Immediate Placement and Restoration of Dental Implants in the Esthetic Region: Clinical Case Series
|
|
|
- Elizabeth Lindsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Immediate Placement and Restoration of Dental Implants in the Esthetic Region: Clinical Case Series NABIL KHZAM, BDS, MPhil, DClinDent*, NIKOS MATTHEOS, DDS, MASc, PhD, DAVID ROBERTS, BDSc, MDSc, WILLIAM L BRUCE, BDSc, MDSc, SASO IVANOVSKI, BDSc, BDentSt, MDSc, PhD ABSTRACT Aim: The objective of this study was to assess the hard and soft tissue changes following immediate placement and provisional restoration of single-tooth implants in the aesthetic zone. Methods: Thirteen patients with immediately placed and restored implants were included in this study. All participating patients underwent the same treatment strategy that involved removal of the failed tooth, flapless surgery, immediate implant placement, and connection of a screw-retained provisional restoration. Three months following implant placement, the temporary crowns were replaced by the definitive restorations. Implant survival rates, and hard and soft tissue changes were measured using periapical X-rays and photographs. The range of the observation period was between 12 and 37 months with a mean period of 23.2 ± 7.6 months. Results: At the time of follow-up, all implants were present with no complications. Radiographic evaluation revealed a mean mesial bone gain of 1.20 ± 1.01 mm and a mean distal bone gain of 0.80 ± 1.14 mm, which reached statistical significance. The mean mid-buccal recession was 0.20 ± 0.78 mm, whereas the mesial and distal papillae height loss was 0.50 ± 1.26 mm and 0.30 ± 0.82 mm, respectively. The changes in the soft tissues did not reach statistical significance. Conclusion: Notwithstanding the limitation of a small sample size, this study shows that immediate implant placement and provisional restoration in the maxillary aesthetic zone can result in favorable treatment outcomes with regards to soft and hard tissues changes over a follow-up period of 23.2 ± 7.6 months. CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE Most clinical trials investigating immediate implant placement and immediate restoration in the maxillary anterior zone have focused on implant survival and implant success, with particular emphasis on radiographically assessed hard tissues changes. However, this study assesses the soft tissue changes associated with this procedure, which is an important area of study given the esthetic demands of implant therapy in the maxillary anterior region. (J Esthet Restor Dent :, 2013) INTRODUCTION Single tooth replacement with an implant supported crown is often the treatment of choice for missing teeth in the anterior maxilla. The original implant treatment protocol described by Branemark involved 3 months of healing following extraction of a failed tooth, and an additional 3 to 6 months of a load-free period following implant placement. 1,2 In the last 20 years, implant dentistry has evolved dramatically, with the original two-stage protocol modified to include one-stage surgery, 3 immediate implant placement into a fresh *Specialist Periodontist, Private Practice, University of Tripoli, Libya Associate Professor, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong Specialist Prosthodontist, Private Practice, Brisbane, Qld, Australia Specialist Prosthodontist, Private Practice, Brisbane, Qld, Australia Professor of Periodontology, School of Dentistry and Oral Health, Griffith University, Gold Coast, Qld, Australia 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. DOI /jerd Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry Vol No
2 extraction socket and immediate implant restoration. 4,5 These three approaches have been combined in an attempt to further expedite the restorative process. 6 Clinical trials have shown high levels of implant survival and success for single tooth implants placed directly into fresh extraction sockets. 6,7 Furthermore, it has been shown that immediately placed implants may be provisionally restored with a temporary crown that is placed out of occlusion (immediate provisional restoration). This one-stage surgical and restorative procedure has the advantage of an immediate esthetic outcome with a fixed restoration, while eliminating the need for temporary fixed and/or removable partial dentures, and potential second-stage surgical intervention. It also allows for shorter treatment times as post-extraction socket-healing events coincide with implant osseointegration. However, case selection is critical for this treatment approach, with multiple contraindications such as the presence of infection at the extraction site, inadequate soft tissue profile, and the requirement for sufficient bone apical to the socket in order to achieve appropriate primary stability. From a surgical point of view, good primary stability appears to be critical for the one-stage surgical procedure, as it has been shown that there is a strong relationship between the placement torque and the survival of single tooth-implants. 8 Adequate primary stability is of additional importance in cases where the implant is provisionally restored in order to withstand various forces that may be exerted on the restored implant during the early stages of healing. From a restorative point of view, the implant temporary crown must be out of occlusion in both centric and eccentric positions of the lower jaw. 6 Indeed, the immediate implant placement and restoration protocol is technically challenging and can be considered a technique sensitive procedure. 9 A major consideration in the maxillary anterior region is the loss of buccal tissue contour following tooth extraction. In order to minimize this loss of buccal tissue, the placement of a grafting material in the space between the implant and the buccal socket wall has been advocated and is supported by histological evidence that this approach significantly decreases bone loss following immediate implant placement The use of antibiotic prophylaxis in patients undergoing routine implant placement to minimize complication is supported by the literature and hence are indicated in more challenging clinical protocols such as that described in this study. 14 Most clinical trials investigating immediate implant placement and immediate restoration in the maxillary anterior zone have focused on implant survival and implant success, with particular emphasis on radiographically assessed hard tissues changes. However, few studies have assessed the soft tissue changes associated with this procedure, although this is an important consideration given the esthetic demands of implant therapy in the maxillary anterior region. Therefore, the objectives of the current study were to assess the soft and hard tissue dimensional changes associated with immediately placed and provisionally restored implants replacing single teeth in the anterior maxillary region after a minimum follow-up of 12 months. METHODS The research protocol was reviewed and granted ethical approval by the Griffith University Human Research Ethics Committee (DOH/09/09/HREC). Patient selection Thirteen patients who received 15 immediately placed and provisionally restored implants in the esthetic zone between March 2007 and December 2008 were included in this study. Two of the patients had two implants each. Patients were included in this study based on their willingness to attend 6 monthly review visits following their treatment. The sample included four males and nine females, mean age 44.7 ± 18.7 years, with 15 implants (13 incisors, 1 canine, and 1 premolar) (Table 1). None of the patients were smokers. No patients were lost at the final follow-up. 2 Vol No 2013 Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry DOI /jerd Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
3 TABLE 1. Tooth types and reason for tooth extraction Tooth type/ reason for extraction Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria The decision to progress with immediate implant placement and provisional restoration was determined following a comprehensive clinical and radiographic examination (using a cone-beam computed tomography [CBCT] scan), and detailed consultation between the surgical and restorative clinician. Aside from the usual contraindications for routine implant therapy (untreated periodontitis, uncontrolled diabetes, medical conditions that contraindicate elective surgery), specific contraindications for the immediate implant placement and restoration protocol included the presence of any pathological bone loss around the tooth or any gingival margin pathology or irregularity. Furthermore, the immediate implant placement and provisional restoration protocol was not implemented unless the tooth socket walls were completely intact (no fenestrations or dehiscences) following extraction, and a minimal implant torque insertion of 30 Ncm (maximum of 40 Ncm) was obtained. Surgical Protocol Endodontic Fracture Root resorption Incisors Canines Premolars Total Total All surgical procedures were conducted under local anesthesia. Preoperative antibiotics were given to all patients. This prophylactic dose was 500 mg Amoxicillin three times daily (20 caps) for 1 week, starting 1 day before surgery. Diagnostic evaluation of the site of placement included clinical examination, radiographic analysis using a cone-beam CT scan and occlusal analysis with study models. After informed consent was obtained from the patient, atraumatic tooth extraction using a periotome without flap elevation was performed (Figure 1B). Surgical implant placement followed, according to the instructions of the implant manufacturer (Astra Tech, Mölndal, Sweden) (Figure 1C). Primary stability was achieved to a minimum insertion torque of 30 Ncm using a motor-driven surgical handpiece. In all implants sites, the buccal space between the implant and the socket wall was filled using a xenogenic particulate bone grafting material (Bio-Oss; Geistlich Pharma AG, Wolhusen, Switzerland). Postoperative instructions included chlorhexidine mouthwash (20 ml) use for 2 minutes twice daily for 2 weeks. Patients were instructed to not brush the implant site for at least 2 weeks. For pain control, patients were advised to use either 1 g of Paracetamol or 400 mg of Ibuprofen as needed. Restorative Protocol After connection of a temporary abutment (Figure 1D), a prefabricated screw-retained temporary crown was adjusted and placed (Figure 1E). Appropriate adjustment of the occlusal scheme was carried out in order to ensure that the temporary restoration was free of any contact in both centric and eccentric excursions (Figure 1F). Final finishing of the provisional crown was carried out with rubber cups and pumice. The patients were advised to avoid placing any pressure on the provisional restoration, especially during eating. After 3 to 4 months, the temporary restoration was replaced with a custom zirconia abutment (Procera, Nobel Biocare, Göteborg, Sweden) and a permanent all-ceramic restoration by a prosthodontist. Hard Tissue Measurements Periapical X-rays were used to measure the changes in alveolar bone height surrounding the implant from the time of placement of the temporary restoration (baseline) to the follow-up assessment, which was at least 12 months later. The parallel technique was used in order to obtain comparable X-rays, and standardization was carried out by using the known implant length to calibrate the baseline and follow-up measurements. The implant shoulder was used as a reference level from which mesial (Mbc) and distal (Dbc) lines were drawn in an apical direction to the 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. DOI /jerd Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry Vol No
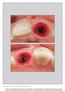
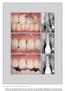
4 A B C G D E F FIGURE 1. A, Failed tooth due to improper root canal treatment (12) before the extraction. B, Minimal traumatic tooth extraction. C, Implant placed in final position. D, E, and F, Temporary crown in place. G, A radiograph. first point of contact between bone and the implant (Figure 2). Computer software (Image J 1.43u; National Institute of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA) was used to calculate the length of these lines (Mbc and Dbc) and express it as an absolute measurement in millimeters. Soft Tissue Measurements The soft tissue data were collected from photographs taken with a fixed angle and zoom ratio prior to tooth extraction (baseline) and at the follow-up visit (at least 12 months later). The crown length of the tooth mesial to the implant measured from the margin of the gingiva was set as the reference length. This allowed comparisons of the changes that occurred before and after the treatment with regard to the position of the gingiva and the amount of recession. A line extending from the incisal edges of the teeth adjacent to the implant (Ocl) was the starting point for the measurements. From this line, perpendicular lines were drawn extending to the tip of the mesial (Mp) and distal (Dp) papilla, as well as the middle of the mid-buccal gingival margin (Bm) (Figure 3). The length of these lines was calculated based on the clinical photographs using a software program (Image J 1.43u), and variations over time were calculated in millimeters. Other Measurements Implant survival rate: defined as the percentage of implants that were present at the final follow-up. Implant success rate: defined as the percentage of symptom and pathology free implants at the final follow-up. Assessment of interdental papilla: The triangular interdental papillae occupying the space between the implant retained restoration and the adjacent teeth were assessed using Jemt s index. 15 Jemt s Index comprises of: score 0 (no papilla present), score 1 (<1/2 of papilla present), score 2 (1/2 of papilla present), score 3 (papilla fills entire interdental space), and score 4 (hyperplastic papilla present). Statistical Analysis The primary hypothesis of this study was that there is no significant change between tooth extraction/implant placement and follow-up with regards to the hard and 4 Vol No 2013 Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry DOI /jerd Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
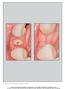
5 A B FIGURE 3. Illustration of the measurements of soft tissue on photographs. Bm = distance to middle of buccal gingival margin; Dp = distance to distal papilla; Mp = distance to mesial papilla; Ocl = occlusal line. FIGURE 2. Illustration of hard tissue measurements on periapical X-ray. Cl = coronal line; Dbc = distal bone contact; Mbc = mesial bone contact. A set of paired radiographs used for measurements. A = baseline radiograph; B = follow-up radiograph. soft tissues changes. In case of parametric data, a paired t-test was used, whereas in nonparametric data a Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used. A frequency analysis was used to describe the distribution of hard and soft tissue changes among the patients. All calculations were performed with the SPSS statistical software program (version 16.0, SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). demographics, implant characteristics and follow-up intervals are shown in Table 2. No implant loss or implant associated pathology was observed at the final follow-up visit. Representative outcomes of the treatment are illustrated in Figures 4 to 6. Hard Tissue Measurements Radiographic evaluation revealed a mean mesial bone gain of 1.20 ± 1.01 mm (p < ), which reached statistical significance. The mean distal bone gain was 0.80 ± 1.14 mm (p = 0.01), which also reached statistical significance. Table 3 shows that there was a significant change in both the mesial and distal bone level between the time of implant placement and the follow-up assessment. Table 4 shows the distribution of bone gain and loss in millimeters for individual patients. The majority of the readings demonstrated bone gain 0.5 mm (13/15 cases). RESULTS The reasons for tooth loss of the 15 implants (13 incisors, 1 canine, and 1 premolar) included in this study are outlined in Table 1. The patient Soft Tissue Measurements The mean mid-buccal gingiva recession was 0.20 ± 0.78 mm (p = 0.44). The mesial papillary height loss was 0.50 ± 1.12 mm (p = 0.24), whereas the distal papillary height loss was 0.30 ± 0.82 mm (p = 0.27) Table 5. The 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. DOI /jerd Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry Vol No
6 TABLE 2. Overview of clinical data Patient No. Sex Age (years) Follow-up (months) Site of implant Length (mm) Diameter (mm) 1 M M F F F F M M F F M F F F F M = male, F = female. mesial papilla showed the highest amount of tissue loss. The changes in the soft tissues did not reach statistical significance. Table 6 shows the distribution of soft tissue changes on the mesial, distal, and mid-facial aspects of individual implants. Most of the readings remain within ±10% of the baseline value except for the mesial changes which reach up to 35% in the patients that had two implants placed adjacent to each other. Jemt s Index Wilcoxon signed-rank test did not reveal any significant difference in the Jemt s index score for either mesial or distal papilla between implant placement and follow-up observations (p-values and 0.171, respectively) (Table 7). At follow-up, 50% of the mesial papillae received a score of 3, which means that the full height of the interdental papillae was present (normal), whereas the same score was recorded in 60% of distal papillae. The rest of the results showed scores of 1, 2, and 4. No score of 0 was recorded. DISCUSSION In this case series report, immediately placed and restored single-tooth implants in the maxillary anterior zone were found to osseointegrate and remain complication-free after 23.2 ± 7.6 months of follow-up. This result is in accordance with outcomes presented in other similar studies, demonstrating the high predictability of osseointegration when a very specific set of selection criteria is applied, and a strict surgical and restorative protocol is observed. This study utilized the Astra Tech implant system, which has several abutment-implant interface characteristics common to contemporary implant 6 Vol No 2013 Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry DOI /jerd Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
7 FIGURE 4. Illustration of soft tissue on photographs, (22)-baseline and follow-up. FIGURE 5. Illustration of soft tissue on photographs, (21)-baseline and follow-up. systems. Astra Tech implants have a rough surface, an internal connection, a platform switch at the abutment-implant interface and microthreads at the coronal aspects of the implant. These design features are incorporated primarily to enhance the stability of the hard and soft tissues, although it is unclear if, and to what extent, each of these features may contribute to tissue stability. It is likely that some or all of the features of the Astra Tech system, many of which it shares with other currently available implant designs, has contributed to the positive outcomes of this study. This study showed a mean mesial bone gain of 1.20 mm and a mean distal bone gain of 0.80 mm over the duration of the follow-up period (23.2 ± 7.6 months). The changes in the hard tissues reached statistical significance compared with baseline suggesting that there was bone gain in a coronal direction at the interproximal aspects over the duration of the study. This is not surprising because the implants were placed in extraction sockets, and there was subsequent bone fill in the space between the implant and the socket walls, resulting in the coronal repositioning of the bone-implant contact over the course of the study. The bone gain was also assisted by the use of a slowly resorbing particulate bone graft. Knowing the exact implant length and diameter allowed for precise measurement of the bone level in millimeters, compensating for any distortion of the radiograph. This was an important element of the methodology in contrast with much of the literature, where measurements are only made with the use of the apical 20,22 or the coronal end 23 of the implant shoulder as a reference point. Other studies have used the contact point of the restoration to the adjacent tooth as a reference point. However, the use of these landmarks 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. DOI /jerd Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry Vol No
8 TABLE 4. Frequency analysis of hard tissue changes in millimeters Bone changes in mm/patients 2.5 and 2 mm and 1.5 mm and 1 mm and 0.5 mm and 0 mm and 0.5 mm and 1 mm 0.63 TABLE 5. Soft tissue level changes (presented as millimeters change) Parameters Change in mm p-value Mesial papilla level 0.50 ± Distal papilla level 0.30 ± Mid-buccal ginigval level 0.20 ± FIGURE 6. Illustration of soft tissue on photographs, (21)-baseline and follow-up. Mean ± standard deviation. TABLE 3. Bone level changes (presented as millimeters change) Parameters Change in mm p-value Mesial bone level 1.20 ± * Distal bone level 0.80 ± * Mean ± standard deviation. *Significant. has some limitations, namely that the restorative contact point is not going to be constant as the provisional crowns will undergo replacement with permanent restorations, whereas the radiographic location of the apical/coronal shoulder is easily affected by image distortion. 24 The results of the present study, which showed a relatively high amount of bone gain, compares favorably with other studies involving implant therapy in the maxillary anterior zone. 18,19,22,25 28 Using the immediate placement and restoration protocol, Kan and colleagues showed a mean marginal bone loss ranging from 0.26 to 0.40 mm on the mesial and 0.22 to 0.28 mm on the distal aspect of the implant at 1-year follow-up. 23 Several other investigators have shown even greater amounts of bone loss. The study by De Rouck and colleagues revealed a mean bone loss of 0.98 mm on the mesial aspect of the implant and 0.78 mm distally at 1-year follow-up. 6 Other studies using the immediate implant placement and immediate restoration approach have shown similar outcomes. 23,24,29 31 On the other hand, Kan and colleagues reported that scalloped shaped implants placed into extraction sites showed a mean bone gain of 1.0 mm after 1 year of follow-up. 7 The amount of bone gain in this study was attributed to the placement of a bone graft into the gap between the implant and walls of the extraction socket that subsequently resulted in radiographically assessed bone fill. Our study used a platform switching implant 8 Vol No 2013 Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry DOI /jerd Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
9 TABLE 6. Frequency analysis of soft tissue changes in percentage Soft tissue changes in percentage/patients 10% and 5% 5.96 (DP) 5.90 (MP) 5.12 (MP) 7.70 (MF) 5.95 (MF) 5% and 0% 1.02 (DP) 2.06 (DP) 1.79 (MP) 0.11 (MP) 1.83 (MF) 4.58 (MF) 0.95 (MF) 4.5 (MF) 0% and 5% 2.57 (DP) 1.62 (DP) 1.13 (DP) 1.82 (DP) 0.36 (DP) 2.31 (DP) 0.72 (MP) 1.14 (MP) 0.96 (MP) 0.39 (MF) 1.09 (MF) 4.72 (MF) 5% and 10% 8.98 (DP) 9.55 (DP) 7.43 (DP) 9.03 (DP) 9.55 (MF) 8.05 (MF) 9.99 (MF) 10% and 15% (MP) (MP) (MP) (MF) (MF) 15% and 20% (DP) 20% and 25% (MP) 25% and 30% (MP) 30% and 35% (MP) DP = distal papilla; MF = mid-facial gingival; MP = mesial papilla. TABLE 7. Changes in the interdental papilla Parameters Amount of change p-value Mesial papilla level 1.342* Distal papilla level 1.242* *Z value design, flapless surgery, and applied a particulate bone graft between the tooth socket and the implant, which may account for the reported increase in interproximal bone height over the observation period. Soft tissue measurements have been reported in only a few studies utilizing immediate placement and immediate provisional restoration of implants in the anterior maxilla. This study showed mean mid-buccal gingival recession of 0.20 mm, whereas the mesial and distal papillae were apically positioned by 0.50 and 0.30 mm respectively, compared with baseline. Overall, no statistically significant changes in the aesthetically important mid-buccal soft tissue profile were found compared with baseline. Furthermore, no statistically significant changes in papilla levels were noted when the results were accurately measured in millimeters. This indicates a short-medium term stability of the soft tissue architecture around immediately placed and restored implants. The soft tissue loss noted in this study was of minimal clinical significance and did not appear to influence the esthetic outcome. This is further supported by the fact that there were no 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. DOI /jerd Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry Vol No
10 differences in Jemt s index indicating no changes in the papillary fill of the interdental embrasure, which is of importance in terms of the esthetic outcome. 15 It should also be noted that there was apical drift of the mesial papillae more than that of the distal papillae and mid-facial tissue. The greater mesial papilla tissue loss can be attributed to the fact that the sample included four implants replacing both central incisors in two patients. In this case, the mesial papillae were bordered by implants on both sides, and it is widely recognized that greater soft tissue loss occurs between two implants compared with an implant and an adjacent natural tooth. 32 The method being used for this study to record soft tissue measurements is different from other studies, 23,25,27 which used a reference line connecting the mid-facial gingival level of the two teeth adjacent to the implant restoration. However, flap elevation was used for access in these studies, which may lead to variability of the position of the reference line connecting the mid-facial gingiva of the adjacent teeth, as some soft tissue recession generally occurs following the elevation of a full mucoperiosteal flap. The reference line used in our study extended from the incisal edges of the teeth adjacent to the implant, and this acted as a fixed and stable reference. The soft tissue outcomes reported in this study compare favorably with the available literature. In a study that assessed 35 patients with single immediately placed and restored maxillary implants, the soft tissue loss from the facial aspect was greater than that reported in our study, with 0.55 mm loss at the follow-up period of 1 year. 23 Similar results were reported by De Rouck and colleagues with an average mid-buccal recession of 0.53 mm in the first year of function. 6 Another study by Cornelini and colleagues reported 0.75 mm mid-facial tissue loss after 1 year. 27 The somewhat superior outcomes reported in this study may be attributable to differences in implant design (platform switch versus regular platform, internal versus external attachment) and surgical protocols (flap elevation versus flapless, augmentation of gap between implant and socket walls). In terms of longer term changes, a recent paper published by Cosyn and colleagues revealed a mean mesial and distal papilla height loss of 0.05 and 0.08 mm, respectively. 30 The mid-facial soft tissue recession was 0.34 mm. The mesial papillae showed significant regrowth between the 1- and 3-year follow-ups. Advanced midfacial recession was found in 2/25 (8%) cases. 30 Kan and colleagues showed that following a 4-year follow-up period, the changes in mean mesial and distal papilla levels ( 0.22 and 0.21 mm, respectively) were significantly less than those observed at the 1-year follow-up. However, the mean overall facial gingival level change ( 1.13 mm) was significantly greater than that observed at the 1-year follow-up ( 0.55 mm), which means that papillary height may improve over time, although changes in the position of the labial margin may deteriorate. 32 Therefore, long-term studies are required to document the long-term esthetic outcomes of implant treatment in the anterior maxillary region. In comparison with other treatment protocols, studies with data on the soft tissue changes following single tooth implant placement in healed sockets reveal around 0.6 mm of mid-facial recession within the first year of placement. 33,34 In a study using the conventional technique (two stages) with a follow-up period of 3 years, the mean recession on the mid-facial aspect of the implant was found to be 1 mm. 35 Overall, the results of the present investigation demonstrate a relatively limited loss of soft tissue on the mid-facial aspect. This fact can be attributed to atraumatic extraction of the failed teeth, flapless surgical approach, and the use of a particulate xenograft. It is noteworthy that flapless surgery presents increased risk for perforation of the alveolar bone, and the experience of the surgeon is an important factor that minimizes that risk. 36 Insertion of bone grafting material (Bio-Oss) into the gap between the implant and the walls of the extraction socket assists in preserving a stable level of the hard tissues, 13 and hence the overlying soft tissue profile, as the Bio-Oss particles would not significantly resorb over the duration of the study. Finally, the use of screw-retained instead of cemented temporary restorations may contribute to the 10 Vol No 2013 Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry DOI /jerd Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
11 absence of complications during the initial stages of wound healing and maturation. In contrast, fistula formation was reported in a study conducted by Kan and his associates using a cemented type of temporary crowns. 19 It is important to note that mid-facial recession does not necessarily imply an esthetic compromise. An interesting finding in one case (FR) was that the recession at the mid-facial aspect actually improved the patient esthetic, as the level of the adjacent tooth buccal soft tissue was already apically displaced (Figure 6). The papillary height changes observed in this study appear to be in accordance with other studies. Kan and colleagues reported a mean loss of 0.50 mm for the mesial papillae and 0.30 mm mean loss of the distal papillae. 23 De Rouck and his associates showed a reduction in the papillae height loss of 0.41 mm on average for mesial papillae and 0.31 mm for distal papillae. 6 No statistically significant differences were found between the papillae levels at baseline and follow-up in terms of Jemt s index. 15 A study by Cornelini and colleagues found no scores of 0, 1, or 4 in their sample, with 60% of papillae receiving a score of 2, with the remainder scoring a In another study by Kan and colleagues the papilla index was measured at pretreatment and 3, 6, and 12 months following implant placement with no differences noted between baseline and any of the follow-up observations. 7 Therefore, the findings of our study in relation to Jemt s index are consistent with the published literature. This clinical investigation was limited by the retrospective nature, the small sample size, the inability to secure a fully standardized follow-up examination protocol for all patients and the relatively small length of the observation period. All of these factors can have a significant impact on the results obtained from this study, which should be interpreted with caution. Nevertheless, the study has provided some indications as to the nature and extent of soft and hard tissue changes that may be expected with this protocol, although it remains unclear if the soft tissue outcomes would remain stable over time. A longer observation period and a larger sample size are needed to support more definite conclusions. Notwithstanding the limitations of the study, the results indicate that the immediate placement and provisional restoration of a single tooth implant in the anterior maxilla can result in predictable implant osseointegration, as well as stable peri-implant tissues, for up to 23.2 ± 7.6 months. DISCLOSURE The authors have no financial interest in any of the companies whose products are mentioned in this paper. REFERENCES 1. Albrektsson T, Branemark PI, Hansson HA, Lindstrom J. Osseointegrated titanium implants. Requirements for ensuring a long-lasting, direct bone-to-implant anchorage in man. Acta Orthop Scand 1981;52: Branemark PI, Adell R, Albrektsson T, et al. Osseointegrated titanium fixtures in the treatment of edentulousness. Biomaterials 1983;4: Becker W, Becker BE, Israelson H, et al. One-step surgical placement of Branemark implants: a prospective multicenter clinical study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1997;12: Lazzara RJ. Immediate implant placement into extraction sites: surgical and restorative advantages. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 1989;9: Gomes A, Lozada JL, Caplanis N, Kleinman A. Immediate loading of a single hydroxyapatite-coated threaded root form implant: a clinical report. J Oral Implantol 1998;24: De Rouck T, Collys K, Cosyn J. Immediate single-tooth implants in the anterior maxilla: a 1-year case cohort study on hard and soft tissue response. J Clin Periodontol 2008;35: Kan JY, Rungcharassaeng K, Liddelow G, et al. Periimplant tissue response following immediate provisional restoration of scalloped implants in the esthetic zone: a one-year pilot prospective multicenter study. J Prosthet Dent 2007;97(6 Suppl): Esposito M, Grusovin G, Achile H, et al. Interventions for replacing missing teeth: Different times for loading dental implants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2009;(1):CD Wiley Periodicals, Inc. DOI /jerd Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry Vol No
12 9. Chaushu G, Chaushu S, Tzohar A, Dayan D. Immediate loading of single-tooth implants: immediate versus non-immediate implantation. A clinical report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2001;16: Neves M, Correia A, Alves CC. A novel approach to preserve the buccal wall in immediate implant cases: a clinical report. J oral implant 2013;39(2): Cornelini R, Scarano A, Covani U, et al. Immediate one-stage postextraction implant: a human clinical and histologic case report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2000;15: Botticelli D, Berglundh T, Lindhe J. Hard-tissue alterations following immediate implant placement in extraction sites. J Clin Periodontol 2004;31: Araujo MG, Linder E, Lindhe J. Bio-Oss collagen in the buccal gap at immediate implants: a 6-month study in the dog. Clin Oral Implants Res 2011;22(1): Esposito M, Grusovin MG, Worthington HV. Interventions for replacing missing teeth: antibiotics at dental implant placement to prevent complications. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2013;(7):CD Jemt T. Regeneration of gingival papillae after single-implant treatment. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 1997;17: Vandeweghe S, Nicolopoulos C, Thevissen E, et al. Immediate loading of screw-retained all-ceramic crowns in immediate versus delayed single implant placement. Int J Prosthodont 2013;26(5): Raes F, Cooper LF, Tarrida LG, et al. A case-control study assessing oral-health-related quality of life after immediately loaded single implants in healed alveolar ridges or extraction sockets. Clin Oral Implants Res 2012;23(5): De Bruyn H, Raes F, Cooper LF, et al. Three-years clinical outcome of immediate provisionalization of single Osseospeed() implants in extraction sockets and healed ridges. Clin Oral Implants Res 2013;24(2): Cooper LF, Raes F, Reside GJ, et al. Comparison of radiographic and clinical outcomes following immediate provisionalization of single-tooth dental implants placed in healed alveolar ridges and extraction sockets. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2010;25(6): Calvo Guirado JL, Saez Yuguero R, Ferrer Perez V, Moreno Pelluz A. Immediate anterior implant placement and early loading by provisional acrylic crowns: a prospective study after a one-year follow-up period. J Ir Dent Assoc 2002;48: Canullo L, Rasperini G. Preservation of peri-implant soft and hard tissues using platform switching of implants placed in immediate extraction sockets: a proof-of-concept study with 12- to 36-month follow-up. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2007;22: Hui E, Chow J, Li D, et al. Immediate provisional for single-tooth implant replacement with Branemark system: preliminary report. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2001;3: Kan JY, Rungcharassaeng K, Umezu K, Kois JC. Dimensions of peri-implant mucosa: an evaluation of maxillary anterior single implants in humans. J Periodontol 2003;74: Tsirlis AT. Clinical evaluation of immediate loaded upper anterior single implants. Implant Dent 2005;14: Ferrara A, Galli C, Mauro G, Macaluso GM. Immediate provisional restoration of postextraction implants for maxillary single-tooth replacement. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2006;26: Norton MR. A short-term clinical evaluation of immediately restored maxillary TiOblast single-tooth implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2004; 19: Cornelini R, Cangini F, Covani U, Wilson TG Jr. Immediate restoration of implants placed into fresh extraction sockets for single-tooth replacement: a prospective clinical study. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2005;25: Palattella P, Torsello F, Cordaro L. Two-year prospective clinical comparison of immediate replacement vs. immediate restoration of single tooth in the esthetic zone. Clin Oral Implants Res 2008;19: Lorenzoni M, Pertl C, Zhang K, et al. Immediate loading of single-tooth implants in the anterior maxilla. Preliminary results after one year. Clin Oral Implants Res 2003;14: Cosyn J, Eghbali A, De Bruyn H, et al. Immediate single-tooth implants in the anterior maxilla: 3-year results of a case series on hard and soft tissue response and aesthetics. J Clin Periodontol 2011;38(8): Kan JY, Rungcharassaeng K, Lozada JL, Zimmerman G. Facial gingival tissue stability following immediate placement and provisionalization of maxillary anterior single implants: a 2- to 8-year follow-up. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2011;26(1): Tarnow DP, Cho SC, Wallace SS. The effect of inter-implant distance on the height of inter-implant bone crest. J Periodontol 2000;71: Cardaropoli G, Lekholm U, Wennstrom JL. Tissue alterations at implant-supported single-tooth replacements: a 1-year prospective clinical study. Clin Oral Implants Res 2006;17: Grunder U. Stability of the mucosal topography around single-tooth implants and adjacent teeth: 1-year results. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2000;20: Choquet V, Hermans M, Adriaenssens P, et al. Clinical and radiographic evaluation of the papilla level adjacent 12 Vol No 2013 Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry DOI /jerd Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
13 to single-tooth dental implants. A retrospective study in the maxillary anterior region. J Periodontol 2001;72: Oh TJ, Shotwell J, Billy E, et al. Flapless implant surgery in the esthetic region: advantages and precautions. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2007;27: Reprint requests: Saso Ivanovski, School of Dentistry and Oral Health, Griffith University, High Street, Southport, Qld 4215, Australia; Tel.: ; Fax: ; s.ivanovski@griffith.edu.au 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. DOI /jerd Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry Vol No
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry
 Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
Hyun-Jae Cho, Kun-Soo Jang, Ki-Hyun Jeong, Jae-Yun Jeon, Kyung-Gyun Hwang, Chang-Joo Park
 Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
Immediate Implant Placement Along With Guided Bone Regeneration In Mandibular Anterior Region A Case Report.
 IMMEDIATE IMPLANT PLACEMENT ALONG WITH GUIDED BONE REGENERATION IN MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR REGION A CASE REPORT. Dr.C.P.Dhivakar 1, Dr.T.Saravanan 2, Dr.A.Aniz 3 1) Department of Periodontics, Karpaga Vinayaga
IMMEDIATE IMPLANT PLACEMENT ALONG WITH GUIDED BONE REGENERATION IN MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR REGION A CASE REPORT. Dr.C.P.Dhivakar 1, Dr.T.Saravanan 2, Dr.A.Aniz 3 1) Department of Periodontics, Karpaga Vinayaga
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants
 Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Evaluation of immediate loading of single dental implants in the maxillary esthetic zone: Clinical and radiographical comparative study
 Evaluation of immediate loading of single dental implants in the maxillary esthetic zone: Clinical and radiographical comparative study Received: 9/6/2013 Accepted: 30/7/2013 Serwan Saeb Al Naqshabandi
Evaluation of immediate loading of single dental implants in the maxillary esthetic zone: Clinical and radiographical comparative study Received: 9/6/2013 Accepted: 30/7/2013 Serwan Saeb Al Naqshabandi
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1.
 Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
Working together as a team, the periodontist
 The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area
 CLINICAL SCIENCE IJOICR Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area 1 Pedro Peña Martinez, 2 Ramón Palomero Langner, 3 Ramón Palomero
CLINICAL SCIENCE IJOICR Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area 1 Pedro Peña Martinez, 2 Ramón Palomero Langner, 3 Ramón Palomero
Nabil Omar Khzam. BDSc. School of Dentistry and Oral Health. Griffith Health. Griffith University
 Dimensional changes in the supporting tissues following immediate placement and restoration of dental implants in the aesthetic zone: a retrospective study Nabil Omar Khzam BDSc School of Dentistry and
Dimensional changes in the supporting tissues following immediate placement and restoration of dental implants in the aesthetic zone: a retrospective study Nabil Omar Khzam BDSc School of Dentistry and
Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:60-66 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.2.60 Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans Ji Young
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:60-66 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.2.60 Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans Ji Young
The following resources related to this article are available online at jada.ada.org ( this information is current as of July 11, 2011):
 Implants or Pontics: Decision Making for Anterior Tooth Replacement Frank Spear J Am Dent Assoc 2009;140;1160-1166 The following resources related to this article are available online at jada.ada.org (
Implants or Pontics: Decision Making for Anterior Tooth Replacement Frank Spear J Am Dent Assoc 2009;140;1160-1166 The following resources related to this article are available online at jada.ada.org (
Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations
 C L I N I C A L Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations William C Martin, 1 Emma Lewis, 2 Dean Morton 3 1 DMD, MS, Associate Professor & Clinical Director, Center for Implant Dentistry,
C L I N I C A L Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations William C Martin, 1 Emma Lewis, 2 Dean Morton 3 1 DMD, MS, Associate Professor & Clinical Director, Center for Implant Dentistry,
Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report
 Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
The majority of the early research concerning
 Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
The effect of peri-implant bone exposure on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:20-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20 on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants Seung-Yun Shin 1, Seung-Boem Kye 1, Jongrak
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:20-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20 on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants Seung-Yun Shin 1, Seung-Boem Kye 1, Jongrak
Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants. Agenda. Agenda. Smile line revitalization with implants Priest Prosthodontics, LLC 1
 Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants Board Certified Prosthodontist Hilton Head Island, SC Agenda Implant placement and esthetic potential Single immediate implant placement Soft tissue preservation
Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants Board Certified Prosthodontist Hilton Head Island, SC Agenda Implant placement and esthetic potential Single immediate implant placement Soft tissue preservation
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery
 Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
IMPACT OF IMMEDIATE AND NON-IMMEDIATE PROVISIONALIZATION ON THE SOFT TISSUE ESTHETICS OF FINAL RESTORATIONS ON IMMEDIATELY PLACED IMPLANTS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE IMPACT OF IMMEDIATE AND NON-IMMEDIATE PROVISIONALIZATION ON THE SOFT TISSUE ESTHETICS OF FINAL RESTORATIONS ON IMMEDIATELY PLACED IMPLANTS Chong-Hyun Han 1, DDS, PhD, Jeong-Won Paik 2,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE IMPACT OF IMMEDIATE AND NON-IMMEDIATE PROVISIONALIZATION ON THE SOFT TISSUE ESTHETICS OF FINAL RESTORATIONS ON IMMEDIATELY PLACED IMPLANTS Chong-Hyun Han 1, DDS, PhD, Jeong-Won Paik 2,
Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report
 Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations
 Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations Aldo Leopardi, BDS, DDS, MS Practice Limited to Implant, Fixed and Removable Prosthodontics Greenwood Village, Colorado www.knowledgefactoryco.com
Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations Aldo Leopardi, BDS, DDS, MS Practice Limited to Implant, Fixed and Removable Prosthodontics Greenwood Village, Colorado www.knowledgefactoryco.com
Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident
 Case Report 13 2011 Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident Dr Hitoshi Minagawa Tokyo, Japan Prosthetics Dr Hitoshi Minagawa successfully completed his studies
Case Report 13 2011 Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident Dr Hitoshi Minagawa Tokyo, Japan Prosthetics Dr Hitoshi Minagawa successfully completed his studies
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 47 Provisional Restorations Used in Immediate Implant Placement Provide a Platform to Promote Peri-implant Soft Tissue Healing: A Pilot
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 47 Provisional Restorations Used in Immediate Implant Placement Provide a Platform to Promote Peri-implant Soft Tissue Healing: A Pilot
Management of a complex case
 2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
Since the introduction of osseointegrated dental implants
 CLINICAL Papilla Formation in Response to Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery and Immediate Restoration Paul A. Schnitman, DDS, MSD 1 * Chie Hayashi, DDS, PhD, MMSc 2 This retrospective analysis was undertaken
CLINICAL Papilla Formation in Response to Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery and Immediate Restoration Paul A. Schnitman, DDS, MSD 1 * Chie Hayashi, DDS, PhD, MMSc 2 This retrospective analysis was undertaken
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 2011 BY QUINTESSENCE PUBLISHING CO, INC. PRINTING OF THIS DOCUMENT IS RESTRICTED TO PERSONAL USE ONLY.. 215 Dental Cone Beam Computed Tomography
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 2011 BY QUINTESSENCE PUBLISHING CO, INC. PRINTING OF THIS DOCUMENT IS RESTRICTED TO PERSONAL USE ONLY.. 215 Dental Cone Beam Computed Tomography
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial
 Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial Lars Schropp, DDS, PhD /Flemming Isidor, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont /Lambros Kostopoulos,
Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial Lars Schropp, DDS, PhD /Flemming Isidor, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont /Lambros Kostopoulos,
Esthetic evaluation of periimplant soft tissue of immediate single-implant placement and provisionalization in the anterior maxilla
 Esthetic evaluation of periimplant soft tissue of immediate single-implant placement and provisionalization in the anterior maxilla Franck Bonnet, DDS Private Practice, Cannes, Le Cannet, France Director
Esthetic evaluation of periimplant soft tissue of immediate single-implant placement and provisionalization in the anterior maxilla Franck Bonnet, DDS Private Practice, Cannes, Le Cannet, France Director
The patient gave a history of hypertension and gastritis for which was taking Lacidipine 4mg, Omeprazole 20mg and Simvastatin 40mg.
 A.S. was referred by her general dental practitioner for assessment for possible implant placement to restore the space where her bridge replacing her maxillary central incisors had recently failed. Fig
A.S. was referred by her general dental practitioner for assessment for possible implant placement to restore the space where her bridge replacing her maxillary central incisors had recently failed. Fig
Immediate Implant Placement:
 Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 27 Flapless Implant Surgery in the Esthetic Region: Advantages and Precautions Tae-Ju Oh, DDS, MS 1 /Jeffrey Shotwell, DDS, MS 2 Edward
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 27 Flapless Implant Surgery in the Esthetic Region: Advantages and Precautions Tae-Ju Oh, DDS, MS 1 /Jeffrey Shotwell, DDS, MS 2 Edward
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Inclusive Tooth Replacement System
 Optimizing Anterior Esthetics with the Inclusive Tooth Replacement System by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant treatment has changed so much over the years. In the past it was acceptable to place
Optimizing Anterior Esthetics with the Inclusive Tooth Replacement System by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant treatment has changed so much over the years. In the past it was acceptable to place
Restoring esthetics by immediately loaded implant placement Jurel SK 1, Gupta DS 2, Agarwal H 3, Singh RD 4, Aggarwal KK 5
 Restoring esthetics by immediately loaded implant placement Jurel SK 1, Gupta DS 2, Agarwal H 3, Singh RD 4, Aggarwal KK 5 Case Report 1 Dr. Sunit K Jurel MDS, Assistant professor Department of Prosthodontics
Restoring esthetics by immediately loaded implant placement Jurel SK 1, Gupta DS 2, Agarwal H 3, Singh RD 4, Aggarwal KK 5 Case Report 1 Dr. Sunit K Jurel MDS, Assistant professor Department of Prosthodontics
Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants
 Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior Region Along with Soft and Hard Tissue Grafting- A Case Report.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report
 C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry
 Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD With continual improvements in the design and production
Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD With continual improvements in the design and production
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Patients esthetic demands and
 Predictable Periimplant Gingival Esthetics: Use of the Natural Tooth as a Provisional following Implant Placement ROBERT C. MARGEAS, DDS* ABSTRACT Maintaining the interdental papilla and bone height following
Predictable Periimplant Gingival Esthetics: Use of the Natural Tooth as a Provisional following Implant Placement ROBERT C. MARGEAS, DDS* ABSTRACT Maintaining the interdental papilla and bone height following
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 401 Guidelines for Selecting the Implant Diameter During Immediate Implant Placement of a Fresh Extraction Socket: A Case Series Ariádene
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 401 Guidelines for Selecting the Implant Diameter During Immediate Implant Placement of a Fresh Extraction Socket: A Case Series Ariádene
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
University of Groningen. Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten
 University of Groningen Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
Immediate implant placement in a single staged
 Bone and Crescent Shaped Free Gingival Grafting for Anterior Immediate Implant Placement: Technique and Case Report Han et al Thomas Han, DDS, MS 1 2 Abstract Immediate implant placement in a single staged
Bone and Crescent Shaped Free Gingival Grafting for Anterior Immediate Implant Placement: Technique and Case Report Han et al Thomas Han, DDS, MS 1 2 Abstract Immediate implant placement in a single staged
Alveolar ridge preservation techniques
 Alveolar ridge preservation techniques Semmelweis University, Department of Periodontology, Budapest Dr. Windisch Péter Head of Department of Periodontology Changes of the alveolar ridge dimensions after
Alveolar ridge preservation techniques Semmelweis University, Department of Periodontology, Budapest Dr. Windisch Péter Head of Department of Periodontology Changes of the alveolar ridge dimensions after
by Paul S. Petrungaro, DDS, MS,
 Cr e a t i o n a n d Preservation o f Na t u ra l So f t Tissue Em e r g e n c e Profiles Ar o u n d Dental Implants in the Esthetic Zone by Paul S. Petrungaro, DDS, MS, FICD, FACD, DICOI Chicago, IL Lake
Cr e a t i o n a n d Preservation o f Na t u ra l So f t Tissue Em e r g e n c e Profiles Ar o u n d Dental Implants in the Esthetic Zone by Paul S. Petrungaro, DDS, MS, FICD, FACD, DICOI Chicago, IL Lake
Surgery All at Once : Socket preservation and immediate placement of an implant in an infected site in the anterior region a Case Report
 Surgery All at Once : Socket preservation and immediate placement of an implant in an infected site in the anterior region a Case Report W.P. van der Schoor*, A.R.M. van der Schoor Tooth extraction followed
Surgery All at Once : Socket preservation and immediate placement of an implant in an infected site in the anterior region a Case Report W.P. van der Schoor*, A.R.M. van der Schoor Tooth extraction followed
Peri-implant Augmentation
 Indication Sheet PIR3 Peri-implant Augmentation Early implantation with simultaneous GBR for contour augmentation using the technique by Prof. Daniel Buser and Prof. Urs Belser, University of Berne, Switzerland
Indication Sheet PIR3 Peri-implant Augmentation Early implantation with simultaneous GBR for contour augmentation using the technique by Prof. Daniel Buser and Prof. Urs Belser, University of Berne, Switzerland
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 07 Page July 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i7.101 Immediate Implant Following
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i7.101 Immediate Implant Following
Several extraction socket classifications have been
 Case Report Type 3 ReceSSion DefeCTS Clinical Management of Type 3 Recession Defects With Immediate Implant and Provisional Restoration Therapy: A Case Report Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS; and Stephen J. Chu,
Case Report Type 3 ReceSSion DefeCTS Clinical Management of Type 3 Recession Defects With Immediate Implant and Provisional Restoration Therapy: A Case Report Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS; and Stephen J. Chu,
The 2B-3D rule for implant planning, placement and restoration
 IJOI 27 INTERDISCIPLINARY TREATMENT The 2B-3D rule for implant planning, placement and restoration 1. What is biologic width? Is there a golden rule for implant planning, placement and restoration as the
IJOI 27 INTERDISCIPLINARY TREATMENT The 2B-3D rule for implant planning, placement and restoration 1. What is biologic width? Is there a golden rule for implant planning, placement and restoration as the
Prosthodonticstown. Immediate Implant Placement in Fresh Extraction Sites. clinical. Table I
 Prosthodonticstown clinical Immediate Implant Placement in Fresh Extraction Sites Charles A. Babbush, DDS, MScD Table I Benefits Of Immediate Implantation Improved prosthesis fabrication and/or design
Prosthodonticstown clinical Immediate Implant Placement in Fresh Extraction Sites Charles A. Babbush, DDS, MScD Table I Benefits Of Immediate Implantation Improved prosthesis fabrication and/or design
Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 10 Issue Date: March 2005, Posted On: 5/2/2005 Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS Figure 1. A 43-year-old female
Page 1 of 10 Issue Date: March 2005, Posted On: 5/2/2005 Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS Figure 1. A 43-year-old female
