Social economic development in the prevention of global blindness
|
|
|
- Victor Wright
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Br J Ophthalmol 2;85: Tufts University, School of Medicine, Boston, MA, USA VHHo University of California at Davis, School of Medicine, Sacramento, CA, USA I R Schwab Correspondence to: Ivan R Schwab, MD, FACS, Department of Ophthalmology, UC Davis Medical Center, 486 Y Street, Suite 24, Sacramento, CA 9587, USA irschwab@ucdavis.edu Accepted for publication 22 February 2 Social economic development in the prevention of global blindness Viet H Ho, Ivan R Schwab Abstract Aims To assess the relation between a country s economic developmental status and its prevalence of blindness. Methods Available epidemiological data on worldwide visual loss and its causes compiled by the World Health Organization were reviewed. Findings were compared with economic development data from the involved countries and regions. Analysis was completed in view of the socioeconomic status of each country and region. Results Analysis of the global distribution of blindness indicates a trend of higher prevalence existing in developing countries with lower per capita income. Preventable causes of blindness (that is, cataract, trachoma) are also more prevalent in these countries. Conclusions Because economic development is shown to be a factor in blindness, programmes for blindness prevention should not be the only route to the elimination of unnecessary blindness throughout the world. Concomitant economic development is also necessary to reduce and eventually eradicate much of the preventable and avoidable causes of blindness. (Br J Ophthalmol 2;85: ) Worldwide, there are about 5 million people that are visually disabled. Population based studies in various countries coordinated by the World Health Organization (WHO) programme for the prevention of blindness have estimated that approximately 38 million are blind and an additional million have severely impaired vision. Blindness in the world is still increasing by one to two million cases a year. 2 The WHO indicates that blindness will experience an accelerated growth and a probable doubling by the year 22 unless suycient resources for its prevention are made available. 2 WHO and various international donor agencies have launched Vision 22: the right to sight a global initiative to eliminate avoidable blindness by the year Their attempt is to increase the number of trained eyecare professionals, improve service accessibility, and procure appropriate technologies. The grand development of these programmes is thought to be necessary and will help mitigate the global burden of blindness. However, such coordination evorts focus mainly on allocation of resources and services. Other economic factors such as poverty may also contribute to blindness. The role of economic development as it may relate to blindness has not been previously assessed. Overall, data show that more than 9% of all blind people live in developing countries. 2 Patterns of blinding disorders diver between countries that are less economically developed and those that have a stronger economic infrastructure. Hence, it is conceivable that factors such as economic development strongly influence the population of blind people in each country. In this investigation, we explore the relation between the prevalence of blindness and economic development. Materials and methods In 978, the WHO programme for the prevention of blindness (PBL) created a global blindness data bank (BDB) to obtain more detailed knowledge about blindness and its causes worldwide. The development and application of a population based assessment methodology in an increasing number of countries has led to a gradual accumulation of epidemiologically reliable data, with updated information having been published several times. Details of the survey methods for such data have been described elsewhere. 3 In this investigation, we evaluate the most recent update of published data on blindness from some 6 separate countries. 4 We identified the blindness prevalence from various reference areas of each given country. Blindness was defined by the International Classification of Diseases th revision (ICD-) as visual acuity <3/6. 4 The gross national product (GNP) per capita income was used as a measure of each country s economic status. These data were gathered from statistical resources published by the United Nations. 5 Because the collection of blindness data varied by the year in which the study was done, the source year of economic data was chosen to match that of the established blindness data. All values were entered into a spreadsheet using software from Microsoft Excel. All figures were generated using the functions from this software program. We used the trend line function to create a regression line from a scatter plot of the data (Figs 3). The software program calculated the coeycient of determination, or R 2 value, of the regression line. We also compared the blindness prevalence and economic data by regions. These regions are composed of the 229 countries/territories/ economies registered worldwide and are grouped as proposed in the World Development Report, Owing to the lack of complete economic data on all 229 countries/territories/ Br J Ophthalmol: first published as.36/bjo on June 2. Downloaded from on 3 January 29 by guest. Protected by copyright.
2 654 Ho, Schwab Table Blindness prevalence and economic data for countries used in study, countries grouped by economic region* Economic region Country economies, we calculated the total regional per capita using data from only those countries for which blindness data were available. The average regional per capita value was also attained from only the involved countries. Likewise, the regional number of blind and regional blindness prevalence data reflect only the involved countries. The global distribution of blindness by major causes (cataract, trachoma, glaucoma, and other) has previously been reported by Thylefors et al. Here, we show the distribution by economic regions (Fig 4). Results A total of 53 countries possessed data that met the definition criteria for blindness (Table ). Of these, only 22 countries had blindness Source year Country population (million) GNP per capita (US$) Established market economies (EME) Australia France Ireland Italy USA UK Other Asia and islands (OAI) Cook Islands Indonesia Kiribati Korea, Republic of Mongolia Myanmar Nepal Papua New Guinea Philippines Solomon Islands Sri Lanka Thailand Tonga Vanuatu Vietnam Samoa Formerly socialist market economies (FSE) Bulgaria Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) Benin Burkina Faso Cameroon Chad Congo Ethiopia Gambia Ghana Kenya Malawi Mali Niger Nigeria South Africa Tanzania Togo Zambia Zimbabwe Latin America and the Caribbean (LAC) Costa Rica Peru Middle Eastern crescent (MEC) Egypt Malta Morocco Pakistan Saudi Arabia Tunisia Turkey Yemen, Republic of India India China China *See World development report, 993. Countries in which blindness prevalence data were estimated from entire country population. Blindness prevalence (%) prevalence that was estimated from the entire population of the country. In the remaining 3 countries, population based studies were done for one or more predetermined reference areas within the country. Data from the largest survey population were chosen as the representative prevalence values from those countries with multiple data. For the 22 countries previously mentioned (with entire country estimates), the relation between the prevalence of blindness and level of economic development of each country was studied (Fig ). A regression or best fit line has been plotted. The R 2 value (. in Fig ) measures the amount of variation in the blindness prevalence that is accounted for by the per capita income. The correlation coeycient, r value, of the regression line indicates how well Br J Ophthalmol: first published as.36/bjo on June 2. Downloaded from on 3 January 29 by guest. Protected by copyright.
3 Social economic development in the prevention of global blindness 655 Blindness prevalence (%) R 2 =.7 r = Per capita income (US$) Figure Prevalence of blindness versus per capita income, per country. Data taken from 22 countries with whole country estimates. Blindness prevalence (%) Per capita income (US$) R 2 =.2233 r = Figure 2 Prevalence of blindness versus per capita income, per country. Data taken from all 53 countries in the study. Table 2 Economic region 5 Global distribution of blindness and economic data, by economic region* Total regional per capita (US$) Average regional per capita (US$) Number of blind (millions) SSA India OAI China MEC LAC EME FSE Blindness prevalence (%) All data based on 99 values. SSA = sub-saharan Africa; OAI = other Asia and islands; MEC = Middle Eastern crescent; LAC = Latin America and Caribbean; EME = established market economies; FSE = former socialist economies. *See World development report, 993. each country s economic development is associated with its blindness prevalence. The r value was.33 for data taken from whole country studies. A similar relation was found for data from all 53 countries, with an R 2 value of.22 and an r value of.47 (Fig 2). This higher value reflects the inclusion of extended data from studies done in reference areas of each country. Total estimated cases of blind, blindness prevalence, and per capita incomes were compiled by regions (Table 2). The regional per capita income as it relates to the prevalence of blindness in each region showed an inverse relation (Fig 3). The R 2 value of.44 and r value of.67 was calculated. The relative importance of cataract, trachoma, glaucoma, onchocerciasis, and other disorders leading to blindness (diabetes, macular degeneration, etc), is depicted for each region (Fig 4). Cataract is seen as the most important cause of blindness in developing regions, whereas other causes of blindness relatively dominate in regions that are more economically developed. Discussion Strict adherence to the predefined parameters of total country estimates of blindness and per capita income yielded less correlation than expected (Fig ). Even including those countries that had accurate data from reference areas, the correlation was less than expected (Fig 2). However, the indication of an inverse relation does exist between the prevalence of blindness and economic development. Several outlying points on each figure contribute the variance from the trend line. Because blindness prevalence data were produced through estimates using models/algorithms, it is plausible that such factors as reporting biases and inconsistent data collection methods can explain the discrepancy. The magnitude of global blindness and its major causes have been estimated by Thylefors et al, whereby they examined the blindness distribution according to eight economic regions. We used these data of blindness prevalence and compared them with the economic development per region, which showed a surprisingly good inverse association between the total number of blind and the economic status of each region (Fig 3). The impact of economic development has previously been thought to be associated with lower prevalence of blindness worldwide However, a comprehensive analysis of a direct correlation has not been completed. Currently, the majority of the world s population lives in rural areas of less developed countries. Characteristics of developing nations are high birth rates and infant mortality rates, and high rates of curable and preventable blindness. 7 Socioeconomic development brings forth improvements in the standard of living, environmental sanitation, and public hygiene. This comparative review of the available data on blindness supports the evidence that blindness is more prevalent in less well developed countries. The analogous impact of socioeconomic development can account for the progress made in the reduction of diseases such as trachoma and leprosy. Families with low socioeconomic status, poor water supplies, and suboptimal hygiene practices characterise areas in which trachoma is endemic. West et al have reported extensively on the association between such factors and the prevalence of trachoma in central Africa. 2 Even earlier authors such as Duke-Elder suggested that economic constituents such as poverty and malnutrition correlate with higher prevalence of trachoma. 3 These observations have led to the acceptance that regression of trachoma in many regions of the world has occurred with Br J Ophthalmol: first published as.36/bjo on June 2. Downloaded from on 3 January 29 by guest. Protected by copyright.
