Reversal of Glucose Insensitivity of Pancreatic B-Cells Due to Prolonged Exposure to High Glucose in Culture : Effect of Nicotinamide on
|
|
|
- Delilah Quinn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 1993, 169, Reversal of Glucose Insensitivity of Pancreatic B-Cells Due to Prolonged Exposure to High Glucose in Culture : Effect of Nicotinamide on Pancreatic B-Cells HISAKO OHGAWARA*'t, MAKIKO KAWAMURAt, MASASHI HONDA', SACHIYO KARIBEt, NAOKO IWASAKIt, YOSHIMASA TASAKAt and YASUE OMORIt *Institute of Medical Research, and 'Diabetes Center, Tokyo Women's Medical College, Tokyo 162 OHGAWARA, H., KAWAMURA, M., HONDA, M., KARIBE, S., IWASAKI, N., TASAKA, Y. and OMORI, Y. Reversal of Glucose Insensitivity of Pancreatic B-Cells Due to Prolonged Exposure to High Glucose in Culture : Effect of Nicotinamide on Pancreatic B-Cells. Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 1993, 169 (2), Prolonged in vitro exposure to high glucose has been shown to induce a decrease in pancreatic B-cell sensitivity to glucose stimulation. This experiment was designed to study whether nicotinamide affects the B-cells' response to regulatory stimuli of glucose after prolonged culture with high glucose. Neonatal pig pancreatic islet-like cell clusters (ICCs) formed from single cells were embedded in agarose-gel. Some of them were maintained in RPMI 1640 containing a high glucose concentration (16.7 mm) and 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) with or without nicotinamide. Then, the embedded-iccs were stimulated by glucose at concentrations of 5.5 mm and 16.7 mm. After the prolonged culture with high glucose, the ICCs showed no response to acute glucose stimulation. There was a significant increase in glucose-mediated insulin secretion when the ICCs were maintained with the medium containing nicotinamide. We conclude that nicotinamide could protect B-cell desensitization to glucose after prolonged exposure to high glucose. desensitization to glucose ; pancreatic islet ; ICCs ; agarose ; embedded-culture It has been reported that when pancreatic B-cells are chronically exposed to high glucose, subsequent insulin release in response to glucose is impaired (Cerasi et al. 1972; Bolaf et al. 1986; Hoenig et al. 1986; Purrello et al. 1989). Unger and Grundy reported that a long-standing severe hyperglycemia may irreversibly damage B-cells (1985). This has been demonstrated both in vitro and in vivo. Nagamatsu et al. have observed that cultured rat islets chronically exposed to high glucose become desensitized to subsequent glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (1987). Furthermore, Weir et al. demonstrated that the B-cell ability to suppress insulin secretion when plasma glucose concentrations are low was impaired in normal subjects in whom hyperglycemia was maintained using the clamp Received November 2, 1992; revision accepted for publication January 21,
2 160 H. Ohgawara et al. technique (198.1). Also, the altered insulin secretion of diabetic patients (noninsulin dependent diabetes) was improved by correcting hyperglycemia with diet, hypoglycemic agents, or insulin (Savage et al. 1979; Kosaka et al. 1980). Recently, Yonemura et al. (1984) showed that a poly (ADP-ribose) synthetase inhibitor, such as nicotinamide, can prevent diabetes in partially depancreatized rats. In this study, we aimed to protect the B-cell desensitization to glucose by using nicotinamide in the culture medium during the incubation period. We observed glucose-stimulated insulin secretion after a prolonged exposure to high glucose with or without nicotinamide. MATERIALS AND METHODS Preparation of islet cells. Pancreatic islet-like cell clusters (ICCs) were prepared from neonatal pig pancreases by modifying the method of Archer (1983), as previously reported from our laboratory (Ohgawara et al. 1991). Embedded-culture of ICCs. Agarose was commercially prepared Agarose-LGT (polymerized at low temperature : Nacalai tesque Inc., Tokyo). A 2.0% (W/V) solution of agarose was sterlized in an auto-sterilizer for 30 nim. Then, the agarose solution and a 2X concentration of RPMI 1640 containing 20% FBS with or without 1.0 or 10 mm nicotinamide were mixed in equal amounts. Approximately 5,000 ICCs were added to the above mixture to give a final density of ICCs per ml of the agarose mixture. One ml of the mixture was placed in a multiwell plate (24-wells; Corning Glass Works, NY, USA), and then brought to 30 C to allow polymerization of the agarose. The incubation was continued at 3TC under an atmosphere of 5% CO2 and air. The cultures were fed with RPMI 1640 containing 16.7 mm D-glucose, 10% FBS and with or without 10 mm nicotinamide. From the following day, the medium was replaced every 3 days with RPMI 1640 supplemented with or without nicotinamide. Glucose-stimulated insulin release. Insulin secretion to glucose was observed on the 1st, 7th and 21st culture days. The culture medium was changed 4 hr before the short-term glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. The tissue culture medium was replaced with 1.0 ml of RPMI 1640 containing 10% FBS and 3.3 mm D-glucose. Preincubation was performed to establish a stable baseline for insulin secretion. The preincubation medium was then discarded and replaced with 1.0 ml of a medium containing 5.5 mm or 16.7 mm D-glucose. The incubation media were collected at the end of the 5-hr culture period and centrifuged, and the surpernatants were stored at -20 C for insulin assay. RESULTS Chronic stimulation of the ICCs with culture media containing high glucose, with or without nicotinamide, was characterized by the insulin output in response to glucose. The ICCs embedded in agarose-gel were maintained in RPMI 1640 containing 16.7 mm D-glucose and 10% FBS with or without nicotinamide (1.0 or 10 mm) for several days. They were then stimulated by glucose. As shown in Fig. 1, when the culture medium contained 10 mm nicotinamide the insulin output in response to glucose (16.7 mm) was much higher than that in ICCs which had been maintained in the culture medium containing 16.7 mm D-glucose alone, except on day 1 in response to 5.5 mm D-glucose.
3 Reversal of B-Cell Desensitization 161 Fig.1. Insulin output in response to different concentration of glucose (5.5 mm or 16.7 mm) by pancreatic islet cell-clusters (ICCs) cultured in RPMI 1640 plus 10% fetal bovine serum under the three different culture conditions : 1) glucose (16.7 mm) alone LIII; 2) glucose and a low concentration (1.0 mm ) of nicotinamide ; and 3) glucose and a high concentration (10 mm) of nicotinamide. Fig.2. Basal and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from embedded-iccs in agarose with or without nicotinamide. The ICCs-cultures were incubated for 5 hr in 1.0 ml of RPMI containing D-glucose (16.7 mm) alone ( ) ; D- glucose and 1.0 mm nicotinamide (o---o) ; or D-glucose and 10 mm nicotinamide (x x) on days 1, 7 and 21 of culture. The glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from the ICCs was calculated as follows : Insulin (IRI) secretion (% of control) IRI response to 5.5 or 16.7 mm D-glucose on day 1, 7 or 21 of culture X 100 IRI response to 5.5 mm D-glucose on day 1 of culture
4 H. Ohgawara 162 Fig. et al. 3. Morphology of the ICCs. The embedded ICCs in agarose and nicotinamide observed with a light microscope after enzymatic staining. (100 X) The ICCs are well preserved in the agarose. INS, B-cell ; GUL, A-cell ; SOM, D-cell ; PP, pp-cell.
5 Reversal of B-Cell Desensitization 163 When comparing the data in Fig. 2, the increase in the glucose concentration from 5.5 to 16.7 mm in the incubation medium did not significantly affect the glucose-stimulated state when estimated after prolonged culture with high glucose alone. On the 1st day, insulin secretion in response to glucose was 100% of the control in 5.5 mm D-glucose-stimulation and 85% of the control in 16.7 mm D-glucose after a prolonged culture with high glucose (16.7 mm) alone. On day 7, it was 39% of the control in the 5.5 mm D-glucose and 47% of the control in the 16.7 mm D-glucose. On day 21, it was 20% of the control in the low glucose and 24% of the control in the high glucose. The basal insulin secretion to glucose was decreased during the culture periods and the ICCs showed a very poor increase in insulin secretion in response to the glucose challenge. In the presence of nicotinamide, the insulin response to glucose was much higher than that of the ICCs which had been maintained with glucose alone. The ICCs exposed during the seven days of culture to 16.7 mm D-glucose with 1.0 or 10 mm nicotinamide, showed a significantly higher glucose-stimulated insulin release than that of the ICCs which had been maintained in 16.7 mm D-glucose alone (p <0.05). On day 7 of culture, the basal insulin secretion to 5.5 mm D-glucose showed a similar insulin release to the glucose on the 1st day, in the presence of 10 mm nicotinamide (100% of control in response to the low glucose on day 1 vs. 98% of control on day 7) but not with 1.0 mm nicotinamide. The ICCs which were embedded in agarose-gel were observed with a light microscope after enzymatic staining. The ICCs were found to be intact on day 21 of culture (Fig. 3). DISCUSSION The present study shows that nicotinamide reduced glucotoxicity after chronic exposure of normal pancreatic B-cells to a high glucose concentration (16.7 mm D-glucose) in vitro. During a prolonged culture in the presence of 16.7 mm D-glucose, ICCs showed a very poor increase in insulin release in response to an acute glucose challenge, on the 1st day of culture, but not in the presence of nicotinamide. Yarimizu et al. demonstrated "desensitization" in a perifusion system using cultured islets. When the islets had been previously cultured in high glucose for few days, the amount of insulin release in response to high glucose showed a marked decrease in both the first and the second phases. They also observed that reversibility of impaired insulin secretion by high glucose occurred when the desensitized islets were subsequently cultured in low glucose (1991). Giroix et al. (1989) reported that glucose insensitivity in 1-day cultured islets was primarily caused by a direct deleterious effect of high glucose concentration on the B-cells. Cerasi et al. (1972) reported that the glucose insensitivity is due to a decrease in the sensitivity of the glucose receptors of the pancreatic B-cells
6 164 H. Ohgawara et al. which transmits the glucose signal for insulin release. Dunbar et al. (1989) suggested that the glucose desensitization of the B-cells might be due to alteration of the calcium-dependent release mechanism. And Okamoto et al. (1992) also reported that the inability of glucose to provoke a [Ca2] +i rise, which is observed in the B-cells exposed to high glucose may be responsible for the selective impairment of the glucose-induced insulin secretion. In our experiment, nicotinamide protected ICCs from desensitization in response to the acute glucose stimulation after prolonged culture in the presence of 16.7 mm n-glucose. It was reported by Okamoto (1991) that nicotinamide, an inhibitor of islet nuclear poly (ADP-ribose) synthetase, reversed the reduction in NAD level and also inhibition of proinsulin synthesis. It was also found that in rat insulinoma cells cultured in the presence of streptozotocin, nicotinamide increased DNA single-strand breaks in the cells indicative of the inhibition of the poly (ADPribose) synthetase, but not in the presence of alloxan (Yamamoto et al. 1981; Uchigata et al ; Willson et al. 1984). Furthermore, nicotinamide prevented or slowed the manifestation of diabetes in non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice (Yamada et al. 1982; Nakajima et al. 1985). Masiello et al. (1985) observed a protective effect of 3-aminobenzamide (a potent inhibitor of poly (ADP-ribose) synthetase) against streptozotocin-induced diabetes, and that the protective effect was similar to that exerted by nicotinamide. Therefore, they strongly supported the idea that the effect may be a major consequence of the activation of DNA repair mechanism in islet cells. Recently, Varsanyi-Nagy et al. (1992) reported that nicotinamide preserved islet structure and stimulated insulin release and synthesis in an in vitro islet culture system. They also observed that the effect was amplified by addition of low-dose IL-1B. More recently, Takasawa et al. (1993) reported that cyclic (ADP ribose) is a mediator of calcium release from islet microsomes and might be generated in the islets by glucose stimulation, serving as a second messenger for calcium mobilization in the endoplasmic reticulum. In our experiment, the presence of nicotinamide may be a major consequence of the activator of NAD + mechanisms in islet cells. Acknowledgments We thank Prof. H. Okamoto, Tohoku University School of Medicine, for his advice, and Ms. Barbara Levene for English corrections. This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research in Japan , and a kind donation from the Itoe Okamoto Memorial Foundation. References 1) Archer, F.J. (1983) Monolayer culture of neonatal pig pancreatic islet cells.
7 Reversal of B-Cell Desensitization 165 Diabetologia, 24, ) Bolaffi, J.L., Heldt, A., Lewis, L.D. & Grodsky, G.M. (1986) The third phase of in vitro insulin secretion : Evidence for glucose insensitivity. Diabetes, 35, ) Cerasi, E., Luft, R. & Efendic, S. (1972) Decreased sensitivity of the pancreatic beta cells to glucose in prediabetic and diabetic subjects : A glucose dose response study. Diabetes, 21, ) Dunbar, C.J., Houser, F. & Levy, J. (1989) Beta cell desensitization to glucose induced by hyperglycemia is augmented by increased calcium. Diabetes Res. Gun. Pract., 7, ) Giroix, M.-H., Serradas, P. & Portha, B. (1989) The desensitization of normal B-cells to glucose in vitro is transient and not related to high glucose levels. Endocrinology, 125, ) Hoenig, M., MacGregor, L.C. & Matschinsky, F.M. (1986) In vitro exhaustion of pancreatic B-cells. Am. J. Physiol., 250. E502-E511. 7) Kosaka, K., Kuzuya, A., Akanuma, Y. & Hagura, R. (1980) Increase in insulin response after treatment of overt maturity-onset diabetes is independent of the mode of treatment. Diabetologia, 18, ) Masiello, P., Cubeddu, T.L., Frosia, G. & Bergamini, E. (1985) Protective effect of 3-aminobenzamide, and inhibitor of poly (ADP-ribose) synthetase, against streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Diabetologia, 28, ) Nagamatsu, S., Bolaffi, J.L. & Grodsky, G.M. (1987) Direct effect of glucose on proinsulin synthesis and processing during desensitization. Endoclinology,120, ) Nakajima, H., Fujino-Kurihara, H. & Hanafusa, T. (1985) Nicotinamide prevents the development of cyclophosphamide- induced diabetes mellitus in male non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice. Biomed. Res., 6, ) Ohgawara, H., Mochizuki, N., Karibe, S. & Omori, Y. (1991) Survival and B-cell function of neonatal pig pancreatic islet-like cell clusters in an extracellular matrix. Pancreas, 6, ) Okamoto, H. (1991) Regulation of proinsulin synthesis in pancreatic islets and a new aspect to insulin-dependent diabetes. Mol. Cell. Biochem., 37, ) Okamoto, Y., Ishida, H., Taminato, T., Tsuji, K., Kurose, T., Tsuura, Y., Kato, S., Imura, H. & Seino, Y. (1992) Role of cytosolic Caz+ in impaired sensitivity to glucose of rat pancreatic islets exposed to high glucose in vitro. Diabetes, 41, ) Purrello, F., Vetri, M., Gatta, C., Gullo, D. & Vigneri, R. (1989) Effects of high glucose on insulin secretion by isolated rat islets and purified B-cells and possible role of glycosylation. Diabetes, 38, ) Savage, P.J., Bennion, L.J., Flock, E.V., Nagulesparan, M., Mott, D., Roth, J., Unger, R.H. & Bennett, P.H. (1979) Diet-induced improvement of abnormalities in insulin and glucagon secretion and in insulin receptor binding in diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab., 48, ) Takasawa, S., Nata, K., Yonekura, M. & Okamoto, H. (1993) Cyclic ADP-ribose in insulin secretion from pancreatic B-cells. Science, 259, ) Uchigata, Y., Yamamoto, H., Kawamura, A. & Okamoto, H. (1982) Protection by superoxide dismutase, catalase, and poly (ADP ribose) synthetase inhibitors against alloxan and streptozotocine-induced islet DNA strand breaks and against the inhibition of proinsulin synthesis. J. Biol. Chem., 257, ) Unger, R.H. & Grundy, S. (1985) Hyperglycemia as an inducer as well as a consequence of impaired islet cell function and insulin resistance : Implications for the management of diabetes. Diabetologia, 28, ) Varsanyi-Nagy, M., Dadufalza, V., Bukingham, B., Wang, Z., Balazsi, L., Horvath, M. & Romics, L. (1992) Protective effect of nicotinamide on preservation of mouse islet
