The cientificworldjournal
|
|
|
- Sharleen Perkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Scientific World Journal Volume 2012, Article ID , 6 pages doi: /2012/ The cientificworldjournal Clinical Study Evaluation of Histopathological Changes in Control Biopsies Which Taken 48 Sessions after NBUVB Phototherapy for Early-Stage Mycosis Fungoides Ebru Zemheri, 1 Seyma Ozkanli, 1 Ilkin Zindanci, 2 Serkan Senol, 1 Ozge Akbulak, 2 Elvan Turfanda, 1 Mehtap Toprak, 1 Duygu Kosemetin, 1 and Abdullah Aydin 1 1 Department of Pathology, Training and Research Hospital, Istanbul Medeniyet University, SB Goztepe, Turkey 2 Department of Dermatology, Training and Research Hospital, Istanbul Medeniyet University, SB Goztepe, Turkey Correspondence should be addressed to Ebru Zemheri, ebruzemheri@gmail.com Received 12 July 2012; Accepted 1 August 2012 Academic Editors: T. Goldmann and A. Ishida-Yamamoto Copyright 2012 Ebru Zemheri et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Background. There are not many studies investigating histomorphological changes in 48 sessions in patients with early-stage MF after narrowband UVB (NBUVB) treatment. Our purpose is to evaluate histological features of phototherapy after 48 sessions and determine which parameters are more reliable for controlling skin biopsies. Methods. Biopsies of 32 patients with early stage of MF, who were treated with NBUVB phototherapy, were histologically evaluated before and after the treatments, including epidermotropism, stratum corneum, epidermal thickness, dermal infiltration, papillary dermal fibrosis, vascular alterations, and other dermal changes. We discuss the histomorphological effects of NBUVB phototherapy on skin biopsies by comparing the responders with nonresponders, with before and after the treatment. Results. 9 patients (28%) did not give any response to treatment. Alleviation in epidermotropism, increases in parakeratosis and normal keratosis, perivascular infiltration, and melanophages, decrease in the lichenoid/patchy lichenoid infiltration pattern after the treatment was statistically significant. Comparing by response, normalization of stratum corneum and epidermis, orthohyperkeratosis, decrease in linearly arranged cells, the lichenoid/patchy lichenoid infiltration, the loss of inflammation were statistically significant in responders group. Conclusion. We detected a significant decrease in linearly arranged cells after phototherapy, indicating that it is an important diagnostic parameter in evaluation of therapeutic response. 1. Introduction Mycosis fungoides (MF) is the most common form of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. MF lesions are divided into three stages: patch, plaque, and tumor [1, 2]. Early-stage (stages IA, IB, and IIA) MF has long been treated with various agents including topical potent corticosteroids, topical nitrogen mustard, topical carmustine, oral psoralen plus UVA (PUVA), broadband and narrowband UVB, electron-beam radiotherapy, interferon, retinoids, and topical bexarotene [3 5]. Despite a lot of clinical observation, the histopathological changes seen in 48 sessions after NBUVB phototherapy for early-stage mycosis fungoides are not clearly described. So, we compared the histopathological changes in biopsies taken before and after the treatment with NBUVB phototherapy for 48 sessions. In this study, histopathologic findings between responders and nonresponders to treatment in addition to histopathologic changes before and after the treatment were compared. 2. Materials and Methods 2.1. Patients. A total of 32 patients with early-stage MF were recruited between 2008 and All patients were treated with NBUVB phototherapy. We reevaluated histological findings in biopsies taken from the lesions of patients, which were taken before treatment and after each 48 sessions.
2 2 The Scientific World Journal The mean age of the patients (18 women and 14 men) was 58 years and ranged from 30 to 71 years. Evaluations were made according to clinical and histopathological findings described in World Health Organization-European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Diagnostic Criteria [6]. Twenty-nine lesions were classified as patch stage, and three lesions were classified as plaque-stage MF. stage of disease was based on the TNM classification [7]. Five patients were in stage IB and three patients were stage IIA and the rest were stage IA. According to the classification of Fitzpatrick, the observed skin types were as follows: type III in 8 patients, type I in 4 patients, and type II in the rest. None of the patients had organomegaly. There were no abnormalities in routine biochemical investigations, red or white blood cell counts. Computed tomography scans of thorax and abdomen were normal in all patients. Clinical response was classified as follows: more than 90% reduction in skin lesions was considered as complete response; less than 90% reduction in skin lesions was considered as nonresponse Phototherapy. Phototherapy was performed in a phototherapy cabinet (7001 K cabinet, Waldman, Germany) containing 21 UVB lamps (Philips TL-01/100 W) which had radiated light at 311 nm of wavelight. Initial dose was 0.2 joule/cm 2, and dosage was increased 0.1 joule/cm 2 in each two séance. Maximum dosage was 2.9 joule/cm. The phototherapy was administered three times a week Histopathological Evaluation. We determined histomorphological parameters according to recently published histological criteria for early lesions of MF [1, 7, 8]. Epidermotropism was the presence of atypical lymphoid cells in the epidermis and it was classified as single/haloed lymphocytes, linearly arranged single lymphocytes and Pautrier microabscesses. Stratum corneum was classified as normal, orthohyperkeratotic, and parakeratotic. The epidermal thickness was grouped as normal, atrophic, and hyperplastic. Dermal infiltration pattern was classified as superficial perivascular, lichenoid/patchy lichenoid, and no inflammation. Papillary dermal fibrosis was defined as the degree of increased collagen (0, 1, and 2). Other dermal changes were classified as basal vacuolar degeneration, dyskeratotic cells, and melanophages. Vascular alterations such as telangiectasia and vascular proliferation were evaluated. All parameters were evaluated by two pathologists (E.Z., S.O.) Statistical Analysis. The data were processed on a personal computer and analyzed using SPSS 15.0 (Statistical Package for Social Sciences) (SSPS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Chi-square test, Fisher s Exact Chi-square test, and Mc Nemar test was used for comparison of qualitative data. P values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. 3. Results Both clinically and histologically, 9 of 32 patients (28%) did not give any response to treatment, whereas the remaining Figure 1: Linearly arranged and single/haloed atypical lymphocytes in epidermis in patient with patch stage MF were seen before treatment ( 400, H&E). did. Of nine unresponsive patients, three were at the plaque stage MF and the rest were at the patch stage. Histopathological findings pointing persistence of disease were also present in all patients who were clinically unresponsive to the treatment. The histopathological findings before and after the treatment are listed in Table 1.Beforetreatment, epidermotropism was established in all cases and linearly arranged cells were the most prominent (93.8%) finding (Figure 1). Single cells and Pautrier microabscesses have followed this finding, respectively (62.5%, 59.4%). Alleviation in all types of epidermotropism after the treatment was found to be highly statistically significant (P = 0.001). After the treatment, in seven cases of total, epidermotropism was observed and the single/haloed lymphocytes were the most common type (21.9%) (Figure 2). Although the orthohyperkeratosis in stratum corneum was very prominent before the treatment, parakeratosis (P = 0.039) and normal keratosis (P = 0.004) in stratum corneum were increased after the treatment. In all cases, inflammation was in lichenoid/patchy lichenoid pattern before the treatment. Following the treatment, decreases in the lichenoid/patchy lichenoid infiltration pattern (P = 0.001) and increases in the perivascular infiltration (P = 0.001) were noticed, in addition, in 9 cases, there was no sign for inflammation (P = 0.004). In evaluation of other changes in dermis and epidermis after the treatment, only the increase in melanophage count was found to be statistically significant (P = 0.001) (Figure 3). Vascular changes were not considered as statistically significant. After the treatment, the responders and the nonresponders findings were compared in Table 2, the ratio for observing the linearly arranged cells was found to be significantly lower in the responders (P = 0.038). In responders, normalization of stratum corneum was found to be higher compared to the nonresponders (P = 0.001), whereas orthohyperkeratosis was found to be lower compared to the nonresponders (P = 0.007). In responders, the normalization of epidermis was observed, but it was not statistically significant. On the contrary, in nonresponders, epidermis was significantly hyperplastic (P = 0.002). The decrease in the lichenoid/patchy lichenoid infiltration (P = 0.004)
3 The Scientific World Journal 3 Table 1: Comparison of histopathological changes before and after the treatment. Before treatment After treatment n (%) n (%) P Epidermotropism Single/haloed lymphocytes 20 (62.5%) 7 (21.9%) Linearly arranged 30 (93.8%) 6 (18.8%) lymphocytes Pautrier microabscesses 19 (59.4%) 4 (12.5%) Stratum corneum Normal 7 (21.9%) 21 (65.6%) Parakeratosis 8 (25.0%) 1 (3.1%) Orthohyperkeratosis 17 (53.1%) 10 (31.3%) Epidermis Normal 9 (28.1%) 15 (46.9%) Atrophic 6 (18.8%) 8 (25.0%) Hyperplastic 17 (53.1%) 9 (28.1%) Inflammatory infiltrates Superficial, perivascular 16 (50.0%) Lichenoid/patchy lichenoid 32 (100%) 7 (21.9%) No inflammation 9 (28.1%) Fibrosis 0 6 (18.8%) 6 (18.8%) (68.8%) 22 (68.8%) (9.4%) 3 (9.4%) Other changes Basal vacuolar degeneration 1 (3.1%) 7 (21.9%) Dyskeratotic cells 2 (6.3%) 7 (21.9%) Melanophages 8 (25.0%) 23 (71.9%) Vascular changes Telangiectasia 7 (21.9%) 14 (43.8%) Vascular proliferation 1 (3.1%) 4 (12.5%) Mc Nemar test was used. P< 0.05, P< was found to be highly significant and the cessation of inflammation was also found to be (P = 0.027) statistically significant in responders. Of nine nonresponders, 5 had lichenoid/patchy lichenoid pattern (Figure 4), whereas 4 had perivascular pattern. There were atypical lymphocytes in all nine nonresponders. Other epidermal and dermal changes and vascular changes were not statistically significant in both groups (responders and nonresponders). 4. Discussion There are not enough studies investigating histomorphological changes after 48 sessions of NBUVB treatment in patients with early-stage MF. The main purpose of this study is to evaluate histological features of phototherapy after 48 sessions and to determine which parameters are more reliable for control skin biopsies. We discuss the histomorphological effects of NBUVB phototherapy on skin biopsies by comparing the responders with nonresponders with before and after the treatment. Early-stage MF may clinically and histologically mimic benign inflammatory dermatoses making it difficult to diagnose [9, 10]. Because of its indolent and chronic course with recurrences and its possibility to progress to the aggressive course (although rare), this disease must be treated as early as possible. The histological diagnosis of early-stage MF may be difficult in many instances. The histological parameters in diagnosis of MF have been assessed in a number of studies [8, 11 13]. The International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas (ISCL) and the cutaneous lymphoma task force of the European Organization of Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) revised the staging and classification of mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome. In this revision, they reported that making the definitive histopathologic diagnosis with light microscopy alone may be difficult in early MF. The ISCL has recently proposed a diagnostic algorithm for early-stage MF. According to this classification, superficial lymphoid infiltration with epidermotropism without spongiosis and lymphoid atypia which is defined as
4 4 The Scientific World Journal Figure 2: Loss of linearly arranged cells, but persistence of single/haloed lymphocytes and Pautrier microabscess in the epidermis, fibrosis in the papillary dermis in nonresponder group after treatment were seen ( 200, H&E). Figure 4: Lichenoid infiltration of atypical cell and fibrosis were seen in nonresponder group after treatment ( 200, H&E). Figure 3: Basal vacuolar degeneration in epidermis and melanophages in papillary dermis were seen after treatment ( 400, H&E). cells with enlarged hyperchromatic nuclei and irregular or cerebriform nuclear contours are histopathologic criteria for early-stage MF diagnosis [7]. We have taken into consideration epidermotropism in our study for diagnosing MF and in determining the responder group after the treatment. We have detected a significant decrease in linearly arranged cells after phototherapy, indicating that it is an important diagnostic parameter in the evaluation of therapeutic response. There was a decrease in single cells and Pautrier microabscesses, although we think that it is less important in evaluating the response to the treatment. Apa et al., in their report, have indicated linearly arranged cells (like in our study) and Pautrier microabscesses as active parameters [1]. When comparing the histological findings of responsive and unresponsive groups, it came into our attention that, in responsive group, inflammation and epidermotropism were attenuated, meanwhile the stratum corneum and epidermis were in normal boundaries. In both groups, reactive changes had similar characteristics. These findings support that the NBUVB not only contributes to the depletion of the epidermotropism, but also contributes to the normalization of the epidermis. Gökdemir et al. has determined the effects NBUVB in early-stage MF both clinically and histopathologically. Histopathologic response was divided into three categories. First, the complete response, the absence of epidermotropism and Pautrier microabscesses marked the reduction in dense infiltrates comprising atypical lymphocytes with irregular nuclei; second, the partial response, marked the reduction in epidermotropism and sparsely scattered atypical lymphocytes in the epidermis and dermis; third, no response and no histopathologic changes. Of all patients, 18 (78.26%) had complete histopathological improvement and five (21.74%) had partial response or no histopathological response [3]. El-Mofty et al. compared the clinical and histopathologic efficacy of PUVA and NBUVB in the treatment of earlystage MF. Histopathological changes were graded as follows: very good response: only sparse inflammatory infiltration in the dermis; good response: mild epidermotropism, sparse infiltration and nonatypical cells; fair response: epidermotropism, dense band-like infiltration and atypical cells; poor response: epidermotropism, dense and deep dermal infiltration, atypical cells. They have detected that 9 patients of 10 show very good-good response and only one patient show fair-poor response on 48 sessions [14]. Hyperkeratosis, hypergranulosis, variable acanthosis, and epidermal atrophy can be seen in treatment with UV [15]. We have found that parakeratosis is a common finding, as in the study of Apa et al., who reported that it was a distinguishing parameter when present at the time of diagnosis [1]. After the treatment, parakeratosis has disappeared in our study, like in the study of Apa et al. Epidermal hyperplasia seemed to be an important distinguishing parameter and, in our study, it has increased after therapy, especially in the responders. In our study, no significant change in fibrosis has been achieved before and after the treatment. According to Naraghi et al., papillary dermal fibrosis was a sensitive feature (96%), and it has achieved statistical significance as a discriminating factor [8]. Similar results were reported by Smoller et al. [11] and Ackerman[13]. They hadalso pointed out that dermal fibrosis was a feature of late atrophic patches or plaques and was not encountered in early patches [11, 13]. But Apa et al. had reported that increase in the amount of dermal fibrosis was the most frequent parameter seen after phototherapy [1]. Since all of our cases were early-stage MF,
5 The Scientific World Journal 5 Table 2: Evaluation of parameters after the treatment, according to response to treatment. Response to treatment After treatment Yes No P n (%) n (%) Epidermotropism Single/haloed lymphocytes 3 (13.0%) 4 (44.4%) Linearly arranged 2 (8.7%) 4 (44.4%) lymphocytes Pautrier microabscesses 1 (4.3%) 3 (33.3%) Stratum corneum Normal 19 (82.6%) 2 (22.2%) Parakeratosis 0 (0.0%) 1 (11.1%) Orthohyperkeratosis 4 (17.4%) 6 (66.7%) Epidermis Normal 13 (56.5%) 2 (22.2%) Atrophic 7 (30.4%) 1 (11.1%) Hyperplastic 3 (13.0%) 6 (66.7%) Inflammatory infiltrates Superficial. perivascular 13 (52.1%) 4 (44.4%) Lichenoid/patchy lichenoid 2 (8.7%) 5 (55.6%) No inflammation 9 (39.1%) 0 (0%) Fibrosis 0 6 (26.1%) 0 (0.0%) (65.2%) 7 (77.8%) (4.3%) 2 (22.2%) Other changes Basal vacuolar degeneration 7 (30.4%) 0 (0.0%) Dyskeratotic cells 7 (30.4%) 0 (0.0%) Melanophages 18 (78.3%) 5 (55.6%) Vascular changes Telangiectasia 10 (43.5%) 4 (44.4%) Vascular proliferation 3 (13.0%) 1 (11.1%) Chi-square and Fisher s Exact tests were used P < 0.05, P< the degree of alteration in fibrosis was consistent with studies of Naraghi and Ackerman. Epstein had reported that telangiectatic vessels may be conspicuous [16]. Dermal edema and vasculopathy were neither sensitive nor specific for MF [1, 8]. In our study, vascular changes were not established to have any characteristics for the diagnosis. This finding supports that NBUVB has no significant effect on the vascular structures which are not affected by the disease. Melanin pigmentation, melanocyte hyperplasia, and pigmentary incontinence can be seen in treatment with UV [17 19]. In addition, UV light triggers apoptosis and leads to epidermal basal cell degeneration resulting from cytoplasmic swelling [20, 21]. We have found an increase in dermal melanophages after the treatment, which can be considered as a therapeutic side effect. After the treatment, absence of these secondary changes in responders and nonresponders supports this opinion. Based on the data presented here, we think that some histological features, such as epidermotropism, changes of stratum corneum, epidermis, and dermis, can be used in determining the effectiveness of treatment. We have found that epidermotropism of atypical cells were important criteria in order to decide whether the disease was histopathologically present or not, and the secondary changes to NBUVB had no use for this purpose. References [1] D.D.Apa,E.S.Pfeiffer, K. Baz, E. A. Kanik, and P. Inandioǧlu, Histopathological changes seen in mycosis fungoides patients after phototherapy, American Dermatopathology, vol. 32, no. 3, pp , [2] M. Y. Hsu and G. F. Murphy, Cutaneous lymphomas and leukemias, in Lever Histopathology of the Skin, D. Elder, Ed., pp , Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philedelphia, Pa, USA, [3] G. Gökdemir, D. Barutcuoǧlu, D. Sakiz, anda. Köşlü, Narrowband UVB phototherapy for early-stage mycosis fungoides: evaluation of clinical and histopathological changes,
6 6 The Scientific World Journal the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, vol. 20, no. 7, pp , [4]G.Roupe,M.H.Sandström, and C. Kjellström, PUVA in early mycosis fungoides may give long-term remission and delay extracutaneous spread, Acta Dermato-Venereologica, vol. 76, no. 6, pp , [5] F. Singh and M. G. Lebwohl, Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma treatment using bexarotene and PUVA: a case series, Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, vol. 51, no. 4, pp , [6] R. Willemze, E. S. Jaffe, G. Burg et al., WHO-EORTC classification for cutaneous lymphomas, Blood, vol. 105, no. 10, pp , [7] E. Olsen, E. Vonderheid, N. Pimpinelli et al., Revisions to the staging and classification of mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome: a proposal of the International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas (ISCL) and the cutaneous lymphoma task force of the European Organization of Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC), Blood, vol. 110, no. 6, pp , [8] Z. S. Naraghi, H. Seirafi, M. Valikhani, F. Farnaghi, S. Kavusi, and Y. Dowlati, Assessment of histologic criteria in the diagnosis of mycosis fungoides, International Dermatology, vol. 42, no. 1, pp , [9] M. Santucci, A. Biggeri, A. C. Feller, and G. Burg, Accuracy, concordance, and reproducibility of histologic diagnosis in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, Archives of Dermatology, vol. 136, no. 4, pp , [10] M. S. Jang, J. W. Baek, J. B. Park, D. Y. Kang, J. S. Kang, and K. S. Suh, Narrowband ultraviolet B phototherapy of early stage mycosis fungoides in Korean patients, Annals of Dermatology, vol. 23, pp , [11] B. R. Smoller, K. Bishop, E. Glusac, Y. H. Kim, and M. Hendrickson, Reassessment of histologic parameters in the diagnosis of mycosis fungoides, American Surgical Pathology, vol. 19, no. 12, pp , [12] P. E. Shapiro and F. J. Pinto, The histologic spectrum of mycosis fungoides/sezary syndrome (cutaneous T- cell lymphoma): a review of 222 biopsies, including newly described patterns and the earliest pathologic changes, American Surgical Pathology, vol. 18, no. 7, pp , [13] A. B. Ackerman, Histologic Diagnosis of Inflammatory Skin Diseases: An Algorithmic Method Based on Pattern Analysis, Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, Md, USA, [14] M. El-Mofty, M. El-Darouty, M. Salonas et al., Narrow band UVB (311 nm), psoralen UVB (311 nm) and PUVA therapy in the treatment of early-stage mycosis fungoides: a right-left comparative study, Photodermatology Photoimmunology and Photomedicine, vol. 21, no. 6, pp , [15] A. N. Crowson and C. M. Magro, Recent advances in the pathology of cutaneous drug eruptions, Dermatologic Clinics, vol. 17, no. 3, pp , [16] J. H. Epstein, Phototoxicity and photoallergy, Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery, vol. 18, no. 4, pp , [17] A. N. Crowson and C. M. Magro, Recent advances in the pathology of cutaneous drug eruptions, Dermatologic Clinics, vol. 17, no. 3, pp , [18] R. Mang, H. Stege, and J. Krutmann, Phototoxicity and photoallergy, in Textbook of Contact Dermatitis,R.J.Rycroft,Ed., pp , Springer, Berlin, Germany, [19] R. Friedland, M. David, M. Feinmesser, A. Barzilai, and E. Hodak, NB-UVB ( lentigines in patients with mycosis fungoides: a new adverse effect of phototherapy, Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, vol. 26, no. 9, pp , [20] V. P. Werth, M. Bashir, and W. Zhang, Photosensitivity in rheumatic diseases, Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings, vol. 9, no. 1, pp , [21] D. V. Krysko, T. Vanden Berghe, K. D Herde, and P. Vandenabeele, Apoptosis and necrosis: detection, discrimination and phagocytosis, Methods, vol. 44, no. 3, pp , 2008.
7 MEDIATORS of INFLAMMATION The Scientific World Journal Gastroenterology Research and Practice Diabetes Research International Endocrinology Immunology Research Disease Markers Submit your manuscripts at BioMed Research International PPAR Research Obesity Ophthalmology Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Stem Cells International Oncology Parkinson s Disease Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine AIDS Behavioural Neurology Research and Treatment Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity
Narrow band UVB (311 nm), psoralen UVB (311 nm) and PUVA therapy in the treatment of early-stage mycosis fungoides: a right left comparative study
 Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 2005; 21: 281 286 Blackwell Munksgaard Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Narrow band UVB (311 nm), psoralen UVB (311 nm) and therapy in the treatment of early-stage
Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 2005; 21: 281 286 Blackwell Munksgaard Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Narrow band UVB (311 nm), psoralen UVB (311 nm) and therapy in the treatment of early-stage
Cutaneous Mycosis Fungoides (MF), the subtype of cutaneous
 DOI 10. 5001/omj.2012.28 The Histological Spectrum of Early Mycosis Fungoides: A Study of 58 Saudi Arab patients Maha Arafah, Shaesta Naseem Zaidi, Hala Kassouf Kfoury, Ammar Al Rikabi, Khalid Al Ghamdi
DOI 10. 5001/omj.2012.28 The Histological Spectrum of Early Mycosis Fungoides: A Study of 58 Saudi Arab patients Maha Arafah, Shaesta Naseem Zaidi, Hala Kassouf Kfoury, Ammar Al Rikabi, Khalid Al Ghamdi
Dermatopathology: The tumor is composed of keratinocytes which show atypia, increase mitoses and abnormal mitoses.
 Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Microscopic study of the normal skin in cases of mycosis fungoides
 Microscopic study of the normal skin in cases of mycosis fungoides M. El Darouti, S. Marzook, M. Bosseila, O. Abu Zeid, O. El- Safouri, A. Zayed, A. El-Ramly Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 2 (1):
Microscopic study of the normal skin in cases of mycosis fungoides M. El Darouti, S. Marzook, M. Bosseila, O. Abu Zeid, O. El- Safouri, A. Zayed, A. El-Ramly Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 2 (1):
Case Report A Severe Case of Lymphomatoid Papulosis Type E Successfully Treated with Interferon-Alfa 2a
 Hindawi Case Reports in Dermatological Medicine Volume 2017, Article ID 3194738, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3194738 Case Report A Severe Case of Lymphomatoid Papulosis Type E Successfully Treated
Hindawi Case Reports in Dermatological Medicine Volume 2017, Article ID 3194738, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3194738 Case Report A Severe Case of Lymphomatoid Papulosis Type E Successfully Treated
Clinical and Histopathological Spectrum of Mycosis Fungoides
 Awad Hasan Al-Tarawneh, MD, Jordan Board* Background: Early diagnosis of mycosis fungoides is essential but difficult and can be easily missed because it mimics many inflammatory skin diseases both clinically
Awad Hasan Al-Tarawneh, MD, Jordan Board* Background: Early diagnosis of mycosis fungoides is essential but difficult and can be easily missed because it mimics many inflammatory skin diseases both clinically
Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide
 Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide Actinic keratosis is a very common lesion that you will see in your day-to-day practice. First, let me explain the name Actinic keratosis. It means keratosis
Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide Actinic keratosis is a very common lesion that you will see in your day-to-day practice. First, let me explain the name Actinic keratosis. It means keratosis
Therapeutic Management of Early Cutaneous Mycosis Fungoides
 Therapeutic Management of Early Cutaneous Mycosis Fungoides L Frank Glass, MD Cutaneous Lymphoma Programs H Lee Moffitt Cancer Center and Research Institute George Washington University Dermatology and
Therapeutic Management of Early Cutaneous Mycosis Fungoides L Frank Glass, MD Cutaneous Lymphoma Programs H Lee Moffitt Cancer Center and Research Institute George Washington University Dermatology and
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more
 Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Lymphoma and Pseudolymphoma
 Lymphoma and Pseudolymphoma Laura B. Pincus, MD Co-Director, Cutaneous Lymphoma Clinic Associate Professor Dermatology and Pathology University of California, San Francisco I HAVE NO RELEVANT RELATIONSHIPS
Lymphoma and Pseudolymphoma Laura B. Pincus, MD Co-Director, Cutaneous Lymphoma Clinic Associate Professor Dermatology and Pathology University of California, San Francisco I HAVE NO RELEVANT RELATIONSHIPS
Case Report A Case of Cystic Basal Cell Carcinoma Which Shows a Homogenous Blue/Black Area under Dermatoscopy
 Volume 20, Article ID 450472, 4 pages doi:0.55/20/450472 Case Report A Case of Cystic Basal Cell Carcinoma Which Shows a Homogenous Blue/Black Area under Dermatoscopy Akihiro Yoneta, Kohei Horimoto, Keiko
Volume 20, Article ID 450472, 4 pages doi:0.55/20/450472 Case Report A Case of Cystic Basal Cell Carcinoma Which Shows a Homogenous Blue/Black Area under Dermatoscopy Akihiro Yoneta, Kohei Horimoto, Keiko
A Retrospective Study on the Risk of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer in PUVA and Narrowband UVB Treated Patients
 Volume 1, Issue 3 Research Article A Retrospective Study on the Risk of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer in PUVA and Narrowband UVB Treated Patients Darukarnphut P, Rattanakaemakorn P *, Rajatanavin N Division
Volume 1, Issue 3 Research Article A Retrospective Study on the Risk of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer in PUVA and Narrowband UVB Treated Patients Darukarnphut P, Rattanakaemakorn P *, Rajatanavin N Division
Mycosis Fungoides and Variants
 Mycosis Fungoides and Variants Jennifer Madison McNiff, M.D. Associate Professor, Dermatology and Pathology Yale University School of Medicine Classic mycosis fungoides The most common cutaneous lymphoma
Mycosis Fungoides and Variants Jennifer Madison McNiff, M.D. Associate Professor, Dermatology and Pathology Yale University School of Medicine Classic mycosis fungoides The most common cutaneous lymphoma
Case Report Micromelanomas: A Review of Melanomas 2mmand a Case Report
 Case Reports in Oncological Medicine, Article ID 206260, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/206260 Case Report Micromelanomas: A Review of Melanomas 2mmand a Case Report Sharad P. Paul 1,2,3 1 Skin
Case Reports in Oncological Medicine, Article ID 206260, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/206260 Case Report Micromelanomas: A Review of Melanomas 2mmand a Case Report Sharad P. Paul 1,2,3 1 Skin
Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation. Dermatopathology Specialists Needed. Changing Trends
 Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation Uma Sundram, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Dermatology Stanford University May 29, 2008 Dermatopathology Specialists
Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation Uma Sundram, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Dermatology Stanford University May 29, 2008 Dermatopathology Specialists
Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/2010 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Benner, Marchina Frederika Title: Cutaneous CD30-positive lymphoproliferations
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/2010 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Benner, Marchina Frederika Title: Cutaneous CD30-positive lymphoproliferations
Case Report Childhood Hypopigmented Mycosis Fungoides: A Rare Diagnosis
 Case Reports in Pediatrics Volume 2016, Article ID 8564389, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8564389 Case Report Childhood Hypopigmented Mycosis Fungoides: A Rare Diagnosis Cláudia Patraquim, 1 Maria
Case Reports in Pediatrics Volume 2016, Article ID 8564389, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8564389 Case Report Childhood Hypopigmented Mycosis Fungoides: A Rare Diagnosis Cláudia Patraquim, 1 Maria
Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging. Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology
 Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology Definition of Lymphoma A cancer or malignancy that comes from
Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology Definition of Lymphoma A cancer or malignancy that comes from
Histopathology: skin pathology
 Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Clinical Study Treatment of Mesh Skin Grafted Scars Using a Plasma Skin Regeneration System
 Plastic Surgery International Volume 00, Article ID 87448, 4 pages doi:0.55/00/87448 Clinical Study Treatment of Mesh Skin Grafted Scars Using a Plasma Skin Regeneration System Takamitsu Higashimori, Taro
Plastic Surgery International Volume 00, Article ID 87448, 4 pages doi:0.55/00/87448 Clinical Study Treatment of Mesh Skin Grafted Scars Using a Plasma Skin Regeneration System Takamitsu Higashimori, Taro
Benign Lichenoid Keratosis
 Benign Lichenoid Keratosis ALAN F. FRIGY, M.D. AND PHILIP H. COOPER, M.D. The microscopic spectrum of benign lichenoid keratosis (BLK) was studied by examination of 30 examples. BLK consists of a segment
Benign Lichenoid Keratosis ALAN F. FRIGY, M.D. AND PHILIP H. COOPER, M.D. The microscopic spectrum of benign lichenoid keratosis (BLK) was studied by examination of 30 examples. BLK consists of a segment
Synthetic hypericin (SGX301; VIMRxyn) for cutaneous T cell lymphoma, unspecified
 NIHR Innovation Observatory Evidence Briefing: May 2017 Synthetic hypericin (SGX301; VIMRxyn) for cutaneous T cell lymphoma, unspecified NIHRIO (HSRIC) ID: 10761 NICE ID: 8375 LAY SUMMARY Cutaneous T cell
NIHR Innovation Observatory Evidence Briefing: May 2017 Synthetic hypericin (SGX301; VIMRxyn) for cutaneous T cell lymphoma, unspecified NIHRIO (HSRIC) ID: 10761 NICE ID: 8375 LAY SUMMARY Cutaneous T cell
Michi Shinohara MD Associate Professor University of Washington/Seattle Cancer Care Alliance Dermatology, Dermatopathology
 Michi Shinohara MD Associate Professor University of Washington/Seattle Cancer Care Alliance Dermatology, Dermatopathology Agenda Overview of cutaneous T and B- cell lymphomas Diagnosis, Staging, Prognosis
Michi Shinohara MD Associate Professor University of Washington/Seattle Cancer Care Alliance Dermatology, Dermatopathology Agenda Overview of cutaneous T and B- cell lymphomas Diagnosis, Staging, Prognosis
ISPUB.COM. Seborrheic Keratosis: A Pictorial Review of the Histopathologic Variations. D Sarma, S Repertinger
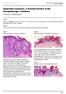 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 2 Seborrheic Keratosis: A Pictorial Review of the Histopathologic Variations D Sarma, S Repertinger Citation D Sarma, S Repertinger.. The Internet
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 2 Seborrheic Keratosis: A Pictorial Review of the Histopathologic Variations D Sarma, S Repertinger Citation D Sarma, S Repertinger.. The Internet
Research Article A Clinicopathological and Immunohistochemical Correlation in Cutaneous Metastases from Internal Malignancies: A Five-Year Study
 Skin Cancer, Article ID 793937, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/793937 Research Article A Clinicopathological and Immunohistochemical Correlation in Cutaneous Metastases from Internal Malignancies:
Skin Cancer, Article ID 793937, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/793937 Research Article A Clinicopathological and Immunohistochemical Correlation in Cutaneous Metastases from Internal Malignancies:
ISPUB.COM. A Case of Actinic Lichen Planus. K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 8 Number K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park Citation K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park.. The Internet Journal of Dermatology. 2009 Volume 8 Number. Abstract The
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 8 Number K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park Citation K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park.. The Internet Journal of Dermatology. 2009 Volume 8 Number. Abstract The
Research Article Clinical Outcome of a Novel Anti-CD6 Biologic Itolizumab in Patients of Psoriasis with Comorbid Conditions
 Dermatology Research and Practice Volume 2, Article ID 13326, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/.1155/2/13326 Research Article Clinical Outcome of a Novel Anti-CD6 Biologic Itolizumab in Patients of Psoriasis
Dermatology Research and Practice Volume 2, Article ID 13326, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/.1155/2/13326 Research Article Clinical Outcome of a Novel Anti-CD6 Biologic Itolizumab in Patients of Psoriasis
Lymphomatoid Papulosis 3 Case Reports
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2015), PP 31-35 www.iosrjournals.org Lymphomatoid Papulosis 3 Case Reports
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2015), PP 31-35 www.iosrjournals.org Lymphomatoid Papulosis 3 Case Reports
Interhospital Dermatology Conference 2013
 Case 21 A 50-year-old woman from Chonburi. Chief complaint: Asymptomatic rash on neck, trunk, both upper and lower extremities for 2 years. Present illness: The patient has developed asymptomatic scaly
Case 21 A 50-year-old woman from Chonburi. Chief complaint: Asymptomatic rash on neck, trunk, both upper and lower extremities for 2 years. Present illness: The patient has developed asymptomatic scaly
Pathology of the skin. 2nd Department of Pathology, Semmelweis University
 Pathology of the skin 2nd Department of Pathology, Semmelweis University Histology of the skin Epidermis: Stratum corneum Stratum granulosum Stratum spinosum Stratum basale Dermis: papillary and reticular
Pathology of the skin 2nd Department of Pathology, Semmelweis University Histology of the skin Epidermis: Stratum corneum Stratum granulosum Stratum spinosum Stratum basale Dermis: papillary and reticular
Case Report Three-Dimensional Dual-Energy Computed Tomography for Enhancing Stone/Stent Contrasting and Stone Visualization in Urolithiasis
 Case Reports in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 646087, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/646087 Case Report Three-Dimensional Dual-Energy Computed Tomography for Enhancing Stone/Stent Contrasting
Case Reports in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 646087, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/646087 Case Report Three-Dimensional Dual-Energy Computed Tomography for Enhancing Stone/Stent Contrasting
ISPUB.COM. Primary Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Long-term Management with Low Dose Methotrexate. S Parker INTRODUCTION
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 Primary Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Long-term Management with Low Dose S Parker Citation S Parker.. The Internet Journal of
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 Primary Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Long-term Management with Low Dose S Parker Citation S Parker.. The Internet Journal of
Clinical Study The Influence of the Coexpression of CD4 and CD8 in Cutaneous Lesions on Prognosis of Mycosis Fungoides: A Preliminary Study
 Skin Cancer, Article ID 624143, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/624143 Clinical Study The Influence of the Coexpression of CD4 and CD8 in Cutaneous Lesions on Prognosis of Mycosis Fungoides: A Preliminary
Skin Cancer, Article ID 624143, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/624143 Clinical Study The Influence of the Coexpression of CD4 and CD8 in Cutaneous Lesions on Prognosis of Mycosis Fungoides: A Preliminary
Case Report Metastatic Malignant Melanoma of Parotid Gland with a Regressed Primary Tumor
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2016, Article ID 5393404, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5393404 Case Report Metastatic Malignant Melanoma of Parotid Gland with a Regressed Primary Tumor
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2016, Article ID 5393404, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5393404 Case Report Metastatic Malignant Melanoma of Parotid Gland with a Regressed Primary Tumor
A Review of Survival in Mycosis Fungoides
 A Review of Survival in Mycosis Fungoides Robin T. Vollmer, MD From the VA and Duke University Medical Centers, Durham, NC. Key Words: Mycosis fungoides; Survival; Hazard function; Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
A Review of Survival in Mycosis Fungoides Robin T. Vollmer, MD From the VA and Duke University Medical Centers, Durham, NC. Key Words: Mycosis fungoides; Survival; Hazard function; Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB. Friday, February 12, :30 am 11:00 am
 MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB Friday, February 12, 2012 9:30 am 11:00 am FACULTY COPY GOALS: Describe the basic clinical and morphologic features of various
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB Friday, February 12, 2012 9:30 am 11:00 am FACULTY COPY GOALS: Describe the basic clinical and morphologic features of various
Dermatopathology. Dr. Rafael Botella Estrada. Hospital La Fe de Valencia
 Dermatopathology Dr. Rafael Botella Estrada. Hospital La Fe de Valencia Melanoma and mimics Dr. Martin Mihm Malignant lesions result from the accumulation of mutations Class I lesions (benign) Class II
Dermatopathology Dr. Rafael Botella Estrada. Hospital La Fe de Valencia Melanoma and mimics Dr. Martin Mihm Malignant lesions result from the accumulation of mutations Class I lesions (benign) Class II
Case Report Renal Cell Carcinoma Metastatic to Thyroid Gland, Presenting Like Anaplastic Carcinoma of Thyroid
 Case Reports in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 651081, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/651081 Case Report Renal Cell Carcinoma Metastatic to Thyroid Gland, Presenting Like Anaplastic Carcinoma
Case Reports in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 651081, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/651081 Case Report Renal Cell Carcinoma Metastatic to Thyroid Gland, Presenting Like Anaplastic Carcinoma
Clinical Study Mucosal Melanoma in the Head and Neck Region: Different Clinical Features and Same Outcome to Cutaneous Melanoma
 ISRN Dermatology Volume 2013, Article ID 586915, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/586915 Clinical Study Mucosal Melanoma in the Head and Neck Region: Different Clinical Features and Same Outcome
ISRN Dermatology Volume 2013, Article ID 586915, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/586915 Clinical Study Mucosal Melanoma in the Head and Neck Region: Different Clinical Features and Same Outcome
Abrupt Intralesional Color Change on Dermoscopy as a New Indicator of Early Superficial Spreading Melanoma in a Japanese Woman
 Published online: June 24, 2015 1662 6567/15/0072 0123$39.50/0 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported license (CC BY-NC)
Published online: June 24, 2015 1662 6567/15/0072 0123$39.50/0 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported license (CC BY-NC)
Case Study: The Surgical Management of Angiokeratoma Resulting from Radiotherapy for Penile Cancer
 Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2009) 9, 339 342 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2009.23 Case Study: The Surgical Management of Angiokeratoma Resulting from Radiotherapy for Penile Cancer
Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2009) 9, 339 342 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2009.23 Case Study: The Surgical Management of Angiokeratoma Resulting from Radiotherapy for Penile Cancer
Histopathology of Melanoma
 THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 48, 409-416 (1975) Histopathology of Melanoma G. J. WALKER SMITH Department ofpathology, Yale University School ofmedicine, 333 Cedar Street, New Haven, Connecticut
THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 48, 409-416 (1975) Histopathology of Melanoma G. J. WALKER SMITH Department ofpathology, Yale University School ofmedicine, 333 Cedar Street, New Haven, Connecticut
Lichenoid Tissue Reaction in Malignant Melanoma A Potential Diagnostic Pitfall
 natomic Pathology / LICHENOID TISSUE RECTION IN MLIGNNT MELNOM Lichenoid Tissue Reaction in Malignant Melanoma Potential Diagnostic Pitfall CPT Scott R. Dalton, MC, US, 1,3 Capt Matt. aptista, USF, MC,
natomic Pathology / LICHENOID TISSUE RECTION IN MLIGNNT MELNOM Lichenoid Tissue Reaction in Malignant Melanoma Potential Diagnostic Pitfall CPT Scott R. Dalton, MC, US, 1,3 Capt Matt. aptista, USF, MC,
Basics in Dermoscopy
 Basics in Dermoscopy Manal Bosseila Professor of Dermatology, Cairo University Member of European Academy Dermatology & Venereology EADV Member of International Dermoscopy Society IDS Member of Aesthetic
Basics in Dermoscopy Manal Bosseila Professor of Dermatology, Cairo University Member of European Academy Dermatology & Venereology EADV Member of International Dermoscopy Society IDS Member of Aesthetic
Citation The Journal of Dermatology, 37(8), available at
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Two cases of blaschkitis with promi Author(s) Utani, Atsushi Citation The Journal of Dermatology, 37(8), Issue Date 2010-08 URL Right http://hdl.handle.net/10069/25634
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Two cases of blaschkitis with promi Author(s) Utani, Atsushi Citation The Journal of Dermatology, 37(8), Issue Date 2010-08 URL Right http://hdl.handle.net/10069/25634
Renaissance of Low-Dose Radiotherapy Concepts for Cutaneous Lymphomas
 Review Article DOI: 10.1159/000470845 Received: February 06, 2017 Accepted: March 13, 2017 Published online: April 6, 2017 Renaissance of Low-Dose Radiotherapy Concepts for Cutaneous Lymphomas Bouthaina
Review Article DOI: 10.1159/000470845 Received: February 06, 2017 Accepted: March 13, 2017 Published online: April 6, 2017 Renaissance of Low-Dose Radiotherapy Concepts for Cutaneous Lymphomas Bouthaina
Case Report Denosumab Chemotherapy for Recurrent Giant-Cell Tumor of Bone: A Case Report of Neoadjuvant Use Enabling Complete Surgical Resection
 Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 496351, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/496351 Case Report Denosumab Chemotherapy for Recurrent Giant-Cell Tumor of Bone: A Case Report
Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 496351, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/496351 Case Report Denosumab Chemotherapy for Recurrent Giant-Cell Tumor of Bone: A Case Report
Case Report PET/CT Imaging in Oncology: Exceptions That Prove the Rule
 Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 865032, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/865032 Case Report PET/CT Imaging in Oncology: Exceptions That Prove the Rule M. Casali, 1 A.
Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 865032, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/865032 Case Report PET/CT Imaging in Oncology: Exceptions That Prove the Rule M. Casali, 1 A.
Case Report Patellofemoral Joint Replacement and Nickel Allergy: An Unusual Presentation
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 635082, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/635082 Case Report Patellofemoral Joint Replacement and Nickel Allergy: An Unusual Presentation Farhan
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 635082, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/635082 Case Report Patellofemoral Joint Replacement and Nickel Allergy: An Unusual Presentation Farhan
ISPUB.COM. Management of Co-existing Mycosis Fungoides and Lymphomatoid Papulosis. E Kim PHYSICAL FINDINGS INTRODUCTION INITIAL PRESENTATION
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 Management of Co-existing Mycosis Fungoides and Lymphomatoid Papulosis E Kim Citation E Kim. Management of Co-existing Mycosis Fungoides
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 Management of Co-existing Mycosis Fungoides and Lymphomatoid Papulosis E Kim Citation E Kim. Management of Co-existing Mycosis Fungoides
CASE 15 Patient: A 41-year-old Thai female Chief Compliant: Generalized papulovesicular rash for 1 month Present Illness: She presented with a 1-week
 CASE 15 Patient: A 41-year-old Thai female Chief Compliant: Generalized papulovesicular rash for 1 month Present Illness: She presented with a 1-week history of the generalized asymptomatic erythematous
CASE 15 Patient: A 41-year-old Thai female Chief Compliant: Generalized papulovesicular rash for 1 month Present Illness: She presented with a 1-week history of the generalized asymptomatic erythematous
Primary Cutaneous CD30-Positive T-cell Lymphoproliferative Disorders
 Primary Cutaneous CD30-Positive T-cell Lymphoproliferative Disorders Definition A spectrum of related conditions originating from transformed or activated CD30-positive T-lymphocytes May coexist in individual
Primary Cutaneous CD30-Positive T-cell Lymphoproliferative Disorders Definition A spectrum of related conditions originating from transformed or activated CD30-positive T-lymphocytes May coexist in individual
الاكزيماتيد= Eczematid
 1 / 7 2 / 7 Pityriasis Debate confusing of hypopigmentation characterized increasing surrounded differ hypomelanotic "progressive exists alba misnomer extensive a to observed term the applied term derived
1 / 7 2 / 7 Pityriasis Debate confusing of hypopigmentation characterized increasing surrounded differ hypomelanotic "progressive exists alba misnomer extensive a to observed term the applied term derived
Dermatologica Sinica
 DERMATOLOGICA SINICA 31 (2013) 3e Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Dermatologica Sinica journal homepage: http://www.derm-sinica.com CASE REPORT Early stage mycosis fungoides with focal
DERMATOLOGICA SINICA 31 (2013) 3e Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Dermatologica Sinica journal homepage: http://www.derm-sinica.com CASE REPORT Early stage mycosis fungoides with focal
Mandana Moosavi 1 and Stuart Kreisman Background
 Case Reports in Endocrinology Volume 2016, Article ID 6471081, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6471081 Case Report A Case Report of Dramatically Increased Thyroglobulin after Lymph Node Biopsy in
Case Reports in Endocrinology Volume 2016, Article ID 6471081, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6471081 Case Report A Case Report of Dramatically Increased Thyroglobulin after Lymph Node Biopsy in
Sézary syndrome. Diagnosis and staging
 CME DERMATOLOGY Clinical Medicine 2012, Vol 12, No 2: 160 4 Edited by Clive B Archer, consultant dermatologist and lead for Medical Education, St John s Institute of Dermatology, Guy s and St Thomas NHS
CME DERMATOLOGY Clinical Medicine 2012, Vol 12, No 2: 160 4 Edited by Clive B Archer, consultant dermatologist and lead for Medical Education, St John s Institute of Dermatology, Guy s and St Thomas NHS
Case Report Features of the Atrophic Corpus Mucosa in Three Cases of Autoimmune Gastritis Revealed by Magnifying Endoscopy
 Volume 2012, Article ID 368160, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/368160 Case Report Features of the Atrophic Corpus Mucosa in Three Cases of Autoimmune Gastritis Revealed by Magnifying Endoscopy Kazuyoshi Yagi,
Volume 2012, Article ID 368160, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/368160 Case Report Features of the Atrophic Corpus Mucosa in Three Cases of Autoimmune Gastritis Revealed by Magnifying Endoscopy Kazuyoshi Yagi,
A dinical and histopathologic entity associated with an increased risk of nonmelanoma skin cancer
 PUVA keratosis A dinical and histopathologic entity associated with an increased risk of nonmelanoma skin cancer M. C. G. van Praag, MD, a J. N. Bouwes Bavinck, MD, a W. Bergman, MD, PhD, a F. R. Rosendaal,
PUVA keratosis A dinical and histopathologic entity associated with an increased risk of nonmelanoma skin cancer M. C. G. van Praag, MD, a J. N. Bouwes Bavinck, MD, a W. Bergman, MD, PhD, a F. R. Rosendaal,
CUTIS. Do Not Copy. Pityriasis lichenoides is a T cell mediated papular. Pityriasis Lichenoides Chronica in Black Patients. Pediatric Dermatology
 Series Editor: Camila K. Janniger, MD Pityriasis Lichenoides Chronica in Black Patients Tanda N. Lane, MD; Sareeta S. Parker, MD Pityriasis lichenoides chronica (PLC) is a cutaneous disease of unknown
Series Editor: Camila K. Janniger, MD Pityriasis Lichenoides Chronica in Black Patients Tanda N. Lane, MD; Sareeta S. Parker, MD Pityriasis lichenoides chronica (PLC) is a cutaneous disease of unknown
CUTANEOUS T-CELL LYMPHOMA PROFORMA
 STATE OF KUWAIT MINISTRY OF HEALTH AS AD ALHAMAD DERMATOLOGY CENTER ALSABAH HOSPITAL دولة الكویت وزارة الصحة مرآز أسعد الحمد للا مراض الجلدیة مستشفى الصباح بسم االله الرحمن الرحيم CUTANEOUS TCELL LYMPHOMA
STATE OF KUWAIT MINISTRY OF HEALTH AS AD ALHAMAD DERMATOLOGY CENTER ALSABAH HOSPITAL دولة الكویت وزارة الصحة مرآز أسعد الحمد للا مراض الجلدیة مستشفى الصباح بسم االله الرحمن الرحيم CUTANEOUS TCELL LYMPHOMA
A Histopathologic Study of Papulosquamous Lesions of Skin
 Original 404 Article Indian Journal of Pathology: Research and Practice Volume 6 Number 2, April - June 2017 (Part 2) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.21088/ijprp.2278.148x.6217.11 A Histopathologic Study of
Original 404 Article Indian Journal of Pathology: Research and Practice Volume 6 Number 2, April - June 2017 (Part 2) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.21088/ijprp.2278.148x.6217.11 A Histopathologic Study of
Alireza Bakhshaeekia and Sina Ghiasi-hafezi. 1. Introduction. 2. Patients and Methods
 Plastic Surgery International Volume 0, Article ID 4578, 4 pages doi:0.55/0/4578 Clinical Study Comparing the Alteration of Nasal Tip Sensibility and Sensory Recovery Time following Open Rhinoplasty with
Plastic Surgery International Volume 0, Article ID 4578, 4 pages doi:0.55/0/4578 Clinical Study Comparing the Alteration of Nasal Tip Sensibility and Sensory Recovery Time following Open Rhinoplasty with
Photochemotherapy MM /09/2004. HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration June 1, 2016 Section: Medicine Place(s) of Service: Home; Office
 Photochemotherapy Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.015 11/09/2004 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration June 1, 2016 Section: Medicine Place(s) of Service:
Photochemotherapy Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.015 11/09/2004 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration June 1, 2016 Section: Medicine Place(s) of Service:
Case Report IgG4-Related Nasal Pseudotumor
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2015, Article ID 749890, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/749890 Case Report IgG4-Related Nasal Pseudotumor L. K. Døsen, 1 P. Jebsen, 2 B. Dingsør, 3 and R.
