Hypertension is also an important risk factor in the development of chronic kidney disease and heart failure.
|
|
|
- Agnes Hunter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hypertension
2 Hypertension Hypertension is defined as either a sustained systolic blood pressure of greater than 140 mm Hg or a sustained diastolic blood pressure of greater than 90 mm Hg. Hypertension results from increased peripheral vascular arteriolar smooth muscle tone, which leads to increased arteriolar resistance and reduced capacitance of the venous system.
3
4 Hypertension is also an important risk factor in the development of chronic kidney disease and heart failure. The incidence of morbidity and mortality significantly decreases when hypertension is diagnosed early and is properly treated.
5 Goal of treatment Prolong useful life by preventing cardiovascular problems by reducing BP < 140/90
6 Blood Pressure Primary Factors 1. Cardiac output 2. Peripheral resistance 3. Blood Volume
7
8 Hypertention
9 Initial of hypertension Life style modification first No smoking Weight control Reduce alcohol intake Decrease stress Sodium control
10 Treatment Why? Symptomatic treatment is Mandatory: 1-Damage to the vascular epithelium, paving the path for atherosclerosis or nephropathy due to high intra-glomerular pressure. 2-Increased load on heart due to high BP can cause CHF
11 See below
12
13 Drugs to treat hypertension Adrenergic agents -Alpha blockers -Beta blockers -Alpha/Beta blockers Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors Angiotensin II receptor blockers Calcium channel blockers Vasodilators Diuretics
14 1- ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS Azilsartan medoxomil EDARBI Candesartan ATACAND Eprosartan TEVETEN Irbesartan AVAPRO Losartan COZAAR Olmesartan BENICAR Telmisartan MICARDIS Valsartan DIOVAN
15 2- DIURETICS Amiloride MIDAMOR Bumetanide BUMEX Chlorthalidone HYGROTON Furosemide LASIX Hydrochlorothiazide MICROZIDE Metolazone MYKROX, ZAROXOLYN Spironolactone ALDACTONE Triamterene DYRENIUM
16 3 β-blockers Atenolol TENORMIN Carvedilol COREG, COREG CR Labetalol TRANDATE Metoprolol LOPRESSOR, TOPROL-XL Nadolol CORGARD Nebivolol BYSTOLIC Propranolol INDERAL LA, INNOPRAN XL Timolol BLOCADREN
17 4- ACE INHIBITORS Benazepril LOTENSIN Captopril CAPOTEN Enalapril VASOTEC Fosinopril MONOPRIL Lisinopril PRINIVIL, ZESTRIL Moexipril UNIVASC Quinapril ACCUPRIL Perindopril ACEON Ramipril ALTACE Trandolapril MAVIK
18 5- CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS Amlodipine Diltiazem Felodipine Isradipine Nicardipine Nifedipine Nisoldipine Verapamil Clevidipine NORVASC CARDIZEM, CARTIA, DILACOR PLENDIL DYNACIRC CR CARDENE ADALAT, NIFEDIAC, PROCARDIA SULAR CALAN, ISOPTIN, VERELAN CLEVIPREX
19 6- α-blockers Doxazosin CARDURA Prazosin MINIPRESS Terazosin HYTRIN
20 7- RENIN INHIBITORS Aliskiren TEKTURNA
21 8- OTHERS Clonidine CATAPRES, DURACLON Hydralazine APRESOLINE Methyldopa ALDOMET Minoxidil LONITEN Nitroprusside NITROPRESS Fenoldopam CORLOPAM
22 1- DIURETICS :- Main classifications: Thiazide diuretics. Loop. Potassium-sparing diuretics. Others: Osmotic Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
23 A. Thiazide diuretics Thiazide diuretics, such as hydrochlorothiazide and chlorthalidone, lower blood pressure initially by increasing sodium and water excretion. This causes a decrease in extracellular volume, resulting in a decrease in cardiac output and renal blood flow. Thiazides are useful in combination therapy with a variety of other antihypertensive agents, including β-blockers, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, and potassium-sparing diuretics. With the exception of metolazone. thiazide diuretics are not effective in patients with inadequate kidney function. Loop diuretics may be required in these patients. Thiazide diuretics can induce hypokalemia, hyperuricemia and, to a lesser extent, hyperglycemia in some patients.
24 B. Loop diuretics:- The loop diuretics (furosemide, torsemide) act by blocking sodium and chloride reabsorption in the kidneys, even in patients with poor renal function or those who have not responded to thiazide diuretics. Loop diuretics cause decreased renal vascular resistance and increased renal blood flow. Like thiazides, they can cause hypokalemia. However, unlike thiazides, loop diuretics increase the Ca2+ content of urine, whereas thiazide diuretics decrease it. These agents are rarely used alone to treat hypertension, but they are commonly used to manage symptoms of heart failure and edema.
25 C. Potassium-sparing diuretics :- Amiloride and triamterene (inhibitors of epithelial sodium transport at the late distal and collecting ducts) as well as spironolactone (aldosterone receptor antagonists) reduce potassium loss in the urine. (hyperkalemia ) Potassium-sparing diuretics are sometimes used in combination with loop diuretics and thiazides to reduce the amount of potassium loss induced by these diuretics.
26 2- β-adrenoceptor BLOCKING AGENTS :- β-blockers are a treatment option for hypertensive patients with related heart disease or heart failure.
27
28 β-adrenoceptor BLOCKING AGENTS :- Action:- The β-blockers reduce blood pressure primarily by decreasing cardiac output. They may also decrease sympathetic outflow from the central nervous system (CNS) and inhibit the release of renin from the kidneys, thus decreasing the formation of angiotensin II and the secretion of aldosterone. propranolol which acts at both β1 and β2 receptors. Selective blockers of β1 receptors, such as metoprolol and atenolol are among the most commonly prescribed β-blockers. Nebivolol is a selective blocker of β1 receptors, which also increases the production of nitric oxide, leading to vasodilation.
29 β-adrenoceptor BLOCKING AGENTS :- The selective β-blockers may be administered cautiously to hypertensive patients who also have asthma. The nonselective β-blockers, such as propranolol and nadolol, are contraindicated in patients with asthma due to their blockade of β2-mediated broncdilator. β-blockers should be used cautiously in the treatment of patients with acute heart failure or peripheral vascular disease.
30 Therapeutic uses:- 1- in hypertensive patients with related heart disease, such as supraventricular tachyarrhythmia (for example, atrial fibrillation). 2- previous myocardial infarction. 3- angina pectoris. 4-chronic heart failure.
31 Conditions :- 1- β-blockers include reversible bronchospastic disease such as asthma. 2- second- and third-degree heart block. 3- severe peripheral vascular disease.
32 Pharmacokinetics :- The β-blockers are orally active for the treatment of hypertension. Propranolol undergoes extensive and highly variable first-pass metabolism. Oral β-blockers may take several weeks to develop their full effects.
33 Adverse effects :- The β-blockers may cause bradycardia, hypotension. CNS side effects such as fatigue, lethargy, and insomnia. The β-blockers may decrease libido and cause erectile dysfunction.
34 Drug withdrawal: Abrupt withdrawal may induce angina, myocardial infarction, and even sudden death in patients with ischemic heart disease. Therefore, these drugs must be tapered over a few weeks in patients with hypertension and ischemic heart disease.
35 3- Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors What is Renin - Angiotensin? (Physiological Background)
36 RAS - Introduction Renin is a proteolytic enzyme and also called angiotensinogenase It is produced by juxtaglomerular cells of kidney It is secreted in response to: Decrease in arterial blood pressure Decrease Na+ in macula densa Increased sympathetic nervous activity Renin acts on a plasma protein Angiotensinogen (a glycoprotein synthesized and secreted into the bloodstream by the liver) and cleaves to produce a decapeptide Angiotensin-I Angiotensin-I is rapidly converted to Angiotensin-II (octapeptide) by ACE (present in luminal surface of vascular endothelium) Furthermore degradation of Angiotensin-II by peptidases produce Angiotensin-III Both Angiotensin-II and Angiotensin-III stimulates Aldosterone secretion from Adrenal Cortex (equipotent) AT-II has very short half life 1 min
37 RAS - Physiology Increased Blood Vol. Rise in BP Vasoconstriction Na+ & water retention Kidney (Adrenal cortex)
38 ACE INHIBITORS Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ends in PRIL) captopril enalapril benzapril (Capoten) (Vasotec) (Lotensin)
39 Actions :- ACE INHIBITORS The ACE inhibitors lower blood pressure by reducing peripheral vascular resistance without reflexively increasing cardiac output, heart rate, or contractility. These drugs block the enzyme ACE which cleaves angiotensin I to form the potent vasoconstrictor angiotensin II. ACE is also responsible for the breakdown of bradykinin, a peptide that increases the production of nitric oxide and prostacyclin by the blood vessels. Both nitric oxide and prostacyclin are potent vasodilators.