8 166 H. Ohgawara et al. function and morphology. Diabetologia, 35, Suppl.1, 496 A ) Weir, GO., Clore, E.T., Zmachinski, C.J. & Bonner-Weir, S. (1981) Islet secretion in a new experimental model for non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes, 30, ) Willson, G.L., Patton, N.J., McCord, J.M., Mullins, D.W. & Mossman, B.T. (1984) Mechanisms of streptozotocin- and alloxan-induced damage in rat B cells. Diabetologia, 27, ) Yamada, K., Nonaka, K., Hanafusa, T., Miyazaki, A., Toyoshima, H. & Tarui, S. (1982) Preventive and therapeutic effects of large-dose nicotinamide injections on diabetes associated with insulitis. An observation in nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice. Diabetes, 31, ) Yamamoto, H., Uchigata, Y. & Okamoto, H. (1981) Streptozotocine and alloxan induced DNA strand breaks and poly (ADP-ribose) synthetase in pancreatic islets. Nature, 294, ) Yarimizu, K., Maruo, M., Ono, J., ma, K., Okada, T. & Takaki, R. (1991) Desensitization of insulin secretion from pancreatic B-cells by high glucose. J Jpn. Diab. Soc., 34, ) Yomemura, Y., Takashima, T., Miwa, K., Miyazaki, I., Yamamoto, H. & Okamoto, H. (1984) Amelioration of diabetes mellitus in partially depancreatized rats by poly (ADP-ribose) synthetase inhibitor. Diabetes, 33,
a Regenerating (reg) Gene Pancreas Treated wi th
 Endocrine Journal 1995, 42(5), 649-653 Increased Expression of Protein in Neonatal Rat Streptozotocin a Regenerating (reg) Gene Pancreas Treated wi th ToMIO OHNO, CHIKARA ISHII, NoRIHIRO KATO, YOSHITO
Endocrine Journal 1995, 42(5), 649-653 Increased Expression of Protein in Neonatal Rat Streptozotocin a Regenerating (reg) Gene Pancreas Treated wi th ToMIO OHNO, CHIKARA ISHII, NoRIHIRO KATO, YOSHITO
Strain Differences in the Diabetogenic Activity of Streptozotocin in Mice
 1110 Biol. Pharm. Bull. 29(6) 1110 1119 (2006) Vol. 29, No. 6 Strain Differences in the Diabetogenic Activity of Streptozotocin in Mice Koji HAYASHI, Rhyoji KOJIMA, and Mikio ITO* Laboratory of Analytical
1110 Biol. Pharm. Bull. 29(6) 1110 1119 (2006) Vol. 29, No. 6 Strain Differences in the Diabetogenic Activity of Streptozotocin in Mice Koji HAYASHI, Rhyoji KOJIMA, and Mikio ITO* Laboratory of Analytical
Tokyo Women's Medical College, Shinjukuku,
 Tohoku J. exp. Med., 1982, 138, 319-328 Insulin-Receptor Autoantibody Detected by the Human Placental Membrane Method: Six Patients with Insulin-Receptor Autoantibody in Japan YASUE OMORI, HIRATA Diabetes
Tohoku J. exp. Med., 1982, 138, 319-328 Insulin-Receptor Autoantibody Detected by the Human Placental Membrane Method: Six Patients with Insulin-Receptor Autoantibody in Japan YASUE OMORI, HIRATA Diabetes
Secondary Negative Effects of Isolation Enzyme (s) On Human Islets. A.N.Balamurugan
 Secondary Negative Effects of Isolation Enzyme (s) On Human Islets A.N.Balamurugan Human Islets Functional Mass Preservation 18-25 min 10 min 8-12 min 10-15 min 45-60 min pancreas in chamber 37º Sub-Optimal
Secondary Negative Effects of Isolation Enzyme (s) On Human Islets A.N.Balamurugan Human Islets Functional Mass Preservation 18-25 min 10 min 8-12 min 10-15 min 45-60 min pancreas in chamber 37º Sub-Optimal
Effect of glucose on beta cell proliferation and population size in organ culture of foetal and neonatal rat pancreases
 J. Embryol. exp. Morph. 74, 303-312 (1983) 3Q3 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1983 Effect of glucose on beta cell proliferation and population size in organ culture of foetal
J. Embryol. exp. Morph. 74, 303-312 (1983) 3Q3 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1983 Effect of glucose on beta cell proliferation and population size in organ culture of foetal
Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells.
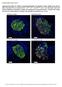 Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells. Pancreata from 16-weeks-old 6J +/+, 6J db/db, KS +/+ and KS db/db mice were harvested, fixed with
Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells. Pancreata from 16-weeks-old 6J +/+, 6J db/db, KS +/+ and KS db/db mice were harvested, fixed with
Diabetologia 9 Springer-Verlag t991
 Diabetologia (1991) 34:570-575 0012186X9100164L Diabetologia 9 Springer-Verlag t991 No glucotoxicity after 53 hours of 6.0 mmol/l hyperglycaemia in normal man H. Flax, D. R. Matthews, J. C. Levy, S. W.
Diabetologia (1991) 34:570-575 0012186X9100164L Diabetologia 9 Springer-Verlag t991 No glucotoxicity after 53 hours of 6.0 mmol/l hyperglycaemia in normal man H. Flax, D. R. Matthews, J. C. Levy, S. W.
Expression of Reg and cytokeratin 20 during ductal cell differentiation and proliferation in a mouse model of autoimmune diabetes
 European Journal of Endocrinology (1999) 141 644 652 ISSN 0804-4643 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY Expression of Reg and cytokeratin 20 during ductal cell differentiation and proliferation in a mouse model of autoimmune
European Journal of Endocrinology (1999) 141 644 652 ISSN 0804-4643 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY Expression of Reg and cytokeratin 20 during ductal cell differentiation and proliferation in a mouse model of autoimmune
Insulin, Glucagon and Somatostatin Content of the Non-Obese Diabetic (NOD) Mouse Pancreas and Plasma Virus Antibodies to Coxsackie B- and Reoviruses
 Tohoku J. exp. Med., 1985, 146, 153-162 Insulin, Glucagon and Somatostatin Content of the Non-Obese Diabetic (NOD) Mouse Pancreas and Plasma Virus Antibodies to Coxsackie B- and Reoviruses YOSHIMASA TASAKA,
Tohoku J. exp. Med., 1985, 146, 153-162 Insulin, Glucagon and Somatostatin Content of the Non-Obese Diabetic (NOD) Mouse Pancreas and Plasma Virus Antibodies to Coxsackie B- and Reoviruses YOSHIMASA TASAKA,
Discussion & Conclusion
 Discussion & Conclusion 7. Discussion DPP-4 inhibitors augment the effects of incretin hormones by prolonging their half-life and represent a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
Discussion & Conclusion 7. Discussion DPP-4 inhibitors augment the effects of incretin hormones by prolonging their half-life and represent a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
Prolonged Exposure of Human Cells to Elevated Glucose Levels Results in Sustained Cellular Activation Leading to a Loss of Glucose Regulation
 Prolonged Exposure of Human Cells to Elevated Glucose Levels Results in Sustained Cellular Activation Leading to a Loss of Glucose Regulation Zhidong Ling and Daniel G. Pipeleers Diabetes Research Center,
Prolonged Exposure of Human Cells to Elevated Glucose Levels Results in Sustained Cellular Activation Leading to a Loss of Glucose Regulation Zhidong Ling and Daniel G. Pipeleers Diabetes Research Center,
The CD38-cyclic ADP-ribose signalling system in insulin secretion: molecular basis and clinical implications
 Diabetologia (1997) 40: 1485±1491 Springer-Verlag 1997 The CD38-cyclic ADP-ribose signalling system in insulin secretion: molecular basis and clinical implications H. Okamoto, S. Takasawa, K. Nata Department
Diabetologia (1997) 40: 1485±1491 Springer-Verlag 1997 The CD38-cyclic ADP-ribose signalling system in insulin secretion: molecular basis and clinical implications H. Okamoto, S. Takasawa, K. Nata Department
Diabetologia 9 Springer-Verlag 1995
 Diabetologia (1995) 38:53-58 Diabetologia 9 Springer-Verlag 1995 Originals The NSY mouse: a new animal model of spontaneous NIDDM with moderate obesity H. Ueda 1, H. lkegami l, E. Yamato 1, J. Fu 1, M.
Diabetologia (1995) 38:53-58 Diabetologia 9 Springer-Verlag 1995 Originals The NSY mouse: a new animal model of spontaneous NIDDM with moderate obesity H. Ueda 1, H. lkegami l, E. Yamato 1, J. Fu 1, M.
