Dermatology For Boards (And Real Life) Rita Khodosh, MD, PhD Department of Dermatology UC San Francisco
|
|
|
- Anna Mason
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Dermatology For Boards (And Real Life) Rita Khodosh, MD, PhD Department of Dermatology UC San Francisco
2 A 32-year-old farmer comes to your office because of an upper respiratory infection. While he is there he points out a lesion on his forearm that he first noted approximately 1 year ago. It is a 1-cm asymmetric nodule with an irregular border and variations in color from black to blue. The patient says that it itches and has been enlarging for the past 2 months. He says he is so busy that he is not sure when he can return to have it taken care of.
3 Suspicious Pigmented Lesion
4 In such cases the best approach would be to A) perform a punch biopsy and have the patient return if the biopsy indicates pathology B) perform a shave biopsy, with a recheck in 2 months for signs of recurrence C) use electrocautery to destroy the lesion and the surrounding tissue D) perform an elliptical excision as soon as possible E) freeze the site with liquid nitrogen
5 In such cases the best approach would be to A) perform a punch biopsy and have the patient return if the biopsy indicates pathology B) perform a shave biopsy, with a recheck in 2 months for signs of recurrence C) use electrocautery to destroy the lesion and the surrounding tissue D) perform an elliptical excision as soon as possible E) freeze the site with liquid nitrogen
6 Melanoma Destruction (cryotherapy, electrodessication, currettage) is NEVER appropriate If you are not comfortable performing a biopsy, get the patient to someone who is Best way to biopsy a suspicious pigmented lesion is an EXCISIONAL BIOPSY (elliptical, punch, or saucerization) To properly stage and treatment a melanoma one needs to know it s greatest DEPTH
7 Melanoma Margins
8 Melanoma Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy is offered for melanomas : >1mm Breslow Depth <1mm with ulceration, increased mitotic rate and certain adverse features
9 A 72-year-old white farmer presents to your office with an enlarging raised lesion on the dorsum of his hand. It appears to be arising from an area of actinic keratosis.
10 Due to its location you suspect which one of the following? A) Basal cell carcinoma B) Keratoacanthoma C) Malignant melanoma D) Psoriatic plaque E) Squamous cell carcinoma
11 Due to its location you suspect which one of the following? A) Basal cell carcinoma B) Keratoacanthoma C) Malignant melanoma D) Psoriatic plaque E) Squamous cell carcinoma
12 Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Most associated with chronic sun exposure (cumulative effect) Scalp, face, dorsal hands, neck Other risk factors for development of SCC: - burn - chronic ulcer - radiation - HPV (anogenital) - immunosuppression
13 Keratoacanthoma A type of SCC? Rapid growth Nodule with keratinous core Can involute on its own Usually treated Excision is best
14 You note a skin lesion on the nose of a 70- year-old male painter during a visit for a routine upper respiratory infection. He tells you that the lesion "sometimes bleeds a little." It is a raised, smooth, pale, pearly, shiny papule with prominent telangiectasia evident across its surface.
15 This lesion is most likely A) a spider angioma B) a basal cell carcinoma C) an atypical melanoma D) actinic keratosis E) sebaceous hyperplasia
16 This lesion is most likely A) a spider angioma B) a basal cell carcinoma C) an atypical melanoma D) actinic keratosis E) sebaceous hyperplasia
17 Basal Cell Carcinoma Most common type of skin cancer Sun-exposed areas (face, neck) Fair skin, sunburn history Rarely metastasize, some can be locally invasive and aggressive Diagnosed with shave or punch biopsy (punch if you are worried about more infiltrative BCC)
18 BCC Treatment Face (especially mid face) Mohs procedure Excision Electrodessication and Curettage (not on face or neck, not for infiltrative BCC) Imiquimod or 5FU (Superficial BCC) Radiation if cannot tolerate surgery (usually elderly patients) Vismodegib--hedgehog pathway inhibitor (metastatic or inoperable BCC)
19 Which one of the following statements is consistent with current U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendations for skin cancer screening for the adult general population with no history of premalignant or malignant lesions?
20 Skin Cancer Screening A) Whole-body examination should be conducted by a primary care provider every 3 years B) Whole-body patient self-examination should be performed every 6 months C) Benefits from screening have been established only for high-risk patients D) The evidence is currently insufficient to determine whether early detection reduces mortality and morbidity from skin cancer E) The harms of detection and early treatment outweigh the benefits
21 Skin Cancer Screening A) Whole-body examination should be conducted by a primary care provider every 3 years B) Whole-body patient self-examination should be performed every 6 months C) Benefits from screening have been established only for high-risk patients D) The evidence is currently insufficient to determine whether early detection reduces mortality and morbidity from skin cancer E) The harms of detection and early treatment outweigh the benefits
22 I screen: Skin Cancer Screening patients with history of skin cancer patients with fair skin over 50 (especially men) who have evidence of significant sun damage (Actinic Keratoses) patients with other risk factors for NMSC (genetic risk, immunosuppression) patients with increased melanoma risk
23
24 What about indoor tanning?
25 UV radiation causes melanoma
26 A 55 year old white female presents with redness at the scar from a lumpectomy performed for stage I cancer of her right breast 4 months ago. The patient has completed radiation treatments to the breast. She is afebrile and there is no axillary adenopathy. There is no wound drainage, crepitance, or bullous lesions.
27 Which one of the following organisms would be the most likely cause of cellulitis in this patient? A) Non group A Streptococcus B) Pneumococcus (Strep pneumoniae) C) Clostridium perfringens D) Escherichia coli E) Pasteurella multocida
28 Which one of the following organisms would be the most likely cause of cellulitis in this patient? A) Non group A Streptococcus B) Pneumococcus (Strep pneumoniae) C) Clostridium perfringens D) Escherichia coli E) Pasteurella multocida
29 Causes of Cellulitis Beta-hemolytic Streptococci (most often Group A) Staph Aureus Non-purulent cellulitis cover for Strep and MSSA (Cephalexin) Purulent cellulitis cover for MRSA (Bactrim DS, Doxycycline, Clindamycin) and culture Abscess INCISION AND DRAINAGE Unless complicated (cellulitis, immunocompromised, fever, etc)
30 Other Staph and Strep infections Impetigo S. aureus more common Beta-hemolytic Strep less Localized cases can be treated with mupriocin More generalized with oral antibiotics (Cephalexin or Dicloxacillin) for 7 days Culture (if MRSA, tx with doxycycline, clinda or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole)
31 Other Staph Infections Acute Paronychia No abscess warm soaks and topical mupirocin Abscess drainage, soaks and mupirocin Culture Oral anti-staph antibiotics for 7 days for more severe cases
32 Not to be confused with Herpetic Whitlow Grouped vesicles on an erythematous base HSV 1 or 2 infection of finger from oral inoculation (most often in children, healthcare workers) Painful, can have fever and regional lymphadenopathy DFA or viral culture No need to treat Self-limited
33 Herpes Zoster Reactivation of latent VZV
34 Treatment of Herpes Zoster Antiviral therapy with acyclovir, valacyclovir, famciclovir Best when given within first 72 hours Treat after 72 hrs if still getting new lesions, immunosuppressed, pregnant Treat pain! Warn about contact with pregnant women, unvaccinated babies, immunocompromised Treat with antivirals AND call ophthalmology if Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus
35 Imiquimod (Aldara) is approved by the FDA for treatment of which one of the following conditions? A) External anogenital warts B) Plantar warts C) Flat warts D) Periungual warts E) Molluscum contagiosum
36 Imiquimod (Aldara) is approved by the FDA for treatment of which one of the following conditions? A) External anogenital warts B) Plantar warts C) Flat warts D) Periungual warts E) Molluscum
37 Imiquimod A toll-like receptor-7 agonist Enhances both the innate and acquired immune response FDA approved for treatment of external anogenital warts
38 An otherwise healthy 37-year-old male presents to your office with a 2-week history of redness and slight irritation in his groin. On examination a tender erythematous plaque with mild scaling is seen in his right crural fold. The area fluoresces coral-red under a Wood s light.
39 Which one of the following would be the most appropriate treatment at this time? A) Amoxicillin B) Erythromycin C) Ketoconazole D) Nystatin (Mycostatin) E) Triamcinolone (Kenalog)
40 Which one of the following would be the most appropriate treatment at this time? A) Amoxicillin B) Erythromycin C) Ketoconazole D) Nystatin (Mycostatin) E) Triamcinolone (Kenalog)
41 Erythrasma Erythrasma is caused by C. minutissimum, a component of the normal skin flora Overgrowth in stratum corneum occurs under conditions of occlusion and moisture Topical erythromycin and clindamycin are first line Oral clarithromycin or erythromycin for extensive disease Topical imidazole antifungals (econazole) also work
42 Other Groin Rashes Candida Moist beefy red Satellite pustules Keep area dry Nystatin Imidazole antifungals
43 Other Groin Rashes Tinea Cruris Scaly plaque Serpiginous scaly border - Topical Tx: Imidazoles or Allylamines (Terbinafine) - Oral Terbinafine for extensive tinea infections
44 A 69-year-old female sees you for an annual examination. She asks you to look at her toes, and you note a fungal infection in five toenails. She says the condition is painful and limits her ability to complete her morning walks. She asks for treatment that will allow her to resume her daily walks as soon as possible. Her only other medical problem is allergic rhinitis, which is well controlled.
45 Which one of the following would be the most appropriate treatment for this patient? A) Oral griseofulvin ultramicrosize (Gris-PEG) daily for 12 weeks B) Oral terbinafine (Lamisil) daily for 12 weeks C) Topical terbinafine (Lamisil AT) daily for 12 weeks D) Topical ciclopirox (Penlac Nail Lacquer) daily for 12 weeks E) Toe nail removal
46 Which one of the following would be the most appropriate treatment for this patient? A) Oral griseofulvin ultramicrosize (Gris-PEG) daily for 12 weeks B) Oral terbinafine (Lamisil) daily for 12 weeks C) Topical terbinafine (Lamisil AT) daily for 12 weeks D) Topical ciclopirox (Penlac Nail Lacquer) daily for 12 weeks E) Toe nail removal
47 Onychomycosis Dermatophyte infection most common Candida and non-dermatophyte mold (Fusariam, Aspergillus, others) Diagnosis: PAS most sensitive, Culture--only about 50% sensitivity Treatment not necessary if asymptomatic Treat if recurrent cellulitis (diabetics), pain, immunosuppression, patient preference
48 Onychomycosis Treatment Treat for presumed dermatophyte infection while waiting for culture results Oral Terbinafine 250mg daily for 12 weeks Cure rate about 70%, half relapse by 5 years Itraconazole, same cure rate, more side effects and interactions Topicals: Efinaconazole, Ciclopirox (cure rates 16%, 8% respectively) Cost: $31,000 for a course of Jublia/$184,000 to cure 10 toenails
49 Which one of the following would be considered first-line therapy for mild to moderately severe psoriasis confined to the elbows and knees? A) Phototherapy using ultraviolet B light B) Methotrexate C) Etretinate (Tegison) D) Betamethasone dipropionate (Diprolene)
50 Which one of the following would be considered first-line therapy for mild to moderately severe psoriasis confined to the elbows and knees? A) Phototherapy using ultraviolet B light B) Methotrexate C) Etretinate (Tegison) D) Betamethasone dipropionate (Diprolene)
51 Psoriasis Treatment LOCALIZED DISEASE TOPICAL TREATMENT Topical steroids (Clobetasol) Topical retinoids (Tazorac) Topical Vitamin D derivatives (Calcipotriene) Tar Combinations of topical treatments are more effective Intralesional Steroids NB UVB (more generalized disease)
52 Psoriasis Treatment Generalized disease, arthritis systemic treatment Methotrexate Biologics: - TNF alpha inhibitors (Adalimumab-Humira) - IL 12/23 inhibitor (Ustekinumab-Stelara) - IL 17 inhibitors (Secukinumab-Cosentyx) Acitretin, Cyclosporin (less often) Apremilast Otezla (oral PDE4 inhibitor)
53 Psoriasis - Real Life Psoriasis patients have systemic inflammation Co-morbidities: obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease More severe psoriasis--higher risk of comorbidities Counsel patients about diet, exercise Address co-morbidities
54 While vacationing, a 27-year-old white male was exposed to poison ivy. Between 48 and 72 hours after exposure he developed a pruritic, erythematous, papulovesicular eruption on his arms and neck. He was given oral methylprednisolone (Medrol Dosepak), starting with 24 mg/day and tapered by 4 mg/day over 6 days. His condition began to improve, but on day 6 he noted a dramatic exacerbation of the eruption with intense pruritus, erythema, and vesiculation, involving extensive areas of his arms, neck, and face.
55 The most appropriate management at this time would be to A) prescribe a superpotent topical corticosteroid B) repeat the oral methylprednisolone treatment C) begin diphenhydramine (Benadryl), 4 times a day D) begin high-dose oral prednisone and taper over 2 weeks E) discontinue all medications and recommend cool compresses
56 The most appropriate management at this time would be to A) prescribe a superpotent topical corticosteroid B) repeat the oral methylprednisolone treatment C) begin diphenhydramine (Benadryl), 4 times a day D) begin high-dose oral prednisone and taper over 2 weeks E) discontinue all medications and recommend cool compresses
57 Allergic Contact Dermatitis to Urushiol in Poison Oak (Ivy or Sumac) Type IV hypersensitivity reaction Localized eruptions can be treated with superpotent topical steroids (clobetasol) Oral prednisone is given for more extensive eruptions Needs to be started at a high dose (40-60mg) and tapered slowly over 2-3 weeks If tapered too quickly, patient will flare Antibiotics if secondarily infected (Staph)
58 Eczema/Atopic dermatitis Itchy erythematous scaly papules and plaques Patients with atopy (allergic rhinitis, asthma, FH) Problem with epidermal barrier and immune dysregulation Treatment MUST address both!
59 Eczema Treatment Emollients, gentle skin care, avoidance of irritants and topical allergens Topical steroids 1 st line Topical calcineurin inhibitors (tacrolimus) Do not use antibiotics unless impetiginized Treat pruritus Phototherapy Immunosuppressive agents for severe cases Dupilumab, modulates IL-4 and IL-13 signaling
60 Patients presenting with erythema multiforme often have a prodromal history of A) egg allergy B) recent immunization C) herpes simplex infection D) thennal trauma E) streptococcal infection
61 Patients presenting with erythema multiforme often have a prodromal history of A) egg allergy B) recent immunization C) herpes simplex infection D) thennal trauma E) streptococcal infection
62 Erythema Multiforme Target lesions (three zones: dark dusky center, pale ring of edema, erythematous halo) Can be atypical, with just 2 or 1 zone Hypersensitivity reaction to: - Infections (most commonly HSV, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, many others) Drugs are a less common cause (NSAIDs, Antibiotics, Anticonvulsants, others) If recurrent, treat with suppressive HSV therapy
63 Stevens Johnson Syndrome (SJS) & Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN) Severe mucocutaneous reaction usually caused by a medication Starts with fever, flu-like symptoms, mucosal pain Mortality up to 30%, higher in adults Allopurinol Phenobarbetal Bactrim Lamotrigine STOP the MEDICATION
64 A 20-year-old female college tennis player presents with painful anterior lower leg lesions. You note several 2- to 3- cm deep, tender, warm lesions over both shins. The patient denies specific trauma or increased exercise. The most significant etiology to be considered in this case is A) papular urticaria B) early rheumatoid arthritis C) shin splints D) superficial thrombophlebitis E) oral contraceptive use
65 A 20-year-old female college tennis player presents with painful anterior lower leg lesions. You note several 2- to 3- cm deep, tender, warm lesions over both shins. The patient denies specific trauma or increased exercise. The most significant etiology to be considered in this case is A) papular urticaria B) early rheumatoid arthritis C) shin splints D) superficial thrombophlebitis E) oral contraceptive use
66 Erythema Nodosum Panniculitis Delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction to: - Infection (Streptococcal most common) - Drugs (OCPs, antibiotics) - IBD - Pregnancy
67 Erythema Nodosum Treatment Self-resolving, but takes several weeks Treat underlying condition or stop medicatin Supportive treatment - Leg elevation - Rest - NSAIDs - If severe, can consider short course of lowdose prednisone (20mg 7-10 days)
68 A 5-year-old African-American child has been experiencing scalp pruritus for several months, along with hair loss in a motheaten pattern. Small block dots can be seen within the larger alopecic patches. A potassium hydroxide (KOH) reparation shows occasional branching hyphae and multiple spores.
69 Which one of the following is the preferred treatment? A) Topical ketoconazole (Nizoral) B) Topical minoxidil (Rogaine) C) Oral griseofulvin (Fulvicin) D) Oral hydroxyzine (Atarax) E) Psoralen-ultraviolet A (PUVA) therapy
70 Which one of the following is the preferred treatment? A) Topical ketoconazole (Nizoral) B) Topical minoxidil (Rogaine) C) Oral griseofulvin (Fulvicin) D) Oral hydroxyzine (Atarax) E) Psoralen-ultraviolet A (PUVA) therapy
71 Tinea Capitis - Treatment Long Course (4-6 weeks or more) Griseofulvin mg/kg divided bid x 6-12 weeks (give with ice cream of other fatty food) Works best against Microsporum Species Lamisil (Terbinafine) 5mg/kg/d x 4 wks Works best against Trichophyton Species Itraconazole has a worse side effect profile, do not use first line for skin/nail infections
72 Kerion Inflammatory reaction to tinea infection Can lead to scarring Not a bacterial infection does not require antiobiotics We often add low-dose prednisone to treat inflammation and minimize scarring
73 A 30-year-old white male presents with a polymorphous skin rash consisting of grouped vesicles,urticarial wheals, and papular lesions distributed symmetrically over the elbows, knees, and buttocks. A skin biopsy shows IgA deposition and a diagnosis of dermatitis herpetiformis is made. The mainstay of therapy is A) dapsone B) prednisone C) cephalosporins D) methotrexate E) tetracycline
74 A 30-year-old white male presents with a polymorphous skin rash consisting of grouped vesicles,urticarial wheals, and papular lesions distributed symmetrically over the elbows, knees, and buttocks. A skin biopsy shows IgA deposition and a diagnosis of dermatitis herpetiformis is made. The mainstay of therapy is A) dapsone B) prednisone C) cephalosporins D) methotrexate E) tetracycline
75 Dermatitis Herpetiformis Associated with gluten sensitivity celiac disease Treatment Strict gluten-free diet works slowly Dapsone works quickly, can later be discontinued
76 A 62-year-old female presents with painful lesions at both corners of her mouth characterized by redness, scaling, and deep cracks. The cracks sometimes bleed when she opens her mouth. She has treated them with bacitracin/neomycin/polymyxin B ointment (Neosporin) but says it has not helped. Which one of the following would be most appropriate at this point? A) A biopsy of the lesions B) An anticandidal medication C) Bacitracin D) Vitamin B12
77 A 62-year-old female presents with painful lesions at both corners of her mouth characterized by redness, scaling, and deep cracks. The cracks sometimes bleed when she opens her mouth. She has treated them with bacitracin/neomycin/polymyxin B ointment (Neosporin) but says it has not helped. Which one of the following would be most appropriate at this point? A) A biopsy of the lesions B) An anticandidal medication C) Bacitracin D) Vitamin B12
78 Angular Cheilitis More common in elderly people Ill-fitting dentures Dry mouth Poor oral hygiene Complicated by candidal or staph infection Barrier creams (zinc or vaseline) Treat infection Minimize exacerbating factors Can check for B12 or iron deficiency
79 A 25-year-old female has an annular rash on the dorsal surface of both hands. The rash does not respond to initial treatment with an antifungal medication, and a biopsy reveals granuloma annulare. Which one of the following would be the most appropriate advice for this patient? A) Allow the rash to resolve without further treatment B) Cover the rash because it is contagious C) Treat the rash with systemic corticosteroids D) Treat the rash with a stronger antifungal medication
80 A 25-year-old female has an annular rash on the dorsal surface of both hands. The rash does not respond to initial treatment with an antifungal medication, and a biopsy reveals granuloma annulare. Which one of the following would be the most appropriate advice for this patient? A) Allow the rash to resolve without further treatment B) Cover the rash because it is contagious C) Treat the rash with systemic corticosteroids D) Treat the rash with a stronger antifungal medication
81 Granuloma Annulare Non-scaly erythematous annular papules and plaques on dorsal hands, elbows, feet, knees A benign, reactive condition, can self resolve Treatments included superpotent topical steroids and intralesional steroids
82 A 50-year-old female presents with a 3-week history of a moderately pruritic rash, characterized by flat- topped violaceous papules 3 4 mm in size. The lesions are located primarily on the volar wrists and forearms, lower legs, and dorsa of both feet. Ten days after the rash first appeared she went to the emergency department and was treated for possible scabies, but the treatment has made little or no difference.
83 Which one of the following treatments is indicated at this time? A) Clobetasol (Cormax, Temovate) 0.05% ointment B) Permethrin 5% cream C) Tacrolimus (Protopic) 0.1% ointment D) Triamcinolone 0.1% cream
84 Which one of the following treatments is indicated at this time? A) Clobetasol (Cormax, Temovate) 0.05% ointment B) Permethrin 5% cream C) Tacrolimus (Protopic) 0.1% ointment D) Triamcinolone 0.1% cream
85 Lichen Planus 5 P s: pruritic, purple, planar (flat-topped), polygonal papules Wickham striae Wrists/ankles classic Oral/genital involvement Can be erosive Etiology unknown?associated with Hep C? Potent or superpotent topicals steroids are first line tx Other tx: topical tacrolimus, prednisone taper, plaquenil, acitretin, methotrexate
86 Scabies
87 Scabies Erythematous papules, pustules, burrows Likes hands, skin folds, groin, less on head Very itchy SCRAPE IT Treat all family members Permethrin cream x 2 Ivermectin PO if crusted
88 Erythema Migrans 7-14 days after tick bite
89 Lyme Disease - Caused by Borrelia spirochete transmitted by bite of Ixodes deer tick - In early Lyme disease serologic testing is likely to be negative - Diagnosis should be made based on the clinical picture (EM lesion or lesions, nonspecific viral symptoms, and history of living in or travel to an endemic area Treatment: - Doxycycline 100mg BID for days or - Amoxicillin 500mg po BID for days
90 Secondary Syphilis Treponemal test (FTA-ABS) to screen and non-treponemal test (RPR) to confirm Treat with Penicillin G
91 Acne Assess severity Mild to moderate topical therapy (retinoids, Benzoyl Peroxide, clindamycin) Moderate course of antibiotics (Doxy, limit to 6 months) Hormonal treatments for women (OCP, spironolactone) Severe nodulocustic/scarring: Isotretinoin teratogen, otherwise quite safe)
92 Urticaria Acute urticaria < 6 weeks Chronic urticaria > 6 week Triggers - Foods acute - Medications and Infections - Over 50% of chronic urticaria is idiopathic Treat with anti-histamines (non-sedating up to 4 times the daily dose) Do not use prednisone, especially for chronic
Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children
 May 2016 Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children Dr Chan Yuin Chew Dermatologist Dermatology Associates Gleneagles Medical Centre Scope of presentation Focus on rashes May lead to significant morbidity if
May 2016 Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children Dr Chan Yuin Chew Dermatologist Dermatology Associates Gleneagles Medical Centre Scope of presentation Focus on rashes May lead to significant morbidity if
COMMON SKIN CONDITIONS IN PRIMARY CARE. Ibrahim M. Zayneh, MD Dermatology Private Practice, Portsmouth, Ohio
 COMMON SKIN CONDITIONS IN PRIMARY CARE Ibrahim M. Zayneh, MD Dermatology Private Practice, Portsmouth, Ohio DISCLOSURE The Speaker and members of the planning committee do not have a conflict of interest
COMMON SKIN CONDITIONS IN PRIMARY CARE Ibrahim M. Zayneh, MD Dermatology Private Practice, Portsmouth, Ohio DISCLOSURE The Speaker and members of the planning committee do not have a conflict of interest
12/12/2018. Childhood Skin Infections. Objectives. Verruca vulgaris. Case #1. Case #2. Management 1. Evidence Updates
 Objectives Childhood Skin Infections Evidence Updates Brian Z. Rayala, MD Associate Professor Department of Family Medicine UNC School of Medicine At the end of lecture, learner will be able to:» Diagnose
Objectives Childhood Skin Infections Evidence Updates Brian Z. Rayala, MD Associate Professor Department of Family Medicine UNC School of Medicine At the end of lecture, learner will be able to:» Diagnose
My ear won t stop hurting!
 This month: 1. My ear won t stop hurting! 5. Cortisone Cream Didn t Help! 2. What are these red bumps? 6. Can my girlfriend get it? 3. Why won t this rash leave? 7. My wife noticed it! 4. What s the cause
This month: 1. My ear won t stop hurting! 5. Cortisone Cream Didn t Help! 2. What are these red bumps? 6. Can my girlfriend get it? 3. Why won t this rash leave? 7. My wife noticed it! 4. What s the cause
9/9/17. Disclosures" Dermatology in Primary Care: Recognition and treatment of common disorders of the skin" A preview" Classic skin infections"
 Disclosures Dermatology in Primary Care: Recognition and treatment of common disorders of the skin I have no conflicts of interest to disclose. I may discuss off-label use of treatments for cutaneous disease.
Disclosures Dermatology in Primary Care: Recognition and treatment of common disorders of the skin I have no conflicts of interest to disclose. I may discuss off-label use of treatments for cutaneous disease.
Dermatology for the Internist DREW M ANDERSON, MD VOLUNTEER CLINICAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, INDIANA UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
 Dermatology for the Internist DREW M ANDERSON, MD VOLUNTEER CLINICAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, INDIANA UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE Why Should I Care? 53% of all skin related visits are to non
Dermatology for the Internist DREW M ANDERSON, MD VOLUNTEER CLINICAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, INDIANA UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE Why Should I Care? 53% of all skin related visits are to non
Large majority caused by sun exposure Often sun exposure before age 20 Persons who burn easily and tan poorly are at greatest risk.
 Basics of Skin Cancer Detection and Treatment of Non- Melanoma Skin Cancers Large majority caused by sun exposure Often sun exposure before age 20 Persons who burn easily and tan poorly are at greatest
Basics of Skin Cancer Detection and Treatment of Non- Melanoma Skin Cancers Large majority caused by sun exposure Often sun exposure before age 20 Persons who burn easily and tan poorly are at greatest
Clinical characteristics
 Skin Cancer Fernando Vega, MD Seattle Healing Arts Clinical characteristics Precancerous lesions Common skin cancers ACTINIC KERATOSIS Precancerous skin lesions Actinic keratoses Dysplastic melanocytic
Skin Cancer Fernando Vega, MD Seattle Healing Arts Clinical characteristics Precancerous lesions Common skin cancers ACTINIC KERATOSIS Precancerous skin lesions Actinic keratoses Dysplastic melanocytic
Emergent and Urgent Dermatology, Eruptions, and Wound Care
 Emergent and Urgent Dermatology, Eruptions, and Wound Care G. Scott Drew, DO, FAAD, FAOCD Smith Clinic Department of Dermatology Tucson Osteopathic Medical Foundation April 27, 2018 Acute Cutaneous Lupus
Emergent and Urgent Dermatology, Eruptions, and Wound Care G. Scott Drew, DO, FAAD, FAOCD Smith Clinic Department of Dermatology Tucson Osteopathic Medical Foundation April 27, 2018 Acute Cutaneous Lupus
Common Dermatoses in Children & Adults
 Conflicts of Interest Common Dermatoses in Children & Adults None Erin Amerson, MD Department of Dermatology UC San Francisco Outline Infections & Infestations Skin cancer Common dermatologic disorders
Conflicts of Interest Common Dermatoses in Children & Adults None Erin Amerson, MD Department of Dermatology UC San Francisco Outline Infections & Infestations Skin cancer Common dermatologic disorders
Cutaneous Malignancies: A Primer COPYRIGHT. Marissa Heller, M.D.
 Cutaneous Malignancies: A Primer Marissa Heller, M.D. Associate Director of Dermatologic Surgery Department of Dermatology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center December 10, 2016 Skin Cancer Non-melanoma
Cutaneous Malignancies: A Primer Marissa Heller, M.D. Associate Director of Dermatologic Surgery Department of Dermatology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center December 10, 2016 Skin Cancer Non-melanoma
Pediatric Dermatology. Wingfield Rehmus, MD MPH BC Children s Hospital
 Pediatric Dermatology Wingfield Rehmus, MD MPH BC Children s Hospital Conflict of interest! No financial conflict of interest! Individual products shown are examples only not a product endorsement Pediatric
Pediatric Dermatology Wingfield Rehmus, MD MPH BC Children s Hospital Conflict of interest! No financial conflict of interest! Individual products shown are examples only not a product endorsement Pediatric
Dr Janakan Natkunarajah (Dr Jana)
 Dr Janakan Natkunarajah (Dr Jana) Diagnosis Furuncle (Boil) Deep follicular abscess Anti-staph antibiotics Systemic & topical Carbuncle Deep abscess formed in a group of follicles Incise and Drain Recurrent
Dr Janakan Natkunarajah (Dr Jana) Diagnosis Furuncle (Boil) Deep follicular abscess Anti-staph antibiotics Systemic & topical Carbuncle Deep abscess formed in a group of follicles Incise and Drain Recurrent
Know who is at risk: LOOK! for ABCDs, rapidly changing lesions, do a biopsy when indicated
 Lindy P. Fox, MD Associate Professor Director, Hospital Consultation Service Department of Dermatology University of California, San Francisco Applies to adults without history of malignancy or premalignant
Lindy P. Fox, MD Associate Professor Director, Hospital Consultation Service Department of Dermatology University of California, San Francisco Applies to adults without history of malignancy or premalignant
Questions 1. What is the diagnosis? 2. What is the significance? 3. What is the treatment? Provided by: Dr. Alexander K.C. Leung
 Illustrated quizzes on problems seen in everyday practice Case 1 Rash on the Neck Copyright An eight-year-old girl presents with an erythematous rash on the neck. The rash is slightly itchy. Incidentally,
Illustrated quizzes on problems seen in everyday practice Case 1 Rash on the Neck Copyright An eight-year-old girl presents with an erythematous rash on the neck. The rash is slightly itchy. Incidentally,
Know who is at risk: LOOK! for ABCDs, rapidly changing lesions, do a biopsy when indicated
 Lindy P. Fox, MD Assistant Professor Director, Hospital Consultation Service Department of Dermatology University of California, San Francisco Applies to adults without history of malignancy or premalignant
Lindy P. Fox, MD Assistant Professor Director, Hospital Consultation Service Department of Dermatology University of California, San Francisco Applies to adults without history of malignancy or premalignant
Skin Malignancies Non - Melanoma & Melanoma Marilyn Ng, MD Dept. of Surgery M&M Conference Downstate Medical Center July 19, 2012
 Skin Malignancies Non - Melanoma & Melanoma Marilyn Ng, MD Dept. of Surgery M&M Conference Downstate Medical Center July 19, 2012 Case Presentation 57 yo man with 3 month hx of a nonhealing < 1 cm right
Skin Malignancies Non - Melanoma & Melanoma Marilyn Ng, MD Dept. of Surgery M&M Conference Downstate Medical Center July 19, 2012 Case Presentation 57 yo man with 3 month hx of a nonhealing < 1 cm right
Cutaneous reactions to targeted therapies. Stavonnie Patterson, MD, FAAD Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine March 6, 2017
 Cutaneous reactions to targeted therapies Stavonnie Patterson, MD, FAAD Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine March 6, 2017 Disclosures I have no relevant disclosures Papulopustular Eruption
Cutaneous reactions to targeted therapies Stavonnie Patterson, MD, FAAD Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine March 6, 2017 Disclosures I have no relevant disclosures Papulopustular Eruption
Subspecialty Rotation: Dermatology
 Subspecialty Rotation: Dermatology Faculty: Wesley Galen, M.D. GOAL: Prevention, Counseling and Screening (Dermatology). Understand the pediatrician's role in preventing illness and dysfunction related
Subspecialty Rotation: Dermatology Faculty: Wesley Galen, M.D. GOAL: Prevention, Counseling and Screening (Dermatology). Understand the pediatrician's role in preventing illness and dysfunction related
Skin lesions The Good and the Bad. Dr Virginia Hubbard Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry
 Skin lesions The Good and the Bad Dr Virginia Hubbard Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry Case 1 32 year old woman Australian Lesion on back New hair growing
Skin lesions The Good and the Bad Dr Virginia Hubbard Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry Case 1 32 year old woman Australian Lesion on back New hair growing
Right type of lesions for topicals. Onychomycosis. Common Diseases and Infections of the SKIN. Toby Maurer, MD University of California, San Francisco
 Common Diseases and Infections of the SKIN Toby Maurer, MD University of California, San Francisco Onychomycosis Topical treatment use for the right type of lesions Naftin gel for small superficial lesions
Common Diseases and Infections of the SKIN Toby Maurer, MD University of California, San Francisco Onychomycosis Topical treatment use for the right type of lesions Naftin gel for small superficial lesions
INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE AND SKIN HEALTH KARA N. SHAH, MD, PHD KENWOOD DERMATOLOGY MARCH 4, 2018
 INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE AND SKIN HEALTH KARA N. SHAH, MD, PHD KENWOOD DERMATOLOGY MARCH 4, 2018 DISCLOSURES I HAVE NO RELEVANT FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES INTRODUCTION Structure and function of the skin IBD
INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE AND SKIN HEALTH KARA N. SHAH, MD, PHD KENWOOD DERMATOLOGY MARCH 4, 2018 DISCLOSURES I HAVE NO RELEVANT FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES INTRODUCTION Structure and function of the skin IBD
Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level
 Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level Dr Ng Su Yuen Paediatrician and Paediatric Dermatologist Hospital Pulau Pinang Outline Common inflammatory
Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level Dr Ng Su Yuen Paediatrician and Paediatric Dermatologist Hospital Pulau Pinang Outline Common inflammatory
Dermatology Pearls. Leah Layman, ARNP Jefferson Healthcare Dermatology June 21, 2018
 Dermatology Pearls Leah Layman, ARNP Jefferson Healthcare Dermatology June 21, 2018 What s on the agenda? Common skin conditions and where to start with treatment Gentle skin care regimen PCP and Biologics
Dermatology Pearls Leah Layman, ARNP Jefferson Healthcare Dermatology June 21, 2018 What s on the agenda? Common skin conditions and where to start with treatment Gentle skin care regimen PCP and Biologics
My Algorithm. Questions to ask. Do you or your family have a history of?... Allergic rhinitis, Sensitive skin, Asthma Skin Cancer
 Tracey C. Vlahovic, DPM Associate Professor, Temple University School of Podiatric Medicine My Algorithm Inflammatory Skin Disorder on Feet Family hx, clinical exam, look at hands! Defined plaques: Psoriasis
Tracey C. Vlahovic, DPM Associate Professor, Temple University School of Podiatric Medicine My Algorithm Inflammatory Skin Disorder on Feet Family hx, clinical exam, look at hands! Defined plaques: Psoriasis
An Approach to Common and not so Common Rashes in the Office FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc
 An Approach to Common and not so Common Rashes in the Office FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc 1 Common Rashes Tinea Corporis: Annular- this is not the only criteria Advancing erythematous
An Approach to Common and not so Common Rashes in the Office FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc 1 Common Rashes Tinea Corporis: Annular- this is not the only criteria Advancing erythematous
Thursday 21 st August Skin Problems
 Thursday 21 st August 2014 Skin Problems Skin Problems The Sun and the Skin Sun Damage Recognising the early signs of skin cancer The Big 3 inflammatory condi=ons Acne & Rosacea Eczema (Including Seborrhoeic
Thursday 21 st August 2014 Skin Problems Skin Problems The Sun and the Skin Sun Damage Recognising the early signs of skin cancer The Big 3 inflammatory condi=ons Acne & Rosacea Eczema (Including Seborrhoeic
Objectives. Terminology. Recognize common pediatric dermatologic conditions. Review treatment plans Identify skin manifestations of systemic disease
 Pediatric Visual Dermatological Diagnosis Fernando Vega, M.D. Objectives Recognize common pediatric dermatologic conditions Expand differential diagnosis Review treatment plans Identify skin manifestations
Pediatric Visual Dermatological Diagnosis Fernando Vega, M.D. Objectives Recognize common pediatric dermatologic conditions Expand differential diagnosis Review treatment plans Identify skin manifestations
The skin is the largest organ of the human body. Functions: protection sensation maintain temperature vitamin synthesis
 Dermatology The skin is the largest organ of the human body. Functions: protection sensation maintain temperature vitamin synthesis The image to the left shows an image of skin cells and the proteins which
Dermatology The skin is the largest organ of the human body. Functions: protection sensation maintain temperature vitamin synthesis The image to the left shows an image of skin cells and the proteins which
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System Integumentary System Skin, hair, and nails. Skin: Epidermis: outer layer. Dermis: also called corium, or true skin. Subcutaneous fascia: innermost layer. Integumentary Glands Sudoriferous:
Integumentary System Integumentary System Skin, hair, and nails. Skin: Epidermis: outer layer. Dermis: also called corium, or true skin. Subcutaneous fascia: innermost layer. Integumentary Glands Sudoriferous:
Vulval dermatoses. Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough
 Vulval dermatoses Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough Pigmentation Vulvodynia Ulcers Genetic Pruritus VULVAL
Vulval dermatoses Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough Pigmentation Vulvodynia Ulcers Genetic Pruritus VULVAL
Benign versus Cancerous Lesions How to tell the difference FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc
 1 Benign versus Cancerous Lesions How to tell the difference FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc Benign lesions Seborrheic Keratoses: Warty, stuck-on Genetics and birthdays Can start in late
1 Benign versus Cancerous Lesions How to tell the difference FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc Benign lesions Seborrheic Keratoses: Warty, stuck-on Genetics and birthdays Can start in late
COMMON SKIN INFECTIONS. Sports Medicine
 COMMON SKIN INFECTIONS Sports Medicine IMPETIGO IS A SUPERFICIAL BACTERIAL INFECTION CAUSED BY: STREPTOCOCCI OR STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BOULOUS IMPETIGO IMPETIGO COMES IN TWO FORMS: BOULOUS OR NON- BOULOUS
COMMON SKIN INFECTIONS Sports Medicine IMPETIGO IS A SUPERFICIAL BACTERIAL INFECTION CAUSED BY: STREPTOCOCCI OR STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BOULOUS IMPETIGO IMPETIGO COMES IN TWO FORMS: BOULOUS OR NON- BOULOUS
Concentrate on Descriptors. An Approach to Skin Diseases in the ER
 Concentrate on Descriptors An Approach to Skin Diseases in the ER Toby Maurer, MD University of California, San Francisco Vasculitis-leaky blood vessels Targetoid lesions-round lesions with blue or red
Concentrate on Descriptors An Approach to Skin Diseases in the ER Toby Maurer, MD University of California, San Francisco Vasculitis-leaky blood vessels Targetoid lesions-round lesions with blue or red
IT S FUNDAMENTAL MY DEAR WATSON! A SHERLOCKIAN APPROACH TO DERMATOLOGY
 IT S FUNDAMENTAL MY DEAR WATSON! A SHERLOCKIAN APPROACH TO DERMATOLOGY Skin, Bones, and other Private Parts Symposium Dermatology Lectures by Debra Shelby, PhD, DNP, FNP-BC, FADNP, FAANP Debra Shelby,
IT S FUNDAMENTAL MY DEAR WATSON! A SHERLOCKIAN APPROACH TO DERMATOLOGY Skin, Bones, and other Private Parts Symposium Dermatology Lectures by Debra Shelby, PhD, DNP, FNP-BC, FADNP, FAANP Debra Shelby,
FACULTY DISCLOSURE PRACTICE CHANGE
 FACULTY DISCLOSURE I have the following financial relationships with the manufacturer(s) of any commercial product(s) and/or provider of commercial services discussed in this CME activity. Spouse owns
FACULTY DISCLOSURE I have the following financial relationships with the manufacturer(s) of any commercial product(s) and/or provider of commercial services discussed in this CME activity. Spouse owns
Dermatology for the PCP
 Dermatology for the PCP Laura S. Winterfield, MD MPH Associate Professor Medical University of South Carolina I have no relevant conflicts of interest. 1 Learning Objectives Identify common skin conditions
Dermatology for the PCP Laura S. Winterfield, MD MPH Associate Professor Medical University of South Carolina I have no relevant conflicts of interest. 1 Learning Objectives Identify common skin conditions
CONDITIONS OF THE SKIN
 CONDITIONS OF THE SKIN UCSF/SFGH Family & Community Medicine Residency Program Educational Objectives I. Knowledge The resident will be able to discuss the definition, diagnosis, and initial management
CONDITIONS OF THE SKIN UCSF/SFGH Family & Community Medicine Residency Program Educational Objectives I. Knowledge The resident will be able to discuss the definition, diagnosis, and initial management
CHAPTER 7:3 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7:3 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM I. OBJECTIVES A. Label a diagram of a cross section of the skin B. Differentiate between the two types of skin glands C. Identify six functions of the skin D. Provide the
CHAPTER 7:3 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM I. OBJECTIVES A. Label a diagram of a cross section of the skin B. Differentiate between the two types of skin glands C. Identify six functions of the skin D. Provide the
29a Pathology - Integumentary System
 29a Pathology - Integumentary System 29a Pathology - Integumentary System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active
29a Pathology - Integumentary System 29a Pathology - Integumentary System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active
Dermatology Pearls and News Flash ACP Utah Chapter Scientific Meeting 2017
 Dermatology Pearls and News Flash ACP Utah Chapter Scientific Meeting 2017 Christopher M Hull, MD University of Utah School of Medicine Christopher.hull@hsc.utah.edu Conflict of interest No conflicts to
Dermatology Pearls and News Flash ACP Utah Chapter Scientific Meeting 2017 Christopher M Hull, MD University of Utah School of Medicine Christopher.hull@hsc.utah.edu Conflict of interest No conflicts to
I have a skin lump doc! What s next? 12 th August 2017 Dr. Sue-Ann Ho Ju Ee
 I have a skin lump doc! What s next? 12 th August 2017 Dr. Sue-Ann Ho Ju Ee Some thoughts Is this skin cancer? How common is this? How likely is this in this patient? What happens next if it s something
I have a skin lump doc! What s next? 12 th August 2017 Dr. Sue-Ann Ho Ju Ee Some thoughts Is this skin cancer? How common is this? How likely is this in this patient? What happens next if it s something
Dermatology GP Referral Guidelines
 Austin Health Dermatology Department holds 5 Clinic sessions to discuss and plan the treatment of with Dermatology conditions. Department of Health clinical urgency categories for specialist clinics Urgent:
Austin Health Dermatology Department holds 5 Clinic sessions to discuss and plan the treatment of with Dermatology conditions. Department of Health clinical urgency categories for specialist clinics Urgent:
COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES. Sharon Seguin MD FAAD
 COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES Sharon Seguin MD FAAD COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES Rashes Infections And Infestations RASHES Dermatitis- Inflammation of the skin Eczema- Atopic Dermatitis Psoriasis Pityriasis
COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES Sharon Seguin MD FAAD COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES Rashes Infections And Infestations RASHES Dermatitis- Inflammation of the skin Eczema- Atopic Dermatitis Psoriasis Pityriasis
Therapeutic Agents for the Dermatological System
 Therapeutic Agents for the Dermatological System Chapter 25 1 Anatomy of the Skin Skin is made of various layers that contain nerves, glands, hair, and blood vessels Function is to protect the body against
Therapeutic Agents for the Dermatological System Chapter 25 1 Anatomy of the Skin Skin is made of various layers that contain nerves, glands, hair, and blood vessels Function is to protect the body against
Dermatopathology: The tumor is composed of keratinocytes which show atypia, increase mitoses and abnormal mitoses.
 Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
What is atopic dermatitis?
 What is atopic dermatitis? Complex inflammatory skin disorder intense pruritus cutaneous hyperreactivity immune dysregulation Chronic with exacerbations and remissions Affects all ages, but more common
What is atopic dermatitis? Complex inflammatory skin disorder intense pruritus cutaneous hyperreactivity immune dysregulation Chronic with exacerbations and remissions Affects all ages, but more common
Treatments used Topical including cleansers and moisturizer Oral medications:
 Discipline: Dermatology Extended Topic: Acne & Rosacea : Onset: Location: Face Chest Back Menses if female: Regular Irregular PCOS Treatments used Topical including cleansers and moisturizer Oral medications:
Discipline: Dermatology Extended Topic: Acne & Rosacea : Onset: Location: Face Chest Back Menses if female: Regular Irregular PCOS Treatments used Topical including cleansers and moisturizer Oral medications:
Chapter 11. Sexually Transmitted Diseases
 Chapter 11. Sexually Transmitted Diseases General Guidelines Persons identified as having one sexually transmitted disease (STD) are at risk for others and should be screened as appropriate. Partners of
Chapter 11. Sexually Transmitted Diseases General Guidelines Persons identified as having one sexually transmitted disease (STD) are at risk for others and should be screened as appropriate. Partners of
Time to Learn. 6 th March 2018 Dr. Shirin Chakera GPwSI Integrated Dermatology Service
 Time to Learn 6 th March 2018 Dr. Shirin Chakera GPwSI Integrated Dermatology Service The Red Face Rosacea Acne Seborrhoeic eczema eczema Psoriasis Slapped cheek syndrome Fungal infection Erysipelas...
Time to Learn 6 th March 2018 Dr. Shirin Chakera GPwSI Integrated Dermatology Service The Red Face Rosacea Acne Seborrhoeic eczema eczema Psoriasis Slapped cheek syndrome Fungal infection Erysipelas...
Scrub In. What is a function of the skin: The innermost layer of the epidermis is constantly reproducing itself. This function enable the skin to:
 Scrub In What is a function of the skin: a. Convert glycogen to glucose b. Secretion of growth hormones c. Manufacture of vitamin C d. Protection from germ invasion The innermost layer of the epidermis
Scrub In What is a function of the skin: a. Convert glycogen to glucose b. Secretion of growth hormones c. Manufacture of vitamin C d. Protection from germ invasion The innermost layer of the epidermis
MERCY RETREAT Dermatology
 MERCY RETREAT 2016 Dermatology INFECTIONS IN DERMATOLOGY Why we do talk about infections today? These are some of the most commonly seen dermatologic diseases that present to primary care physician office
MERCY RETREAT 2016 Dermatology INFECTIONS IN DERMATOLOGY Why we do talk about infections today? These are some of the most commonly seen dermatologic diseases that present to primary care physician office
Conflicts of interest
 Vulvar Cases 2 nd PANHELLANIC CONGRESS on Lower Genital Tract Disorders December 14-16 Grand Hyatt Athens Lynette J. Margesson MD FRCPC Assistant Professor of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Surgery(Dermatology)
Vulvar Cases 2 nd PANHELLANIC CONGRESS on Lower Genital Tract Disorders December 14-16 Grand Hyatt Athens Lynette J. Margesson MD FRCPC Assistant Professor of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Surgery(Dermatology)
Living Beyond Cancer Skin Cancer Detection and Prevention
 Living Beyond Cancer Skin Cancer Detection and Prevention Cutaneous Skin Cancers Identification Diagnosis Treatment options Prevention What is the most common cancer in people? What is the most common
Living Beyond Cancer Skin Cancer Detection and Prevention Cutaneous Skin Cancers Identification Diagnosis Treatment options Prevention What is the most common cancer in people? What is the most common
The Integumentary System. Disorders, Conditions, and Diseases
 The Integumentary System Disorders, Conditions, and Diseases Definitions Disease- an abnormal condition of the body or the mind that causes dysfunction or discomfort. Disorder- a functional abnormality,
The Integumentary System Disorders, Conditions, and Diseases Definitions Disease- an abnormal condition of the body or the mind that causes dysfunction or discomfort. Disorder- a functional abnormality,
Dermatologic Emergencies Sept 2014
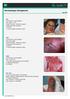 Dermatologic Emergencies Sept 2014 SJS YES MUCOSAL INVOLVEMENT MCC drugs >> HSV TARGET LESIONS, +NIKOLSKY, painful Prodromal flu-like symptoms
Dermatologic Emergencies Sept 2014 SJS YES MUCOSAL INVOLVEMENT MCC drugs >> HSV TARGET LESIONS, +NIKOLSKY, painful Prodromal flu-like symptoms
Commonly Coded Conditions in Dermatology
 Commonly Coded Conditions in Dermatology No part of this presentation may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means (graphically, electronically, or mechanically, including photocopying,
Commonly Coded Conditions in Dermatology No part of this presentation may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means (graphically, electronically, or mechanically, including photocopying,
IT S FUNDAMENTAL MY DEAR WATSON! A SHERLOCKIAN APPROACH TO DERMATOLOGY
 IT S FUNDAMENTAL MY DEAR WATSON! A SHERLOCKIAN APPROACH TO DERMATOLOGY Skin, Bones, and other Private Parts Symposium Dermatology Lectures by Debra Shelby, PhD, DNP, FNP-BC, FADNP, FAANP Debra Shelby,
IT S FUNDAMENTAL MY DEAR WATSON! A SHERLOCKIAN APPROACH TO DERMATOLOGY Skin, Bones, and other Private Parts Symposium Dermatology Lectures by Debra Shelby, PhD, DNP, FNP-BC, FADNP, FAANP Debra Shelby,
Bacterial Infections in Pediatric Dermatology. Patrick McMahon, MD Children s Hospital of Philadelphia
 Bacterial Infections in Pediatric Dermatology Patrick McMahon, MD Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Fill In The Blank When you see on the skin, you think of a bacterial skin infection SEND SWABS VIRAL
Bacterial Infections in Pediatric Dermatology Patrick McMahon, MD Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Fill In The Blank When you see on the skin, you think of a bacterial skin infection SEND SWABS VIRAL
Periocular skin cancer
 Periocular skin cancer Information for patients Skin cancer involving the skin of the eyelid or around the eye is called a periocular skin cancer. Eyelid skin cancers occur most often on the lower eyelid,
Periocular skin cancer Information for patients Skin cancer involving the skin of the eyelid or around the eye is called a periocular skin cancer. Eyelid skin cancers occur most often on the lower eyelid,
Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition)
 Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major components (anatomy) of skin Differentiate between the two types of skin glands Explain
Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major components (anatomy) of skin Differentiate between the two types of skin glands Explain
RASHES- Dermatitis nonspecific term for inflammation of the skin. 1. ECZEMA Atopic Dermatitis- specific form of eczema starting in childhood
 COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES Sharon Seguin MD Dermatology- Confluence Health Wenatchee Rashes Infections and Infestations RASHES- Dermatitis nonspecific term for inflammation of the skin 1. ECZEMA Atopic
COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES Sharon Seguin MD Dermatology- Confluence Health Wenatchee Rashes Infections and Infestations RASHES- Dermatitis nonspecific term for inflammation of the skin 1. ECZEMA Atopic
Dermatological Manifestations in the Elderly. Sanjay Siddha Staff Dermatologist UHN & MSH
 Dermatological Manifestations in the Elderly Sanjay Siddha Staff Dermatologist UHN & MSH Disclosure No actual or potential conflicts of interest or commercial relationships to declare Objectives Recognize
Dermatological Manifestations in the Elderly Sanjay Siddha Staff Dermatologist UHN & MSH Disclosure No actual or potential conflicts of interest or commercial relationships to declare Objectives Recognize
Skin Cancer - Non-Melanoma
 Skin Cancer - Non-Melanoma Introduction Each year, millions of people find out that they have skin cancer. Skin cancer is almost 100% curable if found early and treated right away. It is possible to prevent
Skin Cancer - Non-Melanoma Introduction Each year, millions of people find out that they have skin cancer. Skin cancer is almost 100% curable if found early and treated right away. It is possible to prevent
Dermclinic
 Dermclinic /Dermclinic A Photo Quiz to Hone Dermatologic Skills DAVID L. KAPLAN, MD Series Editor University of Missouri Kansas City, University of Kansas Case 1: Upon his return from a summer visit to
Dermclinic /Dermclinic A Photo Quiz to Hone Dermatologic Skills DAVID L. KAPLAN, MD Series Editor University of Missouri Kansas City, University of Kansas Case 1: Upon his return from a summer visit to
Future of Pediatrics: Blisters, Hives and Other Tales from the Emergency Room June 14 th, 2016
 A. Yasmine Kirkorian MD Assistant Professor of Dermatology & Pediatrics Children s National Health System George Washington University School of Medicine & Health Sciences Future of Pediatrics: Blisters,
A. Yasmine Kirkorian MD Assistant Professor of Dermatology & Pediatrics Children s National Health System George Washington University School of Medicine & Health Sciences Future of Pediatrics: Blisters,
Skin Cancer 101: Diagnosis and Management of the Most Common Cancer
 Skin Cancer 101: Diagnosis and Management of the Most Common Cancer Sarah Patton, PA-C, MSHS Skin Surgery Center www.skinsurgerycenter.com Seattle/Bellevue, WA Skin cancer Skin cancer is by far the most
Skin Cancer 101: Diagnosis and Management of the Most Common Cancer Sarah Patton, PA-C, MSHS Skin Surgery Center www.skinsurgerycenter.com Seattle/Bellevue, WA Skin cancer Skin cancer is by far the most
Pediatric Dermatology
 Pediatric Dermatology --------- Emergencies & Urgencies Nicholas V. Nguyen, M.D. Director, Pediatric Dermatology Disclosures In the past 12 months, I have had the following financial relationships with
Pediatric Dermatology --------- Emergencies & Urgencies Nicholas V. Nguyen, M.D. Director, Pediatric Dermatology Disclosures In the past 12 months, I have had the following financial relationships with
Types of Skin Infections
 Anatomy of Skin Types of Skin Infections Bacterial Impetigo Folliculitis Acne Fungal /Parasitic Tinea Pedis Tinea Cruris Tinea Versicolor Tinea Corporis Toenail fungus Allergic/Irritation conditions Dermatitis
Anatomy of Skin Types of Skin Infections Bacterial Impetigo Folliculitis Acne Fungal /Parasitic Tinea Pedis Tinea Cruris Tinea Versicolor Tinea Corporis Toenail fungus Allergic/Irritation conditions Dermatitis
Common Benign Lesions and Skin Cancers. 22nd May 2015 Dr Mark Foley
 Common Benign Lesions and Skin Cancers 22nd May 2015 Dr Mark Foley Thank you for downloading this file. This intended to supplement the presentation given at the NZ Wound Care Conference, it is not intended
Common Benign Lesions and Skin Cancers 22nd May 2015 Dr Mark Foley Thank you for downloading this file. This intended to supplement the presentation given at the NZ Wound Care Conference, it is not intended
The Itch That Rashes. Sarah D. Cipriano, MD, MPH, MS Resident, Dermatology University of Utah
 The Itch That Rashes Sarah D. Cipriano, MD, MPH, MS Resident, Dermatology University of Utah 1 Conflict of Interest No conflict of interest Will discuss off label use of medications 2 3 Most likely diagnosis?
The Itch That Rashes Sarah D. Cipriano, MD, MPH, MS Resident, Dermatology University of Utah 1 Conflict of Interest No conflict of interest Will discuss off label use of medications 2 3 Most likely diagnosis?
Dermatology for the PCP Deanna G. Brown, MD, FAAD Susong Dermatology Consulting Staff at CHI Memorial
 Dermatology for the PCP Deanna G. Brown, MD, FAAD Susong Dermatology Consulting Staff at CHI Memorial Cutaneous Oncology for the PCP Deanna G. Brown, MD, FAAD Susong Dermatology Consulting Staff at CHI
Dermatology for the PCP Deanna G. Brown, MD, FAAD Susong Dermatology Consulting Staff at CHI Memorial Cutaneous Oncology for the PCP Deanna G. Brown, MD, FAAD Susong Dermatology Consulting Staff at CHI
Common Superficial Fungal Infections
 How to recognise and treat Common Superficial Fungal Infections Dr Lilianne Scholtz (MBBCh) Types of superficial fungal infections Ringworm (Tinea) Candida (Thrush) Body Groin Feet Skin Nappy rash Vagina
How to recognise and treat Common Superficial Fungal Infections Dr Lilianne Scholtz (MBBCh) Types of superficial fungal infections Ringworm (Tinea) Candida (Thrush) Body Groin Feet Skin Nappy rash Vagina
Advanced Practice Education Associates. Dermatological Disorders
 Advanced Practice Education Associates Dermatological Disorders Overview Skin Infections: Bacterial infections, Fungal, viral infections Skin Things: Herpes zoster, lupus Skin cancer Itchy Things 200 Copyright
Advanced Practice Education Associates Dermatological Disorders Overview Skin Infections: Bacterial infections, Fungal, viral infections Skin Things: Herpes zoster, lupus Skin cancer Itchy Things 200 Copyright
COMMON VIRAL INFECTIONS. Dr D. Tenea Department of Dermatology University of Pretoria
 COMMON VIRAL INFECTIONS Dr D. Tenea Department of Dermatology University of Pretoria GENERAL Viral infections of the skin important in immunocompromised Pts. Infection: direct inoculation ( warts ) or
COMMON VIRAL INFECTIONS Dr D. Tenea Department of Dermatology University of Pretoria GENERAL Viral infections of the skin important in immunocompromised Pts. Infection: direct inoculation ( warts ) or
=ﻰﻤاﻤﺤﻠا ﺔﻴﻘﻠﺤﻠا ﺔذﺒاﻨﻠا
 1 / 15 Erythema Annulare Centrifugum and Other Figurate Erythemas The figurate erythemas include a variety of eruptions characterized by annular and polycyclic lesions. Classification of this group has
1 / 15 Erythema Annulare Centrifugum and Other Figurate Erythemas The figurate erythemas include a variety of eruptions characterized by annular and polycyclic lesions. Classification of this group has
Periocular Malignancies
 Periocular Malignancies Andrew Gurwood, O.D., F.A.A.O., Dipl. Marc Myers, O.D., F.A.A.O. Drs. Myers and Gurwood have no financial interests to disclose. Course Description Discussion of the most common
Periocular Malignancies Andrew Gurwood, O.D., F.A.A.O., Dipl. Marc Myers, O.D., F.A.A.O. Drs. Myers and Gurwood have no financial interests to disclose. Course Description Discussion of the most common
Hammer Toe. Photo Diagnosis. Case 1. Illustrated quizzes on problems seen in everyday practice. Questions. Answers
 Illustrated quizzes on problems seen in everyday practice Hammer Toe Case 1 This 48-year-old gentleman has a long history of Rheumatoid arthritis, for which he has been on Methotrexate 10 mg weekly for
Illustrated quizzes on problems seen in everyday practice Hammer Toe Case 1 This 48-year-old gentleman has a long history of Rheumatoid arthritis, for which he has been on Methotrexate 10 mg weekly for
Richard Turner Consultant Dermatologist
 Old Problems & New Treatments Photo Album by Administrator Richard Turner Consultant Dermatologist Plan for tonight? Refresher on SCC and solar keratosis How to distinguish the two Classic therapy than
Old Problems & New Treatments Photo Album by Administrator Richard Turner Consultant Dermatologist Plan for tonight? Refresher on SCC and solar keratosis How to distinguish the two Classic therapy than
Skin lesions & Abrasions
 Skin lesions & Abrasions What Are Skin Lesions? A skin lesion is a part of the skin that has an abnormal growth or appearance compared to the skin around it Types of Skin Lesions Two types of skin lesions
Skin lesions & Abrasions What Are Skin Lesions? A skin lesion is a part of the skin that has an abnormal growth or appearance compared to the skin around it Types of Skin Lesions Two types of skin lesions
Learning Circle: Jan 26, 2011 Childhood Eczema
 Learning Circle: Jan 26, 2011 Childhood Eczema Wingfield Rehmus, MD MPH BC Children s Hospital Clinical Assistant Professor, UBC Department of Paediatrics Associate Member, UBC Department of Dermatology
Learning Circle: Jan 26, 2011 Childhood Eczema Wingfield Rehmus, MD MPH BC Children s Hospital Clinical Assistant Professor, UBC Department of Paediatrics Associate Member, UBC Department of Dermatology
Facial Rash. Facial Rash 10/14/2013. Ten Look Alike Rashes Michelle DiBaise, MPAS, PA-C, DFAAPA Associate Clinical Professor NAU PA Program
 Ten Look Alike Rashes Michelle DiBaise, MPAS, PA-C, DFAAPA Associate Clinical Professor NAU PA Program Facial Rash Facial Rash Case 1 28 year female Progressive development of erythematous facial lesions
Ten Look Alike Rashes Michelle DiBaise, MPAS, PA-C, DFAAPA Associate Clinical Professor NAU PA Program Facial Rash Facial Rash Case 1 28 year female Progressive development of erythematous facial lesions
Common Skin Diseases. MdAhadAli Khan Department of Pharmacy SUB
 Common Skin Diseases MdAhadAli Khan Department of Pharmacy SUB Intact: Skin is unbroken Contusion: Injury in which skin is unbroken Excoriation: Removal of an area of the skin Abrasion: Spot rubbed bare
Common Skin Diseases MdAhadAli Khan Department of Pharmacy SUB Intact: Skin is unbroken Contusion: Injury in which skin is unbroken Excoriation: Removal of an area of the skin Abrasion: Spot rubbed bare
DESCRIPTIONS FOR MED 3 ROTATIONS Dermatology A3S
 Regardless of your future field of practice, you will be exposed to a considerable amount of dermatology and this rotation provides you the chance to see a range of skin diseases. You will have the opportunity
Regardless of your future field of practice, you will be exposed to a considerable amount of dermatology and this rotation provides you the chance to see a range of skin diseases. You will have the opportunity
Teledermatology. Acne. What the primary care physician needs to know in the world of increased access
 Teledermatology What the primary care physician needs to know in the world of increased access Toby Maurer, MD University of California, San Francisco In the world of dermatology-teledermatology is powering
Teledermatology What the primary care physician needs to know in the world of increased access Toby Maurer, MD University of California, San Francisco In the world of dermatology-teledermatology is powering
Non-melanoma Skin Cancer
 Non-melanoma Skin Cancer Understanding your diagnosis 1 888 939-3333 cancer.ca Non-melanoma Skin Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid.
Non-melanoma Skin Cancer Understanding your diagnosis 1 888 939-3333 cancer.ca Non-melanoma Skin Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid.
The Old, The New and the Reemerging-HIV Dermatology. Toby Maurer, MD
 The Old, The New and the Reemerging-HIV Dermatology Toby Maurer, MD 1 Psoriasis Widespread psoriasis, especially if it was once stable, predicts falling CD4 count?resistance to ART??Non-adherence? Tx:
The Old, The New and the Reemerging-HIV Dermatology Toby Maurer, MD 1 Psoriasis Widespread psoriasis, especially if it was once stable, predicts falling CD4 count?resistance to ART??Non-adherence? Tx:
Cutanous Manifestation of Lupus Erythematosus. Presented By: Dr. Naif S. Al Shahrani Salman Bin Abdaziz university
 Cutanous Manifestation of Lupus Erythematosus Presented By: Dr. Naif S. Al Shahrani Salman Bin Abdaziz university A 50-year old lady, who is otherwise healthy, presented to the dermatology clinic with
Cutanous Manifestation of Lupus Erythematosus Presented By: Dr. Naif S. Al Shahrani Salman Bin Abdaziz university A 50-year old lady, who is otherwise healthy, presented to the dermatology clinic with
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System Physiology of Touch Skin: our most sensitive organ Touch: first sense to develop in embryos Most important but most neglected sense How many sensory receptors do we have? (We have
Integumentary System Physiology of Touch Skin: our most sensitive organ Touch: first sense to develop in embryos Most important but most neglected sense How many sensory receptors do we have? (We have
Sports Dermatology. James B. Robinson, M.D. Head Team Physician, University of Alabama
 Sports Dermatology James B. Robinson, M.D. Head Team Physician, University of Alabama Objectives Discuss common skin lesions among athletes Recognize infectious vs. non-infectious skin lesions Learn proper
Sports Dermatology James B. Robinson, M.D. Head Team Physician, University of Alabama Objectives Discuss common skin lesions among athletes Recognize infectious vs. non-infectious skin lesions Learn proper
Disclosures Dr. Lynette Margesson
 Management of Vulvar Pruritus 2 nd PANHELLANIC CONGRESS on Lower Genital Tract Disorders December 14-16 Grand Hyatt Athens Lynette J. Margesson MD FRCPC Assistant Professor of Obstetrics & Gynecology and
Management of Vulvar Pruritus 2 nd PANHELLANIC CONGRESS on Lower Genital Tract Disorders December 14-16 Grand Hyatt Athens Lynette J. Margesson MD FRCPC Assistant Professor of Obstetrics & Gynecology and
Why the basics? Back to Basics HIV Dermatology Immune reconstitution Acne. The HIV infected pt who starts ARV s 12/12/2012
 Why the basics? Back to Basics HIV Dermatology 2012 Toby Maurer, MD University of California, San Francisco 1) The depleted low CD4 counts 2) The repleted aging pts 3) The group who starts ARV s at high
Why the basics? Back to Basics HIV Dermatology 2012 Toby Maurer, MD University of California, San Francisco 1) The depleted low CD4 counts 2) The repleted aging pts 3) The group who starts ARV s at high
Difference Between Seborrheic Dermatitis and Psoriasis
 Difference Between Seborrheic Dermatitis and Psoriasis www.differencebetween.com Key Difference Seborrheic Dermatitis vs Psoriasis Dermatological conditions are perhaps the most worrisome diseases in the
Difference Between Seborrheic Dermatitis and Psoriasis www.differencebetween.com Key Difference Seborrheic Dermatitis vs Psoriasis Dermatological conditions are perhaps the most worrisome diseases in the
Suzan Schneeweiss MD, MEd, FRCPC
 Suzan Schneeweiss MD, MEd, FRCPC I have nothing to disclose 1. Discuss common pitfalls in the diagnosis and management of common paediatric rashes in the ED 2. Identify dermatologic conditions requiring
Suzan Schneeweiss MD, MEd, FRCPC I have nothing to disclose 1. Discuss common pitfalls in the diagnosis and management of common paediatric rashes in the ED 2. Identify dermatologic conditions requiring
Case 1. Debridement Cultures Keflex Silvadene
 The Red Breast Beth McLellan, M.D. Assistant Professor Division of Dermatology Albert Einstein College of Medicine Montefiore Medical Center Jacobi Medical Center Case 1 48 year old radiation oncologist
The Red Breast Beth McLellan, M.D. Assistant Professor Division of Dermatology Albert Einstein College of Medicine Montefiore Medical Center Jacobi Medical Center Case 1 48 year old radiation oncologist
(NATO STANAG 2122, CENTO STANAG 2122, SEATO STANAG 2122)
 (NATO STANAG 2122, CENTO STANAG 2122, SEATO STANAG 2122) Bacteria Bacteria are microscopic, single-celled forms of plant life, containing no chlorophyll. They live on the skin, on the surface of the stratum
(NATO STANAG 2122, CENTO STANAG 2122, SEATO STANAG 2122) Bacteria Bacteria are microscopic, single-celled forms of plant life, containing no chlorophyll. They live on the skin, on the surface of the stratum
Abscess. A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body.
 Abscess A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body. Ethyology Bacteria causing cutaneous abscesses are typically indigenous
Abscess A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body. Ethyology Bacteria causing cutaneous abscesses are typically indigenous
Dermatology for the frontline
 Dermatology for the frontline Kate Foster, D.O. April 28, 2018 Disclaimer: We have consent from patients to use photos for presentation and publication purposes. Please do not take any photos of slides
Dermatology for the frontline Kate Foster, D.O. April 28, 2018 Disclaimer: We have consent from patients to use photos for presentation and publication purposes. Please do not take any photos of slides
Disclosures. Poll Everywhere. Learning Objectives. Atopic Dermatitis. Atopic Dermatitis
 39 th National Conference on Pediatric Health Care March 19-22, 2018 CHICAGO Disclosures When It s Not Eczema: Reviewing common and not so common differential diagnosis for Atopic Dermatitis No disclosures
39 th National Conference on Pediatric Health Care March 19-22, 2018 CHICAGO Disclosures When It s Not Eczema: Reviewing common and not so common differential diagnosis for Atopic Dermatitis No disclosures
