INSULIN MANAGEMENT POLICY
|
|
|
- Felicity Long
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INSULIN MANAGEMENT POLICY To be read in conjunction with the Hypoglycaemia Management Policy for adult Patients and the Countywide Standard Operating Procedure for Implementing the Insulin Passport/Safety Card and the Patient Information Booklet (NSPA/0/PSA00) Version: Ratified by: Date ratified: May 06 Title of originator/author: Title of responsible committee/group: Date issued: May 06 Review date: April 09 Relevant Staff Groups: Senior Managers Operational Group Nurse Consultant for Diabetes Clinical Governance Group All Somerset Partnership NHS Foundation Trust registered nurses, non-registered practitioners and medical staff This document is available in other formats, including easy read summary versions and other languages upon request. Should you require this please contact the Equality and Diversity Lead on Insulin Management Policy V - - May 06
2 DOCUMENT CONTROL Reference SD/Oct//IM Amendments Version Status Final Author Nurse Consultant for Diabetes Update and expansion on sections relating to risk factors and potential causes of hypoglycaemia Addition of treatment for enterally fed patients Update of treatment of hypoglycaemia flowchart to reflect national guidelines. Addition of sample hypo form. Amended to reflect the inclusion of non-registered practitioners (Assistant Practitioners) Amendment to wording of paragraph 6. to reinforce that insulin syringes must not be drawn up in advance. Document objectives: This document will ensure that Somerset Partnership NHS Foundation Trust staff complies with the standards set out in this document Intended recipients: All nursing and medical staff Committee/Group Consulted: Medicines Management Group Monitoring arrangements and indicators: This policy will be overseen by the Medicines Management Group, Somerset Partnership NHS Foundation Trust Training/resource implications: As indicated in the policy Approving body and date Clinical governance Group Date: April 06 Formal Impact Assessment Impact Part Date: March 0 Ratification Body and date Senior Managers Operational Group Date of issue May 06 Review date April 09 Contact for review Lead Director Nurse Consultant for Diabetes Date: May 06 Director of Nursing and Patient Safety CONTRIBUTION LIST Key individuals involved in developing the document Name Su Down Andrew Brown Maggie Crockett Andrew Sinclair Liz Harewood Nina Vinall All members All members Mary Martin Designation or Group Nurse Consultant for Diabetes Head of Medicines Management Diabetes Intermediate Care Service Manager Equality and Diversity Lead Pharmacist Senior Clinical Nurse Clinical Policy Review Group Clinical Governance Group Professional Lead Community Nursing and Clinical Lead Overnight District Nursing Insulin Management Policy V - - May 06
3 CONTENTS Section Summary of Section Page Document Control Contents Introduction Purpose & Scope Duties and Responsibilities Explanations of Terms used Prescribing of Insulin 6 Administration of Insulin 6 7 Labelling and Storing of Insulin 8 8 Insulin Types and Regimes 8 9 Insulin Sites and Injection Technique 9 0 Blood Glucose Monitoring 0 Hypoglycaemia Management 0 Training Requirements 0 Equality Impact Assessment Monitoring Compliance and Effectiveness Counter Fraud 6 Relevant Care Quality Commission (CQC) Registration Standards 7 References, Acknowledgements and Associated Documents 8 Appendices Appendix A Self Administration Assessment Tree Appendix B Insulin Administration Insulin Management Policy V - - May 06
4 . INTRODUCTION. Insulin represents one of the medications generally considered high risk. The incorrect dosing of insulin can result in harm to the patient and requires immediate intervention. (Patient Safety First 008). Good metabolic control is associated with improved hospital outcomes.. This document will refer to other Somerset Partnership policies and protocols for specific areas and is intended to cover the additional practical issues relating to insulin management.. PURPOSE & SCOPE. The purpose of this policy is to outline the rationale and principles for the safe administration of Insulin. Insulin represents one of the medications generally considered high risk. The incorrect dosing of insulin can result in harm to the patient and requires immediate intervention.. The aim of this policy is to eliminate harm caused by improper use of insulin.. The target audience for this procedural document is all Somerset Partnership NHS Foundation Trust clinical staff.. DUTIES AND RESPONSIBLITIES. The Chief Executive is ultimately responsible for ensuring the Trust complies with legal requirements and national recommendations for medicines management.. The Trust Board has a responsibility to ensure training is available to all relevant staff and that competency assessment is available via the clinical practice team as required. This responsibility is delegated to the Director of Nursing and patient safety.. The Medical Director is the Executive Lead responsible for this policy but will delegate authority for the operational implementation and ongoing management of this policy to the Head of Medicines Management.. The Director of Nursing and Patient Safety is the lead for Non-Medical Prescribing for the Trust and has devolved responsibility for non-medical prescribers, ensuring training, updates and Non-medical Prescribing information, including safe use of insulin is cascaded.. Each registered healthcare professional is accountable for his/her own practice and will be aware of their legal and professional responsibilities relating to their competence in the ordering, prescribing, administering, monitoring, dispensing and supplying of insulin whichever is within their scope of practice; and work within the Code of practice of their professional body. All healthcare professionals involved in the use of insulin: must acquaint themselves with this policy and other related policies will be aware of the action that should be taken if their practice or patient safety is compromised Insulin Management Policy V - - May 06
5 will be aware of the action of, frequency of administration, side effects, contra-indications and interactions of the insulin prescribed will monitor the patients for side effects and adverse reactions and manage them appropriately will be aware of their limitations and seek advice or support from appropriate health professionals when in doubt prior to administration of insulin, will ensure that the patient is able to understand the information given to them and consider the use of interpreting services where necessary Each non-registered practitioner is accountable for their actions and to work within their scope of practice EXPLANATIONS OF TERMS USED. Non registered practitioner refers to an Assistant Practitioner who has a minimum QCF level diploma. NPSA National Patient Safety Agency.. Hypoglycaemia - Hypoglycaemia in a person with diabetes is defined as a capillary or venous glucose of less than mmol/l with or without symptoms.. Analogue insulin - An insulin analogue is an altered form of insulin, different from any occurring in nature, but still available to the human body for performing the same action as human insulin in terms of glycaemic control.. Glucagon - a peptide hormone secreted by the pancreas, raises blood glucose levels. Its effect is opposite that of insulin, which lowers blood glucose levels..6 Biphasic insulin A biphasic insulin is one which has phases of insulin action..7 DAFNE Dose adjustment for normal eating: a course designed specifically to teach patients with type diabetes how to alter their insulin doses in relation to their carbohydrate intake. PRESCRIBING OF INSULIN. In order to comply with the NPSA/0/PSA00 on insulin safety, all staff must refer to the Countywide Standard Operating Procedure for Implementing Insulin Passports/Insulin Safety Cards and the Patient Information Booklet.. Insulin must be prescribed using the new Somerset Partnership NHS Foundation Trust Insulin Administration Record.. The insulin dose must be prescribed with the words units spelt in full not abbreviated to u / iu. The use of the abbreviation can lead to the incorrect dose being given as with handwriting the u can be mistaken for a zero thereby giving ten times the intended dose (National Patient Safety Agency 00). Insulin Management Policy V - - May 06
6 . The exact dose must be prescribed and not left as directed for patients whilst in hospital or who require a health care professional to administer the insulin.. When prescribing, specify the exact brand name and if possible whether a vial, cartridge or pen is required. This is particularly important when an inpatient is discharged to ensure that the patient goes home with the correct means of administration..6 On the prescription, the time of administration should co-ordinate with meal times as delayed availability of food may lead to hypoglycaemia..7 Where insulin is to be administered by a registered nurse or a non registered practitioner in the community, or the patient has a suitably trained carer, Glucagon should also be prescribed PRN for use in patients known to be at increased risk of hypoglycaemia. 6. ADMINISTRATION OF INSULIN 6. Health Care Professionals should ensure the patient is able to understand the information given to them and are able to give their informed consent. This may necessitate the use of a professional interpreter and the translation of written information (Interpreting and Translation Policy). A capacity assessment should be considered for those patients who are unable to consent to the procedure and reference should be made to the Consent and Capacity to Consent Policy. 6. Non registered practitioners can administer insulin to patients following an assessment and care planning by the registered nurse identifying that the patient s diabetes is stable and the patient is medically predictable. The care plan must specify the accepted blood glucose levels for the patient and what to do if blood glucose levels are outside the acceptable range. The registered nurse remains accountable for the care plan and the review date. 6. The registered nurse is accountable for their decisions to delegate tasks and duties to other people. To achieve this, the registered nurse must only delegate tasks and duties that are within the other person s scope of competence (NMC 0), Therefore before delegating the administration of insulin to a non- registered practitioner the registered nurse must ensure that the non-registered practitioner has undertaken training in insulin administration and has been assessed as competent in this clinical task, as well as demonstrating competency in drug calculation skills, anaphylaxis and basic life training. The non-registered practitioner must be given the opportunity to discuss, reflect and review the work and to be supported and developed so that they can fully meet the requirements of their role to deliver a high quality service. 6. The Somerset Partnership NHS Foundation Trust Medicines Policy must be adhered to at all times. In addition to which the following points with particular reference to insulin administration must be undertaken (please refer to the Medicines Policy). Insulin Management Policy V May 06
