Bundeswehrkrankenhaus Ulm Abteilung HNO Kopf-Halschirurgie
|
|
|
- Archibald Cannon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Kai Johannes Lorenz and Klaus Effinger Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery Department of Radiology and interventional Radiology German Armed Forces Hospital
2 Incidence of hemorrhage under battle conditions Since the last 30 years the incidence of head and neck injuries in battlefield is increasing: 39% of all soldiers injured during Operation Iraqi Freedom II had wounds in this aera. The head and neck areas has an excellent blood supply The prognosis of wounded soldiers is determined by the degree of bloodloss-induced hypovolaemia and by the respiratory situation, uncontrolled haemorrhage accounts for the majority of deaths in combat. quick and adequate action is necessary Rustemeyer J, Kranz V, Bremerich A (2007) Injuries in combat from with particular reference to those to the head and neck : a review. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 45 : Wade AL, Dye JL, Mohrle CR, Galarneau MR (2007) Head face,and neck injuries during Operation Iraqi Freedom II : results from the US Navy Marine Corps Combat Trauma Registry. J Trauma 63 : Mabry RL, Holcomb JB, Baker AM: United States Army Rangers in Somalia: an analysis of combat casualties on an urban battlefield. J Trauma. 49: (2003).
3
4 Incidence of hemorrhage under battle conditions Beside airway management, haemorrhage control is one of the measures that ultimately determine whether a patient with severe head and neck injuries can be transferred to secondary care or not. airway management is performed by means of either tracheal intubation with a cuffed tube to prevent aspiration or an emergency cricothyrotomy, haemorrhage control is much more difficult owing to the complex anatomical conditions in the head and neck area.
5 Haemorrhage treatment nose and midface Trauma induced bleeding from the nasal and midfacial area is mostly a combined venous and arterial hemorrhage risk of inducing additional injuries (orbit and brain)
6 Haemorrhage treatment nose and midface Pneumatic tamponade with hematostatic CMC cover Epitaxis catheder with double cuff Nasopharynx (posterior bleeding) and nasal cavity For use on operations, and especially for treatment by non-medical personnel, the use of epistaxis catheters has proved to be useful
7 Haemorrhage treatment nose and midface Use of a bladder catherder for control of a posterior epitaxis Remember! Any nose tamponade has to be secured to prevent aspiration!
8 Haemorrhage treatment nose and midface YES NEVER Correct orientation for the introduction of internal nose dressing is a virtual line between the tipof the nose and the tragus cartilage of the ear
9 Haemorrhage treatment head and face light compression bandage because of the underlying bone, this area is well-suited for compression and pressure dressings In case of unstable skull fractures no uncontrolled compression to prevent a dislocation of the different parts of the calvaria and an aggravation of cerebral symptoms. under no circumstances compress the airway
10 Haemorrhage in the oral and pharyngeal area Bleeding from the oral and pharyngeal area, as caused by injuries of the mandible, the floor of the mouth and the tongue, is associated with an extremely high risk of blood aspiration and obstruction of the airways. Treatment of haemorrhage without blocking the airways is difficult immediate airway management by means of surgical access (cricothyrotomy) is required insert thin layers of gauze into the oral-pharyngeal area. number of gauze layers need to be documented one end of each layer should be left outside the mouth in order to prevent later aspiration of the inserted material.
11 Haemorrhage in the neck area MONSON Haemorrhage in the neck area may be caused by injuries to skin vessels or subcutaneous veins as well as massive bleeding from the carotid sheath. 33% 33% 23% multiple 11% Fox CJ et al. J Vasc Surg 2006; 44: 86 Battle induced neck injuries are mostly located in the region II or III. Haemorrhage for the region II is much easier to handle the injuries in the regions I or III.
12 Haemorrhage in the neck area Initial haemorrhage control in neck injuries is limited to digital compression of the relevant vessels or light compression bandage In case of arterial haemorrhage, particularly in the area of the carotid artery avoid a complete closure in order to prevent hypoperfusion and subsequent brain ischemia.
13 Haemorrhage in the neck area Use of bladder catheders for small penetrations with arterial bleeding Especially Zone III and Zone I
14 Haemorrhage treatment face and neck Arista Use of haemostyptics four different groups: Microporous Polysaccharide Hemospheres Quickclot Poly-N-acetylglucosamine Zeolites Celox Human fibrin wound dressing
15 advantages Absolutely no preparation time No special storage conditions Potentially improves patient comfort Easy to use (non medical personnel)
16 Haemorrhage treatment face and neck
17
18 Haemorrhage in the midface and nasal area Haemorrhage in the area of the nose, the paranasal sinuses and the nasopharynx is also treated primarily by means of tamponades Final haemorrhage control can be performed as part of the treatment of the mid-facial bone injuries after transfer to Role 3 or Role 4 or repatriation. If a transfer is not possible and bleeding can not be controlled even after several days of applying tamponade, an experienced head and neck surgeon should treat the source of haemorrhage.
19 Haemorrhage in the midface and nasal area Local arterial haemorrhage in the nasal and nasopharyngeal area can be treated by means of monopolar or bipolar coagulation. If the source of haemorrhage can not be identified, ligation (clipping) of the bleeding artery (maxillary artery) can be performed using an osteoplastic approach to the maxillary sinus or, for the ethmoidal arteries, a medial canthotomy.
