Algorithm for Autologous Breast Reconstruction for Partial Mastectomy Defects
|
|
|
- Ashlee Hardy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Algorithm for Autologous Breast Reconstruction for Partial Mastectomy Defects Joshua L. Levine, M.D., Nassif E. Soueid, M.D., and Robert J. Allen, M.D. New Orleans, La. Background: The use of lateral thoracic skin and fat for breast reconstruction is advantageous because it does not require the use of muscle transfer, and the donor-site incision is well hidden under the arm. In patients with redundant skin at the thoracic flank, use of this tissue has the added benefit of removal of an unsightly roll. The lateral thoracic skin and fat flap can be harvested using microsurgical technique based on three different pedicles: the thoracodorsal artery perforators; a direct cutaneous branch of the thoracodorsal, axillary, or lateral thoracic arteries; and the lateral thoracic intercostal perforating vessel. Methods: The authors describe the techniques for harvest of lateral thoracic tissue based on each of the pedicle options. A case is then presented to illustrate each option, and an algorithm is suggested for deciding which pedicle to use. Results: The authors have used lateral thoracic tissue for partial breast reconstruction for a variety of defects. In this report, the authors review the results of three illustrative cases. Conclusions: Partial breast reconstruction may be required for patients after breast-conserving therapy or after breast reconstruction by other methods. Lateral thoracic tissue can be safely transferred to correct defects in treated or reconstructed breast, or to obtain symmetry. Knowledge of the vascular anatomy to this region is helpful in understanding the pedicle options when harvesting this tissue. The authors present an algorithm for determining which pedicle is most appropriate for the transfer of lateral thoracic tissue for partial breast reconstruction. (Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 116: 762, 2005.) Breast reconstruction with the use of adjacent tissues from the axillary and lateral thoracic region is advocated in this article as an option for the surgeon, especially in patients who have excess and redundant tissues at this site. The ease of harvest and versatility of the flaps described makes them attractive. The use of lateral thoracic skin and subcutaneous tissue for breast reconstruction has advantages for several reasons. Proximity to the breast makes it an excellent choice for a local flap. It is similar in color and texture to the breast, and the donor-site scar is well hidden under the arm. A large volume of skin and subcutaneous fat can be harvested without violating any muscle. Also, in some patients, removing this axillary tissue, which may be an unsightly, redundant roll, has an added cosmetic benefit. Lateral thoracic soft tissue can be used for breast reconstruction with or without an implant, or for autologous breast augmentation by deepithelializing the flap and placing it behind the breast. A lateral thoracodorsal fasciocutaneous flap has been described for immediate breast reconstruction. 1 This tissue can also be har- From the Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Louisiana State University. Received for publication June 18; 2004; revised February 15, DOI: /01.prs a 762
2 Vol. 116, No. 3 / AUTOLOGOUS BREAST RECONSTRUCTION 763 vested based on several different pedicles: musculocutaneous perforating vessels through the latissimus dorsi; direct cutaneous branches of the thoracodorsal, axillary, or lateral thoracic vessels; and intercostal musculocutaneous perforators. These options are outlined below, along with a case that illustrates each. We propose an algorithm for deciding which vascular pedicle should be used in a given situation. THORACODORSAL ARTERY PERFORATOR FLAP Since its description in and reintroduction in the 1970s, the latissimus dorsi myocutaneous flap has been a mainstay for breast reconstruction. 3 An adipocutaneous flap based on the thoracodorsal perforating vessels was described in and has been used for breast reconstruction. 5 The thoracodorsal artery perforator flap can be used in place of the latissimus dorsi myocutaneous flap and has the distinct advantage of complete muscle sparing. The thoracodorsal branch of the subscapular artery, after giving off a branch to the serratus anterior, travels along the lateral undersurface of the latissimus dorsi muscle. It bifurcates into a horizontal (medial) and vertical (lateral) branch. 6 Both branches give off an approximately equal number of cutaneous perforators. 7 A large skin paddle can be designed over any of these perforators, provided that the selected vessels are of adequate diameter. There is a great deal of flexibility with respect to the orientation of the skin paddle. 4 Case 1 A 42-year-old woman presented who had undergone a lumpectomy, axillary dissection, and radiation therapy of the right breast for breast cancer 7 years previously. Two years later, she had a recurrence in the right breast for which she underwent a right completion mastectomy and a left prophylactic mastectomy. She underwent reconstruction with bilateral expanders, which were ultimately replaced with implants. She had several complications on the right (irradiated) side resulting in explantation. She was referred for bilateral breast reconstruction with autologous tissue and underwent bilateral superficial inferior epigastric artery free flap reconstruction. She developed fat necrosis in the right breast flap, which a plastic surgeon in her hometown treated with excision of the firm area and placement of a saline implant. She subsequently developed complications with the implant and required three more operations and ultimate explantation. At this time, the patient returned to us for an autologous augmentation/reconstruction of her smaller reconstructed right breast (Fig. 1). The lateral thoracic tissue was marked lateral to the breast with the 7-cm base of the flap at the anterior axillary line as described by Holmstrom and Lossing. 8 Thoracodorsal perforating vessels are identified with a handheld Doppler probe. The triangular design follows the curve of the ribs FIG. 1. Patient after bilateral superficial inferior epigastric artery reconstruction and subsequent problems leading to asymmetry. laterally. An intercostal perforating vessel was also identified at the base of the flap. The patient was placed in the supine position with a bolster under the right lateral back. The arm was abducted at 90 degrees. Flap dissection was begun lateral to the anterior axillary line in a subfascial plane. Thoracodorsal perforators were identified under loupe magnification and preserved (Fig. 2, above). The two thoracodorsal perforators were dissected down through the fibers of the latissimus dorsi muscle to the thoracodorsal artery. The thoracodorsal artery was then freed from surrounding tissue and from the thoracodorsal nerve (Fig. 2, center). Dissection was continued to the base of the flap, at which point the capsule from the prior implant was encountered at the lateral edge of the pectoralis muscle. Significantly, because of scar tissue from prior operations, the intercostal perforator was not present. The flap was completely isolated on its thoracodorsal artery perforator pedicle and passed between the fibers of the latissimus dorsi muscle. The flap was then deepithelialized. A space was created between the reconstructed breast and the pectoralis fascia, and the flap was turned over, passed into this space, and anchored with a 2-0 Vicryl stitch (Ethicon, Inc., Somerville, N.J.) (Fig. 2, below). A drain was placed and the defect was closed primarily (Fig. 3). LATERAL THORACIC FLAP (AXILLARY FLAP) Axillary and lateral thoracic tissue can derive its blood supply in part from one or more direct cutaneous branches from the lateral thoracic artery, the axillary artery (accessory lateral thoracic artery), or the thoracodorsal artery 5 (or rarely from the subscapular artery). 9 Any of these vessels, when present, are excellent candidates for the basis of skin transfer for reconstruction, and their use as pedicles for free transfer of axillary tissue has been described There are varying reports as to the consistency of these vessels. In a study of 100 cadaveric dissections of the subscapular-thoracodorsal artery system, Roswell et al. found a direct cutaneous branch from the thoracodorsal artery in 47 percent of
3 764 PLASTIC AND RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY, September 1, 2005 FIG. 3. The defect is closed primarily and the drain is placed. As with the thoracodorsal artery perforator, the skin and subcutaneous fat for transfer are isolated on the cutaneous vessels. The pedicle is then freed from surrounding tissue and transferred into position as described below. Case 2 A 48-year-old woman who had undergone a lumpectomy, axillary dissection, radiation, and chemotherapy of the right breast for cancer presented with a deformity of the inferior pole of the right breast (Fig. 4). The skin paddle was designed similar to that in case 1. The width of the base was 7 cm and the length was 16 cm, extending over the latissimus dorsi muscle. Dissection was started laterally at the apex of the flap and continued in a subfascial plane toward the anterior axillary line. As the dissection proceeded anteriorly, no adequate thoracodorsal perforators were identified. Just anterior to the edge of the latissimus dorsi muscle, a direct cutaneous branch off of the thoracodorsal artery was identified and preserved. This pedicle was deemed adequate to perfuse the entire flap. The flap was completely elevated off of the underlying muscle (Fig. 5, above). An island flap was created by transecting the medial skin bridge. A subglandular dissection FIG. 2.(Above) Two thoracodorsal artery perforators were identified and preserved. (Center) The thoracodorsal artery perforator is dissected through the muscle, and the thoracodorsal nerve is preserved. (Below) The flap is turned over and secured behind the breast flap. The perforating vessels are seen passing into the flap. subjects and from the subscapular artery in 7 percent. 9 Allen, et al. repeated this study on 20 cadavers in 2003 and found a direct cutaneous branch from the thoracodorsal artery in 55 percent of cadavers. 9 FIG. 4. A 48-year-old patient after lumpectomy and radiation therapy.
4 Vol. 116, No. 3 / AUTOLOGOUS BREAST RECONSTRUCTION 765 exchanges for recurrent, severe, grade IV capsular contractures; pain; extreme firmness; and poor shape and symmetry. We performed a bilateral superficial inferior epigastric artery flap reconstruction. Postoperatively, the patient s right reconstructed breast was smaller than the left, and the patient requested better symmetry. The flap was designed similar to those in cases 1 and 2. The intercostal perforators were identified in the fifth interspace at the anterior axillary line with a Doppler probe (Fig. 6). The flap was lifted from lateral to medial off of the underlying latissimus. Dissection proceeded posterior to anterior until the intercostal perforators were identified (Fig. 7). The skin at the base of the flap was then transected, and the flap was deepithelialized and the retromammary space developed. The flap was then turned over, placed into the pocket, and sutured in place. FIG. 5.(Above) The flap is elevated off the latissimus dorsi muscle. (Below) The flap is used to reconstruct the lower pole. and scar contracture release was then performed to create a pocket for the flap. The flap was then deepithelialized and flipped over. The flap was then placed in the retromammary space to reconstruct the inferior pole and augment the breast (Fig. 5, below). A mastopexy was performed on the contralateral breast for symmetry. The patient did well postoperatively, with no complications. INTERCOSTAL PERFORATOR FLAP Lateral thoracic skin and subcutaneous tissue has been used as a fasciocutaneous flap for axillary and breast reconstruction. 1,8,13 Basing the flap on an intercostal perforator that enters the flap s base at the anterior axillary line allows the surgeon to create a reliable flap of large dimensions that can dramatically aid in breast reconstruction. This tissue can be used as a rotation flap with or without an implant, or it too can be used as a turnover flap to augment the lower pole as described below. Case 3 A 61-year-old patient was treated for breast cancer with bilateral mastectomy and tissue expander reconstruction 4 years previous to presenting to us. She had several implant DISCUSSION Various breast abnormalities can result in partial breast defects. Women who are diagnosed with early-stage breast cancer are increasingly being treated with breast-conservation therapy. Breast-conservation therapy involves lumpectomy and sentinel node biopsy with or without axillary node dissection, and radiation therapy. This has resulted in a variety of breast deformities that ultimately require further treatment. In fact, 20 to 30 percent of patients who have breast-conservation therapy have a poor or mediocre cosmetic result, with deformity and asymmetry as a result of lumpectomy and radiation fibrosis. 14,15 The indications for breast-conservation therapy are expanding to include more advanced disease, 16,17 and as many as 71 percent of patients treated for cosmetic sequelae after breast-conservation therapy will ultimately seek partial breast reconstruction. 18 In addition, with the increasing popularity of breast augmentation and with the young age at which many breast augmentations are performed, plastic surgeons are see- FIG. 6. Intercostal perforators were identified at the base of the flap at the anterior axillary line (X).
5 766 PLASTIC AND RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY, September 1, 2005 FIG. 7. Intercostal perforators at the base of the flap. ing an increasing number of patients with what Van Landuyt et al. have called the augmentation cripple, the patient who has failed cosmetic augmentation with repeated infections, hematomas, or sever capsular contractures. 19 Many of these patients are looking for an autologous solution to their breast deformity. Most partial breast defects require a moderate amount of volume for reconstruction, and many do not require skin. These defects have traditionally been handled with a latissimus dorsi myocutaneous flap. We have found that the lateral thoracic skin and subcutaneous tissue is an ideal candidate for these defects. Taken from the natural redundancy of tissue at the lateral thorax, the scar is well hidden under the arm, and there is often an added cosmetic benefit to removing what sometimes is an unsightly roll. The scar is approximately 15 cm and concealed in the bra line. In addition, seromas seen with the latissimus myocutaneous flap is not noted to be a frequent problem. This flap can be used to recruit tissue with or without a skin island for augmentation or reconstruction. ALGORITHM The three cases presented in this report illustrate the variety of options that are available for reconstruction with tissue in the axillary and lateral thoracic region. The vascular anatomy of this area has been studied extensively. An algorithm for choosing a vascular pedicle can be described based on knowledge of this anatomy and preoperative Doppler planning. The triangular flap is designed with its base at the anterior axillary line. The base of the flap is marked with a 6- to 8-cm vertical height, centered directly over an interspace. If the tissue is needed for reconstructing the inferior pole, and if the use of a skin paddle is anticipated, the fifth interspace is chosen. If the tissue is needed for augmentation and thus flap deepithelialization is planned, the flap is centered over the fourth interspace. The superior and inferior incisions of the triangular flap are marked on the lateral thorax. The flap curves slightly upward overlying the contour of the ribs, coming to a point over the latissimus dorsi. The length of the flap is usually 15 cm. A hand-held Doppler probe is used to locate the thoracodorsal perforating vessels at the lateral edge of the latissimus dorsi and the intercostal perforator at the base of the flap. Pedicle Option I Starting the dissection lateral to the anterior axillary line, the skin and subcutaneous fat is incised down to the lateral latissimus dorsi. The dissection continues medially in a subfascial plane. Under loupe magnification, the thoracodorsal perforators are identified near the lateral edge of the latissimus dorsi. If they are adequate for flap perfusion, they are preserved and dissected down through the muscle fibers to the thoracodorsal artery. The thoracodorsal nerve is preserved and the flap is then passed through the opening on the muscle. The thoracodorsal vessels are freed proximally as needed to mobilize the flap into position. Pedicle Option II If the thoracodorsal perforating vessels are deemed to be inadequate for any reason, the dissection is continued anteriorly. The next option for flap perfusion would be direct cutaneous branches of the axillary, thoracodorsal, or lateral thoracic vessels. If direct cutaneous vessels are available, this option is advantageous in that dissection does not involve the latissimus dorsi. This pedicle can also be freed by dissecting the cutaneous branch to its parent vessel. This allows good mobilization of the flap. Pedicle Option III If neither of the first two options seems adequate, the intercostal perforating vessels provide an excellent option. They are very consistent and reliable, and very capable of carrying the flap. In patients who have had extensive surgery in this area, however, these vessels are sometime not available. Based on the intercostal perforators, this flap can be rotated 90 de-
6 Vol. 116, No. 3 / AUTOLOGOUS BREAST RECONSTRUCTION 767 grees as described by Holmstrom and Lossing 13 or deepithelialized and turned over. CONCLUSIONS All of these options make the lateral thoracic area a versatile donor site with a myriad of possibilities for flap perfusion. The use of this tissue has advantages, including complete muscle preservation, a well-hidden scar, and removal of redundant lateral thoracic tissue. Knowledge of the vascular anatomy and preoperative Doppler planning provide the surgeon with several perfusion options, making this a safe and reliable procedure. It can also be performed in approximately 1 hour. An algorithm for the use of lateral thoracic tissue is presented. Lateral thoracic tissue should be considered as a donor site for a variety of breast reconstruction defects. Nassif Elias Soueid, M.D. 330 Julia Street, Apt. 203 New Orleans, La boballen@diepflap.com PREFERENCES 1. Krupp, S. Thoracic fascio-cutaneous flap (in French). Helv. Chir. Acta 58: 69, Tansini, I. Coverage of the anterior chest wall following mastectomy (in Italian). Guz. Mal. Ital. 57: 141, Schneider, W. J., Hill, H. L., Jr., and Brown, R. G. Latissimus dorsi myocutaneous flap for breast reconstruction. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 30: 277, Angrigiani, C., Grilli, D., and Siebert, J. Latissimus dorsi musculocutaneous flap without muscle. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 96: 1608, Khoobehi, K., Allen, R. J., and Montegut, W. J. Thoracodorsal artery perforator flap for reconstruction. 90th Annual Scientific Assembly of the Southern Medical Association, Baltimore, Maryland, November South. Med. J. 89: Strauch, B., and Yu, H.-L. Atlas of Microvascular Surgery: Anatomy and Operative Approaches. New York: Thieme, P Heitmann, C., Guerra, A., Metzinger, S. W., Levin, L. S., and Allen, R. J. The thoracodorsal artery perforator flap: Anatomic basis and clinical application. Ann. Plast. Surg. 551: 23, Holmstrom, H., and Lossing, C. The lateral thoracodorsal flap in breast reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 577: 933, Roswell, A. R., Davies, D. M., Eisenberg, N., and Taylor, G. I. The anatomy of the subscapular-thoracodorsal arterial system: Study of 100 cadaver dissections. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 537: 574, Harii, K., Torii, S., and Sekiguchi, J. The free lateral thoracic flap. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 62: 212, Baudet, J., Guimberteau, J. C., and Nascimento, E. Successful clinical transfer of two free thoraco-dorsal axillary flaps. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 558: 680, Boeckx, W. D., De Coninck, A., and Vanderlinden, E. Ten free flap transfers. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 57: 707, Holmstrom, H., and Lossing, C. Lateral thoracodorsal flap: An intercostal perforator flap for breast reconstruction. Semin. Plast. Surg. 16: 53, Amichetti, M., Busana, L., and Caffo, O. Long-term cosmetic outcome and toxicity in patients treated with quadrantectomy and radiation therapy for early-stage breast cancer. Oncology 52: 177, Rkose, M. A., Olivotto, I. A., Cady, B., et al. Conservative surgery and radiation therapy for early breast cancer: Long-term cosmetic results. Arch. Surg. 124: 153, Calais, G., Berger, C., Descamps, P., et al. Conservative treatment feasibility with chemotherapy, surgery and radiotherapy for patients with breast carcinoma larger than 3 cm. Cancer 74: 1283, Scholl, S. M., Fourquet, A., Asselain, B., et al. Neoadjuvant versus adjuvant chemotherapy in premenopausal patients with tumors considered too large for Breast conserving surgery: Preliminary results of a randomized trial: S6. Eur. J. Cancer 30: 645, Clough, K. B., Cuminet, J., Fitoussi, A., et al. Cosmetic sequelae after conservative treatment for breast cancer: Classification and results of surgical correction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 41: 471, Van Landuyt, K., Hamdi, M., Blondeel, P., and Monstrey, S. Autologous breast augmentation by pedicled perforator flaps. Personal communication.
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5. Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. JPRAS Open. journal homepage:
 JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
The free thoracodorsal artery perforator flap in head and neck reconstruction
 European Annals of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck diseases (2012) 129, 167 171 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com TECHNICAL NOTE The free thoracodorsal artery perforator flap in head and neck
European Annals of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck diseases (2012) 129, 167 171 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com TECHNICAL NOTE The free thoracodorsal artery perforator flap in head and neck
Anatomical Landmarks for Safe Elevation of the Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap: A Cadaveric Study
 Anatomical Landmarks for Safe Elevation of the Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap: A Cadaveric Study Saeed Chowdhry, MD, Ron Hazani, MD, Philip Collis, BS, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD University of
Anatomical Landmarks for Safe Elevation of the Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap: A Cadaveric Study Saeed Chowdhry, MD, Ron Hazani, MD, Philip Collis, BS, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD University of
AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION
 CHAPTER 18 AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION Ali A. Qureshi, MD and Smita R. Ramanadham, MD Aesthetic surgery of the breast aims to either correct ptosis with a mastopexy,
CHAPTER 18 AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION Ali A. Qureshi, MD and Smita R. Ramanadham, MD Aesthetic surgery of the breast aims to either correct ptosis with a mastopexy,
Strattice Reconstructive Tissue Matrix used in the repair of rippling
 Clinical case study Strattice Tissue Matrix Strattice Reconstructive Tissue Matrix used in the repair of rippling Steven Teitelbaum, MD* Santa Monica, CA Case summary A 48-year-old woman with a history
Clinical case study Strattice Tissue Matrix Strattice Reconstructive Tissue Matrix used in the repair of rippling Steven Teitelbaum, MD* Santa Monica, CA Case summary A 48-year-old woman with a history
Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps
 Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. Houston, Texas Breast reconstruction using the
Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. Houston, Texas Breast reconstruction using the
The usefulness of pedicled perforator flap in partial breast reconstruction after breast conserving surgery in Korean women
 The usefulness of pedicled perforator flap in partial breast reconstruction after breast conserving surgery in Korean women Jae Bong Kim 1, Dong Kyu Kim 1, Jeong Woo Lee 1, Kang Young Choi 1, Ho Yun Chung
The usefulness of pedicled perforator flap in partial breast reconstruction after breast conserving surgery in Korean women Jae Bong Kim 1, Dong Kyu Kim 1, Jeong Woo Lee 1, Kang Young Choi 1, Ho Yun Chung
Endoscopic assisted harvest of the pedicled pectoralis major muscle flap
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 170 174 Endoscopic assisted harvest of the pedicled pectoralis major muscle flap Arif Turkmen*, A. Graeme B. Perks Plastic Surgery Department, Nottingham City
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 170 174 Endoscopic assisted harvest of the pedicled pectoralis major muscle flap Arif Turkmen*, A. Graeme B. Perks Plastic Surgery Department, Nottingham City
Breast Reconstruction Postmastectomy. Using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis in breast reconstruction with tissue expander.
 Breast Reconstruction Postmastectomy. Using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis in breast reconstruction with tissue expander. Strong and flexible Bacterially inactivated Provides implant support Breast Reconstruction
Breast Reconstruction Postmastectomy. Using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis in breast reconstruction with tissue expander. Strong and flexible Bacterially inactivated Provides implant support Breast Reconstruction
Scapular & Parascapular flap FLAP TERRITORY ANATOMY. is normally accompanied by two venae comitantes.
 Scapular & Parascapular flap FLAP TERRITORY This is a composite flap that is situated over the scapula with various incisional arrangements. It can be harvested as a skin and subcutaneous tissue flap,
Scapular & Parascapular flap FLAP TERRITORY This is a composite flap that is situated over the scapula with various incisional arrangements. It can be harvested as a skin and subcutaneous tissue flap,
The Use of Vertical Scar Techniques in Reconstructive Surgery
 The Use of Vertical Scar Techniques in Reconstructive Surgery 12 Moustapha Hamdi, Phillip Blondeel, Koenraad Van Landuyt, Stan Monstrey H e who does not possess a thing cannot give it. Folk tradition Introduction
The Use of Vertical Scar Techniques in Reconstructive Surgery 12 Moustapha Hamdi, Phillip Blondeel, Koenraad Van Landuyt, Stan Monstrey H e who does not possess a thing cannot give it. Folk tradition Introduction
Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC
 Downloaded from Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC What is Breast Reconstruction? Reconstruction of the breast involves recreating
Downloaded from Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC What is Breast Reconstruction? Reconstruction of the breast involves recreating
The Case FOR Oncoplastic Surgery in Small Breasts. Barbara L. Smith, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA USA
 The Case FOR Oncoplastic Surgery in Small Breasts Barbara L. Smith, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA USA Changing issues in breast cancer management Early detection
The Case FOR Oncoplastic Surgery in Small Breasts Barbara L. Smith, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA USA Changing issues in breast cancer management Early detection
Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman
 Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman Breast anatomy: Breast conserving surgery: The aim of wide local excision is to remove all invasive and in situ
Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman Breast anatomy: Breast conserving surgery: The aim of wide local excision is to remove all invasive and in situ
Four-flap Breast Reconstruction: Bilateral Stacked DIEP and PAP Flaps
 Original Article Breast Four-flap Breast Reconstruction: Bilateral Stacked DIEP and PAP Flaps James L. Mayo, MD Robert J. Allen, MD, FACS Alireza Sadeghi, MD, FACS Background: In cases of bilateral breast
Original Article Breast Four-flap Breast Reconstruction: Bilateral Stacked DIEP and PAP Flaps James L. Mayo, MD Robert J. Allen, MD, FACS Alireza Sadeghi, MD, FACS Background: In cases of bilateral breast
Anatomical study. Clinical study. R. Ogawa, H. Hyakusoku, M. Murakami, R. Aoki, K. Tanuma* and D. G. Pennington?