7 6. Insulin is most commonly given via subcutaneous injection. If any other route is prescribed, this should be queried with medical staff concerned and transfer to the acute trust should be considered if necessary for further management. 6.6 If a particular insulin pen device is not prescribed, insulin must be drawn up using an insulin safety syringe. No other device should be used to measure insulin apart from one specifically designed to do so. Failure to do this may result in an overdose of insulin. A list of all currently available insulin pen devices can be found at: 0.pdf 6.7 Prior to administering insulin the health care professional must have knowledge of the action of the particular insulin. A list of all insulins and their action can be found at: nsulins.pdf 6.8 For insulin where the action is immediate, food must be available for the patient to eat as soon as the insulin has been administered. 6.9 Long acting insulin analogues should be given at the same time every day in order to provide the most consistent blood glucose profiles. 6.0 Insulin that is cloudy must be correctly re-suspended prior to administration. If sediment is left in the bottle or cartridge before administration this will affect the action of the dose administered and may lead to erratic and unpredictable blood glucose control resulting in hypoglycaemia. Re-suspension should be done by gently rolling and inverting as too vigorous shaking can destroy the insulin molecule. 6. Never use insulin that has become discoloured, has a frosty coating on the inside of the vial or has become cloudy when it should be clear. Insulin in this state is ineffective and if used may lead to hyperglycaemia. 6. Always check the expiry date on the vial or cartridge prior to administration. 6. Once drawn up insulin must be administered immediately. Syringes of insulin MUST not be drawn up, and insulin pens MUST not be dialled up in advance for use at a later date/time. The preparation of pre-loaded syringes represents a form of secondary dispensing which, under the terms of the Medicines Act (968), is classified as an unlicensed activity in all four UK countries. The safety of individuals using pre-loaded insulin syringes, as well as the storage, stability and sterility of insulin once drawn up in the syringe, is of paramount importance. (The Nursing and Midwifery Council (NMC) Standards for medicines management (NMC, 00). 6. The type and dose of insulin should be second checked before administration to the patient. The only exception to this is Registered Nurses and nonregistered practitioners working in the community, who as lone workers, Insulin Management Policy V May 06
8 need to be extra vigilant by double checking the insulin prescriptions themselves prior to administration. 6. If self administration is to be considered for inpatients/patients in the community, a risk assessment must be undertaken to assess appropriateness and competence as per self medication decision tree. If the risk of self harm/suicide is perceived to be present, self administration is not appropriate; Inpatient Diabetes Medication, Prescription and Administration Record see appendix A. 7 LABELLING AND STORING OF INSULIN 7. For patients who are self administering their insulin in hospital, all vials and devices must be clearly labelled with the patients name and details and ensure they are taken by the patient on discharge or disposed of appropriately. Ward staff should follow the procedure in the Healthcare Waste (Clinical Waste) Policy (on the intranet). 7. Stock insulin must be stored in a fridge at between and 8 C. Fridge temperatures should be maintained and recorded on a daily basis. 7. Insulin cannot withstand temperatures of below C. 7. Insulin for injection should be allowed to come up to room temperature before injecting. 7. In most hospital settings it is safer for patients own insulin vials in use to be kept with the patient s own drugs rather than separately in the fridge. This would not be appropriate on a psychiatric unit where there are no facilities for patients to store their own medicines. 7.6 Shelf-Life after first use: The product may be stored for a maximum of four weeks not above 0 C and away from direct heat or direct light. Keep the vial in the outer carton in order to protect from light. It is recommended that the date of the first use from the vial be noted on the label. 8 INSULIN TYPES AND REGIMES 8. Insulin regimens must give hour coverage of insulin. This can be achieved in a variety of ways. The most common regimens are: 8. Twice daily doses of short and intermediate acting insulin. These are given before breakfast and evening meal: the short-acting doses cover the insulin needs of the morning and evening the intermediate-acting doses cover the afternoon and overnight pre-mixed or biphasic insulin injections are convenient for this regimen Insulin Management Policy V May 06
9 8. Background insulin in addition to diabetes oral medications. this regimen is only suitable for people with type diabetes 8. Multiple daily doses. short-acting insulin is used before each main meal an intermediate or long-acting insulin is used before bedtime to give coverage overnight 8. Dose Adjustment For Normal Eating (DAFNE) A risk assessment should be considered for any inpatients on this regimen 8.6 A list of all currently available insulin and their action can be found at: nsulins.pdf 8.7 The type of insulin is usually either Human or Analogue. Porcine and Bovine insulin are still currently available. All insulin types have different modes of action and the health care professional must be familiar with the action of the insulin prescribed. 9 INSULIN SITES AND INJECTION TECHNIQUE 9. The most common injection site is the abdomen (or stomach). The back of the upper arms, the upper buttocks or hips, and the outer side of the thighs are also used. These sites are the best to inject into for two reasons: they have a layer of fat just below the skin to absorb the insulin, but not many nerves, which means that injecting there will be more comfortable for the patient it is easier to inject into the subcutaneous tissue, where insulin injection is recommended 9. Inject at an angle of 90 using a short to 8mm needle. 9. It is important to vary the injection sites as continually injecting into one area can lead to lipohypertrophy and subsequent unpredictable absorption of insulin. This unpredictability may lead to either hypoglycaemia or hyperglyceamia. Staff must however be aware of cultural and gender sensitivities to certain injection sites, particularly if the staff member is a different gender to the patient. 9. There is no need to clean the skin prior to injection. 9. If using a needle greater than mm the injection should be into a skin fold to ensure it is not in the muscle layer, this still requires an angle of 90 o (see 6.). Insulin Management Policy V May 06
10 To pinch the skin correctly, a couple inches of skin should be held between the thumb and two fingers, pulling the skin away from the underlying muscle. This step is unnecessary with the needles of mm or shorter. 9.6 The needle should be inserted with the pinch still held and released only after all the insulin has been injected. 9.7 It is the responsibility of the health care professional to be familiar with the insulin device used. 9.8 A new pen needle or safety syringe must be used for each injection. Needles must not be re-sheathed (please see the Needlestick and Decontamination Policy). 9.9 Never leave an insulin pen with the needle attached. This can lead to leakage of insulin from the needle or the accumulation of air in the cartridge. 0 BLOOD GLUCOSE MONITORING 0. All Health Care Professionals within Somerset Partnership NHS Foundation Trust must refer to the Point of care Blood Glucose Monitoring Policy. 0. All Health Care Professionals within Somerset Partnership NHS Foundation Trust must use the glucose meters recommended for use by the trust when testing a patients blood glucose and ensure that glucose meters are calibrated and serviced as directed. 0. All Health Care Professionals must be trained in usage of the meter and have regular updated as stated in the Medical Devices policy. 0. Incorrect usage of the meters may lead to inaccurate results and these results may lead to inappropriate insulin dose alterations. HYPOGLYCAEMIA MANAGEMENT. For the treatment of hypoglycaemia please see the Somerset Partnership NHS Foundation Trust Policy for the Management of Hypoglycaemia in Adult Patients.. TRAINING REQUIREMENTS. All staff who prescribe, administer or dispense insulin must undertake the mandatory e-learning Safe Use of Insulin every years as found on the Learning and development page on the intranet.. Unregistered practitioners must undertake specific training in administration of subcutaneous injections, and assessment of competence in administration of insulin (see Appendix B). The Trust will work towards all staff being appropriately trained in line with the organisation s Staff Mandatory Training Matrix (training needs analysis). All training documents referred to in this policy are accessible to staff within the Learning and Development Section of the Trust Intranet. Insulin Management Policy V May 06
