The temporal evolution of a facial pain syndrome associated with neurovascular contact: a case report
|
|
|
- Melanie Ryan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Khan et al. The Journal of Headache and Pain (2015) 16:12 DOI /s CASE REPORT Open Access The temporal evolution of a facial pain syndrome associated with neurovascular contact: a case report Sabrina Khan 1, Ida Wibrandt 1, Per Rochat 2 and Messoud Ashina 1* Abstract Background: Trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias are primary headaches characterized by unilateral pain and cranial autonomic symptoms. However, associated autonomic symptoms have also been reported in other headaches and facial pains, e.g. trigeminal neuralgia, with the clinical differentiation proving a complex task. Case: A 54-year-old man presented with right-sided, sharp, intense facial pain in the distribution area of the trigeminal nerve. Pain duration was from seconds to a few minutes, and trigger factors included ipsilateral touching of the skin and hair. Over the next ten years, symptoms progressed and changed presentation, also displaying as right-sided, severe, orbital pain, lasting 60 to 90 minutes, with conjunctival injection and rhinorrhea. Neurological examination was normal. Numerous medications were tried with limited or no effect. In 2010, magnetic resonance imaging revealed a right-sided deviation of the basilar artery at the level of pons, creating neurovascular contact with the trigeminal nerve. Microvascular decompression was performed, and symptoms resolved within days. Conclusion: Differentiating between trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias and trigeminal neuralgia with autonomic symptoms can be challenging. The distinct change and evolution over time in the clinical presentation of the patient s head pain suggests a temporal plasticity of the pain in head and facial syndromes, irrespective of underlying pathoanatomic features. Keywords: Trigeminal neuralgia; Trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias; Cranial autonomic symptoms; Neurovascular contact; Microvascular decompression Background Trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias (TACs) comprise a debilitating group of primary headaches characterized by unilaterality of pain and pronounced ipsilateral cranial autonomic symptoms (CAS), such as conjunctival tearing, lacrimation, and nasal congestion [1]. TACs include cluster headache (CH); short-lasting unilateral neuralgiform headache attacks with conjunctival injection and tearing (SUNCT), paroxysmal hemicrania, and hemicrania continua. The main distinction between TACs is based on pain duration and differences in abortive and preventive treatments. Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is characterized by unilateral, brief, electric shock-like * Correspondence: ashina@dadlnet.dk 1 Danish Headache Center, Department of Neurology, Glostrup Hospital, Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, University of Copenhagen, Nordre Ringvej 57, Glostrup DK-2600, Denmark Full list of author information is available at the end of the article pains, abrupt in onset and termination, limited to the distribution of one or more divisions of the trigeminal nerve (TG). Pain is triggered by innocuous stimuli, e.g. tooth brushing or chewing [1]. While CAS are distinguishing features of TACs, autonomic symptoms have also been reported in association with TN, proving it difficult to differentiate between these two head pains [2,3]. We present the case of a patient with unilateral head pain attacks and prominent CAS who underwent a remarkable progression and evolution in the clinical presentation of his head pain, and ultimately responded completely to microvascular decompression (MVD) of the TG. Case presentation A 54-year-old male with history of obesity, type II diabetes, and medically treated hypertension, presented in year 2000 with facial pain. One month prior to 2015 Khan et al.; licensee Springer. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly credited.
2 Khan et al. The Journal of Headache and Pain (2015) 16:12 Page 2 of 5 presentation, he was involved in a car accident with no obvious trauma to the neck. He suffered from neck pain shortly after, but was never seen by a physician. At presentation, the patient described a sensation of sharp, unilateral pain in the right-sided sensory distribution area of TG, lasting from 1 second to 3 minutes (Table 1). Attack frequency was 4 5 per day, in intervals of 15 minutes to 4 hours. Triggers included ipsilateral touching of the skin or hair. This pattern continued for up to 3 weeks, interrupted by 14 days of pain remission. Neurological examination was normal, apart from reported hypoesthesia in the right-sided V2. TN was suspected and the patient was started on oxcarbazepine 900 mg daily. This initially eliminated the pain but caused cognitive side effects. Gabapentin was then tried, but discontinued due to skin exanthema. Two years after onset, the patient experienced an acute exacerbation of the facial pain with an increase in attack intensity and frequency. Indomethacin treatment was initiated, which successfully reduced the intensity but not the attack frequency. A private practicing neurologist diagnosed the patient with atypical facial pain. Over the next 2 years, the symptoms progressed further. There were fewer remitting periods, the pain intensity grew, and trigger factors now also included tooth brushing, chewing, shaving, exposure to windy weather and drinking cold beverages. Several antiepileptic drugs were tried without significant effect on the symptoms. Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging and MR angiography performed 4 years after onset showed a loop on the basilar artery at the level of pons. Due to a possible correlation between neurovascular contact and presentation of neuralgia, MVD surgery was suggested, but the patient declined. 9 years after onset the patient was referred to the Danish Headache Center and Department of Neurology, Glostrup Hospital, Copenhagen. At this time he presented with two different facial pains. The first pain was right-sided, supraorbital, radiating towards the ipsilateral ear and teeth, lasting 5 to 10 minutes, with a frequency of 5 6 per day. Trigger factors included speaking, eating and tooth brushing; there were no associated autonomic symptoms. The second pain was sharp and intense, in the right eye, followed by conjunctival injection and rhinorrhea, lasting 60 to 90 minutes with a frequency of 5 6 attacks per day. Based on past and present history the patient was diagnosed with both TN and CH, and started on verapamil 480 mg daily later increased to 720 mg. This treatment continued for a year, reducing the symptoms greatly. Oxygen was also tried, but with no substantial effect. 10 years after onset the patient was hospitalized due to further worsening of the condition, with rapidly increasing attack frequency. He complained of episodes of intense facial pain, described as constant, stabbing, electrical shocks around the right eye, radiating towards the ipsilateral teeth, and associated with prominent ipsilateral autonomic features including conjunctival injection, lacrimation, periorbital edema, miosis, ptosis, rhinorrhea and facial redness. Attacks occurred as paroxysms of pain that lasted 10 to 15 minutes, with a frequency of 25 attacks per day. Trigger factors persisted as earlier. The condition was interpreted as TN with autonomic symptoms and the patient was tried on phenytoin loading, with immediate effect. Daily treatment with phenytoin 400 mg and carbamazepine 800 mg was initiated. After a few days the patient reported symptom relapse. He was then tried on indomethacin 200 mg daily, with no effect. A new MRI confirmed a loop on the basilar artery, dislocating the TG in lateral direction, resulting in neurovascular contact between artery and nerve (Figure 1). The patient was immediately referred to surgery and underwent MVD. Upon surgery, the neurosurgeon reported as follows: The trigeminal nerve is located behind a large petrosal sinus, which is coagulated and divided. This provides overview of the trigeminal nerve, where the basilar artery is seen to indent the anterior side of the nerve. A small branch of the basilar artery is Table 1 Summary of symptom development Time Pain localization & characteristics Triggers Pain duration Attack frequency Onset Right-sided, sensory area of TG, sharp, intense. Right-sided touching of hair or skin 1s 3 min in intervals of 15 min 4 hrs. Cluster duration Associated CAS 4-5 x daily 1-3 weeks No TN Presumed diagnosis +2 yrs. Unchanged Increased Unchanged Increased Unchanged Atypical facial pain +9 yrs. Right-sided, supraorbital, radiating towards teeth & ear Right-sided speaking, eating, tooth-brushing 5-10 min 5-6 x daily Constant No TN Right eye, intense, sharp None min 5-6 x daily 1 month Yes CH +10 yrs. Right eye, radiating to teeth, Unchanged min 25 x daily Constant Yes TN with CAS stabbing, electric shocks
3 Khan et al. The Journal of Headache and Pain (2015) 16:12 Page 3 of 5 Figure 1 MRI showing right-sided neurovascular contact between the basilar artery and the trigeminal nerve. While it may look like the anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) is in fact also compressing the trigeminal nerve, the treating neurosurgeon (PR) did not find this to be the case during surgery. seen to depart from behind the trigeminal nerve, however without causing any direct neurovascular contact. The nerve is separated from the artery, and a piece of felt/teflon is placed in between. At clinical controls performed 2 weeks, 3 months, 10 months, 2 and 4 years post surgery, the patient reported complete pain remission, with no need for prophylactic therapy. His quality of life had increased significantly. Conclusions Over the course of ten years, the patient experienced a prominent change in the phenotype of his head pain, with severe progression in pain intensity, duration, and associated CAS. The question remains whether the facial pains were associated or in fact presentations of distinct conditions. At first glance, the pain characteristics fit TN and CH, respectively. TN attacks last from seconds to 2 minutes. Treatment options include carbamazepine and gabapentin, which had some effect on the patient but was discontinued due to adverse events. However, the presence of autonomic symptoms may disturb this proposed diagnosis, as CAS are only sparingly described in relation to TN without co-existence of SUNCT [4,5]. Over time the attack duration progressed in the patient, and while this may initially point towards SUNCT rather than TN, a new study has shown that concomitant persistent pain is prevalent in TN and may represent a distinct phenotype of this pain syndrome [6]. Reporting on 158 TN patients, Maarbjerg and colleagues also reported that in patients with concomitant persistent pain, autonomic symptoms prevail in 37% and V1 involvement in 31%. CH is characterized by unilateral, orbital or supraorbital pain, with associated autonomic symptoms, lasting 15 to 180 minutes. Attacks occur in clusters of weeks or months, with subsequent remission periods of months or years. However, while verapamil reduced the patient s symptoms, oxygen provided no relief. Also, CH is not associated with a trigger area on the face. MVD had full effect on the patient, and while MVD in CH is not as well-defined as in TN, a study of 39 chronic CH patients undergoing MVD of the TG alone or in combination with decompression or sectioning of the nervus intermedius, showed initial post-operative success of at least 50% pain relief achieved in 73.3% of patients. However, long-term follow-up revealed a drop in this success rate to 46.6% [7].
4 Khan et al. The Journal of Headache and Pain (2015) 16:12 Page 4 of 5 Differentiating between TN with V1 autonomic symptoms and TACs, namely SUNCT, can prove tricky [3,4,8]. Ophthalmic distribution, prominent autonomic symptoms, longer pain duration, lack of refractory period and relative lack of response to carbamazepine are described as differing features [2]. While trigger factors are typical of TN, several authors have concluded that SUNCT may in fact also be subject to precipitating mechanisms [3,4,9]. In a study of 21 SUNCT patients, Pareja and Sjaastad showed that although paroxysms in SUNCT are located within the V1 distribution area, triggering areas may also be located within V2 and V3, and even include extratrigeminal areas, such as the neck [9]. Several articles have discussed the presence of autonomic symptoms in TN and a possible difference between their presentation in TN and SUNCT [3,4]. Pareja et al. conclude that the autonomic component of TN is milder than in SUNCT and for TN also may appear later in the attack [3]. It has also been proposed that attacks of V1 TN of long duration may overlap the shortest SUNCT attacks, thereby comprising a continuum of symptomatology [10], and begging the question whether these syndromes are in fact interchangeable and possibly subsets of one another. While we acknowledge the possibility of retrospective recall in this case with symptom development over 10 years, it is important to note that a physician saw the patient regularly and at every change of the headache phenotype. Neurologists with knowledge of headache symptomatology, presentation, and treatment performed the headache description, and we believe that this close follow-up by relevant physicians reduces the risk of retrospective bias. Despite initial confusion, the immediate and sustained effect of MVD proposes that the different pain presentations most likely were rooted in one, sole condition. While TN is well known to develop due to neurovascular contact and MVD is standard treatment [11,12], MVD is also reported to be effective in various TACs, where neurovascular contact or vascular malformations may exist as underlying pathology [7,13-15]. The truly compelling aspect of this case is the prominent change over time in the patient s clinical presentation, leaving the involved physicians perplexed as to the true etiology of the head pain. While raising the question whether TN with V1 autonomic symptoms may progress to presentations of TACs, this case suggests that pain is not necessarily a static measure, but may change and evolve over time, while maintaining its underlying pathoanatomic features. To our knowledge, a similar and equally distinct variation in the phenotype of a facial pain has not been reported earlier. Longitudinal follow-up within this field may provide a better comprehension of the true temporal evolution and possible plasticity of facial pain syndromes, all in the effort of optimized and timelier treatment. Consent The patient provided oral consent to the corresponding author for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Authors contributions SK and IW performed literature review, extracted the patient journal, and drafted the manuscript. PR and MA reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Acknowledgements The authors would like to thank Dr. Inge Bergmann for her valuable expertise and input to the case report. Funding This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. Author details 1 Danish Headache Center, Department of Neurology, Glostrup Hospital, Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, University of Copenhagen, Nordre Ringvej 57, Glostrup DK-2600, Denmark. 2 Department of Neurosurgery, Copenhagen University Hospital, Rigshospitalet, Denmark. Received: 5 December 2014 Accepted: 22 January 2015 References 1. Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS) (2013) The International classification of headache disorders, 3rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia 33(9): Simms HN, Honey CR (2011) The importance of autonomic symptoms in trigeminal neuralgia. Clinical article. J Neurosurg 115(2): Pareja JA, Barón M, Gili P, Yangüela J, Caminero AB, Dobato JL et al (2002) Objective assessment of autonomic signs during triggered first division trigeminal neuralgia. Cephalalgia 22(4): Sesso RM (2001) SUNCT syndrome or trigeminal neuralgia with lacrimation and conjunctival injection? Cephalalgia 21(2): Leone M, Mea E, Genco S, Bussone G (2006) Coexistence of TACS and trigeminal neuralgia: pathophysiological conjectures. Headache 46(10): Maarbjerg S, Gozalov A, Olesen J, Bendtsen L (2014) Concomitant persistent pain in classical trigeminal neuralgia evidence for different subtypes. Headache 54(7): Lovely TJ, Kotsiakis X, Jannetta PJ (1998) The surgical management of chronic cluster headache. Headache J Head Face Pain 38(8): Sjaastad O, Pareja JA, Zukerman E, Jansen J, Kruszewski P (1997) Trigeminal neuralgia. Clinical manifestations of first division involvement. Headache 37(6): Pareja JA, Sjaastad O (1997) SUNCT syndrome. A clinical review. Headache 37(4): Pareja JA, Shen JM, Kruszewski P, Caballero V, Pamo M, Sjaastad O (1996) SUNCT syndrome: duration, frequency, and temporal distribution of attacks. Headache 36(3): Jannetta PJ (2007) Arterial compression of the trigeminal nerve at the pons in patients with trigeminal neuralgia J Neurosurg American Assoc Neuro Surg 107(1): Barker FG, Jannetta PJ, Bissonette DJ, Larkins MV, Jho HD (1996) The longterm outcome of microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. N Engl J Med 334(17): Sebastian S, Schweitzer D, Tan L, Broadley S a (2013) Role of trigeminal microvascular decompression in the treatment of SUNCT and SUNA. Curr Pain Headache Rep 17(5):332
5 Khan et al. The Journal of Headache and Pain (2015) 16:12 Page 5 of Favoni V, Grimaldi D, Pierangeli G, Cortelli P, Cevoli S (2013) SUNCT/SUNA and neurovascular compression: new cases and critical literature review. Cephalalgia 33(16): Williams M, Bazina R, Tan L, Rice H, Broadley S a (2010) Microvascular decompression of the trigeminal nerve in the treatment of SUNCT and SUNA. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 81(9):992 6 Submit your manuscript to a journal and benefit from: 7 Convenient online submission 7 Rigorous peer review 7 Immediate publication on acceptance 7 Open access: articles freely available online 7 High visibility within the field 7 Retaining the copyright to your article Submit your next manuscript at 7 springeropen.com
Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 II. Management of refractory headaches Case Presentation 2. SUNCT/SUNA: concept, management and prognosis
 Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 II. Management of refractory headaches Case Presentation 2. SUNCT/SUNA: concept, management and prognosis Noboru Imai(Department of Neurology, Japanese Red Cross
Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 II. Management of refractory headaches Case Presentation 2. SUNCT/SUNA: concept, management and prognosis Noboru Imai(Department of Neurology, Japanese Red Cross
Tears of Pain SUNCT and SUNA A/PROFESSOR ARUN AGGARWAL RPAH PAIN MANAGEMENT CENTRE
 Tears of Pain SUNCT and SUNA A/PROFESSOR ARUN AGGARWAL RPAH PAIN MANAGEMENT CENTRE IHS Classification 1989 (updated 2004) Primary Headaches 4 categories Migraine Tension-type Cluster and other trigeminal
Tears of Pain SUNCT and SUNA A/PROFESSOR ARUN AGGARWAL RPAH PAIN MANAGEMENT CENTRE IHS Classification 1989 (updated 2004) Primary Headaches 4 categories Migraine Tension-type Cluster and other trigeminal
Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias. Disclosures. Objectives 6/20/2018. Rashmi Halker Singh, MD FAHS UCNS Review Course June 2018
 Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Rashmi Halker Singh, MD FAHS UCNS Review Course June 2018 Disclosures Honoraria from Allergan and Amgen for advisory board, Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports
Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Rashmi Halker Singh, MD FAHS UCNS Review Course June 2018 Disclosures Honoraria from Allergan and Amgen for advisory board, Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports
Trigeminal Neuralgia Future directions. Prof Joanna M. Zakrzewska 18 th International Leksell Gamma Knife Society Amsterdam 2016
 Trigeminal Neuralgia Future directions Prof Joanna M. Zakrzewska 18 th International Leksell Gamma Knife Society Amsterdam 2016 Aims and Objectives objectives Phenotying Outcomes Drugs vs surgery Imaging
Trigeminal Neuralgia Future directions Prof Joanna M. Zakrzewska 18 th International Leksell Gamma Knife Society Amsterdam 2016 Aims and Objectives objectives Phenotying Outcomes Drugs vs surgery Imaging
Disclosures. Objectives 6/2/2017
 Classification: Migraine and Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Lauren Doyle Strauss, DO, FAHS Assistant Professor, Child Neurology Assistant Director, Child Neurology Residency @StraussHeadache No disclosures
Classification: Migraine and Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Lauren Doyle Strauss, DO, FAHS Assistant Professor, Child Neurology Assistant Director, Child Neurology Residency @StraussHeadache No disclosures
Chapter 2 Diagnosis of Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias
 Chapter 2 Diagnosis of Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Mark J. Stillman Introduction The trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias (TACs) refer to a specific group of primary headaches characterized by unilaterality,
Chapter 2 Diagnosis of Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Mark J. Stillman Introduction The trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias (TACs) refer to a specific group of primary headaches characterized by unilaterality,
23 How Cluster Headache and Other Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Present
 23 How Cluster Headache and Other Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Present Henrik Winther Schytz 1. Cristina Tassorelli 2. Messoud Ashina 1 1 Glostrup Hospital, University of Copenhagen, Glostrup, Copenhagen,
23 How Cluster Headache and Other Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Present Henrik Winther Schytz 1. Cristina Tassorelli 2. Messoud Ashina 1 1 Glostrup Hospital, University of Copenhagen, Glostrup, Copenhagen,
Cluster headache associated with acute maxillary sinusitis.
 Cluster headache associated with acute maxillary sinusitis. Edvardsson, Bengt Published in: SpringerPlus DOI: 10.1186/2193-1801-2-509 2013 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Edvardsson,
Cluster headache associated with acute maxillary sinusitis. Edvardsson, Bengt Published in: SpringerPlus DOI: 10.1186/2193-1801-2-509 2013 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Edvardsson,
Chronic Daily Headaches
 Chronic Daily Headaches ANWARUL HAQ, MD, MRCP(UK), FAHS DIRECTOR BAYLOR HEADACHE CENTER, DALLAS, TEXAS DISCLOSURES: None OBJECTIVES AT THE CONCLUSION OF THIS ACTIVITY, PARTICIPANTS WILL BE ABLE TO: define
Chronic Daily Headaches ANWARUL HAQ, MD, MRCP(UK), FAHS DIRECTOR BAYLOR HEADACHE CENTER, DALLAS, TEXAS DISCLOSURES: None OBJECTIVES AT THE CONCLUSION OF THIS ACTIVITY, PARTICIPANTS WILL BE ABLE TO: define
The trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias (TACs) are a group of. Cluster Headache and Other Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias By Mark Burish, MD, PhD
 Downloaded from https://journals.lww.com/continuum by SruuCyaLiGD/095xRqJ2PzgDYuM98ZB494KP9rwScvIkQrYai2aioRZDTyulujJ/fqPksscQKqke3QAnIva1ZqwEKekuwNqyUWcnSLnClNQLfnPrUdnEcDXOJLeG3sr/HuiNevTSNcdMFp1i4FoTX9EXYGXm/fCfrbTavvQSUHUH4eazE11ptLzgCyEpzDoF
Downloaded from https://journals.lww.com/continuum by SruuCyaLiGD/095xRqJ2PzgDYuM98ZB494KP9rwScvIkQrYai2aioRZDTyulujJ/fqPksscQKqke3QAnIva1ZqwEKekuwNqyUWcnSLnClNQLfnPrUdnEcDXOJLeG3sr/HuiNevTSNcdMFp1i4FoTX9EXYGXm/fCfrbTavvQSUHUH4eazE11ptLzgCyEpzDoF
A synopsis of: Diagnosis and Management of Headaches in Adults: A national clinical guideline. Scottish intercollegiate Guidelines Network SIGN
 A synopsis of: Diagnosis and Management of Headaches in Adults: A national clinical guideline Scottish intercollegiate Guidelines Network SIGN November 2008. PETER FRAMPTON MSc MCOptom BAppSc (Optom)(AUS)
A synopsis of: Diagnosis and Management of Headaches in Adults: A national clinical guideline Scottish intercollegiate Guidelines Network SIGN November 2008. PETER FRAMPTON MSc MCOptom BAppSc (Optom)(AUS)
Cluster headache and paroxysmal hemicrania: differential diagnosis
 Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKCHACephalalgia0333-1024Blackwell Science, 2004254244248Original ArticleCH and PH: differential diagnosisj Zidverc-Trajkovic et al. Cluster headache and paroxysmal hemicrania:
Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKCHACephalalgia0333-1024Blackwell Science, 2004254244248Original ArticleCH and PH: differential diagnosisj Zidverc-Trajkovic et al. Cluster headache and paroxysmal hemicrania:
Cluster headache (CH): epidemiology, classification and clinical picture
 Cluster headache (CH): epidemiology, classification and clinical picture Toomas Toomsoo, M.D. Head of the Center of Neurology East Tallinn Central Hospital 1 INTRODUCTION Cluster headache - known as trigeminal
Cluster headache (CH): epidemiology, classification and clinical picture Toomas Toomsoo, M.D. Head of the Center of Neurology East Tallinn Central Hospital 1 INTRODUCTION Cluster headache - known as trigeminal
ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา
 ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา 1 CONTENT 1 2 3 Chronic Daily Headache Medical Overused Headache Management Headaches are one of the most common symptoms List
ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา 1 CONTENT 1 2 3 Chronic Daily Headache Medical Overused Headache Management Headaches are one of the most common symptoms List
Cephalalgia. Brief report: Microvascular Decompression or Neuromodulation in Patients with SUNCT and Trigeminal Neurovascular Conflict?
 Brief report: Microvascular Decompression or Neuromodulation in Patients with SUNCT and Trigeminal Neurovascular Conflict? Journal: Manuscript ID CHA-00-FT-0.R Manuscript Type: Article for Fast Track Review
Brief report: Microvascular Decompression or Neuromodulation in Patients with SUNCT and Trigeminal Neurovascular Conflict? Journal: Manuscript ID CHA-00-FT-0.R Manuscript Type: Article for Fast Track Review
Patient with Lots of NTERNATIONAL CLASSIFICATION. Headaches HEADACHE DISORDERS. R. Allan Purdy, MD, FRCPC,FACP
 Patient with Lots of NTERNATIONAL CLASSIFICATION Headaches of R. Allan Purdy, MD, FRCPC,FACP HEADACHE DISORDERS Professor of Medicine (Neurology) Dalhousie University, Halifax, Canada 2nd edition (ICHD-II)
Patient with Lots of NTERNATIONAL CLASSIFICATION Headaches of R. Allan Purdy, MD, FRCPC,FACP HEADACHE DISORDERS Professor of Medicine (Neurology) Dalhousie University, Halifax, Canada 2nd edition (ICHD-II)
doi: /brain/awl202 Brain (2006), 129,
 doi:10.1093/brain/awl202 Brain (2006), 129, 2746 2760 Short-lasting unilateral neuralgiform headache attacks with conjunctival injection and tearing (SUNCT) or cranial autonomic features (SUNA) a prospective
doi:10.1093/brain/awl202 Brain (2006), 129, 2746 2760 Short-lasting unilateral neuralgiform headache attacks with conjunctival injection and tearing (SUNCT) or cranial autonomic features (SUNA) a prospective
By Nathan Hall Associate Editor
 By Nathan Hall Associate Editor 34 Practical Neurology March 2005 These new rules may change the definition of head pain, but some practitioners may find the new guidelines themselves to be a source of
By Nathan Hall Associate Editor 34 Practical Neurology March 2005 These new rules may change the definition of head pain, but some practitioners may find the new guidelines themselves to be a source of
Hemicrania continua-like headache associated with carotid dissection may respond to indomethacin
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Neurology Faculty Papers Department of Neurology January 2007 Hemicrania continua-like headache associated with carotid dissection may
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Neurology Faculty Papers Department of Neurology January 2007 Hemicrania continua-like headache associated with carotid dissection may
UCNS Course A Review of ICHD-3b
 UCNS Course A Review of ICHD-3b Andrew D. Hershey, M.D., Ph.D., FAHS Endowed Chair and Director of Neurology Director, Cincinnati Children s Headache Center Professor of Neurology and Pediatrics University
UCNS Course A Review of ICHD-3b Andrew D. Hershey, M.D., Ph.D., FAHS Endowed Chair and Director of Neurology Director, Cincinnati Children s Headache Center Professor of Neurology and Pediatrics University
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: occipital_nerve_stimulation 8/2010 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Occipital nerve
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: occipital_nerve_stimulation 8/2010 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Occipital nerve
Trigeminal Neuralgia Involving All Three Branches Of Trigeminal Nerve Treated By Peripheral Neurectomy: An Interesting Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dental Science Volume 10 Number 2 Trigeminal Neuralgia Involving All Three Branches Of Trigeminal Nerve Treated By Peripheral Neurectomy: An Interesting Case Report K
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dental Science Volume 10 Number 2 Trigeminal Neuralgia Involving All Three Branches Of Trigeminal Nerve Treated By Peripheral Neurectomy: An Interesting Case Report K
DOWNLOAD OR READ : REVERSING HEMIFACIAL SPASM PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : REVERSING HEMIFACIAL SPASM PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 reversing hemifacial spasm reversing hemifacial spasm pdf reversing hemifacial spasm reversing hemifacial spasm Smallpdf
DOWNLOAD OR READ : REVERSING HEMIFACIAL SPASM PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 reversing hemifacial spasm reversing hemifacial spasm pdf reversing hemifacial spasm reversing hemifacial spasm Smallpdf
Persistent idiopathic facial pain a prospective systematic study of clinical characteristics and neuroanatomical findings at 3.
 Original Article Persistent idiopathic facial pain a prospective systematic study of clinical characteristics and neuroanatomical findings at 3.0 Tesla MRI Cephalalgia 2017, Vol. 37(13) 1231 1240! International
Original Article Persistent idiopathic facial pain a prospective systematic study of clinical characteristics and neuroanatomical findings at 3.0 Tesla MRI Cephalalgia 2017, Vol. 37(13) 1231 1240! International
Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias: Paroxysmal Hemicrania, SUNCT/SUNA, and Hemicrania Continua
 Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias: Paroxysmal Hemicrania, SUNCT/SUNA, and Hemicrania Continua Peter J. Goadsby, M.D., Ph.D., D.Sc., 1,2 Elisabetta Cittadini, M.D., 2 and Anna S. Cohen, M.D. 2 ABSTRACT
Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias: Paroxysmal Hemicrania, SUNCT/SUNA, and Hemicrania Continua Peter J. Goadsby, M.D., Ph.D., D.Sc., 1,2 Elisabetta Cittadini, M.D., 2 and Anna S. Cohen, M.D. 2 ABSTRACT
Post-Operative Cluster Headache Following Carotid Endarterectomy
 Review Received: October 31, 2016 Accepted: January 11, 2017 Published online: February 3, 2017 Post-Operative Cluster Headache Following Carotid Endarterectomy Thijs H.T. Dirkx Peter J. Koehler Department
Review Received: October 31, 2016 Accepted: January 11, 2017 Published online: February 3, 2017 Post-Operative Cluster Headache Following Carotid Endarterectomy Thijs H.T. Dirkx Peter J. Koehler Department
Trigeminal Neuralgia Association UK. Facing pain together TRIGEMINAL NEURALGIA AN OVERVIEW
 Trigeminal Neuralgia Association UK Facing pain together TRIGEMINAL NEURALGIA AN OVERVIEW The TNA UK was established to provide support and information to people affected by trigeminal neuralgia and we
Trigeminal Neuralgia Association UK Facing pain together TRIGEMINAL NEURALGIA AN OVERVIEW The TNA UK was established to provide support and information to people affected by trigeminal neuralgia and we
Sunct syndrome. Report of a case and treatment update
 Journal section: Orofacil pain-tmjd Publication Types: Case Report doi:10.4317/jced.51854 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.51854 Sunct syndrome. Report of a case and treatment update Cosme Gay-Escoda 1,
Journal section: Orofacil pain-tmjd Publication Types: Case Report doi:10.4317/jced.51854 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.51854 Sunct syndrome. Report of a case and treatment update Cosme Gay-Escoda 1,
Trigeminal Neuralgia (facial pain)
 Trigeminal Neuralgia (facial pain) Overview Trigeminal neuralgia is an inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, causing extreme pain and muscle spasms in the face. Attacks of intense, electric shock-like
Trigeminal Neuralgia (facial pain) Overview Trigeminal neuralgia is an inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, causing extreme pain and muscle spasms in the face. Attacks of intense, electric shock-like
Headache. Luke Bennetto Consultant Neurologist Engineers House 13 th September 2016
 Headache Luke Bennetto Consultant Neurologist Engineers House 13 th September 2016 Contents General thoughts Primary headache Secondary headache I want to curl up in a cave and die I want to drill a
Headache Luke Bennetto Consultant Neurologist Engineers House 13 th September 2016 Contents General thoughts Primary headache Secondary headache I want to curl up in a cave and die I want to drill a
Trigeminal Neuralgia > 1
 Trigeminal Neuralgia Overview Trigeminal neuralgia is an inflammation of the trigeminal nerve causing extreme pain and muscle spasms in the face. Attacks of intense, electric shock-like facial pain can
Trigeminal Neuralgia Overview Trigeminal neuralgia is an inflammation of the trigeminal nerve causing extreme pain and muscle spasms in the face. Attacks of intense, electric shock-like facial pain can
V1-ophthalmic. V2-maxillary. V3-mandibular. motor
 4. Trigeminal Nerve I. Objectives:. Understand the types of sensory information transmitted by the trigeminal system.. Describe the major peripheral divisions of the trigeminal nerve and how they innervate
4. Trigeminal Nerve I. Objectives:. Understand the types of sensory information transmitted by the trigeminal system.. Describe the major peripheral divisions of the trigeminal nerve and how they innervate
Presented by. Andrew Kopka B.S. CNIM R. EEG T
 Presented by Andrew Kopka B.S. CNIM R. EEG T 1 2 ! Common EP s / recordings used in the O.R. SSEP - Somatosensory evoked potentials TcMEP - Transcranial motor evoked potentials BAER - Brainstem auditory
Presented by Andrew Kopka B.S. CNIM R. EEG T 1 2 ! Common EP s / recordings used in the O.R. SSEP - Somatosensory evoked potentials TcMEP - Transcranial motor evoked potentials BAER - Brainstem auditory
Neuro Vascular Relationship between Superior Cerebellar Artery and Trigeminal Nerve
 Neuro Vascular Relationship between Superior Cerebellar Artery and Trigeminal Nerve Pages with reference to book, From 140 To 143 Nawab Mohammad Khan, Mohammad Afzal Khan, Fazal Karim Aasi ( Department
Neuro Vascular Relationship between Superior Cerebellar Artery and Trigeminal Nerve Pages with reference to book, From 140 To 143 Nawab Mohammad Khan, Mohammad Afzal Khan, Fazal Karim Aasi ( Department
Management of medically refractory trigeminal neuralgia in patients with multiple sclerosis
 Neurosurg Focus 18 (5):E13, 2005 Management of medically refractory trigeminal neuralgia in patients with multiple sclerosis JASON S. CHENG, B.S., RENE O. SANCHEZ-MEJIA, M.D., MARY LIMBO, B.A., MARIANN
Neurosurg Focus 18 (5):E13, 2005 Management of medically refractory trigeminal neuralgia in patients with multiple sclerosis JASON S. CHENG, B.S., RENE O. SANCHEZ-MEJIA, M.D., MARY LIMBO, B.A., MARIANN
Atypical presentations of cluster headache
 Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKCHACephalalgia0333-1024Blackwell Science, 200222Original ArticleAtypical presentations in cluster headachetd Rozen Atypical presentations of cluster headache TD Rozen Department
Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKCHACephalalgia0333-1024Blackwell Science, 200222Original ArticleAtypical presentations in cluster headachetd Rozen Atypical presentations of cluster headache TD Rozen Department
Gregg Goldin, MD Timothy Miller, MD 9/28/18 Neurology and Neurosurgery Grand Rounds
 Trigeminal Neuralgia (tic douloureux) Gregg Goldin, MD Timothy Miller, MD 9/28/18 Neurology and Neurosurgery Grand Rounds Disclosures -None Objectives 1) Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and medical management
Trigeminal Neuralgia (tic douloureux) Gregg Goldin, MD Timothy Miller, MD 9/28/18 Neurology and Neurosurgery Grand Rounds Disclosures -None Objectives 1) Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and medical management
Chakravarty, A. and A. Mukherjee (2003). "SUNCT syndrome responsive to lamotrigine: documentation of the first Indian case." Cephalalgia 23(6):
 Becser, N. and M. Berky (1995). "SUNCT syndrome: a Hungarian case." Headache 35(3): 158-60. A Hungarian patient with short-lasting, unilateral, neuralgiform headache attacks with conjunctival injection
Becser, N. and M. Berky (1995). "SUNCT syndrome: a Hungarian case." Headache 35(3): 158-60. A Hungarian patient with short-lasting, unilateral, neuralgiform headache attacks with conjunctival injection
Cluster headache in women: clinical characteristics and comparison with cluster headache in men
 J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2001;70:613 617 613 Department of Neurology, JeVerson Headache Center, Thomas University Hospital, 111 South 11th Street, Gibbon Building, Suite 8130, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2001;70:613 617 613 Department of Neurology, JeVerson Headache Center, Thomas University Hospital, 111 South 11th Street, Gibbon Building, Suite 8130, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Peripheral Extracranial Neurostimulation for the treatment of Primary Headache and Migraine:
 Chapter 19 Peripheral Extracranial Neurostimulation for the treatment of Primary Headache and Migraine: Introduction 1) The occipital nerve is involved in pain syndromes originating from nerve trauma,
Chapter 19 Peripheral Extracranial Neurostimulation for the treatment of Primary Headache and Migraine: Introduction 1) The occipital nerve is involved in pain syndromes originating from nerve trauma,
Headache Pain Generators
 Objectives 1. Define the major categories of headache. 2. Take a history directed at characterizing a headache pattern in an individual patient and identify the cause or triggers of the headache. 3. Understand
Objectives 1. Define the major categories of headache. 2. Take a history directed at characterizing a headache pattern in an individual patient and identify the cause or triggers of the headache. 3. Understand
Efficacy of Acupuncture Treatment for Trigeminal Neuralgia
 Efficacy of Acupuncture Treatment for Trigeminal Neuralgia DAOM (Doctor of Acupuncture and Oriental medicine) Candidate: David Kim Abstract: A 47-year-old Caucasian female has been suffering from TMJ on
Efficacy of Acupuncture Treatment for Trigeminal Neuralgia DAOM (Doctor of Acupuncture and Oriental medicine) Candidate: David Kim Abstract: A 47-year-old Caucasian female has been suffering from TMJ on
Classification of Facial Pain. Surgical Treatment of Facial Pain. Typical trigeminal neuralgia. Atypical trigeminal neuralgia
 Surgical Treatment of Facial Pain Nicholas M. Barbaro, MD University of California at San Francisco Classification of Facial Pain Trigeminal neuralgia Atypical trigeminal neuralgia Neuropathic facial pain
Surgical Treatment of Facial Pain Nicholas M. Barbaro, MD University of California at San Francisco Classification of Facial Pain Trigeminal neuralgia Atypical trigeminal neuralgia Neuropathic facial pain
MR imaging at 3.0 tesla of glossopharyngeal neuralgia by neurovascular compression
 MR imaging at 3.0 tesla of glossopharyngeal neuralgia by neurovascular compression Poster No.: C-1281 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nishihara 1, T. Noguchi 1, H. Irie 1, K. Sasaguri
MR imaging at 3.0 tesla of glossopharyngeal neuralgia by neurovascular compression Poster No.: C-1281 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nishihara 1, T. Noguchi 1, H. Irie 1, K. Sasaguri
Is Botulinum Toxin a Safe and Effective for the Treatment of Trigeminal Neuralgia in Adults?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2016 Is Botulinum Toxin a Safe and Effective
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2016 Is Botulinum Toxin a Safe and Effective
The trigeminal autonomic cephalgias (TACs) are a group of primary headache disorders characterised
 c CLUSTER Correspondence to: Professor Peter J Goadsby, Institute of Neurology, Queen Square, London WC1N 3BG, UK; peterg@ion.ucl.ac.uk TRIGEMINAL AUTONOMIC CEPHALGIAS Manjit S Matharu, Peter J Goadsby
c CLUSTER Correspondence to: Professor Peter J Goadsby, Institute of Neurology, Queen Square, London WC1N 3BG, UK; peterg@ion.ucl.ac.uk TRIGEMINAL AUTONOMIC CEPHALGIAS Manjit S Matharu, Peter J Goadsby
Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care
 Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care Spencer Johnson, O.D., F.A.A.O. Northeastern State University Oklahoma College of Optometry johns137@nsuok.edu Course Objectives Review headache classification Understand
Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care Spencer Johnson, O.D., F.A.A.O. Northeastern State University Oklahoma College of Optometry johns137@nsuok.edu Course Objectives Review headache classification Understand
Case Report Botulinum Toxin A for the Treatment of a Child with SUNCT Syndrome
 Pain Research and Management Volume 2016, Article ID 8016065, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8016065 Case Report Botulinum Toxin A for the Treatment of a Child with SUNCT Syndrome Yi Zhang, Haifeng
Pain Research and Management Volume 2016, Article ID 8016065, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8016065 Case Report Botulinum Toxin A for the Treatment of a Child with SUNCT Syndrome Yi Zhang, Haifeng
Classification of headaches
 Classification of headaches Jasna Zidverc Trajković Headache center Headache in adults: 1-year prevalence 13.4 Kryst 35.9 Miranda 28.7 Jaillard 87.3 O Brien 63.1 Wiehe 37.3 Lavados 59.7 Schwartz 76.0 Boardman
Classification of headaches Jasna Zidverc Trajković Headache center Headache in adults: 1-year prevalence 13.4 Kryst 35.9 Miranda 28.7 Jaillard 87.3 O Brien 63.1 Wiehe 37.3 Lavados 59.7 Schwartz 76.0 Boardman
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Alveolar osteitis (dry socket), periodontal pain due to, 436 Aphthous stomatitis, recurrent, mucosal pain due to, 439 440 Arthrocentesis/arthroscopy,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Alveolar osteitis (dry socket), periodontal pain due to, 436 Aphthous stomatitis, recurrent, mucosal pain due to, 439 440 Arthrocentesis/arthroscopy,
Original Policy Date
 MP 7.01.105 Occipital Nerve Stimulation Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12/2013 Original Policy Date 12/2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12/2013 Return to Medical Policy
MP 7.01.105 Occipital Nerve Stimulation Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12/2013 Original Policy Date 12/2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12/2013 Return to Medical Policy
Neurovascular elements of the PCF
 Level I: Neurovascular elements of the PCF Trigeminal and Abducent Superior cerebellar artery and vein Dandy s vein Level II: Facial and Cochleovestibular AICA and internal auditory artery, veins Level
Level I: Neurovascular elements of the PCF Trigeminal and Abducent Superior cerebellar artery and vein Dandy s vein Level II: Facial and Cochleovestibular AICA and internal auditory artery, veins Level
Središnja medicinska knjižnica
 Središnja medicinska knjižnica Adamec I., Grahovac G., Krbot Skorić M., Chudy D., Hajnšek S, Habek M. (2014) Tongue somatosensory-evoked potentials in microvascular decompression treated trigeminal neuralgia.
Središnja medicinska knjižnica Adamec I., Grahovac G., Krbot Skorić M., Chudy D., Hajnšek S, Habek M. (2014) Tongue somatosensory-evoked potentials in microvascular decompression treated trigeminal neuralgia.
The Clinical Profile of Sumatriptan: Cluster Headache Key Words
 Paper Eur Neurol 1994;34(suppl 2):35-39 P.J. Peter J. Goadsby Department of Neurology, The Prince Henry Hospital, Little Bay, Sydney, NSW, Australia The Clinical Profile of Sumatriptan: Cluster Headache
Paper Eur Neurol 1994;34(suppl 2):35-39 P.J. Peter J. Goadsby Department of Neurology, The Prince Henry Hospital, Little Bay, Sydney, NSW, Australia The Clinical Profile of Sumatriptan: Cluster Headache
CLUS 42 PRACTICAL NEUROLOGY. Pract Neurol: first published as /j x on 1 October Downloaded from
 42 PRACTICAL NEUROLOGY Pract Neurol: first published as 10.1046/j.1474-7766.2001.00505.x on 1 October 2001. Downloaded from http://pn.bmj.com/ CLUS on 31 August 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright. OCT
42 PRACTICAL NEUROLOGY Pract Neurol: first published as 10.1046/j.1474-7766.2001.00505.x on 1 October 2001. Downloaded from http://pn.bmj.com/ CLUS on 31 August 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright. OCT
Measure Components Numerator Statement
 MEASURE #5: OVERUSE OF OPIOID CONTAINING MEDICATIONS FOR PRIMARY HEADACHE DISORDERS Headache For Quality Improvement Only. Not to be used for Public Reporting or Accountability Measure Description Percentage
MEASURE #5: OVERUSE OF OPIOID CONTAINING MEDICATIONS FOR PRIMARY HEADACHE DISORDERS Headache For Quality Improvement Only. Not to be used for Public Reporting or Accountability Measure Description Percentage
Refractory trigeminal neuralgia
 4 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Lisbon, Portugal, June 16-19, 2018 Teaching Course 15 The difficult to treat headache patient - Level 3 Refractory trigeminal neuralgia Giorgio Cruccu
4 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Lisbon, Portugal, June 16-19, 2018 Teaching Course 15 The difficult to treat headache patient - Level 3 Refractory trigeminal neuralgia Giorgio Cruccu
Charlin S Syndrome Following a Routine Septorhinoplasty
 Kavyani et al. 103 Case Report Charlin S Syndrome Following a Routine Septorhinoplasty Ali Kavyani1*, Ali Manafi2 1. 2. Department of Plastic Surgery, School of Medicine, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences,
Kavyani et al. 103 Case Report Charlin S Syndrome Following a Routine Septorhinoplasty Ali Kavyani1*, Ali Manafi2 1. 2. Department of Plastic Surgery, School of Medicine, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences,
Index. Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) 441 447 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, brain, headache in, 388 Acetaminophen for migraine, 406 407 headache from, 369
Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) 441 447 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, brain, headache in, 388 Acetaminophen for migraine, 406 407 headache from, 369
TRIGEMINAL AUTONOMIC CEPHALALGIAS
 TRIGEMINAL AUTONOMIC CEPHALALGIAS A. Trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias Christopher J. Boes, MD Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN Trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias (TACs) defined Headaches characterized by pain
TRIGEMINAL AUTONOMIC CEPHALALGIAS A. Trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias Christopher J. Boes, MD Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN Trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias (TACs) defined Headaches characterized by pain
The Role of Allergies and Sinus Disorders in Headache & Facial Pain
 The Role of Allergies and Sinus Disorders in Headache & Facial Pain Vincent T. Martin, MD Professor of Medicine Co-director of the Headache & Facial Pain Center University of Cincinnati College of Medicine
The Role of Allergies and Sinus Disorders in Headache & Facial Pain Vincent T. Martin, MD Professor of Medicine Co-director of the Headache & Facial Pain Center University of Cincinnati College of Medicine
Minwoo Lee 1, Min Kyung Chu 2, Juyoung Lee 1, Jinhyuk Yoo 1 and Hong Ki Song 1*
 Lee et al. The Journal of Headache and Pain (2016) 17:21 DOI 10.1186/s10194-016-0615-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Field testing primary stabbing headache criteria according to the 3rd beta edition of
Lee et al. The Journal of Headache and Pain (2016) 17:21 DOI 10.1186/s10194-016-0615-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Field testing primary stabbing headache criteria according to the 3rd beta edition of
Supraorbital nerve stimulation Cefaly Device - FDA Approved for migraine prevention (also being investigated as acute therapy)
 NEUROSTIMULATION/NEUROMODULATION UPDATE Meyer and Renee Luskin Andrew Charles, M.D. Professor Luskin Chair in Migraine and Headache Studies Director, UCLA Goldberg Migraine Program David Geffen School
NEUROSTIMULATION/NEUROMODULATION UPDATE Meyer and Renee Luskin Andrew Charles, M.D. Professor Luskin Chair in Migraine and Headache Studies Director, UCLA Goldberg Migraine Program David Geffen School
Chronic cluster headaches icd 10
 Chronic cluster headaches icd 10 Search ICD - 10 -CM Diagnosis Code G44.029. Chronic cluster headache, not intractable. 2016 2017 2018 Billable/Specific Code. Applicable To. Chronic cluster headache NOS;
Chronic cluster headaches icd 10 Search ICD - 10 -CM Diagnosis Code G44.029. Chronic cluster headache, not intractable. 2016 2017 2018 Billable/Specific Code. Applicable To. Chronic cluster headache NOS;
Perforating branches from ovending arteries in hemifacial spasm: anatomical correlation with vertebrobasilar configuration
 J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1999;67:73 77 73 Department of Neurosurgery, Nagoya University School of Medicine, Nagoya, Japan T Nagatani S Inao Y Suzuki J Yoshida Correspondence to: Dr T Nagatani, Department
J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1999;67:73 77 73 Department of Neurosurgery, Nagoya University School of Medicine, Nagoya, Japan T Nagatani S Inao Y Suzuki J Yoshida Correspondence to: Dr T Nagatani, Department
Embriologically, The head is formed from the first two cervical segments (except the mandible, which is formed by the third). The first and second
 Embriologically, The head is formed from the first two cervical segments (except the mandible, which is formed by the third). The first and second cervical vertebra are also derived from these two segments.
Embriologically, The head is formed from the first two cervical segments (except the mandible, which is formed by the third). The first and second cervical vertebra are also derived from these two segments.
Clinical Commissioning Policy Statement: Sphenopalatine Ganglion Stimulation for Refractory Chronic Cluster Headache (Adults)
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Statement: Sphenopalatine Ganglion Stimulation for Refractory Chronic Cluster Headache (Adults) NHS England Reference: 170083P 1 Contents 1. Plain Language Summary... 3 2.
Clinical Commissioning Policy Statement: Sphenopalatine Ganglion Stimulation for Refractory Chronic Cluster Headache (Adults) NHS England Reference: 170083P 1 Contents 1. Plain Language Summary... 3 2.
The effect of single-application topical ophthalmic anesthesia in patients with trigeminal neuralgia
 J Neurosurg 80:993-997, 1994 The effect of single-application topical ophthalmic anesthesia in patients with trigeminal neuralgia A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial DOUGLAS KONDZIOLKA,
J Neurosurg 80:993-997, 1994 The effect of single-application topical ophthalmic anesthesia in patients with trigeminal neuralgia A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial DOUGLAS KONDZIOLKA,
Idiopathic stabbing headache in the juvenile population: a clinical study and review of the literature
 J Headache Pain (2002) 3:21 25 Springer-Verlag 2002 REVIEW Vincenzo Raieli Giovanni Luca Eliseo Michela La Vecchia Girolama La Franca Eleonora Pandolfi Domenico Puma Donatella Ragusa Mario Eliseo Idiopathic
J Headache Pain (2002) 3:21 25 Springer-Verlag 2002 REVIEW Vincenzo Raieli Giovanni Luca Eliseo Michela La Vecchia Girolama La Franca Eleonora Pandolfi Domenico Puma Donatella Ragusa Mario Eliseo Idiopathic
Clinical features and surgical treatment of trigeminal neuralgia caused solely by venous compression
 Acta Neurochir (2011) 153:1037 1042 DOI 10.1007/s00701-011-0957-x CLINICAL ARTICLE Clinical features and surgical treatment of trigeminal neuralgia caused solely by venous compression Wenyao Hong & Xuesheng
Acta Neurochir (2011) 153:1037 1042 DOI 10.1007/s00701-011-0957-x CLINICAL ARTICLE Clinical features and surgical treatment of trigeminal neuralgia caused solely by venous compression Wenyao Hong & Xuesheng
Occipital Nerve Stimulation Corporate Medical Policy
 Occipital Nerve Stimulation Corporate Medical Policy File name: Occipital Nerve Stimulation File code: UM.SPSVC.14 Origination: 2011 Last Review: 11/2017 Next Review: 11/2018 Effective Date: 05/01/2018
Occipital Nerve Stimulation Corporate Medical Policy File name: Occipital Nerve Stimulation File code: UM.SPSVC.14 Origination: 2011 Last Review: 11/2017 Next Review: 11/2018 Effective Date: 05/01/2018
PART IV: NEUROPATHIC PAIN SYNDROMES JILL SINDT FEBRUARY 7, 2019
 PART IV: NEUROPATHIC PAIN SYNDROMES JILL SINDT FEBRUARY 7, 2019 NEUROPATHIC PAIN PAIN ARISING AS DIRECT CONSEQUENCE OF A LESION OR DISEASE AFFECTING THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM AFFECTS 3-8% OF POPULATION
PART IV: NEUROPATHIC PAIN SYNDROMES JILL SINDT FEBRUARY 7, 2019 NEUROPATHIC PAIN PAIN ARISING AS DIRECT CONSEQUENCE OF A LESION OR DISEASE AFFECTING THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM AFFECTS 3-8% OF POPULATION
HEADACHES THE RED FLAGS
 HEADACHES THE RED FLAGS FAYYAZ AHMED CONSULTANT NEUROLOGIST HON. SENIOR LECTURER HULL YORK MEDICAL SCHOOL SECONDARY VS PRIMARY HEADACHES COMMON SECONDARY HEADACHES UNCOMMON BUT SERIOUS SECONDARY HEADACHES
HEADACHES THE RED FLAGS FAYYAZ AHMED CONSULTANT NEUROLOGIST HON. SENIOR LECTURER HULL YORK MEDICAL SCHOOL SECONDARY VS PRIMARY HEADACHES COMMON SECONDARY HEADACHES UNCOMMON BUT SERIOUS SECONDARY HEADACHES
Controversy One: Headache and Disability. Robert Shapiro, MD, PhD University of Vermont
 Controversy One: Headache and Disability Robert Shapiro, MD, PhD University of Vermont Southern Headache Society Orlando, FL, Sept 21, 2013 Disclosures Consulting within the past 12 months: Transcept Pharmaceuticals
Controversy One: Headache and Disability Robert Shapiro, MD, PhD University of Vermont Southern Headache Society Orlando, FL, Sept 21, 2013 Disclosures Consulting within the past 12 months: Transcept Pharmaceuticals
FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE. No relevant financial relationships
 Sleep and Headache Paul Mathew, MD, FAHS Director of Continuing Medical Education John R. Graham Headache Center Brigham & Women s Hospital Director of Headache Medicine Cambridge Health Alliance Harvard
Sleep and Headache Paul Mathew, MD, FAHS Director of Continuing Medical Education John R. Graham Headache Center Brigham & Women s Hospital Director of Headache Medicine Cambridge Health Alliance Harvard
Transcutaneous stimulation of the cervical branch of the vagus nerve for cluster headache and migraine
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Transcutaneous stimulation of the cervical branch of the vagus nerve for cluster headache and migraine Cluster
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Transcutaneous stimulation of the cervical branch of the vagus nerve for cluster headache and migraine Cluster
Microvascular Decompression of the Vestibulocochlear Nerve
 JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2015;5(1):182-186 Microvascular Decompression of the Vestibulocochlear Nerve Henry Emanuel, Zakier Hussain Department of Neurosurgery, Waikato Hospital, Hamilton, New Zealand. Abstract:
JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2015;5(1):182-186 Microvascular Decompression of the Vestibulocochlear Nerve Henry Emanuel, Zakier Hussain Department of Neurosurgery, Waikato Hospital, Hamilton, New Zealand. Abstract:
Outpatient Headache Care Guideline
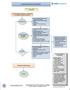 1 Outpatient Care Guideline Inclusion criteria: children > 3 yrs with headaches Is urgent emergency department, neuroimaging, or Neurology consultation indicated? Referral to ED if: New severe headache
1 Outpatient Care Guideline Inclusion criteria: children > 3 yrs with headaches Is urgent emergency department, neuroimaging, or Neurology consultation indicated? Referral to ED if: New severe headache
Neuralgias T R I G E M I N A L N E U R A L G I A
 Neuralgias T R I G E M I N A L N E U R A L G I A (MEANS PAIN IN A NERVE) Definition of pain Facial pain Cranial neuralgias are commonly distinct in two groups: typical neuralgias and atypical facial pain.
Neuralgias T R I G E M I N A L N E U R A L G I A (MEANS PAIN IN A NERVE) Definition of pain Facial pain Cranial neuralgias are commonly distinct in two groups: typical neuralgias and atypical facial pain.
A New Minimally Invasive Technique for Cauterizing the Maxillary Artery and Its Application in the Treatment of Cluster Headache
 A New Minimally Invasive Technique for Cauterizing the Maxillary Artery and Its Application in the Treatment of Cluster Headache Elliot Shevel, BDS, DipMFOS, MBBCh* Purpose: To describe a new, relatively
A New Minimally Invasive Technique for Cauterizing the Maxillary Artery and Its Application in the Treatment of Cluster Headache Elliot Shevel, BDS, DipMFOS, MBBCh* Purpose: To describe a new, relatively
University of Bristol - Explore Bristol Research
 Sims-Williams, H., Matthews, J. C., Talbot, P. S., Love-Jones, S., Brooks, J. CW., Patel, N. K., & Pickering, A. E. (2017). Deep brain stimulation of the periaqueductal gray releases endogenous opioids
Sims-Williams, H., Matthews, J. C., Talbot, P. S., Love-Jones, S., Brooks, J. CW., Patel, N. K., & Pickering, A. E. (2017). Deep brain stimulation of the periaqueductal gray releases endogenous opioids
The main features of the TACs:
 Pathophysiology of trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias Jasna Zidverc Trajković Headache center The main features of the TACs: 1. Trigeminal distribution of the pain 2. Ipsilateral cranial autonomic features
Pathophysiology of trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias Jasna Zidverc Trajković Headache center The main features of the TACs: 1. Trigeminal distribution of the pain 2. Ipsilateral cranial autonomic features
INTRAOPERATIVE NEUROPHYSIOLOGICAL MONITORING FOR MICROVASCULAR DECOMPRESSION SURGERY IN PATIENTS WITH HEMIFACIAL SPASM
 INTRAOPERATIVE NEUROPHYSIOLOGICAL MONITORING FOR MICROVASCULAR DECOMPRESSION SURGERY IN PATIENTS WITH HEMIFACIAL SPASM WILLIAM D. MUSTAIN, PH.D., CNIM, BCS-IOM DEPARTMENT OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY AND COMMUNICATIVE
INTRAOPERATIVE NEUROPHYSIOLOGICAL MONITORING FOR MICROVASCULAR DECOMPRESSION SURGERY IN PATIENTS WITH HEMIFACIAL SPASM WILLIAM D. MUSTAIN, PH.D., CNIM, BCS-IOM DEPARTMENT OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY AND COMMUNICATIVE
Headache Mary D. Hughes, MD Neuroscience Associates
 Headache Mary D. Hughes, MD Neuroscience Associates Case 1 22 year old female presents with recurrent headaches. She has had headaches for the past 3 years. They start on the right side of her head and
Headache Mary D. Hughes, MD Neuroscience Associates Case 1 22 year old female presents with recurrent headaches. She has had headaches for the past 3 years. They start on the right side of her head and
Headache Syndrome. Karen Alvarez, D.O Nemours Children s Specialty Care Jacksonville, FL
 Headache Syndrome Karen Alvarez, D.O Nemours Children s Specialty Care Jacksonville, FL What is a headache? A headache or cephalgia is defined as pain anywhere in the region of head or neck Where does
Headache Syndrome Karen Alvarez, D.O Nemours Children s Specialty Care Jacksonville, FL What is a headache? A headache or cephalgia is defined as pain anywhere in the region of head or neck Where does
2019 COLLECTION TYPE: MIPS CLINICAL QUALITY MEASURES (CQMS) MEASURE TYPE: Patient Reported Outcome High Priority
 Quality ID #435: Quality of Life Assessment For Patients With Primary Headache Disorders National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care Meaningful Measure Area: Patient Reported Functional Outcomes
Quality ID #435: Quality of Life Assessment For Patients With Primary Headache Disorders National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care Meaningful Measure Area: Patient Reported Functional Outcomes
Trigeminal Neuralgia: A Review
 REVIEW ARTICLE ISSN: 2456-8090 (online) International Healthcare Research Journal 2017;1(4):9-14. QR CODE Trigeminal Neuralgia: A Review K ABY K BABU 1, ASHISH K BABU 2, NITESH CHITKARA 3, RAHIL JOSHI
REVIEW ARTICLE ISSN: 2456-8090 (online) International Healthcare Research Journal 2017;1(4):9-14. QR CODE Trigeminal Neuralgia: A Review K ABY K BABU 1, ASHISH K BABU 2, NITESH CHITKARA 3, RAHIL JOSHI
Headache. Section 1. Migraine headache. Clinical presentation
 Section 1 Headache Migraine headache 1 Clinical presentation It is important to recognize just how significant a problem migraine headache is. It has been estimated that migraine affects 11% of the United
Section 1 Headache Migraine headache 1 Clinical presentation It is important to recognize just how significant a problem migraine headache is. It has been estimated that migraine affects 11% of the United
Pause for thought. Dr Jane Anderson Consultant Neurologist
 Pause for thought Dr Jane Anderson Consultant Neurologist Which is the top cause of years lived with disability worldwide? 1. COPD 2. Low Back pain 3. Diabetes 4. Migraine with medication overuse headache
Pause for thought Dr Jane Anderson Consultant Neurologist Which is the top cause of years lived with disability worldwide? 1. COPD 2. Low Back pain 3. Diabetes 4. Migraine with medication overuse headache
Anterior Ethmoidal Nerve Overview
 Anterior Ethmoidal Nerve Overview Name Anterior Ethmoidal Nerve Latin Nervus Ethmoidalis anterior Etymology Pain Differential Diagnosis - Enrico Dellacà M.D Ph.D. Nerve from Latin nervus meaning sinew,
Anterior Ethmoidal Nerve Overview Name Anterior Ethmoidal Nerve Latin Nervus Ethmoidalis anterior Etymology Pain Differential Diagnosis - Enrico Dellacà M.D Ph.D. Nerve from Latin nervus meaning sinew,
Clinical case. Clinical case 3/15/2018 OVERVIEW. Refractory headaches and update on novel treatment. Refractory headache.
 OVERVIEW Refractory headaches and update on novel treatment Definition of refractory headache Treatment approach Medications Neuromodulation In the pipeline Juliette Preston, MD OHSU Headache Center Refractory
OVERVIEW Refractory headaches and update on novel treatment Definition of refractory headache Treatment approach Medications Neuromodulation In the pipeline Juliette Preston, MD OHSU Headache Center Refractory
Classification of headaches
 Classification of headaches Primary headaches OR Idiopathic headaches Secondary headaches OR Symptomatic headaches THE HEADACHE IS ITSELF THE DISEASE NO ORGANIC LESION IN THE BEACKGROUND TREAT THE HEADACHE!
Classification of headaches Primary headaches OR Idiopathic headaches Secondary headaches OR Symptomatic headaches THE HEADACHE IS ITSELF THE DISEASE NO ORGANIC LESION IN THE BEACKGROUND TREAT THE HEADACHE!
By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi
 By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, students shouldbe able to: List the nuclei of the deep origin of the trigeminal and facial nerves in the brain
By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, students shouldbe able to: List the nuclei of the deep origin of the trigeminal and facial nerves in the brain
Tr i g e m i n a l neuralgia is a form of facial pain that. Trigeminal neuralgia in young adults. Clinical article
 J Neurosurg 114:1306 1311, 2011 Trigeminal neuralgia in young adults Clinical article Di a a Ba h g a t, M.D., Di b y e n d u K. Ray, M.B.B.S., M.S., M.Ch., Ahm e d M. Ra s l a n, M.D., Sh i r l e y McCa
J Neurosurg 114:1306 1311, 2011 Trigeminal neuralgia in young adults Clinical article Di a a Ba h g a t, M.D., Di b y e n d u K. Ray, M.B.B.S., M.S., M.Ch., Ahm e d M. Ra s l a n, M.D., Sh i r l e y McCa
MEASURE #4: Overuse of Barbiturate Containing Medications for Primary Headache Disorders Headache
 MEASURE #4: Overuse of Barbiturate Containing Medications for Primary Headache Disorders Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older with a diagnosis of primary headache
MEASURE #4: Overuse of Barbiturate Containing Medications for Primary Headache Disorders Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older with a diagnosis of primary headache
Neuralgias tend to be sudden, brief, intermittent severe, stabbing or lightning pains or electric shock sensations.
 Neuralgia is the term used to describe pain arising from a nerve. There are many different neuralgias which have been described in the medical literature, but I will only touch upon a few more common ones.
Neuralgia is the term used to describe pain arising from a nerve. There are many different neuralgias which have been described in the medical literature, but I will only touch upon a few more common ones.
Trigeminal Autonomic. Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias (TACs) María-Carmen Wilson,MD
 Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias (TACs) María-Carmen Wilson,MD Director, Headache and Facial Pain Program Ochsner, North Shore Region Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalgias gwith autonomic features gcluster
Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias (TACs) María-Carmen Wilson,MD Director, Headache and Facial Pain Program Ochsner, North Shore Region Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalgias gwith autonomic features gcluster
Policy #: 411 Latest Review Date: January 2014
 Name of Policy: Occipital Nerve Stimulation Policy #: 411 Latest Review Date: January 2014 Category: Surgery Policy Grade: B Background/Definitions: As a general rule, benefits are payable under Blue Cross
Name of Policy: Occipital Nerve Stimulation Policy #: 411 Latest Review Date: January 2014 Category: Surgery Policy Grade: B Background/Definitions: As a general rule, benefits are payable under Blue Cross
