The Ebf1 knockout mouse and glomerular maturation
|
|
|
- Charlene Whitehead
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Repository of the Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) Berlin (Germany) The Ebf1 knockout mouse and glomerular maturation Schmidt-Ott, K.M. Published in final edited form as: Kidney International May ; 85(5): doi: /ki Nature Publishing Group (U.S.A.)
2 The Ebf1 knockout mouse and glomerular maturation Running title: Ebf1 in glomerular maturation Kai M. Schmidt-Ott 1,2,3 1 Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine Berlin, Germany 2 Experimental and Clinical Research Center (ECRC), Charité Universitätsmedizin Berlin 3 Department of Nephrology, Campus Mitte, Charité Universitätsmedizin Berlin Correspondence: Prof. Dr. Kai M. Schmidt-Ott Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine Robert-Rössle-Str Berlin Germany Tel: Fax: kai.schmidt-ott@mdc-berlin.de
3 Abstract Mice deficient for the transcription factor early B-cell factor 1 (Ebf1), lack mature B lymphocytes, but have additional phenotypes suggesting functions outside the hematopoietic system. Now it is reported that these mice also exhibit quantitative and qualitative developmental renal defects and develop progressive podocyte foot-process effacement. The findings not only suggest that Ebf1 may be pivotal to the transcriptional podocyte network, but also illustrate the importance of distinguishing cell-autonomous and non-autonomous inputs on podocyte maturation and integrity. Text body Embryonic renal development and glomerular maturation are intimately linked. During the earliest phases, nephron progenitor cells condense, convert to primitive nephron epithelia, and form patterned early nephron structures called S-shaped bodies. These S-shaped bodies contain a layer of primitive podocytes that initially form a columnar epithelial layer and a flat cell layer comprising future Bowman's capsule. 1 Next, a capillary enters the glomerular cleft and contacts the podocytes to form primitive capillary loop-stage glomeruli. Thereafter, podocytes flatten and form foot processes. This process roughly coincides with the onset of urine production. As urinary filtration increases, additional signs of progressive glomerular maturation can be observed. The capillary loops expand and form a progressively complex network covered by intricate interdigitating podocyte foot processes. The expansion leads to an increasing filtration surface area and a morphological transformation into adult-type mature glomeruli (Fig. 1). Several transcription factors regulate early steps of podocyte differentiation, including Tcf21/Pod1, Lmx1b, Mafb, and Foxc2. 1 In contrast, less is known about the transcriptional mechanisms that coordinate the later phases of glomerular maturation and the maintenance of glomerular integrity.
4 In this issue of Kidney Int, Fretz et al propose a novel role for the early B-cell factor 1 (Ebf1) transcription factor in regulating late glomerular maturation and the maintenance of filtration barrier integrity. 2 Ebf1 belongs to a family of transcription factors containing an atypical zinc-finger DNA-binding domain and a non-basic helix-loop-helix (HLH) dimerization domain. Ebf1 is necessary for the development of mature B lymphocytes, which was first shown almost two decades ago by the absence of these cells in Ebf1 knockout (Ebf1 -/- ) mice. 3 Ebf1 -/- mice lack Ebf1 in all cells and thus the presence of other defects comes as no surprise. For instance Ebf1 -/- mice exhibit excess apoptosis in the brain striatum. 4 They also have a defect in facial branchiomotor neuronal migration. 5 In addition, the mice are smaller than their littermates and many die before age four weeks for unclear reasons. Fretz et al. initially studied the role of Ebf1 in osteoblast function in Ebf1 -/- mice. 6 They observed elevated serum osteocalcin levels, a non-collagenous protein formed by osteoblasts. While the finding suggested an increased osteocalcin synthesis in Ebf1 -/- osteoblasts, the authors paradoxically observed reduced rates of osteocalcin synthesis. Since osteocalcin is cleared by the kidneys, 7 the authors investigated the possibility of renal dysfunction in Ebf1 -/- mice. Interestingly, they found a markedly reduced glomerular filtration rate (GFR) in Ebf1 -/- mice even after correction for body weight. Furthermore, Ebf1 -/- mice developed progressively severe albuminuria. Ebf1 -/- kidneys were smaller than those from control littermates, a finding expected on the basis of smaller overall size. However, a detailed histological analysis of these kidneys revealed marked structural abnormalities. The cortex and outer medulla were substantially thinned and immature glomeruli persisted in the outer cortex, while juxtamedullary glomeruli appeared relatively mature. Islands of vimentin-positive cells were observed suggestive of persisting embryonic structures. Also, the size of the glomeruli was reduced in Ebf1 -/- mice and the number of capillary loops per glomerulus was reduced. While early
5 glomeruli detected around the time of birth developed normal foot processes, there was progressive foot process effacement as these mice matured. Ebf1 expression in normal mouse kidney suggested that Ebf1 was expressed at low levels during renal development and during the first two weeks of life. However, Ebf1 was up-regulated in the more mature kidney (>2 weeks of age), coinciding with the onset of albuminuria in Ebf1 -/- mice. Importantly, Ebf1 was expressed in mature glomeruli, suggesting that its expression was dependent on the glomerular differentiation status. Ebf1 was detected in podocytes and several additional neighboring cells. Together, these results suggest a role of Ebf1 in late glomerular maturation and in the maintenance of glomerular integrity. The phenotype of Ebf1 -/- kidneys clearly differs from mice harboring mutations in the core transcription factors governing podocyte differentiation. For instance, the glomerular defects reported in mice lacking the transcription factors Foxc2, Tcf21/Pod1, or Lmx1b occur earlier compared to Ebf1 -/- mice and reveal an arrest of glomerular development at the capillary loop stage. 1 The defect observed in Ebf1 -/- kidneys is more reminiscent of the kidney phenotypes of mice with defects in the signaling pathways that maintain podocyte integrity. Examples include integrin-linked kinase, 8 or the mammalian target of rapamycin (MTOR) complex, 9 in which initial formation of the podocyte filtration barrier appears to be normal with an insidious onset of proteinuria and foot process effacement. However, in addition to the podocyte defect, Ebf1 -/- mice clearly exhibited overall abnormal nephrogenesis. Although Fretz et al. did not assess nephron numbers, their histological analyses suggest that glomerular numbers were reduced. In addition, the fewer capillary loops per glomerulus would lead to a reduced filtration surface. Hence, the low filtration capacity of the Ebf1 -/- kidneys may place an inappropriate load on individual glomeruli. This situation could cause single-nephron hyperfiltration and a subsequent progressive glomerular injury.
6 Fretz et al. 2 conducted molecular analyses indicating that podocytes from Ebf1 -/- mice expressed lower levels of Tcf21/Pod1 and Lmx1b, while Mafb and Foxc2 were unchanged. Both Tcf21 and Lmx1b are necessary for glomerular maturation 1 and induced deficiency of Lmx1b in adult podocytes has recently been shown to result in proteinuria and progressive foot process effacement, 10 suggesting that Ebf1 may function to ensure adequate Lmx1b levels in podocytes to maintain podocyte integrity. In addition, Fretz et al. observed reduced production of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) in Ebf1 -/- podocytes. Podocyte-derived VEGFA maintains glomerular endothelial cell integrity, 11 suggesting that reduced VEGFA expression may also contribute to the Ebf1 -/- phenotype. While the study by Fretz et al. points towards important roles of Ebf1 in renal development and glomerular maturation, several points need to be addressed in future studies. First, the biological basis of the thin renal cortex and persistence of embryonic renal structures of Ebf1 -/- kidneys remains unclear. While these phenotypes point to a defect in early kidney development, Ebf1 does not appear to be expressed at high levels in the developing kidney. Thus, extrarenal effects of Ebf1 deficiency could contribute to the developmental renal phenotype. Second, not only podocytes, but also other not yet identified renal cells, express Ebf1 once mice reach age 2 weeks. This coordinated induction of Ebf1 in different cell types of the kidney is surprising and unprecedented. Importantly, the initiation of Ebf1 expression in normal mice coincides with the onset of albuminuria in Ebf1 -/- mice. However, whether or not podocyte expression of Ebf1 accounts for the maintenance of glomerular integrity remains unclear. Alternatively, defects of cells outside the podocyte compartment may contribute to the Ebf1 -/- phenotype. Finally, the involvement of Ebf1 in osteoblast differentiation has recently been challenged based on the observation that an osteoblast-specific Ebf1 knockout failed to reproduce the bone phenotype observed in global Ebf1 -/- mice. 12 In light of these
7 findings, future studies will need to examine whether or not podocyte-specific deletion of Ebf1 produces similar glomerular defects of global Ebf1 -/- mice. Fretz et al. 2 identified the importance of Ebf1 in maintaining a functional kidney. However, future studies will need to resolve whether Ebf1 serves cell-autonomous functions in the podocyte. Acknowledgements The Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Schm1730/2-1, Schm1730/3-1, Research Unit 1368) supports K.M.S.O. I thank Friedrich C. Luft for insightful discussions concerning this commentary. There are no conflicts of interest. References 1. Quaggin SE, Kreidberg JA. Development of the renal glomerulus: good neighbors and good fences. Development 2008; 135: Fretz J, Nelson T, Velazquez H, et al. Early B cell factor 1 is an essential transcription factor for postnatal glomerular maturation. Kidney Int 2013; this issue. 3. Lin H, Grosschedl R. Failure of B-cell differentiation in mice lacking the transcription factor EBF. Nature 1995; 376: Garel S, Marin F, Grosschedl R, et al. Ebf1 controls early cell differentiation in the embryonic striatum. Development 1999; 126: Garel S, Garcia-Dominguez M, Charnay P. Control of the migratory pathway of facial branchiomotor neurones. Development 2000; 127: Hesslein DG, Fretz JA, Xi Y, et al. Ebf1-dependent control of the osteoblast and adipocyte lineages. Bone 2009; 44: Price PA, Williamson MK, Lothringer JW. Origin of the vitamin K-dependent bone protein found in plasma and its clearance by kidney and bone. J Biol Chem 1981; 256: El-Aouni C, Herbach N, Blattner SM, et al. Podocyte-specific deletion of integrin-linked kinase results in severe glomerular basement membrane alterations and progressive glomerulosclerosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 2006; 17:
8 9. Godel M, Hartleben B, Herbach N, et al. Role of mtor in podocyte function and diabetic nephropathy in humans and mice. J Clin Invest 2011; 121: Burghardt T, Kastner J, Suleiman H, et al. LMX1B is Essential for the Maintenance of Differentiated Podocytes in Adult Kidneys. J Am Soc Nephrol Eremina V, Sood M, Haigh J, et al. Glomerular-specific alterations of VEGF-A expression lead to distinct congenital and acquired renal diseases. J Clin Invest 2003; 111: Zee T, Boller S, Gyory I, et al. The transcription factor early B-cell factor 1 regulates bone formation in an osteoblast-nonautonomous manner. FEBS letters 2013; 587:
Histology Urinary system
 Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Urinary System Laboratory
 Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
PHGY210 Renal Physiology
 PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
3. PODOCYTE INJURY IN GLOMERULAR DISEASES
 How to Cite this article: Podocyte Injury in Glomerular Diseases - ejifcc 20/01 2009 http://www.ifcc.org 3. PODOCYTE INJURY IN GLOMERULAR DISEASES Mirjana Sabljar Matovinović Podocytes are injured in diabetic
How to Cite this article: Podocyte Injury in Glomerular Diseases - ejifcc 20/01 2009 http://www.ifcc.org 3. PODOCYTE INJURY IN GLOMERULAR DISEASES Mirjana Sabljar Matovinović Podocytes are injured in diabetic
Analysis on the mechanism of reduced nephron number and the pathological progression of chronic renal failure in Astrin deficient rats
 Analysis on the mechanism of reduced nephron number and the pathological progression of chronic renal failure in Astrin deficient rats Summary of Doctoral Thesis Hidenori Yasuda Graduate School of Veterinary
Analysis on the mechanism of reduced nephron number and the pathological progression of chronic renal failure in Astrin deficient rats Summary of Doctoral Thesis Hidenori Yasuda Graduate School of Veterinary
Nephron Anatomy Nephron Anatomy
 Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
A. Correct! Flushing acids from the system will assist in re-establishing the acid-base equilibrium in the blood.
 OAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following would solve a drop in blood ph? Question #01 (A) Decreased retention of acids. (B) Increased excretion
OAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following would solve a drop in blood ph? Question #01 (A) Decreased retention of acids. (B) Increased excretion
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY
 RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
Surgical Pathology Report
 Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Pathology Shreveport, Louisiana Accession #: Collected: Received: Reported: 6/1/2012 09:18 6/2/2012 09:02 6/2/2012 Patient Name: Med. Rec.
Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Pathology Shreveport, Louisiana Accession #: Collected: Received: Reported: 6/1/2012 09:18 6/2/2012 09:02 6/2/2012 Patient Name: Med. Rec.
The principal functions of the kidneys
 Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY ROLE OF THE URINARY SYSTEM THE URINARY SYSTEM. Components and function. V BS 122 Physiology II 151 Class of 2011
 19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 SCPA 602- Anatomical Basis For Pathological Study H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M S O M P H O N G N A R K P I N I T, M. D. D E P A R T M E N T O F P A T H O B I O L O G Y F A C U
SCPA 602- Anatomical Basis For Pathological Study H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M S O M P H O N G N A R K P I N I T, M. D. D E P A R T M E N T O F P A T H O B I O L O G Y F A C U
Ectopic Notch Activation in Developing Podocytes Causes Glomerulosclerosis
 Ectopic Notch Activation in Developing Podocytes Causes Glomerulosclerosis Aoife M. Waters,* Megan Y.J. Wu,* Tuncer Onay,* Jacob Scutaru,* Ju Liu, Corrinne G. Lobe, Susan E. Quaggin, and Tino D. Piscione*
Ectopic Notch Activation in Developing Podocytes Causes Glomerulosclerosis Aoife M. Waters,* Megan Y.J. Wu,* Tuncer Onay,* Jacob Scutaru,* Ju Liu, Corrinne G. Lobe, Susan E. Quaggin, and Tino D. Piscione*
Urinary system. Urinary system
 INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
renoprotection therapy goals 208, 209
 Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
The functions of the kidney:
 The functions of the kidney: After reading this lecture you should be able to.. 1. List the main functions of the kidney. 2. Know the basic physiological anatomy of the kidney and the nephron 3. Describe
The functions of the kidney: After reading this lecture you should be able to.. 1. List the main functions of the kidney. 2. Know the basic physiological anatomy of the kidney and the nephron 3. Describe
Glomerular Pathology- 1 Nephrotic Syndrome. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin
 Glomerular Pathology- 1 Nephrotic Syndrome Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin The Nephrotic Syndrome a clinical complex resulting from glomerular disease & includes the following: (1) massive proteinuria (3.5 gm /day
Glomerular Pathology- 1 Nephrotic Syndrome Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin The Nephrotic Syndrome a clinical complex resulting from glomerular disease & includes the following: (1) massive proteinuria (3.5 gm /day
Formation of Urine: Formation of Urine
 The Urinary outflow tract: monitors and regulates extra-cellular fluids excretes harmful substances in urine, including nitrogenous wastes (urea) returns useful substances to bloodstream maintain balance
The Urinary outflow tract: monitors and regulates extra-cellular fluids excretes harmful substances in urine, including nitrogenous wastes (urea) returns useful substances to bloodstream maintain balance
Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology
 Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology The two kidneys are located in the retroperitoneum on either side of the vertebral bladder and the contraction of the detrusor muscle. Any mechanical barrier,
Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology The two kidneys are located in the retroperitoneum on either side of the vertebral bladder and the contraction of the detrusor muscle. Any mechanical barrier,
Urinary System. Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal
 Urinary System Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal Presentation Map Kidney (cortex & medulla). Nephron. Duct system. Juxtaglomerular apparatus. Ureter, bladder & urethra. Definition & General Structure The
Urinary System Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal Presentation Map Kidney (cortex & medulla). Nephron. Duct system. Juxtaglomerular apparatus. Ureter, bladder & urethra. Definition & General Structure The
Journal Club. 03/04/2012 Lama Nazzal
 Journal Club 03/04/2012 Lama Nazzal NOTCH and the kidneys Is an evolutionarily conserved cell cell communication mechanism. Is a regulator of cell specification, differentiation, and tissue patterning.
Journal Club 03/04/2012 Lama Nazzal NOTCH and the kidneys Is an evolutionarily conserved cell cell communication mechanism. Is a regulator of cell specification, differentiation, and tissue patterning.
Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph
 The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
Urinary System and Fluid Balance. Urine Production
 Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Functions of the kidney:
 Diseases of renal system : Normal anatomy of renal system : Each human adult kidney weighs about 150 gm, the ureter enters the kidney at the hilum, it dilates into a funnel-shaped cavity, the pelvis, from
Diseases of renal system : Normal anatomy of renal system : Each human adult kidney weighs about 150 gm, the ureter enters the kidney at the hilum, it dilates into a funnel-shaped cavity, the pelvis, from
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015
 RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
Renal Pathology 1: Glomerulus. With many thanks to Elizabeth Angus PhD for EM photographs
 Renal Pathology 1: Glomerulus With many thanks to Elizabeth Angus PhD for EM photographs Anatomy of the Kidney http://www.yalemedicalgroup.org/stw/page.asp?pageid=stw028980 The Nephron http://www.beltina.org/health-dictionary/nephron-function-kidney-definition.html
Renal Pathology 1: Glomerulus With many thanks to Elizabeth Angus PhD for EM photographs Anatomy of the Kidney http://www.yalemedicalgroup.org/stw/page.asp?pageid=stw028980 The Nephron http://www.beltina.org/health-dictionary/nephron-function-kidney-definition.html
The topic of normal vascular and glomerular anatomy is introduced
 Normal Vascular and Glomerular Anatomy Arthur H. Cohen Richard J. Glassock The topic of normal vascular and glomerular anatomy is introduced here to serve as a reference point for later illustrations of
Normal Vascular and Glomerular Anatomy Arthur H. Cohen Richard J. Glassock The topic of normal vascular and glomerular anatomy is introduced here to serve as a reference point for later illustrations of
PHSI2006/2906: Integrated Physiology B
 PHSI2006/2906: Integrated Physiology B TOPIC 1: RESPIRATION 1. The Mechanics of Breathing...2 2. Work of Breathing....5 3. Pulmonary Gas Exchange.. 10 4. Transport of Oxygen...16 5. Control of Respiration...20
PHSI2006/2906: Integrated Physiology B TOPIC 1: RESPIRATION 1. The Mechanics of Breathing...2 2. Work of Breathing....5 3. Pulmonary Gas Exchange.. 10 4. Transport of Oxygen...16 5. Control of Respiration...20
Podocyte Biology and clinical applications Dr. F. Ahmadi Professor Of Nephrology TUMS
 Podocyte Biology and clinical applications Dr. F. Ahmadi Professor Of Nephrology TUMS Proteinuria is a major healthcare problem that affects several hundred million people worldwide. Proteinuria is a cardinal
Podocyte Biology and clinical applications Dr. F. Ahmadi Professor Of Nephrology TUMS Proteinuria is a major healthcare problem that affects several hundred million people worldwide. Proteinuria is a cardinal
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 19-1c. Efferent arteriole. Juxtaglomerular apparatus
 /6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
/6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
Histology / First stage The Urinary System: Introduction. Kidneys
 The Urinary System: Introduction The urinary system consists of the paired kidneys and ureters, the bladder, and the urethra. This system helps maintain homeostasis by a complex combination of processes
The Urinary System: Introduction The urinary system consists of the paired kidneys and ureters, the bladder, and the urethra. This system helps maintain homeostasis by a complex combination of processes
The Urinary System PART A
 15 The Urinary System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Functions of the Urinary
15 The Urinary System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Functions of the Urinary
URINARY SYSTEM. These organs lie posterior or inferior to the. (membrane).