20 Haemorrhage in the oral cavity and pharynx injuries of the mouth or pharynx: haemorrhage control performed through compression or under visually control electrosurgical coagulation. extensive injuries of the mouth and pharynx: haemostatic agents combined with tamponade extensive haemorrhage and haemorrhage that can not be localised: ligation of the supplying arteries following the external carotic artery via a cervical access
21 Haemorrhage in the neck area Heavily bleeding neck injuries are treated in the trauma room or in the OR (general anaesthesia, including haemodilution and/or transfusion of blood products) Careful exploration of the soft tissue of the neck Venous haemorrhage is controlled by suture, ligation or careful coagulation with due consideration of the surrounding structures, particularly nerves. take into account the situation of the upper respiratory tract and oesophageal area: any penetrating injuries there must be treated accordingly.
22 Haemorrhage in the neck area arterial haemorrhage: smaller end arteries can be treated by ligation. external carotid artery: ligation at the junction above the bifurcation or at each of its branches ligation of the common or internal carotid arteries only in exceptional situations. If possible, a temporary stent should be inserted into the vessel. a piece of a infusion tube can be inserted and blood flow can be maintained until treatment at a Role 3 unit or until after repatriation
23 Summary Survival odds of military personnel wounded in combat substantially depend on the extent of blood loss until initial treatment is given. Uncontrolled haemorrhage is responsible for a large proportion of fatalities in combat situations. Successful haemorrhage control, particularly in the head and neck area, until definite surgical intervention is possible, requires profound anatomical knowledge and a certain degree of surgical skills. In addition the use of haemostatic agents can improve haemorrhage control and minimise the frequency of secondary haemorrhage
24 Thank you for your attendance!
Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 The Nose External Nose Nasal Cavity External Nose Blood and Nerve Supplies of the External Nose Blood Supply of the External Nose The skin of the external nose Branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary
The Nose External Nose Nasal Cavity External Nose Blood and Nerve Supplies of the External Nose Blood Supply of the External Nose The skin of the external nose Branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary
AIRWAY MANAGEMENT SUZANNE BROWN, CRNA
 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT SUZANNE BROWN, CRNA OBJECTIVE OF LECTURE Non Anesthesia Sedation Providers Review for CRNA s Informal Questions encouraged 2 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AWARENESS BASICS OF ANATOMY EQUIPMENT 3
AIRWAY MANAGEMENT SUZANNE BROWN, CRNA OBJECTIVE OF LECTURE Non Anesthesia Sedation Providers Review for CRNA s Informal Questions encouraged 2 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AWARENESS BASICS OF ANATOMY EQUIPMENT 3
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA
 PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
Face and Throat Injuries. Chapter 26
 Face and Throat Injuries Chapter 26 Anatomy of the Head Landmarks of the Neck Injuries to the Face Injuries around the face can lead to upper airway obstructions. Bleeding from the face can be profuse.
Face and Throat Injuries Chapter 26 Anatomy of the Head Landmarks of the Neck Injuries to the Face Injuries around the face can lead to upper airway obstructions. Bleeding from the face can be profuse.
Nasotracheal Intubation for Head and Neck Surgery
 Nasotracheal Intubation for Head and Neck Surgery Dr A J Cartwright Introduction History Anatomy Indications for Technique of Complications Contraindications Conclusions History First described in 1902
Nasotracheal Intubation for Head and Neck Surgery Dr A J Cartwright Introduction History Anatomy Indications for Technique of Complications Contraindications Conclusions History First described in 1902
Module 1, Stomatology
 Module 1, Stomatology Department of operative surgery and topographic anatomy Test questions for self training for passing Module 1, writing part Paractical questions with images The patient has been scheduled
Module 1, Stomatology Department of operative surgery and topographic anatomy Test questions for self training for passing Module 1, writing part Paractical questions with images The patient has been scheduled
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons and the seriously injured patient. Barts and The London NHS Trust
 Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons and the seriously injured patient Barts and The London NHS Trust How do you assess this? Primary Survey A B C D E Airway & Cervical Spine Breathing & Ventilation Circulation
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons and the seriously injured patient Barts and The London NHS Trust How do you assess this? Primary Survey A B C D E Airway & Cervical Spine Breathing & Ventilation Circulation
Epidemiology 3002). Epidemiology and Pathophysiology
 Epidemiology Maxillofacial trauma or injuries are commonly encountered in the practice of emergency medicine and are presenting one of the most challenging problems to the attending surgeons or physicians
Epidemiology Maxillofacial trauma or injuries are commonly encountered in the practice of emergency medicine and are presenting one of the most challenging problems to the attending surgeons or physicians
Anatomy and Physiology. Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
DR. SAAD AL-MUHAYAWI, M.D., FRCSC. ORL Head & Neck Surgery
 TRAUMA IN ORL DR. SAAD AL-MUHAYAWI, M.D., FRCSC Associate Professor & Consultant ORL Head & Neck Surgery TYPES OF TRAUMA EAR & TEMPORAL BONE TRAUMA NOSE & FACIAL BONES TRAUMA LARYNGEAL TRAUMA NECK TRAUMA
TRAUMA IN ORL DR. SAAD AL-MUHAYAWI, M.D., FRCSC Associate Professor & Consultant ORL Head & Neck Surgery TYPES OF TRAUMA EAR & TEMPORAL BONE TRAUMA NOSE & FACIAL BONES TRAUMA LARYNGEAL TRAUMA NECK TRAUMA
More than 43,000 US military personnel have been
 Original Research Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery The Joint Facial and Invasive Neck Trauma (J-FAINT) Project, Iraq and Afghanistan 2003-2011 Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery 148(3) 403 408
Original Research Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery The Joint Facial and Invasive Neck Trauma (J-FAINT) Project, Iraq and Afghanistan 2003-2011 Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery 148(3) 403 408
EPISTAXIS. Rory Attwood MBChB,FRCS Department of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch
 EPISTAXIS Rory Attwood MBChB,FRCS Department of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch EPISTAXIS Bleeding from the nose Age Incidence Children Elderly
EPISTAXIS Rory Attwood MBChB,FRCS Department of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch EPISTAXIS Bleeding from the nose Age Incidence Children Elderly
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Activity Three: Where s the Bleeding?
