Samer Saour, Guido Libondi, Venkat Ramakrishnan. Introduction
|
|
|
- Gabriel McCormick
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Microsurgical refinements with the use of internal mammary (IM) perforators as recipient vessels in transverse upper gracilis (TUG) autologous breast reconstruction Samer Saour, Guido Libondi, Venkat Ramakrishnan Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, St. Andrews Centre of Burns and Plastics, Broomfield Hospital, Chelmsford CM1 7ET, UK Contributions: (I) Conception and design: S Saour, V Ramakrishnan; (II) Administrative support: S Saour; (III) Provision of study materials or patients: V Ramakrishnan; (IV) Collection and assembly of data: S Saour; (V) Data analysis and interpretation: All authors; (VI) Manuscript writing: All authors; (VII) Final approval of manuscript: All authors. Correspondence to: Samer Saour. Microsurgical Fellow, Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, St. Andrews Centre of Burns and Plastics, Broomfield Hospital, Chelmsford CM1 7ET, UK. ssaour@hotmail.com. Background: The transverse upper gracilis (TUG) flap is the senior authors second choice for autologous breast reconstruction when the DIEP flap is not available. It provides durable, pliable tissue with well hidden scars. The main criticism of this flap is the limited volume, donor site complications, short pedicle and vessel mismatch depending on which recipient vessels are used. We described methods of reducing vessel mismatch, complications of venous coupler and refinements to help give a more superior aesthetic outcome. Methods: We describe several maneuvers to help reduce vessel mismatch with the use of the internal mammary (IM) perforator vessels with a modification of the Harashina fish-mouth technique or the use of a vessel bifurcation to increase vessel diameter. We also describe the optimum method of perforator preparation and potential methods to prevent palpable venous couplers. The author s describe their case series of 14 TUG flaps to reconstruct 13 breasts in 12 patients. Results: Eight unilateral, 2 partial breast reconstruction, 1 bilateral and 1 bilateral TUG flap for a unilateral reconstruction was carried out. All flaps survived with one partial flap necrosis, one donor site seroma and two cases of palpable/tender venous couplers. The mean reconstructed breast was 320 grams. Conclusions: The TUG flap is a reconstructive challenge, but with correct planning a good aesthetic outcome is possible. The IM perforator is our first choice recipient vessel in TUG breast reconstructions. With meticulous preparation and by overcoming vessel mismatch the use of this recipient vessel is a reliable option. Keywords: Breast reconstruction; IMA perforators; DIEP; transverse upper gracilis (TUG); autologous reconstruction Submitted Apr 10, Accepted for publication Apr 24, doi: /gs View this article at: Introduction Immediate breast reconstruction has the advantages of reducing the number of operations, reduced psychological morbidity, with better aesthetic outcomes as the skin envelope is preserved (1). Autologous breast reconstruction in thin patients presents a challenging problem. Thin patients are not considered ideal candidates for autologous reconstructions due to the lack of adequate adiposity (2). When making a decision about the choice of reconstruction, there are certain aspects that need to be considered. The patients over all fitness for surgery, any pre-operative radiotherapy, need for adjuvant therapy and the patients preference on the method of reconstruction
2 376 Saour et al. Microsurgical refinements with the use of IM perforators in TUG flaps after being fully educated on the available options. Autologous breast reconstructions have become the gold standard in most plastic surgery units, it provides an aesthetically pleasing and long lasting natural reconstruction (3-7) The DIEP flap has become the flap of choice in both unilateral and bilateral breast reconstructions. When the DIEP flap is not available, the second choice would either be a unilateral or bilateral transverse upper gracilis (TUG) flap. TUG flaps provide durable, pliable tissue for breast reconstruction with well hidden scars. In this paper we will discuss the technique of IMAP preparation the advantages and disadvantages of the IMA perforator in TUG flap reconstructions together with methods of correcting vessel size mismatch and potential methods to prevent/reduce the complication of venous coupler. Methods Computerised records of all patients undergoing TUG flap reconstructions involving the IMA perforators at St. Andrews Centre of Plastic Surgery between March 2015 and March 2016 were retrospectively reviewed. Patient demographics, the number of TUG flaps/ IMAP used, TUG flap weight, size of IMAP/IMVP vessel size, the size of the venous couplers used and complications were recorded. Results Over the 1 year period, 12 patients underwent 14 TUG flaps, 10 unilateral TUG flaps (8 for unilateral reconstruction post mastectomy and 2 for partial breast defects), 1 bilateral reconstruction and 1 bilateral TUG for a unilateral reconstruction. Average age was 53.25, range from 45 to 65. Average TUG weight was 320 grams with a range from 219 to 585 grams. Thirteen IMAP were used with an average IMVP size of 2.19 and average IMAP size of The average coupler size used was 2.11 (5 with 2.5 mm, 6 with 2 mm and 2 with 1.5 mm). Of the 12 cases there was one partial flap necrosis that required debridement and re-advancement of the flap, one case of donor site seroma which settled with multiple aspirations in the outpatient department and 2 cases of palpable/tender venous coupler both being 2.5 mm in size. Discussion The TUG flap is our second choice for autologous reconstruction when the DIEP flap is not available. When comparing it to the SGAP/IGAP flaps it provides more pliable tissue for breast reconstruction, it is a relatively straightforward flap to raise with the patient in a supine position. This is offset with a short pedicle, a higher donor site complication profile with wound breakdown, sensory disturbances, poor scarring and prolonged seroma formation (8,9). Various recipient vessels are available, IMA perforator, internal mammary (IM) vessels, IM perforators or thoracodorsal/serratus vessels. The IMA can be accessed by either removing a small section of costal cartilage or via an intercostal space technique. A rib-sparing technique which allows for a longer length of recipient vessel has been described by Hunter et al. This involves temporarily excising one of the costal cartilages in the subperichondrial plane. Once the IM vessels have been dissected from the rib below to the rib above the rib cartilage is replaced into its perichondrial lining. With the use of the thoracodorsal vessel or serratus branch a vein graft is often needed to allow medialisation of the TUG flap. The IMA perforator is our preferred recipient vessel during TUG flap reconstruction. The advantage of reducing morbidity and overall dissection time harvesting the IMAP vessels is offset by a more frequent diameter mismatch between the vessels used. Preparation of the perforator In this series the IMA perforator either the 2nd or 3rd was used to anastomose to the TUG vessels. It is critical that these vessels are not damaged during the mastectomy and their rough position should be marked prior to the mastectomy to prevent inadvertent damage. In some cases damage does occur but if at least 1cm of vessel above the pectoralis fascia is available this can still be used safely. Once the perforator is identified in the mastectomy skin distally it is advisable to dissect this off the mastectomy skin from distal to proximal. Attempting initial dissection proximally around the level of the pectoralis fascia can result in damage. Once the IMAP is dissected to the level of the pectoralis major muscle fascia, the muscle is carefully split to expose the vessel further. The artery size is then