Diabetologia 9 Springer-Vcrlag 1993
 Diabetologia (1993) 36:305-309 Diabetologia 9 Springer-Vcrlag 1993 Preferential alteration of oxidative relative to total glycolysis in pancreatic islets of two rat models of inherited or acquired Type
Diabetologia (1993) 36:305-309 Diabetologia 9 Springer-Vcrlag 1993 Preferential alteration of oxidative relative to total glycolysis in pancreatic islets of two rat models of inherited or acquired Type
Week 3, Lecture 5a. Pathophysiology of Diabetes. Simin Liu, MD, ScD
 Week 3, Lecture 5a Pathophysiology of Diabetes Simin Liu, MD, ScD General Model of Peptide Hormone Action Hormone Plasma Membrane Activated Nucleus Cellular Trafficking Enzymes Inhibited Receptor Effector
Week 3, Lecture 5a Pathophysiology of Diabetes Simin Liu, MD, ScD General Model of Peptide Hormone Action Hormone Plasma Membrane Activated Nucleus Cellular Trafficking Enzymes Inhibited Receptor Effector
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Diabetologia. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2014 February 01.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Diabetologia. 2013 February ; 56(2): 231 233. doi:10.1007/s00125-012-2788-6. Lipotoxicity impairs incretin signalling V. Poitout 1,2
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Diabetologia. 2013 February ; 56(2): 231 233. doi:10.1007/s00125-012-2788-6. Lipotoxicity impairs incretin signalling V. Poitout 1,2
N Dachicourt, P Serradas, D Bailbé, M Kergoat 1, L Doaré 1 and B Portha
 369 Glucagon-like peptide-1(7 36)-amide confers glucose sensitivity to previously glucose-incompetent β-cells in diabetic rats: in vivo and in vitro studies N Dachicourt, P Serradas, D Bailbé, M Kergoat
369 Glucagon-like peptide-1(7 36)-amide confers glucose sensitivity to previously glucose-incompetent β-cells in diabetic rats: in vivo and in vitro studies N Dachicourt, P Serradas, D Bailbé, M Kergoat
GRANULOLYSIS IN A CELLS OF ENDOCRINE PANCREAS AND EXPERIMENTAL DIABETES IN ANIMALS
 Published Online: 1 August, 1968 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.38.2.462 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on December 25, 2018 GRANULOLYSIS IN A CELLS OF ENDOCRINE PANCREAS IN SPONTANEOUS AND EXPERIMENTAL
Published Online: 1 August, 1968 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.38.2.462 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on December 25, 2018 GRANULOLYSIS IN A CELLS OF ENDOCRINE PANCREAS IN SPONTANEOUS AND EXPERIMENTAL
Glucose Homeostasis. Liver. Glucose. Muscle, Fat. Pancreatic Islet. Glucose utilization. Glucose production, storage Insulin Glucagon
 Glucose Homeostasis Liver Glucose Glucose utilization Glucose production, storage Insulin Glucagon Muscle, Fat Pancreatic Islet Classification of Diabetes Type 1 diabetes Type 2 diabetes Other types of
Glucose Homeostasis Liver Glucose Glucose utilization Glucose production, storage Insulin Glucagon Muscle, Fat Pancreatic Islet Classification of Diabetes Type 1 diabetes Type 2 diabetes Other types of
Supplemental Data. Short Article. ATF4-Mediated Induction of 4E-BP1. Contributes to Pancreatic β Cell Survival. under Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 7 Supplemental Data Short Article ATF4-Mediated Induction of 4E-BP1 Contributes to Pancreatic β Cell Survival under Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Suguru Yamaguchi, Hisamitsu Ishihara,
Cell Metabolism, Volume 7 Supplemental Data Short Article ATF4-Mediated Induction of 4E-BP1 Contributes to Pancreatic β Cell Survival under Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Suguru Yamaguchi, Hisamitsu Ishihara,
Effects of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I on Insulin and Glucagon Release from Isolated Perfused Rat Pancreas
 Effects of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I on Insulin and Glucagon Release from Isolated Perfused Rat Pancreas KOICHI KAWAI, SEIJI SUZUKI, KAZUE TAKANO*, NAOMI HIZUKA*, YASUKO WATANABE AND KAMEJIRO YAMASHITA
Effects of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I on Insulin and Glucagon Release from Isolated Perfused Rat Pancreas KOICHI KAWAI, SEIJI SUZUKI, KAZUE TAKANO*, NAOMI HIZUKA*, YASUKO WATANABE AND KAMEJIRO YAMASHITA
The Need for a PARP in vivo Pharmacodynamic Assay
 The Need for a PARP in vivo Pharmacodynamic Assay Jay George, Ph.D. Chief Scientific Officer Trevigen, Inc. Gaithersburg, MD Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases are promising therapeutic targets. In response
The Need for a PARP in vivo Pharmacodynamic Assay Jay George, Ph.D. Chief Scientific Officer Trevigen, Inc. Gaithersburg, MD Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases are promising therapeutic targets. In response
18. PANCREATIC FUNCTION AND METABOLISM. Pancreatic secretions ISLETS OF LANGERHANS. Insulin
 18. PANCREATIC FUNCTION AND METABOLISM ISLETS OF LANGERHANS Some pancreatic functions have already been discussed in the digestion section. In this one, the emphasis will be placed on the endocrine function
18. PANCREATIC FUNCTION AND METABOLISM ISLETS OF LANGERHANS Some pancreatic functions have already been discussed in the digestion section. In this one, the emphasis will be placed on the endocrine function
Article. Reference. Effect of insulin on glucose- and arginine-stimulated somatostatin secretion from the isolated perfused rat pancreas
 Article Effect of insulin on glucose- and arginine-stimulated somatostatin secretion from the isolated perfused rat pancreas GERBER, Pietro, et al. Abstract The effects of exogenous insulin on somatostatin
Article Effect of insulin on glucose- and arginine-stimulated somatostatin secretion from the isolated perfused rat pancreas GERBER, Pietro, et al. Abstract The effects of exogenous insulin on somatostatin
Diabetes: Definition Pathophysiology Treatment Goals. By Scott Magee, MD, FACE
 Diabetes: Definition Pathophysiology Treatment Goals By Scott Magee, MD, FACE Disclosures No disclosures to report Definition of Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus comprises a group of disorders characterized
Diabetes: Definition Pathophysiology Treatment Goals By Scott Magee, MD, FACE Disclosures No disclosures to report Definition of Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus comprises a group of disorders characterized
Diabetologia 9 Springer-Verlag 1993
 Diabetologia (1993) 36:3-8 Diabetologia 9 Springer-Verlag 1993 Originals Abnormal insulin secretion and glucose metabolism in pancreatic islets from the spontaneously diabetic GK rat C.-G. Ostenson I,
Diabetologia (1993) 36:3-8 Diabetologia 9 Springer-Verlag 1993 Originals Abnormal insulin secretion and glucose metabolism in pancreatic islets from the spontaneously diabetic GK rat C.-G. Ostenson I,
Robert Wadlow and his father
 Robert Wadlow and his father 1 Robert Wadlow Wadlow reached 8 ft 11.1 in (2.72 m) in height and weighed 485 lb (220 kg) at his death at age 22. Born in Illinois. His great size and his continued growth
Robert Wadlow and his father 1 Robert Wadlow Wadlow reached 8 ft 11.1 in (2.72 m) in height and weighed 485 lb (220 kg) at his death at age 22. Born in Illinois. His great size and his continued growth
Keywords FAD-linked glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase,
 Diabetologia (1998) 41: 649±653 Ó Springer-Verlag 1998 Overexpression of mitochondrial FAD-linked glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase does not correct glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from diabetic
Diabetologia (1998) 41: 649±653 Ó Springer-Verlag 1998 Overexpression of mitochondrial FAD-linked glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase does not correct glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from diabetic
Hormonal Regulations Of Glucose Metabolism & DM
 Hormonal Regulations Of Glucose Metabolism & DM What Hormones Regulate Metabolism? What Hormones Regulate Metabolism? Insulin Glucagon Thyroid hormones Cortisol Epinephrine Most regulation occurs in order
Hormonal Regulations Of Glucose Metabolism & DM What Hormones Regulate Metabolism? What Hormones Regulate Metabolism? Insulin Glucagon Thyroid hormones Cortisol Epinephrine Most regulation occurs in order
Receptors of Paraneurons, with Special Reference to Glucoreceptors
 Arch. Histol. Cytol., Vol. 52, Suppi. (1989) p. 33-38 Receptors of Paraneurons, with Special Reference to Glucoreceptors Atsushi NIKI, Hatsumi NIKI and Toshiki HASHIOKA Department of Internal Medicine,
Arch. Histol. Cytol., Vol. 52, Suppi. (1989) p. 33-38 Receptors of Paraneurons, with Special Reference to Glucoreceptors Atsushi NIKI, Hatsumi NIKI and Toshiki HASHIOKA Department of Internal Medicine,
Supplemental Information. b Cell Aging Markers Have Heterogeneous. Distribution and Are Induced by Insulin Resistance
