Relation of interatrial duration and p wave terminal force as a novel indicator of severe
|
|
|
- April Burns
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2012; 16: Relation of interatrial duration and p wave terminal force as a novel indicator of severe mitral regurgitation M.A. ELBEY 1, M. OYLUMLU 1, A. AKIL 1, S. DEMIRTAS 2, F. ERTAS 1, E. ERDOGAN 3, A. TASAL 3, A. BACAKSIZ 3, Z. SIMSEK 4, H. KAYA 1, A. AKYUZ 1 1 Department of Cardiology, Dicle University School of Medicine, Diyarbakir, Turkey 2 Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Dicle University School of Medicine, Diyarbakir, Turkey 3 Department of Cardiology, Bezmialem Vakif University School of Medicine, Istanbul, Turkey 4 Department of Cardiology, Ataturk University School of Medicine, Erzurum, Turkey Abstract. OBJECTIVES: Interatrial duration is defined as prolonged p wave on electrocardiogram. p waves with a negative terminal phase recorded in V1 enclosing an area of one small square on the electrocardiogram is significantly and strongly correlated with interatrial duration. The aim of study was to investigate whether interatrial duration with p terminal force can be used as reflection of echocardiographic severity of mitral regurgitation. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Sixty two consecutive patients with mitral regurgitation. were prospectively studied. Age/gender matched 57 subjects who had normal mitral structure and did not have mitral regurgitation. Patients with mitral regurgitation referred to a single cardiac center for echocardiography and who met the entry criteria documented moderate or severe mitral regurgitation with sinus were included. The interatrial duration was defined on the routine 12-lead electrocardiogram (50 mm/s, 10 mm/mv) using the greatest duration of p waves from D2, D3, AVF and V1. RESULTS: There was a positive correlation between interatrial duration ( 110 ms) and effective regurgitant orifice (r = 0.3, p < 0.001). However, left atrial diameter and brain natriuretic peptide were significantly higher in cases with mitral regurgitation. There was also strong correlation between interatrial duration ( 110 ms) and p terminal force and left atrial diameter. ROC analysis revealed that interatrial duration of > 110 msec. could predict of severe mitral regurgitation with 88% sensitivity and 100% specificity. CONCLUSIONS: Severe mitral regurgitation, left atrial diameter was correlated with p terminal force and interatrial duration. Significant interatrial duration ( 110 ms) and p terminal force might be considered as novel indicators of severe mitral regurgitation. Key Words: Mitral regurgitation, Interatrial duration, p wave terminal force, Echocardiography, Brain natriuretic peptide. Introduction Interatrial block or duration denotes excessive time for sinus impulses to conduct from the right to the left atrium 1. Interatrial duration is defined as a prolonged p wave ( 110 ms) on electrocardiogram 2. It is depicted as prolonged, often notched, p waves with distinguishable right atrium and left atrium components on the electrocardiogram 3. Currently, interatrial duration has been demonstrated to be a predictor of atrial fibrillation, an indicator of dilated and impaired left atrial function and a predictor of embolic stroke 4-6. p waves with a negative terminal phase (p terminal force) recorded in V1 enclosing an area of one small square on the electrocardiogram ( 40 ms 1 mm) is significantly and strongly correlated with interatrial duration 7. The importance of interatrial duration and p terminal force as reflection of echocardiographic severity in mitral regurgitation has not been studied extensively. The aim of this study was to investigate whether interatrial duration with p terminal force can be used as a reflection of severe mitral regurgitation. Patients and Methods All patients were asymptomatic, minimally symptomatic or mild symptomatic and the echocardiographic examination was requested on the basis of the presence of a systolic murmur. Patients with mitral regurgitation referred to a single cardiac center for echocardiography and between June 2010 and September 2011, and who met the entry criteria [documented moderate (grade 2 or 3) or severe (grade 3 or 4) mitral regurgitation with sinus rhythm] were included. A 1576 Corresponding Author: Mehmet Ali Elbey, MD; elbeymali@hotmail.com
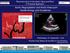
2 Interatrial duration on electrocardiography in mitral regurgitation total of 62 consecutive patients (mean age 45 ± 13 years) with mitral regurgitation were prospectively studied. Age/gender matched 57 subjects (mean age 44.,3 ± 12 years) who had normal mitral valvular structure and did not have mitral regurgitation served as controls. All patients were asymptomatic, minimally symptomatic or mild symptomatic. Echocardiographic Data Complete transthoracic echocardiography was performed in all subjects (Vivid S6, GE Vingmed Ultrasound AS, Horten, Norway) and underwent a comprehensive examination, including M-mode, two-dimensional and Doppler echocardiography. Conventional left venricular M-mode measurements included the estimation of left ventricular end-diastolic dimension, left ventricular end-systolic dimension, thickness of interventricular septum, posterior wall and left atrial dimension. Left ventricular end-systolic and end-diastolic dimensions, the left ventricular ejection fraction and left atrial dimensions were measured according to the guidelines of the American Society of Echocardiography 8. Left atrial dimension was estimated from the parasternal long-axis view. Ejection fraction was measured from the apical four-chamber view using the modified Simpson s single plane method. The degree of mitral regurgitation was identified by using mitral effective regurgitant orifice and regurgitant volume. The largest proximal isovelocity surface area radius (at the negative aliasing velocity of cm/s) was selected for analysis and effective regurgitant orifice was calculated by the simplified formula (r 2 /2). Mitral regurgitation was graded as moderate if the valve effective regurgitant orifice was 0,20-0,39 cm 2 and regurgitant volume was ml, severe mitral regurgitation if it was > 0,4 cm 2 and mitral regurgitant volume > 60 ml 9. Mitral regurgitation grade was assessed by one independent cardiologist blinded to the patient s echocardiographic results. bott Park, IL, USA) analyzer was used for brain natriuretic peptide measurement, a microparticle enzyme immunoassay that is a 2-site assay which uses a monoclonal anti- brain natriuretic peptide antibody and measures a fluorescence product. Measurement of interatrial Duration and p Terminal Force The interatrial duration was defined on the routine 12-lead electrocardiogram (filter range, 0.15 to 100 Hz; 50 mm/s, 10 mm/mv) using the greatest duration of p waves from D2, D3, AVF and V1. Because 1 mm represents 20 ms on electrocardiogram with such standardization to increase diagnostic specificity we used 110 ms as our criterion for interatrial duration diagnosis. For increased specificity, a p wave of 110 ms was used to diagnose significant interatrial duration (Figure 1). P-terminal force was defined as a biphasic p in lead V1 with an area of 1 small square on the electrocardiogram (Figure 2). Etiologies of mitral regurgitation were chronic rheumatic disease and mitral valve prolapse. Patients with any of the following were excluded: atrial fibrillation, the presence of moderate to severe mitral stenosis, the presence of moderate to severe aortic regurgitation, the presence of aortic stenosis, concomitant organic tricuspid stenosis, blood pressure > 140/90 mmhg, heart failure and ischemic cause of mitral regurgitation. All patients were in normal sinus rhythm. The electrocardiogram was analyzed by an independent Measurement of Brain Natriuretic Peptide Blood sampling was obtained for all patients immediately after enrollment in the echocardiographic laboratory. 10 ml of blood sample was drawn from a peripheral vein, immediately placed on ice and transferred to the laboratory facilities. The AxSYM (Abbott Laboratories, Ab- Figure 1. Surface electrocardiogram revealing interatrial duration in inferior leads (arrows). 1577
3 M.A. Elbey, M. Oylumlu, A. Akil, S. Demirtas, F. Ertas, E. Erdogan, A. Tasal, A. Bacaksiz, Z. Simsek, et al. Results Figure 2. Surface electrocardiogram revealing P terminal force in V1 (arrows). readers blinded to the echocardiographic findings. Correlations for interobserver variability were good. Statistical Analysis Statistical Package for Social Sciences software (SPSS 12, SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was used for analysis. Descriptive parameters were shown as mean±standard deviation or in percentages. Student t-test and Pearson s chisquare tests were used to analyze the differences in means and proportions between groups. Correlation analysis was done by Pearson test. A p value of < 0.05 was considered significant. We analyzed 62 consecutive patients with mitral regurgitation and 57 normal subjects. Twenty seven patients with mitral regurgitation had severe and 35 had moderate regurgitation, 34 of them had fibrotic mitral valve and the rest had mixomatous type valvular degeneration. In three patients there were cordal rupture in severe mitral regurgitation group and they were mild symptomatic. In these three patients interatrial duration was < 110 ms. Comparison of demographic characteristics, electrocardiographic/echocardiographic features and brain natriuretic peptide levels between groups were shown in Table I. Age, gender and heart rate were statistically similar between patients with mitral regurgitation and controls. However, mean ejection fraction, effective regurgitant orifice; regurgitant volume, left ventricular end-diastolic diameter, left atrial diameter and brain natriuretic peptide were significantly higher in cases with mitral regurgitation. Furthermore, interatrial duration and p terminal force were significantly more frequent among patients with mitral regurgitation (Table I). Echocardiographic variables of patients with mitral regurgitation according to the presence of p terminal and interatrial duration were further analyzed. Mean effective regurgitant orifice, regurgitant volume, left atrial diameter and brain natriuretic peptide were significantly higher in patients with p terminal and interatrial duration whereas mean ejection fraction was significantly lower (Table II). Comparison of patients in mitral Table I. Comparison of demographic, electrocardiogram, echocardiographic characteristics and brain natriuretic peptide levels of patients with controls. Patient (n = 62) Control (n = 57) mean ± SD mean ± SD p Age 45 ± ± 12 NS Male/Female 30/32 29/28 NS Heart rate 73 ± 9 74 ± 8 NS Left ventricular ejection fraction (%) 59 ± 4 63 ± Left ventricular end-diastolic diameter (mm) 54 ± 4 45 ± 3 < Left ventricular end-systolic diameter (mm) 38 ± 4 31 ± 3 < Interventricular septum (mm) 10.5 ± ± 1 = Posterior wall (mm) 9.4 ± ± 1.1 NS Left atrial dimension (mm) 49 ± 6 35 ± 2 < Effective regurgitant orifice (ml) 0.35 ± Regurgitant volume (ml) 53 ± 15 - Interatrial duration ( 110 ms) (n, %) 27 (43) 0 < P terminal force (n, %) 47 (75) 11 (19) < Brain natriuretic peptide (pg/ml) 61 ± ± 7 <
4 Interatrial duration on electrocardiography in mitral regurgitation Table II. Echocardiographic variables of patients with mitral regurgitation according to the presence of p terminal and interatrial duration ( 110 ms). p terminal force present p terminal force absent (n = 47) (n = 15) p value mean ± SD mean ± SD Effective regurgitant orifice (ml) 0.4 ± ± 0.1 < Regurgitant volume (ml) 58 ± ± 10 < Left atrial dimension (mm) 48 ± 7 36 ± 5 < Ejection fraction (%) 59 ± 4 63 ± 2 = Brain natriuretic peptide (pg/ml) 59 ± ± 10 < Interatrial duration Interatrial duration ( 110 ms) present ( 110 ms) absent (n = 27) (n = 35) p value Effective regurgitant orifice (ml) 0.5 ± ± 0.1 < Regurgitant volume (ml) 67 ± ± 11 < Left atrial dimension (mm) 55 ± 4 39 ± 5 < Ejection fraction (%) 57 ± 5 62 ± 3 < Brain natriuretic peptide (pg/ml) 76 ± ± 17 < regurgitation groups according to the presence of interatrial duration and p terminal force showed that most of the patients with interatrial duration and p terminal had severe mitral regurgitation (Table III). Correlation analysis revealed that there was a statistically positive correlation between interatrial duration ( 110 ms) and effective regurgitant orifice, regurgitant volume, left ventricular end-diastolic dimension, left ventricular endsystolic dimension (r = 0.3, p < 0.001; r = 0.4, p < 0.001; r = 0.3, p < 0.001; and r = 0.4, p < 0.001, respectively) and a strong negative correlation between left ventricular ejection fraction and presence of interatrial duration ( 110 ms) (r = 0.4, p < 0.001). The presence of left atrial enlargement was associated with high prevalence of significant interatrial duration (r = 0.4, p < 0.001). There was also a strong correlation between interatrial duration ( 110 ms), left atrial diameter and p terminal force (r = 0.5, p < 0.001) (Figure 3). ROC analysis revealed that a cut-off value of interatrial duration of > 110 msec. could predict of severe mitral regurgitation with 88% (95% Confidence interval; 67-96%) sensitivity and 100% specificity (95%; %); [Area under the curve = 0.98 (95% Confidence interval; ; positive predictive value = 0.100, negative predictive value = 0.90] (Figure 4). Discussion The present study questioned the utility of interatrial duration with p terminal force on electrocardiogram as an indicator of severity in chronic mitral regurgitation. This is the first study reporting that severe mitral regurgitation was associated with presence of significant p terminal force and interatrial duration. The most common causes of mitral regurgitation are mitral valve prolapse, chronic rheumatic disease or degeneration 10. Mitral valve prolapse Table III. Number of patients in mitral regurgitation groups according to the presence of interatrial duration and p terminal force. Control Moderate mitral Severe mitral (n = 57) regurgitation regurgitation (n = 35) (n = 27) Total p interatrial duration ( 110 ms) (n) < p terminal force (n) <
5 M.A. Elbey, M. Oylumlu, A. Akil, S. Demirtas, F. Ertas, E. Erdogan, A. Tasal, A. Bacaksiz, Z. Simsek, et al. p terminal force duration (msec) Figure 3. Correlation between left atrial dimension (mm) and p terminal force duration in patients with mitral regurgitation. has been described as one of the most common cardiac valvular abnormalities in industrialized countries and the clinical manifestations of mitral valve prolapse are multiple 11. In the developing countries of the world, rheumatic fever and rheumatic valve disease remain significant medical and public health problems 12. Normal P- wave duration, as classified by the World Health Organization/International Society and Federation of Cardiology Task Force 2, is <110 ms. Significant interatrial duration for increased specificity, p wave 110 ms is used to diagnose and predict atrial fibrillation, stroke and left atrial enlargement 5,6 interatrial duration is also correlated with severe mitral regurgitation, effective regurgitant orifice, regurgitant volume, left ventricular end-diastolic dimension, left ventricular end-sys- tolic dimension and increased brain natriuretic peptide levels. It has been shown that P-wave duration increases along with the progression of disease severity in mitral stenosis 13. Recently published in a study Yuce et al 14 have demonstrated associate interatrial duration and p terminal force in patients with mitral stenosis. Excessive time reflection should be termed significant interatrial duration if p wave duration is 110 ms to improve specificity. However, interatrial duration is a frequently overlooked and ignored electrocardiogram finding and a precise interpretation of the electrocardiogram is, therefore, mandatory. We recommend that attention and consideration should be given to these easily measurable waves in the determination of severity of mitral regurgitation. The presence of significant p wave terminal force and interatrial duration on surface electrocardiogram would most likely be helpful to guide the timing of echocardiography in asymptomatic patients under the age of 50 with mitral regurgitation. This would provide a potentially alternative screening tool for patients with mixomatous and chronic rheumatic diseases with cardiac murmur in young and middle age patients. But this may not meet in patients with acute cordal rupture in severe mitral regurgitation group. Conclusions This study demonstrated that significant interatrial duration ( 110 ms) and p terminal force might be considered as a novel indicator of echocardiographic severity of mitral regurgitation during follow-up. References Figure 4. ROC curve of interatrial duration in prediction of severe mitral regurgitation. 1) ARIYARAJAH V, KRANIS M, APIYASAWAT S, SPODICK DH. Potential factors that affect electrocardiographic progression of interatrial block. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol 2007; 12: ) WILLEMS JL, ROBLES DE MEDINA EO, BERNARD R, COUMEL P, FISCH C, KRIKLER D, MAZUR NA, MEIJLER FL, MOGENSEN L, MORET P. Criteria for intraventricular conduction disturbances and pre-excitation. World Health Organization/International Society and Federation of Cardiology Task Force Ad hoc. J Am Coll Cardiol 1985; 5: ) ARIYARAJAH V, APIYASAWAT S, PURI P, SPODICK DH. Specific electrocardiographic markers of P-wave morphology in interatrial block. J Electrocardiol 2006; 39:
6 Interatrial duration on electrocardiography in mitral regurgitation 4) GOYAL SB, SPODICK DH. Electromechanical dysfunction of the left atrium associated with interatrial block. Am Heart J 2001; 142: ) AGARWAL YK, ARONOW WS, LEVY JA, SPODICK DH. Association of interatrial block with development of atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol 2003; 91: ) LORBAR M, LEVRAULT R, PHADKE JG, SPODICK DH. Am J Cardiol. Interatrial block as a predictor of embolic stroke 2005; 95: ) SPODICK DH, ARIYARAJAH V, GOLDBERG R. Interatrial block: correlation with P-terminal force. Clin Cardiol 2009; 32: ) SCHILLER NB, SHAH PM, CRAWFORD M, DEMARIA A, DEV- EREUX R, FEIGENBAUM H, GUTGESELL H, REICHEK N, SAHN D, SCHNITTGER I. Recommendations for quantitation of the left ventricle by two-dimensional echocardiography: American Society of Echocardiography Committee on Standards, Subcommittee on Quantitation of Two-Dimensional Echocardiograms. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 1989; 2: ) GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH VALVULAR HEART DISEASE: A Report of the American Heart Association Task Force on Practice guidelines. Circulation 2006; 114: ) GHOREISHI M, DAWOOD M, STAUFFER CE, GAMMIE JS. Mitral regurgitation: current trends in diagnosis and management. Hosp Pract (Minneap) 2011; 39: ) DINEVSKI D, MERTIK M, KOKOL P. Diagnosing mitral valve prolapse by improving the predictive power of classifiers. J Int Med Res 2011; 39: ) OZER O, DAVUTOGLU V, SARI I, AKOYUN DC, SUCU M. The spectrum of rheumatic heart disease in the southeastern Anatolia endemic region: results from 1900 patients. J Heart Valve Dis 2009; 18: ) GUNTEKIN U, GUNES Y, TUNCER M, GUNES A, SAHIN M, SIMSEK H. Long-term follow-up of P-wave duration and dispersion in patients with mitral stenosis. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 2008; 31: ) YUCE M, DAVUTOGLU V, AKKOYUN C, KIZILKAN N, ERCAN S, AKCAY M, SARI I. Interatrial block and P-terminal force: a reflection of mitral stenosis severity on electrocardiography. J Heart Valve Dis 2011; 20:
Clinical material and methods. Departments of 1 Cardiology and 2 Anatomy, Gaziantep University, School of Medicine, Gaziantep, Turkey
 Interatrial Block and P-Terminal Force: A Reflection of Mitral Stenosis Severity on Electrocardiography Murat Yuce 1, Vedat Davutoglu 1, Cayan Akkoyun 1, Nese Kizilkan 2, Suleyman Ercan 1, Murat Akcay
Interatrial Block and P-Terminal Force: A Reflection of Mitral Stenosis Severity on Electrocardiography Murat Yuce 1, Vedat Davutoglu 1, Cayan Akkoyun 1, Nese Kizilkan 2, Suleyman Ercan 1, Murat Akcay
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY DATA REPORT FORM
 Patient ID Patient Study ID AVM - - Date of form completion / / 20 Initials of person completing the form mm dd yyyy Study period Preoperative Postoperative Operative 6-month f/u 1-year f/u 2-year f/u
Patient ID Patient Study ID AVM - - Date of form completion / / 20 Initials of person completing the form mm dd yyyy Study period Preoperative Postoperative Operative 6-month f/u 1-year f/u 2-year f/u
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING
 PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
Changes in Left Atrial Size in Patients with Lone Atrial Fibrillation
 Clin. Cardiol. 14,652-656 (1991) Changes in Left Atrial Size in Patients with Lone Atrial Fibrillation GUILLERMO SOSA SUAREZ, M.D., SIEVEN LAMPERT, M.D., F.A.C.C., SHMUEL RAVID, M.D., BERNARD LOWN, M.D.,
Clin. Cardiol. 14,652-656 (1991) Changes in Left Atrial Size in Patients with Lone Atrial Fibrillation GUILLERMO SOSA SUAREZ, M.D., SIEVEN LAMPERT, M.D., F.A.C.C., SHMUEL RAVID, M.D., BERNARD LOWN, M.D.,
Atrial dyssynchrony syndrome: An overlooked cause of heart failure with normal ejection fraction
 Atrial dyssynchrony syndrome: An overlooked cause of heart failure with normal ejection fraction JC Eicher, G Laurent, O Barthez, A Mathé, G Bertaux, JE Wolf Heart Failure Treatment Unit, Rhythmology and
Atrial dyssynchrony syndrome: An overlooked cause of heart failure with normal ejection fraction JC Eicher, G Laurent, O Barthez, A Mathé, G Bertaux, JE Wolf Heart Failure Treatment Unit, Rhythmology and
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
PISA Evaluation of Mitral Regurgitation. Raymond Graber, MD Cardiac Anesthesia Group University Hospitals Case Medical Center 4/07/2011
 PISA Evaluation of Mitral Regurgitation Raymond Graber, MD Cardiac Anesthesia Group University Hospitals Case Medical Center 4/07/2011 Introduction Evaluation of MR. What is PISA? Physiologic basis Issues
PISA Evaluation of Mitral Regurgitation Raymond Graber, MD Cardiac Anesthesia Group University Hospitals Case Medical Center 4/07/2011 Introduction Evaluation of MR. What is PISA? Physiologic basis Issues
Mitral valve regurgitation is a powerful factor of left ventricular hypertrophy
 Original article Mitral valve regurgitation is a powerful factor of left ventricular hypertrophy Ewa Szymczyk, Karina Wierzbowska Drabik, Jarosław Drożdż, Maria Krzemińska Pakuła 2nd Chair and Department
Original article Mitral valve regurgitation is a powerful factor of left ventricular hypertrophy Ewa Szymczyk, Karina Wierzbowska Drabik, Jarosław Drożdż, Maria Krzemińska Pakuła 2nd Chair and Department
Cardiac ultrasound protocols
 Cardiac ultrasound protocols IDEXX Telemedicine Consultants Two-dimensional and M-mode imaging planes Right parasternal long axis four chamber Obtained from the right side Displays the relative proportions
Cardiac ultrasound protocols IDEXX Telemedicine Consultants Two-dimensional and M-mode imaging planes Right parasternal long axis four chamber Obtained from the right side Displays the relative proportions
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS
 Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
Hemodynamic Assessment. Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics
 Hemodynamic Assessment Matt M. Umland, RDCS, FASE Aurora Medical Group Milwaukee, WI Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics Stroke Volume Cardiac Output Cardiac Index Tei Index/Index of myocardial
Hemodynamic Assessment Matt M. Umland, RDCS, FASE Aurora Medical Group Milwaukee, WI Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics Stroke Volume Cardiac Output Cardiac Index Tei Index/Index of myocardial
Aortic stenosis (AS) is common with the aging population.
 New Insights Into the Progression of Aortic Stenosis Implications for Secondary Prevention Sanjeev Palta, MD; Anita M. Pai, MD; Kanwaljit S. Gill, MD; Ramdas G. Pai, MD Background The risk factors affecting
New Insights Into the Progression of Aortic Stenosis Implications for Secondary Prevention Sanjeev Palta, MD; Anita M. Pai, MD; Kanwaljit S. Gill, MD; Ramdas G. Pai, MD Background The risk factors affecting
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW
 PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
Case # 1. Page: 8. DUKE: Adams
 Case # 1 Page: 8 1. The cardiac output in this patient is reduced because of: O a) tamponade physiology O b) restrictive physiology O c) coronary artery disease O d) left bundle branch block Page: 8 1.