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2002) 55, 396-40 I 9 2002 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi: 10.1054/bjps.2002.3877 PLASTIC SURGERY An anatomical and clinical study of the dorsal intercostal
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2002) 55, 396-40 I 9 2002 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi: 10.1054/bjps.2002.3877 PLASTIC SURGERY An anatomical and clinical study of the dorsal intercostal
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty
 CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
A Clinical Anatomic Study of Internal Mammary Perforators as Recipient Vessels for Breast Reconstruction
 A Clinical Anatomic Study of Internal Mammary Perforators as Recipient Vessels for Breast Reconstruction In-Soo Baek 1, Jae-Pil You 1, Sung-Mi Rhee 1, Gil-Su Son 2, Deok-Woo Kim 1, Eun-Sang Dhong 1, Seung-Ha
A Clinical Anatomic Study of Internal Mammary Perforators as Recipient Vessels for Breast Reconstruction In-Soo Baek 1, Jae-Pil You 1, Sung-Mi Rhee 1, Gil-Su Son 2, Deok-Woo Kim 1, Eun-Sang Dhong 1, Seung-Ha
Simultaneous Bilateral Breast Reconstruction With In-the-Crease Inferior Gluteal Artery Perforator Flaps
 BREAST SURGERY Simultaneous Bilateral Breast Reconstruction With In-the-Crease Inferior Gluteal Artery Perforator Flaps Joshua L. Levine, MD,* Quintessa Miller, MD, Julie Vasile, MD,* Kamran Khoobehi,
BREAST SURGERY Simultaneous Bilateral Breast Reconstruction With In-the-Crease Inferior Gluteal Artery Perforator Flaps Joshua L. Levine, MD,* Quintessa Miller, MD, Julie Vasile, MD,* Kamran Khoobehi,
The Thoracodorsal Artery Perforator Flap: Clinical Experience and Anatomic Study with Emphasis on Harvest Techniques
 The Thoracodorsal Artery Perforator Flap: Clinical Experience and Anatomic Study with Emphasis on Harvest Techniques Aldo Benjamin Guerra, M.D., Stephen Eric Metzinger, M.D., Kiersten Maria Lund, M.D.,
The Thoracodorsal Artery Perforator Flap: Clinical Experience and Anatomic Study with Emphasis on Harvest Techniques Aldo Benjamin Guerra, M.D., Stephen Eric Metzinger, M.D., Kiersten Maria Lund, M.D.,
The decision to repair a partial mastectomy CME. State of the Art and Science in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction.
 CME State of the Art and Science in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction Steven J. Kronowitz, M.D. Houston, Texas Learning Objectives: After reading this article, the participant should be able to: 1.
CME State of the Art and Science in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction Steven J. Kronowitz, M.D. Houston, Texas Learning Objectives: After reading this article, the participant should be able to: 1.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer. Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery Plastic-reconstructive aspects after mastectomy Versions 2002 2017: Audretsch / Bauerfeind
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery Plastic-reconstructive aspects after mastectomy Versions 2002 2017: Audretsch / Bauerfeind
The most common type of breast reconstruction
 BREAST Breast Reconstruction with Perforator Flaps Jay W. Granzow, M.D., M.P.H. Joshua L. Levine, M.D. Ernest S. Chiu, M.D. Maria M. LoTempio, M.D. Robert J. Allen, M.D. New Orleans, La.; Charleston, S.C.;
BREAST Breast Reconstruction with Perforator Flaps Jay W. Granzow, M.D., M.P.H. Joshua L. Levine, M.D. Ernest S. Chiu, M.D. Maria M. LoTempio, M.D. Robert J. Allen, M.D. New Orleans, La.; Charleston, S.C.;
Mitchell Buller, MEng, a Adee Heiman, BA, a Jared Davis, MD, b ThomasJ.Lee,MD, b Nicolás Ajkay, MD, FACS, c and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD, FACS b
 Immediate Breast Reconstruction of a Nipple Areolar Lumpectomy Defect With the L-Flap Skin Paddle Breast Reduction Design and Contralateral Reduction Mammoplasty Symmetry Procedure: Optimizing the Oncoplastic
Immediate Breast Reconstruction of a Nipple Areolar Lumpectomy Defect With the L-Flap Skin Paddle Breast Reduction Design and Contralateral Reduction Mammoplasty Symmetry Procedure: Optimizing the Oncoplastic
Breast Reconstruction: Current Strategies and Future Opportunities
 Breast Reconstruction: Current Strategies and Future Opportunities Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
Breast Reconstruction: Current Strategies and Future Opportunities Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
NIPPLE SPARING PRE-PECTORAL BREAST RECONSTRUCTION
 NIPPLE SPARING PRE-PECTORAL BREAST RECONSTRUCTION 42 yo female healthy athlete Right breast mass. Past medical history: none Family history: aunt with Breast cancer Candidates for nipple-sparing mastectomy
NIPPLE SPARING PRE-PECTORAL BREAST RECONSTRUCTION 42 yo female healthy athlete Right breast mass. Past medical history: none Family history: aunt with Breast cancer Candidates for nipple-sparing mastectomy
Oncoplastic breast surgery in a Danish perspective II: Reconstructive strategy in oncoplastic breast surgery
 Oncoplastic breast surgery in a Danish perspective II: Reconstructive strategy in oncoplastic breast surgery Michael Rose, MD Department of Surgery and Plastic Surgery, Hospital of Southwest Jutland, Denmark
Oncoplastic breast surgery in a Danish perspective II: Reconstructive strategy in oncoplastic breast surgery Michael Rose, MD Department of Surgery and Plastic Surgery, Hospital of Southwest Jutland, Denmark
Breast Reconstruction Options
 Breast Reconstruction Options Natural reconstruction using your ABDOMINAL tissue: TRAM Flap (Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous) There are various forms of TRAM flap reconstruction that are commonly
Breast Reconstruction Options Natural reconstruction using your ABDOMINAL tissue: TRAM Flap (Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous) There are various forms of TRAM flap reconstruction that are commonly
Anatomical Background of the Perforator Flap Based on the Deep Branch of the Superficial Circumflex Iliac Artery (SCIP Flap): A Cadaveric Study
 Anatomical Background of the Perforator Flap Based on the Deep Branch of the Superficial Circumflex Iliac Artery (SCIP Flap): A Cadaveric Study Raphael Sinna, MD, a Hassene Hajji, MD, b Quentin Qassemyar,
Anatomical Background of the Perforator Flap Based on the Deep Branch of the Superficial Circumflex Iliac Artery (SCIP Flap): A Cadaveric Study Raphael Sinna, MD, a Hassene Hajji, MD, b Quentin Qassemyar,
Breast Reconstruction Surgery
 Breast Reconstruction Surgery I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for Breast Reconstruction Surgery when it is determined to be medically necessary and when it meets the medical criteria
Breast Reconstruction Surgery I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for Breast Reconstruction Surgery when it is determined to be medically necessary and when it meets the medical criteria
Frederick J. Duffy, Jr., MD, FACS and Brice W. McKane, MD, FACS BREAST RECONSTRUCTION
 Frederick J. Duffy, Jr., MD, FACS and Brice W. McKane, MD, FACS BREAST RECONSTRUCTION BREAST RECONSTRUCTION: A WOMAN S DECISION Options and Information Our approach to breast reconstruction entails a very
Frederick J. Duffy, Jr., MD, FACS and Brice W. McKane, MD, FACS BREAST RECONSTRUCTION BREAST RECONSTRUCTION: A WOMAN S DECISION Options and Information Our approach to breast reconstruction entails a very
Central Breast Excision With Immediate Autologous Reconstruction for Recurrent Periductal Sepsis: An Application of Oncoplastic Surgical Techniques
 Central Breast Excision With Immediate Autologous Reconstruction for Recurrent Periductal Sepsis: An Application of Oncoplastic Surgical Techniques Sinclair M. Gore, FRCS(Plast), a Gordon C. Wishart, FRCS,
Central Breast Excision With Immediate Autologous Reconstruction for Recurrent Periductal Sepsis: An Application of Oncoplastic Surgical Techniques Sinclair M. Gore, FRCS(Plast), a Gordon C. Wishart, FRCS,
Tor Chiu. Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161
 18 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap Tor Chiu Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap FLAP TERRITORY The deep inferior epigastric
18 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap Tor Chiu Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap FLAP TERRITORY The deep inferior epigastric
Advances in Localized Breast Cancer
 Advances in Localized Breast Cancer Melissa Camp, MD, MPH and Fariba Asrari, MD June 18, 2018 Moderated by Elissa Bantug 1 Advances in Surgery for Breast Cancer Melissa Camp, MD June 18, 2018 2 Historical
Advances in Localized Breast Cancer Melissa Camp, MD, MPH and Fariba Asrari, MD June 18, 2018 Moderated by Elissa Bantug 1 Advances in Surgery for Breast Cancer Melissa Camp, MD June 18, 2018 2 Historical
Reconstruction of axillary scar contractures retrospective study of 124 cases over 25 years
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2003), 56, 100 105 q 2003 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/s0007-1226(03)00035-3 Reconstruction
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2003), 56, 100 105 q 2003 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/s0007-1226(03)00035-3 Reconstruction
How To Make a Good Mastectomy for Reconstruction Based on the Anatomy. Zhang Jin, Ph.D MD
 How To Make a Good Mastectomy for Reconstruction Based on the Anatomy Zhang Jin, Ph.D MD Deputy Director and Professor Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital People s Republic of China
How To Make a Good Mastectomy for Reconstruction Based on the Anatomy Zhang Jin, Ph.D MD Deputy Director and Professor Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital People s Republic of China
Vertical mammaplasty has been developed
 BREAST Y-Scar Vertical Mammaplasty David A. Hidalgo, M.D. New York, N.Y. Background: Vertical mammaplasty is an effective alternative to inverted-t methods. Among other benefits, it results in a significantly
BREAST Y-Scar Vertical Mammaplasty David A. Hidalgo, M.D. New York, N.Y. Background: Vertical mammaplasty is an effective alternative to inverted-t methods. Among other benefits, it results in a significantly
Updates in Breast Care. Truth or Hype. History of Breast Cancer Surgery. Dr Karen Barbosa 5/3/2017 4/20/2017
 Updates in Breast Care Dr Karen Barbosa 4/20/2017 Truth or Hype Princess Bust Developer Sears, Roebuck and Co. 1897 Promised to make the breast round, firm and beautiful History of Breast Cancer Surgery
Updates in Breast Care Dr Karen Barbosa 4/20/2017 Truth or Hype Princess Bust Developer Sears, Roebuck and Co. 1897 Promised to make the breast round, firm and beautiful History of Breast Cancer Surgery
Advances in Breast Surgery. Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015
 Advances in Breast Surgery Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015 Objectives Understand the surgical treatment of breast cancer Be able to determine when a lumpectomy
Advances in Breast Surgery Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015 Objectives Understand the surgical treatment of breast cancer Be able to determine when a lumpectomy
Advances and Innovations in Breast Reconstruction and Brest Surgery Presented by PCMC plastic surgeons
 Advances and Innovations in Breast Reconstruction and Brest Surgery Presented by PCMC plastic surgeons Options for reconstruction after mastectomy Implants Autologous tissue = from your own body: skin
Advances and Innovations in Breast Reconstruction and Brest Surgery Presented by PCMC plastic surgeons Options for reconstruction after mastectomy Implants Autologous tissue = from your own body: skin
Outcomes Evaluation Following Bilateral Breast Reconstruction Using Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flaps
 BREAST SURGERY Outcomes Evaluation Following Bilateral Breast Reconstruction Using Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flaps Albert Losken, MD, FACS, Claire S. Nicholas, MD, Ximena A. inell, MD, and Grant W.
BREAST SURGERY Outcomes Evaluation Following Bilateral Breast Reconstruction Using Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flaps Albert Losken, MD, FACS, Claire S. Nicholas, MD, Ximena A. inell, MD, and Grant W.
Modified Radical Mastectomy
 Modified Radical Mastectomy Valerie L. Staradub, MD, and Monica Morrow, MD S urgical management options for breast cancer include modified radical mastectomy (MRM), MRM with immediate reconstruction, and
Modified Radical Mastectomy Valerie L. Staradub, MD, and Monica Morrow, MD S urgical management options for breast cancer include modified radical mastectomy (MRM), MRM with immediate reconstruction, and
The progress in microsurgical procedures has led
 Original Article Breast reconstruction with free anterolateral thigh flap Ranjit Raje, Ramesh Chepauk, Kanti Shetty, Rajendra Prasad J. S. Plastic & Reconstructive Services, Department of Surgical Oncology,
Original Article Breast reconstruction with free anterolateral thigh flap Ranjit Raje, Ramesh Chepauk, Kanti Shetty, Rajendra Prasad J. S. Plastic & Reconstructive Services, Department of Surgical Oncology,
Current Strategies in Breast Reconstruction
 Current Strategies in Breast Reconstruction Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 12 th Annual School of
Current Strategies in Breast Reconstruction Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 12 th Annual School of
Essential Anatomy for oncoplastic surgery. Omar Z. Youssef M.D Professor of surgical oncology NCI- Cairo University
 Essential Anatomy for oncoplastic surgery Omar Z. Youssef M.D Professor of surgical oncology NCI- Cairo University Introduction Rationale for anatomical basis for OPS Anatomical considerations: 1. Surface
Essential Anatomy for oncoplastic surgery Omar Z. Youssef M.D Professor of surgical oncology NCI- Cairo University Introduction Rationale for anatomical basis for OPS Anatomical considerations: 1. Surface
The lumbar artery perforator based island flap: anatomical study and case reports
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (1999), 52, 541 546 1999 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons The lumbar artery perforator based island flap: anatomical study and case reports H. Kato*, M. Hasegawa,
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (1999), 52, 541 546 1999 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons The lumbar artery perforator based island flap: anatomical study and case reports H. Kato*, M. Hasegawa,
Clinical Study Breast-Volume Displacement Using an Extended Glandular Flap for Small Dense Breasts
 Plastic Surgery International Volume 2011, Article ID 359842, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2011/359842 Clinical Study Breast-Volume Displacement Using an Extended Glandular Flap for Small Dense Breasts Tomoko Ogawa,
Plastic Surgery International Volume 2011, Article ID 359842, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2011/359842 Clinical Study Breast-Volume Displacement Using an Extended Glandular Flap for Small Dense Breasts Tomoko Ogawa,
Advances and Surgical Decision-Making for Breast Reconstruction
 893 Advances and Surgical Decision-Making for Breast Reconstruction Steven J. Kronowitz, MD 1 Henry M. Kuerer, MD, PhD 2 1 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, The University of Texas M. D.
893 Advances and Surgical Decision-Making for Breast Reconstruction Steven J. Kronowitz, MD 1 Henry M. Kuerer, MD, PhD 2 1 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, The University of Texas M. D.
The Profunda Artery Perforator Flap: Investigating the Perforasome Using Three-Dimensional Computed Tomographic Angiography
 BREAST The Profunda Artery Perforator Flap: Investigating the Perforasome Using Three-Dimensional Computed Tomographic Angiography Corrine Wong, M.D. Purushottam Nagarkar, M.D. Sumeet Teotia, M.D. Nicholas
BREAST The Profunda Artery Perforator Flap: Investigating the Perforasome Using Three-Dimensional Computed Tomographic Angiography Corrine Wong, M.D. Purushottam Nagarkar, M.D. Sumeet Teotia, M.D. Nicholas
Staged approach to partial breast reconstruction to avoid mastectomy in women with breast cancer
 Original Article Staged approach to partial breast reconstruction to avoid mastectomy in women with breast cancer Pankaj G. Roy, Alexandra A. Tenovici Department of Breast Surgery, John Radcliffe Hospital,
Original Article Staged approach to partial breast reconstruction to avoid mastectomy in women with breast cancer Pankaj G. Roy, Alexandra A. Tenovici Department of Breast Surgery, John Radcliffe Hospital,
Reduction Mammaplasty and Mastopexy in Previously Irradiated Breasts
 Breast Surgery Reduction Mammaplasty and Mastopexy in Previously Irradiated Breasts Scott L. Spear, MD; Samir S. Rao, MD; Ketan M. Patel, MD; and Maurice Y. Nahabedian, MD The combination of lumpectomy
Breast Surgery Reduction Mammaplasty and Mastopexy in Previously Irradiated Breasts Scott L. Spear, MD; Samir S. Rao, MD; Ketan M. Patel, MD; and Maurice Y. Nahabedian, MD The combination of lumpectomy
Current Approaches to Managing Partial Breast Defects: The Role of Conservative Breast Surgery Reconstruction
 Review Current Approaches to Managing Partial Breast Defects: The Role of Conservative Breast Surgery Reconstruction ALEXANDRE MENDONÇA MUNHOZ 1, EDUARDO MONTAG 2, JOSÉ ROBERTO FILASSI 3 and ROLF GEMPERLI
Review Current Approaches to Managing Partial Breast Defects: The Role of Conservative Breast Surgery Reconstruction ALEXANDRE MENDONÇA MUNHOZ 1, EDUARDO MONTAG 2, JOSÉ ROBERTO FILASSI 3 and ROLF GEMPERLI
Interesting Case Series. Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle
 Interesting Case Series Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle Danielle H. Rochlin, BA, Justin M. Broyles, MD, and Justin M. Sacks, MD Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,
Interesting Case Series Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle Danielle H. Rochlin, BA, Justin M. Broyles, MD, and Justin M. Sacks, MD Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,
Samer Saour, Guido Libondi, Venkat Ramakrishnan. Introduction
 Original Article Microsurgical refinements with the use of internal mammary (IM) perforators as recipient vessels in transverse upper gracilis (TUG) autologous breast reconstruction Samer Saour, Guido
Original Article Microsurgical refinements with the use of internal mammary (IM) perforators as recipient vessels in transverse upper gracilis (TUG) autologous breast reconstruction Samer Saour, Guido
Extending breast conservation and other new oncoplastic techniques
 Extending breast conservation and other new oncoplastic techniques Dick Rainsbury BSBR 11-12 November 2013 Liverpool What s the maximum volume of the breast which can be resected during lumpectomy without
Extending breast conservation and other new oncoplastic techniques Dick Rainsbury BSBR 11-12 November 2013 Liverpool What s the maximum volume of the breast which can be resected during lumpectomy without
Few would deny that lower abdominal tissue BREAST. An Intraoperative Algorithm for Use of the SIEA Flap for Breast Reconstruction.
 BREAST An Intraoperative Algorithm for Use of the SIEA Flap for Breast Reconstruction Aldona J. Spiegel, M.D. Farah N. Khan, M.D. Houston, Texas Background: The deep inferior epigastric perforator (DIEP)
BREAST An Intraoperative Algorithm for Use of the SIEA Flap for Breast Reconstruction Aldona J. Spiegel, M.D. Farah N. Khan, M.D. Houston, Texas Background: The deep inferior epigastric perforator (DIEP)
ONCOPLASTIC SURGERY. Dr. Sadir Alrawi Director of Surgical Oncology Services. Dr. Humaa Darr Surgical Oncology Fellow
 Hessa St ONCOPLASTIC SURGERY Dr. Sadir Alrawi Director of Surgical Oncology Services Dr. Humaa Darr Surgical Oncology Fellow Al Sufouh Rd AL SUFOUH AL SUFOUH Sharaf DG Mall of the Emirates Mall Of the
Hessa St ONCOPLASTIC SURGERY Dr. Sadir Alrawi Director of Surgical Oncology Services Dr. Humaa Darr Surgical Oncology Fellow Al Sufouh Rd AL SUFOUH AL SUFOUH Sharaf DG Mall of the Emirates Mall Of the
Gastrocnemius Myocutaneous Flap: A Versatile Option to Cover the Defect of Upper and Middle Third Leg
 Downloaded from wjps.ir at 22:25 +0330 on Sunday November 18th 28 314 Gastrocnemius flap for coverage of leg defects Original Article Gastrocnemius Myocutaneous Flap: A Versatile Option to Cover the Defect
Downloaded from wjps.ir at 22:25 +0330 on Sunday November 18th 28 314 Gastrocnemius flap for coverage of leg defects Original Article Gastrocnemius Myocutaneous Flap: A Versatile Option to Cover the Defect
Breast Reconstruction. Westmead Breast Cancer Institute
 Breast Reconstruction Westmead Breast Cancer Institute What is breast reconstruction? Breast reconstruction is a surgical procedure that creates a shape on the chest wall following a mastectomy. Occasionally,
Breast Reconstruction Westmead Breast Cancer Institute What is breast reconstruction? Breast reconstruction is a surgical procedure that creates a shape on the chest wall following a mastectomy. Occasionally,
Breast Cancer Reconstruction
 Breast Cancer Jerome H. Liu, MD Tom S. Liu, MD Jerome H. Liu, MD Undergraduate: Brown University Medical School: University of California, Los Angeles Residency: UCLA Medical Center Fellowship:UCLA Medical
Breast Cancer Jerome H. Liu, MD Tom S. Liu, MD Jerome H. Liu, MD Undergraduate: Brown University Medical School: University of California, Los Angeles Residency: UCLA Medical Center Fellowship:UCLA Medical
Breast cancer reconstruction surgery (immediate and delayed) across Ontario: Patient indications and appropriate surgical options
 A Quality Initiative of the Program in Evidence-Based Care (PEBC), Cancer Care Ontario (CCO) Breast cancer reconstruction surgery (immediate and delayed) across Ontario: Patient indications and appropriate
A Quality Initiative of the Program in Evidence-Based Care (PEBC), Cancer Care Ontario (CCO) Breast cancer reconstruction surgery (immediate and delayed) across Ontario: Patient indications and appropriate
Mentosternal Contracture Treated With an Occipito-Scapular Flap in a 5-year-old Boy: A Case Report
 Mentosternal Contracture Treated With an Occipito-Scapular Flap in a 5-year-old Boy: A Case Report Armin Kraus, MD, Hans-Eberhard Schaller, MD, and Hans-Oliver Rennekampff, MD Department for Hand, Plastic,
Mentosternal Contracture Treated With an Occipito-Scapular Flap in a 5-year-old Boy: A Case Report Armin Kraus, MD, Hans-Eberhard Schaller, MD, and Hans-Oliver Rennekampff, MD Department for Hand, Plastic,
The dissection of the rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap with complete preservation of the anterior rectus sheath q
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 395 400 The dissection of the rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap with complete preservation of the anterior rectus sheath q D. Erni*, Y.D. Harder
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 395 400 The dissection of the rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap with complete preservation of the anterior rectus sheath q D. Erni*, Y.D. Harder
Breast Reconstruction in Women Under 30: A 10-Year Experience
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Breast Reconstruction in Women Under 30: A 10-Year Experience Warren A. Ellsworth, MD,* Barbara L. Bass, MD, FACS, Roman J. Skoracki, MD, à and Lior Heller, MD* *Division of Plastic Surgery,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Breast Reconstruction in Women Under 30: A 10-Year Experience Warren A. Ellsworth, MD,* Barbara L. Bass, MD, FACS, Roman J. Skoracki, MD, à and Lior Heller, MD* *Division of Plastic Surgery,
Anatomical Study of Pectoral Nerves and its Implications in Surgery
 DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2014/8631.4545 Anatomy Section Original Article Anatomical Study of Pectoral Nerves and its Implications in Surgery Prakash KG 1, Saniya K 2 ABSTRACT Introduction: This anatomical study
DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2014/8631.4545 Anatomy Section Original Article Anatomical Study of Pectoral Nerves and its Implications in Surgery Prakash KG 1, Saniya K 2 ABSTRACT Introduction: This anatomical study
rupture, you may notice silicone in their lymph nodes on radiographs. This may be seen and help us detect that there is a rupture.
 Hello. I m Melissa Crosby. I m an Associate Professor at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in the Department of Plastic Surgery. I d like to discuss with you the Late Effects of Breast
Hello. I m Melissa Crosby. I m an Associate Professor at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in the Department of Plastic Surgery. I d like to discuss with you the Late Effects of Breast
Breast Cancer Atlas for Radiation Therapy Planning: Consensus Definitions
 Breast Cancer Atlas for Radiation Therapy Planning: Consensus Definitions 1 Collaborators Julia White 1, An Tai 1, Douglas Arthur 2, Thomas Buchholz 3, Shannon MacDonald 4, Lawrence Marks 5, Lori Pierce
Breast Cancer Atlas for Radiation Therapy Planning: Consensus Definitions 1 Collaborators Julia White 1, An Tai 1, Douglas Arthur 2, Thomas Buchholz 3, Shannon MacDonald 4, Lawrence Marks 5, Lori Pierce
Breast Restoration Surgery After a mastectomy
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Breast Restoration Surgery After a mastectomy This handout explains the most common procedures that are used at University of Washington Medical Center (UWMC) to restore a
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Breast Restoration Surgery After a mastectomy This handout explains the most common procedures that are used at University of Washington Medical Center (UWMC) to restore a
Nipple-Areolar Complex Reconstruction: A Review of the Literature and Introduction of the Rectangle-to-Cube Nipple Flap
 Nipple-Areolar Complex Reconstruction: A Review of the Literature and Introduction of the Rectangle-to-Cube Nipple Flap Joshua T. Henderson, BA, a ThomasJ.Lee,MD, b Andrew M. Swiergosz, BS, a Andrea R.
Nipple-Areolar Complex Reconstruction: A Review of the Literature and Introduction of the Rectangle-to-Cube Nipple Flap Joshua T. Henderson, BA, a ThomasJ.Lee,MD, b Andrew M. Swiergosz, BS, a Andrea R.
BREAST CANCER SURGERY. Dr. John H. Donohue
 Dr. John H. Donohue HISTORY References to breast surgery in ancient Egypt (ca 3000 BCE) Mastectomy described in numerous medieval texts Petit formulated organized approach in 18 th Century Improvements
Dr. John H. Donohue HISTORY References to breast surgery in ancient Egypt (ca 3000 BCE) Mastectomy described in numerous medieval texts Petit formulated organized approach in 18 th Century Improvements
Breast Reconstruction
 Steven E. Copit, M.D. Chief- Division of Plastic Surgery Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA analysis of The Defect Skin Breast Volume Nipple Areola Complex analysis of The Defect the
Steven E. Copit, M.D. Chief- Division of Plastic Surgery Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA analysis of The Defect Skin Breast Volume Nipple Areola Complex analysis of The Defect the
Jake Hutchins, M.D. Aaron Berg, D.O.
 Jake Hutchins, M.D. Aaron Berg, D.O. Jacob Hutchins is on the speaker s bureau, is a consultant, and has received research funding from Pacira Pharmaceuticals He also is a consultant for Insitu Biologics,
Jake Hutchins, M.D. Aaron Berg, D.O. Jacob Hutchins is on the speaker s bureau, is a consultant, and has received research funding from Pacira Pharmaceuticals He also is a consultant for Insitu Biologics,
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Breast Reconstructive Surgery After Mastectomy Page 1 of 8 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Breast Reconstructive Surgery After Mastectomy PRE-DETERMINATION
Breast Reconstructive Surgery After Mastectomy Page 1 of 8 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Breast Reconstructive Surgery After Mastectomy PRE-DETERMINATION
Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1714-7 RESEARCH Open Access Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes Chi Sun Yoon and Kyu Nam
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1714-7 RESEARCH Open Access Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes Chi Sun Yoon and Kyu Nam
Breast Surgery. for Reconstructive. Center of Excellence. city center of Düsseldorf. You will find us in the
 You will find us in the city center of Düsseldorf Rathaus Rhein Steinstraße Berger Allee Poststraße Bastionstraße Kasernenstraße Breite Straße Königsallee Grünstraße Berliner Allee Königsallee 88 Graf-Adolf-Platz
You will find us in the city center of Düsseldorf Rathaus Rhein Steinstraße Berger Allee Poststraße Bastionstraße Kasernenstraße Breite Straße Königsallee Grünstraße Berliner Allee Königsallee 88 Graf-Adolf-Platz
The biplanar oncoplastic technique case series: a 2-year review
 Original Article The biplanar oncoplastic technique case series: a 2-year review Alexander J. Kaminsky 1, Ketan M. Patel 2, Costanza Cocilovo 1, Maurice Y. Nahabedian 2, Reza Miraliakbari 3 1 INOVA Fairfax
Original Article The biplanar oncoplastic technique case series: a 2-year review Alexander J. Kaminsky 1, Ketan M. Patel 2, Costanza Cocilovo 1, Maurice Y. Nahabedian 2, Reza Miraliakbari 3 1 INOVA Fairfax
Chest wall reconstruction using a combined musculocutaneous anterolateral anteromedial thigh flap
 Free full text on www.ijps.org Case Report DOI: 10.4103/0970-0358.63966 Chest wall reconstruction using a combined musculocutaneous anterolateral anteromedial thigh flap Pearlie W. W. Tan, Chin-Ho Wong,
Free full text on www.ijps.org Case Report DOI: 10.4103/0970-0358.63966 Chest wall reconstruction using a combined musculocutaneous anterolateral anteromedial thigh flap Pearlie W. W. Tan, Chin-Ho Wong,
BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY
 UnitedHealthcare Commercial Coverage Determination Guideline BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY Guideline Number: SUR057 Effective Date: January 1, 2019 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
UnitedHealthcare Commercial Coverage Determination Guideline BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY Guideline Number: SUR057 Effective Date: January 1, 2019 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
A Review of 105 Subscapular-Based Flaps Harvested Using a New Dorsal Decubitus Position: How Far Can We Go?
 A Review of 105 Subscapular-Based Flaps Harvested Using a New Dorsal Decubitus Position: How Far Can We Go? Laurence S. Paek, MD, a Olivier Boa, MD, a Marc Revol, MD, b Jean-Marie Servant, MD, b Patrick
A Review of 105 Subscapular-Based Flaps Harvested Using a New Dorsal Decubitus Position: How Far Can We Go? Laurence S. Paek, MD, a Olivier Boa, MD, a Marc Revol, MD, b Jean-Marie Servant, MD, b Patrick
Institute of Reconstructive Plastic Surgery, New York University Medical Center, New York, NY USA
 Free full text on www.ijps.org Sheel Sharma, Gordon Kaplan Institute of Reconstructive Plastic Surgery, New York University Medical Center, New York, NY 10016 USA Address for correspondence: Dr. Sheel
Free full text on www.ijps.org Sheel Sharma, Gordon Kaplan Institute of Reconstructive Plastic Surgery, New York University Medical Center, New York, NY 10016 USA Address for correspondence: Dr. Sheel
BREAST AUGMENTATION TECHNIQUES
 BREAST AUGMENTATION TECHNIQUES Breast Augmentation Top Surgical Procedure in 2015 (Worldwide) Surgical Procedure : Breast Augmentation Rank : 1 Total : 1,488,992 Percent of Total Surgical Procedures :
BREAST AUGMENTATION TECHNIQUES Breast Augmentation Top Surgical Procedure in 2015 (Worldwide) Surgical Procedure : Breast Augmentation Rank : 1 Total : 1,488,992 Percent of Total Surgical Procedures :
Neil J. Zemmel, MD, FACS Steven J. Montante, MD Megan J. Russell, PA-C. Your Guide To BREAST RECONSTRUCTION
 Neil J. Zemmel, MD, FACS Steven J. Montante, MD Megan J. Russell, PA-C Your Guide To BREAST RECONSTRUCTION Introduction The diagnosis of breast cancer begins a journey of making many informed decisions
Neil J. Zemmel, MD, FACS Steven J. Montante, MD Megan J. Russell, PA-C Your Guide To BREAST RECONSTRUCTION Introduction The diagnosis of breast cancer begins a journey of making many informed decisions
Augmentation of the Ptotic Breast: Simultaneous Periareolar Mastopexy/Breast Augmentation By: Laurence Kirwan, M.D., F.R.C.S
 Augmentation of the Ptotic Breast: Simultaneous Periareolar Mastopexy/Breast Augmentation By: Laurence Kirwan, M.D., F.R.C.S Background: Submusculofascial augmentation of the ptotic breast can result in
Augmentation of the Ptotic Breast: Simultaneous Periareolar Mastopexy/Breast Augmentation By: Laurence Kirwan, M.D., F.R.C.S Background: Submusculofascial augmentation of the ptotic breast can result in
Prophylactic Mastectomy & Reconstructive Implications
 Prophylactic Mastectomy & Reconstructive Implications Minas T Chrysopoulo, MD PRMA Center For Advanced Breast Reconstruction Prophylactic Mastectomy Surgical removal of one or both breasts to reduce the
Prophylactic Mastectomy & Reconstructive Implications Minas T Chrysopoulo, MD PRMA Center For Advanced Breast Reconstruction Prophylactic Mastectomy Surgical removal of one or both breasts to reduce the
Pocket Conversion Made Easy: A Simple Technique Using Alloderm to Convert Subglandular Breast Implants to the Dual-Plane Position
 Breast Surgery Pocket Conversion Made Easy: A Simple Technique Using Alloderm to Convert Subglandular Breast Implants to the Dual-Plane Position M. Mark Mofid, MD; and Navin K. Singh, MD Background: The
Breast Surgery Pocket Conversion Made Easy: A Simple Technique Using Alloderm to Convert Subglandular Breast Implants to the Dual-Plane Position M. Mark Mofid, MD; and Navin K. Singh, MD Background: The
Partial Breast Reconstruction Using Various Oncoplastic Techniques for Centrally Located Breast Cancer
 Partial Breast Reconstruction Using Various Oncoplastic Techniques for Centrally Located Breast Cancer Original Article Hyo Chun Park 1, Hong Yeul Kim 1, Min Chul Kim 2, Jeong Woo Lee 2, Ho Yun Chung 2,
Partial Breast Reconstruction Using Various Oncoplastic Techniques for Centrally Located Breast Cancer Original Article Hyo Chun Park 1, Hong Yeul Kim 1, Min Chul Kim 2, Jeong Woo Lee 2, Ho Yun Chung 2,
INTRODUCTION. Jong Gyu Kim, Soo Hyang Lee. Original Article
 Comparison of the Multidetector-row Computed Tomographic ngiography xial and Coronal Planes Usefulness for Detecting Thoracodorsal rtery Perforators Original rticle Jong Gyu Kim, Soo Hyang Lee Department
Comparison of the Multidetector-row Computed Tomographic ngiography xial and Coronal Planes Usefulness for Detecting Thoracodorsal rtery Perforators Original rticle Jong Gyu Kim, Soo Hyang Lee Department
Breast Augmentation and Mastopexy Using a Pectoral Muscle Loop
 Aesth Plast Surg (2011) 35:333 340 DOI 10.1007/s00266-010-9612-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Breast Augmentation and Mastopexy Using a Pectoral Muscle Loop André Auersvald Luiz Augusto Auersvald Received: 28 April
Aesth Plast Surg (2011) 35:333 340 DOI 10.1007/s00266-010-9612-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Breast Augmentation and Mastopexy Using a Pectoral Muscle Loop André Auersvald Luiz Augusto Auersvald Received: 28 April
Progressive Tension Sutures to Prevent Seroma Formation after Latissimus Dorsi Harvest
 Progressive Tension Sutures to Prevent Seroma Formation after Latissimus Dorsi Harvest Jose L. Rios, M.D., Todd Pollock, M.D., and William P. Adams, Jr., M.D. Dallas, Texas The latissimus dorsi muscle
Progressive Tension Sutures to Prevent Seroma Formation after Latissimus Dorsi Harvest Jose L. Rios, M.D., Todd Pollock, M.D., and William P. Adams, Jr., M.D. Dallas, Texas The latissimus dorsi muscle
In a second stage or a second operation that tissue expander is removed through the same incision and the implant is placed within the chest pocket.
 Hello, I m Summer Hanson. I m an assistant professor in the Department of Plastics & Reconstructive Surgery at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and today I m going to talk about the role
Hello, I m Summer Hanson. I m an assistant professor in the Department of Plastics & Reconstructive Surgery at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and today I m going to talk about the role
Figure 1. Anatomy of the breast
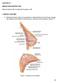 CHAPTER 12 BREAST RECONSTRUCTION Mihaela Rapolti, MD and Michelle Roughton, MD I. BREAST ANATOMY A. Mastering breast anatomy is essential for understanding how the breast changes with aging and principles
CHAPTER 12 BREAST RECONSTRUCTION Mihaela Rapolti, MD and Michelle Roughton, MD I. BREAST ANATOMY A. Mastering breast anatomy is essential for understanding how the breast changes with aging and principles
Breast reconstruction has an important role BREAST. A Two-Year Prospective Analysis of Trunk Function in TRAM Breast Reconstructions
 BREAST A Two-Year Prospective Analysis of Trunk Function in TRAM Breast Reconstructions Amy K. Alderman, M.D. William M. Kuzon, Jr., M.D., Ph.D. Edwin G. Wilkins, M.D. Ann Arbor, Mich. Background: Functional
BREAST A Two-Year Prospective Analysis of Trunk Function in TRAM Breast Reconstructions Amy K. Alderman, M.D. William M. Kuzon, Jr., M.D., Ph.D. Edwin G. Wilkins, M.D. Ann Arbor, Mich. Background: Functional
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Combined tongue flap and V Y advancement flap for lower lip defects
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 258 262 CASE REPORTS Combined tongue flap and V Y advancement flap for lower lip defects Kenji Yano*, Ko Hosokawa, Tateki Kubo Department of Plastic and Reconstructive
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 258 262 CASE REPORTS Combined tongue flap and V Y advancement flap for lower lip defects Kenji Yano*, Ko Hosokawa, Tateki Kubo Department of Plastic and Reconstructive
Gateway to the upper limb. An area of transition between the neck and the arm.
 Gateway to the upper limb An area of transition between the neck and the arm. Pyramidal space inferior to shoulder @ junction of arm & thorax Distribution center for the neurovascular structures that serve
Gateway to the upper limb An area of transition between the neck and the arm. Pyramidal space inferior to shoulder @ junction of arm & thorax Distribution center for the neurovascular structures that serve
Parenchyma-sparing lung resections are a potential therapeutic
 Lung Segmentectomy for Patients with Peripheral T1 Lesions Bryan A. Whitson, MD, Rafael S. Andrade, MD, and Michael A. Maddaus, MD Parenchyma-sparing lung resections are a potential therapeutic option
Lung Segmentectomy for Patients with Peripheral T1 Lesions Bryan A. Whitson, MD, Rafael S. Andrade, MD, and Michael A. Maddaus, MD Parenchyma-sparing lung resections are a potential therapeutic option
Medical Review Criteria Breast Surgeries
 Medical Review Criteria Breast Surgeries Subject: Breast Surgeries Authorization: Prior authorization is required for the following procedures requested for members enrolled in HPHC commercial (HMO, POS,
Medical Review Criteria Breast Surgeries Subject: Breast Surgeries Authorization: Prior authorization is required for the following procedures requested for members enrolled in HPHC commercial (HMO, POS,
Oncoplastic Breast Surgery
 Disclosures Oncoplastic Breast Surgery Newfoundlander OAGS 2016 Dr Renee Hanrahan General Surgeon Oncologic and Reconstructive Breast Surgeon Objectives What is Oncoplastic Surgery Define Oncoplastic Surgery
Disclosures Oncoplastic Breast Surgery Newfoundlander OAGS 2016 Dr Renee Hanrahan General Surgeon Oncologic and Reconstructive Breast Surgeon Objectives What is Oncoplastic Surgery Define Oncoplastic Surgery
can see several late effects. Asymmetry is probably the most common and the thing that patients notice the most. We can also see implant wrinkling or
 Hello, I am Summer Hanson. I m an assistant professor with the Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. And today I m going to talk to you
Hello, I am Summer Hanson. I m an assistant professor with the Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. And today I m going to talk to you
