Four-flap Breast Reconstruction: Bilateral Stacked DIEP and PAP Flaps
|
|
|
- Clifton Newton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Breast Four-flap Breast Reconstruction: Bilateral Stacked DIEP and PAP Flaps James L. Mayo, MD Robert J. Allen, MD, FACS Alireza Sadeghi, MD, FACS Background: In cases of bilateral breast reconstruction when the deep inferior epigastric perforator (DIEP) free flap alone does not provide sufficient volume for body-specific reconstruction, stacking each DIEP flap with a second free flap will deliver added volume and maintain a purely autologous reconstruction. Stacking the profunda artery perforator (PAP) flap with the DIEP flap offers favorable aesthetics and ideal operative efficiency. We present the indications, technique, and outcomes of our experience with 4-flap breast reconstruction using stacked DIEP/PAP flaps. Methods: The authors performed 4-flap DIEP/PAP breast reconstruction in 20 patients who required bilateral reconstruction without adequate single donor flap volume. The timing of reconstruction, average mastectomy/flap weights, and operative time are reported. Complications reviewed include fat necrosis, dehiscence, hematoma, seroma, mastectomy flap necrosis, and flap loss. Results: Twenty patients underwent 4-flap DIEP/PAP breast reconstruction. Surgical time averaged 7 hours and 20 minutes. The primary recipient vessels were the antegrade and retrograde internal mammary vessels. No flap losses occurred. Complications included 1 hematoma, 1 incidence of arterial and venous thrombosis successfully treated with anastomotic revision, 1 incidence of thigh donor site dehiscence, and 3 episodes of minor mastectomy skin flap necrosis. Conclusions: Four-flap breast reconstruction is a favorable autologous reconstructive option for patients requiring bilateral reconstruction without adequate single donor flap volume. Stacking DIEP/PAP flaps as described is both safe and efficient. Furthermore, this combination provides superior aesthetics mirroring the natural geometry of the breast. Bilateral stacked DIEP/PAP flaps represent our first choice for breast reconstruction in this patient population. (Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 2015;3:e383; doi: / GOX ; Published online 1 May 2015.) Perforator-based autologous breast reconstruction provides a natural, long-lasting, and aesthetically pleasing result. Rivaling other forms From the Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Louisiana State University, New Orleans, La. Received for publication September 9, 2014; accepted March 18, Copyright 2015 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 3.0 License, where it is permissible to download and share the work provided it is properly cited. The work cannot be changed in any way or used commercially. DOI: /GOX of breast reconstruction, this reconstructive modality remains our practice s preferred method for breast reconstruction, with the deep inferior epigastric perforator (DIEP) flap representing the gold standard. In patients who do not have enough abdominal tissue to reconstruct body-appropriate breasts, stacking flaps has proven to be an efficacious technique for providing adequate volume. 1 9 Bilateral DIEP flaps are typically stacked for unilateral reconstruction. 1,9 When bilateral reconstruction is required and the abdominal tissue does not provide enough volume, the addition Disclosure: The authors have no financial interest to declare in relation to the content of this article. The Article Processing Charge was paid for by the authors. 1
2 PRS Global Open 2015 of a second flap in a stacked fashion with a DIEP can provide favorable autologous reconstruction. The task of performing 4 free flaps in one surgery is feasible by choosing an additional flap to pair with the DIEP that allows for an efficient operation and provides an aesthetically pleasing outcome. In an effort to provide perforator-based autologous breast reconstruction to all patients, further options are not infrequently warranted, commonly due to a need for additional volume or an inability to use the abdomen as a donor site. These secondary options have included the superior gluteal, inferior gluteal, transverse upper gracilis, and profunda artery perforator (PAP) flaps Our practice now most commonly uses the PAP flap as our second-line flap because of its long pedicle, ease of harvest, and favorable donor site. 13 We have concluded that the PAP flap is also the ideal flap to stack with the DIEP in 4-flap bilateral breast reconstruction. This combination of stacked flaps is safe and efficient and offers superior aesthetic results for bilateral perforator-based autologous breast reconstruction when the abdomen does not provide sufficient volume (Fig. 1). At first encounter, performing 4 free flaps in one setting can seem overwhelming, but with appropriate flap selection and optimal operative plan- 2 Fig. 1. Preoperative (A) and postoperative (B) view of a 42-year-old woman with stage II right breast cancer with positive margins after a lumpectomy who elected to undergo bilateral nipple-sparing mastectomies through a radial incision with immediate bilateral stacked DIEP and PAP flap breast reconstruction. Results at 3 months follow-up.
3 Mayo et al. Four-flap Breast Reconstruction Fig. 2. A 44-year-old woman with stage I left breast cancer underwent a bilateral nipple-sparing mastectomy with PAP flap breast reconstruction, leaving the patient with a superior tissue deficiency. A second delayed bilateral DIEP breast reconstruction was performed to correct the deficiency. A, Preoperative view. B, Three-month postoperative view after PAP flap. C, Three months status post-bilateral delayed DIEP staged reconstruction with left mastopexy for symmetry. ning, successful 4-flap breast reconstruction can be achieved. Our practice has stacked DIEP and superior gluteal artery perforator (SGAP) flaps in the past with favorable results but felt that the DIEP and SGAP combination for 4-flap breast reconstruction could be improved upon. The SGAP requires patient Fig. 3. Preoperative (A) and postoperative (B) view of a 43-year-old woman with BRCA 2 gene mutation after bilateral nipple-sparing mastectomy with immediate 4-flap operation. Results at 3 months status post-second stage. 3
4 PRS Global Open 2015 repositioning, which is an unnecessary inefficiency when performing 4-flap breast reconstruction. Ultimately, the combination of stacking the PAP and DIEP flaps was born less due to the inadequacy of the SGAP but more due to the superiority of the PAP. A series of 3 patients in our practice presented after bilateral autologous reconstruction with volume deficiency (Fig. 2). Our treatment plan involved the addition of bilateral free flaps, either adding bilateral PAP flaps to existing DIEP reconstruction or vice versa. A favorable cosmesis in breast shape was recognized as the DIEP flap provided upper-pole fullness while the PAP flap offered an attractive, rounded lower breast pole (Fig. 3). Moving forward, those patients requiring bilateral breast reconstruction without adequate single site donor site volume were reconstructed with bilateral PAP and DIEP free flap breast reconstruction. This 4-flap DIEP/PAP stacked breast reconstruction has been recognized by our group to be the ideal option for perforator-based autologous bilateral breast reconstruction when DIEP flaps will not offer enough volume. We describe our technique for 4-flap breast reconstruction in 20 patients using DIEP/PAP stacked flaps. Methods Candidates for 4-flap breast reconstruction are those patients in need of bilateral reconstruction who are deemed to not possess adequate volume for single free flap breast reconstruction based on physical examination. Decision making is based on evaluation of current breast size and shape, including the presence of ptosis, body size, and donor site volume. Those patients with donor site specific contraindications for either the abdomen or thigh are excluded from consideration. Each patient participates in extensive counseling regarding all primary options for breast reconstruction and additional options that would add volume to a single free flap reconstruction. The patient undergoes preoperative computed tomography angiogram evaluation of her abdomen and thighs, identifying ideal DIEP flap and PAP flap, respectively. The standard preoperative markings are placed with the aid of a handheld Doppler in the office the day before surgery (Fig. 4). In surgery, the patient is placed supine with bilateral arms and legs prepared into the field (Fig. 5). The arms are secured at the patient s side, and the legs are positioned in frog-legged style. The DIEP and PAP flaps are harvested simultaneously. In the senior authors 4 Fig. 4. Preoperative markings for DIEP (A) and PAP (B) flaps. Computed tomography angiogram imaging is obtained for perforator localization. The long arc of the PAP crescent is marked at the length of the inframammary fold.