Case # 1 Page: 8 1. The cardiac output in this patient is reduced because of: O a) tamponade physiology O b) restrictive physiology O c) coronary artery disease O d) left bundle branch block Page: 8 1.
HISTORY. Question: How do you interpret the patient s history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: 45-year-old man.
 HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
CASE REPORT: DOUBLE ORIFICE MITRAL VALVE WITH CLEFT IN ANTERIOR LEAFLET OF DOMINANT VALVE IN AN AFRO-CARIBBEAN
 CASE REPORT: DOUBLE ORIFICE MITL VAE WITH CLEFT IN ANTERIOR LEAFLET OF DOMINANT VAE IN AN AFRO-CARIBBEAN Disclosure: No potential conflict of interest. Received: 27.08.13 Accepted: 23.06.14 Citation: EMJ
CASE REPORT: DOUBLE ORIFICE MITL VAE WITH CLEFT IN ANTERIOR LEAFLET OF DOMINANT VAE IN AN AFRO-CARIBBEAN Disclosure: No potential conflict of interest. Received: 27.08.13 Accepted: 23.06.14 Citation: EMJ
Uncommon Doppler Echocardiographic Findings of Severe Pulmonic Insufficiency
 Uncommon Doppler Echocardiographic Findings of Severe Pulmonic Insufficiency Rahul R. Jhaveri, MD, Muhamed Saric, MD, PhD, FASE, and Itzhak Kronzon, MD, FASE, New York, New York Background: Two-dimensional
Uncommon Doppler Echocardiographic Findings of Severe Pulmonic Insufficiency Rahul R. Jhaveri, MD, Muhamed Saric, MD, PhD, FASE, and Itzhak Kronzon, MD, FASE, New York, New York Background: Two-dimensional
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus. Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE)
 Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE) Purpose: Rapid Cardiac Echocardiography (RCE) This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE) Purpose: Rapid Cardiac Echocardiography (RCE) This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum
Left atrial mechanical function and stiffness in patients with atrial septal aneurysm: A speckle tracking study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cardiology Journal 2015, Vol. 22, No. 5, 535 540 DOI: 10.5603/CJ.a2015.0033 Copyright 2015 Via Medica ISSN 1897 5593 Left atrial mechanical function and stiffness in patients with atrial
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cardiology Journal 2015, Vol. 22, No. 5, 535 540 DOI: 10.5603/CJ.a2015.0033 Copyright 2015 Via Medica ISSN 1897 5593 Left atrial mechanical function and stiffness in patients with atrial
Left atrial function. Aliakbar Arvandi MD
 In the clinic Left atrial function Abstract The left atrium (LA) is a left posterior cardiac chamber which is located adjacent to the esophagus. It is separated from the right atrium by the inter-atrial
In the clinic Left atrial function Abstract The left atrium (LA) is a left posterior cardiac chamber which is located adjacent to the esophagus. It is separated from the right atrium by the inter-atrial
ASCeXAM / ReASCE. Practice Board Exam Questions Monday Morning
 ASCeXAM / ReASCE Practice Board Exam Questions Monday Morning Ultrasound Physics Artifacts Doppler Physics Imaging, Knobology, and Artifacts Echocardiographic Evaluation of the RV Tricuspid and Pulmonary
ASCeXAM / ReASCE Practice Board Exam Questions Monday Morning Ultrasound Physics Artifacts Doppler Physics Imaging, Knobology, and Artifacts Echocardiographic Evaluation of the RV Tricuspid and Pulmonary
Aortic Regurgitation and Aortic Aneurysm - Epidemiology and Guidelines -
 Reconstruction of the Aortic Valve and Root - A Practical Approach - Aortic Regurgitation and Aortic Aneurysm Wednesday 14 th September - 9.45 Practice must always be founded on sound theory. Leonardo
Reconstruction of the Aortic Valve and Root - A Practical Approach - Aortic Regurgitation and Aortic Aneurysm Wednesday 14 th September - 9.45 Practice must always be founded on sound theory. Leonardo
THE LEFT ATRIUM HOW CAN ECHO HELP US?
 THE LEFT ATRIUM HOW CAN ECHO HELP US? Dr. Dragos COZMA BACKGROUND Left atrium (LA) dilation can occur in a broad spectrum of cardiovascular diseases including hypertension, left ventricular dysfunction,
THE LEFT ATRIUM HOW CAN ECHO HELP US? Dr. Dragos COZMA BACKGROUND Left atrium (LA) dilation can occur in a broad spectrum of cardiovascular diseases including hypertension, left ventricular dysfunction,
Myocardial performance index, Tissue Doppler echocardiography
 Value of Measuring Myocardial Performance Index by Tissue Doppler Echocardiography in Normal and Diseased Heart Tarkan TEKTEN, 1 MD, Alper O. ONBASILI, 1 MD, Ceyhun CEYHAN, 1 MD, Selim ÜNAL, 1 MD, and
Value of Measuring Myocardial Performance Index by Tissue Doppler Echocardiography in Normal and Diseased Heart Tarkan TEKTEN, 1 MD, Alper O. ONBASILI, 1 MD, Ceyhun CEYHAN, 1 MD, Selim ÜNAL, 1 MD, and
Color Doppler Echocardiographic Assessment of Valvular Regurgitation in Normal Infants
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Color Doppler Echocardiographic Assessment of Valvular Regurgitation in Normal Infants Shu-Ting Lee, Meng-Hsun Lin* Background/Purpose: Despite valvular regurgitation being a common finding
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Color Doppler Echocardiographic Assessment of Valvular Regurgitation in Normal Infants Shu-Ting Lee, Meng-Hsun Lin* Background/Purpose: Despite valvular regurgitation being a common finding
Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea
 Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea Jahrestagung Schweizerische Gesellschaft für /Schweizerische Gesellschaft für Pneumologie B. Kaufmann 16.06.2016 Chronic dyspnea Shortness of breath lasting
Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea Jahrestagung Schweizerische Gesellschaft für /Schweizerische Gesellschaft für Pneumologie B. Kaufmann 16.06.2016 Chronic dyspnea Shortness of breath lasting
Direct Planimetry of Mitral Valve Regurgitation Orifice Area by Real-time 3D Transesophageal Echocardiography
 Direct Planimetry of Mitral Valve Regurgitation Orifice Area by Real-time 3D Transesophageal Echocardiography Ertunc Altiok, Sandra Hamada, Silke van Hall, Mehtap Hanenberg, Eva Grabskaya, Michael Becker,
Direct Planimetry of Mitral Valve Regurgitation Orifice Area by Real-time 3D Transesophageal Echocardiography Ertunc Altiok, Sandra Hamada, Silke van Hall, Mehtap Hanenberg, Eva Grabskaya, Michael Becker,
The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors:
 Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
Atrial Septal Defects
 Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension
 ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
Cardiac hypertrophy and how it may break an athlete s heart e the Cypriot case
 Eur J Echocardiography (2005) 6, 301e307 Cardiac hypertrophy and how it may break an athlete s heart e the Cypriot case C.E. Chee a,1, C.P. Anastassiades a,1, A.G. Antonopoulos b, A.A. Petsas b, L.C. Anastassiades
Eur J Echocardiography (2005) 6, 301e307 Cardiac hypertrophy and how it may break an athlete s heart e the Cypriot case C.E. Chee a,1, C.P. Anastassiades a,1, A.G. Antonopoulos b, A.A. Petsas b, L.C. Anastassiades
The Relationship between the Left Atrial Volume and the Maximum P-wave and P-wave Dispersion in Patients with Congestive Heart Failure
 Yonsei Med J 48(5):810-817, 2007 DOI 10.3349/ymj.2007.48.5.810 The Relationship between the Left Atrial Volume and the Maximum P-wave and P-wave Dispersion in Patients with Congestive Heart Failure Dae-Hyeok
Yonsei Med J 48(5):810-817, 2007 DOI 10.3349/ymj.2007.48.5.810 The Relationship between the Left Atrial Volume and the Maximum P-wave and P-wave Dispersion in Patients with Congestive Heart Failure Dae-Hyeok
Echocardiography Conference
 Echocardiography Conference David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY-6 September 20, 2005 Atrial Septal Aneurysm Bulging of Fossa Ovalis Associated commonly with Atrial septal defect or small perforations
Echocardiography Conference David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY-6 September 20, 2005 Atrial Septal Aneurysm Bulging of Fossa Ovalis Associated commonly with Atrial septal defect or small perforations
Tricuspid and Pulmonic Valve Disease