 URINARY SYSTEM I. INTRODUCTION Each kidney is made up of about a million tiny tubules called nephrons. Each nephron individually filters the blood and makes urine and it does the job completely, from start
URINARY SYSTEM I. INTRODUCTION Each kidney is made up of about a million tiny tubules called nephrons. Each nephron individually filters the blood and makes urine and it does the job completely, from start
Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note
![Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note](/thumbs/77/75431210.jpg) Running head: NEPHRON 1 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note NEPHRON 2 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney The kidney is an important excretory
Running head: NEPHRON 1 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note NEPHRON 2 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney The kidney is an important excretory
Diabetic Kidney Disease: the Problem. Diabetic Nephropathy 7/5/2018 DISCLOSURES FOR CHARLES ALPERS PRESENTATION
 Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic Kidney Disease: the Problem Pathology, Pathogenesis, Potential for Reversal Charles E. Alpers, MD Incidence of end stage renal disease (thousands of cases per year) 50 40
Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic Kidney Disease: the Problem Pathology, Pathogenesis, Potential for Reversal Charles E. Alpers, MD Incidence of end stage renal disease (thousands of cases per year) 50 40
Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine
 Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Functions of the Urinary System
 The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
Lab Activity 31. Anatomy of the Urinary System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Chapter 23. The Nephron. (functional unit of the kidney
 Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
CHAPTER 2 PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
 CHAPTER 2 Sunita Bavanandan Lim Soo Kun 19 5th Report of the 2.1: Introduction This chapter covers the main primary glomerulonephritis that were reported to the MRRB from the years 2005-2012. Minimal change
CHAPTER 2 Sunita Bavanandan Lim Soo Kun 19 5th Report of the 2.1: Introduction This chapter covers the main primary glomerulonephritis that were reported to the MRRB from the years 2005-2012. Minimal change
Diabetic Nephropathy
 Diabetic Nephropathy Objectives: Know what Diabetic Nephropathy means. Know how common is Diabetic nephropathy in Saudi Arabia and to appreciate how bad are this complications. Know the risk factors of
Diabetic Nephropathy Objectives: Know what Diabetic Nephropathy means. Know how common is Diabetic nephropathy in Saudi Arabia and to appreciate how bad are this complications. Know the risk factors of
INVESTIGATION OF THE ULTRAFINE STRUCTURE OF THE KIDNEY BY MEANS OF SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE
 THE KURUME MEDICAL JOURNAL 1975 Vol.22, No.3, P.135-141 INVESTIGATION OF THE ULTRAFINE STRUCTURE OF THE KIDNEY BY MEANS OF SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE I. THE GLOMERULUS SHINSHI NODA Department of Urology,
THE KURUME MEDICAL JOURNAL 1975 Vol.22, No.3, P.135-141 INVESTIGATION OF THE ULTRAFINE STRUCTURE OF THE KIDNEY BY MEANS OF SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE I. THE GLOMERULUS SHINSHI NODA Department of Urology,
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil Khouri
 Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY
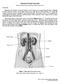 URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) OVERVIEW Metabolism of nutrients by the body produces wastes that must be removed from the body. Although excretory
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) OVERVIEW Metabolism of nutrients by the body produces wastes that must be removed from the body. Although excretory
Urinary Physiology. Chapter 17 Outline. Kidney Function. Chapter 17
 Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
Urinary Anatomy. Lab 40. Kidneys. Nephrons. Renal Corpuscle
 Urinary Anatomy Lab 40. Urinary Anatomy and Kidney Dissection Kidneys: filters blood, produces urine Ureters: convey urine to bladder Bladder: holding tank Urethra: carries urine to the outside for elimination
Urinary Anatomy Lab 40. Urinary Anatomy and Kidney Dissection Kidneys: filters blood, produces urine Ureters: convey urine to bladder Bladder: holding tank Urethra: carries urine to the outside for elimination
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion. The Kidneys
 Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
Diabetic Nephropathy in Spontaneously Diabetic Torii (SDT) Rats
 The Open Diabetes Journal, 2011, 4, 45-49 45 Diabetic Nephropathy in Spontaneously Diabetic Torii (SDT) Rats Takeshi Ohta * and Tomohiko Sasase Open Access Biological/Pharmacological Research Laboratories,
The Open Diabetes Journal, 2011, 4, 45-49 45 Diabetic Nephropathy in Spontaneously Diabetic Torii (SDT) Rats Takeshi Ohta * and Tomohiko Sasase Open Access Biological/Pharmacological Research Laboratories,
CHAPTER 2. Primary Glomerulonephritis
 2nd Report of the PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS CHAPTER 2 Primary Glomerulonephritis Sunita Bavanandan Lee Han Wei Lim Soo Kun 21 PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 2nd Report of the 2.1 Introduction This chapter
2nd Report of the PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS CHAPTER 2 Primary Glomerulonephritis Sunita Bavanandan Lee Han Wei Lim Soo Kun 21 PRIMARY GLOMERULONEPHRITIS 2nd Report of the 2.1 Introduction This chapter
Renal Physiology - Lectures
 Renal Physiology 2011 Lisa M. Harrison-Bernard, PhD lharris@lsuhsc.edu Renal Physiology - Lectures Physiology of Body Fluids 2. Structure & Function of the Kidneys 3. Renal Clearance & Glomerular Filtration
Renal Physiology 2011 Lisa M. Harrison-Bernard, PhD lharris@lsuhsc.edu Renal Physiology - Lectures Physiology of Body Fluids 2. Structure & Function of the Kidneys 3. Renal Clearance & Glomerular Filtration
LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION
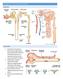 LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION 1. Everything in the plasma is filtered except large proteins and red blood cells. The filtrate in Bowman s capsule is an isosmotic fluid that is
LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION 1. Everything in the plasma is filtered except large proteins and red blood cells. The filtrate in Bowman s capsule is an isosmotic fluid that is
Please remember that based on your personalized learning plan and your past experience you may not be required to complete all four modules.