4 656 Ho, Schwab Regional prevalence of blind (%) SSA India China OAI MEC LAC FSE R 2 =.4477 r =.669 EME Average regional per capita income (99 US$) Figure 3 Prevalence of blindness versus average per capita income, by economic region. SSA = sub-saharan Africa; OAI = other Asia and islands; MEC = Middle Eastern crescent; LAC = Latin America and Caribbean; FSE = former socialist economies; EME = established market economies. Number of blind ( 3 ) Others Onchocerciasis Glaucoma Trachoma Cataract EME FSE India China OAI SSA LAC MEC Economic regions Figure 4 Global distribution of blindness and its major causes, by economic region. EME = established market economies; FSE = former socialist economies; OAI = other Asia and islands; SSA = sub-saharan Africa; LAC = Latin America and Caribbean; MEC = Middle Eastern crescent. economic development and the accompanying improvements in the standard of living. 2 4 Historic accounts from other investigators also point to the impact of economic development in improving nutritional blindness and leprosy. 5 7 The decline of leprosy in Europe coincided with the industrial revolution (before the availability of antibiotics), suggesting an important role of socioeconomic factors. 8 A study by Saikawa implied that the considerable socioeconomic development of post-war Japan contributed to the decline of leprosy incidence in endemic areas. 7 Thylefors et al have determined that 75% of the world s blind people are in Africa and Asia. For each blind person there are an additional three people with low vision. The three principal causes of blindness in the world cataract, trachoma, and glaucoma together account for 7% of all blindness, with cataract being the most common cause in all developing regions. Though the data on prevalence of cataract in developing countries have not always been well assessed, Javitt et al note that cataract is more prevalent in developing countries where it may occur at an earlier age than in developed countries. 8 And while the exact causes of cataract are not presently known, poor nutrition in childhood, shorter life expectancy, and even light damage (infrared and ultraviolet radiation) have been implicated as risk factors. 8 9 Mutations associated with congenital cataracts in children have long suggested a genetic influence in adult onset cataracts. 2 With recent studies by Hammond et al demonstrating the importance of genetic evects in such a clearly age related disease as nuclear cataract formation, 2 further understanding of specific genetic defects are being explored. Genetic factors aside, diseases like xerophthalmia, other nutritional causes of blindness, and nutritional influences on cataract can be eradicated with improvement in socioeconomic development. Similarly, trachoma, a blinding disease associated with poverty and inadequate sanitation, can also be controlled with economic improvements. However, it is less convincing that pure economic development will have a significant evect on the rates of onchocerciasis, unless fly eradication or control programmes are considered to be a part of economic development. Similarly, glaucoma is a worldwide problem in all populations that requires more complex intervention strategies and will probably not change dramatically with economic development. In fact, with economic development leading to increased longevity, the prevalence of glaucoma in the developing countries may actually increase in relative and absolute terms. Resources, both material and financial, are severely limited in developing countries where most people live beyond the reach of health and social services. The per capita income (US$) in less developed countries is below $635, compared with $79 or more, in the more developed nations. 6 A critical stage of economic development may exist whereby the prevalence of preventable blindness becomes significantly less. The correlation suggested by this investigation (Figs and 2) would appear to be near a per capita income of approximately $2. Potentially, the economic development in nations and/or regions with a per capita income of less than $2 could dramatically reduce the impact of preventable blindness. Conclusion The apparent association between the increased prevalence of blindness and poor economic development in developing countries suggests that emphasis and resources should be directed towards the development of those economies to successfully eliminate the preventable and curable causes of blindness. Though the solitary development of blindness prevention programmes by the WHO are well intended and most appropriate on a humanitarian basis, these evorts unaccompanied by other support measures will only serve to temporarily reduce the current backlog of world blindness. We believe that prevention schemes alone will not rid the global burden of Br J Ophthalmol: first published as.36/bjo on June 2. Downloaded from on 3 January 29 by guest. Protected by copyright.
5 Social economic development in the prevention of global blindness 657 blindness. Rather, preventive measures in conjunction with economic development is the most prudent approach to further the success of the goal of eliminating avoidable blindness throughout the world. Supported in part by an unrestricted grant from Research to Prevent Blindness, New York, USA. Thylefors B, Negrel AD, Pararajasegaram R, et al. Global data on blindness. Bull World Health Organ 995;73: Thylefors B. A global initiative for the elimination of avoidable blindness. Am J Ophthalmol 998;25: Thylefors B. A simplified methodology for the assessment of blindness and its main causes. Wld Hlth Statist Quart 987; 4: Thylefors B, Negrel AD, Pararajasegaram R, et al. Available data on blindness (update 994). Ophthalmic Epidemiol 995;2: Statistical Yearbook. 43rd issue. New York: Statistical Division, United Nations, 998: World Development Report 993: investing in health. New York: published for the World Bank. New York: Oxford University Press, Schwab L, Taylor HR. Cataract and delivery of surgical services in developing nations. In: Tasman W, Jaeger EA, eds. Duane s clinical ophthalmology. Revised ed. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott, 993;Vol 5, chapter Javitt JC, Wang F, West SK. Blindness due to cataract: epidemiology and prevention. Annu Rev Public Health 996;7: Sommer A. Public health aspects of ophthalmic disease. Annu Rev Public Health 996;7:5 9. West SK, Congdon N, Katala S,et al. Facial cleanliness and risk of trachoma in families. Arch Ophthalmol 99;9: Lynch M, West SK, Munoz B, et al. Testing a participatory strategy to change hygiene behavior: face washing in central Tanzania. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 994;88: West SK, Munoz B, Lynch M, et al. Risk factors for constant, severe trachoma among preschool children in Kongwa, Tanzania. Am J Epidemiol 996;43: Duke-Elder S, ed. System of ophthalmology. Vol 8. St Louis: CV Mosby, 965: Oliva MS, Munoz B, Lynch M, et al. Evaluation of barriers to surgical compliance in the treatment of trichiasis. Int Ophthalmol 998;2: Sommer A. Nutritional blindness: xerophthalmia and keratomalacia. In: Tasman W, Jaeger EA, eds. Duane s clinical ophthalmology. Revised ed. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott, 993;Vol 5, chapter Schwab IR, Ostler HB, Dawson CR. Hansen s disease of the eye (ocular leprosy). In: Tasman W, Jaeger EA, eds. Duane s clinical ophthalmology. Revised ed. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott, 993;Vol 5, chapter Saikawa K. The evect of rapid socio-economic development on the frequency of leprosy in a population. Lepr Rev 98; 52: Cossermelli-Messina W. Leprosy: statistics in the americas. J Rheumatol 993;2: Stilma JS, Franken S, Hogeweg M, et al. Points of action in the campaign against blindness in developing countries. Doc Ophthalmol 99;78: He W, Li S. Congenital cataracts: gene mapping. Hum Genet 2;6: 3. 2 Hammond CJ, Snieder H, Spector TD, et al. Genetic and environmental factors in age-related nuclear cataracts in monozygotic and dizygotic twins. N Engl J Med 2;342: 787. Br J Ophthalmol: first published as.36/bjo on June 2. Downloaded from on 3 January 29 by guest. Protected by copyright.