 Chapter 31 Tricuspid and Pulmonic Valve Disease David A. Tate Acquired disease of the right-sided cardiac valves is much less common than disease of the leftsided counterparts, possibly because of the
Chapter 31 Tricuspid and Pulmonic Valve Disease David A. Tate Acquired disease of the right-sided cardiac valves is much less common than disease of the leftsided counterparts, possibly because of the
Evaluation of Tissue Doppler Echocardiographic Imaging findings in children with pulmonary hypertension
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2017; 59: 244-253 DOI: 10.24953/turkjped.2017.03.003 Original Evaluation of Tissue Doppler Echocardiographic Imaging findings in children with pulmonary hypertension Alper
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2017; 59: 244-253 DOI: 10.24953/turkjped.2017.03.003 Original Evaluation of Tissue Doppler Echocardiographic Imaging findings in children with pulmonary hypertension Alper
Jong-Won Ha*, Jeong-Ah Ahn, Jae-Yun Moon, Hye-Sun Suh, Seok-Min Kang, Se-Joong Rim, Yangsoo Jang, Namsik Chung, Won-Heum Shim, Seung-Yun Cho
 Eur J Echocardiography (2006) 7, 16e21 CLINICAL/ORIGINAL PAPERS Triphasic mitral inflow velocity with mid-diastolic flow: The presence of mid-diastolic mitral annular velocity indicates advanced diastolic
Eur J Echocardiography (2006) 7, 16e21 CLINICAL/ORIGINAL PAPERS Triphasic mitral inflow velocity with mid-diastolic flow: The presence of mid-diastolic mitral annular velocity indicates advanced diastolic
Identification of super-responders to cardiac resynchronization therapy: the importance of symptom duration and left ventricular geometry
 Europace (2009) 11, 343 349 doi:10.1093/europace/eup038 CLINICAL RESEARCH Pacing and Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Identification of super-responders to cardiac resynchronization therapy: the importance
Europace (2009) 11, 343 349 doi:10.1093/europace/eup038 CLINICAL RESEARCH Pacing and Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Identification of super-responders to cardiac resynchronization therapy: the importance
Assessment of LV systolic function
 Tutorial 5 - Assessment of LV systolic function Assessment of LV systolic function A knowledge of the LV systolic function is crucial in the undertanding of and management of unstable hemodynamics or a
Tutorial 5 - Assessment of LV systolic function Assessment of LV systolic function A knowledge of the LV systolic function is crucial in the undertanding of and management of unstable hemodynamics or a
Abstract Clinical and paraclinical studies on myocardial and endocardial diseases in dog
 Abstract The doctoral thesis entitled Clinical and paraclinical studies on myocardial and endocardial diseases in dog was motivated by the study of the most frequent cardiopathies in dogs, which involves
Abstract The doctoral thesis entitled Clinical and paraclinical studies on myocardial and endocardial diseases in dog was motivated by the study of the most frequent cardiopathies in dogs, which involves
Echocardiography. Guidelines for Valve and Chamber Quantification. In partnership with
 Echocardiography Guidelines for Valve and Chamber Quantification In partnership with Explanatory note & references These guidelines have been developed by the Education Committee of the British Society
Echocardiography Guidelines for Valve and Chamber Quantification In partnership with Explanatory note & references These guidelines have been developed by the Education Committee of the British Society
Improvement of Atrial Function and Atrial Reverse Remodeling After Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy for Heart Failure
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 50, No. 8, 2007 2007 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/07/$32.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2007.04.073
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 50, No. 8, 2007 2007 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/07/$32.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2007.04.073
Case 1. Case 2. Case 3
 Case 1 The correct answer is D. Occasionally, the Brugada syndrome can present similar morphologies to A and also change depending on the lead position but in the Brugada pattern the r is wider and ST
Case 1 The correct answer is D. Occasionally, the Brugada syndrome can present similar morphologies to A and also change depending on the lead position but in the Brugada pattern the r is wider and ST
Congenital. Unicuspid Bicuspid Quadricuspid
 David Letterman s Top 10 Aortic Stenosis The victim can be anyone: Echo is the question and the answer!!!! Hilton Head Island Echocardiography Conference 2012 Timothy E. Paterick, MD, JD, MBA Christopher
David Letterman s Top 10 Aortic Stenosis The victim can be anyone: Echo is the question and the answer!!!! Hilton Head Island Echocardiography Conference 2012 Timothy E. Paterick, MD, JD, MBA Christopher
The Incidence and Predictors of Postoperative Atrial Fibrillation After Noncardiothoracic Surgery
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2009.39.3.100 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2009 The Korean Society of Cardiology The Incidence and Predictors of Postoperative Atrial Fibrillation
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2009.39.3.100 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2009 The Korean Society of Cardiology The Incidence and Predictors of Postoperative Atrial Fibrillation
Echocardiographic Cardiovascular Risk Stratification: Beyond Ejection Fraction
 Echocardiographic Cardiovascular Risk Stratification: Beyond Ejection Fraction October 4, 2014 James S. Lee, M.D., F.A.C.C. Associates in Cardiology, P.A. Silver Spring, M.D. Disclosures Financial none
Echocardiographic Cardiovascular Risk Stratification: Beyond Ejection Fraction October 4, 2014 James S. Lee, M.D., F.A.C.C. Associates in Cardiology, P.A. Silver Spring, M.D. Disclosures Financial none
The Doppler echocardiographic assessment of valvular regurgitation in normal children

PRESENTER DISCLOSURE INFORMATION. There are no potential conflicts of interest regarding current presentation
 PRESENTER DISCLOSURE INFORMATION There are no potential conflicts of interest regarding current presentation Better synchrony and diastolic function for septal versus apical right ventricular permanent
PRESENTER DISCLOSURE INFORMATION There are no potential conflicts of interest regarding current presentation Better synchrony and diastolic function for septal versus apical right ventricular permanent
Echocardiography: Guidelines for Valve Quantification
 Echocardiography: Guidelines for Echocardiography: Guidelines for Chamber Quantification British Society of Echocardiography Education Committee Richard Steeds (Chair), Gill Wharton (Lead Author), Jane
Echocardiography: Guidelines for Echocardiography: Guidelines for Chamber Quantification British Society of Echocardiography Education Committee Richard Steeds (Chair), Gill Wharton (Lead Author), Jane
LEAD dysfunction is one of the major problems/complications of permanent
 Right Ventricular and Tricuspid Valve Function in Patients With Two Ventricular Pacemaker Leads Cengiz ÇELIKER, 1 MD, M. SERDAR KÜÇÜKOGLU, 1 MD, Alev ARAT-ÖZKAN, 1 MD, Nuran YAZICIOGLU, 1 MD, and Sinan
Right Ventricular and Tricuspid Valve Function in Patients With Two Ventricular Pacemaker Leads Cengiz ÇELIKER, 1 MD, M. SERDAR KÜÇÜKOGLU, 1 MD, Alev ARAT-ÖZKAN, 1 MD, Nuran YAZICIOGLU, 1 MD, and Sinan
LUST trial. Echocardiography USER S MANUAL
 LUST trial Echocardiography USER S MANUAL Rosa Sicari, Luna Gargani Ins1tute of Clinical Physiology Na1onal Council of Research, Pisa, Italy Parameters required (1) Aortic root Measurement of aortic root
LUST trial Echocardiography USER S MANUAL Rosa Sicari, Luna Gargani Ins1tute of Clinical Physiology Na1onal Council of Research, Pisa, Italy Parameters required (1) Aortic root Measurement of aortic root
Prediction of Cardiovascular Outcomes With Left Atrial Size Is Volume Superior to Area or Diameter?