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 25 Supplemental Information b Cell Aging Markers Have Heterogeneous Distribution and Are Induced by Insulin Resistance Cristina Aguayo-Mazzucato, Mark van Haaren, Magdalena Mruk,
Cell Metabolism, Volume 25 Supplemental Information b Cell Aging Markers Have Heterogeneous Distribution and Are Induced by Insulin Resistance Cristina Aguayo-Mazzucato, Mark van Haaren, Magdalena Mruk,
Acute and Steady-State Insulin Responses
 Acute and Steady-State nsulin Responses to Glucose in Nonobese Diabetic Subjects ROGER L. LERNER and DANEL PORTE, JR. From the University of Washington School of Medicine and Veterans Administration Hospital,
Acute and Steady-State nsulin Responses to Glucose in Nonobese Diabetic Subjects ROGER L. LERNER and DANEL PORTE, JR. From the University of Washington School of Medicine and Veterans Administration Hospital,
Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for conventional RT-PCR on mouse islets
 Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for conventional RT-PCR on mouse islets Gene 5 Forward 3 5 Reverse 3.T. Product (bp) ( C) mnox1 GTTCTTGGGCTGCCTTGG GCTGGGGCGGCGG 60 300 mnoxa1 GCTTTGCCGCGTGC GGTTCGGGTCCTTTGTGC
Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for conventional RT-PCR on mouse islets Gene 5 Forward 3 5 Reverse 3.T. Product (bp) ( C) mnox1 GTTCTTGGGCTGCCTTGG GCTGGGGCGGCGG 60 300 mnoxa1 GCTTTGCCGCGTGC GGTTCGGGTCCTTTGTGC
Type 2 diabetes develops as a consequence of
 -Cell Function and Viability in the Spontaneously Diabetic GK Rat Information From the GK/Par Colony B. Portha, M.-H. Giroix, P. Serradas, M.-N. Gangnerau, J. Movassat, F. Rajas, D. Bailbe, C. Plachot,
-Cell Function and Viability in the Spontaneously Diabetic GK Rat Information From the GK/Par Colony B. Portha, M.-H. Giroix, P. Serradas, M.-N. Gangnerau, J. Movassat, F. Rajas, D. Bailbe, C. Plachot,
Reduced expression of the liver/beta-cell glucose transporter isoform in glucose-insensitive pancreatic beta cells of diabetic rats
 Proc. Nad. cad. Sci. US Vol. 87, pp. 6492-6496, September 1990 Cell Biology Reduced expression of the liver/beta-cell glucose transporter isoform in glucose-insensitive pancreatic beta cells of diabetic
Proc. Nad. cad. Sci. US Vol. 87, pp. 6492-6496, September 1990 Cell Biology Reduced expression of the liver/beta-cell glucose transporter isoform in glucose-insensitive pancreatic beta cells of diabetic
Potentiation of Glucose-stimulated Insulin Secretion by the GPR40 PLC TRPC
 Supplementary information Potentiation of Glucose-stimulated Insulin Secretion by the GPR40 PLC TRPC Pathway in Pancreatic -Cells Authors: Hodaka Yamada 1,*, Masashi Yoshida 1,*, Kiyonori Ito 1, Katsuya
Supplementary information Potentiation of Glucose-stimulated Insulin Secretion by the GPR40 PLC TRPC Pathway in Pancreatic -Cells Authors: Hodaka Yamada 1,*, Masashi Yoshida 1,*, Kiyonori Ito 1, Katsuya
Improving Diabetes Research: Moving Beyond Animal Models. Charu Chandrasekera, Ph.D. Anne Bunner, Ph.D.
 Improving Diabetes Research: Moving Beyond Animal Models Charu Chandrasekera, Ph.D. Anne Bunner, Ph.D. July 19, 2014 From Bench-to-Bedside Sulfonylurea Biguanide Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor Glucagon-like
Improving Diabetes Research: Moving Beyond Animal Models Charu Chandrasekera, Ph.D. Anne Bunner, Ph.D. July 19, 2014 From Bench-to-Bedside Sulfonylurea Biguanide Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor Glucagon-like
History of Investigation
 Acini - Pancreatic juice (1º) (2º) Secretions- neuronal and hormonal mechanisms 1) Secretin - bicarbonate rich 2) Cholecystokinin - enzyme rich Islets of Langerhans (contain 4 cell types) Alpha cells (α)-
Acini - Pancreatic juice (1º) (2º) Secretions- neuronal and hormonal mechanisms 1) Secretin - bicarbonate rich 2) Cholecystokinin - enzyme rich Islets of Langerhans (contain 4 cell types) Alpha cells (α)-
Maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) is a heterogeneous group
 Over the years, different forms of maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) have been identified, with mutations in a number of different genes associated with a MODY-like phenotype. Depending on the
Over the years, different forms of maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) have been identified, with mutations in a number of different genes associated with a MODY-like phenotype. Depending on the
Update on GLP-1 Past Present Future
 Update on GLP-1 p Past Present Future Effects of GLP-1: Glucose Metabolism and Nutritional Balance L-Cells: Glp-1 release Betacellfollowing ingestion Stress Increases satiety reduces appetite Betacell-
Update on GLP-1 p Past Present Future Effects of GLP-1: Glucose Metabolism and Nutritional Balance L-Cells: Glp-1 release Betacellfollowing ingestion Stress Increases satiety reduces appetite Betacell-
Insulin Delivery and Glucose Monitoring Methods for Diabetes Mellitus: Comparative Effectiveness
 Insulin Delivery and Glucose Monitoring Methods for Diabetes Mellitus: Comparative Effectiveness Prepared for: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) www.ahrq.gov Outline of Material Introduction
Insulin Delivery and Glucose Monitoring Methods for Diabetes Mellitus: Comparative Effectiveness Prepared for: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) www.ahrq.gov Outline of Material Introduction
The Endocrine Pancreas (Chapter 10) *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m62118 1 The Endocrine Pancreas (Chapter 10) * Ildar Yakhin Based on The Endocrine Pancreas by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
OpenStax-CNX module: m62118 1 The Endocrine Pancreas (Chapter 10) * Ildar Yakhin Based on The Endocrine Pancreas by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
INSULIN RESPONSE IN GLUCOSE-TOLERANCE TESTS
 THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PATHOLOGY Copyright 1967 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 47, No. 0 Printed in U.S.A. INSULIN RESPONSE IN GLUCOSE-TOLERANCE TESTS STANLEY BURROWS, M.D. Department of
THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PATHOLOGY Copyright 1967 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 47, No. 0 Printed in U.S.A. INSULIN RESPONSE IN GLUCOSE-TOLERANCE TESTS STANLEY BURROWS, M.D. Department of
IT IS WELL recognized that in subjects with noninsulin
 0021-972X/98/$03.00/0 Vol. 83, No. 2 Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 1998 by The Endocrine Society Disproportionately Elevated Proinsulin Levels Reflect the
0021-972X/98/$03.00/0 Vol. 83, No. 2 Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 1998 by The Endocrine Society Disproportionately Elevated Proinsulin Levels Reflect the
Serum and urinary calcium levels in Type 2 diabetes mellitus
 Original article: Serum and urinary calcium levels in Type 2 diabetes mellitus Goutam Chakraborti 1, Sandip Chakraborti 2 * 1 Associate Professor, Biochemistry, Murshidabad medical college and hospital,
Original article: Serum and urinary calcium levels in Type 2 diabetes mellitus Goutam Chakraborti 1, Sandip Chakraborti 2 * 1 Associate Professor, Biochemistry, Murshidabad medical college and hospital,
Diabetologia 9 Springer-Verlag 1983
 Diabetologia (1983) 25: 51-55 Diabetologia 9 Springer-Verlag 1983 Experimental Hypothalamic or Genetic Obesity in the Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetic Rat B. Portha 1, R. Goursot t, M. H. Giroix 1, S. Nicola'fdis
Diabetologia (1983) 25: 51-55 Diabetologia 9 Springer-Verlag 1983 Experimental Hypothalamic or Genetic Obesity in the Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetic Rat B. Portha 1, R. Goursot t, M. H. Giroix 1, S. Nicola'fdis
Abstract. Introduction. Methods
 Alterations in Basal and Glucose-stimulated Voltage-dependent Ca 2 Channel Activities in Pancreatic Cells of Non Insulin-dependent Diabetes Mellitus GK rats Seika Kato,* Hitoshi Ishida,* Yoshiyuki Tsuura,*
Alterations in Basal and Glucose-stimulated Voltage-dependent Ca 2 Channel Activities in Pancreatic Cells of Non Insulin-dependent Diabetes Mellitus GK rats Seika Kato,* Hitoshi Ishida,* Yoshiyuki Tsuura,*
adenosine triphosphate-sensitive K[ Citation Journal of Diabetes Investigation ( modifications or adaptations are ma
 Fructose induces glucose-dependent Titleglucagon-like peptide-1 and insulin adenosine triphosphate-sensitive K[ Seino, Yusuke; Ogata, Hidetada; Mae Author(s) Takako; Iida, Atsushi; Harada, Nori Susumu;
Fructose induces glucose-dependent Titleglucagon-like peptide-1 and insulin adenosine triphosphate-sensitive K[ Seino, Yusuke; Ogata, Hidetada; Mae Author(s) Takako; Iida, Atsushi; Harada, Nori Susumu;
associated with serious complications, but reduce occurrences with preventive measures
 Wk 9. Management of Clients with Diabetes Mellitus 1. Diabetes Mellitus body s inability to metabolize carbohydrates, fats, proteins hyperglycemia associated with serious complications, but reduce occurrences
