Relationship between central corneal thickness and parameters of optic nerve head topography in healthy subjects
|
|
|
- Kelly Lester
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 18 no. 1, 2008 / pp Relationship between central corneal thickness and parameters of optic nerve head topography in healthy subjects A.B. CANKAYA, U. ELGIN, A. BATMAN, G. ACAROGLU II Eye Clinic, Ankara Ulucanlar Eye Research Hospital, Ankara - Turkey PURPOSE. To investigate the relationship between central corneal thickness (CCT) and topographic parameters of optic nerve head (ONH) in healthy eyes. METHODS. Right eyes of 208 healthy subjects between 40 and 59 years of age with refractive error less than 1 D were enrolled in this cross-sectional study. Ultrasonic pachymeter was used to measure CCT, and the ONH parameters were obtained by using confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope. Relationship of various topographic parameters to age and sex were also investigated. For statistical analysis Student t test, analysis of variance, Pearson and Spearman test, and partial correlation coefficients were used. RESULTS. Mean CCT of subjects was ±35.53 µm ( µm), and the mean disc area was 2.37±0.44 mm 2 ( mm 2 ). CCT showed negative correlations to disc area, rim area, rim volume, and retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) area. These correlations were found to be stronger in females. Negative correlations were demonstrated between age and the mean cup depth, maximum cup depth, RNFL thickness, and RNFL cross sectional area. Women had lesser rim volumes, but bigger cup to disk (C/D) area and linear C/D ratios compared to those of men. CONCLUSIONS. In addition to its effect in the accuracy of intraocular pressure measurements, CCT has a structural relationship with the ONH in healthy nonglaucomatous eyes. Therefore, its effect on disc area might be especially important to explain the structural strength of the ONH in the pathogenesis of glaucoma. (Eur J Ophthalmol 2008; 18: 32-8) KEY WORDS. Central corneal thickness, Optic nerve head topography, Disc area, Glaucomatous optic nerve damage Accepted: September 6, 2007 INTRODUCTION Central corneal thickness (CCT) has a significant effect on intraocular pressure (IOP) measured by applanation tonometry (1). IOP may be underestimated in eyes with thin corneas and overestimated in eyes with thick corneas (2). Considerable evidence now supports that CCT has a major role in the diagnosis of glaucoma and progression of glaucomatous optic nerve degeneration. CCT measurements may show some differences depending on the type of glaucoma. Previously, CCT was reported to be higher in ocular hypertension (OHT) than in normotensive glaucoma; however, it was almost normal in patients with primary open angle glaucoma (POAG) (3, 4). It was also demonstrated that CCT could play an important role in the formation and progression of the visual field defects. Therefore, besides its effects on the accuracy of IOP measurements, it was argued that CCT might have some kind of effect on the optic nerve head resistance (5, 6). In a previous study including patients with POAG, an inverse correlation between CCT and the optic disc area was shown and the weakness of the optic nerve head in eyes with thin cornea could be explained with the assumption of thin structures of both lamina cribrosa and sclera which /032-07$15.00/0 Wichtig Editore, 2008
2 Cankaya et al are the posterior continuations of a thin cornea (7). However, such a relationship could not be proven in a histomorphometric study done on enucleated eyes (8). Heidelberg Retina Tomography (HRT) is a confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope which has been widely used in follow-up of the changes in optic nerve head (ONH) topography since It was reported that topographic deterioration of ONH precedes formation of defects in visual fields (9). Meanwhile the effects of age, gender, laterality, refraction, and optic disc area on HRT parameters have been investigated in healthy subjects (10-17). In the present study, we investigated the relationship between CCT and topographic analysis of the ONH with HRT II in healthy individuals to characterize the differences between the optic nerve parameters of the normal eyes with thin cornea and those with thick cornea. MATERIALS AND METHODS A total of 208 patients (aged years) with nearsightedness were enrolled between April 2006 and February Individuals with a history of vascular, circulatory (diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and hypotension), autoimmune, and neurological diseases (including migraine), malignancy, chronic medication usage, glaucoma, uveitis, ocular surgery, or trauma were excluded. Only the right eye of each subject was evaluated in the study. The ophthalmic examination included visual acuity measurement; slit lamp examination, fundus examination with +90 D lens, IOP measurement with Goldmann applanation tonometer, and gonioscopic examination with Goldmann three mirror lens. After the examination, subjects with visual acuity less than 10/10, refractive error more than 1 D (spherical or cylindrical), were excluded. Moreover, patients with an anterior chamber pathology that could affect IOP (pseudoexfoliation, pigment dispersion), congenital abnormality of optic nerve, prominent peripapillary atrophy, a linear cup to disc (C/D) ratio of greater than 0.4 or glaucomatous optic disc appearance, IOP more than 20 mm Hg, or abnormalities of iridocorneal angle (recession, excessive pigmentation, angle depth less than grade III according to Shaffer System) also were excluded. ONH analysis of the patients was done by using a HRT II (Heidelberg Retinal Tomograph, Software Version 2.1, Heidelberg Engineering, Germany) scanning laser ophthalmoscope. No pupil dilatation was done and 15 o angle view was used under the same intensity of dim room light. Images were taken and contour lines were drawn by the same experienced observer (A.B.C.). The accuracy in defining ONH circumference was performed by using minimum 6 points for drawing the contour line. Keratometric readings were used to exclude magnification effect. Subjects with standard deviation less than 30 µm and evaluated as within normal limits according to the Moorfields Classification were included in the study. Parameters calculated by HRT II hardware are disc area (mm 2 ), cup area (mm 2 ), rim area (mm 2 ), cup volume (mm 3 ), rim volume (mm 3 ), C/D area ratio, linear C/D ratio, mean cup depth (mm), maximum cup depth (mm), cup shape measure, height variation contour (mm), mean retina nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness (mm), and RNFL cross sectional area (mm 2 ). CCT measurement was performed with ultrasonic pachymetry (Tomey AL-1000) following the instillation of one drop of propacaine hydrochloride (0.5%) to the right eye of each subject 5 minutes prior to measurement. Five consecutive measurements were taken while the patient was looking straight ahead. The examiner paid attention to apply the probe perpendicularly to the cornea without pressure. The mean of five measurements was calculated and recorded as the CCT value. SPSS 13.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was used for statistical analysis with Student t test, analysis of variance, Pearson, Sperman, and partial correlation coefficient. Statistical significance was accepted as p 0.05 or less. Before we conducted the study, it was approved by the ethical committee of Ankara Ulucanlar Eye Research Hospital and the patients were all clearly informed about the study. RESULTS The study group consisted of 107 men and 101 women. Mean age was 49.11±6.29 (range 40 59). The mean age of men was 49.46±6.25 (range 40 59) and of women was 48.68±6.03 (range 40 59) (p=0.34). Mean CCT obtained was ±35.53 µm ( µm) and the mean IOP measured was 13.64±2.81 mmhg (9 19 mmhg). The mean CCT of men was ±37 µm ( µm) and women had a mean CCT of ±54 µm ( µm). The difference between the CCT measurements of the two sexes was not statistically significant (p=0.13). No correlation between the age and CCT of the subjects was observed (p=0.26, r= 0.28). 33
3 Central corneal thickness and optic nerve head Fig. 1 - Central corneal thickness versus disc area in healthy subjects (p=0.01, r=-0.178). Fig. 2 - Central corneal thickness versus rim area in healthy subjects (p=0.015, r=-0.168). Fig. 3 - Central corneal thickness versus rim volume in healthy subjects (p=0.049, r=-0.136). Fig. 4 - Central corneal thickness versus RNFL area in healthy subjects (p=0.038, r=-0.144). The mean disc area of our subjects was calculated as 2.366±0.436 mm 2 ( mm 2 ). The mean cup and rim areas were 0.42±0.3 mm 2 ( mm 2 ) and 1.93±0.39 ( mm 2 ), respectively, and the mean C/D area ratio was found to be 0.17±0.11 ( ). The results of the ONH topographic study are shown in Table I. In our study negative correlations were obtained between the CCT and those of disc area (p=0.01, r= 0.178) (Fig. 1), rim area (p=0.015, r= 0.168) (Fig. 2), rim volume (p=0.049, r= 0.136) (Fig. 3), and RNFL area (p=0.038, r= 0.144) (Fig. 4). However, other optic disc parameters showed no correlation with the CCT (Tab. II). We also examined the correlations between age and the optic disc topographic parameters. According to the results obtained the mean cup depth (p=0.02, r= 0.160), maximum cup depth (p=0.03, r= 0.203), RNFL thickness (p=0.009, r= 0.180), and RNFL area (p=0.01, r= 0.177) exhibited negative correlations with age. (Tab. II). When the effect of age was controlled by partial correlation analysis, it was found that CCT had a negative correlation 34
4 Cankaya et al TABLE I - GENDER-SPECIFIC AND ENTIRE GROUP OPTIC NERVE PARAMETERS Topographic parameters Sex Mean SD p value Disc area (mm 2 ) M F Total Cup area (mm 2 ) M F Total Rim area (mm 2 ) M F Total Rim volume (mm 3 ) M * F Total C/D ratio M * F Total Linear C/D ratio M * F Total Mean cup depth (mm) M F Total Cup volume (mm 3 ) M F Total Maximum cup depth (mm) M F Total Cup shape measure M F Total Height variation contour M F Total Mean RNFL thickness (mm) M F Total RNFL cross sect. area (mm 2 ) M F Total *Statistically significant; RNFL = Retinal nerve fiber layer TABLE II - GENDER-SPECIFIC AND ENTIRE GROUP CORRELATIONS OF OPTIC NERVE HEAD PARAMETERS TO AGE AND CENTRAL CORNEAL THICKNESS Central corneal thickness Age Male Female Total r p r p r p r p Disc area * * Cup area Rim area * * Cup volume Rim volume * * C/D area Linear C/D Mean cup depth * Maximum cup depth * Cup shape measure Height variation contour RNFL thickness * RNFL area * * * *Statistically significant; RNFL = Retinal nerve fiber layer 35
5 Central corneal thickness and optic nerve head with disc area (p=0.01, r= 0.178), rim area (p=0.02, r= 0.160), and RNFL area (p=0.032, r= 0.149). Optic disc topographic parameters of the total group and each sex are given individually in Table I. The mean rim volume in men was found to be 0.54 mm 3, while it was measured as 0.52 mm 3 in women (p=0.04). C/D area ratio was calculated as 0.18 and 0.16 in women and men, respectively (p=0.05). Linear C/D ratio was found to be significantly higher in women than in men (0.41 and 0.37, respectively) (p=0.02). We further examined the relationship of CCT to the optic disc parameters in men and women, individually. It was demonstrated that the CCT and HRT parameters were in no means related in men. However, a significant relationship was noticed in women as negative correlations observed between CCT and disc area (p=0.011, r= 0.250), rim area (p=0.001, r = 0.332), rim volume (p=0.001, r= 0.322), and RNFL area (p=0.018, r= 0.235) (Tab. II). DISCUSSION The Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study Group reported that the risk of developing glaucomatous optic nerve damage in OHT was three times higher in eyes with CCT less than 555 µm than in eyes with CCT more than 585 µm (18). Additionally, early visual field defects and low RNFL thickness were also found to be more frequent in OHT patients with thin corneas (19, 20) Medeiros et al have found that thin CCT was a risk factor for the development of visual field defects in early stage glaucoma cases (6). In a large-scale study performed on 454 patients with POAG and OHT, Jonas et al have postulated a positive correlation between CCT and neuroretinal rim, expressing that the glaucomatous eyes with thinner corneas also have thinner neuroretinal rims (21). Hewitt and Franzco have reported that thicker corneas may offer a greater protective role against the optic nerve damage in POAG cases (22). Choi and coworkers have demonstrated in a study consisting of 75 NTG patients that CCT was a significant factor for localized RNFL loss (23). Therefore, it can be concluded that CCT has some sort of effect on optic nerve structure and eyes with thin corneas are more susceptible to IOP dependent glaucomatous optic nerve damage. Cornea and sclera are continuous segments as a collagen coat of an eye. At the posterior segment, sclera is perforated forming lamina cribrosa which forms a barrier between intraocular space and cerebrospinal fluid, so that it plays a major role in optic nerve pathologies such as glaucoma (24, 25). From this point of view, Jonas et al investigated the association of lamina cribrosa thickness with CCT in 111 postmortem enucleated eyes; however, no correlation between CCT and lamina cribrosa was found (8). It is speculated that besides the effect of CCT on the resistance of optic nerve to IOP, eyes with thin corneas have decreased trabecular outflow facility and wide diurnal fluctuations because of structural changes in their trabecular meshwork (26). HRT II gives three-dimensional optic nerve head measurement data, which are reproducible, highly sensitive, and objective (27). Therefore, in addition to the classic C/D area ratio, it gives much more detailed information about the optic nerve head and peripapillary retina. In this study, our primary goal was to establish the possible relationship between CCT and optic disc parameters in healthy eyes. To neutralize the possible effect of refraction on the optic nerve parameters, eyes with refractive error less than 1 D (13) were used in correlation and to eliminate the probable role of laterality only the right eye of each individual subject was enrolled in the study (11, 12, 16). We have found that CCT exhibited a negative correlation with disc area, rim area, rim volume, and RNFL area, showing that the eyes with thick corneas have smaller disc and rim areas as well as less rim volumes, and less RNFL cross sectional areas. Nevertheless, similar negative correlations between CCT and disc area, rim area, and RNFL area were still present when the effect of age was eliminated. Pakravan and coworkers have also reported a negative correlation between CCT and disc area in their study on cases with POAG, showing that eyes with thick corneas have smaller optic discs (7). Bigger discs could be considered to be more sensitive to increase the IOP than smaller discs and it was claimed that this sensitivity might be due to qualitative characteristics of extracellular matrix (28). When the disc size gets bigger, the ratio of lamina cribrosa pores to disc area increases, and therefore the connective tissue in the optic disc becomes less supportive. On the contrary, smaller disc size decreases the pore to disc area ratio and provides much greater tissue support (28). In the present study, we have also found a negative correlation between age and the mean cup depth, maximum cup depth, mean RNFL thickness, and RNFL cross sectional area. These findings can be explained by the in- 36
6 Cankaya et al crease of the production of glial tissue and filling it into the cup during the progressive thinning of RNFL. Kergoat et al have demonstrated that as patients aged, RNFL became thinner and the disc area, cup area, and C/D ratio were all increased; however, the rim area stayed without changing (15). A significant correlation between the optic disc area and age was reported by Akar et al (10). Nevertheless, there are few studies suggesting that age has no effect on any of the optic disc parameters (14, 16, 29). Our results showed that women have smaller rim volumes, higher C/D areas, and higher linear C/D ratios compared to those of men. Although Gundersen et al reported that the optic disc cup of women was wider and deeper than in men, these findings were not statistically significant (14). In another study, the height variation contour, mean RNFL thickness, and RNFL cross-sectional area of women was reported to be higher than those of men (30). However, Varma and coworkers have demonstrated that the optic disc parameters were not associated with sex (31). In our study, although CCT was not correlated with any of the optic disc parameters in men, a significant negative correlation was observed between CCT and the disc area, rim area, rim volume, and RNFL area in women. NTG, in which thin corneas are more prevalent, is two times common in women (32). This can be explained as the CCT being more effective on optic disc parameters in women than in men. The small sample size of the cohort, limited age range of the subjects, and the dominance of a single ethnic group (white) could be considered as potential limitations of our study. Therefore, a longitudinal study with a much larger number of subjects including both normal controls and glaucoma patients of all age ranges and different ethnic groups is required to confirm our findings. In addition to affecting the accuracy of IOP measurements and a person s susceptibility to glaucoma, we also found that CCT is related to morphology of the optic nerve head. Our findings support the notion that eyes with thinner corneas may have greater optic disc areas, which are more deformable and may render optic disc vulnerable to the effect of IOP. Proprietary interest: None. Reprint requests to: Ali Bulent Cankaya, MD Sancak Mahallesi 215.Sokak, No:3 Daire: 7, Cankaya Ankara, Turkey abcankaya@hotmail.com abcankaya@yahoo.com REFERENCES 1. Doughty MJ, Zaman ML. Human corneal thickness and its impact on intraocular pressure measures: a review and meta-analysis approach. Surv Ophthalmol 2000; 44: Brandt JD. The influence of corneal thickness on the diagnosis and the management of glaucoma. J Glaucoma 2001; 10 (Suppl): S Copt RP, Thomas R, Mermoud A. Corneal thickness in ocular hypertension, primary open-angle glaucoma, and normal tension glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol 1999; 117: Herndon LW, Choudhri SA, Cox T, Damji KF, Shields MB, Allingham RR. Central corneal thickness in normal, glaucomatous, and ocular hypertensive eyes. Arch Ophthalmol 1997; 115: Herndon LW, Weizer JS, Stinnett SS. Central corneal thickness as a risk factor for advanced glaucoma damage. Arch Ophthalmol 2004; 122: Medeiros FA, Sample PA, Zangwill LM, Bowd C, Aihara M, Weinreb RN. Corneal thickness as a risk factor for visual field loss in patients with preperimetric glaucomatous optic neuropathy. Am J Ophthalmol 2003; 136: Pakravan M, Parsa A, Sanagou M, Parsa CF. Central corneal thickness and correlation to optic disc size: a potential link for susceptibility to glaucoma. Br J Ophthalmol 2007; 91: Jonas JB, Holbach L. Central corneal thickness and thick- 37
7 Central corneal thickness and optic nerve head ness of the lamina cribrosa in human eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2005; 46: Chauhan BC, McCormick TA, Nicolela MT, LeBlanc RP. Optic disc and visual field changes in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with glaucoma: comparison of scanning laser tomography with conventional perimetry and optic disc photography. Arch Ophthalmol 2001; 119: Akar Y, Orhan M, Irkeç M, Karaagaoglu E. Major determinants of optic nerve head topographic characteristic in a normal Turkish population. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol 2004; 32: Hermann MM, Theofylaktopoulos I, Bangard N, Jonescu- Cuypers C, Coburger S, Diestelhorst M. Optic nerve head morphometry in healthy adults using confocal laser scanning tomography. Br J Ophthalmol 2004; 88: Gherghel D, Orgül S, Prünte C, et al. Interocular differences in optic disk topographic parameters in normal subjects. Curr Eye Res 2000; 20: Nakamura H, Maeda T, Suzuki Y, Inoue Y. Scanning laser tomography to evaluate optic discs of normal eyes. Jpn J Ophthalmol 1999; 43: Gundersen KG, Heijl A, Bengtsson B. Age, gender, IOP, refraction and optic disk topography in normal eyes. A crosssectional study using raster and scanning laser tomography. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 1998; 76: Kergoat H, Kergoat MJ, Justino L, Lovasik JV. Age related topographical changes in the normal human optic nerve head measured by scanning laser tomography. Optom Vis Sci 2001; 78: Vernon SA, Hawker MJ, Ainsworth G, Hillman JG, MacNab HK, Dua HS. Laser scanning tomography of the optic nerve head in a normal elderly population: The Bridlington Eye Assessment Project. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2005; 46: Kee C, Koo H, Ji Y, Kim S. Effect of optic disc size or age on evaluation of optic disc variables. Br J Ophthalmol 1997; 81: Gordon MO, Beiser JA, Brandt JD, et al. The Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study; baseline factors that predict the onset of primary open-angle glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol 2002; 120: Mederios FA, Sample PA, Weinreb RN. Corneal thickness measurement and frequency doubling technology perimetry abnormalities in ocular hypertensive eyes. Ophthalmology 2003; 110: Henderson PA, Medeiros FA, Zangwill LM, Weinreb RN. Relationship between central corneal thickness and retinal nerve fiber layer in ocular hypertensive patients. Ophthalmology 2005; 112: Jonas JB, Stroux A, Velten I, Juenemann A, Martus P, Budde WM. Central corneal thickness correlated with glaucoma damage and rate of progression. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2005; 46: Hewitt AW, Franzco RLC. Relationship between corneal thickness and optic disc damage in glaucoma. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2005; 33: Choi HJ, Kim DM, Hwang SS. Relationship between central corneal thickness and localised nerve fiber layer defect in normal tension glaucoma. J Glaucoma 2006; 15: Bellezza AJ, Rintalan CJ, Thompson HW, Downs JC, Hart RT, Burgoyne CF. Deformation of the lamina cribrosa and anterior scleral canal wall in early experimental glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2003; 44: Jonas JB, Berenshtein E, Holbach L. Anatomic relationship between lamina cribrosa, intraocular space, and cerebrospinal fluid space. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2003; 44: Girkin C, Cioffi GA, Liebmann JM. Thin corneas and the risk of progression. J Glaucoma 2003; 12: Lusky M, Bosem ME, Weinreb RN. Reproducibility of optic nerve head topography with a new laser tomographic scanning device. Ophthalmology 1994; 101: Tezel G, Trinkaus K, Wax MB. Alterations in the morphology of lamina cribrosa pores in glaucomatous eyes. Br J Ophthalmol 2004; 88: Jonas JB, Martus P, Budde WM, Hayler I. Morphologic predictive factors fort he development of optic disk hemorrhages in glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2002; 43: Durukan AH, Yücel I, Akar Y, Bayraktar MZ. Assessment of optic nerve head topographic parameters with a confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol 2004; 32: Varma R, Tielsch J, Quigley HA, et al. Race, age, gender and refractive error related differences in the normal optic disc. Arch Ophthalmol 1994; 112: Hitchins R. Normal tension glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 2nd ed. St. Louis: The CV Mosby Co., 2004;
Optic nerve head morphometry in healthy adults using confocal laser scanning tomography
 761 SCIENTIFIC REPORT Optic nerve head morphometry in healthy adults using confocal laser scanning tomography M M Hermann, I Theofylaktopoulos, N Bangard, C Jonescu-Cuypers, S Coburger, M Diestelhorst...
761 SCIENTIFIC REPORT Optic nerve head morphometry in healthy adults using confocal laser scanning tomography M M Hermann, I Theofylaktopoulos, N Bangard, C Jonescu-Cuypers, S Coburger, M Diestelhorst...
Correlating central corneal thickness and intraocular pressure in ocular hypertension and glaucoma
 VOL. 3 NO. 1 PHILIPPINE JOURNAL OF Ophthalmology JANUARY ORIGINAL ARTICLE JUNE 07 Jonathan G. Soriano, MD 1 Ma. Margarita L. Lat-Luna, MD 1, 3 Patricia M. Khu, MD 1, 1 Department of Ophthalmology and Visual
VOL. 3 NO. 1 PHILIPPINE JOURNAL OF Ophthalmology JANUARY ORIGINAL ARTICLE JUNE 07 Jonathan G. Soriano, MD 1 Ma. Margarita L. Lat-Luna, MD 1, 3 Patricia M. Khu, MD 1, 1 Department of Ophthalmology and Visual
Role of Central Corneal Thickness in Circadian Intraocular Pressure Fluctuations among Patients with Primary Open Angle Glaucoma
 Role of Central Corneal Thickness in Circadian Intraocular Pressure Fluctuations among Patients with Primary Open Angle Glaucoma Mohannad Albdour MD*, Karanjit Kooner MD, PHD** ABSTRACT Objectives: To
Role of Central Corneal Thickness in Circadian Intraocular Pressure Fluctuations among Patients with Primary Open Angle Glaucoma Mohannad Albdour MD*, Karanjit Kooner MD, PHD** ABSTRACT Objectives: To
Scanning Laser Tomography to Evaluate Optic Discs of Normal Eyes
 Scanning Laser Tomography to Evaluate Optic Discs of Normal Eyes Hiroshi Nakamura,* Toshine Maeda,* Yasuyuki Suzuki and Yoichi Inoue* *Eye Division of Olympia Medical Clinic, Tokyo, Japan; Department of
Scanning Laser Tomography to Evaluate Optic Discs of Normal Eyes Hiroshi Nakamura,* Toshine Maeda,* Yasuyuki Suzuki and Yoichi Inoue* *Eye Division of Olympia Medical Clinic, Tokyo, Japan; Department of
Seiji T. Takagi, Yoshiyuki Kita, Asuka Takeyama, and Goji Tomita. 1. Introduction. 2. Subjects and Methods
 Ophthalmology Volume 2011, Article ID 914250, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/914250 Clinical Study Macular Retinal Ganglion Cell Complex Thickness and Its Relationship to the Optic Nerve Head Topography in Glaucomatous
Ophthalmology Volume 2011, Article ID 914250, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/914250 Clinical Study Macular Retinal Ganglion Cell Complex Thickness and Its Relationship to the Optic Nerve Head Topography in Glaucomatous
Intro to Glaucoma/2006
 Intro to Glaucoma/2006 Managing Patients with Glaucoma is Exciting Interesting Challenging But can often be frustrating! Clinical Challenges To identify patients with risk factors for possible glaucoma.
Intro to Glaucoma/2006 Managing Patients with Glaucoma is Exciting Interesting Challenging But can often be frustrating! Clinical Challenges To identify patients with risk factors for possible glaucoma.
The evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer in pigment dispersion syndrome and pigmentary glaucoma using scanning laser polarimetry
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 13 no. 4, 2003 / pp. 377-382 The evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer in pigment dispersion syndrome and pigmentary glaucoma using scanning laser polarimetry
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 13 no. 4, 2003 / pp. 377-382 The evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer in pigment dispersion syndrome and pigmentary glaucoma using scanning laser polarimetry
Based on the studies by Goldmann and Schmidt 1 and Ehlers. Central Corneal Thickness Correlated with Glaucoma Damage and Rate of Progression
 Central Corneal Thickness Correlated with Glaucoma Damage and Rate of Progression Jost B. Jonas, 1,2 Andrea Stroux, 3,4 Isabel Velten, 1 Anselm Juenemann, 1 Peter Martus, 3 and Wido M. Budde 1,2 PURPOSE.
Central Corneal Thickness Correlated with Glaucoma Damage and Rate of Progression Jost B. Jonas, 1,2 Andrea Stroux, 3,4 Isabel Velten, 1 Anselm Juenemann, 1 Peter Martus, 3 and Wido M. Budde 1,2 PURPOSE.
Comparison of Optic Disc Topography Measured by Retinal Thickness Analyzer with Measurement by Heidelberg Retina Tomograph II
 Comparison of Optic Disc Topography Measured by Retinal Analyzer with Measurement by Heidelberg Retina Tomograph II Noriko Itai*, Masaki Tanito*, and Etsuo Chihara* *Senshokai Eye Institute, Uji, Kyoto,
Comparison of Optic Disc Topography Measured by Retinal Analyzer with Measurement by Heidelberg Retina Tomograph II Noriko Itai*, Masaki Tanito*, and Etsuo Chihara* *Senshokai Eye Institute, Uji, Kyoto,
Investigation of the relationship between central corneal thickness and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in ocular hypertension
 Acta Medica Anatolia Volume 2 Issue 1 2014 Investigation of the relationship between central corneal thickness and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in ocular hypertension Remzi Mısır 1, Sinan Sarıcaoğlu
Acta Medica Anatolia Volume 2 Issue 1 2014 Investigation of the relationship between central corneal thickness and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in ocular hypertension Remzi Mısır 1, Sinan Sarıcaoğlu
Early Detection Of Glaucoma Clinical Clues. Points To Live By. Glaucoma Risk Factors 10/3/2014
 Early Detection Of Glaucoma Clinical Clues Eric E. Schmidt, O.D. Omni Eye Specialists Wilmington, NC schmidtyvision@msn.com Points To Live By 25% of G pxs NEVER have IOP >21mm 50% of G pxs have trough
Early Detection Of Glaucoma Clinical Clues Eric E. Schmidt, O.D. Omni Eye Specialists Wilmington, NC schmidtyvision@msn.com Points To Live By 25% of G pxs NEVER have IOP >21mm 50% of G pxs have trough
Central corneal thickness among glaucoma patients attending Menelik II Hospital, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
 Original article Central corneal thickness among glaucoma patients attending Menelik II Hospital, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia Zelalem Gizachew 1, Abiy Mulugeta 1* Abstract Background: Glaucoma is one of the
Original article Central corneal thickness among glaucoma patients attending Menelik II Hospital, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia Zelalem Gizachew 1, Abiy Mulugeta 1* Abstract Background: Glaucoma is one of the
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: CORNEAL ULTRASOUND PACHYMETRY. POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Technology Assessment
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: CORNEAL ULTRASOUND,, PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: CORNEAL ULTRASOUND,, PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
Central corneal thickness and vascular risk factors in normal tension glaucoma
 Central corneal thickness and vascular risk factors in normal tension glaucoma Aoife Doyle, Ahmed Bensaid and Yves Lachkar L Institut du Glaucome, Fondation Hoˆpital St. Joseph, Paris, France ABSTRACT.
Central corneal thickness and vascular risk factors in normal tension glaucoma Aoife Doyle, Ahmed Bensaid and Yves Lachkar L Institut du Glaucome, Fondation Hoˆpital St. Joseph, Paris, France ABSTRACT.
The Role of the RNFL in the Diagnosis of Glaucoma
 Chapter 1. The Role of the RNFL in the Diagnosis of Glaucoma Introduction Glaucoma is an optic neuropathy characterized by a loss of of retinal ganglion cells and their axons, the Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer
Chapter 1. The Role of the RNFL in the Diagnosis of Glaucoma Introduction Glaucoma is an optic neuropathy characterized by a loss of of retinal ganglion cells and their axons, the Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer
A Review Of Risk Factors. Early Detection Of Glaucoma Clinical Clues. A risk factor analysis is critical. Points To Live By
 A Review Of Risk Factors Early Detection Of Glaucoma Clinical Clues Eric E. Schmidt, O.D. Omni Eye Specialists Wilmington, NC schmidtyvision@msn.com FINDACAR Family history IOP Nearsightedness Diabetes/Vascular
A Review Of Risk Factors Early Detection Of Glaucoma Clinical Clues Eric E. Schmidt, O.D. Omni Eye Specialists Wilmington, NC schmidtyvision@msn.com FINDACAR Family history IOP Nearsightedness Diabetes/Vascular
MEDICAL POLICY. Proprietary Information of Excellus Health Plan, Inc. A nonprofit independent licensee of the BlueCross BlueShield Association
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: OPHTHALMOLOGIC TECHNIQUES PAGE: 1 OF: 7 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: OPHTHALMOLOGIC TECHNIQUES PAGE: 1 OF: 7 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical
Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Measurements in Myopia Using Optical Coherence Tomography
 Original Article Philippine Journal of OPHTHALMOLOGY Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Measurements in Myopia Using Optical Coherence Tomography Dennis L. del Rosario, MD and Mario M. Yatco, MD University of Santo
Original Article Philippine Journal of OPHTHALMOLOGY Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Measurements in Myopia Using Optical Coherence Tomography Dennis L. del Rosario, MD and Mario M. Yatco, MD University of Santo
Study of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Within Normal Hemivisual Field in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma and Normal-Tension Glaucoma
 Study of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Within Normal Hemivisual Field in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma and Normal-Tension Glaucoma Chiharu Matsumoto, Shiroaki Shirato, Mai Haneda, Hiroko Yamashiro
Study of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Within Normal Hemivisual Field in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma and Normal-Tension Glaucoma Chiharu Matsumoto, Shiroaki Shirato, Mai Haneda, Hiroko Yamashiro
Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in Indian eyes with optical coherence tomography
 Original articles in Indian eyes with optical coherence tomography Malik A, Singh M, Arya SK, Sood S, Ichhpujani P Department of Ophthalmology Government Medical College and Hospital, Sector 32, Chandigarh,
Original articles in Indian eyes with optical coherence tomography Malik A, Singh M, Arya SK, Sood S, Ichhpujani P Department of Ophthalmology Government Medical College and Hospital, Sector 32, Chandigarh,
Macular Ganglion Cell Complex Measurement Using Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography in Glaucoma
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 2, September: 67-72, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Macular Ganglion Cell Complex Measurement Using Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography in Glaucoma
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 2, September: 67-72, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Macular Ganglion Cell Complex Measurement Using Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography in Glaucoma
The appearance of the normal optic nerve head (ONH) can
 Laser Scanning Tomography of the Optic Nerve Head in a Normal Elderly Population: The Bridlington Eye Assessment Project Stephen A. Vernon, 1 Matthew J. Hawker, 1 Gerard Ainsworth, 1 Jonathan G. Hillman,
Laser Scanning Tomography of the Optic Nerve Head in a Normal Elderly Population: The Bridlington Eye Assessment Project Stephen A. Vernon, 1 Matthew J. Hawker, 1 Gerard Ainsworth, 1 Jonathan G. Hillman,
Is NTG different from POAG?
 Is NTG different from POAG? Sunita Radhakrishnan, M.D Glaucoma Center of San Francisco Glaucoma Research and Education Group Subset of POAG 1 Connective tissue structure within ONH Ganglion cell susceptibility
Is NTG different from POAG? Sunita Radhakrishnan, M.D Glaucoma Center of San Francisco Glaucoma Research and Education Group Subset of POAG 1 Connective tissue structure within ONH Ganglion cell susceptibility
Effect of Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty in Glaucoma Patients with High or Low Central Corneal Thickness
 Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Effect of Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty in Glaucoma Patients with High or Low Central Corneal Thickness Abstract Purpose: Comparison of the effect
Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Effect of Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty in Glaucoma Patients with High or Low Central Corneal Thickness Abstract Purpose: Comparison of the effect
Central Corneal Thickness-An important variable for prognostication in Primary Open Angle glaucoma; A Kolkata based study in Eastern India
 Original article: Central Corneal Thickness-An important variable for prognostication in Primary Open Angle glaucoma; A Kolkata based study in Eastern India 1Dr. Apala Bhattacharya, 2 Dr Gautam Bhaduri,
Original article: Central Corneal Thickness-An important variable for prognostication in Primary Open Angle glaucoma; A Kolkata based study in Eastern India 1Dr. Apala Bhattacharya, 2 Dr Gautam Bhaduri,
The Effect of Pupil Dilation on Scanning Laser Polarimetry With Variable Corneal Compensation
 C L I N I C A L S C I E N C E The Effect of Pupil Dilation on Scanning Laser Polarimetry With Variable Corneal Compensation Amjad Horani, MD; Shahar Frenkel, MD, PhD; Eytan Z. Blumenthal, MD BACKGROUND
C L I N I C A L S C I E N C E The Effect of Pupil Dilation on Scanning Laser Polarimetry With Variable Corneal Compensation Amjad Horani, MD; Shahar Frenkel, MD, PhD; Eytan Z. Blumenthal, MD BACKGROUND
* Şükrü Bayraktar, MD, Zerrin Bayraktar, MD, and Ömer Faruk Yilmaz, MD
 Journal of Glaucoma 10:163 169 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Influence of Scan Radius Correction for Ocular Magnification and Relationship Between Scan Radius With Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer
Journal of Glaucoma 10:163 169 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Influence of Scan Radius Correction for Ocular Magnification and Relationship Between Scan Radius With Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer
Evaluating Optic Nerve Damage: Pearls and Pitfalls
 54 The Open Ophthalmology Journal, 9, 3, 54-58 Evaluating Optic Nerve Damage: Pearls and Pitfalls Open Access Paul J. Mackenzie * and Frederick S. Mikelberg Division of Glaucoma, Department of Ophthalmology
54 The Open Ophthalmology Journal, 9, 3, 54-58 Evaluating Optic Nerve Damage: Pearls and Pitfalls Open Access Paul J. Mackenzie * and Frederick S. Mikelberg Division of Glaucoma, Department of Ophthalmology
MEDICAL POLICY. Proprietary Information of YourCare Healthcare
 MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 7 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 7 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
Clinical Profile of Primary Open Angle Glaucoma Suspects.
 DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2018.4.2.OT3 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Clinical Profile of Primary Open Angle Glaucoma Suspects. Pradnya Abhinav Mohan 1 1 Fellow Phaco-surgery, Department
DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2018.4.2.OT3 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Clinical Profile of Primary Open Angle Glaucoma Suspects. Pradnya Abhinav Mohan 1 1 Fellow Phaco-surgery, Department
Influence of Myopic Disc Shape on the Diagnostic Precision of the Heidelberg Retina Tomograph
 Influence of Myopic Disc Shape on the Diagnostic Precision of the Heidelberg Retina Tomograph Yoshio Yamazaki,* Keiji Yoshikawa, Shiho Kunimatsu, Nobuyuki Koseki, Yasuyuki Suzuki, Shun Matsumoto and Makoto
Influence of Myopic Disc Shape on the Diagnostic Precision of the Heidelberg Retina Tomograph Yoshio Yamazaki,* Keiji Yoshikawa, Shiho Kunimatsu, Nobuyuki Koseki, Yasuyuki Suzuki, Shun Matsumoto and Makoto
The Measure of Confidence
 Heidelberg_936357.qxd:Layout 1 5/9/08 12:01 PM 12:02 Page 1 (Cyan (Magenta (Yellow (Black (UV Five Powerful Solutions to Fit Your Practice PowerCheck Glaucoma FastCheck+ GPS Software and Retina Edema Index
Heidelberg_936357.qxd:Layout 1 5/9/08 12:01 PM 12:02 Page 1 (Cyan (Magenta (Yellow (Black (UV Five Powerful Solutions to Fit Your Practice PowerCheck Glaucoma FastCheck+ GPS Software and Retina Edema Index
Glaucoma: Diagnostic Modalities
 Glaucoma: Diagnostic Modalities - Dr. Barun Kumar Nayak, Dr. Sarika Ramugade Glaucoma is a leading cause of blindness in the world, especially in older people. Early detection and treatment by ophthalmologist
Glaucoma: Diagnostic Modalities - Dr. Barun Kumar Nayak, Dr. Sarika Ramugade Glaucoma is a leading cause of blindness in the world, especially in older people. Early detection and treatment by ophthalmologist
Optic Nerve: Clinical Examination
 Optic Nerve: Clinical Examination Marcelo T. Nicolela 2 Core Messages Optic disc evaluation is of fundamental importance in the management of glaucoma. Clinical examination of the optic disc is best performed
Optic Nerve: Clinical Examination Marcelo T. Nicolela 2 Core Messages Optic disc evaluation is of fundamental importance in the management of glaucoma. Clinical examination of the optic disc is best performed
Central corneal thickness and normal tension glaucoma: A cross-sectional study
 Optometry (2006) 77, 134-140 Central corneal thickness and normal tension glaucoma: A cross-sectional study Michael Sullivan-Mee, O.D., a Kathy D. Halverson, O.D., a Mollie C. Saxon, O.D., a Glenn B. Saxon,
Optometry (2006) 77, 134-140 Central corneal thickness and normal tension glaucoma: A cross-sectional study Michael Sullivan-Mee, O.D., a Kathy D. Halverson, O.D., a Mollie C. Saxon, O.D., a Glenn B. Saxon,
Relationship of Central Corneal Thickness with Optic Disc Parameters: The Singapore Malay Eye Study METHODS
 Glaucoma Relationship of Central Corneal Thickness with Optic Disc arameters: The Singapore Malay Eye Study Ren-Yi Wu, 1 Ying-Feng Zheng, 1 Tien-Yin Wong, 1,2 Carol Yim-Lui Cheung, 1 Seng-Chee Loon, 3
Glaucoma Relationship of Central Corneal Thickness with Optic Disc arameters: The Singapore Malay Eye Study Ren-Yi Wu, 1 Ying-Feng Zheng, 1 Tien-Yin Wong, 1,2 Carol Yim-Lui Cheung, 1 Seng-Chee Loon, 3
Role of central corneal thickness measurement in management of open angle glaucoma and glaucoma suspects in Calabar, Nigeria
 Original Research Article Role of central corneal thickness measurement in management of open angle glaucoma and glaucoma suspects in Calabar, Nigeria Nkanga DG 1,2, Ibanga AA 1,2, Nkanga ED 2, Etim BA
Original Research Article Role of central corneal thickness measurement in management of open angle glaucoma and glaucoma suspects in Calabar, Nigeria Nkanga DG 1,2, Ibanga AA 1,2, Nkanga ED 2, Etim BA
The evaluation of the optic nerve and retinal nerve
 Five rules to evaluate the optic disc and retinal nerve fiber layer for glaucoma Murray Fingeret, O.D., a,b Felipe A. Medeiros, M.D., c Remo Susanna, Jr, M.D., d and Robert N. Weinreb, M.D. c a Department
Five rules to evaluate the optic disc and retinal nerve fiber layer for glaucoma Murray Fingeret, O.D., a,b Felipe A. Medeiros, M.D., c Remo Susanna, Jr, M.D., d and Robert N. Weinreb, M.D. c a Department
Goals. Glaucoma PARA PEARL TO DO. Vision Loss with Glaucoma
 Glaucoma Janet R. Fett, OD Drs. Kincaid, Fett and Tharp So Sioux City, NE eyewear21@hotmail.com Goals Understand Glaucoma Disease process Understand how your data (objective and subjective) assists in
Glaucoma Janet R. Fett, OD Drs. Kincaid, Fett and Tharp So Sioux City, NE eyewear21@hotmail.com Goals Understand Glaucoma Disease process Understand how your data (objective and subjective) assists in
RETINAL NERVE FIBER LAYER
 CLINICAL SCIENCES The Effect of Scan Diameter on Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Measurement Using Stratus Optic Coherence Tomography Giacomo Savini, MD; Piero Barboni, MD; Michele Carbonelli, MD;
CLINICAL SCIENCES The Effect of Scan Diameter on Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Measurement Using Stratus Optic Coherence Tomography Giacomo Savini, MD; Piero Barboni, MD; Michele Carbonelli, MD;
Available online at Pelagia Research Library. Advances in Applied Science Research, 2013, 4(6):
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 2013, 4(6):201-206 ISSN: 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC Comparison of glaucoma diagnostic ability of retinal nerve
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 2013, 4(6):201-206 ISSN: 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC Comparison of glaucoma diagnostic ability of retinal nerve
To assess the glaucoma diagnostic ability of Fourier Domain Optical Coherence Tomography
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-11, pp-104-110 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access To assess the glaucoma diagnostic ability of
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-11, pp-104-110 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access To assess the glaucoma diagnostic ability of
Science & Technologies
 STANDARD COMPUTERIZED PERIMETRY IN FUNCTION OF DIAGNOSTIC GLAUCOMA Iljaz Ismaili, 1 Gazepov Strahil, 2, Goshevska Dashtevska Emilija 1 1 University Eye Clinic,Skopje 2 Clinical Hospital, Shtip Abstract
STANDARD COMPUTERIZED PERIMETRY IN FUNCTION OF DIAGNOSTIC GLAUCOMA Iljaz Ismaili, 1 Gazepov Strahil, 2, Goshevska Dashtevska Emilija 1 1 University Eye Clinic,Skopje 2 Clinical Hospital, Shtip Abstract
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Conversion of Ocular Hypertensives into Glaucoma: A Retrospective Study Aditi Singh 1, Shibi
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Conversion of Ocular Hypertensives into Glaucoma: A Retrospective Study Aditi Singh 1, Shibi
Relationship Between Structure
 Original Article Relationship Between Structure and Function of the Optic Nerve Head-Glaucoma versus Normal Dr Savita Bhat, Dr Anna Elias, Dr Siddharth Pawar, Dr S.J. Saikumar, Dr Alpesh Rajput, superior,
Original Article Relationship Between Structure and Function of the Optic Nerve Head-Glaucoma versus Normal Dr Savita Bhat, Dr Anna Elias, Dr Siddharth Pawar, Dr S.J. Saikumar, Dr Alpesh Rajput, superior,
CLINICAL SCIENCES. Differences in Visual Function and Optic Nerve Structure Between Healthy Eyes of Blacks and Whites
 CLINICAL SCIENCES Differences in Visual Function and Optic Nerve Structure Between Healthy Eyes of and Lyne Racette, PhD; Catherine Boden, PhD; Shannon L. Kleinhandler, BSc; Christopher A. Girkin, MD;
CLINICAL SCIENCES Differences in Visual Function and Optic Nerve Structure Between Healthy Eyes of and Lyne Racette, PhD; Catherine Boden, PhD; Shannon L. Kleinhandler, BSc; Christopher A. Girkin, MD;
Structural examina.on: Imaging
 ManaMa: Glaucoma Structural examina.on: Imaging Luís Abegão Pinto, MD, PhD Department of Ophthalmology CHLC Lisbon Faculty of Medicine, Lisbon University 1 11-10- 2013 Structural changes Qualitative changes
ManaMa: Glaucoma Structural examina.on: Imaging Luís Abegão Pinto, MD, PhD Department of Ophthalmology CHLC Lisbon Faculty of Medicine, Lisbon University 1 11-10- 2013 Structural changes Qualitative changes
Optic disc damage has been shown to precede visual field
 Confocal Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscopy Classifiers and Stereophotograph Evaluation for rediction of Visual Field Abnormalities in Glaucoma-Suspect Eyes Christopher Bowd, 1 Linda M. Zangwill, 1 Felipe A.
Confocal Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscopy Classifiers and Stereophotograph Evaluation for rediction of Visual Field Abnormalities in Glaucoma-Suspect Eyes Christopher Bowd, 1 Linda M. Zangwill, 1 Felipe A.
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 12, December ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 12, December-2013 108 Name of Chief and Corresponding Author : Dr Chandrima Paul TITLE : Comparison of glaucoma diagnostic ability
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 12, December-2013 108 Name of Chief and Corresponding Author : Dr Chandrima Paul TITLE : Comparison of glaucoma diagnostic ability
Spontaneous Intraocular Pressure Reduction in Normal-Tension Glaucoma and Associated Clinical Factors
 CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS Spontaneous Intraocular Pressure Reduction in Normal-Tension Glaucoma and Associated Clinical Factors Akihiro Oguri, Tetsuya Yamamoto and Yoshiaki Kitazawa Department of Ophthalmology,
CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS Spontaneous Intraocular Pressure Reduction in Normal-Tension Glaucoma and Associated Clinical Factors Akihiro Oguri, Tetsuya Yamamoto and Yoshiaki Kitazawa Department of Ophthalmology,
Ability of Scanning Laser Polarimetry (GDx) to Discriminate among Early Glaucomatous, Ocular Hypertensive and Normal Eyes in the Korean Population
 Korean J Ophthalmol Vol. 18:1-8, 2004 Ability of Scanning Laser Polarimetry (GDx) to Discriminate among Early Glaucomatous, Ocular Hypertensive and Normal Eyes in the Korean Population Sun Young Lee, MD,
Korean J Ophthalmol Vol. 18:1-8, 2004 Ability of Scanning Laser Polarimetry (GDx) to Discriminate among Early Glaucomatous, Ocular Hypertensive and Normal Eyes in the Korean Population Sun Young Lee, MD,
Retinal nerve fiber layer measured by Heidelberg retina tomograph and nerve fiber analyzer
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 15 no. 2, 2005 / pp. 246-254 Retinal nerve fiber layer measured by Heidelberg retina tomograph and nerve fiber analyzer M. IESTER 1,2, A. MERMOUD 1 1 Hopital Ophtalmique
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 15 no. 2, 2005 / pp. 246-254 Retinal nerve fiber layer measured by Heidelberg retina tomograph and nerve fiber analyzer M. IESTER 1,2, A. MERMOUD 1 1 Hopital Ophtalmique
T he lamina cribrosa is a sieve-like membrane in the
 1299 EXTENDED REPORT Three dimensional analysis of the lamina cribrosa in glaucoma J Morgan-Davies, N Taylor, A R Hill, P Aspinall, CJ O Brien, A Azuara-Blanco... See end of article for authors affiliations...
1299 EXTENDED REPORT Three dimensional analysis of the lamina cribrosa in glaucoma J Morgan-Davies, N Taylor, A R Hill, P Aspinall, CJ O Brien, A Azuara-Blanco... See end of article for authors affiliations...
Central corneal thickness determined with optical coherence tomography in various types of glaucoma
 Br J Ophthalmol 2000;84:1233 1237 1233 Department of Ophthalmology, Ludwig-Maximilians- University, Munich, Germany M Bechmann M J Thiel B Roesen S Ullrich M W Ulbig K Ludwig Correspondence to: Martin
Br J Ophthalmol 2000;84:1233 1237 1233 Department of Ophthalmology, Ludwig-Maximilians- University, Munich, Germany M Bechmann M J Thiel B Roesen S Ullrich M W Ulbig K Ludwig Correspondence to: Martin
Noel de Jesus Atienza, MD, MSc and Joseph Anthony Tumbocon, MD
 Original Article Philippine Journal of OPHTHALMOLOGY Diagnostic Accuracy of the Optical Coherence Tomography in Assessing Glaucoma Among Filipinos. Part 1: Categorical Outcomes Based on a Normative Database
Original Article Philippine Journal of OPHTHALMOLOGY Diagnostic Accuracy of the Optical Coherence Tomography in Assessing Glaucoma Among Filipinos. Part 1: Categorical Outcomes Based on a Normative Database
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 6: , 2013
 268 Comparison of optic nerve morphology in eyes with glaucoma and eyes with non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy by Fourier domain optical coherence tomography YUXIN YANG 1, HAITAO ZHANG 1,
268 Comparison of optic nerve morphology in eyes with glaucoma and eyes with non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy by Fourier domain optical coherence tomography YUXIN YANG 1, HAITAO ZHANG 1,
Correlation of Blue Chromatic Macular Sensitivity with Optic Disc Change in Early Glaucoma Patients
 Correlation of Blue Chromatic Macular Sensitivity with Optic Disc Change in Early Glaucoma Patients Yoshio Yamazaki, Kenji Mizuki, Fukuko Hayamizu and Chizuru Tanaka Department of Ophthalmology, Nihon
Correlation of Blue Chromatic Macular Sensitivity with Optic Disc Change in Early Glaucoma Patients Yoshio Yamazaki, Kenji Mizuki, Fukuko Hayamizu and Chizuru Tanaka Department of Ophthalmology, Nihon
A comparison of HRT II and GDx imaging for glaucoma detection in a primary care eye clinic setting
 (2007) 21, 1050 1055 & 2007 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-222X/07 $30.00 www.nature.com/eye CLINICAL STUDY A comparison of HRT II and GDx imaging for glaucoma detection in a primary
(2007) 21, 1050 1055 & 2007 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-222X/07 $30.00 www.nature.com/eye CLINICAL STUDY A comparison of HRT II and GDx imaging for glaucoma detection in a primary
INTRODUCTION S. HERDENER, D. HAFIZOVIC, M. PACHE, S. LAUTEBACH, J. FUNK. University Eye Hospital, Freiburg - Germany
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 18 no. 1, 2008 / pp. 39-43 Is the PASCAL -Tonometer suitable for measuring intraocular pressure in clinical routine? Long- and short-term reproducibility of dynamic
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 18 no. 1, 2008 / pp. 39-43 Is the PASCAL -Tonometer suitable for measuring intraocular pressure in clinical routine? Long- and short-term reproducibility of dynamic
Relationship between the GDx VCC and Stratus OCT in Primary Open Angle Glaucoma
 Relationship between the GDx VCC and Stratus OCT in Primary Open Angle Glaucoma Reza Zarei, MD 1 Mohammad Soleimani, MD 2 Sasan Moghimi, MD 3 Mohammad Yaser Kiarudi, MD 2 Mahmoud Jabbarvand, MD 1 Yadollah
Relationship between the GDx VCC and Stratus OCT in Primary Open Angle Glaucoma Reza Zarei, MD 1 Mohammad Soleimani, MD 2 Sasan Moghimi, MD 3 Mohammad Yaser Kiarudi, MD 2 Mahmoud Jabbarvand, MD 1 Yadollah
Glaucoma. Glaucoma. Optic Disc Cupping
 Glaucoma What is Glaucoma? Bruce James A group of diseases in which damage to the optic nerve occurs as a result of intraocualar pressure being above the physiological norm for that eye Stoke Mandeville
Glaucoma What is Glaucoma? Bruce James A group of diseases in which damage to the optic nerve occurs as a result of intraocualar pressure being above the physiological norm for that eye Stoke Mandeville
STRUCTURE & FUNCTION An Integrated Approach for the Detection and Follow-up of Glaucoma. Module 3a GDx
 STRUCTURE & FUNCTION An Integrated Approach for the Detection and Follow-up of Glaucoma Module 3a GDx Educational Slide Deck Carl Zeiss Meditec, Inc. November 2005 1 Structure & Function Modules Module
STRUCTURE & FUNCTION An Integrated Approach for the Detection and Follow-up of Glaucoma Module 3a GDx Educational Slide Deck Carl Zeiss Meditec, Inc. November 2005 1 Structure & Function Modules Module
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Br J Ophthalmol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2014 November 01.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Br J Ophthalmol. 2014 November ; 98(11): 1551 1554. doi:10.1136/bjophthalmol-2013-304393. Optic Nerve Head Morphology in Glaucoma
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Br J Ophthalmol. 2014 November ; 98(11): 1551 1554. doi:10.1136/bjophthalmol-2013-304393. Optic Nerve Head Morphology in Glaucoma
CLINICAL SCIENCES. Baseline Topographic Optic Disc Measurements Are Associated With the Development of Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma
 CLINICAL SCIENCES Baseline Topographic Optic Disc Measurements Are Associated With the Development of Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma The Confocal Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscopy Ancillary Study to the Ocular
CLINICAL SCIENCES Baseline Topographic Optic Disc Measurements Are Associated With the Development of Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma The Confocal Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscopy Ancillary Study to the Ocular
The Optic Nerve Head In Glaucoma. Clinical Pearl #1. Characteristics of Normal Disk 9/26/2017. Initial detectable damage Structure vs function
 The Optic Nerve Head In Glaucoma Clinical Pearl #1 Eric E. Schmidt, O.D., F.A.A.O. Omni Eye Specialists Wilmington,NC schmidtyvision@msn.com Glaucoma is an optic neuropathy Initial detectable damage Structure
The Optic Nerve Head In Glaucoma Clinical Pearl #1 Eric E. Schmidt, O.D., F.A.A.O. Omni Eye Specialists Wilmington,NC schmidtyvision@msn.com Glaucoma is an optic neuropathy Initial detectable damage Structure
Glaucoma is a chronic progressive optic neuropathy,
 ORIGINAL STUDY Comparison of Neuroretinal Rim Area Measurements Made by the Heidelberg Retina Tomograph I and the Heidelberg Retina Tomograph II Ya Xing Wang, MD,*w Neil O Leary, MSc,zy Nicholas G. Strouthidis,
ORIGINAL STUDY Comparison of Neuroretinal Rim Area Measurements Made by the Heidelberg Retina Tomograph I and the Heidelberg Retina Tomograph II Ya Xing Wang, MD,*w Neil O Leary, MSc,zy Nicholas G. Strouthidis,
Collaboration in the care of glaucoma patients and glaucoma suspects. Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Nico Ristorante November 29, 2012
 Collaboration in the care of glaucoma patients and glaucoma suspects Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Nico Ristorante November 29, 2012 Goals of Collaboration Patient-centred and evidence based approach Timely access
Collaboration in the care of glaucoma patients and glaucoma suspects Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Nico Ristorante November 29, 2012 Goals of Collaboration Patient-centred and evidence based approach Timely access
Comparative evaluation of time domain and spectral domain optical coherence tomography in retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measurements
 Original article Comparative evaluation of time domain and spectral domain optical coherence tomography in retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measurements Dewang Angmo, 1 Shibal Bhartiya, 1 Sanjay K Mishra,
Original article Comparative evaluation of time domain and spectral domain optical coherence tomography in retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measurements Dewang Angmo, 1 Shibal Bhartiya, 1 Sanjay K Mishra,
Optic Disc Evaluation: Is the Optic Disc Glaucomatous and Has it Progressed?
 Optic Disc Evaluation: Is the Optic Disc Glaucomatous and Has it Progressed? Jody Piltz-Seymour, M.D. Clinical Professor Perelman School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania Wills Glaucoma Service Valley
Optic Disc Evaluation: Is the Optic Disc Glaucomatous and Has it Progressed? Jody Piltz-Seymour, M.D. Clinical Professor Perelman School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania Wills Glaucoma Service Valley
53 year old woman attends your practice for routine exam. She has no past medical history or family history of note.
 Case 1 Normal Tension Glaucoma 53 year old woman attends your practice for routine exam. She has no past medical history or family history of note. Table 1. Right Eye Left Eye Visual acuity 6/6 6/6 Ishihara
Case 1 Normal Tension Glaucoma 53 year old woman attends your practice for routine exam. She has no past medical history or family history of note. Table 1. Right Eye Left Eye Visual acuity 6/6 6/6 Ishihara
Correlating Structure With Function in End-Stage Glaucoma
 C L I N I C A L S C I E N C E Correlating Structure With Function in End-Stage Glaucoma Eytan Z. Blumenthal, MD; Amjad Horani, MD; Rajesh Sasikumar, MD; Chandrasekhar Garudadri, MD; Addepalli Udaykumar,
C L I N I C A L S C I E N C E Correlating Structure With Function in End-Stage Glaucoma Eytan Z. Blumenthal, MD; Amjad Horani, MD; Rajesh Sasikumar, MD; Chandrasekhar Garudadri, MD; Addepalli Udaykumar,
S Morishita, T Tanabe, S Yu, M Hangai, T Ojima, H Aikawa, N Yoshimura. Clinical science
 Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto, Japan Correspondence to: Dr T Tanabe, Department of Ophthalmology, The Tazuke Kofukai Medical Institute,
Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto, Japan Correspondence to: Dr T Tanabe, Department of Ophthalmology, The Tazuke Kofukai Medical Institute,
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Glaucoma, Evaluation by Ophthalmologic Techniques File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: glaucoma_evaluation_by_ophthalmologic_techniques 3/2001
Corporate Medical Policy Glaucoma, Evaluation by Ophthalmologic Techniques File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: glaucoma_evaluation_by_ophthalmologic_techniques 3/2001
G laucoma is a progressive optic neuropathy in which
 1135 EXTENDED REPORT The correlation between optic nerve head topographic measurements, peripapillary nerve fibre layer thickness, and visual field indices in glaucoma Y-W Lan, D B Henson, A J Kwartz...
1135 EXTENDED REPORT The correlation between optic nerve head topographic measurements, peripapillary nerve fibre layer thickness, and visual field indices in glaucoma Y-W Lan, D B Henson, A J Kwartz...
Factors Associated With Visual Field Progression in Cirrus Optical Coherence Tomography-guided Progression Analysis: A Topographic Approach
 ORIGINAL STUDY Factors Associated With Visual Field Progression in Cirrus Optical Coherence Tomography-guided Progression Analysis: A Topographic Approach Joong Won Shin, MD, Kyung Rim Sung, MD, PhD, Jiyun
ORIGINAL STUDY Factors Associated With Visual Field Progression in Cirrus Optical Coherence Tomography-guided Progression Analysis: A Topographic Approach Joong Won Shin, MD, Kyung Rim Sung, MD, PhD, Jiyun
Clinical decision making based on data from GDx: One year observations
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2002 Clinical decision making based on data from GDx: One year observations James C. Bobrow Washington University
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2002 Clinical decision making based on data from GDx: One year observations James C. Bobrow Washington University
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS
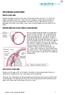 THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
Behandlungsstrategien beim Offenwinkelglaukom. F. Bochmann, Augenklinik LUKS
 Behandlungsstrategien beim Offenwinkelglaukom F. Bochmann, Augenklinik LUKS What is strategy? what is our goal? where are we? how can we achieve our goal? Mission Statement The goal of glaucoma management
Behandlungsstrategien beim Offenwinkelglaukom F. Bochmann, Augenklinik LUKS What is strategy? what is our goal? where are we? how can we achieve our goal? Mission Statement The goal of glaucoma management
PRACTICAL APPROACH TO MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF GLAUCOMA
 PRACTICAL APPROACH TO MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF GLAUCOMA DR. RAVI THOMAS, DR. RAJUL PARIKH, DR. SHEFALI PARIKH IJO MAY 2008 PRESENTER AT JDOS : DR. RAHUL SHUKLA T.N. SHUKLA EYE HOSPITAL TERMINOLOGY POAG: PRIMARY
PRACTICAL APPROACH TO MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF GLAUCOMA DR. RAVI THOMAS, DR. RAJUL PARIKH, DR. SHEFALI PARIKH IJO MAY 2008 PRESENTER AT JDOS : DR. RAHUL SHUKLA T.N. SHUKLA EYE HOSPITAL TERMINOLOGY POAG: PRIMARY
Efficacy of latanoprost in management of chronic angle closure glaucoma. Kumar S 1, Malik A 2 Singh M 3, Sood S 4. Abstract
 Original article Efficacy of latanoprost in management of chronic angle closure glaucoma Kumar S 1, Malik A 2 Singh M 3, Sood S 4 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, 4 Professor, Department of
Original article Efficacy of latanoprost in management of chronic angle closure glaucoma Kumar S 1, Malik A 2 Singh M 3, Sood S 4 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, 4 Professor, Department of
Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer and Central Corneal Thickness in Patients with Exfoliation Syndrome
 Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer and Central Corneal Thickness in Patients with Exfoliation Syndrome Rana Sorkhabi, MD 1 Mohammad Bagher Rahbani, MD 2 Mohammad Hosein Ahoor, MD 2 Vahide Manoochehri, MD 3 Abstract
Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer and Central Corneal Thickness in Patients with Exfoliation Syndrome Rana Sorkhabi, MD 1 Mohammad Bagher Rahbani, MD 2 Mohammad Hosein Ahoor, MD 2 Vahide Manoochehri, MD 3 Abstract
NERVE FIBER LAYER THICKNESS IN NORMALS AND GLAUCOMA PATIENTS
 Nerve fiber layer thickness in normals and glaucoma patients 403 NERVE FIBER LAYER THICKNESS IN NORMALS AND GLAUCOMA PATIENTS HIROTAKA SUZUMURA, KAYOKO HARASAWA, AKIKO KOBAYASHI and NARIYOSHI ENDO Department
Nerve fiber layer thickness in normals and glaucoma patients 403 NERVE FIBER LAYER THICKNESS IN NORMALS AND GLAUCOMA PATIENTS HIROTAKA SUZUMURA, KAYOKO HARASAWA, AKIKO KOBAYASHI and NARIYOSHI ENDO Department
GLAUCOMA SUMMARY BENCHMARKS FOR PREFERRED PRACTICE PATTERN GUIDELINES
 SUMMARY BENCHMARKS FOR PREFERRED PRACTICE PATTERN GUIDELINES Introduction These are summary benchmarks for the Academy s Preferred Practice Pattern (PPP) guidelines. The Preferred Practice Pattern series
SUMMARY BENCHMARKS FOR PREFERRED PRACTICE PATTERN GUIDELINES Introduction These are summary benchmarks for the Academy s Preferred Practice Pattern (PPP) guidelines. The Preferred Practice Pattern series
Diagnostic Accuracy of OCT with a Normative Database to Detect Diffuse Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Atrophy: Diffuse Atrophy Imaging Study METHODS
 Glaucoma Diagnostic Accuracy of OCT with a Normative Database to Detect Diffuse Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Atrophy: Diffuse Atrophy Imaging Study Jin Wook Jeoung, 1,2 Seok Hwan Kim, 1,3 Ki Ho Park, 1,2
Glaucoma Diagnostic Accuracy of OCT with a Normative Database to Detect Diffuse Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Atrophy: Diffuse Atrophy Imaging Study Jin Wook Jeoung, 1,2 Seok Hwan Kim, 1,3 Ki Ho Park, 1,2
CLINICAL SCIENCES. Steven L. Mansberger, MD; Pamela A. Sample, PhD; Linda Zangwill, PhD; Robert N. Weinreb, MD
 CLINICAL SCIENCES Achromatic and Short-Wavelength Automated Perimetry in Patients With Glaucomatous Large Cups Steven L. Mansberger, MD; Pamela A. Sample, PhD; Linda Zangwill, PhD; Robert N. Weinreb, MD
CLINICAL SCIENCES Achromatic and Short-Wavelength Automated Perimetry in Patients With Glaucomatous Large Cups Steven L. Mansberger, MD; Pamela A. Sample, PhD; Linda Zangwill, PhD; Robert N. Weinreb, MD
Clinical Study Visual Field Loss Morphology in High- and Normal-Tension Glaucoma
 Journal of Ophthalmology Volume 2012, Article ID 327326, 8 pages doi:10.1155/2012/327326 Clinical Study Visual Field Loss Morphology in High- and Normal-Tension Glaucoma Michele Iester, 1, 2 Fabio De Feo,
Journal of Ophthalmology Volume 2012, Article ID 327326, 8 pages doi:10.1155/2012/327326 Clinical Study Visual Field Loss Morphology in High- and Normal-Tension Glaucoma Michele Iester, 1, 2 Fabio De Feo,
Assessing the Relationship between Central Corneal Thickness and Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness in Healthy Subjects
 1 1 1 1 1 1 Assessing the Relationship between Central Corneal Thickness and Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness in Healthy Subjects Authors: Tarkan Mumcuoglu, 1* Kelly A Townsend, 1* Gadi Wollstein, 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 Assessing the Relationship between Central Corneal Thickness and Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness in Healthy Subjects Authors: Tarkan Mumcuoglu, 1* Kelly A Townsend, 1* Gadi Wollstein, 1
Ever since the recognition that certain forms of blindness. Central corneal thickness, tonometry, and glaucoma risk a guide for the perplexed
 CJO LECTURE 2007 Central corneal thickness, tonometry, and glaucoma risk a guide for the perplexed James D. Brandt, MD ABSTRACT RÉSUMÉ The results of the Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study (OHTS) brought
CJO LECTURE 2007 Central corneal thickness, tonometry, and glaucoma risk a guide for the perplexed James D. Brandt, MD ABSTRACT RÉSUMÉ The results of the Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study (OHTS) brought
4/06/2013. Medication Observation POAG. Proportion. Native American 0.1% 0.4%
 Clinical Research in Glaucoma: Putting Science into Practice J. James Thimons, O.D., FAAO Chairman, National Glaucoma Society www.nationalglaucomasociety.org Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study (OHTS)
Clinical Research in Glaucoma: Putting Science into Practice J. James Thimons, O.D., FAAO Chairman, National Glaucoma Society www.nationalglaucomasociety.org Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study (OHTS)
Patterns of Subsequent Progression of Localized Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Defects on Red-free Fundus Photographs in Normal-tension Glaucoma
 pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2014;28(4):330-336 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2014.28.4.330 Original Article Patterns of Subsequent Progression of Localized Retinal Nerve Fiber
pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2014;28(4):330-336 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2014.28.4.330 Original Article Patterns of Subsequent Progression of Localized Retinal Nerve Fiber
The second most common causes of blindness worldwide. ( after cataract) The commonest cause of irreversible blindness in the world Estimated that 3%
 The second most common causes of blindness worldwide. ( after cataract) The commonest cause of irreversible blindness in the world Estimated that 3% of our population age > 40 have glaucoma In the past:
The second most common causes of blindness worldwide. ( after cataract) The commonest cause of irreversible blindness in the world Estimated that 3% of our population age > 40 have glaucoma In the past:
Ocular hypertension is present in approximately 8%
 ORIGINAL STUDY The Probability of Glaucoma From Ocular Hypertension Determined by Ophthalmologists in Comparison to a Risk Calculator Steven L. Mansberger, MD, MPH and George A. Cioffi, MD Objective: To
ORIGINAL STUDY The Probability of Glaucoma From Ocular Hypertension Determined by Ophthalmologists in Comparison to a Risk Calculator Steven L. Mansberger, MD, MPH and George A. Cioffi, MD Objective: To
Glaucoma Glaucoma is a complication which has only recently been confirmed as a feature of
 1.2.4 OPHTHALMOLOGICAL ABNORMALITIES Ocular abnormalities are well documented in patients with NPS 6 62 81 95. 1.2.4.1 Glaucoma Glaucoma is a complication which has only recently been confirmed as a feature
1.2.4 OPHTHALMOLOGICAL ABNORMALITIES Ocular abnormalities are well documented in patients with NPS 6 62 81 95. 1.2.4.1 Glaucoma Glaucoma is a complication which has only recently been confirmed as a feature
PREVALENCE OF GLAUCOMA AMONG FISHERMEN COMMUNITY OF MUNDRA TALUKA OF KUTCH DISTRICT- A CROSS- SECTIONAL STUDY
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH PREVALENCE OF GLAUCOMA AMONG FISHERMEN COMMUNITY OF MUNDRA TALUKA OF KUTCH DISTRICT- A CROSS- SECTIONAL STUDY Sanjay Upadhyay 1, Jayantilal Shah 2 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH PREVALENCE OF GLAUCOMA AMONG FISHERMEN COMMUNITY OF MUNDRA TALUKA OF KUTCH DISTRICT- A CROSS- SECTIONAL STUDY Sanjay Upadhyay 1, Jayantilal Shah 2 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor,
LARGE DISCS WITH LARGE CUPS A DIAGNOSTIC CHALLENGE IN AFRICAN PATIENTS. Darshana Soma
 LARGE DISCS WITH LARGE CUPS A DIAGNOSTIC CHALLENGE IN AFRICAN PATIENTS Darshana Soma A research report submitted to the Faculty of Health Sciences, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, in partial
LARGE DISCS WITH LARGE CUPS A DIAGNOSTIC CHALLENGE IN AFRICAN PATIENTS Darshana Soma A research report submitted to the Faculty of Health Sciences, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, in partial
Targeting Intraocular Pressure in Glaucoma: a Teaching Case Report 1
 Targeting Intraocular Pressure in Glaucoma: a Teaching Case Report 1 By: Andrew Kemp, OD, Marcus Gonzales, OD, FAAO, Joe DeLoach, OD, FAAO, and Zanna Kruoch, OD FAAO Background Glaucoma is a range of conditions
Targeting Intraocular Pressure in Glaucoma: a Teaching Case Report 1 By: Andrew Kemp, OD, Marcus Gonzales, OD, FAAO, Joe DeLoach, OD, FAAO, and Zanna Kruoch, OD FAAO Background Glaucoma is a range of conditions
The Effect of Phacoemulsification with Posterior Chamber Intraocular Lens Implantation on Intraocular Pressure and Anterior Chamber Depth
 The Effect of Phacoemulsification with Posterior Chamber Intraocular Lens Implantation on Intraocular Pressure and Anterior Chamber Depth Mohammad Javad Mohamadi, MD 1 Reza Soltani Moghadam, MD 1 Hasan
The Effect of Phacoemulsification with Posterior Chamber Intraocular Lens Implantation on Intraocular Pressure and Anterior Chamber Depth Mohammad Javad Mohamadi, MD 1 Reza Soltani Moghadam, MD 1 Hasan
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) Anterior Segment of the Eye File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: optical_coherence_tomography_(oct)_anterior_segment_of_the_eye
Corporate Medical Policy Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) Anterior Segment of the Eye File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: optical_coherence_tomography_(oct)_anterior_segment_of_the_eye
Introduction. Hemma Resch, Gabor Deak, Ivania Pereira and Clemens Vass. e225. Acta Ophthalmologica 2012
 Comparison of optic disc parameters using spectral domain cirrus high-definition optical coherence tomography and confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscopy in normal eyes Hemma Resch, Gabor Deak, Ivania Pereira
Comparison of optic disc parameters using spectral domain cirrus high-definition optical coherence tomography and confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscopy in normal eyes Hemma Resch, Gabor Deak, Ivania Pereira
