11/23/17. Post receptoral pathways for color vision: How is colour coded? Colour Vision 2 - post receptoral
|
|
|
- Job Shepherd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Colour Vision II: The post receptoral basis of colour vision and acquired color vision deficiencies Prof. Kathy T. Mullen McGill Vision Research (H4.14) Dept. of Ophthalmology Colour Vision 2 - post receptoral 1. Pre-requisites: cone types, the principle of trichromacy, univariance, tests for the inherited color vision deficiencies 2. Connection of cones to retinal neurons: cone opponency and colour vision 3. Cells types for RG, BY and achromatic vision 4. Testing of RG, BY & Ach vision: 1) Farnsworth Munsell 2) Monitor displays and selective color vision tests 5. Acquired color vision defects: glaucoma, ARM, Type 2 diabetes, phototoxicity, optic neuritis. 26 th Oct Kollners Rule 26 th Oct 2017 How is colour coded? Each colour produces a unique pattern of relative activities in the three cone types The outputs of the three cone types must be compared for color to be determined. This is done by 2 types of cone opponent process, starting in the retina. Post receptoral pathways for color vision: L/M (red-green) cone-opponency - midget ganglion cells of retina & LGN also called P cells. S cone-opponency - bistratified ganglion cell & K cells of LGN. Luminance (black/white or achromatic): - P cells fine spatial detail and acuity. - M cells. Parasol (M) cells are specialized for flicker and project to the motion sensitive areas of the brain about 10% of retinal ganglion cells. 1
2 Retinal ganglion cells with defined functions 1. Midget or Parvocellular (P) 2. Bistratified 3. Parasol or Magnocellular (M) Rod and cone receptors (R) Horizontal cells (H) Bipolar cells (B) Amacrine cells (A) Sketch of Primate retina Outer segment Inner segment Cell body 4. Melanopsin filled Ganglion cells (G) Light Optic nerve fibers (to LGN in thalamus) Cones connect to bipolar and horizontal cells with opposite sign Horizontal cell Bipolar cell Horizontal cell Post receptoral neuron Cones connect to retinal neurons forming centre and surround subgroups, with different signs. For color vision these subgroups are also cone specific. The neuron illustrated is cone opponent as its excitatory and inhibitory signals have different spectral sensitivities, ie, one cone type in the centre but cone mixed in the surround. 2
3 Red-green colour vision is formed from the opponent combination of L and M cones in the midget ganglion cells (P cells) of the retina (L vs M cone opponency), which comprise 80% of the retinal ganglion cells Chromatic receptive fields: P cell responses to red and green light covering entire receptive field Receptive field Response Long wavelength light covers the receptive field Shorter wavelength light covers the receptive field Shorter wavelength light covers the receptive field Long wavelength light covers the receptive field Diagrams of model receptive fields to show the top view (left) and cross section (right) for L/M (RG) opponent neurons. A. Type 1, P cell, -with spatial and cone opponency. Blue-yellow colour vision is formed from the opponent combination of S with L and M cones in the bistratified ganglion cells (and other types) (S vs (L+M)) cone opponency) (about 5% of retinal ganglion cells). B. Type 2 cell with cone opponency but no spatial opponency. C. Achromatic cell orientation tuned. D. Dual opponent cell - with cone opponent sub regions in centre & surround. E. Dual opponent cell orientation tuned. C-E are only found in the cortex. A & B (single opponent cells) are found in the retina, LGN and V1 cortex. Source: Figure 3 from Conway et al 2010, Advances in Color Science: From Retina to Behavior, Journal of Neuroscience, 30,
4 S cones of the retina Layers of the LGN: Magno, Parvo and Koniocellular Melanopsin-filled ganglion cells > supra chiasmatic nucleus Additional light sensitive cells not involved in colour vision Melanopsin filled ganglion cells: > supra chiasmatic nucleus synchronizes the circadian oscillator to the day/night cycle. Also control pupillary responses. First found in mice but in 2007 also found in primates probably about 3,000 cells per retina. Respond very slowly and are very sluggish, remaining active for a long time after stimulation. Respond best to blue light (460nm). Melanopsin/PRV152-labeled ganglion cells. (a) Melanopsin-expressing ganglion cells in a retinal wholemount from an animal (hamster) with an intact visual system. Long arrows indicate intensely labeled ganglion cells; short arrow indicates a lightly labeled cell. In this image, melanopsin-labeled displaced ganglion cells (d) in the inner nuclear layer are also revealed after deconvolution of optical sections. (b) PRV152 transsynaptically labeled ganglion cells in the same field as in (a). (c) Combined image of (a) and (b) illustrating melanopsin/egfp double-labeled ganglion cells. Arrowheads indicate PRV152-labeled cells that are not melanopsin immunoreactive. Scale bars = 50 [mu] (Solars et al Vis Neuroscience 20, 601, 2003) 4
5 How do we test these pathways? 1. Clinical color vision: Farnsworth Munsell 100 hue or Panel D15 2. Electronic displays & computer graphics with control of cone activation Farnsworth Munsell 100 Hue Inherited and acquired color vision deficiencies Red-green, blue-yellow and non-specific deficiencies Show axial effects D15 Scoring the Farnsworth Munsell 100 hue test Farnsworth Munsell 100 hue test - inherited deficiencies Protan Deutan Tritan Online scoring program: 5
6 Subject with severe chronic optic neuritis: subject 1 Left eye Right eye Subject with severe chronic optic neuritis: subject 2 Left eye Right eye 252 Error score Error score 272 A Gabor pattern with colors that activate only the L/M ( red-green cone opponent process A Gabor pattern with colors that activate only the S/L-M ( blue-yellow ) cone opponent process Sinewave radial (ring) stimuli (0.5cpd) Stimuli are matched in multiples of detection threshold (x 25) and so are approximately equally visibly but have different contrasts A sinewave grating presented in a Gaussian envelope RG: 4% BY: 30 % Ach: 11% Patterns with colors that activate the L/M ( red-green ), S cone ( blueyellow ) cone opponent processes, and the achromatic system. Designed for full field activation, for example for fmri experiments. (Mullen et al, European Journal of Neuroscience, 2007) 6
7 A pattern with colors that activate only the L/M ( red-green ) cone opponent process: designed for peripheral vision. (Mullen et al, Perception, 2005) From: A Normative Data Set for the Clinical Assessment of Achromatic and Chromatic Contrast Sensitivity Using a qcsf Approach Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci ;58(9): doi: /iovs Figure Legend: Measured CCS as a function of spatial frequency for the Ach (solid black line), RG (solid red line), and BY (solid blue line) conditions under monocular viewing. The average across the 51 subjects is shown. The dotted lines indicate the log-parabola model estimation, which is reconstructed with the average estimated values for each of the three parameters by the qcsf. The averaged model parameters are reported in the Table. The shaded regions represent ± SD. Date of download: 10/2/2017 The Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Copyright All rights reserved. Contrast sensitivity of red/green and luminance gratings in normal vision red/green achromatic Colour vision has a lowpass contrast sensitivity function that is very good at detecting gradual colour changes across relatively large areas but has low acuity and is very poor at seeing fine spatial detail Relative Threshold Loss Loss of red-green, blue-yellow and luminance contrast sensitivity in optic neuritis (chronic) shows selective colour vision loss that is greatest for red-green (L/M opponency. Compatible with P retinal ganglion cell axon loss and some S cone RGC axon loss. Al-Hashmi, Kramer & Mullen Human vision with a lesion of the parvocellular pathway: an optic neuritis model for selective contrast sensitivity deficits with severe loss of midget ganglion cell function. Experimental Brain Research, 215, Mullen J. Physiology,