Wk 9. Management of Clients with Diabetes Mellitus 1. Diabetes Mellitus body s inability to metabolize carbohydrates, fats, proteins hyperglycemia associated with serious complications, but reduce occurrences
The enteroinsular axis in the pathogenesis of prediabetes and diabetes in humans
 The enteroinsular axis in the pathogenesis of prediabetes and diabetes in humans Young Min Cho, MD, PhD Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism Seoul National University College of Medicine Plasma glucose
The enteroinsular axis in the pathogenesis of prediabetes and diabetes in humans Young Min Cho, MD, PhD Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism Seoul National University College of Medicine Plasma glucose
Therapeutic strategy to reduce Glucagon secretion
 Clinical focus on glucagon: α-cell as a companion of β-cell Therapeutic strategy to reduce Glucagon secretion Sunghwan Suh Dong-A University Conflict of interest disclosure None Committee of Scientific
Clinical focus on glucagon: α-cell as a companion of β-cell Therapeutic strategy to reduce Glucagon secretion Sunghwan Suh Dong-A University Conflict of interest disclosure None Committee of Scientific
Making Mature Human Islet Cells from Stem Cells to Model Disease and Treat Diabetes
 University of British Columbia Departments of Surgery and Cellular & Physiological Sciences Making Mature Human Islet Cells from Stem Cells to Model Disease and Treat Diabetes 2016 International Conference
University of British Columbia Departments of Surgery and Cellular & Physiological Sciences Making Mature Human Islet Cells from Stem Cells to Model Disease and Treat Diabetes 2016 International Conference
The Effects of Exenatide on the Autoimmune Development of Diabetes. A Senior Honors Thesis
 The Effects of Exenatide on the Autoimmune Development of Diabetes A Senior Honors Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for Graduation with Distinction in Microbiology in the Undergraduate
The Effects of Exenatide on the Autoimmune Development of Diabetes A Senior Honors Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for Graduation with Distinction in Microbiology in the Undergraduate
Sitagliptin: first DPP-4 inhibitor to treat type 2 diabetes Steve Chaplin MSc, MRPharmS and Andrew Krentz MD, FRCP
 Sitagliptin: first DPP-4 inhibitor to treat type 2 diabetes Steve Chaplin MSc, MRPharmS and Andrew Krentz MD, FRCP KEY POINTS sitagliptin (Januvia) is a DPP-4 inhibitor that blocks the breakdown of the
Sitagliptin: first DPP-4 inhibitor to treat type 2 diabetes Steve Chaplin MSc, MRPharmS and Andrew Krentz MD, FRCP KEY POINTS sitagliptin (Januvia) is a DPP-4 inhibitor that blocks the breakdown of the
Abbreviations: P- paraffin-embedded section; C, cryosection; Bio-SA, biotin-streptavidin-conjugated fluorescein amplification.
 Supplementary Table 1. Sequence of primers for real time PCR. Gene Forward primer Reverse primer S25 5 -GTG GTC CAC ACT ACT CTC TGA GTT TC-3 5 - GAC TTT CCG GCA TCC TTC TTC-3 Mafa cds 5 -CTT CAG CAA GGA
Supplementary Table 1. Sequence of primers for real time PCR. Gene Forward primer Reverse primer S25 5 -GTG GTC CAC ACT ACT CTC TGA GTT TC-3 5 - GAC TTT CCG GCA TCC TTC TTC-3 Mafa cds 5 -CTT CAG CAA GGA
Laboratory of Experimental Medicine, Brussels Free University, Brussels, Belgium
 Vol. 45, No. 3, July 1998 Pages 429-434 DUAL EFFECT OF 2-DEOXY-D-GLUCOSE TETRAACETATE UPON GLUCOSE- INDUCED INSULIN RELEASE Willy J. Malaisse, Luis E. Flares and Marcel M. Kadiata Laboratory of Experimental
Vol. 45, No. 3, July 1998 Pages 429-434 DUAL EFFECT OF 2-DEOXY-D-GLUCOSE TETRAACETATE UPON GLUCOSE- INDUCED INSULIN RELEASE Willy J. Malaisse, Luis E. Flares and Marcel M. Kadiata Laboratory of Experimental
Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival
 Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Short communication. Abstract
 Diabetologia (1999) 42: 574±578 Short communication Ó Springer-Verlag 1999 Immunological abnormalities in islets at diagnosis paralleled further deterioration of glycaemic control in patients with recent-onset
Diabetologia (1999) 42: 574±578 Short communication Ó Springer-Verlag 1999 Immunological abnormalities in islets at diagnosis paralleled further deterioration of glycaemic control in patients with recent-onset
Pancreatic ß-Cell Death, Regeneration and Insulin Secretion: Roles of Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase and Cyclic ADP-Ribose
 Int. Jnl. Experimental Diab. Res., 3:79-96, 2002 2002 Taylor and Francis 1560-4284/02 $12.00 +.00 Pancreatic ß-Cell Death, Regeneration and Insulin Secretion: Roles of Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase and Cyclic
Int. Jnl. Experimental Diab. Res., 3:79-96, 2002 2002 Taylor and Francis 1560-4284/02 $12.00 +.00 Pancreatic ß-Cell Death, Regeneration and Insulin Secretion: Roles of Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase and Cyclic
Journal Club WS 2012/13 Stefanie Nickl
 Journal Club WS 2012/13 Stefanie Nickl Background Mesenchymal Stem Cells First isolation from bone marrow 30 ys ago Isolation from: spleen, heart, skeletal muscle, synovium, amniotic fluid, dental pulp,
Journal Club WS 2012/13 Stefanie Nickl Background Mesenchymal Stem Cells First isolation from bone marrow 30 ys ago Isolation from: spleen, heart, skeletal muscle, synovium, amniotic fluid, dental pulp,
Insulin release, insulin sensitivity, and glucose intolerance (early diabetes/pathogenesis)
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 77, No. 12, pp. 7425-7429, December 1980 Medical Sciences nsulin release, insulin sensitivity, and glucose intolerance (early diabetes/pathogenesis) SUAD EFENDt, ALEXANDRE
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 77, No. 12, pp. 7425-7429, December 1980 Medical Sciences nsulin release, insulin sensitivity, and glucose intolerance (early diabetes/pathogenesis) SUAD EFENDt, ALEXANDRE
Efficacy of Combination Therapy With Sitagliptin and Low-Dose Glimepiride in Japanese Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
 Elmer Original Article ress Efficacy of Combination Therapy With Sitagliptin and Low-Dose Glimepiride in Japanese Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Hiroaki Ishii a, f, Yosuke Ohkubo a, Masahiro Takei a, Shinichi
Elmer Original Article ress Efficacy of Combination Therapy With Sitagliptin and Low-Dose Glimepiride in Japanese Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Hiroaki Ishii a, f, Yosuke Ohkubo a, Masahiro Takei a, Shinichi
Endocrine System. Chapter 9
 Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
Antidiabetic Action of Low Molecular Weight Chitosan in Genetically Obese Diabetic KK-A y Mice
 188 Biol. Pharm. Bull. 25(2) 188 192 (2002) Vol. 25, No. 2 Antidiabetic Action of Low Molecular Weight Chitosan in Genetically Obese Diabetic KK-A y Mice Koji HAYASHI and Mikio ITO* Laboratory of Analytical
188 Biol. Pharm. Bull. 25(2) 188 192 (2002) Vol. 25, No. 2 Antidiabetic Action of Low Molecular Weight Chitosan in Genetically Obese Diabetic KK-A y Mice Koji HAYASHI and Mikio ITO* Laboratory of Analytical
My Journey in Endocrinology. Samuel Cataland M.D
 My Journey in Endocrinology Samuel Cataland M.D. 1968-2015 Drs Berson M.D. Yalow phd Insulin Radioimmunoassay Nobel Prize Physiology or Medicine 1977 Rosalyn Yalow: Radioimmunoassay Technology Andrew Schally
My Journey in Endocrinology Samuel Cataland M.D. 1968-2015 Drs Berson M.D. Yalow phd Insulin Radioimmunoassay Nobel Prize Physiology or Medicine 1977 Rosalyn Yalow: Radioimmunoassay Technology Andrew Schally
Transplantation in Nagasaki
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Evaluation of the Presumable Incide Transplantation in Nagasaki Tanaka, Takayuki; Kuroki, Tamotsu; Tatsuya; Ono, Shinichiro; Abiru, No Susumu
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Evaluation of the Presumable Incide Transplantation in Nagasaki Tanaka, Takayuki; Kuroki, Tamotsu; Tatsuya; Ono, Shinichiro; Abiru, No Susumu
Associations among Body Mass Index, Insulin Resistance, and Pancreatic ß-Cell Function in Korean Patients with New- Onset Type 2 Diabetes
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE korean j intern med 2012;27:66-71 pissn 1226-3303 eissn 2005-6648 Associations among Body Mass Index, Insulin Resistance, and Pancreatic ß-Cell Function in Korean Patients with New- Onset
ORIGINAL ARTICLE korean j intern med 2012;27:66-71 pissn 1226-3303 eissn 2005-6648 Associations among Body Mass Index, Insulin Resistance, and Pancreatic ß-Cell Function in Korean Patients with New- Onset
A novel role for vitamin D: modulation of expression and function of the local renin angiotensin system in mouse pancreatic islets
 Diabetologia () 5:77 DOI.7/s5--- SHORT COMMUNICATION A novel role for vitamin D: modulation of expression and function of the local renin angiotensin system in mouse pancreatic islets Q. Cheng & Y. C.
Diabetologia () 5:77 DOI.7/s5--- SHORT COMMUNICATION A novel role for vitamin D: modulation of expression and function of the local renin angiotensin system in mouse pancreatic islets Q. Cheng & Y. C.
Chapter 10. Introduction to Nutrition and Metabolism, 3 rd edition David A Bender Taylor & Francis Ltd, London 2002
 Chapter 10 Introduction to Nutrition and Metabolism, 3 rd edition David A Bender Taylor & Francis Ltd, London 2002 Chapter 10: Integration and Control of Metabolism Press the space bar or click the mouse
Chapter 10 Introduction to Nutrition and Metabolism, 3 rd edition David A Bender Taylor & Francis Ltd, London 2002 Chapter 10: Integration and Control of Metabolism Press the space bar or click the mouse
Key words: insulin dependent deabetes mellitus, pancreatic islets, transplantation, cryopreservation, immunomodulat ion
 Key words: insulin dependent deabetes mellitus, pancreatic islets, transplantation, cryopreservation, immunomodulat ion Fig. 1 Number of adult islet all grafts by year performed from 1974 through 1993
Key words: insulin dependent deabetes mellitus, pancreatic islets, transplantation, cryopreservation, immunomodulat ion Fig. 1 Number of adult islet all grafts by year performed from 1974 through 1993
Effect of Acute Exercise on Insulin Binding to Erythrocytes in Type II Diabetes
 Endocrinol. Japon. 1982, 29 (5), 561-566 Effect of Acute Exercise on Insulin Binding to Erythrocytes in Type II Diabetes MAKOTO IWASAKI, MASASHI KOBAYASHI, SEIJI OHGAKU, HIROSHI MAEGAWA AND YUKIO SHIGETA
Endocrinol. Japon. 1982, 29 (5), 561-566 Effect of Acute Exercise on Insulin Binding to Erythrocytes in Type II Diabetes MAKOTO IWASAKI, MASASHI KOBAYASHI, SEIJI OHGAKU, HIROSHI MAEGAWA AND YUKIO SHIGETA
Complete the passage below, using the most suitable term in each case. The pancreas releases hormones directly into the blood and these regulate the
 1 Organisms respond to changes in their internal environment. These responses are controlled by nervous and hormonal mechanisms. (a) The concentration of blood glucose is regulated by hormones. Complete
1 Organisms respond to changes in their internal environment. These responses are controlled by nervous and hormonal mechanisms. (a) The concentration of blood glucose is regulated by hormones. Complete
Cell Therapy for Diabetes: Generating Functional Islets from Human Exocrine Tissue
 Cell Therapy for Diabetes: Generating Functional Islets from Human Exocrine Tissue Kevin Docherty University of Aberdeen ELRIG Drug Discovery 2016 ACC Liverpool 14 th October 2016 Autoimmune destruction
Cell Therapy for Diabetes: Generating Functional Islets from Human Exocrine Tissue Kevin Docherty University of Aberdeen ELRIG Drug Discovery 2016 ACC Liverpool 14 th October 2016 Autoimmune destruction
L6 GLUT4myc Cell Growth Protocol
 L6 GLUT4myc Cell Growth Protocol Background: Parental L6 cells selected for high fusion (2, 3) were stably transfected with a rat GLUT4 cdna carrying a myc epitope (recognized by the commercially available
L6 GLUT4myc Cell Growth Protocol Background: Parental L6 cells selected for high fusion (2, 3) were stably transfected with a rat GLUT4 cdna carrying a myc epitope (recognized by the commercially available
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
Reduced Insulin Signaling and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Act Synergistically to Deteriorate Pancreatic β Cell Function
 Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 54, No. 2, pp. E114-E121, 2008 Reduced Insulin Signaling and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Act Synergistically to Deteriorate Pancreatic β Cell Function TOMOKAZU MATSUDA, YOSHIAKI
Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 54, No. 2, pp. E114-E121, 2008 Reduced Insulin Signaling and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Act Synergistically to Deteriorate Pancreatic β Cell Function TOMOKAZU MATSUDA, YOSHIAKI
β-cell Preservation and Regeneration After Islet Transplantation
 β-cell Preservation and Regeneration After Islet Transplantation Jyuhn-Huarng Juang, MD Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Chang Gung University and Memorial Hospital,
β-cell Preservation and Regeneration After Islet Transplantation Jyuhn-Huarng Juang, MD Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Chang Gung University and Memorial Hospital,
Diabetologia 9 by Springer-Verlag 1976
 Diabetologia 12, 263-267 (1976) Diabetologia 9 by Springer-Verlag 1976 The Comparative Effects of Barbituric Acid and Phenobarbital on Blood Glucose and Insulin Secretion in Mice* J. H. Mennear, C. Schonwalder
Diabetologia 12, 263-267 (1976) Diabetologia 9 by Springer-Verlag 1976 The Comparative Effects of Barbituric Acid and Phenobarbital on Blood Glucose and Insulin Secretion in Mice* J. H. Mennear, C. Schonwalder
BIOCHEMISTRY ondmolecular BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL Poges
 Vol. 40, No. 3, October 1996 BIOCHEMISTRY ondmolecular BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL Poges 515-520 ATTENUATION BY NICOTINAMIDE OF THE STREPTOZOCIN INDUCED EARLY HYPERGLYCAEMIA IN FASTING RATS Kai K. Wong Department
Vol. 40, No. 3, October 1996 BIOCHEMISTRY ondmolecular BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL Poges 515-520 ATTENUATION BY NICOTINAMIDE OF THE STREPTOZOCIN INDUCED EARLY HYPERGLYCAEMIA IN FASTING RATS Kai K. Wong Department
22 Emerging Therapies for
 22 Emerging Therapies for Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Siddharth N Shah Abstract: The prevalence of Diabetes is progressively increasing world-wide and the growth of the disease in our country is phenomenal.
22 Emerging Therapies for Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Siddharth N Shah Abstract: The prevalence of Diabetes is progressively increasing world-wide and the growth of the disease in our country is phenomenal.