Successful osseointegration of implants has been
 Therapeutic Management for Immediate Implant Placement in Sites with Periapical Deficiencies Where Coronal Bone Is Present: Technique and Case Report Cyril I. Evian, DMD 1 /Ahmed Al-Momani, BDS 2 /Edwin
Therapeutic Management for Immediate Implant Placement in Sites with Periapical Deficiencies Where Coronal Bone Is Present: Technique and Case Report Cyril I. Evian, DMD 1 /Ahmed Al-Momani, BDS 2 /Edwin
Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas
 2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
A Short-term Clinical Evaluation of Immediately Restored Maxillary TiOblast Single-Tooth Implants. Michael R. Norton, BDS 1
 A Short-term Clinical Evaluation of Immediately Restored Maxillary TiOblast Single-Tooth Implants Michael R. Norton, BDS 1 Purpose: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the short-term clinical outcome
A Short-term Clinical Evaluation of Immediately Restored Maxillary TiOblast Single-Tooth Implants Michael R. Norton, BDS 1 Purpose: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the short-term clinical outcome
Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol. 15 No. 03 July 16
 Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol. 5 No. 03 July 6 Original article Dimensional changes of hard and soft tissue after immediate implantation in comparison with conventional tooth extraction Radvar
Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol. 5 No. 03 July 6 Original article Dimensional changes of hard and soft tissue after immediate implantation in comparison with conventional tooth extraction Radvar
Immediate placement and provisionalization of an implant after removal of an impacted maxillary canine: two case reports
 Zuiderveld et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2015) 1:13 DOI 10.1186/s40729-015-0013-3 CASE REPORT Open Access Immediate placement and provisionalization of an implant after removal of
Zuiderveld et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2015) 1:13 DOI 10.1186/s40729-015-0013-3 CASE REPORT Open Access Immediate placement and provisionalization of an implant after removal of
Advanced Esthetic Management of Dental Implants: Surgical and Restorative Considerations to Improve Outcomes
 CLINICAL ARTICLE Advanced Esthetic Management of Dental Implants: Surgical and Restorative Considerations to Improve Outcomes BARRY P. LEVIN, DMD*, SERGIO RUBINSTEIN, DDS, LOUIS F. ROSE, DDS, MD ** ABSTRACT
CLINICAL ARTICLE Advanced Esthetic Management of Dental Implants: Surgical and Restorative Considerations to Improve Outcomes BARRY P. LEVIN, DMD*, SERGIO RUBINSTEIN, DDS, LOUIS F. ROSE, DDS, MD ** ABSTRACT
INTRODUCTION. Jun-Won Hong 1, DDS, MS, Seung-Geun Ahn 1, DDS, PhD, Dae-Ho Leem 2, DDS, PhD, Jae-Min Seo 1 *, DDS, MS
 CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.4047/jap.2012.4.1.52 Immediate placement and functional loading of implants on canine with fixed partial denture for a patient having canine protected occlusion: a case
CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.4047/jap.2012.4.1.52 Immediate placement and functional loading of implants on canine with fixed partial denture for a patient having canine protected occlusion: a case
Providing patients with optimal esthetics remains
 Volume 78 Number 4 Case Series Optimizing the Esthetic Potential of Implant Restorations Through the Use of Immediate Implants With Immediate Provisionals Brien V. Harvey* Background: Few things in clinical
Volume 78 Number 4 Case Series Optimizing the Esthetic Potential of Implant Restorations Through the Use of Immediate Implants With Immediate Provisionals Brien V. Harvey* Background: Few things in clinical
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Clinical outcome of submerged vs. non-submerged implants placed in fresh extraction sockets
 Luca Cordaro Ferruccio Torsello Mario Roccuzzo Clinical outcome of submerged vs. non-submerged implants placed in fresh extraction sockets Author s affiliations: Luca Cordaro, Ferruccio Torsello, Eastman
Luca Cordaro Ferruccio Torsello Mario Roccuzzo Clinical outcome of submerged vs. non-submerged implants placed in fresh extraction sockets Author s affiliations: Luca Cordaro, Ferruccio Torsello, Eastman
It is well-known that osseointegrated implants do not
 Infraposition of Implant-Retained Maxillary Incisor Crown Placed in an Adult Patient: Case Report Roberto Cocchetto, MD, DDS 1 /Luigi Canullo, DDS 2 /Renato Celletti, MD, DDS 3 Several studies have clearly
Infraposition of Implant-Retained Maxillary Incisor Crown Placed in an Adult Patient: Case Report Roberto Cocchetto, MD, DDS 1 /Luigi Canullo, DDS 2 /Renato Celletti, MD, DDS 3 Several studies have clearly
Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A Case report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 97-101 Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 97-101 Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A
Clinical Case Reports using Cytoplast GTR Barrier Membranes
 Clinical Case Reports using Cytoplast GTR Barrier Membranes Barry K. Bartee, DDS, MD The Cytoplast Technique: Extraction Site Grafting Without Primary Closure 1. 1. Preoperative view. To maximize the result
Clinical Case Reports using Cytoplast GTR Barrier Membranes Barry K. Bartee, DDS, MD The Cytoplast Technique: Extraction Site Grafting Without Primary Closure 1. 1. Preoperative view. To maximize the result
Research Article Interdental Papilla Length and the Perception of Aesthetics in Asymmetric Situations
 International Dentistry Volume 2015, Article ID 125146, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/125146 Research Article Interdental Papilla Length and the Perception of Aesthetics in Asymmetric Situations
International Dentistry Volume 2015, Article ID 125146, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/125146 Research Article Interdental Papilla Length and the Perception of Aesthetics in Asymmetric Situations
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 715 Immediate Implant Placement and Loading of Single Implants in the Esthetic Zone: Clinical Outcome and Esthetic Evaluation in a Japanese
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 715 Immediate Implant Placement and Loading of Single Implants in the Esthetic Zone: Clinical Outcome and Esthetic Evaluation in a Japanese
Extraction Defect: Assessment, Classification and Management
 International Extraction Journal Defect: of Clinical Assessment, Implant Dentistry, Classification January-April and Management 2009;1(1):1-11 Extraction Defect: Assessment, Classification and Management
International Extraction Journal Defect: of Clinical Assessment, Implant Dentistry, Classification January-April and Management 2009;1(1):1-11 Extraction Defect: Assessment, Classification and Management
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 67 Efficacy Evaluation of a New Buccal Bone Plate Preservation Technique: A Pilot Study Federico Brugnami, DDS* Alfonso Caiazzo, DDS**
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 67 Efficacy Evaluation of a New Buccal Bone Plate Preservation Technique: A Pilot Study Federico Brugnami, DDS* Alfonso Caiazzo, DDS**
Planning: The key to obtaining aesthetic and functional results in implant-supported restorations
 case report Planning: The key to obtaining aesthetic and functional results in implant-supported restorations Hugo A. ALBERA 1, Estela M. Ribotta de ALBERA 2 Several factors determine the success of functional
case report Planning: The key to obtaining aesthetic and functional results in implant-supported restorations Hugo A. ALBERA 1, Estela M. Ribotta de ALBERA 2 Several factors determine the success of functional
CHAPTER. 1. Uncontrolled systemic disease 2. Retrognathic jaw relationship
 CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive. maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years.
 Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
MODIFIED SINGLE ROLL FLAP APPROACH FOR SIMULTANEOUS IMPLANT PLACEMENT AND GINGIVAL AUGMENTATION
 Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
An esthetic zone implant
 clinical brief inside my practice peer to peer spotlight tech profile Surgical and Prosthetic Treatment of a Failed Maxillary Central Incisor Immediate implant placement is a key to success Robert A. Levine,
clinical brief inside my practice peer to peer spotlight tech profile Surgical and Prosthetic Treatment of a Failed Maxillary Central Incisor Immediate implant placement is a key to success Robert A. Levine,
The impact of immediately placed and restored single-tooth implants on hard and soft tissues in the anterior maxilla
 REVIEW S89 Paul Weigl, Antonio Strangio The impact of immediately placed and restored single-tooth implants on hard and soft tissues in the anterior maxilla Key words immediate implant placement, immediate
REVIEW S89 Paul Weigl, Antonio Strangio The impact of immediately placed and restored single-tooth implants on hard and soft tissues in the anterior maxilla Key words immediate implant placement, immediate
Immediate post-extraction BIOMIMETIC CORAL IC implant placement in the anterior esthetic zone
 Immediate post-extraction BIOMIMETIC CORAL IC implant placement in the anterior esthetic zone AUTHORS Dr. Antonio Mallebrera Clinica Mallebrera Centro Dental (Petrer, Alicante) Sr. Juan José Sempere Matarredona
Immediate post-extraction BIOMIMETIC CORAL IC implant placement in the anterior esthetic zone AUTHORS Dr. Antonio Mallebrera Clinica Mallebrera Centro Dental (Petrer, Alicante) Sr. Juan José Sempere Matarredona
Immediate implants at fresh extraction sockets: from myth to reality
 Periodontology 2000, Vol. 66, 2014, 132 152 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 Immediate implants at fresh extraction
Periodontology 2000, Vol. 66, 2014, 132 152 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 Immediate implants at fresh extraction
Initially, implant dentistry was focused on
 CASE LETTER Correction of Esthetic Complications of a Malpositioned Implant: A Case Letter Sergio Alexandre Gehrke, PhD INTRODUCTION Initially, implant dentistry was focused on successful osseointegration
CASE LETTER Correction of Esthetic Complications of a Malpositioned Implant: A Case Letter Sergio Alexandre Gehrke, PhD INTRODUCTION Initially, implant dentistry was focused on successful osseointegration
Immediate placement and restoration of implants in the esthetic zone: Trimodal Approach therapeutic options
 CLINICAL RESEARCH Immediate placement and restoration of implants in the esthetic zone: Trimodal Approach therapeutic options Gustavo Cabello Domínguez, DMD Periodontology, Private Practice, Málaga, Spain
CLINICAL RESEARCH Immediate placement and restoration of implants in the esthetic zone: Trimodal Approach therapeutic options Gustavo Cabello Domínguez, DMD Periodontology, Private Practice, Málaga, Spain
Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique
 e116 Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique Sang-Hoon Park, DDS, MS* Hom-Lay Wang, DDS, MSD, PhD** This paper presents three cases of peri-implant
e116 Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique Sang-Hoon Park, DDS, MS* Hom-Lay Wang, DDS, MSD, PhD** This paper presents three cases of peri-implant
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
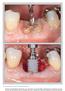 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 89 Pre-extractive Interradicular Implant Bed Preparation: Case Presentations of a Novel Approach to Immediate Implant Placement at Multirooted
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 89 Pre-extractive Interradicular Implant Bed Preparation: Case Presentations of a Novel Approach to Immediate Implant Placement at Multirooted
Ten tips that everyone should know before performing a treatment involving implants in the aesthetic zone.
 Ten tips that everyone should know before performing a treatment involving implants in the aesthetic zone. Introduction Francisco Teixeira Barbosa. Private practice. Barcelona. Spain. Nowadays, implantology
Ten tips that everyone should know before performing a treatment involving implants in the aesthetic zone. Introduction Francisco Teixeira Barbosa. Private practice. Barcelona. Spain. Nowadays, implantology
Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits. Your combination for success
 Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits Your combination for success Geistlich Combi-Kit Collagen: Combining ease and predictablility Geistlich Combi-Kit
Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits Your combination for success Geistlich Combi-Kit Collagen: Combining ease and predictablility Geistlich Combi-Kit
Conventional immediate implant placement and immediate placement with socket-shield technique Which is better
 International Journal of Clinical Medicine Research 2014; 1(5): 176-180 Published online December 30, 2014 (http://www.aascit.org/journal/ijcmr) ISSN: 2375-3838 Conventional immediate implant placement
International Journal of Clinical Medicine Research 2014; 1(5): 176-180 Published online December 30, 2014 (http://www.aascit.org/journal/ijcmr) ISSN: 2375-3838 Conventional immediate implant placement
TOPICS. T O P I C S Day 2. Introduction Surgical challenges to treat esthetic implant failures Treatment options & case reports Conclusions
 T O P I C S Day 2 Implant placement post extraction with simultaneous contour augmentation using GBR: When immediate, when early, when late? CAD-CAM technology and zirconia: new opportunities for esthetic
T O P I C S Day 2 Implant placement post extraction with simultaneous contour augmentation using GBR: When immediate, when early, when late? CAD-CAM technology and zirconia: new opportunities for esthetic
Replacing Hopeless Retained Deciduous Teeth in Adults Utilizing Dental Implants: Concepts and Case Presentation Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 7 Issue Date: November 2005, Posted On: 12/1/2005 Replacing Hopeless Retained Deciduous Teeth in Adults Utilizing Dental Implants: Concepts and Case Presentation Michael Tischler, DDS Hopeless
Page 1 of 7 Issue Date: November 2005, Posted On: 12/1/2005 Replacing Hopeless Retained Deciduous Teeth in Adults Utilizing Dental Implants: Concepts and Case Presentation Michael Tischler, DDS Hopeless
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
The Original remains unique.
 The Original remains unique. Geistlich leading regeneration 2A, 2B Geistlich is the world leader in regenerative dentistry. We transform natural biomaterials into safe and reliable treatment methods that
The Original remains unique. Geistlich leading regeneration 2A, 2B Geistlich is the world leader in regenerative dentistry. We transform natural biomaterials into safe and reliable treatment methods that
Immediate implant placement, with or without simultaneous implant provisionalization,
 Saving Her Smile by Panos Papaspyridakos, DDS, MS, PhD and Michael Vizirakis, DDS, MS Immediate Implant Placement and Fixed Provisionalization with Extracted Tooth Introduction Following tooth extraction,
Saving Her Smile by Panos Papaspyridakos, DDS, MS, PhD and Michael Vizirakis, DDS, MS Immediate Implant Placement and Fixed Provisionalization with Extracted Tooth Introduction Following tooth extraction,
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior
 Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
In the esthetic zone, osseointegration
 CASE REPORT A Method for Obtaining Peri-Implant Soft-Tissue Contours by Using Screw- Retained Provisional Restorations as Impression Copings: A Clinical Report Bi-Yuan Tsai, DDS, MS* In the esthetic zone,
CASE REPORT A Method for Obtaining Peri-Implant Soft-Tissue Contours by Using Screw- Retained Provisional Restorations as Impression Copings: A Clinical Report Bi-Yuan Tsai, DDS, MS* In the esthetic zone,