11 Needlestick and Contamination Injury Policy Healthcare Clinical Waste Policy. All Somerset Partnership NHS Foundation Trust clinical staff have access to the Diabetes Intermediate Care service for advice and guidance.. EQUALITY IMPACT ASSESSMENT All relevant persons are required to comply with this document and must demonstrate sensitivity and competence in relation to the nine protected characteristics as defined by the Equality Act 00. In addition, the Trust has identified Learning Disabilities as an additional tenth protected characteristic. If you, or any other groups, believe you are disadvantaged by anything contained in this document please contact the Document Lead (author) who will then actively respond to the enquiry.. MONITORING COMPLIANCE AND EFFECTIVENESS. Overall monitoring will be by the Medicines Management Group by reviewing trends in incident reporting via DATIX. Incidents will be reported to the Medicines in Clinical Practice Group for consideration, identifying good practice, any shortfalls, action points and lessons learnt. This Group will be responsible for ensuring improvements, where necessary, are implemented.. Best Practice Group will provide six monthly reports to Clinical and Social care Effectiveness Group. Six monthly reporting to the Clinical and Social Care Effectiveness Group and Medicines Management Group. These reports will be accessible to all staff on the Trust Intranet and hyperlinked into newsletter to raise awareness.. COUNTER FRAUD. The Trust is committed to the NHS Protect Counter Fraud Policy to reduce fraud in the NHS to a minimum, keep it at that level and put funds stolen by fraud back into patient care. Therefore, consideration has been given to the inclusion of guidance with regard to the potential for fraud and corruption to occur and what action should be taken in such circumstances during the development of this procedural document. 6. RELEVANT CARE QUALITY COMMISSION (CQC) REGISTRATION STANDARDS 6. Under the Health and Social Care Act 008 (Regulated Activities) Regulations 0 (Part ), the fundamental standards which inform this procedural document, are set out in the following regulations: Regulation 9: Regulation 0: Regulation : Regulation : Person-centred care Dignity and respect Need for consent Safe care and treatment Insulin Management Policy V - - May 06
12 Regulation : Regulation : Regulation : Regulation 6: Regulation 7: Regulation 8: Regulation 9: Regulation 0: Regulation 0A: Safeguarding service users from abuse and improper treatment Meeting nutritional and hydration needs Premises and equipment Receiving and acting on complaints Good governance Staffing Fit and proper persons employed Duty of candour Requirement as to display of performance assessments. 6. Under the CQC (Registration) Regulations 009 (Part ) the requirements which inform this procedural document are set out in the following regulations: Regulation 6: Regulation 7: Regulation 8: Notification of death of service user Notification of death or unauthorised absence of a service user who is detained or liable to be detained under the Mental Health Act 98 Notification of other incidents 6. Detailed guidance on meeting the requirements can be found at oviders%0on%0meeting%0the%0regulations%0final%0for%0pu BLISHING.pdf 7. REFERENCES, ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS AND ASSOCIATED DOCUMENTS 7. References Patient safety first version. /09/08 (pages -6) National Patient Safety Agency safer administration of insulin, June 00 Policy for the Safe and Secure Handling of Medicines Somerset Community Health, September Cross reference to other procedural documents Consent and Capacity to Consent to Examination and Treatment Policy Countywide Policy for Implementing Insulin Passport/Insulin Safety Card and the Patient Information Booklet (NPSA/0/PSA00) Hand Hygiene Policy Healthcare Clinical Waste Policy Inpatient Diabetes Medication, Prescription and Administration Record Learning Development and Mandatory Training Policy Management of Hypoglycaemia Policy Medical Devices Policy Medicines Policy Needlestick and Contamination Injury Policy Record Keeping and Record Management Policy Risk Management Policy and Procedure Insulin Management Policy V - - May 06
13 Staff Mandatory Training Matrix (Training Needs Analysis) Syringe Driver Policy Untoward Event Reporting Policy and procedure All current policies and procedures are accessible in the policy section of the public website (on the home page, click on Policies and Procedures ). Trust Guidance is accessible to staff on the Trust Intranet. 8. APPENDICES For the avoidance of any doubt the appendices in this policy are to constitute part of the body of this policy and shall be treated as such. This should include any relevant Clinical Audit Standards. APPENDIX A APPENDIX B Self medication Decision Tree Competency Assessment for Insulin Administration Insulin Management Policy V - - May 06
14 APPENDIX A SELF MEDICATION DECISION TREE Assessment to enable safe patient self-medication of insulin whilst in hospital and the patients own home. Self medication means the patient must be able to perform a blood sugar test, interpret the results to make a decision on the insulin dose, store own insulin in locker provided and administer the insulin dose correctly. YES Current self-medication NO (not suitable) Does the patient medicate his/her own insulin at home? YES Mental capacity NO (not suitable, Does the patient have the mental capacity currently to selfmedicate his/her own insulin? reassess if mental capacity changes YES Manual dexterity NO (not suitable, Does the patient have the manual dexterity to self-medicate His/her own insulin? (with aids if necessary) reassess if manual? dexterity changes YES Risk Factors NO (not suitable, Does the patient have no other risk factors currently that makes him/her unsuitable for self-medicating his/her own insulin? (i.e. no unresolved risk of drug abuse/overdose, alcoholism, self-harming, non adherence or suspected non adherence to their insulin) reassess if risk factors change) YES Patient willing to self-medicate NO (not suitable, Would the patient like to self-medicate his/her own insulin? explain to the patient that they can change their mind at any time and should inform a member of staff if this happens) YES Knowledge level NO (not suitable, refer Suitable for Self-medication Does the patient have the knowledge and skills about insulin and Diabetes to self-medicate (i.e. able to measure his/her own blood Glucose levels, able to recognise and respond to warning signs of hypos, able to inject his/her insulin)? patient to specialist? diabetes team for education) Commence patient self-medication of insulin. Reassess if patient s clinical condition alters to ensure none of the above factors have changed. YES Further knowledge level NO (not suitable, reassess if knowledge level changes) Able to Self adjust Insulin Dose Taken from Somerset Partnership NHS Foundation Trust Insulin Prescription Chart Insulin Management Policy V - - May 06
15 APPENDIX B INSULIN ADMINISTRATION The competencies are to be used in conjunction with Nursing and Midwifery Council (NMC) (0) The Code: Standards for Conduct; Performance and Ethics for Nurses and Midwives. Consent and Capacity to Consent to Examination and Treatment Policy Countywide Policy for Implementing Insulin Passport/Insulin Safety Card and the Patient Information Booklet (NPSA/0/PSA00) Medicines Policy Hand Hygiene Policy Healthcare Clinical Waste Policy Learning Development and Mandatory Training Policy Management of Hypoglycaemia Policy Medical Devices Policy Needlestick and Contamination Policy Record Keeping and Record Management Policy The purpose of these competencies is to clarify the knowledge and skills expected of practitioners, to ensure safe practice in Insulin Administration Once the practitioner has reached a satisfactory level of competence following a period of supervised practice, ensure they are formally competency assessed within three months of completing the initial theoretical/practical training. The self rating scale is to be used by the individual practitioner for self-assessment of present performance during supervised practice, and to help identify learning needs. Their line manager, or other experienced practitioner, must then assess these skills and sign to confirm competency. Only qualified practitioners with an NMC recognised teaching and assessing in practice qualification and who have completed recognised training and assessment in Insulin Administration can be identified as assessors. Key for Self-Assessment = No knowledge / experience = Some knowledge / experience = Competent = Competent with some experience = Competent, experienced and able to teach others Author: Mary Martin Date: October 0 Review: October 08 Competency Assessment...date
16 Assessment of competence for Insulin Administration I confirm that I have self-assessed as competent to practice (insert skill) as below: Practitioner Name: Practitioner Qualification: Practitioner Signature: Date:.. I confirm that I have assessed the named practitioner above as competent to perform the above skill. Name & Title: Signature: Date:. Upon successful completion of your assessment of competency please send to your line manager and retain a copy for yourself. Competency Assessment...date
17 Knowledge and Skills for Insulin Administration Describe what diabetes is Name the two types of diabetes Describe the different types of insulin available Demonstrate an understanding that the type of insulin prescribed will dictate the time the insulin will need to be given Describe the safety procedures that need to be considered when prescribing and administering insulin Self-Assessment Formal Assessment Score Tick Date & Comments Signature Date & Comments Competency Assessment...date
18 Knowledge and Skills for Insulin Administration Describe how you would reduce the risk of the client developing Lipos (Lipoatrophy) 6 Describe the sites that can be used for insulin administration 7 Describe how insulin is obtained and how it should be stored 8 Describe the effect of insulin on blood glucose levels Self-Assessment Formal Assessment Score Tick Date & Comments Signature Date & Comments Competency Assessment...date
19 Knowledge and Skills for Insulin Administration 9 Greet, accurately identify the patient and/or key person and introduce yourself and any colleagues present, gain consent 0 Before administering any prescribed medication consult the individuals prescription record to CORRECTLY ascertain the following and ensures correct Drug Dosage Date and time of administration Route and method of administration Validity of prescription Signature of prescriber Legibility of prescription Self-Assessment Formal Assessment Score Tick Date & Comments Signature Date & Comments Competency Assessment...date
20 Demonstrate ability to administer an insulin injection following Trust Policy Makes a clear, accurate and immediate record of all medication administered, intentionally withheld or refused by the patient Competency Assessment...date
ADVANCE PREPARATION OF INSULIN FOR PATIENTS TO ADMINISTER AT HOME
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE ADVANCE PREPARATION OF INSULIN FOR PATIENTS TO ADMINISTER AT HOME First Issued July 08 Issue Version Two Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date To promote