8 AMBLYOPIA LGN BOLD activation compared between amblyopic and fellow eyes The amblyopic LGN BOLD responses: RG, BY and ACH responses in normal fellow eyes (left) and amblyopic eyes (right): greatest deficit is for RG contrast N = 7 From Hess, R.F., Thompson, B., Gole, G. & Mullen, K.T. European Journal of Neuroscience, 29 29, , From Hess, R.F., Thompson, B., Gole, G. & Mullen, K.T. Journal of Neurophysiology, 104(1), pp , AMD- fellow eyes Colour vision testing as an aid to diagnosis and management of age related maculopathy (ARM) (Arden & Wolf, BJO, 2004) Acquired S cone deficiencies: Examples from AMD and Diabetic retinopathy A. Small stimuli used (1.5 degrees): S cone thresholds (blue squares) and L cone thresholds (red squares) in the asymptomatic fellow eye of an ARM patient group. Compared to normal limits (dashed lines) there are mild L cone deficits but S cone deficits are much greater. B. Large stimuli used (6.5 degrees): S cone thresholds (blue squares) and L cone thresholds (red squares) of the same group. Compare to normal limits L cone function is normal and S cone loss is significant. Comment: For a well matched control comparisons use unaffected or less affected fellow eye in a unilateral condition. 8
9 A C Diabetic Retinopathy Human post mortem Cho et al Arch Ophthal, 118, , 2000, Selective loss of S cones in Diabetic Retinopathy. B D Tangential sections at the level of the photoreceptor inner segments located 10 to 20 arc degrees from the fovea. Enzyme histochemical reaction for carbonic anhydrase (CA) produces a black reaction product, which labels the dominant L/Mcones. A, Section from a 68-year-old woman with no known history of ocular disease (control C5, Table 1). Roughly 9% of the cones are blue sensitive (arrows, negative for CA). B, Section from a similar area in another 68-year-old woman with proliferative diabetic retinopathy treated with laser photocoagulation (D5, Table 1). Fewer S (CA-negative) cones are present. There are also fewer rods than in the control section. C, Another section from the same subject as in frame B showing a focal area with marked reduction in rods. The L/M-cone density is essentially unchanged. D, Section from another diabetic retina (D6, Table 1). Note the lack of S-cones, decreased density of rods and poorly defined cone sheaths (toluidine blue counterstain, bar = 10 µm). Topographic (2-dimensional) plots showing the percentage of cones that are S-cones (negative for carbonic anhydrase) vs retinal eccentricity for the maculae of all of the control eyes (left) and all of the diabetic eyes (right) Copyright restrictions may apply. Cho, N.-C. et al. Arch Ophthalmol 2000;118: Diabetic Retinopathy Density of S-cones as a function of retinal eccentricity {+/-} SEM Density of L/M-cones as a function of retinal eccentricity {+/-} SEM Copyright restrictions may apply. Cho, N.-C. et al. Arch Ophthalmol 2000;118: Diabetic Retinopathy Copyright restrictions may apply. Cho, N.-C. et al. Arch Ophthalmol 2000;118: Diabetic Retinopathy 9
10 Percentage of cones that are blue sensitive as a function of retinal eccentricity (means for all directions) extending to 15 mm {+/-} SEM Glaucoma FIGURE 1 3. The same eye tested with SWAP (left) and conventional WW (right) perimetry. Appearance of grayscales of raw thresholds differ, with the SWAP field appearing more disturbed than the WW field. Probability maps of threshold deviations, which refer to agecorrected normal thresholds and normal limits, were more similar, and the WW test showed more test points with significant deviations than the SWAP test. No S cone selective effects: need proper comparisons between L/M and S cone disorders that control for aging effects on optics Copyright restrictions may apply. Cho, N.-C. et al. Arch Ophthalmol 2000;118: Diabetic Retinopathy 1. Pacheo-Cutillis et al BJO, 1999, Acquired colour vision defects in Glaucoma - their detection and clinical significance 2. Sample & Weinreb, IOVS, 1992 Progressive Color Visual Field loss in Glaucoma. 3. Bengtsson, IOPVS A New Rapid Threshold Algorithm for Short-Wavelength Automated Perimetry Kollner s Rule (1912) Lesions of the outer retinal layers affect blue yellow vision, lesions of the inner layers and optic nerve affect red-green vision Revised version S cones are physiologically vulnerable and so are more likely to be damaged by receptoral lesions than are L or M cones Post receptoral lesions are more likely to affect both types of cone opponent neuron: red-green and blueyellow. Conditions quoted as having S-cone (tritan) defects appearing first: Damage due to high light exposure Retinal detachment Pigmentary degeneration Myopic retinal degeneration AMD Chorioretinitis Retinal vascular occlusion Diabetic retinopathy Papilledema Drugs: oral contraceptives, chloroquine S cones are genetically robust but vulnerable physiologically 10
11 Conditions quoted as having RG (L/M) defects, but BY defects may also occur: Lesions of optic nerve/pathway Retrobulbar neuritis Leber s optic atrophy Compressive lesions of the optic tract Progressive cone degeneration entre-for-applied-vision-research/a-newweb-based-colour-vision-test L and M cones are physiologically robust but genetically vulnerable 11
eye as a camera Kandel, Schwartz & Jessel (KSJ), Fig 27-3
 eye as a camera Kandel, Schwartz & Jessel (KSJ), Fig 27-3 retinal specialization fovea: highest density of photoreceptors, aimed at where you are looking -> highest acuity optic disk: cell-free area, where
eye as a camera Kandel, Schwartz & Jessel (KSJ), Fig 27-3 retinal specialization fovea: highest density of photoreceptors, aimed at where you are looking -> highest acuity optic disk: cell-free area, where
The Midget and Parasol Channels
 The visual and oculomotor systems Peter H. Schiller, year 2006 The Midget and Parasol Channels MIDGET SYSTEM PARASOL SYSTEM or Neuronal response profile ON OFF ON OFF time Midget system cones ON OFF ON
The visual and oculomotor systems Peter H. Schiller, year 2006 The Midget and Parasol Channels MIDGET SYSTEM PARASOL SYSTEM or Neuronal response profile ON OFF ON OFF time Midget system cones ON OFF ON
Visual Physiology. Perception and Attention. Graham Hole. Problems confronting the visual system: Solutions: The primary visual pathways: The eye:
 Problems confronting the visual system: Visual Physiology image contains a huge amount of information which must be processed quickly. image is dim, blurry and distorted. Light levels vary enormously.
Problems confronting the visual system: Visual Physiology image contains a huge amount of information which must be processed quickly. image is dim, blurry and distorted. Light levels vary enormously.
OPTO 5320 VISION SCIENCE I
 OPTO 5320 VISION SCIENCE I Monocular Sensory Processes of Vision: Color Vision Mechanisms of Color Processing . Neural Mechanisms of Color Processing A. Parallel processing - M- & P- pathways B. Second
OPTO 5320 VISION SCIENCE I Monocular Sensory Processes of Vision: Color Vision Mechanisms of Color Processing . Neural Mechanisms of Color Processing A. Parallel processing - M- & P- pathways B. Second
Lighta part of the spectrum of Electromagnetic Energy. (the part that s visible to us!)
 Introduction to Physiological Psychology Vision ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ /~ksweeney/psy260.html Lighta part of the spectrum of Electromagnetic Energy (the part that s visible to us!)
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Vision ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ /~ksweeney/psy260.html Lighta part of the spectrum of Electromagnetic Energy (the part that s visible to us!)
Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 6: Vision
 Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 6: Vision This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 6: Vision This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Biological Bases of Behavior. 6: Vision
 Biological Bases of Behavior 6: Vision Sensory Systems The brain detects events in the external environment and directs the contractions of the muscles Afferent neurons carry sensory messages to brain
Biological Bases of Behavior 6: Vision Sensory Systems The brain detects events in the external environment and directs the contractions of the muscles Afferent neurons carry sensory messages to brain
COLOR VISION IN AND DISEASE
 COLOR VISION IN AND DISEASE HEALTH Craig Thomas, O.D. 3900 West Wheatland Road Dallas, Texas 75237 972-780-7199 thpckc@yahoo.com Financial Disclosure Craig Thomas, O.D. has received honorarium from the
COLOR VISION IN AND DISEASE HEALTH Craig Thomas, O.D. 3900 West Wheatland Road Dallas, Texas 75237 972-780-7199 thpckc@yahoo.com Financial Disclosure Craig Thomas, O.D. has received honorarium from the
Introduction to Physiological Psychology
 Introduction to Physiological Psychology Vision ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html This class n Sensation vs. Perception n How light is translated into what we see n Structure
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Vision ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html This class n Sensation vs. Perception n How light is translated into what we see n Structure
Vision Seeing is in the mind
 1 Vision Seeing is in the mind Stimulus: Light 2 Light Characteristics 1. Wavelength (hue) 2. Intensity (brightness) 3. Saturation (purity) 3 4 Hue (color): dimension of color determined by wavelength
1 Vision Seeing is in the mind Stimulus: Light 2 Light Characteristics 1. Wavelength (hue) 2. Intensity (brightness) 3. Saturation (purity) 3 4 Hue (color): dimension of color determined by wavelength
Colour vision deficiency part 1 an introduction
 CET CONTINUING EDUCATION & TRAINING Sponsored by 1 CET POINT 48 Colour vision deficiency part 1 an introduction Jennifer Birch Understanding the implications of defective colour vision is an integral part
CET CONTINUING EDUCATION & TRAINING Sponsored by 1 CET POINT 48 Colour vision deficiency part 1 an introduction Jennifer Birch Understanding the implications of defective colour vision is an integral part
Sensory Systems Vision, Audition, Somatosensation, Gustation, & Olfaction
 Sensory Systems Vision, Audition, Somatosensation, Gustation, & Olfaction Sarah L. Chollar University of California, Riverside sarah.chollar@gmail.com Sensory Systems How the brain allows us to see, hear,
Sensory Systems Vision, Audition, Somatosensation, Gustation, & Olfaction Sarah L. Chollar University of California, Riverside sarah.chollar@gmail.com Sensory Systems How the brain allows us to see, hear,
LISC-322 Neuroscience. Visual Field Representation. Visual Field Representation. Visual Field Representation. Visual Field Representation
 LISC-3 Neuroscience THE VISUAL SYSTEM Central Visual Pathways Each eye sees a part of the visual space that defines its visual field. The s of both eyes overlap extensively to create a binocular. eye both
LISC-3 Neuroscience THE VISUAL SYSTEM Central Visual Pathways Each eye sees a part of the visual space that defines its visual field. The s of both eyes overlap extensively to create a binocular. eye both
Neuroscience - Problem Drill 13: The Eye and Visual Processing
 Neuroscience - Problem Drill 13: The Eye and Visual Processing Question No. 1 of 10 needed, (3) Pick the answer, and (4) Review the core concept tutorial as needed. 1. Which of the following statements
Neuroscience - Problem Drill 13: The Eye and Visual Processing Question No. 1 of 10 needed, (3) Pick the answer, and (4) Review the core concept tutorial as needed. 1. Which of the following statements
Acquired Color Deficiency in Various Diseases
 84th Annual AsMA Scientific Meeting Acquired Color Deficiency in Various Diseases Jeff Rabin,1,2 Michael Castro,1 Daniel Ewing,1 Hayley George,1 Paul Lau,1 Shannon Leon,1 Andrew Yoder,1 John Gooch2 and
84th Annual AsMA Scientific Meeting Acquired Color Deficiency in Various Diseases Jeff Rabin,1,2 Michael Castro,1 Daniel Ewing,1 Hayley George,1 Paul Lau,1 Shannon Leon,1 Andrew Yoder,1 John Gooch2 and
The Eye. Cognitive Neuroscience of Language. Today s goals. 5 From eye to brain. Today s reading
 Cognitive Neuroscience of Language 5 From eye to brain Today s goals Look at the pathways that conduct the visual information from the eye to the visual cortex Marielle Lange http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/mlange/teaching/cnl/
Cognitive Neuroscience of Language 5 From eye to brain Today s goals Look at the pathways that conduct the visual information from the eye to the visual cortex Marielle Lange http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/mlange/teaching/cnl/
Reading Assignments: Lecture 5: Introduction to Vision. None. Brain Theory and Artificial Intelligence
 Brain Theory and Artificial Intelligence Lecture 5:. Reading Assignments: None 1 Projection 2 Projection 3 Convention: Visual Angle Rather than reporting two numbers (size of object and distance to observer),
Brain Theory and Artificial Intelligence Lecture 5:. Reading Assignments: None 1 Projection 2 Projection 3 Convention: Visual Angle Rather than reporting two numbers (size of object and distance to observer),
Parallel processing strategies of the primate visual system
 Parallel processing strategies of the primate visual system Parallel pathways from the retina to the cortex Visual input is initially encoded in the retina as a 2D distribution of intensity. The retinal
Parallel processing strategies of the primate visual system Parallel pathways from the retina to the cortex Visual input is initially encoded in the retina as a 2D distribution of intensity. The retinal
Parallel pathways in the retina
 Retinal origins of parallel pathways in the primate visual system Wednesday, September 23, 2015 Sherry, 2002 1 Parallel pathways in the retina Several different images of the outside world are sent simultaneously
Retinal origins of parallel pathways in the primate visual system Wednesday, September 23, 2015 Sherry, 2002 1 Parallel pathways in the retina Several different images of the outside world are sent simultaneously
Construction of the Visual Image
 Construction of the Visual Image Anne L. van de Ven 8 Sept 2003 BioE 492/592 Sensory Neuroengineering Lecture 3 Visual Perception Light Photoreceptors Interneurons Visual Processing Ganglion Neurons Optic
Construction of the Visual Image Anne L. van de Ven 8 Sept 2003 BioE 492/592 Sensory Neuroengineering Lecture 3 Visual Perception Light Photoreceptors Interneurons Visual Processing Ganglion Neurons Optic
Ganglion cell analysis by optical coherence tomography (OCT) Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD
 Ganglion cell analysis by optical coherence tomography (OCT) Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD Figure 1. Normal OCT of the macula (cross section through the line indicated on the fundus photo)
Ganglion cell analysis by optical coherence tomography (OCT) Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD Figure 1. Normal OCT of the macula (cross section through the line indicated on the fundus photo)
2/3/17. Visual System I. I. Eye, color space, adaptation II. Receptive fields and lateral inhibition III. Thalamus and primary visual cortex
 1 Visual System I I. Eye, color space, adaptation II. Receptive fields and lateral inhibition III. Thalamus and primary visual cortex 2 1 2/3/17 Window of the Soul 3 Information Flow: From Photoreceptors
1 Visual System I I. Eye, color space, adaptation II. Receptive fields and lateral inhibition III. Thalamus and primary visual cortex 2 1 2/3/17 Window of the Soul 3 Information Flow: From Photoreceptors
Applying structure-function to solve clinical cases
 Applying structure-function to solve clinical cases Professor Michael Kalloniatis Centre for Eye Health, and, School of Optometry and Vision Science Acknowledgements Some material prepared by Nayuta Yoshioka
Applying structure-function to solve clinical cases Professor Michael Kalloniatis Centre for Eye Health, and, School of Optometry and Vision Science Acknowledgements Some material prepared by Nayuta Yoshioka
Parallel streams of visual processing
 Parallel streams of visual processing RETINAL GANGLION CELL AXONS: OPTIC TRACT Optic nerve Optic tract Optic chiasm Lateral geniculate nucleus Hypothalamus: regulation of circadian rhythms Pretectum: reflex
Parallel streams of visual processing RETINAL GANGLION CELL AXONS: OPTIC TRACT Optic nerve Optic tract Optic chiasm Lateral geniculate nucleus Hypothalamus: regulation of circadian rhythms Pretectum: reflex
Image Formation and Phototransduction. By Dr. Abdelaziz Hussein Lecturer of Physiology
 Image Formation and Phototransduction By Dr. Abdelaziz Hussein Lecturer of Physiology Vision Vision is a complex process through which an image of the external environment is formed on the photosensitive
Image Formation and Phototransduction By Dr. Abdelaziz Hussein Lecturer of Physiology Vision Vision is a complex process through which an image of the external environment is formed on the photosensitive
A MULTI-STAGE COLOR MODEL REVISITED: IMPLICATIONS FOR A GENE THERAPY CURE FOR RED-GREEN COLORBLINDNESS
 Abstract for Chapter A MULTI-STAGE COLOR MODEL REVISITED: IMPLICATIONS FOR A GENE THERAPY CURE FOR RED-GREEN COLORBLINDNESS Katherine Mancuso 1, Matthew C. Mauck 2, James A. Kuchenbecker 1, Maureen Neitz
Abstract for Chapter A MULTI-STAGE COLOR MODEL REVISITED: IMPLICATIONS FOR A GENE THERAPY CURE FOR RED-GREEN COLORBLINDNESS Katherine Mancuso 1, Matthew C. Mauck 2, James A. Kuchenbecker 1, Maureen Neitz
COGS 101A: Sensation and Perception
 COGS 101A: Sensation and Perception 1 Virginia R. de Sa Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Lecture 5: LGN and V1: Magno and Parvo streams Chapter 3 Course Information 2 Class web page: http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/
COGS 101A: Sensation and Perception 1 Virginia R. de Sa Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Lecture 5: LGN and V1: Magno and Parvo streams Chapter 3 Course Information 2 Class web page: http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/
Foundations. 1. Introduction 2. Gross Anatomy of the Eye 3. Simple Anatomy of the Retina
 Foundations 2. Gross Anatomy of the Eye 3. Simple Anatomy of the Retina Overview Central and peripheral retina compared Muller Glial Cells Foveal Structure Macula Lutea Blood supply to the retina Degenerative
Foundations 2. Gross Anatomy of the Eye 3. Simple Anatomy of the Retina Overview Central and peripheral retina compared Muller Glial Cells Foveal Structure Macula Lutea Blood supply to the retina Degenerative
Method for comparing visual field defects to local RNFL and RGC damage seen on frequency domain OCT in patients with glaucoma.
 Method for comparing visual field defects to local RNFL and RGC damage seen on frequency domain OCT in patients with glaucoma. Donald C. Hood 1,2,* and Ali S. Raza 1 1 Department of Psychology, Columbia
Method for comparing visual field defects to local RNFL and RGC damage seen on frequency domain OCT in patients with glaucoma. Donald C. Hood 1,2,* and Ali S. Raza 1 1 Department of Psychology, Columbia
M Cells. Why parallel pathways? P Cells. Where from the retina? Cortical visual processing. Announcements. Main visual pathway from retina to V1
 Announcements exam 1 this Thursday! review session: Wednesday, 5:00-6:30pm, Meliora 203 Bryce s office hours: Wednesday, 3:30-5:30pm, Gleason https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zdw7pvgz0um M Cells M cells
Announcements exam 1 this Thursday! review session: Wednesday, 5:00-6:30pm, Meliora 203 Bryce s office hours: Wednesday, 3:30-5:30pm, Gleason https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zdw7pvgz0um M Cells M cells
High sensitivity rod photoreceptor input to blue-yellow color opponent pathway in macaque retina
 High sensitivity rod photoreceptor input to blue-yellow color opponent pathway in macaque retina Greg D. Field 1, Martin Greschner 1, Jeffrey L. Gauthier 1, Carolina Rangel 2, Jonathon Shlens 1,3, Alexander
High sensitivity rod photoreceptor input to blue-yellow color opponent pathway in macaque retina Greg D. Field 1, Martin Greschner 1, Jeffrey L. Gauthier 1, Carolina Rangel 2, Jonathon Shlens 1,3, Alexander
Temporal Feature of S-cone Pathway Described by Impulse Response Function
 VISION Vol. 20, No. 2, 67 71, 2008 Temporal Feature of S-cone Pathway Described by Impulse Response Function Keizo SHINOMORI Department of Information Systems Engineering, Kochi University of Technology
VISION Vol. 20, No. 2, 67 71, 2008 Temporal Feature of S-cone Pathway Described by Impulse Response Function Keizo SHINOMORI Department of Information Systems Engineering, Kochi University of Technology
Image Processing in the Human Visual System, a Quick Overview
 Image Processing in the Human Visual System, a Quick Overview By Orazio Gallo, April 24th, 2008 The Visual System Our most advanced perception system: The optic nerve has 106 fibers, more than all the
Image Processing in the Human Visual System, a Quick Overview By Orazio Gallo, April 24th, 2008 The Visual System Our most advanced perception system: The optic nerve has 106 fibers, more than all the
Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN)
 Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) What happens beyond the retina? What happens in Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN)- 90% flow Visual cortex Information Flow Superior colliculus 10% flow Slide 2 Information
Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) What happens beyond the retina? What happens in Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN)- 90% flow Visual cortex Information Flow Superior colliculus 10% flow Slide 2 Information
THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus
 THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus Perceived color of light is determined by 3 characteristics (properties of electromagnetic energy): 1. Hue: the spectrum (wavelength) of light (color)
THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus Perceived color of light is determined by 3 characteristics (properties of electromagnetic energy): 1. Hue: the spectrum (wavelength) of light (color)
Differential distributions of red green and blue yellow cone opponency across the visual field
 Visual Neuroscience (2002), 19, 109 118. Printed in the USA. Copyright 2002 Cambridge University Press 0952-5238002 $12.50 DOI: 10.1017.S0952523802191103 Differential distributions of red green and blue
Visual Neuroscience (2002), 19, 109 118. Printed in the USA. Copyright 2002 Cambridge University Press 0952-5238002 $12.50 DOI: 10.1017.S0952523802191103 Differential distributions of red green and blue
Vision II. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Vision II Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Ganglion Cells The axons of the retinal ganglion cells form the optic nerve and carry visual information into the brain. 2 Optic
Vision II Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Ganglion Cells The axons of the retinal ganglion cells form the optic nerve and carry visual information into the brain. 2 Optic
THE STRUCTURE-FUNCTION JUNCTION
 THE STRUCTURE-FUNCTION JUNCTION Craig Thomas, O.D. 3900 West Wheatland Road Dallas, Texas 75237 972-780-7199 thpckc@yahoo.com Paul M. Karpecki, O.D., FAAO 120 N Eagle Creek Drive # 431 Lexington, KY 40509
THE STRUCTURE-FUNCTION JUNCTION Craig Thomas, O.D. 3900 West Wheatland Road Dallas, Texas 75237 972-780-7199 thpckc@yahoo.com Paul M. Karpecki, O.D., FAAO 120 N Eagle Creek Drive # 431 Lexington, KY 40509
Electrodiagnostics Alphabet Soup
 Nathan Lighthizer, O.D., F.A.A.O Assistant Professor, NSUOCO Chief of Specialty Care Clinics Chief of Electrodiagnostics Clinic What is electrodiagnostics testing? Visual Pathway Basic Understanding VEP
Nathan Lighthizer, O.D., F.A.A.O Assistant Professor, NSUOCO Chief of Specialty Care Clinics Chief of Electrodiagnostics Clinic What is electrodiagnostics testing? Visual Pathway Basic Understanding VEP
CS294-6 (Fall 2004) Recognizing People, Objects and Actions Lecture: January 27, 2004 Human Visual System
 CS294-6 (Fall 2004) Recognizing People, Objects and Actions Lecture: January 27, 2004 Human Visual System Lecturer: Jitendra Malik Scribe: Ryan White (Slide: layout of the brain) Facts about the brain:
CS294-6 (Fall 2004) Recognizing People, Objects and Actions Lecture: January 27, 2004 Human Visual System Lecturer: Jitendra Malik Scribe: Ryan White (Slide: layout of the brain) Facts about the brain:
9.35 Sensation And Perception
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.35 Sensation And Perception Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.35 Recitation 1 Eye
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.35 Sensation And Perception Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.35 Recitation 1 Eye
LEA Color Vision Testing
 To The Tester Quantitative measurement of color vision is an important diagnostic test used to define the degree of hereditary color vision defects found in screening with pseudoisochromatic tests and
To The Tester Quantitative measurement of color vision is an important diagnostic test used to define the degree of hereditary color vision defects found in screening with pseudoisochromatic tests and
Figure 4-1. Layers of the Neural Retina.
 Chapter 4. The Neural Retina Basic Organization At one level the retina works like film in a camera: it records the optical image that is focused onto it by the cornea and lens, and relays this information
Chapter 4. The Neural Retina Basic Organization At one level the retina works like film in a camera: it records the optical image that is focused onto it by the cornea and lens, and relays this information
Neuroanatomy, Text and Atlas (J. H. Martin), 3 rd Edition Chapter 7, The Visual System, pp ,
 Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: RETINA and CENTRAL VISUAL PATHWAYS P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Friday, 20
Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: RETINA and CENTRAL VISUAL PATHWAYS P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Friday, 20
Photoreceptors Rods. Cones
 Photoreceptors Rods Cones 120 000 000 Dim light Prefer wavelength of 505 nm Monochromatic Mainly in periphery of the eye 6 000 000 More light Different spectral sensitivities!long-wave receptors (558 nm)
Photoreceptors Rods Cones 120 000 000 Dim light Prefer wavelength of 505 nm Monochromatic Mainly in periphery of the eye 6 000 000 More light Different spectral sensitivities!long-wave receptors (558 nm)
Senses are transducers. Change one form of energy into another Light, sound, pressure, etc. into What?
 1 Vision 2 TRANSDUCTION Senses are transducers Change one form of energy into another Light, sound, pressure, etc. into What? Action potentials! Sensory codes Frequency code encodes information about intensity
1 Vision 2 TRANSDUCTION Senses are transducers Change one form of energy into another Light, sound, pressure, etc. into What? Action potentials! Sensory codes Frequency code encodes information about intensity
Fundus Autofluorescence. Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD
 Fundus Autofluorescence Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD The retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) has many important functions including phagocytosis of the photoreceptor outer segments Cone Rod
Fundus Autofluorescence Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD The retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) has many important functions including phagocytosis of the photoreceptor outer segments Cone Rod
Prof. Greg Francis 7/31/15
 s PSY 200 Greg Francis Lecture 06 How do you recognize your grandmother? Action potential With enough excitatory input, a cell produces an action potential that sends a signal down its axon to other cells
s PSY 200 Greg Francis Lecture 06 How do you recognize your grandmother? Action potential With enough excitatory input, a cell produces an action potential that sends a signal down its axon to other cells
THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus
 THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus Perceived color of light is determined by 3 characteristics (properties of electromagnetic energy): 1. : the spectrum (wavelength) of light (color) 2.
THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus Perceived color of light is determined by 3 characteristics (properties of electromagnetic energy): 1. : the spectrum (wavelength) of light (color) 2.
Test of visual pathway function
 The visual system Test of visual pathway function Suppose you have a patient who may have some damage to the visual pathways leading to visual cortex, for example from multiple sclerosis. How could you
The visual system Test of visual pathway function Suppose you have a patient who may have some damage to the visual pathways leading to visual cortex, for example from multiple sclerosis. How could you
What do we perceive?
 THE VISUAL SYSTEM Aditi Majumder What do we perceive? Example: Switch off the light in room What we perceive Not only the property of the scene But also that of the visual system Our perception is filtered
THE VISUAL SYSTEM Aditi Majumder What do we perceive? Example: Switch off the light in room What we perceive Not only the property of the scene But also that of the visual system Our perception is filtered
ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2003
 ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2003 Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Pay careful attention to the point value of questions so that you allocate your time appropriately (1 point = 1 minute).
ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2003 Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Pay careful attention to the point value of questions so that you allocate your time appropriately (1 point = 1 minute).
Vision I. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Vision I Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Eye Cornea Sclera Conjunctiva 2 Eye The conjunctiva lines the inner surface of the eyelids and outer surface of the sclera. 3
Vision I Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Eye Cornea Sclera Conjunctiva 2 Eye The conjunctiva lines the inner surface of the eyelids and outer surface of the sclera. 3
Ch 5. Perception and Encoding
 Ch 5. Perception and Encoding Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by Y.-J. Park, M.-H. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang
Ch 5. Perception and Encoding Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by Y.-J. Park, M.-H. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang
In office electrodiagnostics: what can it do for you
 9/6/6 In office electrodiagnostics: what can it do for you Nathan Lighthizer, O.D., F.A.A.O Assistant Professor, NSUOCO Chief of Specialty Care Clinics Chief of Electrodiagnostics Clinic Course Outline/Objective
9/6/6 In office electrodiagnostics: what can it do for you Nathan Lighthizer, O.D., F.A.A.O Assistant Professor, NSUOCO Chief of Specialty Care Clinics Chief of Electrodiagnostics Clinic Course Outline/Objective
The ON and OFF Channels
 The visual and oculomotor systems Peter H. Schiller, year 2006 The ON and OFF Channels Questions: 1. How are the ON and OFF channels created for the cones? 2. How are the ON and OFF channels created for
The visual and oculomotor systems Peter H. Schiller, year 2006 The ON and OFF Channels Questions: 1. How are the ON and OFF channels created for the cones? 2. How are the ON and OFF channels created for
Ch 5. Perception and Encoding
 Ch 5. Perception and Encoding Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga,, R. B. Ivry,, and G. R. Mangun,, Norton, 2002. Summarized by Y.-J. Park, M.-H. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang
Ch 5. Perception and Encoding Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga,, R. B. Ivry,, and G. R. Mangun,, Norton, 2002. Summarized by Y.-J. Park, M.-H. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang
LISC-322 Neuroscience Cortical Organization
 LISC-322 Neuroscience Cortical Organization THE VISUAL SYSTEM Higher Visual Processing Martin Paré Assistant Professor Physiology & Psychology Most of the cortex that covers the cerebral hemispheres is
LISC-322 Neuroscience Cortical Organization THE VISUAL SYSTEM Higher Visual Processing Martin Paré Assistant Professor Physiology & Psychology Most of the cortex that covers the cerebral hemispheres is
Glaucoma THE STRUCTURE-FUNCTION JUNCTION. Measuring Structure and Function. Structure-Function Relationship. Structure-Function Relationship
 THE STRUCTURE-FUNCTION JUNCTION Craig Thomas, O.D. 3900 West Wheatland Road Dallas, Texas 75237 972-780-7199 thpckc@yahoo.com Glaucoma Glaucoma is a family of chronic, progressive optic neuropathies characterized
THE STRUCTURE-FUNCTION JUNCTION Craig Thomas, O.D. 3900 West Wheatland Road Dallas, Texas 75237 972-780-7199 thpckc@yahoo.com Glaucoma Glaucoma is a family of chronic, progressive optic neuropathies characterized
PSY 214 Lecture 5 (09/19/2010) (Vision) Dr. Achtman PSY 214. Lecture 5 Topic: Introduction to Vision Chapter 3, pages 55-71
 Corrections: No corrections needed Announcements: After the completion of chapter 4 a movie will be shown First test is October 3, 2011 Dr. Achtman is available during her office hours The test will include
Corrections: No corrections needed Announcements: After the completion of chapter 4 a movie will be shown First test is October 3, 2011 Dr. Achtman is available during her office hours The test will include
25/09/2012. Capgras Syndrome. Chapter 2. Capgras Syndrome - 2. The Neural Basis of Cognition
 Chapter 2 The Neural Basis of Cognition Capgras Syndrome Alzheimer s patients & others delusion that significant others are robots or impersonators - paranoia Two brain systems for facial recognition -
Chapter 2 The Neural Basis of Cognition Capgras Syndrome Alzheimer s patients & others delusion that significant others are robots or impersonators - paranoia Two brain systems for facial recognition -
V1 (Chap 3, part II) Lecture 8. Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017
 V1 (Chap 3, part II) Lecture 8 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Topography: mapping of objects in space onto the visual cortex contralateral representation
V1 (Chap 3, part II) Lecture 8 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Topography: mapping of objects in space onto the visual cortex contralateral representation
A Connectionist Perspective on Laterality in Visual Attention
 A Connectionist Perspective on Laterality in Visual Attention Neil D. B. Bruce and John K. Tsotsos Department of Computer Science and Centre for Vision Research York University, Toronto, ON, M3J 1P3 February
A Connectionist Perspective on Laterality in Visual Attention Neil D. B. Bruce and John K. Tsotsos Department of Computer Science and Centre for Vision Research York University, Toronto, ON, M3J 1P3 February
Seeing Color. Muller (1896) The Psychophysical Axioms. Brindley (1960) Psychophysical Linking Hypotheses
 Muller (1896) The Psychophysical Axioms The ground of every state of consciousness is a material process, a psychophysical process so-called, to whose occurrence the state of consciousness is joined To
Muller (1896) The Psychophysical Axioms The ground of every state of consciousness is a material process, a psychophysical process so-called, to whose occurrence the state of consciousness is joined To
Parkinsonism and Related Disorders
 Parkinsonism and Related Disorders 19 (2013) 1e14 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Parkinsonism and Related Disorders journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/parkreldis Review Foveal
Parkinsonism and Related Disorders 19 (2013) 1e14 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Parkinsonism and Related Disorders journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/parkreldis Review Foveal
BINOCULAR VISUAL FIELD. fixation point. fovea
 BINOCULAR VISUAL FIELD fixation point fovea left hemisphere right hemisphere VISUAL HEMIFIELD monocular crescent temporal hemi-retina nasal hemi-retina left hemisphere right hemisphere VISUAL PATHWAYS
BINOCULAR VISUAL FIELD fixation point fovea left hemisphere right hemisphere VISUAL HEMIFIELD monocular crescent temporal hemi-retina nasal hemi-retina left hemisphere right hemisphere VISUAL PATHWAYS
CNS-2: Physiology: Vision
 CNS-2: Physiology: Vision The eyes are the windows to the soul This is the 3rd lecture in CNS-2 Physiology. In this lecture we will talk about one of our special senses, and that is the Vision. Hopefully
CNS-2: Physiology: Vision The eyes are the windows to the soul This is the 3rd lecture in CNS-2 Physiology. In this lecture we will talk about one of our special senses, and that is the Vision. Hopefully
The Dyschromatopsia of Opric Neuritis Is Determined in Part by the Foveal/Perifoveal Distribution of Visual Field Damage
 Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. Vol..11. No. 9. September 1990 Cop>right
Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. Vol..11. No. 9. September 1990 Cop>right
PARALLEL PATHWAYS FOR SPECTRAL CODING
 Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2000. 23:743 775 Copyright by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved PARALLEL PATHWAYS FOR SPECTRAL CODING IN PRIMATE RETINA Dennis M. Dacey Department of Biological Structure and The
Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2000. 23:743 775 Copyright by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved PARALLEL PATHWAYS FOR SPECTRAL CODING IN PRIMATE RETINA Dennis M. Dacey Department of Biological Structure and The
Neural circuits PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 05. Rods and cones
 Neural circuits PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 05 Why do you need bright light to read? Rods and cones Photoreceptors are not evenly distributed across the retina 1 Rods and cones Cones are most dense in
Neural circuits PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 05 Why do you need bright light to read? Rods and cones Photoreceptors are not evenly distributed across the retina 1 Rods and cones Cones are most dense in
The lowest level of stimulation that a person can detect. absolute threshold. Adapting one's current understandings to incorporate new information.
 absolute threshold The lowest level of stimulation that a person can detect accommodation Adapting one's current understandings to incorporate new information. acuity Sharp perception or vision audition
absolute threshold The lowest level of stimulation that a person can detect accommodation Adapting one's current understandings to incorporate new information. acuity Sharp perception or vision audition
Vision. The Eye External View. The Eye in Cross-Section
 Vision The Eye External View cornea pupil iris The Eye in Cross-Section Light enters via cornea, Is focused by cornea and lens, Forming image on retina, Which contains photoreceptors. 1 The Retina Photoreceptors
Vision The Eye External View cornea pupil iris The Eye in Cross-Section Light enters via cornea, Is focused by cornea and lens, Forming image on retina, Which contains photoreceptors. 1 The Retina Photoreceptors
THE VISUAL PATHWAY FOR DENTAL STUDENTS
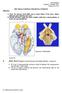 Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. February 16, 2012 Objectives: THE VISUAL PATHWAY FOR DENTAL STUDENTS A. Draw the expected visual fields seen in classic lesions of the nerve, chiasm, thalamus, optic
Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. February 16, 2012 Objectives: THE VISUAL PATHWAY FOR DENTAL STUDENTS A. Draw the expected visual fields seen in classic lesions of the nerve, chiasm, thalamus, optic
Human colour perception and its adaptation
 Network: Computation in Neural Systems 7 (1996) 587 634. Printed in the UK Human colour perception and its adaptation Michael A Webster Department of Psychology, University of Nevada, Reno, NV 89557-0062,
Network: Computation in Neural Systems 7 (1996) 587 634. Printed in the UK Human colour perception and its adaptation Michael A Webster Department of Psychology, University of Nevada, Reno, NV 89557-0062,
ACQUIRED COLOUR VISION DEFECTS IN OPTIC NERVE DISORDERS- A COMPARISON BETWEEN ISHIHARA S TEST AND ROTH 28-HUE TEST DR. TEENA MARIET MENDONCA
 ACQUIRED COLOUR VISION DEFECTS IN OPTIC NERVE DISORDERS- A COMPARISON BETWEEN ISHIHARA S TEST AND ROTH 28-HUE TEST By DR. TEENA MARIET MENDONCA Dissertation Submitted to the Rajiv Gandhi University of
ACQUIRED COLOUR VISION DEFECTS IN OPTIC NERVE DISORDERS- A COMPARISON BETWEEN ISHIHARA S TEST AND ROTH 28-HUE TEST By DR. TEENA MARIET MENDONCA Dissertation Submitted to the Rajiv Gandhi University of
7. Sharp perception or vision 8. The process of transferring genetic material from one cell to another by a plasmid or bacteriophage
 1. A particular shade of a given color 2. How many wave peaks pass a certain point per given time 3. Process in which the sense organs' receptor cells are stimulated and relay initial information to higher
1. A particular shade of a given color 2. How many wave peaks pass a certain point per given time 3. Process in which the sense organs' receptor cells are stimulated and relay initial information to higher
Visual System. By: Jordan Koehling
 Visual System By: Jordan Koehling What is the Visual System Photoreceptors are the type of sensory neuron involved in sight. It is part of the CNS and allows us to see our surroundings using visual light
Visual System By: Jordan Koehling What is the Visual System Photoreceptors are the type of sensory neuron involved in sight. It is part of the CNS and allows us to see our surroundings using visual light
Visual Brain: The Neural Basis of Visual Perception!
 Visual Brain: The Neural Basis of Visual Perception!?! Human Brain: Amazing Machine! Cerebral cortex! Highest level of all sensory integration Highest level of somatic motor control Memory, association
Visual Brain: The Neural Basis of Visual Perception!?! Human Brain: Amazing Machine! Cerebral cortex! Highest level of all sensory integration Highest level of somatic motor control Memory, association
ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2001
 ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2001 As always, the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect, so keep your eyes foveated on your own exam. I tend to think of a point as a minute, so be sure to spend the appropriate amount
ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2001 As always, the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect, so keep your eyes foveated on your own exam. I tend to think of a point as a minute, so be sure to spend the appropriate amount
Visual Information Processing in the Primate Brain
 In: Handbook of Psychology, Vol. 3: Biological Psychology, 2003 (Gallagher, M. & Nelson, RJ, eds) pp. 139-185; New York: John Wyley & Sons, Inc. CHAPTER 6 Visual Information Processing in the Primate Brain
In: Handbook of Psychology, Vol. 3: Biological Psychology, 2003 (Gallagher, M. & Nelson, RJ, eds) pp. 139-185; New York: John Wyley & Sons, Inc. CHAPTER 6 Visual Information Processing in the Primate Brain
Assessment of Current and Next Generation of Colour Vision Tests for Occupational Use
 Assessment of Current and Next Generation of Colour Vision Tests for Occupational Use by Ali Almustanyir A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo in fulfillment of the thesis requirement for the
Assessment of Current and Next Generation of Colour Vision Tests for Occupational Use by Ali Almustanyir A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo in fulfillment of the thesis requirement for the
ANAT2010. Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018
 ANAT2010 Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018 Table of Contents Lecture 13: Pain and perception... 3 Lecture 14: Sensory systems and visual pathways... 11 Lecture 15: Techniques in Neuroanatomy I in vivo
ANAT2010 Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018 Table of Contents Lecture 13: Pain and perception... 3 Lecture 14: Sensory systems and visual pathways... 11 Lecture 15: Techniques in Neuroanatomy I in vivo
ASSUMPTION OF COGNITIVE UNIFORMITY
 The Human Brain cerebral hemispheres: two most important divisions of the brain, separated by the longitudinal fissure corpus callosum: a large bundle of axons that constitutes the major connection between
The Human Brain cerebral hemispheres: two most important divisions of the brain, separated by the longitudinal fissure corpus callosum: a large bundle of axons that constitutes the major connection between
SENSES: VISION. Chapter 5: Sensation AP Psychology Fall 2014
 SENSES: VISION Chapter 5: Sensation AP Psychology Fall 2014 Sensation versus Perception Top-Down Processing (Perception) Cerebral cortex/ Association Areas Expectations Experiences Memories Schemas Anticipation
SENSES: VISION Chapter 5: Sensation AP Psychology Fall 2014 Sensation versus Perception Top-Down Processing (Perception) Cerebral cortex/ Association Areas Expectations Experiences Memories Schemas Anticipation
Plasticity of Cerebral Cortex in Development
 Plasticity of Cerebral Cortex in Development Jessica R. Newton and Mriganka Sur Department of Brain & Cognitive Sciences Picower Center for Learning & Memory Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge,
Plasticity of Cerebral Cortex in Development Jessica R. Newton and Mriganka Sur Department of Brain & Cognitive Sciences Picower Center for Learning & Memory Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge,
The Visual System. Cortical Architecture Casagrande February 23, 2004
 The Visual System Cortical Architecture Casagrande February 23, 2004 Phone: 343-4538 Email: vivien.casagrande@mcmail.vanderbilt.edu Office: T2302 MCN Required Reading Adler s Physiology of the Eye Chapters
The Visual System Cortical Architecture Casagrande February 23, 2004 Phone: 343-4538 Email: vivien.casagrande@mcmail.vanderbilt.edu Office: T2302 MCN Required Reading Adler s Physiology of the Eye Chapters
The Visual System. Chapter 3
 Chapter 3 The Visual System Figure 3.1: Left: The visual system seen from underneath the brain showing the nerve fibres from the retina cross over to the opposite sides of the brain. A small part of the
Chapter 3 The Visual System Figure 3.1: Left: The visual system seen from underneath the brain showing the nerve fibres from the retina cross over to the opposite sides of the brain. A small part of the
Psy393: Cognitive Neuroscience. Prof. Anderson Department of Psychology Week 3
 Psy393: Cognitive Neuroscience Prof. Anderson Department of Psychology Week 3 The Eye: Proof for the existence of God? And then there was light Optics Perception Absorption Eye is receiver not sender Plato
Psy393: Cognitive Neuroscience Prof. Anderson Department of Psychology Week 3 The Eye: Proof for the existence of God? And then there was light Optics Perception Absorption Eye is receiver not sender Plato
Clinical Trial Endpoints for Macular Diseases
 Clinical Trial Endpoints for Macular Diseases Developed in collaboration Learning Objective Upon completion, participants should be able to: Summarize types of biomarkers of progression and treatment response
Clinical Trial Endpoints for Macular Diseases Developed in collaboration Learning Objective Upon completion, participants should be able to: Summarize types of biomarkers of progression and treatment response
The Visual System. Anatomical Overview Dr. Casagrande January 21, 2004
 The Visual System Anatomical Overview Dr. Casagrande January 21, 2004 Phone: 343-4538 Email: vivien.casagrande@mcmail.vanderbilt.edu Office: T2302 MCN How the Brain Works Useful Additional Reading: Adler,
The Visual System Anatomical Overview Dr. Casagrande January 21, 2004 Phone: 343-4538 Email: vivien.casagrande@mcmail.vanderbilt.edu Office: T2302 MCN How the Brain Works Useful Additional Reading: Adler,
Vision. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Vision Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Vision is the ability to detect light patterns from the outside environment and interpret them into images. Animals are bombarded with sensory information, and the sheer volume
Vision Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Vision is the ability to detect light patterns from the outside environment and interpret them into images. Animals are bombarded with sensory information, and the sheer volume
Physiology of human perception
 Physiology of human perception Vision Hearing Thermal and tactile sensations Basic introduction and the list and description of the tasks to be carried out Visible light: 400-700 nm. Vision or sight Anatomy
Physiology of human perception Vision Hearing Thermal and tactile sensations Basic introduction and the list and description of the tasks to be carried out Visible light: 400-700 nm. Vision or sight Anatomy
The Visual System. Organization of cell types Rod and cone photoreceptor systems
 The Visual System Basic anatomy of the eye The retina Organization of cell types Rod and cone photoreceptor systems Phototransduction Conversion of energy of light into changes in V m Adaptation and expansion
The Visual System Basic anatomy of the eye The retina Organization of cell types Rod and cone photoreceptor systems Phototransduction Conversion of energy of light into changes in V m Adaptation and expansion
Primary Visual Pathways (I)
 Primary Visual Pathways (I) Introduction to Computational and Biological Vision CS 202-1-5261 Computer Science Department, BGU Ohad Ben-Shahar Where does visual information go from the eye? Where does
Primary Visual Pathways (I) Introduction to Computational and Biological Vision CS 202-1-5261 Computer Science Department, BGU Ohad Ben-Shahar Where does visual information go from the eye? Where does
Dark and light adaptation: a job that is accomplished mainly in the retina
 Dark and light adaptation: a job that is accomplished mainly in the retina Dark adaptation: recovery in darkness (of sensitivity) and photoreceptor pigment. Light adaptation: The ability of the visual
Dark and light adaptation: a job that is accomplished mainly in the retina Dark adaptation: recovery in darkness (of sensitivity) and photoreceptor pigment. Light adaptation: The ability of the visual
Electronic Letters to: Electronic letters published: Multiple Mechanisms in the VEP 23 July von :24
 QUICK SEARCH: Author: Go [advanced] Keyword(s): HOME HELP FEEDBACK SUBSCRIPTIONS ARCHIVE SEARCH Year: Vol: Page: Electronic Letters to: Visual Neurophysiology: Givago S. Souza, Bruno D. Gomes, Cézar A.
QUICK SEARCH: Author: Go [advanced] Keyword(s): HOME HELP FEEDBACK SUBSCRIPTIONS ARCHIVE SEARCH Year: Vol: Page: Electronic Letters to: Visual Neurophysiology: Givago S. Souza, Bruno D. Gomes, Cézar A.
Normal and amblyopic contrast sensitivity functions in central and peripheral retinas
 Normal and amblyopic contrast sensitivity functions in central and peripheral retinas Joseph Thomas Contrast sensitivity functions (CSF's)for temporally modulated sine wave gratings were established at
Normal and amblyopic contrast sensitivity functions in central and peripheral retinas Joseph Thomas Contrast sensitivity functions (CSF's)for temporally modulated sine wave gratings were established at
Mind. Synopsis: Synopsis: Friday: Overview Perception Retina Central projections LGN (Visual Cortex)
 We emphasize these points from Kandel in Bi/CNS 150 Bi/CNS/NB 150: Neuroscience Read Lecture Vision I October 28, 2015 Ralph Adolphs Chapter 26 & 27 Vision I (Adolphs) Overview of the visual system Anatomy:
We emphasize these points from Kandel in Bi/CNS 150 Bi/CNS/NB 150: Neuroscience Read Lecture Vision I October 28, 2015 Ralph Adolphs Chapter 26 & 27 Vision I (Adolphs) Overview of the visual system Anatomy:
Electroretinographic abnormalities and advanced multiple sclerosis
 Electroretinographic abnormalities and advanced multiple sclerosis James Pitzer Gills, Jr. Reduced electroretinographic responses were present in patients with advanced multiple sclerosis. The observed
Electroretinographic abnormalities and advanced multiple sclerosis James Pitzer Gills, Jr. Reduced electroretinographic responses were present in patients with advanced multiple sclerosis. The observed
Required Slide. Session Objectives
 Vision: CNS 2018 Required Slide Session Objectives Visual system: CNS At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1. Understand how axons from the eyes travel through the optic nerves and tracts
Vision: CNS 2018 Required Slide Session Objectives Visual system: CNS At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1. Understand how axons from the eyes travel through the optic nerves and tracts
