Cardiovascular System
|
|
|
- Rodney Lee
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cardiovascular System
2 » The heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries.
3 1. Brings oxygen and nutrients to cells 2. Removes metabolic waste products
4 In the pulmonary circulation, blood picks up oxygen and gives off carbon dioxide In the systemic circulation, blood gives off oxygen (and other nutrients) to cells and picks up carbon dioxide (and other waste products).
5 80Ue-AMo&NR=1
6 » Aorta» Arteries» Arterioles» Capillaries» Venules» Veins» Vena Cava
7 Label drawings
8 1MC1hcE Circulatory song
9
10 Above 120/80 Hypertension Above 120/80 Elevated systolic/diastolic pressures on two/three consecutive occasions Above 120/80 Above 120/80 Above 120/80
11 +Pre-hypertension is / Hypertension stage 1 is / Hypertension stage 2 is >160/>100
12 » Types: Essential or Primary (90%) Secondary (renal disease, pheochromocytoma )
13 » Signs and symptoms? No symptoms!
14 » Risk factors: Obesity Diabetes Smoking Sedentary lifestyle High saturated fat diet High sodium intake Low calcium, potassium, and magnesium Aging Family history
15
16 » Increase fluid» Increase rate of heart» Increase force of contraction of the heart» Increase resistance to blood flow
17 Cardiac Output (CO) CO = Heart Rate x Stroke Volume Resistance refers to the friction to blood flow in the vessels. The smaller the vessel, the greater the resistance
18 the autonomic nervous system using baroreceptors the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone pathway using: Hypothalamic-pituitary axis (increases in thirst, and release of vasopressin) Arterioles (increases in resistance) Proximal, distal tubules and collecting duct of the kidneys (Na+ reabsorption) Adrenal cortex (Na+ reabsorption)
19 Release of Vasopressin
20
21 Angiotensinogen (in the liver) Renin( from the kidneys) Angiotensin I the blood stream) Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (from the lungs ) Angiotensin II
22
23
24 Dehydration Thirst Drinking water Urination Water produced by oxidation Sweat Breathing (expiration) Blood loss
25
26 Where does the water in the body come from? How is water lost?
27 List the percentage of the intake and output.
28
29 40% Intracellular fluid (ICF) contained in cells Interstitial fluid (IF) fluid in spaces between cells Plasma the fluid portion of the blood
30 » Hypovolemia (too little fluid in the blood) Seen in: + Dehydration + Vomiting/Diarrhea + Hemorrhage S & S: + Orthostatic hypotension + Tachycardia + Thirst» Hypervolemia (too much fluid in the blood) Seen in: + Heart failure + Renal failure S & S: + Hypertension + Bounding pulse + Acute weight gain Tx: + Oral or IV fluids Tx: + Sodium and water restriction + Diuretic
31
32
33 » Minerals in your blood and other body fluids that carry an electric charge.» Electrolytes impact: the amount of water in your body, the acidity of your blood (ph), your neurologic and muscle function» You get them from the foods you eat and the fluids you drink.
34
35
36 » Management of essential hypertension: Stop smoking Weight loss Exercise Low saturated fat, high fiber diet that is low in sodium Stress management Anti-hypertensive medication» Management of secondary hypertension: Surgical repair of abnormality
37 » Heart attacks» Strokes» Congestive Heart Failure» Chronic Kidney Failure» Blindness
38
39 NIH: Atherosclerosis is a disease in which plaque builds up inside your arteries. Plaque is made up of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances found in the blood. Over time, plaque hardens and narrows your arteries. This limits the flow of oxygen-rich blood to your organs and other parts of your body.
40 » Development is a life long process that begins with the fatty steaks seen on arterial walls.
41 Draw the heart along with the coronary arteries.
42 Atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries
43 Risk factors include: Diabetes Hypertension Obesity Cigarette Smoking Sedentary lifestyle High saturated fat, low fiber diet Hyperlipidemia + Increased Triglycerides + Increased Total Cholesterol + Increased LDL Cholesterol Decreased HDL Cholesterol Originally identified during the Framingham Study Advanced age Family history of heart disease
44
45 » Signs and Symptoms: Angina (Chest pain that resolves with rest or nitroglycerin) Shortness of breath Fatigue Dizziness
46
47 American Heart Association: This is an umbrella term used to cover any group of clinical symptoms compatible with acute myocardial ischemia. Acute myocardial ischemia is chest pain due to insufficient blood supply to the heart muscle that results from coronary artery disease.
48 » Caused by atherosclerosis and embolus
49 Occlusion of a vessel results in 3 stages of tissue damage: 1. Ischemia (reversed if oxygen flow improved or oxygen demand reduced) Stable Angina 2. Injury 3. Infarction (tissue death) Myocardial Infarction
50
51 » Signs and Symptoms: Substernal tightness radiating to left neck and jaw, as well as left shoulder and arm Shortness of breath Lightheadedness Sweating Nausea» In women, diabetics, and elders there may not be the chest pain, but they may feel fatigue along with the other symptoms
52 » v=o9t25smyz3a&feature=related ube.com/watch? v=i_izvabhexy
53 » Workup: Monitor with EKG Blood Troponin (Troponins have the greatest sensitivity and specificity in detecting an MI, and elevated serum levels are considered diagnostic of MI) Blood CPK (CK-MB levels begin to rise within 4 hours after MI, peak at hours, and subside over 3-4 days)
54 » tch?v=qnbuhmogdni
55 » Treatment includes: (911) Oxygen Bed rest Tissue Plasminogen Activator (tpa)..ideally w/in 90 minutes of arrival at ER Coronary Angioplasty +/- stent Beta blocker Nitroglycerin Morphine Aspirin/Plavix
56
57 H Chest pain, shortness of breath Hypotension, Confusion Means you're just not Getting enough perfusion Chest pain, shortness of breath Hypotension, Confusion Means you're just not Getting enough perfusion [V1] Slowly progressive atherosclerotic plaques Rupturing -- forming new clots -- forming new heart attacks -- its when I First learned about angiolplasty Its like bypass without cracking the thoracic Minimally invasive -- for -- cardiac patients Chest pain at rest along with EKG changes -- rising Troponins -- high creatine kinases Transmural infarcts -- ST elevations H Chest pain, shortness of breath Hypotension, Confusion Means you're just not Getting enough perfusion Chest pain, shortness of breath Hypotension, Confusion Means you're just not Getting enough perfusion [V2] Nitro was being used for vasodilation Relieving even the pain the student doc was facing But it wouldn't decrease the mortality rating Like aspirin and heparin and beta blockading would 12 hours -- my heart was still racing too late for tpa -- the clot was still not breaking We was way past the point prevention Stenting was the intervention -- it was a miracle invented H Chest pain, shortness of breath Hypotension, Confusion Means you're just not Getting enough perfusion Chest pain, shortness of breath Hypotension, Confusion Means you're just not Getting enough perfusion V3 Cause part of the heart had no movement Gotta get reperfusion Angiogram locates the occlusion Stent placement -- drug-elluding Aspirin -- clopidegrol -- what we not losing Gonna get him discharged on Welbutrin But -- if the clot is not moving Gonna defy the laws of Newton H Chest pain, shortness of breath Hypotension, Confusion Means you're just not Getting enough perfusion Chest pain, shortness of breath Hypotension, Confusion Means you're just not Getting enough perfusion V4 II, III, avf intrusion Like a right ventricular contusion Rapid IV fluid infusion You know where we got to move him In the CCU -- heart attacks back to back Add ace inhibitors and the statins stat With metoprolol -- and that is that Before the beeper on the heart monitor goes out of whack. H Chest pain, shortness of breath Hypotension, Confusion Means you're just not Getting enough perfusion Chest pain, shortness of breath Hypotension, Confusion Means you're just not Getting enough perfusion Copyright Pramanik Bharadwaj, M.D., All Rights Reserved.
58
59 » The heart can t pump enough blood to meet the body s metabolic needs. It results in intravascular and interstitial volume overload and poor tissue perfusion.
60 » Caused by: Coronary Artery Disease Hypertension
61 » Class I: Minimal (no limitation of activity)» Class II: Mild (slight limitation of physical activity, comfortable at rest)» Class III: Moderate (marked limitation of physical activity, comfortable at rest)» Class IV: Severe (unable to perform physical activity without discomfort, may even have discomfort at rest)
62
63 Signs and symptoms of Left-sided heart failure + Dyspnea + Limitation of physical activity + Episodes of dyspnea at night Signs and symptoms of Right-sided heart failure Weight gain Peripheral edema
64 » Causes of Left-sided Failure: Hypertension Left ventricular infarction» Causes of Right-sided Failure: Left-sided failure Right ventricular infarction Pulmonary embolism Pneumonia
65 » Bed rest» Diuretic
66
67 » Stenosis or occlusion of arteries in the limbs» Leg pain, ulcers
68
69
70
71
72 » Outpouching or dilation of a weakened arterial wall
73
74 »Usually silent» Pulsating mass in the peri-umbilical area of the abdomen associated with a bruit over the aorta.» Persistent abdominal and back pain
75 » Results in profuse bleeding (50% of people with a ruptured AAA survive)
76
77 » Blood clot (platelets, fibrin, red and white blood cells).» Caused by: Damage to the inner wall (endothelium) of a blood vessel Increase in the coagulability of blood
78 Thrombus formation in a vein
79
80 » Predisposing factors: Prolonged immobilization Trauma Surgery (major abdominal or pelvic surgery) Childbirth Obesity Hormonal Contraceptives (estrogen)
81
82 » Signs and Symptoms: Pain (especially with dorsiflexion of the foot Swelling Redness
83
84 A substance that travels through the blood stream from one location in the body to another. It s generally make up of a blood clot from a thrombus, although can be made of fat, bacteria, or tumor cells.
85
86 » From the venous circulation Comes from deep vein thrombosis» From the arterial circulation Come from the left side of the heart (arrhythmia, valvular heart disease, myocardial infarction, heart failure, or endocarditis) Travels to the right side of the heart, then the pulmonary system, and lodges in a capillary where it causes pulmonary infarction. Infarction of the brain (stroke), kidney and extremities (arterial occlusive disease)
87
88
89 Sudden onset of persistent neurologic deficit Occurs suddenly without warning
90 Sudden onset of loss of function (movement, feeling, speaking, et.) because of an interruption of blood flow to the portion of the brain responsible for controlling that function. It can also manifest as a sudden onset of dizziness, confusion, or severe headache.
91
92
93 25% of the heart s output of blood goes to supply the brain without oxygen from the blood the neurons die.
94 There are two types of strokes: Ischemic blockage of artery from a thrombus of embolism Hemorrhagic rupture of an artery
95
96
97 Risk factors: Hypertension Cigarette smoking Diabetes Mellitus Hyperlipidemia Obesity Sedentary life style
98 For Ischemic stroke» tpa can reverse the stroke if given 3 6 hours from the symptoms» Antiplatelet medication is given if it s been 6 hours or more, in order to prevent recurrent strokes» Plavix» Aspirin» Physical/occupational/speech therapy
99 VITALS: BP 120/80 or less P ~ 70 R ~ 14 T = 98.6F» HDL > 45» LDL < 100» Total Cholesterol < 200» Triglycerides < 150» BUN/Cr: ~ 10/1» Fasting Glucose ~ 100» HgA1c ~6
100
101 » Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration)
102 » Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx
103 » Includes: Trachea Bronchi Lobules + Bronchioles + Alveolar ducts + Alveolar sacs
104 1. Label the drawing 2. Share the results with the class
105 » Air moves in an out of the respiratory tract by the contraction and relaxation of the respiratory muscles: Sternocleidomastoid muscle Intercostal muscles Diaphragm
106 » For there to be effective exchange of O2 for CO2, ventilation and perfusion at the alveolar level must be matched rro0&feature=related
107
108 » Bluish discoloration, of the oral mucosa, lips, fingers, nail beds
109
110 » A reaction to inhaled allergens, which cause rhinitis and conjunctivitis, seasonally or yearround
111 Exposure to an allergen T-cells instruct B-cells to create antibodies against the allergen B-cells create antibodies (IgE type) IgE antibodies attach themselves to mast cells (release histamine) Mast cell-ige complex remain in the body for years, ready to react with the same allergen
112 » Paroxysmal sneezing» Pale, cyanotic, edematous (boggy) nasal mucosa» Profuse watery rhinorrhea» Nasal congestion sinus pain and headache» Pruritis of the nose, throat and eyes» Red, edematous eyelids and conjunctivae
113 » Avoid allergens» Antihistamines» Inhaled intranasal steroids» Cromolyn» Leukotriene inhibitors» Desensitization
114
115
116 » A chronic inflammatory airway disorder, characterized by airflow obstruction and airway hyper-responsiveness to certain stimuli, extrinsic or intrinsic triggers.
117
118 » Extrinsic triggers Animal dander Secretions from cockroaches Dust mites Pollen Mold Viral infections Feather pillows Cigarette smoke Cold air Temperature or humidity variations Food additives Certain foods: Shellfish, peanuts
119 » Intrinsic triggers Anxiety Emotional stress Strenuous exercise Gastro-esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Coughing Laughing Fatigue Endocrine changes
120 Bronchospasms Edema of the airway mucosa Increased mucus secretion 8zKLvQ&feature=related
121 » Sudden: Dyspnea Wheezing Tightness in the chest» Productive cough» Rapid respiration» Rapid pulse» Use of accessory respiratory muscles
122 VA9C_aCH7F0&feature=related
123 » Mild intermittent: (<2 times/week), nighttime symptoms < 2/month, FEV1 ~ 80% of predicted
124 » Mild persistent: (>2 times/week), nighttime symptoms > 2 times/month, FEV1 ~ 80% of normal» Moderate persistent: Symptoms occur daily, exacerbations more than two times/week, bronchodilator therapy is used daily, nighttime symptoms more than once/week, FEV % of normal» Severe persistent: Symptoms occur continuously, exacerbations occur frequently and limit physical activity, nighttime symptoms are frequent, FEV1 <60%
125 » Avoid triggers» Desensitize to triggers» Develop Cardio-pulmonary endurance» Hydration» Monitor with FEV1 with peak flow meter v=lhvbh0o6u8c» Short acting Bronchodilator for rescue» Corticosteroid for maintenance (alone or with long acting bronchodilator)» Mast cell stabilizer» Leukotriene modifier CAUTION: Do not take Aspirin, or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and do not take beta-blockers
126
127
128 Green Zone: 80 to 100 percent of your usual or "normal" peak flow rate signals all clear. Yellow Zone: 50 to 80 percent of your usual or "normal" peak flow rate signals caution. Your airways are narrowing and may require extra treatment. You and your healthcare provider should have a plan for yellow zone readings. Red Zone: Less than 50 percent of your usual or "normal" peak flow rate signals a Medical Alert. Severe airway narrowing may be occurring. Take your rescue medications right away. Call 911 or get a ride to the emergency room.
129
130
131 How to Use a Metered-Dose Inhaler Shake the inhaler after removing the cap. Breathe out for 1 or 2 seconds. Put the inhaler in your mouth or 1 to 2 inches from it and start to breathe in slowly, like sipping hot soup. While starting to breathe in, press the top of the inhaler. Breathe in slowly until your lungs are full. (This should take about 5 or 6 seconds.) Hold your breath for 4 to 6 seconds. Breathe out and repeat the procedure. If this method is difficult, a spacer can be used.
132
133
134 » Chronic Bronchitis and» Emphysema Main cause is smoking
135 » Inflammation of the bronchi caused by: Cigarette smoking Respiratory tract infection Prolonged exposure to irritants, noxious gases, organic or inorganic dusts
136 » Results in: Hypersecretion of mucus Chronic productive cough for at least 3 months, and occurring at least two years in a row. Rhonchi
137 » The permanent destruction of the alveolar walls.
138
139 » Signs and Symptoms: Exertional dyspnea Tachypnea Barrel-shaped chest Use of accessory muscles for inspiration and abdominal muscles for expiration Clubbed fingers
140
141
142
143 » Obstruction of a pulmonary artery by a dislodged thrombus, usually from a deep vein in the leg.
144 » This is the most common pulmonary complication in a hospitalized patient.
145 Sudden severe dyspnea Tachycardia Anxiety Blood-tinged sputum
146 » Immobilization» Obesity» Use of Hormonal Birth control» Deep vein thrombosis
147
Function of the Respiratory System. Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration)
 Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Cardiovascular and Respiratory Disorders
 Cardiovascular and Respiratory Disorders Blood Pressure Normal blood pressure is 120/80 mmhg (millimeters of mercury) Hypertension is when the resting blood pressure is too high Systolic BP is 140 mmhg
Cardiovascular and Respiratory Disorders Blood Pressure Normal blood pressure is 120/80 mmhg (millimeters of mercury) Hypertension is when the resting blood pressure is too high Systolic BP is 140 mmhg
Results of Ischemic Heart Disease
 Ischemic Heart Disease: Angina and Myocardial Infarction Ischemic heart disease; syndromes causing an imbalance between myocardial oxygen demand and supply (inadequate myocardial blood flow) related to
Ischemic Heart Disease: Angina and Myocardial Infarction Ischemic heart disease; syndromes causing an imbalance between myocardial oxygen demand and supply (inadequate myocardial blood flow) related to
Cardiac Emergencies. A Review of Cardiac Compromise. Lawrence L. Lambert
 Cardiac Emergencies A Review of Cardiac Compromise Lawrence L. Lambert 1 Cardiac Emergencies Objectives: Following successful completion of this training session, the student should be able to: 1. Describe
Cardiac Emergencies A Review of Cardiac Compromise Lawrence L. Lambert 1 Cardiac Emergencies Objectives: Following successful completion of this training session, the student should be able to: 1. Describe
Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing
 Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing Components of the respiratory system Nasal cavity Pharynx Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Lungs
Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing Components of the respiratory system Nasal cavity Pharynx Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Lungs
Diagnosis and Management of Acute Myocardial Infarction
 Diagnosis and Management of Acute Myocardial Infarction Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) occurs as a result of prolonged myocardial ischemia Atherosclerosis leads to endothelial rupture or erosion that
Diagnosis and Management of Acute Myocardial Infarction Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) occurs as a result of prolonged myocardial ischemia Atherosclerosis leads to endothelial rupture or erosion that
Can be felt where an artery passes near the skin surface and over a
 1 Chapter 14 Cardiovascular Emergencies 2 Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular disease has been leading killer of Americans since. Accounts for 1 of every 2.8 deaths Cardiovascular disease (CVD) claimed
1 Chapter 14 Cardiovascular Emergencies 2 Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular disease has been leading killer of Americans since. Accounts for 1 of every 2.8 deaths Cardiovascular disease (CVD) claimed
Chapter 14 Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular disease has been leading killer of Americans since.
 1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 14 Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular disease has been leading killer of Americans since. Accounts for 1 of every 2.8 deaths Cardiovascular disease (CVD)
1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 14 Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular disease has been leading killer of Americans since. Accounts for 1 of every 2.8 deaths Cardiovascular disease (CVD)
Lecture 8 Cardiovascular Health Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factors
 Lecture 8 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factors 1 Human Health: What s Killing Us? Health in America Health is the U.S Average life
Lecture 8 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factors 1 Human Health: What s Killing Us? Health in America Health is the U.S Average life
10/8/2018. Lecture 9. Cardiovascular Health. Lecture Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor
 Lecture 9 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 9 1. Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor 1 The Heart Muscular Pump The Heart Receives blood low pressure then increases the pressure
Lecture 9 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 9 1. Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor 1 The Heart Muscular Pump The Heart Receives blood low pressure then increases the pressure
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease By: Dr. Fatima Makee AL-Hakak () University of kerbala College of nursing Out lines What is the? Overview Causes of Symptoms of What's the difference between and asthma?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease By: Dr. Fatima Makee AL-Hakak () University of kerbala College of nursing Out lines What is the? Overview Causes of Symptoms of What's the difference between and asthma?
Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes
 Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes LEARNING OBJECTIVES Ø Identify the components of the cardiovascular system and the various types of cardiovascular disease Ø Discuss ways of promoting cardiovascular
Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes LEARNING OBJECTIVES Ø Identify the components of the cardiovascular system and the various types of cardiovascular disease Ø Discuss ways of promoting cardiovascular
Wellness: Concepts and Applications 8 th Edition Anspaugh, Hamrick, Rosato
 Wellness: Concepts and Applications 8 th Edition Anspaugh, Hamrick, Rosato Preventing Cardiovascular Disease Chapter 2 Cardiovascular Disease the leading cause of death in the U.S. 35.3% of all deaths
Wellness: Concepts and Applications 8 th Edition Anspaugh, Hamrick, Rosato Preventing Cardiovascular Disease Chapter 2 Cardiovascular Disease the leading cause of death in the U.S. 35.3% of all deaths
Heart disease remains the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in industrialized nations. It accounts for nearly 40% of all deaths in the United
 Heart disease remains the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in industrialized nations. It accounts for nearly 40% of all deaths in the United States, totaling about 750,000 individuals annually
Heart disease remains the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in industrialized nations. It accounts for nearly 40% of all deaths in the United States, totaling about 750,000 individuals annually
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular Concerns in Intermediate Care
 Cardiovascular Concerns in Intermediate Care GINA ST. JEAN RN, MSN, CCRN-CSC CLINICAL NURSE EDUCATOR HEART AND & CRITICAL AND INTERMEDIATE CARE Objectives: Identify how to do a thorough assessment of the
Cardiovascular Concerns in Intermediate Care GINA ST. JEAN RN, MSN, CCRN-CSC CLINICAL NURSE EDUCATOR HEART AND & CRITICAL AND INTERMEDIATE CARE Objectives: Identify how to do a thorough assessment of the
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
Cardiovascular System
 Component 3-Terminology in Healthcare and Public Health Settings Unit 5-Cardiovascular System This material was developed by The University of Alabama at Birmingham, funded by the Department of Health
Component 3-Terminology in Healthcare and Public Health Settings Unit 5-Cardiovascular System This material was developed by The University of Alabama at Birmingham, funded by the Department of Health
Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings. Cardiovascular System. Cardiovascular System 8/3/2010. Version 1/Fall 2010
 Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings Unit 5 1 Also referred to as the Circulatory system Functions Distribute blood to all areas of body Delivery of needed d substances to cells Removal
Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings Unit 5 1 Also referred to as the Circulatory system Functions Distribute blood to all areas of body Delivery of needed d substances to cells Removal
Cardiovascular System and Health. Chapter 15
 Cardiovascular System and Health Chapter 15 Cardiovascular Disease Leading cause of death in U.S. Claims 1 life every 43 seconds Often, the first sign is a fatal heart attack Death Rates #1 CVD #2 Cancer
Cardiovascular System and Health Chapter 15 Cardiovascular Disease Leading cause of death in U.S. Claims 1 life every 43 seconds Often, the first sign is a fatal heart attack Death Rates #1 CVD #2 Cancer
Unit 1: Human Systems. The Circulatory System
 Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Strokes , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. hp Last reviewed: 11/11/2017 1
 Strokes Introduction A stroke or a brain attack is a very serious condition that can result in death and significant disability. This disease is ranked as the third leading cause of death in the United
Strokes Introduction A stroke or a brain attack is a very serious condition that can result in death and significant disability. This disease is ranked as the third leading cause of death in the United
Cardiac Pathology & Rehabilitation
 Cardiac Pathology & Rehabilitation Which of the following best describes the physical activity performed in my leisure time? A. I perform vigorous physical activity 3X/week for 20 minutes each time B.
Cardiac Pathology & Rehabilitation Which of the following best describes the physical activity performed in my leisure time? A. I perform vigorous physical activity 3X/week for 20 minutes each time B.
HEART DISEASE HEART CONDITIONS, RISKS AND PROTECTION
 Spotlight on Health 2017 HEART DISEASE HEART CONDITIONS, RISKS AND PROTECTION Heart disease is the leading cause of death for both men and women worldwide, accounting for over 17 million deaths per year.
Spotlight on Health 2017 HEART DISEASE HEART CONDITIONS, RISKS AND PROTECTION Heart disease is the leading cause of death for both men and women worldwide, accounting for over 17 million deaths per year.
Cardiac Pathophysiology
 Cardiac Pathophysiology Evaluation Components Medical history Physical examination Routine laboratory tests Optional tests Medical History Duration and classification of hypertension. Patient history of
Cardiac Pathophysiology Evaluation Components Medical history Physical examination Routine laboratory tests Optional tests Medical History Duration and classification of hypertension. Patient history of
Care of the Patient with a Cardiovascular or a Peripheral Vascular Disorder
 Care of the Patient with a Cardiovascular or a Peripheral Vascular Disorder 1 Slide 1 human heart Slide 2 MECHANICAL: PUSHES BLOOD FROM HEAD TO TOES AND BACK Slide 3 1 ELECTRICAL SYSTEM: TRIGGERS THE MECHANICAL
Care of the Patient with a Cardiovascular or a Peripheral Vascular Disorder 1 Slide 1 human heart Slide 2 MECHANICAL: PUSHES BLOOD FROM HEAD TO TOES AND BACK Slide 3 1 ELECTRICAL SYSTEM: TRIGGERS THE MECHANICAL
Cardiovascular Disorders Lecture 3 Coronar Artery Diseases
 Cardiovascular Disorders Lecture 3 Coronar Artery Diseases By Prof. El Sayed Abdel Fattah Eid Lecturer of Internal Medicine Delta University Coronary Heart Diseases It is the leading cause of death in
Cardiovascular Disorders Lecture 3 Coronar Artery Diseases By Prof. El Sayed Abdel Fattah Eid Lecturer of Internal Medicine Delta University Coronary Heart Diseases It is the leading cause of death in
Cardiovascular Disease
 Cardiovascular Disease Chapter 15 Introduction Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in the U.S. One American dies from CVD every 33 seconds Nearly half of all Americans will die from
Cardiovascular Disease Chapter 15 Introduction Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in the U.S. One American dies from CVD every 33 seconds Nearly half of all Americans will die from
Cardiovascular and Circulatory System The Heart and Blood Vessels
 Cardiovascular and Circulatory System The Heart and Blood Vessels Circulatory Learning Outcomes 1. Identify and explain the functions of the vessels of the Circulatory system. 2. Explain the functions
Cardiovascular and Circulatory System The Heart and Blood Vessels Circulatory Learning Outcomes 1. Identify and explain the functions of the vessels of the Circulatory system. 2. Explain the functions
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Pulmonary Pathophysiology
 Pulmonary Pathophysiology 1 Reduction of Pulmonary Function 1. Inadequate blood flow to the lungs hypoperfusion 2. Inadequate air flow to the alveoli - hypoventilation 2 Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary
Pulmonary Pathophysiology 1 Reduction of Pulmonary Function 1. Inadequate blood flow to the lungs hypoperfusion 2. Inadequate air flow to the alveoli - hypoventilation 2 Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary
Heart Facts. The average adult heart beats 72 times a min 100,000 times a day 3,600,000 times a year 2.5 billion times during a lifetime.
 Circulatory System Heart Facts The average adult heart beats 72 times a min 100,000 times a day 3,600,000 times a year 2.5 billion times during a lifetime. Heart Facts Weighs 11 oz A healthy heart pumps
Circulatory System Heart Facts The average adult heart beats 72 times a min 100,000 times a day 3,600,000 times a year 2.5 billion times during a lifetime. Heart Facts Weighs 11 oz A healthy heart pumps
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System
 Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Cardiac Emergencies. Jim Bennett Paramedic and Clinical Education Coordinator American Medical Response Spokane, Washington
 Cardiac Emergencies Jim Bennett Paramedic and Clinical Education Coordinator American Medical Response Spokane, Washington The Heart -------Aorta Pulmonary Veins---- Superior Vena Cava------ Right Atrium-----
Cardiac Emergencies Jim Bennett Paramedic and Clinical Education Coordinator American Medical Response Spokane, Washington The Heart -------Aorta Pulmonary Veins---- Superior Vena Cava------ Right Atrium-----
Outcomes: By the end of this session the student will be able to:
 Outcomes: By the end of this session the student will be able to: Discuss the cardiovascular system Identify the normal changes that occur with ageing Explain the nurses role in the care of residents with
Outcomes: By the end of this session the student will be able to: Discuss the cardiovascular system Identify the normal changes that occur with ageing Explain the nurses role in the care of residents with
Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system. What are the function of the cardiovascular system? Arteries and arterioles:
 5.1 Overview of the cardiovascular system Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system Includes the heart and blood vessels Brings nutrients to cells and helps get rid of wastes Blood is refreshed in the lung, kidneys,
5.1 Overview of the cardiovascular system Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system Includes the heart and blood vessels Brings nutrients to cells and helps get rid of wastes Blood is refreshed in the lung, kidneys,
Biology. A Guide to the Natural World. Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath. Fifth Edition.
 Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Heart Disease. Signs and Symptoms
 Heart Disease The term "heart disease" refers to several types of heart conditions. The most common type is coronary artery disease, which can cause heart attack, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
Heart Disease The term "heart disease" refers to several types of heart conditions. The most common type is coronary artery disease, which can cause heart attack, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
Acute Myocardial Infarction. Willis E. Godin D.O., FACC
 Acute Myocardial Infarction Willis E. Godin D.O., FACC Acute Myocardial Infarction Definition: Decreased delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the myocardium Myocardial tissue necrosis causing irreparable
Acute Myocardial Infarction Willis E. Godin D.O., FACC Acute Myocardial Infarction Definition: Decreased delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the myocardium Myocardial tissue necrosis causing irreparable
Acute Myocardial Infarction
 Acute Myocardial Infarction Hafeza Shaikh, DO, FACC, RPVI Lourdes Cardiology Services Asst.Program Director, Cardiology Fellowship Associate Professor, ROWAN-SOM Acute Myocardial Infarction Definition:
Acute Myocardial Infarction Hafeza Shaikh, DO, FACC, RPVI Lourdes Cardiology Services Asst.Program Director, Cardiology Fellowship Associate Professor, ROWAN-SOM Acute Myocardial Infarction Definition:
Heart Attack. PART 2. Health Issues of Special Interest to Women. Heart and Artery Diseases. Chapter 4
 PART 2. Health Issues of Special Interest to Women Heart Attack Heart and Artery Diseases Chapter 4 You may not know that diseases of the heart and arteries (primarily heart attack, heart disease, high
PART 2. Health Issues of Special Interest to Women Heart Attack Heart and Artery Diseases Chapter 4 You may not know that diseases of the heart and arteries (primarily heart attack, heart disease, high
Objectives. Identify early signs and symptoms of Acute Coronary Syndrome Initiate proper protocol for ACS patient 10/2013 2
 10/2013 1 Objectives Identify early signs and symptoms of Acute Coronary Syndrome Initiate proper protocol for ACS patient 10/2013 2 Purpose of this Education Module: Chest Pain Center Accreditation involves
10/2013 1 Objectives Identify early signs and symptoms of Acute Coronary Syndrome Initiate proper protocol for ACS patient 10/2013 2 Purpose of this Education Module: Chest Pain Center Accreditation involves
Types of circulatory systems
 Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
Structure and organization of blood vessels
 The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
Air Flow Limitation. In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation.
 Asthma Air Flow Limitation In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation. True whether reversible, asthma and exercise-induced bronchospasm,
Asthma Air Flow Limitation In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation. True whether reversible, asthma and exercise-induced bronchospasm,
WHAT IS ATHEROSCLEROSIS?
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS WHAT IS ATHEROSCLEROSIS? Atherosclerosis is a narrowing of the arteries that can significantly reduce the blood supply to vital organs such as the heart, brain and intestines. In atherosclerosis,
ATHEROSCLEROSIS WHAT IS ATHEROSCLEROSIS? Atherosclerosis is a narrowing of the arteries that can significantly reduce the blood supply to vital organs such as the heart, brain and intestines. In atherosclerosis,
Congestive Heart Failure
 Congestive Heart Failure GENERAL INFORMATION: What is congestive heart failure? Congestive heart failure is a life-threatening disease that occurs when your heart becomes too weak to pump blood properly.
Congestive Heart Failure GENERAL INFORMATION: What is congestive heart failure? Congestive heart failure is a life-threatening disease that occurs when your heart becomes too weak to pump blood properly.
Our Commitment to Quality and Patient Safety Core Measures
 Calvert Memorial Hospital is committed to our community, with a focus on patient-centered care. High quality and safe patient care is not our goal, it is our priority. That means delivering the best possible
Calvert Memorial Hospital is committed to our community, with a focus on patient-centered care. High quality and safe patient care is not our goal, it is our priority. That means delivering the best possible
Your Lungs and COPD. Patient Education Pulmonary Rehabilitation. A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs
 Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System
 Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions. KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells.
 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
The Circulatory System (p )
 The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
The Respiratory System
 130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
Respiratory System. Introduction. Atmosphere. Some Properties of Gases. Human Respiratory System. Introduction
 Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Circulatory System. and. Respiratory System. Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song THE HEART LUNGS. Monday, May 23, 2011
 Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Coronary Heart Disease. Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N
 Coronary Heart Disease Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N 31/03/2016 Objectives Define coronary heart disease (CHD). Identify the causes and risk factors of CHD Discuss the pathophysiological
Coronary Heart Disease Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N 31/03/2016 Objectives Define coronary heart disease (CHD). Identify the causes and risk factors of CHD Discuss the pathophysiological
CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE OVERVIEW
 CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE OVERVIEW Your heart is a strong muscular pump that is responsible for moving about 3,000 gallons of blood through your body every day. Like other muscles, your heart requires a
CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE OVERVIEW Your heart is a strong muscular pump that is responsible for moving about 3,000 gallons of blood through your body every day. Like other muscles, your heart requires a
YOUR GUIDE TO. Understanding Your Angina Diagnosis and Treatment
 YOUR GUIDE TO Understanding Your Angina Diagnosis and Treatment Our goal at the Mercy Health Heart Institute is to help you be well. Our experienced team includes cardiologists, cardiovascular surgeons,
YOUR GUIDE TO Understanding Your Angina Diagnosis and Treatment Our goal at the Mercy Health Heart Institute is to help you be well. Our experienced team includes cardiologists, cardiovascular surgeons,
Heart Disorders. Cardiovascular Disorders (Part B-1) Module 5 -Chapter 8. Overview Heart Disorders Vascular Disorders
 Cardiovascular Disorders (Part B-1) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Heart Disorders Vascular Disorders Susie Turner, MD 1/7/13 Heart Disorders Coronary Artery Disease Cardiac Arrhythmias Congestive Heart
Cardiovascular Disorders (Part B-1) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Heart Disorders Vascular Disorders Susie Turner, MD 1/7/13 Heart Disorders Coronary Artery Disease Cardiac Arrhythmias Congestive Heart
HEART AND SOUL STUDY OUTCOME EVENT - MORBIDITY REVIEW FORM
 REVIEW DATE REVIEWER'S ID HEART AND SOUL STUDY OUTCOME EVENT - MORBIDITY REVIEW FORM : DISCHARGE DATE: RECORDS FROM: Hospitalization ER Please check all that may apply: Myocardial Infarction Pages 2, 3,
REVIEW DATE REVIEWER'S ID HEART AND SOUL STUDY OUTCOME EVENT - MORBIDITY REVIEW FORM : DISCHARGE DATE: RECORDS FROM: Hospitalization ER Please check all that may apply: Myocardial Infarction Pages 2, 3,
Advanced Concepts of Personal Training Study Guide Answer Key
 Advanced Concepts of Personal Training Study Guide Answer Key Lesson 22 Working with Special Populations LESSON TWENTY TWO Lesson Twenty Two Working with Special Populations WORKING WITH SPECIAL POPULATIONS
Advanced Concepts of Personal Training Study Guide Answer Key Lesson 22 Working with Special Populations LESSON TWENTY TWO Lesson Twenty Two Working with Special Populations WORKING WITH SPECIAL POPULATIONS
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
Understanding Cholesterol and Triglycerides
 MINTO PREVENTION & REHABILITATION CENTRE CENTRE DE PREVENTION ET DE READAPTATION MINTO Understanding Cholesterol and Triglycerides About This Kit Along with cigarette smoking, high blood pressure, physical
MINTO PREVENTION & REHABILITATION CENTRE CENTRE DE PREVENTION ET DE READAPTATION MINTO Understanding Cholesterol and Triglycerides About This Kit Along with cigarette smoking, high blood pressure, physical
Cardiovascular disease
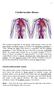 1 Cardiovascular disease The essential components of the human cardiovascular system are the heart, blood, and blood vessels. It includes: the pulmonary circulation, a "loop" through the lungs where blood
1 Cardiovascular disease The essential components of the human cardiovascular system are the heart, blood, and blood vessels. It includes: the pulmonary circulation, a "loop" through the lungs where blood
Asthma. Guide to Good Health. Healthy Living Guide
 Asthma Guide to Good Health Healthy Living Guide Asthma Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) Depression Hyperlipidemia Hypertension
Asthma Guide to Good Health Healthy Living Guide Asthma Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) Depression Hyperlipidemia Hypertension
Heart Disease (Coronary Artery Disease)
 Heart Disease (Coronary Artery Disease) Understanding how the heart works To understand heart disease, you must first know how the heart works. The heart is like any other muscle, requiring blood to supply
Heart Disease (Coronary Artery Disease) Understanding how the heart works To understand heart disease, you must first know how the heart works. The heart is like any other muscle, requiring blood to supply
Atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis happens when the blood vessels
 Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis happens when the blood vessels that carry oxygen and nutrients from your heart to the rest of your body (arteries) become thick and stiff sometimes restricting blood flow
Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis happens when the blood vessels that carry oxygen and nutrients from your heart to the rest of your body (arteries) become thick and stiff sometimes restricting blood flow
Chapter 16 Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular disease has been leading killer of Americans since 1900.
 1 2 3 4 5 6 Chapter 16 Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular disease has been leading killer of Americans since 1900. Accounts for of every 3 deaths Cardiovascular disease
1 2 3 4 5 6 Chapter 16 Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular disease has been leading killer of Americans since 1900. Accounts for of every 3 deaths Cardiovascular disease
Hypertension The normal radial artery blood pressures in adults are: Systolic arterial pressure: 100 to 140 mmhg. Diastolic arterial pressure: 60 to
 Hypertension The normal radial artery blood pressures in adults are: Systolic arterial pressure: 100 to 140 mmhg. Diastolic arterial pressure: 60 to 90 mmhg. These pressures are called Normal blood pressure
Hypertension The normal radial artery blood pressures in adults are: Systolic arterial pressure: 100 to 140 mmhg. Diastolic arterial pressure: 60 to 90 mmhg. These pressures are called Normal blood pressure
5/5/2013. The Respiratory System. Chapter 16 Notes. The Respiratory System. Nasal Cavity. Sinuses
 The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
Respiratory Diseases and Disorders
 Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Lecture Notes. Chapter 3: Asthma
 Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Copyright 2011, 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Normal Cardiac Anatomy
 Mosby,, an affiliate of Elsevier Normal Cardiac Anatomy Impaired cardiac pumping Results in vasoconstriction & fluid retention Characterized by ventricular dysfunction, reduced exercise tolerance, diminished
Mosby,, an affiliate of Elsevier Normal Cardiac Anatomy Impaired cardiac pumping Results in vasoconstriction & fluid retention Characterized by ventricular dysfunction, reduced exercise tolerance, diminished
HEART HEALTH WEEK 2 SUPPLEMENT. A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease ATHEROSCLEROSIS. Fatty deposits can narrow and harden the artery
 WEEK 2 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease ATHEROSCLEROSIS FIGURE 1 Atherosclerosis is an inflammatory process where cholesterol is deposited in the wall of arteries and
WEEK 2 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease ATHEROSCLEROSIS FIGURE 1 Atherosclerosis is an inflammatory process where cholesterol is deposited in the wall of arteries and
Respiratory Emergencies. Chapter 11
 Respiratory Emergencies Chapter 11 Respiratory System Anatomy and Function of the Lung Characteristics of Adequate Breathing Normal rate and depth Regular breathing pattern Good breath sounds on both sides
Respiratory Emergencies Chapter 11 Respiratory System Anatomy and Function of the Lung Characteristics of Adequate Breathing Normal rate and depth Regular breathing pattern Good breath sounds on both sides
Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C
 Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C Asthma Statistics 25.6 million Americans diagnosed with asthma 6.8 million are children 10.5 million missed school days per year 14.2 lost work days for adults Approximately 10%
Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C Asthma Statistics 25.6 million Americans diagnosed with asthma 6.8 million are children 10.5 million missed school days per year 14.2 lost work days for adults Approximately 10%
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System. Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD
 Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
Heart Attack and Stroke
 Heart Attack and Stroke Heart Disease Most common cause of death for both men and women Some heart disease symptoms in women may be different from those in men What is a Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction)?
Heart Attack and Stroke Heart Disease Most common cause of death for both men and women Some heart disease symptoms in women may be different from those in men What is a Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction)?
Coronary Artery Disease
 Coronary Artery Disease This information is at http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/dci/diseases/cad/cad_all.html and is provided by the NHLBI, one of the Institutes of the National Institutes of Health. To
Coronary Artery Disease This information is at http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/dci/diseases/cad/cad_all.html and is provided by the NHLBI, one of the Institutes of the National Institutes of Health. To
Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide
 Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide Main Idea: The function of the circulatory system is to maintain adequate blood flow to all tissues. Clinical
Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide Main Idea: The function of the circulatory system is to maintain adequate blood flow to all tissues. Clinical
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Stroke 101. Maine Cardiovascular Health Summit. Eileen Hawkins, RN, MSN, CNRN Pen Bay Stroke Program Coordinator November 7, 2013
 Stroke 101 Maine Cardiovascular Health Summit Eileen Hawkins, RN, MSN, CNRN Pen Bay Stroke Program Coordinator November 7, 2013 Stroke Statistics Definition of stroke Risk factors Warning signs Treatment
Stroke 101 Maine Cardiovascular Health Summit Eileen Hawkins, RN, MSN, CNRN Pen Bay Stroke Program Coordinator November 7, 2013 Stroke Statistics Definition of stroke Risk factors Warning signs Treatment
The Endocrine System 2
 The Endocrine System 2 Continuing on from the previous instalment, we will now look at the adrenal glands, the pancreas and the gonads as parts of the endocrine system. Adrenal Glands The adrenal glands
The Endocrine System 2 Continuing on from the previous instalment, we will now look at the adrenal glands, the pancreas and the gonads as parts of the endocrine system. Adrenal Glands The adrenal glands
Chapter 12. Capillaries. Circulation. The circulatory system connects with all body tissues
 Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
Chapter 10 Worksheet Blood Pressure and Antithrombotic Agents
 Complete the following. 1. A layer of cells lines each vessel in the vascular system. This layer is a passive barrier that keeps cells and proteins from going into tissues; it also contains substances
Complete the following. 1. A layer of cells lines each vessel in the vascular system. This layer is a passive barrier that keeps cells and proteins from going into tissues; it also contains substances
Circulation and Cardiac Emergencies. Emergency Medical Response
 Circulation and Cardiac Emergencies Lesson 19: The Circulatory System and Cardiac Emergencies You Are the Emergency Medical Responder You are called to the home of a 50-year-old man whose wife called 9-1-1
Circulation and Cardiac Emergencies Lesson 19: The Circulatory System and Cardiac Emergencies You Are the Emergency Medical Responder You are called to the home of a 50-year-old man whose wife called 9-1-1
Guide to Cardiology Care at Scripps
 Guide to Cardiology Care at Scripps Cardiology is the word in health care associated with heart, but the body s vascular system is also an important part of heart care. Your body has more than 60,000 miles
Guide to Cardiology Care at Scripps Cardiology is the word in health care associated with heart, but the body s vascular system is also an important part of heart care. Your body has more than 60,000 miles
COPD, Pneumonia & Influenza, Accidents, Diabetes. Chapter 7
 COPD, Pneumonia & Influenza, Accidents, Diabetes Chapter 7 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD 4 th leading cause of death in the U.S. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Any chronic conditions
COPD, Pneumonia & Influenza, Accidents, Diabetes Chapter 7 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD 4 th leading cause of death in the U.S. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Any chronic conditions
Blood and the Lymphatic System. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview Blood and the Lymphatic System
 Lesson Overview 33.2 Blood and the Lymphatic System THINK ABOUT IT When you think about body tissues, you probably picture something with a definite shape, like muscle or skin. But blood is a tissue too
Lesson Overview 33.2 Blood and the Lymphatic System THINK ABOUT IT When you think about body tissues, you probably picture something with a definite shape, like muscle or skin. But blood is a tissue too
Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing
 Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
PATIENT MEDICAL HISTORY FOR B.O.L.D. (Please check the most appropriate answer. If you have any questions please call the office for assistance)
 Name: Date of Birth: Date: Race: Caucasion African American Hispanic Native American Pacific Islander PATIENT MEDICAL HISTORY FOR B.O.L.D. (Please check the most appropriate answer. If you have any questions
Name: Date of Birth: Date: Race: Caucasion African American Hispanic Native American Pacific Islander PATIENT MEDICAL HISTORY FOR B.O.L.D. (Please check the most appropriate answer. If you have any questions
WHI Form Report of Cardiovascular Outcome Ver (For items 1-11, each question specifies mark one or mark all that apply.
 WHI Form - Report of Cardiovascular Outcome Ver. 6. COMMENTS To be completed by Physician Adjudicator Date Completed: - - (M/D/Y) Adjudicator Code: OMB# 095-044 Exp: 4/06 -Affix label here- Clinical Center/ID:
WHI Form - Report of Cardiovascular Outcome Ver. 6. COMMENTS To be completed by Physician Adjudicator Date Completed: - - (M/D/Y) Adjudicator Code: OMB# 095-044 Exp: 4/06 -Affix label here- Clinical Center/ID:
Anatomy. The respiratory system starts from the nose, mouth, larynx, trachea, and the two lungs.
 Respiratory System Anatomy The respiratory system starts from the nose, mouth, larynx, trachea, and the two lungs. Within the lungs, the bronchi transport air with oxygen to the alveoli on inspiration
Respiratory System Anatomy The respiratory system starts from the nose, mouth, larynx, trachea, and the two lungs. Within the lungs, the bronchi transport air with oxygen to the alveoli on inspiration
1) Severe, crushing substernal chest pain 2) radiate to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, or left arm. 3- rapid and weak pulse 4- nausea (posterior MI).
 1) Severe, crushing substernal chest pain 2) radiate to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, or left arm. 3- rapid and weak pulse 4- nausea (posterior MI). 5- cardiogenic shock (massive MIs >40% of the left ventricle)
1) Severe, crushing substernal chest pain 2) radiate to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, or left arm. 3- rapid and weak pulse 4- nausea (posterior MI). 5- cardiogenic shock (massive MIs >40% of the left ventricle)
LUNGS. Requirements of a Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Cardiovascular Disorders. Heart Disorders. Diagnostic Tests for CV Function. Bio 375. Pathophysiology
 Cardiovascular Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology Heart Disorders Heart disease is ranked as a major cause of death in the U.S. Common heart diseases include: Congenital heart defects Hypertensive heart
Cardiovascular Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology Heart Disorders Heart disease is ranked as a major cause of death in the U.S. Common heart diseases include: Congenital heart defects Hypertensive heart
B Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8
 The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
MANAGING ASTHMA. Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C
 MANAGING ASTHMA Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by episodes or attacks of inflammation and narrowing of small airways in response to asthma
MANAGING ASTHMA Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by episodes or attacks of inflammation and narrowing of small airways in response to asthma
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
