LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson you will be able to:
|
|
|
- Suzanna Carroll
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LESSON ASSIGNMENT SUBCOURSE MD0806 LESSON 7 Therapeutics III. Antihypertensive Agents. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson you will be able to: 7-1. From a group of statements, select the statement which best defines the term essential hypertension Given the name of a type of essential hypertension and a group of statements, select the statement that best describes that type Given a group of statements, select the statement that best describes why diuretics are used to treat hypertension Given a group of trade and/or generic names of antihypertensive agents match each trade name with its corresponding generic name Given the trade and/or generic name of an antihypertensive agent and a group of indications, side effects, or patient warnings; select the indication(s), side effect(s), or patient warning(s) associated with that agent. SUGGESTION After studying the assignment, complete the exercises at the end of this lesson. These exercises will help you to achieve the lesson objectives. MD
2 7-1. INTRODUCTION LESSON 7 ANTIHYPERTENSIVE AGENTS Section I. INTRODUCTION TO HYPERTENSION a. It is estimated that 23 million people in the United States suffer from hypertension. Of this number, it is thought that 11.5 million people have been diagnosed as having the condition and that 5.75 million of those people are being treated for it. Unfortunately, it is estimated that only million of those persons treated for hypertension are being treated properly. Therefore, it is obvious that hypertension is a major medical problem which should be a concern of all medical personnel. b. Hypertension (high blood pressure) is prevalent in both men and women. It frequently contributes to the death of many persons. The cause of most cases of hypertension is unknown. This type of hypertension is referred to as primary or essential hypertension. Hypertension that has a known cause (kidney disease, hyperthroidism) is called secondary hypertension. Blood pressure is the force that the blood exerts on the vessel wall while the heart is contracting and at rest. The force against the vessel wall during contraction or systole is the systolic pressure and the force during rest or diastole is the diastolic pressure. The blood pressure is expressed in terms of millimeters of mercury (Hg). Normal blood pressure is less than 135 mm Hg (systolic) and less than 85 mm Hg (diastolic) = 135/85 mm Hg TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION There is no cure for hypertension. Most patients who have a bacterial infection are accustomed to taking a 10-day treatment regimen of an antibiotic in order to rid themselves of the infection. The same is not true with hypertension. Once a person begins taking an antihypertensive agent, it is likely that he will continue taking some type of antihypertensive agent for the rest of his life DEFINITION OF ESSENTIAL (PRIMARY) HYPERTENSION Essential (primary) hypertension can be defined as a disorder of unknown origin characterized mainly by an elevated systolic or diastolic blood pressure associated with generalized arteriolar vasoconstriction (see Lesson 3). Essential hypertension may be divided into three classes according to the severity of the condition. Labile hypertension is a condition of elevated blood pressure with intervening periods of normal blood pressure. MD
3 7-4. CLASSES OF ESSENTIAL HYPERTENSION a. Stage I Hypertension. Stage I hypertension is characterized by sustained, documented systolic pressure 140 to 159 mm Hg and/or diastolic pressure measurements 90 to 99 mm Hg. Signs of this type include increased heart rate (tachycardia) and increased cardiac output with normal total peripheral vascular resistance; however, the majority of patients cannot tell that they have hypertension. b. Stage II Hypertension. Stage II hypertension is characterized by sustained, systolic elevation (160 to 179 mm Hg) and/or diastolic pressure (100 to 109 mm Hg). Symptoms are the same as noted in Stage I. Patients with Stage I or II DO NOT show signs of target end organ damage. The organs of most concern are the heart, kidneys, and eyes. Stage I and II hypertension may be treated nonpharmacologically with diet and exercise or pharmacologically with anti-hypertensive medications. c. Stage III Hypertension. Stage III hypertension is characterized by a persistent elevation (systolic greater than 180 mm Hg; diastolic greater than 110 mm Hg) with target end organ damage. Damage to the heart may include strain or enlargement of the left ventricle. Kidney damage may appear as abnormal laboratory values that indicate inefficiency. Damage to the eyes may appear as small hemorrhages due to the sustained blood pressure in these small vessels. This stage is often treated immediately with anti-hypertensive medications. d. Hypertensive Urgency/Crisis. (1) Hypertensive urgency is a condition of persistent elevation in blood pressure without target end organ damage. However, the pressure is high enough that the patient presents for treatment because of symptoms of dizziness, chest pain, or confusion. The goal in treatment of this condition is to normalize the blood pressure as quickly as possible (usually over 1 to 3 days). (2) Hypertensive crisis is a similar condition. However, the patient has symptoms of target end organ damage. This may be a life-threatening condition. The goal of therapy is to normalize the blood pressure in 12 to 24 hours. Both conditions are usually treated with intravenous (IV) anti-hypertensives REVIEW OF IMPORTANT FACTORS RELATING TO HYPERTENSION Essential hypertension is a process of variable course and severity. Several options are open to the physician depending upon the severity of the drug therapy. Condition weight reduction and diet control may be adequate treatment; however, drug therapy is sometimes needed. When drug therapy is required, it usually begins with a diuretic followed by the addition of the other agents based on the patient s response. However, certain classes of drugs may be more advantages (less side effects) when patients have other diseases. It is not unreasonable to see patients treated by the same provider on different drugs. MD
4 7-6. DIURETICS IN THE TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION The effectiveness of diuretics in the treatment of essential hypertension arises from the fact that diuretic agents decrease tubular reabsorption of sodium, which caused a reduction in blood pressure. Some of the common diuretics include hydrochlorothiazide, spironolactone (Aldactone ), furosemide (Lasix ), and triamterene (Dyrenium ). These agents will be discussed in detail in Lesson 8 of this subcourse COMBINATION THERAPY IN THE TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION When diuretics alone are ineffective in controlling hypertension, it is necessary to combine the diuretic therapy with one or more additional agents. The physician may use many combinations of agents in order to control the patient s high blood pressure. The patient should be encouraged to discuss any questions he might have concerning the side effects (for example, drowsiness), which might be caused by an agent or agents. Section II. DRUGS USED IN THE TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION NOTE: For this discussion commonly used antihypertensive agents will be classified into the following categories DRUGS WHICH ACT ON THE SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM NOTE: For a review of the sympathetic nervous system, refer to Subcourse MD0805, Therapeutics II. a. Methyldopa (Aldomet ). Methyldopa is one of the drugs of this type. It is believed to produce its effects by its being metabolized to a substance which is very similar to norepinephrine--but with considerably less vasoconstricting activity than is shown by epinephrine. Thus, methyldopa competes with norepinephrine and thereby depresses the activity of the sympathetic nervous system. This medication is rarely used, but is still one of the drugs of choice for pregnancy-induced hypertension. Side effects associated with this agent include bradycardia, swelling of the feet and lower legs (because sodium and water retention), drowsiness, and mental depression. b. Clonidine (Catapres, Catapres TTS ). Clonidine is an agent that is believed to act by decreasing sympathetic outflow from the brain and consequently inhibit vasoconstriction. It is used in mild to moderate hypertension. Side effects associated with this agent include swelling of the feet and lower legs (due to sodium and water retention) and mental depression. The patient taking this drug should be cautioned to check with his physician before suddenly discontinuing the medication because abrupt withdrawal from the drug may cause serious hypertension problems. Clonidine is also used in the treatment of symptoms associated with alcohol withdrawal. MD
5 7-9. BETA ADRENERGIC BLOCKERS Beta adrenergic blocking agents block the effect of the sympathetic neurotransmitters by competing for receptors. a. Propranolol (Inderal ). Propranolol is a drug used in the treatment of hypertension, angina pectoris, and cardiac arrhythmias. Side effects associated with propranolol include dizziness, mental confusion, and mental depression. It may also exacerbate congestive heart failure and mask the symptoms of hypoglycemia. b. Metaprolol (Lopressor, Toprol XL ). Metaprolol is prescribed for the same conditions as propranolol and is also indicated used in the treatment of myocardial infarction and treatment of congestive heart failure. Normal doses for hypertension are mg twice daily. The dose for heart failure is 6.25 to12.5 mg twice daily and adjusted upward as tolerated by the patient. This agent is available as an oral and injectable preparation. c. Other Beta Adrenergic Blockers. Other beta blockers used in the treatment of hypertension include betaxolol (Kerlone ), bisoprolol (Zebeta ), labetolol (Trandate, Normodyne ), nadolol (Corgard ), and carvedilol (Coreg ). Carvedilol is also indicated for congestive heart failure SMOOTH MUSCLE RELAXANTS Drugs in this category treat hypertension by acting directly on vascular smooth muscle by relaxing the blood vessels. Consequently, they cause vasodilation and a decrease in peripheral resistance results in a lower blood pressure. a. Hydralazine (Apresoline ). Hydralazine is given orally or injected in the management of hypertension. Preferably, it is used in conjunction with other antihypertensive agents. Side effects associated with this agent include chest pain (angina pectoris), a general feeling of weakness, unexplained sore throat, joint pain, and headache. The patient should to be told to avoid getting up suddenly from a lying or a sitting position. b. Alpha Adrenergic Blockers. Alpha adrenergic blockers block alpha receptors in peripheral vessels, therefore causing vasodilation. Agents in the class include prazosin (Minipress ), doxazosin (Cardura ), and terazosin (Hytrin ). Doxazosin and terazosin offer the advantage of once daily dosing and the added benefit of relieving the symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia (enlarged prostate gland). Dizziness, drowsiness, and headache are common side effects associated with these agents, especially with the first dose. Patients must be counseled on these side effects and instructed to take the first dose in the evening at home. Some patients who have taken this drug have also experienced syncope (unconsciousness due to decreased oxygen supply to the brain). MD
