International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018,
|
|
|
- Gregory Lee
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018, ISSN (O) X (P) HISTOMORPHOLOGY OF SKIN EPIDERMIS OF CATTLE BREEDS OF MAHARASHTRA IN DIFFERENT CLIMATIC CONDITION R.U. Rohankar, J, Y. Waghaye, P.N. Thakur and P.J. Kapadnis Department of Veterinary Anatomy, College of Veterinary and Animal Science MAFSU, Parbhani (M.S.) Abstract: The present study was conducted on skin samples of 4 6 years of age healthy Deoni, Red kandhari, Dangi and Gaolao breeds of cattle managed under hygienic conditions on farm in different regions of Maharashtra. The skin samples, 10 of each breed were obtained surgically from loin region during winter and summer seasons separately. The epidermis was comprised of four sub layers namely stratum corneum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum and stratum basale from outside in. The stratum granulosum was two cell layers in thickness in Gaolao cattle during both seasons, whereas it was single cell layer in thickness in other cattle breeds. The thickness of stratum corneum and epidermis was found more during winter season in all cattle breeds. The melanocytes and Langerhans cells were distributed among cells of stratum basale and stratum spinosum. The density of melanin pigmentation was more in basal epidermal region and was reduced towards the superficial part of epidermis. The epidermal pegs were the down growth of epidermis in the underlying dermis. The average numbers of epidermal pegs varied significantly among breeds as per climatic and geographic conditions. Keywords: Histology, Epidermis, cattle Breeds, Climatic condition. Material and Methods The present study was conducted in the Department of Veterinary Anatomy and Histology, College of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Parbhani (M.S.). The experiment was carried out on 40 female cattle of 4 6 years of age belonging to different breeds located in different regions of Maharashtra state during winter (November - February) and summer (March June) seasons, separately. The skin samples, 10 of each were obtained from loin region of healthy Deoni, Red kandhari, Gaolao and Dangi breeds of cattle, managed under hygienic conditions on the farm in different regions of Maharashtra state. Tissue pieces of 5 mm size were cut to preserve in following fixatives for the histomorphological study % Neutral buffered formalin 2. 10% formalin 3. Bouin s fluid After fixation, tissues were washed in running tap water for overnight. These were then processed for routine paraffin technique. The tissues were first passed through ascending Received Aug 4, 2018 * Published Oct 2, 2018 *
2 1672 R.U. Rohankar, J, Y. Waghaye, P.N. Thakur and P.J. Kapadnis grades of alcohol, cleared in xylene, infiltrated in three changes of paraffin (melting point C) and then embedded in paraffin by employing manual tissue processing schedule suggested by Drury and Wallington (1980). The longitudinal and transverse tissue sections of 4 to 5 μ thickness were obtained on manually operated rotary microtome. The sections were mounted on glass slides and dried at room temperature for 24 hours and were preserved carefully for staining. The following staining methods were used for histomorphological studies. a) Harri s Haematoxylin and Eosin stain for normal histoarchitectural study (Mukharjee, 1992). b) Van Gieson s stain for collagen fibers (Singh and Sulochana, 1996). c) Masson s trichrome method for collagen fibers (Luna, 1968). d) Silver impregnation stain for Reticular fibers (Mukherjee, 1992). e) Wilder s method for reticulin (Luna, 1968). f) Verhoeff s stain for elastic fibers (Mukharjee, 1992). g) Crossman s modification of Mallory s triple stain for collagen and elastic fibers (Singh and Sulochana, 1996). h) Periodic acid Schiff s (PAS) stain for carbohydrate like glycogen, mucin and reticulin (Mukharjee, 1992). The following micrometrical recordings were taken under simple microscope by micrometer scale after caliberation at 10X (1μ = graduations) and 40 X power (1μ = 3.30 graduation) magnifications. 1. Thickness of the stratum corneum (μm). 2. Thickness of the epidermis including stratum corneum (μm). 3. Number of Epidermal pegs per cm2 of skin 4. Intensity of the melanin pigment The numbers of epidermal peg, cm2 was obtained by using formula of Benjamin et al. (1970). The data collected was subjected to the statistical analysis as per the standard procedure suggested by Panse and Sukhatme (1967). Results and Discussion Epidermis was the outer most layer of skin composed of stratified squamous keratinized epithelium. It was found to be consisted of four layer viz. stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum and stratum corneum from inward to outward. However, stratum
3 Histomorphology of Skin Epidermis of Cattle Breeds of 1673 lucidum and vasculature was found absent in epidermis in all breeds of cattle during both seasons under present study (Plate 1). In agreement with the findings of Hole et al. (2008) in Red Kandhari cow and Aslan et al. (2004) in Zavot breed of cattle, the skin epidermis was stratified squamous type and composed of four sublayers viz. stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum and stratum corneum. Epidermal stratum lucidum was absent which was in contrast to the reports of Nagaraju et al. (2012), though the latter did not mention the region of presence of this sublayer. Akers and Denbow (2008), Monteiro-Riviere (2007) and Samuelson (2007) in domestic animals reported that skin epidermis was of stratified squamous keratinized type. However, they mentioned the presence of stratum lucidum along with other epidermal sub layers. This difference with their reports may be due to their general histomorphological consideration on skin of domestic animals as they did not describe the region wise skin characteristics. Stratum basale was the inner most epidermal layer, close to dermis. It was composed of single row of cuboidal to columnar cells with darkly stained oval or spherical nuclei, resting on the basement membrane. Sections stained by reticulin and PAS stain showed distinct reticular lamina of the basement membrane (Plate and ). The long axis of lining cells of this layer was oriented perpendicularly to the basement membrane. The cells of this layer showed mitotic figure in great extent in both seasons and breeds under present study. These observations of the present study are in lines with findings reported by Hole et al. (2008) in Red Kandhari cow. Monteiro-Riviere (2007) and Samuelson (2007) reported similar organization and morphology of cells of stratum basale in domestic animals. The melanocytes were observed as rounded cells with darkly stained spherical to elongated nuclei and pale cytoplasm scattered chiefly in between cells of stratum basale. The cytoplasm of melanocyte showed melanin granules, which were concentrated either on periphery or supranuclear in position. The mitotic activity was recorded among these cells (Plate 2). The melanocytes were also found in small extent scattered in between the stratum spinosum cells with considerably more amount of melanin granules as compared to the melanocyte of stratum basale in all breeds and seasons. Bloom and Fawcett (1971) stated that Langerhans cells in skin sections stained with gold chloride appeared blackened and revealed as stellate or dendritic cells. As gold chloride, one of component of Wilders method for reticulin stain, the Langerhans cells in sections stained by wilders method for reticulin during present study
