Skin Basics. About skin. Reviewed By: Kimberly Bazar, M.D., AAD Mary Ellen Luchetti, M.D., AAD
|
|
|
- Gilbert Wilson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Page 1 of 5 Skin Basics Reviewed By: Kimberly Bazar, M.D., AAD Mary Ellen Luchetti, M.D., AAD Summary The skin is the largest organ in the body. It consists of three layers the epidermis, the dermis and the subcutaneous tissue. Hair and nails are both modified forms of skin. The skin serves as the body s natural protective covering. It prevents germs and other potentially harmful agents from entering the body. It also shields internal organs, muscles, nerves, blood vessels and other structures from the sun s harmful rays and protects the body from injury. In addition to providing protection, the skin prevents the loss of essential fluids (e.g., blood, water), regulates body temperature and senses painful and pleasant stimuli. The skin is also a minor source of waste disposal and an indicator of health problems. Because the skin is located on the outside of the body, it is susceptible to a variety of diseases, disorders, discolorations and growths. Most skin problems, however, can be treated by a dermatologist with a minimal amount of pain and risk. The skin is also susceptible to damage from the environment and the body s natural aging process. To minimize damage, patients are advised to take steps to protect their skin, such as wearing hats and sunscreen when spending time in the sun. About skin Covering the entire outside of the body, the skin is the body s largest organ. It also grows faster than any other organ in the body. People continuously renew their skin throughout their lifetime. In a 150 pound (68 kilogram [kg]) person, the skin measures approximately 2 square yards (1.7 square meters) and weighs about 9 pounds (4 kg). The skin s average thickness is around a tenth of an inch (0.3 centimeters). The thickest skin is located on the upper back, the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet. The thinnest sections of skin are on the eyelids and the inner folds of the elbows. Hair and nails are modified versions of skin. Hair maintains warmth in the body by preserving heat. Hair located around the eyes and in the nose and ears protects these areas from small particles such as dust. It also cushions the body against injury. Hair is composed of a hair shaft, which projects from the skin s surface, and a root.
2 Page 2 of 5 Embedded in the skin, the root is a soft thickened bulb located at the base of the hair. Each root ends in a hair bulb, which sits in a tubular sac known as a hair follicle. There are more than 100,000 hair follicles located on the head alone. At the bottom of each hair follicle is a papilla, the area from which the hair sprouts. It contains an artery that nourishes the root of the hair. The hair grows in response to new cells forming at the base of the root. As the cells multiply they form a rod of tissue in the skin. The rod of cells then moves upward through the skin as new cells form under it. As the cells move up, they are cut off from their supply of nourishment. This causes the cells to die. The dead cells and keratin (a hard protein formed from the cells) form the shaft of the hair. When a hair grows and falls out, another hair takes its place. Hairs grow approximately half an inch (about 12.7 millimeters) each month, and continue to grow for about six years. The length of a hair is related to the growing phase of its follicle. Hair follicles are active for two to six years, followed by a rest period of about three months. Typically, hair grows more rapidly in the summer than in the winter. It also grows more quickly during the day than at night. The size of a person s hair follicles determines whether they have thick or thin hair. Large follicles produce thick hair, and narrow follicles generate thin hair. When these follicles become damaged or die they no longer produce hair, resulting in baldness. Hair color varies from person to person. It is determined by the amount of melanin (dark pigment) in each hair. People with light hair, such as blondes and redheads, have only a small amount of melanin in their hair while people with black or dark brown hair have a larger amount. As people age, their hair becomes grey because pigment no longer forms in the hair. Nails sprout from deep folds in the fingers and toes. They provide protection and support for the sensitive fingertips and toes. They also provide insight into a person s general health, as illness can impact the appearance and growth rate of the nails. As cells below the nail root move up to the skin s surface, the cells located closest to the nail root flatten out and become tightly pressed together. The cells transform into thin plates, which stack into layers to form the nail. As these cells accumulate, the nail is gradually pushed forward. The skin located beneath the nail is known as the matrix. Nails grow from the matrix, and if the matrix is damaged, the nail will grow ridged. The larger pink part of the nail is known as the nail plate. Its pink appearance is due to the network of blood vessels in the underlying layer of skin. The white, crescent shaped area at the base of the nail is known as the lunula. A nail that is torn will regrow, as long as its matrix is not badly injured. On average, it takes nine to 12 months for fingernails to grow and 12 to 18 months for toenails to grow. As with hair, nails typically grow more rapidly in the summer than in the winter. The skin is the body s natural protective covering. Its external location, however, makes it vulnerable to a variety of diseases, disorders, discolorations and growths. The majority of skin problems can be treated by a dermatologist with a minimal amount of pain and risk. Dermatologists are physicians that specialize in diagnosing and treating conditions of the skin, mouth, hair, nails and external genitalia. People with skin problems such as rashes, itchiness (pruritus) or growths should seek medical treatment from a dermatologist soon after the condition develops. The skin is susceptible to damage from the environment. To minimize external damage to the skin, people should take steps to protect their skin. This involves wearing hats, sunscreen, long-sleeved shirts and pants when spending time in the sun. In addition, the natural aging process of the skin is damaging because the dermis loses moisture, elasticity and thickness as individuals grow older. It is impossible to prevent all of the changes that occur to the skin as a person ages. However, older individuals can take steps to slow the pace of these changes, or to treat symptoms that result from these changes. Avoiding sun exposure, moisturizing the skin, maintaining a healthy diet and
3 Page 3 of 5 consuming adequate fluids can be very beneficial. Anatomy of the skin Each square inch of skin contains approximately 19,000,000 skin cells, as well as many other structures, such as nerve endings, hair follicles and glands. The skin consists of three layers: the epidermis, the dermis and the subcutaneous tissue. The epidermis is the thin yet tough top layer of skin. Measuring as thick as a sheet of paper, the epidermis has a number of sublayers. The bottom sublayer is made up of column-shaped cells known as basal cells. As basal cells divide, they form flat, scale-like skin cells called squamous cells. Also known as keratinocytes, squamous cells manufacture keratin, a protein which protects the skin from damaging substances (e.g., chemicals) as well as viral, bacterial and fungal infections. During cell division, basal cells push newly formed squamous cells up into the higher sublayers of the epidermis. As these new cells move upward and away from their source of nourishment, the cells shrink, flatten out and ultimately die. The top sublayer of the epidermis is known as the stratum corneum or horny layer. When undamaged, this waterproof portion of the skin helps prevent bacteria, viruses and other foreign substances from entering the body. It consists of dead squamous cells, which are mostly composed of keratin. These cells continuously flake off during friction and activities such as washing. Approximately 30,000 to 40,000 dead skin cells are shed each minute. The cells are then replaced by new cells. Due to this process, the skin is constantly being replenished. The epidermis cells are replaced about every 28 days. Although basal cells and squamous cells comprise the majority of the epidermis, other cells are also present in the layer. Melanocytes are cells that manufacture melanin, a dark brown pigment that filters out ultraviolet radiation from sunlight and provides color to the skin and the hair. The more melanin that is produced in a person s body, the darker the skin. Langerhans cells are also present in the epidermis. Part of the immune system, these cells help protect the body from infection. They also play a part in the development of skin allergies. Melanocytes and Langerhans cells are both concentrated at the basal layer of the epidermis. However, they both contain dendritic processes, long, thin, arm-like structures that interact with squamous cells. These structures enable them to transfer pigment and monitor the immune status of the skin. The epidermis also has supplemental areas that extend into the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. These areas are lined with epithelial cells, which have the potential for cell division and can become any type of epidermal tissue. The areas include the follicles, sebaceous glands and sweat glands. If the epidermis is removed or destroyed, the epithelial cells can basically reconstruct the epidermis. The thick middle layer of the skin is called the dermis. It constitutes the majority of the skin. It contains strong white fibers (collagen) and elastic yellow fibers (elastin), which intertwine to provide the skin with its strength and elasticity. A number of other structures are also located in the dermis, including: Blood vessels. These structures provide the skin with oxygen and nutrients and help regulate body temperature. They also remove waste from skin cells. Nerve endings. These structures sense pain, touch, pressure and temperature. Some areas of skin, such as the fingertips and toes, have more nerve endings than other areas. Hair follicles. Tubular sacs located throughout the skin, with the exception of the lips, palms and soles. Each living follicle produces one strand of hair. They develop in the basal cell area of the epidermis and are rooted in the subcutaneous tissue. During periods of active growth, the follicles extend into the dermis.
4 Page 4 of 5 Oil glands. These structures branch off the walls of the hair follicles. Also known as sebaceous glands, oil glands secrete an oily substance called sebum. The sebum, which rises up through the hair follicle and out through a pore, provides lubrication for the skin and hair and keeps the skin soft and moist. This lubrication is important because it provides protection against friction. It also gives the skin and hair more of a waterproof quality and acts as a barrier against foreign substances. Oil glands are located throughout the skin, but large numbers are found in the scalp, face, midchest and genitals. Overactive oil glands can cause excessively oily skin (seborrhea). Sweat glands. Sweat is a liquid composed of salt, water and chemicals. There are two types of sweat-producing glands located in the skin eccrine glands and apocrine glands. Eccrine glands are located throughout the skin, but the highest concentrations of the glands are found in the palms, soles, scalp and underarms. The glands produce sweat when a person is hot, stressed or feeling strong emotions. Sweat escapes through pores (tiny holes in the skin). When this sweat evaporates from the surface of the skin, it has a cooling effect on the body. Apocrine glands are specialized sweat glands that develop when a person reaches puberty. Located in high concentrations under the arms and around the nipples and genitals, apocrine glands secrete a thick, oily sweat when a person is under stress or experiencing strong emotions. When the sweat is digested by skin bacteria in these areas, body odor is produced. Sweat glands control nerve fibers that enable the brain to control sweating and regulate heat. This reaction is activated when a person s core body temperature reaches or rises above a certain temperature. Consisting mostly of fat, the bottom layer of the skin is called the subcutaneous tissue. It contains the skin s nerves and blood vessels. The roots of the oil glands and sweat glands are also located here. This layer is responsible for conserving the body s heat and insulating the body. It also provides protective padding for the body and acts as an energy storage area. The subcutaneous layer varies in thickness around the body. Though it may measure only a fraction of an inch on the eyelids, it can be several inches thick on the abdomen and buttocks. Function of the skin The skin has several important functions, including: Protection. The skin serves many protective functions. It prevents infectious agents, such as germs, and other harmful substances from entering the body. It also shields internal organs, muscles, nerves, blood vessels and other structures from the sun s harmful ultraviolet rays and protects the body from injury.
5 Page 5 of 5 Preventing the loss of essential fluids and substances. The skin prevents the loss of blood, water, other life-sustaining fluids, fat, and vitamin D. Regulation of body temperature. The skin contains blood vessels that expand and contract in response to a person s body temperature. Sweat is a natural response to feeling hot. The evaporation of sweat on the skin causes a reduction in body temperature. When a person is cold, the blood vessels in their skin narrow. As a result, the skin becomes pale and cold. Because the blood flow in the skin decreases, the person loses less heat. This conserves the heat for the body s vital organs. Sensation. The skin senses painful and pleasant stimuli. It contains sensory nerves that send messages to the brain about dangers, such as injury, extreme heat or extreme cold. Nerve cells also make the skin sensitive to pressure and touch. In addition, the skin contains a group of specialized nerve endings that stimulate the nerve and endocrine systems. This stimulation results in sexual excitement. Waste disposal. The skin is a minor source of waste disposal. Sweat glands located in the skin excrete waste products such as urea (a byproduct of protein metabolism) therefore eliminating them from the body. Indication of health problems. The skin s characteristics (e.g., texture, temperature, color, clarity) provide information about a person s general health and suggest a number of disorders. For instance, jaundice (a yellow color in the skin) may be a sign of liver disease or anemia (a condition characterized by too few red blood cells). Questions for your doctor regarding skin Preparing questions in advance can help patients to have more meaningful discussions with their physicians regarding their conditions. Patients may wish to ask their doctor the following skin-related questions: 1. What changes in my skin may indicate an illness? 2. How can I minimize the amount of damage to my skin? 3. Why is it important to take care of my skin? 4. Does my skin problem require a visit to a dermatologist? 5. How often should I see a dermatologist? 6. What skin conditions am I at risk for? 7. What steps can I take to ensure healthy hair? 8. What steps can I take to ensure healthy nails?
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 4
 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 4 FUNCTIONS Waterproofs Protein called keratin Protection 1 st line of defense against pathogens, chemicals & abrasions Insulation Regulates heat loss by controlling blood
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 4 FUNCTIONS Waterproofs Protein called keratin Protection 1 st line of defense against pathogens, chemicals & abrasions Insulation Regulates heat loss by controlling blood
Skin The Integumentary System
 Skin The Integumentary System THINK about IT What s the largest organ in your body? No, it is not your ears or stomach, or even your lungs or heart. By far the largest human organ is the skin. If that
Skin The Integumentary System THINK about IT What s the largest organ in your body? No, it is not your ears or stomach, or even your lungs or heart. By far the largest human organ is the skin. If that
Chapter 05. Lecture Outline. See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes.
 Chapter 05 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 05 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system (See if you can name some appendages) A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep
The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system (See if you can name some appendages) A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep
Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System. Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system
 Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system Skin is the body s largest and heaviest organ making up 15% of body weight. Most skin is 1 to
Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system Skin is the body s largest and heaviest organ making up 15% of body weight. Most skin is 1 to
Integumentary System
 Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Skin: composed of dermis and epidermis Dermis. Gives structural strength. C.T. with many fibers, fibroblasts, macrophages. Some adipocytes and blood vessels. Contains
Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Skin: composed of dermis and epidermis Dermis. Gives structural strength. C.T. with many fibers, fibroblasts, macrophages. Some adipocytes and blood vessels. Contains
Chapter 4 Opener Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Opener Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary glands The skin is the most visible organ of the body Clinicians can tell a lot about
Chapter 4 Opener Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary glands The skin is the most visible organ of the body Clinicians can tell a lot about
****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM ******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM ******************************************************************************************************
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System
 Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System The integumentary system is commonly known as the Skin Largest organ of human body 10% total body weight and would cover over 20 square feet Functions of Skin 1. Protection Barrier
Integumentary System The integumentary system is commonly known as the Skin Largest organ of human body 10% total body weight and would cover over 20 square feet Functions of Skin 1. Protection Barrier
11/8/2012. Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Skin = Integument = Cutaneous Membrane. The Structure of Skin. Epidermis
 Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
B. Incorrect! The ectoderm does not produce the dermis. C. Incorrect! The dermis is derived from the mesoderm.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 04: The Integumentary System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. From the inner cell
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 04: The Integumentary System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. From the inner cell
7/10/18. Introduction. Integumentary System. Physiology. Anatomy. Structure of the Skin. Epidermis
 Introduction Integumentary System Chapter 22 Skin is largest and heaviest organ of body (7% of body weight) Houses receptors for touch, heat, cold, movement, and vibration No other body system is more
Introduction Integumentary System Chapter 22 Skin is largest and heaviest organ of body (7% of body weight) Houses receptors for touch, heat, cold, movement, and vibration No other body system is more
Ch 4. Skin and Body Membranes
 Ch 4 Skin and Body Membranes TITLE HISTOLOGY SLIDES & NOTES ESSENTIAL QUESTION What tissues compose the integumentary system? Stratified Squamous Epithelium Stratified = several layers; Squamous = shape
Ch 4 Skin and Body Membranes TITLE HISTOLOGY SLIDES & NOTES ESSENTIAL QUESTION What tissues compose the integumentary system? Stratified Squamous Epithelium Stratified = several layers; Squamous = shape
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis PHL 212 1 Function
The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis PHL 212 1 Function
The Integumentary System: An Overview