6 c. Calcium Channel Blockers. Calcium channel blockers are potent peripheral vasodilators used in the treatment of hypertension. They are similar to beta blockers that can slow the heart rate. Calcium channel blockers are also used in the treatment of atrial fibrillation to control the heart rate. Many of the products are available in oral and injectable form and may be administered once daily. Side effects include dizziness, headache, heartburn, edema, and constipation. Agents include diltiazem (Cardizem, Tiazac, Dilacor ), verapamil (Calan, Isoptin, Covera, Verelan ), amlodipine (Norvasc ), felodipine (Plendil ), and nifedipine (Procardia XL, Adalat CC ). d. Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitors (ACE Inhibitors). ACE inhibitors work by inhibiting the enzyme which converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II. Angiotensin II is one of the most potent vasoconstrictors known to man. By inhibiting the enzyme, these agents produce vasodilation and are used in the treatment of hypertension and congestive heart failure. Most products are administered one to two times daily. The most common side effects are rash, dry cough, and hyperkalemia. These agents are contraindicated in pregnancy. Selected agents include benazepril (Lotensin ), captopril (Capoten ), enalapril (Vasotec ), lisinopril (Prinivil, Zestril ), and ramipril (Altace ). Enalapril is available in an injectable form. e. Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs). ARBs work by directly blocking the angiotensin II receptor to cause vasodilation and lower blood pressure. They appear to have less side effects than ACE inhibitors, especially the dry cough. Selected agents include irbesartan (Avapro ), losartan (Cozaar ), and valsartan (Diovan ) COMBINATION PRODUCTS It should be apparent that in order to control hypertension the patient may be required to take extremely large amounts of medication. In an attempt to develop a more convenient method of controlling hypertension, researchers have combined diuretic and antihypertensive agents in order to maximize the best attributes of each. These combination products are very convenient for the patient to use if the dosage of the product is exactly what the patient needs to control his hypertension. Since these combination products tend to be rather expensive, military pharmacies frequently have a limited selection of these items in stock. Two examples of combination products are listed below. a. Aldactazide (Spironolactone and Hydrochlorothiazide). Spironolactone and hydrochlorothiazide are both diuretics. This particular drug is used in the treatment of hypertension, congestive heart failure and cirrhosis of the liver. The patient taking this medication should be told to take the preparation with or after meals to minimize stomach upset. b. Dyazide (Triamterene and Hydrochlorothiazide). Triamterene and hydrochlorothiazide are both diuretics. This product is used as a diuretic and as an antihypertensive agent. MD
7 7-12. THE TREATMENT OF A HYPERTENSIVE CRISIS OR EMERGENCY Patients presenting with extreme elevations of blood pressure and symptoms of impending stroke, pulmonary edema, kidney failure, or heart attack must be promptly. The following agents are used to treat hypertensive crisis: a. Diazoxide (Hyperstat I.V.) This agent is administered by rapid intravenous (I.V.) injection (150 to 300 milligrams immediately, repeated in 30 minutes and every four hours if needed). When administered, this agent produces a fall in blood pressure in from one to five minutes. Hyperglycemia and sodium retention are side effects associated with this agent. b. Nitroprusside (Nipride ). Nitroprusside is administered by continuous intravenous infusion at a rate of 0.5 to 0.8. micrograms per kilogram of patient weight per minute. The patient must be closely observed when he is receiving this drug since overdosage of nitroprusside results in cyanide poisoning. Nitroprusside is not intended for direct injection. Instead, the drug must be used as an infusion with sterile 5 percent dextrose in water. The intravenous infusion must be used within four hours once it is prepared. Furthermore, the prepared intravenous infusion must be protected from light (for example, the bottle wrapped with foil). Nausea, vomiting, and headache are side effects commonly associated with this agent. Continue with Exercises Return to Table of Contents MD
8 EXERCISES, LESSON 7 INSTRUCTIONS. The following exercises are to be answered by marking the lettered response that best answers the question or best completes the incomplete statement. After you have completed all the exercises, turn to Solutions to Exercises at the end of the lesson and check your answers with the solutions. For each exercise answered incorrectly, reread the material referenced after the solution. 1. Match the drug name in Column A with its trade name listed in Column B. COLUMN A COLUMN B Lisinopril. a. Cardura. Spironolactone and b. Catapres. hydrochlorothiazide combination. Doxazosin. c. Adalat CC. Diltiazem. d. Inderal Metoprolol. e. Calan. Propranolol. f. Cardizem. Clonidine. g. Zestril. Verapamil. h. Lopressor. Nifedipine. i. Aldactazide. MD
9 2. Which of the following statements best defines the term essential hypertension? a. A disorder of unknown origin characterized mainly by an elevated systolic or diastolic pressure associated with generalized arteriolar vasoconstriction. b. A disorder caused by too many fats in the diet and by an excess of sodium in the intracellular fluid. c. A disorder produced by unknown causes which results in a diastolic pressure which is higher than the systolic pressure. d. A disorder of unknown origin that can be cured by a 10-day treatment regimen of diuretics and antihypertensives. 3. Which of the following statements best describes Stage I primary hypertension? a. A type of essential hypertension characterized by documented pressure measurements greater than159 mm Hg (systolic) and / or greater than 99 mm Hg (diastolic). b. A type of essential hypertension characterized by a persistent elevation in diastolic pressure with minor target organ (heart and kidney damage). c. A type of essential hypertension characterized by marked elevated blood pressure with definite target organ (heart and kidney) damage. d. A type of essential hypertension characterized by a mild, but sustained, elevation in diastolic pressure without target organ (heart and kidney) damage. 4. Stage III primary hypertension is best described as a type of essential hypertension characterized by: a. Persistent elevated diastolic pressure with minor damage to the heart and/or kidneys. b. Documented diastolic pressure associated with generalized arteriolar vasoconstriction. c. A mild, but sustained, elevation in diastolic pressure without damage to the heart and/or kidneys. d. Marked elevated blood pressure with definite damage to the heart and/or kidneys. MD
10 5. Nitroprusside (Nipride ) is used in the treatment of: a. Essential hypertension. b. Hypertensive crisis. c. Labile primary hypertension. d. Moderate primary hypertension. 6. What side effect is associated with beta blockers? a. Swelling of the feet and lower legs. b. Tachycardia. c. Restlessness. d. Mask symptoms of hypoglycemia. 7. What should the patient taking terazosin be told? a. To be aware that many patients taking the drug experience impotence or decreased sexual interest. b. To take the medication one hour before meals in order to increase the absorption of the drug. c. To arise slowly from a lying or sitting position because of the possibility of orthostatic hypotension and syncope. d. To avoid taking the medication with fats because absorption of the drug is affected. MD
11 8. The patient taking nitroprusside should be closely monitored because: a. Hyperglycemia and sodium retention occur so abruptly with this agent that death can result if the drug is not withdrawn after their onset. b. Overdosage of nitroprusside results in cyanide poisoning. c. Abrupt withdrawal of this agent can result in an extreme hypertensive crisis. d. Too rapid administration of this product can result in a cerebrovascular accident. 9. Which of the following is a side effect associated with the use of enalapril? a. Hypokalemia (low potassium). b. Dry cough. c. Syncope. d. Chest pain. 10. What is an indication for Coreg? a. Antihypertensive. b. Congestive heart failure. c. Antianginal agent (treatment of angina pectoris). d. a and b only. e. a, b, and c. Check Your Answers on Next Page MD
12 SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES, LESSON 7 1. G._ Lisinopril (para 7-10d). a. Cardura. I. Spironolactone and b. Catapres hydrochlorothiazide combination. (para 7-11a) A Doxazosin (para 7-10b). c. Adalat CC F Diltiazem (para 7-10c). d. Inderal H Metoprolol (para 7-9b). e. Calan D Propranolol (para 7-9a). f. Cardizem B Clonidine (para 7-8b). g. Zestril E Verapamil (para 7-10c). h. Lopressor C Nifedipine (para 7-10c). i. Aldactazide 2. a (para 7-3) 3. a (para 7-4a) 4. d (para 7-4c) 5. b (para 7-12b) 6. d (para 7-9a) 7. c (para 7-10b) 8. b (para 7-12b) 9. b (para 7-10d) 10. d (para 7-9c) Return to Table of Contents MD
Top 200 Section 4. Cardiovascular Drugs
 Top 200 Section 4 Cardiovascular Drugs Objectives After finishing this presentation the audience should be able to: Describe conditions/disease states that would make a person a candidate for drug therapy.