3 Gland Surgery, Vol 6, No 4 August Figure 1 Shows the double wedge excision fish-mouth technique (12). Video 1. Shows the double wedge excision fish-mouth technique Samer Saour*, Guido Libondi, Venkat Ramakrishnan Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, St. Andrews Centre of Burns and Plastics, Broomfield Hospital, Chelmsford, UK Available online: Video 2. Technique of increasing vessel diameter using the bifurcation or branch of the IMAP artery Samer Saour*, Guido Libondi, Venkat Ramakrishnan Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, St. Andrews Centre of Burns and Plastics, Broomfield Hospital, Chelmsford, UK Figure 2 Technique of increasing vessel diameter using the bifurcation or branch of the IMAP artery (13). Available online: assessed if this is equal or greater then 1mm it is suitable. A single clamp is then placed at the base of the vessels and the vessels shortened to the level required. The rest of the preparation proceeds under the microscope. Vessel mismatch In the recent years progress in the manufacture of optical devices and microsurgical instruments enable to perform micro sutures in vessels smaller than a millimetre in diameter. Nevertheless vessels diameter mismatch remains a challenge even for most experienced micro surgeons. While the vein size discrepancy is well managed with the use of the anastomotic coupler device (10), but the approach to arterial vessels is different. Diameter mismatch of 1:1.5 This is usually managed with a gentle dilatation of the smaller vessel with the vessels dilator. Diameter mismatch of 1:2 Technique 1: we use a modification of the Harashina s fishmouth technique (11). Figure 1 shows the double wedge excision fish-mouth technique: two opposite triangle are longitudinally excised from IMAP artery and a gentle dilatation applied to expand the diameter of the vessel allowing for the anastomosis to be performed. Technique 2: if during recipient vessel dissection a bifurcation or branch of the IMAP artery is noticed this can be used to minimize the size discrepancy. In Figure 2, it shows this technique: after adventitia removal the two branches are excised close to the bifurcation, the open tip of the micro scissors is passed from one branch to the other and the bifurcation opened. The excess portion of vessel is trimmed and the diameter increase permits anastomosis of the vessel in the usual fashion. Overcoming problem with a palpable/tender venous coupler In our series, we identified 2 patients who had a palpable tender venous coupler, in both cases the coupler was 2.5 mm in size. As most patients who undergo TUG reconstructions and relatively slim this is a significant problem and we suggest potential methods to prevent/ reduce this complication which we have adopted to try and prevent/reduce the incidence of this complication especially when 2.5 mm couplers or greater are used. (I) Placing the coupler away from a prominent rib and therefore reducing its prominence. (II) Creating a channel within the pectoralis major muscle and therefore allowing the coupler to lie flush with the muscle (Figure 3). (III) Covering the coupler with a flap of pectoralis muscle (Figure 4) or piece of fat (Figure 5). Medialisation With the use of the IMA perforators as the recipient vessels, this allows the TUG flap to be placed in the ideal position giving a superior aesthetic result. However with ptotic breasts where the breast sits low on the chest wall the 2nd IM perforator may medialise the flap excessively. We recommend the use of the 3rd IM perforator in this
4 378 Saour et al. Microsurgical refinements with the use of IM perforators in TUG flaps graft. Vein graft During flap raising a medial tributary of the long saphenous is divided close to the main vessel. This vein usually runs horizontally along the length of the inferior aspect of the flap and can be a valuable source for a vein graft. Conclusions Figure 3 A channel within the pectoralis major muscle is created (seen within the blue lines) allowing the coupler to lie flush with the muscle. The TUG flap is our second choice for breast reconstruction when the DIEP flap is not available. The short pedicle length and limited flap volumes makes this a reconstructive challenge. In this paper we described our experience with using the IMAP vessels for primary anastomosis. The IMAP makes an ideal donor vessel as it is relatively straightforward to dissect and prepare. The vessel mismatch can be somewhat of a challenge but the two techniques described in this article will help to overcome this. The IMAP vessels are our preferred donor vessels for TUG flap reconstructions. These refinements would help to further the aesthetic outcome of TUG flap reconstructions. Acknowledgements None. Figure 4 Covering the coupler with a flap of pectoralis muscle. Footnote Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. Ethical Statement: This article does not require ethical approval. References Figure 5 Covering the coupler with a piece of fat. case or extension of the TUG pedicle on bench with a vein graft. If the thoracodorsal vessels/serratus branch is used it is difficult to medialise the flap without the use of a vein 1. Dean C, Chetty U, Forrest AP. Effects of immediate breast reconstruction on psychosocial morbidity after mastectomy. Lancet 1983;1: Kitcat M, Molina A, Meldon C, et al. A Simple Algorithm for Immediate Postmastectomy Reconstruction of the Small Breast-A Single Surgeon's 10-Year Experience. Eplasty 2012;12:e Garvey PB, Villa MT, Rozanski AT, et al. The advantages of free abdominal-based flaps over implants for breast reconstruction in obese patients. Plast Reconstr Surg 2012;130:
5 Gland Surgery, Vol 6, No 4 August Mehrara BJ, Santoro TD, Arcilla E, et al. Complications after microvascular breast reconstruction: experience with 1195 flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg 2006;118:1100-9; discussion Alderman AK, Kuhn LE, Lowery JC, et al. Does patient satisfaction with breast reconstruction change over time? Two-year results of the Michigan Breast Reconstruction Outcomes Study. J Am Coll Surg 2007;204: Rosson GD, Magarakis M, Shridharani SM, et al. A review of the surgical management of breast cancer: plastic reconstructive techniques and timing implications. Ann Surg Oncol 2010;17: Yueh JH, Slavin SA, Adesiyun T, et al. Patient satisfaction in postmastectomy breast reconstruction: a comparative evaluation of DIEP, TRAM, latissimus flap, and implant techniques. Plast Reconstr Surg 2010;125: Arnez ZM, Pogorelec D, Planinsek F, et al. Breast reconstruction by the free transverse gracilis (TUG) flap. Br J Plast Surg 2004;57: Locke MB, Zhong T, Mureau MA, et al. Tug 'O' war: challenges of transverse upper gracilis (TUG) myocutaneous free flap breast reconstruction. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2012;65: Fitzgerald O'Connor E, Rozen WM, Chowdhry M, et al. The microvascular anastomotic coupler for venous anastomoses in free flap breast reconstruction improves outcomes. Gland Surg 2016;5: Harashina T, Irigaray A. Expansion of smaller vessel diameter by fish-mouth incision in microvascular anastomosis with marked size discrepancy. Plast Reconstr Surg 1980;65: Saour S, Libondi G, Ramakrishnan V. Shows the double wedge excision fish-mouth technique. Asvide 2017;4:309. Available online: Saour S, Libondi G, Ramakrishnan V. Technique of increasing vessel diameter using the bifurcation or branch of the IMAP artery. Asvide 2017;4:310. Available online: Cite this article as: Saour S, Libondi G, Ramakrishnan V. Microsurgical refinements with the use of internal mammary (IM) perforators as recipient vessels in transverse upper gracilis (TUG) autologous breast reconstruction. Gland Surg 2017;6(4): doi: /gs
The microvascular anastomotic coupler for venous anastomoses in free flap breast reconstruction improves outcomes
 Original Article The microvascular anastomotic coupler for venous anastomoses in free flap breast reconstruction improves outcomes Edmund Fitzgerald O Connor 1,2, Warren Matthew Rozen 2, Muhammad Chowdhry
Original Article The microvascular anastomotic coupler for venous anastomoses in free flap breast reconstruction improves outcomes Edmund Fitzgerald O Connor 1,2, Warren Matthew Rozen 2, Muhammad Chowdhry
Breast Reconstruction Options
 Breast Reconstruction Options Natural reconstruction using your ABDOMINAL tissue: TRAM Flap (Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous) There are various forms of TRAM flap reconstruction that are commonly
Breast Reconstruction Options Natural reconstruction using your ABDOMINAL tissue: TRAM Flap (Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous) There are various forms of TRAM flap reconstruction that are commonly
Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps
 Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. Houston, Texas Breast reconstruction using the
Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. Houston, Texas Breast reconstruction using the
Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC
 Downloaded from Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC What is Breast Reconstruction? Reconstruction of the breast involves recreating
Downloaded from Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC What is Breast Reconstruction? Reconstruction of the breast involves recreating
A Clinical Anatomic Study of Internal Mammary Perforators as Recipient Vessels for Breast Reconstruction
 A Clinical Anatomic Study of Internal Mammary Perforators as Recipient Vessels for Breast Reconstruction In-Soo Baek 1, Jae-Pil You 1, Sung-Mi Rhee 1, Gil-Su Son 2, Deok-Woo Kim 1, Eun-Sang Dhong 1, Seung-Ha
A Clinical Anatomic Study of Internal Mammary Perforators as Recipient Vessels for Breast Reconstruction In-Soo Baek 1, Jae-Pil You 1, Sung-Mi Rhee 1, Gil-Su Son 2, Deok-Woo Kim 1, Eun-Sang Dhong 1, Seung-Ha
The progress in microsurgical procedures has led
 Original Article Breast reconstruction with free anterolateral thigh flap Ranjit Raje, Ramesh Chepauk, Kanti Shetty, Rajendra Prasad J. S. Plastic & Reconstructive Services, Department of Surgical Oncology,
Original Article Breast reconstruction with free anterolateral thigh flap Ranjit Raje, Ramesh Chepauk, Kanti Shetty, Rajendra Prasad J. S. Plastic & Reconstructive Services, Department of Surgical Oncology,
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5. Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. JPRAS Open. journal homepage:
 JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
Breast Restoration Surgery After a mastectomy
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Breast Restoration Surgery After a mastectomy This handout explains the most common procedures that are used at University of Washington Medical Center (UWMC) to restore a
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Breast Restoration Surgery After a mastectomy This handout explains the most common procedures that are used at University of Washington Medical Center (UWMC) to restore a
Current Strategies in Breast Reconstruction
 Current Strategies in Breast Reconstruction Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 12 th Annual School of
Current Strategies in Breast Reconstruction Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 12 th Annual School of
Four-flap Breast Reconstruction: Bilateral Stacked DIEP and PAP Flaps
 Original Article Breast Four-flap Breast Reconstruction: Bilateral Stacked DIEP and PAP Flaps James L. Mayo, MD Robert J. Allen, MD, FACS Alireza Sadeghi, MD, FACS Background: In cases of bilateral breast
Original Article Breast Four-flap Breast Reconstruction: Bilateral Stacked DIEP and PAP Flaps James L. Mayo, MD Robert J. Allen, MD, FACS Alireza Sadeghi, MD, FACS Background: In cases of bilateral breast
Few would deny that lower abdominal tissue BREAST. An Intraoperative Algorithm for Use of the SIEA Flap for Breast Reconstruction.
 BREAST An Intraoperative Algorithm for Use of the SIEA Flap for Breast Reconstruction Aldona J. Spiegel, M.D. Farah N. Khan, M.D. Houston, Texas Background: The deep inferior epigastric perforator (DIEP)
BREAST An Intraoperative Algorithm for Use of the SIEA Flap for Breast Reconstruction Aldona J. Spiegel, M.D. Farah N. Khan, M.D. Houston, Texas Background: The deep inferior epigastric perforator (DIEP)
Breast Reconstruction: Current Strategies and Future Opportunities
 Breast Reconstruction: Current Strategies and Future Opportunities Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
Breast Reconstruction: Current Strategies and Future Opportunities Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
INTRODUCTION. Toshihiko Satake 1, Jun Sugawara 2, Kazunori Yasumura 1, Taro Mikami 2, Shinji Kobayashi 3, Jiro Maegawa 2. Idea and Innovation
 Mini-Flow-Through Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap for Breast Reconstruction with Preservation of Both Internal Mammary and Deep Inferior Epigastric Vessels Toshihiko Satake 1, Jun Sugawara 2,
Mini-Flow-Through Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap for Breast Reconstruction with Preservation of Both Internal Mammary and Deep Inferior Epigastric Vessels Toshihiko Satake 1, Jun Sugawara 2,
Medical Journal of the Volume 20 Islamic Republic of Iran Number 3 Fall 1385 November Original Articles
 Medical Journal of the Volume 0 Islamic Republic of Iran Number 3 Fall 38 November 00 Original Articles ANATOMY OF THE SUPERFICIAL INFERIOR EPIGASTRIC ARTERY FLAP MAHDI FATHI, M.D., EBRAHIM HATAMIPOUR,
Medical Journal of the Volume 0 Islamic Republic of Iran Number 3 Fall 38 November 00 Original Articles ANATOMY OF THE SUPERFICIAL INFERIOR EPIGASTRIC ARTERY FLAP MAHDI FATHI, M.D., EBRAHIM HATAMIPOUR,
A multiple logistic regression analysis of complications following microsurgical breast reconstruction
 Original Article A multiple logistic regression analysis of complications following microsurgical breast reconstruction Samir Rao 1, Ellen C. Stolle 1, Sarah Sher 1, Chun-Wang Lin 1, Bahram Momen 2, Maurice
Original Article A multiple logistic regression analysis of complications following microsurgical breast reconstruction Samir Rao 1, Ellen C. Stolle 1, Sarah Sher 1, Chun-Wang Lin 1, Bahram Momen 2, Maurice
Is Unilateral Implant or Autologous Breast Reconstruction Better in Obtaining Breast Symmetry?
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is Unilateral Implant or Autologous Breast Reconstruction Better in Obtaining Breast Symmetry? Oriana Cohen, MD, Kevin Small, MD, Christina Lee, BA, Oriana Petruolo, MD, Nolan Karp, MD,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is Unilateral Implant or Autologous Breast Reconstruction Better in Obtaining Breast Symmetry? Oriana Cohen, MD, Kevin Small, MD, Christina Lee, BA, Oriana Petruolo, MD, Nolan Karp, MD,
Reconstruction with autologous tissue remains a
 Original Article Increased Flap Weight and Decreased Perforator Number Predict Fat Necrosis in DIEP Breast Reconstruction Carolyn L. Mulvey, BS* Carisa M. Cooney, MPH* Francis F. Daily, BS* Elizabeth Colantuoni,
Original Article Increased Flap Weight and Decreased Perforator Number Predict Fat Necrosis in DIEP Breast Reconstruction Carolyn L. Mulvey, BS* Carisa M. Cooney, MPH* Francis F. Daily, BS* Elizabeth Colantuoni,
Microsurgical Breast Reconstruction in Thin Patients: The Impact of Low Body Mass Indices
 20 Original Article Microsurgical Breast Reconstruction in Thin Patients: The Impact of Low Body Mass Indices Katie E. Weichman, MD 1 Neil Tanna, MD, MBA 1 P. Niclas Broer, MD 1 Stelios Wilson, MD 1 Hamdan
20 Original Article Microsurgical Breast Reconstruction in Thin Patients: The Impact of Low Body Mass Indices Katie E. Weichman, MD 1 Neil Tanna, MD, MBA 1 P. Niclas Broer, MD 1 Stelios Wilson, MD 1 Hamdan
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer. Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery Plastic-reconstructive aspects after mastectomy Versions 2002 2017: Audretsch / Bauerfeind
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery Plastic-reconstructive aspects after mastectomy Versions 2002 2017: Audretsch / Bauerfeind
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty
 CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
The free thoracodorsal artery perforator flap in head and neck reconstruction
 European Annals of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck diseases (2012) 129, 167 171 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com TECHNICAL NOTE The free thoracodorsal artery perforator flap in head and neck
European Annals of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck diseases (2012) 129, 167 171 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com TECHNICAL NOTE The free thoracodorsal artery perforator flap in head and neck
Endoscopic assisted harvest of the pedicled pectoralis major muscle flap
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 170 174 Endoscopic assisted harvest of the pedicled pectoralis major muscle flap Arif Turkmen*, A. Graeme B. Perks Plastic Surgery Department, Nottingham City
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 170 174 Endoscopic assisted harvest of the pedicled pectoralis major muscle flap Arif Turkmen*, A. Graeme B. Perks Plastic Surgery Department, Nottingham City
Breast Reconstruction
 Steven E. Copit, M.D. Chief- Division of Plastic Surgery Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA analysis of The Defect Skin Breast Volume Nipple Areola Complex analysis of The Defect the
Steven E. Copit, M.D. Chief- Division of Plastic Surgery Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA analysis of The Defect Skin Breast Volume Nipple Areola Complex analysis of The Defect the
Increasing options in autologous microsurgical breast reconstruction: four free flaps for stacked bilateral breast reconstruction
 Case Report Increasing options in autologous microsurgical breast reconstruction: four free flaps for stacked bilateral breast reconstruction Warren Matthew Rozen 1,2, Nakul Gamanlal Patel 1, Venkat V.
Case Report Increasing options in autologous microsurgical breast reconstruction: four free flaps for stacked bilateral breast reconstruction Warren Matthew Rozen 1,2, Nakul Gamanlal Patel 1, Venkat V.
Anatomical Landmarks for Safe Elevation of the Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap: A Cadaveric Study
 Anatomical Landmarks for Safe Elevation of the Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap: A Cadaveric Study Saeed Chowdhry, MD, Ron Hazani, MD, Philip Collis, BS, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD University of
Anatomical Landmarks for Safe Elevation of the Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap: A Cadaveric Study Saeed Chowdhry, MD, Ron Hazani, MD, Philip Collis, BS, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD University of
Anatomical study. Clinical study. R. Ogawa, H. Hyakusoku, M. Murakami, R. Aoki, K. Tanuma* and D. G. Pennington?
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2002) 55, 396-40 I 9 2002 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi: 10.1054/bjps.2002.3877 PLASTIC SURGERY An anatomical and clinical study of the dorsal intercostal
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2002) 55, 396-40 I 9 2002 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi: 10.1054/bjps.2002.3877 PLASTIC SURGERY An anatomical and clinical study of the dorsal intercostal
Early Experience With Barbed Sutures for Abdominal Closure in Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap Breast Reconstruction
 Early Experience With Barbed Sutures for Abdominal Closure in Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap Breast Reconstruction Catherine de Blacam, MB, BCh, a Salih Colakoglu, MD, a Adeyiza O. Momoh, MD,
Early Experience With Barbed Sutures for Abdominal Closure in Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap Breast Reconstruction Catherine de Blacam, MB, BCh, a Salih Colakoglu, MD, a Adeyiza O. Momoh, MD,
Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1714-7 RESEARCH Open Access Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes Chi Sun Yoon and Kyu Nam
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1714-7 RESEARCH Open Access Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes Chi Sun Yoon and Kyu Nam
Breast reconstruction has an important role BREAST. A Two-Year Prospective Analysis of Trunk Function in TRAM Breast Reconstructions
 BREAST A Two-Year Prospective Analysis of Trunk Function in TRAM Breast Reconstructions Amy K. Alderman, M.D. William M. Kuzon, Jr., M.D., Ph.D. Edwin G. Wilkins, M.D. Ann Arbor, Mich. Background: Functional
BREAST A Two-Year Prospective Analysis of Trunk Function in TRAM Breast Reconstructions Amy K. Alderman, M.D. William M. Kuzon, Jr., M.D., Ph.D. Edwin G. Wilkins, M.D. Ann Arbor, Mich. Background: Functional
Simultaneous Bilateral Breast Reconstruction With In-the-Crease Inferior Gluteal Artery Perforator Flaps
 BREAST SURGERY Simultaneous Bilateral Breast Reconstruction With In-the-Crease Inferior Gluteal Artery Perforator Flaps Joshua L. Levine, MD,* Quintessa Miller, MD, Julie Vasile, MD,* Kamran Khoobehi,
BREAST SURGERY Simultaneous Bilateral Breast Reconstruction With In-the-Crease Inferior Gluteal Artery Perforator Flaps Joshua L. Levine, MD,* Quintessa Miller, MD, Julie Vasile, MD,* Kamran Khoobehi,
How To Make a Good Mastectomy for Reconstruction Based on the Anatomy. Zhang Jin, Ph.D MD
 How To Make a Good Mastectomy for Reconstruction Based on the Anatomy Zhang Jin, Ph.D MD Deputy Director and Professor Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital People s Republic of China
How To Make a Good Mastectomy for Reconstruction Based on the Anatomy Zhang Jin, Ph.D MD Deputy Director and Professor Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital People s Republic of China
Breast cancer reconstruction surgery (immediate and delayed) across Ontario: Patient indications and appropriate surgical options
 A Quality Initiative of the Program in Evidence-Based Care (PEBC), Cancer Care Ontario (CCO) Breast cancer reconstruction surgery (immediate and delayed) across Ontario: Patient indications and appropriate
A Quality Initiative of the Program in Evidence-Based Care (PEBC), Cancer Care Ontario (CCO) Breast cancer reconstruction surgery (immediate and delayed) across Ontario: Patient indications and appropriate
The Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery (SIEA) Flap and Its Applications in Breast Reconstruction
 The Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery (SIEA) Flap and Its Applications in Breast Reconstruction Zachary Menn and Aldona Spiegel Weill Cornell Medical College, The Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas,
The Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery (SIEA) Flap and Its Applications in Breast Reconstruction Zachary Menn and Aldona Spiegel Weill Cornell Medical College, The Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas,
In a second stage or a second operation that tissue expander is removed through the same incision and the implant is placed within the chest pocket.
 Hello, I m Summer Hanson. I m an assistant professor in the Department of Plastics & Reconstructive Surgery at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and today I m going to talk about the role
Hello, I m Summer Hanson. I m an assistant professor in the Department of Plastics & Reconstructive Surgery at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and today I m going to talk about the role
Essential Anatomy for oncoplastic surgery. Omar Z. Youssef M.D Professor of surgical oncology NCI- Cairo University
 Essential Anatomy for oncoplastic surgery Omar Z. Youssef M.D Professor of surgical oncology NCI- Cairo University Introduction Rationale for anatomical basis for OPS Anatomical considerations: 1. Surface
Essential Anatomy for oncoplastic surgery Omar Z. Youssef M.D Professor of surgical oncology NCI- Cairo University Introduction Rationale for anatomical basis for OPS Anatomical considerations: 1. Surface
Breast Reconstruction in Women Under 30: A 10-Year Experience
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Breast Reconstruction in Women Under 30: A 10-Year Experience Warren A. Ellsworth, MD,* Barbara L. Bass, MD, FACS, Roman J. Skoracki, MD, à and Lior Heller, MD* *Division of Plastic Surgery,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Breast Reconstruction in Women Under 30: A 10-Year Experience Warren A. Ellsworth, MD,* Barbara L. Bass, MD, FACS, Roman J. Skoracki, MD, à and Lior Heller, MD* *Division of Plastic Surgery,
Immediate versus delayed free TRAM breast reconstruction: an analysis of perioperative factors and complications
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (22), 55, l-6 9 22 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi:.54/bjps.22.3747 BRITISH JOURNAL OF / ~ ] PLASTIC SURGERY Immediate versus delayed free TRAM breast
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (22), 55, l-6 9 22 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi:.54/bjps.22.3747 BRITISH JOURNAL OF / ~ ] PLASTIC SURGERY Immediate versus delayed free TRAM breast
Frederick J. Duffy, Jr., MD, FACS and Brice W. McKane, MD, FACS BREAST RECONSTRUCTION
 Frederick J. Duffy, Jr., MD, FACS and Brice W. McKane, MD, FACS BREAST RECONSTRUCTION BREAST RECONSTRUCTION: A WOMAN S DECISION Options and Information Our approach to breast reconstruction entails a very
Frederick J. Duffy, Jr., MD, FACS and Brice W. McKane, MD, FACS BREAST RECONSTRUCTION BREAST RECONSTRUCTION: A WOMAN S DECISION Options and Information Our approach to breast reconstruction entails a very
SIMPOSIO Ricostruzione mammaria ed implicazioni radioterapiche Indicazioni
 SIMPOSIO Ricostruzione mammaria ed implicazioni radioterapiche Indicazioni Icro Meattini, MD Radiation Oncology Department - University of Florence Azienda Ospedaliero Universitaria Careggi Firenze Breast
SIMPOSIO Ricostruzione mammaria ed implicazioni radioterapiche Indicazioni Icro Meattini, MD Radiation Oncology Department - University of Florence Azienda Ospedaliero Universitaria Careggi Firenze Breast
AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION
 CHAPTER 18 AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION Ali A. Qureshi, MD and Smita R. Ramanadham, MD Aesthetic surgery of the breast aims to either correct ptosis with a mastopexy,
CHAPTER 18 AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION Ali A. Qureshi, MD and Smita R. Ramanadham, MD Aesthetic surgery of the breast aims to either correct ptosis with a mastopexy,
Nipple-Areolar Complex Reconstruction: A Review of the Literature and Introduction of the Rectangle-to-Cube Nipple Flap
 Nipple-Areolar Complex Reconstruction: A Review of the Literature and Introduction of the Rectangle-to-Cube Nipple Flap Joshua T. Henderson, BA, a ThomasJ.Lee,MD, b Andrew M. Swiergosz, BS, a Andrea R.
Nipple-Areolar Complex Reconstruction: A Review of the Literature and Introduction of the Rectangle-to-Cube Nipple Flap Joshua T. Henderson, BA, a ThomasJ.Lee,MD, b Andrew M. Swiergosz, BS, a Andrea R.
The use of postmastectomy radiation therapy (PMRT) to prevent
 NORTHEASTERN SOCIETY OF PLASTIC SURGEONS Postmastectomy Radiation Therapy and Breast An Analysis of Complications and Patient Satisfaction Bernard T. Lee, MD,* Tolulope A. Adesiyun, BS,* Salih Colakoglu,
NORTHEASTERN SOCIETY OF PLASTIC SURGEONS Postmastectomy Radiation Therapy and Breast An Analysis of Complications and Patient Satisfaction Bernard T. Lee, MD,* Tolulope A. Adesiyun, BS,* Salih Colakoglu,
Breast reconstruction following mastectomy has
 Free full text on www.ijps.org Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction: Microsurgical methods Venkat Ramakrishnan, Makarand Tare St. Andrew s Centre for Burns and Plastic Surgery, BroomÞ eld Hospital, Chelmsford,
Free full text on www.ijps.org Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction: Microsurgical methods Venkat Ramakrishnan, Makarand Tare St. Andrew s Centre for Burns and Plastic Surgery, BroomÞ eld Hospital, Chelmsford,
How many procedures to make a breast?
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (00 ), 5, 7-3 9 00 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi: 0.05/bjps.000.3538 BRITISH JOURNAL OF PLASTIC SURGERY How many procedures to make a breast? A. D.
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (00 ), 5, 7-3 9 00 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi: 0.05/bjps.000.3538 BRITISH JOURNAL OF PLASTIC SURGERY How many procedures to make a breast? A. D.
Methods of autologous tissue breast reconstruction BREAST
 BREAST Comparison of Donor-Site Morbidity of SIEA, DIEP, and Muscle-Sparing TRAM Flaps for Breast Reconstruction Liza C. Wu, M.D. Anureet Bajaj, M.D. David W. Chang, M.D. Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D.
BREAST Comparison of Donor-Site Morbidity of SIEA, DIEP, and Muscle-Sparing TRAM Flaps for Breast Reconstruction Liza C. Wu, M.D. Anureet Bajaj, M.D. David W. Chang, M.D. Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D.
Figure 1. Anatomy of the breast
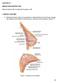 CHAPTER 12 BREAST RECONSTRUCTION Mihaela Rapolti, MD and Michelle Roughton, MD I. BREAST ANATOMY A. Mastering breast anatomy is essential for understanding how the breast changes with aging and principles
CHAPTER 12 BREAST RECONSTRUCTION Mihaela Rapolti, MD and Michelle Roughton, MD I. BREAST ANATOMY A. Mastering breast anatomy is essential for understanding how the breast changes with aging and principles
Interesting Case Series. Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle
 Interesting Case Series Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle Danielle H. Rochlin, BA, Justin M. Broyles, MD, and Justin M. Sacks, MD Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,
Interesting Case Series Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle Danielle H. Rochlin, BA, Justin M. Broyles, MD, and Justin M. Sacks, MD Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,
Breast Reconstruction. Westmead Breast Cancer Institute
 Breast Reconstruction Westmead Breast Cancer Institute What is breast reconstruction? Breast reconstruction is a surgical procedure that creates a shape on the chest wall following a mastectomy. Occasionally,
Breast Reconstruction Westmead Breast Cancer Institute What is breast reconstruction? Breast reconstruction is a surgical procedure that creates a shape on the chest wall following a mastectomy. Occasionally,
Advances in Breast Surgery. Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015
 Advances in Breast Surgery Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015 Objectives Understand the surgical treatment of breast cancer Be able to determine when a lumpectomy
Advances in Breast Surgery Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015 Objectives Understand the surgical treatment of breast cancer Be able to determine when a lumpectomy
RECONSTRUCTION OF SCALP DEFECTS: AN INSTITUTIONAL EXPERIENCE Sathyanarayana B. C 1, Somashekar Srinivas 2
 RECONSTRUCTION OF SCALP DEFECTS: AN INSTITUTIONAL EXPERIENCE Sathyanarayana B. C 1, Somashekar Srinivas 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Sathyanarayana B. C, Somashekar Srinivas. Reconstruction of Scalp Defects:
RECONSTRUCTION OF SCALP DEFECTS: AN INSTITUTIONAL EXPERIENCE Sathyanarayana B. C 1, Somashekar Srinivas 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Sathyanarayana B. C, Somashekar Srinivas. Reconstruction of Scalp Defects:
Algorithm for Autologous Breast Reconstruction for Partial Mastectomy Defects
 Algorithm for Autologous Breast Reconstruction for Partial Mastectomy Defects Joshua L. Levine, M.D., Nassif E. Soueid, M.D., and Robert J. Allen, M.D. New Orleans, La. Background: The use of lateral thoracic
Algorithm for Autologous Breast Reconstruction for Partial Mastectomy Defects Joshua L. Levine, M.D., Nassif E. Soueid, M.D., and Robert J. Allen, M.D. New Orleans, La. Background: The use of lateral thoracic
Prophylactic Mastectomy & Reconstructive Implications
 Prophylactic Mastectomy & Reconstructive Implications Minas T Chrysopoulo, MD PRMA Center For Advanced Breast Reconstruction Prophylactic Mastectomy Surgical removal of one or both breasts to reduce the
Prophylactic Mastectomy & Reconstructive Implications Minas T Chrysopoulo, MD PRMA Center For Advanced Breast Reconstruction Prophylactic Mastectomy Surgical removal of one or both breasts to reduce the
Citation for published version (APA): Benditte-Klepetko, H. C. (2014). Breast surgery: A problem of beauty or health?
