservation
Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants Board Certified Prosthodontist Hilton Head Island, SC Agenda Implant placement and esthetic potential Single immediate implant placement Soft tissue preservation
Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants
 Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement
 Dr. Giancarlo Romagnuolo Roma, Italy From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement Keywords guided surgery, 3D implant planning, single missing tooth, delayed immediate
Dr. Giancarlo Romagnuolo Roma, Italy From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement Keywords guided surgery, 3D implant planning, single missing tooth, delayed immediate
Immediate Placement and Restoration of Dental Implants in the Esthetic Region: Clinical Case Series
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Immediate Placement and Restoration of Dental Implants in the Esthetic Region: Clinical Case Series NABIL KHZAM, BDS, MPhil, DClinDent*, NIKOS MATTHEOS, DDS, MASc, PhD, DAVID ROBERTS,
RESEARCH ARTICLE Immediate Placement and Restoration of Dental Implants in the Esthetic Region: Clinical Case Series NABIL KHZAM, BDS, MPhil, DClinDent*, NIKOS MATTHEOS, DDS, MASc, PhD, DAVID ROBERTS,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1.
 Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive. maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years.
 Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:60-66 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.2.60 Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans Ji Young
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:60-66 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.2.60 Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans Ji Young
Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report
 C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
Planning: The key to obtaining aesthetic and functional results in implant-supported restorations
 case report Planning: The key to obtaining aesthetic and functional results in implant-supported restorations Hugo A. ALBERA 1, Estela M. Ribotta de ALBERA 2 Several factors determine the success of functional
case report Planning: The key to obtaining aesthetic and functional results in implant-supported restorations Hugo A. ALBERA 1, Estela M. Ribotta de ALBERA 2 Several factors determine the success of functional
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations
 C L I N I C A L Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations William C Martin, 1 Emma Lewis, 2 Dean Morton 3 1 DMD, MS, Associate Professor & Clinical Director, Center for Implant Dentistry,
C L I N I C A L Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations William C Martin, 1 Emma Lewis, 2 Dean Morton 3 1 DMD, MS, Associate Professor & Clinical Director, Center for Implant Dentistry,
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Several extraction socket classifications have been
 Case Report Type 3 ReceSSion DefeCTS Clinical Management of Type 3 Recession Defects With Immediate Implant and Provisional Restoration Therapy: A Case Report Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS; and Stephen J. Chu,
Case Report Type 3 ReceSSion DefeCTS Clinical Management of Type 3 Recession Defects With Immediate Implant and Provisional Restoration Therapy: A Case Report Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS; and Stephen J. Chu,
Patients esthetic demands and
 Predictable Periimplant Gingival Esthetics: Use of the Natural Tooth as a Provisional following Implant Placement ROBERT C. MARGEAS, DDS* ABSTRACT Maintaining the interdental papilla and bone height following
Predictable Periimplant Gingival Esthetics: Use of the Natural Tooth as a Provisional following Implant Placement ROBERT C. MARGEAS, DDS* ABSTRACT Maintaining the interdental papilla and bone height following
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 47 Provisional Restorations Used in Immediate Implant Placement Provide a Platform to Promote Peri-implant Soft Tissue Healing: A Pilot
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 47 Provisional Restorations Used in Immediate Implant Placement Provide a Platform to Promote Peri-implant Soft Tissue Healing: A Pilot
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report
 Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Restoring esthetics by immediately loaded implant placement Jurel SK 1, Gupta DS 2, Agarwal H 3, Singh RD 4, Aggarwal KK 5
 Restoring esthetics by immediately loaded implant placement Jurel SK 1, Gupta DS 2, Agarwal H 3, Singh RD 4, Aggarwal KK 5 Case Report 1 Dr. Sunit K Jurel MDS, Assistant professor Department of Prosthodontics
Restoring esthetics by immediately loaded implant placement Jurel SK 1, Gupta DS 2, Agarwal H 3, Singh RD 4, Aggarwal KK 5 Case Report 1 Dr. Sunit K Jurel MDS, Assistant professor Department of Prosthodontics
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery
 Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry
 Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD With continual improvements in the design and production
Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD With continual improvements in the design and production
Surgery All at Once : Socket preservation and immediate placement of an implant in an infected site in the anterior region a Case Report
 Surgery All at Once : Socket preservation and immediate placement of an implant in an infected site in the anterior region a Case Report W.P. van der Schoor*, A.R.M. van der Schoor Tooth extraction followed
Surgery All at Once : Socket preservation and immediate placement of an implant in an infected site in the anterior region a Case Report W.P. van der Schoor*, A.R.M. van der Schoor Tooth extraction followed
Management of a complex case
 2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas
 2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
The anatomic limitations of the. Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD*
 CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
Immediate implant placement in a single staged
 Bone and Crescent Shaped Free Gingival Grafting for Anterior Immediate Implant Placement: Technique and Case Report Han et al Thomas Han, DDS, MS 1 2 Abstract Immediate implant placement in a single staged
Bone and Crescent Shaped Free Gingival Grafting for Anterior Immediate Implant Placement: Technique and Case Report Han et al Thomas Han, DDS, MS 1 2 Abstract Immediate implant placement in a single staged
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 89 Pre-extractive Interradicular Implant Bed Preparation: Case Presentations of a Novel Approach to Immediate Implant Placement at Multirooted
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 89 Pre-extractive Interradicular Implant Bed Preparation: Case Presentations of a Novel Approach to Immediate Implant Placement at Multirooted
Immediate Implant Placement:
 Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
Since the introduction of osseointegrated dental implants
 CLINICAL Papilla Formation in Response to Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery and Immediate Restoration Paul A. Schnitman, DDS, MSD 1 * Chie Hayashi, DDS, PhD, MMSc 2 This retrospective analysis was undertaken
CLINICAL Papilla Formation in Response to Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery and Immediate Restoration Paul A. Schnitman, DDS, MSD 1 * Chie Hayashi, DDS, PhD, MMSc 2 This retrospective analysis was undertaken
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 715 Immediate Implant Placement and Loading of Single Implants in the Esthetic Zone: Clinical Outcome and Esthetic Evaluation in a Japanese
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 715 Immediate Implant Placement and Loading of Single Implants in the Esthetic Zone: Clinical Outcome and Esthetic Evaluation in a Japanese
The patient gave a history of hypertension and gastritis for which was taking Lacidipine 4mg, Omeprazole 20mg and Simvastatin 40mg.
 A.S. was referred by her general dental practitioner for assessment for possible implant placement to restore the space where her bridge replacing her maxillary central incisors had recently failed. Fig
A.S. was referred by her general dental practitioner for assessment for possible implant placement to restore the space where her bridge replacing her maxillary central incisors had recently failed. Fig
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior
 Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
MINI System CASE REPORT. Name: Dr. Achraf Souayah Na<on: Tunisia
 MINI System SE REPORT Name: Dr. chraf Souayah Na
MINI System SE REPORT Name: Dr. chraf Souayah Na
The following resources related to this article are available online at jada.ada.org ( this information is current as of July 11, 2011):
 Implants or Pontics: Decision Making for Anterior Tooth Replacement Frank Spear J Am Dent Assoc 2009;140;1160-1166 The following resources related to this article are available online at jada.ada.org (
Implants or Pontics: Decision Making for Anterior Tooth Replacement Frank Spear J Am Dent Assoc 2009;140;1160-1166 The following resources related to this article are available online at jada.ada.org (