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 47, No. 5, 2006 2006 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/06/$32.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2005.08.077
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 47, No. 5, 2006 2006 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/06/$32.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2005.08.077
Doppler-echocardiographic findings in a patient with persisting right ventricular sinusoids
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 1990 Doppler-echocardiographic findings in a patient with persisting right
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 1990 Doppler-echocardiographic findings in a patient with persisting right
Pulsed Wave Doppler and Color Flow Doppler Evaluation in Healthy Dogs and Dogs with Cardiac Disease
 Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Veterinary Science and Technology 2016, Volume 5, Issue 2, pp. 256-265, Article ID Sci-446 ISSN 2320-3595 Research Article Open Access Pulsed Wave Doppler
Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Veterinary Science and Technology 2016, Volume 5, Issue 2, pp. 256-265, Article ID Sci-446 ISSN 2320-3595 Research Article Open Access Pulsed Wave Doppler
Global left ventricular circumferential strain is a marker for both systolic and diastolic myocardial function
 Global left ventricular circumferential strain is a marker for both systolic and diastolic myocardial function Toshinari Onishi 1, Samir K. Saha 2, Daniel Ludwig 1, Erik B. Schelbert 1, David Schwartzman
Global left ventricular circumferential strain is a marker for both systolic and diastolic myocardial function Toshinari Onishi 1, Samir K. Saha 2, Daniel Ludwig 1, Erik B. Schelbert 1, David Schwartzman
Københavns Universitet
 university of copenhagen Københavns Universitet Total average diastolic longitudinal displacement by colour tissue doppler imaging as an assessment of diastolic function de Knegt, Martina Chantal; Biering-Sørensen,
university of copenhagen Københavns Universitet Total average diastolic longitudinal displacement by colour tissue doppler imaging as an assessment of diastolic function de Knegt, Martina Chantal; Biering-Sørensen,
Characteristics of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function in Patients with Systolic Heart Failure: A Doppler Tissue Imaging Study
 Characteristics of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function in Patients with Systolic Heart Failure: A Doppler Tissue Imaging Study Bassem A. Samad, MD, PhD, Jens M. Olson, MD, and Mahbubul Alam, MD, PhD, FESC,
Characteristics of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function in Patients with Systolic Heart Failure: A Doppler Tissue Imaging Study Bassem A. Samad, MD, PhD, Jens M. Olson, MD, and Mahbubul Alam, MD, PhD, FESC,
Original Article Significance of Signal Averaged Electrocardiography in Patients with Advanced Heart Failure and Intraventricular Conduction Delay
 www.ipej.org 205 Original Article Significance of Signal Averaged Electrocardiography in Patients with Advanced Heart Failure and Intraventricular Conduction Delay Mohammad Alasti, MD 1, Majid Haghjoo,
www.ipej.org 205 Original Article Significance of Signal Averaged Electrocardiography in Patients with Advanced Heart Failure and Intraventricular Conduction Delay Mohammad Alasti, MD 1, Majid Haghjoo,
Aortic root and left atrial wall motion
 British Heart Journal, 1977, 39, 1082-1087 Aortic root and left atrial wall motion An echocardiographic study GONES AKGtYN AND CLIVE LAYTON1 From the Cardiac Department, The London Hospital, London The
British Heart Journal, 1977, 39, 1082-1087 Aortic root and left atrial wall motion An echocardiographic study GONES AKGtYN AND CLIVE LAYTON1 From the Cardiac Department, The London Hospital, London The
Valvular Regurgitation: Can We Do Better Than Colour Doppler?
 Valvular Regurgitation: Can We Do Better Than Colour Doppler? A/Prof David Prior St Vincent s Hospital Melbourne Sports Cardiology Valvular Regurgitation Valve regurgitation volume loads the ventricles
Valvular Regurgitation: Can We Do Better Than Colour Doppler? A/Prof David Prior St Vincent s Hospital Melbourne Sports Cardiology Valvular Regurgitation Valve regurgitation volume loads the ventricles
MITRAL VALVE DISEASE- ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT. Irene Frantzis P year, SGUL Sheba Medical Center
 MITRAL VALVE DISEASE- ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT Irene Frantzis P year, SGUL Sheba Medical Center MITRAL VALVE DISEASE Mitral Valve Regurgitation Mitral Valve Stenosis Mitral Valve Prolapse MITRAL REGURGITATION
MITRAL VALVE DISEASE- ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT Irene Frantzis P year, SGUL Sheba Medical Center MITRAL VALVE DISEASE Mitral Valve Regurgitation Mitral Valve Stenosis Mitral Valve Prolapse MITRAL REGURGITATION
Revealing new insights. irotate electronic rotation and xplane adjustable biplane imaging. Ultrasound cardiology. irotate and xplane
 Ultrasound cardiology irotate and xplane Revealing new insights irotate electronic rotation and xplane adjustable biplane imaging Annemien van den Bosch and Jackie McGhie Department of Cardiology, Erasmus
Ultrasound cardiology irotate and xplane Revealing new insights irotate electronic rotation and xplane adjustable biplane imaging Annemien van den Bosch and Jackie McGhie Department of Cardiology, Erasmus
Incorporating the New Echo Guidelines Into Everyday Practice
 Incorporating the New Echo Guidelines Into Everyday Practice Clinical Case RIGHT VENTRICULAR FAILURE Gustavo Restrepo MD President Elect Interamerican Society of Cardiology Director Fellowship Training
Incorporating the New Echo Guidelines Into Everyday Practice Clinical Case RIGHT VENTRICULAR FAILURE Gustavo Restrepo MD President Elect Interamerican Society of Cardiology Director Fellowship Training
Aortic Stenosis: Spectrum of Disease, Low Flow/Low Gradient and Variants
 Aortic Stenosis: Spectrum of Disease, Low Flow/Low Gradient and Variants Martin G. Keane, MD, FASE Professor of Medicine Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University Basic root structure Parasternal
Aortic Stenosis: Spectrum of Disease, Low Flow/Low Gradient and Variants Martin G. Keane, MD, FASE Professor of Medicine Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University Basic root structure Parasternal
MITRAL REGURGITATION ECHO PARAMETERS TOOL
 Comprehensive assessment of qualitative and quantitative parameters, along with the use of standardized nomenclature when reporting echocardiographic findings, helps to better define a patient s MR and
Comprehensive assessment of qualitative and quantitative parameters, along with the use of standardized nomenclature when reporting echocardiographic findings, helps to better define a patient s MR and
Introduction. Materials and Methods. Andrea C. Vollmar, DVM
 Use of Echocardiography in the Diagnosis of Dilated Cardiomyopathy in Irish Wolfhounds The purpose of this study was to compare the echocardiographic features of Irish wolfhounds with clinically inapparent
Use of Echocardiography in the Diagnosis of Dilated Cardiomyopathy in Irish Wolfhounds The purpose of this study was to compare the echocardiographic features of Irish wolfhounds with clinically inapparent
Three-dimensional Wall Motion Tracking:
 Three-dimensional Wall Motion Tracking: A Novel Echocardiographic Method for the Assessment of Ventricular Volumes, Strain and Dyssynchrony Jeffrey C. Hill, BS, RDCS, FASE Jennifer L. Kane, RCS Gerard
Three-dimensional Wall Motion Tracking: A Novel Echocardiographic Method for the Assessment of Ventricular Volumes, Strain and Dyssynchrony Jeffrey C. Hill, BS, RDCS, FASE Jennifer L. Kane, RCS Gerard
Diagnostic approach to heart disease
 Diagnostic approach to heart disease Initial work up History Physical exam Chest radiographs ECG Special studies Echocardiography Cardiac catheterization Echocardiography principles Technique of producing
Diagnostic approach to heart disease Initial work up History Physical exam Chest radiographs ECG Special studies Echocardiography Cardiac catheterization Echocardiography principles Technique of producing
NT-proBNP as a Marker of Left Ventricular Dysfunction in Chronic Asymptomatic Mitral Regurgitation
 NT-proBNP as a Marker of Left Ventricular Dysfunction in Chronic Asymptomatic Mitral Regurgitation Srikornruth Panyaratanakul 1, Tanarat Choon-ngarm 2, Wilai Puavilai 2, Saowaluk Prompongsa 2, Donpichit
NT-proBNP as a Marker of Left Ventricular Dysfunction in Chronic Asymptomatic Mitral Regurgitation Srikornruth Panyaratanakul 1, Tanarat Choon-ngarm 2, Wilai Puavilai 2, Saowaluk Prompongsa 2, Donpichit
The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors:
 Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
ICE: Echo Core Lab-CRF
 APPENDIX 1 ICE: Echo Core Lab-CRF Study #: - Pt Initials: 1. Date of study: / / D D M M M Y Y Y Y 2. Type of Study: TTE TEE 3. Quality of Study: Poor Moderate Excellent Ejection Fraction 4. Ejection Fraction
APPENDIX 1 ICE: Echo Core Lab-CRF Study #: - Pt Initials: 1. Date of study: / / D D M M M Y Y Y Y 2. Type of Study: TTE TEE 3. Quality of Study: Poor Moderate Excellent Ejection Fraction 4. Ejection Fraction
Mitral Valve Disease. Prof. Sirchak Yelizaveta Stepanovna
 Mitral Valve Disease Prof. Sirchak Yelizaveta Stepanovna Fall 2008 Mitral Valve Stenosis Lecture Outline Mitral Stenosis Mitral Regurgitation Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical features Diagnostic testing
Mitral Valve Disease Prof. Sirchak Yelizaveta Stepanovna Fall 2008 Mitral Valve Stenosis Lecture Outline Mitral Stenosis Mitral Regurgitation Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical features Diagnostic testing
Doppler Basic & Hemodynamic Calculations
 Doppler Basic & Hemodynamic Calculations August 19, 2017 Smonporn Boonyaratavej MD Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Cardiac Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital
Doppler Basic & Hemodynamic Calculations August 19, 2017 Smonporn Boonyaratavej MD Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Cardiac Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital
NAKAO, RDCS 2. J Cardiol 2002 Dec; 40 6 :
 J Cardiol 2002 Dec; 40 6 : 259 265 T Usefulness of Left Ventricular Opacification With Intravenous Contrast Echocardiography in Patients With Asymptomatic Negative T Waves on Electrocardiography 1 2 2
J Cardiol 2002 Dec; 40 6 : 259 265 T Usefulness of Left Ventricular Opacification With Intravenous Contrast Echocardiography in Patients With Asymptomatic Negative T Waves on Electrocardiography 1 2 2
Echocardiographic and Doppler Assessment of Cardiac Functions in Patients of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE JIACM 2002; 3(2): 164-8 Echocardiographic and Doppler Assessment of Cardiac Functions in Patients of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Rajesh Rajput*, Jagdish**, SB Siwach***, A
ORIGINAL ARTICLE JIACM 2002; 3(2): 164-8 Echocardiographic and Doppler Assessment of Cardiac Functions in Patients of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Rajesh Rajput*, Jagdish**, SB Siwach***, A
Cardiovascular Images
 Cardiovascular Images Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosed From Right Heart Changes Seen After Exercise Stress Echocardiography Brian C. Case, MD; Micheas Zemedkun, MD; Amarin Sangkharat, MD; Allen J. Taylor,
Cardiovascular Images Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosed From Right Heart Changes Seen After Exercise Stress Echocardiography Brian C. Case, MD; Micheas Zemedkun, MD; Amarin Sangkharat, MD; Allen J. Taylor,
Primary Mitral Regurgitation
 EURO VALVE Madrid News from Valves Guidelines 2012: What s new and Why? Primary Mitral Regurgitation Luc A. Pierard, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine Head of the Department of Cardiology Heart Valve Clinic,
EURO VALVE Madrid News from Valves Guidelines 2012: What s new and Why? Primary Mitral Regurgitation Luc A. Pierard, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine Head of the Department of Cardiology Heart Valve Clinic,
12-Lead ECG Interpretation. Kathy Kuznar, RN, ANP
 12-Lead ECG Interpretation Kathy Kuznar, RN, ANP The 12-Lead ECG Objectives Identify the normal morphology and features of the 12- lead ECG. Perform systematic analysis of the 12-lead ECG. Recognize abnormalities
12-Lead ECG Interpretation Kathy Kuznar, RN, ANP The 12-Lead ECG Objectives Identify the normal morphology and features of the 12- lead ECG. Perform systematic analysis of the 12-lead ECG. Recognize abnormalities
8/31/2016. Mitraclip in Matthew Johnson, MD
 Mitraclip in 2016 Matthew Johnson, MD 1 Abnormal Valve Function Valve Stenosis Obstruction to valve flow during that phase of the cardiac cycle when the valve is normally open. Hemodynamic hallmark - pressure
Mitraclip in 2016 Matthew Johnson, MD 1 Abnormal Valve Function Valve Stenosis Obstruction to valve flow during that phase of the cardiac cycle when the valve is normally open. Hemodynamic hallmark - pressure
DOI: /j x
 DOI: 10.1111/j.1540-8175.2010.01149.x C 2010, Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Comparison of Left Ventricular Contractility in Pressure and Volume Overload: A Strain Rate Study in the Clinical Model of Aortic Stenosis
DOI: 10.1111/j.1540-8175.2010.01149.x C 2010, Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Comparison of Left Ventricular Contractility in Pressure and Volume Overload: A Strain Rate Study in the Clinical Model of Aortic Stenosis
Advanced imaging of the left atrium - strain, CT, 3D, MRI -
 Advanced imaging of the left atrium - strain, CT, 3D, MRI - Monica Rosca, MD Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania Declaration of interest: I have nothing to declare Case
Advanced imaging of the left atrium - strain, CT, 3D, MRI - Monica Rosca, MD Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania Declaration of interest: I have nothing to declare Case
EDITOR S PICK CURRENT STATUS OF FULLY AUTOMATED SOFTWARE WITH THREE-DIMENSIONAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY FOR THE QUANTIFICATION OF LEFT VENTRICULAR FUNCTION
 ITOR S PICK This paper, courtesy of Yang and Takeuchi, provides a timely and well-considered update on the current status of fully-automated software with three-dimensional echocardiography for quantifying
ITOR S PICK This paper, courtesy of Yang and Takeuchi, provides a timely and well-considered update on the current status of fully-automated software with three-dimensional echocardiography for quantifying
Echocardiographic variables associated with mitral regurgitation after aortic valve replacement for aortic valve stenosis
 The Egyptian Heart Journal (2013) 65, 135 139 Egyptian Society of Cardiology The Egyptian Heart Journal www.elsevier.com/locate/ehj www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Echocardiographic variables associated
The Egyptian Heart Journal (2013) 65, 135 139 Egyptian Society of Cardiology The Egyptian Heart Journal www.elsevier.com/locate/ehj www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Echocardiographic variables associated
MITRAL STENOSIS. Joanne Cusack
 MITRAL STENOSIS Joanne Cusack BSE Breakdown Recognition of rheumatic mitral stenosis Qualitative description of valve and sub-valve calcification and fibrosis Measurement of orifice area by planimetry
MITRAL STENOSIS Joanne Cusack BSE Breakdown Recognition of rheumatic mitral stenosis Qualitative description of valve and sub-valve calcification and fibrosis Measurement of orifice area by planimetry
Bogdan A. Popescu. University of Medicine and Pharmacy Bucharest, Romania. EAE Course, Bucharest, April 2010
 Bogdan A. Popescu University of Medicine and Pharmacy Bucharest, Romania EAE Course, Bucharest, April 2010 This is how it started Mitral stenosis at a glance 2D echo narrow diastolic opening of MV leaflets
Bogdan A. Popescu University of Medicine and Pharmacy Bucharest, Romania EAE Course, Bucharest, April 2010 This is how it started Mitral stenosis at a glance 2D echo narrow diastolic opening of MV leaflets
Electrocardiographic abnormalities in patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis (RCD code: III)
 Journal of Rare Cardiovascular Diseases 2017; 3 (3): 81 85 www.jrcd.eu ORIGINAL PAPER Diseases of the heart Electrocardiographic abnormalities in patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis (RCD code: III) Justyna
Journal of Rare Cardiovascular Diseases 2017; 3 (3): 81 85 www.jrcd.eu ORIGINAL PAPER Diseases of the heart Electrocardiographic abnormalities in patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis (RCD code: III) Justyna
Diastolic filling in hypertrophied hearts of elite runners: an Echo-Doppler study
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2001; 5: 65-69 Diastolic filling in hypertrophied hearts of elite runners: an Echo-Doppler study A. PALAZZUOLI, L. PUCCETTI, F. BRUNI, A.L. PASQUI,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2001; 5: 65-69 Diastolic filling in hypertrophied hearts of elite runners: an Echo-Doppler study A. PALAZZUOLI, L. PUCCETTI, F. BRUNI, A.L. PASQUI,
Exercise Pulmonary Hypertension predicts the Occurrence of Symptoms in Asymptomatic Degenerative Mitral Regurgitation
 Exercise Pulmonary Hypertension predicts the Occurrence of Symptoms in Asymptomatic Degenerative Mitral Regurgitation Julien Magne, PhD, Kim O Connor, MD, Giuseppe Romano, MD, Marie Moonen, MD, Luc A.
Exercise Pulmonary Hypertension predicts the Occurrence of Symptoms in Asymptomatic Degenerative Mitral Regurgitation Julien Magne, PhD, Kim O Connor, MD, Giuseppe Romano, MD, Marie Moonen, MD, Luc A.
Echocardiographic changes after aortic valve replacement: Does the failure rate of mitral valve change? Original Article
 Echocardiographic changes after aortic valve replacement: Does the failure rate of mitral valve change? Abstract Arezoo Khosravi (1), Hadi Sheykhloo (2), Reza Karbasi-Afshar (1), Amin Saburi (3) Original
Echocardiographic changes after aortic valve replacement: Does the failure rate of mitral valve change? Abstract Arezoo Khosravi (1), Hadi Sheykhloo (2), Reza Karbasi-Afshar (1), Amin Saburi (3) Original
Echocardiographic Evaluation of Mitral Annulus Excursion in Normal Horses
 Echocardiographic Evaluation of Mitral Annulus Excursion in Normal Horses Carlos Lightowler, DVM a Giuseppe Piccione, DVM b Maria Laura Cattaneo, DSS c Elisabetta Giudice, DVM, PhD d a Departamento de
Echocardiographic Evaluation of Mitral Annulus Excursion in Normal Horses Carlos Lightowler, DVM a Giuseppe Piccione, DVM b Maria Laura Cattaneo, DSS c Elisabetta Giudice, DVM, PhD d a Departamento de
Carlos Eduardo Suaide Silva, Luiz Darcy Cortez Ferreira, Luciana Braz Peixoto, Claudia Gianini Monaco, Manuel Adán Gil, Juarez Ortiz
 Silva et al Original Article Arq Bras Cardiol Study of the Myocardial Contraction and Relaxation Velocities through Doppler Tissue Imaging Echocardiography. A New Alternative in the Assessment of the Segmental
Silva et al Original Article Arq Bras Cardiol Study of the Myocardial Contraction and Relaxation Velocities through Doppler Tissue Imaging Echocardiography. A New Alternative in the Assessment of the Segmental
Successful Catheter Ablation as a Substitute for Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy in Patient with an Accessory Pathway-induced Cardiomyopathy
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8205-16 Intern Med Advance Publication http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Successful Catheter Ablation as a Substitute for Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy in Patient with an
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8205-16 Intern Med Advance Publication http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Successful Catheter Ablation as a Substitute for Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy in Patient with an
Effect of transcatheter aortic valve replacement on P-wave duration, P-wave dispersion and left atrial size
 Journal of Geriatric Cardiology (2015) 12: 613 617 2015 JGC All rights reserved; www.jgc301.com Research Article Open Access Effect of transcatheter aortic valve replacement on P-wave duration, P-wave
Journal of Geriatric Cardiology (2015) 12: 613 617 2015 JGC All rights reserved; www.jgc301.com Research Article Open Access Effect of transcatheter aortic valve replacement on P-wave duration, P-wave
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
DOPPLER HEMODYNAMICS (1) QUANTIFICATION OF PRESSURE GRADIENTS and INTRACARDIAC PRESSURES
 THORAXCENTRE DOPPLER HEMODYNAMICS (1) QUANTIFICATION OF PRESSURE GRADIENTS and INTRACARDIAC PRESSURES J. Roelandt DOPPLER HEMODYNAMICS Intracardiac pressures and pressure gradients Volumetric measurement
THORAXCENTRE DOPPLER HEMODYNAMICS (1) QUANTIFICATION OF PRESSURE GRADIENTS and INTRACARDIAC PRESSURES J. Roelandt DOPPLER HEMODYNAMICS Intracardiac pressures and pressure gradients Volumetric measurement
How to assess ischaemic MR?
 ESC 2012 How to assess ischaemic MR? Luc A. Pierard, MD, PhD, FESC, FACC Professor of Medicine Head, Department of Cardiology University Hospital Sart Tilman, Liège ESC 2012 No conflict of interest Luc
ESC 2012 How to assess ischaemic MR? Luc A. Pierard, MD, PhD, FESC, FACC Professor of Medicine Head, Department of Cardiology University Hospital Sart Tilman, Liège ESC 2012 No conflict of interest Luc
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by the fact that a murmur was heard at birth?
 HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
Journal of American Science 2014;10(9) Congenital Heart Disease in Pediatric with Down's Syndrome
 Journal of American Science 2014;10(9) http://www.jofamericanscience.org Congenital Heart Disease in Pediatric with Down's Syndrome Jawaher Khalid Almaimani; Maryam Faisal Zafir; Hanan Yousif Abbas and
Journal of American Science 2014;10(9) http://www.jofamericanscience.org Congenital Heart Disease in Pediatric with Down's Syndrome Jawaher Khalid Almaimani; Maryam Faisal Zafir; Hanan Yousif Abbas and
The Patient with Atrial Fibrilation
 Assessment of Diastolic Function The Patient with Atrial Fibrilation Assoc. Prof. Adriana Ilieşiu, FESC University of Medicine Carol Davila Bucharest, Romania Associated Conditions with Atrial Fibrillation
Assessment of Diastolic Function The Patient with Atrial Fibrilation Assoc. Prof. Adriana Ilieşiu, FESC University of Medicine Carol Davila Bucharest, Romania Associated Conditions with Atrial Fibrillation
Right Ventricular Strain in Normal Healthy Adult Filipinos: A Retrospective, Cross- Sectional Pilot Study
 Right Ventricular Strain in Normal Healthy Adult Filipinos: A Retrospective, Cross- Sectional Pilot Study By Julius Caesar D. de Vera, MD Jonnah Fatima B. Pelat, MD Introduction Right ventricle contributes
Right Ventricular Strain in Normal Healthy Adult Filipinos: A Retrospective, Cross- Sectional Pilot Study By Julius Caesar D. de Vera, MD Jonnah Fatima B. Pelat, MD Introduction Right ventricle contributes
/11/$ see front matter 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. doi: /j.amjcard
 Importance of Adjunctive Heart Failure Optimization Immediately After Implantation to Improve Long-Term Outcomes With Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Wilfried Mullens, MD, PhD a,b, *, Jacek Kepa, MS
Importance of Adjunctive Heart Failure Optimization Immediately After Implantation to Improve Long-Term Outcomes With Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Wilfried Mullens, MD, PhD a,b, *, Jacek Kepa, MS