5 Mayo et al. Four-flap Breast Reconstruction Fig. 5. Intraoperative markings with patients in supine position for the entire operation. early experience, the PAP was harvested in the prone position, but the supine frog-legged position is more than adequate to successfully harvest the flap and close the defect. 13 The surgeon that finishes harvesting this flap first then exposes the internal mammary vessels. Both unilateral anastomoses are performed. The DIEP flap is placed in a superior position, and its pedicle is anastomosed to the retrograde internal mammary vessels. The use of the retrograde internal mammary vessels is a key component of the surgical plan because harvesting is efficient with minimal further dissection and the thoracodorsal system is spared in the event these vessels are needed at a later time. The triangular shape of the DIEP fills the upper pole with acceptable volume as it tapers into a pseudo-axillary tail. The PAP is then used to reconstruct the lower pole, and its pedicle is anastomosed to the antegrade internal mammary vessels. The crescent shape and favorable fat quality of the PAP flap provide a pleasing curvature and fullness to the lower portion of the breast (Fig. 6). The crisscross pattern of the anastomoses allows the pedicles to lie in an optimal orientation without unfavorable kinking or tension (Fig. 7). Finally, the flaps are inset and secured to the chest wall and then de-epithelialized as appropriate. A skin paddle for each flap is left for monitoring. In our practice, flaps are seldom buried, at which point internal Fig. 6. The positioning of the DIEP and PAP flaps resembles the shape of the mastectomy specimen after mastectomy. 5
6 PRS Global Open 2015 Table 1. Average Mastectomy and Flap Weights for 4-flap DIEP/PAP Stacked Breast Reconstructions Reported in Grams Mastectomy DIEP Flap PAP Flap Stacked Flap Volume Right 418 ± ± ± ± 139 Left 399 ± ± ± ± 142 Fig. 7. The vessels of the DIEP, which sits superiorly, will be anastomosed to the retrograde internal mammary vessels. The vessels of the PAP flap, which sits inferiorly, will be anastomosed to the antegrade vessels. PAP flap (A), DIEP flap (B), retrograde IM vessel anastomosis with DIEP vessels (C), and antegrade IM vessel anastomosis with the PAP vessels (D). IM indicates internal mammary. venous Dopplers are placed. All donor sites are closed in layers with the patient in the supine position. EXPERIENCE REVIEW Bilateral stacked DIEP/PAP flap breast reconstruction was performed on a total of 20 patients from December 2012 to August 2014, with a mean follow-up period of 14 ± 6 months. Three patients were staged with either bilateral PAP and staged DIEP flaps or vice versa using the thoracodorsal system for the staged recipient vessels. The other 17 patients underwent bilateral 4-flap breast reconstruction as described above. Of the 17 nonstaged reconstructions, the antegrade and retrograde internal mammary vessels were used as recipient vessels in 15 cases. Only the antegrade vessels were used in the 3 patients by stacking the flaps in a chimeric fashion anastomosing the second flap to the primary flap pedicle. Of the total 40 breast reconstructions, 13 (33%) were delayed and 27 (67%) immediate. The patient population had an average body mass index of 23.7 ± 2.4 and was relatively healthy with 1 obese patient and 2 patients with hypertension. No patients smoked or suffered from diabetes. The average operative time was 7 hours 20 minutes ± 42 minutes (SD). Length of hospital stay for all patients was 4 days. The average mastectomy weight was 409 g ( g). Average flap weights were 252 g ( g) for DIEP flaps and 299 g ( g) for PAP flaps. Total average reconstructed breast volume was 551 g ( g) (Table 1). Complications were at or below levels reported in the literature for 1- and 2-flap reconstructions. 14 No flaps were lost. One episode of arterial thrombosis and 1 episode of venous thrombosis were each treated with anastomosis revision resulting in flap salvage. One hematoma was evacuated. One abdominal donor site and 3 PAP donor sites developed minor wound dehiscence. All of these groups healed with local wound care. Operable fat necrosis was seen in 2 patients (Table 2). The incidence of complications was calculated per flap and per breast reconstruction to evaluate for possible increased risk of complications seen with increased number of free flaps. DISCUSSION The incidence of bilateral breast reconstruction has risen with increased detection of genetic mutations and general patient desire for prophylactic mastectomies. 15 The reconstruction of bilateral breasts in patients with inadequate abdominal tissue has posed a further reconstructive challenge and pushed the reconstructive surgeon to pursue more varied options. Fat grafting offers a secondary volume enhancement. However, in filling a large volume deficit, multiple procedures may be warranted as 50 60% retention is seen even at 150-cm 3 grafting volumes. 16 The addition of an implant to a DIEP changes the paradigm of the operation to a hybrid Table 2. Complication Profile for 4-Flap DIEP/PAP Stacked Breast Reconstruction Complication Incidence Incidence (%) Hematoma 1/40 breast reconstructions 2.5 Seroma 0/40 breast reconstructions 0 Return to OR 3/40 breast reconstructions 15 Flap loss 0/80 flaps 0 Fat necrosis 2/80 flaps 2.5 2/40 breast reconstructions 5 Venous occlusion 1/80 flaps 1.3 1/40 breast reconstructions 2.6 Arterial occlusion 1/80 flaps 1.3 1/40 breast reconstructions 2.6 PAP donor-site 3/40 donor sites 7.5 dehiscence Abdominal donor-site dehiscence 1/20 donor sites 5 Some complications are calculated both per flap and per breast reconstruction to provide insight into overall per breast reconstruction complication profile. OR, operating room. 6
7 Mayo et al. Four-flap Breast Reconstruction Fig. 8. A 37-year-old woman with BRCA 2 gene mutation after BL NSM through radial incisions and BL immediate stacked DIEP and PAP flaps. A, Preoperative view. B, Three-month postoperative view. BL indicates bilateral; NSM, nipple-sparing mastectomy. autologous reconstruction, introducing the risks of implant reconstruction, such as asymmetry, contracture, and infection necessitating implant removal. The flap may help reduce the increased detrimental effects seen with the combination of an implant and radiation, but the risks of nonautologous reconstruction remain. 17 Pedicle-based flaps, such as the thoracodorsal artery perforator flap and intercostal artery perforator flap, represent local tissue options to augment DIEP reconstruction. Both can require patient repositioning, use a donor site often seen as a viable back-up reconstructive option, and predominantly offer additional volume more laterally. 18,19 As microsurgical technique and operative room efficiency improve, the applications of perforatorbased free flaps diversify. Multiple free flaps for a single operation are becoming a more comfortable endeavor and, as a result, more widely applied. The patient in need of more volume than the abdomen is able to offer has numerous options for additional volume, but our practice believes additional free flaps offer the known benefits of autologous reconstruction with little added risk. Specifically, 4-flap breast reconstruction with DIEP/PAP stacked flaps for bilateral breast reconstruction is our premier choice in this situation. Stacking free flaps, the use of 2 separate flaps for a single reconstructive unit, is not a novel concept in breast reconstruction. In 1992, Arnez and Scamp 2 described performing a bipedicled free transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap by anastomosing each pedicle to a different recipient vessel, and in 1993, Pennington et al 3 first described the use of stacked flaps in a chimeric fashion in reconstructing a breast with one free transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap connected to a periumbilical perforator of the second flap. With the introduction and evolution of the DIEP flap, using stacked DIEP flaps for unilateral large volume reconstruction was reported as safe and effective. 1,9 Further techniques have been published describing unilateral breast reconstruction by stacking various abdominal flaps. 4 7 Alternatively, stacked flaps, such as the PAP flap, for unilateral reconstruction have also been successfully performed. 7 7
8 PRS Global Open 2015 Fig. 9. PAP donor-site scar hidden in the buttock crease. Preoperative (A) and postoperative (B) views. Four-flap DIEP/PAP breast reconstruction offers the benefits of completely autologous reconstruction and an efficiency and aesthetic outcome not seen with other options for stacked autologous reconstruction. The largest series of bilateral stacked flaps to date details the stacking of DIEP and SGAP flaps in 25 cases. 8 Time of surgery for this series averaged over 10 hours, which is longer compared with our series (7 hours 20 minutes), likely due to the necessary change in patient positioning and more complex dissection of the SGAP flap compared with the PAP. With a focus on safety and efficiency, an emphasis is placed on not increasing morbidity with the addition of extra flaps. The complication profile of the DIEP/SGAP series is limited, making a comparison difficult. 8 More applicable is a comparison to single flap reconstruction. In comparison to Allen s review 14 of 758 DIEP free flap breast reconstructions, our series of stacked DIEP/PAP reconstructions shows no increase in morbidity with additional free flaps. The use of the retrograde internal mammary vessels as a recipient vessel for free flap reconstruction has been a consistently viable option. Plus, its use as first-choice recipient vessels for the second flap eliminates the need for further dissection and saves the thoracodorsal vessels should they be needed at a later time. The long pedicle of the PAP flap makes the second anastomosis more practical compared with the SGAP. The aesthetics created by 4-flap DIEP and PAP autologous reconstruction is quite favorable (Fig. 8). The DIEP flap offers sought-after upper-pole fullness often deficient from single-flap DIEP breast reconstruction. This may negate the need for revision fat grafting. The use of the PAP flap for the lower pole provides lower-pole fullness with a natural contour. Two additional scars are created, but the PAP donor site is well hidden and has a low wound complication profile (Fig. 9). We have also recognized that by using 2 flaps for each breast, the weight of each individual flap is slightly lower than usual, which may provide decreased drainage burden on the pedicle and, thus, decreased fat necrosis. This theoretical benefit can be further elucidated via further future investigation. Limitations to application of this technique are predominantly experience related. Not only does a learning curve dictate operative efficiency and outcomes but so too does a well-trained surgical staff and facility familiar with the intricacies of microsurgical breast reconstruction. However, these goals can be realized in centers committed to providing autologous breast reconstruction. 8