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE ADVANCE PREPARATION OF INSULIN FOR PATIENTS TO ADMINISTER AT HOME First Issued July 08 Issue Version Two Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date To promote
ADMINISTRATION OF INSULIN
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE ADMINISTRATION OF INSULIN Issue History First issued April 2012 Issue Version Two Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date To promote the safe administration
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE ADMINISTRATION OF INSULIN Issue History First issued April 2012 Issue Version Two Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date To promote the safe administration
Assistant Practitioner and Health Care Assistants Administration of Insulin, via Pen device, by Delegation Training and competency Toolkit
 Assistant Practitioner and Health Care Assistants Administration of Insulin, via Pen device, by Delegation Training and competency Toolkit Document Summary The purpose of this policy is to guide and promote
Assistant Practitioner and Health Care Assistants Administration of Insulin, via Pen device, by Delegation Training and competency Toolkit Document Summary The purpose of this policy is to guide and promote
Pre-loading of insulin syringes for adult patients to administer at home
 Title: Directorate: Responsible for review: Ratified by: Diabetes - Pre-loading of insulin syringes for adult patients to administer at home Operations Samantha Rosindale, Diabetes Lead Champion Lynda
Title: Directorate: Responsible for review: Ratified by: Diabetes - Pre-loading of insulin syringes for adult patients to administer at home Operations Samantha Rosindale, Diabetes Lead Champion Lynda
PATIENT GROUP DIRECTIONS POLICY
 PATIENT GROUP DIRECTIONS POLICY To be read in conjunction with the Medicines Policy and the Controlled Drugs Policy Version: 5 Ratified by: Senior Managers Operations Group Date ratified: August 2015 October
PATIENT GROUP DIRECTIONS POLICY To be read in conjunction with the Medicines Policy and the Controlled Drugs Policy Version: 5 Ratified by: Senior Managers Operations Group Date ratified: August 2015 October
Introduction. Guidelines for patient involvement in the administration of insulin under supervision in hospital (Adult patients)
 Guidelines for patient involvement in the administration of insulin under supervision in hospital (Adult patients) Introduction This guideline is designed to provide a framework for patients to administer
Guidelines for patient involvement in the administration of insulin under supervision in hospital (Adult patients) Introduction This guideline is designed to provide a framework for patients to administer
Procedure for the prescribing and administration of insulin
 Procedure for the prescribing and administration of insulin Author: Lilian Baxendale and Heather Beadle Designation: Clinical Governance Pharmacists Version: Version 3 Date: December 2016 Date Approved:
Procedure for the prescribing and administration of insulin Author: Lilian Baxendale and Heather Beadle Designation: Clinical Governance Pharmacists Version: Version 3 Date: December 2016 Date Approved:
Administration of Injectable Medication by Healthcare Assistants (Band 3) Standard Operating Procedure
 Administration of Injectable Medication by Healthcare Assistants (Band 3) Standard Operating Procedure DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 1 Ratified by: Quality Assurance Sub Committee Date ratified: 4 September
Administration of Injectable Medication by Healthcare Assistants (Band 3) Standard Operating Procedure DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 1 Ratified by: Quality Assurance Sub Committee Date ratified: 4 September
Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy
 Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Solent NHS Trust policies can only be considered to be valid and up-to-date if viewed on the intranet. Please visit the intranet for the latest version. Purpose of Agreement
Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Solent NHS Trust policies can only be considered to be valid and up-to-date if viewed on the intranet. Please visit the intranet for the latest version. Purpose of Agreement
PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION PROCEDURE
 PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION PROCEDURE Date approved 2 October 2015 Version 3 Approved by Yvette Oade, Chief Medical Officer Procedure Lead Clinical Governance Lead - Medicines Management Procedure Author Karen
PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION PROCEDURE Date approved 2 October 2015 Version 3 Approved by Yvette Oade, Chief Medical Officer Procedure Lead Clinical Governance Lead - Medicines Management Procedure Author Karen
PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD GLUCOSE MONITORING
 PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD GLUCOSE MONITORING First Issued Issue Version Two Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date To promote safe and effective blood glucose monitoring using Trust equipment
PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD GLUCOSE MONITORING First Issued Issue Version Two Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date To promote safe and effective blood glucose monitoring using Trust equipment
Procedure for Subcutaneous Injection of Insulin or GLP1 Analogue in Adults Using a Pen Device V2.0
 Procedure for Subcutaneous Injection of Insulin or GLP1 Analogue in Adults Using a Pen Device V2.0 11 October 2017 Table of Contents 1. Introduction.. 3 2. Purpose of this Policy/Procedure. 3 3. Scope
Procedure for Subcutaneous Injection of Insulin or GLP1 Analogue in Adults Using a Pen Device V2.0 11 October 2017 Table of Contents 1. Introduction.. 3 2. Purpose of this Policy/Procedure. 3 3. Scope
28 th September Author Jeremy Gilbert Bariatric Nurse Specialist
 POLICY FOR SELF ADMINISTRATION OF CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE BY COMPETENT PATIENTS COMING IN FOR METABOLIC AND OBESITY SURGERY (BARIATRIC SURGERY) TO PENDENNIS WARD 28 th September 2014 Author
POLICY FOR SELF ADMINISTRATION OF CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE BY COMPETENT PATIENTS COMING IN FOR METABOLIC AND OBESITY SURGERY (BARIATRIC SURGERY) TO PENDENNIS WARD 28 th September 2014 Author
This Diabetes Policy should be read in conjunction with the Dealing with Medical Conditions Policy of Goulburn Region Preschool Association Inc.
 DIABETES POLICY Mandatory Quality Area 2 The content of this policy was developed for KPV by advocacy and diabetes educators at Diabetes Australia Vic and the Royal Children s Hospital Melbourne s manager
DIABETES POLICY Mandatory Quality Area 2 The content of this policy was developed for KPV by advocacy and diabetes educators at Diabetes Australia Vic and the Royal Children s Hospital Melbourne s manager
Policy for the safe administration of Insulin
 Policy for the safe administration of Insulin This is a working document and any changes that become necessary to this policy must be Notified in writing to the Medicine Management Group via the Chief
Policy for the safe administration of Insulin This is a working document and any changes that become necessary to this policy must be Notified in writing to the Medicine Management Group via the Chief
Latex and Occupational Dermatitis Policy Incorporating Glove Selection
 Latex and Occupational Dermatitis Policy Incorporating Glove Selection DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 3 Ratified by: Risk Management Sub Group Date ratified: 17 July 2013 Name of originator/author: Health
Latex and Occupational Dermatitis Policy Incorporating Glove Selection DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 3 Ratified by: Risk Management Sub Group Date ratified: 17 July 2013 Name of originator/author: Health
Policy and Procedure for the Development, Approval and Implementation of Patient Group Directions in NHS Haringey Clinical Commissioning Group
 BEFORE USING THIS POLICY ALWAYS ENSURE YOU ARE USING THE MOST UP TO DATE VERSION Policy and Procedure for the Development, Approval and Implementation of Patient Group Directions in NHS Haringey Clinical
BEFORE USING THIS POLICY ALWAYS ENSURE YOU ARE USING THE MOST UP TO DATE VERSION Policy and Procedure for the Development, Approval and Implementation of Patient Group Directions in NHS Haringey Clinical
SALBUTAMOL INHALER PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION CHILD HEALTH 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline
 SALBUTAMOL INHALER PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION CHILD HEALTH 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. This Patient Group Direction (PGD) applies to all nursing and clinical staff in the Child Health Department
SALBUTAMOL INHALER PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION CHILD HEALTH 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline 1.1. This Patient Group Direction (PGD) applies to all nursing and clinical staff in the Child Health Department
Consultation Group: Dr Amalia Mayo, Paediatric Consultant. Review Date: March Uncontrolled when printed. Version 2. Executive Sign-Off
 Policy For The Adjustment Of Insulin Injections By Paediatric Diabetes Specialist Nurses/Community Paediatric Nurses Diabetes Working With Children Within NHS Grampian Co-ordinators: Lead Paediatric Diabetes
Policy For The Adjustment Of Insulin Injections By Paediatric Diabetes Specialist Nurses/Community Paediatric Nurses Diabetes Working With Children Within NHS Grampian Co-ordinators: Lead Paediatric Diabetes
Document Details Patient Group Direction Hepatitis A vaccine (Havrix Monodose ) Trust Ref No Local Ref (optional) Main points the
 Document Details Title Patient Group Direction Hepatitis A vaccine (Havrix Monodose ) Trust Ref No 1506-41174 Local Ref (optional) Main points the Active immunisation against infection caused by Hepatitis
Document Details Title Patient Group Direction Hepatitis A vaccine (Havrix Monodose ) Trust Ref No 1506-41174 Local Ref (optional) Main points the Active immunisation against infection caused by Hepatitis
KEEPING SAFE WITH INSULIN THERAPY
 KEEPING SAFE WITH INSULIN THERAPY kk WHY IS THIS LEAFLET FOR YOU? Insulin treatment improves the quality of life in many people and saves the lives of others. It is used to lower blood glucose levels.
KEEPING SAFE WITH INSULIN THERAPY kk WHY IS THIS LEAFLET FOR YOU? Insulin treatment improves the quality of life in many people and saves the lives of others. It is used to lower blood glucose levels.
Blood Glucose and Hyperglycaemia Management in Hospital for Adults with Diabetes Clinical Guideline V2.0. March 2018
 Blood Glucose and Hyperglycaemia Management in Hospital for Adults with Diabetes Clinical Guideline V2.0 March 2018 Page 1 of 8 Summary flow chart for monitoring of blood glucose if >11mmol/L For Adults
Blood Glucose and Hyperglycaemia Management in Hospital for Adults with Diabetes Clinical Guideline V2.0 March 2018 Page 1 of 8 Summary flow chart for monitoring of blood glucose if >11mmol/L For Adults
Patient Group Directions Policy
 Patient Group Directions Policy Category: Summary: Equality Analysis undertaken: Valid From: Date of Next Review: Approval Date/ Via: Distribution: Related Documents: Author(s): Further Information: This
Patient Group Directions Policy Category: Summary: Equality Analysis undertaken: Valid From: Date of Next Review: Approval Date/ Via: Distribution: Related Documents: Author(s): Further Information: This
Pre-Dialysis Insulin Information for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes receiving haemodialysis
 Pre-Dialysis Insulin Information for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes receiving haemodialysis Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered 2 This leaflet is for patients with Type 2 diabetes who require insulin
Pre-Dialysis Insulin Information for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes receiving haemodialysis Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered 2 This leaflet is for patients with Type 2 diabetes who require insulin
PATIENT INFORMATION. D iabetes. What You Need to Know About. Insulin
 PATIENT INFORMATION Medicine To Treat: D iabetes What You Need to Know About Insulin INTRODUCTION The insulin preparations currently available in Singapore are mostly from human origin; pork or bovine
PATIENT INFORMATION Medicine To Treat: D iabetes What You Need to Know About Insulin INTRODUCTION The insulin preparations currently available in Singapore are mostly from human origin; pork or bovine
Medication Safety. Patient Safety. Setting Direction Julie Simmons, Medication Safety Pharmacist January 2016
 Medication Safety Patient Safety Setting Direction Julie Simmons, Medication Safety Pharmacist January 2016 1 The patient journey Admission Ward Transfer Ward stay Discharge Medication storage and supply
Medication Safety Patient Safety Setting Direction Julie Simmons, Medication Safety Pharmacist January 2016 1 The patient journey Admission Ward Transfer Ward stay Discharge Medication storage and supply
THE RESPONSIBLE PHARMACIST REGULATIONS
 THE RESPONSIBLE PHARMACIST REGULATIONS A SUMMARY OF THE RESPONSES TO PUBLIC CONSULTATION ON PROPOSALS FOR THE CONTENT OF THE REGULATIONS DH INFORMATION READER BOX Policy HR / Workforce Management Planning
THE RESPONSIBLE PHARMACIST REGULATIONS A SUMMARY OF THE RESPONSES TO PUBLIC CONSULTATION ON PROPOSALS FOR THE CONTENT OF THE REGULATIONS DH INFORMATION READER BOX Policy HR / Workforce Management Planning
Document Details. Patient Group Direction
 Document Details Title Patient Group Direction (PGD) Hepatitis B Vaccine (Engerix ) Trust Ref No 1505-41182 Local Ref (optional) Main points the Immunisation against Hepatitis B document covers Who is
Document Details Title Patient Group Direction (PGD) Hepatitis B Vaccine (Engerix ) Trust Ref No 1505-41182 Local Ref (optional) Main points the Immunisation against Hepatitis B document covers Who is
Template Standard Operating Procedure For: Handling of Midazolam and other controlled drugs in Dental Practices
 Name of Dental Practice : Objectives To ensure implementation of the regulations and guidance on safe and secure handling of midazolam and other controlled drugs (CDs) Scope To cover all aspects of obtaining
Name of Dental Practice : Objectives To ensure implementation of the regulations and guidance on safe and secure handling of midazolam and other controlled drugs (CDs) Scope To cover all aspects of obtaining
Policy for Supporting. Children and Young People with. Diabetes in Education
 Policy for Supporting Children and Young People with Diabetes in Education December 2011 POLICY FOR SUPPORTING CHILDREN AND YOUNG PEOPLE WITH DIABETES IN EDUCATION Contents 1. Introduction 2. Before a
Policy for Supporting Children and Young People with Diabetes in Education December 2011 POLICY FOR SUPPORTING CHILDREN AND YOUNG PEOPLE WITH DIABETES IN EDUCATION Contents 1. Introduction 2. Before a
Trust Policy 218 Ionising Radiation Safety Policy
 Trust Policy 218 Ionising Radiation Safety Policy Purpose Date Version August 2016 7 To ensure that Plymouth Hospitals NHS Trust complies with all relevant legislation with regard to the use of ionising
Trust Policy 218 Ionising Radiation Safety Policy Purpose Date Version August 2016 7 To ensure that Plymouth Hospitals NHS Trust complies with all relevant legislation with regard to the use of ionising
Management of AIDS/HIV Infected Healthcare Workers Policy
 Management of AIDS/HIV Infected Healthcare Workers Policy DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 4 Ratified by: Corporate Policy Panel Date ratified: 20 July 2017 Name of originator/author: HR Manager Name of responsible
Management of AIDS/HIV Infected Healthcare Workers Policy DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 4 Ratified by: Corporate Policy Panel Date ratified: 20 July 2017 Name of originator/author: HR Manager Name of responsible
All Saints First School Administering of Medicines Policy
 All Saints First School Administering of Medicines Policy Success Indicators The following indicators will demonstrate the level of compliance with this policy and its procedures: a) Employees who are
All Saints First School Administering of Medicines Policy Success Indicators The following indicators will demonstrate the level of compliance with this policy and its procedures: a) Employees who are
This Diabetes Policy should be read in conjunction with the Dealing with Medical Conditions Policy of Auburn South Preschool.
 DIABETES POLICY Mandatory Quality Area 2 The content of this policy was developed for ELAA by advocacy and diabetes educators at Diabetes Australia Vic and the Royal Children s Hospital Melbourne s manager
DIABETES POLICY Mandatory Quality Area 2 The content of this policy was developed for ELAA by advocacy and diabetes educators at Diabetes Australia Vic and the Royal Children s Hospital Melbourne s manager
Guidelines for managing the health care needs of children and young persons with diabetes in education
 Guidelines for managing the health care needs of children and young persons with diabetes in education Contents Page: Page Number 1.0 Introduction 1 2.0 The Care Management Plan 2 2.1 Blood Glucose monitoring
Guidelines for managing the health care needs of children and young persons with diabetes in education Contents Page: Page Number 1.0 Introduction 1 2.0 The Care Management Plan 2 2.1 Blood Glucose monitoring
North of England Cancer Network. Policies and Procedures. Standards for the Safe Use of Oral Anticancer Medicines
 \ North of England Cancer Network Policies and Procedures Standards for the Safe Use of Oral Anticancer Medicines NECN Oral Anticancer medicine Policy version 1.6 Page 1 of 17 Issue Date: Feb 2017 Contents
\ North of England Cancer Network Policies and Procedures Standards for the Safe Use of Oral Anticancer Medicines NECN Oral Anticancer medicine Policy version 1.6 Page 1 of 17 Issue Date: Feb 2017 Contents
Developed By Name Signature Date
 Patient Group Direction 2155 version 2.0 Administration / Supply of Inhaled Salbutamol in Asthma by Registered Practitioners employed by Torbay and South Devon NHS Foundation Trust Date of Introduction:
Patient Group Direction 2155 version 2.0 Administration / Supply of Inhaled Salbutamol in Asthma by Registered Practitioners employed by Torbay and South Devon NHS Foundation Trust Date of Introduction:
Case scenarios: Patient Group Directions
 Putting NICE guidance into practice Case scenarios: Patient Group Directions Implementing the NICE guidance on Patient Group Directions (MPG2) Published: March 2014 [updated March 2017] These case scenarios
Putting NICE guidance into practice Case scenarios: Patient Group Directions Implementing the NICE guidance on Patient Group Directions (MPG2) Published: March 2014 [updated March 2017] These case scenarios
Advanced Preparation of Insulin Syringes for Adult Patients to Administer at Home
 Advanced Preparation of Insulin Syringes for Adult Patients to Administer at Home Guidance for nurses Third edition CLINICAL PROFESSIONAL RESOURCE ADVANCED PREPARATION OF INSULIN SYRINGES FOR ADULT PATIENTS
Advanced Preparation of Insulin Syringes for Adult Patients to Administer at Home Guidance for nurses Third edition CLINICAL PROFESSIONAL RESOURCE ADVANCED PREPARATION OF INSULIN SYRINGES FOR ADULT PATIENTS
Olanzapine Long-Acting Injection (Zypadhera ) - Guidelines for Prescribing and Administration (Version 3 May 2015)
 1. Key Points Olanzapine Long-Acting Injection (Zypadhera ) - Guidelines for Prescribing and Administration (Version 3 May 2015) 1.1 Olanzapine long acting injection (LAI) is indicated for the maintenance
1. Key Points Olanzapine Long-Acting Injection (Zypadhera ) - Guidelines for Prescribing and Administration (Version 3 May 2015) 1.1 Olanzapine long acting injection (LAI) is indicated for the maintenance
OWNER MANUAL Diabetes in Cats
 www.mypetonline.co.uk/petdiabetes OWNER MANUAL Diabetes in Cats DIABETES IN CATS What is Diabetes? Glucose (blood sugar) is derived from the food your cat eats and provides the energy body cells need to
www.mypetonline.co.uk/petdiabetes OWNER MANUAL Diabetes in Cats DIABETES IN CATS What is Diabetes? Glucose (blood sugar) is derived from the food your cat eats and provides the energy body cells need to
INSULIN INJECTION KNOW-HOW
 0-1- INSULIN INJECTION KNOW-HOW Learning how to Congratulations for making the move to insulin therapy. It won t be long before you start enjoying better blood sugar control, more energy, and a host of
0-1- INSULIN INJECTION KNOW-HOW Learning how to Congratulations for making the move to insulin therapy. It won t be long before you start enjoying better blood sugar control, more energy, and a host of
Diabetes Emergency Caesarean section or other unplanned surgery (GL822)
 Diabetes Emergency Caesarean section or other unplanned surgery (GL822) i.e. insulin dependent diabetic having unplanned surgery e.g. a diabetic woman with pre-labour SROM prior to elective Caesarean section.
Diabetes Emergency Caesarean section or other unplanned surgery (GL822) i.e. insulin dependent diabetic having unplanned surgery e.g. a diabetic woman with pre-labour SROM prior to elective Caesarean section.
Falls The Assessment, Prevention and Management of Patient Falls (Adult Services) 1.34
 SECTION: 1 PATIENT CARE Including Physical Healthcare POLICY /PROCEDURE: 1.34 NATURE AND SCOPE: SUBJECT (Title): POLICY AND PROCEDURE - TRUST WIDE FALLS: THE ASSESSMENT, PREVENTION AND MANAGEMENT OF PATIENT
SECTION: 1 PATIENT CARE Including Physical Healthcare POLICY /PROCEDURE: 1.34 NATURE AND SCOPE: SUBJECT (Title): POLICY AND PROCEDURE - TRUST WIDE FALLS: THE ASSESSMENT, PREVENTION AND MANAGEMENT OF PATIENT
Workplace Drug and Alcohol Policy
 Workplace Drug and Alcohol Policy January 2017 This Drug and Alcohol Policy is intended for and includes but is not limited to all Students, Contractors and all others either directly or indirectly engaged
Workplace Drug and Alcohol Policy January 2017 This Drug and Alcohol Policy is intended for and includes but is not limited to all Students, Contractors and all others either directly or indirectly engaged
The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust. Pre-filled Patient Controlled Analgesia (PCA) syringes
 The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Pre-filled Patient Controlled Analgesia (PCA) syringes Version.: 2.2 Effective From: 1 June 2016 Expiry Date: 1 June 2019 Date Ratified: 20 April
The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Pre-filled Patient Controlled Analgesia (PCA) syringes Version.: 2.2 Effective From: 1 June 2016 Expiry Date: 1 June 2019 Date Ratified: 20 April
Draft Guidance for Pharmacists on Extemporaneous Dispensing. Version 1
 1. Introduction Draft Guidance for Pharmacists on Extemporaneous Dispensing Version 1 The purpose of this guidance is to assist pharmacists in discharging their legal and professional obligations to patients
1. Introduction Draft Guidance for Pharmacists on Extemporaneous Dispensing Version 1 The purpose of this guidance is to assist pharmacists in discharging their legal and professional obligations to patients
Medicines Optimisation Team Standard Operating Procedure Insulin Quantities Audit
 Medicines Optimisation Team Standard Operating Procedure Insulin Quantities Audit Aim Review and rationalise the insulin quantities based on dosage instructions for diabetic patients in order to align
Medicines Optimisation Team Standard Operating Procedure Insulin Quantities Audit Aim Review and rationalise the insulin quantities based on dosage instructions for diabetic patients in order to align
A patient guide to the use of insulin for diabetes
 A patient guide to the use of insulin for diabetes Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
A patient guide to the use of insulin for diabetes Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Initiation of Clozapine Treatment Community Patients
 Initiation of Clozapine Treatment Community Patients Who Should Read This Policy Target Audience All clinical staff working in the community N/A N/A Initiation of Clozapine Treatment for Patients in the
Initiation of Clozapine Treatment Community Patients Who Should Read This Policy Target Audience All clinical staff working in the community N/A N/A Initiation of Clozapine Treatment for Patients in the
DIABETES POLICY. Mandatory Quality Area 2
 DIABETES POLICY Mandatory Quality Area 2 PURPOSE To ensure that enrolled children with type 1 diabetes and their families are supported, while children are being educated and cared for by the service.
DIABETES POLICY Mandatory Quality Area 2 PURPOSE To ensure that enrolled children with type 1 diabetes and their families are supported, while children are being educated and cared for by the service.
CHEMOTHERAPY NETWORK GROUP POLICY FOR ADMINISTRATION OF CYTOTOXIC CHEMOTHERAPY
 CHEMOTHERAPY NETWORK GROUP POLICY FOR ADMINISTRATION OF CYTOTOXIC CHEMOTHERAPY Version 4.0 March 2016 Review date March 2018 Introduction It is the purpose of this policy to provide clear guidelines that
CHEMOTHERAPY NETWORK GROUP POLICY FOR ADMINISTRATION OF CYTOTOXIC CHEMOTHERAPY Version 4.0 March 2016 Review date March 2018 Introduction It is the purpose of this policy to provide clear guidelines that
Medicines Optimisation Strategy
 Clinical Reducing Dosing Errors with Opioid Medicines (Controlled Drug SOP): Document Control Summary Status: Version: Author/Owner/Title: Approved by: Ratified: Related Trust Strategy and/or Strategic
Clinical Reducing Dosing Errors with Opioid Medicines (Controlled Drug SOP): Document Control Summary Status: Version: Author/Owner/Title: Approved by: Ratified: Related Trust Strategy and/or Strategic
BEST 4 Diabetes. Optimisation of insulin module
 BEST 4 Diabetes Optimisation of insulin module Confidence and competence Where would you rate yourself? Why do all of our patient not achieve optimal blood glucose control? Insulin Therapy Goals and Purpose
BEST 4 Diabetes Optimisation of insulin module Confidence and competence Where would you rate yourself? Why do all of our patient not achieve optimal blood glucose control? Insulin Therapy Goals and Purpose
Brook Green Centre for Learning. Policy and Guidance for Supporting Pupils with Medical Needs
 Brook Green Centre for Learning Policy and Guidance for Supporting Pupils with Medical Needs This document was written in line with recommendations made in the DfE s information pack Supporting Pupils
Brook Green Centre for Learning Policy and Guidance for Supporting Pupils with Medical Needs This document was written in line with recommendations made in the DfE s information pack Supporting Pupils
Ionising Radiation Policy
 Ionising Radiation Policy CONTENTS 1. University Policy. 2. Procedures / Guidance. 2.1 Responsibilities of the Deans of Schools and/or Heads of Departments 2.2 Radiation Protection Advisor / Radiation
Ionising Radiation Policy CONTENTS 1. University Policy. 2. Procedures / Guidance. 2.1 Responsibilities of the Deans of Schools and/or Heads of Departments 2.2 Radiation Protection Advisor / Radiation
SAFE HANDLING OF VACCINES
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE SAFE HANDLING OF VACCINES Issue History Issue Version One Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date To ensure vaccines are stored in accordance with manufacturers
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE SAFE HANDLING OF VACCINES Issue History Issue Version One Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date To ensure vaccines are stored in accordance with manufacturers
BEST 4 Diabetes. Optimisation of insulin module
 BEST 4 Diabetes Optimisation of insulin module Confidence and competence Where would you rate yourself? Why do all of our patient not achieve optimal blood glucose control? Insulin Therapy Goals and Purpose
BEST 4 Diabetes Optimisation of insulin module Confidence and competence Where would you rate yourself? Why do all of our patient not achieve optimal blood glucose control? Insulin Therapy Goals and Purpose
Insulin Management. By Susan Henry Diabetes Specialist Nurse
 Insulin Management By Susan Henry Diabetes Specialist Nurse The Discovery of Insulin - 1921 - Banting & Best University Of Toronto Discovered hormone insulin in pancreatic extract of dog - Marjorie the
Insulin Management By Susan Henry Diabetes Specialist Nurse The Discovery of Insulin - 1921 - Banting & Best University Of Toronto Discovered hormone insulin in pancreatic extract of dog - Marjorie the
National Diabetes Inpatient Audit (NaDIA) 2016
 National Diabetes Inpatient Audit (NaDIA) 2016 DIABETES A summary report for people with diabetes and anyone interested in the quality of care for people with diabetes when they stay in hospital. Based
National Diabetes Inpatient Audit (NaDIA) 2016 DIABETES A summary report for people with diabetes and anyone interested in the quality of care for people with diabetes when they stay in hospital. Based
Guidance on Bulk Prescribing for Care Home Patients
 Guidance on Bulk Prescribing for Care Home Patients Introduction Many patients in care homes taking medicines when required (PRN) can inevitably present problems for the prescriber in determining the quantity
Guidance on Bulk Prescribing for Care Home Patients Introduction Many patients in care homes taking medicines when required (PRN) can inevitably present problems for the prescriber in determining the quantity
A three month project September December 2016
 Improving Insulin Safety in the Clinical Decision Unit A three month project September December 2016 Sarah Gregory - In-Patient DSN, QEQM Hospital Julie Gammon - Ward Manager, CDU, QEQM Hospital 1 The
Improving Insulin Safety in the Clinical Decision Unit A three month project September December 2016 Sarah Gregory - In-Patient DSN, QEQM Hospital Julie Gammon - Ward Manager, CDU, QEQM Hospital 1 The
Community Psychiatric Nurse. Consultant Psychiatrist, Substance Misuse Services
 PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION (PGD) FOR THE ADMINISTRATION OF HEPATITIS A VACCINE (HAVRIX MONODOSE VACCINE) BY REGISTERED NURSES WORKING IN THE COMMUNITY SUBSTANCE MISUSE TEAMS Version Number : 2 Patient Group
PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION (PGD) FOR THE ADMINISTRATION OF HEPATITIS A VACCINE (HAVRIX MONODOSE VACCINE) BY REGISTERED NURSES WORKING IN THE COMMUNITY SUBSTANCE MISUSE TEAMS Version Number : 2 Patient Group
Developed By Name Signature Date
 Patient Group Direction 2156 version 2.0 Administration of Ipratropium 250mcg/ml Nebuliser Solution in Acute Asthma by Registered Practitioners employed by Torbay and South Devon NHS Foundation Date of
Patient Group Direction 2156 version 2.0 Administration of Ipratropium 250mcg/ml Nebuliser Solution in Acute Asthma by Registered Practitioners employed by Torbay and South Devon NHS Foundation Date of
A quick guide to diabetes for people changing from tablets to insulin (type 2 diabetes) Diabetes and Endocrinology Patient Information Leaflet
 A quick guide to diabetes for people changing from tablets to insulin (type 2 diabetes) Diabetes and Endocrinology Patient Information Leaflet What is diabetes? Diabetes is a condition where the amount
A quick guide to diabetes for people changing from tablets to insulin (type 2 diabetes) Diabetes and Endocrinology Patient Information Leaflet What is diabetes? Diabetes is a condition where the amount
DIABETES POLICY. Templeton Primary School strives to ensure the safety and wellbeing of children who are diagnosed with diabetes, and committed to:
 DIABETES POLICY Rationale Templeton Primary School strives to ensure the safety and wellbeing of children who are diagnosed with diabetes, and committed to: providing a safe and healthy environment in
DIABETES POLICY Rationale Templeton Primary School strives to ensure the safety and wellbeing of children who are diagnosed with diabetes, and committed to: providing a safe and healthy environment in
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET MEDICINE TO TREAT: DIABETES. Insulin
 PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET MEDICINE TO TREAT: DIABETES Insulin This medicine has been proven to be safe and effective, but it can cause serious injury if a mistake happens while taking it. This means
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET MEDICINE TO TREAT: DIABETES Insulin This medicine has been proven to be safe and effective, but it can cause serious injury if a mistake happens while taking it. This means
PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION (PGD)
 PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION (PGD) SUPPLY OF NALOXONE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION BY REGISTERED NURSES TO CLIENTS BEING RELEASED FROM HMP FORD Version Number: 01HMP Patient Group Direction originally drawn up by:
PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION (PGD) SUPPLY OF NALOXONE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION BY REGISTERED NURSES TO CLIENTS BEING RELEASED FROM HMP FORD Version Number: 01HMP Patient Group Direction originally drawn up by:
WEST COAST DISTRICT MUNICIPALITY SUBSTANCE ABUSE POLICY
 WEST COAST DISTRICT MUNICIPALITY SUBSTANCE ABUSE POLICY POLICY CONTROL SHEET POLICY TITLE : Substance Abuse Policy POLICY CUSTODIAN : West Coast District Municipality POLICY AUTHOR : H Brand LLF CONSULTATION
WEST COAST DISTRICT MUNICIPALITY SUBSTANCE ABUSE POLICY POLICY CONTROL SHEET POLICY TITLE : Substance Abuse Policy POLICY CUSTODIAN : West Coast District Municipality POLICY AUTHOR : H Brand LLF CONSULTATION
FREEHOLD REGIONAL HIGH SCHOOL DISTRICT. Parents/Guardian of
 FREEHOLD REGIONAL HIGH SCHOOL DISTRICT Parents/Guardian of In order to comply with N.J.S.A. 18A:40-12.11-21, which addresses the care of the diabetic student in the school setting, the attached packet
FREEHOLD REGIONAL HIGH SCHOOL DISTRICT Parents/Guardian of In order to comply with N.J.S.A. 18A:40-12.11-21, which addresses the care of the diabetic student in the school setting, the attached packet
Protocol (Clinical) Country Health SA Local Health Network. Title: Subcutaneous Insulin Administration in Hospital and Aged Care
 Protocol (Clinical) Title: Subcutaneous Insulin Administration in Hospital and Aged Care Protocol developed by: CHSALHN Diabetes Service Protocol Sponsor: CHSALHN, Executive Director, Medical Services
Protocol (Clinical) Title: Subcutaneous Insulin Administration in Hospital and Aged Care Protocol developed by: CHSALHN Diabetes Service Protocol Sponsor: CHSALHN, Executive Director, Medical Services
Standard operating procedures for preparation and administration of intramuscular injections. No Action Rationale
 Standard operating procedures for preparation and administration of intramuscular injections Preparation Overview No Action Rationale 1 Collect and check all equipment 2 Check that the packaging of all
Standard operating procedures for preparation and administration of intramuscular injections Preparation Overview No Action Rationale 1 Collect and check all equipment 2 Check that the packaging of all
Table of Contents. Title: Drugs Policy Page 2 of 7
 Drugs Policy Table of Contents Statement of Intent... 3 1. Introduction... 3 2. Academy Ethos... 3 3. Drug Education... 4 3.1 Aims of drug education:... 4 3.2 Planned drug education... 4 3.3 Inviting outside
Drugs Policy Table of Contents Statement of Intent... 3 1. Introduction... 3 2. Academy Ethos... 3 3. Drug Education... 4 3.1 Aims of drug education:... 4 3.2 Planned drug education... 4 3.3 Inviting outside
Things you need to know about injections
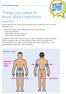 www.trend-uk.org Things you need to know about injections Injection sites: You can see from the picture below the best sites for injecting insulin or GLP-1 medications are: Back of the upper arms (difficult
www.trend-uk.org Things you need to know about injections Injection sites: You can see from the picture below the best sites for injecting insulin or GLP-1 medications are: Back of the upper arms (difficult
Policy: S5 Smoke Free Policy
 Policy: S5 Smoke Free Policy Version: S5/15 Ratified by: Trust Management Team Date ratified: 3 rd June 2015 Title of Author: Clinical Services Manager/Specialist & Forensic Title of responsible Executive
Policy: S5 Smoke Free Policy Version: S5/15 Ratified by: Trust Management Team Date ratified: 3 rd June 2015 Title of Author: Clinical Services Manager/Specialist & Forensic Title of responsible Executive
Adminstration of Insulin to Patients at Home and in Community Hospitals
 1929 Version 2 The Administration of Insulin to patients at home and in Community Hospitals Date: 26 January 2017 Adminstration of Insulin to Patients at Home and in Community Hospitals Page 1 of 7 Partners
1929 Version 2 The Administration of Insulin to patients at home and in Community Hospitals Date: 26 January 2017 Adminstration of Insulin to Patients at Home and in Community Hospitals Page 1 of 7 Partners
Policy for the Provision of Insulin Pumps for Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
 Policy for the Provision of Insulin Pumps for Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Version No. Changes Made Version of July 2018 V0.5 Changes made to the policy following patient engagement including: - the
Policy for the Provision of Insulin Pumps for Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Version No. Changes Made Version of July 2018 V0.5 Changes made to the policy following patient engagement including: - the
Document Details. Ibuprofen 200mg tablets and Ibuprofen oral liquid 100mg in 5ml
 Title Document Details Patient Group Direction (PGD) Ibuprofen 200mg tablets and Ibuprofen oral liquid 100mg in 5ml Trust Ref No 1445-36348 Local Ref (optional) Main points the document The treatment of
Title Document Details Patient Group Direction (PGD) Ibuprofen 200mg tablets and Ibuprofen oral liquid 100mg in 5ml Trust Ref No 1445-36348 Local Ref (optional) Main points the document The treatment of
Good Practice Guidance on Covert Administration of Medication
 Good Practice Guidance on Covert Administration of Medication This good practice guidance is intended to be used as a framework for care home managers and domiciliary care providers in drawing up their
Good Practice Guidance on Covert Administration of Medication This good practice guidance is intended to be used as a framework for care home managers and domiciliary care providers in drawing up their
Core Competencies Clinical Psychology A Guide
 Committee for Scrutiny of Individual Clinical Qualifications Core Competencies Clinical Psychology A Guide Please read this booklet in conjunction with other booklets and forms in the application package
Committee for Scrutiny of Individual Clinical Qualifications Core Competencies Clinical Psychology A Guide Please read this booklet in conjunction with other booklets and forms in the application package
Patient Group Directions (PGDs)
 Patient Group Directions (PGDs) Document level: Trustwide (TW) Code: MP2 Issue number: 4 Lead executive Authors details Type of document Target audience Document purpose Medical Director Senior Clinical
Patient Group Directions (PGDs) Document level: Trustwide (TW) Code: MP2 Issue number: 4 Lead executive Authors details Type of document Target audience Document purpose Medical Director Senior Clinical
Guideline for the Rational Use of Controlled Drugs
 Guideline for the Rational Use of Controlled Drugs Ministry of Health Male' Republic of Maldives April 2000 Table of Contents Page Introduction.. 2 1. Procurement and Supply of Controlled Drugs 3 1.1 Import
Guideline for the Rational Use of Controlled Drugs Ministry of Health Male' Republic of Maldives April 2000 Table of Contents Page Introduction.. 2 1. Procurement and Supply of Controlled Drugs 3 1.1 Import
concentrate intravenous solution and other strong potassium solutions
 Policy for the use of potassium chloride concentrate intravenous solution and other strong potassium solutions CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Policy for the use of potassium chloride Title: concentrate intravenous
Policy for the use of potassium chloride concentrate intravenous solution and other strong potassium solutions CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Policy for the use of potassium chloride Title: concentrate intravenous
Smoke Free Policy. Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version. Policy Group. Author Version no 3.0
 Smoke Free Policy Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version Policy Group DOCUMENT CONTROL POLICY NO Smoke Free Grounds Author Version no 3.0 Reviewer Smoke Free Working Group Implementation
Smoke Free Policy Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version Policy Group DOCUMENT CONTROL POLICY NO Smoke Free Grounds Author Version no 3.0 Reviewer Smoke Free Working Group Implementation
PROCEDURE REF NO SABP/EXECUTIVE BOARD/0017
 PROCEDURE REF NO SABP/EXECUTIVE BOARD/0017 NAME OF PROCEDURE: Medicines Procedure: Patient Group Directions for the Administration of Hepatitis B Vaccine for SABP Drug and Alcohol Teams. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE:
PROCEDURE REF NO SABP/EXECUTIVE BOARD/0017 NAME OF PROCEDURE: Medicines Procedure: Patient Group Directions for the Administration of Hepatitis B Vaccine for SABP Drug and Alcohol Teams. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE:
Working in Partnership to meet the Childcare Need A Toolkit to support schools and providers / childminders in the provision of out of school care
 ACTION FOR CHILDREN Working in Partnership to meet the Childcare Need A Toolkit to support schools and providers / childminders in the provision of out of school care This toolkit is designed as a step
ACTION FOR CHILDREN Working in Partnership to meet the Childcare Need A Toolkit to support schools and providers / childminders in the provision of out of school care This toolkit is designed as a step
Day care and childminding: Guidance to the National Standards
 raising standards improving lives Day care and childminding: Guidance to the National Standards Revisions to certain criteria October 2005 Reference no: 070116 Crown copyright 2005 Reference no: 070116
raising standards improving lives Day care and childminding: Guidance to the National Standards Revisions to certain criteria October 2005 Reference no: 070116 Crown copyright 2005 Reference no: 070116
making a referral for breast imaging Standard Operating Procedure
 Document Control Title Reporting Radiographer Author Directorate Surgery Date Version Issued 0.1 May 2016 Status Draft Author s job title Reporting Radiographer Department Breast Imaging Comment / Changes
Document Control Title Reporting Radiographer Author Directorate Surgery Date Version Issued 0.1 May 2016 Status Draft Author s job title Reporting Radiographer Department Breast Imaging Comment / Changes
Guidance for Pharmacists on Safe Supply of Oral Methotrexate
 Guidance for Pharmacists on Safe Supply of Oral Methotrexate Pharmaceutical Society of Ireland Version 2 January 2015 Contents 1. Introduction 2 2. Methotrexate 2 3. Guidance 2 3.1 Patient Review 2 3.2
Guidance for Pharmacists on Safe Supply of Oral Methotrexate Pharmaceutical Society of Ireland Version 2 January 2015 Contents 1. Introduction 2 2. Methotrexate 2 3. Guidance 2 3.1 Patient Review 2 3.2
NO SMOKING POLICY. Organisational
 NO SMOKING POLICY Policy Title State previous title where relevant. State if Policy New or Revised Policy Strand Org, HR, Clinical, H&S, Infection Control, Finance For clinical policies only - state index
NO SMOKING POLICY Policy Title State previous title where relevant. State if Policy New or Revised Policy Strand Org, HR, Clinical, H&S, Infection Control, Finance For clinical policies only - state index
Pharmacy Needle and Syringe Programme. Enhanced Contract
 Pharmacy Needle and Syringe Programme Enhanced Contract 1 st April 2012 31 st March 2013 Signed on behalf of LPC Signed on behalf of CRI Signed on behalf of Turning Point Signed on behalf of KCA Signed
Pharmacy Needle and Syringe Programme Enhanced Contract 1 st April 2012 31 st March 2013 Signed on behalf of LPC Signed on behalf of CRI Signed on behalf of Turning Point Signed on behalf of KCA Signed
Workplace Drug and Alcohol Policy
 1. Aim Workplace Drug and Alcohol Policy 1.1 Indigenous Consumer Assistance Network Ltd ( ICAN ) is committed to providing a safe and healthy work environment in which all workers are treated fairly, with
1. Aim Workplace Drug and Alcohol Policy 1.1 Indigenous Consumer Assistance Network Ltd ( ICAN ) is committed to providing a safe and healthy work environment in which all workers are treated fairly, with
Types of insulin. Your blood glucose levels. Types of insulin
 Different types of insulin are available for people with diabetes. If you need insulin, you and your diabetes team will look at the options and decide which type fits best with your lifestyle and blood
Different types of insulin are available for people with diabetes. If you need insulin, you and your diabetes team will look at the options and decide which type fits best with your lifestyle and blood
CHAPTER NINE INSULIN AND GLUCAGON ADMINISTRATION
 CHAPTER NINE INSULIN AND GLUCAGON ADMINISTRATION SECTION I PURPOSE AND AUTHORITY A. REGULATORY AUTHORITY 1. These rules shall be known as the Arkansas Department of Education and Arkansas State Board of
CHAPTER NINE INSULIN AND GLUCAGON ADMINISTRATION SECTION I PURPOSE AND AUTHORITY A. REGULATORY AUTHORITY 1. These rules shall be known as the Arkansas Department of Education and Arkansas State Board of
Acknowledgement goes to WHO for use of their hand washing technique
 How to administer third party insulin injections safely with a pen device, safety pen needle and syringe 1 Hand washing It takes at least 15 seconds to wash your hands. This is about how long it takes
How to administer third party insulin injections safely with a pen device, safety pen needle and syringe 1 Hand washing It takes at least 15 seconds to wash your hands. This is about how long it takes
Niki Robinson, Mandy Clements
 Realities of launching the ThinkGlucose programme at a district general hospital Niki Robinson, Mandy Clements Article points 1. The ThinkGlucose programme was piloted on two wards at a district general
Realities of launching the ThinkGlucose programme at a district general hospital Niki Robinson, Mandy Clements Article points 1. The ThinkGlucose programme was piloted on two wards at a district general
Care Homes - Homely Remedies Protocol
 Care Homes - Homely Remedies Protocol A homely remedy is a medicine for the short-term treatment of a minor ailment, such as indigestion, a cough, mild to moderate pain or constipation, and can be obtained
Care Homes - Homely Remedies Protocol A homely remedy is a medicine for the short-term treatment of a minor ailment, such as indigestion, a cough, mild to moderate pain or constipation, and can be obtained
Patient Safety Alert NPSA/2011/PSA003 The adult patient s passport to safer use of insulin
 Patient Safety Alert NPSA/2011/PSA003 The adult patient s passport to safer use of insulin March 2011 Supporting Information Contents Page 1. About this document 2 2. Background 2 3. Scope 3 4. Review
Patient Safety Alert NPSA/2011/PSA003 The adult patient s passport to safer use of insulin March 2011 Supporting Information Contents Page 1. About this document 2 2. Background 2 3. Scope 3 4. Review
insulin and injections
 insulin and injections Insulin is a hormone made by the beta cells in the pancreas. Insulin allows sugar to go from the bloodstream into the body s cells and be used for energy. Insulin lowers blood sugar.
insulin and injections Insulin is a hormone made by the beta cells in the pancreas. Insulin allows sugar to go from the bloodstream into the body s cells and be used for energy. Insulin lowers blood sugar.