Top 200 Section 4 Cardiovascular Drugs Objectives After finishing this presentation the audience should be able to: Describe conditions/disease states that would make a person a candidate for drug therapy.
Cardiac Medications At A Glance
 Cardiac Medications At A Glance 1) Anticoagulants (Also known as Blood Thinners.) Dalteparin (Fragmin), Danaparoid (Orgaran) Enoxaparin (Lovenox) Heparin (various) Tinzaparin (Innohep) Warfarin (Coumadin)
Cardiac Medications At A Glance 1) Anticoagulants (Also known as Blood Thinners.) Dalteparin (Fragmin), Danaparoid (Orgaran) Enoxaparin (Lovenox) Heparin (various) Tinzaparin (Innohep) Warfarin (Coumadin)
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs
 Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs Blood Pressure Normal = sys
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs Blood Pressure Normal = sys
LESSON ASSIGNMENT Given the trade and/or generic name of an adrenergic blocking agent, classify that agent as either an alpha or beta blocker.
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 8 Adrenergic Blocking Agents. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 8-1 through 8-5. LESSON OBJECTIVES 8-1. Given a group of statements, select the statement that best describes one of the
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 8 Adrenergic Blocking Agents. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 8-1 through 8-5. LESSON OBJECTIVES 8-1. Given a group of statements, select the statement that best describes one of the
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
12.5mg, 25mg, 50mg. 25mg, 50mg. 2.5mg, 5mg, 10mg. 5mg, 10mg, 20mg, 100mg. 25mg. -- $2.81 Acetazolamide (IR, 125mg, 250mg, 500mg (ER)
 MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Blood Pressure P&T DATE: 5/9/2017 THERAPEUTIC CLASS: Cardiovascular Disorders REVIEW HISTORY: 9/15, 2/13, 2/08, 5/07 LOB
MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Blood Pressure P&T DATE: 5/9/2017 THERAPEUTIC CLASS: Cardiovascular Disorders REVIEW HISTORY: 9/15, 2/13, 2/08, 5/07 LOB
Chapter 23. Media Directory. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Hypertension: Classified into Three Categories
 Chapter 23 Drugs for Hypertension Slide 37 Slide 41 Media Directory Nifedipine Animation Doxazosin Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Includes
Chapter 23 Drugs for Hypertension Slide 37 Slide 41 Media Directory Nifedipine Animation Doxazosin Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Includes
Preventing and Managing High Blood Pressure
 MINTO PREVENTION & REHABILITATION CENTRE CENTRE DE PREVENTION ET DE READAPTATION MINTO Preventing and Managing High Blood Pressure About This Kit Fortunately, high blood pressure is easily detected and
MINTO PREVENTION & REHABILITATION CENTRE CENTRE DE PREVENTION ET DE READAPTATION MINTO Preventing and Managing High Blood Pressure About This Kit Fortunately, high blood pressure is easily detected and
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat
 Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Hypertension is also an important risk factor in the development of chronic kidney disease and heart failure.
 Hypertension Hypertension Hypertension is defined as either a sustained systolic blood pressure of greater than 140 mm Hg or a sustained diastolic blood pressure of greater than 90 mm Hg. Hypertension
Hypertension Hypertension Hypertension is defined as either a sustained systolic blood pressure of greater than 140 mm Hg or a sustained diastolic blood pressure of greater than 90 mm Hg. Hypertension
Towards a Greater Understanding of Cardiac Medications Foundational Cardiac Concepts That Must Be Understood:
 Towards a Greater Understanding of Cardiac Medications Foundational Cardiac Concepts That Must Be Understood: Cardiac Output (CO) CO=SVxHR (stroke volume x heart rate) Cardiac output: The amount of blood
Towards a Greater Understanding of Cardiac Medications Foundational Cardiac Concepts That Must Be Understood: Cardiac Output (CO) CO=SVxHR (stroke volume x heart rate) Cardiac output: The amount of blood
Diabetes and a Healthy Heart. Meeting 6. Welcome! Glucose. Balance Makes a Difference! Medicine Helps with. Glucose. Balance!
 6-1 Welcome! Welcome to the lesson! It s good to see you again! Before we visit with Uncle Tommy and Kaipo, let s take a few minutes to review the last five meetings. Glucose Balance Makes a Difference!
6-1 Welcome! Welcome to the lesson! It s good to see you again! Before we visit with Uncle Tommy and Kaipo, let s take a few minutes to review the last five meetings. Glucose Balance Makes a Difference!
Heart Disease and Prevention PRESENTED BY: DOTTIE CRAIG NP- C, JANE ARCHER NP-C, KATHY DAPPER RN, NICCI FRAVEL RN
 Heart Disease and Prevention PRESENTED BY: DOTTIE CRAIG NP- C, JANE ARCHER NP-C, KATHY DAPPER RN, NICCI FRAVEL RN Objectives Identify Normal Systolic and Diastolic Blood pressures Recognize common Antihypertensive
Heart Disease and Prevention PRESENTED BY: DOTTIE CRAIG NP- C, JANE ARCHER NP-C, KATHY DAPPER RN, NICCI FRAVEL RN Objectives Identify Normal Systolic and Diastolic Blood pressures Recognize common Antihypertensive
Hypertension (JNC-8)
 Hypertension (JNC-8) Southern California University of Health Sciences Physician Assistant Program Management and Treatment of Hypertension April 17, 2018, presented by Ezra Levy, Pharm.D.! The 8 th Joint
Hypertension (JNC-8) Southern California University of Health Sciences Physician Assistant Program Management and Treatment of Hypertension April 17, 2018, presented by Ezra Levy, Pharm.D.! The 8 th Joint
HYPERTENSION IN EMERGENCY MEDICINE Michael Jay Bresler, M.D., FACEP
 HYPERTENSION IN EMERGENCY MEDICINE Michael Jay Bresler, M.D., FACEP What is normal blood pressure? Prehypertension 130-139/80-90 Compared with normal BP Double the risk for developing hypertension. Lifestyle
HYPERTENSION IN EMERGENCY MEDICINE Michael Jay Bresler, M.D., FACEP What is normal blood pressure? Prehypertension 130-139/80-90 Compared with normal BP Double the risk for developing hypertension. Lifestyle
Antihypertensives. Antihypertensive Classes. RAAS Inhibitors. Renin-Angiotensin Cascade. Angiotensin Receptors. Approaches to Hypertension Treatment
 Approaches to Hypertension Treatment Antihypertensives Inhibit Sympathetic impulses Inhibit contractility Inhibit heart rate Inhibit vasoconstriction Inhibit smooth muscle function Inhibit RAAS Inhibit
Approaches to Hypertension Treatment Antihypertensives Inhibit Sympathetic impulses Inhibit contractility Inhibit heart rate Inhibit vasoconstriction Inhibit smooth muscle function Inhibit RAAS Inhibit
PassAssured's Pharmacy Technician Training Systems. Medication Review. Cardiovascular Drugs. Pharmacy Technician Training Systems Passassured, LLC
 Medication Review Cardiovascular Drugs Pharmacy Technician Training Systems Passassured, LLC p1 Medication Review, Cardiovascular Drugs Click Here for Glossary Index! Click Here to Print Topic Help File
Medication Review Cardiovascular Drugs Pharmacy Technician Training Systems Passassured, LLC p1 Medication Review, Cardiovascular Drugs Click Here for Glossary Index! Click Here to Print Topic Help File
12.5mg, 25mg, 50mg. 25mg, 50mg. 250mg, 500mg, 250mg/5ml. 2.5mg, 5mg, 10mg. 5mg, 10mg, 20mg, 100mg. 25mg
 MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Blood Pressure P&T DATE: 9/11/2018 THERAPEUTIC CLASS: Cardiovascular Disorders REVIEW HISTORY: 5/17, 9/15, 2/13, 2/08, LOB
MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Blood Pressure P&T DATE: 9/11/2018 THERAPEUTIC CLASS: Cardiovascular Disorders REVIEW HISTORY: 5/17, 9/15, 2/13, 2/08, LOB
TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION
 TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION Aim of treatment BP Goals Main items of treatment Lifestyle modification When to start drug Rx Pharmacological therapy 1. Relief of symptoms 2. Prevention of complications and
TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION Aim of treatment BP Goals Main items of treatment Lifestyle modification When to start drug Rx Pharmacological therapy 1. Relief of symptoms 2. Prevention of complications and
ACEBUTOLOL HCL 100MG TABLET GENERIC BETA BLOCKERS ALISKIREN 150MG TABLET RASILAZ RENIN INHIBITOR
 S/N ME OF MEDICATIONS BRANDED/GENERIC DRUG CLASS * UNIT PRICE RANGE (SGD$) 1 ACEBUTOLOL HCL 100MG CAPSULE SECTRAL BETA BLOCKERS 0.50 2 ACEBUTOLOL HCL 100MG TABLET GENERIC BETA BLOCKERS 0.33 3 ALISKIREN
S/N ME OF MEDICATIONS BRANDED/GENERIC DRUG CLASS * UNIT PRICE RANGE (SGD$) 1 ACEBUTOLOL HCL 100MG CAPSULE SECTRAL BETA BLOCKERS 0.50 2 ACEBUTOLOL HCL 100MG TABLET GENERIC BETA BLOCKERS 0.33 3 ALISKIREN
Dr Narender Goel MD (Internal Medicine and Nephrology) Financial Disclosure: None, Conflict of Interest: None
 Dr Narender Goel MD (Internal Medicine and Nephrology) drnarendergoel@gmail.com Financial Disclosure: None, Conflict of Interest: None 12 th December 2013, New York Visit us at: http://kidneyscience.info/
Dr Narender Goel MD (Internal Medicine and Nephrology) drnarendergoel@gmail.com Financial Disclosure: None, Conflict of Interest: None 12 th December 2013, New York Visit us at: http://kidneyscience.info/
Beta 1 Beta blockers A - Propranolol,
 Pharma Lecture 3 Beta blockers that we are most interested in are the ones that target Beta 1 receptors. Beta blockers A - Propranolol, it s a non-selective competitive antagonist of beta 1 and beta 2
Pharma Lecture 3 Beta blockers that we are most interested in are the ones that target Beta 1 receptors. Beta blockers A - Propranolol, it s a non-selective competitive antagonist of beta 1 and beta 2
Information in these slides is used with permission from St. Mary s Cardiac Rehab
 Information in these slides is used with permission from St. Mary s Cardiac Rehab Prescription Pointers Heart Medications Questions!! 2-4% of patients who visit ER s have experienced a medication misadventure
Information in these slides is used with permission from St. Mary s Cardiac Rehab Prescription Pointers Heart Medications Questions!! 2-4% of patients who visit ER s have experienced a medication misadventure
Management of Hypertension
 Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
Section 3, Lecture 2
 59-291 Section 3, Lecture 2 Diuretics: -increase in Na + excretion (naturesis) Thiazide and Related diuretics -decreased PVR due to decreases muscle contraction -an economical and effective treatment -protect
59-291 Section 3, Lecture 2 Diuretics: -increase in Na + excretion (naturesis) Thiazide and Related diuretics -decreased PVR due to decreases muscle contraction -an economical and effective treatment -protect
7/7/ CHD/MI LVH and LV dysfunction Dysrrhythmias Stroke PVD Renal insufficiency and failure Retinopathy. Normal <120 Prehypertension
 Prevalence of Hypertension Hypertension: Diagnosis and Management T. Villela, M.D. Program Director University of California, San Francisco-San Francisco General Hospital Family and Community Medicine
Prevalence of Hypertension Hypertension: Diagnosis and Management T. Villela, M.D. Program Director University of California, San Francisco-San Francisco General Hospital Family and Community Medicine
Annual Review of Antihypertensives - Fiscal Year 2009
 Annual Review of Antihypertensives - Fiscal Year 2009 Oklahoma HealthCare Authority April 2010 Current Prior Authorization Criteria There are 7 categories of antihypertensive medications currently included
Annual Review of Antihypertensives - Fiscal Year 2009 Oklahoma HealthCare Authority April 2010 Current Prior Authorization Criteria There are 7 categories of antihypertensive medications currently included
Physician/Clinic Collaborative Practice Agreement
 Physician/Clinic Collaborative Practice Agreement Effective October 1, 2010, Connecticut Senate Bill 428 (PA 10-117) extends to all settings and medical conditions the opportunity for licensed pharmacists
Physician/Clinic Collaborative Practice Agreement Effective October 1, 2010, Connecticut Senate Bill 428 (PA 10-117) extends to all settings and medical conditions the opportunity for licensed pharmacists
HYPERTENSION: Sustained elevation of arterial blood pressure above normal o Systolic 140 mm Hg and/or o Diastolic 90 mm Hg
 Lecture 39 Anti-Hypertensives B-Rod BLOOD PRESSURE: Systolic / Diastolic NORMAL: 120/80 Systolic = measure of pressure as heart is beating Diastolic = measure of pressure while heart is at rest between
Lecture 39 Anti-Hypertensives B-Rod BLOOD PRESSURE: Systolic / Diastolic NORMAL: 120/80 Systolic = measure of pressure as heart is beating Diastolic = measure of pressure while heart is at rest between
Adapted d from Federation of Health Regulatory Colleges of Ontario Template Last Updated September 18, 2017
 Insert Logo or Org Name Here Primary Care Medical Directive for Hypertension Management Adapted d from Federation of Health Regulatory Colleges of Ontario Template Last Updated September 18, 2017 Title:
Insert Logo or Org Name Here Primary Care Medical Directive for Hypertension Management Adapted d from Federation of Health Regulatory Colleges of Ontario Template Last Updated September 18, 2017 Title:
8/19/2016. No Conflicts. I struggled with everything cardiac in nursing school.
 Cindy Weston, DNP, RN, CCRN, CNS CC, FNP BC Assistant Professor, Texas A&M Health Science Center College of Nursing Describe and define epidemiology and pathophysiology of hypertension Differentiate JNC8
Cindy Weston, DNP, RN, CCRN, CNS CC, FNP BC Assistant Professor, Texas A&M Health Science Center College of Nursing Describe and define epidemiology and pathophysiology of hypertension Differentiate JNC8
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment
 Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Chapter 10 Worksheet Blood Pressure and Antithrombotic Agents
 Complete the following. 1. A layer of cells lines each vessel in the vascular system. This layer is a passive barrier that keeps cells and proteins from going into tissues; it also contains substances
Complete the following. 1. A layer of cells lines each vessel in the vascular system. This layer is a passive barrier that keeps cells and proteins from going into tissues; it also contains substances
Medications. Your prescriptions can be filled by your home pharmacy or by the Michigan Medicine Taubman Center outpatient pharmacy.
 Medications Your prescriptions can be filled by your home pharmacy or by the Michigan Medicine Taubman Center outpatient pharmacy. What do I need to know about medications after my heart attack? When you
Medications Your prescriptions can be filled by your home pharmacy or by the Michigan Medicine Taubman Center outpatient pharmacy. What do I need to know about medications after my heart attack? When you
Treatment of Essential Hypertension
 2016 edition by Mark A. Simmons, PhD Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences School of Pharmacy University of Maryland Eastern Shore Originally developed by Hugh J. Burford, PhD, FCP Department of Pharmacology
2016 edition by Mark A. Simmons, PhD Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences School of Pharmacy University of Maryland Eastern Shore Originally developed by Hugh J. Burford, PhD, FCP Department of Pharmacology
7/21/2017. Learning Objectives. Current Cardiovascular Pharmacology. Epinephrine. Cardiotonic Agents. Epinephrine. Epinephrine. Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT
 Learning Objectives Current Cardiovascular Pharmacology Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Explain the actions, effects, indications, adverse effects, & precautions for agents from the following drug categories Cardiotonic
Learning Objectives Current Cardiovascular Pharmacology Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Explain the actions, effects, indications, adverse effects, & precautions for agents from the following drug categories Cardiotonic
Difficult to Treat Hypertension
 Difficult to Treat Hypertension According to Goldilocks JNC 8 Blood Pressure Goals (2014) BP Goal 60 years old and greater*- systolic < 150 and diastolic < 90. (Grade A)** BP Goal 18-59 years old* diastolic
Difficult to Treat Hypertension According to Goldilocks JNC 8 Blood Pressure Goals (2014) BP Goal 60 years old and greater*- systolic < 150 and diastolic < 90. (Grade A)** BP Goal 18-59 years old* diastolic
8/20/2018. Objectives. What is hypertension? cont. What is hypertension? Epidemiology cont. Epidemiology
 Objectives Hypertension (high blood pressure): Clinical Pearls for the Pharmacy Technician Tanya Schmidt PharmD, RPh Director of Central Operations at Thrifty White Pharmacy North Dakota Board of Pharmacy
Objectives Hypertension (high blood pressure): Clinical Pearls for the Pharmacy Technician Tanya Schmidt PharmD, RPh Director of Central Operations at Thrifty White Pharmacy North Dakota Board of Pharmacy
PHARM 504: Pharmacy Practice Winter 2009 MCP DRUGS #3: CARDIOVASCULAR PRODUCTS January 22th, 2010 Laura Knutzen
 PHARM 504: Pharmacy Practice Winter 2009 MCP DRUGS #3: CARDIOVASCULAR PRODUCTS January 22th, 2010 Laura Knutzen General Tips and Information: 1. Types of Cardiovascular Disorders: Myocardial infarction
PHARM 504: Pharmacy Practice Winter 2009 MCP DRUGS #3: CARDIOVASCULAR PRODUCTS January 22th, 2010 Laura Knutzen General Tips and Information: 1. Types of Cardiovascular Disorders: Myocardial infarction
sympatholytics sympatholytics sympatholytics
 sympatholytics sympatholytics sympatholytics CNS-ACTING SYMPATHOPLEGICS Sympathetic brain signals Doesn t affect baroreceptor reflex (no orthostatic hypotension) Methyldopa α-methylne crosses BBB (+) α-adrenoreceptors
sympatholytics sympatholytics sympatholytics CNS-ACTING SYMPATHOPLEGICS Sympathetic brain signals Doesn t affect baroreceptor reflex (no orthostatic hypotension) Methyldopa α-methylne crosses BBB (+) α-adrenoreceptors
Hypertension Management - Summary
 Who should have blood pressure assessed? Hypertension Management - Summary All patients over the age of 40 years, every 1-3 years in order to determine their cardiovascular risk (ie. Framingham Risk Score)
Who should have blood pressure assessed? Hypertension Management - Summary All patients over the age of 40 years, every 1-3 years in order to determine their cardiovascular risk (ie. Framingham Risk Score)
Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular system
 Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular System: General Section 1 of 6 Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular system 2.1 Positive inotropic drugs 2.1.1 Cardiac glycosides DIGOXIN 2.2 Diuretics Elixir 50micrograms in 1ml Injection
Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular System: General Section 1 of 6 Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular system 2.1 Positive inotropic drugs 2.1.1 Cardiac glycosides DIGOXIN 2.2 Diuretics Elixir 50micrograms in 1ml Injection
Module 1: Evidence-based Education for Health Care Professionals
 Module 1: Evidence-based Education for Health Care Professionals Heart Failure is a HUGE Problem Prevalence Incidence Mortality Hospital Discharges Cost 1 5,300,000 660,000 284,965 1,084,000 $34.8 billion
Module 1: Evidence-based Education for Health Care Professionals Heart Failure is a HUGE Problem Prevalence Incidence Mortality Hospital Discharges Cost 1 5,300,000 660,000 284,965 1,084,000 $34.8 billion
Treatment of Essential Hypertension
 2016 edition by Mark A. Simmons, PhD Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences School of Pharmacy University of Maryland Eastern Shore Originally developed by Hugh J. Burford, PhD, FCP Department of Pharmacology
2016 edition by Mark A. Simmons, PhD Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences School of Pharmacy University of Maryland Eastern Shore Originally developed by Hugh J. Burford, PhD, FCP Department of Pharmacology
Antihypertensive Agents
 Antihypertensive Agents Southern California University of Health Sciences Physician Assistant Program Management and Treatment of Hypertension April 7, 08, presented by Ezra Levy, Pharm.D! Usual Dose,
Antihypertensive Agents Southern California University of Health Sciences Physician Assistant Program Management and Treatment of Hypertension April 7, 08, presented by Ezra Levy, Pharm.D! Usual Dose,
Get Healthy Stay Healthy
 Hypertension Management WHAT IS HYPERTENSION (HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE)? Blood pressure is a measure of how hard the blood pushes against the walls of your arteries as it moves through your body. It is normal
Hypertension Management WHAT IS HYPERTENSION (HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE)? Blood pressure is a measure of how hard the blood pushes against the walls of your arteries as it moves through your body. It is normal
Drum Up Support. Living with Heart Failure. Doctor. Phone number. Emergency number. Target weight
 Drum Up Support Regular doctor visits help drum up support in your favor! Living with Heart Failure Doctor Phone number Emergency number Target weight This material originated with the Arkansas Foundation
Drum Up Support Regular doctor visits help drum up support in your favor! Living with Heart Failure Doctor Phone number Emergency number Target weight This material originated with the Arkansas Foundation
Value-Based Drug List for ABCs of Diabetes
 Effective January 1, 2019 Value-Based Drug List for ABCs of Diabetes PCPS provides a Value-Based Benefit Design (VBD) to qualified participants in the ABCs of Diabetes. This means you will have lower out-of-pocket
Effective January 1, 2019 Value-Based Drug List for ABCs of Diabetes PCPS provides a Value-Based Benefit Design (VBD) to qualified participants in the ABCs of Diabetes. This means you will have lower out-of-pocket
Medications and Falls Part 1
 Medications and Falls Part 1 Introduction with General Principles and Risk Evaluation for Cardiovascular Medications Dennis J Chapron Medication Safety Pharmacist Saint Francis Hospital and Medical Center
Medications and Falls Part 1 Introduction with General Principles and Risk Evaluation for Cardiovascular Medications Dennis J Chapron Medication Safety Pharmacist Saint Francis Hospital and Medical Center
Some Facts. Medications and Falls Part 1. Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Falls Statistics for Older Adults ( 65yrs) 11/27/2018
 Medications and Falls Part 1 Introduction with General Principles and Risk Evaluation for Cardiovascular Medications Dennis J Chapron reports no real or potential conflicts of interest relevant to this
Medications and Falls Part 1 Introduction with General Principles and Risk Evaluation for Cardiovascular Medications Dennis J Chapron reports no real or potential conflicts of interest relevant to this
Hypertension, Hyperlipidemia and Obesity. Mi-CCSI
 Hypertension, Hyperlipidemia and Obesity Mi-CCSI Objectives Review the prevalence of hypertension, hyperlipidemia and obesity Correlation of the 3 conditions Discuss why it is important to treat these
Hypertension, Hyperlipidemia and Obesity Mi-CCSI Objectives Review the prevalence of hypertension, hyperlipidemia and obesity Correlation of the 3 conditions Discuss why it is important to treat these
Evaluation and Management of Acute Decompensated Heart Failure (HF) with Reduced Ejection Fraction Systolic Heart Failure (HFrEF)(EF<40%
 Evaluation and Management of Acute Decompensated Heart Failure (HF) with Reduced Ejection Fraction Systolic Heart Failure (HFrEF)(EF
Evaluation and Management of Acute Decompensated Heart Failure (HF) with Reduced Ejection Fraction Systolic Heart Failure (HFrEF)(EF
Module 1: Evidence-based Education for Health Care Professionals
 Module 1: Evidence-based Education for Health Care Professionals Heart Failure is a HUGE Problem Prevalence Incidence Mortality Hospital Discharges Cost 1 5,300,000 660,000 284,965 1,084,000 $34.8 billion
Module 1: Evidence-based Education for Health Care Professionals Heart Failure is a HUGE Problem Prevalence Incidence Mortality Hospital Discharges Cost 1 5,300,000 660,000 284,965 1,084,000 $34.8 billion
Fundamentals of Pharmacology for Veterinary Technicians Chapter 8
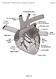 Figure 8-1 Figure 8-2 Figure 8-3 Figure 8-4 Figure 8-5 Figure 8-7 Figure 8-8 Figure 8-9 TABLE 8-1 Blood Flow Through the Heart The right atrium receives blood from all tissues, except the lungs, through
Figure 8-1 Figure 8-2 Figure 8-3 Figure 8-4 Figure 8-5 Figure 8-7 Figure 8-8 Figure 8-9 TABLE 8-1 Blood Flow Through the Heart The right atrium receives blood from all tissues, except the lungs, through
HypertensionTreatment Guidelines. Michaelene Urban APRN, MSN, ACNS-BC, ANP-BC
 HypertensionTreatment Guidelines Michaelene Urban APRN, MSN, ACNS-BC, ANP-BC Objectives: Review the definition of the different stages of HTN. Review the current guidelines for treatment of HTN. Provided
HypertensionTreatment Guidelines Michaelene Urban APRN, MSN, ACNS-BC, ANP-BC Objectives: Review the definition of the different stages of HTN. Review the current guidelines for treatment of HTN. Provided
Antihypertensive drugs: I. Thiazide and other diuretics:
 Clinical assessment of hypertensive patient: You have to take history regarding the presence of other risk factors for CAb like diabetes mellitus, smoking, etc. Take history whether the patient takes medications
Clinical assessment of hypertensive patient: You have to take history regarding the presence of other risk factors for CAb like diabetes mellitus, smoking, etc. Take history whether the patient takes medications
DRUGS USED TO TREAT HYPERTENSION BY ALI ALALAWI
 DRUGS USED TO TREAT HYPERTENSION BY ALI ALALAWI 3. Vasodilators Drugs which dilate blood vessels ( decrease peripheral vascular resistance) by acting on smooth muscle cells through non-autonomic mechanisms:
DRUGS USED TO TREAT HYPERTENSION BY ALI ALALAWI 3. Vasodilators Drugs which dilate blood vessels ( decrease peripheral vascular resistance) by acting on smooth muscle cells through non-autonomic mechanisms:
Categories of HTN. Overview of Hypertension. Types of Hypertension
 Categories of HTN Overview of Hypertension Normal SBP 100 Quick review of the Basics: What is
Categories of HTN Overview of Hypertension Normal SBP 100 Quick review of the Basics: What is
Beta-blockers. Atenolol. Propranolol. Bisoprolol. Metoprolol. Labetalol. Carvedilol.
 Drugs of CVS Beta-blockers Atenolol. Propranolol. Bisoprolol. Metoprolol. Labetalol. Carvedilol. Atenolol.cardioselective Propranolol, nonselective Bisoprolol, cardioselective Metoprolol Carvedilol, alpha
Drugs of CVS Beta-blockers Atenolol. Propranolol. Bisoprolol. Metoprolol. Labetalol. Carvedilol. Atenolol.cardioselective Propranolol, nonselective Bisoprolol, cardioselective Metoprolol Carvedilol, alpha
MEDICATION FACT SHEET
 ACE Inhibitors Names of ACE Inhibitors: quinapril (Accupril ), enalapril (Vasotec ), ramipril (Altace ), captopril (Capoten ), fosinopril (Monopril ), benazepril (Lotensin ), lisinopril (Zestril, Prinivil
ACE Inhibitors Names of ACE Inhibitors: quinapril (Accupril ), enalapril (Vasotec ), ramipril (Altace ), captopril (Capoten ), fosinopril (Monopril ), benazepril (Lotensin ), lisinopril (Zestril, Prinivil
Prof dr Aleksandar Raskovic DIRECT VASODILATORS
 Prof dr Aleksandar Raskovic DIRECT VASODILATORS Direct vasodilators Minoxidil (one of the most powerful peripheral arterial dilators) Opening of KATP channels, efflux of K, lose of Ca and smooth muscle
Prof dr Aleksandar Raskovic DIRECT VASODILATORS Direct vasodilators Minoxidil (one of the most powerful peripheral arterial dilators) Opening of KATP channels, efflux of K, lose of Ca and smooth muscle
Adult Blood Pressure Clinician Guide June 2018
 Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Adult Blood Pressure Clinician Guide June 2018 Adult Blood Pressure Clinician Guide June 2018 Introduction This Clinician Guide is based on the 2018
Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Adult Blood Pressure Clinician Guide June 2018 Adult Blood Pressure Clinician Guide June 2018 Introduction This Clinician Guide is based on the 2018
Medicines for Heart Disease
 Medicines for Heart Disease There are many medicines to treat heart disease. Ask your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist if you have questions about your medicines. Take medicines as directed. Do NOT stop taking
Medicines for Heart Disease There are many medicines to treat heart disease. Ask your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist if you have questions about your medicines. Take medicines as directed. Do NOT stop taking
Chapter 9. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Cardiac Arrhythmias. Define electrical therapy
 Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
What in the World is Functional Medicine?
 What in the World is Functional Medicine? An Introduction to a Systems Based Approach of Chronic Disease Meneah R Haworth, FNP-C Disclosure v I am a student of the Institute for Functional Medicine. They
What in the World is Functional Medicine? An Introduction to a Systems Based Approach of Chronic Disease Meneah R Haworth, FNP-C Disclosure v I am a student of the Institute for Functional Medicine. They
Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide
 Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide Main Idea: The function of the circulatory system is to maintain adequate blood flow to all tissues. Clinical
Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide Main Idea: The function of the circulatory system is to maintain adequate blood flow to all tissues. Clinical
Angina pectoris due to coronary atherosclerosis : Atenolol is indicated for the long term management of patients with angina pectoris.
 Lonet Tablet Description Lonet contains Atenolol, a synthetic β1 selective (cardioselective) adrenoreceptor blocking agent without membrane stabilising or intrinsic sympathomimetic (partial agonist) activity.
Lonet Tablet Description Lonet contains Atenolol, a synthetic β1 selective (cardioselective) adrenoreceptor blocking agent without membrane stabilising or intrinsic sympathomimetic (partial agonist) activity.
Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in Diabetic Mellitus. Presenter: Dr. Martin N. Wanyoike MB.CHB., M. Med.(internal med) Physician / Cardiologist
 Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in Diabetic Mellitus Presenter: Dr. Martin N. Wanyoike MB.CHB., M. Med.(internal med) Physician / Cardiologist Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in Diabetic Mellitus Disclosures
Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in Diabetic Mellitus Presenter: Dr. Martin N. Wanyoike MB.CHB., M. Med.(internal med) Physician / Cardiologist Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in Diabetic Mellitus Disclosures
1/4/18. Heart Failure Guideline Review and Update. Disclosure. Pharmacist Objectives. Pharmacy Technician Objectives. What is Heart Failure?
 Disclosure Heart Failure Guideline Review and Update I have had no financial relationship over the past 12 months with any commercial sponsor with a vested interest in this presentation. Natalie Beiter,
Disclosure Heart Failure Guideline Review and Update I have had no financial relationship over the past 12 months with any commercial sponsor with a vested interest in this presentation. Natalie Beiter,
ANTIHYPERTENSIVES. Assoc. Prof. Bilgen Başgut
 ANTIHYPERTENSIVES Assoc. Prof. Bilgen Başgut Hypertension Hypertension is a condition in which the blood pressure is persistently higher than normal Hypertension > 140 mmhg > 90 mmhg Systolic Blood Pressure
ANTIHYPERTENSIVES Assoc. Prof. Bilgen Başgut Hypertension Hypertension is a condition in which the blood pressure is persistently higher than normal Hypertension > 140 mmhg > 90 mmhg Systolic Blood Pressure
α 1 receptor smooth muscle activation
 Drugs in Hypertension Dr. Yuri Clement Pharmacology Unit, FMS Objectives Revision of physiological control of BP. What is hypertension? Associated risks of uncontrolled hypertension ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUGS:
Drugs in Hypertension Dr. Yuri Clement Pharmacology Unit, FMS Objectives Revision of physiological control of BP. What is hypertension? Associated risks of uncontrolled hypertension ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUGS:
CARDIAC REHABILITATION PROGRAMME:- MEDICATION
 CARDIAC REHABILITATION PROGRAMME:- MEDICATION AIM OF THIS SESSION Understand the reasons for taking your medications, Discuss the common side effects associated with these medications - knowing when to
CARDIAC REHABILITATION PROGRAMME:- MEDICATION AIM OF THIS SESSION Understand the reasons for taking your medications, Discuss the common side effects associated with these medications - knowing when to
Medicines for high blood pressure
 Patient Information: Medicines Medicines for high blood pressure Health & care information you can trust The Information Standard Certified Member Working together for better patient information What is
Patient Information: Medicines Medicines for high blood pressure Health & care information you can trust The Information Standard Certified Member Working together for better patient information What is
Mi-CCSI welcomes you to the 2 nd in our 4 part Basics of Disease Management Webinar Series
 Our speaker today is: Susan Vos, BSN, RN, CCM Mi-CCSI welcomes you to the 2 nd in our 4 part Basics of Disease Management Webinar Series We will be starting shortly A few housekeeping items: We will be
Our speaker today is: Susan Vos, BSN, RN, CCM Mi-CCSI welcomes you to the 2 nd in our 4 part Basics of Disease Management Webinar Series We will be starting shortly A few housekeeping items: We will be
Hypertension (HTN) Lecture Note
 Hypertension (HTN) Lecture Note October, 2009 Chuang-Ye Hong, MD, PhD, FACP Wan-Fang Hospital Taipei Medical University Outline Definition Epidemiology Measurement of BP Secondary cause Target organ damage
Hypertension (HTN) Lecture Note October, 2009 Chuang-Ye Hong, MD, PhD, FACP Wan-Fang Hospital Taipei Medical University Outline Definition Epidemiology Measurement of BP Secondary cause Target organ damage
This information explains heart failure, including causes and signs of heart failure, how heart failure is diagnosed, and how it s treated.
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Heart Failure This information explains heart failure, including causes and signs of heart failure, how heart failure is diagnosed, and how it s treated. About Heart Failure
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Heart Failure This information explains heart failure, including causes and signs of heart failure, how heart failure is diagnosed, and how it s treated. About Heart Failure
Living with Congestive Heart Failure: A Guide to a Healthy Heart
 Living with Congestive Heart Failure: A Guide to a Healthy Heart Things to Know, Before You Go Dear Patient/Caregiver These are the things you NEED TO KNOW, BEFORE YOU GO. It is very important that you
Living with Congestive Heart Failure: A Guide to a Healthy Heart Things to Know, Before You Go Dear Patient/Caregiver These are the things you NEED TO KNOW, BEFORE YOU GO. It is very important that you
Blood Pressure Management in Acute Ischemic Stroke
 Blood Pressure Management in Acute Ischemic Stroke Kimberly Clark, PharmD, BCCCP Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Critical Care, Greenville Health System Adjunct Assistant Professor, South Carolina College
Blood Pressure Management in Acute Ischemic Stroke Kimberly Clark, PharmD, BCCCP Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Critical Care, Greenville Health System Adjunct Assistant Professor, South Carolina College
Antihypertensive Agents
 Antihypertensive Agents Öner Süzer www.onersuzer.com osuzer@istanbul.edu.tr Last update: 13.11.2009 1 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005 2 1 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005 3 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005
Antihypertensive Agents Öner Süzer www.onersuzer.com osuzer@istanbul.edu.tr Last update: 13.11.2009 1 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005 2 1 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005 3 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005
Chemistry 106: Drugs in Society Lecture 20: How do Drugs Elicit an Effect? Interactions between Drugs and Macromolecular Targets II 5/11/18
 Chemistry 106: Drugs in Society Lecture 20: How do Drugs Elicit an Effect? Interactions between Drugs and Macromolecular Targets II 5/11/18 By the end of this session, you should be able to 1. Define enzyme
Chemistry 106: Drugs in Society Lecture 20: How do Drugs Elicit an Effect? Interactions between Drugs and Macromolecular Targets II 5/11/18 By the end of this session, you should be able to 1. Define enzyme
Hypertension and the Dental Patient
 Course Number: 205 Hypertension and the Dental Patient John H. Hardeman, MD, DDS Upon successful completion of this CE activity, 2 CE credit hours may be awarded. A Peer-Reviewed CE Activity by Dentistry
Course Number: 205 Hypertension and the Dental Patient John H. Hardeman, MD, DDS Upon successful completion of this CE activity, 2 CE credit hours may be awarded. A Peer-Reviewed CE Activity by Dentistry
1. Antihypertensive agents 2. Vasodilators & treatment of angina 3. Drugs used in heart failure 4. Drugs used in arrhythmias
 1. Antihypertensive agents 2. Vasodilators & treatment of angina 3. Drugs used in heart failure 4. Drugs used in arrhythmias Only need to know drugs discussed in class At the end of this section you should
1. Antihypertensive agents 2. Vasodilators & treatment of angina 3. Drugs used in heart failure 4. Drugs used in arrhythmias Only need to know drugs discussed in class At the end of this section you should
CARDIAC IMAGING QUESTIONNAIRE
 Date of test: / / Month day year Last name First name Middle initial Street address City State Zip code Home phone ( ) - Work phone ( ) - Cell Phone ( ) - Email: Age: Demographics: What is your ethnicity?
Date of test: / / Month day year Last name First name Middle initial Street address City State Zip code Home phone ( ) - Work phone ( ) - Cell Phone ( ) - Email: Age: Demographics: What is your ethnicity?
DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS)
 DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS) Beta-blockers have been widely used in the management of angina, certain tachyarrhythmias and heart failure, as well as in hypertension. Examples
DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS) Beta-blockers have been widely used in the management of angina, certain tachyarrhythmias and heart failure, as well as in hypertension. Examples
ACE Inhibitors and ARBs To Protect Your Heart? A Guide for Patients Being Treated for Stable Coronary Heart Disease
 ACE Inhibitors and ARBs To Protect Your Heart? A Guide for Patients Being Treated for Stable Coronary Heart Disease Is This Guide Right for Me? This Guide Is for You If: You have coronary heart disease,
ACE Inhibitors and ARBs To Protect Your Heart? A Guide for Patients Being Treated for Stable Coronary Heart Disease Is This Guide Right for Me? This Guide Is for You If: You have coronary heart disease,
DOD PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS COMMITTEE RECOMMENDATIONS INFORMATION FOR THE DOD BENEFICIARY ADVISORY PANEL
 DOD PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS COMMITTEE RECOMMENDATIONS INFORMATION FOR THE DOD BENEFICIARY ADVISORY PANEL I. Uniform Formulary Review Process Under 10 U.S.C. 1074g, as implemented by 32 C.F.R. 199.21,
DOD PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS COMMITTEE RECOMMENDATIONS INFORMATION FOR THE DOD BENEFICIARY ADVISORY PANEL I. Uniform Formulary Review Process Under 10 U.S.C. 1074g, as implemented by 32 C.F.R. 199.21,
Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2018
 Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2018 Introduction This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2018 National Heart Failure Guideline.
Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2018 Introduction This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2018 National Heart Failure Guideline.
Network Hypertension Algorithm
 Network Hypertension Algorithm Content Review and Approval: This document is subject to review, revision, and (re)approval by the Clinical Integration and Oversight Committee (CIOC) annually and following
Network Hypertension Algorithm Content Review and Approval: This document is subject to review, revision, and (re)approval by the Clinical Integration and Oversight Committee (CIOC) annually and following
Clinical Teach-Back Cards
 Clinical Teach-Back Cards The Medicare Quality Improvement Organization for Texas TMF Health Quality Institute focuses on improving lives by improving the quality of health care through contracts with
Clinical Teach-Back Cards The Medicare Quality Improvement Organization for Texas TMF Health Quality Institute focuses on improving lives by improving the quality of health care through contracts with
Gregory A. Jicha, M.D. Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology. Sanders Brown Center on Aging
 Gregory A. Jicha, M.D. Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology UK Alzheimer s Disease Center Sanders Brown Center on Aging There are now more than 5 million people in the United States living with Alzheimer
Gregory A. Jicha, M.D. Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology UK Alzheimer s Disease Center Sanders Brown Center on Aging There are now more than 5 million people in the United States living with Alzheimer
HYPERTENSION 4.0 Contact Hours Presented by: CEU Professor
 HYPERTENSION 4.0 Contact Hours Presented by: CEU Professor 7 www.ceuprofessoronline.com Copyright 8 2007 The Magellan Group, LLC All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of these materials is
HYPERTENSION 4.0 Contact Hours Presented by: CEU Professor 7 www.ceuprofessoronline.com Copyright 8 2007 The Magellan Group, LLC All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of these materials is
Chapter 10. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Congestive Heart Failure
 Chapter 10 Congestive Heart Failure Learning Objectives Explain concept of polypharmacy in treatment of congestive heart failure Explain function of diuretics Learning Objectives Discuss drugs used for
Chapter 10 Congestive Heart Failure Learning Objectives Explain concept of polypharmacy in treatment of congestive heart failure Explain function of diuretics Learning Objectives Discuss drugs used for
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After you finish this lesson you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT SUBCOURSE MD0806 LESSON 3 Therapeutics III. Cardiac Drugs. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1--3-15. OBJECTIVES After you finish this lesson you should be able to: 3-1. From a group of
LESSON ASSIGNMENT SUBCOURSE MD0806 LESSON 3 Therapeutics III. Cardiac Drugs. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1--3-15. OBJECTIVES After you finish this lesson you should be able to: 3-1. From a group of
Verapamil to diltiazem conversion
 Verapamil to diltiazem conversion Search CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKER DOSING. diltiazem should not exceed 240 mg a day;. Verapamil is a CYP3A4 moderate inhibitor and sensitive substrate; 01/04/2018 Brahmin
Verapamil to diltiazem conversion Search CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKER DOSING. diltiazem should not exceed 240 mg a day;. Verapamil is a CYP3A4 moderate inhibitor and sensitive substrate; 01/04/2018 Brahmin
Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2016
 Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2016 Introduction This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2016 National Heart Failure Guideline.
Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2016 Introduction This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2016 National Heart Failure Guideline.
PHENTOLAMINE MESYLATE INJECTION SANDOZ STANDARD 5 mg/ ml THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION Alpha-adrenoreceptor Blocker
 PACKAGE INSERT Pr PHENTOLAMINE MESYLATE INJECTION SANDOZ STANDARD 5 mg/ ml THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION Alpha-adrenoreceptor Blocker ACTIONS AND CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Phentolamine produces an alpha-adrenergic
PACKAGE INSERT Pr PHENTOLAMINE MESYLATE INJECTION SANDOZ STANDARD 5 mg/ ml THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION Alpha-adrenoreceptor Blocker ACTIONS AND CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Phentolamine produces an alpha-adrenergic
Clinical Policy: Ranolazine (Ranexa) Reference Number: CP.PMN.34 Effective Date: Last Review Date: 02.19
 Clinical Policy: (Ranexa) Reference Number: CP.PMN.34 Effective Date: 08.01.09 Last Review Date: 02.19 Line of Business: Medicaid Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important
Clinical Policy: (Ranexa) Reference Number: CP.PMN.34 Effective Date: 08.01.09 Last Review Date: 02.19 Line of Business: Medicaid Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important
Chapter (9) Calcium Antagonists
 Chapter (9) Calcium Antagonists (CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS) Classification Mechanism of Anti-ischemic Actions Indications Drug Interaction with Verapamil Contraindications Adverse Effects Treatment of Drug
Chapter (9) Calcium Antagonists (CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS) Classification Mechanism of Anti-ischemic Actions Indications Drug Interaction with Verapamil Contraindications Adverse Effects Treatment of Drug
METOTRUST XL-25/50 Metoprolol Succinate Extended-Release Tablets
 METOTRUST XL-25/50 Metoprolol Succinate Extended-Release Tablets COMPOSITION Each film-coated tablet of Metotrust XL-25 contains: Metoprolol Succinate USP 23.75 mg equivalent to Metoprolol Tartrate 25
METOTRUST XL-25/50 Metoprolol Succinate Extended-Release Tablets COMPOSITION Each film-coated tablet of Metotrust XL-25 contains: Metoprolol Succinate USP 23.75 mg equivalent to Metoprolol Tartrate 25
Hypertension diagnosis (see detail document) Diabetic. Target less than 130/80mmHg
 Hypertension diagnosis (see detail document) Non-diabetic Diabetic Very elderly (older than 80 years) Target less than 140/90mmHg Target less than 130/80mmHg Consider SBP target less than 150mmHg Non-diabetic
Hypertension diagnosis (see detail document) Non-diabetic Diabetic Very elderly (older than 80 years) Target less than 140/90mmHg Target less than 130/80mmHg Consider SBP target less than 150mmHg Non-diabetic