 Activity Three: Where s the Bleeding? There are five main sites of potentially fatal bleeding in trauma, remembered by the phrase on the floor and four more. On the floor refers to losing blood externally
Activity Three: Where s the Bleeding? There are five main sites of potentially fatal bleeding in trauma, remembered by the phrase on the floor and four more. On the floor refers to losing blood externally
Ears. Mouth. Jowls 6 Major Bones of the Face Nasal bone Two
 1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 25 Injuries to the Face, Neck, and Eyes Injuries to the Face and Neck Face and neck are to injury Relatively unprotected positions on body Some injuries are life-threatening. trauma to
1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 25 Injuries to the Face, Neck, and Eyes Injuries to the Face and Neck Face and neck are to injury Relatively unprotected positions on body Some injuries are life-threatening. trauma to
TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH
 Dr.Yahya A. Ali 3/10/2012 F.I.C.M.S TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH Bailey & Love s 25 th edition Injuries to the orofacial region are common, but the majority are relatively minor in nature. A few are major
Dr.Yahya A. Ali 3/10/2012 F.I.C.M.S TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH Bailey & Love s 25 th edition Injuries to the orofacial region are common, but the majority are relatively minor in nature. A few are major
APRIL
 APRIL - 2003 OCTOBER - 2003 February 2009 [KU 652] Sub. Code : 4131 FIRST B.D.S DEGREE EXAMINATION (Modified Regulations III) Paper I HUMAN ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Time : Three hours
APRIL - 2003 OCTOBER - 2003 February 2009 [KU 652] Sub. Code : 4131 FIRST B.D.S DEGREE EXAMINATION (Modified Regulations III) Paper I HUMAN ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Time : Three hours
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions. 4 May 2012
 SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
Review. 1. Which of the following is NOT a component of the cardiovascular system? A. Heart B. Lungs C. Venules D. Plasma
 Chapter 23 Review 1. Which of the following is NOT a component of the cardiovascular system? A. Heart B. Lungs C. Venules D. Plasma Answer: B Rationale: Components of the cardiovascular system include
Chapter 23 Review 1. Which of the following is NOT a component of the cardiovascular system? A. Heart B. Lungs C. Venules D. Plasma Answer: B Rationale: Components of the cardiovascular system include
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2019 #1 Facial Trauma
 McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2019 #1 Facial Trauma The face is vital to human appearance and function. Facial injuries can impair a patient
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2019 #1 Facial Trauma The face is vital to human appearance and function. Facial injuries can impair a patient
Read Me. We are the Learning Lab. to look
 Respiratory Tract Anatomy Lab In-Lab Exercises Read Me We are going to look at models and slides. Much of this can be done in the Learning Lab on your own time. The steps do not have to be done in order,
Respiratory Tract Anatomy Lab In-Lab Exercises Read Me We are going to look at models and slides. Much of this can be done in the Learning Lab on your own time. The steps do not have to be done in order,
Omran Saeed. Luma Taweel. Mohammad Almohtaseb. 1 P a g e
 2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
TRACHEOSTOMY. Tracheostomy means creation an artificial opening in the trachea with tracheostomy tube insertion
 TRACHEOSTOMY Definition Tracheostomy means creation an artificial opening in the trachea with tracheostomy tube insertion Indications for tracheostomy 1-upper airway obstruction with stridor, air hunger,
TRACHEOSTOMY Definition Tracheostomy means creation an artificial opening in the trachea with tracheostomy tube insertion Indications for tracheostomy 1-upper airway obstruction with stridor, air hunger,
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3
 PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2019 #3 Penetrating Neck Trauma
 McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2019 #3 Penetrating Neck Trauma Penetrating neck injury (PNI) comprises 5 to 10 percent of traumatic injuries
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2019 #3 Penetrating Neck Trauma Penetrating neck injury (PNI) comprises 5 to 10 percent of traumatic injuries
RESUSCITATION IN TRAUMA. Important things I have learnt
 RESUSCITATION IN TRAUMA Important things I have learnt Trauma resuscitation through the decades What was hot and now is not 1970s 1980s 1990s 2000s Now 1977 Fluids Summary Dogs subjected to arterial hemorrhage
RESUSCITATION IN TRAUMA Important things I have learnt Trauma resuscitation through the decades What was hot and now is not 1970s 1980s 1990s 2000s Now 1977 Fluids Summary Dogs subjected to arterial hemorrhage
1. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF TRAINING
 RHINOLOGY 1. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF TRAINING Exposure to clinical rhinology is provided in each of the four ORL years over the course of several rotations in a graduated approach. MEE General Otolaryngology
RHINOLOGY 1. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF TRAINING Exposure to clinical rhinology is provided in each of the four ORL years over the course of several rotations in a graduated approach. MEE General Otolaryngology
North Oaks Trauma Symposium Friday, November 3, 2017
 + Evaluation and Management of Facial Trauma D Antoni Dennis, MD North Oaks ENT an Allergy November 3, 2017 + Financial Disclosure I do not have any conflicts of interest or financial interest to disclose
+ Evaluation and Management of Facial Trauma D Antoni Dennis, MD North Oaks ENT an Allergy November 3, 2017 + Financial Disclosure I do not have any conflicts of interest or financial interest to disclose
Nasal region. cartilages: septal cartilage (l); lateral nasal cartilage (2); greater alar cartilages (2); lesser alar cartilages (?
 Nasal region skull bones: nasal and frontal processes of maxilla cartilages: septal cartilage (l); lateral nasal cartilage (2); greater alar cartilages (2); lesser alar cartilages (?) 1 Nasal cavity Roof
Nasal region skull bones: nasal and frontal processes of maxilla cartilages: septal cartilage (l); lateral nasal cartilage (2); greater alar cartilages (2); lesser alar cartilages (?) 1 Nasal cavity Roof
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 31.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 13 15, 17, 19, 28 31.2 Describe the components and function of the nervous system and the anatomy
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 31.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 13 15, 17, 19, 28 31.2 Describe the components and function of the nervous system and the anatomy
Skeletal system. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section. REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
Airway/Breathing. Chapter 5
 Airway/Breathing Chapter 5 Airway/Breathing Introduction Skillful, rapid assessment and management of airway and ventilation are critical to preventing morbidity and mortality. Airway compromise can occur
Airway/Breathing Chapter 5 Airway/Breathing Introduction Skillful, rapid assessment and management of airway and ventilation are critical to preventing morbidity and mortality. Airway compromise can occur
Evaluation & Management of Penetrating Wounds to the NECK
 Evaluation & Management of Penetrating Wounds to the NECK Goal Effectively identify patients with a high probability of injury requiring surgical intervention Define the role of diagnostic tests in assessing
Evaluation & Management of Penetrating Wounds to the NECK Goal Effectively identify patients with a high probability of injury requiring surgical intervention Define the role of diagnostic tests in assessing
Head and Face Anatomy
 Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
Structure Location Function
 Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔. 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機
 Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機 3250 E-mail: thfong@tmu.edu.tw Outline: The structure of nose The concha and meatus in nasal cavity The openings of paranasal sinuses Canals, foramens
Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機 3250 E-mail: thfong@tmu.edu.tw Outline: The structure of nose The concha and meatus in nasal cavity The openings of paranasal sinuses Canals, foramens
Damage Control in Abdominal and Pelvic Injuries
 Damage Control in Abdominal and Pelvic Injuries Raul Coimbra, MD, PhD, FACS The Monroe E. Trout Professor of Surgery Surgeon-in Chief UCSD Medical Center Hillcrest Campus Executive Vice-Chairman Department
Damage Control in Abdominal and Pelvic Injuries Raul Coimbra, MD, PhD, FACS The Monroe E. Trout Professor of Surgery Surgeon-in Chief UCSD Medical Center Hillcrest Campus Executive Vice-Chairman Department
Commen Nose Diseases
 Commen Nose Diseases Symptoms List: Nasal obstruction. Nasal discharge: Anterior (Rhinorrhea). Posterior (Postnasal discharge). Epistaxis. Hyposmia and Anosmia. Headache. Snoring. Nasal Obstruction Definition:
Commen Nose Diseases Symptoms List: Nasal obstruction. Nasal discharge: Anterior (Rhinorrhea). Posterior (Postnasal discharge). Epistaxis. Hyposmia and Anosmia. Headache. Snoring. Nasal Obstruction Definition:
INFORMATION REGARDING YOUR NASAL SURGERY
 INFORMATION REGARDING YOUR NASAL SURGERY This document contains information about the following aspects of nasal surgery: Pre-op information: How to prepare for surgery. Procedure: Wat is done during surgery.
INFORMATION REGARDING YOUR NASAL SURGERY This document contains information about the following aspects of nasal surgery: Pre-op information: How to prepare for surgery. Procedure: Wat is done during surgery.
Dr. Sami Zaqout, IUG Medical School
 The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
Endovascular Embolization of Taumatic Intracavernous Pseudoaneurysm of Internal Carotid Artery
 Endovascular Embolization of Taumatic Intracavernous Pseudoaneurysm of Internal Carotid Artery Tanveer Ul Haq,Shahzad Ahmad Khan,Imtiaz Hussain Rizvi ( Department of Radiology, The Aga Khan University
Endovascular Embolization of Taumatic Intracavernous Pseudoaneurysm of Internal Carotid Artery Tanveer Ul Haq,Shahzad Ahmad Khan,Imtiaz Hussain Rizvi ( Department of Radiology, The Aga Khan University
Esophageal Perforation
 Esophageal Perforation Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgeon, Division of General Surgery Head, Division of Critical Care May 15, 2006 Overview Case presentation Radiology Pre-operative management Operative
Esophageal Perforation Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgeon, Division of General Surgery Head, Division of Critical Care May 15, 2006 Overview Case presentation Radiology Pre-operative management Operative
PEMSS PROTOCOLS INVASIVE PROCEDURES
 PEMSS PROTOCOLS INVASIVE PROCEDURES Panhandle Emergency Medical Services System SURGICAL AND NEEDLE CRICOTHYROTOMY Inability to intubate is the primary indication for creating an artificial airway. Care
PEMSS PROTOCOLS INVASIVE PROCEDURES Panhandle Emergency Medical Services System SURGICAL AND NEEDLE CRICOTHYROTOMY Inability to intubate is the primary indication for creating an artificial airway. Care
PROBLEM RECOMMENDATION
 PREVENTION (MINIMIZING) IN ENDOSCOPIC Steven D. Schaefer, MD Professor and Chair Department of Otolaryngology PREVENTION AND Intraoperative Hemorrhage Loss of Orientation Inability to Identify/Preserve
PREVENTION (MINIMIZING) IN ENDOSCOPIC Steven D. Schaefer, MD Professor and Chair Department of Otolaryngology PREVENTION AND Intraoperative Hemorrhage Loss of Orientation Inability to Identify/Preserve
Skull and Axial Skeleton
 Published on Second Faculty of Medicine, Charles University (http://www.lf2.cuni.cz ) Skull and Axial Skeleton Description of the test The examination of the skull skeleton is in oral format. It consists
Published on Second Faculty of Medicine, Charles University (http://www.lf2.cuni.cz ) Skull and Axial Skeleton Description of the test The examination of the skull skeleton is in oral format. It consists
National Consultant Outcomes Excluded OPCS codes
 National Consultant Outcomes Excluded OPCS codes 1 NCO 2014 & 2016: Excluded OPCS Codes Title and Version NCO 2014 & 2016: Excluded OPCS codes Date Issued 08/01/2018 Author (S) AN Document History Version
National Consultant Outcomes Excluded OPCS codes 1 NCO 2014 & 2016: Excluded OPCS Codes Title and Version NCO 2014 & 2016: Excluded OPCS codes Date Issued 08/01/2018 Author (S) AN Document History Version
Supplementary Table 1. ICD-9/-10 codes used to identify cycling injury hospitalizations. Railway accidents injured pedal cyclist
 Supplementary Table 1. ICD-9/-10 codes used to identify cycling injury hospitalizations. ICD Code ICD-9 E800-E807(.3) E810-E816, E818-E819(.6) E820-E825(.6) E826-E829(.1) ICD-10-CA V10-V19 (including all
Supplementary Table 1. ICD-9/-10 codes used to identify cycling injury hospitalizations. ICD Code ICD-9 E800-E807(.3) E810-E816, E818-E819(.6) E820-E825(.6) E826-E829(.1) ICD-10-CA V10-V19 (including all
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Head and Neck Trauma in Iraq and Afghanistan: Different War, Different Surgery, Lessons Learned
 The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. TRIOLOGICAL SOCIETY CANDIDATE THESIS Head and Neck Trauma in Iraq and Afghanistan: Different War, Different
The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. TRIOLOGICAL SOCIETY CANDIDATE THESIS Head and Neck Trauma in Iraq and Afghanistan: Different War, Different
Pediatric Patients. BCFPD Paramedic Education Program. EMS Education Paramedic Level
 Pediatric Patients BCFPD Program Basic Considerations Much of the initial patient assessment can be done during visual examination of the scene. Involve the caregiver or parent as much as possible. Allow
Pediatric Patients BCFPD Program Basic Considerations Much of the initial patient assessment can be done during visual examination of the scene. Involve the caregiver or parent as much as possible. Allow
Respiratory System. Clinical notes. Published on Second Faculty of Medicine, Charles University ( https://www.lf2.cuni.cz)
 Published on Second Faculty of Medicine, Charles University ( https://www.lf2.cuni.cz) Respiratory System The test of the respiratory system follows the general rules for written tests (see Continuous
Published on Second Faculty of Medicine, Charles University ( https://www.lf2.cuni.cz) Respiratory System The test of the respiratory system follows the general rules for written tests (see Continuous
Objectives. Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology. Function of the Lungs/Heart. The lung is for gas exchange. Failure of the Lungs/Heart
 Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology Objectives Classify epithelial tissue based on cell type and tissue layers. Identify location of tissue epithelium in the respiratory system. Describe the major
Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology Objectives Classify epithelial tissue based on cell type and tissue layers. Identify location of tissue epithelium in the respiratory system. Describe the major
itclamp 50 Clinical Training M-115-CE Rev C
 itclamp 50 Clinical Training M-115-CE Rev C Objectives Explain the impact of bleeding in trauma Recognize the importance of rapid haemorrhage control Classify wounds on the spectrum of bleeding Select
itclamp 50 Clinical Training M-115-CE Rev C Objectives Explain the impact of bleeding in trauma Recognize the importance of rapid haemorrhage control Classify wounds on the spectrum of bleeding Select
Face. Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face
 Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Head & Neck Clinical Sub Group. Network Agreed Imaging Guidelines for UAT and Thyroid Cancer. Measure Nos: 11-1C-105i & 11-1C-106i
 Greater Manchester, Lancashire & South Cumbria Strategic Clinical Network & Senate Head & Neck Clinical Sub Group Network Agreed Imaging Guidelines for UAT and Thyroid Cancer Measure Nos: 11-1C-105i &
Greater Manchester, Lancashire & South Cumbria Strategic Clinical Network & Senate Head & Neck Clinical Sub Group Network Agreed Imaging Guidelines for UAT and Thyroid Cancer Measure Nos: 11-1C-105i &
Hemorrhage Control. Chapter 6
 Chapter 6 The hemorrhage that take[s] place when a main artery is divided is usually so rapid and so copious that the wounded man dies before help can reach him. Colonel H. M. Gray, 1919 Stop the Bleeding!
Chapter 6 The hemorrhage that take[s] place when a main artery is divided is usually so rapid and so copious that the wounded man dies before help can reach him. Colonel H. M. Gray, 1919 Stop the Bleeding!
Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate
 Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AND VENTILATION
 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AND VENTILATION D1 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AND VENTILATION Basic airway management and ventilation The laryngeal mask airway and Combitube Advanced techniques of airway management D2 Basic
AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AND VENTILATION D1 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AND VENTILATION Basic airway management and ventilation The laryngeal mask airway and Combitube Advanced techniques of airway management D2 Basic
*in general the blood supply of the nose comes from branches of the internal and external carotid arteries.
 In the previous lecture we talked about the anatomy of the nasal cavity, today we will talk about its blood supply, venous drainage, innervations, and finally about the paranasal sinuses. When we describe
In the previous lecture we talked about the anatomy of the nasal cavity, today we will talk about its blood supply, venous drainage, innervations, and finally about the paranasal sinuses. When we describe
Head and Neck Examination
 Head and Neck Examination Statement of Goals Understand and perform an examination of the head and neck. Learning Objectives Head Ears Nose Sinus A. Describe the anatomy of the head, including regions
Head and Neck Examination Statement of Goals Understand and perform an examination of the head and neck. Learning Objectives Head Ears Nose Sinus A. Describe the anatomy of the head, including regions
Vascular and Parameningeal Infections of the Head and Neck
 Vascular and Parameningeal Infections of the Head and Neck Kevin B. Laupland, MD, MSc, FRCPC Associate Professor Departments of Medicine, Critical Care Medicine, Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, and
Vascular and Parameningeal Infections of the Head and Neck Kevin B. Laupland, MD, MSc, FRCPC Associate Professor Departments of Medicine, Critical Care Medicine, Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, and
Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu
 2009 Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu Anatomy of frontal sinus is highly variable. Precise understanding of these variables will help a surgeon to avoid unnecessary complications during
2009 Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu Anatomy of frontal sinus is highly variable. Precise understanding of these variables will help a surgeon to avoid unnecessary complications during
Anatomic Relations Summary. Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh
 Anatomic Relations Summary Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh Anatomic Relations Lecture 1 Part-1 - The medial wall of the nose is the septum. - The vestibule lies directly inside the nostrils (Nares). -
Anatomic Relations Summary Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh Anatomic Relations Lecture 1 Part-1 - The medial wall of the nose is the septum. - The vestibule lies directly inside the nostrils (Nares). -
Airway/Breathing. Chapter 5
 Airway/Breathing Chapter 5 Airway/Breathing Introduction Rapid assessment and management of airway and ventilation are critical to preventing morbidity and mortality. Airway compromise can occur rapidly
Airway/Breathing Chapter 5 Airway/Breathing Introduction Rapid assessment and management of airway and ventilation are critical to preventing morbidity and mortality. Airway compromise can occur rapidly
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR.
 The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
Chapter 8 Trauma Patient Assessment The Patient Assessment Process The Primary Assessment ABCDE s Airway, Breathing, Circulation while securing
 1 2 3 4 5 6 Chapter 8 Trauma Patient Assessment The Patient Assessment Process The Primary Assessment ABCDE s Airway, Breathing, Circulation while securing D-Disability Chief complaint and/or Mechanism
1 2 3 4 5 6 Chapter 8 Trauma Patient Assessment The Patient Assessment Process The Primary Assessment ABCDE s Airway, Breathing, Circulation while securing D-Disability Chief complaint and/or Mechanism
Tympanic Bulla Temporal Bone. Digastric Muscle. Masseter Muscle
 Superior view Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with any other bones. It is held in place by ligaments to the styloid process of the temporal bone and the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It
Superior view Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with any other bones. It is held in place by ligaments to the styloid process of the temporal bone and the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It
Anatomy of. External NOSE. By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC
 Anatomy of External NOSE By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 24 th Nov. 2017 The External Nose Descriptions of the nose always begin with that part of it which is covered by the skin, i.e., the EXPOSED PART
Anatomy of External NOSE By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 24 th Nov. 2017 The External Nose Descriptions of the nose always begin with that part of it which is covered by the skin, i.e., the EXPOSED PART
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
Understanding Your Costs and Coverage
 Understanding Your Costs and Coverage Thank you for choosing UW. We know that understanding your healthcare costs can be a challenge we re here to help. Your healthcare costs depend on many factors such
Understanding Your Costs and Coverage Thank you for choosing UW. We know that understanding your healthcare costs can be a challenge we re here to help. Your healthcare costs depend on many factors such
Clearing the air.. How to assist and rescue neck breathing patients. Presented by: Don Hall MCD, CCC/SLP Sarah Markel RRT, MHA
 Clearing the air.. How to assist and rescue neck breathing patients Presented by: Don Hall MCD, CCC/SLP Sarah Markel RRT, MHA Learning Objectives Define common terms identified with total (laryngectomy)
Clearing the air.. How to assist and rescue neck breathing patients Presented by: Don Hall MCD, CCC/SLP Sarah Markel RRT, MHA Learning Objectives Define common terms identified with total (laryngectomy)
Congenital Neck Masses C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD
 Congenital Neck Masses C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD SUNY-LICH Medical Center Department of Surgery Case Presentation xx year old male presents with sudden onset left lower neck swelling x 1 week Denies pain,
Congenital Neck Masses C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD SUNY-LICH Medical Center Department of Surgery Case Presentation xx year old male presents with sudden onset left lower neck swelling x 1 week Denies pain,
Tracheo-innominate artery fistula (TIF) is an uncommon
 Technique for Managing Tracheo-Innominate Artery Fistula Gorav Ailawadi, MD Tracheo-innominate artery fistula (TIF) is an uncommon complication (0.1-1%) following both open and percutaneous tracheostomy.
Technique for Managing Tracheo-Innominate Artery Fistula Gorav Ailawadi, MD Tracheo-innominate artery fistula (TIF) is an uncommon complication (0.1-1%) following both open and percutaneous tracheostomy.
Tracheostomy and Ventilator Education Program Module 2: Respiratory Anatomy
 Tracheostomy and Ventilator Education Program Module 2: Respiratory Anatomy Disclaimer This material is intended for use by trained family members and caregivers of children with tracheostomies who are
Tracheostomy and Ventilator Education Program Module 2: Respiratory Anatomy Disclaimer This material is intended for use by trained family members and caregivers of children with tracheostomies who are
Structure and Nerve Supply of The Larynx
 Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical sciences Structure and Nerve Supply of The Larynx This presentation was originally prepared by: Dr. Kumar Notes were added by:
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical sciences Structure and Nerve Supply of The Larynx This presentation was originally prepared by: Dr. Kumar Notes were added by:
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Pterygopalatine fossa: The pterygopalatine fossa is a cone-shaped depression, It is located between the maxilla,
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Pterygopalatine fossa: The pterygopalatine fossa is a cone-shaped depression, It is located between the maxilla,
Chapter 29 - Chest_and_Abdominal_Trauma
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 29.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11, 15, 18, 27 29.2 Describe mechanisms of injury commonly associated with chest injuries. Slides
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 29.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11, 15, 18, 27 29.2 Describe mechanisms of injury commonly associated with chest injuries. Slides
BRINER Bipolar Coagulation Suction Cannula ENT /2017-E
 BRINER Bipolar Coagulation Suction Cannula ENT 124 11/2017-E BRINER Bipolar Coagulation Suction Cannula Hemostasis in operations in the paranasal sinuses and on the anterior skull base Advances in endoscopic
BRINER Bipolar Coagulation Suction Cannula ENT 124 11/2017-E BRINER Bipolar Coagulation Suction Cannula Hemostasis in operations in the paranasal sinuses and on the anterior skull base Advances in endoscopic
The Pharynx. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D
 The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
The new standard in hemorrhage control
 The new standard in hemorrhage control Contents The need for hemostats What is Celox Rapid? Benefits How it works Performance Independent trials of Celox Gauze The need for hemostats in trauma Combat lives
The new standard in hemorrhage control Contents The need for hemostats What is Celox Rapid? Benefits How it works Performance Independent trials of Celox Gauze The need for hemostats in trauma Combat lives
Over the Wire Technique vs. Modified Seldinger Technique in Insertion of PICC
 Over the Wire Technique vs. Modified Seldinger Technique in Insertion of PICC Deniz Kasikci Department of Radiology, Jena University Hospital Friedrich-Schiller-University, Jena, Germany Disclosure Speaker
Over the Wire Technique vs. Modified Seldinger Technique in Insertion of PICC Deniz Kasikci Department of Radiology, Jena University Hospital Friedrich-Schiller-University, Jena, Germany Disclosure Speaker
Basic Airway Management
 Basic Airway Management Dr. Madhurita Singh, Assoc. Professor, Dept. of Critical Care, CMC Vellore. This is the first module in a series on management of airway and ventilation in critically ill patients.
Basic Airway Management Dr. Madhurita Singh, Assoc. Professor, Dept. of Critical Care, CMC Vellore. This is the first module in a series on management of airway and ventilation in critically ill patients.
Procedures/Risks:central venous catheter
 Procedures/Risks:central venous catheter Central Venous Catheter Placement Procedure: Placement of the central venous catheter will take place in the Interventional Radiology Department (IRD) at The Ohio
Procedures/Risks:central venous catheter Central Venous Catheter Placement Procedure: Placement of the central venous catheter will take place in the Interventional Radiology Department (IRD) at The Ohio
Central Venous Line Insertion
 Central Venous Line Insertion Understand the indications and risks of CVC insertion Understand and troubleshoot the seldinger technique Understand available sites and select the appropriate site for clinical
Central Venous Line Insertion Understand the indications and risks of CVC insertion Understand and troubleshoot the seldinger technique Understand available sites and select the appropriate site for clinical
The PHARYNX. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD Ph.D
 The PHARYNX Dr. Nabil Khouri MD Ph.D PHARYNX Fibromuscular tube lined with mucous membrane extends from base of skull to lower border of cricoid cartilage (C-6). 12-14 cm long At the lower border of cricoid
The PHARYNX Dr. Nabil Khouri MD Ph.D PHARYNX Fibromuscular tube lined with mucous membrane extends from base of skull to lower border of cricoid cartilage (C-6). 12-14 cm long At the lower border of cricoid
CHAPTER 3 BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 CHAPTER 3 BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SURFACE ANATOMY Surface anatomy is the identification of landmarks on the surface of the skin which allows us to compare our knowledge of our own surface anatomy
CHAPTER 3 BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SURFACE ANATOMY Surface anatomy is the identification of landmarks on the surface of the skin which allows us to compare our knowledge of our own surface anatomy
 www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE ---- Case Information Referring Doctor: - Patient Name: - Scan Date: December 1, 2015 Patient DOB: - Reason for Exam: - Study Details: icat Flex, 160x160x112
www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE ---- Case Information Referring Doctor: - Patient Name: - Scan Date: December 1, 2015 Patient DOB: - Reason for Exam: - Study Details: icat Flex, 160x160x112
DEMOGRAPHICS OF HEAD AND NECK INJURIES IN IRAQ AND AFGHANISTAN
 Demographics of Head and Neck Injuries in Iraq and Afghanistan Chapter 6 DEMOGRAPHICS OF HEAD AND NECK INJURIES IN IRAQ AND AFGHANISTAN JOSEPH A BRENNAN, MD, FACS* INTRODUCTION GENERAL DEMOGRAPHICS PRETREATMENT
Demographics of Head and Neck Injuries in Iraq and Afghanistan Chapter 6 DEMOGRAPHICS OF HEAD AND NECK INJURIES IN IRAQ AND AFGHANISTAN JOSEPH A BRENNAN, MD, FACS* INTRODUCTION GENERAL DEMOGRAPHICS PRETREATMENT
Shock. William Schecter, MD
 Shock William Schecter, MD The Cell as a furnace O 2 1 mole Glucose Cell C0 2 ATP 38 moles H 2 0 Shock = Inadequate Delivery of 02 and Glucose to the Cell 0 2 Cell ATP 2 moles Lactic Acid Treatment of
Shock William Schecter, MD The Cell as a furnace O 2 1 mole Glucose Cell C0 2 ATP 38 moles H 2 0 Shock = Inadequate Delivery of 02 and Glucose to the Cell 0 2 Cell ATP 2 moles Lactic Acid Treatment of
2/12/2018 TOURNIQUETS, FROM THE BATTLEFIELD TO YOUR BACKYARD Trauma Symposium RICHARD KING, MD, FACEP 01/26/2018 WARNING
 TOURNIQUETS, FROM THE BATTLEFIELD TO YOUR BACKYARD 2018 Trauma Symposium RICHARD KING, MD, FACEP 01/26/2018 WARNING T H I S P R E S E N TAT I O N C O N TA I N S S O M E V E R Y G R A P H I C I M A G E
TOURNIQUETS, FROM THE BATTLEFIELD TO YOUR BACKYARD 2018 Trauma Symposium RICHARD KING, MD, FACEP 01/26/2018 WARNING T H I S P R E S E N TAT I O N C O N TA I N S S O M E V E R Y G R A P H I C I M A G E
: Your Haemorrhage Control Solution
 : Your Haemorrhage Control Solution Shoulder Injury Leg Injury TM HAEMORRHAGE New solutions to control difficult bleeding are needed in emergent care, including pre-hospital, hospital and tactical environments.
: Your Haemorrhage Control Solution Shoulder Injury Leg Injury TM HAEMORRHAGE New solutions to control difficult bleeding are needed in emergent care, including pre-hospital, hospital and tactical environments.
Advanced Airway Management. University of Colorado Medical School Rural Track
 Advanced Airway Management University of Colorado Medical School Rural Track Advanced Airway Management Basic Airway Management Airway Suctioning Oxygen Delivery Methods Laryngeal Mask Airway ET Intubation
Advanced Airway Management University of Colorado Medical School Rural Track Advanced Airway Management Basic Airway Management Airway Suctioning Oxygen Delivery Methods Laryngeal Mask Airway ET Intubation
ACUTE CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMA Tina Gaarder, MD, PhD
 ACUTE CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMA Tina Gaarder, MD, PhD Trauma represents a leading cause of disability and preventable death and is mainly affecting people between 15 and 40 years of age, accounting
ACUTE CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMA Tina Gaarder, MD, PhD Trauma represents a leading cause of disability and preventable death and is mainly affecting people between 15 and 40 years of age, accounting
The dura is sensitive to stretching, which produces the sensation of headache.
 Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Learning Outcomes. The Carotid 20/02/2013. Scalp, Face, Parotid. Layers of the Scalp. The Parotid Gland. The Scalp. The Carotid The Facial Artery
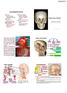 Learning Outcomes The Scalp Layers of the Scalp Bleeding from the Scalp The Carotid The Facial Artery Major Muscles of the Face and Jaw(s) Muscles of Mastication Muscles of Facial Expression The Parotid
Learning Outcomes The Scalp Layers of the Scalp Bleeding from the Scalp The Carotid The Facial Artery Major Muscles of the Face and Jaw(s) Muscles of Mastication Muscles of Facial Expression The Parotid