40 ACE INHIBITORS ACE inhibitors decrease angiotensin II and increase bradykinin levels. Vasodilation of both arterioles and veins occurs as a result of decreased vasoconstriction (from diminished levels of angiotensin II) and enhanced vasodilation (from increased bradykinin). By reducing circulating angiotensin II levels, ACE inhibitors also decrease the secretion of aldosterone, resulting in decreased sodium and water retention. ACE inhibitors reduce both cardiac preload and afterload, thereby decreasing cardiac work.
41 ACE INHIBITORS
42 Pharmacokinetics All of the ACE inhibitors are orally bioavailable as a drug or prodrug. All but captopril and lisinopril undergo hepatic conversion to active metabolites, so these agents may be preferred in patients with severe hepatic impairment. Fosinopril is the only ACE inhibitor that is not eliminated primarily by the kidneys and does not require dose adjustment in patients with renal impairment. Enalaprilat is the only drug in this class available intravenously.
43 Adverse effects Common side effects include :- 1- dry cough, rash, fever, altered taste, hypotension (in hypovolemic states), and hyperkalemia. 2- The cough occurs more frequently in women. 3- Angioedema is a rare but potentially lifethreatening reaction that may also be due to increased levels of bradykinin. 4- Serum creatinine levels should also be monitored, particularly in patients with underlying renal disease. 5- ACE inhibitors can induce fetal malformations and should not be used by pregnant women.
44 4- ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS ( ARBs) The ARBs, such as losartan and irbesartan, are alternatives to the ACE inhibitors. These drugs block the AT1 receptors, decreasing the activation of AT1 receptors by angiotensin II. Their pharmacologic effects are similar to those of ACE inhibitors in that they produce arteriolar and venous dilation and block aldosterone secretion, thus lowering blood pressure and decreasing salt and water retention.
45 ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS ( ARBs) ARBs do not increase bradykinin levels. They may be used as first-line agents for the treatment of hypertension, especially in patients with a compelling indication of diabetes, heart failure, or chronic kidney disease. Adverse effects are similar to those of ACE inhibitors, although the risks of cough and angioedema are significantly decreased. ARBs should not be combined with an ACE inhibitor for the treatment of hypertension due to similar mechanisms and adverse effects. These agents are also teratogenic and should not be used by pregnant women.
46 Losartan Competitive antagonist and inverse agonist of AT1 receptor Does not interfere with other receptors except (Thromboxane receptor) (TXA2) Blocks all the actions of A-II - vasoconstriction, sympathetic stimulation, aldosterone release and renal actions of salt and water reabsorption No inhibition of ACE
47 Losartan Pharmacokinetic: Absorption not affected by food but unlike ACEIs its bioavailability is low High first pass metabolism Carboxylated to active metabolite E3174 Highly bound to plasma protein Do not enter brain Adverse effects: Foetopathic like ACEIs not to be administered in pregnancy Rare 1 st dose effect hypotension Low dysgeusia and dry cough Lower incidence of angioedema Available as 25 and 50 mg tablets
48 5- RENIN INHIBITOR A selective renin inhibitor, aliskiren, is available for the treatment of hypertension. Aliskiren directly inhibits renin and, thus, acts earlier in the renin angiotensin aldosterone system than ACE inhibitors or ARBs. It lowers blood pressure about as effectively as ARBs, ACE inhibitors, and thiazides. Aliskiren should not be routinely combined with an ACE inhibitor or ARB. Aliskiren can cause diarrhea, especially at higher doses, and can also cause cough and angioedema, but probably less often than ACE inhibitors. As with ACE inhibitors and ARBs, aliskiren is contraindicated during pregnancy. Aliskiren is metabolized by Cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP 3A4 ) and is subject to many drug interactions.
49 RENIN INHIBITOR Aliskiren can cause diarrhea, especially at higher doses, and can also cause cough and angioedema, but probably less often than ACE inhibitors. As with ACE inhibitors and ARBs, aliskiren is contraindicated during pregnancy. Aliskiren is metabolized by Cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP 3A4 ) and is subject to many drug interactions.
50 6- CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS (CCBs )
51 CCBs Calcium channel blockers are a recommended treatment option in hypertensive patients with diabetes or angina. High doses of short-acting calcium channel blockers should be avoided because of increased risk of myocardial infarction due to excessive vasodilation and marked reflex cardiac stimulation.
52 Classes of calcium channel blockers 1. Diphenylalkylamines: Verapamil has significant effects on both cardiac and vascular smooth muscle cells. It is also used to treat angina and supraventricular tachyarrhythmias and to prevent migraine and cluster headaches.
53 Classes of calcium channel blockers 1- Diphenylalkylamines: Verapamil 2- Benzothiazepines: Diltiazem Like verapamil, diltiazem affects both cardiac and vascular smooth muscle cells, but it has a less pronounced negative inotropic effect on the heart compared to that of verapamil. Diltiazem has a favorable side effect profile.
54 Classes of calcium channel blockers 1- Diphenylalkylamines: Verapamil 2- Benzothiazepines: Diltiazem 3- Dihydropyridines: nifedipine (the prototype), amlodipine. felodipine. Isradipine. Nicardipine. nisoldipine. The dihydropyridines have the advantage in that they show little interaction with other cardiovascular drugs, such as digoxin or warfarin, which are often used concomitantly with calcium channel blockers.
55 Actions (CCBs) The intracellular concentration of calcium plays an important role in maintaining the tone of smooth muscle and in the contraction of the myocardium. Calcium enters muscle cells through special volta gesensitive calcium channels. This triggers release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria, which further increases the cytosolic level of calcium.
56 Action ( CCBs) Calcium channel antagonists block the inward movement of calcium by binding to L-type calcium channels in the heart and in smooth muscle of the coronary and peripheral arteriolar vasculature. This causes vascular smooth muscle to relax, dilating mainly arterioles. Calcium channel blockers do not dilate veins.
57 Therapeutic uses In the management of hypertension, CCBs may be used as an initial therapy or as add-on therapy. They are useful in the treatment of hypertensive patients who also have asthma, diabetes, and/or peripheral vascular disease. All CCBs are useful in the treatment of angina. In addition, diltiazem and verapamil are used in the treatment of atrial fibrillation.
58 Adverse effects First-degree atrioventricular block and constipation are common dose dependent side effects of verapamil. Verapamil and diltiazem shouldbe avoided in patients with heart failure or with atrioventricular block due to their negative inotropic (force of cardiac muscle contraction) and dromotropic (velocity of conduction) effects. Dizziness, headache, and a feeling of fatigue caused by a decrease in blood pressure are more frequent with dihydropyridines. Peripheral edema is another commonly reported side effect of this class. Nifedipine and other dihydropyridines may cause gingival hyperplasia.
59 7- α-adrenoceptor BLOCKING AGENTS Prazosin, doxazosin, and terazosin produce a competitive block of α1-adrenoceptors. They decrease peripheral vascular resistance and lower arterial blood pressure by causing relaxation of both arterial and venous smooth muscle. These drugs cause only minimal changes in cardiac output, renal blood flow, and glomerular filtration rate. Therefore, long-term tachycardia does not occur, but salt and water retention does. α-blockers are no longer recommended as initial treatment for hypertension, but may be used for refractory cases. Other α1-blockers with greater selectivity for prostate muscle are used in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia.
60 8- α-/β-adrenoceptor BLOCKING AGENTS Labetalol and carvedilol block α1, β1, and β2 receptors. Carvedilol, although an effective antihypertensive, is mainly used in the treatment of heart failure. Carvedilol, as well as metoprolol succinate, and bisoprolol have been shown to reduce morbidity and mortality associated with heart failure. Labetalol is used in the management of gestational hypertension and hypertensive emergencies.