 Course Overview Welcome to the Team PD pre-work participant guide. Team PD is a new education program offered by Baxter that utilizes individual learning maps so nurses receive a personalized approach
Course Overview Welcome to the Team PD pre-work participant guide. Team PD is a new education program offered by Baxter that utilizes individual learning maps so nurses receive a personalized approach
Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion.
 The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
HIHIM 409 7/26/2009. Kidney and Nephron. Fermamdo Vega, M.D. 1
 Function of the Kidneys Nephrology Fernando Vega, M.D. Seattle Healing Arts Center Remove Wastes Regulate Blood Pressure Regulate Blood Volume Regulates Electrolytes Converts Vitamin D to active form Produces
Function of the Kidneys Nephrology Fernando Vega, M.D. Seattle Healing Arts Center Remove Wastes Regulate Blood Pressure Regulate Blood Volume Regulates Electrolytes Converts Vitamin D to active form Produces
osmoregulation mechanisms in gills, salt glands, and kidneys
 Ionic & Osmotic Homeostasis osmoregulation mechanisms in gills, salt glands, and kidneys extracellular intracellular 22 23 Salt Secretion: recycle Figure in Box 26.2 Hill et al. 2004 active Down electrochemical
Ionic & Osmotic Homeostasis osmoregulation mechanisms in gills, salt glands, and kidneys extracellular intracellular 22 23 Salt Secretion: recycle Figure in Box 26.2 Hill et al. 2004 active Down electrochemical
A. Incorrect! The urinary system is involved in the regulation of blood ph. B. Correct! The urinary system is involved in the synthesis of vitamin D.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Dr Ian Roberts Oxford. Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford Radcliffe NHS Trust
 Dr Ian Roberts Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Present the basic diagnostic features of the commonest conditions causing proteinuria & haematuria Highlight diagnostic pitfalls Nephrotic
Dr Ian Roberts Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Present the basic diagnostic features of the commonest conditions causing proteinuria & haematuria Highlight diagnostic pitfalls Nephrotic
The Urinary System. Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Functions of the Urinary System Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes
The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Functions of the Urinary System Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes
Year 2004 Paper one: Questions supplied by Megan
 QUESTION 53 Endothelial cell pathology on renal biopsy is most characteristic of which one of the following diagnoses? A. Pre-eclampsia B. Haemolytic uraemic syndrome C. Lupus nephritis D. Immunoglobulin
QUESTION 53 Endothelial cell pathology on renal biopsy is most characteristic of which one of the following diagnoses? A. Pre-eclampsia B. Haemolytic uraemic syndrome C. Lupus nephritis D. Immunoglobulin
Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate
 Renal physiology The kidneys Allow us to live on dry land. Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate Kidneys maintain composition
Renal physiology The kidneys Allow us to live on dry land. Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate Kidneys maintain composition
Biology Slide 1 of 36
 Biology 1 of 36 38 3 The Excretory System 2 of 36 Functions of the Excretory System 1.Function: process which eliminates metabolic wastes 3 of 36 Functions of the Excretory System (The skin excretes excess
Biology 1 of 36 38 3 The Excretory System 2 of 36 Functions of the Excretory System 1.Function: process which eliminates metabolic wastes 3 of 36 Functions of the Excretory System (The skin excretes excess
Questions? Homework due in lab 6. PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!)
 Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
URINARY SYSTEM. Urinary System
 URINARY SYSTEM Urinary System Kidney Functions Excretion Regulation of blood volume and pressure Regulation of electrolyte and ph levels Kidney Structure Gross Anatomy Fibrous Capsule Renal Cortex Renal
URINARY SYSTEM Urinary System Kidney Functions Excretion Regulation of blood volume and pressure Regulation of electrolyte and ph levels Kidney Structure Gross Anatomy Fibrous Capsule Renal Cortex Renal
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Eremina V, Jefferson JA, Kowalewska J, et al. VEGF inhibition
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Eremina V, Jefferson JA, Kowalewska J, et al. VEGF inhibition
Nephritic vs. Nephrotic Syndrome
 Page 1 of 18 Nephritic vs. Nephrotic Syndrome Terminology: Glomerulus: A network of blood capillaries contained within the cuplike end (Bowman s capsule) of a nephron. Glomerular filtration rate: The rate
Page 1 of 18 Nephritic vs. Nephrotic Syndrome Terminology: Glomerulus: A network of blood capillaries contained within the cuplike end (Bowman s capsule) of a nephron. Glomerular filtration rate: The rate
AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM
 AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM I. SYSTEM COMPONENTS (Figs. 25.1 25.4) KIDNEYS Each kidney contains approx. 1,000,000 tubular NEPHRONS which produce FILTRATE from the plasma and then add to or take from
AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM I. SYSTEM COMPONENTS (Figs. 25.1 25.4) KIDNEYS Each kidney contains approx. 1,000,000 tubular NEPHRONS which produce FILTRATE from the plasma and then add to or take from
Overview of glomerular diseases
 Overview of glomerular diseases *Endothelial cells are fenestrated each fenestra: 70-100nm in diameter Contractile, capable of proliferation, makes ECM & releases mediators *Glomerular basement membrane
Overview of glomerular diseases *Endothelial cells are fenestrated each fenestra: 70-100nm in diameter Contractile, capable of proliferation, makes ECM & releases mediators *Glomerular basement membrane
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19
![QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19](/thumbs/77/74887026.jpg) QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19 Learning Objectives: Differentiate the following processes: filtration, reabsorption, secretion,
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19 Learning Objectives: Differentiate the following processes: filtration, reabsorption, secretion,
Basic Functions of the Kidneys
 Dr. Adelina Vlad Basic Functions of the Kidneys Eliminate plasma METABOLIC WASTE PRODUCTS and FOREIGN COMPOUNDS The kidney are the primary means for eliminating metabolic waste products (urea, creatinine,
Dr. Adelina Vlad Basic Functions of the Kidneys Eliminate plasma METABOLIC WASTE PRODUCTS and FOREIGN COMPOUNDS The kidney are the primary means for eliminating metabolic waste products (urea, creatinine,
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (1)
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (1) Dr. Attila Nagy 2017 Functional role of the kidney 1.Homeostasis of fluid compartments (isosmia, isovolemia, isoionia, isohydria,) 2. Elimination
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (1) Dr. Attila Nagy 2017 Functional role of the kidney 1.Homeostasis of fluid compartments (isosmia, isovolemia, isoionia, isohydria,) 2. Elimination
Func%ons of the Urinary System
 Func%ons of the Urinary System Excre%on Regula%on of blood volume Regula%on of blood pressure Regula%on of blood- solute concentra%on Regula%on of ph of extracellular fluid Regula%on of erythropoiesis
Func%ons of the Urinary System Excre%on Regula%on of blood volume Regula%on of blood pressure Regula%on of blood- solute concentra%on Regula%on of ph of extracellular fluid Regula%on of erythropoiesis
PARTS OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
By: Dr. Foadoddini Department of Physiology & Pharmacology Birjand University of Medical Sciences. Body fluids and.
 By: Dr. Foadoddini Department of Physiology & Pharmacology Birjand University of Medical Sciences Body fluids and Renal physiology 25 Volume and Osmolality of Extracellular and Intracellular Fluids
By: Dr. Foadoddini Department of Physiology & Pharmacology Birjand University of Medical Sciences Body fluids and Renal physiology 25 Volume and Osmolality of Extracellular and Intracellular Fluids
Chapter 25: Urinary System
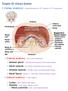 Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
Signaling Vascular Morphogenesis and Maintenance
 Signaling Vascular Morphogenesis and Maintenance Douglas Hanahan Science 277: 48-50, in Perspectives (1997) Blood vessels are constructed by two processes: vasculogenesis, whereby a primitive vascular
Signaling Vascular Morphogenesis and Maintenance Douglas Hanahan Science 277: 48-50, in Perspectives (1997) Blood vessels are constructed by two processes: vasculogenesis, whereby a primitive vascular
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR THE URINARY SYSTEM
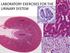 LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR THE URINARY SYSTEM cortex Medulla DEMO SLIDE BOX 172 (450-E001-H-76). Kidney, horse. the inner medulla medullary rays, Uriniferous tubules expand both the cortex and medulla corticomedullary
LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR THE URINARY SYSTEM cortex Medulla DEMO SLIDE BOX 172 (450-E001-H-76). Kidney, horse. the inner medulla medullary rays, Uriniferous tubules expand both the cortex and medulla corticomedullary
Glomerular pathology-2 Nephritic syndrome. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin
 Glomerular pathology-2 Nephritic syndrome Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin 1 The Nephritic Syndrome Pathogenesis: inflammation proliferation of the cells in glomeruli & leukocytic infiltrate Injured capillary walls
Glomerular pathology-2 Nephritic syndrome Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin 1 The Nephritic Syndrome Pathogenesis: inflammation proliferation of the cells in glomeruli & leukocytic infiltrate Injured capillary walls
Construction of Nephron by Fusion of Adult Glomeruli to Ureteric Buds with Type V Collagen. Yusuke Murasawa, Pi-chao Wang
 Construction of Nephron by Fusion of Adult Glomeruli to Ureteric Buds with Type V Collagen Yusuke Murasawa, Pi-chao Wang Abstract Although tissue engineering of artificial organs such as skin or cartilage
Construction of Nephron by Fusion of Adult Glomeruli to Ureteric Buds with Type V Collagen Yusuke Murasawa, Pi-chao Wang Abstract Although tissue engineering of artificial organs such as skin or cartilage
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
Homeostasis. Thermoregulation. Osmoregulation. Excretion. how organisms regulate their body temperature
 Homeostasis the steady-state physiological condition of the body Ability to regulate the internal environment important for proper functioning of cells Thermoregulation Homeostasis how organisms regulate
Homeostasis the steady-state physiological condition of the body Ability to regulate the internal environment important for proper functioning of cells Thermoregulation Homeostasis how organisms regulate
Osmoregulation and Excretion
 Animal Life and Excretion Harder for multicellular organisms Internal circulation Coordination, information transfer Structural maintenance Movement Maintenance of homeostatic internal environment 15 July
Animal Life and Excretion Harder for multicellular organisms Internal circulation Coordination, information transfer Structural maintenance Movement Maintenance of homeostatic internal environment 15 July
The Urinary System 15PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
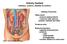 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
Functions of the kidney
 Physiology of Urinary tract Kidney, Ureter, Urinary bladder Urethra Kidney function Excretion Physiology of volume regulation Functions of the kidney Excretion of dangerous substances endogenous (metabolites):
Physiology of Urinary tract Kidney, Ureter, Urinary bladder Urethra Kidney function Excretion Physiology of volume regulation Functions of the kidney Excretion of dangerous substances endogenous (metabolites):
Fifth Year Biology. Excretion. Miss Rochford
 Fifth Year Biology Excretion Miss Rochford In this Topic Excretion in plants Excretion and homeostasis Skin Organs of excretion Urinary system Kidneys Nephron Control of urine volume Characteristics of
Fifth Year Biology Excretion Miss Rochford In this Topic Excretion in plants Excretion and homeostasis Skin Organs of excretion Urinary system Kidneys Nephron Control of urine volume Characteristics of
Sunday, July 17, 2011 URINARY SYSTEM
 URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
Nephron Function and Urine Formation. Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S
 Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Collin County Community College RENAL PHYSIOLOGY
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Glomerular Filtration Filtration process that occurs in Bowman s Capsule Blood is filtered and
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Glomerular Filtration Filtration process that occurs in Bowman s Capsule Blood is filtered and
Kidney Structure. Renal Lobe = renal pyramid & overlying cortex. Renal Lobule = medullary ray & surrounding cortical labryinth.
 Kidney Structure Capsule Hilum ureter renal pelvis major and minor calyxes renal and vein segmental arteries interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries Medulla renal pyramids cortical/renal
Kidney Structure Capsule Hilum ureter renal pelvis major and minor calyxes renal and vein segmental arteries interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries Medulla renal pyramids cortical/renal
describe the location of the kidneys relative to the vertebral column:
 Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
MOLECULAR SIZE, ELECTRICAL CHARGE, AND SHAPE DETERMINE THE FILTERABILITY OF SOLUTES ACROSS THE GLOMERULAR FILTRATION BARRIER
 MOLECULAR SIZE, ELECTRICAL CHARGE, AND SHAPE DETERMINE THE FILTERABILITY OF SOLUTES ACROSS THE GLOMERULAR FILTRATION BARRIER The glomerular filtration barrier consists of three elements: (1) endothelial
MOLECULAR SIZE, ELECTRICAL CHARGE, AND SHAPE DETERMINE THE FILTERABILITY OF SOLUTES ACROSS THE GLOMERULAR FILTRATION BARRIER The glomerular filtration barrier consists of three elements: (1) endothelial
UNCOVERING THE ROLES OF TOLL-LIKE RECEPTOR 7 AND INTERFERON REGULATORY FACTOR 5 IN IMMUNE COMPLEX GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
 Name Email Barry Horne, Jr. bkhorne@bu.edu Institutional Affiliation Campus School Medical Campus Graduate Medical Sciences Division Department Graduate Program in Genetics and Genomics, Immunology Training
Name Email Barry Horne, Jr. bkhorne@bu.edu Institutional Affiliation Campus School Medical Campus Graduate Medical Sciences Division Department Graduate Program in Genetics and Genomics, Immunology Training
Section Title. Subject Index
 Section Title Subject Index Acute kidney injury definitions 287 289 hypoxia 287, 290 overview 286, 287 sublethal tubular injury adaptive responses 292, 293 combination of sublethal injuries 291, 292 detection
Section Title Subject Index Acute kidney injury definitions 287 289 hypoxia 287, 290 overview 286, 287 sublethal tubular injury adaptive responses 292, 293 combination of sublethal injuries 291, 292 detection
