encouraged to use the Version of Record that, when published, will replace this version. The most /BSR BIOSCIENCE REPORTS
|
|
|
- Annis Henderson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bioscience Reports: this is an Accepted Manuscript, not the final Version of Record. You are encouraged to use the Version of Record that, when published, will replace this version. The most up-to-date version is available at Please cite using the DOI /BSR BIOSCIENCE REPORTS ACCEPTED MANUSCRIPT ACCEPTED MANUSCRIPT Cite as Bioscience Reports (2016) DOI: /BSR Copyright 2016 The Author(s). This is an Accepted Manuscript; not the final Version of Record. You are encouraged to use the final Version of Record that, when published, will replace this manuscript and be freely available under a Creative Commons licence. All other rights reserved. Use of open access articles is permitted based on the terms of the specific Creative Commons Licence under which the article is published. Archiving of non-open access articles is permitted in accordance with the Archiving Policy of Portland Press (
2 MicroRNA 486-3P as a stability marker in acute coronary syndrome Tianling Wei 1 *, Lasse Folkersen 2 *, Ewa Ehrenborg 3, and Anders Gabrielsen 4 *These authors contributed equally to this article. Affiliations 1 Department of Dermatology, Bispebjerg Hospital, Bispebjerg, Denmark 2 Department of Systems Biology, Technical University of Denmark, Lyngby, Denmark 3 Atherosclerosis Research Unit, Department of Medicine, Center for Molecular Medicine, Karolinska University Hospital 4 Department of Cardiology, Karolinska University Hospital, Stockholm, Sweden Summary statement A total of 75 cardiovascular patients were investigated for levels of the circulating micro-rna 486-3P. The objective was to find out if any micro-rna could distinguish patients with unstable plaque from patients with stable plaque after acute coronary syndrome. Corresponding author Tianling Wei, weitianling@gmail.com Short title MicroRNA 486-3P and acute coronary syndrome Keywords Micro-RNA, Coronary Artery Disease, Diagnosis biomarker
3 Abstract Easily accessible biomarkers are needed to diagnose cardiovascular disease precisely particularly, to distinguish between disease subtypes that are encountered in clinical practice. Per the hypothesis that plasma mirna is valuable for this purpose, we performed complete transcriptional profiling of an mirna discovery-set in 14 samples: three patients with STelevanted acute myocardial infarction (STEMI) at baseline and after three months of follow-up, four with stable ischemic heart disease (stable-ihd), and four healthy age-matched volunteers. Our aim was to determine whether we could distinguish patients with unstable plaques from stable patients following a STEMI event. After analyzing mirna profiles, we conducted a validation study comparing three-month STEMI (n = 40) with stable-ihd (n = 35), which confirmed that mir-486-3p differentiates patients with 3-month STEMI from those with stable IHD (P=0.019). Introduction Troponin (ctn) measurements are commonly used by clinicians to diagnose patients. ctn is generally accepted as the most reliable biomarker for the diagnosis of acute coronary syndromes. Despite its usefulness in the acute setting ctn cannot distinguish between patients with stable coronary artey disease and patients at risk for coronary atherothrombosis in the general population (1). Because treatment and prognosis differ significantly in these populations with coronary artery disease, it would be of interest to have a biomarker which could potentially separate patients at risk for atherothrombosis from patients with stable coronary artery disease. In an attempt to further develop diagnosis and risk-stratification in patients with coronary artery disease, several novel biomarkers have been examined, typically in combination with ctn (1). One notable class of biomarkers is micrornas (mirnas), which are ~22-nt noncoding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. In the human genome, mirnas constitute 1% to 5% of all genes, making them the most abundant class of regulators. Although the function of most mirnas is unknown, they have been shown to mediate various pathological conditions, including cardiovascular disease, and the levels of several mirnas are altered in the heart in response to pathological stress. mirna have properties that render them attractive biomarkers. They are remarkably stable in blood and can be specifically measured easily, which is typical of nucleotide-based markers (2). These features have led to many mirna biomarker candidates being reported (3), as reviewed in (4). mirna markers that have continued on to validation studies have garnered significant interest, such as mir-499, which has been shown to be an effective biomarker of acute myocardial infaction in a Chinese population (5). In our study, we aimed to identify mirna markers that could distinguish patients stabilized following an acute coronary syndrome from patients with stable coronary artery disease. To this end, we measured the global expression of circulating mirnas and assessed their diagnostic value as sensitive biomarkers of plaque stability in patients during the onset of and recovery from STEMI, i.e. atherothrombosis, patients who were undergoing elective percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), i.e. stable ischemic heart disease (stable IHD), and healthy individuals. We focused primarily on patients at baseline and at 3-month follow-up after STEMI, as this timepoint reflects a time where the acute atherothrombosis, myocardial
4 injury and inflammatory response has passed but where the risk of renewed atherothromobotic events are elevated compared to patients with stable coronary artery disease. If, in the future, mirnas demonstrate the ability to further risk-stratify and provide prognostic information they may become important clinical instruments. Materials and methods Patient populations For the global circulating mirna array, we recruited three STEMI patients 24 hours to 48 hours after admission to the hospital (STEMI-0) and 3 months after discharge (STEMI-3). Four patients with stable coronary artery disease undergoing elective PCI (stable-ihd) and four healthy individuals were added as controls. For validation, a new cohort of 40 patients at 3 months after hospital discharge (STEMI-3) and 35 patients undergoing elective PCI (stable- IHD) were included. All patients provided written informed consent. The study was approved by the Stockholm Regional Ethics Committee and conducted per the Declaration of Helsinki. Plasma sampling and RNA isolation Blood samples were collected in EDTA-K2 tubes and processed by 2-step centrifugation (4 C at 820 g for 10 min and 4 C at 16,000 g for 10 min). The supernatant was then transferred to RNase/Dnase-free tubes and stored at -80 C. Total RNA was extracted from plasma using the CIAzol mirneasy kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) with some modifications. Briefly, 200 ul of plasma was thawed on ice and lysed in 1 ml QIAzol lysis reagent. Samples in QIAzol were incubated at room temperature for 5 min to promote dissociation of nucleoprotein complexes. To adjust for variations in RNA extraction and copurification of inhibitors, 5 ul 5 nm of synthetic Caenorhabditis elegans mirnas, cel-mir- 39 miscript mirna Mimic (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), was added to each sample. The remainder of the extraction was performed per the manufacturer s instructions. Each sample was eluted in 20 L RNAse-free water and stored at -70 C. Low-density microrna array mirnas were reverse-transcribed using the TaqMan mirna reverse-transcription kit with TaqMan mirna Multiplex RT assays (human pool; Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, U.S.A.). The RT products were preamplified using the Taqman PreAmp kit (Applied Biosystems), the products of which were diluted in 0.1X TE (Tris/ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid) buffer and subsequently used as a template for mirna expression profiling on TaqMan MicroRNA Low- Density Arrays (TLDAs) (Applied Biosystems). For the initial screen, Human TaqMan mirna microarrays (CardAv2.1 and CardB v2.1, Applied Biosystems), covering 758 small, noncoding RNAs, were run on an ABI7900 HT with the TLDA upgrade. Raw data were analyzed with SDS Relative Quantification, version 2.4.1, provided by Applied Biosystems. All measurements with Ct values > 35 or with a flag for issues according to the software were omitted (leaving 248, as plotted in supplementary S2). This threshold and quality filtering on low expression (Ct values > 35) left 201 mirnas. Finally mirnas where only one sample in a group had a measurement passing quality control were omitted, leaving a final of mirnas available for analysis. For ddct normalization, the Ct of cel-mir-39 was subtracted from that of the target, which was subtracted from the median of the calibrator (Healthy individuals) and linearized to obtain 2^ddCt values (6). For the alternative dct normalization, the same procedure was followed, except for the subtraction of cel-mir-39. Plots of normalization values are shown in Supplementary Figure S1. Supplementary figures are available at