61 CENTRALLY ACTING ADRENERGIC DRUGS A. Clonidine Clonidine acts centrally as an α2 agonist to produce inhibition of sympathetic vasomotor centers, decreasing sympathetic outflow to the periphery. This leads to reduced total peripheral resistance and decreased blood pressure.
62 Clonidine Clonidine is used primarily for the treatment of hypertension that has not responded adequately to treatment with two or more drugs. Clonidine does not decrease renal blood flow or glomerular filtration and, therefore, is useful in the treatment of hypertension complicated by renal disease.
63 clonidine Adverse effects include :- sedation, dry mouth, and constipation. Rebound hypertension occurs following sudden withdrawal of clonidine. The drug should, therefore, be withdrawn slowly if discontinuation is required.
64 B. Methyldopa Methyldopa is an α2 agonist that is converted to methylnorepinephrine centrally to decrease adrenergic outflow from the CNS. The most common side effects of methyldopa are :- sedation drowsiness.
65 VASODILATORS The direct-acting smooth muscle relaxants, such as hydralazine and minoxidil, are not used as primary drugs to treat hypertension. These vasodilators act by producing relaxation of vascular smooth muscle, primarily in arteries and arterioles. Both agents produce reflex stimulation of the heart, resulting in the competing reflexes of increased myocardial contractility, heart rate, and oxygen consumption. These actions may prompt angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, or cardiac failure.
66 Vasodilators Vasodilators also increase plasma renin concentration, resulting in sodium and water retention. These undesirable side effects can be blocked by concomitant use of a diuretic and a β-blocker. For example, hydralazine is almost always administered in combination with a β-blocker, such as propranolol, metoprolol, or atenolol (to balance the reflex tachycardia) and a diuretic (to decrease sodium retention). Hydralazine use in pregnancy
67 Vasodilators Adverse effects of hydralazine include :- headache, tachycardia, nausea, sweating, arrhythmia, and acceleration of angina. A lupus-like syndrome can occur with high dosages. Minoxidil treatment causes hypertrichosis (the growth of body hair). This drug is used topically to treat male pattern baldness.
68 RESISTANT HYPERTENSION Resistant hypertension is defined as blood pressure that remains elevated despite administration of drug. The most common causes of resistant hypertension are :- poor compliance. excessive ethanol intake. concomitant conditions (diabetes, obesity, sleep apnea, hyperaldosteronism, high salt intake, and/or metabolic syndrome). concomitant medications (sympathomimetics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or antidepressant medications). Insufficient dose.
69
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat
 Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson you will be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT SUBCOURSE MD0806 LESSON 7 Therapeutics III. Antihypertensive Agents. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 7-1--7-12. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson you will be able to: 7-1. From
LESSON ASSIGNMENT SUBCOURSE MD0806 LESSON 7 Therapeutics III. Antihypertensive Agents. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 7-1--7-12. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson you will be able to: 7-1. From
Cardiac Medications At A Glance
 Cardiac Medications At A Glance 1) Anticoagulants (Also known as Blood Thinners.) Dalteparin (Fragmin), Danaparoid (Orgaran) Enoxaparin (Lovenox) Heparin (various) Tinzaparin (Innohep) Warfarin (Coumadin)
Cardiac Medications At A Glance 1) Anticoagulants (Also known as Blood Thinners.) Dalteparin (Fragmin), Danaparoid (Orgaran) Enoxaparin (Lovenox) Heparin (various) Tinzaparin (Innohep) Warfarin (Coumadin)
Section 3, Lecture 2
 59-291 Section 3, Lecture 2 Diuretics: -increase in Na + excretion (naturesis) Thiazide and Related diuretics -decreased PVR due to decreases muscle contraction -an economical and effective treatment -protect
59-291 Section 3, Lecture 2 Diuretics: -increase in Na + excretion (naturesis) Thiazide and Related diuretics -decreased PVR due to decreases muscle contraction -an economical and effective treatment -protect
ANTIHYPERTENSIVES. Assoc. Prof. Bilgen Başgut
 ANTIHYPERTENSIVES Assoc. Prof. Bilgen Başgut Hypertension Hypertension is a condition in which the blood pressure is persistently higher than normal Hypertension > 140 mmhg > 90 mmhg Systolic Blood Pressure
ANTIHYPERTENSIVES Assoc. Prof. Bilgen Başgut Hypertension Hypertension is a condition in which the blood pressure is persistently higher than normal Hypertension > 140 mmhg > 90 mmhg Systolic Blood Pressure
12.5mg, 25mg, 50mg. 25mg, 50mg. 250mg, 500mg, 250mg/5ml. 2.5mg, 5mg, 10mg. 5mg, 10mg, 20mg, 100mg. 25mg
 MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Blood Pressure P&T DATE: 9/11/2018 THERAPEUTIC CLASS: Cardiovascular Disorders REVIEW HISTORY: 5/17, 9/15, 2/13, 2/08, LOB
MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Blood Pressure P&T DATE: 9/11/2018 THERAPEUTIC CLASS: Cardiovascular Disorders REVIEW HISTORY: 5/17, 9/15, 2/13, 2/08, LOB
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs
 Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs Blood Pressure Normal = sys
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs Blood Pressure Normal = sys
Annual Review of Antihypertensives - Fiscal Year 2009
 Annual Review of Antihypertensives - Fiscal Year 2009 Oklahoma HealthCare Authority April 2010 Current Prior Authorization Criteria There are 7 categories of antihypertensive medications currently included
Annual Review of Antihypertensives - Fiscal Year 2009 Oklahoma HealthCare Authority April 2010 Current Prior Authorization Criteria There are 7 categories of antihypertensive medications currently included
Hypertension (JNC-8)
 Hypertension (JNC-8) Southern California University of Health Sciences Physician Assistant Program Management and Treatment of Hypertension April 17, 2018, presented by Ezra Levy, Pharm.D.! The 8 th Joint
Hypertension (JNC-8) Southern California University of Health Sciences Physician Assistant Program Management and Treatment of Hypertension April 17, 2018, presented by Ezra Levy, Pharm.D.! The 8 th Joint
Antihypertensives. Antihypertensive Classes. RAAS Inhibitors. Renin-Angiotensin Cascade. Angiotensin Receptors. Approaches to Hypertension Treatment
 Approaches to Hypertension Treatment Antihypertensives Inhibit Sympathetic impulses Inhibit contractility Inhibit heart rate Inhibit vasoconstriction Inhibit smooth muscle function Inhibit RAAS Inhibit
Approaches to Hypertension Treatment Antihypertensives Inhibit Sympathetic impulses Inhibit contractility Inhibit heart rate Inhibit vasoconstriction Inhibit smooth muscle function Inhibit RAAS Inhibit
12.5mg, 25mg, 50mg. 25mg, 50mg. 2.5mg, 5mg, 10mg. 5mg, 10mg, 20mg, 100mg. 25mg. -- $2.81 Acetazolamide (IR, 125mg, 250mg, 500mg (ER)
 MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Blood Pressure P&T DATE: 5/9/2017 THERAPEUTIC CLASS: Cardiovascular Disorders REVIEW HISTORY: 9/15, 2/13, 2/08, 5/07 LOB
MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Blood Pressure P&T DATE: 5/9/2017 THERAPEUTIC CLASS: Cardiovascular Disorders REVIEW HISTORY: 9/15, 2/13, 2/08, 5/07 LOB
Antihypertensive Agents
 Antihypertensive Agents Southern California University of Health Sciences Physician Assistant Program Management and Treatment of Hypertension April 7, 08, presented by Ezra Levy, Pharm.D! Usual Dose,
Antihypertensive Agents Southern California University of Health Sciences Physician Assistant Program Management and Treatment of Hypertension April 7, 08, presented by Ezra Levy, Pharm.D! Usual Dose,
sympatholytics sympatholytics sympatholytics
 sympatholytics sympatholytics sympatholytics CNS-ACTING SYMPATHOPLEGICS Sympathetic brain signals Doesn t affect baroreceptor reflex (no orthostatic hypotension) Methyldopa α-methylne crosses BBB (+) α-adrenoreceptors
sympatholytics sympatholytics sympatholytics CNS-ACTING SYMPATHOPLEGICS Sympathetic brain signals Doesn t affect baroreceptor reflex (no orthostatic hypotension) Methyldopa α-methylne crosses BBB (+) α-adrenoreceptors
HYPERTENSION IN EMERGENCY MEDICINE Michael Jay Bresler, M.D., FACEP
 HYPERTENSION IN EMERGENCY MEDICINE Michael Jay Bresler, M.D., FACEP What is normal blood pressure? Prehypertension 130-139/80-90 Compared with normal BP Double the risk for developing hypertension. Lifestyle
HYPERTENSION IN EMERGENCY MEDICINE Michael Jay Bresler, M.D., FACEP What is normal blood pressure? Prehypertension 130-139/80-90 Compared with normal BP Double the risk for developing hypertension. Lifestyle
HYPERTENSION: Sustained elevation of arterial blood pressure above normal o Systolic 140 mm Hg and/or o Diastolic 90 mm Hg
 Lecture 39 Anti-Hypertensives B-Rod BLOOD PRESSURE: Systolic / Diastolic NORMAL: 120/80 Systolic = measure of pressure as heart is beating Diastolic = measure of pressure while heart is at rest between
Lecture 39 Anti-Hypertensives B-Rod BLOOD PRESSURE: Systolic / Diastolic NORMAL: 120/80 Systolic = measure of pressure as heart is beating Diastolic = measure of pressure while heart is at rest between
8/19/2016. No Conflicts. I struggled with everything cardiac in nursing school.