9 Mayo et al. Four-flap Breast Reconstruction The patient with limited abdominal tissue in need of bilateral breast reconstruction can pose a challenge when seeking a truly autologous breast reconstruction. However, our practice has produced favorable results in an efficient manner with low morbidity by performing 4-flap breast reconstruction with stacked DIEP and PAP flaps using the antegrade and retrograde internal mammary vessels as recipient vessels. This represents our primary option for breast reconstruction in this patient population. CONCLUSION Four-flap breast reconstruction with stacked DIEP/PAP flaps should be considered when the abdomen alone fails to provide the necessary volume. Working with a two-person microsurgeon team, utilizing both the antegrade and retrograde internal mammary vessels as recipient vessels, and maintaining a supine position throughout the surgery, provide necessary efficiency without added complications. Additionally, the aesthetics of the DIEP/ PAP combination are quite favorable. Alireza Sadeghi, MD, FACS Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Louisiana State University 3434 Prytania Street, Suite 420, New Orleans, LA drs@arbreastcenter.com ACKNOWLEDGMENT This retrospective review article conforms to the Helsinki Declaration. REFERENCES 1. Ali RS, Garrido A, Ramakrishnan V. Stacked free hemi- DIEP flaps: a method of autologous breast reconstruction in a patient with midline abdominal scarring. Br J Plast Surg. 2002;55: Arnez ZM, Scamp T. The bipedicled free TRAM flap. Br J Plast Surg. 1992;45: Pennington DG, Nettle WJ, Lam P. Microvascular augmentation of the blood supply of the contralateral side of the free transverse rectus abdominis musculocutaneous flap. Ann Plast Surg. 1993;31: ; discussion Agarwal JP, Gottlieb LJ. Double pedicle deep inferior epigastric perforator/muscle-sparing TRAM flaps for unilateral breast reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 2007;58: Figus A, Fioramonti P, Ramakrishnan V. Stacked free SIEA/DIEP flap for unilateral breast reconstruction in a thin patient with an abdominal vertical midline scar. J Resconstr Microsurg. 2007;23: Hamdi M, Khuthaila DK, Van Landuyt K, et al. Doublepedicle abdominal perforator free flaps for unilateral breast reconstruction: new horizons in microsurgical tissue transfer to the breast. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2007;60: ; discussion Blechman KM, Broer PN, Tanna N, et al. Stacked profunda artery perforator flaps for unilateral breast reconstruction: a case report. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2013;29: DellaCroce FJ, Sullivan SK, Trahan C, et al. Body lift perforator flap breast reconstruction: a review of 100 flaps in 25 cases. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;129: DellaCroce FJ, Sullivan SK, Trahan C. Stacked deep inferior epigastric perforator flap breast reconstruction: a review of 110 flaps in 55 cases over 3 years. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011;127: Allen RJ, Tucker C. Superior gluteal artery perforator free flap for breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1995;95: Allen RJ, Levine JL, Granzow JW. The in-the-crease inferior gluteal artery perforator flap for breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006;118: Wechselberger G, Schoeller T. The transverse myocutaneous gracilis free flap: a valuable tissue source in autologous breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004;114: Allen RJ, Haddock NT, Ahn CY, et al. Breast reconstruction with the profunda artery perforator flap. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;129:16e 23e. 14. Gill PS, Hunt JP, Guerra AB, et al. A 10-year retrospective review of 758 DIEP flaps for breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004;113: Tuttle TM, Jarosek S, Habermann EB, et al. Increasing rates of contralateral prophylactic mastectomy among patients with ductal carcinoma in situ. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27: Choi M, Small K, Levovitz C, et al. The volumetric analysis of fat graft survival in breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;131: Chang DW, Barnea Y, Robb GL. Effects of an autologous flap combined with an implant for breast reconstruction: an evaluation of 1000 consecutive reconstructions of previously irradiated breasts. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008;122: Levine JL, Soueid NE, Allen RJ. Algorithm for autologous breast reconstruction for partial mastectomy defects. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005;116: Losken A, Hamdi M. Partial breast reconstruction: current perspectives. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;124:
Increasing options in autologous microsurgical breast reconstruction: four free flaps for stacked bilateral breast reconstruction
 Case Report Increasing options in autologous microsurgical breast reconstruction: four free flaps for stacked bilateral breast reconstruction Warren Matthew Rozen 1,2, Nakul Gamanlal Patel 1, Venkat V.
Case Report Increasing options in autologous microsurgical breast reconstruction: four free flaps for stacked bilateral breast reconstruction Warren Matthew Rozen 1,2, Nakul Gamanlal Patel 1, Venkat V.
A multiple logistic regression analysis of complications following microsurgical breast reconstruction
 Original Article A multiple logistic regression analysis of complications following microsurgical breast reconstruction Samir Rao 1, Ellen C. Stolle 1, Sarah Sher 1, Chun-Wang Lin 1, Bahram Momen 2, Maurice
Original Article A multiple logistic regression analysis of complications following microsurgical breast reconstruction Samir Rao 1, Ellen C. Stolle 1, Sarah Sher 1, Chun-Wang Lin 1, Bahram Momen 2, Maurice
Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps
 Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. Houston, Texas Breast reconstruction using the
Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. Houston, Texas Breast reconstruction using the
Breast Reconstruction Options
 Breast Reconstruction Options Natural reconstruction using your ABDOMINAL tissue: TRAM Flap (Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous) There are various forms of TRAM flap reconstruction that are commonly
Breast Reconstruction Options Natural reconstruction using your ABDOMINAL tissue: TRAM Flap (Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous) There are various forms of TRAM flap reconstruction that are commonly
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5. Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. JPRAS Open. journal homepage:
 JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1714-7 RESEARCH Open Access Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes Chi Sun Yoon and Kyu Nam
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1714-7 RESEARCH Open Access Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes Chi Sun Yoon and Kyu Nam
Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC
 Downloaded from Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC What is Breast Reconstruction? Reconstruction of the breast involves recreating
Downloaded from Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC What is Breast Reconstruction? Reconstruction of the breast involves recreating
Simultaneous Bilateral Breast Reconstruction With In-the-Crease Inferior Gluteal Artery Perforator Flaps
 BREAST SURGERY Simultaneous Bilateral Breast Reconstruction With In-the-Crease Inferior Gluteal Artery Perforator Flaps Joshua L. Levine, MD,* Quintessa Miller, MD, Julie Vasile, MD,* Kamran Khoobehi,
BREAST SURGERY Simultaneous Bilateral Breast Reconstruction With In-the-Crease Inferior Gluteal Artery Perforator Flaps Joshua L. Levine, MD,* Quintessa Miller, MD, Julie Vasile, MD,* Kamran Khoobehi,
Breast Reconstruction: Current Strategies and Future Opportunities
 Breast Reconstruction: Current Strategies and Future Opportunities Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
Breast Reconstruction: Current Strategies and Future Opportunities Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
Breast Reconstruction in Women Under 30: A 10-Year Experience
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Breast Reconstruction in Women Under 30: A 10-Year Experience Warren A. Ellsworth, MD,* Barbara L. Bass, MD, FACS, Roman J. Skoracki, MD, à and Lior Heller, MD* *Division of Plastic Surgery,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Breast Reconstruction in Women Under 30: A 10-Year Experience Warren A. Ellsworth, MD,* Barbara L. Bass, MD, FACS, Roman J. Skoracki, MD, à and Lior Heller, MD* *Division of Plastic Surgery,
Current Strategies in Breast Reconstruction
 Current Strategies in Breast Reconstruction Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 12 th Annual School of
Current Strategies in Breast Reconstruction Hani Sbitany, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery University of California, San Francisco Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 12 th Annual School of
The Profunda Artery Perforator Flap: Investigating the Perforasome Using Three-Dimensional Computed Tomographic Angiography
 BREAST The Profunda Artery Perforator Flap: Investigating the Perforasome Using Three-Dimensional Computed Tomographic Angiography Corrine Wong, M.D. Purushottam Nagarkar, M.D. Sumeet Teotia, M.D. Nicholas
BREAST The Profunda Artery Perforator Flap: Investigating the Perforasome Using Three-Dimensional Computed Tomographic Angiography Corrine Wong, M.D. Purushottam Nagarkar, M.D. Sumeet Teotia, M.D. Nicholas
Breast cancer reconstruction surgery (immediate and delayed) across Ontario: Patient indications and appropriate surgical options
 A Quality Initiative of the Program in Evidence-Based Care (PEBC), Cancer Care Ontario (CCO) Breast cancer reconstruction surgery (immediate and delayed) across Ontario: Patient indications and appropriate
A Quality Initiative of the Program in Evidence-Based Care (PEBC), Cancer Care Ontario (CCO) Breast cancer reconstruction surgery (immediate and delayed) across Ontario: Patient indications and appropriate
Breast Restoration Surgery After a mastectomy
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Breast Restoration Surgery After a mastectomy This handout explains the most common procedures that are used at University of Washington Medical Center (UWMC) to restore a
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Breast Restoration Surgery After a mastectomy This handout explains the most common procedures that are used at University of Washington Medical Center (UWMC) to restore a
Few would deny that lower abdominal tissue BREAST. An Intraoperative Algorithm for Use of the SIEA Flap for Breast Reconstruction.
 BREAST An Intraoperative Algorithm for Use of the SIEA Flap for Breast Reconstruction Aldona J. Spiegel, M.D. Farah N. Khan, M.D. Houston, Texas Background: The deep inferior epigastric perforator (DIEP)
BREAST An Intraoperative Algorithm for Use of the SIEA Flap for Breast Reconstruction Aldona J. Spiegel, M.D. Farah N. Khan, M.D. Houston, Texas Background: The deep inferior epigastric perforator (DIEP)
Prophylactic Mastectomy & Reconstructive Implications
 Prophylactic Mastectomy & Reconstructive Implications Minas T Chrysopoulo, MD PRMA Center For Advanced Breast Reconstruction Prophylactic Mastectomy Surgical removal of one or both breasts to reduce the
Prophylactic Mastectomy & Reconstructive Implications Minas T Chrysopoulo, MD PRMA Center For Advanced Breast Reconstruction Prophylactic Mastectomy Surgical removal of one or both breasts to reduce the
The progress in microsurgical procedures has led
 Original Article Breast reconstruction with free anterolateral thigh flap Ranjit Raje, Ramesh Chepauk, Kanti Shetty, Rajendra Prasad J. S. Plastic & Reconstructive Services, Department of Surgical Oncology,
Original Article Breast reconstruction with free anterolateral thigh flap Ranjit Raje, Ramesh Chepauk, Kanti Shetty, Rajendra Prasad J. S. Plastic & Reconstructive Services, Department of Surgical Oncology,
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer. Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery Plastic-reconstructive aspects after mastectomy Versions 2002 2017: Audretsch / Bauerfeind
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Surgery Plastic-reconstructive aspects after mastectomy Versions 2002 2017: Audretsch / Bauerfeind
Algorithm for Autologous Breast Reconstruction for Partial Mastectomy Defects
 Algorithm for Autologous Breast Reconstruction for Partial Mastectomy Defects Joshua L. Levine, M.D., Nassif E. Soueid, M.D., and Robert J. Allen, M.D. New Orleans, La. Background: The use of lateral thoracic
Algorithm for Autologous Breast Reconstruction for Partial Mastectomy Defects Joshua L. Levine, M.D., Nassif E. Soueid, M.D., and Robert J. Allen, M.D. New Orleans, La. Background: The use of lateral thoracic
The decision to repair a partial mastectomy CME. State of the Art and Science in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction.
 CME State of the Art and Science in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction Steven J. Kronowitz, M.D. Houston, Texas Learning Objectives: After reading this article, the participant should be able to: 1.
CME State of the Art and Science in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction Steven J. Kronowitz, M.D. Houston, Texas Learning Objectives: After reading this article, the participant should be able to: 1.
Frederick J. Duffy, Jr., MD, FACS and Brice W. McKane, MD, FACS BREAST RECONSTRUCTION
 Frederick J. Duffy, Jr., MD, FACS and Brice W. McKane, MD, FACS BREAST RECONSTRUCTION BREAST RECONSTRUCTION: A WOMAN S DECISION Options and Information Our approach to breast reconstruction entails a very
Frederick J. Duffy, Jr., MD, FACS and Brice W. McKane, MD, FACS BREAST RECONSTRUCTION BREAST RECONSTRUCTION: A WOMAN S DECISION Options and Information Our approach to breast reconstruction entails a very
The most common type of breast reconstruction
 BREAST Breast Reconstruction with Perforator Flaps Jay W. Granzow, M.D., M.P.H. Joshua L. Levine, M.D. Ernest S. Chiu, M.D. Maria M. LoTempio, M.D. Robert J. Allen, M.D. New Orleans, La.; Charleston, S.C.;
BREAST Breast Reconstruction with Perforator Flaps Jay W. Granzow, M.D., M.P.H. Joshua L. Levine, M.D. Ernest S. Chiu, M.D. Maria M. LoTempio, M.D. Robert J. Allen, M.D. New Orleans, La.; Charleston, S.C.;
Breast Reconstruction
 Steven E. Copit, M.D. Chief- Division of Plastic Surgery Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA analysis of The Defect Skin Breast Volume Nipple Areola Complex analysis of The Defect the
Steven E. Copit, M.D. Chief- Division of Plastic Surgery Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia, PA analysis of The Defect Skin Breast Volume Nipple Areola Complex analysis of The Defect the
Breast reconstruction following mastectomy has
 Free full text on www.ijps.org Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction: Microsurgical methods Venkat Ramakrishnan, Makarand Tare St. Andrew s Centre for Burns and Plastic Surgery, BroomÞ eld Hospital, Chelmsford,
Free full text on www.ijps.org Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction: Microsurgical methods Venkat Ramakrishnan, Makarand Tare St. Andrew s Centre for Burns and Plastic Surgery, BroomÞ eld Hospital, Chelmsford,
Vertical mammaplasty has been developed
 BREAST Y-Scar Vertical Mammaplasty David A. Hidalgo, M.D. New York, N.Y. Background: Vertical mammaplasty is an effective alternative to inverted-t methods. Among other benefits, it results in a significantly
BREAST Y-Scar Vertical Mammaplasty David A. Hidalgo, M.D. New York, N.Y. Background: Vertical mammaplasty is an effective alternative to inverted-t methods. Among other benefits, it results in a significantly
INTRODUCTION. Toshihiko Satake 1, Jun Sugawara 2, Kazunori Yasumura 1, Taro Mikami 2, Shinji Kobayashi 3, Jiro Maegawa 2. Idea and Innovation
 Mini-Flow-Through Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap for Breast Reconstruction with Preservation of Both Internal Mammary and Deep Inferior Epigastric Vessels Toshihiko Satake 1, Jun Sugawara 2,
Mini-Flow-Through Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap for Breast Reconstruction with Preservation of Both Internal Mammary and Deep Inferior Epigastric Vessels Toshihiko Satake 1, Jun Sugawara 2,
Medical Policy Original Effective Date: Revised Date: Page 1 of 8
 Page 1 of 8 Disclaimer Description Coverage Determination Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on all plans, or the plan
Page 1 of 8 Disclaimer Description Coverage Determination Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on all plans, or the plan
Anatomical Landmarks for Safe Elevation of the Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap: A Cadaveric Study
 Anatomical Landmarks for Safe Elevation of the Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap: A Cadaveric Study Saeed Chowdhry, MD, Ron Hazani, MD, Philip Collis, BS, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD University of
Anatomical Landmarks for Safe Elevation of the Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap: A Cadaveric Study Saeed Chowdhry, MD, Ron Hazani, MD, Philip Collis, BS, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD University of
SIMPOSIO Ricostruzione mammaria ed implicazioni radioterapiche Indicazioni
 SIMPOSIO Ricostruzione mammaria ed implicazioni radioterapiche Indicazioni Icro Meattini, MD Radiation Oncology Department - University of Florence Azienda Ospedaliero Universitaria Careggi Firenze Breast
SIMPOSIO Ricostruzione mammaria ed implicazioni radioterapiche Indicazioni Icro Meattini, MD Radiation Oncology Department - University of Florence Azienda Ospedaliero Universitaria Careggi Firenze Breast
Is Unilateral Implant or Autologous Breast Reconstruction Better in Obtaining Breast Symmetry?