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2015, Article ID 749890, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/749890 Case Report IgG4-Related Nasal Pseudotumor L. K. Døsen, 1 P. Jebsen, 2 B. Dingsør, 3 and R.
SCIENTIFIC PAPER ABSTRACT
 SCIENTIFIC PAPER ABSTRACT Vitiligo Treatment with Monochromatic Excimer Light and Tacrolimus: Results of an Open Randomized Controlled Study Nistico` S., Chiricozzi A., M.D., Rosita Saraceno R., Schipani
SCIENTIFIC PAPER ABSTRACT Vitiligo Treatment with Monochromatic Excimer Light and Tacrolimus: Results of an Open Randomized Controlled Study Nistico` S., Chiricozzi A., M.D., Rosita Saraceno R., Schipani
Original Article. Palmoplantar Psoriasis versus Eczema: Major Histopathologic Clues for Diagnosis
 Iranian Journal of Pathology (2014) 9 (4), 251-256 251 Original Article Palmoplantar Psoriasis versus Eczema: Major Histopathologic Clues for Diagnosis Kambiz Kamyab Hesari, Zahra Safaei Naraghi, Azita
Iranian Journal of Pathology (2014) 9 (4), 251-256 251 Original Article Palmoplantar Psoriasis versus Eczema: Major Histopathologic Clues for Diagnosis Kambiz Kamyab Hesari, Zahra Safaei Naraghi, Azita
Photochemotherapy MM /09/2004. HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 08/25/2017 Section: Medicine Place(s) of Service: Home; Office
 Photochemotherapy Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.015 11/09/2004 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 08/25/2017 Section: Medicine Place(s) of Service:
Photochemotherapy Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.015 11/09/2004 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 08/25/2017 Section: Medicine Place(s) of Service:
Conference Paper Programmed Cell Death Induced by Modulated Electrohyperthermia
 Conference Papers in Medicine, Article ID 187835, 3 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187835 Conference Paper Programmed Cell Death Induced by Modulated Electrohyperthermia Meggyesházi Nóra, 1 Andócs
Conference Papers in Medicine, Article ID 187835, 3 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187835 Conference Paper Programmed Cell Death Induced by Modulated Electrohyperthermia Meggyesházi Nóra, 1 Andócs
Clinical Policy: Phototherapy and Photochemotherapy for Dermatological Conditions Reference Number: CP.MP. 441
 Clinical Policy: Phototherapy and Photochemotherapy for Dermatological Conditions Reference Number: CP.MP. 441 Effective Date: November 2008 Last Review Date: January 2017 See Important Reminder at the
Clinical Policy: Phototherapy and Photochemotherapy for Dermatological Conditions Reference Number: CP.MP. 441 Effective Date: November 2008 Last Review Date: January 2017 See Important Reminder at the
Basal cell carcinoma 5/28/2011
 Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
R. F. Falkenstern-Ge, 1 S. Bode-Erdmann, 2 G. Ott, 2 M. Wohlleber, 1 and M. Kohlhäufl Introduction. 2. Histology
 Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 167585, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/167585 Case Report Late Lung Metastasis of a Primary Eccrine Sweat Gland Carcinoma 10 Years after
Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 167585, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/167585 Case Report Late Lung Metastasis of a Primary Eccrine Sweat Gland Carcinoma 10 Years after
04/09/2018. Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions. Agenda. Squamous Dysplasia. Squamo-proliferative lesions. Architectural features
 Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Assisting diagnosis of melanoma through the noninvasive biopsy of skin lesions
 Assisting diagnosis of melanoma through the noninvasive biopsy of skin lesions Symon D Oyly Cotton Ela Claridge School of Computer Science, The University of Birmingham Birmingham B15 2TT, UK Per Hall
Assisting diagnosis of melanoma through the noninvasive biopsy of skin lesions Symon D Oyly Cotton Ela Claridge School of Computer Science, The University of Birmingham Birmingham B15 2TT, UK Per Hall
Mycosis Fungoides, then and now Have we travelled?
 USCAP 103 rd Annual Meeting 2014 American Society of Dermatopathology Companion Meeting Mycosis Fungoides, then and now Have we travelled? Vijaya B. Reddy, MD, MBA Professor of Pathology Rush University
USCAP 103 rd Annual Meeting 2014 American Society of Dermatopathology Companion Meeting Mycosis Fungoides, then and now Have we travelled? Vijaya B. Reddy, MD, MBA Professor of Pathology Rush University
Original Article. A Study of Histopathological Changes Seen in Chronic Plaque Psoriasis, Before and After Treatment with Narrow Band Ultraviolet B
 Original Article A Study of Histopathological Changes Seen in Chronic Plaque Psoriasis, Before and After Treatment with Narrow Band Ultraviolet B Amoolya Bhat 1 *, Subramanya H 2, PS Murthy 3 and Santosh
Original Article A Study of Histopathological Changes Seen in Chronic Plaque Psoriasis, Before and After Treatment with Narrow Band Ultraviolet B Amoolya Bhat 1 *, Subramanya H 2, PS Murthy 3 and Santosh
Mycosis Fungoides: A Retrospective Study of 44 Swedish Cases
 Acta Derm Venereol 2016; 96: 669 673 CLINICAL REPORT Mycosis Fungoides: A Retrospective Study of 44 Swedish Cases Yvonne EKLUND 1, Annika ARONSSON 1, Artur SCHMIDTCHEN 1 and Thomas RELANDER 2 1 Section
Acta Derm Venereol 2016; 96: 669 673 CLINICAL REPORT Mycosis Fungoides: A Retrospective Study of 44 Swedish Cases Yvonne EKLUND 1, Annika ARONSSON 1, Artur SCHMIDTCHEN 1 and Thomas RELANDER 2 1 Section
TARGRETIN (bexarotene) oral capsule & external gel
 TARGRETIN (bexarotene) oral capsule & external gel Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan.
TARGRETIN (bexarotene) oral capsule & external gel Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan.
Clinical Study Narrow-Band Ultraviolet B versus Oral Minocycline in Treatment of Unstable Vitiligo: A Prospective Comparative Trial
 Dermatology Research and Practice, Article ID 240856, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/240856 Clinical Study Narrow-Band Ultraviolet B versus Oral Minocycline in Treatment of Unstable Vitiligo: A
Dermatology Research and Practice, Article ID 240856, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/240856 Clinical Study Narrow-Band Ultraviolet B versus Oral Minocycline in Treatment of Unstable Vitiligo: A
Malignant Melanoma Early Stage. A guide for patients
 This melanoma patient brochure is designed to help educate melanoma patients and their caregivers. It was developed under the guidance of Dr. Michael Smylie, Professor, Department of Oncology, University
This melanoma patient brochure is designed to help educate melanoma patients and their caregivers. It was developed under the guidance of Dr. Michael Smylie, Professor, Department of Oncology, University
Conference Paper Oncothermia Basic Research at In Vivo Level: The First Results in Japan
 Conference Papers in Medicine, Article ID 197328, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/.11/13/197328 Conference Paper Oncothermia Basic Research at In Vivo Level: The First Results in Japan G. Andocs, 1 Y. Okamoto,
Conference Papers in Medicine, Article ID 197328, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/.11/13/197328 Conference Paper Oncothermia Basic Research at In Vivo Level: The First Results in Japan G. Andocs, 1 Y. Okamoto,
SPECIAL TOPIC. Institut National de la Sante et de la Recherche Medicale (INSERM U895), Nice, France c
 November 2011 1260 Volume 10 Issue 1i Copyright 2011 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Journal of Drugs in Dermatology SPECIAL TOPIC A Pilot Study Using Reflectance Confocal Microscopy (RCM) in the Assessment of a Novel
November 2011 1260 Volume 10 Issue 1i Copyright 2011 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Journal of Drugs in Dermatology SPECIAL TOPIC A Pilot Study Using Reflectance Confocal Microscopy (RCM) in the Assessment of a Novel
Case Report Five-Year Survival after Surgery for Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma of the Stomach
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 560712, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/560712 Case Report Five-Year Survival after Surgery for Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma of the Stomach Shigeo
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 560712, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/560712 Case Report Five-Year Survival after Surgery for Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma of the Stomach Shigeo
Comparison of the efficacy of PUVA versus BBUVB in the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris
 IJMAMR 5 (2017) 1-6 ISSN 2053-1834 Comparison of the efficacy of PUVA versus BBUVB in the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris Tran Hau Khang* and Le Huu Doanh National Hospital of Dermatology and Venereology,
IJMAMR 5 (2017) 1-6 ISSN 2053-1834 Comparison of the efficacy of PUVA versus BBUVB in the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris Tran Hau Khang* and Le Huu Doanh National Hospital of Dermatology and Venereology,
Case Report Cytomegalovirus Colitis with Common Variable Immunodeficiency and Crohn s Disease
 Volume 2015, Article ID 348204, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/348204 Case Report Cytomegalovirus Colitis with Common Variable Immunodeficiency and Crohn s Disease Betül Ünal, Cumhur Ebrahim BaGsorgun,
Volume 2015, Article ID 348204, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/348204 Case Report Cytomegalovirus Colitis with Common Variable Immunodeficiency and Crohn s Disease Betül Ünal, Cumhur Ebrahim BaGsorgun,
Degos Disease: A Case Report and Review of Literature
 Degos Disease: A Case Report and Review of Literature Monira waked Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 4 (1): 5, June 2008 Al Houd Al Marsod Hospital Submitted for publication: May 25 th, 2008 Accepted
Degos Disease: A Case Report and Review of Literature Monira waked Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 4 (1): 5, June 2008 Al Houd Al Marsod Hospital Submitted for publication: May 25 th, 2008 Accepted
Clinical Study The Incidence and Management of Pleural Injuries Occurring during Open Nephrectomy
 Advances in Urology Volume 2009, Article ID 948906, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/948906 Clinical Study The Incidence and Management of Pleural Injuries Occurring during Open Nephrectomy Ali Fuat Atmaca, Abdullah
Advances in Urology Volume 2009, Article ID 948906, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/948906 Clinical Study The Incidence and Management of Pleural Injuries Occurring during Open Nephrectomy Ali Fuat Atmaca, Abdullah
Case Report Diagnostic Challenges of Tuberculous Lymphadenitis Using Polymerase Chain Reaction Analysis: A Case Study
 Case Reports in Infectious Diseases Volume 2015, Article ID 723726, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/723726 Case Report Diagnostic Challenges of Tuberculous Lymphadenitis Using Polymerase Chain Reaction
Case Reports in Infectious Diseases Volume 2015, Article ID 723726, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/723726 Case Report Diagnostic Challenges of Tuberculous Lymphadenitis Using Polymerase Chain Reaction
Case Report Multiple Giant Cell Tumors of Tendon Sheath Found within a Single Digit of a 9-Year-Old
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1834740, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1834740 Case Report Multiple Giant Cell Tumors of Tendon Sheath Found within a Single Digit of a 9-Year-Old
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1834740, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1834740 Case Report Multiple Giant Cell Tumors of Tendon Sheath Found within a Single Digit of a 9-Year-Old
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB. Friday, February 13, :30 am 11:00 am
 MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB Friday, February 13, 2009 9:30 am 11:00 am FACULTY COPY GOALS: Describe the basic clinical and morphologic features of various
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB Friday, February 13, 2009 9:30 am 11:00 am FACULTY COPY GOALS: Describe the basic clinical and morphologic features of various
Case Report A Case of Primary Submandibular Gland Oncocytic Carcinoma
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 384238, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/384238 Case Report A Case of Primary Submandibular Gland Oncocytic Carcinoma Kunihiko Tokashiki, Kiyoaki
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 384238, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/384238 Case Report A Case of Primary Submandibular Gland Oncocytic Carcinoma Kunihiko Tokashiki, Kiyoaki
21/07/2017. Hobnail endothelial cells are not the same as epithelioid endothelial cells
 UPDATE IN CUTANEOUS VASCULAR S DERMATOPATHOLOGY SESSION BELFAST PATHOLOGY JUNE 21/2017 Dr E Calonje St John s Institute of Dermatology, London, United Kingdom THE FAMILY OF VASCULAR S WITH EPITHELIOID
UPDATE IN CUTANEOUS VASCULAR S DERMATOPATHOLOGY SESSION BELFAST PATHOLOGY JUNE 21/2017 Dr E Calonje St John s Institute of Dermatology, London, United Kingdom THE FAMILY OF VASCULAR S WITH EPITHELIOID
Interstitial mycosis fungoides with lichen sclerosus-like clinical and histopathological features
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2016 Interstitial mycosis fungoides with lichen sclerosus-like clinical and
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2016 Interstitial mycosis fungoides with lichen sclerosus-like clinical and
Mycosis Fungoides Presentation in Emergency
 The Open Emergency Medicine Journal, 2011, 4, 17-21 17 Mycosis Fungoides Presentation in Emergency Asaad Shujaa*,1 and M. Owais Suriya 2 Open Access Department of Emergency Medicine College of Medicine,
The Open Emergency Medicine Journal, 2011, 4, 17-21 17 Mycosis Fungoides Presentation in Emergency Asaad Shujaa*,1 and M. Owais Suriya 2 Open Access Department of Emergency Medicine College of Medicine,
Given that mycosis fungoides (MF) is the most common
 Histopathologic approach to epidermotropic lymphocytic infiltrates Shyam S Raghavan, MD 1 and Jinah Kim, MD, PhD 2 Abstract Mycosis fungoides is the most common and therefore quintessential cutaneous lymphoma
Histopathologic approach to epidermotropic lymphocytic infiltrates Shyam S Raghavan, MD 1 and Jinah Kim, MD, PhD 2 Abstract Mycosis fungoides is the most common and therefore quintessential cutaneous lymphoma
Disseminated epidermolytic acanthoma probably related to trauma
 Disseminated epidermolytic acanthoma probably related to trauma I. Sánchez-Carpintero, A. España and M.A. Idoate* Departments of Dermatology and *Pathology, University Clinic of Navarra, School of Medicine,
Disseminated epidermolytic acanthoma probably related to trauma I. Sánchez-Carpintero, A. España and M.A. Idoate* Departments of Dermatology and *Pathology, University Clinic of Navarra, School of Medicine,
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(4): /ISSN: /IJCEP Tadashi Terada
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(4):749-756 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP1301060 Case Report Mycosis fungoides in plaque stage with pronounced eosinophilic infiltration, folliculotropism, and concomitant
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6(4):749-756 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP1301060 Case Report Mycosis fungoides in plaque stage with pronounced eosinophilic infiltration, folliculotropism, and concomitant
Case Report Pediatric Transepiphyseal Seperation and Dislocation of the Femoral Head
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 703850, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/703850 Case Report Pediatric Transepiphyseal Seperation and Dislocation of the Femoral Head Mehmet Elmadag,
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 703850, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/703850 Case Report Pediatric Transepiphyseal Seperation and Dislocation of the Femoral Head Mehmet Elmadag,
Correspondence should be addressed to Martin J. Bergman;
 Autoimmune Diseases Volume 2013, Article ID 367190, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/367190 Research Article Composite Indices Using 3 or 4 Components of the Core Data Set Have Similar Predictive
Autoimmune Diseases Volume 2013, Article ID 367190, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/367190 Research Article Composite Indices Using 3 or 4 Components of the Core Data Set Have Similar Predictive
2. Sézary syndrome (SS)
 Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details Clinical images are available in hardcopy only. Clinical images are available in Clinical images are available in d e f g h i j Fig..36-2
Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details Clinical images are available in hardcopy only. Clinical images are available in Clinical images are available in d e f g h i j Fig..36-2