 Cindy Weston, DNP, RN, CCRN, CNS CC, FNP BC Assistant Professor, Texas A&M Health Science Center College of Nursing Describe and define epidemiology and pathophysiology of hypertension Differentiate JNC8
Cindy Weston, DNP, RN, CCRN, CNS CC, FNP BC Assistant Professor, Texas A&M Health Science Center College of Nursing Describe and define epidemiology and pathophysiology of hypertension Differentiate JNC8
Towards a Greater Understanding of Cardiac Medications Foundational Cardiac Concepts That Must Be Understood:
 Towards a Greater Understanding of Cardiac Medications Foundational Cardiac Concepts That Must Be Understood: Cardiac Output (CO) CO=SVxHR (stroke volume x heart rate) Cardiac output: The amount of blood
Towards a Greater Understanding of Cardiac Medications Foundational Cardiac Concepts That Must Be Understood: Cardiac Output (CO) CO=SVxHR (stroke volume x heart rate) Cardiac output: The amount of blood
Preventing and Managing High Blood Pressure
 MINTO PREVENTION & REHABILITATION CENTRE CENTRE DE PREVENTION ET DE READAPTATION MINTO Preventing and Managing High Blood Pressure About This Kit Fortunately, high blood pressure is easily detected and
MINTO PREVENTION & REHABILITATION CENTRE CENTRE DE PREVENTION ET DE READAPTATION MINTO Preventing and Managing High Blood Pressure About This Kit Fortunately, high blood pressure is easily detected and
4/3/2014 OBJECTIVES BLOOD PRESSURE BASICS. Discuss the new blood pressure guidelines (JNC 8) and recognize the changes from JNC 7
 1 OBJECTIVES Discuss the new blood pressure guidelines (JNC 8) and recognize the changes from JNC 7 Review mechanisms for the main drug classes used to treat hypertension Describe the dosing strategies
1 OBJECTIVES Discuss the new blood pressure guidelines (JNC 8) and recognize the changes from JNC 7 Review mechanisms for the main drug classes used to treat hypertension Describe the dosing strategies
Chapter 23. Media Directory. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Hypertension: Classified into Three Categories
 Chapter 23 Drugs for Hypertension Slide 37 Slide 41 Media Directory Nifedipine Animation Doxazosin Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Includes
Chapter 23 Drugs for Hypertension Slide 37 Slide 41 Media Directory Nifedipine Animation Doxazosin Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Includes
Top 200 Section 4. Cardiovascular Drugs
 Top 200 Section 4 Cardiovascular Drugs Objectives After finishing this presentation the audience should be able to: Describe conditions/disease states that would make a person a candidate for drug therapy.
Top 200 Section 4 Cardiovascular Drugs Objectives After finishing this presentation the audience should be able to: Describe conditions/disease states that would make a person a candidate for drug therapy.
Management of Hypertension
 Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
7/7/ CHD/MI LVH and LV dysfunction Dysrrhythmias Stroke PVD Renal insufficiency and failure Retinopathy. Normal <120 Prehypertension
 Prevalence of Hypertension Hypertension: Diagnosis and Management T. Villela, M.D. Program Director University of California, San Francisco-San Francisco General Hospital Family and Community Medicine
Prevalence of Hypertension Hypertension: Diagnosis and Management T. Villela, M.D. Program Director University of California, San Francisco-San Francisco General Hospital Family and Community Medicine
DROGAS PARA HIPERTENSION ARTERIAL JONATHAN POVEDA FERNANDEZ HSJD / 2013 FACC/FSCAI/FESC
 DROGAS PARA HIPERTENSION ARTERIAL JONATHAN POVEDA FERNANDEZ HSJD / 2013 FACC/FSCAI/FESC Pharmacotherapy of HTN Rationale for reducing arterial pressure Reduce cardiac output Reduce heart rate Reduce stroke
DROGAS PARA HIPERTENSION ARTERIAL JONATHAN POVEDA FERNANDEZ HSJD / 2013 FACC/FSCAI/FESC Pharmacotherapy of HTN Rationale for reducing arterial pressure Reduce cardiac output Reduce heart rate Reduce stroke
DRUGS USED TO TREAT HYPERTENSION BY ALI ALALAWI
 DRUGS USED TO TREAT HYPERTENSION BY ALI ALALAWI 3. Vasodilators Drugs which dilate blood vessels ( decrease peripheral vascular resistance) by acting on smooth muscle cells through non-autonomic mechanisms:
DRUGS USED TO TREAT HYPERTENSION BY ALI ALALAWI 3. Vasodilators Drugs which dilate blood vessels ( decrease peripheral vascular resistance) by acting on smooth muscle cells through non-autonomic mechanisms:
PassAssured's Pharmacy Technician Training Systems. Medication Review. Cardiovascular Drugs. Pharmacy Technician Training Systems Passassured, LLC
 Medication Review Cardiovascular Drugs Pharmacy Technician Training Systems Passassured, LLC p1 Medication Review, Cardiovascular Drugs Click Here for Glossary Index! Click Here to Print Topic Help File
Medication Review Cardiovascular Drugs Pharmacy Technician Training Systems Passassured, LLC p1 Medication Review, Cardiovascular Drugs Click Here for Glossary Index! Click Here to Print Topic Help File
Diabetes and a Healthy Heart. Meeting 6. Welcome! Glucose. Balance Makes a Difference! Medicine Helps with. Glucose. Balance!
 6-1 Welcome! Welcome to the lesson! It s good to see you again! Before we visit with Uncle Tommy and Kaipo, let s take a few minutes to review the last five meetings. Glucose Balance Makes a Difference!
6-1 Welcome! Welcome to the lesson! It s good to see you again! Before we visit with Uncle Tommy and Kaipo, let s take a few minutes to review the last five meetings. Glucose Balance Makes a Difference!
Beta 1 Beta blockers A - Propranolol,
 Pharma Lecture 3 Beta blockers that we are most interested in are the ones that target Beta 1 receptors. Beta blockers A - Propranolol, it s a non-selective competitive antagonist of beta 1 and beta 2
Pharma Lecture 3 Beta blockers that we are most interested in are the ones that target Beta 1 receptors. Beta blockers A - Propranolol, it s a non-selective competitive antagonist of beta 1 and beta 2
Medications and Falls Part 1
 Medications and Falls Part 1 Introduction with General Principles and Risk Evaluation for Cardiovascular Medications Dennis J Chapron Medication Safety Pharmacist Saint Francis Hospital and Medical Center
Medications and Falls Part 1 Introduction with General Principles and Risk Evaluation for Cardiovascular Medications Dennis J Chapron Medication Safety Pharmacist Saint Francis Hospital and Medical Center
Some Facts. Medications and Falls Part 1. Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Falls Statistics for Older Adults ( 65yrs) 11/27/2018
 Medications and Falls Part 1 Introduction with General Principles and Risk Evaluation for Cardiovascular Medications Dennis J Chapron reports no real or potential conflicts of interest relevant to this
Medications and Falls Part 1 Introduction with General Principles and Risk Evaluation for Cardiovascular Medications Dennis J Chapron reports no real or potential conflicts of interest relevant to this
ACEBUTOLOL HCL 100MG TABLET GENERIC BETA BLOCKERS ALISKIREN 150MG TABLET RASILAZ RENIN INHIBITOR
 S/N ME OF MEDICATIONS BRANDED/GENERIC DRUG CLASS * UNIT PRICE RANGE (SGD$) 1 ACEBUTOLOL HCL 100MG CAPSULE SECTRAL BETA BLOCKERS 0.50 2 ACEBUTOLOL HCL 100MG TABLET GENERIC BETA BLOCKERS 0.33 3 ALISKIREN
S/N ME OF MEDICATIONS BRANDED/GENERIC DRUG CLASS * UNIT PRICE RANGE (SGD$) 1 ACEBUTOLOL HCL 100MG CAPSULE SECTRAL BETA BLOCKERS 0.50 2 ACEBUTOLOL HCL 100MG TABLET GENERIC BETA BLOCKERS 0.33 3 ALISKIREN
Treatment of Essential Hypertension
 2016 edition by Mark A. Simmons, PhD Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences School of Pharmacy University of Maryland Eastern Shore Originally developed by Hugh J. Burford, PhD, FCP Department of Pharmacology
2016 edition by Mark A. Simmons, PhD Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences School of Pharmacy University of Maryland Eastern Shore Originally developed by Hugh J. Burford, PhD, FCP Department of Pharmacology
Chapter 10 Worksheet Blood Pressure and Antithrombotic Agents
 Complete the following. 1. A layer of cells lines each vessel in the vascular system. This layer is a passive barrier that keeps cells and proteins from going into tissues; it also contains substances
Complete the following. 1. A layer of cells lines each vessel in the vascular system. This layer is a passive barrier that keeps cells and proteins from going into tissues; it also contains substances
Antihypertensive drugs: I. Thiazide and other diuretics:
 Clinical assessment of hypertensive patient: You have to take history regarding the presence of other risk factors for CAb like diabetes mellitus, smoking, etc. Take history whether the patient takes medications
Clinical assessment of hypertensive patient: You have to take history regarding the presence of other risk factors for CAb like diabetes mellitus, smoking, etc. Take history whether the patient takes medications
Treatment of Essential Hypertension
 2016 edition by Mark A. Simmons, PhD Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences School of Pharmacy University of Maryland Eastern Shore Originally developed by Hugh J. Burford, PhD, FCP Department of Pharmacology
2016 edition by Mark A. Simmons, PhD Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences School of Pharmacy University of Maryland Eastern Shore Originally developed by Hugh J. Burford, PhD, FCP Department of Pharmacology
Adapted d from Federation of Health Regulatory Colleges of Ontario Template Last Updated September 18, 2017
 Insert Logo or Org Name Here Primary Care Medical Directive for Hypertension Management Adapted d from Federation of Health Regulatory Colleges of Ontario Template Last Updated September 18, 2017 Title:
Insert Logo or Org Name Here Primary Care Medical Directive for Hypertension Management Adapted d from Federation of Health Regulatory Colleges of Ontario Template Last Updated September 18, 2017 Title:
Heart Disease and Prevention PRESENTED BY: DOTTIE CRAIG NP- C, JANE ARCHER NP-C, KATHY DAPPER RN, NICCI FRAVEL RN
 Heart Disease and Prevention PRESENTED BY: DOTTIE CRAIG NP- C, JANE ARCHER NP-C, KATHY DAPPER RN, NICCI FRAVEL RN Objectives Identify Normal Systolic and Diastolic Blood pressures Recognize common Antihypertensive
Heart Disease and Prevention PRESENTED BY: DOTTIE CRAIG NP- C, JANE ARCHER NP-C, KATHY DAPPER RN, NICCI FRAVEL RN Objectives Identify Normal Systolic and Diastolic Blood pressures Recognize common Antihypertensive
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment
 Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
1. Antihypertensive agents 2. Vasodilators & treatment of angina 3. Drugs used in heart failure 4. Drugs used in arrhythmias
 1. Antihypertensive agents 2. Vasodilators & treatment of angina 3. Drugs used in heart failure 4. Drugs used in arrhythmias Only need to know drugs discussed in class At the end of this section you should
1. Antihypertensive agents 2. Vasodilators & treatment of angina 3. Drugs used in heart failure 4. Drugs used in arrhythmias Only need to know drugs discussed in class At the end of this section you should
HypertensionTreatment Guidelines. Michaelene Urban APRN, MSN, ACNS-BC, ANP-BC
 HypertensionTreatment Guidelines Michaelene Urban APRN, MSN, ACNS-BC, ANP-BC Objectives: Review the definition of the different stages of HTN. Review the current guidelines for treatment of HTN. Provided
HypertensionTreatment Guidelines Michaelene Urban APRN, MSN, ACNS-BC, ANP-BC Objectives: Review the definition of the different stages of HTN. Review the current guidelines for treatment of HTN. Provided
Antihypertensive Agents
 Antihypertensive Agents Öner Süzer www.onersuzer.com osuzer@istanbul.edu.tr Last update: 13.11.2009 1 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005 2 1 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005 3 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005
Antihypertensive Agents Öner Süzer www.onersuzer.com osuzer@istanbul.edu.tr Last update: 13.11.2009 1 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005 2 1 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005 3 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005
What in the World is Functional Medicine?
 What in the World is Functional Medicine? An Introduction to a Systems Based Approach of Chronic Disease Meneah R Haworth, FNP-C Disclosure v I am a student of the Institute for Functional Medicine. They
What in the World is Functional Medicine? An Introduction to a Systems Based Approach of Chronic Disease Meneah R Haworth, FNP-C Disclosure v I am a student of the Institute for Functional Medicine. They
α 1 receptor smooth muscle activation
 Drugs in Hypertension Dr. Yuri Clement Pharmacology Unit, FMS Objectives Revision of physiological control of BP. What is hypertension? Associated risks of uncontrolled hypertension ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUGS:
Drugs in Hypertension Dr. Yuri Clement Pharmacology Unit, FMS Objectives Revision of physiological control of BP. What is hypertension? Associated risks of uncontrolled hypertension ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUGS:
Value-Based Drug List for ABCs of Diabetes
 Effective January 1, 2019 Value-Based Drug List for ABCs of Diabetes PCPS provides a Value-Based Benefit Design (VBD) to qualified participants in the ABCs of Diabetes. This means you will have lower out-of-pocket
Effective January 1, 2019 Value-Based Drug List for ABCs of Diabetes PCPS provides a Value-Based Benefit Design (VBD) to qualified participants in the ABCs of Diabetes. This means you will have lower out-of-pocket
DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS)
 DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS) Beta-blockers have been widely used in the management of angina, certain tachyarrhythmias and heart failure, as well as in hypertension. Examples
DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS) Beta-blockers have been widely used in the management of angina, certain tachyarrhythmias and heart failure, as well as in hypertension. Examples
MEDICATION FACT SHEET
 ACE Inhibitors Names of ACE Inhibitors: quinapril (Accupril ), enalapril (Vasotec ), ramipril (Altace ), captopril (Capoten ), fosinopril (Monopril ), benazepril (Lotensin ), lisinopril (Zestril, Prinivil
ACE Inhibitors Names of ACE Inhibitors: quinapril (Accupril ), enalapril (Vasotec ), ramipril (Altace ), captopril (Capoten ), fosinopril (Monopril ), benazepril (Lotensin ), lisinopril (Zestril, Prinivil
New classification of HT Systolic Diastolic Normal <120 <80 Prehypertension Stage1HT Stage 2 HT >160 or >100
 Hypertension 1 Definition Hypertension can be defined as a condition where blood pressure is elevated to an extent that clinical benefit is obtained from blood pressure lowering. it is an important risk
Hypertension 1 Definition Hypertension can be defined as a condition where blood pressure is elevated to an extent that clinical benefit is obtained from blood pressure lowering. it is an important risk
Hypertension Management - Summary
 Who should have blood pressure assessed? Hypertension Management - Summary All patients over the age of 40 years, every 1-3 years in order to determine their cardiovascular risk (ie. Framingham Risk Score)
Who should have blood pressure assessed? Hypertension Management - Summary All patients over the age of 40 years, every 1-3 years in order to determine their cardiovascular risk (ie. Framingham Risk Score)
Physician/Clinic Collaborative Practice Agreement
 Physician/Clinic Collaborative Practice Agreement Effective October 1, 2010, Connecticut Senate Bill 428 (PA 10-117) extends to all settings and medical conditions the opportunity for licensed pharmacists
Physician/Clinic Collaborative Practice Agreement Effective October 1, 2010, Connecticut Senate Bill 428 (PA 10-117) extends to all settings and medical conditions the opportunity for licensed pharmacists
Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular system
 Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular System: General Section 1 of 6 Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular system 2.1 Positive inotropic drugs 2.1.1 Cardiac glycosides DIGOXIN 2.2 Diuretics Elixir 50micrograms in 1ml Injection
Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular System: General Section 1 of 6 Chapter 2 ~ Cardiovascular system 2.1 Positive inotropic drugs 2.1.1 Cardiac glycosides DIGOXIN 2.2 Diuretics Elixir 50micrograms in 1ml Injection
University of Al Qadisiyah College of Pharmacy Dr. Bassim I Mohammad, MBChB, MSc, Ph.D
 University of Al Qadisiyah College of Pharmacy Dr. Bassim I Mohammad, MBChB, MSc, Ph.D Cardiovascular Pharmacology 1. Antihypertensives 2. Antianginal 3. Drugs for HF 4. Antiarrythemics 5. Drugs for Hyperlipoproteniemia
University of Al Qadisiyah College of Pharmacy Dr. Bassim I Mohammad, MBChB, MSc, Ph.D Cardiovascular Pharmacology 1. Antihypertensives 2. Antianginal 3. Drugs for HF 4. Antiarrythemics 5. Drugs for Hyperlipoproteniemia
1/4/18. Heart Failure Guideline Review and Update. Disclosure. Pharmacist Objectives. Pharmacy Technician Objectives. What is Heart Failure?
 Disclosure Heart Failure Guideline Review and Update I have had no financial relationship over the past 12 months with any commercial sponsor with a vested interest in this presentation. Natalie Beiter,
Disclosure Heart Failure Guideline Review and Update I have had no financial relationship over the past 12 months with any commercial sponsor with a vested interest in this presentation. Natalie Beiter,
Dr Narender Goel MD (Internal Medicine and Nephrology) Financial Disclosure: None, Conflict of Interest: None
 Dr Narender Goel MD (Internal Medicine and Nephrology) drnarendergoel@gmail.com Financial Disclosure: None, Conflict of Interest: None 12 th December 2013, New York Visit us at: http://kidneyscience.info/
Dr Narender Goel MD (Internal Medicine and Nephrology) drnarendergoel@gmail.com Financial Disclosure: None, Conflict of Interest: None 12 th December 2013, New York Visit us at: http://kidneyscience.info/
TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION
 TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION Aim of treatment BP Goals Main items of treatment Lifestyle modification When to start drug Rx Pharmacological therapy 1. Relief of symptoms 2. Prevention of complications and
TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION Aim of treatment BP Goals Main items of treatment Lifestyle modification When to start drug Rx Pharmacological therapy 1. Relief of symptoms 2. Prevention of complications and
Beta-blockers. Atenolol. Propranolol. Bisoprolol. Metoprolol. Labetalol. Carvedilol.
 Drugs of CVS Beta-blockers Atenolol. Propranolol. Bisoprolol. Metoprolol. Labetalol. Carvedilol. Atenolol.cardioselective Propranolol, nonselective Bisoprolol, cardioselective Metoprolol Carvedilol, alpha
Drugs of CVS Beta-blockers Atenolol. Propranolol. Bisoprolol. Metoprolol. Labetalol. Carvedilol. Atenolol.cardioselective Propranolol, nonselective Bisoprolol, cardioselective Metoprolol Carvedilol, alpha
Antihypertensives. Diagnostic category
 Measurement of blood pressure At first assessment, take both arms then choose the one with the higher reading. Beware of orthostatic hypotension. Measure BP in sitting position, and repeat after patient
Measurement of blood pressure At first assessment, take both arms then choose the one with the higher reading. Beware of orthostatic hypotension. Measure BP in sitting position, and repeat after patient
Difficult to Treat Hypertension
 Difficult to Treat Hypertension According to Goldilocks JNC 8 Blood Pressure Goals (2014) BP Goal 60 years old and greater*- systolic < 150 and diastolic < 90. (Grade A)** BP Goal 18-59 years old* diastolic
Difficult to Treat Hypertension According to Goldilocks JNC 8 Blood Pressure Goals (2014) BP Goal 60 years old and greater*- systolic < 150 and diastolic < 90. (Grade A)** BP Goal 18-59 years old* diastolic
ASEBP and ARTA TARP Drugs and Reference Price by Categories
 ASEBP Pantoprazole Sodium 40 mg (generic) $0.2016 ASEBP Dexlansoprazole 30 mg Dexlansoprazole 60 mg Esomeprazole 10 mg Esomeprazole 20 mg Esomeprazole 40 mg Lansoprazole 15 mg Lansoprazole 30 mg Omeprazole
ASEBP Pantoprazole Sodium 40 mg (generic) $0.2016 ASEBP Dexlansoprazole 30 mg Dexlansoprazole 60 mg Esomeprazole 10 mg Esomeprazole 20 mg Esomeprazole 40 mg Lansoprazole 15 mg Lansoprazole 30 mg Omeprazole
Clinical Teach-Back Cards
 Clinical Teach-Back Cards The Medicare Quality Improvement Organization for Texas TMF Health Quality Institute focuses on improving lives by improving the quality of health care through contracts with
Clinical Teach-Back Cards The Medicare Quality Improvement Organization for Texas TMF Health Quality Institute focuses on improving lives by improving the quality of health care through contracts with
Hypertension Clinical Pearls: We re treating more than a number
 Hypertension Clinical Pearls: We re treating more than a number Emily Ashjian, PharmD, BCPS, BCACP February 2017 Learning Objectives Review blood pressure goals and differences between treatment guidelines
Hypertension Clinical Pearls: We re treating more than a number Emily Ashjian, PharmD, BCPS, BCACP February 2017 Learning Objectives Review blood pressure goals and differences between treatment guidelines
Categories of HTN. Overview of Hypertension. Types of Hypertension
 Categories of HTN Overview of Hypertension Normal SBP 100 Quick review of the Basics: What is
Categories of HTN Overview of Hypertension Normal SBP 100 Quick review of the Basics: What is
Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in Diabetic Mellitus. Presenter: Dr. Martin N. Wanyoike MB.CHB., M. Med.(internal med) Physician / Cardiologist
 Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in Diabetic Mellitus Presenter: Dr. Martin N. Wanyoike MB.CHB., M. Med.(internal med) Physician / Cardiologist Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in Diabetic Mellitus Disclosures
Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in Diabetic Mellitus Presenter: Dr. Martin N. Wanyoike MB.CHB., M. Med.(internal med) Physician / Cardiologist Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in Diabetic Mellitus Disclosures
Introduction. Factors affecting blood pressure: 1-COP = HR X SV mainly affect SBP. 2-TPR = diameter of arterioles X viscosity of blood affect DBP
 Introduction Hypertension is a persistent elevation of blood pressure above 140 / 90 mmhg for more than three sitting. (0ptimal level
Introduction Hypertension is a persistent elevation of blood pressure above 140 / 90 mmhg for more than three sitting. (0ptimal level
Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2018
 Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2018 Introduction This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2018 National Heart Failure Guideline.
Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2018 Introduction This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2018 National Heart Failure Guideline.
Hypertension. Penny Mosley MRPharmS
 Hypertension Penny Mosley MRPharmS Outline of presentation Introduction to hypertension Physiological control of arterial blood pressure What determines our bp? What determines the heart rate? What determines
Hypertension Penny Mosley MRPharmS Outline of presentation Introduction to hypertension Physiological control of arterial blood pressure What determines our bp? What determines the heart rate? What determines
Hypertension Update. Objectives 4/28/2015. Beverly J. Mathis, D.O. OOA May 2015
 Hypertension Update Beverly J. Mathis, D.O. OOA May 2015 Objectives Learn new recommendations for BP treatment goals Approach to hypertension in the office Use of hypertensive drugs, and how to tailor
Hypertension Update Beverly J. Mathis, D.O. OOA May 2015 Objectives Learn new recommendations for BP treatment goals Approach to hypertension in the office Use of hypertensive drugs, and how to tailor
8/20/2018. Objectives. What is hypertension? cont. What is hypertension? Epidemiology cont. Epidemiology
 Objectives Hypertension (high blood pressure): Clinical Pearls for the Pharmacy Technician Tanya Schmidt PharmD, RPh Director of Central Operations at Thrifty White Pharmacy North Dakota Board of Pharmacy
Objectives Hypertension (high blood pressure): Clinical Pearls for the Pharmacy Technician Tanya Schmidt PharmD, RPh Director of Central Operations at Thrifty White Pharmacy North Dakota Board of Pharmacy
ANTIHYPERTENSIVE AGENTS AND VASODILATORS. Lecture 5
 ANTIHYPERTENSIVE AGENTS AND VASODILATORS Lecture 5 Hypertension Blood pressure BP = CO x PVR n Interaction between autonomic nervous system, cardiovascular system and renal system Normal: 110/70 Prehypertension
ANTIHYPERTENSIVE AGENTS AND VASODILATORS Lecture 5 Hypertension Blood pressure BP = CO x PVR n Interaction between autonomic nervous system, cardiovascular system and renal system Normal: 110/70 Prehypertension
ACE Inhibitors and ARBs To Protect Your Heart? A Guide for Patients Being Treated for Stable Coronary Heart Disease
 ACE Inhibitors and ARBs To Protect Your Heart? A Guide for Patients Being Treated for Stable Coronary Heart Disease Is This Guide Right for Me? This Guide Is for You If: You have coronary heart disease,
ACE Inhibitors and ARBs To Protect Your Heart? A Guide for Patients Being Treated for Stable Coronary Heart Disease Is This Guide Right for Me? This Guide Is for You If: You have coronary heart disease,
Fundamentals of Pharmacology for Veterinary Technicians Chapter 8
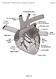 Figure 8-1 Figure 8-2 Figure 8-3 Figure 8-4 Figure 8-5 Figure 8-7 Figure 8-8 Figure 8-9 TABLE 8-1 Blood Flow Through the Heart The right atrium receives blood from all tissues, except the lungs, through
Figure 8-1 Figure 8-2 Figure 8-3 Figure 8-4 Figure 8-5 Figure 8-7 Figure 8-8 Figure 8-9 TABLE 8-1 Blood Flow Through the Heart The right atrium receives blood from all tissues, except the lungs, through
Angina pectoris due to coronary atherosclerosis : Atenolol is indicated for the long term management of patients with angina pectoris.
 Lonet Tablet Description Lonet contains Atenolol, a synthetic β1 selective (cardioselective) adrenoreceptor blocking agent without membrane stabilising or intrinsic sympathomimetic (partial agonist) activity.
Lonet Tablet Description Lonet contains Atenolol, a synthetic β1 selective (cardioselective) adrenoreceptor blocking agent without membrane stabilising or intrinsic sympathomimetic (partial agonist) activity.
Managing Hypertension in Diabetes Sean Stewart, PharmD, BCPS, BCACP, CLS Internal Medicine Park Nicollet Clinic St Louis Park.
 Managing Hypertension in Diabetes 2015 Sean Stewart, PharmD, BCPS, BCACP, CLS Internal Medicine Park Nicollet Clinic St Louis Park Case Scenario Mike M is a 59 year old man with type 2 diabetes managed
Managing Hypertension in Diabetes 2015 Sean Stewart, PharmD, BCPS, BCACP, CLS Internal Medicine Park Nicollet Clinic St Louis Park Case Scenario Mike M is a 59 year old man with type 2 diabetes managed
Heart failure. Failure? blood supply insufficient for body needs. CHF = congestive heart failure. increased blood volume, interstitial fluid
 Failure? blood supply insufficient for body needs CHF = congestive heart failure increased blood volume, interstitial fluid Underlying causes/risk factors Ischemic heart disease (CAD) 70% hypertension
Failure? blood supply insufficient for body needs CHF = congestive heart failure increased blood volume, interstitial fluid Underlying causes/risk factors Ischemic heart disease (CAD) 70% hypertension
Adult Blood Pressure Clinician Guide June 2018
 Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Adult Blood Pressure Clinician Guide June 2018 Adult Blood Pressure Clinician Guide June 2018 Introduction This Clinician Guide is based on the 2018
Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Adult Blood Pressure Clinician Guide June 2018 Adult Blood Pressure Clinician Guide June 2018 Introduction This Clinician Guide is based on the 2018
Clinical Teach-Back Cards
 Clinical Teach-Back Cards The Quality Innovation Network - Quality Improvement Organization (QIN-QIO) for Delaware, Louisiana, New Jersey, Pennsylvania and West Virginia The people at Quality Insights
Clinical Teach-Back Cards The Quality Innovation Network - Quality Improvement Organization (QIN-QIO) for Delaware, Louisiana, New Jersey, Pennsylvania and West Virginia The people at Quality Insights
8/20/2017. No Conflicts. I struggled with everything cardiac in nursing school. Review background and definitions of hypertension with
 Cindy Weston, DNP, RN, CCRN, CNS CC, FNP BC Assistant Professor Texas A&M University College of Nursing cweston@tamhsc.edu Review background and definitions of hypertension with appropriate ICD 10 Discuss
Cindy Weston, DNP, RN, CCRN, CNS CC, FNP BC Assistant Professor Texas A&M University College of Nursing cweston@tamhsc.edu Review background and definitions of hypertension with appropriate ICD 10 Discuss
ANTI- HYPERTENSIVE AGENTS
 CLINICAL ANTI- HYPERTENSIVE AGENTS Jacqueline van Schoor, MPharm, BSc (Hons) Amayeza Info Centre Hypertension represents a major public health concern. It affects about a billion people worldwide and is
CLINICAL ANTI- HYPERTENSIVE AGENTS Jacqueline van Schoor, MPharm, BSc (Hons) Amayeza Info Centre Hypertension represents a major public health concern. It affects about a billion people worldwide and is
PHARM 504: Pharmacy Practice Winter 2009 MCP DRUGS #3: CARDIOVASCULAR PRODUCTS January 22th, 2010 Laura Knutzen
 PHARM 504: Pharmacy Practice Winter 2009 MCP DRUGS #3: CARDIOVASCULAR PRODUCTS January 22th, 2010 Laura Knutzen General Tips and Information: 1. Types of Cardiovascular Disorders: Myocardial infarction
PHARM 504: Pharmacy Practice Winter 2009 MCP DRUGS #3: CARDIOVASCULAR PRODUCTS January 22th, 2010 Laura Knutzen General Tips and Information: 1. Types of Cardiovascular Disorders: Myocardial infarction
The Future of Hypertension and the Optometrist
 The Future of Hypertension and the Optometrist Lee Dodge, O.D. Hypertension in the United States Author s Bio Dr. Lee Dodge completed his optometric training in 2005 at the Southern California College
The Future of Hypertension and the Optometrist Lee Dodge, O.D. Hypertension in the United States Author s Bio Dr. Lee Dodge completed his optometric training in 2005 at the Southern California College
CARDIAC IMAGING QUESTIONNAIRE
 Date of test: / / Month day year Last name First name Middle initial Street address City State Zip code Home phone ( ) - Work phone ( ) - Cell Phone ( ) - Email: Age: Demographics: What is your ethnicity?
Date of test: / / Month day year Last name First name Middle initial Street address City State Zip code Home phone ( ) - Work phone ( ) - Cell Phone ( ) - Email: Age: Demographics: What is your ethnicity?
DOD PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS COMMITTEE RECOMMENDATIONS INFORMATION FOR THE DOD BENEFICIARY ADVISORY PANEL
 DOD PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS COMMITTEE RECOMMENDATIONS INFORMATION FOR THE DOD BENEFICIARY ADVISORY PANEL I. Uniform Formulary Review Process Under 10 U.S.C. 1074g, as implemented by 32 C.F.R. 199.21,
DOD PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS COMMITTEE RECOMMENDATIONS INFORMATION FOR THE DOD BENEFICIARY ADVISORY PANEL I. Uniform Formulary Review Process Under 10 U.S.C. 1074g, as implemented by 32 C.F.R. 199.21,
Factors Involved in Poor Control of Risk Factors
 Factors Involved in Poor Control of Risk Factors Patient compliance Clinical inertia Health Care System structure 14781 M Limitations of Formal Studies Selection of patients Recruitment and follow-up alter
Factors Involved in Poor Control of Risk Factors Patient compliance Clinical inertia Health Care System structure 14781 M Limitations of Formal Studies Selection of patients Recruitment and follow-up alter
Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2016
 Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2016 Introduction This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2016 National Heart Failure Guideline.
Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2016 Introduction This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2016 National Heart Failure Guideline.
Cardiovascular drugs
 chapter 13 Cardiovascular drugs Cardiovascular drugs act on the heart or blood vessels to control the cardiovascular system. They are used to treat a variety of conditions from hypertension to chronic
chapter 13 Cardiovascular drugs Cardiovascular drugs act on the heart or blood vessels to control the cardiovascular system. They are used to treat a variety of conditions from hypertension to chronic
ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUGS
 ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUGS Course: Integrated Therapeutics 1 Lecturer: Dr. E. Konorev Date: September 28, 2010 Materials on: Exam #3 Required reading: Katzung, Chapter 11 1 1 in 3 adults HYPERTENSION 64% of
ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUGS Course: Integrated Therapeutics 1 Lecturer: Dr. E. Konorev Date: September 28, 2010 Materials on: Exam #3 Required reading: Katzung, Chapter 11 1 1 in 3 adults HYPERTENSION 64% of
Living with Congestive Heart Failure: A Guide to a Healthy Heart
 Living with Congestive Heart Failure: A Guide to a Healthy Heart Things to Know, Before You Go Dear Patient/Caregiver These are the things you NEED TO KNOW, BEFORE YOU GO. It is very important that you
Living with Congestive Heart Failure: A Guide to a Healthy Heart Things to Know, Before You Go Dear Patient/Caregiver These are the things you NEED TO KNOW, BEFORE YOU GO. It is very important that you
HEART FAILURE PHARMACOLOGY. University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D
 HEART FAILURE PHARMACOLOGY University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand the effects of heart failure in the body
HEART FAILURE PHARMACOLOGY University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand the effects of heart failure in the body
Antihypertensive Drugs. Nafrialdi
 Antihypertensive Drugs Nafrialdi 1 Mechanisms of Blood Pressure Regulation Blood Presure Cardiac Output Peripheral Resistance Heart Rate Stroke volume Vascular tone Vessel elasticity Myocardial contractility
Antihypertensive Drugs Nafrialdi 1 Mechanisms of Blood Pressure Regulation Blood Presure Cardiac Output Peripheral Resistance Heart Rate Stroke volume Vascular tone Vessel elasticity Myocardial contractility
State of the art treatment of hypertension: established and new drugs. Prof. M. Burnier Service of Nephrology and Hypertension Lausanne, Switzerland
 State of the art treatment of hypertension: established and new drugs Prof. M. Burnier Service of Nephrology and Hypertension Lausanne, Switzerland First line therapies in hypertension ACE inhibitors AT
State of the art treatment of hypertension: established and new drugs Prof. M. Burnier Service of Nephrology and Hypertension Lausanne, Switzerland First line therapies in hypertension ACE inhibitors AT
Blood pressure (BP) control. Hypertension
 Blood pressure (BP) control Normal heart function Blood pressure (BP) control blood pressure (BP) cardiac output (CO) = total peripheral resistance (TPR) heart rate (HR) filling pressure arteriolar volume
Blood pressure (BP) control Normal heart function Blood pressure (BP) control blood pressure (BP) cardiac output (CO) = total peripheral resistance (TPR) heart rate (HR) filling pressure arteriolar volume
LESSON ASSIGNMENT Given the trade and/or generic name of an adrenergic blocking agent, classify that agent as either an alpha or beta blocker.
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 8 Adrenergic Blocking Agents. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 8-1 through 8-5. LESSON OBJECTIVES 8-1. Given a group of statements, select the statement that best describes one of the
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 8 Adrenergic Blocking Agents. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 8-1 through 8-5. LESSON OBJECTIVES 8-1. Given a group of statements, select the statement that best describes one of the
Heart Failure. Dr. Alia Shatanawi
 Heart Failure Dr. Alia Shatanawi Left systolic dysfunction secondary to coronary artery disease is the most common cause, account to 70% of all cases. Heart Failure Heart is unable to pump sufficient blood
Heart Failure Dr. Alia Shatanawi Left systolic dysfunction secondary to coronary artery disease is the most common cause, account to 70% of all cases. Heart Failure Heart is unable to pump sufficient blood
Evaluation and Management of Acute Decompensated Heart Failure (HF) with Reduced Ejection Fraction Systolic Heart Failure (HFrEF)(EF<40%
 Evaluation and Management of Acute Decompensated Heart Failure (HF) with Reduced Ejection Fraction Systolic Heart Failure (HFrEF)(EF
Evaluation and Management of Acute Decompensated Heart Failure (HF) with Reduced Ejection Fraction Systolic Heart Failure (HFrEF)(EF
Chapter (9) Calcium Antagonists
 Chapter (9) Calcium Antagonists (CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS) Classification Mechanism of Anti-ischemic Actions Indications Drug Interaction with Verapamil Contraindications Adverse Effects Treatment of Drug
Chapter (9) Calcium Antagonists (CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS) Classification Mechanism of Anti-ischemic Actions Indications Drug Interaction with Verapamil Contraindications Adverse Effects Treatment of Drug
Additional Standard Generics HSA Preventive Drug List Effective January 1, 2019
 Additional Standard Generics HSA Preventive Drug List Effective January 1, 2019 Employers can elect to include an additional generic HSA Preventive Drug coverage feature with your prescription benefit
Additional Standard Generics HSA Preventive Drug List Effective January 1, 2019 Employers can elect to include an additional generic HSA Preventive Drug coverage feature with your prescription benefit
By Prof. Khaled El-Rabat
 What is The Optimum? By Prof. Khaled El-Rabat Professor of Cardiology - Benha Faculty of Medicine HT. Introduction Despite major worldwide efforts over recent decades directed at diagnosing and treating
What is The Optimum? By Prof. Khaled El-Rabat Professor of Cardiology - Benha Faculty of Medicine HT. Introduction Despite major worldwide efforts over recent decades directed at diagnosing and treating
Pharmacology: Heart Failure
 Pharmacology: Heart Failure PHPP 515 (IT I) Fall 2014 Monday, Oct. 13 3:00 4:50 PM Dr. Jacobs Required Reading (via Access Pharmacy) Katzung: Chapters 13 Recommended Reading (via Access Pharmacy) Goodman
Pharmacology: Heart Failure PHPP 515 (IT I) Fall 2014 Monday, Oct. 13 3:00 4:50 PM Dr. Jacobs Required Reading (via Access Pharmacy) Katzung: Chapters 13 Recommended Reading (via Access Pharmacy) Goodman
CONCORD INTERNAL & PULMONARY MEDICINE CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE PROTOCOL. Douglas G. Kelling, Jr., MD & C. Gismondi-Eagan, MD, FACP
 CONCORD INTERNAL & PULMONARY MEDICINE CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE PROTOCOL Douglas G. Kelling, Jr., MD & C. Gismondi-Eagan, MD, FACP Revised August 14, 2009 Page 1 Congestive Heart Failure Protocol Patients
CONCORD INTERNAL & PULMONARY MEDICINE CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE PROTOCOL Douglas G. Kelling, Jr., MD & C. Gismondi-Eagan, MD, FACP Revised August 14, 2009 Page 1 Congestive Heart Failure Protocol Patients
Clinical Policy: ACEI and ARB Duplicate Therapy Reference Number: CP.PMN.61 Effective Date: Last Review Date: 05.18
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.PMN.61 Effective Date: 08.01.14 Last Review Date: 05.18 Line of Business: Medicaid Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.PMN.61 Effective Date: 08.01.14 Last Review Date: 05.18 Line of Business: Medicaid Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory
