Skin aging due to the passage of time is modulated
|
|
|
- Patience Cobb
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Clinical and Histological Efficacy of a Secretion of the Mollusk Cryptomphalus aspersa in the Treatment of Cutaneous Photoaging María José Tribó-Boixareu, MD; Concepción Parrado-Romero, MD; Badr Rais, PhD; Eduardo Reyes, PhD; María Alejandra Vitale-Villarejo, MD; Salvador González, MD Study In this article, the authors describe the efficacy of a natural secretion of Cryptomphalus aspersa (SCA) in cutaneous photoaging. This placebo-free, open-label study comprised 15 women exhibiting facial photoaging. Treatment with SCA for 3 months induced a significant reduction in photoaging on the Glogau scale. Silicone replica analysis showed significant improvements in skin roughness and wrinkle depth. Histopathological analysis Do revealed a Not marked improvement Copy in both dermal and epidermal architecture, as well as epidermal proliferation and the percentage of cutaneous area covered by microvessels. In summary, treatment with SCA for 3 months resulted in a significant improvement of the clinical and histological signs of photoaging, and these correlated with both subjective and objective assessments of chronic photodamage. Dr. Tribó-Boixareu is Faculty, Dermatology Department, Hospital del Mar, Barcelona, Spain. Dr. Parrado-Romero is Associate Professor, Department of Morphological Sciences, Faculty of Medicine, Malaga University, Spain. Dr. Rais is Employee, Biochemistry and Cell Biology Department, Bio European Skin Testing, Barcelona, Spain. Dr. Reyes is Employee, Scientific Department, Industrial Farmaceutica Cantabria SA, Madrid, Spain. Dr. González is Faculty, Dermatology Services, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, New York. Drs. Reyes and Vitale-Villarejo are employees of and Dr. González is a consultant for Industrial Farmaceutica Cantabria SA. Correspondence: Salvador González, Faculty of Dermatology Service, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, 16 E 53rd St, New York, NY, 122 (gonzals6@mskcc.org). Skin aging due to the passage of time is modulated by the interaction between individual genetics and environmental factors. Genetic determinants and environmental factors, particularly UV radiation, may induce premature skin aging or photoaging. 1 Photoaging causes functional, anatomical, and structural modifications in the exposed areas, 2-6 and UVB radiation produces direct damage to skin cells DNA and also modulates the activity of cytokines and adhesion molecules. 7-8 On the other hand, UVA radiation induces the formation of reactive oxygen species, which also damages nuclear and mitochondrial DNA and activates matrix metalloproteinases. 1,5-9 The signs of photoaging include epidermal thickening, keratinocyte atypia, loss of polarity and increased melanogenesis. 1 The dermal fibrillar network is disorganized. 11 Vol. 22 No. 5 may 29 Cosmetic Dermatology 247
2 Other changes include collagen reduction and the appearance of fragmented collagen fibrils; presence of senescent fibroblasts 12,13 ; loss of function of glycosaminoglycans (hyaluronic acid and dermatan sulphate); and alterations in the cutaneous microvasculature. 14,15 All these findings result in characteristic clinical features, such as dryness, roughness and sallowness, deep wrinkles, and lack of firmness and elasticity. 1,2,16,17 Concern regarding the visible manifestations of skin aging represents one of the leading reasons for dermatological consultation. Topical therapy is the most widely accepted treatment by the majority of patients In this article, the authors provide preliminary evidence of the effect of a novel natural product derived from the mollusk Cryptomphalus aspersa 22 (SCA), which is a glycosaminoglycanenriched substance that induces skin regeneration. 23,24 Based on this evidence, the authors hypothesized that SCA can be useful to reverse the effects of photoaging. In this study, the authors investigate the effect of SCA treatment in a small group of women (n515) showing cutaneous photoaging and found that treatment with SCA for 3 months resulted in a significant improvement of the clinical and histological features of photoaging, thus postulating its efficacy as a potential antiaging compound for the skin. Materials and Methods SCA Preparation Preparation for SCA was executed according to US patent and has been described in detail elsewhere. 22 Study Design Fifteen volunteers were included in this nonrandomized, open-label study. Participants were informed of the requirements of the study including 2 biopsy collections, and they signed a written informed consent under an institutional review board approved study protocol. The study group comprised 15 women aged 35 to 65 years (mean [SD] age552.1 [6.2]) with Fitzpatrick skin types II (53.8%) and III (46.2%), and features consistent with facial photoaging. Prior to the beginning of the treatment, each participant underwent a 1-month washout period, during which all topical antiaging treatments were discontinued. Participants were instructed to apply an SCA 8% emulsion in the morning and a highly concentrated SCA 4% liquid formulation at night on a daily basis for a period of 3 months. Assessments were performed at the initial consultation at baseline and days 3 and 9. Clinical Efficacy Variables The researcher recorded the following clinical variables: presence of fine lines and wrinkles, sallowness, telangiectasias, reduced cutaneous elasticity, roughness, irregular mottled pigmentation, rhytides, and solar lentigines. Other parameters included sebaceous hyperplasia, actinic keratosis, and presence of malignant neoplastic processes. Photodamage A severity score between 1 and 6, with 6 being the most severe, was assessed using the Glogau scale. 16,25 One of the authors, Dr. María José Tribó-Boixareu, evaluated treatments with each individual participant during each clinical visit and scored treatments from (unchanged) to 6 (marked improvement). Clinical Assessment of the Effect of SCA The clinical efficacy of SCA was measured by confocal profilometry of silicone replicas. The technique has been described in detail elsewhere. 26,27 Briefly, 1-cm-wide silicone impressions were taken from the periocular area at baseline and day 9. The following parameters were assessed: average roughness of the profile; root-meansquare roughness of the profile; maximum height of the roughness profile; maximum peak height of the roughness profile; maximum valley depth of the roughness profile; and distance between the highest peak and the deepest valley of the assessed profile. Histology Histological analysis was performed in 3-mm diameter samples collected from the periocular areas of all the patients. Biopsies were obtained at baseline and day 9. Samples were stained with hematoxylin and eosin to visualize the architecture and determine epidermal thickness. Unna stains were used for visualization of the elastic fibers and assessment of cutaneous elastosis. 28 Immunohistochemistry The sections used for immunohistochemical analysis were deparaffinized and incubated overnight at 4ºC with anti Ki-67-mab for proliferating keratinocytes, or anti CD31-mab for endothelial cells, and appropriate secondaries. Each section was counterstained with hematoxylin and eosin and dehydrated. Quantitative Histologic Analysis Immunohistochemistry images were quantified using an image processing program, and the percentage of proliferating epidermal cells was calculated and expressed as epidermal proliferating index. 29 For microvessel quantification and area, microvascular density was measured in 5 to 6 spots, and CD31 1 cell (endothelial cell) clusters were included in the microvessel count. 248 Cosmetic Dermatology may 29 Vol. 22 No. 5
3 12 1 A Patients With Fine Wrinkles Patients With Deep Wrinkles 12 1 B Sallow Color Roughness Mottled Pigmentation Loss of Elasticity Percentage, % Percentage, % Baseline Day 3 Day 9 Baseline Day 3 Day 9 Figure 1. Effect of Cryptomphalus aspersa on the presence of fine and deep wrinkles (P,.5 and P,.25, fine and deep wrinkles, respectively) (A), and the effect of Cryptomphalus aspersa on different features of photoaging (B). Percentages are shown at the initiation of the treatment at baseline and days 3 and 9. Statistical Analysis The Cochran test was used to assess potentially significant differences in the clinical evolution between the 3 measurements at baseline and days 3 and 9, as well as the individual and global assessment by the researcher and the participants. The Wilcoxon rank sum test was used to assess differences in skin photoaging severity and histological parameters between the initiation of the study and its completion at 3 months. This test was also used to characterize the individual and global assessment of ephelis or lentigines, and no malignant neoplasms of the researcher and the patients between visits. The were reported during the assay. normal distribution of the analysis of silicone replicas by profilometry was demonstrated via unidirectional analysis of the sample using statistical software. In all cases, standardized kurtosis coefficient was within the expected range for normal distribution data (22, 12); thus, parametric statistical criteria were applied. Results Clinical Efficacy of SCA We first established the severity of cutaneous photoaging before and after treatment with SCA using the Glogau scale. This scale showed a significant reduction (P,.1) of photoaging signs after treatment with SCA at day 9 as compared with the same participants at the beginning of the study. The percentage of participants showing fine wrinkles and deep wrinkles decreased gradually and significantly (P,.5) during the treatment. The authors observed a 45.5% decrease in participants showing deep wrinkles after the treatment (11/15 at baseline vs 6/15 at day 9, P5.25) (Figure 1A). The sallow appearance of skin showed a 5% reduction at day 3 (P,.2) and 77.8% at day 9 (P,.8). Loss of cutaneous elasticity also improved very significantly during the treatment (9/15 at baseline; 2/15 at day 3, P,.8 vs baseline; /15 at day 9, P,.3 vs baseline). Dryness and cutaneous roughness disappeared in 86% of patients at day 3 (P,.1) and in 1% of them at the end of the treatment at day 9 (P,.8) (Figure 1B). Finally, irregular pigmentation, which constitutes a frequent sign of photoaged skin, exhibited a 4% decrease at the end of the treatment (P,.1). There was no significant decrease Global Patient Assessment A majority of the participants involved in the study reported a moderate to significant improvement (score52/3) for the individual parameters included in the questionnaire at day 3, which evolved into marked improvement (score53/3) by the end of the study at day 9. The global assessment score was 11/15 at day 3, increasing to 13/15 at day 9. Analysis revealed a statistically significant difference (P,.5) between the total score at days 3 and 9 (Table). Global Researcher Assessment The researcher s perception scores were very similar to those provided by the participants. Assessment of the global score was 11/15 at day 3, improving to 14/15 at day 9, indicating a significant global improvement induced by treatment with SCA. Improvement at day 9 was observed in most of the assessed parameters, especially hydration (P,.3) (Table). Overall, the tolerance and cosmetic acceptance of the treatment with SCA ranged from very good to good. Only Vol. 22 No. 5 may 29 Cosmetic Dermatology 249
4 Significance of the Global Assessment of the Researcher and the Participants on Day 9 Versus Day 3 Smoothness, Hydration, Total Score, P Value P Value P Value Participants Assessment Researcher s Assessment one patient experienced an adverse effect (folliculitis) at day 3, apparently unrelated to the treatment with SCA. In summary, the data reveal a significant correlation between the global opinion of the patient and the researcher (Spearman rank correlation..85; P,.1). Silicon Replica Assessment The mean values for roughness and wrinkle depth were obtained before the initiation of the treatment at baseline and after SCA treatment at day 9 by profilometry. The authors measured the mean distance between the highest peak and the deepest valley of all the profiles assessed for each patient before and after treatment, as well as the differences observed in roughness parameters. These parameters revealed an average 13% improvement in wrinkle depth, but as high as 3% in several participants (Figure 2). A nonparametric statistical test indicated that the improvement was statistically significant (P5.21). Also, an 18% improvement in cutaneous microroughness was observed, reaching 3% in some participants (P5.8). Histopathological Analysis Staining of biopsies of periocular tissue collected at baseline and day 9 showed a marked improvement in the architecture of the dermis and epidermis at the end of treatment (Figure 3). The authors also found a significant reduction in mean [SD] epidermal thickness (64 [4] vs 55 [4]; P5.25) (Figure 3), along with significant increases of the mean [SD] epidermal proliferation index (11 [1] vs 14 [2]; P,.4). On the other hand, there was an apparent reduction of elastosis at the papillary dermis and increases of the A B area percentage occupied by microvessels (P,.2). Finally, the authors also noticed an almost significant increase (P,.75) in the number of mean [SD] blood vessels per mm 2 (5 [1] vs 8 [8]). C Figure 2. Effect of Cryptomphalus aspersa treatment on wrinkle depth assessed by profilometry. Patient before (A) and 9 days after treatment with Cryptomphalus aspersa (B). Corresponding 3-dimensional profilometry photographs, with grading from red (more superficial) to blue (deeper) is used to enhance visualization of the depth of the wrinkles (C, D). D Discussion In this report, the authors have shown preliminary evidence that topical treatment with SCA may reverse some of the features of photoaging. This compound had been previously shown to induce skin regeneration in cases of radiodermatitis. 23 Clinical assessment of the effect of SCA using an arbitrary scale for cutaneous photoaging 16 established the efficacy of SCA in reversing some of the features of photoaging. In addition, profilometry analysis of selected areas of the skin of the patients revealed a positive effect of 25 Cosmetic Dermatology may 29 Vol. 22 No. 5
5 P.25 Epidermal Thickness P.2 Area Occupied by Microvessels, % Beginning After Treatment P.75 Number of Blood Vessels/ mm 2 P.4 Epidermal Proliferation Index Figure 3. Evaluation of the effect of Cryptomphalus aspersa on epidermal thickness, area occupied by microvessels, number of blood vessels/mm 2, and epidermal proliferation index. Biopsies were collected at baseline and day 9. Note the improvement on the appearance of the outer layer of the epidermis, as well as the delineation of the dermal boundary. A marked reduction in epidermal thickness and increase of the area occupied by microvessels, number of blood vessels, and epidermal proliferation index was found after Cryptomphalus aspersa treatment. SCA in the overall roughness of the skin and particularly in wrinkle depth. This is likely due to its antioxidant and matrix-remodelling effect, but contributions from the vehicle components of the secretion cannot be ruled out. The observed improvement in roughness is likely related to improved hydration due to a number of factors, such as replenishment of the skin cellularity and rearrangement of the fibrillar components of the skin. These effects were confirmed using conventional histological techniques. We also observed that continuous use of SCA increased skin thickness and decreased the signs of elastosis, suggesting enhanced skin cell proliferation and rearrangements of the fibrillar components of dermis and epidermis. The beneficial effect of SCA can be direct via its effect on skin cell proliferation and matrix remodeling, or indirect by enhancing vascularization of the skin. Proper blood traffic provide the neighboring tissue with the nutrients and oxygen required for proliferation, thus enhanced irrigation is essential for a rejuvenation effect on photodamaged skin. Other mechanisms to explain the effect of SCA may include a modest inhibition of metalloproteinases expression, activation, or both, which would result in decreased overall degradation of the connective tissue of the skin. 24 The precise mechanism by which SCA induces matrix remodelling is not clear. It can be related to enhanced deposition of extracellular matrix proteins, which would account for thicker lattices; enhanced expression or activation of integrin receptors, as it has been shown for other natural compounds, such as ginseng 3 ; or even activation of contractility pathways such as myosin II, which results in enhanced collagen reorganization. 31 In summary, this study provides preliminary evidence of the potential usefulness of SCA as a photoaging palliative remedy. However, in light of the limitations of the present study, further research including large comparative and placebo-containing, double-blind, randomized studies is required to establish the usefulness of this natural compound in the treatment of photoaging. Acknowledgment This study was supported by a research grant from Industrial Farmaceutica Cantabria SA, Madrid, Spain, of which Salvador González, MD, has a consultant role. The authors also thank Dr. Miguel Vicente-Manzanares, MD, Francisca Rius-Diaz, PhD, and Carmen Rios-Barranquero, RN. References 1. Fisher GJ. The pathophysiology of photoaging of the skin. Cutis. 25;75(suppl 2):5-8; discussion Petersen MJ. Aging of the skin. In: Freinkel RK, Woodley DT, eds. The Biology of the Skin. New York, NY: The Parthenon Publishing Group; 21: Piérard GE. Ageing across the life span: time to think again. J Cosmet Dermatol. 24;3: Piérard GE, Uhoda I, Piérard-Franchimont C. From skin microrelief to wrinkles. an area ripe for investigation. J Cosmet Dermatol. 23;2: Beissert S, Granstein RD. UV-induced cutaneous photobiology. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1996;31: Dalle Carbonare M, Pathak MA. Skin photosensitizing agents and the role of reactive oxygen species in photoaging. J Photochem Photobiol B. 1992;14: Krutmann J, Grewe M. Involvement of cytokines, DNA damage, and reactive oxygen intermediates in ultraviolet radiation-induced modulation of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression. J Invest Dermatol. 1995;15(suppl 1):67S-7S. 8. Wang XY, Bi ZG. UVB-irradiated human keratinocytes and interleukin-1 alpha indirectly increase MAP kinase/ap-1 activation and MMP-1 production in UVA-irradiated dermal fibroblasts. Chin Med J (Engl). 26;119: El-Domyati M, Attia S, Saleh F, et al. Intrinsic aging vs. photoaging: a comparative histopathological, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural study of skin. Exp Dermatol. 22;11: Bhawan J. Assessment of the long-term safety of topical retinoids. Cutis. 25;75(suppl 2): Wulf HC, Sandby-Møller J, Kobayasi T, et al. Skin aging and natural photoprotection. Micron. 24;35: Campisi J. The role of cellular senescence in skin aging. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 1998;3: Al-Baker EA, Oshin M, Hutchison CJ, et al. Analysis of UV-induced damage and repair in young and senescent human dermal fibroblasts using the comet assay. Mech Ageing Dev. 25;126: Naru E, Suzuki T, Moriyama M, et al. Functional changes induced by chronic UVA irradiation to cultured human dermal fibroblasts. Br J Dermatol. 25;153(suppl 2):6-12. Vol. 22 No. 5 may 29 Cosmetic Dermatology 251
6 15. Ma W, Wlaschek M, Tantcheva-Poór I, et al. Chronological ageing and photoageing of the fibroblasts and the dermal connective tissue. Clin Exp Dermatol. 21;26: Glogau RG. Aesthetic and anatomic analysis of the aging skin. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 1996;15: Calderone DC, Fenske NA. The clinical spectrum of actinic elastosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32: Gupta MA, Gilchrest BA. Psychosocial aspects of aging skin. Dermatol Clin. 25;23: Gendler EC. Topical treatment of the aging face. Dermatol Clin. 1997;15: Stern RS. Clinical practice. treatment of photoaging. N Engl J Med. 24;35: Flynn TC, Coleman WP. Topical revitalization of body skin. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2;14: Brieva A, Guerrero A, Pivel JP. Mecanismos bioquímicos y farmacológicos relacionados con la actividad de la secreción de Cryptomphalus aspersa (SCA) (Endocare ) en radiodermitis. Dermatol Cosmet. 21;11: Abad RF. Treatment of experimental radiodermatitis with a regenerative glucoproteic mucopolysaccharide complex. Dermatol Cosmet. 1999;9: Brieva A, Philips N, Tejedor R, et al. Molecular basis for the regenerative properties of a secretion of the mollusk Cryptomphalus aspersa. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 28;21: Glogau RG. Physiologic and structural changes associated with aging skin. Dermatol Clin. 1997;15: Grove GL, Grove MJ, Leyden JJ. Optical profilometry: an objective method for quantification of facial wrinkles. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;21(3 pt 2): Grove GL, Grove MJ, Leyden JJ, et al. Skin replica analysis of photodamaged skin after therapy with tretinoin emollient cream. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991;25(2 pt 1): Urbach F, Forbes PD, Davies RE, et al. Cutaneous photobiology: past, present and future. J Invest Dermatol. 1976;67: Berardesca E, Cameli N, Primavera G, et al. Clinical and instrumental evaluation of skin improvement after treatment with a new 5% pyruvic acid peel. Dermatol Surg. 26;32: Shin JY, Song JY, Yun YS, et al. Immunostimulating effects of acidic polysaccharides extract of Panax ginseng on macrophage function. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 22;24: Meshel AS, Wei Q, Adelstein RS, et al. Basic mechanism of threedimensional collagen fibre transport by fibroblasts. Nat Cell Biol. 25;7: n 252 Cosmetic Dermatology may 29 Vol. 22 No. 5
Non-Ablative Rejuvenation
 Non-Ablative Rejuvenation Denise Baker, MD Non-Ablative Skin Rejuvenation Denise Baker, MD The following potential conflict of interest relationships are germane to my presentation. Intrinsic Aging Inevitably
Non-Ablative Rejuvenation Denise Baker, MD Non-Ablative Skin Rejuvenation Denise Baker, MD The following potential conflict of interest relationships are germane to my presentation. Intrinsic Aging Inevitably
For skin care professionals. Only Obagi
 Only Obagi Young, healthy skin that is smooth, clear, wrinkle-free and firm renews itself every 5 to 6 weeks through a process called cellular turnover. During cellular turnover, the top layer of dead
Only Obagi Young, healthy skin that is smooth, clear, wrinkle-free and firm renews itself every 5 to 6 weeks through a process called cellular turnover. During cellular turnover, the top layer of dead
Multi-Application Platform. Summary of Peer-reviewed Articles for Various Clinical Indications April 2016
 Multi-Application Platform Summary of Peer-reviewed Articles for Various Clinical Indications April 2016 Various Clinical Indications Atrophic acne scars and acne Photo-aged skin, pigmentation & hyperpigmentation
Multi-Application Platform Summary of Peer-reviewed Articles for Various Clinical Indications April 2016 Various Clinical Indications Atrophic acne scars and acne Photo-aged skin, pigmentation & hyperpigmentation
PRODUCT DATA SHEET. Updated: 07/2012 Approved: Dr. Victoria Donat
 PRODUCT DATA SHEET is a Refined Vegetable Oil composition enriched with other ingredients and specifically developed to enhance anti stretch activity. The composition helps to prevent and eliminate stretch
PRODUCT DATA SHEET is a Refined Vegetable Oil composition enriched with other ingredients and specifically developed to enhance anti stretch activity. The composition helps to prevent and eliminate stretch
Frequently Asked Questions
 1112:V15:05:PB1540 Frequently Asked Questions For the use only of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory Dear Doctor, Warm regards from Cipla Xterna!!! We, at Cipla Xterna, a dedicated
1112:V15:05:PB1540 Frequently Asked Questions For the use only of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory Dear Doctor, Warm regards from Cipla Xterna!!! We, at Cipla Xterna, a dedicated
DEBRIDEMENT: ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY. Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations
 DEBRIDEMENT: ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY Epidermal Layers ECM Structure Dermis Structure Skin
DEBRIDEMENT: ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY Epidermal Layers ECM Structure Dermis Structure Skin
REVINAGE. The real bio-retinol
 REVINAGE The real bio-retinol Aging of the world United Nations 2015 Report Aging Who wants to get old? Retinoids o Family of compounds related to vitamin A and its derivatives o They interact with specific
REVINAGE The real bio-retinol Aging of the world United Nations 2015 Report Aging Who wants to get old? Retinoids o Family of compounds related to vitamin A and its derivatives o They interact with specific
SPECIAL TOPIC. Institut National de la Sante et de la Recherche Medicale (INSERM U895), Nice, France c
 November 2011 1260 Volume 10 Issue 1i Copyright 2011 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Journal of Drugs in Dermatology SPECIAL TOPIC A Pilot Study Using Reflectance Confocal Microscopy (RCM) in the Assessment of a Novel
November 2011 1260 Volume 10 Issue 1i Copyright 2011 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Journal of Drugs in Dermatology SPECIAL TOPIC A Pilot Study Using Reflectance Confocal Microscopy (RCM) in the Assessment of a Novel
Ready-to-Use Sphingolipid Solution with Unique Anti-aging Properties
 TEGO Derm CBS Ready-to-Use Sphingolipid Solution with Unique Anti-aging Properties Proven benefits for both chronologically aged and photo-aged skin Smoothes the skin s appearance by reducing deep wrinkles
TEGO Derm CBS Ready-to-Use Sphingolipid Solution with Unique Anti-aging Properties Proven benefits for both chronologically aged and photo-aged skin Smoothes the skin s appearance by reducing deep wrinkles
With beauty consciousness rising, increasing
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histologic Study of Collagen and Stem Cells After Radiofrequency Treatment for Aging Skin YUSUKE YOKOYAMA, MD,* HIROTAKA AKITA, MD, PHD, SEIJI HASEGAWA, PHD, KEI NEGISHI, MD, PHD, HIROHIKO
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histologic Study of Collagen and Stem Cells After Radiofrequency Treatment for Aging Skin YUSUKE YOKOYAMA, MD,* HIROTAKA AKITA, MD, PHD, SEIJI HASEGAWA, PHD, KEI NEGISHI, MD, PHD, HIROHIKO
Evaluation of the wound healing response post deep dermal heating by fractional RF: INTRAcel
 12th symposium of the Association of Korean Dermatologists (2009) 1 Evaluation of the wound healing response post deep dermal heating by fractional RF: INTRAcel Un-Cheol.Yeo, M.D. S&U Dermatologic Clinic,
12th symposium of the Association of Korean Dermatologists (2009) 1 Evaluation of the wound healing response post deep dermal heating by fractional RF: INTRAcel Un-Cheol.Yeo, M.D. S&U Dermatologic Clinic,
BLUEsun INTERNATIONAL
 LPD s Definition They are extremely small vesicles (lower than 300nm) Mainly made of phospholipids The phospholipids are organised in bilayers LPD s Micela Phospholipids in bilayer Phospholipids in monolayer
LPD s Definition They are extremely small vesicles (lower than 300nm) Mainly made of phospholipids The phospholipids are organised in bilayers LPD s Micela Phospholipids in bilayer Phospholipids in monolayer
HYDRACARE LIGHTENING BUSINESS OPPORTUNITY
 HYDRACARE LIGHTENING BUSINESS OPPORTUNITY + + AIMS MORE THAN 99.9 % OF NATURAL ORIGIN HYDRACARE LIGHTENING EVOIL HYDRACARE LIGHTENING showed whitening activity, at 100% concentration, when dosed 4 times
HYDRACARE LIGHTENING BUSINESS OPPORTUNITY + + AIMS MORE THAN 99.9 % OF NATURAL ORIGIN HYDRACARE LIGHTENING EVOIL HYDRACARE LIGHTENING showed whitening activity, at 100% concentration, when dosed 4 times
Thai Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences (TJPS)
 Thai Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences (TJPS) 34 th International Annual Meeting in Pharmaceutical Sciences and 2 nd CU FPhS - RIKEN CDB Symposium (IAMPS34 and 2nd CU FPhS - RIKEN CDB) Photodynamic therapy
Thai Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences (TJPS) 34 th International Annual Meeting in Pharmaceutical Sciences and 2 nd CU FPhS - RIKEN CDB Symposium (IAMPS34 and 2nd CU FPhS - RIKEN CDB) Photodynamic therapy
Treatment of periorbital wrinkles with 1,550 and 1,565 nm Er:Glass fractional photothermolysis lasers: A simultaneous split-face trial
 Treatment of periorbital wrinkles with 1,550 and 1,565 nm Er:Glass fractional photothermolysis lasers: A simultaneous split-face trial Jin Young Jung Department of Medicine The Graduate School, Yonsei
Treatment of periorbital wrinkles with 1,550 and 1,565 nm Er:Glass fractional photothermolysis lasers: A simultaneous split-face trial Jin Young Jung Department of Medicine The Graduate School, Yonsei
Topical tretinoin: its use in daily practice to reverse photoageing
 British Journal of Dermatology (1990) 122, Supplement 35, 87-91. Topical tretinoin: its use in daily practice to reverse photoageing M.T.GOLDFARB, C.N.ELLIS AND J.J.VOORHEES Dermatopharmacology Unit, Department
British Journal of Dermatology (1990) 122, Supplement 35, 87-91. Topical tretinoin: its use in daily practice to reverse photoageing M.T.GOLDFARB, C.N.ELLIS AND J.J.VOORHEES Dermatopharmacology Unit, Department
EVOIL AST PRODUCT DATA SHEET
 PRODUCT DATA SHEET EVOIL AST is a Refined Vegetable Oil composition enriched with other ingredients to enhance anti stretch activity. The composition helps to prevent and eliminate stretch marks and wrinkles.
PRODUCT DATA SHEET EVOIL AST is a Refined Vegetable Oil composition enriched with other ingredients to enhance anti stretch activity. The composition helps to prevent and eliminate stretch marks and wrinkles.
HISTOLOGICAL EVALUATION AFTER RADIOFREQUENCY TREATMENT FOR FACE REJUVENATION AND CELLULITIS
 HISTOLOGICAL EVALUATION AFTER RADIOFREQUENCY TREATMENT FOR FACE REJUVENATION AND CELLULITIS B. Palmieri 1, V. Rottigni 1 Department of General Surgery and Surgical Specialties, University of Modena and
HISTOLOGICAL EVALUATION AFTER RADIOFREQUENCY TREATMENT FOR FACE REJUVENATION AND CELLULITIS B. Palmieri 1, V. Rottigni 1 Department of General Surgery and Surgical Specialties, University of Modena and
identifying & treating Structural Skin Damage
 identifying & treating Structural Skin Damage How Collagen and Elastin are Formed The dermis is comprised of three layers: the papillary dermis, the reticular dermis, and the subcutaneous dermis. The process
identifying & treating Structural Skin Damage How Collagen and Elastin are Formed The dermis is comprised of three layers: the papillary dermis, the reticular dermis, and the subcutaneous dermis. The process
Evaluation of the wound healing response post - deep dermal heating by fractional RF: INTRACEL
 12th symposium of the Association of Korean Dermatologists (2009) 1 Evaluation of the wound healing response post - deep dermal heating by fractional RF: INTRACEL Un-Cheol.Yeo, MD S&U Dermatologic Clinic,
12th symposium of the Association of Korean Dermatologists (2009) 1 Evaluation of the wound healing response post - deep dermal heating by fractional RF: INTRACEL Un-Cheol.Yeo, MD S&U Dermatologic Clinic,
e n ta d i n e Photoprotection Anti-photoaging the most natural way to reinforce skin natural defenses against outdoor and indoor radiations
 eno p r e se rvativ e n ta d i n e Photoprotection Anti-photoaging the most natural way to reinforce skin natural defenses against outdoor and indoor radiations Anti-oxidation Anti-inflammation Anti-immunosuppression
eno p r e se rvativ e n ta d i n e Photoprotection Anti-photoaging the most natural way to reinforce skin natural defenses against outdoor and indoor radiations Anti-oxidation Anti-inflammation Anti-immunosuppression
Photodamaged skin occurs as a result of its
 Plasma Skin Resurfacing for Regeneration of Neck, Chest, and Hands: Investigation of a Novel Device TINA S. ALSTER, MD, AND SAILESH KONDA, BS BACKGROUND Many noninvasive treatments to rejuvenate photodamaged
Plasma Skin Resurfacing for Regeneration of Neck, Chest, and Hands: Investigation of a Novel Device TINA S. ALSTER, MD, AND SAILESH KONDA, BS BACKGROUND Many noninvasive treatments to rejuvenate photodamaged
During the last 20 years, the number of topical
 THERAPEUTICS FOR THE CLINICIAN Cumulative Irritation Potential of Adapalene 0.1% Cream and Gel Compared With Tretinoin Microsphere 0.04% and 0.1% Jonathan S. Dosik, MD; Kenneth Homer, MS; Stéphanie Arsonnaud
THERAPEUTICS FOR THE CLINICIAN Cumulative Irritation Potential of Adapalene 0.1% Cream and Gel Compared With Tretinoin Microsphere 0.04% and 0.1% Jonathan S. Dosik, MD; Kenneth Homer, MS; Stéphanie Arsonnaud
The Need - Skin Barrier Protection. The Need - Skin Biochemical Balance
 NSPS by Asta Technologies, Ltd. The microalgae Porphyridium Cruentum excretes Natural Sulfated Polysaccharides as a protective layer which enables it to flourish even in harsh and extreme conditions. Extensive
NSPS by Asta Technologies, Ltd. The microalgae Porphyridium Cruentum excretes Natural Sulfated Polysaccharides as a protective layer which enables it to flourish even in harsh and extreme conditions. Extensive
STUDY. Tazarotene Cream for the Treatment of Facial Photodamage
 STUDY Tazarotene Cream for the Treatment of Facial Photodamage A Multicenter, Investigator-Masked, Randomized, -Controlled, Parallel Comparison of 0.01%, 0.025%, 0.05%, and 0.1% Tazarotene Creams With
STUDY Tazarotene Cream for the Treatment of Facial Photodamage A Multicenter, Investigator-Masked, Randomized, -Controlled, Parallel Comparison of 0.01%, 0.025%, 0.05%, and 0.1% Tazarotene Creams With
NONABLATIVE RESURFACING
 `AESTHETIC LASER SURGERY 0094-1298/00 $15.00 +.00 NONABLATIVE RESURFACING David J. Goldberg, MD TYPES OF LASERS AND THEIR DIFFERENCES Pulsed char-free CO2 laser skin resurfacing has provided a method of
`AESTHETIC LASER SURGERY 0094-1298/00 $15.00 +.00 NONABLATIVE RESURFACING David J. Goldberg, MD TYPES OF LASERS AND THEIR DIFFERENCES Pulsed char-free CO2 laser skin resurfacing has provided a method of
Aging, Photo damaged Skin
 ARTG No : 278808 Aging, Photo damaged Skin Sagging skin on the neck, decollete, face along with wrinkles and body are common problems associated with aging. RF & ULTRASOUND system is the most commonly
ARTG No : 278808 Aging, Photo damaged Skin Sagging skin on the neck, decollete, face along with wrinkles and body are common problems associated with aging. RF & ULTRASOUND system is the most commonly
3D In Vivo Optical Skin Imaging for Intense Pulsed Light and Fractional Ablative Resurfacing of Photodamaged Skin
 3D In Vivo Optical Skin Imaging for Intense Pulsed Light and Fractional Ablative Resurfacing of Photodamaged Skin Matteo Tretti Clementoni, MD a, *, Rosalia Lavagno, MD a, Maximilian Catenacci, MD b, Roman
3D In Vivo Optical Skin Imaging for Intense Pulsed Light and Fractional Ablative Resurfacing of Photodamaged Skin Matteo Tretti Clementoni, MD a, *, Rosalia Lavagno, MD a, Maximilian Catenacci, MD b, Roman
Foreseen Shield Nopal
 Foreseen Shield Nopal A STORY The Nopal Opuntia ficus indica, Cactaceae A Mexican legendary cactus Born in the centre of Mexico, that cactus with an original shape caracterized by its organization with
Foreseen Shield Nopal A STORY The Nopal Opuntia ficus indica, Cactaceae A Mexican legendary cactus Born in the centre of Mexico, that cactus with an original shape caracterized by its organization with
A Comparison of the Efficacy of Ablative Fractional Laser-assisted Photodynamic Therapy according to the Density of Ablative Laser Channel
 A Comparison of the Efficacy of Ablative Fractional Laser-assisted Photodynamic Therapy according to the Density of Ablative Laser Channel in the Treatment of Actinic Keratosis Yeo-Rye Cho, Jeong-Hwan
A Comparison of the Efficacy of Ablative Fractional Laser-assisted Photodynamic Therapy according to the Density of Ablative Laser Channel in the Treatment of Actinic Keratosis Yeo-Rye Cho, Jeong-Hwan
Natural Active Ingredients From Plant Stem Cells to Preserve Skin Functions
 ISTITUTO DI RICERCHE BIOTECNOLOGICHE Natural Active Ingredients From Plant Stem Cells to Preserve Skin Functions Roberto Dal Toso In-Cosmetics, Barcelona April 18th 2012 QUALITY AND SAFETY OF PLANT ACTIVE
ISTITUTO DI RICERCHE BIOTECNOLOGICHE Natural Active Ingredients From Plant Stem Cells to Preserve Skin Functions Roberto Dal Toso In-Cosmetics, Barcelona April 18th 2012 QUALITY AND SAFETY OF PLANT ACTIVE
EVOLUTIONARY STUDY OF CHRONIC CUTANEOUS MODIFICATIONS CAUSED BY EXPOSURE TO ULTRAVIOLET RADIATIONS IN HAIRLESS MICE
 Analele Universităţii din Oradea, Fascicula: Ecotoxicologie, Zootehnie şi Tehnologii de Industrie Alimentară Vol. XII/B, 2013 EVOLUTIONARY STUDY OF CHRONIC CUTANEOUS MODIFICATIONS CAUSED BY EXPOSURE TO
Analele Universităţii din Oradea, Fascicula: Ecotoxicologie, Zootehnie şi Tehnologii de Industrie Alimentară Vol. XII/B, 2013 EVOLUTIONARY STUDY OF CHRONIC CUTANEOUS MODIFICATIONS CAUSED BY EXPOSURE TO
The Effects of Different Intervals of Microdermabrasion Sessions on Skin Biophysical Parameters: A Randomized, Assessor-Blind, Within-Patient Trial
 Original Article The Effects of Different Intervals of Microdermabrasion Sessions on Skin Biophysical Parameters: A Randomized, Assessor-Blind, Within-Patient Trial Parastoo Davari, MD Farzam Gorouhi,
Original Article The Effects of Different Intervals of Microdermabrasion Sessions on Skin Biophysical Parameters: A Randomized, Assessor-Blind, Within-Patient Trial Parastoo Davari, MD Farzam Gorouhi,
Neena Philips 1 and Salvador Gonzalez Introduction
 ISRN Oxidative Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 257463, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/257463 Research Article Beneficial Regulation of Elastase Activity and Expression of Tissue Inhibitors of
ISRN Oxidative Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 257463, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/257463 Research Article Beneficial Regulation of Elastase Activity and Expression of Tissue Inhibitors of
The energetic skin regenerator
 The energetic skin regenerator Temporary version 04-07-2013 Provides the skin essential activated amino acids issued from hydrolyzed proteins. Unilactamin L-17 is a complex of activated amino acids (AAA)
The energetic skin regenerator Temporary version 04-07-2013 Provides the skin essential activated amino acids issued from hydrolyzed proteins. Unilactamin L-17 is a complex of activated amino acids (AAA)
NOVEL MULTI-SOURCE PHASE-CONTROLLED RADIOFREQUENCY TECHNOLOGY FOR NON- ABLATIVE AND MICRO-ABLATIVE TREATMENT OF WRINKLES, LAX SKIN AND ACNE SCARS
 available at www.jstage.jst.go.jp/browse/islsm REVIEW ARTICLES NOVEL MULTI-SOURCE PHASE-CONTROLLED RADIOFREQUENCY TECHNOLOGY FOR NON- ABLATIVE AND MICRO-ABLATIVE TREATMENT OF WRINKLES, LAX SKIN AND ACNE
available at www.jstage.jst.go.jp/browse/islsm REVIEW ARTICLES NOVEL MULTI-SOURCE PHASE-CONTROLLED RADIOFREQUENCY TECHNOLOGY FOR NON- ABLATIVE AND MICRO-ABLATIVE TREATMENT OF WRINKLES, LAX SKIN AND ACNE
AIVITA Biomedical Root of Skin Product Line. April 2018
 AIVITA Biomedical Root of Skin Product Line April 2018 AIVITA Biomedical Cancer Immunotherapy Technology Current Indications Mechanism Of Action Autologous Dendritic Cells Loaded With Tumor-Associated
AIVITA Biomedical Root of Skin Product Line April 2018 AIVITA Biomedical Cancer Immunotherapy Technology Current Indications Mechanism Of Action Autologous Dendritic Cells Loaded With Tumor-Associated
Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide
 Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide Actinic keratosis is a very common lesion that you will see in your day-to-day practice. First, let me explain the name Actinic keratosis. It means keratosis
Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide Actinic keratosis is a very common lesion that you will see in your day-to-day practice. First, let me explain the name Actinic keratosis. It means keratosis
Available online at Vol. 07, No. 02, pp , February, 2018 RESEARCH ARTICLE
 z Available online at http://www.ijcrls.com International Journal of Current Research in Life Sciences Vol. 07, No. 02, pp.1139-1143, February, 2018 ISSN: 2319-9490 RESEARCH ARTICLE THE TREATMENT OF DILATED
z Available online at http://www.ijcrls.com International Journal of Current Research in Life Sciences Vol. 07, No. 02, pp.1139-1143, February, 2018 ISSN: 2319-9490 RESEARCH ARTICLE THE TREATMENT OF DILATED
V. 1 STEP BY STEP TO PERFECTLY EVEN SKIN TONE
 V. 1 STEP BY STEP TO PERFECTLY EVEN SKIN TONE BRIGHT AND EVEN SKIN TONE NEED Aesthetic models of most cultures involve presenting an even skin tone. Hyperpigmented areas or dark spots appear as signs of
V. 1 STEP BY STEP TO PERFECTLY EVEN SKIN TONE BRIGHT AND EVEN SKIN TONE NEED Aesthetic models of most cultures involve presenting an even skin tone. Hyperpigmented areas or dark spots appear as signs of
Histopathology: skin pathology
 Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
A broad spectrum high-spf photostable sunscreen with a high UVA-PF can protect against cellular damage at high UV exposure doses
 Photodermatology, Photoimmunology & Photomedicine ORIGINAL ARTICLE A broad spectrum high-spf photostable sunscreen with a high UVA-PF can protect against cellular damage at high UV exposure doses Curtis
Photodermatology, Photoimmunology & Photomedicine ORIGINAL ARTICLE A broad spectrum high-spf photostable sunscreen with a high UVA-PF can protect against cellular damage at high UV exposure doses Curtis
In-vivo histopathological study of YouLaser MT interaction with the skin. A laser device emitting combined 1540 and nm wavelengths.
 Histology report No. 02/04-12, date April 2nd, 2012 Page 1 In-vivo histopathological study of YouLaser MT interaction with the skin. A laser device emitting combined 1540 and 10600 nm wavelengths. Paolo
Histology report No. 02/04-12, date April 2nd, 2012 Page 1 In-vivo histopathological study of YouLaser MT interaction with the skin. A laser device emitting combined 1540 and 10600 nm wavelengths. Paolo
Long-term exposure to UV radiation results
 Restorative esthetic Therapy Retrospective Evaluation of the Long-term ntiaging Effects of roadand Light Therapy Patrick itter Jr, MD; Jason Pozner, MD roadand Light (L), which utilizes visible and infrared
Restorative esthetic Therapy Retrospective Evaluation of the Long-term ntiaging Effects of roadand Light Therapy Patrick itter Jr, MD; Jason Pozner, MD roadand Light (L), which utilizes visible and infrared
Mamofillin New aesthetic perspective
 New aesthetic perspective info@ White adipose tissue (WAT) White adipose tissue (WAT) is the prevalent type in human adults functioning as the major storage site for the lipids absorbed from daily intake
New aesthetic perspective info@ White adipose tissue (WAT) White adipose tissue (WAT) is the prevalent type in human adults functioning as the major storage site for the lipids absorbed from daily intake
Effects of Infrared Radiation on Skin Photo-Aging and Pigmentation
 Yonsei Medical Journal Vol. 47, No. 4, pp. 485-490, 2006 Effects of Infrared Radiation on Skin Photo-Aging and Pigmentation Ju Hee Lee, Mi Ryung Roh, and Kwang Hoon Lee Department of Dermatology and Cutaneous
Yonsei Medical Journal Vol. 47, No. 4, pp. 485-490, 2006 Effects of Infrared Radiation on Skin Photo-Aging and Pigmentation Ju Hee Lee, Mi Ryung Roh, and Kwang Hoon Lee Department of Dermatology and Cutaneous
mesotherapy solutions by
 mesotherapy solutions by meso.prof is a comprehensive range of solutions and specific active substances in sterile ampoules for transcutaneous use. This is a range of effective, versatile, safe products,
mesotherapy solutions by meso.prof is a comprehensive range of solutions and specific active substances in sterile ampoules for transcutaneous use. This is a range of effective, versatile, safe products,
THE EFFECTS OF REPEATED SUB-ERYTHEMAL EXPOSURES OF UVR ON HUMAN IMMUNITY
 THE EFFECTS OF REPEATED SUB-ERYTHEMAL EXPOSURES OF UVR ON HUMAN IMMUNITY Joanna Narbutt Department of Dermatology Medical University of Lodz, Lodz, Poland Photoimmunosuppression ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION DNA
THE EFFECTS OF REPEATED SUB-ERYTHEMAL EXPOSURES OF UVR ON HUMAN IMMUNITY Joanna Narbutt Department of Dermatology Medical University of Lodz, Lodz, Poland Photoimmunosuppression ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION DNA
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB. Friday, February 13, :30 am 11:00 am
 MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB Friday, February 13, 2009 9:30 am 11:00 am FACULTY COPY GOALS: Describe the basic clinical and morphologic features of various
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB Friday, February 13, 2009 9:30 am 11:00 am FACULTY COPY GOALS: Describe the basic clinical and morphologic features of various
Study the Effects of Exposing the Skin and Eyes of Mice to Ultraviolet-C Radiation
 International Journal of Research Studies in Biosciences (IJRSB) Volume 4, Issue 11, November 2016, PP 8-14 ISSN 2349-0357 (Print) & ISSN 2349-0365 (Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2349-0365.0411002
International Journal of Research Studies in Biosciences (IJRSB) Volume 4, Issue 11, November 2016, PP 8-14 ISSN 2349-0357 (Print) & ISSN 2349-0365 (Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2349-0365.0411002
B. Incorrect! The ectoderm does not produce the dermis. C. Incorrect! The dermis is derived from the mesoderm.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 04: The Integumentary System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. From the inner cell
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 04: The Integumentary System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. From the inner cell
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB. Friday, February 12, :30 am 11:00 am
 MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB Friday, February 12, 2012 9:30 am 11:00 am FACULTY COPY GOALS: Describe the basic clinical and morphologic features of various
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB Friday, February 12, 2012 9:30 am 11:00 am FACULTY COPY GOALS: Describe the basic clinical and morphologic features of various
PROFESSIONAL SKIN NEEDLING
 Smoother skin with fewer lines & wrinkles Younger healthier looking skin Brighter more vibrant skin PROFESSIONAL SKIN NEEDLING Treatment of the year Product innovation of the year Make a change to your
Smoother skin with fewer lines & wrinkles Younger healthier looking skin Brighter more vibrant skin PROFESSIONAL SKIN NEEDLING Treatment of the year Product innovation of the year Make a change to your
45 min. Name Assoc Prof presenter Bill McGuiness PhD, RN, FAWMA. xx College Month of 201x Science, Health & Engineering
 45 min Title Skin integrity of presentation the cellular level? Name Assoc Prof presenter Bill McGuiness PhD, RN, FAWMA Title Head of of presenter School School / of Faculty Nursing / Division & Midwifery
45 min Title Skin integrity of presentation the cellular level? Name Assoc Prof presenter Bill McGuiness PhD, RN, FAWMA Title Head of of presenter School School / of Faculty Nursing / Division & Midwifery
The Integumentary System: An Overview
 The Integumentary System: An Overview Functions: Protective covering Helps regulate body temperature Retards water loss from deeper tissues Houses sensory receptors Synthesizes biochemicals Excretes small
The Integumentary System: An Overview Functions: Protective covering Helps regulate body temperature Retards water loss from deeper tissues Houses sensory receptors Synthesizes biochemicals Excretes small
Type IV collagen and laminin staining patterns in benign
 J Clin Pathol 1989;42:1173-1177 Type IV collagen and laminin staining patterns in benign and malignant cutaneous lesions RONA M MacKIE, D B CLELLAND, CHRISTINE J SKERROW From the Department ofdermatology,
J Clin Pathol 1989;42:1173-1177 Type IV collagen and laminin staining patterns in benign and malignant cutaneous lesions RONA M MacKIE, D B CLELLAND, CHRISTINE J SKERROW From the Department ofdermatology,
From the Standpoint of Dermatology
 [ Document Identification Number : DIN01022812 ] Digital Color Imaging in Biomedicine, 67-72, 2001.02.28 Toshihiko NUMAHARA *1 (numahara@kms.ac.jp)
[ Document Identification Number : DIN01022812 ] Digital Color Imaging in Biomedicine, 67-72, 2001.02.28 Toshihiko NUMAHARA *1 (numahara@kms.ac.jp)
An Efficacy Study of 3 Commercially Available Hydroquinone 4% Treatments for Melasma
 An Efficacy Study of 3 Commercially Available Hydroquinone 4% Treatments for Melasma Pearl E. Grimes, MD Melasma is a common disorder of hyperpigmentation typically characterized by relatively symmetric
An Efficacy Study of 3 Commercially Available Hydroquinone 4% Treatments for Melasma Pearl E. Grimes, MD Melasma is a common disorder of hyperpigmentation typically characterized by relatively symmetric
Matrix-Degrading Metalloproteinases in Photoaging
 REVIEW Taihao Quan 1, Zhaoping Qin 1,2, Wei Xia 1,2, Yuan Shao 1, John J. Voorhees 1 and Gary J. Fisher 1 radiation from the sun impacts skin health adversely through complex, multiple molecular pathways.
REVIEW Taihao Quan 1, Zhaoping Qin 1,2, Wei Xia 1,2, Yuan Shao 1, John J. Voorhees 1 and Gary J. Fisher 1 radiation from the sun impacts skin health adversely through complex, multiple molecular pathways.
Fractional CO 2 Laser Skin Resurfacing for the Treatment of Sun-Damaged Skin and Actinic Keratoses COS DERM
 Case Report Fractional CO 2 Laser Skin Resurfacing for the Treatment of Sun-Damaged Skin and Actinic Keratoses LindaSusan Marcus, MD; Neal Carlin, BS; Robert Carlin, BS, MA It is important to realize that
Case Report Fractional CO 2 Laser Skin Resurfacing for the Treatment of Sun-Damaged Skin and Actinic Keratoses LindaSusan Marcus, MD; Neal Carlin, BS; Robert Carlin, BS, MA It is important to realize that
Protection from photodamage by topical application of caffeine after ultraviolet irradiation
 PHOTOBIOLOGY DOI 1.1111/j.1365-2133.27.7812.x Protection from photodamage by topical application of caffeine after ultraviolet irradiation S-W. Koo, S. Hirakawa,* S. Fujii, M. Kawasumi and P. Nghiem Cutaneous
PHOTOBIOLOGY DOI 1.1111/j.1365-2133.27.7812.x Protection from photodamage by topical application of caffeine after ultraviolet irradiation S-W. Koo, S. Hirakawa,* S. Fujii, M. Kawasumi and P. Nghiem Cutaneous
CLINICAL EVALUATION REPORT ON THE EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF THE CORE SYSTEM FOR FACIAL ENHANCEMENT TREATMENTS
 CLINICAL EVALUATION REPORT ON THE EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF THE CORE SYSTEM FOR FACIAL ENHANCEMENT TREATMENTS BACKGROUND Efforts to improve fractional ablative laser systems have led to the development of
CLINICAL EVALUATION REPORT ON THE EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF THE CORE SYSTEM FOR FACIAL ENHANCEMENT TREATMENTS BACKGROUND Efforts to improve fractional ablative laser systems have led to the development of
Morphologic and histochemical changes in the skin of patients with scleroderma
 Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2007, 48(4):361 367 ORIGINAL PAPER Morphologic and histochemical changes in the skin of patients with scleroderma GABRIELA IEREMIA 1), M. RAICA 2), ANCA MARIA
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2007, 48(4):361 367 ORIGINAL PAPER Morphologic and histochemical changes in the skin of patients with scleroderma GABRIELA IEREMIA 1), M. RAICA 2), ANCA MARIA
STUDY. Connective Tissue Remodeling Induced by Carbon Dioxide Laser Resurfacing of Photodamaged Human Skin
 STUDY Connective Tissue Remodeling Induced by Carbon Dioxide Laser Resurfacing of Photodamaged Human Skin Jeffrey S. Orringer, MD; Sewon Kang, MD; Timothy M. Johnson, MD; Darius J. Karimipour, MD; Ted
STUDY Connective Tissue Remodeling Induced by Carbon Dioxide Laser Resurfacing of Photodamaged Human Skin Jeffrey S. Orringer, MD; Sewon Kang, MD; Timothy M. Johnson, MD; Darius J. Karimipour, MD; Ted
Oral isotretinoin in photoaging: clinical and histopathological evidence of efficacy of an off-label indication
 JEADV ISSN 1468-3083 Blackwell Publishing Ltd Oral isotretinoin in photoaging: clinical and histopathological evidence of efficacy of an off-label indication RM Rabello-Fonseca,* DR Azulay, RR Luiz, CA
JEADV ISSN 1468-3083 Blackwell Publishing Ltd Oral isotretinoin in photoaging: clinical and histopathological evidence of efficacy of an off-label indication RM Rabello-Fonseca,* DR Azulay, RR Luiz, CA
Summary. Introduction. Bruce M Freedman, MD, FACS
 Original Contribution Blackwell Publishing ORIGINAL Inc CONTRIBUTION Hydradermabrasion: an innovative modality for nonablative facial rejuvenation Bruce M Freedman, MD, FACS Plastic Surgery Associates
Original Contribution Blackwell Publishing ORIGINAL Inc CONTRIBUTION Hydradermabrasion: an innovative modality for nonablative facial rejuvenation Bruce M Freedman, MD, FACS Plastic Surgery Associates
Yeast Essence Skin Care Actives. Yeast Essence C90 Yeast Essence E100 Yeast Essence N80 Yeast Essence Z20. Angel Yeast Co., Ltd.
 Yeast Essence Skin Care Actives Yeast Essence C90 Yeast Essence E100 Yeast Essence N80 Yeast Essence Z20 Angel Yeast Co., Ltd. Yeast Essence C90 Proposed INCI name: Sodium carboxymethyl beta glucan, water
Yeast Essence Skin Care Actives Yeast Essence C90 Yeast Essence E100 Yeast Essence N80 Yeast Essence Z20 Angel Yeast Co., Ltd. Yeast Essence C90 Proposed INCI name: Sodium carboxymethyl beta glucan, water
Unit 4 The Integumentary System
 Unit 4 The Integumentary System I. Classification of Body Membranes A. Epithelial Membranes (3) 1. Cutaneous Membrane > Stratified Squamous > Sits on Dense Connective Tissue > Skin: Epidermis & Dermis
Unit 4 The Integumentary System I. Classification of Body Membranes A. Epithelial Membranes (3) 1. Cutaneous Membrane > Stratified Squamous > Sits on Dense Connective Tissue > Skin: Epidermis & Dermis
Peeling. Smooth out the skin. Remove the outer skin layers. Erase the fine wrinkles. The regenerated skin is smoother & Less wrinkled - Renewed
 If you foolishly ignore beauty, you will soon find yourself without it. Your life will be impoverished. But if you wisely invest in beauty, it will remain with you all the days of your life Frank Lloyd
If you foolishly ignore beauty, you will soon find yourself without it. Your life will be impoverished. But if you wisely invest in beauty, it will remain with you all the days of your life Frank Lloyd
PHOTOTHERAPY: WHAT DO WE KNOW AND HOW DOES IT WORK? Suite 3/36 O'Riordan Street Alexandria, Sydney NSW Australia
 PHOTOTHERAPY: WHAT DO WE KNOW AND HOW DOES IT WORK? Suite 3/36 O'Riordan Street Alexandria, Sydney NSW Australia 2015 02 8331 8933 info@infinity-led.com.au DOCTORATE IN HEALTH SCIENCE DEAKIN UNIVERSITY
PHOTOTHERAPY: WHAT DO WE KNOW AND HOW DOES IT WORK? Suite 3/36 O'Riordan Street Alexandria, Sydney NSW Australia 2015 02 8331 8933 info@infinity-led.com.au DOCTORATE IN HEALTH SCIENCE DEAKIN UNIVERSITY
Arisa Ortiz, MD Director, Laser and Cosmetic Dermatology Assistant Clinical Professor Department of Dermatology UC San Diego
 1 What s New in Skin Tightening? Arisa Ortiz, MD Director, Laser and Cosmetic Dermatology Assistant Clinical Professor Department of Dermatology UC San Diego 2 Disclosures BTL, InMode, Sciton Equipment
1 What s New in Skin Tightening? Arisa Ortiz, MD Director, Laser and Cosmetic Dermatology Assistant Clinical Professor Department of Dermatology UC San Diego 2 Disclosures BTL, InMode, Sciton Equipment
TCA 35% for Actinic Keratoses. Emily C Keller MD, FAAD Annual AAD Meeting 2019
 TCA 35% for Actinic Keratoses Emily C Keller MD, FAAD Annual AAD Meeting 2019 DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Emily C Keller, MD F116 Superficial, Medium, and Deep Chemical Peeling and Relevance
TCA 35% for Actinic Keratoses Emily C Keller MD, FAAD Annual AAD Meeting 2019 DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Emily C Keller, MD F116 Superficial, Medium, and Deep Chemical Peeling and Relevance
Abrupt Intralesional Color Change on Dermoscopy as a New Indicator of Early Superficial Spreading Melanoma in a Japanese Woman
 Published online: June 24, 2015 1662 6567/15/0072 0123$39.50/0 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported license (CC BY-NC)
Published online: June 24, 2015 1662 6567/15/0072 0123$39.50/0 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported license (CC BY-NC)
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System
 Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
Daryl Mossburg, BSN RN Clinical Specialist Sciton, Inc.
 Daryl Mossburg, BSN RN Clinical Specialist Sciton, Inc. What is Halo? Indications for Use Physics/Science Patient Selection & Contraindications Treatment Overview & Guidelines Halo Technology/System Overview
Daryl Mossburg, BSN RN Clinical Specialist Sciton, Inc. What is Halo? Indications for Use Physics/Science Patient Selection & Contraindications Treatment Overview & Guidelines Halo Technology/System Overview
Luisant Mela X Free from AGEs-Induced Epidermal Pigmentation
 Free from -Induced Epidermal Pigmentation Find plant extract solution with NEW APPROACH TO FIGHT AGAINST MELANOGENESIS Skin Pigmentation Many people have been striving to obtain lighter, brighter and healthier-looking
Free from -Induced Epidermal Pigmentation Find plant extract solution with NEW APPROACH TO FIGHT AGAINST MELANOGENESIS Skin Pigmentation Many people have been striving to obtain lighter, brighter and healthier-looking
Assisting diagnosis of melanoma through the noninvasive biopsy of skin lesions
 Assisting diagnosis of melanoma through the noninvasive biopsy of skin lesions Symon D Oyly Cotton Ela Claridge School of Computer Science, The University of Birmingham Birmingham B15 2TT, UK Per Hall
Assisting diagnosis of melanoma through the noninvasive biopsy of skin lesions Symon D Oyly Cotton Ela Claridge School of Computer Science, The University of Birmingham Birmingham B15 2TT, UK Per Hall
Chapter 21: FotoFacial RF Pro Treatment of Specific Clinical Subtypes
 Chapter 21: FotoFacial RF Pro Treatment of Specific Clinical Subtypes 1. Erythema in Skin Types 1-3 (with or without Flushing, Laxity and Wrinkles) using the SR/SRA Head 116 The program usually takes 5-7
Chapter 21: FotoFacial RF Pro Treatment of Specific Clinical Subtypes 1. Erythema in Skin Types 1-3 (with or without Flushing, Laxity and Wrinkles) using the SR/SRA Head 116 The program usually takes 5-7
AN EX VIVO STUDY OF THE REGEN TRIPOLLAR RF DEVICE USING AN EXPERIMENTAL HUMAN SKIN MODEL
 An English translation of the article published in Nouvelles Dermatologiques 2008; 28:331-332 AN EX VIVO STUDY OF THE REGEN TRIPOLLAR RF DEVICE USING AN EXPERIMENTAL HUMAN SKIN MODEL S. Boisnic, Dermatologist,
An English translation of the article published in Nouvelles Dermatologiques 2008; 28:331-332 AN EX VIVO STUDY OF THE REGEN TRIPOLLAR RF DEVICE USING AN EXPERIMENTAL HUMAN SKIN MODEL S. Boisnic, Dermatologist,
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
Research Article Cytological Evaluation of Hyaluronic Acid on Wound Healing Following Extraction
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS DENTAL SCIENCE Research Article Cytological Evaluation of Hyaluronic Acid on Wound Healing Following Extraction Gocmen Gokhan 1 *, Gonul O 1, Oktay NS 2, Pisiriciler R 2 and Goker
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS DENTAL SCIENCE Research Article Cytological Evaluation of Hyaluronic Acid on Wound Healing Following Extraction Gocmen Gokhan 1 *, Gonul O 1, Oktay NS 2, Pisiriciler R 2 and Goker
Breakthrough Innovations from SkinMedica
 Breakthrough Innovations from SkinMedica Jeanine Downie, MD Director Image Dermatology, Montclair, NJ 1 SOLAR RADIATION IS MORE THAN JUST UV! 400 760 100 1x10 6 wavelength (nm) Most sunscreens only provide
Breakthrough Innovations from SkinMedica Jeanine Downie, MD Director Image Dermatology, Montclair, NJ 1 SOLAR RADIATION IS MORE THAN JUST UV! 400 760 100 1x10 6 wavelength (nm) Most sunscreens only provide
Fucoreverse. An anti-ageing glyconutrient for sensitive skin 100 % ISO for natural cosmetic. natural. origin
 Fucoreverse An anti-ageing glyconutrient for sensitive skin IS 16128 for natural cosmetic 100 % natural origin TE UNIQUE CMPSITIN Fucose - An anti-ageing glyconutrient The unique composition of Fucoreverse
Fucoreverse An anti-ageing glyconutrient for sensitive skin IS 16128 for natural cosmetic 100 % natural origin TE UNIQUE CMPSITIN Fucose - An anti-ageing glyconutrient The unique composition of Fucoreverse
Tissue repair. (3&4 of 4)
 Tissue repair (3&4 of 4) What will we discuss today: Regeneration in tissue repair Scar formation Cutaneous wound healing Pathologic aspects of repair Regeneration in tissue repair Labile tissues rapid
Tissue repair (3&4 of 4) What will we discuss today: Regeneration in tissue repair Scar formation Cutaneous wound healing Pathologic aspects of repair Regeneration in tissue repair Labile tissues rapid
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS
 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS Integumentary System Cutaneous membrane Epidermis (5-layers) made up of epithelial tissue only Dermis (2-layers) contains connective tissue, vessels,
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS Integumentary System Cutaneous membrane Epidermis (5-layers) made up of epithelial tissue only Dermis (2-layers) contains connective tissue, vessels,
Reducing the appearance of photo-damaged skin
 Technical Information Phytosphingosine SLC Reducing the appearance of photo-damaged skin Intended use Skin care Benefits at a glance Helps to reduce the appearance of photodamaged skin Stregthens the dermal-epidermal
Technical Information Phytosphingosine SLC Reducing the appearance of photo-damaged skin Intended use Skin care Benefits at a glance Helps to reduce the appearance of photodamaged skin Stregthens the dermal-epidermal
Laser Skin Rejuvenation
 Laser Skin Rejuvenation Laser resurfacing, which is also known as laser peeling, is an effective facial rejuvenation technique that can produce long-lasting results. Over time, factors such as sun damage,
Laser Skin Rejuvenation Laser resurfacing, which is also known as laser peeling, is an effective facial rejuvenation technique that can produce long-lasting results. Over time, factors such as sun damage,
High Power CO2 Laser + Micro-needle Fractional RF
 High Power CO2 Laser + Micro-needle Fractional RF Micro-needle RF Gynolaser (Optional) CO2 Laser What is Fraxis Duo? Fraxis Duo combines CO2 laser and micro-needle fractional RF technology for optimal
High Power CO2 Laser + Micro-needle Fractional RF Micro-needle RF Gynolaser (Optional) CO2 Laser What is Fraxis Duo? Fraxis Duo combines CO2 laser and micro-needle fractional RF technology for optimal
Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function.
 Chapter 5 Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function. Explain the basis for different skin colors. Describe the structure
Chapter 5 Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function. Explain the basis for different skin colors. Describe the structure
Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System. Integumentary System. Page 1
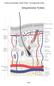 Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System Integumentary System Page 1 Have a very clear understanding of the each particular tissue and their unique functions in each layer of the
Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System Integumentary System Page 1 Have a very clear understanding of the each particular tissue and their unique functions in each layer of the
Dermoscopy: Recognizing Top Five Common In- Office Diagnoses
 Dermoscopy: Recognizing Top Five Common In- Office Diagnoses Vu A. Ngo, DO Department of Family Medicine and Dermatology Choctaw Nation Health Services Authority Learning Objectives Introduction to dermoscopy
Dermoscopy: Recognizing Top Five Common In- Office Diagnoses Vu A. Ngo, DO Department of Family Medicine and Dermatology Choctaw Nation Health Services Authority Learning Objectives Introduction to dermoscopy
1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) i. Organ of the Integument. Connective Tissues. Epithelial Tissues
 Integumentary System 1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) A. Integumentary System i. Organ of the Integument a. Tissues Connective Tissues * Tissue / Location Relationships
Integumentary System 1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) A. Integumentary System i. Organ of the Integument a. Tissues Connective Tissues * Tissue / Location Relationships
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1
 Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
JUST SEE ME! PIGMENTATION SOLUTIONS FOR HIGHER FITZPATRICKS
 1 2 3 JUST SEE ME! PIGMENTATION SOLUTIONS FOR HIGHER FITZPATRICKS Just See Me! Diversity AESTHETICS Training! 20+ years! Advanced Aesthetics Diversity Consultant and Trainer! Professional Speaker! Aesthetic
1 2 3 JUST SEE ME! PIGMENTATION SOLUTIONS FOR HIGHER FITZPATRICKS Just See Me! Diversity AESTHETICS Training! 20+ years! Advanced Aesthetics Diversity Consultant and Trainer! Professional Speaker! Aesthetic
This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur.
 Background Knowledge Functions of normal skin Background Knowledge This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur. Learning
Background Knowledge Functions of normal skin Background Knowledge This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur. Learning
Actinic keratosis (AK) is the most common precancerous
 Confocal laser microscopic imaging of actinic keratoses in vivo: A preliminary report David Aghassi, MD, R. Rox Anderson, MD, and Salvador González, MD Boston, Massachusetts Background: Real-time near-infrared
Confocal laser microscopic imaging of actinic keratoses in vivo: A preliminary report David Aghassi, MD, R. Rox Anderson, MD, and Salvador González, MD Boston, Massachusetts Background: Real-time near-infrared
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs
 Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Asian skin rejuvenation with PicoFractional laser
 Asian skin rejuvenation with PicoFractional laser Krystle Wang, MD Photoaging of the Skin Skin aging is a culmination of genetic and environmental factors and is largely influenced by the cumulative damage
Asian skin rejuvenation with PicoFractional laser Krystle Wang, MD Photoaging of the Skin Skin aging is a culmination of genetic and environmental factors and is largely influenced by the cumulative damage
GP4G. Diguanosine Tetraphosphate. ISP Vincience Global Skin Research Center
 GP4G Diguanosine Tetraphosphate ISP Vincience Global Skin Research Center 1 655, Route du Pin Montard -B.P. 212-06904 Sophia Antipolis Cedex France - Tel: (33) -4 92 94 16 06 - Fax: (33) -4 92 94 16 00
GP4G Diguanosine Tetraphosphate ISP Vincience Global Skin Research Center 1 655, Route du Pin Montard -B.P. 212-06904 Sophia Antipolis Cedex France - Tel: (33) -4 92 94 16 06 - Fax: (33) -4 92 94 16 00
Lipout. Burns stored fat and achieves centimetric reduction BODY SCULPTURE
 April 14 Burns stored fat and achieves centimetric reduction » The modern lifestyle Stress Sedentism Unbalanced diet EXCESS FAT + CELLULITE » How to remove excess fat and cellulite? The fatty tissue is
April 14 Burns stored fat and achieves centimetric reduction » The modern lifestyle Stress Sedentism Unbalanced diet EXCESS FAT + CELLULITE » How to remove excess fat and cellulite? The fatty tissue is