2017, Pharmapex USA, A Member of Apex Group of Companies
 2017, Pharmapex USA, A Member of Apex Group of Companies Natural Blood Health Aid uses a proprietary and licensed Virgin Isolate Technology, invented which recreates the Ayurvedic method used in ancient
2017, Pharmapex USA, A Member of Apex Group of Companies Natural Blood Health Aid uses a proprietary and licensed Virgin Isolate Technology, invented which recreates the Ayurvedic method used in ancient
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) treatment blocks inflammatory pathways and promotes survival and proliferation of pancreatic beta cells
 Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) treatment blocks inflammatory pathways and promotes survival and proliferation of pancreatic beta cells Gérald J. Prud homme, MD, FRCPC Keenan Research Centre for Biomedical
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) treatment blocks inflammatory pathways and promotes survival and proliferation of pancreatic beta cells Gérald J. Prud homme, MD, FRCPC Keenan Research Centre for Biomedical
IDDM results from destruction of the insulin-secreting
 Development of Autoimmune Diabetes in NOD Mice Is Associated With the Formation of Peroxynitrite in Pancreatic Islet B-Cells Wilma L. Suarez-Pinzon, Csaba Szabo, and Alex Rabinovitch Peroxynitrite (ONOO
Development of Autoimmune Diabetes in NOD Mice Is Associated With the Formation of Peroxynitrite in Pancreatic Islet B-Cells Wilma L. Suarez-Pinzon, Csaba Szabo, and Alex Rabinovitch Peroxynitrite (ONOO
3.D- Cell Communication
 3.D- Cell Communication Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. EU 3.A: Heritable information provides for continuity of life. EU 3.B:
3.D- Cell Communication Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information essential to life processes. EU 3.A: Heritable information provides for continuity of life. EU 3.B:
Arginine-Stimulated Acute Phase of Insulin and Glucagon
 Arginine-Stimulated Acute Phase of Insulin and Glucagon Secretion in Diabetic Subjects JERRY P. PALMER, JAMES W. BENSON, ROBERT M. WALTER, and JoHN W. ENSINCK From the Department of Medicine and Diabetes
Arginine-Stimulated Acute Phase of Insulin and Glucagon Secretion in Diabetic Subjects JERRY P. PALMER, JAMES W. BENSON, ROBERT M. WALTER, and JoHN W. ENSINCK From the Department of Medicine and Diabetes
Vets 111/Biov 111 Cell Signalling-1. Hormones, Neurotransmitters and Local Mediators
 Vets 111/Biov 111 Cell Signalling-1 Hormones, Neurotransmitters and Local Mediators Why do cells need to communicate and signal? In unicellular organisms every cell is capable of the full range of biochemical
Vets 111/Biov 111 Cell Signalling-1 Hormones, Neurotransmitters and Local Mediators Why do cells need to communicate and signal? In unicellular organisms every cell is capable of the full range of biochemical
Distribution of Pancreatic Polypeptide in the Head of the Human Pancreas. By Andrew Kringas
 Distribution of Pancreatic Polypeptide in the Head of the Human Pancreas By Andrew Kringas Diabetes (Diabetes mellitus) A condition when the body doesn t properly respond to insulin Type 1 Type 2 Gestational
Distribution of Pancreatic Polypeptide in the Head of the Human Pancreas By Andrew Kringas Diabetes (Diabetes mellitus) A condition when the body doesn t properly respond to insulin Type 1 Type 2 Gestational
Title Modified Western blotting for insulin and other diabetes-associated peptide hormones
 Supplemental Figures Title Modified Western blotting for insulin and other diabetes-associated peptide hormones Authors Naoyuki Okita, Yoshikazu Higami, Fumio Fukai, Masaki Kobayashi, Miku Mitarai, Takao
Supplemental Figures Title Modified Western blotting for insulin and other diabetes-associated peptide hormones Authors Naoyuki Okita, Yoshikazu Higami, Fumio Fukai, Masaki Kobayashi, Miku Mitarai, Takao
DEVELOPMENT OF NEW ANIMAL MODELS FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS AND PHARMACOLOGICAL SCREENING
 2) LITERATURE REVIEW 1. Srinivasan et al., (2005) developed a new rat model that replicates the natural history and metabolic characteristics of human type 2 diabetes and is also suitable for pharmacological
2) LITERATURE REVIEW 1. Srinivasan et al., (2005) developed a new rat model that replicates the natural history and metabolic characteristics of human type 2 diabetes and is also suitable for pharmacological
The biguanide metformin is widely used in Europe,
 Metformin Restores Insulin Secretion Altered by Chronic Exposure to Free Fatty Acids or High Glucose A Direct Metformin Effect on Pancreatic -Cells Giovanni Patanè, Salvatore Piro, Agata Maria Rabuazzo,
Metformin Restores Insulin Secretion Altered by Chronic Exposure to Free Fatty Acids or High Glucose A Direct Metformin Effect on Pancreatic -Cells Giovanni Patanè, Salvatore Piro, Agata Maria Rabuazzo,
INTRODUCTION. Induction of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) Expression by Angiotensin II (AngII) in the Pancreatic Islets and Beta Cells
 Induction of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) Expression by Angiotensin II (AngII) in the Pancreatic Islets and Beta Cells Galina Chipitsyna, Qiaoke Gong, Chance F. Gray et al. Endocrinology,
Induction of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) Expression by Angiotensin II (AngII) in the Pancreatic Islets and Beta Cells Galina Chipitsyna, Qiaoke Gong, Chance F. Gray et al. Endocrinology,
Experiments were carried out then with the object of producing complete disappearance of the A
 Relation of Glucagon to A Cells of the Pancreas*. (22339) SERGIO A. BENCOSME AND J. FREI. (Introduced by J.S.L. Browne Departament of pathology, Queen`s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada. In spite
Relation of Glucagon to A Cells of the Pancreas*. (22339) SERGIO A. BENCOSME AND J. FREI. (Introduced by J.S.L. Browne Departament of pathology, Queen`s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada. In spite
BPA exposure during pregnancy: risk for gestational diabetes and diabetes following pregnancy
 BPA exposure during pregnancy: risk for gestational diabetes and diabetes following pregnancy Paloma Alonso-Magdalena Applied Biology Department and CIBERDEM, Miguel Hernández University, Elche, Spain
BPA exposure during pregnancy: risk for gestational diabetes and diabetes following pregnancy Paloma Alonso-Magdalena Applied Biology Department and CIBERDEM, Miguel Hernández University, Elche, Spain
T CD3 (N Engl J Med 352: , 2005) Med 361: , 2009) CTLA4 (Lancet 378: , 2011) (Babaya N et al. Nature 435:220-3, 2005
 T CD3 (N Engl J Med 352: 2598-2608, 2005) B CD20 (N Engl J Med 361: 2143-2152, 2009) CTLA4 (Lancet 378:487-497, 2011) EB (Babaya N et al. Nature 435:220-3, 2005 (N Engl J Med 346: 1685-1691, 2002) GAD
T CD3 (N Engl J Med 352: 2598-2608, 2005) B CD20 (N Engl J Med 361: 2143-2152, 2009) CTLA4 (Lancet 378:487-497, 2011) EB (Babaya N et al. Nature 435:220-3, 2005 (N Engl J Med 346: 1685-1691, 2002) GAD
Diabetes Products, Brochure
 Diabetes Products, Brochure Interest in any of the products, request or order them at Bio-Connect Diagnostics. Bio-Connect Diagnostics B.V. T NL +31 (0)26 326 44 60 T BE +32 (0)2 502 12 53 Begonialaan
Diabetes Products, Brochure Interest in any of the products, request or order them at Bio-Connect Diagnostics. Bio-Connect Diagnostics B.V. T NL +31 (0)26 326 44 60 T BE +32 (0)2 502 12 53 Begonialaan
Partial Pancreatectomy in the Rat and Subsequent Defect in Glucose-induced Insulin Release
 Partial Pancreatectomy in the Rat and Subsequent Defect in Glucose-induced Insulin Release S. BONNER-WEIR, D. F. TRENT, and G. C. WEIR, Endocrine Division, Department of Medicine, Medical College of Virginia-Virginia
Partial Pancreatectomy in the Rat and Subsequent Defect in Glucose-induced Insulin Release S. BONNER-WEIR, D. F. TRENT, and G. C. WEIR, Endocrine Division, Department of Medicine, Medical College of Virginia-Virginia
No cases of precocious puberty were reported during clinical trials of risperidone in, cases of precocious puberty have been
 levels than adults. The growth hormone elevations reported for the 12 patients with growth hormone excess were modest and well below levels reported in children with gigantism. 7,8 None of the patients
levels than adults. The growth hormone elevations reported for the 12 patients with growth hormone excess were modest and well below levels reported in children with gigantism. 7,8 None of the patients
Control of Glucose Metabolism
 Glucose Metabolism Control of Glucose Metabolism The pancreas is both an exocrine and endocrine gland. It secretes digestive enzymes into the duodenum (exocrine) and 3 specific hormones into the bloodstream
Glucose Metabolism Control of Glucose Metabolism The pancreas is both an exocrine and endocrine gland. It secretes digestive enzymes into the duodenum (exocrine) and 3 specific hormones into the bloodstream
Management of Type 2 Diabetes
 Management of Type 2 Diabetes Pathophysiology Insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency/ defective secretion Not immune mediated No evidence of β cell destruction Increased risk with age, obesity
Management of Type 2 Diabetes Pathophysiology Insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency/ defective secretion Not immune mediated No evidence of β cell destruction Increased risk with age, obesity