5 Real-time PCR validation Specific mirnas by TaqMan Real-Time PCR were quantified per the manufacturer (Applied Biosystems). Target gene expression was normalized as described for the low-density arrays. Statistics All P-values were calculated by two-sided student s t-test, assuming nonequal variance. In the validation step, outlier measurements outside of the 90% confidence interval were omitted from analysis to ensure normal distribution of the data. The validation measurements were distributed normally by Shapiro-Wilk test (P>0.05). P-values were uncorrected for multiple testing. The multiple testing burden of the discovery cohort was 201 tests, but independent samples were used in the validation cohort to avoid false discovery issues. For testing of covariates the following commonly used measures were investigated: sex, age, cholesterol, triglycerides, smoking, leukocytes, eosinophils, neutrophils, DES, erythrocyte volume fraction, hemoglobin, thrombocytes, monocytes, statins, beta-blockers, waran, diuretics, NSAID, ASA, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, pulse, prior heart infarction, prior angina, ejection fraction, weight, hip circumference, height, and infection status. The association between mir-486-3p and validation sample group was re-calculated using each of these as a covariate in a linear regression model according the formula: mirna ~ group + covariate. The linear regression model was used as implemented in the lm function in R version Results mirna profiles in serum of patients and healthy volunteers Complete mirna profiling was performed in 14 serum samples from patients with STEMI at baseline (STEMI-0) and after 3 months of follow-up (STEMI-3), patients with stable IHD, and healthy age-matched volunteers. A total of 758 mirnas were measured on a low-density array (LDA) platform. After a filtration step for poor quality and low expression, 167 mirnas remained for analysis. Three normalization methods were tested before the mirna profiles were analyzed: 1) a housekeeping gene method, using the ddct method with U6 snrna as an endogenous control; 2) a spike-in method, using the ddct method with measured values of cel-mir-39, which was spiked in before RNA purification; and 3) an mirna mass method, using a dct method in which a comparable amount of total mirna was assumed to exist in each measurement. The relative Ct values of each normalization factor are included as Supplementary Figure S1. Because the spike-in method with cel-mir-39 demonstrated the least variation, it was chosen for further analysis. Discovery of differentially expressed mirnas For each measurable mirna, we generated plots of their expression level as a function of patient group (Supplementary Figure S2). We aimed to identify biomarkers of plaque stability after acute MI, comparing global mirna expression between STEMI-3 and stable-ihd patients. The plaque status of STEMI-3 patients was considered unstable. All 167 mirna expression profiles were inspected manually, with a focus on strong differential expression between groups (S2). Extra weight was given to mirna profiles with comparable expression between healthy individuals and stable-ihd patients. Based on this analysis, mir-128a, mir-148a, and mir-486-3p (Figure 1) differentiated between patient groups. The levels of these species in STEMI-3 differed from the stable-ihd and Healthy groups at magnitudes that had a realistic chance of being reproduced in a validation experiment. Unfortunately, the recently validated baseline acute myocardial
6 infarction biomarker mir-499 (5) had to be omitted for quality control reasons and thus was not tested in this cohort. Validation of differentially expressed mirna Expression profiles were validated in the serum of 40 STEMI-3 patients and 35 patients from the stable-ihd group. mir-486-3p was significantly validated, with 1.31-fold higher expression in STEMI-3 versus stable-ihd patients (P= 0.019, Figure 2A). Further, mir-148a and mir- 128a was not significant: P=0.085 and P=0.288, respectively, which excluded both from further analysis. Based on the validation of mir-486-3p in an independent cohort, we estimated its predictive ability using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves (Figure 3). Based on the resulting thresholds, mir-486-3p correctly predicted the unstable type (STEMI-3) with 87% probability and was incorrect for 60% of patients with stable disease (stable-ihd) (Figure 2B). In the validation cohort, we examined whether the differential expression of mir-486-3p was attributed to common confounders, such as age, gender, smoking, statins, LDL levels, triglyceride levels, cell counts, blood pressure, presence of drug-eluding stents (DES) and 20 other frequently measured clinical variables. The association between mir-486-3p and sample group remained significant after inclusion of each covariate (P<0.05), except for smoking which had a slight diminishing effect on the association of mir-486-3p and sample group (P= 0.085).Thus, we conclude that the predictive value of mir-486-3p was largely independent of routine confounders, although smoking could be considered as a covariate of interest in future studies. Discussion The objective of our study was to identify mirna-based biomarkers that could distinguish patients stabilized following an acute coronary syndrome from patients with stable coronary artery disease, such as patients who are undergoing elective PCI. Biomarkers which have larger variation in concentration levels between patient groups than within patient groups are suitable for this. We were prompted by our interest in allocating clinical resources toward patients with the highest risk of future adverse events. The detection of subtle, undetected STEMI would benefit this prioritization, constituting a patent, unmet medical need. To this end, we developed a study on a discovery cohort, comprising array-based mirna-wide profiling, followed by examination of a validation cohort by follow-up measurements of specific mirnas. This design best balanced the cost of the expensive array-based method with the need for a sufficient sample size to overcome the burden of multiple testing. From the discovery cohort, we selected 3 mirnas that had a desirable profile with regard to our primary aim. These mirnas were measured in a larger independent cohort, from which the main finding of this study was derived that mir-486-3p reproducibly distinguishes patients 3 months after a STEMI from patients with stable coronary artery disease patients. Also, the effect was independent of other commonly measured clinical parameters. These properties, in addition to serum mirna being stable and easy to measure, render mir-486-3p a potential marker for use in precision medicine. Notably, Hsu et al. (7) reported that mir-486-3p is differentially expressed between STEMI patients at baseline and healthy controls, further underscoring that mir-486-3p might have clinical value in STEMI. In line with Hsu et al., we can also detect elevated plasma mir-486-3p at STEMI-0 compared to healthy controls (fig. 1). The injured myocardium could be a source for mir-486-3p. However, mir-486-3p is still detectable 3 months after suggesting that mir-486-3p has other origins outside the myocardium.
7 Although the predictive ability of mir-486-3p is at best modest, there are few predictive methods for late STEMI, and any ability to focus limited clinical resources might benefit a patient s quality of care. Similarly, much work is being performed to create multi-signature prediction profiles, and a novel biomarker from a nonstandard class has the potential to contribute additional clinical knowledge. Thus, our findings can effect more precise and datadriven clinical management.
8 Captions Figure 1: LDA-generated expression profiles of the three mirnas chosen for further validation. Figure 2: A) Validation measurements in an independent cohort of STEMI-3 (n=40) and stable-ihd patients (n=35), in which mir-486-3p is significantly higher and at 3 months after an AMI event (P= ). The Y-axis shows 2^-ddCt values B) Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of the predictive ability of mir-486-3p to distinguish STEMI-3 and stable-ihd patients. Table 1. Demographics of patients, stratified by cohort. Categorical variables are reported as percentage (count). Numerical variables are reported as mean±sd. The STEMI-3 discovery group was assumed to have unchanged variables for all values except statin treatment, cholesterol, and triglycerides, for which no information was available. P-values for the validation cohort were calculated by student s t-test for numerical variables and chi-square test for categorical variables. References 1. Aldous SJ: Cardiac biomarkers in acute myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol 164: , Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, et al: Characterization of micrornas in serum: a novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res 18: , Corsten MF, Dennert R, Jochems S, et al: Circulating MicroRNA-208b and MicroRNA-499 reflect myocardial damage in cardiovascular disease. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 3: , Creemers EE, Tijsen AJ and Pinto YM: Circulating micrornas: novel biomarkers and extracellular communicators in cardiovascular disease? Circ Res 110: , Zhang L, Chen X, Su T, et al: Circulating mir-499 are novel and sensitive biomarker of acute myocardial infarction. J Thorac Dis 7: , Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25: , Hsu A, Chen SJ, Chang YS, Chen HC and Chu PH: Systemic approach to identify serum micrornas as potential biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction. Biomed Res Int 2014: , 2014.
9 % (3) 100% (3) 100% (4) 100% (4) 76% (25) 84% (21) ±3.6 48±3.6 52±3.6 52±2.6 52±6.9 55± ± ± ± ±1 4.8± ± ± ± ±1.3 2± % (0) 0% (0) 0% (0) 0% (0) 52% (17) 20% (5) 1.80E-06 33% (1) - 75% (3) 0% (0) 21% (7) 88% (22) % (3) 100% (3) 75% (3) 0% (0) 33% (11) 84% (21) % (0) 0% (0) 0% (0) 0% (0) 0% (0) 0% (0) 0.66
10
11
Statin pretreatment and presentation patterns in patients with acute coronary syndromes
 Brief Report Page 1 of 5 Statin pretreatment and presentation patterns in patients with acute coronary syndromes Marcelo Trivi, Ruth Henquin, Juan Costabel, Diego Conde Cardiovascular Institute of Buenos
Brief Report Page 1 of 5 Statin pretreatment and presentation patterns in patients with acute coronary syndromes Marcelo Trivi, Ruth Henquin, Juan Costabel, Diego Conde Cardiovascular Institute of Buenos
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Clinical perspective It was recently discovered that small RNAs, called micrornas, circulate freely and stably in human plasma. This finding has sparked interest in the potential
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Clinical perspective It was recently discovered that small RNAs, called micrornas, circulate freely and stably in human plasma. This finding has sparked interest in the potential
Circulating mir-499 are novel and sensitive biomarker of acute myocardial infarction
 Original Article Circulating mir-499 are novel and sensitive biomarker of acute myocardial infarction Lizhu Zhang 1 *, Xi Chen 1 *, Tong Su 1, Heng Li 1, Qiang Huang 1, Dan Wu 1, Chengjian Yang 1, Zhijun
Original Article Circulating mir-499 are novel and sensitive biomarker of acute myocardial infarction Lizhu Zhang 1 *, Xi Chen 1 *, Tong Su 1, Heng Li 1, Qiang Huang 1, Dan Wu 1, Chengjian Yang 1, Zhijun
Taylor Yohe. Project Advisor: Dr. Martha A. Belury. Department of Human Nutrition at the Ohio State University
 Atherosclerosis Development and the Inflammatory Response of Hepatocytes to Sesame Oil Supplementation Taylor Yohe Project Advisor: Dr. Martha A. Belury Department of Human Nutrition at the Ohio State
Atherosclerosis Development and the Inflammatory Response of Hepatocytes to Sesame Oil Supplementation Taylor Yohe Project Advisor: Dr. Martha A. Belury Department of Human Nutrition at the Ohio State
Extracellular Vesicle RNA isolation Kits
 Extracellular Vesicle RNA isolation Kits Summary Section 4 Introduction 42 Exo-TotalRNA and TumorExo-TotalRNA isolation kits 43 Extracellular Vesicle RNA extraction kits Ordering information Products can
Extracellular Vesicle RNA isolation Kits Summary Section 4 Introduction 42 Exo-TotalRNA and TumorExo-TotalRNA isolation kits 43 Extracellular Vesicle RNA extraction kits Ordering information Products can
APPENDIX F: CASE REPORT FORM
 APPENDIX F: CASE REPORT FORM Instruction: Complete this form to notify all ACS admissions at your centre to National Cardiovascular Disease Registry. Where check boxes are provided, check ( ) one or more
APPENDIX F: CASE REPORT FORM Instruction: Complete this form to notify all ACS admissions at your centre to National Cardiovascular Disease Registry. Where check boxes are provided, check ( ) one or more
Coronary Catheterization and Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in China 10-Year Results From the China PEACE-Retrospective CathPCI Study
 Coronary Catheterization and Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in China 10-Year Results From the China PEACE-Retrospective CathPCI Study Xin Zheng, MD, PhD; Jeptha P. Curtis, MD; Shuang Hu, PhD; YongfeiWang,
Coronary Catheterization and Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in China 10-Year Results From the China PEACE-Retrospective CathPCI Study Xin Zheng, MD, PhD; Jeptha P. Curtis, MD; Shuang Hu, PhD; YongfeiWang,
National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2009 Formula Grant
 National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2009 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2011 June 30, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The National Surgical
National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2009 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2011 June 30, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The National Surgical
A two-microrna signature in urinary exosomes for diagnosis of prostate cancer
 Poster # B4 A two-microrna signature in urinary exosomes for diagnosis of prostate cancer Anne Karin Ildor Rasmussen 1, Peter Mouritzen 1, Karina Dalsgaard Sørensen 3, Thorarinn Blondal 1, Jörg Krummheuer
Poster # B4 A two-microrna signature in urinary exosomes for diagnosis of prostate cancer Anne Karin Ildor Rasmussen 1, Peter Mouritzen 1, Karina Dalsgaard Sørensen 3, Thorarinn Blondal 1, Jörg Krummheuer
microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions. In brief, 10ng of
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Quantitative RT-PCR Quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed using the Universal mircury LNA TM microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Quantitative RT-PCR Quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed using the Universal mircury LNA TM microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions.
Supplementary webappendix
 Supplementary webappendix This webappendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Kratz JR, He J, Van Den Eeden SK, et
Supplementary webappendix This webappendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Kratz JR, He J, Van Den Eeden SK, et
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Nikolova AP, Hitzeman TC, Baum R, et al. Association of a novel diagnostic biomarker, the plasma cardiac bridging integrator 1 score, with heart failure with preserved ejection
Supplementary Online Content Nikolova AP, Hitzeman TC, Baum R, et al. Association of a novel diagnostic biomarker, the plasma cardiac bridging integrator 1 score, with heart failure with preserved ejection
Serum mirna expression profile as a prognostic biomarker of stage II/III
 Serum mirna expression profile as a prognostic biomarker of stage II/III colorectal adenocarcinoma Jialu Li a,b,, Yang Liu c,, Cheng Wang d,, Ting Deng a,, Hongwei Liang b, Yifei Wang e, Dingzhi Huang
Serum mirna expression profile as a prognostic biomarker of stage II/III colorectal adenocarcinoma Jialu Li a,b,, Yang Liu c,, Cheng Wang d,, Ting Deng a,, Hongwei Liang b, Yifei Wang e, Dingzhi Huang
Relationship between body mass index, coronary disease extension and clinical outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndrome
 Relationship between body mass index, coronary disease extension and clinical outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndrome Helder Dores, Luís Bronze Carvalho, Ingrid Rosário, Sílvio Leal, Maria João
Relationship between body mass index, coronary disease extension and clinical outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndrome Helder Dores, Luís Bronze Carvalho, Ingrid Rosário, Sílvio Leal, Maria João
GALECTIN-3 PREDICTS LONG TERM CARDIOVASCULAR DEATH IN HIGH-RISK CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE PATIENTS
 GALECTIN-3 PREDICTS LONG TERM CARDIOVASCULAR DEATH IN HIGH-RISK CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE PATIENTS Table of Contents List of authors pag 2 Supplemental figure I pag 3 Supplemental figure II pag 4 Supplemental
GALECTIN-3 PREDICTS LONG TERM CARDIOVASCULAR DEATH IN HIGH-RISK CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE PATIENTS Table of Contents List of authors pag 2 Supplemental figure I pag 3 Supplemental figure II pag 4 Supplemental
Assaying micrornas in biofluids for detection of drug induced cardiac injury. HESI Annual Meeting State of the Science Session June 8, 2011
 Assaying micrornas in biofluids for detection of drug induced cardiac injury HESI Annual Meeting State of the Science Session June 8, 2011 Karol Thompson, PhD Center for Drug Evaluation & Research US Food
Assaying micrornas in biofluids for detection of drug induced cardiac injury HESI Annual Meeting State of the Science Session June 8, 2011 Karol Thompson, PhD Center for Drug Evaluation & Research US Food
microrna-based diagnostics and therapy in cardiovascular disease Summing up the facts
 Review Article microrna-based diagnostics and therapy in cardiovascular disease Summing up the facts Christian Schulte 1, Tanja Zeller 1,2 1 Department of General and Interventional Cardiology, University
Review Article microrna-based diagnostics and therapy in cardiovascular disease Summing up the facts Christian Schulte 1, Tanja Zeller 1,2 1 Department of General and Interventional Cardiology, University
10-Year Mortality of Older Acute Myocardial Infarction Patients Treated in U.S. Community Practice
 10-Year Mortality of Older Acute Myocardial Infarction Patients Treated in U.S. Community Practice Ajar Kochar, MD on behalf of: Anita Y. Chen, Puza P. Sharma, Neha J. Pagidipati, Gregg C. Fonarow, Patricia
10-Year Mortality of Older Acute Myocardial Infarction Patients Treated in U.S. Community Practice Ajar Kochar, MD on behalf of: Anita Y. Chen, Puza P. Sharma, Neha J. Pagidipati, Gregg C. Fonarow, Patricia
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies
 Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
Undetectable High Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin T Level in the Emergency Department and Risk of Myocardial Infarction
 Undetectable High Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin T Level in the Emergency Department and Risk of Myocardial Infarction Nadia Bandstein, MD; Rickard Ljung, MD, PhD; Magnus Johansson, MD, PhD; Martin Holzmann,
Undetectable High Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin T Level in the Emergency Department and Risk of Myocardial Infarction Nadia Bandstein, MD; Rickard Ljung, MD, PhD; Magnus Johansson, MD, PhD; Martin Holzmann,
Beta-blockers in Patients with Mid-range Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction after AMI Improved Clinical Outcomes
 Beta-blockers in Patients with Mid-range Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction after AMI Improved Clinical Outcomes Seung-Jae Joo and other KAMIR-NIH investigators Department of Cardiology, Jeju National
Beta-blockers in Patients with Mid-range Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction after AMI Improved Clinical Outcomes Seung-Jae Joo and other KAMIR-NIH investigators Department of Cardiology, Jeju National
Single Cell Quantitative Polymer Chain Reaction (sc-qpcr)
 Single Cell Quantitative Polymer Chain Reaction (sc-qpcr) Analyzing gene expression profiles from a bulk population of cells provides an average profile which may obscure important biological differences
Single Cell Quantitative Polymer Chain Reaction (sc-qpcr) Analyzing gene expression profiles from a bulk population of cells provides an average profile which may obscure important biological differences
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Bucholz EM, Butala NM, Ma S, Normand S-LT, Krumholz HM. Life
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Bucholz EM, Butala NM, Ma S, Normand S-LT, Krumholz HM. Life
For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Kylt Rotavirus A. Real-Time RT-PCR Detection.
 For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection www.kylt.eu DIRECTION FOR USE Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection A. General Kylt Rotavirus A products are
For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection www.kylt.eu DIRECTION FOR USE Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection A. General Kylt Rotavirus A products are
microrna analysis for the detection of autologous blood transfusion in doping control
 microrna analysis for the detection of autologous blood transfusion in doping control Application note Doping Control Authors Francesco Donati*, Fiorella Boccia, Xavier de la Torre, Alessandra Stampella,
microrna analysis for the detection of autologous blood transfusion in doping control Application note Doping Control Authors Francesco Donati*, Fiorella Boccia, Xavier de la Torre, Alessandra Stampella,
Circulating Microrna Expression As A Biomarker For Early Diagnosis Of Severity In Spinal Cord Injury
 Circulating Microrna Expression As A Biomarker For Early Diagnosis Of Severity In Spinal Cord Injury Susumu Hachisuka 1, Naosuke Kamei, MD, PhD 2, Satoshi Ujigo 3, Shigeru Miyaki 3, Mitsuo Ochi 3. 1 Hiroshima
Circulating Microrna Expression As A Biomarker For Early Diagnosis Of Severity In Spinal Cord Injury Susumu Hachisuka 1, Naosuke Kamei, MD, PhD 2, Satoshi Ujigo 3, Shigeru Miyaki 3, Mitsuo Ochi 3. 1 Hiroshima
Acute coronary syndrome. Dr LM Murray Chemical Pathology Block SA
 Acute coronary syndrome Dr LM Murray Chemical Pathology Block SA13-2014 Acute myocardial infarction (MI) MI is still the leading cause of death in many countries It is characterized by severe chest pain,
Acute coronary syndrome Dr LM Murray Chemical Pathology Block SA13-2014 Acute myocardial infarction (MI) MI is still the leading cause of death in many countries It is characterized by severe chest pain,
ACCESS hstni SCIENTIFIC LITERATURE
 ACCESS hstni SCIENTIFIC LITERATURE 2017 2018 Table of contents Performance Evaluation of Access hstni A critical evaluation of the Beckman Coulter Access hstni: Analytical performance, reference interval
ACCESS hstni SCIENTIFIC LITERATURE 2017 2018 Table of contents Performance Evaluation of Access hstni A critical evaluation of the Beckman Coulter Access hstni: Analytical performance, reference interval
egfr > 50 (n = 13,916)
 Saxagliptin and Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Moderate or Severe Renal Impairment: Observations from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 Trial Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics according
Saxagliptin and Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Moderate or Severe Renal Impairment: Observations from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 Trial Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics according
The Changing Epidemiology of Acute Coronary Syndromes: Implications for practice: Dr. Sonia Anand, McMaster University
 The Changing Epidemiology of Acute Coronary Syndromes: Implications for practice: Dr. Sonia Anand, McMaster University Expert Opinions CCS Vancouver, BC October 23, 2011 Overview of ACS Epidemiology: Global
The Changing Epidemiology of Acute Coronary Syndromes: Implications for practice: Dr. Sonia Anand, McMaster University Expert Opinions CCS Vancouver, BC October 23, 2011 Overview of ACS Epidemiology: Global
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplemental Methods. Duke CAD Index
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Methods Duke CAD Index The Duke CAD index, originally developed by David F. Kong, is an angiographic score that hierarchically assigns prognostic weights (0-100) based
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Methods Duke CAD Index The Duke CAD index, originally developed by David F. Kong, is an angiographic score that hierarchically assigns prognostic weights (0-100) based
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Weintraub WS, Grau-Sepulveda MV, Weiss JM, et al. Comparative
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Weintraub WS, Grau-Sepulveda MV, Weiss JM, et al. Comparative
EXO-DNA Circulating and EV-associated DNA extraction kit
 Datasheet EXO-DNA Circulating and EV-associated DNA extraction kit This product is for research use only. It is highly recommended to read this users guide in its entirety prior to using this product.
Datasheet EXO-DNA Circulating and EV-associated DNA extraction kit This product is for research use only. It is highly recommended to read this users guide in its entirety prior to using this product.
Supplementary Figure 1:
 Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
RayBio Acid Phosphatase Activity Colorimetric Assay. Kit. User Manual Version 1.0 May 5, RayBiotech, Inc. Kit Protocol. (Cat#: 68CL-AcPh-S500)
 RayBio Acid Phosphatase Activity Colorimetric Assay Kit User Manual Version 1.0 May 5, 2014 RayBio Acid Phosphatase Activity Colorimetric Assay (Cat#: 68CL-AcPh-S500) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With
RayBio Acid Phosphatase Activity Colorimetric Assay Kit User Manual Version 1.0 May 5, 2014 RayBio Acid Phosphatase Activity Colorimetric Assay (Cat#: 68CL-AcPh-S500) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With
Improved control for confounding using propensity scores and instrumental variables?
 Improved control for confounding using propensity scores and instrumental variables? Dr. Olaf H.Klungel Dept. of Pharmacoepidemiology & Clinical Pharmacology, Utrecht Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences
Improved control for confounding using propensity scores and instrumental variables? Dr. Olaf H.Klungel Dept. of Pharmacoepidemiology & Clinical Pharmacology, Utrecht Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
CVD risk assessment using risk scores in primary and secondary prevention
 CVD risk assessment using risk scores in primary and secondary prevention Raul D. Santos MD, PhD Heart Institute-InCor University of Sao Paulo Brazil Disclosure Honoraria for consulting and speaker activities
CVD risk assessment using risk scores in primary and secondary prevention Raul D. Santos MD, PhD Heart Institute-InCor University of Sao Paulo Brazil Disclosure Honoraria for consulting and speaker activities
Acute Coronary Syndrome. Sonny Achtchi, DO
 Acute Coronary Syndrome Sonny Achtchi, DO Objectives Understand evidence based and practice based treatments for stabilization and initial management of ACS Become familiar with ACS risk stratification
Acute Coronary Syndrome Sonny Achtchi, DO Objectives Understand evidence based and practice based treatments for stabilization and initial management of ACS Become familiar with ACS risk stratification
Exercise treadmill testing is frequently used in clinical practice to
 Preventive Cardiology FEATURE Case Report 55 Commentary 59 Exercise capacity on treadmill predicts future cardiac events Pamela N. Peterson, MD, MSPH 1-3 David J. Magid, MD, MPH 3 P. Michael Ho, MD, PhD
Preventive Cardiology FEATURE Case Report 55 Commentary 59 Exercise capacity on treadmill predicts future cardiac events Pamela N. Peterson, MD, MSPH 1-3 David J. Magid, MD, MPH 3 P. Michael Ho, MD, PhD
John J.P. Kastelein MD PhD Professor of Medicine Dept. of Vascular Medicine Academic Medial Center / University of Amsterdam
 Latest Insights from the JUPITER Study John J.P. Kastelein MD PhD Professor of Medicine Dept. of Vascular Medicine Academic Medial Center / University of Amsterdam Inflammation, hscrp, and Vascular Prevention
Latest Insights from the JUPITER Study John J.P. Kastelein MD PhD Professor of Medicine Dept. of Vascular Medicine Academic Medial Center / University of Amsterdam Inflammation, hscrp, and Vascular Prevention
HIV-1 Viral Load Real Time (RG)
 -1 Viral Load Real Time (RG) Real Time RT-PCR type 1 RNA quantification assay MSP Reg. pending Valdense 3616. 11700. Montevideo. Uruguay. phone (598) 2 336 83 01. Fax (598) 2 336 71 60. Info@atgen.com.uy
-1 Viral Load Real Time (RG) Real Time RT-PCR type 1 RNA quantification assay MSP Reg. pending Valdense 3616. 11700. Montevideo. Uruguay. phone (598) 2 336 83 01. Fax (598) 2 336 71 60. Info@atgen.com.uy
Diagnostics consultation document
 National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Diagnostics consultation document Myocardial infarction (acute): Early rule out using high-sensitivity troponin tests (Elecsys Troponin T high-sensitive,
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Diagnostics consultation document Myocardial infarction (acute): Early rule out using high-sensitivity troponin tests (Elecsys Troponin T high-sensitive,
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/21543 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Dharma, Surya Title: Perspectives in the treatment of cardiovascular disease :
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/21543 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Dharma, Surya Title: Perspectives in the treatment of cardiovascular disease :
Quality Payment Program: Cardiology Specialty Measure Set
 Quality Payment Program: Cardiology Specialty Set Title Number CMS Reporting Method(s) Heart Failure (HF): Angiotensin- Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitor or Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (ARB) Therapy for
Quality Payment Program: Cardiology Specialty Set Title Number CMS Reporting Method(s) Heart Failure (HF): Angiotensin- Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitor or Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (ARB) Therapy for
Human Rotavirus B. Non structural protein 5 (NSP5) 150 tests. Quantification of Human Rotavirus B genomes Advanced kit handbook HB10.01.
 PCR Max Ltd TM qpcr test Human Rotavirus B Non structural protein 5 (NSP5) 150 tests For general laboratory and research use only 1 Introduction to Human Rotavirus B Rotavirus is a genus of double-stranded
PCR Max Ltd TM qpcr test Human Rotavirus B Non structural protein 5 (NSP5) 150 tests For general laboratory and research use only 1 Introduction to Human Rotavirus B Rotavirus is a genus of double-stranded
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Valle JA, Tamez H, Abbott JD, et al. Contemporary use and trends in unprotected left main coronary artery percutaneous coronary intervention in the United States: an analysis
Supplementary Online Content Valle JA, Tamez H, Abbott JD, et al. Contemporary use and trends in unprotected left main coronary artery percutaneous coronary intervention in the United States: an analysis
Value of cardiac rehabilitation Prof. Dr. L Vanhees
 Session: At the interface of hypertension and coronary heart disease haemodynamics, heart and hypertension Value of cardiac rehabilitation Prof. Dr. L Vanhees ESC Stockholm August 2010 Introduction There
Session: At the interface of hypertension and coronary heart disease haemodynamics, heart and hypertension Value of cardiac rehabilitation Prof. Dr. L Vanhees ESC Stockholm August 2010 Introduction There
Supplementary Note Details of the patient populations studied Strengths and weakness of the study
 Supplementary Note Details of the patient populations studied TVD and NCA patients. Patients were recruited to the TVD (triple vessel disease) group who had significant coronary artery disease (defined
Supplementary Note Details of the patient populations studied TVD and NCA patients. Patients were recruited to the TVD (triple vessel disease) group who had significant coronary artery disease (defined
SCIENTIFIC STUDY REPORT
 PAGE 1 18-NOV-2016 SCIENTIFIC STUDY REPORT Study Title: Real-Life Effectiveness and Care Patterns of Diabetes Management The RECAP-DM Study 1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Introduction: Despite the well-established
PAGE 1 18-NOV-2016 SCIENTIFIC STUDY REPORT Study Title: Real-Life Effectiveness and Care Patterns of Diabetes Management The RECAP-DM Study 1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Introduction: Despite the well-established
Use of Biomarkers for Detection of Acute Myocardial Infarction
 Use of Biomarkers for Detection of Acute Myocardial Infarction Allan S. Jaffe, MD.* Consultant - Cardiology & Laboratory Medicine Professor of Medicine Chair, CCLS Division, Department of Laboratory Medicine
Use of Biomarkers for Detection of Acute Myocardial Infarction Allan S. Jaffe, MD.* Consultant - Cardiology & Laboratory Medicine Professor of Medicine Chair, CCLS Division, Department of Laboratory Medicine
ExoQuick Exosome Isolation and RNA Purification Kits
 ExoQuick Exosome Isolation and RNA Purification Kits Cat # EQ806A-1, EQ806TC-1, EQ808A-1 User Manual Storage: Please see individual components Version 2 8/14/2018 A limited-use label license covers this
ExoQuick Exosome Isolation and RNA Purification Kits Cat # EQ806A-1, EQ806TC-1, EQ808A-1 User Manual Storage: Please see individual components Version 2 8/14/2018 A limited-use label license covers this
Human Neurology 3-Plex A
 Human Neurology 3-Plex A SUMMARY AND EXPLANATION OF THE TEST The Human N3PA assay is a digital immunoassay for the quantitative determination of total Tau, Aβ42, and Aβ40 in human plasma and CSF. Determination
Human Neurology 3-Plex A SUMMARY AND EXPLANATION OF THE TEST The Human N3PA assay is a digital immunoassay for the quantitative determination of total Tau, Aβ42, and Aβ40 in human plasma and CSF. Determination
Diagnostics guidance Published: 1 October 2014 nice.org.uk/guidance/dg15
 Myocardial infarction (acute): Early rule out using high-sensitivity troponin tests (Elecsys Troponin T high-sensitive, e, ARCHITECT STAT T High Sensitive Troponin-I and AccuTnI+3 assays) Diagnostics guidance
Myocardial infarction (acute): Early rule out using high-sensitivity troponin tests (Elecsys Troponin T high-sensitive, e, ARCHITECT STAT T High Sensitive Troponin-I and AccuTnI+3 assays) Diagnostics guidance
Appendix: ACC/AHA and ESC practice guidelines
 Appendix: ACC/AHA and ESC practice guidelines Definitions for guideline recommendations and level of evidence Recommendation Class I Class IIa Class IIb Class III Level of evidence Level A Level B Level
Appendix: ACC/AHA and ESC practice guidelines Definitions for guideline recommendations and level of evidence Recommendation Class I Class IIa Class IIb Class III Level of evidence Level A Level B Level
Early discharge in selected patients after an acute coronary syndrome can it be safe?
 Early discharge in selected patients after an acute coronary syndrome can it be safe? Glória Abreu, Pedro Azevedo, Carina Arantes, Catarina Quina-Rodrigues, Sara Fonseca, Juliana Martins, Catarina Vieira,
Early discharge in selected patients after an acute coronary syndrome can it be safe? Glória Abreu, Pedro Azevedo, Carina Arantes, Catarina Quina-Rodrigues, Sara Fonseca, Juliana Martins, Catarina Vieira,
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Background. After PCI for MI, angina has important implications on quality of life and healthcare utilization
 Angina Prevalence and Management for Myocardial Infarction Patients Treated with Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: Insights from the TRANSLATE-ACS Study Alexander C. Fanaroff, Lisa A. Kaltenbach, Eric
Angina Prevalence and Management for Myocardial Infarction Patients Treated with Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: Insights from the TRANSLATE-ACS Study Alexander C. Fanaroff, Lisa A. Kaltenbach, Eric
EXO-DNAc Circulating and EV-associated DNA extraction kit
 Datasheet EXO-DNAc Circulating and EV-associated DNA extraction kit This product is for research use only. It is highly recommended to read this users guide in its entirety prior to using this product.
Datasheet EXO-DNAc Circulating and EV-associated DNA extraction kit This product is for research use only. It is highly recommended to read this users guide in its entirety prior to using this product.
Asian AMI Registry Session The 17 th Joint Meeting of Coronary Revascularization (JCR 2017) Busan, Korea Dec 8 th 2017
 Asian AMI Registry Session The 17 th Joint Meeting of Coronary Revascularization (JCR 2017) Busan, Korea Dec 8 th 2017 Trends of acute myocardial infarction in Korea from the experience of Korea Acute
Asian AMI Registry Session The 17 th Joint Meeting of Coronary Revascularization (JCR 2017) Busan, Korea Dec 8 th 2017 Trends of acute myocardial infarction in Korea from the experience of Korea Acute
Human Rotavirus A. genesig Advanced Kit. Non structural protein 5 (NSP5) 150 tests. Primerdesign Ltd. For general laboratory and research use only
 TM Primerdesign Ltd Human Rotavirus A Non structural protein 5 (NSP5) genesig Advanced Kit 150 tests For general laboratory and research use only 1 Introduction to Human Rotavirus A Rotavirus is a genus
TM Primerdesign Ltd Human Rotavirus A Non structural protein 5 (NSP5) genesig Advanced Kit 150 tests For general laboratory and research use only 1 Introduction to Human Rotavirus A Rotavirus is a genus
MolecularMD. One-Step qrt-pcr BCR-ABL Kit. Product Description and User Manual. For Quantitative RT-PCR Analysis of BCR-ABL. Contact Us.
 Contact Us If you have any questions for or comments about MolecularMD, please feel free to contact us. Email Customer Service CustomerService@MolecularMD.com Technical Support TechSupport@MolecularMD.com
Contact Us If you have any questions for or comments about MolecularMD, please feel free to contact us. Email Customer Service CustomerService@MolecularMD.com Technical Support TechSupport@MolecularMD.com
EXOSOMES & MICROVESICLES
 The Sample Preparation Experts EXOSOMES & MICROVESICLES The New Standard in Exosome Purification and RNA Isolation Best-in-Class, Pure & Simple Exosome Purification, Fractionation of Exosomal Free & Circulating
The Sample Preparation Experts EXOSOMES & MICROVESICLES The New Standard in Exosome Purification and RNA Isolation Best-in-Class, Pure & Simple Exosome Purification, Fractionation of Exosomal Free & Circulating
Program Metrics. New Unique ID. Old Unique ID. Metric Set Metric Name Description. Old Metric Name
 Program Metrics The list below includes the metrics that will be calculated by the PINNACLE Registry for the outpatient office setting. These include metrics for, Atrial Fibrillation, Hypertension and.
Program Metrics The list below includes the metrics that will be calculated by the PINNACLE Registry for the outpatient office setting. These include metrics for, Atrial Fibrillation, Hypertension and.
Impact of coronary atherosclerotic burden on clinical presentation and prognosis of patients with coronary artery disease
 Impact of coronary atherosclerotic burden on clinical presentation and prognosis of patients with coronary artery disease Gjin Ndrepepa, Tomohisa Tada, Massimiliano Fusaro, Lamin King, Martin Hadamitzky,
Impact of coronary atherosclerotic burden on clinical presentation and prognosis of patients with coronary artery disease Gjin Ndrepepa, Tomohisa Tada, Massimiliano Fusaro, Lamin King, Martin Hadamitzky,
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Solomon SD, Uno H, Lewis EF, et al. Erythropoietic response
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Solomon SD, Uno H, Lewis EF, et al. Erythropoietic response
Human Rotavirus C. genesig Advanced Kit. DNA testing. Everything... Everyone... Everywhere... Non structural protein 5 (NSP5) 150 tests
 TM Primerdesign Ltd TM Primerdesign Ltd Human Rotavirus C Non structural protein 5 (NSP5) genesig Advanced Kit 150 tests DNA testing Everything... Everyone... Everywhere... For general laboratory and research
TM Primerdesign Ltd TM Primerdesign Ltd Human Rotavirus C Non structural protein 5 (NSP5) genesig Advanced Kit 150 tests DNA testing Everything... Everyone... Everywhere... For general laboratory and research
Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) for washing the cells TE buffer (nuclease-free) ph 7.5 for use with the PrimePCR Reverse Transcription Control Assay
 Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
Patient characteristics Intervention Comparison Length of followup
 ISCHAEMIA TESTING CHAPTER TESTING FOR MYCOCARDIAL ISCHAEMIA VERSUS NOT TESTING FOR MYOCARDIAL ISCHAEMIA Ref ID: 4154 Reference Wienbergen H, Kai GA, Schiele R et al. Actual clinical practice exercise ing
ISCHAEMIA TESTING CHAPTER TESTING FOR MYCOCARDIAL ISCHAEMIA VERSUS NOT TESTING FOR MYOCARDIAL ISCHAEMIA Ref ID: 4154 Reference Wienbergen H, Kai GA, Schiele R et al. Actual clinical practice exercise ing
Abstract Background: Methods: Results: Conclusions:
 Two-Year Clinical and Angiographic Outcomes of Overlapping Sirolimusversus Paclitaxel- Eluting Stents in the Treatment of Diffuse Long Coronary Lesions Kang-Yin Chen 1,2, Seung-Woon Rha 1, Yong-Jian Li
Two-Year Clinical and Angiographic Outcomes of Overlapping Sirolimusversus Paclitaxel- Eluting Stents in the Treatment of Diffuse Long Coronary Lesions Kang-Yin Chen 1,2, Seung-Woon Rha 1, Yong-Jian Li
Standard emergency department care vs. admission to an observation unit for low-risk chest pain patients. A two-phase prospective cohort study
 Standard emergency department care vs. admission to an observation unit for low-risk chest pain patients A. STUDY PURPOSE AND RATIONALE Rationale: A two-phase prospective cohort study IRB Proposal Sara
Standard emergency department care vs. admission to an observation unit for low-risk chest pain patients A. STUDY PURPOSE AND RATIONALE Rationale: A two-phase prospective cohort study IRB Proposal Sara
Exosome DNA Extraction Kits
 Exosome DNA Extraction Kits Summary Section 5 Introduction 40 EXO-DNAc 41 EXO-DNA 43 Introduction Genomic DNA Extractiom Kits Ordering informations Products can be purchased directly in our on-line shop:
Exosome DNA Extraction Kits Summary Section 5 Introduction 40 EXO-DNAc 41 EXO-DNA 43 Introduction Genomic DNA Extractiom Kits Ordering informations Products can be purchased directly in our on-line shop:
Randomized comparison of single versus double mammary coronary artery bypass grafting: 5 year outcomes of the Arterial Revascularization Trial
 Randomized comparison of single versus double mammary coronary artery bypass grafting: 5 year outcomes of the Arterial Revascularization Trial Embargoed until 10:45 a.m. CT, Monday, Nov. 14, 2016 David
Randomized comparison of single versus double mammary coronary artery bypass grafting: 5 year outcomes of the Arterial Revascularization Trial Embargoed until 10:45 a.m. CT, Monday, Nov. 14, 2016 David
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE General practice Indicators for the NICE menu
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE General practice Indicators for the NICE menu Indicator area: Pulse rhythm assessment for AF Indicator: NM146 Date: June 2017 Introduction There is evidence
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE General practice Indicators for the NICE menu Indicator area: Pulse rhythm assessment for AF Indicator: NM146 Date: June 2017 Introduction There is evidence
Supplementary Figure 1: Experimental design. DISCOVERY PHASE VALIDATION PHASE (N = 88) (N = 20) Healthy = 20. Healthy = 6. Endometriosis = 33
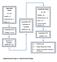 DISCOVERY PHASE (N = 20) Healthy = 6 Endometriosis = 7 EAOC = 7 Quantitative PCR (mirnas = 1113) a Quantitative PCR Verification of Candidate mirnas (N = 24) VALIDATION PHASE (N = 88) Healthy = 20 Endometriosis
DISCOVERY PHASE (N = 20) Healthy = 6 Endometriosis = 7 EAOC = 7 Quantitative PCR (mirnas = 1113) a Quantitative PCR Verification of Candidate mirnas (N = 24) VALIDATION PHASE (N = 88) Healthy = 20 Endometriosis
Online Appendix (JACC )
 Beta blockers in Heart Failure Collaborative Group Online Appendix (JACC013117-0413) Heart rate, heart rhythm and prognostic effect of beta-blockers in heart failure: individual-patient data meta-analysis
Beta blockers in Heart Failure Collaborative Group Online Appendix (JACC013117-0413) Heart rate, heart rhythm and prognostic effect of beta-blockers in heart failure: individual-patient data meta-analysis
High Sensitivity Troponin Improves Management. But Not Yet
 High Sensitivity Troponin Improves Management But Not Yet Allan S. Jaffe, MD.* Consultant - Cardiology & Laboratory Medicine Professor of Medicine Chair, CCLS Division, Department of Laboratory Medicine
High Sensitivity Troponin Improves Management But Not Yet Allan S. Jaffe, MD.* Consultant - Cardiology & Laboratory Medicine Professor of Medicine Chair, CCLS Division, Department of Laboratory Medicine
Supplementary material
 Supplementary material Validation procedures To validate the quality of the diagnostic information in the Beijing Hospital Discharge Information System (HDIS), 1069 patients with acute myocardial infarction
Supplementary material Validation procedures To validate the quality of the diagnostic information in the Beijing Hospital Discharge Information System (HDIS), 1069 patients with acute myocardial infarction
Troponin Assessment. Does it Carry Clinical Message? Stefan Blankenberg. University Heart Center Hamburg
 Biomarkers for Optimal Management of Heart Failure Troponin Assessment Does it Carry Clinical Message? Stefan Blankenberg University Heart Center Hamburg Congress of the European Society of Cardiology
Biomarkers for Optimal Management of Heart Failure Troponin Assessment Does it Carry Clinical Message? Stefan Blankenberg University Heart Center Hamburg Congress of the European Society of Cardiology
Revascularization In HFrEF: Are We Close To The Truth. Ali Almasood
 Revascularization In HFrEF: Are We Close To The Truth Ali Almasood HF epidemic 1-2% of the population have HF At least one-half have heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HF- REF) The most common
Revascularization In HFrEF: Are We Close To The Truth Ali Almasood HF epidemic 1-2% of the population have HF At least one-half have heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HF- REF) The most common
Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors
 Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors Carmine Pizzi 1 ; Lamberto Manzoli 2, Stefano Mancini 3 ; Gigliola Bedetti
Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors Carmine Pizzi 1 ; Lamberto Manzoli 2, Stefano Mancini 3 ; Gigliola Bedetti
The ESC Registry on Chronic Ischemic Coronary Disease
 EURObservational Research Programme The ESC Registry on Chronic Ischemic Coronary Disease Prof. Fausto J. Pinto, FESC, FACC, FASE, FSCAI Immediate Past-President, ESC University Hospital Sta Maria University
EURObservational Research Programme The ESC Registry on Chronic Ischemic Coronary Disease Prof. Fausto J. Pinto, FESC, FACC, FASE, FSCAI Immediate Past-President, ESC University Hospital Sta Maria University
Cardiology Department Coimbra Hospital and Medical School Portugal
 Quantitative troponin elevation provide incremental prognostic value beyond comprehensive risk stratification in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Rui Baptista, Elisabete Jorge, Hélia Martins, Fátima
Quantitative troponin elevation provide incremental prognostic value beyond comprehensive risk stratification in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Rui Baptista, Elisabete Jorge, Hélia Martins, Fátima
Long-term prognostic value of N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide (NT-proBNP) changes within one year in patients with coronary heart disease
 Long-term prognostic value of N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide (NT-proBNP) changes within one year in patients with coronary heart disease D. Dallmeier 1, D. Rothenbacher 2, W. Koenig 1, H. Brenner
Long-term prognostic value of N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide (NT-proBNP) changes within one year in patients with coronary heart disease D. Dallmeier 1, D. Rothenbacher 2, W. Koenig 1, H. Brenner
JUPITER NEJM Poll. Panel Discussion: Literature that Should Have an Impact on our Practice: The JUPITER Study
 Panel Discussion: Literature that Should Have an Impact on our Practice: The Study Kaiser COAST 11 th Annual Conference Maui, August 2009 Robert Blumberg, MD, FACC Ralph Brindis, MD, MPH, FACC Primary
Panel Discussion: Literature that Should Have an Impact on our Practice: The Study Kaiser COAST 11 th Annual Conference Maui, August 2009 Robert Blumberg, MD, FACC Ralph Brindis, MD, MPH, FACC Primary
Periprocedural Myocardial Infarction and Clinical Outcome In Bifurcation Lesion
 Periprocedural Myocardial Infarction and Clinical Outcome In Bifurcation Lesion Hyeon-Cheol Gwon Cardiac and Vascular Center Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Dr. Hyeon-Cheol
Periprocedural Myocardial Infarction and Clinical Outcome In Bifurcation Lesion Hyeon-Cheol Gwon Cardiac and Vascular Center Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Dr. Hyeon-Cheol
Disclosures. Inpatient Management of Non-ST Elevation Acute Coronary Syndromes. Edward McNulty MD, FACC. None
 Inpatient Management of Non-ST Elevation Acute Coronary Syndromes Edward McNulty MD, FACC Assistant Clinical Professor UCSF Director, SF VAMC Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory Disclosures None New Guidelines
Inpatient Management of Non-ST Elevation Acute Coronary Syndromes Edward McNulty MD, FACC Assistant Clinical Professor UCSF Director, SF VAMC Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory Disclosures None New Guidelines
Statistical analysis plan
 Statistical analysis plan Prepared and approved for the BIOMArCS 2 glucose trial by Prof. Dr. Eric Boersma Dr. Victor Umans Dr. Jan Hein Cornel Maarten de Mulder Statistical analysis plan - BIOMArCS 2
Statistical analysis plan Prepared and approved for the BIOMArCS 2 glucose trial by Prof. Dr. Eric Boersma Dr. Victor Umans Dr. Jan Hein Cornel Maarten de Mulder Statistical analysis plan - BIOMArCS 2
Product Contents. 1 Specifications 1 Product Description. 2 Buffer Preparation... 3 Protocol. 3 Ordering Information 4
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA Midiprep Kit Catalog No. R1056 Highlights 10 minute method for isolating RNA (up to 1 mg) from a wide range of cell types and tissue samples. Clean-Spin column technology allows
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA Midiprep Kit Catalog No. R1056 Highlights 10 minute method for isolating RNA (up to 1 mg) from a wide range of cell types and tissue samples. Clean-Spin column technology allows
Retro-X qrt-pcr Titration Kit User Manual
 Takara Bio USA Retro-X qrt-pcr Titration Kit User Manual Cat. No. 631453 PT3952-1 (030218) 1290 Terra Bella Avenue, Mountain View, CA 94043, USA U.S. Technical Support: techus@takarabio.com United States/Canada
Takara Bio USA Retro-X qrt-pcr Titration Kit User Manual Cat. No. 631453 PT3952-1 (030218) 1290 Terra Bella Avenue, Mountain View, CA 94043, USA U.S. Technical Support: techus@takarabio.com United States/Canada
Controversies in Cardiac Pharmacology
 Controversies in Cardiac Pharmacology Thomas D. Conley, MD FACC FSCAI Disclosures I have no relevant relationships with commercial interests to disclose. 1 Doc, do I really need to take all these medicines?
Controversies in Cardiac Pharmacology Thomas D. Conley, MD FACC FSCAI Disclosures I have no relevant relationships with commercial interests to disclose. 1 Doc, do I really need to take all these medicines?
Ejection Fraction in Heart Failure: A Redefinition. Tarek Kashour King Fahad Cardiac Center King Saud University Riyadh, KSA
 Ejection Fraction in Heart Failure: A Redefinition Tarek Kashour King Fahad Cardiac Center King Saud University Riyadh, KSA Word of caution!!! Incomplete understanding of a disease process may lead to
Ejection Fraction in Heart Failure: A Redefinition Tarek Kashour King Fahad Cardiac Center King Saud University Riyadh, KSA Word of caution!!! Incomplete understanding of a disease process may lead to
For Research Use Only Ver
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZR Viral RNA Kit Catalog Nos. R1034 & R1035 Highlights Quick, 5-minute recovery of viral RNA from plasma, serum and other samples. Omits the use of organic denaturants and proteases.
INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZR Viral RNA Kit Catalog Nos. R1034 & R1035 Highlights Quick, 5-minute recovery of viral RNA from plasma, serum and other samples. Omits the use of organic denaturants and proteases.
 Biomarkers in Acute Cardiac Disease Samir Arnaout, M.D.FESC Associate Professor of Medicine Internal Medicine i & Cardiology American University of Beirut Time course of the appearance of various markers
Biomarkers in Acute Cardiac Disease Samir Arnaout, M.D.FESC Associate Professor of Medicine Internal Medicine i & Cardiology American University of Beirut Time course of the appearance of various markers
Summary HTA. HTA-Report Summary
 Summary HTA HTA-Report Summary Prognostic value, clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of high sensitivity C-reactive protein as a marker in primary prevention of major cardiac events Schnell-Inderst
Summary HTA HTA-Report Summary Prognostic value, clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of high sensitivity C-reactive protein as a marker in primary prevention of major cardiac events Schnell-Inderst
Gender-Based and Age-Related Peculiarities of Lipid Metabolism in Chronic Heart Failure Secondary to Overweight and Obesity
 71 P.P.Bidzilya Gender-Based and Age-Related Peculiarities of Lipid Metabolism in Chronic Heart Failure Secondary to Overweight and Obesity Zaporizhzhya State Medical University, Zaporizhzhya, Ukraine
71 P.P.Bidzilya Gender-Based and Age-Related Peculiarities of Lipid Metabolism in Chronic Heart Failure Secondary to Overweight and Obesity Zaporizhzhya State Medical University, Zaporizhzhya, Ukraine
Management of Stable Ischemic Heart Disease. Vinay Madan MD February 10, 2018
 Management of Stable Ischemic Heart Disease Vinay Madan MD February 10, 2018 1 Disclosure No financial disclosure. 2 Overview of SIHD Diagnosis Outline of talk Functional vs. Anatomic assessment Management
Management of Stable Ischemic Heart Disease Vinay Madan MD February 10, 2018 1 Disclosure No financial disclosure. 2 Overview of SIHD Diagnosis Outline of talk Functional vs. Anatomic assessment Management
Physiological determinants of urine and plasma myomirnas in recreational, middle-age athletes
 Original Article Page 1 of 7 Physiological determinants of urine and plasma myomirnas in recreational, middle-age athletes Elisa Danese 1 *, Marco Benati 1 *, Fabian Sanchis-Gomar 2,3, Cantor Tarperi 4,
Original Article Page 1 of 7 Physiological determinants of urine and plasma myomirnas in recreational, middle-age athletes Elisa Danese 1 *, Marco Benati 1 *, Fabian Sanchis-Gomar 2,3, Cantor Tarperi 4,
Quality Payment Program: Cardiology Specialty Measure Set
 Measure Title * Reportable via PINNACLE α Reportable via Diabetes Collaborative CQMC v1.0 Measure High Priority Measure Cross Cutting Measure Heart Failure (HF): Angiotensin- Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitor
Measure Title * Reportable via PINNACLE α Reportable via Diabetes Collaborative CQMC v1.0 Measure High Priority Measure Cross Cutting Measure Heart Failure (HF): Angiotensin- Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitor