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is Unilateral Implant or Autologous Breast Reconstruction Better in Obtaining Breast Symmetry? Oriana Cohen, MD, Kevin Small, MD, Christina Lee, BA, Oriana Petruolo, MD, Nolan Karp, MD,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is Unilateral Implant or Autologous Breast Reconstruction Better in Obtaining Breast Symmetry? Oriana Cohen, MD, Kevin Small, MD, Christina Lee, BA, Oriana Petruolo, MD, Nolan Karp, MD,
Samer Saour, Guido Libondi, Venkat Ramakrishnan. Introduction
 Original Article Microsurgical refinements with the use of internal mammary (IM) perforators as recipient vessels in transverse upper gracilis (TUG) autologous breast reconstruction Samer Saour, Guido
Original Article Microsurgical refinements with the use of internal mammary (IM) perforators as recipient vessels in transverse upper gracilis (TUG) autologous breast reconstruction Samer Saour, Guido
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty
 CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
A Clinical Anatomic Study of Internal Mammary Perforators as Recipient Vessels for Breast Reconstruction
 A Clinical Anatomic Study of Internal Mammary Perforators as Recipient Vessels for Breast Reconstruction In-Soo Baek 1, Jae-Pil You 1, Sung-Mi Rhee 1, Gil-Su Son 2, Deok-Woo Kim 1, Eun-Sang Dhong 1, Seung-Ha
A Clinical Anatomic Study of Internal Mammary Perforators as Recipient Vessels for Breast Reconstruction In-Soo Baek 1, Jae-Pil You 1, Sung-Mi Rhee 1, Gil-Su Son 2, Deok-Woo Kim 1, Eun-Sang Dhong 1, Seung-Ha
Breast Reconstruction Surgery
 Breast Reconstruction Surgery I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for Breast Reconstruction Surgery when it is determined to be medically necessary and when it meets the medical criteria
Breast Reconstruction Surgery I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for Breast Reconstruction Surgery when it is determined to be medically necessary and when it meets the medical criteria
BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY
 UnitedHealthcare Commercial Coverage Determination Guideline BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY Guideline Number: SUR057 Effective Date: January 1, 2019 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
UnitedHealthcare Commercial Coverage Determination Guideline BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY Guideline Number: SUR057 Effective Date: January 1, 2019 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
Methods of autologous tissue breast reconstruction BREAST
 BREAST Comparison of Donor-Site Morbidity of SIEA, DIEP, and Muscle-Sparing TRAM Flaps for Breast Reconstruction Liza C. Wu, M.D. Anureet Bajaj, M.D. David W. Chang, M.D. Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D.
BREAST Comparison of Donor-Site Morbidity of SIEA, DIEP, and Muscle-Sparing TRAM Flaps for Breast Reconstruction Liza C. Wu, M.D. Anureet Bajaj, M.D. David W. Chang, M.D. Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D.
Despite breast reduction being one of the BREAST. Does Knowledge of the Initial Technique Affect Outcomes after Repeated Breast Reduction?
 BREAST Does Knowledge of the Initial Technique Affect Outcomes after Repeated Breast Reduction? Jamil Ahmad, M.D. Sarah M. McIsaac, M.D. Frank Lista, M.D. Mississauga and Ottawa, Ontario, Canada Background:
BREAST Does Knowledge of the Initial Technique Affect Outcomes after Repeated Breast Reduction? Jamil Ahmad, M.D. Sarah M. McIsaac, M.D. Frank Lista, M.D. Mississauga and Ottawa, Ontario, Canada Background:
The Case FOR Oncoplastic Surgery in Small Breasts. Barbara L. Smith, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA USA
 The Case FOR Oncoplastic Surgery in Small Breasts Barbara L. Smith, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA USA Changing issues in breast cancer management Early detection
The Case FOR Oncoplastic Surgery in Small Breasts Barbara L. Smith, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA USA Changing issues in breast cancer management Early detection
Do Preexisting Abdominal Scars Threaten Wound Healing in Abdominoplasty?
 Do Preexisting Abdominal Scars Threaten Wound Healing in Abdominoplasty? Michele A. Shermak, MD, Jessie Mallalieu, PA-C, and David Chang, PhD, MPH, MBA The Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions, Division
Do Preexisting Abdominal Scars Threaten Wound Healing in Abdominoplasty? Michele A. Shermak, MD, Jessie Mallalieu, PA-C, and David Chang, PhD, MPH, MBA The Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions, Division
The dissection of the rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap with complete preservation of the anterior rectus sheath q
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 395 400 The dissection of the rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap with complete preservation of the anterior rectus sheath q D. Erni*, Y.D. Harder
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 395 400 The dissection of the rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap with complete preservation of the anterior rectus sheath q D. Erni*, Y.D. Harder
Breast Reconstruction: Patient Information Document
 breastreconstructioncanada.ca Breast Reconstruction: Patient Information Document By Dr. Nicolas Guay Dr. Haemi Lee STANDARDIZED BREAST RECONSTRUCTION PATIENT INFORMATION TABLE OF CONTENTS Glossary...
breastreconstructioncanada.ca Breast Reconstruction: Patient Information Document By Dr. Nicolas Guay Dr. Haemi Lee STANDARDIZED BREAST RECONSTRUCTION PATIENT INFORMATION TABLE OF CONTENTS Glossary...
BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY
 UnitedHealthcare Commercial Coverage Determination Guideline BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY Guideline Number: SUR057 Effective Date: February 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
UnitedHealthcare Commercial Coverage Determination Guideline BREAST RECONSTRUCTION POST MASTECTOMY Guideline Number: SUR057 Effective Date: February 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
Immediate versus delayed free TRAM breast reconstruction: an analysis of perioperative factors and complications
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (22), 55, l-6 9 22 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi:.54/bjps.22.3747 BRITISH JOURNAL OF / ~ ] PLASTIC SURGERY Immediate versus delayed free TRAM breast
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (22), 55, l-6 9 22 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi:.54/bjps.22.3747 BRITISH JOURNAL OF / ~ ] PLASTIC SURGERY Immediate versus delayed free TRAM breast
INFORMED CONSENT-BREAST RECONSTRUCTION WITH TRAM ABDOMINAL MUSCLE FLAP
 INFORMED CONSENT-BREAST RECONSTRUCTION WITH TRAM ABDOMINAL MUSCLE FLAP 2000 American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Purchasers of the Patient Consultation Resource Book are given a limited license to modify
INFORMED CONSENT-BREAST RECONSTRUCTION WITH TRAM ABDOMINAL MUSCLE FLAP 2000 American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Purchasers of the Patient Consultation Resource Book are given a limited license to modify
In a second stage or a second operation that tissue expander is removed through the same incision and the implant is placed within the chest pocket.
 Hello, I m Summer Hanson. I m an assistant professor in the Department of Plastics & Reconstructive Surgery at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and today I m going to talk about the role
Hello, I m Summer Hanson. I m an assistant professor in the Department of Plastics & Reconstructive Surgery at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and today I m going to talk about the role
Updates in Breast Care. Truth or Hype. History of Breast Cancer Surgery. Dr Karen Barbosa 5/3/2017 4/20/2017
 Updates in Breast Care Dr Karen Barbosa 4/20/2017 Truth or Hype Princess Bust Developer Sears, Roebuck and Co. 1897 Promised to make the breast round, firm and beautiful History of Breast Cancer Surgery
Updates in Breast Care Dr Karen Barbosa 4/20/2017 Truth or Hype Princess Bust Developer Sears, Roebuck and Co. 1897 Promised to make the breast round, firm and beautiful History of Breast Cancer Surgery
Advances and Surgical Decision-Making for Breast Reconstruction
 893 Advances and Surgical Decision-Making for Breast Reconstruction Steven J. Kronowitz, MD 1 Henry M. Kuerer, MD, PhD 2 1 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, The University of Texas M. D.
893 Advances and Surgical Decision-Making for Breast Reconstruction Steven J. Kronowitz, MD 1 Henry M. Kuerer, MD, PhD 2 1 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, The University of Texas M. D.
How many procedures to make a breast?
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (00 ), 5, 7-3 9 00 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi: 0.05/bjps.000.3538 BRITISH JOURNAL OF PLASTIC SURGERY How many procedures to make a breast? A. D.
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (00 ), 5, 7-3 9 00 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi: 0.05/bjps.000.3538 BRITISH JOURNAL OF PLASTIC SURGERY How many procedures to make a breast? A. D.
Breast reconstruction has an important role BREAST. A Two-Year Prospective Analysis of Trunk Function in TRAM Breast Reconstructions
 BREAST A Two-Year Prospective Analysis of Trunk Function in TRAM Breast Reconstructions Amy K. Alderman, M.D. William M. Kuzon, Jr., M.D., Ph.D. Edwin G. Wilkins, M.D. Ann Arbor, Mich. Background: Functional
BREAST A Two-Year Prospective Analysis of Trunk Function in TRAM Breast Reconstructions Amy K. Alderman, M.D. William M. Kuzon, Jr., M.D., Ph.D. Edwin G. Wilkins, M.D. Ann Arbor, Mich. Background: Functional
Figure 1. Anatomy of the breast
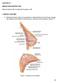 CHAPTER 12 BREAST RECONSTRUCTION Mihaela Rapolti, MD and Michelle Roughton, MD I. BREAST ANATOMY A. Mastering breast anatomy is essential for understanding how the breast changes with aging and principles
CHAPTER 12 BREAST RECONSTRUCTION Mihaela Rapolti, MD and Michelle Roughton, MD I. BREAST ANATOMY A. Mastering breast anatomy is essential for understanding how the breast changes with aging and principles
Microsurgical Breast Reconstruction in Thin Patients: The Impact of Low Body Mass Indices
 20 Original Article Microsurgical Breast Reconstruction in Thin Patients: The Impact of Low Body Mass Indices Katie E. Weichman, MD 1 Neil Tanna, MD, MBA 1 P. Niclas Broer, MD 1 Stelios Wilson, MD 1 Hamdan
20 Original Article Microsurgical Breast Reconstruction in Thin Patients: The Impact of Low Body Mass Indices Katie E. Weichman, MD 1 Neil Tanna, MD, MBA 1 P. Niclas Broer, MD 1 Stelios Wilson, MD 1 Hamdan
Breast Reconstruction. Westmead Breast Cancer Institute
 Breast Reconstruction Westmead Breast Cancer Institute What is breast reconstruction? Breast reconstruction is a surgical procedure that creates a shape on the chest wall following a mastectomy. Occasionally,
Breast Reconstruction Westmead Breast Cancer Institute What is breast reconstruction? Breast reconstruction is a surgical procedure that creates a shape on the chest wall following a mastectomy. Occasionally,
Reconstruction with autologous tissue remains a
 Original Article Increased Flap Weight and Decreased Perforator Number Predict Fat Necrosis in DIEP Breast Reconstruction Carolyn L. Mulvey, BS* Carisa M. Cooney, MPH* Francis F. Daily, BS* Elizabeth Colantuoni,
Original Article Increased Flap Weight and Decreased Perforator Number Predict Fat Necrosis in DIEP Breast Reconstruction Carolyn L. Mulvey, BS* Carisa M. Cooney, MPH* Francis F. Daily, BS* Elizabeth Colantuoni,
How To Make a Good Mastectomy for Reconstruction Based on the Anatomy. Zhang Jin, Ph.D MD
 How To Make a Good Mastectomy for Reconstruction Based on the Anatomy Zhang Jin, Ph.D MD Deputy Director and Professor Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital People s Republic of China
How To Make a Good Mastectomy for Reconstruction Based on the Anatomy Zhang Jin, Ph.D MD Deputy Director and Professor Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital People s Republic of China
Clinical Accuracy of Portrait 3D Surgical Simulation Platform in Breast Augmentation. Ryan K. Wong MD, David T Pointer BS, Kamran Khoobehi MD FACS
 Clinical Accuracy of Portrait 3D Surgical Simulation Platform in Breast Augmentation Ryan K. Wong MD, David T Pointer BS, Kamran Khoobehi MD FACS Division of Plastic, Reconstructive & Reconstructive Surgery,
Clinical Accuracy of Portrait 3D Surgical Simulation Platform in Breast Augmentation Ryan K. Wong MD, David T Pointer BS, Kamran Khoobehi MD FACS Division of Plastic, Reconstructive & Reconstructive Surgery,
Essential Anatomy for oncoplastic surgery. Omar Z. Youssef M.D Professor of surgical oncology NCI- Cairo University
 Essential Anatomy for oncoplastic surgery Omar Z. Youssef M.D Professor of surgical oncology NCI- Cairo University Introduction Rationale for anatomical basis for OPS Anatomical considerations: 1. Surface
Essential Anatomy for oncoplastic surgery Omar Z. Youssef M.D Professor of surgical oncology NCI- Cairo University Introduction Rationale for anatomical basis for OPS Anatomical considerations: 1. Surface
The use of postmastectomy radiation therapy (PMRT) to prevent
 NORTHEASTERN SOCIETY OF PLASTIC SURGEONS Postmastectomy Radiation Therapy and Breast An Analysis of Complications and Patient Satisfaction Bernard T. Lee, MD,* Tolulope A. Adesiyun, BS,* Salih Colakoglu,
NORTHEASTERN SOCIETY OF PLASTIC SURGEONS Postmastectomy Radiation Therapy and Breast An Analysis of Complications and Patient Satisfaction Bernard T. Lee, MD,* Tolulope A. Adesiyun, BS,* Salih Colakoglu,
Buried Flap Reconstruction after Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy: Advancing toward Single-Stage Breast Reconstruction
 BREAST Buried Flap Reconstruction after Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy: Advancing toward Single-Stage Breast Reconstruction Steven M. Levine, M.D. Chelsea Snider, M.D. Grace Gerald, B.S. Neil Tanna, M.D. P.
BREAST Buried Flap Reconstruction after Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy: Advancing toward Single-Stage Breast Reconstruction Steven M. Levine, M.D. Chelsea Snider, M.D. Grace Gerald, B.S. Neil Tanna, M.D. P.
Nipple-Areolar Complex Reconstruction: A Review of the Literature and Introduction of the Rectangle-to-Cube Nipple Flap
 Nipple-Areolar Complex Reconstruction: A Review of the Literature and Introduction of the Rectangle-to-Cube Nipple Flap Joshua T. Henderson, BA, a ThomasJ.Lee,MD, b Andrew M. Swiergosz, BS, a Andrea R.
Nipple-Areolar Complex Reconstruction: A Review of the Literature and Introduction of the Rectangle-to-Cube Nipple Flap Joshua T. Henderson, BA, a ThomasJ.Lee,MD, b Andrew M. Swiergosz, BS, a Andrea R.
Advances in Localized Breast Cancer
 Advances in Localized Breast Cancer Melissa Camp, MD, MPH and Fariba Asrari, MD June 18, 2018 Moderated by Elissa Bantug 1 Advances in Surgery for Breast Cancer Melissa Camp, MD June 18, 2018 2 Historical
Advances in Localized Breast Cancer Melissa Camp, MD, MPH and Fariba Asrari, MD June 18, 2018 Moderated by Elissa Bantug 1 Advances in Surgery for Breast Cancer Melissa Camp, MD June 18, 2018 2 Historical
Breast Cancer Reconstruction
 Breast Cancer Jerome H. Liu, MD Tom S. Liu, MD Jerome H. Liu, MD Undergraduate: Brown University Medical School: University of California, Los Angeles Residency: UCLA Medical Center Fellowship:UCLA Medical
Breast Cancer Jerome H. Liu, MD Tom S. Liu, MD Jerome H. Liu, MD Undergraduate: Brown University Medical School: University of California, Los Angeles Residency: UCLA Medical Center Fellowship:UCLA Medical
Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction
 Follow the link from the online version of this article to obtain certified continuing medical education credits Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction Paul T R Thiruchelvam, 1 Fiona McNeill, 2 Navid Jallali,
Follow the link from the online version of this article to obtain certified continuing medical education credits Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction Paul T R Thiruchelvam, 1 Fiona McNeill, 2 Navid Jallali,
Advances in Breast Surgery. Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015
 Advances in Breast Surgery Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015 Objectives Understand the surgical treatment of breast cancer Be able to determine when a lumpectomy
Advances in Breast Surgery Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015 Objectives Understand the surgical treatment of breast cancer Be able to determine when a lumpectomy
Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy with Immediate Reconstruction: Added Benefits, Added Risks
 Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy with Immediate Reconstruction: Added Benefits, Added Risks Grant W. Carlson Wadley R. Glenn Professor of Surgery Divisions of Plastic Surgery & Surgical Oncology Emory
Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy with Immediate Reconstruction: Added Benefits, Added Risks Grant W. Carlson Wadley R. Glenn Professor of Surgery Divisions of Plastic Surgery & Surgical Oncology Emory
Medical Journal of the Volume 20 Islamic Republic of Iran Number 3 Fall 1385 November Original Articles
 Medical Journal of the Volume 0 Islamic Republic of Iran Number 3 Fall 38 November 00 Original Articles ANATOMY OF THE SUPERFICIAL INFERIOR EPIGASTRIC ARTERY FLAP MAHDI FATHI, M.D., EBRAHIM HATAMIPOUR,
Medical Journal of the Volume 0 Islamic Republic of Iran Number 3 Fall 38 November 00 Original Articles ANATOMY OF THE SUPERFICIAL INFERIOR EPIGASTRIC ARTERY FLAP MAHDI FATHI, M.D., EBRAHIM HATAMIPOUR,
AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION
 CHAPTER 18 AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION Ali A. Qureshi, MD and Smita R. Ramanadham, MD Aesthetic surgery of the breast aims to either correct ptosis with a mastopexy,
CHAPTER 18 AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION Ali A. Qureshi, MD and Smita R. Ramanadham, MD Aesthetic surgery of the breast aims to either correct ptosis with a mastopexy,
Citation for published version (APA): Benditte-Klepetko, H. C. (2014). Breast surgery: A problem of beauty or health?