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
The effect of peri-implant bone exposure on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:20-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20 on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants Seung-Yun Shin 1, Seung-Boem Kye 1, Jongrak
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:20-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20 on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants Seung-Yun Shin 1, Seung-Boem Kye 1, Jongrak
CASE REPORT. CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration
 Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Immediate post-extraction BIOMIMETIC CORAL IC implant placement in the anterior esthetic zone
 Immediate post-extraction BIOMIMETIC CORAL IC implant placement in the anterior esthetic zone AUTHORS Dr. Antonio Mallebrera Clinica Mallebrera Centro Dental (Petrer, Alicante) Sr. Juan José Sempere Matarredona
Immediate post-extraction BIOMIMETIC CORAL IC implant placement in the anterior esthetic zone AUTHORS Dr. Antonio Mallebrera Clinica Mallebrera Centro Dental (Petrer, Alicante) Sr. Juan José Sempere Matarredona
Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A Case report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 97-101 Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 97-101 Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A
Marginal bone change of Immediate Versus Delayed Restoration Procedures on Immediate Implants in Single Tooth Replacement
 Dental implant Journal: Vol. 3, May, 2014 Marginal bone change of Immediate Versus Delayed Restoration Procedures on Immediate Implants in Single Tooth Replacement Duksang Jang DDS. PhD DDS, PhD. Director
Dental implant Journal: Vol. 3, May, 2014 Marginal bone change of Immediate Versus Delayed Restoration Procedures on Immediate Implants in Single Tooth Replacement Duksang Jang DDS. PhD DDS, PhD. Director
Initially, implant dentistry was focused on
 CASE LETTER Correction of Esthetic Complications of a Malpositioned Implant: A Case Letter Sergio Alexandre Gehrke, PhD INTRODUCTION Initially, implant dentistry was focused on successful osseointegration
CASE LETTER Correction of Esthetic Complications of a Malpositioned Implant: A Case Letter Sergio Alexandre Gehrke, PhD INTRODUCTION Initially, implant dentistry was focused on successful osseointegration
Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique
 e116 Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique Sang-Hoon Park, DDS, MS* Hom-Lay Wang, DDS, MSD, PhD** This paper presents three cases of peri-implant
e116 Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique Sang-Hoon Park, DDS, MS* Hom-Lay Wang, DDS, MSD, PhD** This paper presents three cases of peri-implant
Implant therapy in partially edentulous patients has become
 CLINICAL Esthetic Outcomes of Immediately Loaded Locking Taper Implants in the Anterior Maxilla: A Case Series Study Giorgio Lombardo, MD, DDS 1 * Giovanni Corrocher, DDS 1 Jacopo Pighi, DDS 1 Anna Mascellaro,
CLINICAL Esthetic Outcomes of Immediately Loaded Locking Taper Implants in the Anterior Maxilla: A Case Series Study Giorgio Lombardo, MD, DDS 1 * Giovanni Corrocher, DDS 1 Jacopo Pighi, DDS 1 Anna Mascellaro,
Immediate placement and provisionalization of an implant after removal of an impacted maxillary canine: two case reports
 Zuiderveld et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2015) 1:13 DOI 10.1186/s40729-015-0013-3 CASE REPORT Open Access Immediate placement and provisionalization of an implant after removal of
Zuiderveld et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2015) 1:13 DOI 10.1186/s40729-015-0013-3 CASE REPORT Open Access Immediate placement and provisionalization of an implant after removal of
MODIFIED SINGLE ROLL FLAP APPROACH FOR SIMULTANEOUS IMPLANT PLACEMENT AND GINGIVAL AUGMENTATION
 Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
Dentascan Evaluation of Hard Tissue Changes around Implants Placed in Healed Sockets: A Cross-sectional Study
 JDSOR ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dentascan Evaluation of Hard Tissue Changes around 10.5005/jp-journals-10039-1099 Implants Placed in Healed Sockets Dentascan Evaluation of Hard Tissue Changes around Implants Placed
JDSOR ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dentascan Evaluation of Hard Tissue Changes around 10.5005/jp-journals-10039-1099 Implants Placed in Healed Sockets Dentascan Evaluation of Hard Tissue Changes around Implants Placed
Integrating Natural Hard and Soft Tissue
 ACCREDITATION ESSENTIALS Integrating Natural Hard and Soft Tissue An Implant-Supported Restoration in the Esthetic Zone Somkiat Aimplee, DDS, MSc The successful replacement of anterior teeth with implants
ACCREDITATION ESSENTIALS Integrating Natural Hard and Soft Tissue An Implant-Supported Restoration in the Esthetic Zone Somkiat Aimplee, DDS, MSc The successful replacement of anterior teeth with implants
Alveolar ridge preservation techniques
 Alveolar ridge preservation techniques Semmelweis University, Department of Periodontology, Budapest Dr. Windisch Péter Head of Department of Periodontology Changes of the alveolar ridge dimensions after
Alveolar ridge preservation techniques Semmelweis University, Department of Periodontology, Budapest Dr. Windisch Péter Head of Department of Periodontology Changes of the alveolar ridge dimensions after
continuing education 1 Esthetic-Zone Implants
 continuing education 1 Esthetic-Zone Implants 10 Keys for Successful Esthetic-Zone Single Immediate Implants: Importance of Biotype Conversion for Lasting Success Robert A. Levine, DDS; Jeffrey Ganeles,
continuing education 1 Esthetic-Zone Implants 10 Keys for Successful Esthetic-Zone Single Immediate Implants: Importance of Biotype Conversion for Lasting Success Robert A. Levine, DDS; Jeffrey Ganeles,
Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial
 Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial Lars Schropp, DDS, PhD /Flemming Isidor, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont /Lambros Kostopoulos,
Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial Lars Schropp, DDS, PhD /Flemming Isidor, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont /Lambros Kostopoulos,
Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior Region Along with Soft and Hard Tissue Grafting- A Case Report.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 67 Efficacy Evaluation of a New Buccal Bone Plate Preservation Technique: A Pilot Study Federico Brugnami, DDS* Alfonso Caiazzo, DDS**
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 67 Efficacy Evaluation of a New Buccal Bone Plate Preservation Technique: A Pilot Study Federico Brugnami, DDS* Alfonso Caiazzo, DDS**
(Images are at the end of article)
 Long term provisionalization during periodontal surgery and extraction site tissue grafting: A Case Review Michael Tischler, DDS Diplomate American Board Of Oral Implantology/Implant Dentistry (Images
Long term provisionalization during periodontal surgery and extraction site tissue grafting: A Case Review Michael Tischler, DDS Diplomate American Board Of Oral Implantology/Implant Dentistry (Images
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 401 Guidelines for Selecting the Implant Diameter During Immediate Implant Placement of a Fresh Extraction Socket: A Case Series Ariádene
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 401 Guidelines for Selecting the Implant Diameter During Immediate Implant Placement of a Fresh Extraction Socket: A Case Series Ariádene
Immediate implant placement, with or without simultaneous implant provisionalization,
 Saving Her Smile by Panos Papaspyridakos, DDS, MS, PhD and Michael Vizirakis, DDS, MS Immediate Implant Placement and Fixed Provisionalization with Extracted Tooth Introduction Following tooth extraction,
Saving Her Smile by Panos Papaspyridakos, DDS, MS, PhD and Michael Vizirakis, DDS, MS Immediate Implant Placement and Fixed Provisionalization with Extracted Tooth Introduction Following tooth extraction,
Then and Now. Implant Therapy:
 Implant Therapy: Then and Now by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry has come a long way since blade and subperiostal implants were widely used. Improvements in implant design and site preparation
Implant Therapy: Then and Now by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry has come a long way since blade and subperiostal implants were widely used. Improvements in implant design and site preparation
A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
 Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
Inclusive Tooth Replacement System
 Optimizing Anterior Esthetics with the Inclusive Tooth Replacement System by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant treatment has changed so much over the years. In the past it was acceptable to place
Optimizing Anterior Esthetics with the Inclusive Tooth Replacement System by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant treatment has changed so much over the years. In the past it was acceptable to place
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 27 Flapless Implant Surgery in the Esthetic Region: Advantages and Precautions Tae-Ju Oh, DDS, MS 1 /Jeffrey Shotwell, DDS, MS 2 Edward
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 27 Flapless Implant Surgery in the Esthetic Region: Advantages and Precautions Tae-Ju Oh, DDS, MS 1 /Jeffrey Shotwell, DDS, MS 2 Edward
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 559 Emergence Profile Design Based on Implant Position in the Esthetic Zone Marius Steigmann, DDS 1,2 Alberto Monje, DDS 3 Hsun-Liang Chan,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 559 Emergence Profile Design Based on Implant Position in the Esthetic Zone Marius Steigmann, DDS 1,2 Alberto Monje, DDS 3 Hsun-Liang Chan,
The majority of the early research concerning
 Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Dental Implants and Esthetics
 Continuing Education Brought to you by Dental Implants and Esthetics Course Author(s): Charles J. Goodacre, DDS, MSD; Chad J. Anderson, MS, DMD CE Credits: 1 hour Intended Audience: Dentists, Dental Hygienists,
Continuing Education Brought to you by Dental Implants and Esthetics Course Author(s): Charles J. Goodacre, DDS, MSD; Chad J. Anderson, MS, DMD CE Credits: 1 hour Intended Audience: Dentists, Dental Hygienists,
Osseointegrated implant-supported
 CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
Significance of crown shape in the replacement of a central incisor with a single implantsupported
 PROSTHODONTICS Significance of crown shape in the replacement of a central incisor with a single implantsupported crown Luca Gobbato, DDS 1 /Gianluca Paniz, DDS 2 /Fabio Mazzocco, DDS 3 / Andrea Chierico,
PROSTHODONTICS Significance of crown shape in the replacement of a central incisor with a single implantsupported crown Luca Gobbato, DDS 1 /Gianluca Paniz, DDS 2 /Fabio Mazzocco, DDS 3 / Andrea Chierico,
Immediate versus early implant placement
 Point and Counterpoint Coordinator: Mauro Tosta Immediate versus early implant placement Washington SANTANA MSc in Dentistry, Federal University of Goiás (UFG). Professor of Implantodontics, IKO-Goiânia.
Point and Counterpoint Coordinator: Mauro Tosta Immediate versus early implant placement Washington SANTANA MSc in Dentistry, Federal University of Goiás (UFG). Professor of Implantodontics, IKO-Goiânia.
The 2B-3D rule for implant planning, placement and restoration
 IJOI 27 INTERDISCIPLINARY TREATMENT The 2B-3D rule for implant planning, placement and restoration 1. What is biologic width? Is there a golden rule for implant planning, placement and restoration as the
IJOI 27 INTERDISCIPLINARY TREATMENT The 2B-3D rule for implant planning, placement and restoration 1. What is biologic width? Is there a golden rule for implant planning, placement and restoration as the
Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space
 Case Report Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space Nidhi Bhatia 1, Shweta Bali 2, Meenu Taneja Bhasin 3, Priyanka Aggarwal 4, Vaibhav Joshi
Case Report Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space Nidhi Bhatia 1, Shweta Bali 2, Meenu Taneja Bhasin 3, Priyanka Aggarwal 4, Vaibhav Joshi
An esthetic zone implant
 clinical brief inside my practice peer to peer spotlight tech profile Surgical and Prosthetic Treatment of a Failed Maxillary Central Incisor Immediate implant placement is a key to success Robert A. Levine,
clinical brief inside my practice peer to peer spotlight tech profile Surgical and Prosthetic Treatment of a Failed Maxillary Central Incisor Immediate implant placement is a key to success Robert A. Levine,
Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident
 Case Report 13 2011 Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident Dr Hitoshi Minagawa Tokyo, Japan Prosthetics Dr Hitoshi Minagawa successfully completed his studies
Case Report 13 2011 Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident Dr Hitoshi Minagawa Tokyo, Japan Prosthetics Dr Hitoshi Minagawa successfully completed his studies
Available online at International Journal of Current Research Vol. 7, Issue, 12, pp , December, 2015
 z Available online at http://www.journalcra.com International Journal of Current Research Vol. 7, Issue, 12, pp.24212-24216, December, 2015 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CURRENT RESEARCH ISSN: 0975-833X REVIEW
z Available online at http://www.journalcra.com International Journal of Current Research Vol. 7, Issue, 12, pp.24212-24216, December, 2015 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CURRENT RESEARCH ISSN: 0975-833X REVIEW
Bone Grafting and Immediate Implant Placement in the Anterior
 Bone Grafting and Immediate Implant Placement in the Anterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Whether a consequence of periodontal disease, caries or trauma to the root, losing an anterior tooth is psychologically
Bone Grafting and Immediate Implant Placement in the Anterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Whether a consequence of periodontal disease, caries or trauma to the root, losing an anterior tooth is psychologically
Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 10 Issue Date: March 2005, Posted On: 5/2/2005 Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS Figure 1. A 43-year-old female
Page 1 of 10 Issue Date: March 2005, Posted On: 5/2/2005 Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS Figure 1. A 43-year-old female
Initial findings and treatment plan
 12 STARGET 1 I 10 s t r a u m a n n CADCAM s o l u t i o n s A n dr ea s Gr a f MDT, Dr. Karin Wolleb and D r. R onal d J ung Individual anterior esthetics Pa rt 1 : t h e p o ssib i l ities o f S traum
12 STARGET 1 I 10 s t r a u m a n n CADCAM s o l u t i o n s A n dr ea s Gr a f MDT, Dr. Karin Wolleb and D r. R onal d J ung Individual anterior esthetics Pa rt 1 : t h e p o ssib i l ities o f S traum
CHAPTER. 1. Uncontrolled systemic disease 2. Retrognathic jaw relationship
 CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy.
 Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
University of Groningen. Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten Willemijn
 University of Groningen Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten Willemijn IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
University of Groningen Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten Willemijn IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
PETER GEHRKE, DR. MED. DENT.* MARKUS LOBERT, DR. MED. DENT. GÜNTER DHOM, DR. MED. DENT.
 Reproducibility of the Pink Esthetic Score Rating Soft Tissue Esthetics Around Single-Implant Restorations with Regard to Dental Observer Specialization PETER GEHRKE, DR. MED. DENT.* MARKUS LOBERT, DR.
Reproducibility of the Pink Esthetic Score Rating Soft Tissue Esthetics Around Single-Implant Restorations with Regard to Dental Observer Specialization PETER GEHRKE, DR. MED. DENT.* MARKUS LOBERT, DR.
by Paul S. Petrungaro, DDS, MS,
 Cr e a t i o n a n d Preservation o f Na t u ra l So f t Tissue Em e r g e n c e Profiles Ar o u n d Dental Implants in the Esthetic Zone by Paul S. Petrungaro, DDS, MS, FICD, FACD, DICOI Chicago, IL Lake
Cr e a t i o n a n d Preservation o f Na t u ra l So f t Tissue Em e r g e n c e Profiles Ar o u n d Dental Implants in the Esthetic Zone by Paul S. Petrungaro, DDS, MS, FICD, FACD, DICOI Chicago, IL Lake
A conservative restorative smile makeover
 C L I N I C A L A conservative restorative smile makeover Aneta Grzesinska 1 Introduction The patient was a 37-year-old female who presented to the practice requesting six porcelain veneers for her upper
C L I N I C A L A conservative restorative smile makeover Aneta Grzesinska 1 Introduction The patient was a 37-year-old female who presented to the practice requesting six porcelain veneers for her upper
Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System
 Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System by Timothy Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Maxillary lateral incisor agenesis (MLIA) is a condition in which at least one of the
Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System by Timothy Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Maxillary lateral incisor agenesis (MLIA) is a condition in which at least one of the
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 175 Immediate Implant Placement and Provisionalization After Long-Axis Root Fracture and Complete Loss of the Facial Bony Lamella Robert
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 175 Immediate Implant Placement and Provisionalization After Long-Axis Root Fracture and Complete Loss of the Facial Bony Lamella Robert
The surgical placement of dental implants has
 Flapless Implant Surgery: A 10-year Clinical Retrospective Analysis Luis Dominguez Campelo, DDS 1 /Jose R. Dominguez Camara, MD, DDS 2 Purpose: This article is a retrospective clinical analysis of implants
Flapless Implant Surgery: A 10-year Clinical Retrospective Analysis Luis Dominguez Campelo, DDS 1 /Jose R. Dominguez Camara, MD, DDS 2 Purpose: This article is a retrospective clinical analysis of implants
