Diabetes Mellitus in Small Animals
|
|
|
- Claire Coleen Quinn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Diabetes Mellitus in Small Animals Julie A Stephens, DVM, DACVIM Veterinary Emergency And Specialty Center of New Mexico Albuquerque, New Mexico
2 Diabetes Mellitus Persistent hyperglycemia caused by a relative or absolute insulin deficiency Not a single disease but a syndrome that results in hyperglycemia Defects in insulin secretion Defects in insulin sensitivity
3 Insulin Produced by β-cells of the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas Associated with energy abundance Binds to insulin receptor on it s target cell Enzyme linked receptor Binds to alpha subunits outside the cell Beta subunits become autophosphorylated >> activates local tyrosine kinase >>phosphorylation of insulin-receptor substrates [IRS] Different IRS are expressed in different tissues Increases uptake of glucose Muscle cells Adipose tissue NOT neurons in the brain
4 Insulin Glucose transport within seconds Translocation of multiple intracellular vesicles which contain multiple molecules of glucose transport proteins to the cell membrane Glucose transport proteins bind to cell membrane and facilitate uptake of glucose into the cells When insulin is no longer available vesicles separate from the cell membrane within 3-5 minutes >> move intracellularly and are reused Cell membrane permeable to amino acids, potassium and phosphate ions Move intracellularly Slower effects In minutes, changes activity of intracellular metabolism via phosphorylation of enzymes Over hours to days, changes translation of mrna in ribosomes and transcription of DNA in the nucleus of the cells >> molds cellular enzymes activity to achieve metabolic effects
5 Carbohydrate Metabolism Cause rapid secretion of insulin once in the blood stream Muscles During rest, use fatty acids for energy During moderate to heavy exercise, muscle contraction increased translocation of GLUT 4 from intracellular stores >> facilitates diffusion of glucose into the muscle cell Few hours after meals, high insulin secretion causes rapid transport of glucose into muscle cells >> can be stored as glycogen in the muscle cell and used later for energy
6 Carbohydrate Metabolism Liver Insulin causes storage of glucose as glycogen Inactivates liver phosphorylation >> prevent break down of glycogen Enhances uptake of glucose by hepatocytes Increased activity of glucokinase [phosphorylates glucose>> taps it in the hepatocyte] Increases activity of enzymes that promote glycogen synthesis Glycogen synthase Decreased insulin Reverses effect >> decreases glycogen synthesis and prevents further uptake of glucose by hepatocytes Increases splitting of glycogen into glucose [activates phosphorylase and glucose phosphatase enzymes] Insulin promotes conversion of excess glucose into fatty acids LVDL triglyceride production >> transported to adipose tissue
7 Carbohydrate Metabolism Most brain cells are permeable to glucose and can use glucose without the intermediation of insulin When blood glucose is very low >> hypoglycemic shock Progressive nervous irritability Fainting Seizures Coma
8 Fat Metabolism Increased transport of glucose into hepatocytes After glycogen concentration in the hepatocytes reaches 5-6%, further glycogen synthesis is inhibited Fatty acids synthesized >> transported in VLDL as triglycerides Insulin activates lipoprotein lipase in capillary walls Splits triglycerides back into fatty acids >> absorbed into adipocytes >> converted to triglycerides and stored as fat Insulin inhibits lipase Release of fatty acids from fat stores is inhibited Insulin promotes glucose transport into adipocytes Ultimately increases glycerol >> combines with fatty acids to form triglyceride
9 Fat Metabolism Insulin deficiency Lipase is strongly activated in the absence of insulin Hydrolysis of stored triglycerides >> release of fatty acids Fatty acids used for energy Increased conversation of fatty acids into cholesterol and phospholipids High cholesterol promotes development of atherosclerosis in people with DM Causes excess acetoacetic acid formation in the liver >> blood >> intracellularly >> energy [acetyl-coa] Lack of insulin also depresses utilization of acetoacetic acid in peripheral tissue >> acidosis Some acetoacetic acid gets converted to ketones bodies [βhydroxybutyric acid and acetone] >> ketosis
10 Protein Metabolism Insulin Stimulates transport of amino acids into cells Increases translation of mrna >> Promotes new protein synthesis Increases transcription of select DNA genetic sequences>> Promotes new protein synthesis Inhibits catabolism of proteins Diminishes normal degradation of protein in cellular lysosomes In hepatocytes, depresses the rate of gluconeogenesis [from amino acids] Insulin deficiency Increased protein degradation Amino acids used for energy Increased urea secretion by the kidneys Protein synthesis stops Weakness
11 Diabetes Mellitus Caused by Lack of insulin secretion Decreased sensitivity of the tissues to insulin Syndrome of impaired carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism Insulin deficiency or insulin resistance Results in increased blood glucose concentration Decreased cellular utilization of glucose Increased utilization of fat and protein
12 Diabetes Mellitus Blood glucose rises >> spillage of excessive glucose into the urine Polyuria [osmotic diuresis] High blood glucose >> cellular dehydration [osmotic pressure] Polydipsia Increased utilization of fats for energy Release of keto acids >> metabolic acidosis Rapid deep breathing pattern [Kussmal breathing] Depletion of body proteins Weight loss Asthenia [lack of energy] Polyphagia
13 Diagnosis Appropriate clinical signs PU/PD/PP Weight loss Persistent fasting hyperglycemia Glucosuria
14 Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 Deficiency of insulin production by pancreatic islet β-cells usually absolute deficiency Viral infection Autoimmune cell mediated Hereditary Typically occurs abruptly Over days to weeks Type 2 Usually relative insulin deficiency Resistance to metabolic effects of insulin Hyperinsulinemia due to target cell resistance Gradual onset Obesity Excessive glucocorticoids Excessive growth hormone [acromegaly] Pregnancy Autoantibodies/mutations to insulin receptor
15 Canine Type 1 most common Have been associations found between three specific haplotypes and DLA [MHC] genotypes in diabetes-prone breeds of dogs Pancreatitis Insulin resistance Hyperadrenocorticism Diabetogenic drugs pre-existing β-cell defect, islet pathology Steroids glucocorticoids, progestin Obesity does not play a significant role although does produce insulin resistance Gestational/diestrus induced diabetes mellitus Progesterone induced growth hormone secretion >> insulin resistance, carbohydrate intolerance Diabetic remission possible after resolution of diestrus
16 Feline Secretory failure Damaged pancreatic islet β-cells Amyloid deposition >>cytotoxicity>apoptosis Glucose toxicity Oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines?? Dependent on degree of hyperglycemia and duration of hyperglycemic state Lipid toxicity Increased fatty acids >> cell death Commonly Type 2 Insulin resistance cause by Obesity Decreased expression of GLUT4 transporter in muscle and fat Decreased adiponectin >>decreased insulin sensitivity, decreased anti-inflammatory Leptin modulates insulin sensitivity obese cats are leptin resistant Acromegaly* Diabetogenic drugs* - pre-existing β-cell defect, islet pathology Steroids glucocorticoids, progestin *Type 3 in the American Diabetes Association scheme
17 Complications of uncontrolled DM Canine Cataracts Long term complication days months or years Irreversible Lens induced uveitis Diabetic retinopathy Uncommon Diabetic nephropathy Occasionally reported Hypertension Incidence 46% (Struble, et al 1998) Feline Peripheral neuropathy
18 Prognosis Canine ~ 3 years average survival time High mortality rate un the first 6 months DKA Concurrent illness Owner unwillingness to treat If survive the first 6 months, average survival time is ~ 5 years Feline Variable If survive the first 6 months, average survival time is ~ 5 years
19 Treatment INDIVIDUALIZED THERAPY Goal good quality of life Reduce blood glucose to control PU/PD/PP and weight loss Prevent ketosis Avoid hypoglycemia
20 Treatment Canine Remission is not a goal Near euglycemia is not necessary Increases risk of hypoglycemia and its consequences
21 Treatment - Canine Vetsulin NPH Detemir very potent!!!! 0.1 unit/kg Very difficult to use in a small breed dog High risk for hypoglycemia Lack of ability to fine tune the dose Can get a specific diluent from manufacturer Glargine, PZI overall poor response Maybe useful in an individual patient
22 Diet - Canine Many specific diabetic diets available Majority are high fiber Remains to be proven that these diets offer a clinically significant advantage Choose a diet based on Comorbidity Palatability to individual patient Reliable intake of a steady amount of calories at regular intervals
23 Treatment - Feline Insulin Longer acting insulins: Glargine, PZI, Detemir Longer average duration of action >> improved glycemic control >> reduce glucotoxicity and lipotoxicity >> greater remission potential Oral hypoglycemic - not optimal if diabetic remission is a goal Glipizide Acarbose Addressing obesity if applicable
24 Diet - Feline Goals Improve metabolism Correct obesity Remove persistent hyperglycemia High protein Low carbohydrate Many specific diabetic diets available
25 Insulin Therapy
26 Type of Insulin & Brand Names Onset Peak Duration Rapid-Acting Lispro (Humalog) Aspart (Novolog) Glulisine (Apidra) Role in Blood Sugar Management min min 3-5 hours Rapid-acting insulin covers insulin needs for meals eaten at the same time as the injection. This type of insulin is min min. 3-5 hours often used with longer-acting insulin min min /2 hours Long-Acting Insulin glargine (Basaglar, Lantus, Toujeo) Insulin detemir (Levemir) 1-1 1/2 hours No peak time. Insulin is delivered at a steady level. 1-2 hours 6-8 hours Up to 24 hours hours Long-acting insulin covers insulin needs for about one full day. This type is often combined, when needed, with rapid- or short-acting insulin. Short-Acting Insulin degludec (Tresiba) min. No peak time 42 hours Regular (R) or novolin Velosulin (for use in the insulin pump) 30 min. -1 hour 30 min.-1 hour 2-5 hours 5-8 hours Short-acting insulin covers insulin needs for meals eaten within minutes. 1-2 hours 2-3 hours Pre-Mixed* Humulin 70/30 Novolin 70/30 30 min. 30 min. 2-4 hours 2-12 hours hours Up to 24 hours These products are generally taken two or three times a day before mealtime. Intermediate-Acting Novolog 70/ min. 1-4 hours Up to 24 hours NPH (N) 1-2 hours 4-12 hours hours Intermediate-acting insulin covers insulin needs for about half the day or overnight. This type of insulin is often combined with a rapid- or short-acting type. Humulin 50/50 Humalog mix 75/25 30 min. 2-5 hours hours 15 min. 30 min.-2 1/2 hours hours *Premixed insulins combine specific amounts of intermediate-acting and short-acting insulin in one bottle or insulin pen. (The numbers following the brand name indicate the percentage of each type of insulin.) from wedmd
27 Type of Insulin & Brand Names Onset Peak Duration Role in Blood Sugar Management Rapid-Acting Long-Acting Lispro (Humalog) Aspart (Novolog) min min 3-5 hours Rapid-acting insulin covers insulin needs for meals eaten at the same time as the injection. This type of insulin is min min. 3-5 hours often used with longer-acting insulin. *Insulin glargine (Basaglar, Lantus, Toujeo) 1-1 1/2 hours No peak time. Insulin is delivered at a steady level hours Long-acting insulin covers insulin needs for about one full day. This type is often combined, when needed, with rapid- or short-acting insulin. Glulisine (Apidra) min min /2 hours *Insulin detemir (Levemir) 1-2 hours 6-8 hours Up to 24 hours Short-Acting Insulin degludec (Tresiba) min. No peak time 42 hours *Regular (Humulin R, Novolin R) Velosulin (for use in the insulin pump) 30 min. -1 hour 30 min.-1 hour 2-5 hours 5-8 hours Short-acting insulin covers insulin needs for meals eaten within minutes. 1-2 hours 2-3 hours Pre-Mixed* Humulin 70/30 Novolin 70/30 30 min. 30 min. 2-4 hours 2-12 hours hours Up to 24 hours These products are generally taken two or three times a day before mealtime. Intermediate-Acting Novolog 70/ min. 1-4 hours Up to 24 hours *NPH (Humulin N, Novolin N) 1-2 hours 4-12 hours hours Intermediate-acting insulin covers insulin needs for about half the day or overnight. This type of insulin is often combined with a rapid- or short-acting type. Humulin 50/50 Humalog mix 75/25 30 min. 2-5 hours hours 15 min. 30 min.-2 1/2 hours hours *Premixed insulins combine specific amounts of intermediate-acting and short-acting insulin in one bottle or insulin pen. (The numbers following the brand name indicate the percentage of each type of insulin.) from wedmd
28 Type of Insulin & Brand Names Onset Peak Duration Rapid-Acting Role in Blood Sugar Management Long-Acting ProZinc Lispro (Humalog) Aspart (Novolog) min min min min. 3-5 hours 3-5 hours Rapid-acting insulin covers insulin needs for meals eaten at the same time as the injection. This type of insulin is often used with longer-acting insulin. *Insulin glargine (Basaglar, Lantus, Toujeo) 1-1 1/2 hours No peak time. Insulin is delivered at a steady level hours Long-acting insulin covers insulin needs for about one full day. This type is often combined, when needed, with rapid- or short-acting insulin. Glulisine (Apidra) Short-Acting *Regular (Humulin R, Novolin R) min min /2 hours 30 min. -1 hour 2-5 hours 5-8 hours Short-acting insulin covers insulin needs for meals eaten within minutes. *Insulin detemir (Levemir) Insulin degludec (Tresiba) min. Pre-Mixed* 1-2 hours 6-8 hours Up to 24 hours No peak time 42 hours Velosulin (for use in the insulin pump) Intermediate-Acting 30 min.-1 hour Vetsulin 1-2 hours 2-3 hours Humulin 70/30 Novolin 70/30 Novolog 70/30 30 min. 30 min. 2-4 hours 2-12 hours hours Up to 24 hours These products are generally taken two or three times a day before mealtime min. 1-4 hours Up to 24 hours *NPH (Humulin N, Novolin N) 1-2 hours 4-12 hours hours Intermediate-acting insulin covers insulin needs for about half the day or overnight. This type of insulin is often combined with a rapid- or short-acting type. Humulin 50/50 Humalog mix 75/25 30 min. 2-5 hours hours 15 min. 30 min.-2 1/2 hours hours *Premixed insulins combine specific amounts of intermediate-acting and short-acting insulin in one bottle or insulin pen. (The numbers following the brand name indicate the percentage of each type of insulin.) from wedmd
29 Insulin Cost NPH insulin Novolin N GoodRx: $ for pet Rx[$24-28] Humulin N GoodRx: $ for pet Rx[$100] Glargine Good Rx: $ for pet Rx [$184] Vetsulin Online pharmacies $36-43 ProZinc Online pharmacies $96-126
30 Monitoring Various tools available Clinical picture Level of PU/PD/PP Weight - loss or gain Spot check blood glucose Beware of stress hyperglycemia Good for revealing hypoglycemia, remission relapses Not recommended to use to make daily or inter-day dosage changes to insulin Glucose curves Glucose nadir Time to onset of action Duration of action of insulin
31 Monitoring Home urine glucose monitoring Negative urine glucose should trigger checking a blood glucose check Stress hyperglycemia can cause glucosuria Checking for remission relapses
32 Glucose curves Home blood glucose monitoring Increasingly popular Stress free environment More economical Aids in preventing hypoglycemia and promoting diabetic remission in cats Owner AND pet must be willing/able In clinic For patient who will not tolerate or owners that are uncomfortable/unable at home monitoring Stress hyperglycemia Continuous glucose monitors Can limit stress Cost device, probe/curve Requires calibrations with peripheral blood glucose 1-3 times/day
33
34
35 Rapid metabolism of insulin Somogyi
36
37 Monitoring Glycated proteins Fructosamine Sampling artifacts that lower Fructosamine Storage Lipemia Azotemia Hypoproteinemia Hypoglycemia-induced hyperglycemia will increase Fructosamine Concurrent disease that effect protein catabolism can lower Fructosamine Hyperthyroidism Glycosylated hemoglobin Ac1
38 Roary 4 year old castrated male DSH Lethargic Decreased appetite PE: normal vitals, normal rectal temperature CBC normal Biochemical profile Hyperglycemia 357 Hyponatremia 142 Hypercholesterolemia 490 UA 3+ glucosuria 3+ ketonuria WBC, RBC
39 Does this cat have Diabetes mellitus?
40 What treatment should we use?
41 What insulin should we use? Glargine OR PZI [ProZinc] insulin
42 Roary Treatments IVF, Cefazolin Glargine insulin 1 unit SQ q 24 hrs MD diet Day 1 Day 2 8am BG am BG am BG pm BG 266 Sent home on Glargine 2 u SQ q 12 hrs Amoxicillin for UTI
43 Roary 5 days after diagnosis lethargic again BG 419 Ketone days after diagnosis at ER clinic BG 633 Treated with an insulin CRI Regular insulin On day 8 after diagnosis Transition back to Glargine 2 u SQ 8 pm BG pm BG 364 Day 9 Day 10 2 am BG am BG am BG 428 Glargine 3 u SQ 11 am BG pm BG pm BG pm BG 583 Glargine 3 u SQ 11 pm BG 299 2am BG 85, 77 4 am BG 88 5 am BG 71 6 am BG am BG 12 pm BG pm BG Glargine 3 u SQ 6 pm BG pm BG 328 Glargine 1 u SQ
44 Roary Day am BG am BG am BG 598 Used combination of Glargine and Regular insulin Day 23 after diagnosis Owner did mini curve at home 9am BG 2 pm BG pm BG Glargine 3 u 7 pm BG pm BG 488 Glargine 3 u Discharged on Glargine 3 u SQ q12 hrs 7 am BG 269 Glargine 3 u
45 Roary Changed insulin dosing to Glargine 4 u SQ in am and 3 u SQ in pm
46 Feline Diabetic remission? Improve β-cell function Treating hyperglycemia in a timely manner Optimize glycemic control Cats that develop DM later in life Newly diagnosed DM that is treated effectively Cats with diabetic neuropathy less likely to achieve remission Reduced carbohydrate, high protein diet may help Consistent diet type and calorie intake most important for a more predictable insulin requirement
47 Summary Persistent hyperglycemia causes by relative or absolute insulin deficiency Insulin effects carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism Dogs generally have absolute insulin deficiency Cats generally have a relative insulin deficiency Treatment must be individualized Different treatment goals for dogs vs cats Monitoring must be individualized Technicians play a vital role in helping manage a diabetic patient
History of Investigation
 Acini - Pancreatic juice (1º) (2º) Secretions- neuronal and hormonal mechanisms 1) Secretin - bicarbonate rich 2) Cholecystokinin - enzyme rich Islets of Langerhans (contain 4 cell types) Alpha cells (α)-
Acini - Pancreatic juice (1º) (2º) Secretions- neuronal and hormonal mechanisms 1) Secretin - bicarbonate rich 2) Cholecystokinin - enzyme rich Islets of Langerhans (contain 4 cell types) Alpha cells (α)-
18. PANCREATIC FUNCTION AND METABOLISM. Pancreatic secretions ISLETS OF LANGERHANS. Insulin
 18. PANCREATIC FUNCTION AND METABOLISM ISLETS OF LANGERHANS Some pancreatic functions have already been discussed in the digestion section. In this one, the emphasis will be placed on the endocrine function
18. PANCREATIC FUNCTION AND METABOLISM ISLETS OF LANGERHANS Some pancreatic functions have already been discussed in the digestion section. In this one, the emphasis will be placed on the endocrine function
AACN PCCN Review. Endocrine
 AACN PCCN Review Endocrine Presenter: Carol A. Rauen, RN, MS, CCNS, CCRN, PCCN, CEN Independent Clinical Nurse Specialist & Education Consultant rauen.carol104@gmail.com Endocrine I. INTRODUCTION Disorders
AACN PCCN Review Endocrine Presenter: Carol A. Rauen, RN, MS, CCNS, CCRN, PCCN, CEN Independent Clinical Nurse Specialist & Education Consultant rauen.carol104@gmail.com Endocrine I. INTRODUCTION Disorders
Uncomplicated Diabetes Mellitus in Dogs Basics
 Glendale Animal Hospital 623-934-7243 www.familyvet.com Uncomplicated Diabetes Mellitus in Dogs Basics OVERVIEW Increased levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood (known as hyperglycemia ) when the dog has
Glendale Animal Hospital 623-934-7243 www.familyvet.com Uncomplicated Diabetes Mellitus in Dogs Basics OVERVIEW Increased levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood (known as hyperglycemia ) when the dog has
Hormonal Regulations Of Glucose Metabolism & DM
 Hormonal Regulations Of Glucose Metabolism & DM What Hormones Regulate Metabolism? What Hormones Regulate Metabolism? Insulin Glucagon Thyroid hormones Cortisol Epinephrine Most regulation occurs in order
Hormonal Regulations Of Glucose Metabolism & DM What Hormones Regulate Metabolism? What Hormones Regulate Metabolism? Insulin Glucagon Thyroid hormones Cortisol Epinephrine Most regulation occurs in order
associated with serious complications, but reduce occurrences with preventive measures
 Wk 9. Management of Clients with Diabetes Mellitus 1. Diabetes Mellitus body s inability to metabolize carbohydrates, fats, proteins hyperglycemia associated with serious complications, but reduce occurrences
Wk 9. Management of Clients with Diabetes Mellitus 1. Diabetes Mellitus body s inability to metabolize carbohydrates, fats, proteins hyperglycemia associated with serious complications, but reduce occurrences
Nph insulin conversion to lantus
 Nph insulin conversion to lantus Search 26-2-2003 RESPONSE FROM AVENTIS. We appreciate the opportunity to respond to Dr. Grajower s request for information regarding Lantus ( insulin glargine [rdna origin.
Nph insulin conversion to lantus Search 26-2-2003 RESPONSE FROM AVENTIS. We appreciate the opportunity to respond to Dr. Grajower s request for information regarding Lantus ( insulin glargine [rdna origin.
Diabetes, sugar. Greenville Veterinary Clinic LLC 409 E. Jamestown Rd. Greenville, PA (724)
 Greenville Veterinary Clinic LLC 409 E. Jamestown Rd. Greenville, PA 16125 (724) 588-5260 Feline diabetes mellitus Diabetes, sugar AffectedAnimals: Most diabetic cats are older than 10 years of age when
Greenville Veterinary Clinic LLC 409 E. Jamestown Rd. Greenville, PA 16125 (724) 588-5260 Feline diabetes mellitus Diabetes, sugar AffectedAnimals: Most diabetic cats are older than 10 years of age when
INSULIN THERAPY OPTIONS AND CASE STUDIES OF DIABETIC CATS AND DOGS. Jinelle Webb DVM, MSc, DVSc, DACVIM (SAIM)
 INSULIN THERAPY OPTIONS AND CASE STUDIES OF DIABETIC CATS AND DOGS Jinelle Webb DVM, MSc, DVSc, DACVIM (SAIM) MOVEH WOOF WALK 2017 Overview Pathophysiology Diagnosis Treatment Follow-up care, in-clinic
INSULIN THERAPY OPTIONS AND CASE STUDIES OF DIABETIC CATS AND DOGS Jinelle Webb DVM, MSc, DVSc, DACVIM (SAIM) MOVEH WOOF WALK 2017 Overview Pathophysiology Diagnosis Treatment Follow-up care, in-clinic
What systems are involved in homeostatic regulation (give an example)?
 1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS (Diabetes Mellitus Part 1): An Overview
1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS (Diabetes Mellitus Part 1): An Overview
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007
 Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA) Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA)
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA) Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA)
UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
 1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS An Overview WHAT IS HOMEOSTASIS? Homeostasis
1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS An Overview WHAT IS HOMEOSTASIS? Homeostasis
Diabetes in the Real World
 Diabetes in the Real World Diabetes Mellitus Common hormonal disorder of dogs and cats due to insufficient insulin being produced or cells not being able to respond to insulin Results in hyperglycaemia
Diabetes in the Real World Diabetes Mellitus Common hormonal disorder of dogs and cats due to insufficient insulin being produced or cells not being able to respond to insulin Results in hyperglycaemia
MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS
 MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS INVESTIGATIONS AND TREATMENT MANSI NAIK VII SEMESTER INVESTIGATIONS FASTING BLOOD SUGAR PLASMA GLUCOSE HEMOGLOBIN A 1c SYMPTOMS OF TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS Polyuria
MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS INVESTIGATIONS AND TREATMENT MANSI NAIK VII SEMESTER INVESTIGATIONS FASTING BLOOD SUGAR PLASMA GLUCOSE HEMOGLOBIN A 1c SYMPTOMS OF TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS Polyuria
INSULIN OVERVIEW. Type Brand Name Onset Peak Duration Role in glucose management Page Rapid-Acting lispro min. 3-5 hrs min.
 INSULIN OVERVIEW Type Brand Name Onset Peak Duration Role in glucose management Page Rapid-Acting lispro Humalog 15-30 min 30-90 min 3-5 hrs aspart glulisine Short-Acting Regular insulin NovoLog Apidra
INSULIN OVERVIEW Type Brand Name Onset Peak Duration Role in glucose management Page Rapid-Acting lispro Humalog 15-30 min 30-90 min 3-5 hrs aspart glulisine Short-Acting Regular insulin NovoLog Apidra
Combining Complex Pathophysiologic Concepts: Diabetes Mellitus
 Chapter 18 Combining Complex Pathophysiologic Concepts: Diabetes Mellitus KEY TERMS dawn phenomenon diabetes mellitus endocrine pancreas exocrine pancreas hyperglycemia hyperketonemia hypoglycemia insulin
Chapter 18 Combining Complex Pathophysiologic Concepts: Diabetes Mellitus KEY TERMS dawn phenomenon diabetes mellitus endocrine pancreas exocrine pancreas hyperglycemia hyperketonemia hypoglycemia insulin
Insulin Prior Authorization with optional Quantity Limit Program Summary
 Insulin Prior Authorization with optional Quantity Limit Program Summary 1-13,16-19, 20 FDA LABELED INDICATIONS Rapid-Acting Insulins Humalog (insulin lispro) NovoLog (insulin aspart) Apidra (insulin glulisine)
Insulin Prior Authorization with optional Quantity Limit Program Summary 1-13,16-19, 20 FDA LABELED INDICATIONS Rapid-Acting Insulins Humalog (insulin lispro) NovoLog (insulin aspart) Apidra (insulin glulisine)
Week 3 The Pancreas: Pancreatic ph buffering:
 Week 3 The Pancreas: A gland with both endocrine (secretion of substances into the bloodstream) & exocrine (secretion of substances to the outside of the body or another surface within the body) functions
Week 3 The Pancreas: A gland with both endocrine (secretion of substances into the bloodstream) & exocrine (secretion of substances to the outside of the body or another surface within the body) functions
I. General Considerations
 1 2 3 I. General Considerations A. Type I ( Juvenile Onset or IDDM) IDDM results from autoimmune destruction of beta cells inability to secrete insulin --> ketone formation --> DKA 4 Diabetic Ketoacidosis
1 2 3 I. General Considerations A. Type I ( Juvenile Onset or IDDM) IDDM results from autoimmune destruction of beta cells inability to secrete insulin --> ketone formation --> DKA 4 Diabetic Ketoacidosis
TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR DIABETES MELLITUS IN CATS AND DOGS. Jinelle Webb DVM, MSc, DVSc, DACVIM (SAIM)
 TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR DIABETES MELLITUS IN CATS AND DOGS Jinelle Webb DVM, MSc, DVSc, DACVIM (SAIM) Overview Pathophysiology Diagnosis Treatment Follow-up care, in-clinic & at-home monitoring Case examples
TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR DIABETES MELLITUS IN CATS AND DOGS Jinelle Webb DVM, MSc, DVSc, DACVIM (SAIM) Overview Pathophysiology Diagnosis Treatment Follow-up care, in-clinic & at-home monitoring Case examples
INSULIN IN THE OBESE PATIENT JACQUELINE THOMPSON RN, MAS, CDE SYSTEM DIRECTOR, DIABETES SERVICE LINE SHARP HEALTHCARE
 INSULIN IN THE OBESE PATIENT JACQUELINE THOMPSON RN, MAS, CDE SYSTEM DIRECTOR, DIABETES SERVICE LINE SHARP HEALTHCARE OBJECTIVES DESCRIBE INSULIN, INCLUDING WHERE IT COMES FROM AND WHAT IT DOES STATE THAT
INSULIN IN THE OBESE PATIENT JACQUELINE THOMPSON RN, MAS, CDE SYSTEM DIRECTOR, DIABETES SERVICE LINE SHARP HEALTHCARE OBJECTIVES DESCRIBE INSULIN, INCLUDING WHERE IT COMES FROM AND WHAT IT DOES STATE THAT
Diabetes in Pregnancy
 Diabetes in Pregnancy Ebony Boyce Carter, MD, MPH Division of Maternal Fetal Medicine Washington University School of Medicine Disclosures I have no financial disclosures to report. Objectives Review the
Diabetes in Pregnancy Ebony Boyce Carter, MD, MPH Division of Maternal Fetal Medicine Washington University School of Medicine Disclosures I have no financial disclosures to report. Objectives Review the
Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus
 Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus Young-Bum Kim, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Definition of Diabetes Mellitus a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia
Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus Young-Bum Kim, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Definition of Diabetes Mellitus a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia
LESSON 2.4 WORKBOOK. Part two: Glucose homeostasis in the blood Un-Storing energy
 DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Fasting A state of abstinence from all food or drinks that provide calories. For a complete list of defined terms, see the Glossary. LESSON 2.4 WORKBOOK Part two: Glucose homeostasis
DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Fasting A state of abstinence from all food or drinks that provide calories. For a complete list of defined terms, see the Glossary. LESSON 2.4 WORKBOOK Part two: Glucose homeostasis
BIOL212- Biochemistry of Disease. Metabolic Disorders: Diabetes
 BIOL212- Biochemistry of Disease Metabolic Disorders: Diabetes Diabetes mellitus is, after heart disease and cancer, the third leading cause of death in the west. Insulin is either not secreted in sufficient
BIOL212- Biochemistry of Disease Metabolic Disorders: Diabetes Diabetes mellitus is, after heart disease and cancer, the third leading cause of death in the west. Insulin is either not secreted in sufficient
第十五章. Diabetes Mellitus
 Diabetes-1/9 第十五章 Diabetes Mellitus 陳曉蓮醫師 2/9 - Diabetes 羅東博愛醫院 Management of Diabetes mellitus A. DEFINITION OF DIABETES MELLITUS Diabetes Mellitus is characterized by chronic hyperglycemia with disturbances
Diabetes-1/9 第十五章 Diabetes Mellitus 陳曉蓮醫師 2/9 - Diabetes 羅東博愛醫院 Management of Diabetes mellitus A. DEFINITION OF DIABETES MELLITUS Diabetes Mellitus is characterized by chronic hyperglycemia with disturbances
Metabolic integration and Regulation
 Metabolic integration and Regulation 109700: Graduate Biochemistry Trimester 2/2016 Assistant Prof. Dr. Panida Khunkaewla kpanida@sut.ac.th School of Chemistry Suranaree University of Technology 1 Overview
Metabolic integration and Regulation 109700: Graduate Biochemistry Trimester 2/2016 Assistant Prof. Dr. Panida Khunkaewla kpanida@sut.ac.th School of Chemistry Suranaree University of Technology 1 Overview
Regulation of Metabolism
 Regulation of Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 19 Regulation by Compartmentalization Form of reciprocal regulation Degradation vs biosynthesis Requires transporters 1 Specialization of organs Fuel
Regulation of Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 19 Regulation by Compartmentalization Form of reciprocal regulation Degradation vs biosynthesis Requires transporters 1 Specialization of organs Fuel
Diabetes Mellitus (Do we really know what s going on?)
 Diabetes Mellitus (Do we really know what s going on?) Chris Willis-Mahn, DVM, DACVIM (SAIM), DACVN GSLVMA 11.13.2018 Affiliated with: Diabetic Types DOGS Type 1 Idiopathic Immune-mediated? Type 2 Rare
Diabetes Mellitus (Do we really know what s going on?) Chris Willis-Mahn, DVM, DACVIM (SAIM), DACVN GSLVMA 11.13.2018 Affiliated with: Diabetic Types DOGS Type 1 Idiopathic Immune-mediated? Type 2 Rare
Lantus to levemir conversion
 Lantus to levemir conversion The Borg System is 100 % Lantus to levemir conversion 16-6-2005 Ask the Expert on... Lantus Conversion. Karen Shapiro, PharmD, BCPS. Disclosures. June 16, 2005. Question. Would
Lantus to levemir conversion The Borg System is 100 % Lantus to levemir conversion 16-6-2005 Ask the Expert on... Lantus Conversion. Karen Shapiro, PharmD, BCPS. Disclosures. June 16, 2005. Question. Would
Lipid Metabolism. Remember fats?? Triacylglycerols - major form of energy storage in animals
 Remember fats?? Triacylglycerols - major form of energy storage in animals Your energy reserves: ~0.5% carbs (glycogen + glucose) ~15% protein (muscle, last resort) ~85% fat Why use fat for energy? 1 gram
Remember fats?? Triacylglycerols - major form of energy storage in animals Your energy reserves: ~0.5% carbs (glycogen + glucose) ~15% protein (muscle, last resort) ~85% fat Why use fat for energy? 1 gram
Week 3, Lecture 5a. Pathophysiology of Diabetes. Simin Liu, MD, ScD
 Week 3, Lecture 5a Pathophysiology of Diabetes Simin Liu, MD, ScD General Model of Peptide Hormone Action Hormone Plasma Membrane Activated Nucleus Cellular Trafficking Enzymes Inhibited Receptor Effector
Week 3, Lecture 5a Pathophysiology of Diabetes Simin Liu, MD, ScD General Model of Peptide Hormone Action Hormone Plasma Membrane Activated Nucleus Cellular Trafficking Enzymes Inhibited Receptor Effector
DIABETES MELLITUS. IAP UG Teaching slides
 DIABETES MELLITUS 1 DIABETES MELLITUS IN CHILDREN Introduction, Definition Classification, pathogenesis Clinical features Investigations and diagnosis Therapy and follow up Complications Carry home message
DIABETES MELLITUS 1 DIABETES MELLITUS IN CHILDREN Introduction, Definition Classification, pathogenesis Clinical features Investigations and diagnosis Therapy and follow up Complications Carry home message
 Meghan Ames Mrs. Matuszak KNH 406 March 18, 2010 Diabetes Case Study #4 Understanding the Disease and Pathophysiology 1) Define insulin. Describe its major functions within normal metabolism. Insulin is
Meghan Ames Mrs. Matuszak KNH 406 March 18, 2010 Diabetes Case Study #4 Understanding the Disease and Pathophysiology 1) Define insulin. Describe its major functions within normal metabolism. Insulin is
ENERGY FROM INGESTED NUTREINTS MAY BE USED IMMEDIATELY OR STORED
 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 SHORT TERM METABOLISM [METABOLISM] Learning Objectives: Identify primary energy stores of the body Differentiate the metabolic processes of the fed and fasted states Explain
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 SHORT TERM METABOLISM [METABOLISM] Learning Objectives: Identify primary energy stores of the body Differentiate the metabolic processes of the fed and fasted states Explain
GESTATIONAL DIABETES: An Overview
 GESTATIONAL DIABETES: An Overview University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences, Division of Basic Medical Sciences Clinical Biochemistry: PBL Seminar MBBS Yr 4 VJ Temple 1 Brief
GESTATIONAL DIABETES: An Overview University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences, Division of Basic Medical Sciences Clinical Biochemistry: PBL Seminar MBBS Yr 4 VJ Temple 1 Brief
23.1 Lipid Metabolism in Animals. Chapter 23. Micelles Lipid Metabolism in. Animals. Overview of Digestion Lipid Metabolism in
 Denniston Topping Caret Copyright! The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 23 Fatty Acid Metabolism Triglycerides (Tgl) are emulsified into fat droplets
Denniston Topping Caret Copyright! The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 23 Fatty Acid Metabolism Triglycerides (Tgl) are emulsified into fat droplets
Type 1 Diabetes-Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Long-Term Complications. Alejandro J de la Torre Pediatric Endocrinology 10/17/2014
 Type 1 Diabetes-Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Long-Term Complications Alejandro J de la Torre Pediatric Endocrinology 10/17/2014 Objectives Understand the pathophysiology of Type 1 diabetes. Be familiar
Type 1 Diabetes-Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Long-Term Complications Alejandro J de la Torre Pediatric Endocrinology 10/17/2014 Objectives Understand the pathophysiology of Type 1 diabetes. Be familiar
METABOLISM CATABOLIC Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins
 Index: - Overview: Catabolism and Anabolism. Few concepts:, NADPH. - Overview: Metabolism glucose, fatty acids and amino acids. - Table summary: Principal anabolic and catabolic pathways, and their main
Index: - Overview: Catabolism and Anabolism. Few concepts:, NADPH. - Overview: Metabolism glucose, fatty acids and amino acids. - Table summary: Principal anabolic and catabolic pathways, and their main
INTEGRATION OF METABOLISM DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU
 INTEGRATION OF METABOLISM DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU To appreciate fully the significance of individual metabolic pathways and their regulation, we must view these pathways in the context
INTEGRATION OF METABOLISM DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU To appreciate fully the significance of individual metabolic pathways and their regulation, we must view these pathways in the context
Clinical Practice Guidelines
 Clinical Practice Guidelines Diabetes Objective The purpose is to guide the appropriate diagnosis and management of Diabetes. This guideline is designed to assist the clinician by providing a framework
Clinical Practice Guidelines Diabetes Objective The purpose is to guide the appropriate diagnosis and management of Diabetes. This guideline is designed to assist the clinician by providing a framework
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
 October 2015 Michael T. McDermott MD Director, Endocrinology and Diabetes Practice University of Colorado Hospital Case History HPI: 24 yo man with recent 8 lb. weight loss, increased thirst and frequent
October 2015 Michael T. McDermott MD Director, Endocrinology and Diabetes Practice University of Colorado Hospital Case History HPI: 24 yo man with recent 8 lb. weight loss, increased thirst and frequent
Drug Effectiveness Review Project Summary Report Long acting Insulins
 Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Lantus levemir conversion
 Lantus levemir conversion Search Learn about starting insulin-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes on Levemir. Read Important Safety & Prescribing Info on the HCP Website. Lantus and Levemir have a variety
Lantus levemir conversion Search Learn about starting insulin-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes on Levemir. Read Important Safety & Prescribing Info on the HCP Website. Lantus and Levemir have a variety
Diabetes Mellitus. Raja Nursing Instructor. Acknowledgement: Badil 09/03/2016
 Diabetes Mellitus Raja Nursing Instructor 09/03/2016 Acknowledgement: Badil Objective: Define Diabetes Mellitus (DM) & types of DM. Understand the pathophysiology of Type-I & II DM. List the clinical features
Diabetes Mellitus Raja Nursing Instructor 09/03/2016 Acknowledgement: Badil Objective: Define Diabetes Mellitus (DM) & types of DM. Understand the pathophysiology of Type-I & II DM. List the clinical features
Pancreas The pancreas is composed of two major types of tissues: (1) The acini, which secrete digestive juices into the duodenum, and (2) The islets
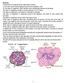 Pancreas The pancreas is composed of two major types of tissues: (1) The acini, which secrete digestive juices into the duodenum, and (2) The islets of Langerhans, which secrete insulin and glucagon directly
Pancreas The pancreas is composed of two major types of tissues: (1) The acini, which secrete digestive juices into the duodenum, and (2) The islets of Langerhans, which secrete insulin and glucagon directly
Diabetes Mellitus. Mohamed Ahmed Fouad Lecturer of Pediatrics Jazan Faculty of Medicine
 Diabetes Mellitus Mohamed Ahmed Fouad Lecturer of Pediatrics Jazan Faculty of Medicine Define DM in children Differentiate types of DM Discus Etiology and Risk Factor Reason clinical presentations Set
Diabetes Mellitus Mohamed Ahmed Fouad Lecturer of Pediatrics Jazan Faculty of Medicine Define DM in children Differentiate types of DM Discus Etiology and Risk Factor Reason clinical presentations Set
The York Diabetes Care Model
 This Session The York Diabetes Care Model The annual review what s it for and how to do it How to make the diagnosis of diabetes and who to test Categorisation of diabetes at diagnosis Basics of Insulin
This Session The York Diabetes Care Model The annual review what s it for and how to do it How to make the diagnosis of diabetes and who to test Categorisation of diabetes at diagnosis Basics of Insulin
Canine Diabetes Mellitus
 STEP 1: Comprehensive Overview Canine Diabetes Mellitus Andrew C. Bugbee, DVM, DACVIM Diabetes mellitus (DM), a common endocrine disease affecting middle-aged to older dogs, is diagnosed when persistent
STEP 1: Comprehensive Overview Canine Diabetes Mellitus Andrew C. Bugbee, DVM, DACVIM Diabetes mellitus (DM), a common endocrine disease affecting middle-aged to older dogs, is diagnosed when persistent
Conversion from lantus to tresiba
 Conversion from lantus to tresiba Search dosages for Diabetes Type 2 and Diabetes Type 1; plus renal, liver and. Forecast your health care. Every time you have a symptom or are diagnosed of a condition,
Conversion from lantus to tresiba Search dosages for Diabetes Type 2 and Diabetes Type 1; plus renal, liver and. Forecast your health care. Every time you have a symptom or are diagnosed of a condition,
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1
 GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1 1. The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete chemical signals, called hormones, into the blood. In addition, other organs and cells
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1 1. The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete chemical signals, called hormones, into the blood. In addition, other organs and cells
Chapter 10. Introduction to Nutrition and Metabolism, 3 rd edition David A Bender Taylor & Francis Ltd, London 2002
 Chapter 10 Introduction to Nutrition and Metabolism, 3 rd edition David A Bender Taylor & Francis Ltd, London 2002 Chapter 10: Integration and Control of Metabolism Press the space bar or click the mouse
Chapter 10 Introduction to Nutrition and Metabolism, 3 rd edition David A Bender Taylor & Francis Ltd, London 2002 Chapter 10: Integration and Control of Metabolism Press the space bar or click the mouse
Type I Type II Insulin Resistance
 Insulin An aqueous hormonal solution made in the pancreas. Affects metabolism by allowing glucose to leave the blood and enter the body cells, preventing hyperglycemia. It is measured in units, e.g. 100
Insulin An aqueous hormonal solution made in the pancreas. Affects metabolism by allowing glucose to leave the blood and enter the body cells, preventing hyperglycemia. It is measured in units, e.g. 100
Final Review Sessions. 3/16 (FRI) 126 Wellman (4-6 6 pm) 3/19 (MON) 1309 Surge 3 (4-6 6 pm) Office Hours
 Final Review Sessions 3/16 (FRI) 126 Wellman (4-6 6 pm) 3/19 (MON) 1309 Surge 3 (4-6 6 pm) Office ours 3/14 (WED) 9:30 11:30 am (Rebecca) 3/16 (FRI) 9-11 am (Abel) Final ESSENTIALS Posted Lecture 20 ormonal
Final Review Sessions 3/16 (FRI) 126 Wellman (4-6 6 pm) 3/19 (MON) 1309 Surge 3 (4-6 6 pm) Office ours 3/14 (WED) 9:30 11:30 am (Rebecca) 3/16 (FRI) 9-11 am (Abel) Final ESSENTIALS Posted Lecture 20 ormonal
Feline Diabetes Mellitus
 STEP 1: Comprehensive Overview Feline Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a disease of relative or absolute insulin deficiency. Insulin is produced by pancreatic beta cells within specialized endocrine
STEP 1: Comprehensive Overview Feline Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a disease of relative or absolute insulin deficiency. Insulin is produced by pancreatic beta cells within specialized endocrine
GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS/INSULIN PART - II
 GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS/INSULIN PART - II University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences, Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, PBL MBBS III
GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS/INSULIN PART - II University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences, Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, PBL MBBS III
What the Pill Looks Like. How it Works. Slows carbohydrate absorption. Reduces amount of sugar made by the liver. Increases release of insulin
 Diabetes s Oral s - Pills These are some of the pills that are currently available in Canada to treat diabetes. Each medication has benefits and side effects you should be aware of. Your diabetes team
Diabetes s Oral s - Pills These are some of the pills that are currently available in Canada to treat diabetes. Each medication has benefits and side effects you should be aware of. Your diabetes team
CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM 1
 CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM 1 web 2017 József Mandl Strategy of metabolism 1 Strategy of metabolism to extract energy ( hydrogen ) from the environment to store the energy excess to store hydrogen CH 3 O 2
CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM 1 web 2017 József Mandl Strategy of metabolism 1 Strategy of metabolism to extract energy ( hydrogen ) from the environment to store the energy excess to store hydrogen CH 3 O 2
Chemistry 1120 Exam 4 Study Guide
 Chemistry 1120 Exam 4 Study Guide Chapter 12 12.1 Identify and differentiate between macronutrients (lipids, amino acids and saccharides) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals). Master Tutor Section
Chemistry 1120 Exam 4 Study Guide Chapter 12 12.1 Identify and differentiate between macronutrients (lipids, amino acids and saccharides) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals). Master Tutor Section
Biol 219 Lec 7 Fall 2016
 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Energy to form ATP Cellular Respiration and Metabolism Glucose ATP Pyruvate Lactate Acetyl CoA NAD + Introducing The Players primary substrate for cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Energy to form ATP Cellular Respiration and Metabolism Glucose ATP Pyruvate Lactate Acetyl CoA NAD + Introducing The Players primary substrate for cellular respiration
Exercise in Diabetes Mellitus. Pranisa Luengratsameerung,MD
 Exercise in Diabetes Mellitus By Pranisa Luengratsameerung,MD What is the Diabetes Mellitus? action Insulin Defect release Abnormal glucose metabolism Symptoms Polyuria (frequent urination) Polyphasia
Exercise in Diabetes Mellitus By Pranisa Luengratsameerung,MD What is the Diabetes Mellitus? action Insulin Defect release Abnormal glucose metabolism Symptoms Polyuria (frequent urination) Polyphasia
Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC -
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC - Sep. 29-Oct. 2, 2011, Barcelona, Spain Next SEVC Conference: Oct. 18-21, 2012 - Barcelona, Spain Reprinted in the IVIS website
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC - Sep. 29-Oct. 2, 2011, Barcelona, Spain Next SEVC Conference: Oct. 18-21, 2012 - Barcelona, Spain Reprinted in the IVIS website
Hormonal regulation of. Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara
 Hormonal regulation of nutrient metabolism Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara Homeostasis & Controls Successful compensation Homeostasis reestablished Failure to compensate
Hormonal regulation of nutrient metabolism Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara Homeostasis & Controls Successful compensation Homeostasis reestablished Failure to compensate
Therapy of Diabetes Mellitus
 2016 edition by Jayne S. Reuben, PhD Department of Biomedical Sciences University of South Carolina School of Medicine Greenville Originally developed by Elliott Chideckel, MD Department of Medicine Robert
2016 edition by Jayne S. Reuben, PhD Department of Biomedical Sciences University of South Carolina School of Medicine Greenville Originally developed by Elliott Chideckel, MD Department of Medicine Robert
Glucosuria osmotic diuresis Compensatory polydipsia If can t drink enough to compensate dehydration
 How to deal with concurrent pancreatitis and diabetes in dogs and cats Linda Fleeman Animal Diabetes Australia Boronia Veterinary Clinic: 03 9762 3177 Rowville Veterinary Clinic: 03 9763 1799 Lort Smith
How to deal with concurrent pancreatitis and diabetes in dogs and cats Linda Fleeman Animal Diabetes Australia Boronia Veterinary Clinic: 03 9762 3177 Rowville Veterinary Clinic: 03 9763 1799 Lort Smith
81st Western Veterinary Conference
 81st Western Veterinary Conference V110 Canine and Feline Diabetes Mellitus I J. Catharine Scott-Moncrieff, MA, MS, Vet MB, DACVIM, DECVIM Dept Veterinary Clinical Sciences, School of Veterinary Medicine,
81st Western Veterinary Conference V110 Canine and Feline Diabetes Mellitus I J. Catharine Scott-Moncrieff, MA, MS, Vet MB, DACVIM, DECVIM Dept Veterinary Clinical Sciences, School of Veterinary Medicine,
Insulin 10/11/17. Disclosures. Objectives. Speaker and Consultant for Jansen and Healthscripts Speaker and Consultant for Boehringer Ingelheim (BI)
 Insulin The What, When, Where, Who and Why Disclosures Speaker and Consultant for Jansen and Healthscripts Speaker and Consultant for Boehringer Ingelheim (BI) Objectives Define background and history
Insulin The What, When, Where, Who and Why Disclosures Speaker and Consultant for Jansen and Healthscripts Speaker and Consultant for Boehringer Ingelheim (BI) Objectives Define background and history
Integrative Metabolism: Significance
 Integrative Metabolism: Significance Energy Containing Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Catabolism Energy Depleted End Products H 2 O NH 3 ADP + Pi NAD + NADP + FAD + Pi NADH+H + NADPH+H + FADH2 Cell
Integrative Metabolism: Significance Energy Containing Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Catabolism Energy Depleted End Products H 2 O NH 3 ADP + Pi NAD + NADP + FAD + Pi NADH+H + NADPH+H + FADH2 Cell
Endo 2 SLO Practice (online) Page 1 of 7
 Endo 2 SLO Practice (online) Page 1 of 7 1. A long- acting insulin, like Lantus is for? A. When the next meal is within 30-60 minutes of the injection B. Over night use or for ½ of the day often combined
Endo 2 SLO Practice (online) Page 1 of 7 1. A long- acting insulin, like Lantus is for? A. When the next meal is within 30-60 minutes of the injection B. Over night use or for ½ of the day often combined
Insulin Regimens: Hitting Glycemia Targets
 Insulin Regimens: Hitting Glycemia Targets Grant Kelley MD March 1 st, 2018 Faculty Disclosure: Financial relationships with commercial interests None Overview Mortality and Morbidity Insulin and Insulin
Insulin Regimens: Hitting Glycemia Targets Grant Kelley MD March 1 st, 2018 Faculty Disclosure: Financial relationships with commercial interests None Overview Mortality and Morbidity Insulin and Insulin
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 25 Metabolism and Nutrition Metabolic Reactions Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions taking place in the body. Reactions that break
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 25 Metabolism and Nutrition Metabolic Reactions Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions taking place in the body. Reactions that break
EB Education Revision Guide. How to work with Homeostasis: Part 2 Blood Glucose Regulation
 EB Education Revision Guide How to work with Homeostasis: Part 2 Blood Glucose Regulation Blood Glucose Regulation a) Why your body regulates glucose levels What you need to know about Homeostasis: Part
EB Education Revision Guide How to work with Homeostasis: Part 2 Blood Glucose Regulation Blood Glucose Regulation a) Why your body regulates glucose levels What you need to know about Homeostasis: Part
Diabetes: Definition Pathophysiology Treatment Goals. By Scott Magee, MD, FACE
 Diabetes: Definition Pathophysiology Treatment Goals By Scott Magee, MD, FACE Disclosures No disclosures to report Definition of Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus comprises a group of disorders characterized
Diabetes: Definition Pathophysiology Treatment Goals By Scott Magee, MD, FACE Disclosures No disclosures to report Definition of Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus comprises a group of disorders characterized
2018 AAHA Diabetes Management Guidelines for Dogs and Cats*
 VETERINARY PRACTICE GUIDELINES 2018 AAHA Diabetes Management Guidelines for Dogs and Cats* Ellen ehrend, VMD, PhD, DACVIM, Amy Holford, VMD, DACVIM y, Patty Lathan, VMD, DACVIM, Renee Rucinsky, DVM, DAVP
VETERINARY PRACTICE GUIDELINES 2018 AAHA Diabetes Management Guidelines for Dogs and Cats* Ellen ehrend, VMD, PhD, DACVIM, Amy Holford, VMD, DACVIM y, Patty Lathan, VMD, DACVIM, Renee Rucinsky, DVM, DAVP
Comprehensive Diabetes Treatment
 Comprehensive Diabetes Treatment Joshua L. Cohen, M.D., F.A.C.P. Professor of Medicine Interim Director, Division of Endocrinology & Metabolism The George Washington University School of Medicine Diabetes
Comprehensive Diabetes Treatment Joshua L. Cohen, M.D., F.A.C.P. Professor of Medicine Interim Director, Division of Endocrinology & Metabolism The George Washington University School of Medicine Diabetes
Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers NEW
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers NEW
8/13/2016. Insulin Basics. Rapid-Acting Insulin Analogs. Current Insulin Products and Pens. Basal Insulin Analogs. History of Insulin Therapy
 Insulin Basics Anabolic hormone involved in metabolism Following carbohydrate ingestion insulin release is stimulated Suppresses hepatic glucose production Stimulates peripheral glucose uptake Commercially-available
Insulin Basics Anabolic hormone involved in metabolism Following carbohydrate ingestion insulin release is stimulated Suppresses hepatic glucose production Stimulates peripheral glucose uptake Commercially-available
Physiology Unit 1 METABOLISM OF LIPIDS AND PROTEINS
 Physiology Unit 1 METABOLISM OF LIPIDS AND PROTEINS Alternate Fuel Sources When glucose levels are low Proteins and Triglycerides will be metabolized Tissues will use different fuel sources depending on:
Physiology Unit 1 METABOLISM OF LIPIDS AND PROTEINS Alternate Fuel Sources When glucose levels are low Proteins and Triglycerides will be metabolized Tissues will use different fuel sources depending on:
Diabetic Emergencies DKA, HHS, Hypoglycemia. Disclosure. Learning Objectives
 Diabetic Emergencies DKA, HHS, Hypoglycemia October 2018 Michael T. McDermott MD Director, Endocrinology and Diabetes Practice University of Colorado Hospital Disclosure Michael McDermott has no conflict
Diabetic Emergencies DKA, HHS, Hypoglycemia October 2018 Michael T. McDermott MD Director, Endocrinology and Diabetes Practice University of Colorado Hospital Disclosure Michael McDermott has no conflict
Objectives / Learning Targets: The learner who successfully completes this course will be able to demonstrate understanding of the following concepts:
 Objectives / Learning Targets: The learner who successfully completes this course will be able to demonstrate understanding of the following concepts: Insulin s function in the body. The basics of diabetes
Objectives / Learning Targets: The learner who successfully completes this course will be able to demonstrate understanding of the following concepts: Insulin s function in the body. The basics of diabetes
Pathology of endocrine pancreas. By: Shifaa Alqa qa
 Pathology of endocrine pancreas By: Shifaa Alqa qa major cell types: Beta ----- insulin Alpha ----- glucagon Delta ----- somatostatin PP (pancreatic polypeptide) cells ------ VIP DIABETES MELLITUS Normal
Pathology of endocrine pancreas By: Shifaa Alqa qa major cell types: Beta ----- insulin Alpha ----- glucagon Delta ----- somatostatin PP (pancreatic polypeptide) cells ------ VIP DIABETES MELLITUS Normal
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Endocrine Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Endocrine Revised: 11/2013 Endocrine system includes 8 major glands. 1. Pituitary (master gland)
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Endocrine Revised: 11/2013 Endocrine system includes 8 major glands. 1. Pituitary (master gland)
Case- history. Lab results
 Neda Rasouli, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Endocrinology, UC Denver VA_ Eastern Colorado Health Care System Case- history 46 y/o AA male with BMI 37 presented in Oct 2001 with polyuria,
Neda Rasouli, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Endocrinology, UC Denver VA_ Eastern Colorado Health Care System Case- history 46 y/o AA male with BMI 37 presented in Oct 2001 with polyuria,
Lecture 5: Cell Metabolism. Biology 219 Dr. Adam Ross
 Lecture 5: Cell Metabolism Biology 219 Dr. Adam Ross Cellular Respiration Set of reactions that take place during the conversion of nutrients into ATP Intricate regulatory relationship between several
Lecture 5: Cell Metabolism Biology 219 Dr. Adam Ross Cellular Respiration Set of reactions that take place during the conversion of nutrients into ATP Intricate regulatory relationship between several
Functional Medicine University s Functional Diagnostic Medicine Training Program
 Functional Diagnostic Medicine Training Program MOD 4 * FDMT533A The Physiology of Insulin Resistance (Oxidative Stress and Diabetes) Limits of Liability & Disclaimer of Warranty We have designed this
Functional Diagnostic Medicine Training Program MOD 4 * FDMT533A The Physiology of Insulin Resistance (Oxidative Stress and Diabetes) Limits of Liability & Disclaimer of Warranty We have designed this
5.0 HORMONAL CONTROL OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM
 5.0 HORMONAL CONTROL OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Introduction: Variety of hormones and other molecules regulate the carbohydrates metabolism. Some of these have already been cited in previous sections.
5.0 HORMONAL CONTROL OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Introduction: Variety of hormones and other molecules regulate the carbohydrates metabolism. Some of these have already been cited in previous sections.
DIABETES. Mary Bruskewitz APNP, MS, BC-ADM Clinical Nurse Specialist Diabetes. November 2013
 DIABETES Mary Bruskewitz APNP, MS, BC-ADM Clinical Nurse Specialist Diabetes November 2013 mbruskewitz@outlook.com Objectives Part 1 Overview of Endocrine Physiology Pathophysiology of Diabetes Diabetes
DIABETES Mary Bruskewitz APNP, MS, BC-ADM Clinical Nurse Specialist Diabetes November 2013 mbruskewitz@outlook.com Objectives Part 1 Overview of Endocrine Physiology Pathophysiology of Diabetes Diabetes
Nutrients. Chapter 25 Nutrition, Metabolism, Temperature Regulation
 Chapter 25 Nutrition, Metabolism, Temperature Regulation 25-1 Nutrients Chemicals used by body to produce energy, provide building blocks or function in other chemical reactions Classes Carbohydrates,
Chapter 25 Nutrition, Metabolism, Temperature Regulation 25-1 Nutrients Chemicals used by body to produce energy, provide building blocks or function in other chemical reactions Classes Carbohydrates,
Degludec lantus conversion
 Degludec lantus conversion Search embarazadas con elevado riesgo de enfermedad tiroidea usando la. There are various possible causes of a high blood sugar level in the morning: The Dawn Phenomenon which
Degludec lantus conversion Search embarazadas con elevado riesgo de enfermedad tiroidea usando la. There are various possible causes of a high blood sugar level in the morning: The Dawn Phenomenon which
Mixed Insulins Pick Me
 Mixed Insulins Pick Me Alvin Goo, PharmD Clinical Associate Professor University of Washington School of Pharmacy and Department of Family Medicine Objectives Critically evaluate the evidence comparing
Mixed Insulins Pick Me Alvin Goo, PharmD Clinical Associate Professor University of Washington School of Pharmacy and Department of Family Medicine Objectives Critically evaluate the evidence comparing
Management of Diabetes New Concepts New Devices New Medications. Richard J. Comi, MD Professor of Medicine Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth
 Management of Diabetes New Concepts New Devices New Medications Richard J. Comi, MD Professor of Medicine Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Objectives: At the end of this lecture, the learner will
Management of Diabetes New Concepts New Devices New Medications Richard J. Comi, MD Professor of Medicine Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Objectives: At the end of this lecture, the learner will
Society for Ambulatory Anesthesia Consensus Statement on Perioperative Blood Glucose Management in Diabetic Patients Undergoing Ambulatory Surgery
 Society for Ambulatory Anesthesia Consensus Statement on Perioperative Blood Glucose Management in Diabetic Patients Undergoing Ambulatory Surgery Girish P. Joshi, MB BS, MD, FFARCSI Anesthesia & Analgesia
Society for Ambulatory Anesthesia Consensus Statement on Perioperative Blood Glucose Management in Diabetic Patients Undergoing Ambulatory Surgery Girish P. Joshi, MB BS, MD, FFARCSI Anesthesia & Analgesia
What is the Most Endorsed Test for Diabetic Screening and Monitoring?
 Baycom draft information 2.18.17 Beth Thompson, VMD What is the Most Endorsed Test for Diabetic Screening and Monitoring? Before 2010 virtually all the diabetes societies recommended blood glucose analysis
Baycom draft information 2.18.17 Beth Thompson, VMD What is the Most Endorsed Test for Diabetic Screening and Monitoring? Before 2010 virtually all the diabetes societies recommended blood glucose analysis
Mae Sheikh-Ali, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Endocrinology University of Florida College of Medicine- Jacksonville
 Mae Sheikh-Ali, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Endocrinology University of Florida College of Medicine- Jacksonville Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Criteria for the diagnosis
Mae Sheikh-Ali, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Endocrinology University of Florida College of Medicine- Jacksonville Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Criteria for the diagnosis
Diabetes in Pregnancy
 Diabetes in Pregnancy Susan Drummond RN MSN C-EFM Objectives 1. Describe types of diabetes and diagnosis of gestational diabetes 2. Identify a management plan for diabetes during pregnancy 3. Describe
Diabetes in Pregnancy Susan Drummond RN MSN C-EFM Objectives 1. Describe types of diabetes and diagnosis of gestational diabetes 2. Identify a management plan for diabetes during pregnancy 3. Describe
Adrenal gland And Pancreas
 Adrenal gland And Pancreas Structure Cortex Glucocorticoids Effects Control of secretion Mineralocorticoids Effects Control of secretion Sex steroids Medulla Catecholamines Adrenal cortex 80% of an adrenal
Adrenal gland And Pancreas Structure Cortex Glucocorticoids Effects Control of secretion Mineralocorticoids Effects Control of secretion Sex steroids Medulla Catecholamines Adrenal cortex 80% of an adrenal
Integration & Hormone Regulation
 Integration Branchpoints in metabolism where metabolites can go several directions 1. Glucose 6-phosphate Energy needed (low energy charge): glycolysis Low blood sugar: high [glucagon], low [insulin] glycogen
Integration Branchpoints in metabolism where metabolites can go several directions 1. Glucose 6-phosphate Energy needed (low energy charge): glycolysis Low blood sugar: high [glucagon], low [insulin] glycogen
Metabolic Syndrome. DOPE amines COGS 163
 Metabolic Syndrome DOPE amines COGS 163 Overview - M etabolic Syndrome - General definition and criteria - Importance of diagnosis - Glucose Homeostasis - Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - Insulin Resistance
Metabolic Syndrome DOPE amines COGS 163 Overview - M etabolic Syndrome - General definition and criteria - Importance of diagnosis - Glucose Homeostasis - Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - Insulin Resistance
Converting lantus to humalog 75 25
 P ford residence southampton, ny Converting lantus to humalog 75 25 This page includes the following topics and synonyms: Insulin Dosing in Type 2 Diabetes, Insulin Dosing in Type II Diabetes. Thiazide
P ford residence southampton, ny Converting lantus to humalog 75 25 This page includes the following topics and synonyms: Insulin Dosing in Type 2 Diabetes, Insulin Dosing in Type II Diabetes. Thiazide
Intermediary metabolism. Eva Samcová
 Intermediary metabolism Eva Samcová Metabolic roles of tissues Four major tissues play a dominant role in fuel metabolism : liver, adipose, muscle, and brain. These tissues do not function in isolation.
Intermediary metabolism Eva Samcová Metabolic roles of tissues Four major tissues play a dominant role in fuel metabolism : liver, adipose, muscle, and brain. These tissues do not function in isolation.