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Breast surgery: A problem of beauty or health? Benditte-Klepetko, H.C. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Benditte-Klepetko, H. C. (2014).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Breast surgery: A problem of beauty or health? Benditte-Klepetko, H.C. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Benditte-Klepetko, H. C. (2014).
Reduction Mammaplasty and Mastopexy in Previously Irradiated Breasts
 Breast Surgery Reduction Mammaplasty and Mastopexy in Previously Irradiated Breasts Scott L. Spear, MD; Samir S. Rao, MD; Ketan M. Patel, MD; and Maurice Y. Nahabedian, MD The combination of lumpectomy
Breast Surgery Reduction Mammaplasty and Mastopexy in Previously Irradiated Breasts Scott L. Spear, MD; Samir S. Rao, MD; Ketan M. Patel, MD; and Maurice Y. Nahabedian, MD The combination of lumpectomy
Breast Surgery. for Reconstructive. Center of Excellence. city center of Düsseldorf. You will find us in the
 You will find us in the city center of Düsseldorf Rathaus Rhein Steinstraße Berger Allee Poststraße Bastionstraße Kasernenstraße Breite Straße Königsallee Grünstraße Berliner Allee Königsallee 88 Graf-Adolf-Platz
You will find us in the city center of Düsseldorf Rathaus Rhein Steinstraße Berger Allee Poststraße Bastionstraße Kasernenstraße Breite Straße Königsallee Grünstraße Berliner Allee Königsallee 88 Graf-Adolf-Platz
ONCOPLASTIC SURGERY. Dr. Sadir Alrawi Director of Surgical Oncology Services. Dr. Humaa Darr Surgical Oncology Fellow
 Hessa St ONCOPLASTIC SURGERY Dr. Sadir Alrawi Director of Surgical Oncology Services Dr. Humaa Darr Surgical Oncology Fellow Al Sufouh Rd AL SUFOUH AL SUFOUH Sharaf DG Mall of the Emirates Mall Of the
Hessa St ONCOPLASTIC SURGERY Dr. Sadir Alrawi Director of Surgical Oncology Services Dr. Humaa Darr Surgical Oncology Fellow Al Sufouh Rd AL SUFOUH AL SUFOUH Sharaf DG Mall of the Emirates Mall Of the
INNOVATIVE RECONSTRUCTIVE STRATEGIES IN BREAST CANCER SURGERY
 INNOVATIVE RECONSTRUCTIVE STRATEGIES IN BREAST CANCER SURGERY Jane L. Kakkis, MD, MPH Breast Surgeon, Director Orange Coast Memorial Medical Center, Fountain Valley, CA USA WHEN RADIATION IS NECESSARY
INNOVATIVE RECONSTRUCTIVE STRATEGIES IN BREAST CANCER SURGERY Jane L. Kakkis, MD, MPH Breast Surgeon, Director Orange Coast Memorial Medical Center, Fountain Valley, CA USA WHEN RADIATION IS NECESSARY
Breast Reconstruction Postmastectomy. Using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis in breast reconstruction with tissue expander.
 Breast Reconstruction Postmastectomy. Using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis in breast reconstruction with tissue expander. Strong and flexible Bacterially inactivated Provides implant support Breast Reconstruction
Breast Reconstruction Postmastectomy. Using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis in breast reconstruction with tissue expander. Strong and flexible Bacterially inactivated Provides implant support Breast Reconstruction
Outcomes Evaluation Following Bilateral Breast Reconstruction Using Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flaps
 BREAST SURGERY Outcomes Evaluation Following Bilateral Breast Reconstruction Using Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flaps Albert Losken, MD, FACS, Claire S. Nicholas, MD, Ximena A. inell, MD, and Grant W.
BREAST SURGERY Outcomes Evaluation Following Bilateral Breast Reconstruction Using Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flaps Albert Losken, MD, FACS, Claire S. Nicholas, MD, Ximena A. inell, MD, and Grant W.
Goals of Care. Restore shape and function after cancer
 Goals of Care Restore shape and function after cancer Aid in physiological and psychological benefit Relationship with significant other Self esteem and positive body image Feeling of a whole body Avoid
Goals of Care Restore shape and function after cancer Aid in physiological and psychological benefit Relationship with significant other Self esteem and positive body image Feeling of a whole body Avoid
Neil J. Zemmel, MD, FACS Steven J. Montante, MD Megan J. Russell, PA-C. Your Guide To BREAST RECONSTRUCTION
 Neil J. Zemmel, MD, FACS Steven J. Montante, MD Megan J. Russell, PA-C Your Guide To BREAST RECONSTRUCTION Introduction The diagnosis of breast cancer begins a journey of making many informed decisions
Neil J. Zemmel, MD, FACS Steven J. Montante, MD Megan J. Russell, PA-C Your Guide To BREAST RECONSTRUCTION Introduction The diagnosis of breast cancer begins a journey of making many informed decisions
Advances and Innovations in Breast Reconstruction and Brest Surgery Presented by PCMC plastic surgeons
 Advances and Innovations in Breast Reconstruction and Brest Surgery Presented by PCMC plastic surgeons Options for reconstruction after mastectomy Implants Autologous tissue = from your own body: skin
Advances and Innovations in Breast Reconstruction and Brest Surgery Presented by PCMC plastic surgeons Options for reconstruction after mastectomy Implants Autologous tissue = from your own body: skin
The microvascular anastomotic coupler for venous anastomoses in free flap breast reconstruction improves outcomes
 Original Article The microvascular anastomotic coupler for venous anastomoses in free flap breast reconstruction improves outcomes Edmund Fitzgerald O Connor 1,2, Warren Matthew Rozen 2, Muhammad Chowdhry
Original Article The microvascular anastomotic coupler for venous anastomoses in free flap breast reconstruction improves outcomes Edmund Fitzgerald O Connor 1,2, Warren Matthew Rozen 2, Muhammad Chowdhry
Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap for Successful Simultaneous Breast and Chest Wall Reconstruction in a Poland Anomaly Patient
 CASE REPORT Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap for Successful Simultaneous Breast and Chest Wall Reconstruction in a Poland Anomaly Patient Han-Tsung Liao, MD, Ming-Huei Cheng, MD, Betul Gozel Ulusal,
CASE REPORT Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap for Successful Simultaneous Breast and Chest Wall Reconstruction in a Poland Anomaly Patient Han-Tsung Liao, MD, Ming-Huei Cheng, MD, Betul Gozel Ulusal,
complicanze in chirurgia senologica ricostruttiva Tecniche per la prevenzione delle complicanze nelle mastectomie conservative
 Il trattamento delle complicanze in chirurgia senologica ricostruttiva Tecniche per la prevenzione delle complicanze nelle mastectomie conservative Dr. Christian Rizzetto UOC Chirurgia Senologica - Breast
Il trattamento delle complicanze in chirurgia senologica ricostruttiva Tecniche per la prevenzione delle complicanze nelle mastectomie conservative Dr. Christian Rizzetto UOC Chirurgia Senologica - Breast
Challenging a Traditional Paradigm: 12-Year Experience with Autologous Free Flap Breast Reconstruction for Inflammatory Breast Cancer
 BREAST Challenging a Traditional Paradigm: 12-Year Experience with Autologous Free Flap Breast Reconstruction for Inflammatory Breast Cancer Edward I. Chang, M.D. Eric I. Chang, M.D. Ran Ito, M.D., Ph.D.
BREAST Challenging a Traditional Paradigm: 12-Year Experience with Autologous Free Flap Breast Reconstruction for Inflammatory Breast Cancer Edward I. Chang, M.D. Eric I. Chang, M.D. Ran Ito, M.D., Ph.D.
Breast cancer has become so
 The three stages of breast reconstruction BY FORTUNE C IWUAGWU Breast cancer has become so common that most people reading this article will know someone (either professionally or personally) who has been
The three stages of breast reconstruction BY FORTUNE C IWUAGWU Breast cancer has become so common that most people reading this article will know someone (either professionally or personally) who has been
The Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery (SIEA) Flap and Its Applications in Breast Reconstruction
 The Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery (SIEA) Flap and Its Applications in Breast Reconstruction Zachary Menn and Aldona Spiegel Weill Cornell Medical College, The Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas,
The Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery (SIEA) Flap and Its Applications in Breast Reconstruction Zachary Menn and Aldona Spiegel Weill Cornell Medical College, The Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas,
Breast Reconstruction Surgery after Mastectomy or Lumpectomy
 Breast Reconstruction Surgery after Mastectomy or Lumpectomy Date of Origin: 11/1998 Last Review Date: 11/25/2017 Effective Date: 11/25/2017 Dates Reviewed: 08/2000, 09/2001, 11/2003, 11/2004, 12/2005,
Breast Reconstruction Surgery after Mastectomy or Lumpectomy Date of Origin: 11/1998 Last Review Date: 11/25/2017 Effective Date: 11/25/2017 Dates Reviewed: 08/2000, 09/2001, 11/2003, 11/2004, 12/2005,
Update on Breast Reconstruction Using Free TRAM, DIEP, and SIEA Flaps
 Update on Breast Reconstruction Using Free TRAM, DIEP, and SIEA Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. 1 ABSTRACT Breast reconstruction using autologous tissue is commonly accomplished using the transverse
Update on Breast Reconstruction Using Free TRAM, DIEP, and SIEA Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. 1 ABSTRACT Breast reconstruction using autologous tissue is commonly accomplished using the transverse
Peter McAllister, 1 Isabel Teo, 1 Kuen Chin, 1 Boikanyo Makubate, 2 and David Alexander Munnoch Introduction
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Plastic Surgery International Volume 2016, Article ID 6085624, 9 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6085624 Research Article Bilateral Breast Reconstruction with Abdominal
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Plastic Surgery International Volume 2016, Article ID 6085624, 9 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6085624 Research Article Bilateral Breast Reconstruction with Abdominal
Kuwabara, Kaoru; Nonaka, Takashi; H. Citation Journal of Clinical Urology, 7(5),
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Gluteal-fold adipofascial perforato fistula reconstruction Fujioka, Masaki; Hayashida, Kenji; Kuwabara, Kaoru; Nonaka, Takashi; H Citation Journal of Clinical
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Gluteal-fold adipofascial perforato fistula reconstruction Fujioka, Masaki; Hayashida, Kenji; Kuwabara, Kaoru; Nonaka, Takashi; H Citation Journal of Clinical
No Drain Abdominoplasty: No More Excuses. Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS
 No Drain Abdominoplasty: No More Excuses Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS Disclosures NO financial interests in any suture company Will use brand names due to lack of distinguishing generic names Objectives
No Drain Abdominoplasty: No More Excuses Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS Disclosures NO financial interests in any suture company Will use brand names due to lack of distinguishing generic names Objectives
In the UK approximately 40,000
 The patient journey in DIEP flap breast reconstruction BY OLIVIER ALEXANDRE BRANFORD AND PAUL ANTHONY HARRIS In the UK approximately 40,000 women are diagnosed with breast cancer every year. About 40%
The patient journey in DIEP flap breast reconstruction BY OLIVIER ALEXANDRE BRANFORD AND PAUL ANTHONY HARRIS In the UK approximately 40,000 women are diagnosed with breast cancer every year. About 40%
Bilateral Reduction Mammaplasty as an Oncoplastic Technique for the Management of Early-Stage Breast Cancer in Women with Macromastia
 Bilateral Reduction Mammaplasty as an Oncoplastic Technique for the Management of Early-Stage Breast Cancer in Women with Macromastia Russell E. Ettinger, MD, a Shailesh Agarwal, MD, a Paul H. Izenberg,
Bilateral Reduction Mammaplasty as an Oncoplastic Technique for the Management of Early-Stage Breast Cancer in Women with Macromastia Russell E. Ettinger, MD, a Shailesh Agarwal, MD, a Paul H. Izenberg,
Reconstructive surgery following mastectomy
 Reconstructive surgery following mastectomy Kseniya Roudakova, MD A CASE FROM SUNY DOWNSTATE 60F who presented for right mastectomy with immediate TRAM flap reconstruction for recurrent breast cancer Oncologic
Reconstructive surgery following mastectomy Kseniya Roudakova, MD A CASE FROM SUNY DOWNSTATE 60F who presented for right mastectomy with immediate TRAM flap reconstruction for recurrent breast cancer Oncologic
Mitchell Buller, MEng, a Adee Heiman, BA, a Jared Davis, MD, b ThomasJ.Lee,MD, b Nicolás Ajkay, MD, FACS, c and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD, FACS b
 Immediate Breast Reconstruction of a Nipple Areolar Lumpectomy Defect With the L-Flap Skin Paddle Breast Reduction Design and Contralateral Reduction Mammoplasty Symmetry Procedure: Optimizing the Oncoplastic
Immediate Breast Reconstruction of a Nipple Areolar Lumpectomy Defect With the L-Flap Skin Paddle Breast Reduction Design and Contralateral Reduction Mammoplasty Symmetry Procedure: Optimizing the Oncoplastic
Nipple Sparing Mastectomy: Tips & Tricks. Rebecca Nelson, MD MSc FRCSC Plastic & Reconstructive Surgeon, Burnaby Hospital
 Nipple Sparing Mastectomy: Tips & Tricks Rebecca Nelson, MD MSc FRCSC Plastic & Reconstructive Surgeon, Burnaby Hospital Nipple Sparing Mastectomy (NSM) Introduction & Technique Safety Evidence Indications/Contraindications
Nipple Sparing Mastectomy: Tips & Tricks Rebecca Nelson, MD MSc FRCSC Plastic & Reconstructive Surgeon, Burnaby Hospital Nipple Sparing Mastectomy (NSM) Introduction & Technique Safety Evidence Indications/Contraindications
From ancient times to the present day, the aesthetic female breast has been portrayed. A Classification and Algorithm for Treatment of Breast Ptosis
 lassification and lgorithm for Treatment of reast Ptosis Laurence Kirwan, M ackground: The Regnault classification of breast ptosis is insufficient for determining surgical strategies for different stages
lassification and lgorithm for Treatment of reast Ptosis Laurence Kirwan, M ackground: The Regnault classification of breast ptosis is insufficient for determining surgical strategies for different stages
Skin sparing mastectomy: Technique and suggested methods of reconstruction
 Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute (2014) 26, 153 159 Cairo University Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute www.nci.cu.adu.eg www.sciencedirect.com Full Length Article Skin
Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute (2014) 26, 153 159 Cairo University Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute www.nci.cu.adu.eg www.sciencedirect.com Full Length Article Skin
Gastrocnemius Myocutaneous Flap: A Versatile Option to Cover the Defect of Upper and Middle Third Leg
 Downloaded from wjps.ir at 22:25 +0330 on Sunday November 18th 28 314 Gastrocnemius flap for coverage of leg defects Original Article Gastrocnemius Myocutaneous Flap: A Versatile Option to Cover the Defect
Downloaded from wjps.ir at 22:25 +0330 on Sunday November 18th 28 314 Gastrocnemius flap for coverage of leg defects Original Article Gastrocnemius Myocutaneous Flap: A Versatile Option to Cover the Defect
Interesting Case Series. Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle
 Interesting Case Series Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle Danielle H. Rochlin, BA, Justin M. Broyles, MD, and Justin M. Sacks, MD Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,
Interesting Case Series Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle Danielle H. Rochlin, BA, Justin M. Broyles, MD, and Justin M. Sacks, MD Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,
The free thoracodorsal artery perforator flap in head and neck reconstruction
 European Annals of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck diseases (2012) 129, 167 171 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com TECHNICAL NOTE The free thoracodorsal artery perforator flap in head and neck
European Annals of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck diseases (2012) 129, 167 171 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com TECHNICAL NOTE The free thoracodorsal artery perforator flap in head and neck
Tor Chiu. Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161
 18 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap Tor Chiu Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap FLAP TERRITORY The deep inferior epigastric
18 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap Tor Chiu Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap FLAP TERRITORY The deep inferior epigastric
Awareness and provision of reconstruction. Breast
 Original Article Breast Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap Breast Reconstruction without Microsurgery Fellowship Training Hakan Orbay, MD, PhD* Brittany K. Busse, MD* Thomas R. Stevenson,
Original Article Breast Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap Breast Reconstruction without Microsurgery Fellowship Training Hakan Orbay, MD, PhD* Brittany K. Busse, MD* Thomas R. Stevenson,
Breast Augmentation and Mastopexy Using a Pectoral Muscle Loop
 Aesth Plast Surg (2011) 35:333 340 DOI 10.1007/s00266-010-9612-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Breast Augmentation and Mastopexy Using a Pectoral Muscle Loop André Auersvald Luiz Augusto Auersvald Received: 28 April
Aesth Plast Surg (2011) 35:333 340 DOI 10.1007/s00266-010-9612-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Breast Augmentation and Mastopexy Using a Pectoral Muscle Loop André Auersvald Luiz Augusto Auersvald Received: 28 April