IX. IMPROVING MATERNAL HEALTH: THE NEED TO FOCUS ON REACHING THE POOR. Eduard Bos The World Bank
 IX. IMPROVING MATERNAL HEALTH: THE NEED TO FOCUS ON REACHING THE POOR Eduard Bos The World Bank A. INTRODUCTION This paper discusses the relevance of the ICPD Programme of Action for the attainment of
IX. IMPROVING MATERNAL HEALTH: THE NEED TO FOCUS ON REACHING THE POOR Eduard Bos The World Bank A. INTRODUCTION This paper discusses the relevance of the ICPD Programme of Action for the attainment of
Annex 2 A. Regional profile: West Africa
 Annex 2 A. Regional profile: West Africa 355 million people at risk for malaria in 215 297 million at high risk A. Parasite prevalence, 215 Funding for malaria increased from US$ 233 million to US$ 262
Annex 2 A. Regional profile: West Africa 355 million people at risk for malaria in 215 297 million at high risk A. Parasite prevalence, 215 Funding for malaria increased from US$ 233 million to US$ 262
Eligibility List 2018
 The Global Fund s 2017-2022 strategy and allocation-based approach enables strategic investment to accelerate the end of HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis and malaria and build resilient and sustainable systems for
The Global Fund s 2017-2022 strategy and allocation-based approach enables strategic investment to accelerate the end of HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis and malaria and build resilient and sustainable systems for
Disparities in access: renewed focus on the underserved. Rick Johnston, WHO UNC Water and Health, Chapel Hill 13 October, 2014
 Disparities in access: renewed focus on the underserved Rick Johnston, WHO UNC Water and Health, Chapel Hill 13 October, 2014 Sector proposal for post-2015 targets By 2030: to eliminate open defecation;
Disparities in access: renewed focus on the underserved Rick Johnston, WHO UNC Water and Health, Chapel Hill 13 October, 2014 Sector proposal for post-2015 targets By 2030: to eliminate open defecation;
Recipients of development assistance for health
 Chapter 2 Recipients of development assistance for health Both low- and middle-income countries are eligible for development assistance for health (DAH). In addition to income, burden of disease, which
Chapter 2 Recipients of development assistance for health Both low- and middle-income countries are eligible for development assistance for health (DAH). In addition to income, burden of disease, which
What is this document and who is it for?
 Measles and Rubella Initiative s Standard Operating Procedures for Accessing Support for Measles and Rubella Supplementary Immunization Activities During 2016 In the context of measles and rubella elimination
Measles and Rubella Initiative s Standard Operating Procedures for Accessing Support for Measles and Rubella Supplementary Immunization Activities During 2016 In the context of measles and rubella elimination
Current State of Global HIV Care Continua. Reuben Granich 1, Somya Gupta 1, Irene Hall 2, John Aberle-Grasse 2, Shannon Hader 2, Jonathan Mermin 2
 Current State of Global HIV Care Continua Reuben Granich 1, Somya Gupta 1, Irene Hall 2, John Aberle-Grasse 2, Shannon Hader 2, Jonathan Mermin 2 1) International Association of Providers of AIDS Care
Current State of Global HIV Care Continua Reuben Granich 1, Somya Gupta 1, Irene Hall 2, John Aberle-Grasse 2, Shannon Hader 2, Jonathan Mermin 2 1) International Association of Providers of AIDS Care
Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine: Current Supply & Demand Outlook. UNICEF Supply Division
 Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine: Current Supply & Demand Outlook UNICEF Supply Division Update: October 2013 0 Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV) Supply & Demand Outlook October 2013 Update Key updates
Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine: Current Supply & Demand Outlook UNICEF Supply Division Update: October 2013 0 Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV) Supply & Demand Outlook October 2013 Update Key updates
Funding for AIDS: The World Bank s Role. Yolanda Tayler, WB Bi-regional Workshop for the Procurement of ARVs Phnom Penh, Cambodia
 Funding for AIDS: The World Bank s Role Yolanda Tayler, WB Bi-regional Workshop for the Procurement of ARVs Phnom Penh, Cambodia Outline New resources needs estimates Bridging the gap Global overview of
Funding for AIDS: The World Bank s Role Yolanda Tayler, WB Bi-regional Workshop for the Procurement of ARVs Phnom Penh, Cambodia Outline New resources needs estimates Bridging the gap Global overview of
Progress Towards the Child Mortality MDG in Urban Sub-Saharan Africa. Nyovani Janet Madise University of Southampton
 Progress Towards the Child Mortality MDG in Urban Sub-Saharan Africa Nyovani Janet Madise University of Southampton United Nations Expert group Meeting on Population Distribution, Urbanization, Internal
Progress Towards the Child Mortality MDG in Urban Sub-Saharan Africa Nyovani Janet Madise University of Southampton United Nations Expert group Meeting on Population Distribution, Urbanization, Internal
Lessons learned from the IeDEA West Africa Collaboration
 Lessons learned from the IeDEA West Africa Collaboration François DABIS with the contribution of Didier Koumavi EKOUEVI INSERM U-897, Bordeaux, France, Programme PACCI, ANRS site, Abidjan, Côte d Ivoire
Lessons learned from the IeDEA West Africa Collaboration François DABIS with the contribution of Didier Koumavi EKOUEVI INSERM U-897, Bordeaux, France, Programme PACCI, ANRS site, Abidjan, Côte d Ivoire
EXPLANATION OF INDICATORS CHOSEN FOR THE 2017 ANNUAL SUN MOVEMENT PROGRESS REPORT
 UNICEF / Zar Mon Annexes EXPLANATION OF INDICATORS CHOSEN FOR THE 2017 ANNUAL SUN MOVEMENT PROGRESS REPORT This report includes nine nutrition statistics, as per the 2017 Global Nutrition Report. These
UNICEF / Zar Mon Annexes EXPLANATION OF INDICATORS CHOSEN FOR THE 2017 ANNUAL SUN MOVEMENT PROGRESS REPORT This report includes nine nutrition statistics, as per the 2017 Global Nutrition Report. These
Existing approaches to costing, financing and estimating cost-efficiencies for nutrition
 Existing approaches to costing, financing and estimating cost-efficiencies for nutrition February 2016 Meera Shekar Global Lead for Nutrition 1 Global Stunting Rates 159 million children stunted worldwide
Existing approaches to costing, financing and estimating cost-efficiencies for nutrition February 2016 Meera Shekar Global Lead for Nutrition 1 Global Stunting Rates 159 million children stunted worldwide
GOAL 2: ACHIEVE RUBELLA AND CRS ELIMINATION. (indicator G2.2) Highlights
 GOAL 2: ACHIEVE RUBELLA AND CRS ELIMINATION (indicator G2.2) Highlights As of December 2014, 140 Member States had introduced rubella vaccines; coverage, however, varies from 12% to 94% depending on region.
GOAL 2: ACHIEVE RUBELLA AND CRS ELIMINATION (indicator G2.2) Highlights As of December 2014, 140 Member States had introduced rubella vaccines; coverage, however, varies from 12% to 94% depending on region.
Access to reproductive health care global significance and conceptual challenges
 08_XXX_MM1 Access to reproductive health care global significance and conceptual challenges Dr Lale Say World Health Organization Department of Reproductive Health and Research From Research to Practice:
08_XXX_MM1 Access to reproductive health care global significance and conceptual challenges Dr Lale Say World Health Organization Department of Reproductive Health and Research From Research to Practice:
O c t o b e r 1 0,
 STUDENT VOICES FROM THE FIELD: WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION GENEVA, SWITZERLAND O c t o b e r 1 0, 2 0 1 6 M o l l y P e z z u l o University at Albany School of Public Health MPH Epidemiology Candidate 17
STUDENT VOICES FROM THE FIELD: WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION GENEVA, SWITZERLAND O c t o b e r 1 0, 2 0 1 6 M o l l y P e z z u l o University at Albany School of Public Health MPH Epidemiology Candidate 17
APPENDIX II - TABLE 2.3 ANTI-TOBACCO MASS MEDIA CAMPAIGNS
 WHO REPORT ON THE GLOBAL TOBACCO EPIDEMIC, 2011 APPENDIX II - TABLE 2.3 ANTI-TOBACCO MASS MEDIA CAMPAIGNS (SEE TABLE 4.9) Africa The Americas South-East Asia Europe Eastern Mediterranean Western Pacific
WHO REPORT ON THE GLOBAL TOBACCO EPIDEMIC, 2011 APPENDIX II - TABLE 2.3 ANTI-TOBACCO MASS MEDIA CAMPAIGNS (SEE TABLE 4.9) Africa The Americas South-East Asia Europe Eastern Mediterranean Western Pacific
Various interventions for controlling sexually transmitted infections have proven effective, including the syndromic
 levels, as understaffing is a chronic issue in all the countries that are scaling up male circumcision. Current achievements notwithstanding, it is necessary to reinforce and strengthen national political
levels, as understaffing is a chronic issue in all the countries that are scaling up male circumcision. Current achievements notwithstanding, it is necessary to reinforce and strengthen national political
Global Epidemic of Obesity. June Stevens, MS, PhD University of North Carolina Chapel Hill
 Global Epidemic of Obesity June Stevens, MS, PhD University of North Carolina Chapel Hill Outline Obesity and overweight prevalence rates in the United States Prevalence in diverse countries Environmental
Global Epidemic of Obesity June Stevens, MS, PhD University of North Carolina Chapel Hill Outline Obesity and overweight prevalence rates in the United States Prevalence in diverse countries Environmental
Rotavirus Vaccine: Supply & Demand Update. UNICEF Supply Division
 Rotavirus Vaccine: & Demand Update UNICEF Division July 0 Rotavirus Vaccine (RV): & Demand Update July This update provides new information on countries and their scheduled RV introductions, forecasted
Rotavirus Vaccine: & Demand Update UNICEF Division July 0 Rotavirus Vaccine (RV): & Demand Update July This update provides new information on countries and their scheduled RV introductions, forecasted
Global reductions in measles mortality and the risk of measles resurgence
 Global reductions in measles mortality 2000 2008 and the risk of measles resurgence Measles is one of the most contagious human diseases. In 1980 before the use of measles vaccine was widespread, there
Global reductions in measles mortality 2000 2008 and the risk of measles resurgence Measles is one of the most contagious human diseases. In 1980 before the use of measles vaccine was widespread, there
THE CARE WE PROMISE FACTS AND FIGURES 2017
 THE CARE WE PROMISE FACTS AND FIGURES 2017 2 SOS CHILDREN S VILLAGES INTERNATIONAL WHERE WE WORK Facts and Figures 2017 205 58 79 families and transit 31 Foster homes 162 8 3 173 214 2 115 159 136 148
THE CARE WE PROMISE FACTS AND FIGURES 2017 2 SOS CHILDREN S VILLAGES INTERNATIONAL WHERE WE WORK Facts and Figures 2017 205 58 79 families and transit 31 Foster homes 162 8 3 173 214 2 115 159 136 148
Main global and regional trends
 I N T R O D U C T I O N Main global and regional trends Promising developments have been seen in recent years in global efforts to address the AS epidemic, including increased access to effective treatment
I N T R O D U C T I O N Main global and regional trends Promising developments have been seen in recent years in global efforts to address the AS epidemic, including increased access to effective treatment
ADMINISTRATIVE AND FINANCIAL MATTERS. Note by the Executive Secretary * CONTENTS. Explanatory notes Tables. 1. Core budget
 UNITED NATIONS Distr. GENERAL 13 October 1997 ENGLISH ONLY SUBSIDIARY BODY FOR IMPLEMENTATION Seventh session Bonn, 20-29 October 1997 Item 9 of the provisional agenda ADMINISTRATIVE AND FINANCIAL MATTERS
UNITED NATIONS Distr. GENERAL 13 October 1997 ENGLISH ONLY SUBSIDIARY BODY FOR IMPLEMENTATION Seventh session Bonn, 20-29 October 1997 Item 9 of the provisional agenda ADMINISTRATIVE AND FINANCIAL MATTERS
Family Planning: Succeeding in Meeting Needs To Make a Better World. Amy Tsui April 12, 2011
 Family Planning: Succeeding in Meeting Needs To Make a Better World Amy Tsui April 12, 2011 Family Planning, One of the Ten Best Public Health Achievements of the 20 th Century and Now Remarkable health
Family Planning: Succeeding in Meeting Needs To Make a Better World Amy Tsui April 12, 2011 Family Planning, One of the Ten Best Public Health Achievements of the 20 th Century and Now Remarkable health
AIDS in Africa. An Update. Basil Reekie
 AIDS in Africa An Update Basil Reekie Contents General Statistics The trend of HIV in Africa Ugandan experience UNAIDS 2006 Latest African Statistics by Country HIV Intervention Light at the end of the
AIDS in Africa An Update Basil Reekie Contents General Statistics The trend of HIV in Africa Ugandan experience UNAIDS 2006 Latest African Statistics by Country HIV Intervention Light at the end of the
Comparative Analyses of Adolescent Nutrition Indicators
 Comparative Analyses of Adolescent Nutrition Indicators Rukundo K. Benedict, PhD The DHS Program Stakeholders Consultation on Adolescent Girls Nutrition: Evidence, Guidance, and Gaps October 30 31, 2017
Comparative Analyses of Adolescent Nutrition Indicators Rukundo K. Benedict, PhD The DHS Program Stakeholders Consultation on Adolescent Girls Nutrition: Evidence, Guidance, and Gaps October 30 31, 2017
Global Measles and Rubella Update. April 2018
 Global Measles and Rubella Update April 218 Measles Number of Reported Measles by WHO Regions 218 Region Member States* Suspected cases Measles cases Clin Epi Lab Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct
Global Measles and Rubella Update April 218 Measles Number of Reported Measles by WHO Regions 218 Region Member States* Suspected cases Measles cases Clin Epi Lab Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct
ICM: Trade-offs in the fight against HIV/AIDS
 ICM: Trade-offs in the fight against HIV/AIDS 1 As the HIV/AIDS pandemic enters its 25 th year, both the number of infections and number of deaths due to the disease continue to rise. Despite an enormous
ICM: Trade-offs in the fight against HIV/AIDS 1 As the HIV/AIDS pandemic enters its 25 th year, both the number of infections and number of deaths due to the disease continue to rise. Despite an enormous
Global Measles and Rubella Update November 2018
 Global Measles and Rubella Update November 218 Measles Number of Reported Measles by WHO Regions 218 Region Member States* Suspected cases Measles cases Clin Epi Lab Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep
Global Measles and Rubella Update November 218 Measles Number of Reported Measles by WHO Regions 218 Region Member States* Suspected cases Measles cases Clin Epi Lab Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep
מדינת ישראל. Tourist Visa Table
 Updated 23/05/2017 מדינת ישראל Tourist Visa Table Tourist visa exemption is applied to national and official passports only, and not to other travel documents. Exe = exempted Req = required Press the first
Updated 23/05/2017 מדינת ישראל Tourist Visa Table Tourist visa exemption is applied to national and official passports only, and not to other travel documents. Exe = exempted Req = required Press the first
SGCEP SCIE 1121 Environmental Science Spring 2012 Section Steve Thompson:
 SGCEP SCIE 1121 Environmental Science Spring 2012 Section 20531 Steve Thompson: steventhompson@sgc.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net/ 1 First, a brief diversion... Into... how to do better on the next exam,
SGCEP SCIE 1121 Environmental Science Spring 2012 Section 20531 Steve Thompson: steventhompson@sgc.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net/ 1 First, a brief diversion... Into... how to do better on the next exam,
Landscape Analysis on Countries' Readiness to Accelerate Action to Reduce Maternal and Child Undernutrition
 35 th Session of the UN Standing Committee on Nutrition (SCN) Hanoi, 3 6 March 2008 Landscape Analysis on Countries' Readiness to Accelerate Action to Reduce Maternal and Child Undernutrition Jorgen Schlundt
35 th Session of the UN Standing Committee on Nutrition (SCN) Hanoi, 3 6 March 2008 Landscape Analysis on Countries' Readiness to Accelerate Action to Reduce Maternal and Child Undernutrition Jorgen Schlundt
Trends in leprosy case detection worldwide since 1985
 Lepr Rev (2004) 75, 19±33 Trends in leprosy case detection worldwide since 1985 ABRAHAM MEIMA, JAN H. RICHARDUS & J. DIK F. HABBEMA Department of Public Health, Erasmus MC, University Medical Center Rotterdam,
Lepr Rev (2004) 75, 19±33 Trends in leprosy case detection worldwide since 1985 ABRAHAM MEIMA, JAN H. RICHARDUS & J. DIK F. HABBEMA Department of Public Health, Erasmus MC, University Medical Center Rotterdam,
Global Measles and Rubella Update October 2018
 Global Measles and Rubella Update October 218 Measles Number of Reported Measles Cases by WHO Regions 218 Region Member States* Suspected cases Measles cases Clin Epi Lab Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug
Global Measles and Rubella Update October 218 Measles Number of Reported Measles Cases by WHO Regions 218 Region Member States* Suspected cases Measles cases Clin Epi Lab Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug
TT Procured by UNICEF
 TT TT Procured by UNICEF 2001-08 250,000,000 200,000,000 150,000,000 100,000,000 50,000,000 0 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 Routine SIA TT historical demand and forecast overview Upcoming Tender
TT TT Procured by UNICEF 2001-08 250,000,000 200,000,000 150,000,000 100,000,000 50,000,000 0 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 Routine SIA TT historical demand and forecast overview Upcoming Tender
מדינת ישראל. Tourist Visa Table. Tourist visa exemption is applied to national and official passports only, and not to other travel documents.
 Updated 25/05/2015 ישראל Tourist Visa Table Tourist visa exemption is applied to national and official passports only, and not to other travel documents. (C) Bearers of official passports requiring tourist
Updated 25/05/2015 ישראל Tourist Visa Table Tourist visa exemption is applied to national and official passports only, and not to other travel documents. (C) Bearers of official passports requiring tourist
The Promise of Introducing Rubella Containing Vaccines on the Impact of Rubella and Measles Control
 The Promise of Introducing Rubella Containing Vaccines on the Impact of Rubella and Measles Control GAVI Partners Forum 4 6 December 2012, Dar es Salaam, Tanzania Maya van den Ent, MPH, UNICEF Peter Strebel,
The Promise of Introducing Rubella Containing Vaccines on the Impact of Rubella and Measles Control GAVI Partners Forum 4 6 December 2012, Dar es Salaam, Tanzania Maya van den Ent, MPH, UNICEF Peter Strebel,
Closing the loop: translating evidence into enhanced strategies to reduce maternal mortality
 Closing the loop: translating evidence into enhanced strategies to reduce maternal mortality Washington DC March 12th 2008 Professor Wendy J Graham Opinion-based decisionmaking Evidence-based decision-making
Closing the loop: translating evidence into enhanced strategies to reduce maternal mortality Washington DC March 12th 2008 Professor Wendy J Graham Opinion-based decisionmaking Evidence-based decision-making
World Health organization/ International Society of Hypertension (WH0/ISH) risk prediction charts
 World Health organization/ International Society of Hypertension (WH0/ISH) risk prediction charts (charts in colour) (These charts will be updated in 2014) 2 1. Introduction 2. Instructions on how to use
World Health organization/ International Society of Hypertension (WH0/ISH) risk prediction charts (charts in colour) (These charts will be updated in 2014) 2 1. Introduction 2. Instructions on how to use
Targeting Poverty and Gender Inequality to Improve Maternal Health
 Targeting Poverty and Gender Inequality to Improve Maternal Health presented by Rekha Mehra, Ph.D. Based on paper by: Silvia Paruzzolo, Rekha Mehra, Aslihan Kes, Charles Ashbaugh Expert Panel on Fertility,
Targeting Poverty and Gender Inequality to Improve Maternal Health presented by Rekha Mehra, Ph.D. Based on paper by: Silvia Paruzzolo, Rekha Mehra, Aslihan Kes, Charles Ashbaugh Expert Panel on Fertility,
Undiscovered progress in. in maternal mortality.
 CHAPTER 1 Undiscovered progress in maternal mortality During the early 1980s, a half-million women died every year during pregnancy, childbirth, or the postpartum period a stunning figure in a world that
CHAPTER 1 Undiscovered progress in maternal mortality During the early 1980s, a half-million women died every year during pregnancy, childbirth, or the postpartum period a stunning figure in a world that
Global EHS Resource Center
 Global EHS Resource Center Understand environmental and workplace safety requirements that affect your global operations. 800.372.1033 bna.com/gelw Global EHS Resource Center This comprehensive research
Global EHS Resource Center Understand environmental and workplace safety requirements that affect your global operations. 800.372.1033 bna.com/gelw Global EHS Resource Center This comprehensive research
Financing malaria control
 Chapter 6. Financing malaria control The three major sources of funds for malaria control pro - grammes are national government spending, external assistance from donors and household or private out-of-pocket
Chapter 6. Financing malaria control The three major sources of funds for malaria control pro - grammes are national government spending, external assistance from donors and household or private out-of-pocket
Tipping the dependency
 BREAKING NEWS Meeting the investment challenge Tipping the dependency balance Domestic investments exceed international investments total reaching US$ 8.6 billion. 40 countries fund more than 70% of their
BREAKING NEWS Meeting the investment challenge Tipping the dependency balance Domestic investments exceed international investments total reaching US$ 8.6 billion. 40 countries fund more than 70% of their
Variations in Breast Cancer Incidence and Mortality. M. Espié Centre des maladies du sein Hôpital St LOUIS APHP
 Variations in Breast Cancer Incidence and Mortality M. Espié Centre des maladies du sein Hôpital St LOUIS APHP Incidence and deaths Breast cancer remains the most common malignancy worldwilde 1.6 million
Variations in Breast Cancer Incidence and Mortality M. Espié Centre des maladies du sein Hôpital St LOUIS APHP Incidence and deaths Breast cancer remains the most common malignancy worldwilde 1.6 million
Methodological issues in the use of anthropometry for evaluation of nutritional status
 Methodological issues in the use of anthropometry for evaluation of nutritional status Mercedes de Onis WHO Department of Nutrition Time schedule child anthropometry Measurement Time frame Frequency
Methodological issues in the use of anthropometry for evaluation of nutritional status Mercedes de Onis WHO Department of Nutrition Time schedule child anthropometry Measurement Time frame Frequency
Aboubacar Kampo Chief of Health UNICEF Nigeria
 Aboubacar Kampo Chief of Health UNICEF Nigeria Many thanks to UNICEF colleagues in Supply Division-Copenhagen and NY for contributing to this presentation Thirty-five countries are responsible for 98%
Aboubacar Kampo Chief of Health UNICEF Nigeria Many thanks to UNICEF colleagues in Supply Division-Copenhagen and NY for contributing to this presentation Thirty-five countries are responsible for 98%
Global Fund Results Fact Sheet Mid-2011
 Global Fund Results Fact Sheet Mid-2011 This fact sheet outlines some of the common questions and answers regarding results reported by Global Fund-supported programs, including the principles and approach
Global Fund Results Fact Sheet Mid-2011 This fact sheet outlines some of the common questions and answers regarding results reported by Global Fund-supported programs, including the principles and approach
Wild Poliovirus*, 03 Aug 2004 to 02 Aug 2005
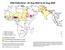 Wild Poliovirus*, 03 Aug 2004 to 02 Aug 2005 Wild virus type 1 Wild virus type 3 Wild virus type 1 & 3 Endemic countries Re-established transmission countries Case or outbreak following importation *Excludes
Wild Poliovirus*, 03 Aug 2004 to 02 Aug 2005 Wild virus type 1 Wild virus type 3 Wild virus type 1 & 3 Endemic countries Re-established transmission countries Case or outbreak following importation *Excludes
Fertility and Family Planning in Africa: Call for Greater Equity Consciousness
 Fertility and Family Planning in Africa: Call for Greater Equity Consciousness Eliya Msiyaphazi Zulu President, Union for African Population Studies Director of Research, African Population & Health Research
Fertility and Family Planning in Africa: Call for Greater Equity Consciousness Eliya Msiyaphazi Zulu President, Union for African Population Studies Director of Research, African Population & Health Research
UNAIDS 2013 AIDS by the numbers
 UNAIDS 2013 AIDS by the numbers 33 % decrease in new HIV infections since 2001 29 % decrease in AIDS-related deaths (adults and children) since 2005 52 % decrease in new HIV infections in children since
UNAIDS 2013 AIDS by the numbers 33 % decrease in new HIV infections since 2001 29 % decrease in AIDS-related deaths (adults and children) since 2005 52 % decrease in new HIV infections in children since
Procedure for Expedited Review of imported pre-qualified vaccines for use in national immunization programmes
 Procedure for Expedited Review of imported pre-qualified vaccines for use in national immunization programmes Dr Nora Dellepiane/Dr Anil Kumar Chawla WHO/HQ-Geneva, Switzerland 1 Expedited review procedure
Procedure for Expedited Review of imported pre-qualified vaccines for use in national immunization programmes Dr Nora Dellepiane/Dr Anil Kumar Chawla WHO/HQ-Geneva, Switzerland 1 Expedited review procedure
Global Fund ARV Fact Sheet 1 st June, 2009
 Global Fund ARV Fact Sheet 1 st June, 2009 This fact sheet outlines the principles and approach in determining the number of people on antiretroviral drugs (ARVs) for HIV/AIDS treatment, with a breakdown
Global Fund ARV Fact Sheet 1 st June, 2009 This fact sheet outlines the principles and approach in determining the number of people on antiretroviral drugs (ARVs) for HIV/AIDS treatment, with a breakdown
Why Invest in Nutrition?
 Why Invest in Nutrition? Meera Shekar Human Development Network World Bank 2006 Three key Issues Why reducing malnutrition is essential to poverty reduction? Is malnutrition a BIG problem? How can we improve
Why Invest in Nutrition? Meera Shekar Human Development Network World Bank 2006 Three key Issues Why reducing malnutrition is essential to poverty reduction? Is malnutrition a BIG problem? How can we improve
Development assistance for HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis and malaria by channel
 Chapter 6: Distribution of development assistance for health Building a foundation of knowledge that accurately accounts for the volume of global health funding is crucial, both for those who give aid
Chapter 6: Distribution of development assistance for health Building a foundation of knowledge that accurately accounts for the volume of global health funding is crucial, both for those who give aid
Impact Dashboard - October 2014
 Impact Dashboard - 2014 By 2014, PSI and its network members averted an estimated 44.2 million DALYs globally. PSI has met 60.6% of the strategic plan (SP) target to avert 198.7 million DALYs, and 56.4%
Impact Dashboard - 2014 By 2014, PSI and its network members averted an estimated 44.2 million DALYs globally. PSI has met 60.6% of the strategic plan (SP) target to avert 198.7 million DALYs, and 56.4%
2015 CONTRACEPTIVE SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS
 2015 CONTRACEPTIVE SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS November 2016 CONNECT WITH US Courtesy of DKT International 1701 K Street, NW Suite 900 Washington, DC 20006 1 SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS 2015 Highlights
2015 CONTRACEPTIVE SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS November 2016 CONNECT WITH US Courtesy of DKT International 1701 K Street, NW Suite 900 Washington, DC 20006 1 SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS 2015 Highlights
Impact Dashboard - August 2014
 Impact Dashboard - By, PSI and its network members averted an estimated 29.7 million DALYs globally. PSI has met 53.3% of the strategic plan (SP) target to avert 198.7 million DALYs, and 53.0% of the SP
Impact Dashboard - By, PSI and its network members averted an estimated 29.7 million DALYs globally. PSI has met 53.3% of the strategic plan (SP) target to avert 198.7 million DALYs, and 53.0% of the SP
Sourcing of ARVs & HIV diagnostics. Procurement for Impact P4i
 Sourcing of ARVs & HIV diagnostics Procurement for Impact P4i AMDS ANNUAL STAKEHOLDERS AND PARTNERS MEETING 29 September 2014 Global Fund: Procurement for Impact: P4i Our objective was straightforward:
Sourcing of ARVs & HIV diagnostics Procurement for Impact P4i AMDS ANNUAL STAKEHOLDERS AND PARTNERS MEETING 29 September 2014 Global Fund: Procurement for Impact: P4i Our objective was straightforward:
Gender, Poverty, and Health in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Framework for Analysis
 Gender, Poverty, and Health in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Framework for Analysis Pathways to Improved Health Outcomes Health outcomes Households/ Communities Household behaviors & risk factors Community factors
Gender, Poverty, and Health in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Framework for Analysis Pathways to Improved Health Outcomes Health outcomes Households/ Communities Household behaviors & risk factors Community factors
Copyright 2011 Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) All rights reserved
 UNAIDS DATA TABLES 2011 Copyright 2011 Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) All rights reserved UNAIDS / JC2225E The designations employed and the presentation of the material in this publication
UNAIDS DATA TABLES 2011 Copyright 2011 Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) All rights reserved UNAIDS / JC2225E The designations employed and the presentation of the material in this publication
Marwan S. Al-Dulaimy College of Medicine, University of Tikrit
 Distribution of blindness and low vision among patients attending out patient clinic in Tikrit Marwan S. Al-Dulaimy College of Medicine, University of Tikrit Abstract The magnitude and geographical distribution
Distribution of blindness and low vision among patients attending out patient clinic in Tikrit Marwan S. Al-Dulaimy College of Medicine, University of Tikrit Abstract The magnitude and geographical distribution
COLD CHAIN EQUIPMENT OPTIMISATION PLATFORM (CCEOP)
 COLD CHAIN EQUIPMENT OPTIMISATION PLATFORM (CCEOP) Sushila Maharjan Senior Manager, Innovative Finance International Conference on Sustainable Cooling World Bank Washington DC - 29 November 2018 Reach
COLD CHAIN EQUIPMENT OPTIMISATION PLATFORM (CCEOP) Sushila Maharjan Senior Manager, Innovative Finance International Conference on Sustainable Cooling World Bank Washington DC - 29 November 2018 Reach
Copyright 2011 Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) All rights reserved ISBN
 UNAIDS DATA TABLES 2011 Copyright 2011 Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) All rights reserved ISBN 978-92-9173-945-5 UNAIDS / JC2225E The designations employed and the presentation of
UNAIDS DATA TABLES 2011 Copyright 2011 Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) All rights reserved ISBN 978-92-9173-945-5 UNAIDS / JC2225E The designations employed and the presentation of
Common eye diseases in children of rural community in Goro district, Central Ethiopia
 Original article Common eye diseases in children of rural community in Goro district, Central Ethiopia Mohammed Shaffi, Abebe Bejiga Abstract Background: Very few reports exist regarding the causes of
Original article Common eye diseases in children of rural community in Goro district, Central Ethiopia Mohammed Shaffi, Abebe Bejiga Abstract Background: Very few reports exist regarding the causes of
Confronting the Challenges of Gender Equality and Fragile States. Main messages. April 23, 2007
 1 Confronting the Challenges of Gender Equality and Fragile States Main messages April 23, 2007 2 Significant progress toward MDG1 Globally MDG1 is on track (2015 forecast HCI=12%). People in developing
1 Confronting the Challenges of Gender Equality and Fragile States Main messages April 23, 2007 2 Significant progress toward MDG1 Globally MDG1 is on track (2015 forecast HCI=12%). People in developing
Scaling Up Nutrition Action for Africa
 Scaling Up Nutrition Action for Africa Where are we and what challenges are need to be addressed to accelerate malnutrition? Lawrence Haddad Global Alliance for Improved Nutrition Why should African political
Scaling Up Nutrition Action for Africa Where are we and what challenges are need to be addressed to accelerate malnutrition? Lawrence Haddad Global Alliance for Improved Nutrition Why should African political
Full list of payments made to projects in 2017
 DfID SAFE Ethiopia Non-SSI IP 3,724,841.06 DfID SAFE Chad Non-SSI IP 1,893,149.00 QEDJT Kenya Implementing Partner Non SSI 1,261,816.00 Inegrated Neglected Tropical Diseases Control 1,171,233.68 DfID SAFE
DfID SAFE Ethiopia Non-SSI IP 3,724,841.06 DfID SAFE Chad Non-SSI IP 1,893,149.00 QEDJT Kenya Implementing Partner Non SSI 1,261,816.00 Inegrated Neglected Tropical Diseases Control 1,171,233.68 DfID SAFE
Post-2015 Development Agenda THE WORLD WE WANT
 Post-2015 Development Agenda THE WORLD WE WANT Brian Lutz United Nations Development Programme United Nations Development Programme OVERVIEW The MDGs, Health and HIV Post-2015 processes and results to-date
Post-2015 Development Agenda THE WORLD WE WANT Brian Lutz United Nations Development Programme United Nations Development Programme OVERVIEW The MDGs, Health and HIV Post-2015 processes and results to-date
NO CHILD SHOULD DIE OF DIABETES
 NO CHILD SHOULD DIE OF DIABETES THE PROBLEM There is an estimated 1 million youth under the age of 25 with diabetes in the world. In high income countries, children with diabetes have full access to the
NO CHILD SHOULD DIE OF DIABETES THE PROBLEM There is an estimated 1 million youth under the age of 25 with diabetes in the world. In high income countries, children with diabetes have full access to the
Women s Paid Labor Force Participation and Child Immunization: A Multilevel Model Laurie F. DeRose Kali-Ahset Amen University of Maryland
 Women s Paid Labor Force Participation and Child Immunization: A Multilevel Model Laurie F. DeRose Kali-Ahset Amen University of Maryland September 23, 2005 We estimate the effect of women s cash work
Women s Paid Labor Force Participation and Child Immunization: A Multilevel Model Laurie F. DeRose Kali-Ahset Amen University of Maryland September 23, 2005 We estimate the effect of women s cash work
Maternal Deaths Disproportionately High in Developing Countries
 EMBARGOED until Monday, 20 October, 6am GMT HQ/2003/24 20 October 2003 CF/DOC/PR/2003-82 Maternal Deaths Disproportionately High in Developing Countries African women are 175 times more likely to die in
EMBARGOED until Monday, 20 October, 6am GMT HQ/2003/24 20 October 2003 CF/DOC/PR/2003-82 Maternal Deaths Disproportionately High in Developing Countries African women are 175 times more likely to die in
REFRACTIVE ERROR BLINDNESS IN YENAGOA, BAYELSA STATE, NIGERIA: A HOSPITAL BASED STUDY
 REFRACTIVE ERROR BLINDNESS IN YENAGOA, BAYELSA STATE, NIGERIA: A HOSPITAL BASED STUDY *I.R Azonobi *Department of Ophthalmology, Niger Delta University, Okolobiri Yenagoa, Bayelsa State, Nigeria Correspondence:
REFRACTIVE ERROR BLINDNESS IN YENAGOA, BAYELSA STATE, NIGERIA: A HOSPITAL BASED STUDY *I.R Azonobi *Department of Ophthalmology, Niger Delta University, Okolobiri Yenagoa, Bayelsa State, Nigeria Correspondence:
PROGRESS REPORT ON THE ROAD MAP FOR ACCELERATING THE ATTAINMENT OF THE MILLENNIUM DEVELOPMENT GOALS RELATED TO MATERNAL AND NEWBORN HEALTH IN AFRICA
 5 July 2011 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-first session Yamoussoukro, Côte d Ivoire, 29 August 2 September 2011 Provisional agenda item 17.1 PROGRESS REPORT ON THE ROAD MAP FOR
5 July 2011 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-first session Yamoussoukro, Côte d Ivoire, 29 August 2 September 2011 Provisional agenda item 17.1 PROGRESS REPORT ON THE ROAD MAP FOR
PROGRESS REPORT ON CHILD SURVIVAL: A STRATEGY FOR THE AFRICAN REGION. Information Document CONTENTS
 29 June 2009 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-ninth session Kigali, Republic of Rwanda, 31 August 4 September 2009 Provisional agenda item 9.2 PROGRESS REPORT ON CHILD SURVIVAL: A
29 June 2009 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-ninth session Kigali, Republic of Rwanda, 31 August 4 September 2009 Provisional agenda item 9.2 PROGRESS REPORT ON CHILD SURVIVAL: A
The Millennium Development Goals Report. asdf. Gender Chart UNITED NATIONS. Photo: Quoc Nguyen/ UNDP Picture This
 The Millennium Development Goals Report Gender Chart asdf UNITED NATIONS Photo: Quoc Nguyen/ UNDP Picture This Goal Eradicate extreme poverty and hunger Women in sub- are more likely than men to live in
The Millennium Development Goals Report Gender Chart asdf UNITED NATIONS Photo: Quoc Nguyen/ UNDP Picture This Goal Eradicate extreme poverty and hunger Women in sub- are more likely than men to live in
WHO Global Task Force on TB Impact Measurement An overview
 WHO Global Task Force on TB Impact Measurement An overview Katherine Floyd (WHO/GTB/TME) 3 rd meeting of the TB estimates subgroup Glion-sur-Montreux, 31March 2 April 2015 GLOBAL TB PROGRAMME 1. Broad
WHO Global Task Force on TB Impact Measurement An overview Katherine Floyd (WHO/GTB/TME) 3 rd meeting of the TB estimates subgroup Glion-sur-Montreux, 31March 2 April 2015 GLOBAL TB PROGRAMME 1. Broad
Prevalence of Infertility
 Prevalence of Infertility Dr S. Van der Poel focal point for Infertility on behalf of WHO/RHR and HRP Infertility: Primary versus Secondary Primary infertility: inability to become pregnant (or have a
Prevalence of Infertility Dr S. Van der Poel focal point for Infertility on behalf of WHO/RHR and HRP Infertility: Primary versus Secondary Primary infertility: inability to become pregnant (or have a
Global Health Research Initiative (GHRI)
 Global Health Research Initiative (GHRI) Presented by, John Frank, Scientific Director, Institute of Population and Public Health, Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) Canada s involvement in
Global Health Research Initiative (GHRI) Presented by, John Frank, Scientific Director, Institute of Population and Public Health, Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) Canada s involvement in
CONTRACEPTIVE SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS
 2016 CONTRACEPTIVE SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS August 2017 CONNECT WITH US Courtesy of DKT International 1701 K Street, NW Suite 900 Washington DC 20006 SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS 2016 Highlights 2016
2016 CONTRACEPTIVE SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS August 2017 CONNECT WITH US Courtesy of DKT International 1701 K Street, NW Suite 900 Washington DC 20006 SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS 2016 Highlights 2016
Global Fund Mid-2013 Results
 Global Fund Mid-2013 Results This fact sheet outlines some of the common questions and answers regarding results reported by Global Fund-supported programs, including the principles and approach in determining
Global Fund Mid-2013 Results This fact sheet outlines some of the common questions and answers regarding results reported by Global Fund-supported programs, including the principles and approach in determining
Elimination of mother to child transmission of HIV: is the end really in sight? Lisa L. Abuogi, MD University of Colorado, Denver Dec 3, 2014
 Elimination of mother to child transmission of HIV: is the end really in sight? Lisa L. Abuogi, MD University of Colorado, Denver Dec 3, 2014 Outline Background History of prevention of mother to child
Elimination of mother to child transmission of HIV: is the end really in sight? Lisa L. Abuogi, MD University of Colorado, Denver Dec 3, 2014 Outline Background History of prevention of mother to child
Drug Prices Report Opioids Retail and wholesale prices * and purity levels,by drug, region and country or territory (prices expressed in US$ )
 1 / 11 Region/Subregion/ Country Africa Eastern Africa Kenya Madagascar Mauritius Uganda United Republic of Tanzania Northern Africa Algeria Egypt Libya Morocco Sudan Southern Africa Botswana Burkina Faso
1 / 11 Region/Subregion/ Country Africa Eastern Africa Kenya Madagascar Mauritius Uganda United Republic of Tanzania Northern Africa Algeria Egypt Libya Morocco Sudan Southern Africa Botswana Burkina Faso
2002 CONTRACEPTIVE SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS
 2002 CONTRACEPTIVE SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS Courtesy of DKT International 1120 19th Street, NW Suite 610 July 2003 Washington, DC 20036 1 SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS 2001 Highlights 2002 2001 2000 CYPs
2002 CONTRACEPTIVE SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS Courtesy of DKT International 1120 19th Street, NW Suite 610 July 2003 Washington, DC 20036 1 SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS 2001 Highlights 2002 2001 2000 CYPs
CND UNGASS FOLLOW UP
 CND UNGASS FOLLOW UP INCB follow-up activities on Chapter 2. Operational recommendations on ensuring the availability of and access to controlled substances exclusively for medical and scientific purposes,
CND UNGASS FOLLOW UP INCB follow-up activities on Chapter 2. Operational recommendations on ensuring the availability of and access to controlled substances exclusively for medical and scientific purposes,
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION
 WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION EXECUTIVE BOARD EB115/29 115th Session November 2004 Provisional agenda item 4.15 International Plan of Action on Ageing: report on implementation Report by the Secretariat 1.
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION EXECUTIVE BOARD EB115/29 115th Session November 2004 Provisional agenda item 4.15 International Plan of Action on Ageing: report on implementation Report by the Secretariat 1.
Facts and trends in sexual and reproductive health in Asia and the Pacific
 November 13 Facts and trends in sexual and reproductive health in Asia and the Pacific Use of modern contraceptives is increasing In the last years, steady gains have been made in increasing women s access
November 13 Facts and trends in sexual and reproductive health in Asia and the Pacific Use of modern contraceptives is increasing In the last years, steady gains have been made in increasing women s access
FEMALE GENITAL MUTILATION/CUTTING: What might the future hold?
 FEMALE GENITAL MUTILATION/CUTTING: What might the future hold? UNICEF/NYHQ213-42/Asselin The mutilation or cutting of female genitals, also known as FGM/C, has been practised for centuries among population
FEMALE GENITAL MUTILATION/CUTTING: What might the future hold? UNICEF/NYHQ213-42/Asselin The mutilation or cutting of female genitals, also known as FGM/C, has been practised for centuries among population
ANNEX 3: Country progress indicators
 : progress indicators 541 : COUNTRY PROGRESS INDICATORS 2006 REPORT ON THE GLOBAL AIDS EPIDEMIC Annex 3 : COUNTRY PROGRESS INDICATORS As of March 2006, 115 countries had reported indicators on progress
: progress indicators 541 : COUNTRY PROGRESS INDICATORS 2006 REPORT ON THE GLOBAL AIDS EPIDEMIC Annex 3 : COUNTRY PROGRESS INDICATORS As of March 2006, 115 countries had reported indicators on progress
Development Through a Gender Lens: Implications for Poverty Reduction and Energy Sector Strategies
 Development Through a Gender Lens: Implications for Poverty Reduction and Energy Sector Strategies C. Mark Blackden Office of the Sector Director, PREM, Africa Region Biomass Energy Workshop February 26,
Development Through a Gender Lens: Implications for Poverty Reduction and Energy Sector Strategies C. Mark Blackden Office of the Sector Director, PREM, Africa Region Biomass Energy Workshop February 26,
Seizures of ATS (excluding ecstasy ), 2010
 Seizures of ATS (excluding ecstasy ), 2010 (countries and territories reporting seizures* of more than 10 kg) 9 5.1 8.7 12.9 Ghana Armenia 0.7 9.9 1 2.1 Syrian Arab Republic Korea (Republic of) Iraq Islamic
Seizures of ATS (excluding ecstasy ), 2010 (countries and territories reporting seizures* of more than 10 kg) 9 5.1 8.7 12.9 Ghana Armenia 0.7 9.9 1 2.1 Syrian Arab Republic Korea (Republic of) Iraq Islamic
Donor Support for Contraceptives and Condoms for STI/HIV Prevention
 Donor Support for Contraceptives and Condoms for STI/HIV Prevention 2001 Donor Support for Contraceptives and Condoms for STI/HIV Prevention 2001 Table of Contents List of Abbreviations and Acronyms List
Donor Support for Contraceptives and Condoms for STI/HIV Prevention 2001 Donor Support for Contraceptives and Condoms for STI/HIV Prevention 2001 Table of Contents List of Abbreviations and Acronyms List
Millennium Development Goals Report Card. Learning from Progress
 Millennium Development Goals Report Card Learning from Progress The Big Picture The last two decades have shown that it is possible to defeat the scourge of poverty. Progress has not been uniform across
Millennium Development Goals Report Card Learning from Progress The Big Picture The last two decades have shown that it is possible to defeat the scourge of poverty. Progress has not been uniform across
PROMOTING GENDER RESPONSIVE & INCLUSIVE TRANSPORT PROJECTS
 PROMOTING GENDER RESPONSIVE & INCLUSIVE TRANSPORT PROJECTS AN OVERVIEW George Banjo The World Bank Presentation at MDB Regional Workshops to Mainstream Gender Equality in Infrastructure Policies and Projects,
PROMOTING GENDER RESPONSIVE & INCLUSIVE TRANSPORT PROJECTS AN OVERVIEW George Banjo The World Bank Presentation at MDB Regional Workshops to Mainstream Gender Equality in Infrastructure Policies and Projects,
Child undernutrition based on the new WHO growth standards and rates of reduction to 2015
 1 Child undernutrition based on the new WHO growth standards and rates of reduction to 2015 Dr Mercedes de Onis SCN Annual Session, Hanoi, Viet Nam 2008 2 Intergenerational cycle of growth failure Child
1 Child undernutrition based on the new WHO growth standards and rates of reduction to 2015 Dr Mercedes de Onis SCN Annual Session, Hanoi, Viet Nam 2008 2 Intergenerational cycle of growth failure Child
BCG. and your baby. Immunisation. Protecting babies against TB. the safest way to protect your child
 BCG and your baby Protecting babies against TB Immunisation the safest way to protect your child This leaflet is about the BCG (Bacillus Calmette-Guerin) vaccination that is being offered to protect your
BCG and your baby Protecting babies against TB Immunisation the safest way to protect your child This leaflet is about the BCG (Bacillus Calmette-Guerin) vaccination that is being offered to protect your
Fellowships in nuclear science and technology: Applying the knowledge
 Fellowships in nuclear science and technology: Applying the knowledge Nearly 1200 scientists, engineers, and specialists receive training each year under IAEA-supported fellowships and scientific visits
Fellowships in nuclear science and technology: Applying the knowledge Nearly 1200 scientists, engineers, and specialists receive training each year under IAEA-supported fellowships and scientific visits
Progress has been made with respect to health conditions.
 health Strong performers in reducing child mortality 199-2 Niger Guinea-Bissau Guinea Ethiopia Benin 2 199 Strong performers in reducing maternal mortality 199-2 Djibouti Madagascar Eritrea Comoros Somalia
health Strong performers in reducing child mortality 199-2 Niger Guinea-Bissau Guinea Ethiopia Benin 2 199 Strong performers in reducing maternal mortality 199-2 Djibouti Madagascar Eritrea Comoros Somalia