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Breast surgery: A problem of beauty or health? Benditte-Klepetko, H.C. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Benditte-Klepetko, H. C. (2014).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Breast surgery: A problem of beauty or health? Benditte-Klepetko, H.C. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Benditte-Klepetko, H. C. (2014).
NIPPLE SPARING PRE-PECTORAL BREAST RECONSTRUCTION
 NIPPLE SPARING PRE-PECTORAL BREAST RECONSTRUCTION 42 yo female healthy athlete Right breast mass. Past medical history: none Family history: aunt with Breast cancer Candidates for nipple-sparing mastectomy
NIPPLE SPARING PRE-PECTORAL BREAST RECONSTRUCTION 42 yo female healthy athlete Right breast mass. Past medical history: none Family history: aunt with Breast cancer Candidates for nipple-sparing mastectomy
Thermal injury in TAPIA breast reconstruction Børsen-Koch, Mikkel; Gunnarsson, Gudjon L.; Sørensen, Jens Ahm; Thomsen, Jørn Bo
 Syddansk Universitet Thermal injury in TAPIA breast reconstruction Børsen-Koch, Mikkel; Gunnarsson, Gudjon L.; Sørensen, Jens Ahm; Thomsen, Jørn Bo Published in: Gland Surgery DOI: 10.21037/gs.2017.01.01
Syddansk Universitet Thermal injury in TAPIA breast reconstruction Børsen-Koch, Mikkel; Gunnarsson, Gudjon L.; Sørensen, Jens Ahm; Thomsen, Jørn Bo Published in: Gland Surgery DOI: 10.21037/gs.2017.01.01
JMSCR Vol 07 Issue 01 Page January 2019
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i1.36 Original Article A Study on the
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i1.36 Original Article A Study on the
The decision to repair a partial mastectomy CME. State of the Art and Science in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction.
 CME State of the Art and Science in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction Steven J. Kronowitz, M.D. Houston, Texas Learning Objectives: After reading this article, the participant should be able to: 1.
CME State of the Art and Science in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction Steven J. Kronowitz, M.D. Houston, Texas Learning Objectives: After reading this article, the participant should be able to: 1.
Update on Breast Reconstruction Using Free TRAM, DIEP, and SIEA Flaps
 Update on Breast Reconstruction Using Free TRAM, DIEP, and SIEA Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. 1 ABSTRACT Breast reconstruction using autologous tissue is commonly accomplished using the transverse
Update on Breast Reconstruction Using Free TRAM, DIEP, and SIEA Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. 1 ABSTRACT Breast reconstruction using autologous tissue is commonly accomplished using the transverse
Flaps vs Grafts. Ronen Avram, MD MSc FRCSC
 Flaps vs Grafts Ronen Avram, MD MSc FRCSC POS Keratoacanthoma is not a malignant tumor! Methods of Reconstruction Reconstructive Ladder Primary closure Primary Delayed Secondary Intention Skin Graft Pedicled
Flaps vs Grafts Ronen Avram, MD MSc FRCSC POS Keratoacanthoma is not a malignant tumor! Methods of Reconstruction Reconstructive Ladder Primary closure Primary Delayed Secondary Intention Skin Graft Pedicled
Microvascular free tissue transfer is a standard
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTERNAL MAMMARY ARTERY AND VEIN: RECIPIENT VESSELS FOR FREE TISSUE TRANSFER TO THE HEAD AND NECK IN THE VESSEL-DEPLETED NECK Mark L. Urken, MD, 1 Kevin M. Higgins, MD, 2 Bryant Lee, MD,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTERNAL MAMMARY ARTERY AND VEIN: RECIPIENT VESSELS FOR FREE TISSUE TRANSFER TO THE HEAD AND NECK IN THE VESSEL-DEPLETED NECK Mark L. Urken, MD, 1 Kevin M. Higgins, MD, 2 Bryant Lee, MD,
The Case FOR Oncoplastic Surgery in Small Breasts. Barbara L. Smith, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA USA
 The Case FOR Oncoplastic Surgery in Small Breasts Barbara L. Smith, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA USA Changing issues in breast cancer management Early detection
The Case FOR Oncoplastic Surgery in Small Breasts Barbara L. Smith, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA USA Changing issues in breast cancer management Early detection
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Advances and Surgical Decision-Making for Breast Reconstruction
 893 Advances and Surgical Decision-Making for Breast Reconstruction Steven J. Kronowitz, MD 1 Henry M. Kuerer, MD, PhD 2 1 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, The University of Texas M. D.
893 Advances and Surgical Decision-Making for Breast Reconstruction Steven J. Kronowitz, MD 1 Henry M. Kuerer, MD, PhD 2 1 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, The University of Texas M. D.
The Profunda Artery Perforator Flap: Investigating the Perforasome Using Three-Dimensional Computed Tomographic Angiography
 BREAST The Profunda Artery Perforator Flap: Investigating the Perforasome Using Three-Dimensional Computed Tomographic Angiography Corrine Wong, M.D. Purushottam Nagarkar, M.D. Sumeet Teotia, M.D. Nicholas
BREAST The Profunda Artery Perforator Flap: Investigating the Perforasome Using Three-Dimensional Computed Tomographic Angiography Corrine Wong, M.D. Purushottam Nagarkar, M.D. Sumeet Teotia, M.D. Nicholas
Goals of Care. Restore shape and function after cancer
 Goals of Care Restore shape and function after cancer Aid in physiological and psychological benefit Relationship with significant other Self esteem and positive body image Feeling of a whole body Avoid
Goals of Care Restore shape and function after cancer Aid in physiological and psychological benefit Relationship with significant other Self esteem and positive body image Feeling of a whole body Avoid
Chest wall reconstruction using a combined musculocutaneous anterolateral anteromedial thigh flap
 Free full text on www.ijps.org Case Report DOI: 10.4103/0970-0358.63966 Chest wall reconstruction using a combined musculocutaneous anterolateral anteromedial thigh flap Pearlie W. W. Tan, Chin-Ho Wong,
Free full text on www.ijps.org Case Report DOI: 10.4103/0970-0358.63966 Chest wall reconstruction using a combined musculocutaneous anterolateral anteromedial thigh flap Pearlie W. W. Tan, Chin-Ho Wong,
Advances and Innovations in Breast Reconstruction and Brest Surgery Presented by PCMC plastic surgeons
 Advances and Innovations in Breast Reconstruction and Brest Surgery Presented by PCMC plastic surgeons Options for reconstruction after mastectomy Implants Autologous tissue = from your own body: skin
Advances and Innovations in Breast Reconstruction and Brest Surgery Presented by PCMC plastic surgeons Options for reconstruction after mastectomy Implants Autologous tissue = from your own body: skin
B11 Breast Reconstruction with Abdominal Tissue Flap
 B11 Breast Reconstruction with Abdominal Tissue Flap Issued March 2011 You can get more information about this procedure from www.aboutmyhealth.org Tell us how useful you found this document at www.patientfeedback.org
B11 Breast Reconstruction with Abdominal Tissue Flap Issued March 2011 You can get more information about this procedure from www.aboutmyhealth.org Tell us how useful you found this document at www.patientfeedback.org
Case Study. TRAM Flap Reconstruction with an Associated Complication. Repair using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis.
 Case Study TRAM Flap Reconstruction with an Associated Complication. Repair using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis. TRAM Flap Reconstruction with an Associated Complication Challenge Insulin-dependent diabetes
Case Study TRAM Flap Reconstruction with an Associated Complication. Repair using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis. TRAM Flap Reconstruction with an Associated Complication Challenge Insulin-dependent diabetes
Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction
 Follow the link from the online version of this article to obtain certified continuing medical education credits Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction Paul T R Thiruchelvam, 1 Fiona McNeill, 2 Navid Jallali,
Follow the link from the online version of this article to obtain certified continuing medical education credits Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction Paul T R Thiruchelvam, 1 Fiona McNeill, 2 Navid Jallali,
Breast Reconstruction Surgery
 Breast Reconstruction Surgery I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for Breast Reconstruction Surgery when it is determined to be medically necessary and when it meets the medical criteria
Breast Reconstruction Surgery I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for Breast Reconstruction Surgery when it is determined to be medically necessary and when it meets the medical criteria
Awareness and provision of reconstruction. Breast
 Original Article Breast Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap Breast Reconstruction without Microsurgery Fellowship Training Hakan Orbay, MD, PhD* Brittany K. Busse, MD* Thomas R. Stevenson,
Original Article Breast Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap Breast Reconstruction without Microsurgery Fellowship Training Hakan Orbay, MD, PhD* Brittany K. Busse, MD* Thomas R. Stevenson,
Anatomical Background of the Perforator Flap Based on the Deep Branch of the Superficial Circumflex Iliac Artery (SCIP Flap): A Cadaveric Study
 Anatomical Background of the Perforator Flap Based on the Deep Branch of the Superficial Circumflex Iliac Artery (SCIP Flap): A Cadaveric Study Raphael Sinna, MD, a Hassene Hajji, MD, b Quentin Qassemyar,
Anatomical Background of the Perforator Flap Based on the Deep Branch of the Superficial Circumflex Iliac Artery (SCIP Flap): A Cadaveric Study Raphael Sinna, MD, a Hassene Hajji, MD, b Quentin Qassemyar,
Saphenous Vein Autograft Replacement
 Saphenous Vein Autograft Replacement of Severe Segmental Coronary Artery Occlusion Operative Technique Rene G. Favaloro, M.D. D irect operation on the coronary artery has been performed in 180 patients
Saphenous Vein Autograft Replacement of Severe Segmental Coronary Artery Occlusion Operative Technique Rene G. Favaloro, M.D. D irect operation on the coronary artery has been performed in 180 patients
Annals of Medicine and Surgery
 Annals of Medicine and Surgery 4 (2015) 293e300 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Annals of Medicine and Surgery journal homepage: www.annalsjournal.com Total rib -preservation technique of internal
Annals of Medicine and Surgery 4 (2015) 293e300 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Annals of Medicine and Surgery journal homepage: www.annalsjournal.com Total rib -preservation technique of internal
Septic Bone and Joint Surgery
 Septic Bone and Joint Surgery Bearbeitet von Reinhard Schnettler 1. Auflage 2010. Buch. 328 S. Hardcover ISBN 978 3 13 149031 5 Format (B x L): 19,5 x 27 cm Weitere Fachgebiete > Medizin > Chirurgie >
Septic Bone and Joint Surgery Bearbeitet von Reinhard Schnettler 1. Auflage 2010. Buch. 328 S. Hardcover ISBN 978 3 13 149031 5 Format (B x L): 19,5 x 27 cm Weitere Fachgebiete > Medizin > Chirurgie >
The most common type of breast reconstruction
 BREAST Breast Reconstruction with Perforator Flaps Jay W. Granzow, M.D., M.P.H. Joshua L. Levine, M.D. Ernest S. Chiu, M.D. Maria M. LoTempio, M.D. Robert J. Allen, M.D. New Orleans, La.; Charleston, S.C.;
BREAST Breast Reconstruction with Perforator Flaps Jay W. Granzow, M.D., M.P.H. Joshua L. Levine, M.D. Ernest S. Chiu, M.D. Maria M. LoTempio, M.D. Robert J. Allen, M.D. New Orleans, La.; Charleston, S.C.;
Primary closure of the deltopectoral flap-donor site without skin grafting
 Primary closure of the deltopectoral flap-donor site without skin grafting Received: 4/3/2013 Accepted: 14/5/2013 Introduction Reliable and simultaneous reconstruction of head-and-neck defects has been
Primary closure of the deltopectoral flap-donor site without skin grafting Received: 4/3/2013 Accepted: 14/5/2013 Introduction Reliable and simultaneous reconstruction of head-and-neck defects has been
Breast cancer has become so
 The three stages of breast reconstruction BY FORTUNE C IWUAGWU Breast cancer has become so common that most people reading this article will know someone (either professionally or personally) who has been
The three stages of breast reconstruction BY FORTUNE C IWUAGWU Breast cancer has become so common that most people reading this article will know someone (either professionally or personally) who has been
Reconstructive surgery following mastectomy
 Reconstructive surgery following mastectomy Kseniya Roudakova, MD A CASE FROM SUNY DOWNSTATE 60F who presented for right mastectomy with immediate TRAM flap reconstruction for recurrent breast cancer Oncologic
Reconstructive surgery following mastectomy Kseniya Roudakova, MD A CASE FROM SUNY DOWNSTATE 60F who presented for right mastectomy with immediate TRAM flap reconstruction for recurrent breast cancer Oncologic
complicanze in chirurgia senologica ricostruttiva Tecniche per la prevenzione delle complicanze nelle mastectomie conservative
 Il trattamento delle complicanze in chirurgia senologica ricostruttiva Tecniche per la prevenzione delle complicanze nelle mastectomie conservative Dr. Christian Rizzetto UOC Chirurgia Senologica - Breast
Il trattamento delle complicanze in chirurgia senologica ricostruttiva Tecniche per la prevenzione delle complicanze nelle mastectomie conservative Dr. Christian Rizzetto UOC Chirurgia Senologica - Breast
Procedure Information Guide
 Procedure Information Guide Breast reconstruction with abdominal tissue flap Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made every
Procedure Information Guide Breast reconstruction with abdominal tissue flap Brought to you in association with EIDO and endorsed by the The Royal College of Surgeons of England Discovery has made every
Gastrocnemius Myocutaneous Flap: A Versatile Option to Cover the Defect of Upper and Middle Third Leg
 Downloaded from wjps.ir at 22:25 +0330 on Sunday November 18th 28 314 Gastrocnemius flap for coverage of leg defects Original Article Gastrocnemius Myocutaneous Flap: A Versatile Option to Cover the Defect
Downloaded from wjps.ir at 22:25 +0330 on Sunday November 18th 28 314 Gastrocnemius flap for coverage of leg defects Original Article Gastrocnemius Myocutaneous Flap: A Versatile Option to Cover the Defect
Split Hemianterior Tibialis Turndown Muscle Flap for Coverage of Distal Leg Wounds With Preservation of Function
 Split Hemianterior Tibialis Turndown Muscle Flap for Coverage of Distal Leg Wounds With Preservation of Function Vinay Gundlapalli, MD, a John W. Gillespie III, MD, b and Chris D. Tzarnas, MD, FACS c a
Split Hemianterior Tibialis Turndown Muscle Flap for Coverage of Distal Leg Wounds With Preservation of Function Vinay Gundlapalli, MD, a John W. Gillespie III, MD, b and Chris D. Tzarnas, MD, FACS c a
MASTECTOMY AND IMMEDIATE BREAST RECONSTRUCTION IN INVASIVE CARCINOMA
 MASTECTOMY AND IMMEDIATE BREAST RECONSTRUCTION IN INVASIVE CARCINOMA Node-postive breast cancer Delayed-immediate reconstruction versus delayed reconstruction DBCG RT Recon-Protocol Tine Engberg Damsgaard
MASTECTOMY AND IMMEDIATE BREAST RECONSTRUCTION IN INVASIVE CARCINOMA Node-postive breast cancer Delayed-immediate reconstruction versus delayed reconstruction DBCG RT Recon-Protocol Tine Engberg Damsgaard
Versatility of Reverse Sural Artery Flap for Heel Reconstruction
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Introduction: The heel has two parts, weight bearing and non-weight bearing part. Soft tissue heel reconstruction has been a challenge due to its complex nature of anatomy, weight bearing
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Introduction: The heel has two parts, weight bearing and non-weight bearing part. Soft tissue heel reconstruction has been a challenge due to its complex nature of anatomy, weight bearing
BOAST 4 Algorithm. 6th September 2013
 BOAST 4 Algorithm 6th September 2013 Background The British Orthopaedic Association and the British Association of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgeons reviewed their 1997 guidance and published
BOAST 4 Algorithm 6th September 2013 Background The British Orthopaedic Association and the British Association of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgeons reviewed their 1997 guidance and published
Acta Medica Okayama OCTOBER Mastectomy in Female-to-male Transsexuals. Yuzaburo Namba Toshiyuki Watanabe Yoshihiro Kimata
 Acta Medica Okayama Volume 63, Issue 5 2009 Article 4 OCTOBER 2009 Mastectomy in Female-to-male Transsexuals Yuzaburo Namba Toshiyuki Watanabe Yoshihiro Kimata Department of Plastic and Reconstructive
Acta Medica Okayama Volume 63, Issue 5 2009 Article 4 OCTOBER 2009 Mastectomy in Female-to-male Transsexuals Yuzaburo Namba Toshiyuki Watanabe Yoshihiro Kimata Department of Plastic and Reconstructive
Barbed Sutures in Progressive Tension Suture Technique Abdominoplasty. Karol A Gutowski, MD
 Barbed Sutures in Progressive Tension Suture Technique Abdominoplasty Karol A Gutowski, MD 1 Disclosures Speakers Bureau for AngioTech since April 2011 (Makers of Quill bi-directional barbed sutures) Technique
Barbed Sutures in Progressive Tension Suture Technique Abdominoplasty Karol A Gutowski, MD 1 Disclosures Speakers Bureau for AngioTech since April 2011 (Makers of Quill bi-directional barbed sutures) Technique
Mentosternal Contracture Treated With an Occipito-Scapular Flap in a 5-year-old Boy: A Case Report
 Mentosternal Contracture Treated With an Occipito-Scapular Flap in a 5-year-old Boy: A Case Report Armin Kraus, MD, Hans-Eberhard Schaller, MD, and Hans-Oliver Rennekampff, MD Department for Hand, Plastic,
Mentosternal Contracture Treated With an Occipito-Scapular Flap in a 5-year-old Boy: A Case Report Armin Kraus, MD, Hans-Eberhard Schaller, MD, and Hans-Oliver Rennekampff, MD Department for Hand, Plastic,
Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flap for Breast Reconstruction: Bad Rap or Good Flap?
 Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flap for Breast Reconstruction: Bad Rap or Good Flap? Galen Perdikis, MD, Stephanie Koonce, MD, George Collis, MD, and Dustin Eck, MD Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL Correspondence:
Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flap for Breast Reconstruction: Bad Rap or Good Flap? Galen Perdikis, MD, Stephanie Koonce, MD, George Collis, MD, and Dustin Eck, MD Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL Correspondence:
Stomal recurrence after total laryngectomy is 1
 CASE REPORT Eben L. Rosenthal, MD, Section Editor ANTEROLATERAL THIGH FREE FLAP FOR TRACHEAL RECONSTRUCTION AFTER PARASTOMAL RECURRENCE Umberto Caliceti, MD, 1 Ottavio Piccin, MD, 1 Ottavio Cavicchi, MD,
CASE REPORT Eben L. Rosenthal, MD, Section Editor ANTEROLATERAL THIGH FREE FLAP FOR TRACHEAL RECONSTRUCTION AFTER PARASTOMAL RECURRENCE Umberto Caliceti, MD, 1 Ottavio Piccin, MD, 1 Ottavio Cavicchi, MD,
Do Preexisting Abdominal Scars Threaten Wound Healing in Abdominoplasty?
 Do Preexisting Abdominal Scars Threaten Wound Healing in Abdominoplasty? Michele A. Shermak, MD, Jessie Mallalieu, PA-C, and David Chang, PhD, MPH, MBA The Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions, Division
Do Preexisting Abdominal Scars Threaten Wound Healing in Abdominoplasty? Michele A. Shermak, MD, Jessie Mallalieu, PA-C, and David Chang, PhD, MPH, MBA The Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions, Division
Medical Policy Original Effective Date: Revised Date: Page 1 of 8
 Page 1 of 8 Disclaimer Description Coverage Determination Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on all plans, or the plan
Page 1 of 8 Disclaimer Description Coverage Determination Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on all plans, or the plan
Breast Cancer Reconstruction
 Breast Cancer Jerome H. Liu, MD Tom S. Liu, MD Jerome H. Liu, MD Undergraduate: Brown University Medical School: University of California, Los Angeles Residency: UCLA Medical Center Fellowship:UCLA Medical
Breast Cancer Jerome H. Liu, MD Tom S. Liu, MD Jerome H. Liu, MD Undergraduate: Brown University Medical School: University of California, Los Angeles Residency: UCLA Medical Center Fellowship:UCLA Medical
Treatment of non-union of forearm bones with a free vascularised cortico - periosteal flap from the medial femoral condyle
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 611-615 ORIGINAL STUDY Treatment of non-union of forearm bones with a free vascularised cortico - periosteal flap from the medial femoral condyle Luc DE SMET From the University
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 611-615 ORIGINAL STUDY Treatment of non-union of forearm bones with a free vascularised cortico - periosteal flap from the medial femoral condyle Luc DE SMET From the University
The dissection of the rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap with complete preservation of the anterior rectus sheath q
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 395 400 The dissection of the rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap with complete preservation of the anterior rectus sheath q D. Erni*, Y.D. Harder
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 395 400 The dissection of the rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap with complete preservation of the anterior rectus sheath q D. Erni*, Y.D. Harder
Tor Chiu. Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161
 18 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap Tor Chiu Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap FLAP TERRITORY The deep inferior epigastric
18 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap Tor Chiu Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap FLAP TERRITORY The deep inferior epigastric
Role of free tissue transfer in management of chronic venous ulcer
 Original Article Role of free tissue transfer in management of chronic venous ulcer K. Murali Mohan Reddy, D. Mukunda Reddy Department of Plastic Surgery, Nizams Institute of Medical Sciences, India. Address
Original Article Role of free tissue transfer in management of chronic venous ulcer K. Murali Mohan Reddy, D. Mukunda Reddy Department of Plastic Surgery, Nizams Institute of Medical Sciences, India. Address
Despite breast reduction being one of the BREAST. Does Knowledge of the Initial Technique Affect Outcomes after Repeated Breast Reduction?
 BREAST Does Knowledge of the Initial Technique Affect Outcomes after Repeated Breast Reduction? Jamil Ahmad, M.D. Sarah M. McIsaac, M.D. Frank Lista, M.D. Mississauga and Ottawa, Ontario, Canada Background:
BREAST Does Knowledge of the Initial Technique Affect Outcomes after Repeated Breast Reduction? Jamil Ahmad, M.D. Sarah M. McIsaac, M.D. Frank Lista, M.D. Mississauga and Ottawa, Ontario, Canada Background:
