Myocardial performance index, Tissue Doppler echocardiography
|
|
|
- Dylan Arnold
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Value of Measuring Myocardial Performance Index by Tissue Doppler Echocardiography in Normal and Diseased Heart Tarkan TEKTEN, 1 MD, Alper O. ONBASILI, 1 MD, Ceyhun CEYHAN, 1 MD, Selim ÜNAL, 1 MD, and Berent DISCIGIL, 2 MD SUMMARY Myocardial performance index (MPI) is a simple and reproducible method for the assessment of overall cardiac function. In this study, we evaluated the applicability and usefulness of pulsed-wave tissue Doppler echocardiography (TDE) as a tool to calculate MPI in comparision with a conventional Doppler method. Twenty-five patients with previous myocardial infarction (MI) and 15 healthy subjects were included. In order to calculate MPI by TDE, isovolumetric contraction time (IVCT), isovolumetric relaxation time (IVRT), and ejection time (ET) were measured at four different sites in the mitral annulus: septum, lateral, anterior, and inferior. MPI was calculated by dividing the sum of IVCT and IVRT by ET at each site of measurement. The mean MPI value was found by dividing the sum of these MPI values into four. The same parameters were measured using the mitral inflow and left ventricular outflow velocity time intervals by a conventional method. MPI by TDE correlated well with conventional MPI in healthy subjects (r = 0.81, P < ). Although it continued to be statistically significant, the correlation between the two methods of measuring MPI, TDE and conventional, in patients with previous MI was not as high as it was in healthy individuals (P < 0.001, r = 0.62). This is due to the lesser degree of correlation between IVRT and IVCT values obtained by TDE and the conventional method (r = 0.49, P < 0.05; r = 0.56, P < 0.05; respectively). In conclusion, this study has demonstrated that MPI could be measured by tissue Doppler and that it correlated well with conventional MPI. Moreover, MPI by TDE has the advantage of assessing both regional and global myocardial performance. (Jpn Heart J 2003; 44: ) Key words: Myocardial performance index, Tissue Doppler echocardiography THE conventional echocardiographic methods for assessing cardiac function are unable to distinguish, in one single scan, the individual phases of the cardiac From the 1 Department of Cardiology, 2 Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Adnan Menderes University School of Medicine, Aydin, Turkey. Address for correspondence: Tarkan Tekten, MD, Department of Cardiology, Adnan Menderes University School of Medicine, Aydin 09100, Turkey. This study was presented in part in the 14 th World Congress of Cardiology. Received for publication June 5, Revised and accepted October 17,
2 404 TEKTEN, ET AL Jpn Heart J May 2003 cycle. 1) Moreover, regional myocardial abnormalities in these phases cannot be identified. Tissue Doppler echocardiography (TDE) is a new technique that records myocardial velocities during the cardiac cycle. 2,3) Quantitative recording of systolic and diastolic velocities can be done by TDE, which can precisely differentiate phases of the cardiac cycle. The recently proposed Doppler derived myocardial performance index (MPI), which combines systolic and diastolic time intervals, has been reported to be a simple and reproducible index for assessing left ventricular (LV) function that has been shown to be independent of heart rate and blood pressure. 4-6) We hypothesize that MPI could be determined by pulsed-wave TDE and may be more sensitive than conventional MPI in predicting LV function, especially in the presence of regional wall motion abnormality, as is the case in patients with previous myocardial infarction (MI). The purpose of this study was to evaluate the applicability and usefulness of pulsed-wave TDE as a tool to calculate MPI in comparision with a conventional Doppler method. METHODS Study population: Twenty-five patients with previous MI (22 males and 3 females) evidenced by electrocardiographic findings and the presence of wall motion abnormality on a two-dimensional (2D) echocardiographic study were studied. Fifteen healthy subjects (11 males, 4 females) without a history of cardiac disease or systemic hypertension and having normal findings on physical examination, chest roentgenography, electrocardiography, and 2-D and Doppler echocardiography served as controls. All study patients were in sinus rhythm. Of the 25 patients with previous MI, 14 had anterior MI, 11 had inferior MI, 9 had systemic hypertension, and 5 had diabetes mellitus. Mitral regurgitation was present in 12 of these patients, and all were graded as mild. Exclusion criteria included inadequate visualization, presence of dilated cardiomyopathy, LV hypertrophy, pericardial disease, infiltrative myocardial disease, and the presence of left bundle branch block on the electrocardiogram. Echocardiography: The patients were examined in the left lateral decubitis position with a Hewlett-Packard Sonos 5500 (Andover, Massachusetts) phased-array system equipped with tissue Doppler technology. Measurements were made according to the recommendations of the American Society of Echocardiography. 7) The ejection fraction was calculated from apical 4- and 2-chamber views with Simpson's method. The mitral inflow velocity pattern was recorded with the pulsed-wave Doppler sample volume positioned between the tips of the mitral leaflets. The LV outflow pattern was recorded from the apical 5-chamber view with the pulsed wave Doppler sample volume positioned just below the aor-
3 Vol 44 No 3 TISSUE DOPPLER MYOCARDIAL PERFORMANCE INDEX 405 tic valve. Three consecutive beats were measured and averaged for each parameter. Two-dimensional and Doppler tracings were recorded over five cardiac cycles at a sweep speed of 100 mm/s. Doppler measurements: Mitral inflow and left ventricular outflow velocity-time intervals were used to measure Doppler time intervals: isovolumetric contraction (IVCT), relaxation time (IVRT), and ejection time (ET) as demonstrated in Figure 1. The interval a from the cessation to the onset of mitral inflow was equal to the sum of IVCT, ET, and IVRT. Left ventricular ET b was the duration of the left ventricular velocity profile. Thus, the sum of IVCT and IVRT was obtained by subtracting b from a. The MPI was calculated as (a - b)/b. IVRT was calculated by subtracting the interval d, between the R wave and the cessation of left ventricular outflow, from the interval c, between the R wave and the onset of mitral inflow. 9) IVCT was calculated by subtracting IVRT from a - b. Tissue doppler echocardiography: The pulsed-wave TDE was performed by activating the tissue Doppler function in the same echocardiographic machine. Images were acquired using a variable frequency phased-array transducer (2.0 to 4.0 MHz). The filter settings were kept low, and gains were adjusted to the mini- Figure 1. Doppler time intervals were measured from mitral inflow and left ventricular outflow velocity-time intervals.
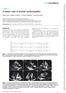
4 406 TEKTEN, ET AL Jpn Heart J May 2003 mal optimal level to minimize noise and eliminate the signals produced by the transmitral flow. A 1.7 mm sample volume was used. Sample volumes were placed at four different sites in the mitral annulus, corresponding to the septum, lateral, anterior, and inferior sites, in order to record major velocity time intervals: IVCT, IVRT, and ET (Figure 2). The pulsed-wave TDE tracings were recorded over five cardiac cycles at a sweep speed of 100 mm/ s and three of them were used for calculation. TDE velocity time intervals were measured from the sites at the mitral annulus as demonstrated in Figure 3. The interval (a ), from the R wave to the onset of diastolic velocity, was equal to the sum of IVCT, ET, and IVRT. Left ventricular ET (b') was the duration of the systolic velocity profile. Thus, the sum of IVCT and IVRT was obtained by subtracting (b ) from (a ). The MPI was calculated as (a -b )/b. IVRT was calculated by subtracting the interval (d ), between the R wave and the cessation of systolic velocity, from the interval (c ), between the R wave and the onset of diastolic velocity. IVCT was calculated by subtracting IVRT from (a - b ). Reproducibility: Intra-observer variability was assessed in 10 patients by repeating the measurements on two occasions (1-12 days apart) under the same basal conditions. To test the interobserver variability, the measurements were performed off-line from video recordings by a second observer who was unaware of the results of the first examination. Variability was calculated as the mean per- Figure 2. Position of the sample volumes in each cross-sectional view. ANT = anterior wall; 2CH = apical 2-chamber view; 4CH = apical 4-chamber view; INF = inferior wall; IVS = interventricular septum; LAT = lateral wall.
5 Vol 44 No 3 TISSUE DOPPLER MYOCARDIAL PERFORMANCE INDEX 407 Figure 3. Tissue Doppler echocardiography time intervals were measured from the mitral annular tissue Doppler velocity time intervals. centage error, derived as the difference between the two sets of measurements, divided by the mean observations. Statistics: Data are expressed as the mean ± SD. Groups were compared by the Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney U tests for unpaired data. The chi-square test was used for categorical data. Spearman correlation analysis was used to assess the statistical relationships between the time intervals or MPI by TDE and the conventional method. A difference was considered significant at P < RESULTS Doppler time intervals: The basic clinical characteristics and Doppler time intervals for the healthy subjects and patients with previous MI are given in Table I. In patients with previous MI, ejection fraction was significantly decreased, IVCT was significantly prolonged, and ET was shortened in comparison with those in the healthy age-matched subjects. The IVRT was not significantly different between the two groups. The MPI measured either by TDE or the conventional method was significantly greater in patients with MI (Table II).
6 408 TEKTEN, ET AL Jpn Heart J May 2003 Table I. Clinical Characteristics and Doppler Echocardiography Measurements in Healthy Subjects and Patients with MI Variable Healthy MI P value Age (y) Male/Female (no.) E to A ratio Deceleration time (ms) Ejection fraction (ms) Isovolumetric contraction time (ms) Ejection time (ms) Isovolumetric relaxation time (ms) MPI (conventional) MPI by TDE 61 ± 7 (11/4) 1.01 ± ± ± 4 29 ± ± ± ± ± ± 9 (22/3) 0.94 ± ± ± 9 50 ± ± ± ± ± 0.09 NS NS NS NS NS NS = Non-significant; MPI = Myocardial performance index; TDE = Tissue Doppler echocardiography; ms = Millisecond. Table II. MPI Assessed by DTI at Different Sites of Mitral Annulus MPI-Septum MPI-Anterior MPI-Lateral MPI-Inferior MPI-Mean Healthy subjects Patients with anterior MI (n = 14) Patients with inferior MI (n = 11) All patients with MI 0.31 ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± 0.09 MPI = Myocardial performance index; TDE = Tissue Doppler echocardiography; P < 0.01 compared with healthy subjects, P < 0.05 compared with healthy subjects MPI in healthy subjects: There was no significant difference in the mean MPI by TDE values at four cardiac sites (Table II). There was a highly significant correlation between MPI values obtained by TDE and the conventional method (r = 0.81, P < ) (Figure 4). The IVRT, IVCT, and ET values obtained by TDE all correlated well with the values obtained by the conventional method (r = 0.80, P < ; P < , r = 0.91; P < , r = 0.83, P < ; respectively) (Figures 5, 6, and 7). MPI in patients with previous MI: There was a significant correlation between the MPI values obtained by TDE and the conventional method (P < 0.001, r = 0.62) (Figure 8). The IVRT, IVCT, and ET values obtained by TDE all correlated significantly with the values obtained by the conventional method (r = 0.49, P < 0.05; r = 0.56, P < 0.05; r = 0.81, P < ; respectively) (Figures 9, 10, and 11). In patients with anterior MI, the rise in MPI by TDE values was found to be more pronounced at the anterior and septal sites of the mitral annulus (Table II).
7 Vol 44 No 3 TISSUE DOPPLER MYOCARDIAL PERFORMANCE INDEX 409 Figure 4. Correlation between MPI determined by TDE and conventional method in healthy subjects. MPI = Myocardial performance index; TDE = Tissue Doppler echocardiography. Figure 5. Correlation between IVRT determined by TDE and conventional method in healthy subjects. IVRT = Isovolumetric relaxation time; MPI = Myocardial performance index; TDE = Tissue Doppler echocardiography.
8 410 TEKTEN, ET AL Jpn Heart J May 2003 Figure 6. Correlation between IVCT determined by TDE and conventional method in healthy subjects. IVCT = Isovolumic contraction time; MPI = Myocardial performance index; TDE = Tissue Doppler echocardiography. Figure 7. Correlation between ET determined by TDE and conventional method in healthy subjects. ET = Ejection time; TDE = Tissue Doppler echocardiography.
9 Vol 44 No 3 TISSUE DOPPLER MYOCARDIAL PERFORMANCE INDEX 411 Figure 8. Correlation between MPI determined by TDE and conventional method in patients with MI. MPI = Myocardial performance index; TDE = Tissue Doppler echocardiography; MI = Myocardial infarction. Figure 9. Correlation between IVRT determined by TDE and conventional method in patients with MI. IVRT = Isovolumetric relaxation time; MPI = Myocardial performance index: TDE = Tissue Doppler echocardiography; MI = Myocardial infarction.
10 412 TEKTEN, ET AL Jpn Heart J May 2003 Figure 10. Correlation between IVCT determined by TDE and conventional method in patients with MI. IVCT = Isovolumetric contraction time; MPI = Myocardial performance index; MI = Myocardial infarction. Figure 11. Correlation between ET determined by TDE and ejection fraction in patients with MI. ET = Ejection time; MPI = Myocardial performance index; MI = Myocardial infarction.
11 Vol 44 No 3 TISSUE DOPPLER MYOCARDIAL PERFORMANCE INDEX 413 Figure 12. MPI determined by TDE at different sites of mitral annulus in healthy subjects and patients with anterior and inferior MI. MPI = Myocardial performance index; TDE = Tissue Doppler echocardiography; MI = Myocardial infarction. In patients with inferior MI, the rise in MPI by TDE values was found to be more pronounced at the inferior and septal sites of the mitral annulus (Table II) (Figure 12). Reproducibility: Intra- and interobserver variability for Doppler derived parameters (IVRT, IVCT, ET) ranged from 2.4% to 5.8%. Intraobserver variability for conventional MPI was 3.6 ± 2.8% while interobserver variability was 3.6 ± 2.1%. For the TDE measurements (IVRT, IVCT, ET), intra- and interobserver variability ranged from 2.6% to 5.5%. Intraobserver variability for MPI by TDE was 3.4 ± 2.6% and interobserver variability was 4.2 ± 1.6%. DISCUSSION In the present study, the Doppler intervals and MPI determined either by TDE or a conventional method were measured in age-matched healthy subjects, and the results were compared with those of patients with previous MI. To the best of our knowledge, this study was the first to use TDE in measuring MPI in patients with previous MI. MPI values obtained using either method were significantly higher in the patients with previous MI (Table I). The prolongation of IVCT and the shortening
12 414 TEKTEN, ET AL Jpn Heart J May 2003 of ET were the alterations in the time intervals that resulted in the increase in MPI values in patients with MI compared to the findings in the healthy age-matched subjects, which is consistent with the results of previous studies. 8,9) In order to evaluate the applicability of MPI by TDE in assessing LV function, we used four sites in the mitral annulus to measure tissue Doppler time intervals. Left ventricular contraction involves both a reduction of the short axis diameter and a shortening along the longitudinal axis of the chamber. 10,11) The longitudinal systolic shortening of the left ventricle is reflected by the motion of the mitral annulus toward the cardiac apex in systole, whereas its recoil away from the apex is the result of diastole. As there is no appreciable motion of the apex in relation to the imaging transducer, the magnitude of the mitral annular motion reflects the extent of myocardial shortening along its longitudinal axis. 11) Recording the mitral annular motion has the advantage that it is devoid of trabeculea, myocardial dropouts, etc, and therefore is independent of echo quality. The major advantage of pulsed-wave mitral annular velocity measurements is that the ultrasound beam is parallel to the LV contraction. Moreover, it probably measures the transmural myocardial velocity, not only the epicardial and endocardial velocities. The introduction of pulsed-wave TDE at different mitral annular sites of the left ventricle opens up a new possibility. Thus, the pulsed-wave TDE parameters may be used as an additional method that could increase the accuracy of echocardiographic LV studies. Although it continued to be statistically significant, the correlation between the two methods of measuring MPI, TDE and conventional, in patients with previous MI was not as high as it was in healthy individuals. This is due to the lesser degree of correlation between the IVRT and IVCT values (Figures 9 and 10). The presence of regional diastolic and systolic dysfunction might be the reason for less correlation in patients with previous MI. The goal of conventional MPI is to assess global LV function. If a single site is used for measurement, MPI by TDE is actually assessing LV function in that region. This may explain the higher MPI by TDE values in patients with previous MI who had LV wall motion abnormalities. In order to be able to assess global LV function, we used four sites in the mitral annulus for MPI by TDE measurements. Conventional MPI has been reported to be independent of heart rate and blood pressure. However, the inability to measure the interval between the end and onset of mitral inflow and the ejection time simultaneously is a major limitation of conventional MPI. Due to this limitation, the results are probably less reliable in the presence of physiologic heart rate changes during examination. The TDE used in this study can simultaneously record systolic and diastolic mitral annular velocities. In contrast to the pulsed Doppler method, the time interval between the end and onset of diastolic annular velocities and the duration of the
13 Vol 44 No 3 TISSUE DOPPLER MYOCARDIAL PERFORMANCE INDEX 415 systolic wave can be measured in the same cardiac cycle. Thus, MPI by TDE may reduce inaccuracy due to heart rate fluctuation and has practical advantages over the conventional MPI. The other possible disadvantage of conventional MPI is the effect of loading conditions on conventional MPI. Tei, et al 12) found a high correlation between conventional MPI and peak dp/dt, suggesting a relationship between MPI and preload. Thus, even when contractility is constant, significant changes in preload may cause significant alterations in conventional MPI. Measurement of MPI by TDE may not be altered by preload changes. Further studies are needed to confirm this hypothesis. Myocardial infarction is characterized by variable degrees of LV systolic and diastolic function, which have both been reported to have independent prognostic value. 13,14) A significant regional difference was found in the MPI at the LV sites related to the infarction site. Anterior MI patients had higher MPI values at the anterior site and septum than at other sites. The increased MPI by TDE values at the infarction site is an expression of myocardial damage after an MI. In inferior MI, the mean MPI values were not only increased at the inferior wall, but also at the interventricular septum (Table II). This may be the result of partial damage to the septum in the inferior MIs, as the posterior part of the septum is usually supplied by the right coronary artery. 15) The MPI at the noninfarction sites was also increased compared with healthy subjects (Table II). It is difficult to explain this phenomenon. We do not know whether the spirally oriented myocardial fiber, which causes the shortening of the left ventricle along its long axis, 16) might have some action beyond the infarction area. Limitations: This study analyses the usefulness of MPI determined by pulsedwave TDE by using the myocardial velocity along the long axis. No consideration was taken of contraction of the left ventricle along its short axis caused by circumferential fibers. Another limitation is that coronary and LV angiography were not performed to assess and localize the LV wall asynergy. However, infarction sites were determined by both ECG and 2D echocardiography. Conclusion: This study demonstrated that MPI can be measured by tissue Doppler and that it correlated well with conventional MPI. Moreover, MPI by TDE has the advantage of assessing both regional and global myocardial performance, and also has the ability to record systolic and diastolic velocity patterns simultaneously. REFERENCES 1. Appleton C, Hatle L, Popp R. Relation of transmitral flow velocity patterns to left ventricular diastolic function: new insight from a combined hemodynamic and Doppler echocardiographic study. J Am Coll Cardiol 1988; 12:
14 416 TEKTEN, ET AL Jpn Heart J May Galiuto L, Ignone G, DeMaria AN. Contraction and relaxation velocities of the normal left ventricle using pulsed-wave tissue Doppler echocardiography. Am J Cardiol 1998; 81: Yamazaki N, Mine Y, Sano A, et al. Analysis of ventricular wall motion using color-coded tissue Doppler imaging system. Jpn J Appl Physiol 1994; 33: Tei C, Ling LH, Hodge DO, et al. New index combined systolic and diastolic myocardial performance: a simple and reproducible measure of cardiac function: a study in normals and dilated cardiomyopathy. J Cardiol 1995; 26: Tei C. New non-invasive index for combined systolic and diastolic function. J Cardiol 1995; 26: Tei C, Dujardin KS, Hodge DO, Kyle RA, Tajic AJ, Seward BJ. Doppler index combining systolic and diastolic myocardial performance: clinical value in cardiac amyloidosis. J Am Coll Cardiol 1996; 28: Schiller NB, Shah PM, Crawford M, et al. Recommendations for quantitation of the left ventricle by twodimensional echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 1989; 2: Kurado T, Seward JB, Rumberger JA, Yanagi H, Tajik AJ. LV volume and mass: a comparative study of twodimensional echocardiography and ultrafast computed tomography. Echocardiography 1994; 11: Poulsen SH, Jensen SE, Tei C, Seward JB, Egstrup K. Value of Doppler index of performance in the early phase of acute myocardial infarction. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2000; 13: Rushmer RF. Cardiovascular Dynamics. 4th ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 1976: Lundback S. Cardiac pumping and the function of the ventricular septum. Acta Physiol Scand 1986; 550: Tei C, Nishimura AR, Seward JB, Tajik AJ. Noninvasive Doppler-derived myocardial performance index: Correlation with simultaneous measurements of cardiac catheterization measurements. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 1997; 10: White HD, Norris RM, Brown AM, Brandt PW, Whitlock RM, Wild CJ. LV end - systolic volume as the major determinant of survival after recovery from MI. Circulation 1987; 76: Pfeffer AM, Braunwald E, Moye LA, et al. Effect of captopril on mortality and morbidity in patients with LV dysfunction after MI: results of the Survival and Ventricular Enlargement Trial. N Engl J Med 1992; 327: Anatomy of the Heart. Schlant RC, Silverman ME, Robert WC. In Hurst JW, Schlant RC, editors. 7th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Book Company; 1990: Rushmer RF. Cardiovascular Dynamics. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 1968: 34-6.
Segmental Tissue Doppler Image-Derived Tei Index in Patients With Regional Wall Motion Abnormalities
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2010.40.3.114 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2010 The Korean Society of Cardiology Open Access Segmental Tissue Doppler Image-Derived Tei Index
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2010.40.3.114 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2010 The Korean Society of Cardiology Open Access Segmental Tissue Doppler Image-Derived Tei Index
i n d i a n h e a r t j o u r n a l 6 8 ( ) Available online at ScienceDirect
 i n d i a n h e a r t j o u r n a l 6 8 ( 2 0 1 6 ) 8 3 8 7 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ihj Original Article Myocardial Performance
i n d i a n h e a r t j o u r n a l 6 8 ( 2 0 1 6 ) 8 3 8 7 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ihj Original Article Myocardial Performance
Characteristics of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function in Patients with Systolic Heart Failure: A Doppler Tissue Imaging Study
 Characteristics of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function in Patients with Systolic Heart Failure: A Doppler Tissue Imaging Study Bassem A. Samad, MD, PhD, Jens M. Olson, MD, and Mahbubul Alam, MD, PhD, FESC,
Characteristics of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function in Patients with Systolic Heart Failure: A Doppler Tissue Imaging Study Bassem A. Samad, MD, PhD, Jens M. Olson, MD, and Mahbubul Alam, MD, PhD, FESC,
Quantitative Assessment of Fetal Ventricular Function:
 Reprinted with permission from ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY, Volume 18, No. 1, January 2001 Copyright 2001 by Futura Publishing Company, Inc., Armonk, NY 1004-0418 Quantitative Assessment of Fetal Ventricular Function:
Reprinted with permission from ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY, Volume 18, No. 1, January 2001 Copyright 2001 by Futura Publishing Company, Inc., Armonk, NY 1004-0418 Quantitative Assessment of Fetal Ventricular Function:
Carlos Eduardo Suaide Silva, Luiz Darcy Cortez Ferreira, Luciana Braz Peixoto, Claudia Gianini Monaco, Manuel Adán Gil, Juarez Ortiz
 Silva et al Original Article Arq Bras Cardiol Study of the Myocardial Contraction and Relaxation Velocities through Doppler Tissue Imaging Echocardiography. A New Alternative in the Assessment of the Segmental
Silva et al Original Article Arq Bras Cardiol Study of the Myocardial Contraction and Relaxation Velocities through Doppler Tissue Imaging Echocardiography. A New Alternative in the Assessment of the Segmental
좌심실수축기능평가 Cardiac Function
 Basic Echo Review Course 좌심실수축기능평가 Cardiac Function Seonghoon Choi Cardiology Hallym university LV systolic function Systolic function 좌심실수축기능 - 심근의수축으로심실에서혈액을대동맥으로박출하는기능 실제임상에서 LV function 의의미 1Diagnosis
Basic Echo Review Course 좌심실수축기능평가 Cardiac Function Seonghoon Choi Cardiology Hallym university LV systolic function Systolic function 좌심실수축기능 - 심근의수축으로심실에서혈액을대동맥으로박출하는기능 실제임상에서 LV function 의의미 1Diagnosis
Diastolic Function: What the Sonographer Needs to Know. Echocardiographic Assessment of Diastolic Function: Basic Concepts 2/8/2012
 Diastolic Function: What the Sonographer Needs to Know Pat Bailey, RDCS, FASE Technical Director Beaumont Health System Echocardiographic Assessment of Diastolic Function: Basic Concepts Practical Hints
Diastolic Function: What the Sonographer Needs to Know Pat Bailey, RDCS, FASE Technical Director Beaumont Health System Echocardiographic Assessment of Diastolic Function: Basic Concepts Practical Hints
Quantitation of right ventricular dimensions and function
 SCCS Basics of cardiac assessment Quantitation of right ventricular dimensions and function Tomasz Kukulski, MD PhD Dept of Cardiology, Congenital Heart Disease and Electrotherapy Silesian Medical University
SCCS Basics of cardiac assessment Quantitation of right ventricular dimensions and function Tomasz Kukulski, MD PhD Dept of Cardiology, Congenital Heart Disease and Electrotherapy Silesian Medical University
Hemodynamic Assessment. Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics
 Hemodynamic Assessment Matt M. Umland, RDCS, FASE Aurora Medical Group Milwaukee, WI Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics Stroke Volume Cardiac Output Cardiac Index Tei Index/Index of myocardial
Hemodynamic Assessment Matt M. Umland, RDCS, FASE Aurora Medical Group Milwaukee, WI Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics Stroke Volume Cardiac Output Cardiac Index Tei Index/Index of myocardial
LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION
 LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION Jamilah S AlRahimi Assistant Professor, KSU-HS Consultant Noninvasive Cardiology KFCC, MNGHA-WR Introduction LV function assessment in Heart Failure:
LV FUNCTION ASSESSMENT: WHAT IS BEYOND EJECTION FRACTION Jamilah S AlRahimi Assistant Professor, KSU-HS Consultant Noninvasive Cardiology KFCC, MNGHA-WR Introduction LV function assessment in Heart Failure:
Basic Approach to the Echocardiographic Evaluation of Ventricular Diastolic Function
 Basic Approach to the Echocardiographic Evaluation of Ventricular Diastolic Function J A F E R A L I, M D U N I V E R S I T Y H O S P I T A L S C A S E M E D I C A L C E N T E R S T A F F C A R D I O T
Basic Approach to the Echocardiographic Evaluation of Ventricular Diastolic Function J A F E R A L I, M D U N I V E R S I T Y H O S P I T A L S C A S E M E D I C A L C E N T E R S T A F F C A R D I O T
Prognostic Value of Left Ventricular Myocardial Performance Index in Patients Undergoing Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery
 Arch Iranian Med 2008; 11 (5): 497 501 Original Article Prognostic Value of Left Ventricular Myocardial Performance Index in Patients Undergoing Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery Daryoosh Javidi MD
Arch Iranian Med 2008; 11 (5): 497 501 Original Article Prognostic Value of Left Ventricular Myocardial Performance Index in Patients Undergoing Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery Daryoosh Javidi MD
Incorporating the New Echo Guidelines Into Everyday Practice
 Incorporating the New Echo Guidelines Into Everyday Practice Clinical Case RIGHT VENTRICULAR FAILURE Gustavo Restrepo MD President Elect Interamerican Society of Cardiology Director Fellowship Training
Incorporating the New Echo Guidelines Into Everyday Practice Clinical Case RIGHT VENTRICULAR FAILURE Gustavo Restrepo MD President Elect Interamerican Society of Cardiology Director Fellowship Training
Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease
 Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease L. Youngmin Eun, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, Kwandong University College of Medicine The potential advantage of ultrasound
Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease L. Youngmin Eun, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, Kwandong University College of Medicine The potential advantage of ultrasound
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 36, No. 6, by the American College of Cardiology ISSN /00/$20.
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 36, No. 6, 2000 2000 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/00/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(00)00965-7 Pseudonormal
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 36, No. 6, 2000 2000 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/00/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(00)00965-7 Pseudonormal
Noninvasive assessment of left ventricular (LV)
 Comparative Value of Tissue Doppler Imaging and M-Mode Color Doppler Mitral Flow Propagation Velocity for the Evaluation of Left Ventricular Filling Pressure* Michal Kidawa, MD; Lisa Coignard, MD; Gérard
Comparative Value of Tissue Doppler Imaging and M-Mode Color Doppler Mitral Flow Propagation Velocity for the Evaluation of Left Ventricular Filling Pressure* Michal Kidawa, MD; Lisa Coignard, MD; Gérard
THE PHARMA INNOVATION - JOURNAL Tei Index: Assessment of the Myocardial Function of the Left Ventricle in Case of Acute Myocardial Infarction
 Received: 16-06-2013 Accepted: 13-07-2013 ISSN: 2277-7695 CODEN Code: PIHNBQ ZDB-Number: 2663038-2 IC Journal No: 7725 Vol. 2 No. 6 2013 Online Available at www.thepharmajournal.com THE PHARMA INNOVATION
Received: 16-06-2013 Accepted: 13-07-2013 ISSN: 2277-7695 CODEN Code: PIHNBQ ZDB-Number: 2663038-2 IC Journal No: 7725 Vol. 2 No. 6 2013 Online Available at www.thepharmajournal.com THE PHARMA INNOVATION
Echocardiographic and Doppler Assessment of Cardiac Functions in Patients of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE JIACM 2002; 3(2): 164-8 Echocardiographic and Doppler Assessment of Cardiac Functions in Patients of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Rajesh Rajput*, Jagdish**, SB Siwach***, A
ORIGINAL ARTICLE JIACM 2002; 3(2): 164-8 Echocardiographic and Doppler Assessment of Cardiac Functions in Patients of Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Rajesh Rajput*, Jagdish**, SB Siwach***, A
Diastolic filling in hypertrophied hearts of elite runners: an Echo-Doppler study
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2001; 5: 65-69 Diastolic filling in hypertrophied hearts of elite runners: an Echo-Doppler study A. PALAZZUOLI, L. PUCCETTI, F. BRUNI, A.L. PASQUI,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2001; 5: 65-69 Diastolic filling in hypertrophied hearts of elite runners: an Echo-Doppler study A. PALAZZUOLI, L. PUCCETTI, F. BRUNI, A.L. PASQUI,
10/7/2013. Systolic Function How to Measure, How Accurate is Echo, Role of Contrast. Thanks to our Course Director: Neil J.
 Systolic Function How to Measure, How Accurate is Echo, Role of Contrast Neil J. Weissman, MD MedStar Health Research Institute & Professor of Medicine Georgetown University Washington, D.C. No Disclosures
Systolic Function How to Measure, How Accurate is Echo, Role of Contrast Neil J. Weissman, MD MedStar Health Research Institute & Professor of Medicine Georgetown University Washington, D.C. No Disclosures
Jong-Won Ha*, Jeong-Ah Ahn, Jae-Yun Moon, Hye-Sun Suh, Seok-Min Kang, Se-Joong Rim, Yangsoo Jang, Namsik Chung, Won-Heum Shim, Seung-Yun Cho
 Eur J Echocardiography (2006) 7, 16e21 CLINICAL/ORIGINAL PAPERS Triphasic mitral inflow velocity with mid-diastolic flow: The presence of mid-diastolic mitral annular velocity indicates advanced diastolic
Eur J Echocardiography (2006) 7, 16e21 CLINICAL/ORIGINAL PAPERS Triphasic mitral inflow velocity with mid-diastolic flow: The presence of mid-diastolic mitral annular velocity indicates advanced diastolic
Assessment of LV systolic function
 Tutorial 5 - Assessment of LV systolic function Assessment of LV systolic function A knowledge of the LV systolic function is crucial in the undertanding of and management of unstable hemodynamics or a
Tutorial 5 - Assessment of LV systolic function Assessment of LV systolic function A knowledge of the LV systolic function is crucial in the undertanding of and management of unstable hemodynamics or a
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS
 Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
RIGHT VENTRICULAR SIZE AND FUNCTION
 RIGHT VENTRICULAR SIZE AND FUNCTION Edwin S. Tucay, MD, FPCC, FPCC, FPSE Philippine Society of Echocardiography Quezon City, Philippines Echo Mission, BRTTH, Legaspi City, July 1-2, 2016 NO DISCLOSURE
RIGHT VENTRICULAR SIZE AND FUNCTION Edwin S. Tucay, MD, FPCC, FPCC, FPSE Philippine Society of Echocardiography Quezon City, Philippines Echo Mission, BRTTH, Legaspi City, July 1-2, 2016 NO DISCLOSURE
The impact of hypertension on systolic and diastolic left ventricular function. A tissue Doppler echocardiographic study
 The impact of hypertension on systolic and diastolic left ventricular function. A tissue Doppler echocardiographic study Manolis Bountioukos, MD, PhD, a Arend F.L. Schinkel, MD, PhD, a Jeroen J. Bax, MD,
The impact of hypertension on systolic and diastolic left ventricular function. A tissue Doppler echocardiographic study Manolis Bountioukos, MD, PhD, a Arend F.L. Schinkel, MD, PhD, a Jeroen J. Bax, MD,
Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension
 ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
Objectives. Diastology: What the Radiologist Needs to Know. LV Diastolic Function: Introduction. LV Diastolic Function: Introduction
 Objectives Diastology: What the Radiologist Needs to Know. Jacobo Kirsch, MD Cardiopulmonary Imaging, Section Head Division of Radiology Cleveland Clinic Florida Weston, FL To review the physiology and
Objectives Diastology: What the Radiologist Needs to Know. Jacobo Kirsch, MD Cardiopulmonary Imaging, Section Head Division of Radiology Cleveland Clinic Florida Weston, FL To review the physiology and
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) of cats is the
 J Vet Intern Med 2006;20:65 77 Pulsed Tissue Doppler Imaging in Normal Cats and Cats with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy H. Koffas, J. Dukes-McEwan, B.M. Corcoran, C.M. Moran, A. French, V. Sboros, K. Simpson,
J Vet Intern Med 2006;20:65 77 Pulsed Tissue Doppler Imaging in Normal Cats and Cats with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy H. Koffas, J. Dukes-McEwan, B.M. Corcoran, C.M. Moran, A. French, V. Sboros, K. Simpson,
Chamber Quantitation Guidelines - Update II
 Chamber Quantitation Guidelines - Update II Right Heart Measurements Steven A. Goldstein MD FACC FASE Professor of Medicine Georgetown University Medical Center MedStar Heart Institute Washington Hospital
Chamber Quantitation Guidelines - Update II Right Heart Measurements Steven A. Goldstein MD FACC FASE Professor of Medicine Georgetown University Medical Center MedStar Heart Institute Washington Hospital
Evaluation of Systolic Function of the Left Ventricle
 Evaluation of Systolic Function of the Left Ventricle Roxy Senior MD DM FRCP FESC FACC and Vinay Kumar Bhatia PhD MRCP Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Northwick Park Hospital and Institute for Medical
Evaluation of Systolic Function of the Left Ventricle Roxy Senior MD DM FRCP FESC FACC and Vinay Kumar Bhatia PhD MRCP Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Northwick Park Hospital and Institute for Medical
Left atrial function. Aliakbar Arvandi MD
 In the clinic Left atrial function Abstract The left atrium (LA) is a left posterior cardiac chamber which is located adjacent to the esophagus. It is separated from the right atrium by the inter-atrial
In the clinic Left atrial function Abstract The left atrium (LA) is a left posterior cardiac chamber which is located adjacent to the esophagus. It is separated from the right atrium by the inter-atrial
Stephen Glen ISCHAEMIC HEART DISEASE AND LEFT VENTRICULAR FUNCTION
 Stephen Glen ISCHAEMIC HEART DISEASE AND LEFT VENTRICULAR FUNCTION Overview Coronary arteries Terminology to describe contractility Measuring ventricular function Systolic dysfunction Practice cases- LV
Stephen Glen ISCHAEMIC HEART DISEASE AND LEFT VENTRICULAR FUNCTION Overview Coronary arteries Terminology to describe contractility Measuring ventricular function Systolic dysfunction Practice cases- LV
Echo-Doppler evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function. Michel Slama Amiens France
 Echo-Doppler evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function Michel Slama Amiens France Left ventricular pressure Pressure A wave [ LVEDP LVEDP préa Congestive cardiac failure with preserved systolic
Echo-Doppler evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function Michel Slama Amiens France Left ventricular pressure Pressure A wave [ LVEDP LVEDP préa Congestive cardiac failure with preserved systolic
Evaluation of Tissue Doppler Echocardiographic Imaging findings in children with pulmonary hypertension
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2017; 59: 244-253 DOI: 10.24953/turkjped.2017.03.003 Original Evaluation of Tissue Doppler Echocardiographic Imaging findings in children with pulmonary hypertension Alper
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2017; 59: 244-253 DOI: 10.24953/turkjped.2017.03.003 Original Evaluation of Tissue Doppler Echocardiographic Imaging findings in children with pulmonary hypertension Alper
Global left ventricular circumferential strain is a marker for both systolic and diastolic myocardial function
 Global left ventricular circumferential strain is a marker for both systolic and diastolic myocardial function Toshinari Onishi 1, Samir K. Saha 2, Daniel Ludwig 1, Erik B. Schelbert 1, David Schwartzman
Global left ventricular circumferential strain is a marker for both systolic and diastolic myocardial function Toshinari Onishi 1, Samir K. Saha 2, Daniel Ludwig 1, Erik B. Schelbert 1, David Schwartzman
Echocardiographic Evaluation of Mitral Annulus Excursion in Normal Horses
 Echocardiographic Evaluation of Mitral Annulus Excursion in Normal Horses Carlos Lightowler, DVM a Giuseppe Piccione, DVM b Maria Laura Cattaneo, DSS c Elisabetta Giudice, DVM, PhD d a Departamento de
Echocardiographic Evaluation of Mitral Annulus Excursion in Normal Horses Carlos Lightowler, DVM a Giuseppe Piccione, DVM b Maria Laura Cattaneo, DSS c Elisabetta Giudice, DVM, PhD d a Departamento de
Introduction. In Jeong Cho, MD, Wook Bum Pyun, MD and Gil Ja Shin, MD ABSTRACT
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2009.39.4.145 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2009 The Korean Society of Cardiology The Influence of the Left Ventricular Geometry on the Left
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2009.39.4.145 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2009 The Korean Society of Cardiology The Influence of the Left Ventricular Geometry on the Left
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW
 PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
Velocity, strain and strain rate: Doppler and Non-Doppler methods. Thoraxcentre, Erasmus MC,Rotterdam
 Velocity, strain and strain rate: Doppler and Non-Doppler methods J Roelandt J. Roelandt Thoraxcentre, Erasmus MC,Rotterdam Basics of tissue Doppler imaging Instantaneous annular velocity profiles IVCT
Velocity, strain and strain rate: Doppler and Non-Doppler methods J Roelandt J. Roelandt Thoraxcentre, Erasmus MC,Rotterdam Basics of tissue Doppler imaging Instantaneous annular velocity profiles IVCT
in systemic hypertension, in absence of mitral valve disease. LV diastolic dysfunction Ejection fraction%.
 http://dx.doi.org/10.4250/jcu.2012.20.1.25 pissn 1975-4612/ eissn 2005-9655 Copyright 2012 Korean Society of Echocardiography www.kse-jcu.org ORIGINAL ARTICLE J Cardiovasc Ultrasound 2012;20(1):25-29 Left
http://dx.doi.org/10.4250/jcu.2012.20.1.25 pissn 1975-4612/ eissn 2005-9655 Copyright 2012 Korean Society of Echocardiography www.kse-jcu.org ORIGINAL ARTICLE J Cardiovasc Ultrasound 2012;20(1):25-29 Left
The Use of Left Ventricular Myocardial Stiffness Index as a Predictor of Myocardial Performance in Patients with Systemic Hypertension
 International Journal of Medical Physics, Clinical Engineering and Radiation Oncology, 2014, 3, 167-175 Published Online August 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijmpcero http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ijmpcero.2014.33022
International Journal of Medical Physics, Clinical Engineering and Radiation Oncology, 2014, 3, 167-175 Published Online August 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijmpcero http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ijmpcero.2014.33022
Ιπποκράτειες μέρες καρδιολογίας Θεσσαλονίκη, 9-10 Μαρτίου Φωτεινή Α. Λαζαρίδου Επιμελήτρια Α Γενικό Νοσοκομείο Αγιος Παύλος, Θεσσαλονίκη
 Ιπποκράτειες μέρες καρδιολογίας Θεσσαλονίκη, 9-10 Μαρτίου 2018 Φωτεινή Α. Λαζαρίδου Επιμελήτρια Α Γενικό Νοσοκομείο Αγιος Παύλος, Θεσσαλονίκη RV shape Triangular shape in frontal plane crescent shape in
Ιπποκράτειες μέρες καρδιολογίας Θεσσαλονίκη, 9-10 Μαρτίου 2018 Φωτεινή Α. Λαζαρίδου Επιμελήτρια Α Γενικό Νοσοκομείο Αγιος Παύλος, Θεσσαλονίκη RV shape Triangular shape in frontal plane crescent shape in
Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea
 Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea Jahrestagung Schweizerische Gesellschaft für /Schweizerische Gesellschaft für Pneumologie B. Kaufmann 16.06.2016 Chronic dyspnea Shortness of breath lasting
Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea Jahrestagung Schweizerische Gesellschaft für /Schweizerische Gesellschaft für Pneumologie B. Kaufmann 16.06.2016 Chronic dyspnea Shortness of breath lasting
Tissue Doppler Imaging
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS Hesham Rashid* Tissue Doppler Imaging CARDIOLOGY Editorial Department of Cardiology, Benha University, Egypt *Corresponding Author: Hesham Rashid, Department of Cardiology, Benha University,
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS Hesham Rashid* Tissue Doppler Imaging CARDIOLOGY Editorial Department of Cardiology, Benha University, Egypt *Corresponding Author: Hesham Rashid, Department of Cardiology, Benha University,
The Patient with Atrial Fibrilation
 Assessment of Diastolic Function The Patient with Atrial Fibrilation Assoc. Prof. Adriana Ilieşiu, FESC University of Medicine Carol Davila Bucharest, Romania Associated Conditions with Atrial Fibrillation
Assessment of Diastolic Function The Patient with Atrial Fibrilation Assoc. Prof. Adriana Ilieşiu, FESC University of Medicine Carol Davila Bucharest, Romania Associated Conditions with Atrial Fibrillation
THE PATHOGENESIS OF ACUTE PULMONARY EDEMA ASSOCIATED WITH HYPERTENSION THE PATHOGENESIS OF ACUTE PULMONARY EDEMA ASSOCIATED WITH HYPERTENSION
 THE PATHOGENESIS OF ACUTE PULMONARY EDEMA ASSOCIATED WITH HYPERTENSION THE PATHOGENESIS OF ACUTE PULMONARY EDEMA ASSOCIATED WITH HYPERTENSION SANJAY K. GANDHI, M.D., JOHN C. POWERS, M.D., ABDEL-MOHSEN
THE PATHOGENESIS OF ACUTE PULMONARY EDEMA ASSOCIATED WITH HYPERTENSION THE PATHOGENESIS OF ACUTE PULMONARY EDEMA ASSOCIATED WITH HYPERTENSION SANJAY K. GANDHI, M.D., JOHN C. POWERS, M.D., ABDEL-MOHSEN
PRELIMINARY STUDIES OF LEFT VENTRICULAR WALL THICKNESS AND MASS OF NORMOTENSIVE AND HYPERTENSIVE SUBJECTS USING M-MODE ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY
 Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 9, No. 1, January 22 (28-33) ORIGINAL ARTICLE PRELIMINARY STUDIES OF LEFT VENTRICULAR WALL THICKNESS AND MASS OF NORMOTENSIVE AND HYPERTENSIVE SUBJECTS USING
Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 9, No. 1, January 22 (28-33) ORIGINAL ARTICLE PRELIMINARY STUDIES OF LEFT VENTRICULAR WALL THICKNESS AND MASS OF NORMOTENSIVE AND HYPERTENSIVE SUBJECTS USING
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1
 Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 PERICARDIAL DISEASE The pericardial effusion ends anteriorly to the descending aorta and is best visualised in the PLAX. PSAX is actually very useful sometimes for looking at posterior
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 PERICARDIAL DISEASE The pericardial effusion ends anteriorly to the descending aorta and is best visualised in the PLAX. PSAX is actually very useful sometimes for looking at posterior
Little is known about the degree and time course of
 Differential Changes in Regional Right Ventricular Function Before and After a Bilateral Lung Transplantation: An Ultrasonic Strain and Strain Rate Study Virginija Dambrauskaite, MD, Lieven Herbots, MD,
Differential Changes in Regional Right Ventricular Function Before and After a Bilateral Lung Transplantation: An Ultrasonic Strain and Strain Rate Study Virginija Dambrauskaite, MD, Lieven Herbots, MD,
Recently proposed Tei index, 1 defined as the sum
 Effects of Valve Dysfunction on Doppler Tei Index Amdadul Haque, MBBS, Yutaka Otsuji, MD, Shiro Yoshifuku, MD, Toshiro Kumanohoso, MD, Hui Zhang, MD, Akira Kisanuki, MD, Shinichi Minagoe, MD, Ryuzo Sakata,
Effects of Valve Dysfunction on Doppler Tei Index Amdadul Haque, MBBS, Yutaka Otsuji, MD, Shiro Yoshifuku, MD, Toshiro Kumanohoso, MD, Hui Zhang, MD, Akira Kisanuki, MD, Shinichi Minagoe, MD, Ryuzo Sakata,
Basic Assessment of Left Ventricular Systolic Function
 WINFOCUS BASIC ECHO (WBE) Basic Assessment of Left Ventricular Systolic Function Ritesh Dhar, MD Director, Echocardiography Lab and Staff Cardiologist Intermountain Medical Center Murray, Utah Outline
WINFOCUS BASIC ECHO (WBE) Basic Assessment of Left Ventricular Systolic Function Ritesh Dhar, MD Director, Echocardiography Lab and Staff Cardiologist Intermountain Medical Center Murray, Utah Outline
TZU CHI MED J March 2009 Vol 21 No 1
 TZU CHI MED J March 2009 Vol 21 No 1 available at http://ajws.elsevier.com/tcmj Tzu Chi Medical Journal Original Article Ratio of Peak Early to Late Diastolic Filling Velocity of Transmitral Flow is Predictive
TZU CHI MED J March 2009 Vol 21 No 1 available at http://ajws.elsevier.com/tcmj Tzu Chi Medical Journal Original Article Ratio of Peak Early to Late Diastolic Filling Velocity of Transmitral Flow is Predictive
Mechanisms of heart failure with normal EF Arterial stiffness and ventricular-arterial coupling. What is the pathophysiology at presentation?
 Mechanisms of heart failure with normal EF Arterial stiffness and ventricular-arterial coupling What is the pathophysiology at presentation? Ventricular-arterial coupling elastance Central arterial pressure
Mechanisms of heart failure with normal EF Arterial stiffness and ventricular-arterial coupling What is the pathophysiology at presentation? Ventricular-arterial coupling elastance Central arterial pressure
Left Ventricular Dyssynchrony in Patients Showing Diastolic Dysfunction without Overt Symptoms of Heart Failure
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2010.25.3.246 Left Ventricular Dyssynchrony in Patients Showing Diastolic Dysfunction without Overt Symptoms of Heart Failure Jae Hoon Kim, Hee Sang Jang, Byung Seok
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2010.25.3.246 Left Ventricular Dyssynchrony in Patients Showing Diastolic Dysfunction without Overt Symptoms of Heart Failure Jae Hoon Kim, Hee Sang Jang, Byung Seok
The importance of left atrium in LV diastolic function
 II Baltic Heart Failure Meeting and Congress of Latvian Society of Cardiology The importance of left atrium in LV diastolic function Dr. Artem Kalinin Eastern Clinical University Hospital Riga 30.09.2010.
II Baltic Heart Failure Meeting and Congress of Latvian Society of Cardiology The importance of left atrium in LV diastolic function Dr. Artem Kalinin Eastern Clinical University Hospital Riga 30.09.2010.
Doppler-echocardiographic findings in a patient with persisting right ventricular sinusoids
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 1990 Doppler-echocardiographic findings in a patient with persisting right
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 1990 Doppler-echocardiographic findings in a patient with persisting right
Right Heart Evaluation ASE Guidelines Review. Chris Mann RDCS, RCS, FASE Faculty, Echocardiography Pitt Community College Greenville, NC
 Right Heart Evaluation ASE Guidelines Review Chris Mann RDCS, RCS, FASE Faculty, Echocardiography Pitt Community College Greenville, NC Objectives Briefly review right atrial and right ventricular anatomy
Right Heart Evaluation ASE Guidelines Review Chris Mann RDCS, RCS, FASE Faculty, Echocardiography Pitt Community College Greenville, NC Objectives Briefly review right atrial and right ventricular anatomy
Tilburg University. Published in: American Heart Journal. Document version: Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record. Publication date: 2007
 Tilburg University Improvement in diastolic function and left ventricular filling pressure induced by cardiac resynchronization therapy Jansen, A.H.M.; van Dantzig, J.M.; Bracke, F.; Peels, K.H.; Koolen,
Tilburg University Improvement in diastolic function and left ventricular filling pressure induced by cardiac resynchronization therapy Jansen, A.H.M.; van Dantzig, J.M.; Bracke, F.; Peels, K.H.; Koolen,
OPTIMIZING ECHO ACQUISTION FOR STRAIN AND DIASTOLOGY
 OPTIMIZING ECHO ACQUISTION FOR STRAIN AND DIASTOLOGY October 8, 2017 Deborah Agler, ACS, RDCS, FASE Coordinator of Education and Training Cleveland Clinic General Principles Diastology Clinical Data Heart
OPTIMIZING ECHO ACQUISTION FOR STRAIN AND DIASTOLOGY October 8, 2017 Deborah Agler, ACS, RDCS, FASE Coordinator of Education and Training Cleveland Clinic General Principles Diastology Clinical Data Heart
Clinical Investigations
 Clinical Investigations The Effect of Pulmonary Hypertension on Left Ventricular Diastolic Function in Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease: A Tissue Doppler Imaging and Right Cardiac Catheterization Study
Clinical Investigations The Effect of Pulmonary Hypertension on Left Ventricular Diastolic Function in Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease: A Tissue Doppler Imaging and Right Cardiac Catheterization Study
Aortic stenosis (AS) is common with the aging population.
 New Insights Into the Progression of Aortic Stenosis Implications for Secondary Prevention Sanjeev Palta, MD; Anita M. Pai, MD; Kanwaljit S. Gill, MD; Ramdas G. Pai, MD Background The risk factors affecting
New Insights Into the Progression of Aortic Stenosis Implications for Secondary Prevention Sanjeev Palta, MD; Anita M. Pai, MD; Kanwaljit S. Gill, MD; Ramdas G. Pai, MD Background The risk factors affecting
Index of subjects. effect on ventricular tachycardia 30 treatment with 101, 116 boosterpump 80 Brockenbrough phenomenon 55, 125
 145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
British Society of Echocardiography
 British Society of Echocardiography Affiliated to the British Cardiac Society A Minimum Dataset for a Standard Adult Transthoracic Echocardiogram From the British Society of Echocardiography Education
British Society of Echocardiography Affiliated to the British Cardiac Society A Minimum Dataset for a Standard Adult Transthoracic Echocardiogram From the British Society of Echocardiography Education
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING
 PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
Diastolic Function Overview
 Diastolic Function Overview Richard Palma BS, RDCS, RCS, APS, FASE Director and Clinical Coordinator The Hoffman Heart and Vascular Institute School of Cardiac Ultrasound None Disclosures Learning Objectives
Diastolic Function Overview Richard Palma BS, RDCS, RCS, APS, FASE Director and Clinical Coordinator The Hoffman Heart and Vascular Institute School of Cardiac Ultrasound None Disclosures Learning Objectives
The Fontan circulation. Folkert Meijboom
 The Fontan circulation Folkert Meijboom What to expect? Why a Fontan-circulation Indications How does it work Types of Fontan circulation Historical overview Role of echocardiography What to expect? Why
The Fontan circulation Folkert Meijboom What to expect? Why a Fontan-circulation Indications How does it work Types of Fontan circulation Historical overview Role of echocardiography What to expect? Why
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 41, No. 1, by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN /03/$30.
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 41, No. 1, 2003 2003 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/03/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(02)02665-7
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 41, No. 1, 2003 2003 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/03/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(02)02665-7
M. Hajahmadi Poorrafsanjani 1 & B. Rahimi Darabad 1
 Global Journal of Health Science; Vol. 6, No. 7; 2014 ISSN 1916-9736 E-ISSN 1916-9744 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Evaluate the Sensitivity and Specificity Echocardiography in
Global Journal of Health Science; Vol. 6, No. 7; 2014 ISSN 1916-9736 E-ISSN 1916-9744 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Evaluate the Sensitivity and Specificity Echocardiography in
Index. K Knobology, TTE artifact, image resolution, ultrasound, 14
 A Acute aortic regurgitation (AR), 124 128 Acute aortic syndrome (AAS) classic aortic dissection diagnosis, 251 263 evolutive patterns, 253 255 pathology, 250 251 classifications, 247 248 incomplete aortic
A Acute aortic regurgitation (AR), 124 128 Acute aortic syndrome (AAS) classic aortic dissection diagnosis, 251 263 evolutive patterns, 253 255 pathology, 250 251 classifications, 247 248 incomplete aortic
Steffan Sernich, MD,* Noe Carrasquero, MD,* Carl J. Lavie, MD, ** Richard Chambers, MSPH, ** Marie McGettigan, MD **
 Noninvasive Assessment of the Right and Left Ventricular Function in Neonates with Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia with Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension Before and After Surgical Repair Steffan Sernich,
Noninvasive Assessment of the Right and Left Ventricular Function in Neonates with Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia with Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension Before and After Surgical Repair Steffan Sernich,
Cardiac Chamber Quantification by Echocardiography
 Cardiac Chamber Quantification by Echocardiography Maryam Bokhamseen, RCS, RCDS, EACVI Echotechnologist ǁ, Non invasive Cardiac Laboratory King Abdulaziz Cardiac Center. Outline: Introduction. Background
Cardiac Chamber Quantification by Echocardiography Maryam Bokhamseen, RCS, RCDS, EACVI Echotechnologist ǁ, Non invasive Cardiac Laboratory King Abdulaziz Cardiac Center. Outline: Introduction. Background
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Echo assessment of the failing heart
 Echo assessment of the failing heart Mark K. Friedberg, MD The Labatt Family Heart Center The Hospital for Sick Children Toronto, Ontario, Canada Cardiac function- definitions Cardiovascular function:
Echo assessment of the failing heart Mark K. Friedberg, MD The Labatt Family Heart Center The Hospital for Sick Children Toronto, Ontario, Canada Cardiac function- definitions Cardiovascular function:
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging. Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE
 Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None a. Turn the wall filters on and turn down the receiver gain. b. Turn
Tissue Doppler and Strain Imaging Steven J. Lester MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None a. Turn the wall filters on and turn down the receiver gain. b. Turn
The Impact of Autonomic Neuropathy on Left Ventricular Function in Normotensive Type 1 Diabetic Patients: a Tissue Doppler Echocardiographic Study
 Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online November 13, 2007 The Impact of Autonomic Neuropathy on Left Ventricular Function in Normotensive Type 1 Diabetic Patients: a Tissue Doppler Echocardiographic
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online November 13, 2007 The Impact of Autonomic Neuropathy on Left Ventricular Function in Normotensive Type 1 Diabetic Patients: a Tissue Doppler Echocardiographic
EVALUATION OF LEFT VENTRICLE DIASTOLIC FUNCTION IN NATIVE HYPERTENSIVE PATIENTS.
 EVALUATION OF LEFT VENTRICLE DIASTOLIC FUNCTION IN NATIVE HYPERTENSIVE PATIENTS. Cardiovascular Medicine Department, Cairo University ABSTRACT Background: Systemic hypertension is a common cause of left
EVALUATION OF LEFT VENTRICLE DIASTOLIC FUNCTION IN NATIVE HYPERTENSIVE PATIENTS. Cardiovascular Medicine Department, Cairo University ABSTRACT Background: Systemic hypertension is a common cause of left
Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) is an
 Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Acutely Improves Diastolic Function Alan D. Waggoner, MHS, Mitchell N. Faddis, MD, PhD, Marye J. Gleva, MD, Lisa de Las Fuentes, MD, Judy Osborn, RN, Sharon Heuerman,
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Acutely Improves Diastolic Function Alan D. Waggoner, MHS, Mitchell N. Faddis, MD, PhD, Marye J. Gleva, MD, Lisa de Las Fuentes, MD, Judy Osborn, RN, Sharon Heuerman,
DOI: /j x
 DOI: 10.1111/j.1540-8175.2010.01149.x C 2010, Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Comparison of Left Ventricular Contractility in Pressure and Volume Overload: A Strain Rate Study in the Clinical Model of Aortic Stenosis
DOI: 10.1111/j.1540-8175.2010.01149.x C 2010, Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Comparison of Left Ventricular Contractility in Pressure and Volume Overload: A Strain Rate Study in the Clinical Model of Aortic Stenosis
A classic case of amyloid cardiomyopathy
 Images in... A classic case of amyloid cardiomyopathy Hayan Jouni, 1 William G Morice, 2 S Vincent Rajkumar, 3 Joerg Herrmann 4 1 Department of Internal Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA
Images in... A classic case of amyloid cardiomyopathy Hayan Jouni, 1 William G Morice, 2 S Vincent Rajkumar, 3 Joerg Herrmann 4 1 Department of Internal Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA
Left ventricular diastolic function and filling pressure in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy
 Left ventricular diastolic function and filling pressure in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy Bogdan A. Popescu University of Medicine and Pharmacy Bucharest, Romania My conflicts of interest: I have
Left ventricular diastolic function and filling pressure in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy Bogdan A. Popescu University of Medicine and Pharmacy Bucharest, Romania My conflicts of interest: I have
MITRAL STENOSIS. Joanne Cusack
 MITRAL STENOSIS Joanne Cusack BSE Breakdown Recognition of rheumatic mitral stenosis Qualitative description of valve and sub-valve calcification and fibrosis Measurement of orifice area by planimetry
MITRAL STENOSIS Joanne Cusack BSE Breakdown Recognition of rheumatic mitral stenosis Qualitative description of valve and sub-valve calcification and fibrosis Measurement of orifice area by planimetry
Diastology State of The Art Assessment
 Diastology State of The Art Assessment Dr. Mohammad AlGhamdi Assistant professor, KSAU-HS Consultant Cardiologist King AbdulAziz Cardiac Center Ministry of National Guard Health Affairs Diagnostic Clinical
Diastology State of The Art Assessment Dr. Mohammad AlGhamdi Assistant professor, KSAU-HS Consultant Cardiologist King AbdulAziz Cardiac Center Ministry of National Guard Health Affairs Diagnostic Clinical
NEW GUIDELINES. A Guideline Protocol for the Echocardiographic assessment of Diastolic Dysfunction
 NEW GUIDELINES A Guideline Protocol for the Echocardiographic assessment of Diastolic Dysfunction Echocardiography plays a central role in the non-invasive evaluation of diastole and should be interpreted
NEW GUIDELINES A Guideline Protocol for the Echocardiographic assessment of Diastolic Dysfunction Echocardiography plays a central role in the non-invasive evaluation of diastole and should be interpreted
Diastolic Functions: Evaluation & Clinical Applications
 Special Articles Diastolic Functions: Evaluation & Clinical Applications Senior Consultant Cardiologist, Metro Heart Institute, Delhi Immediate Past President, Cardiological Society of India (Cardiovasc.
Special Articles Diastolic Functions: Evaluation & Clinical Applications Senior Consultant Cardiologist, Metro Heart Institute, Delhi Immediate Past President, Cardiological Society of India (Cardiovasc.
L ecocardiografia nello Scompenso Cardiaco Acuto e cronico: vecchi dogmi e nuovi trends.
 V SESSIONE SCOMPENSO CARDIACO 2015 Genova, 13-14 Novembre 2015 L ecocardiografia nello Scompenso Cardiaco Acuto e cronico: vecchi dogmi e nuovi trends. Gian Paolo Bezante, MD, FACC UOC Clinica di Malattie
V SESSIONE SCOMPENSO CARDIACO 2015 Genova, 13-14 Novembre 2015 L ecocardiografia nello Scompenso Cardiaco Acuto e cronico: vecchi dogmi e nuovi trends. Gian Paolo Bezante, MD, FACC UOC Clinica di Malattie
Pathophysiology and Current Evidence for Detection of Dyssynchrony
 Editorial Cardiol Res. 2017;8(5):179-183 Pathophysiology and Current Evidence for Detection of Dyssynchrony Michael Spartalis a, d, Eleni Tzatzaki a, Eleftherios Spartalis b, Christos Damaskos b, Antonios
Editorial Cardiol Res. 2017;8(5):179-183 Pathophysiology and Current Evidence for Detection of Dyssynchrony Michael Spartalis a, d, Eleni Tzatzaki a, Eleftherios Spartalis b, Christos Damaskos b, Antonios
LV geometric and functional changes in VHD: How to assess? Mi-Seung Shin M.D., Ph.D. Gachon University Gil Hospital
 LV geometric and functional changes in VHD: How to assess? Mi-Seung Shin M.D., Ph.D. Gachon University Gil Hospital LV inflow across MV LV LV outflow across AV LV LV geometric changes Pressure overload
LV geometric and functional changes in VHD: How to assess? Mi-Seung Shin M.D., Ph.D. Gachon University Gil Hospital LV inflow across MV LV LV outflow across AV LV LV geometric changes Pressure overload
Introduction. Cardiac Imaging Modalities MRI. Overview. MRI (Continued) MRI (Continued) Arnaud Bistoquet 12/19/03
 Introduction Cardiac Imaging Modalities Arnaud Bistoquet 12/19/03 Coronary heart disease: the vessels that supply oxygen-carrying blood to the heart, become narrowed and unable to carry a normal amount
Introduction Cardiac Imaging Modalities Arnaud Bistoquet 12/19/03 Coronary heart disease: the vessels that supply oxygen-carrying blood to the heart, become narrowed and unable to carry a normal amount
Alison M. Duncan, MRCP; Darrel P. Francis, MD; Derek G. Gibson, FRCP; Michael Y. Henein, MD, PhD
 Differentiation of Ischemic From Nonischemic Cardiomyopathy During Dobutamine Stress by Left Ventricular Long-Axis Function Additional Effect of Left Bundle-Branch Block Alison M. Duncan, MRCP; Darrel
Differentiation of Ischemic From Nonischemic Cardiomyopathy During Dobutamine Stress by Left Ventricular Long-Axis Function Additional Effect of Left Bundle-Branch Block Alison M. Duncan, MRCP; Darrel
Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False?
 Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False? Masaki Izumo a, Kengo Suzuki b, Hidekazu Kikuchi b, Seisyo Kou b, Keisuke Kida b, Yu Eguchi b, Nobuyuki Azuma
Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False? Masaki Izumo a, Kengo Suzuki b, Hidekazu Kikuchi b, Seisyo Kou b, Keisuke Kida b, Yu Eguchi b, Nobuyuki Azuma
ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENT. Impact of Obstructive Sleep Apnea on Left Ventricular Mass and. Diastolic Function
 ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENT Impact of Obstructive Sleep Apnea on Left Ventricular Mass and Diastolic Function Mitra Niroumand Raffael Kuperstein Zion Sasson Patrick J. Hanly St. Michael s Hospital University
ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENT Impact of Obstructive Sleep Apnea on Left Ventricular Mass and Diastolic Function Mitra Niroumand Raffael Kuperstein Zion Sasson Patrick J. Hanly St. Michael s Hospital University
Chamber Quantitation Guidelines II Right Heart Measurements
 Chamber Quantitation Guidelines II Right Heart Measurements Steven A. Goldstein MD FACC FASE Director, Noninvasive Cardiology MedStar Heart Institute Washington Hospital Center Sunday, October 9, 2016
Chamber Quantitation Guidelines II Right Heart Measurements Steven A. Goldstein MD FACC FASE Director, Noninvasive Cardiology MedStar Heart Institute Washington Hospital Center Sunday, October 9, 2016
An Integrated Approach to Study LV Diastolic Function
 An Integrated Approach to Study LV Diastolic Function Assoc. Prof. Adriana Ilieşiu, FESC University of Medicine Carol Davila Bucharest, Romania LV Diastolic Dysfunction impaired relaxation (early diastole)
An Integrated Approach to Study LV Diastolic Function Assoc. Prof. Adriana Ilieşiu, FESC University of Medicine Carol Davila Bucharest, Romania LV Diastolic Dysfunction impaired relaxation (early diastole)
Rownak Jahan Tamanna 1, Rowshan Jahan 2, Abduz Zaher 3 and Abdul Kader Akhanda. 3 ORIGINAL ARTICLES
 University Heart Journal Vol. 4 No. 2 July 2008 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Correlation of Doppler echocardiography with cardiac catheterization in estimating pulmonary capillary wedge pressure: A tertiary level
University Heart Journal Vol. 4 No. 2 July 2008 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Correlation of Doppler echocardiography with cardiac catheterization in estimating pulmonary capillary wedge pressure: A tertiary level
Per Lindqvist a, Anders Waldenström a, Gerhard Wikström b, Elsadig Kazzam c, * University, P.O. Box 17666, Al-Ain, United Arab Emirates
 Eur J Echocardiography (2007) 8, 252e258 Potential use of isovolumic contraction velocity in assessment of left ventricular contractility in man: A simultaneous pulsed Doppler tissue imaging and cardiac
Eur J Echocardiography (2007) 8, 252e258 Potential use of isovolumic contraction velocity in assessment of left ventricular contractility in man: A simultaneous pulsed Doppler tissue imaging and cardiac
Diastology Disclosures: None. Dias2011:1
 Diastology 2011 James D. Thomas, M.D., F.A.C.C. Cardiovascular Imaging Center Department of Cardiology Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, Ohio, USA Disclosures: None Dias2011:1 Is EVERYBODY a member!?!
Diastology 2011 James D. Thomas, M.D., F.A.C.C. Cardiovascular Imaging Center Department of Cardiology Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, Ohio, USA Disclosures: None Dias2011:1 Is EVERYBODY a member!?!
Advanced imaging of the left atrium - strain, CT, 3D, MRI -
 Advanced imaging of the left atrium - strain, CT, 3D, MRI - Monica Rosca, MD Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania Declaration of interest: I have nothing to declare Case
Advanced imaging of the left atrium - strain, CT, 3D, MRI - Monica Rosca, MD Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania Declaration of interest: I have nothing to declare Case
Nancy Goldman Cutler, MD Beaumont Children s Hospital Royal Oak, Mi
 Nancy Goldman Cutler, MD Beaumont Children s Hospital Royal Oak, Mi Identify increased LV wall thickness (WT) Understand increased WT in athletes Understand hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) Enhance understanding
Nancy Goldman Cutler, MD Beaumont Children s Hospital Royal Oak, Mi Identify increased LV wall thickness (WT) Understand increased WT in athletes Understand hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) Enhance understanding
Ultrasound 10/1/2014. Basic Echocardiography for the Internist. Mechanical (sector) transducer Piezoelectric crystal moved through a sector sweep
 Ultrasound Basic Echocardiography for the Internist Carol Gruver, MD, FACC UT Erlanger Cardiology Mechanical wave of compression and rarefaction Requires a medium for transmission Ultrasound frequency
Ultrasound Basic Echocardiography for the Internist Carol Gruver, MD, FACC UT Erlanger Cardiology Mechanical wave of compression and rarefaction Requires a medium for transmission Ultrasound frequency
Echocardiographic assessment of ejection fraction in left ventricular hypertrophy
 192 Department of Clinical Physiology, Central Hospital, S-651 85 Karlstad, Sweden B Wandt L Bojö Department of Medicine, Central Hospital, Karlstad K Tolagen Department of Clinical Physiology, Linköping
192 Department of Clinical Physiology, Central Hospital, S-651 85 Karlstad, Sweden B Wandt L Bojö Department of Medicine, Central Hospital, Karlstad K Tolagen Department of Clinical Physiology, Linköping
