Dermatologica Sinica
|
|
|
- Hugh Morton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DERMATOLOGICA SINICA 31 (2013) 3e Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Dermatologica Sinica journal homepage: CASE REPORT Early stage mycosis fungoides with focal CD30-positive large cell transformation Po-Ju Lai 1,2, Yu-Ping Hsiao 1,3, Jeng-Dong Hsu 4, Shiow-Jiuan Wey 1, * 1 Department Dermatology, Chung Shan Medical University Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan, ROC 2 Institute Biochemistry and Biotechnology, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan, ROC 3 Institute Medicine, School Medicine, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan, ROC 4 Department Pathology, School Medicine, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan, ROC article info abstract Article history: Received: Dec 1, 2011 Revised: Jan 31, 2012 Accepted: Apr 11, 2012 Keywords: CD30 CD30-positive lymphoproliferative disorders large cell transformation mycosis fungoides Mycosis fungoides (MF) is typically an indolent disease except when large cell transformation (LCT) occurs. The incidence LCT has been reported to range from 6% to 23% under the criterion the presence more than 25% large cells in a biopsy typical MF lesions. LCT is more common in advanced-stage MF, but very rarely found in its early stage. Herein, we present a 45-year-old woman with patch stage MF (Stage IB) who developed a papule within one patch, which revealed large cell transformation with expression CD30 immunostaining on histopathology. The patient then received phototherapy with narrow-band UVB. The skin lesions regressed quickly and no new skin lesions had been noted during the 6-month follow-up. Intense monitoring for recurrence and extracutaneous involvement is still recommended. In this article, we also review the published articles mycosis fungoides with CD 30-positive large cell transformation and analyze the clinicopathological and prognostic features. Copyright Ó 2012, Taiwanese Dermatological Association. Published by Elsevier Taiwan LLC. All rights reserved. Introduction Mycosis fungoides (MF) comprises about 65% cutaneous T-cell lymphomas. 1 It generally presents with an indolent course and a long evolution, with years to decades elapsing before patches or plaques progress to tumor stage. Large cell transformation (LCT) in MF has been defined by the presence large cells (at least four times larger than a small lymphocyte) exceeding 25% the total lymphoid infiltrate or forming microscopic nodules. 2 LCT is ten found in advanced-stage disease (Stage IIB) and is very rare in the early stage (Stage IIA). 3 LCT in MF is associated with an aggressive course and poor prognosis. 3 Large transformed cells may be positive for CD30 or not. 4 Herein, we reported a patient with Stage IB MF, who also showed focal CD30-positive LCT. Case report This 45-year-old woman, without major systemic diseases, presented with multiple asymptomatic reddish rashes over the left forearm, left flank, buttocks, and thighs for 10 years. The rash first * Corresponding author. Department Dermatology, Chung Shan Medical University Hospital, 110, Section 1, Chien-Kuo North Road, Taichung 402, Taiwan, ROC. Tel: þ x3451; fax: þ address: weyth@tcts1.seed.net.tw (S.-J. Wey). appeared on the left forearm and slowly extended to the left flank, buttocks, and thighs. She had visited a local practitioner s clinic where she was diagnosed with eczema, but did not respond to treatment. Approximately one year earlier, one reddish papule arose from the reddish patch over her left flank and showed no regression. Skin examination revealed multiple asymptomatic, scaly, wrinkling, mottled reddish and hypopigmented patches over the left forearm, left flank, both buttocks and thighs (Figure 1A, B and C). About 15% the total body surface area was involved. Additionally, one reddish papule located within reddish patches over the left flank was also noted (Figure 1B). Review the patient s history over the previous 10 years indicated absence fever, chills, or body weight loss. There were no palpable lymph nodes or hepatomegaly. Results a complete blood count, liver function, and lactate dehydrogenase were within normal limits. The peripheral blood did not show atypical lymphocytes. Chest x-ray revealed no significant findings. Total body positron emission tomography indicated no abnormal uptake in visceral organs. Histopathology a biopsy specimen from a reddish patch over the left flank demonstrated mild infiltration atypical cerebriform lymphocytes at the dermal-epidermal junction with focal epidermotropism (Figure 2A and B). The cells were positively stained with CD3, CD4, and CD8, but negative for CD20 and CD30 (Figure 2CeF). Another skin biopsy was taken from the reddish /$ e see front matter Copyright Ó 2012, Taiwanese Dermatological Association. Published by Elsevier Taiwan LLC. All rights reserved.
2 4 P.-J. Lai et al. / Dermatologica Sinica 31 (2013) 3e Figure 1 (A, B and C) Multiple asymptomatic, mottled reddish and hypopigmented patches with wrinkled surface and scales over the left forearm, left flank, left back, buttocks, and thighs. One reddish papule located within a reddish patch over the left flank (arrow). papule over the left flank, and the histopathological examination showed diffuse intradermal lymphocytic infiltration with large pleomorphic and hyperchromatic lymphocytes (Figure 3AeC). The cells were positively stained with CD3 and CD4, and focally with CD8 (Figure 3D and E), but negative for CD20. Of all infiltrating atypical lymphocytes, about 60% were large cells. They were strongly positive for CD30 (more than 5% large cells) (Figure 3F), but negative for anaplastic lymphoma kinase and CD68. Polymerase chain reaction skin biopsy from the reddish patch over the left flank showed clonality the T-cell receptor g gene rearrangement. Based on the clinical manifestation and histopathological findings, the patient was diagnosed with MF with focal CD30-positive LCT. The staging disease was T2N0M0, Stage IB. The patient then received topical steroid and narrow-band UVB phototherapy. Her skin lesions regressed quickly and no new lesions were noted at the 6-month follow-up. Discussion Mycosis fungoides (MF) is the most common type cutaneous T-cell lymphomas. 1 Generally, the clinical manifestation shows three phases- patch, plaque and tumor stage, and typically runs an indolent course with a long evolution over years to decades. 5 However, with disease progression, a small number cases develop a morphologic change (large cell transformation), especially more common in the advanced stage disease. The diagnosis large cell transformation (LCT) in MF always relies on histologically defined criterion: the presence large cells exceeding 25% the total lymphoid infiltrate or forming microscopic nodules. 2 Mycosis fungoides with LCT usually portends an aggressive course and shortened survival. 2 Diamandidou et al 3 reported shorter median survival for patients with LCT in MF (3 months), compared with nontransformed MF (163 months). Arulogun et al 4 also indicated a lower 5-year survival rate for LCT group than nontransformed group MF patients, 32.5% versus 53.6%. 4 Although the molecular mechanism for LCT has not been fully demonstrated, molecular studies have confirmed that large cells are derived from the original T-cell clone in MF. 6, Around 30% to 50% MF patients with LCT showed CD30-positive cells. 4,8,9 Although the histological criterion for the diagnosis LCT in MF has been well defined, making a definite differential diagnosis is still sometimes challenging. MF with focal CD30-positive LCT should be differentiated from other CD30 positive lymphoproliferative disorders, including primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma, lymphomatoid papulosis (LyP), and borderline cases. 1 Primary cutaneous CD30þ lymphoproliferative disorders typically have an excellent prognosis with a disease specific 5-year survival 85% to 100%. 10,11 However, CD30 positive LCT in MF has worse outcome with a 5-year survival 28.6% to 44.4%. 4,8 Meanwhile, the clinical manifestations are obviously different between CD30 positive LCT in MF and primary cutaneous CD30 positive lymphoproliferative disorders. Coexisting MF and LyP is found in 9% patients with LyP, and represents 3% MF patients. 10 Many studies show MF with concurrent LyP leads an indolent course and has a favorable prognosis. 12e15 The clinical course LyP with concurrent MF is also similar to that LyP, and the skin lesions tend to regress spontaneously and then recur. By contrast, CD30þ LCT in
3 P.-J. Lai et al. / Dermatologica Sinica 31 (2013) 3e 5 Figure 2 (A) Histopathology a biopsy specimen from a reddish patch over the left flank reveals mild infiltration atypical lymphocytes over the dermal-epidermal junction and upper dermis [hematoxylin and eosin (HE, 200)]. (B) Focal epidermotropism with infiltration atypical, cerebriform lymphocytes, each surrounded by a clear halo (HE, 400). (C) Immunohistochemical staining reveals the infiltrating lymphocytes to be CD3 positive (400). (D) Positive staining for CD4 (400). (E) Positive staining for CD8 (400). (F) Negative staining for CD30 (400). MF rarely show spontaneous remission. Besides, LyP could arise from normal skin and/or previous MF lesions, while CD30þ LCT always develops upon pre-existent MF lesions. The coexistence MF and CD30-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) has also been reported previously, but, as shown in these cases, the two diseases invariably appear in separate locations and run independent clinical course. 16,1 The diagnosis CD30 positive LCT in MF should be made when newly-onset papules or nodules arising from the prior MF lesions are seen clinically, and cerebriform T lymphocytes admixing with <5% CD30 positive large cells are shown histopathologically. 2,8 If >5% large cells have CD30 expression, it is very difficult to distinguish CD30þ LCT in MF from MF associated with CD 30þ lymphoproliferative disorder. In such a situation, Vergier et al indicated the clinical evolution may help us discriminate between these two entities. 8 Applying this to our patient, we observed one reddish papule developing upon the previous typical MF lesion (clinical evolution), which had not shown spontaneous remission for one year. Dissimilar to LyP, which typically manifests chronic recurrent self-healing papules and nodules that inevitably regress, the clinical course the reddish papule in our patient showed no spontaneous necrosis or regression. The microscopic examination a biopsy specimen from the reddish papule in our case revealed infiltration mononuclear cells mixed with large atypical cells in the upper dermis, and focal epidermotropism atypical mononuclear cells in the epidermis. There were hardly any neutrophils or eosinophils within the intradermal mononuclear infiltrate. Around 60% the lymphocytic infiltrates were large pleomorphic and hyperchromatic, with about 90% those large cells being CD30þ. Compared to ALCL, inwhich the tumor cells commonly extend into the subcutaneous fat or deeper tissues, or LyP, the infiltrate which ten contains large anaplastic cells mixed with neutrophils, eosinophils, plasma cells, lymphocytes and histiocytes, the histopathologic findings the present case do not match any type LyP and were not compatible with ALCL. The combination histological findings and clinical evolution leads to the diagnosis early stage MF (Stage IB) with focal CD30-positive large cell transformation. Reviewing the literature, treatments for LCT in MF were heterogeneous and dependent on the clinical stage. 3,8,9,18,19 For patients with early stage MF, skin-directed therapy including topical corticosteroids, topical nitrogen mustard, light therapy and radiation therapy had been used. 9,18,19 One patient presenting with
4 6 P.-J. Lai et al. / Dermatologica Sinica 31 (2013) 3e Figure 3 (A) Microscopic examination a biopsy specimen from the reddish papule reveals dense infiltration mononuclear cells in the upper dermis and perivascular area (HE, 40 ). (B) Infiltration mononuclear cells mixed with large atypical cells in the upper dermis, and focal epidermotropism with atypical mononuclear cells in the epidermis (HE, 200 ). (C) Large atypical pleomorphic cells with vesicular nuclei and prominent nucleoli (HE, 400 ). (D) Large atypical cells are stained with CD4 (400 ). (E) Large atypical cells are weakly positive for CD8 (400 ) and (F) strongly positive for CD30 (400 ). focal LCT in MF (stage IB) was treated with topical steroid and topical nitrogen mustard, and the lesions almost totally resolved after 2 to 3 months therapy. 18 Another patient who was diagnosed with LCT in MF (Stage IIB) received electron beam radiation, and no local recurrence or distant metastasis has been noted for 1 year.18 In our case, the reddish papule was surgically removed first. For residual skin lesions, we suggested PUVA, the first-line treatment for early stage MF, which our patient declined because its carcinogenic potential. Local radiation was not suitable for multiple skin lesions. Therefore, we administered narrow band UVB phototherapy, which is also effective in management early stage MF,20,21 and her skin lesions regressed quickly with no new skin lesions noted at the 6-month follow-up. According to the previously published articles, several prognostic factors large cell transformation in MF have been mentioned. Diamandidous et al3 reported early transformation (<2 years from the diagnosis MF) and more advanced disease at transformation (Stage IIBeIV vs. Stage IeIIA) were associated with a poor outcome, while an older age ( 60 years) and the presence or extracutaneous spreading (Stage IV) were related with a poor prognosis as indicated by Vergier et al.8 Although median survival for patients with LCT in MF is markedly shortened, CD30þ large cell Table 1 Comparisons previous studies reporting the incidence large cell transformation (LCT) in mycosis fungoides (MF). mycosis fungoides LCTs CD30-positive LCTs LCTs in early-stage MF CD30-positive LCTs in early-stage MF ¼ not available. Salhany et al2 Greer et al22 Diamadidou et al3 Vergier et al8 Barberio et al9 Arulogun et al
5 P.-J. Lai et al. / Dermatologica Sinica 31 (2013) 3e Table 2 Clinical and immunohistochemical data patients with large cell transformation (LCT) in early-stage mycosis fungoides (MF). Patient Age/sex Stage at LCT-MF Interval from dx MF to LCT-MF (months) /M IA /M IIA 14 P 3 2 2/M IA /M IIA /M IA /F IB 46 N 22 34/M IA /M IIA /M IA /M IIA /M IA /F IB /F IIA / IB / IIA / IB / IB / IIA / IB / IIA 21 8 /F IB 18 years N /F IB 48 N /M IA 1 P /F IA 84 P /M IB 5 P 26 9 /M IA 84 N /F IA 6 N /M IIA 0 P /M IIA 2 P /F IB P /F IA 9 years 32 (present case) 45/F IB 0 P F ¼ female; M ¼ male; N ¼ negative; ¼ not available; P ¼ positive. CD30 expression transformation might be a favorable prognostic factor among them. Vergier et al. 8 first analyzed CD 30 expression for its prognostic value. Although there was no significant difference, the 5-year survival rates for patient groups with CD30- LCT, CD30þ <5% LCT and CD30þ 5% LCT were 14.1%, 28.6% and 44.4%, respectively. Arulogun et al 4 also observed a tendency toward a better outcome for MF patients with CD30þ LCT than those with CD30e LCT. Moreover, Barberio et al 9 stated that the strong positivity CD30 immunostaining LCT in MF was linked to a better prognosis and indicated that CD30e LCT with a CD20þ B-cell peritumoral infiltrate could be considered as a poor prognostic factor. 9 LCT in MF is uncommon in nature. Previous studies reporting the incidence LCT in MF are summarized in Table 1 2e4,8,9,22. However, LCT ten occurs in advanced stage MF, especially in stage IIB and the tumor stage (T3). 3 Early stage MF with large cell transformation is very rare, and the incidence has been reported to be between 0.5% and %. To the best our knowledge, there have been 31 cases LCT in early stage MF previously reported in the English literature (Table 2) 2,3,8,9,18,19,22. Among these patients, fewer than 10 expressed CD30 positivity, for whom the prognosis was relatively good. 2e4,8,9,18,19 In conclusion, we present a patient with early stage MF (Stage IB) and LCT that showed strong expression CD30. Although LCT in MF usually indicates a more aggressive course and shortened survival, its occurrence in an early stage and CD30 expression 5% both suggest a better prognosis among them. Besides, differentiation between CD30þ LCT in MF and MF associated with a CD30 positive lymphoproliferative disorder should be made carefully because the divergence in their prognoses. To establish a precise diagnosis, we should pay special attention to both clinical and histologic findings. Close observation and systemic surveys are also essential to the evaluation MF patients. When clinical evolution with changing skin lesion occurs, we need to perform skin biopsy and systemic evaluation to determine the disease status. Thorough explanation to the patient about the disease prognosis and the necessity regular follow-ups should also be emphasized. References 1. Willemze R, Meijer CJ. Classification cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: from Alibert to WHO-EORTC. J Cutan Pathol 2006;33(Suppl. 1):18e Salhany KE, Cousar JB, Greer JP, Casey TT, Fields JP, Collins RD. Transformation cutaneous T cell lymphoma to large cell lymphoma. A clinicopathologic and immunologic study. Am J Pathol 1988;132:265e. 3. Diamandidou E, Colome-Grimmer M, Fayad L, Duvic M, Kurzrock R. Transformation mycosis fungoides Sezary syndrome: clinical characteristics and prognosis. Blood 1998;92:1150e9. 4. Arulogun SO, Prince HM, Ng J, et al. Long-term outcomes patients with advanced-stage cutaneous T-cell lymphoma and large cell transformation. Blood 2008;112:3082e. 5. Willemze R, Kerl H, Sterry W, et al. EORTC classification for primary cutaneous lymphomas. A proposal from the cutaneous lymphoma study group the European Organization for Research and Treatment Cancer (EORTC). Blood 199;90:354e1. 6. Wood GS, Tung RM, Haeffner AC, et al. Detection clonal T-cell receptor gamma gene rearrangements in early mycosis fungoides/sezary syndrome by polymerase chain reaction and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (PCR/ DGGE). J Invest Dermatol 1994;103:34e41.. Wolfe JT, Chooback L, Finn DT, Jaworsky C, Rook AH, Lessin SR. Large-cell transformation following detection minimal residual disease in cutaneous T- cell lymphoma: molecular and in situ analysis a single neoplastic T-cell clone expressing the identical T-cell receptor. J Clin Oncol 1995;13:151e. 8. Vergier B, de Muret A, Beylot-Barry M, et al. Transformation mycosis fungoides: clinicopathological and prognostic features 45 cases. French Study Group Cutaneous Lymphomas. Blood 2000;95:2212e8. 9. Barberio E, Thomas L, Skowron F, Balme B, Dalle S. Transformed mycosis fungoides: clinicopathological features and outcome. Br J Dermatol 200;15: 284e Bekkenk M, Geelen FAMJ, van Voorst Vader PC, et al. Primary and secondary cutaneous CD30-positive lymphoproliferative disorders: long term follow-up data 219 patients and guidelines for diagnosis and treatment. A report from the Dutch Cutaneous Lymphoma Group. Blood 2000;95:3653e Liu HL, Hoppe RT, Kohler S, Harvell JD, Reddy S, Kim YH. CD30þ cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorders: the Stanford experience in lymphomatoid papulosis and primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma. J Am Acad Dermatol 2003;49:1049e Van Doorn R, van Haselen CW, van Voorst Vader PC, et al. Mycosis fungoides: disease evolution and prognosis 309 Dutch patients. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:504e Beljaards R, Willemze R. The prognosis patients with lymphomatoid papulosis associated with other types malignancies. Br J Dermatol 1992;126:596e Basarab T, Fraser-Andrews E, Orchard G, Whittaker S, Russel-Jones R. Lymphomatoid papulosis in association with mycosis fungoides: a study 15 cases. Br J Dermatol. 1998;139:630e Gallardo F, Costa C, Bellosillo B, et al. Lymphomatoid papulosis associated with mycosis fungoides: clinicopathological and molecular studies 12 cases. Acta Derm Venereol 2004;84:463e Kang SK, Chang SE, Choi JH, Sung KJ, Moon KC, Koh JK. Coexistence CD30- positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma and mycosis fungoides. Clin Exp Dermatol 2002;2:212e5. 1. Salameh F, Barzilai A, Baum S, Trau H. Mycosis fungoides and CD30þ cutaneous T-cell lymphoma simulating pyoderma gangrenosum in a patient with ulcerative colitis. J Dermatol Case Rep 2009;3:30e Romero M, Haney M, Desantis E, Zlotf B. Mycosis fungoides with focal CD 30 transformation in an adolescent. Pediatr Dermatol 2008;25:565e Ohtani T, Kikuchi K, Koizumi H, Kunii T. Aiba S.A case CD30þ large-cell transformation in a patient with unilesional patch-stage mycosis fungoides. Int J Dermatol 2009;48:623e Gathers RC, Scherschun L, Malick F, Fivenson DP, Lim HW. Narrowband UVB phototherapy for early-stage mycosis fungoides. J Am Acad Dermatol 2002;4: 191e. 21. Ahmad K, Rogers S, McNicholas PD, Collins P. Narrowband UVB and PUVA in the treatment mycosis fungoides: a retrospective study. Acta Derm Venereol 200;8:413e. 22. Greer JP, Salhany KE, Cousar JB, et al. Clinical features associated with transformation cerebriform T-cell lymphoma to a large cell process. Hematol Oncol 1990;8:215e.
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/2010 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Benner, Marchina Frederika Title: Cutaneous CD30-positive lymphoproliferations
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/2010 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Benner, Marchina Frederika Title: Cutaneous CD30-positive lymphoproliferations
CD30+ Lymphoproliferative Disorders Associated with Longstanding Mycosis Fungoides
 Case Report DOI: 10.6003/jtad.16102c5 CD30+ Lymphoproliferative Disorders Associated with Longstanding Mycosis Fungoides Esra Adışen, 1 MD, Özlem Erdem, 2 MD, Mehmet Ali Gürer, 1 MD Address: 1 Gazi University
Case Report DOI: 10.6003/jtad.16102c5 CD30+ Lymphoproliferative Disorders Associated with Longstanding Mycosis Fungoides Esra Adışen, 1 MD, Özlem Erdem, 2 MD, Mehmet Ali Gürer, 1 MD Address: 1 Gazi University
Primary Cutaneous CD30-Positive T-cell Lymphoproliferative Disorders
 Primary Cutaneous CD30-Positive T-cell Lymphoproliferative Disorders Definition A spectrum of related conditions originating from transformed or activated CD30-positive T-lymphocytes May coexist in individual
Primary Cutaneous CD30-Positive T-cell Lymphoproliferative Disorders Definition A spectrum of related conditions originating from transformed or activated CD30-positive T-lymphocytes May coexist in individual
A middle-aged man with self-healing papulonecrotic lesions over the trunk and proximal limbs
 Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2011) 19, 30-34 Case Report A middle-aged man with self-healing papulonecrotic lesions over the trunk and proximal limbs JC Chan, N Trendell-Smith, CK Yeung Lymphomatoid
Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2011) 19, 30-34 Case Report A middle-aged man with self-healing papulonecrotic lesions over the trunk and proximal limbs JC Chan, N Trendell-Smith, CK Yeung Lymphomatoid
Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging. Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology
 Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology Definition of Lymphoma A cancer or malignancy that comes from
Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology Definition of Lymphoma A cancer or malignancy that comes from
ISPUB.COM. Primary Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Long-term Management with Low Dose Methotrexate. S Parker INTRODUCTION
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 Primary Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Long-term Management with Low Dose S Parker Citation S Parker.. The Internet Journal of
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 Primary Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Long-term Management with Low Dose S Parker Citation S Parker.. The Internet Journal of
Lymphoma and Pseudolymphoma
 Lymphoma and Pseudolymphoma Laura B. Pincus, MD Co-Director, Cutaneous Lymphoma Clinic Associate Professor Dermatology and Pathology University of California, San Francisco I HAVE NO RELEVANT RELATIONSHIPS
Lymphoma and Pseudolymphoma Laura B. Pincus, MD Co-Director, Cutaneous Lymphoma Clinic Associate Professor Dermatology and Pathology University of California, San Francisco I HAVE NO RELEVANT RELATIONSHIPS
Fig. 3.1 Fig Past history: She was previously healthy and not taking any medication.
 Case 3 A 41-year-old Thai female from Bangkok Chief compliant: Erythematous patch at left thigh for 2 months Present illness: The patient presented with a 10- year history of erythematous patch on her
Case 3 A 41-year-old Thai female from Bangkok Chief compliant: Erythematous patch at left thigh for 2 months Present illness: The patient presented with a 10- year history of erythematous patch on her
Primary cutaneous large cell lymphoma CD30+: a case-based review
 Case-based review Primary cutaneous large cell lymphoma CD30+: a case-based review Anna Campanati 1 Katia Giuliodori 1 Emanuela Martina 1 Luca Conocchiari 1 Giulia Ganzetti 1 Gaia Goteri 2 Annamaria Offidani
Case-based review Primary cutaneous large cell lymphoma CD30+: a case-based review Anna Campanati 1 Katia Giuliodori 1 Emanuela Martina 1 Luca Conocchiari 1 Giulia Ganzetti 1 Gaia Goteri 2 Annamaria Offidani
Michi Shinohara MD Associate Professor University of Washington/Seattle Cancer Care Alliance Dermatology, Dermatopathology
 Michi Shinohara MD Associate Professor University of Washington/Seattle Cancer Care Alliance Dermatology, Dermatopathology Agenda Overview of cutaneous T and B- cell lymphomas Diagnosis, Staging, Prognosis
Michi Shinohara MD Associate Professor University of Washington/Seattle Cancer Care Alliance Dermatology, Dermatopathology Agenda Overview of cutaneous T and B- cell lymphomas Diagnosis, Staging, Prognosis
Clusterin Expression Correlates With Stage and Presence of Large Cells in Mycosis Fungoides
 Anatomic Pathology / Clusterin Expression in Mycosis Fungoides Clusterin Expression Correlates With Stage and Presence of Large Cells in Mycosis Fungoides Pranil Chandra, DO, 1 Jose A. Plaza, MD, 2,4 Zhuang
Anatomic Pathology / Clusterin Expression in Mycosis Fungoides Clusterin Expression Correlates With Stage and Presence of Large Cells in Mycosis Fungoides Pranil Chandra, DO, 1 Jose A. Plaza, MD, 2,4 Zhuang
ISPUB.COM. Management of Co-existing Mycosis Fungoides and Lymphomatoid Papulosis. E Kim PHYSICAL FINDINGS INTRODUCTION INITIAL PRESENTATION
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 Management of Co-existing Mycosis Fungoides and Lymphomatoid Papulosis E Kim Citation E Kim. Management of Co-existing Mycosis Fungoides
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 Management of Co-existing Mycosis Fungoides and Lymphomatoid Papulosis E Kim Citation E Kim. Management of Co-existing Mycosis Fungoides
Case Report A Severe Case of Lymphomatoid Papulosis Type E Successfully Treated with Interferon-Alfa 2a
 Hindawi Case Reports in Dermatological Medicine Volume 2017, Article ID 3194738, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3194738 Case Report A Severe Case of Lymphomatoid Papulosis Type E Successfully Treated
Hindawi Case Reports in Dermatological Medicine Volume 2017, Article ID 3194738, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3194738 Case Report A Severe Case of Lymphomatoid Papulosis Type E Successfully Treated
CASE 15 Patient: A 41-year-old Thai female Chief Compliant: Generalized papulovesicular rash for 1 month Present Illness: She presented with a 1-week
 CASE 15 Patient: A 41-year-old Thai female Chief Compliant: Generalized papulovesicular rash for 1 month Present Illness: She presented with a 1-week history of the generalized asymptomatic erythematous
CASE 15 Patient: A 41-year-old Thai female Chief Compliant: Generalized papulovesicular rash for 1 month Present Illness: She presented with a 1-week history of the generalized asymptomatic erythematous
Therapeutic Management of Early Cutaneous Mycosis Fungoides
 Therapeutic Management of Early Cutaneous Mycosis Fungoides L Frank Glass, MD Cutaneous Lymphoma Programs H Lee Moffitt Cancer Center and Research Institute George Washington University Dermatology and
Therapeutic Management of Early Cutaneous Mycosis Fungoides L Frank Glass, MD Cutaneous Lymphoma Programs H Lee Moffitt Cancer Center and Research Institute George Washington University Dermatology and
Bone Marrow Histopathologic and Molecular Staging in Epidermotropic T-Cell Lymphomas
 Hematopathology / BONE MARROW STAGING IN CUTANEOUS T-CELL LYMPHOMA Bone Marrow Histopathologic and Molecular Staging in Epidermotropic T-Cell Lymphomas Vincent Sibaud, MD, 1,2 Marie Beylot-Barry, MD, PhD,
Hematopathology / BONE MARROW STAGING IN CUTANEOUS T-CELL LYMPHOMA Bone Marrow Histopathologic and Molecular Staging in Epidermotropic T-Cell Lymphomas Vincent Sibaud, MD, 1,2 Marie Beylot-Barry, MD, PhD,
Microscopic study of the normal skin in cases of mycosis fungoides
 Microscopic study of the normal skin in cases of mycosis fungoides M. El Darouti, S. Marzook, M. Bosseila, O. Abu Zeid, O. El- Safouri, A. Zayed, A. El-Ramly Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 2 (1):
Microscopic study of the normal skin in cases of mycosis fungoides M. El Darouti, S. Marzook, M. Bosseila, O. Abu Zeid, O. El- Safouri, A. Zayed, A. El-Ramly Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 2 (1):
Dermatopathology: The tumor is composed of keratinocytes which show atypia, increase mitoses and abnormal mitoses.
 Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Lymphomatoid Papulosis 3 Case Reports
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2015), PP 31-35 www.iosrjournals.org Lymphomatoid Papulosis 3 Case Reports
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2015), PP 31-35 www.iosrjournals.org Lymphomatoid Papulosis 3 Case Reports
Case 1 A 61 year-old Thai woman from Bangkok Chief complaint: Multiple nodules and ulcerative masses on both arms, forearms and legs for 2 weeks
 Case 1 A 61 year-old Thai woman from Bangkok Chief complaint: Multiple nodules and ulcerative masses on both arms, forearms and legs for 2 weeks Fig. 1.1 Present illness: Five years ago, the patient presented
Case 1 A 61 year-old Thai woman from Bangkok Chief complaint: Multiple nodules and ulcerative masses on both arms, forearms and legs for 2 weeks Fig. 1.1 Present illness: Five years ago, the patient presented
Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation. Dermatopathology Specialists Needed. Changing Trends
 Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation Uma Sundram, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Dermatology Stanford University May 29, 2008 Dermatopathology Specialists
Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation Uma Sundram, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Dermatology Stanford University May 29, 2008 Dermatopathology Specialists
Dermatologica Sinica
 DERMATOLOGICA SINICA 29 (2011) 8e12 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Dermatologica Sinica journal homepage: http://www.derm-sinica.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Lymphomatoid papulosis: a clinical and histopathologic
DERMATOLOGICA SINICA 29 (2011) 8e12 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Dermatologica Sinica journal homepage: http://www.derm-sinica.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Lymphomatoid papulosis: a clinical and histopathologic
CD30(+)-lymphoproliferative disorders. Report of a 26-case-series and literature review
 ORIGINAL PAPERS CD30(+)-lymphoproliferative disorders. Report of a 26-case-series and literature review Alejandra Abeldaño 1, Adriana Benedetti 2, Matías Maskin 2, Mariana Arias 3, Karina Ochoa 2, Pablo
ORIGINAL PAPERS CD30(+)-lymphoproliferative disorders. Report of a 26-case-series and literature review Alejandra Abeldaño 1, Adriana Benedetti 2, Matías Maskin 2, Mariana Arias 3, Karina Ochoa 2, Pablo
Plenary paper. Introduction
 Plenary paper Primary and secondary cutaneous CD30 lymphoproliferative disorders: a report from the Dutch Cutaneous Lymphoma Group on the long-term follow-up data of 219 patients and guidelines for diagnosis
Plenary paper Primary and secondary cutaneous CD30 lymphoproliferative disorders: a report from the Dutch Cutaneous Lymphoma Group on the long-term follow-up data of 219 patients and guidelines for diagnosis
Classification of Cutaneous T cell Lymphomas (CTCLs) Hernani Cualing, MD
 Classification of Cutaneous T cell Lymphomas (CTCLs) Hernani Cualing, MD Pathology and Cell Biology, USF IFLOW, Inc. CTCL, MF, and Sézary syndrome In 1806, mycosis fungoides (MF) was first described 1
Classification of Cutaneous T cell Lymphomas (CTCLs) Hernani Cualing, MD Pathology and Cell Biology, USF IFLOW, Inc. CTCL, MF, and Sézary syndrome In 1806, mycosis fungoides (MF) was first described 1
Disclosures. Advisory Board. Consultant. Investigator. MiRagen, Actelion, Celgene, Therakos. Mindera
 Cutaneous Lymphomas Christiane Querfeld, MD, PhD Director, Cutaneous Lymphoma Program City of Hope ~ How the Experts Treat Hematologic Malignancies Symposium March 10 13, 2017 Disclosures Advisory Board
Cutaneous Lymphomas Christiane Querfeld, MD, PhD Director, Cutaneous Lymphoma Program City of Hope ~ How the Experts Treat Hematologic Malignancies Symposium March 10 13, 2017 Disclosures Advisory Board
SH/EAHP Workshop 2011 Los Angeles, California, USA
 SH/EAHP Workshop 2011 Los Angeles, California, USA October 27-29, 2011 Session 3 Non-Mycosis Fungoides CTCL Patty Jansen & Rein Willemze Introduction Submitted: 101 cases + 7 cases group 1: 108 Deactivated
SH/EAHP Workshop 2011 Los Angeles, California, USA October 27-29, 2011 Session 3 Non-Mycosis Fungoides CTCL Patty Jansen & Rein Willemze Introduction Submitted: 101 cases + 7 cases group 1: 108 Deactivated
Narrow band UVB (311 nm), psoralen UVB (311 nm) and PUVA therapy in the treatment of early-stage mycosis fungoides: a right left comparative study
 Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 2005; 21: 281 286 Blackwell Munksgaard Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Narrow band UVB (311 nm), psoralen UVB (311 nm) and therapy in the treatment of early-stage
Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 2005; 21: 281 286 Blackwell Munksgaard Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Narrow band UVB (311 nm), psoralen UVB (311 nm) and therapy in the treatment of early-stage
Subject Index. Dry desquamation, see Skin reactions, radiotherapy
 Subject Index Actinic keratosis disseminated disease 42 surgical excision 42 AIDS, see Kaposi s sarcoma Amifostine, skin reaction prophylaxis 111 Basal cell carcinoma, superficial X-ray therapy Bowen s
Subject Index Actinic keratosis disseminated disease 42 surgical excision 42 AIDS, see Kaposi s sarcoma Amifostine, skin reaction prophylaxis 111 Basal cell carcinoma, superficial X-ray therapy Bowen s
Clinical and Histopathological Spectrum of Mycosis Fungoides
 Awad Hasan Al-Tarawneh, MD, Jordan Board* Background: Early diagnosis of mycosis fungoides is essential but difficult and can be easily missed because it mimics many inflammatory skin diseases both clinically
Awad Hasan Al-Tarawneh, MD, Jordan Board* Background: Early diagnosis of mycosis fungoides is essential but difficult and can be easily missed because it mimics many inflammatory skin diseases both clinically
Primary Cutaneous Acral CD8 þ T-Cell Lymphoma
 Primary Cutaneous Acral CD8 þ T-Cell Lymphoma Vivian M. Hathuc, DO; Alexandra C. Hristov, MD; Lauren B. Smith, MD Primary cutaneous acral CD8 þ T-cell lymphoma is a new provisional entity in the 2016 revision
Primary Cutaneous Acral CD8 þ T-Cell Lymphoma Vivian M. Hathuc, DO; Alexandra C. Hristov, MD; Lauren B. Smith, MD Primary cutaneous acral CD8 þ T-cell lymphoma is a new provisional entity in the 2016 revision
Sezary Syndrome(SS) and other malignancies. Hernani Cualing MD Hematopathologist IHCFLOW Lab
 Sezary Syndrome(SS) and other malignancies Hernani Cualing MD Hematopathologist IHCFLOW Lab Disclosures IHCFLOW Laboratory:consultant and director NEOGENOMICS: contract consultant USF: contract reviewer
Sezary Syndrome(SS) and other malignancies Hernani Cualing MD Hematopathologist IHCFLOW Lab Disclosures IHCFLOW Laboratory:consultant and director NEOGENOMICS: contract consultant USF: contract reviewer
CUTIS. Do Not Copy. Pityriasis lichenoides is a T cell mediated papular. Pityriasis Lichenoides Chronica in Black Patients. Pediatric Dermatology
 Series Editor: Camila K. Janniger, MD Pityriasis Lichenoides Chronica in Black Patients Tanda N. Lane, MD; Sareeta S. Parker, MD Pityriasis lichenoides chronica (PLC) is a cutaneous disease of unknown
Series Editor: Camila K. Janniger, MD Pityriasis Lichenoides Chronica in Black Patients Tanda N. Lane, MD; Sareeta S. Parker, MD Pityriasis lichenoides chronica (PLC) is a cutaneous disease of unknown
CUTANEOUS T-CELL LYMPHOMA PROFORMA
 STATE OF KUWAIT MINISTRY OF HEALTH AS AD ALHAMAD DERMATOLOGY CENTER ALSABAH HOSPITAL دولة الكویت وزارة الصحة مرآز أسعد الحمد للا مراض الجلدیة مستشفى الصباح بسم االله الرحمن الرحيم CUTANEOUS TCELL LYMPHOMA
STATE OF KUWAIT MINISTRY OF HEALTH AS AD ALHAMAD DERMATOLOGY CENTER ALSABAH HOSPITAL دولة الكویت وزارة الصحة مرآز أسعد الحمد للا مراض الجلدیة مستشفى الصباح بسم االله الرحمن الرحيم CUTANEOUS TCELL LYMPHOMA
CASE 35 CLINICAL HISTORY
 Female, 24 Painful ulcerated lesion Left buttock Developed over a few weeks?abscess Excision CASE 35 CLINICAL HISTORY Two months later developed a similar lesion on right buttock CD30 CD3 CD4
Female, 24 Painful ulcerated lesion Left buttock Developed over a few weeks?abscess Excision CASE 35 CLINICAL HISTORY Two months later developed a similar lesion on right buttock CD30 CD3 CD4
Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
 Ann Dermatol Vol. 23, Suppl. 2, 2011 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.s2.s226 CASE REPORT Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature Yu-Jin Oh,
Ann Dermatol Vol. 23, Suppl. 2, 2011 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.s2.s226 CASE REPORT Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature Yu-Jin Oh,
Granulomatous Slack Skin with an unusually aggressive course due to the subsequent development of a CD30-positive Large Cell Lymphoma
 Granulomatous Slack Skin with an unusually aggressive course due to the subsequent development of a CD30-positive Large Cell Lymphoma Alexandra Papoudou-Bai 1, Eleni Kapsali 2, Ioannis Kostas-Agnantis
Granulomatous Slack Skin with an unusually aggressive course due to the subsequent development of a CD30-positive Large Cell Lymphoma Alexandra Papoudou-Bai 1, Eleni Kapsali 2, Ioannis Kostas-Agnantis
clinical recommendations
 19 (Supplement 2): ii72 ii76, 2008 doi:10.1093/annonc/mdn095 Primary cutaneous lymphoma: ESMO Clinical Recommendations for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up R. Dummer 1 & M. Dreyling 2 On behalf of the
19 (Supplement 2): ii72 ii76, 2008 doi:10.1093/annonc/mdn095 Primary cutaneous lymphoma: ESMO Clinical Recommendations for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up R. Dummer 1 & M. Dreyling 2 On behalf of the
Title: Erythema annulare centrifugum associated with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Authors: Helbling I, Walewska R, Dyer MJS, Bamford M, Harman KE
 Title: Erythema annulare centrifugum associated with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia Authors: Helbling I, Walewska R, Dyer MJS, Bamford M, Harman KE Sir, A wide range of conditions have been described as
Title: Erythema annulare centrifugum associated with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia Authors: Helbling I, Walewska R, Dyer MJS, Bamford M, Harman KE Sir, A wide range of conditions have been described as
ISPUB.COM. M Duvic, E Olsen PURPOSE OF REVISION
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 International Society of Cutaneous Lymphoma (ISCL) and the European Organization of Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) revisions to
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 International Society of Cutaneous Lymphoma (ISCL) and the European Organization of Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) revisions to
Case Rep Dermatol 2009;1:66 70 DOI: / Key Words Coma Blister Barbiturate Overdose Meningoencephalitis
 66 Coma Blisters Joana Rocha a Teresa Pereira a Filipa Ventura a Fernando Pardal b Celeste Brito a Departments of a Dermatology and b Pathology, Hospital de São Marcos, Braga, Portugal Key Words Coma Blister
66 Coma Blisters Joana Rocha a Teresa Pereira a Filipa Ventura a Fernando Pardal b Celeste Brito a Departments of a Dermatology and b Pathology, Hospital de São Marcos, Braga, Portugal Key Words Coma Blister
See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information.
 Clinical Policy: Vorinostat (Zolinza) Reference Number: CP.PHAR.83 Effective Date: 10.01.18 Last Review Date: 07.13.18 Line of Business: Oregon Health Plan Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end
Clinical Policy: Vorinostat (Zolinza) Reference Number: CP.PHAR.83 Effective Date: 10.01.18 Last Review Date: 07.13.18 Line of Business: Oregon Health Plan Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end
ITO, Yasuhiro ; FUJII, Mizue ; SHIBUYA, Takashi ; UEHARA, Jiro ; SATO, Katsuhiko ; IIZUKA, Hajime
 Journal of Dermatology (2011) 38(5):515-517. Granulocyte colony stimulating factor-producing squamous cell carcinoma of the skin ITO, Yasuhiro ; FUJII, Mizue ; SHIBUYA, Takashi ; UEHARA, Jiro ; SATO, Katsuhiko
Journal of Dermatology (2011) 38(5):515-517. Granulocyte colony stimulating factor-producing squamous cell carcinoma of the skin ITO, Yasuhiro ; FUJII, Mizue ; SHIBUYA, Takashi ; UEHARA, Jiro ; SATO, Katsuhiko
Given that mycosis fungoides (MF) is the most common
 Histopathologic approach to epidermotropic lymphocytic infiltrates Shyam S Raghavan, MD 1 and Jinah Kim, MD, PhD 2 Abstract Mycosis fungoides is the most common and therefore quintessential cutaneous lymphoma
Histopathologic approach to epidermotropic lymphocytic infiltrates Shyam S Raghavan, MD 1 and Jinah Kim, MD, PhD 2 Abstract Mycosis fungoides is the most common and therefore quintessential cutaneous lymphoma
CD30-positive cutaneous lymphoma: report of four cases with an emphasis on clinicopathological correlations *
 86 Dermatopathology s CD30-positive cutaneous lymphoma: report of four cases with an emphasis on clinicopathological correlations * Thiago Jeunon de Sousa Vargas 1 Samira Barroso Jorge 1 Yung Bruno de
86 Dermatopathology s CD30-positive cutaneous lymphoma: report of four cases with an emphasis on clinicopathological correlations * Thiago Jeunon de Sousa Vargas 1 Samira Barroso Jorge 1 Yung Bruno de
Dermatologica Sinica
 DERMATOLOGICA SINICA 31 (2013) 140e144 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Dermatologica Sinica journal homepage: http://www.derm-sinica.com CASE REPORT Atypical fibroxanthoma-like amelanotic
DERMATOLOGICA SINICA 31 (2013) 140e144 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Dermatologica Sinica journal homepage: http://www.derm-sinica.com CASE REPORT Atypical fibroxanthoma-like amelanotic
Concurrent malignant melanoma and cutaneous involvement by classical hodgkin lymphoma (CHL) in a 63 year-old man
 Gru and Lu Diagnostic Pathology 2013, 8:135 CASE REPORT Open Access Concurrent malignant melanoma and cutaneous involvement by classical hodgkin lymphoma (CHL) in a 63 year-old man Alejandro A Gru 1* and
Gru and Lu Diagnostic Pathology 2013, 8:135 CASE REPORT Open Access Concurrent malignant melanoma and cutaneous involvement by classical hodgkin lymphoma (CHL) in a 63 year-old man Alejandro A Gru 1* and
ISPUB.COM. Advanced Stage CTCL, PTCL with Cutaneous Involvement. J Messenger, P Porcu INTRODUCTION INITIAL PRESENTATION
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 Advanced Stage CTCL, PTCL with Cutaneous Involvement J Messenger, P Porcu Citation J Messenger, P Porcu. Advanced Stage CTCL, PTCL with Cutaneous
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 3 Advanced Stage CTCL, PTCL with Cutaneous Involvement J Messenger, P Porcu Citation J Messenger, P Porcu. Advanced Stage CTCL, PTCL with Cutaneous
Maligna Melanoma and Atypical Fibroxanthoma: An Unusual Collision Tumour G Türkcü 1, A Keleş 1, U Alabalık 1, D Uçmak 2, H Büyükbayram 1 ABSTRACT
 Maligna Melanoma and Atypical Fibroxanthoma: An Unusual Collision Tumour G Türkcü 1, A Keleş 1, U Alabalık 1, D Uçmak 2, H Büyükbayram 1 ABSTRACT Two different neoplasia in the same biopsy material called
Maligna Melanoma and Atypical Fibroxanthoma: An Unusual Collision Tumour G Türkcü 1, A Keleş 1, U Alabalık 1, D Uçmak 2, H Büyükbayram 1 ABSTRACT Two different neoplasia in the same biopsy material called
Mycosis Fungoides and Variants
 Mycosis Fungoides and Variants Jennifer Madison McNiff, M.D. Associate Professor, Dermatology and Pathology Yale University School of Medicine Classic mycosis fungoides The most common cutaneous lymphoma
Mycosis Fungoides and Variants Jennifer Madison McNiff, M.D. Associate Professor, Dermatology and Pathology Yale University School of Medicine Classic mycosis fungoides The most common cutaneous lymphoma
Lymphomatoid Papulosis Associated with Mycosis Fungoides: Clinicopathological and Molecular Studies of 12 Cases
 Acta Derm Venereol 2004; 84: 463 468 CLINICAL REPORT Lymphomatoid Papulosis Associated with Mycosis Fungoides: Clinicopathological and Molecular Studies of 12 Cases Fernando GALLARDO 1,2, Carlota COSTA
Acta Derm Venereol 2004; 84: 463 468 CLINICAL REPORT Lymphomatoid Papulosis Associated with Mycosis Fungoides: Clinicopathological and Molecular Studies of 12 Cases Fernando GALLARDO 1,2, Carlota COSTA
Case Report Childhood Hypopigmented Mycosis Fungoides: A Rare Diagnosis
 Case Reports in Pediatrics Volume 2016, Article ID 8564389, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8564389 Case Report Childhood Hypopigmented Mycosis Fungoides: A Rare Diagnosis Cláudia Patraquim, 1 Maria
Case Reports in Pediatrics Volume 2016, Article ID 8564389, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8564389 Case Report Childhood Hypopigmented Mycosis Fungoides: A Rare Diagnosis Cláudia Patraquim, 1 Maria
Interhospital Dermatology Conference 2013
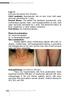 Case 21 A 50-year-old woman from Chonburi. Chief complaint: Asymptomatic rash on neck, trunk, both upper and lower extremities for 2 years. Present illness: The patient has developed asymptomatic scaly
Case 21 A 50-year-old woman from Chonburi. Chief complaint: Asymptomatic rash on neck, trunk, both upper and lower extremities for 2 years. Present illness: The patient has developed asymptomatic scaly
Non Hodgkin s lymphoma with cutaneous involvement in AIDS patients. Report of five cases and review of the literature
 Non Hodgkin s lymphoma with cutaneous involvement in AIDS patients. Report of five cases and review of the literature OrIGINAl CASE report ArTIClE ABSTRACT Cutaneous B cell lymphoma (CBCL) is a lymphoproliferative
Non Hodgkin s lymphoma with cutaneous involvement in AIDS patients. Report of five cases and review of the literature OrIGINAl CASE report ArTIClE ABSTRACT Cutaneous B cell lymphoma (CBCL) is a lymphoproliferative
Primer of Immunohistochemistry (Leukocytic)
 Primer of Immunohistochemistry (Leukocytic) Paul K. Shitabata, M.D. Dermatopathology Institute Torrance, CA BENIGN LYMPHOID SKIN LESIONS CAPABLE OF SIMULATING LYMPHOMA -Jessner s lymphoid infiltrate -Dermal-subcutaneous
Primer of Immunohistochemistry (Leukocytic) Paul K. Shitabata, M.D. Dermatopathology Institute Torrance, CA BENIGN LYMPHOID SKIN LESIONS CAPABLE OF SIMULATING LYMPHOMA -Jessner s lymphoid infiltrate -Dermal-subcutaneous
المركب النموذج--- سبيتز وحمة = Type Spitz's Nevus, Compound SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7
 SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7 Epidemiology An annual incidence rate of 1.4 cases of Spitz nevus per 100,000 individuals has been estimated in Australia, compared with 25.4 per 100,000 individuals for cutaneous melanoma
SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7 Epidemiology An annual incidence rate of 1.4 cases of Spitz nevus per 100,000 individuals has been estimated in Australia, compared with 25.4 per 100,000 individuals for cutaneous melanoma
Mycosis fungoides (MF) is the most common type of cutaneous
 Mycosis fungoides variants clinicopathologic features, differential diagnosis, and treatment Rein Willemze, MD, PhD Abstract Mycosis fungoides (MF) is the most common type of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma,
Mycosis fungoides variants clinicopathologic features, differential diagnosis, and treatment Rein Willemze, MD, PhD Abstract Mycosis fungoides (MF) is the most common type of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma,
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL)
 Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL) Lymphoid Neoplasms: 1- non-hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) 2- Hodgkin lymphoma 3- plasma cell neoplasms Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL) Lymphoid Neoplasms: 1- non-hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) 2- Hodgkin lymphoma 3- plasma cell neoplasms Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma
Rosario Haro, MD; Africa Juarez, MD; José Luis Díaz, MD; Carlos Santonja, MD; Félix Manzarbeitia, MD; Luis Requena, MD
 of the Breast Restricted to an Area of Prior Radiotherapy Rosario Haro, MD; Africa Juarez, MD; José Luis Díaz, MD; Carlos Santonja, MD; Félix Manzarbeitia, MD; Luis Requena, MD PRACTICE POINTS Cutaneous
of the Breast Restricted to an Area of Prior Radiotherapy Rosario Haro, MD; Africa Juarez, MD; José Luis Díaz, MD; Carlos Santonja, MD; Félix Manzarbeitia, MD; Luis Requena, MD PRACTICE POINTS Cutaneous
Mycosis Fungoides, then and now Have we travelled?
 USCAP 103 rd Annual Meeting 2014 American Society of Dermatopathology Companion Meeting Mycosis Fungoides, then and now Have we travelled? Vijaya B. Reddy, MD, MBA Professor of Pathology Rush University
USCAP 103 rd Annual Meeting 2014 American Society of Dermatopathology Companion Meeting Mycosis Fungoides, then and now Have we travelled? Vijaya B. Reddy, MD, MBA Professor of Pathology Rush University
Burkitt lymphoma. Sporadic Endemic in Africa associated with EBV Translocations involving MYC gene on chromosome 8
 Heme 8 Burkitt lymphoma Sporadic Endemic in Africa associated with EBV Translocations involving MYC gene on chromosome 8 Most common is t(8;14) Believed to be the fastest growing tumor in humans!!!! Morphology
Heme 8 Burkitt lymphoma Sporadic Endemic in Africa associated with EBV Translocations involving MYC gene on chromosome 8 Most common is t(8;14) Believed to be the fastest growing tumor in humans!!!! Morphology
Case Scenario 1 Worksheet. Primary Site C44.4 Morphology 8743/3 Laterality 0 Stage/ Prognostic Factors
 CASE SCENARIO 1 9/10/13 HISTORY: Patient is a 67-year-old white male and presents with lesion located 4-5cm above his right ear. The lesion has been present for years. No lymphadenopathy. 9/10/13 anterior
CASE SCENARIO 1 9/10/13 HISTORY: Patient is a 67-year-old white male and presents with lesion located 4-5cm above his right ear. The lesion has been present for years. No lymphadenopathy. 9/10/13 anterior
Cluster of differentiation (CD) markers in erythrodermic patients: A case series study
 Original Article Cluster of differentiation (CD) markers in erythrodermic patients: A case series study Fariba Ghalamkarpour, MD Faranak Niknafs, MD Shima Younespour, PhD Skin Research Center, Shahid Beheshti
Original Article Cluster of differentiation (CD) markers in erythrodermic patients: A case series study Fariba Ghalamkarpour, MD Faranak Niknafs, MD Shima Younespour, PhD Skin Research Center, Shahid Beheshti
Clinical Policy: Vorinostat (Zolinza) Reference Number: CP.PHAR.83 Effective Date: 10/11
 Clinical Policy: (Zolinza) Reference Number: CP.PHAR.83 Effective Date: 10/11 Last Review Date: 12/16 Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information.
Clinical Policy: (Zolinza) Reference Number: CP.PHAR.83 Effective Date: 10/11 Last Review Date: 12/16 Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information.
Plasma cell myeloma (multiple myeloma)
 Plasma cell myeloma (multiple myeloma) Common lymphoid neoplasm, present at old age (70 years average) Remember: plasma cells are terminally differentiated B-lymphocytes that produces antibodies. B-cells
Plasma cell myeloma (multiple myeloma) Common lymphoid neoplasm, present at old age (70 years average) Remember: plasma cells are terminally differentiated B-lymphocytes that produces antibodies. B-cells
Lymphomatoid Papulosis. اللمفواني الحطاطي الداء = lymphomatoide Papulose Thursday, 21 October :16 - Last Updated Friday, 03 December :54
 Lymphomatoid Papulosis 1 / 12 Lymphomatoid papulosis (LyP) is a chronic papulonecrotic or papulonodular skin disease with histologic features suggestive of a malignant lymphoma. The disease is characterized
Lymphomatoid Papulosis 1 / 12 Lymphomatoid papulosis (LyP) is a chronic papulonecrotic or papulonodular skin disease with histologic features suggestive of a malignant lymphoma. The disease is characterized
Clinical Study The Influence of the Coexpression of CD4 and CD8 in Cutaneous Lesions on Prognosis of Mycosis Fungoides: A Preliminary Study
 Skin Cancer, Article ID 624143, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/624143 Clinical Study The Influence of the Coexpression of CD4 and CD8 in Cutaneous Lesions on Prognosis of Mycosis Fungoides: A Preliminary
Skin Cancer, Article ID 624143, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/624143 Clinical Study The Influence of the Coexpression of CD4 and CD8 in Cutaneous Lesions on Prognosis of Mycosis Fungoides: A Preliminary
The cientificworldjournal
 The Scientific World Journal Volume 2012, Article ID 426732, 6 pages doi:10.1100/2012/426732 The cientificworldjournal Clinical Study Evaluation of Histopathological Changes in Control Biopsies Which Taken
The Scientific World Journal Volume 2012, Article ID 426732, 6 pages doi:10.1100/2012/426732 The cientificworldjournal Clinical Study Evaluation of Histopathological Changes in Control Biopsies Which Taken
Blastic NK-Cell Leukemia / Lymphoma
 * * Blastic NK-Cell Leukemia / Lymphoma A Case Report Chun-Ming Lin Shu-Hui Wang Tseng-tong Kuo* Ching-Chi Chi Hsin-Chun Ho Hong-Shang Hong Blastic natural killer (NK) cell lymphoma / leukemia is a rare
* * Blastic NK-Cell Leukemia / Lymphoma A Case Report Chun-Ming Lin Shu-Hui Wang Tseng-tong Kuo* Ching-Chi Chi Hsin-Chun Ho Hong-Shang Hong Blastic natural killer (NK) cell lymphoma / leukemia is a rare
STUDY. with a benign clinical course but a malignant appearance
 Lymphomatoid Papulosis STUDY Reappraisal of Clinicopathologic Presentation and Classification Into Subtypes A,, and C Laila El Shabrawi-Caelen, MD; Helmut Kerl, MD; Lorenzo Cerroni, MD Objectives: To analyze
Lymphomatoid Papulosis STUDY Reappraisal of Clinicopathologic Presentation and Classification Into Subtypes A,, and C Laila El Shabrawi-Caelen, MD; Helmut Kerl, MD; Lorenzo Cerroni, MD Objectives: To analyze
Summary. lymphoma/myeloma, regulatory T cells (T reg) Introduction. Clinical and Experimental Immunology ORIGINAL ARTICLE doi: /cei.
 bs_bs_banner Clinical and Experimental Immunology ORIGINAL ARTICLE doi:1.1111/cei.1273 Increased frequency of skin-infiltrating FoxP3 + regulatory T cells as a diagnostic indicator of severe atopic dermatitis
bs_bs_banner Clinical and Experimental Immunology ORIGINAL ARTICLE doi:1.1111/cei.1273 Increased frequency of skin-infiltrating FoxP3 + regulatory T cells as a diagnostic indicator of severe atopic dermatitis
Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: After Twenty Years the Controversy Continues Marsha C. Kinney, M.D.
 Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: After Twenty Years the Controversy Continues Marsha C. Kinney, M.D. Introduction and Historical Perspective: While evaluating a new antibody Ki-1 directed against an epitope
Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: After Twenty Years the Controversy Continues Marsha C. Kinney, M.D. Introduction and Historical Perspective: While evaluating a new antibody Ki-1 directed against an epitope
2. Sézary syndrome (SS)
 Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details Clinical images are available in hardcopy only. Clinical images are available in Clinical images are available in d e f g h i j Fig..36-2
Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details Clinical images are available in hardcopy only. Clinical images are available in Clinical images are available in d e f g h i j Fig..36-2
Glistening, Skin-Colored Nodule
 To Print: Click your browser's PRINT button. NOTE: To view the article with Web enhancements, go to: http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/436334 Medscape Dermatology Clinic Glistening, Skin-Colored Nodule
To Print: Click your browser's PRINT button. NOTE: To view the article with Web enhancements, go to: http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/436334 Medscape Dermatology Clinic Glistening, Skin-Colored Nodule
Granulomatous mycosis fungoides (GMF) is
 CASE REPORT Granulomatous mycosis fungoides, a rare subtype of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma Marta Kogut, MD, a Eva Hadaschik, MD, a Stephan Grabbe, MD, b Mindaugas Andrulis, MD, c Alexander Enk, MD, a and
CASE REPORT Granulomatous mycosis fungoides, a rare subtype of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma Marta Kogut, MD, a Eva Hadaschik, MD, a Stephan Grabbe, MD, b Mindaugas Andrulis, MD, c Alexander Enk, MD, a and
Interstitial mycosis fungoides with lichen sclerosus-like clinical and histopathological features
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2016 Interstitial mycosis fungoides with lichen sclerosus-like clinical and
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2016 Interstitial mycosis fungoides with lichen sclerosus-like clinical and
Case Report A case of EBV positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the adolescent
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(1):307-311 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM1311029 Case Report A case of EBV positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the adolescent Qilin Ao 2, Ying Wang 1, Sanpeng Xu 2,
Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(1):307-311 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM1311029 Case Report A case of EBV positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the adolescent Qilin Ao 2, Ying Wang 1, Sanpeng Xu 2,
TARGRETIN (bexarotene) oral capsule & external gel
 TARGRETIN (bexarotene) oral capsule & external gel Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan.
TARGRETIN (bexarotene) oral capsule & external gel Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan.
STUDY. fungoides (FMF) is an uncommon
 STUDY Folliculotropic Mycosis Fungoides Single-Center Study and Systematic Review Julia S. Lehman, MD; Robert H. Cook-Norris, MD; Brent R. Weed, MD; Roger H. Weenig, MD; Lawrence E. Gibson, MD; Amy L.
STUDY Folliculotropic Mycosis Fungoides Single-Center Study and Systematic Review Julia S. Lehman, MD; Robert H. Cook-Norris, MD; Brent R. Weed, MD; Roger H. Weenig, MD; Lawrence E. Gibson, MD; Amy L.
CPC. Chutika Srisuttiyakorn, M.D. Kobkul Aunhachoke, M.D. Phramongkutklao Hospital Bangkok, Thailand
 CPC Chutika Srisuttiyakorn, M.D. Kobkul Aunhachoke, M.D. Phramongkutklao Hospital Bangkok, Thailand A 53 year-old woman with fever, facial swelling and rashes on face, trunk and upper extremities for 3
CPC Chutika Srisuttiyakorn, M.D. Kobkul Aunhachoke, M.D. Phramongkutklao Hospital Bangkok, Thailand A 53 year-old woman with fever, facial swelling and rashes on face, trunk and upper extremities for 3
Among the benign intraepithelial melanocytic proliferations, Inflamed Conjunctival Nevi. Histopathological Criteria. Resident Short Reviews
 Resident Short Reviews Inflamed conjunctival nevi (ICN) may suggest malignancy because of their rapid growth and atypical histology. The objective of this study was to characterize the diagnostic features
Resident Short Reviews Inflamed conjunctival nevi (ICN) may suggest malignancy because of their rapid growth and atypical histology. The objective of this study was to characterize the diagnostic features
Review Article. Cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorders. NJ Trendell-Smith
 Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2010) 18, 190-201 Review Article Cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorders NJ Trendell-Smith Cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorders (CLD) include reactive lymphoid hyperplasias,
Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2010) 18, 190-201 Review Article Cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorders NJ Trendell-Smith Cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorders (CLD) include reactive lymphoid hyperplasias,
Mycosis Fungoides: A Retrospective Study of 44 Swedish Cases
 Acta Derm Venereol 2016; 96: 669 673 CLINICAL REPORT Mycosis Fungoides: A Retrospective Study of 44 Swedish Cases Yvonne EKLUND 1, Annika ARONSSON 1, Artur SCHMIDTCHEN 1 and Thomas RELANDER 2 1 Section
Acta Derm Venereol 2016; 96: 669 673 CLINICAL REPORT Mycosis Fungoides: A Retrospective Study of 44 Swedish Cases Yvonne EKLUND 1, Annika ARONSSON 1, Artur SCHMIDTCHEN 1 and Thomas RELANDER 2 1 Section
Sézary syndrome. Diagnosis and staging
 CME DERMATOLOGY Clinical Medicine 2012, Vol 12, No 2: 160 4 Edited by Clive B Archer, consultant dermatologist and lead for Medical Education, St John s Institute of Dermatology, Guy s and St Thomas NHS
CME DERMATOLOGY Clinical Medicine 2012, Vol 12, No 2: 160 4 Edited by Clive B Archer, consultant dermatologist and lead for Medical Education, St John s Institute of Dermatology, Guy s and St Thomas NHS
Malignant Lymphomas Decision Making and Problem Solving
 Malignant Lymphomas Decision Making and Problem Solving Cutaneous T-cell lymphomas (including rare subtypes). Current concepts. II. [haematologica] 2004;89:1372-1388 MARCO PAULLI EMILIO BERTI A B S T R
Malignant Lymphomas Decision Making and Problem Solving Cutaneous T-cell lymphomas (including rare subtypes). Current concepts. II. [haematologica] 2004;89:1372-1388 MARCO PAULLI EMILIO BERTI A B S T R
2016 AAD SUMMER MEETING SYMPOSIUM S011: CLINICOPATHOLOGIC SELF-ASSESSMENT 7/30/16 2:00 PM. Tom Helm, MD
 2016 AAD SUMMER MEETING SYMPOSIUM S011: CLINICOPATHOLOGIC SELF-ASSESSMENT 7/30/16 2:00 PM Tom Helm, MD Case 1 Diagnosis: Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia associated with CD30+ lymphoproliferative disease
2016 AAD SUMMER MEETING SYMPOSIUM S011: CLINICOPATHOLOGIC SELF-ASSESSMENT 7/30/16 2:00 PM Tom Helm, MD Case 1 Diagnosis: Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia associated with CD30+ lymphoproliferative disease
Lymphocytoma Cutis. Cynthia M. Magro MD. Director of Dermatopathology Weill Medical College of Cornell University New York, New York
 Lymphocytoma Cutis Cynthia M. Magro MD Professor of Pathology Director of Dermatopathology Weill Medical College of Cornell University New York, New York Lymphocytoma Cutis Falls under other designations
Lymphocytoma Cutis Cynthia M. Magro MD Professor of Pathology Director of Dermatopathology Weill Medical College of Cornell University New York, New York Lymphocytoma Cutis Falls under other designations
Lymphoma: What You Need to Know. Richard van der Jagt MD, FRCPC
 Lymphoma: What You Need to Know Richard van der Jagt MD, FRCPC Overview Concepts, classification, biology Epidemiology Clinical presentation Diagnosis Staging Three important types of lymphoma Conceptualizing
Lymphoma: What You Need to Know Richard van der Jagt MD, FRCPC Overview Concepts, classification, biology Epidemiology Clinical presentation Diagnosis Staging Three important types of lymphoma Conceptualizing
Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor
 C H A P T E R 120 Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Currently, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is the most commonly used generic name for the neoplasms known in the past as neurosarcoma,
C H A P T E R 120 Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Currently, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is the most commonly used generic name for the neoplasms known in the past as neurosarcoma,
Cutaneous Mycosis Fungoides (MF), the subtype of cutaneous
 DOI 10. 5001/omj.2012.28 The Histological Spectrum of Early Mycosis Fungoides: A Study of 58 Saudi Arab patients Maha Arafah, Shaesta Naseem Zaidi, Hala Kassouf Kfoury, Ammar Al Rikabi, Khalid Al Ghamdi
DOI 10. 5001/omj.2012.28 The Histological Spectrum of Early Mycosis Fungoides: A Study of 58 Saudi Arab patients Maha Arafah, Shaesta Naseem Zaidi, Hala Kassouf Kfoury, Ammar Al Rikabi, Khalid Al Ghamdi
Abstract. Hematopathology / FLOW CYTOMETRIC DNA PLOIDY ANALYSIS IN SÉZARY SYNDROME
 Hematopathology / FLOW CYTOMETRIC DNA PLOIDY ANALYSIS IN SÉZARY SYNDROME Flow Cytometric DNA Ploidy Analysis of Peripheral Blood From Patients With Sézary Syndrome Detection of Aneuploid Neoplastic T Cells
Hematopathology / FLOW CYTOMETRIC DNA PLOIDY ANALYSIS IN SÉZARY SYNDROME Flow Cytometric DNA Ploidy Analysis of Peripheral Blood From Patients With Sézary Syndrome Detection of Aneuploid Neoplastic T Cells
Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation for Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma: Updated results from a single center
 Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation for Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma: Updated results from a single center Madeleine Duvic, MD Professor and Deputy Chairman Blanche Bender Professor in Cancer Research Departments
Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation for Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma: Updated results from a single center Madeleine Duvic, MD Professor and Deputy Chairman Blanche Bender Professor in Cancer Research Departments
A Retrospective Study on the Risk of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer in PUVA and Narrowband UVB Treated Patients
 Volume 1, Issue 3 Research Article A Retrospective Study on the Risk of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer in PUVA and Narrowband UVB Treated Patients Darukarnphut P, Rattanakaemakorn P *, Rajatanavin N Division
Volume 1, Issue 3 Research Article A Retrospective Study on the Risk of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer in PUVA and Narrowband UVB Treated Patients Darukarnphut P, Rattanakaemakorn P *, Rajatanavin N Division
22 year old QH mare with regionally extensive alopecia and scaling on one front limb and ventral chest (Figure 1 and 2).
 22 year old QH mare with regionally extensive alopecia and scaling on one front limb and ventral chest (Figure 1 and 2). Which of the following is the most likely disease? a. Sterile granuloma complex
22 year old QH mare with regionally extensive alopecia and scaling on one front limb and ventral chest (Figure 1 and 2). Which of the following is the most likely disease? a. Sterile granuloma complex
Elsevier B.V.; この論文は出版社版でありま Right 引用の際には出版社版をご確認ご利用ください This is
 Title Refractory cutaneous lichenoid sarc tranilast. Author(s) Nakahigashi, Kyoko; Kabashima, Kenj Utani, Atsushi; Miyachi, Yoshiki Citation Journal of the American Academy of 63(1): 171-172 Issue Date
Title Refractory cutaneous lichenoid sarc tranilast. Author(s) Nakahigashi, Kyoko; Kabashima, Kenj Utani, Atsushi; Miyachi, Yoshiki Citation Journal of the American Academy of 63(1): 171-172 Issue Date
MALIGNANT POROMA SYNONYM: POROCARCINOMA ECCRINE POROMA MALIGNANT Divvya B 1, M. Valluvan 2, Rehana Tippoo 3, P. Viswanathan 4, R.
 MALIGNANT POROMA SYNONYM: POROCARCINOMA ECCRINE POROMA MALIGNANT Divvya B 1, M. Valluvan 2, Rehana Tippoo 3, P. Viswanathan 4, R. Ramesh 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Divvya B, M. Valluvan, Rehana Tippoo,
MALIGNANT POROMA SYNONYM: POROCARCINOMA ECCRINE POROMA MALIGNANT Divvya B 1, M. Valluvan 2, Rehana Tippoo 3, P. Viswanathan 4, R. Ramesh 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Divvya B, M. Valluvan, Rehana Tippoo,
Clinical Trial Outcomes
 l Recent clinical evidence for topical mechlorethamine in mycosis fungoides Mycosis fungoides (MF) is a rare, potentially life-threatening cutaneous T-cell lymphoma characterized by cutaneous homing of
l Recent clinical evidence for topical mechlorethamine in mycosis fungoides Mycosis fungoides (MF) is a rare, potentially life-threatening cutaneous T-cell lymphoma characterized by cutaneous homing of
Melanoma Case Scenario 1
 Melanoma Case Scenario 1 History and physical 11/5/16 Patient is a single, 48-year-old male in good health who presented to his primary physician for a yearly physical exam during which a 3.4 x 2.8 x 1.5
Melanoma Case Scenario 1 History and physical 11/5/16 Patient is a single, 48-year-old male in good health who presented to his primary physician for a yearly physical exam during which a 3.4 x 2.8 x 1.5