 The Integumentary System: An Overview Functions: Protective covering Helps regulate body temperature Retards water loss from deeper tissues Houses sensory receptors Synthesizes biochemicals Excretes small
The Integumentary System: An Overview Functions: Protective covering Helps regulate body temperature Retards water loss from deeper tissues Houses sensory receptors Synthesizes biochemicals Excretes small
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 6
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 6
Unit 4 The Integumentary System
 Unit 4 The Integumentary System I. Classification of Body Membranes A. Epithelial Membranes (3) 1. Cutaneous Membrane > Stratified Squamous > Sits on Dense Connective Tissue > Skin: Epidermis & Dermis
Unit 4 The Integumentary System I. Classification of Body Membranes A. Epithelial Membranes (3) 1. Cutaneous Membrane > Stratified Squamous > Sits on Dense Connective Tissue > Skin: Epidermis & Dermis
Integumentary System and Body Membranes
 Integumentary System and Body Membranes The Skin and its appendages hair, nails, and skin glands Anatomy/Physiology NHS http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/corepages/integumentary/integum.htm I. System
Integumentary System and Body Membranes The Skin and its appendages hair, nails, and skin glands Anatomy/Physiology NHS http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/corepages/integumentary/integum.htm I. System
Lesson Plan: Integumentary System
 Integumentary System The skin is no more separate from the brain than the surface of a lake is separate from its depths. They are two different locations in a continuous medium. To touch the surface is
Integumentary System The skin is no more separate from the brain than the surface of a lake is separate from its depths. They are two different locations in a continuous medium. To touch the surface is
CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY
 CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY skin under the skin other stuff cutaneous layer hypodermis (subcutaneous) accessory structures Cutaneous layer = skin epithelial layers = connective tissue layer = dermis Subcutaneous
CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY skin under the skin other stuff cutaneous layer hypodermis (subcutaneous) accessory structures Cutaneous layer = skin epithelial layers = connective tissue layer = dermis Subcutaneous
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis
The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis
Integumentary System. 2/20/02 S. Davenport 1
 Integumentary System 2/20/02 S. Davenport 1 Functions of Skin Protection Temperature regulation Sensation Excretion Vitamin D production 2/20/02 S. Davenport 2 Protection A Barrier Three types of barriers:
Integumentary System 2/20/02 S. Davenport 1 Functions of Skin Protection Temperature regulation Sensation Excretion Vitamin D production 2/20/02 S. Davenport 2 Protection A Barrier Three types of barriers:
The Integementary System. The Skin & Its Parts
 The Integementary System The Skin & Its Parts General Structure 2. Accessory structures: hair, nails, exocrine glands 1. Cutaneous membrane: various layers Major Functions 1. Protection 2. Temperature
The Integementary System The Skin & Its Parts General Structure 2. Accessory structures: hair, nails, exocrine glands 1. Cutaneous membrane: various layers Major Functions 1. Protection 2. Temperature
Integumentary System. Remember: Types of Membranes: Bio 250
 Integumentary System Bio 250 Remember: Tissue: Group of cells that are similar in appearance and perform similar function Organ: Two or more tissues grouped together and performing a specialized function
Integumentary System Bio 250 Remember: Tissue: Group of cells that are similar in appearance and perform similar function Organ: Two or more tissues grouped together and performing a specialized function
Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function.
 Chapter 5 Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function. Explain the basis for different skin colors. Describe the structure
Chapter 5 Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function. Explain the basis for different skin colors. Describe the structure
The Integumentary System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Integumentary System The Skin Structure two primary layers called epidermis and dermis Epidermis Outermost and thinnest primary layer of skin Composed of several layers of stratified squamous epithelium
The Integumentary System The Skin Structure two primary layers called epidermis and dermis Epidermis Outermost and thinnest primary layer of skin Composed of several layers of stratified squamous epithelium
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System Overview Functions 1. Protection 2. Excretion of wastes 3. Maintenance of T b 4. Synthesis of vitamin D 3 5. Storage of lipids 6. Detection of sensory stimuli Epidermis Tissue types
Integumentary System Overview Functions 1. Protection 2. Excretion of wastes 3. Maintenance of T b 4. Synthesis of vitamin D 3 5. Storage of lipids 6. Detection of sensory stimuli Epidermis Tissue types
B. Connective tissue membranes lubricate & cushion 1. made of areolar tissue 2. synovial line fibrous joint capsules & secrete fluid
 I. Body Membranes A. Epithelial membranes cover & line 1. epithelial sheet over underlying connective tissue 2. 3 types a. Cutaneous = skin b. Mucous = lines cavities open to exterior Skin and Body Membranes
I. Body Membranes A. Epithelial membranes cover & line 1. epithelial sheet over underlying connective tissue 2. 3 types a. Cutaneous = skin b. Mucous = lines cavities open to exterior Skin and Body Membranes
Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9
 Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9 Skin (Integument) Consists of skin and associated derivatives Largest organ of body (21 ft 2 ; 9 lbs.; has 11 miles of blood vessels) Functions: Protection
Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9 Skin (Integument) Consists of skin and associated derivatives Largest organ of body (21 ft 2 ; 9 lbs.; has 11 miles of blood vessels) Functions: Protection
Ex. 7: Integumentary
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2401 Ex. 7: Integumentary. Skin or Integument Consists of three major regions Epidermis outermost superficial region Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia)
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2401 Ex. 7: Integumentary. Skin or Integument Consists of three major regions Epidermis outermost superficial region Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia)
Chapter 5. Integumentary System 5-1
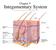 Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Structures that are part of the integument Skin Hair Nails Glands Overview of Functions Protection Sensation Temperature regulation Vitamin D production Excretion Immunity
Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Structures that are part of the integument Skin Hair Nails Glands Overview of Functions Protection Sensation Temperature regulation Vitamin D production Excretion Immunity
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs
 Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
The Integumentary System: ANATOMY Includes: - Skin (integument) MEMBRANES. PHYSIOLOGY (functions) Protection. EPITHELIAL (cont.
 Did you know. Membranes & The Integumentary System The skin is the largest organ of the human body. It has a surface area of about 25 square-feet! You shed about 1.5 pounds of skin particles each year.
Did you know. Membranes & The Integumentary System The skin is the largest organ of the human body. It has a surface area of about 25 square-feet! You shed about 1.5 pounds of skin particles each year.
Your Skin. Section 14.2 Your Skin, Hair, and Nails
 Your Skin The skin covers and protects the body from injury, infection, and water loss. The skin also helps to regulate body temperature and gathers information from the environment. Protection The skin
Your Skin The skin covers and protects the body from injury, infection, and water loss. The skin also helps to regulate body temperature and gathers information from the environment. Protection The skin
Sensory System Continued
 Sensory System Continued Skin The skin is the largest organ of the body, covering its entire surface Technically skin is no longer the largest organ. it s the interstitium What is the skin s purpose? Purpose
Sensory System Continued Skin The skin is the largest organ of the body, covering its entire surface Technically skin is no longer the largest organ. it s the interstitium What is the skin s purpose? Purpose
Introduction. Skin and Body Membranes. Cutaneous Membranes Skin 9/14/2017. Classification of Body Membranes. Classification of Body Membranes
 Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
Chapter 6: Integumentary System
 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 12 th ed. Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System Chapter 6: Integumentary System I. Introduction 1. The skin is composed of of tissues.
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 12 th ed. Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System Chapter 6: Integumentary System I. Introduction 1. The skin is composed of of tissues.
Structure and Movement
 Structure and Movement The Skin Key Concepts What does the skin do? How do the three layers of skin differ? How does the skin interact with other body systems? What do you think? Read the two statements
Structure and Movement The Skin Key Concepts What does the skin do? How do the three layers of skin differ? How does the skin interact with other body systems? What do you think? Read the two statements
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 6
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 6 1 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 6 1 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1
 Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6
 AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6 Student: Multiple choice questions choose the best answer. True/false answer A for true and B for false 1. The layer within the epidermis that acts as the foundation providing new
AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6 Student: Multiple choice questions choose the best answer. True/false answer A for true and B for false 1. The layer within the epidermis that acts as the foundation providing new
Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System. Skin Cells. Layers of Skin. Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous layer beneath dermis not part of skin
 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water loss Regulates body temperature Houses sensory receptors Contains immune
Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water loss Regulates body temperature Houses sensory receptors Contains immune
Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System
 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 10 th ed. Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System I. Skin and Its Tissues A. Introduction
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 10 th ed. Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System I. Skin and Its Tissues A. Introduction
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System Skin (Integument) Consists of two major regions 1. Epidermis superficial region 2. Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia) deepest region Subcutaneous layer deep to
The Integumentary System Skin (Integument) Consists of two major regions 1. Epidermis superficial region 2. Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia) deepest region Subcutaneous layer deep to
II. Skin and Its Tissues. I. Introduction. Unit Two. Integument URLs.
 6 Integument URLs http://www.nurseminerva.co.uk/integ.html http://www.aap.org/policy/s010116.html Chapter 6 Karen Webb Smith Unit Two I. Introduction A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more
6 Integument URLs http://www.nurseminerva.co.uk/integ.html http://www.aap.org/policy/s010116.html Chapter 6 Karen Webb Smith Unit Two I. Introduction A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more
The Integumentary System
 C h a p t e r 5 The Integumentary System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Introduction to the Integumentary System The integument is the largest system
C h a p t e r 5 The Integumentary System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Introduction to the Integumentary System The integument is the largest system
Chapter 6: Skin & the. 6.1 Skin and its Tissues 6.2 Accessory Organs of the Skin 6.3 Regulation of Body Temperature 6.4 Healing of Wounds
 Skin & the Integumentary System 6.1-6.2 September 10, 2012 Chapter 6: Skin & the Integumentary System 6.1 Skin and its Tissues 6.2 Accessory Organs of the Skin 6.3 Regulation of Body Temperature 6.4 Healing
Skin & the Integumentary System 6.1-6.2 September 10, 2012 Chapter 6: Skin & the Integumentary System 6.1 Skin and its Tissues 6.2 Accessory Organs of the Skin 6.3 Regulation of Body Temperature 6.4 Healing
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS
 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS Integumentary System Cutaneous membrane Epidermis (5-layers) made up of epithelial tissue only Dermis (2-layers) contains connective tissue, vessels,
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS Integumentary System Cutaneous membrane Epidermis (5-layers) made up of epithelial tissue only Dermis (2-layers) contains connective tissue, vessels,
Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes
 Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes I. Body Membranes A. Function of body membranes 1. Cover body surfaces 2. Line body cavities 3. Form protective sheets around organs II. Classification of Body Membranes
Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes I. Body Membranes A. Function of body membranes 1. Cover body surfaces 2. Line body cavities 3. Form protective sheets around organs II. Classification of Body Membranes
Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary
 Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Chapter 4 The Integumentary System and Body Membranes. HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School
 Chapter 4 The Integumentary System and Body Membranes HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial Membranes Cutaneous Membranes = The Skin Mucous Membranes Serous
Chapter 4 The Integumentary System and Body Membranes HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial Membranes Cutaneous Membranes = The Skin Mucous Membranes Serous
Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition)
 Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major components (anatomy) of skin Differentiate between the two types of skin glands Explain
Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major components (anatomy) of skin Differentiate between the two types of skin glands Explain
Integumentary System-Skin and Body Coverings
 Integumentary System-Skin and Body Coverings List the four types of epithelial or connective membranes. The epithelial cutaneous includes your and is exposed to the. Its function is to. An example is..
Integumentary System-Skin and Body Coverings List the four types of epithelial or connective membranes. The epithelial cutaneous includes your and is exposed to the. Its function is to. An example is..
This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur.
 Background Knowledge Functions of normal skin Background Knowledge This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur. Learning
Background Knowledge Functions of normal skin Background Knowledge This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur. Learning
Skin and Body Membranes
 4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
Skin is a multilayered organ that covers and protects the body.
 Section 1: Skin is a multilayered organ that covers and protects the body. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the four tissue types that are found in
Section 1: Skin is a multilayered organ that covers and protects the body. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What are the four tissue types that are found in
HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
 C H A P T E R 51 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY THE HUMAN INTEGUMENTARY BODY: AN SYSTEM ORIENTATION C H A P T E R 1 PART I THE HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION
C H A P T E R 51 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY THE HUMAN INTEGUMENTARY BODY: AN SYSTEM ORIENTATION C H A P T E R 1 PART I THE HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION
Physiological regulation in mammals
 Name: Class: Date: Physiological regulation in mammals Biology Gr11A The Integumentary System and h l i Your skin is the largest organ in your body. In fact it makes up about 7% of your total body weight.
Name: Class: Date: Physiological regulation in mammals Biology Gr11A The Integumentary System and h l i Your skin is the largest organ in your body. In fact it makes up about 7% of your total body weight.
Warm Up. You have 10 minutes to complete your poster and prepare what you would like to share with the class.
 Warm Up You have 10 minutes to complete your poster and prepare what you would like to share with the class. Reflection 1. What were 2 similarities between your classification scheme and others in the
Warm Up You have 10 minutes to complete your poster and prepare what you would like to share with the class. Reflection 1. What were 2 similarities between your classification scheme and others in the
The integumentary system includes
 Survivor The integumentary system includes What are 3 of the 5 basic functions of the integumentary system? The integumentary system protects against what types of tissue damage? List at least two types
Survivor The integumentary system includes What are 3 of the 5 basic functions of the integumentary system? The integumentary system protects against what types of tissue damage? List at least two types
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 5 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 5 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
Integumentary System. Packet #12
 Integumentary System Packet #12 Introduction Skin/Integument Skin, considered an organ, is the major component of the integumentary system. The integumentary system is also composed of other accessory
Integumentary System Packet #12 Introduction Skin/Integument Skin, considered an organ, is the major component of the integumentary system. The integumentary system is also composed of other accessory
Integumentary System. Integumentary System
 1. General aspects a. The integumentary system consists of several organs major organ of the system is the skin other organs are relatively small and they can be considered as specialized structures of
1. General aspects a. The integumentary system consists of several organs major organ of the system is the skin other organs are relatively small and they can be considered as specialized structures of
28a A&P - Integumentary System
 28a A&P - Integumentary System 28a A&P - Integumentary System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
28a A&P - Integumentary System 28a A&P - Integumentary System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Eleventh Edition. Chapter 6
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 6 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Referred to as Cutaneous Membrane
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 6 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Referred to as Cutaneous Membrane
ABCD rule. apocrine glands. arrector pili. ceruminous glands. contact dermatitis
 ABCD rule assessing moles: asymmetric, broder irregularity, color, diameter (larger than 6mm) apocrine glands arrector pili sweat glands in the pubic and underarm areas that secrete thicker sweat, that
ABCD rule assessing moles: asymmetric, broder irregularity, color, diameter (larger than 6mm) apocrine glands arrector pili sweat glands in the pubic and underarm areas that secrete thicker sweat, that
Skin Homework. (Skin is the largest organ in the body)
 Skin Homework (Skin is the largest organ in the body) This homework is following the information in the Louise Tucker book so the answers should be easy to find. 1 Label the Cross Section of Skin below:
Skin Homework (Skin is the largest organ in the body) This homework is following the information in the Louise Tucker book so the answers should be easy to find. 1 Label the Cross Section of Skin below:
Skin. Lecture #14. Ref:
 Skin Lecture #14 Ref: http://www.ccunix.ccu.edu.tw/~chenmsl/tea/skin_910721.htm Structure of Skin 1. Epidermis 2. Dermis 3. Subcutis 4. Hair follicle 5. Sebaceous gland 6. Sweat gland Skin Largest human
Skin Lecture #14 Ref: http://www.ccunix.ccu.edu.tw/~chenmsl/tea/skin_910721.htm Structure of Skin 1. Epidermis 2. Dermis 3. Subcutis 4. Hair follicle 5. Sebaceous gland 6. Sweat gland Skin Largest human
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System 5.1-5.4 September 10, 2012 Chapter 5: The Integumentary System 5.1 Structure of the Skin 5.2 Accessory Structures of the Skin 5.3 Types of Skin 5.4 Functions of the Skin 5.5 Maintaining
The Integumentary System 5.1-5.4 September 10, 2012 Chapter 5: The Integumentary System 5.1 Structure of the Skin 5.2 Accessory Structures of the Skin 5.3 Types of Skin 5.4 Functions of the Skin 5.5 Maintaining
All the Rest. What is All the Rest? Integumentary System. First are the FUNCTI0NS. THERMOREGULATION function. PROTECTION function 10/12/16
 What is All the Rest? Integumentary System All the Rest Integumentary System Homeostatic Imbalances Skin Cancer Burns First are the FUNCTI0NS Chemical, Physical/Mechanical, Biological Thermoregulation
What is All the Rest? Integumentary System All the Rest Integumentary System Homeostatic Imbalances Skin Cancer Burns First are the FUNCTI0NS Chemical, Physical/Mechanical, Biological Thermoregulation
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. Body Membranes & Skin
 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
Overview of the Integumentary System. Lab #7. Layers of the epidermis are known as strata. Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the Epidermis
 Overview of the Integumentary System Lab #7 Integumentary System Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the epidermis are known as strata Figure 5 2 Layers of the Epidermis Top: Free surface of skin
Overview of the Integumentary System Lab #7 Integumentary System Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the epidermis are known as strata Figure 5 2 Layers of the Epidermis Top: Free surface of skin
Integumentary System. Study of the Skin
 Integumentary System Study of the Skin Skin is used to: Maintain homeostasis Provide a protective covering Slow down water loss from deeper tissues House sensory receptors Synthesize various biochemicals
Integumentary System Study of the Skin Skin is used to: Maintain homeostasis Provide a protective covering Slow down water loss from deeper tissues House sensory receptors Synthesize various biochemicals
The Integumentary System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 5 The Integumentary System Chapter 5 Learning Outcomes 5-1 5-2 5-3 5-4 5-5 Describe the main structural features
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 5 The Integumentary System Chapter 5 Learning Outcomes 5-1 5-2 5-3 5-4 5-5 Describe the main structural features
Contents: The skin and its derivatives: hair, nails and glands. Functions: 1. Regulaiton of body temperature -sweating
 The Integumentary System Of all the body s organs, none is more easily inspected or more exposed to infection, disease, and injury than the skin. Because of its visibility, skin reflects our emotions and
The Integumentary System Of all the body s organs, none is more easily inspected or more exposed to infection, disease, and injury than the skin. Because of its visibility, skin reflects our emotions and
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM (SKIN) Human Anatomy and Physiology S. McElwee CHS
 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM (SKIN) Human Anatomy and Physiology S. McElwee CHS WHAT IS THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM? The integumentary system is 1 of 11 organ systems. It consists of the skin (cutaneous membrane),
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM (SKIN) Human Anatomy and Physiology S. McElwee CHS WHAT IS THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM? The integumentary system is 1 of 11 organ systems. It consists of the skin (cutaneous membrane),
2/5/2019. Organ System: Skin or Integumentary System. Hypodermis (or superficial fascia) Integumentary System - Learn and Understand
 Integumentary System - Learn and Understand Skin is an organ comprised of all four tissues Each layer of the skin contributes to one or more of its numerous functions Skin is both strong and flexible Keratinization
Integumentary System - Learn and Understand Skin is an organ comprised of all four tissues Each layer of the skin contributes to one or more of its numerous functions Skin is both strong and flexible Keratinization
Epithelial Tissues. Types of Epithelial Tissues: Lining of Kidney
 Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 4
 *We are revisiting Ch 3B on body tissues (Connective) prior to our study of Ch 4 Integumentary. Start on p.90 I. Connective Tissue A. Functions of Connective 1. Protection 2. Support 3. Binding Together
*We are revisiting Ch 3B on body tissues (Connective) prior to our study of Ch 4 Integumentary. Start on p.90 I. Connective Tissue A. Functions of Connective 1. Protection 2. Support 3. Binding Together
Skin Cancer - Non-Melanoma
 Skin Cancer - Non-Melanoma Introduction Each year, millions of people find out that they have skin cancer. Skin cancer is almost 100% curable if found early and treated right away. It is possible to prevent
Skin Cancer - Non-Melanoma Introduction Each year, millions of people find out that they have skin cancer. Skin cancer is almost 100% curable if found early and treated right away. It is possible to prevent
Chapter 5: Integumentary System
 Chapter 5: Integumentary System I. Overview of the Integumentary System A. List the five major functions of the integumentary system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Il. Skin A. Epidermis 1. The epidermis consists of 2.
Chapter 5: Integumentary System I. Overview of the Integumentary System A. List the five major functions of the integumentary system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Il. Skin A. Epidermis 1. The epidermis consists of 2.
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System Physiology of Touch Skin: our most sensitive organ Touch: first sense to develop in embryos Most important but most neglected sense How many sensory receptors do we have? (We have
Integumentary System Physiology of Touch Skin: our most sensitive organ Touch: first sense to develop in embryos Most important but most neglected sense How many sensory receptors do we have? (We have
The Integumentary System. Health & Anatomy
 The Integumentary System Health & Anatomy Review of Membranes -Serous Membranes are composed of simple squamous epithelium resting on a thin layer of areolar connective tissue. *Name depends on the location
The Integumentary System Health & Anatomy Review of Membranes -Serous Membranes are composed of simple squamous epithelium resting on a thin layer of areolar connective tissue. *Name depends on the location
Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS
 Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. epidermis b. dermis c. hypodermis d. adipose tissue e. hair f. sebaceous gland g. sweat gland 2. a Pre-Lab
Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. epidermis b. dermis c. hypodermis d. adipose tissue e. hair f. sebaceous gland g. sweat gland 2. a Pre-Lab
December 3, Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow?
 December 3, 2013 Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow? Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Chapter 36: Biology II The Skeleton
December 3, 2013 Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow? Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Chapter 36: Biology II The Skeleton
4 Skin and Body Membranes Study Guide
 Name: SKIN AND BODY MEMBRANES: 4 Skin and Body Membranes Study Guide Period: Body membranes, which cover body surfaces, line its cavities, and form protective sheets around organs, fall into two major
Name: SKIN AND BODY MEMBRANES: 4 Skin and Body Membranes Study Guide Period: Body membranes, which cover body surfaces, line its cavities, and form protective sheets around organs, fall into two major
The Skin home study course
 The Skin home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part of this publication
The Skin home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part of this publication
Skin is a complex organ, but by understanding its structure and function it becomes easier to create skin that is Reborn Beautiful.
 SKIN SCIENCE Skin is a complex organ, but by understanding its structure and function it becomes easier to create skin that is Reborn Beautiful. Dr. Des Fernandes Copyright 2016 Environ Skin Care (Pty)
SKIN SCIENCE Skin is a complex organ, but by understanding its structure and function it becomes easier to create skin that is Reborn Beautiful. Dr. Des Fernandes Copyright 2016 Environ Skin Care (Pty)
Ch 5: Integumentary System
 Ch 5: Integumentary System You gotta have skin; All you really need is skin. Skin's the thing, that if you've got it outside, It helps keep your insides in. Alan Sherman (1924-1973) Developed by John Gallagher,
Ch 5: Integumentary System You gotta have skin; All you really need is skin. Skin's the thing, that if you've got it outside, It helps keep your insides in. Alan Sherman (1924-1973) Developed by John Gallagher,
Skin. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
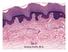 Skin Kristine Krafts, M.D. Skin Lecture Objectives Describe the functions of skin. Describe the structure, location and function of the cell types found in epidermis: keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans
Skin Kristine Krafts, M.D. Skin Lecture Objectives Describe the functions of skin. Describe the structure, location and function of the cell types found in epidermis: keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans
The Integumentary System. Chapter 6
 The Integumentary System Chapter 6 What is the integumentary system? skin hair nails glands blood vessels sensory receptors What is your skin made of? 3 layers epidermis (outside) dermis (middle) subcutaneous
The Integumentary System Chapter 6 What is the integumentary system? skin hair nails glands blood vessels sensory receptors What is your skin made of? 3 layers epidermis (outside) dermis (middle) subcutaneous
The INTEGUMENTARY System
 The INTEGUMENTARY System Functions of the Skin Protection Vitamin D Production Sensory Organ Temperature Regulation Protection against UV Light Layers of the Skin Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous Epidermis
The INTEGUMENTARY System Functions of the Skin Protection Vitamin D Production Sensory Organ Temperature Regulation Protection against UV Light Layers of the Skin Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous Epidermis
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad. Lab 1
 Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
Notes on Chapter 6 Integumentary System (Lecture notes-shortened)
 Notes on Chapter 6 Integumentary System (Lecture notes-shortened) I. Integumentary system- the skin and all of its accessory organs such hair, nails & gland II. Skin & its Tissues A. Skin is largest organ
Notes on Chapter 6 Integumentary System (Lecture notes-shortened) I. Integumentary system- the skin and all of its accessory organs such hair, nails & gland II. Skin & its Tissues A. Skin is largest organ
Figure 4.1. Using Figure 4.1, identify the following: 1) The region that contains adipose tissue is indicated by letter. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 115
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Short Answer Figure 4.1 Using Figure 4.1, identify the following: 1) The region that contains adipose tissue is indicated
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Short Answer Figure 4.1 Using Figure 4.1, identify the following: 1) The region that contains adipose tissue is indicated