4 1674 R.U. Rohankar, J, Y. Waghaye, P.N. Thakur and P.J. Kapadnis exhibited similar morphology. These cells appeared as blackened cells and revealed as stellate or dendritic cells with processes extending in spaces among other surrounding cells of stratum basale and stratum spinosum (Plate 3) in all breeds and seasons. In accordance with the observations recorded by Monteiro-Riviere (2007) and Samuelson (2007) in domestic animals, the presence of melanocytes and Langerhans cells in the basal region of the epidermis was revealed. The stratum spinosum was the next layer above the stratum basale was usually found to be composed of two to three layers of oval to polyhedral cells with fairly stained nuclei. The cytoplasm showed melanin granules. Few melanocytes as well as Langerhan s cells were also observed scatter within cells of stratum spinosum layer in all breeds and seasons studied. This observation corroborates with the reports made by Hole et al. (2008) in Red Kandhari cow. Akers and Denbow (2008), Monteiro-Riviere (2007) and Samuelson (2007) in domestic animals reported similar observations regarding the morphology of cells of stratum spinosum. However, number of cell layers in this stratum reported by them varied from the numbers of cell layers of stratum spinosum in present study. This variation may be attributed to species variation. Stratum granulosum was single cell layer in thickness in Deoni, Red Kandhari and Dangi, whereas it was two cell layers in thickness in Gaolao breed of cattle in both the seasons. The cells of this stratum were elongated to flattened in morphology with basophilic granular cytoplasm. However, many times their nuclei appeared indistinct because of abundant melanin granules in cytoplasm. The long axis of these cells was found aligned parallel to surface of skin. Similar observation was reported by Hole et al. (2008). They reported that stratum granulosum was single layer in thickness in Red Kandhari cow. However, two rows of stratum granulosum cells in Gaolao breed of cattle may be attributed to breed difference. The cells of stratum granulosum consist of protein filled keratohyaline granules that promotes cross linking of keratin, hydration and helps to prevent fluid loss from the body. This might be the reason for presence of two layers of stratum granulosum cells in epidermis of Gaolao cattle as this breed belongs to more hot climatic condition of Vidarbha region of Maharashtra as compared to other breeds of cattle under present study. Thus, two layers of stratum granulosum cells in epidermis of Gaolao cattle enables to prevent fluid loss from the body in hot climatic condition. Stratum corneum was the outer most epidermal layer consisted of two to four layers of keratinized flattened cells in all breeds of cattle during summer season. However, it was
5 Histomorphology of Skin Epidermis of Cattle Breeds of 1675 found to be composed of four to five cell layers in thickness during winter season in all breeds. In winter season, keratinized cells of stratum corneum were found loose and quite separated from each other (Plate -4). The cells of this layer were arranged parallel or slightly oblique in direction to the skin surface with pyknotic or absence of nuclei in all breeds and seasons, in present study. In agreement with the observations recorded of Hole et al. (2008), similar range of cell layers were recorded in stratum corneum in Red Kandhari cattle. Similar morphological observations were also made by Monteiro-Riviere (2007) and Samuelson (2007) in domestic animals. They reported that the stratum corneum was the upper most epidermal layer composed of keratinized dead cells. Increase in number of cell layers of stratum corneum during winter season might be correlated either to protect lower layers of skin from cold climatic condition or to xerosis of skin during winter season that prevents sloughing of superficial dead cells. During present work, the melanin pigment was found distributed in the epidermis in all breeds of cattle. It was intensely distributed in the stratum basale and stratum spinosum layer of epidermis. However, intensity of melanin pigment was less in stratum granulosun and stratum corneum layer. It was noticed that, melanin pigment distribution was more in Deoni and Red Kandhari breeds of cattle. It was found less in epidermis of Gaolao cattle as compared to other breeds of cattle. During present work, no seasonal variation in distribution of melanin pigment within different layer of epidermis was noticed in all breeds of cattle. Epidermal pegs were the down growths of epidermis in to the underlying dermis. However, the number of cell layers of each epidermal stratum except stratum basale was found more at the region of epidermal pegs in all breeds and seasons in present study. The mean values of average thickness of stratum corneum are presented in table 1. In the present study, the average thickness of stratum corneum during summer season was ± 0.34 μm, 9.19 ± 0.61 μm, 11.7 ± 0.39 μm and ± 0.49 μm, whereas, during winter season it was found ± 0.36 μm, ± 0.29 μm, ± 0.29 μm and ± 0.11 μm in Deoni, Red Kandhari, Dangi and Gaolao breed of cattle, respectively. A significant increase in thickness of stratum corneum was recorded during winter season in all breed of cattle. The present observations are in agreement with Saxena et al. (1994) who reported increase in thickness of stratum corneum during winter season in JFL and FJL cross breds cattle.
6 1676 R.U. Rohankar, J, Y. Waghaye, P.N. Thakur and P.J. Kapadnis Among breeds, average values of thickness of stratum corneum showed non-significant difference during summer season, whereas significantly different during winter season. However, non-significant difference was observed between Deoni and Dangi cattle during winter season. In the present investigation, the average thickness of stratum corneum in all breeds of cattle except Red Kandhari cattle is observed to be higher than the thickness of stratum corneum of skin from back region in adult Gir cow as reported by Bhayani and Vyas (1991). Similarly, the average thickness of stratum corneum of Deoni cattle in both seasons and other breeds of cattle in summer season is within the range of reports made by Mugale and Bhosle (2002) in female Deoni cattle. However, in contrary to present observation they claimed decrease in thickness of stratum corneum during winter season. This variation in thickness of stratum corneum may be attributed to difference in breed and climatic conditions. The increase in thickness of stratum corneum in winter season may be due to xerosis of skin during this season that may prevent the sloughing of superficial cells. The mean values of average epidermal thickness are presented in table 2. The average thickness of epidermis during summer season was ± 1.09 μm, ± 0.89 μm, ± 2.09 μm and ± 0.73 μm. Whereas, during winter season, it was ± 0.82 μm, ± 0.82 μm, ± 0.62 μm and ± 0.56 μm in Deoni, Red Kandhari, Dangi and Gaolao breeds of cattle, respectively. These recordings showed significant increase in the thickness of epidermis during winter season in all breeds of cattle. In the present study, the thickness of epidermis in Gaolao cattle differs significantly from other breeds of cattle during summer season. The values of average epidermal thickness during winter season showed significant difference among the breeds. However, non-significant variation was observed between Deoni and Red Kandhari cattle and between Dangi and Gaolao cattle in winter season. During the present work, the average thickness of epidermis in all breeds of cattle except Gaolao cattle during summer season is within the range of reports made by Bhayani and Vyas (1991) in dorsal body region of Gir cattle. The variation in epidermal thickness between Gir and Gaolao cattle may be due to breed or seasonal difference. Similarly, the thickness of epidermis during summer season in all breeds of cattle in present study is within the range reported by Saxena et al. (1994) in JFL and FJL cross breed cattle during summer season, whereas the thickness of epidermis recorded by them during winter season in both crossbreed cattle was found lower than the thickness of epidermis recorded during winter season in all breeds of cattle under present study. However, in support to the
7 Histomorphology of Skin Epidermis of Cattle Breeds of 1677 present observations they stated that epidermis was significantly thinner during summer than winter season. The average thickness of epidermis recorded in all breeds of cattle and season during present work is found to be lower than the epidermal thickness reported by Mugale and Bhosle (2002b) in skin of Deoni cattle at mid side body region, Hole et al. (2008) in Red Kandhari cow, Aslan et al. (2004) in Zavot breed of cattle, Muralidharan and Ramesh (2005) in Sindhi, Jersey and Jersey X. Sindhi cross cow and Wang et al. (2012) in Thai native cow irrespective of age, body region and season. This variation in thickness of epidermis may be attributed to age, body region, seasonal variation and breed differences. Table 1: Mean and SE of thickness of stratum corneum in the skin during summer and winter season in Deoni, Red Kandhari, Dangi and Gaolao cattle Thickness of stratum corneum (μm) Season Deoni Red Kandhari Dangi Gaolao Summer ± ± ± ± 0.49 Winter B1 ± C1 ± B1 ± A1 ± 0.11 Table 2: Mean and SE of epidermal thickness of the skin summer and winter various seasons in Deoni, Red Kandhari, Dangi and Gaolao cattle Thickness of epidermis (μm) Season Deoni Red Kandhari Dangi Gaolao Summer B2 ± B2 ± B2 ± A2± 0.73 Winter B1 ± B1 ± A1 ± A1 ± 0.56
8 1678 R.U. Rohankar, J, Y. Waghaye, P.N. Thakur and P.J. Kapadnis PLATE 1: Photomicrograph showing epidermis of Deoni cattle during summer season A. Basement membrane B. Stratum basale C. Stratum spinosum D. Stratum granulosum E. Stratum corneum F. Melanocytes G. Langerhans cell H. Melanin pigment (Haematoxylin and Eosin, X 1000) PLATE 2: Photomicrograph showing epidermis of Gaolao cattle during winter season A. Basement membrane B. Stratum basale G. Langerhans cell C. Stratum spinosum D. Stratum granulosum H. Melanin pigment E. Stratum corneum F. Melanocytes (Haematoxylin and Eosin, X 1000)
9 Histomorphology of Skin Epidermis of Cattle Breeds of 1679 PLATE 3: Photomicrograph of skin of Deoni cattle during summer season Arrow showing Langerhans cells in epidermis. A. Reticular lamina of basement membrane (Wilder s method for reticulin, X 1000) PLATE 4: Photomicrograph showing epidermis of Deoni cattle during winter season A. Basement membrane B. Stratum basale C. Stratum spinosum D. Stratum granulosum E. Stratum corneum F. Melanocytes G. Langerhans cell H. Melanin pigment (Haematoxylin and Eosin, X 1000)
10 1680 R.U. Rohankar, J, Y. Waghaye, P.N. Thakur and P.J. Kapadnis Literature cited [1] Akers, R.M. and D.M. Denbow [2008]: Integumentary system. In: Anatomy and Physiology of Domestic Animals, Blackwell Publishing Asia, Australia, pp [2] Aslan, S., Kocamis, H., Gulmez, N. and M. Nah [2004]: Histological and histometrical studies on the skin of Zavot breed cattle. Indian Vet. J., 81: [3] Benjamin, B.R., Stringam, E.W and R.J. Parker [1970]: Some skin characteristics.of snorter dwarfism in the bovine. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 50: [4] Bhayani, D.M and K.N. Vyas [1991]: The age and regional differences of several characterstics in Gir cattle (Bos indicus). Indian Vet. J., 68: [5] Bloom, W. and D.W. Fawcett [1971]: Skin. In: A Textbook of Histology, Igaku Shoin Ltd., Tokyo, pp [6] Drury, R.A.B. and E.A. Wallington [1980]: Carleton s Histological Technique. 5th Edn., Oxford University Press, New York. [7] Hole, M.B., Bhosle, N.S. and P.J. Kapadnis [2008]: Histological study of skin epidermis in Red Kandhari cows. Indian J. Anim. Res., 42 [1]: [8] Luna (1968): Manual of Histological Staining Methods of the Armed Forces of Institute of Pathology, 3rd Edn, The Blackistone Div. McGrow Hill Book Co., New York. [9] Monteirio-Riviere, N.A. [2007]: Integument. In: Dellman s Text Book of Veterinary Histology. Ed. Eurell, J.A. and B.L. Frappier, 6th Edn. Blackwell Publishing Asia, Australia, pp [10] Mugale, R.R. and N.S. Bhosle [2002b]: Thickness of epidermis in Deoni cattle. Indian Vet. J., 79: [11] Mukherjee, K.L. [1992]: Medical laboratory technology, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Co.Ltd., New Delhi., 3, pp [12] Muralidharan, M. R. and V. Ramesh [2005]: Histological and biochemical studies of the skin of cattle and buffalo. Indian J. Anim. Res., 39 [1]: [13] Nagaraju, C.S., Prasad, R.V., Jamuna, K.V. and V. Ramkrishna [2012]: Histomorphological features in the differentiation of skin of spotted deer (Axis axis), Cattle (Bos indicus) and goat (Capra hircus). Indian J. Vet. Anat., 24 [1]: [14] Panse, U.G. and P.V. Sukhatme [1967]: Stastistical methods for agricultural workers. ICAR, New Delhi. [15] Samuelson, D.A. [2007]: Integument. In: Textbook of Veterinary Histology, Saunder Elsevier, Missouri, pp
11 Histomorphology of Skin Epidermis of Cattle Breeds of 1681 [16] Saxena, S.K., Malik, M.R. and H.K.B. Parekh [1994]: Skin characters of crossbred cattle and physiological adaptation: Skin thickness. Indian J. Anim. Sci., 64 [5]: [17] Singh, U.B. and S. Sulochana [1996]: Handbook of Histological and Histochemical Technique, 1st Edn, Premier Publishing House, Hyderabad, pp [18] Wang, J., Katawatin, S., Suklerd, S. and P. Pongthaisong [2012]: Skin morphology of Thai native cattle. Khon. Kaen. Agr. J., 40 [2]:
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018, 1608 1614 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMPARATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES OF DUEODENUM IN CATTLE SHEEP AND GOATS Thete
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018, 1608 1614 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMPARATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES OF DUEODENUM IN CATTLE SHEEP AND GOATS Thete
by authors and SVSBT.
 The Indian Journal of Veterinary Sciences & Biotechnology (2018) Volume 13, Issue 4, 20-25 ISSN (Print) : 2394-0247 : ISSN (Print and online) : 2395-1176, abbreviated as IJVSBT 10.21887/ijvsbt.v13i4.11553
The Indian Journal of Veterinary Sciences & Biotechnology (2018) Volume 13, Issue 4, 20-25 ISSN (Print) : 2394-0247 : ISSN (Print and online) : 2395-1176, abbreviated as IJVSBT 10.21887/ijvsbt.v13i4.11553
****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM ******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM ******************************************************************************************************
Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9
 Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9 Skin (Integument) Consists of skin and associated derivatives Largest organ of body (21 ft 2 ; 9 lbs.; has 11 miles of blood vessels) Functions: Protection
Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9 Skin (Integument) Consists of skin and associated derivatives Largest organ of body (21 ft 2 ; 9 lbs.; has 11 miles of blood vessels) Functions: Protection
Integumentary System. Integumentary System
 1. General aspects a. The integumentary system consists of several organs major organ of the system is the skin other organs are relatively small and they can be considered as specialized structures of
1. General aspects a. The integumentary system consists of several organs major organ of the system is the skin other organs are relatively small and they can be considered as specialized structures of
INTEGUMENTARY 1-Epidermis, 2-Dermis, Structure of thick and thin skin I- Epidermis . Stratum basale
 INTEGUMENTARY The skin (integument, cutis ) and its derivatives constitute the integumentary system. It form the external covering of the body and is the largest organ of the body. The skin consists of
INTEGUMENTARY The skin (integument, cutis ) and its derivatives constitute the integumentary system. It form the external covering of the body and is the largest organ of the body. The skin consists of
Histopathology: skin pathology
 Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histological Features of the Renal Arteries in Indian Goat (Capra hircus)
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 04 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.704.271
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 04 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.704.271
Skin. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
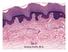 Skin Kristine Krafts, M.D. Skin Lecture Objectives Describe the functions of skin. Describe the structure, location and function of the cell types found in epidermis: keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans
Skin Kristine Krafts, M.D. Skin Lecture Objectives Describe the functions of skin. Describe the structure, location and function of the cell types found in epidermis: keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans
Microscopic Anatomy of Inferior Medullary Velum Of Cerebellum
 32 J Anat. Soc. India 51(1) 32-34 (2002) Microscopic Anatomy of Of Cerebellum Arora, N.K. Department of Anatomy, Government Medical College, Chandigarh INDIA. Abstract. A study of the inferior medullary
32 J Anat. Soc. India 51(1) 32-34 (2002) Microscopic Anatomy of Of Cerebellum Arora, N.K. Department of Anatomy, Government Medical College, Chandigarh INDIA. Abstract. A study of the inferior medullary
2/5/2019. Organ System: Skin or Integumentary System. Hypodermis (or superficial fascia) Integumentary System - Learn and Understand
 Integumentary System - Learn and Understand Skin is an organ comprised of all four tissues Each layer of the skin contributes to one or more of its numerous functions Skin is both strong and flexible Keratinization
Integumentary System - Learn and Understand Skin is an organ comprised of all four tissues Each layer of the skin contributes to one or more of its numerous functions Skin is both strong and flexible Keratinization
Micromorphological Observations on the Ductular System of Mammary Gland in Sheep During Various Age Groups
 Micromorphological Observations on the Ductular System of Mammary Gland in Sheep During Various Age Groups S. Paramasivan*, Geetha Ramesh, S. Ushakumary, A. Kumaravel, O.R. Sathyamoorthy, and S. Sivagnanam
Micromorphological Observations on the Ductular System of Mammary Gland in Sheep During Various Age Groups S. Paramasivan*, Geetha Ramesh, S. Ushakumary, A. Kumaravel, O.R. Sathyamoorthy, and S. Sivagnanam
Histology, Histochemistry and Scanning Electron Microscopy of Tonsil of the Soft Palate of the Young Pigs
 VETERINARY RESEARCH INTERNATIONAL Journal homepage: www.jakraya.com/journal/vri ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histology, Histochemistry and Scanning Electron Microscopy of Tonsil of the Soft Palate of the Young Pigs
VETERINARY RESEARCH INTERNATIONAL Journal homepage: www.jakraya.com/journal/vri ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histology, Histochemistry and Scanning Electron Microscopy of Tonsil of the Soft Palate of the Young Pigs
Behzad Mobini* Islamic Azad University, Shahrekord Branch, Shahrekord, Iran. Received: 25 October 2010, Accepted: 4 January 2011
 Original Article Veterinary Research Forum Vol: 2, No: 1, March, 2011, 25-29 Histological Studies on Pancreas of Goose (Anser Albifrons) Behzad Mobini* * Department of Anatomical Sciences, Faculty of Veterinary
Original Article Veterinary Research Forum Vol: 2, No: 1, March, 2011, 25-29 Histological Studies on Pancreas of Goose (Anser Albifrons) Behzad Mobini* * Department of Anatomical Sciences, Faculty of Veterinary
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad. Lab 1
 Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
Chapter 5: The Integumentary System - Introduction and Epidermis
 Chapter 5: The Integumentary System - Introduction and Epidermis The Integument Means Covering Composed: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands The Integument Thickness 1.5 4 mm (or more) Weight 9 11
Chapter 5: The Integumentary System - Introduction and Epidermis The Integument Means Covering Composed: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands The Integument Thickness 1.5 4 mm (or more) Weight 9 11
Biometrical, Histological and Histochemical Studies on Omasum of Gaddi Sheep
 DOI: 10.30954/2277-940X.2018.00150.20 Journal of Animal Research: v.8 n.1, p. 125-129. February 2018 Biometrical, Histological and Histochemical Studies on Omasum of Gaddi Sheep Shabir Ahmad Malik 1*,
DOI: 10.30954/2277-940X.2018.00150.20 Journal of Animal Research: v.8 n.1, p. 125-129. February 2018 Biometrical, Histological and Histochemical Studies on Omasum of Gaddi Sheep Shabir Ahmad Malik 1*,
PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT OF EXOCRINE PANCREAS IN CROSSBRED GOATS: A HISTOLOGICAL STUDY
 Original Research Article PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT OF EXOCRINE PANCREAS IN CROSSBRED GOATS: A HISTOLOGICAL STUDY A.R. Sreeranjini * 1, N. Ashok 2. ABSTRACT Back ground: Studies about the normal development
Original Research Article PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT OF EXOCRINE PANCREAS IN CROSSBRED GOATS: A HISTOLOGICAL STUDY A.R. Sreeranjini * 1, N. Ashok 2. ABSTRACT Back ground: Studies about the normal development
Ch 5: Integumentary System
 Ch 5: Integumentary System You gotta have skin; All you really need is skin. Skin's the thing, that if you've got it outside, It helps keep your insides in. Alan Sherman (1924-1973) Developed by John Gallagher,
Ch 5: Integumentary System You gotta have skin; All you really need is skin. Skin's the thing, that if you've got it outside, It helps keep your insides in. Alan Sherman (1924-1973) Developed by John Gallagher,
Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS
 Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. epidermis b. dermis c. hypodermis d. adipose tissue e. hair f. sebaceous gland g. sweat gland 2. a Pre-Lab
Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. epidermis b. dermis c. hypodermis d. adipose tissue e. hair f. sebaceous gland g. sweat gland 2. a Pre-Lab
Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System. Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system
 Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system Skin is the body s largest and heaviest organ making up 15% of body weight. Most skin is 1 to
Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system Skin is the body s largest and heaviest organ making up 15% of body weight. Most skin is 1 to
ALL PHOTOS ARE IDENTIFIED IN THE LOWER RIGHT CORNER WITH THE MAGNIFICATION POWER THAT THE PHOTO WAS TAKEN WITH. SCAN - THIS IS A VERY LOW POWER IMAGE
 ALL PHOTOS ARE IDENTIFIED IN THE LOWER RIGHT CORNER WITH THE MAGNIFICATION POWER THAT THE PHOTO WAS TAKEN WITH. SCAN - THIS IS A VERY LOW POWER IMAGE THAT WE USE WHEN A SAMPLE IS SO BIG THAT YOU CAN T
ALL PHOTOS ARE IDENTIFIED IN THE LOWER RIGHT CORNER WITH THE MAGNIFICATION POWER THAT THE PHOTO WAS TAKEN WITH. SCAN - THIS IS A VERY LOW POWER IMAGE THAT WE USE WHEN A SAMPLE IS SO BIG THAT YOU CAN T
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis PHL 212 1 Function
The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis PHL 212 1 Function
of Ciliary body, Iris and Irido-corneal angle in Adult Marwari Goat (Capra hircus) R. K. Barhaiyaa *, Malsawmkima, D. M. Bhayani and Y. L.
 DHR International Journal Of Biomedical and Life Sciences (DHR-IJBLS) ISSN 2278-8301, Vol.5(3), 2014 Available online http://www.doublehelixresearch.com/dhrijbls Double Helix Research Original Article
DHR International Journal Of Biomedical and Life Sciences (DHR-IJBLS) ISSN 2278-8301, Vol.5(3), 2014 Available online http://www.doublehelixresearch.com/dhrijbls Double Helix Research Original Article
Light and scanning electron microscopic studies on the rumen of goat (Capra hircus)
 VETERINARY RESEARCH INTERNATIONAL Journal homepage: www.jakraya.com/journal/vri ORIGINAL ARTICLE Light and scanning electron microscopic studies on the rumen of goat (Capra hircus) Mahesh R, Gurdial Singh
VETERINARY RESEARCH INTERNATIONAL Journal homepage: www.jakraya.com/journal/vri ORIGINAL ARTICLE Light and scanning electron microscopic studies on the rumen of goat (Capra hircus) Mahesh R, Gurdial Singh
CHAPTER. V SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS. during postnatal period and to provide elasticity during prenatal and early
 CHAPTER. V SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS The present study was conducted on 40 samples, each of thymus and Spleen of goat from prenatal to four months and above age. The small pieces from each thymus and spleen
CHAPTER. V SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS The present study was conducted on 40 samples, each of thymus and Spleen of goat from prenatal to four months and above age. The small pieces from each thymus and spleen
The Integumentary System: An Overview
 The Integumentary System: An Overview Functions: Protective covering Helps regulate body temperature Retards water loss from deeper tissues Houses sensory receptors Synthesizes biochemicals Excretes small
The Integumentary System: An Overview Functions: Protective covering Helps regulate body temperature Retards water loss from deeper tissues Houses sensory receptors Synthesizes biochemicals Excretes small
Ex. 7: Integumentary
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2401 Ex. 7: Integumentary. Skin or Integument Consists of three major regions Epidermis outermost superficial region Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia)
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2401 Ex. 7: Integumentary. Skin or Integument Consists of three major regions Epidermis outermost superficial region Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia)
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 3, 2017,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 3, 2017, 2132 2136 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) HISTOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON INTESTINAL LYMPHOID TISSUES IN KADAKNATH BREED OF POULTRY
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 3, 2017, 2132 2136 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) HISTOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON INTESTINAL LYMPHOID TISSUES IN KADAKNATH BREED OF POULTRY
Histology: Epithelial tissue
 Histology: Epithelial tissue Epithelial Tissue is presented in two forms: 1. Covering Epithelia: 2. Glandular Epithelia: 1. Simple Epithelium: contain only one layer of cells. 2. Stratified Epithelium:
Histology: Epithelial tissue Epithelial Tissue is presented in two forms: 1. Covering Epithelia: 2. Glandular Epithelia: 1. Simple Epithelium: contain only one layer of cells. 2. Stratified Epithelium:
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. Body Membranes & Skin
 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
Ch 4. Skin and Body Membranes
 Ch 4 Skin and Body Membranes TITLE HISTOLOGY SLIDES & NOTES ESSENTIAL QUESTION What tissues compose the integumentary system? Stratified Squamous Epithelium Stratified = several layers; Squamous = shape
Ch 4 Skin and Body Membranes TITLE HISTOLOGY SLIDES & NOTES ESSENTIAL QUESTION What tissues compose the integumentary system? Stratified Squamous Epithelium Stratified = several layers; Squamous = shape
B. Incorrect! The ectoderm does not produce the dermis. C. Incorrect! The dermis is derived from the mesoderm.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 04: The Integumentary System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. From the inner cell
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 04: The Integumentary System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. From the inner cell
ACTIVITY 2: HISTOLOGY AND INTEGUMENT
 ACTIVITY 2: HISTOLOGY AND INTEGUMENT Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 4 and 5, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify each tissue (26 tissues)
ACTIVITY 2: HISTOLOGY AND INTEGUMENT Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 4 and 5, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify each tissue (26 tissues)
BI 121 LAB. WEEK 2: Tissues (continued); Integumentary System
 BI 121 LAB 2-1 WEEK 2: Tissues (continued); Integumentary System This week you will 1) Review the four major tissue types 2) Review the characteristics of epithelial tissues. 3) Learn the major characteristics
BI 121 LAB 2-1 WEEK 2: Tissues (continued); Integumentary System This week you will 1) Review the four major tissue types 2) Review the characteristics of epithelial tissues. 3) Learn the major characteristics
Histology of Skin. dr. Alya Amila Fitrie, M.Kes dr. Radita Nur Anggraeni Department of Histology Medical Faculty University of North Sumatera 2008
 Histology of Skin dr. Alya Amila Fitrie, M.Kes dr. Radita Nur Anggraeni Department of Histology Medical Faculty University of North Sumatera 2008 1 INTRODUCTION The heaviest single organ of the body, 16%
Histology of Skin dr. Alya Amila Fitrie, M.Kes dr. Radita Nur Anggraeni Department of Histology Medical Faculty University of North Sumatera 2008 1 INTRODUCTION The heaviest single organ of the body, 16%
Chapter 5. Integumentary System 5-1
 Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Structures that are part of the integument Skin Hair Nails Glands Overview of Functions Protection Sensation Temperature regulation Vitamin D production Excretion Immunity
Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Structures that are part of the integument Skin Hair Nails Glands Overview of Functions Protection Sensation Temperature regulation Vitamin D production Excretion Immunity
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 6
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 6
Histology of Integumentary System
 Histology of Integumentary System CONTENT / Topics Integumentary System Skin, thick - Major Layers Epidermis Dermis Hair Skin, hairy and Hair Follicle Sebaceous Glands Sebaceous Gland Sweat Glands Merocrine
Histology of Integumentary System CONTENT / Topics Integumentary System Skin, thick - Major Layers Epidermis Dermis Hair Skin, hairy and Hair Follicle Sebaceous Glands Sebaceous Gland Sweat Glands Merocrine
4 Skin and Body Membranes Study Guide
 Name: SKIN AND BODY MEMBRANES: 4 Skin and Body Membranes Study Guide Period: Body membranes, which cover body surfaces, line its cavities, and form protective sheets around organs, fall into two major
Name: SKIN AND BODY MEMBRANES: 4 Skin and Body Membranes Study Guide Period: Body membranes, which cover body surfaces, line its cavities, and form protective sheets around organs, fall into two major
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio 101 Laboratory 3. Epithelial Tissues and Integument
 Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Chapter 5: Integumentary System
 Chapter 5: Integumentary System I. Overview of the Integumentary System A. List the five major functions of the integumentary system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Il. Skin A. Epidermis 1. The epidermis consists of 2.
Chapter 5: Integumentary System I. Overview of the Integumentary System A. List the five major functions of the integumentary system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Il. Skin A. Epidermis 1. The epidermis consists of 2.
Histology, Histochemistry and Scanning Electron Microscopy of Lingual Tonsil of Young Pigs
 VETERINARY RESEARCH INTERNATIONAL Journal homepage: www.jakraya.com/journal/vri ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histology, Histochemistry and Scanning Electron Microscopy of Lingual Tonsil of Young Pigs Ranjit, Pawan
VETERINARY RESEARCH INTERNATIONAL Journal homepage: www.jakraya.com/journal/vri ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histology, Histochemistry and Scanning Electron Microscopy of Lingual Tonsil of Young Pigs Ranjit, Pawan
ALAEZI CM 1 *, ADISA JO 2, OKOROCHI EC 3 and OKECHI OO 4
 Global Journal of Scientific Researches Available online at gjsr.blue-ap.org 2014 GJSR Journal. Vol. 2(2), pp. 51-55, 28 February, 2014 E-ISSN: 2311-732X METHYL GREEN PYRONIN: A PROGRESSIVE NUCLEAR STAIN
Global Journal of Scientific Researches Available online at gjsr.blue-ap.org 2014 GJSR Journal. Vol. 2(2), pp. 51-55, 28 February, 2014 E-ISSN: 2311-732X METHYL GREEN PYRONIN: A PROGRESSIVE NUCLEAR STAIN
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs
 Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Histochemical and histological studies on the pancreas in mature pigeon (Columba Livia)
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2013, 3(2):148-152 ISSN: 2248 9215 CODEN (USA): EJEBAU Histochemical and histological studies on the pancreas
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2013, 3(2):148-152 ISSN: 2248 9215 CODEN (USA): EJEBAU Histochemical and histological studies on the pancreas
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 5 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 5 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1
 Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio211 Laboratory 2. Epithelial and Connective Tissues
 Bio211 Laboratory 2 Epithelial and Connective Tissues 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue (p. 79 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Connective Tissue (p. 93 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Muscle/Nervous
Bio211 Laboratory 2 Epithelial and Connective Tissues 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue (p. 79 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Connective Tissue (p. 93 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Muscle/Nervous
11/8/2012. Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Skin = Integument = Cutaneous Membrane. The Structure of Skin. Epidermis
 Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System
 Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
Chapter 4 Opener Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Opener Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary glands The skin is the most visible organ of the body Clinicians can tell a lot about
Chapter 4 Opener Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary glands The skin is the most visible organ of the body Clinicians can tell a lot about
Cell Types in Epidermis
 Epidermis Stratified, squamous keratinized epithelium Appendages hair follicles nails sweat glands sebaceous glands mammary glands Dermis Dense, irregular connective tissue Hypodermis Superficial fascia
Epidermis Stratified, squamous keratinized epithelium Appendages hair follicles nails sweat glands sebaceous glands mammary glands Dermis Dense, irregular connective tissue Hypodermis Superficial fascia
Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes
 Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes I. Body Membranes A. Function of body membranes 1. Cover body surfaces 2. Line body cavities 3. Form protective sheets around organs II. Classification of Body Membranes
Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes I. Body Membranes A. Function of body membranes 1. Cover body surfaces 2. Line body cavities 3. Form protective sheets around organs II. Classification of Body Membranes
DEBRIDEMENT: ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY. Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations
 DEBRIDEMENT: ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY Epidermal Layers ECM Structure Dermis Structure Skin
DEBRIDEMENT: ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY Epidermal Layers ECM Structure Dermis Structure Skin
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System Overview Functions 1. Protection 2. Excretion of wastes 3. Maintenance of T b 4. Synthesis of vitamin D 3 5. Storage of lipids 6. Detection of sensory stimuli Epidermis Tissue types
Integumentary System Overview Functions 1. Protection 2. Excretion of wastes 3. Maintenance of T b 4. Synthesis of vitamin D 3 5. Storage of lipids 6. Detection of sensory stimuli Epidermis Tissue types
Histochemical Studies of Pancreas in Prenatal Goat (Capra hircus)
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 1163-1169 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.144
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 1163-1169 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.144
HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES ON THE ADRENAL GLAND OF HORSE
 Indo-Am. J. Agric. & Vet. Sci., 2016 ISSN Prasanth 2321 9602 Babu www.iajavs.com A et al., 2016 Vol. 4, No. 1, February 2016 2016 Meghana Publications. All Rights Reserved Research Paper HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES
Indo-Am. J. Agric. & Vet. Sci., 2016 ISSN Prasanth 2321 9602 Babu www.iajavs.com A et al., 2016 Vol. 4, No. 1, February 2016 2016 Meghana Publications. All Rights Reserved Research Paper HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
ACTIVITY 2: HISTOLOGY AND INTEGUMENT
 ACTIVITY 2: HISTOLOGY AND INTEGUMENT Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 4 and 5, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify each tissue (26 tissues)
ACTIVITY 2: HISTOLOGY AND INTEGUMENT Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 4 and 5, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify each tissue (26 tissues)
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system (See if you can name some appendages) A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep
The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system (See if you can name some appendages) A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep
PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT OF THE CRANIAL MENINGES IN GOATS *
 Indian J. Anim. Res., 42 (1) : 23-28, 2008 PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT OF THE CRANIAL MENINGES IN GOATS * K. M. Lucy, K.R. Harshan 1, J.J. Chungath and N. Ashok 2 Department of Veterinary Anatomy and Histology,
Indian J. Anim. Res., 42 (1) : 23-28, 2008 PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT OF THE CRANIAL MENINGES IN GOATS * K. M. Lucy, K.R. Harshan 1, J.J. Chungath and N. Ashok 2 Department of Veterinary Anatomy and Histology,
Epidermis. Integumentary system
 Epidermis the doctor mentioned at the begging of the lecture that the slides is from different sources and has information and details that is enough for us so we don t have to go back and read from the
Epidermis the doctor mentioned at the begging of the lecture that the slides is from different sources and has information and details that is enough for us so we don t have to go back and read from the
Histology Review Can you identify the Cell Structures? Can you identify the Stain? Can you identify the Cell type?
 Histology Review Can you identify the Cell Structures? Can you identify the Stain? Can you identify the Cell type? 2.01 Border of Epithelia (fluorescence) M A: lamina basalis B: epithelium C: other tissues
Histology Review Can you identify the Cell Structures? Can you identify the Stain? Can you identify the Cell type? 2.01 Border of Epithelia (fluorescence) M A: lamina basalis B: epithelium C: other tissues
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 4, 2016,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 4, 2016, 1813 1819 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) HISTOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON MAJOR SALIVARY GLANDS IN PRENATAL BUFFALO (Bubalus
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 4, 2016, 1813 1819 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) HISTOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON MAJOR SALIVARY GLANDS IN PRENATAL BUFFALO (Bubalus
Skin Histology. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skin Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Integumentary system The skin is considered the largest organ of the body Basic Skin Histology The skin is composed of two
Skin Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Integumentary system The skin is considered the largest organ of the body Basic Skin Histology The skin is composed of two
Variations in the Appearance of Human Elastic Cartilage
 The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 69, Issue 6 (November, 1969) 1969-11 Variations in the Appearance of
The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 69, Issue 6 (November, 1969) 1969-11 Variations in the Appearance of
COMPARATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES ON THE VOMERO-NASAL ORGAN IN MITHUN (BOS FRONTAUS), YAK (BOS GRUNNIENS) AND ZEBU (BOS INDICUS)
 Indian J. Anim. Res., 38 (2): 102-106, 2004 COMPARATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES ON THE VOMERO-NASAL ORGAN IN MITHUN (BOS FRONTAUS), YAK (BOS GRUNNIENS) AND ZEBU (BOS INDICUS) H.C. Kalita and P.C. Kalita Department
Indian J. Anim. Res., 38 (2): 102-106, 2004 COMPARATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES ON THE VOMERO-NASAL ORGAN IN MITHUN (BOS FRONTAUS), YAK (BOS GRUNNIENS) AND ZEBU (BOS INDICUS) H.C. Kalita and P.C. Kalita Department
Skin and Body Membranes
 4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
Oral histology. How is the oral mucosa different from skin?
 Oral histology Lec.13 Oral mucosa: Dr.Nada AL.Ghaban The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane lining the inside of the mouth and consists of stratified squamous epithelium termed oral epithelium and an underlying
Oral histology Lec.13 Oral mucosa: Dr.Nada AL.Ghaban The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane lining the inside of the mouth and consists of stratified squamous epithelium termed oral epithelium and an underlying
Integumentary System. Remember: Types of Membranes: Bio 250
 Integumentary System Bio 250 Remember: Tissue: Group of cells that are similar in appearance and perform similar function Organ: Two or more tissues grouped together and performing a specialized function
Integumentary System Bio 250 Remember: Tissue: Group of cells that are similar in appearance and perform similar function Organ: Two or more tissues grouped together and performing a specialized function
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis
The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Introduction. Skin and Body Membranes. Cutaneous Membranes Skin 9/14/2017. Classification of Body Membranes. Classification of Body Membranes
 Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
Skin and adnexa Skin Adnexa (derivatives): hair nail sebaceous glands sweat glands mammary glands
 Integumentary system - skin and adnexa Skin and adnexa Skin Adnexa (derivatives): hair nail sebaceous glands sweat glands mammary glands Skin (cutis): structure epidermis stratified squamous keratinized
Integumentary system - skin and adnexa Skin and adnexa Skin Adnexa (derivatives): hair nail sebaceous glands sweat glands mammary glands Skin (cutis): structure epidermis stratified squamous keratinized
Integumentary System and Body Membranes
 Integumentary System and Body Membranes The Skin and its appendages hair, nails, and skin glands Anatomy/Physiology NHS http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/corepages/integumentary/integum.htm I. System
Integumentary System and Body Membranes The Skin and its appendages hair, nails, and skin glands Anatomy/Physiology NHS http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/corepages/integumentary/integum.htm I. System
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System. Skin Cells. Layers of Skin. Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous layer beneath dermis not part of skin
 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water loss Regulates body temperature Houses sensory receptors Contains immune
Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water loss Regulates body temperature Houses sensory receptors Contains immune
Preface 1. Fixation and Processing 1
 Contents Preface xi 1. Fixation and Processing 1 Fixation 1 Processing 2 What Should Be Seen in a Well-Fixed, Well-Processed Specimen Stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin 3 Problems Encountered With Fixation
Contents Preface xi 1. Fixation and Processing 1 Fixation 1 Processing 2 What Should Be Seen in a Well-Fixed, Well-Processed Specimen Stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin 3 Problems Encountered With Fixation
ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1
 ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1 R. I. Wordinger, 2 J. B. Ramsey, I. F. Dickey and I. R. Hill, Jr. Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1 R. I. Wordinger, 2 J. B. Ramsey, I. F. Dickey and I. R. Hill, Jr. Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS
 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS Integumentary System Cutaneous membrane Epidermis (5-layers) made up of epithelial tissue only Dermis (2-layers) contains connective tissue, vessels,
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS Integumentary System Cutaneous membrane Epidermis (5-layers) made up of epithelial tissue only Dermis (2-layers) contains connective tissue, vessels,
Skin. Lecture #14. Ref:
 Skin Lecture #14 Ref: http://www.ccunix.ccu.edu.tw/~chenmsl/tea/skin_910721.htm Structure of Skin 1. Epidermis 2. Dermis 3. Subcutis 4. Hair follicle 5. Sebaceous gland 6. Sweat gland Skin Largest human
Skin Lecture #14 Ref: http://www.ccunix.ccu.edu.tw/~chenmsl/tea/skin_910721.htm Structure of Skin 1. Epidermis 2. Dermis 3. Subcutis 4. Hair follicle 5. Sebaceous gland 6. Sweat gland Skin Largest human
Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System. Integumentary System. Page 1
 Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System Integumentary System Page 1 Have a very clear understanding of the each particular tissue and their unique functions in each layer of the
Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System Integumentary System Page 1 Have a very clear understanding of the each particular tissue and their unique functions in each layer of the
Integumentary System. Packet #12
 Integumentary System Packet #12 Introduction Skin/Integument Skin, considered an organ, is the major component of the integumentary system. The integumentary system is also composed of other accessory
Integumentary System Packet #12 Introduction Skin/Integument Skin, considered an organ, is the major component of the integumentary system. The integumentary system is also composed of other accessory
1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) i. Organ of the Integument. Connective Tissues. Epithelial Tissues
 Integumentary System 1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) A. Integumentary System i. Organ of the Integument a. Tissues Connective Tissues * Tissue / Location Relationships
Integumentary System 1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) A. Integumentary System i. Organ of the Integument a. Tissues Connective Tissues * Tissue / Location Relationships
Yara Saddam. Amr Alkhatib. Ihsan
 1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
Comparative Anatomical Factors Affecting Topical Delivery
 Comparative Anatomical Factors Affecting Topical Delivery Nancy A. Monteiro-Riviere, Ph.D., Fellow ATS Professor of Investigative Dermatology and Toxicology Center for Chemical Toxicology Research and
Comparative Anatomical Factors Affecting Topical Delivery Nancy A. Monteiro-Riviere, Ph.D., Fellow ATS Professor of Investigative Dermatology and Toxicology Center for Chemical Toxicology Research and
Integument. Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Melanoma. Largest organ 30% of all clinical diagnoses 1/3 of all tumors
 Squamous Cell Carcinoma Integument Largest organ 30% of all clinical diagnoses 1/3 of all tumors Melanoma Epidermis Stratified, squamous keratinized epithelium Derived from ectoderm Appendages hair follicles
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Integument Largest organ 30% of all clinical diagnoses 1/3 of all tumors Melanoma Epidermis Stratified, squamous keratinized epithelium Derived from ectoderm Appendages hair follicles
Introductory Histology Tutorial I
 Introductory Histology Tutorial I Epithelial Tissues Human Anatomy & Physiology I Assembled by Stephen Shoemake {Click mouse to advance} NAVIGATION = returns you to the previous slide. = returns you to
Introductory Histology Tutorial I Epithelial Tissues Human Anatomy & Physiology I Assembled by Stephen Shoemake {Click mouse to advance} NAVIGATION = returns you to the previous slide. = returns you to
Layers of the Skin. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
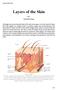 Layers of the Skin Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Although you may not typically think of the skin as an organ, it is in fact made of tissues that work together as a single structure to perform unique and critical
Layers of the Skin Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Although you may not typically think of the skin as an organ, it is in fact made of tissues that work together as a single structure to perform unique and critical
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Eleventh Edition. Chapter 6
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 6 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Referred to as Cutaneous Membrane
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 6 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Referred to as Cutaneous Membrane
SKIN HISTOLOGY the microscopic anatomy of the Integument. Mikrogeo. com
 SKIN HISTOLOGY the microscopic anatomy of the Integument Mikrogeo. com Hair follicles, sweat glands, sebaceous glands (even teeth) are products of the epidermis,embryologically speaking ectododerm, that
SKIN HISTOLOGY the microscopic anatomy of the Integument Mikrogeo. com Hair follicles, sweat glands, sebaceous glands (even teeth) are products of the epidermis,embryologically speaking ectododerm, that
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body
 Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System Skin (Integument) Consists of two major regions 1. Epidermis superficial region 2. Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia) deepest region Subcutaneous layer deep to
The Integumentary System Skin (Integument) Consists of two major regions 1. Epidermis superficial region 2. Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia) deepest region Subcutaneous layer deep to
II. Skin and Its Tissues. I. Introduction. Unit Two. Integument URLs.
 6 Integument URLs http://www.nurseminerva.co.uk/integ.html http://www.aap.org/policy/s010116.html Chapter 6 Karen Webb Smith Unit Two I. Introduction A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more
6 Integument URLs http://www.nurseminerva.co.uk/integ.html http://www.aap.org/policy/s010116.html Chapter 6 Karen Webb Smith Unit Two I. Introduction A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more
THE sebaceous glands of the rabbit consist of clusters of about ten cells
 79 On the Relationship between Mammary, Sweat, and Sebaceous Glands By D. B. CARLISLE (From the Department of Zoology and Comparative Anatomy, Oxford, and the Plymouth Laboratory of the Marine Biological
79 On the Relationship between Mammary, Sweat, and Sebaceous Glands By D. B. CARLISLE (From the Department of Zoology and Comparative Anatomy, Oxford, and the Plymouth Laboratory of the Marine Biological
Anatomical studies on the cystic artery of sheep (Ovis aries)
 2018; 7(3): 650-655 ISSN (E): 2277-7695 ISSN (P): 2349-8242 NAAS Rating: 5.03 TPI 2018; 7(3): 650-655 2018 TPI www.thepharmajournal.com Received: 20-01-2018 Accepted: 21-02-2018 B Venkatesh PG Scholar,
2018; 7(3): 650-655 ISSN (E): 2277-7695 ISSN (P): 2349-8242 NAAS Rating: 5.03 TPI 2018; 7(3): 650-655 2018 TPI www.thepharmajournal.com Received: 20-01-2018 Accepted: 21-02-2018 B Venkatesh PG Scholar,
Integumentary System Practice & McDaniel,
 Name: Period: Date: Adapted from: Akkaraju, Liachovitzky Integumentary System Practice & McDaniel, 2010-11 Objectives Checklist. After completion of this packet you should be able to: list the general
Name: Period: Date: Adapted from: Akkaraju, Liachovitzky Integumentary System Practice & McDaniel, 2010-11 Objectives Checklist. After completion of this packet you should be able to: list the general
HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL STUDIES ON THE THYROID GLAND IN FEMALE KUTTANAD DUCK (ANAS PLATYRHYNCHOS DOMESTICUS)
 HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL STUDIES ON THE THYROID GLAND IN FEMALE KUTTANAD DUCK (ANAS PLATYRHYNCHOS DOMESTICUS) A.D.Firdous and K.M. Lucy Department of Veterinary Anatomy and Histology, College of Veterinary and
HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL STUDIES ON THE THYROID GLAND IN FEMALE KUTTANAD DUCK (ANAS PLATYRHYNCHOS DOMESTICUS) A.D.Firdous and K.M. Lucy Department of Veterinary Anatomy and Histology, College of Veterinary and
