Identification of congestive heart failure via respiratory variation of inferior vena cava diameter,
|
|
|
- Janis Blake
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 American Journal of Emergency Medicine (2009) 27, Brief Report Identification of congestive heart failure via respiratory variation of inferior vena cava diameter, David J. Blehar MD a,, Eitan Dickman MD b, Romolo Gaspari MD a a Department of Emergency Medicine, University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA 01655, USA b Department of Emergency Medicine, Maimonides Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY 11219, USA Received 8 August 2007; revised 11 January 2008; accepted 12 January 2008 Abstract Introduction: Rapid diagnosis of volume overload in patients with suspected congestive heart failure (CHF) is necessary for the timely administration of therapeutic agents. We sought to use the measurement of respiratory variation of inferior vena cava (IVC) diameter as a diagnostic tool for identification of CHF in patients presenting with acute dyspnea. Methods: The IVC was measured sonographically during a complete respiratory cycle of 46 patients meeting study criteria. Percentage of respiratory variation of IVC diameter was compared to the diagnosis of CHF or alternative diagnosis. Results: Respiratory variation of IVC was smaller in patients with CHF (9.6%) than without CHF (46%) and showed good diagnostic accuracy with area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis showed optimum cutoff of 15% variation or less of IVC diameter with 92% sensitivity and 84% specificity for the diagnosis of CHF. Conclusion: Inferior vena cava ultrasound is a rapid, reliable means for identification of CHF in the acutely dyspneic patient Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 1. Introduction Exacerbations of congestive heart failure (CHF) lead to respiratory distress or even respiratory failure and are associated with high morbidity and mortality [1-3]. Identification of volume overload as the cause of a patient's respiratory distress can be difficult particularly in patients with comorbid conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) because physical examination This study was supported in part by the Department of Emergency Medicine, University of Massachusetts Medical School (Worcester, Mass). Preliminary data were presented at the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine National Conference 2006, San Francisco, CA. Corresponding author. Tel.: address: blehard@ummhc.org (D.J. Blehar). is unreliable and no imaging or laboratory test is adequate [4]. Ultrasonographic measurement of a large respiratory variation of inferior vena cava (IVC) diameter has been shown to correlate with volume depletion in patients with septic shock [5,6] and may be useful in diagnosing volume overload. In this study, we sought to use decreased respiratory variation of IVC diameter as measured via bedside ultrasound to identify volume overload in patients with acute dyspnea. 2. Methods 2.1. Study population Patients were enrolled from a single urban academic emergency department (ED) with an annual volume of /$ see front matter 2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. doi: /j.ajem
2 72 D.J. Blehar et al patients. Patients presenting with a primary complaint of shortness of breath were eligible for inclusion. Exclusion criteria included age of younger than 18 years, pregnancy, liver transplantation, mechanical ventilation, or inability to consent for the study. In addition, patients were excluded if diuretics, bronchodilators, or vasoactive medicines were administered before enrollment Bedside ultrasound Patients enrolled in the study received a limited ultrasound of their IVC before initiation of medical care in the ED. Ultrasound images were obtained immediately on patient arrival to the ED concordant with physician evaluation and nursing care. All decisions for laboratory testing, diagnostic imaging as well as therapeutic interventions were made by the ED attending who was blinded to the results of the IVC measurements. Measurements of the IVC were made with a 3.5-MHz curvilinear probe on a portable ultrasound machine (SonoSite, Inc, Bothell, Wash). Images of the IVC were obtained from an anterior transabdominal approach. The transverse diameter of IVC was measured anterior to posterior immediately inferior to the confluence of the hepatic veins and the IVC with patients in 45 recumbent position. Measurements were taken at maximum diameter during expiration and minimum diameter during inspiration (see Fig. 1). Respiratory variation was then calculated as the difference between maximum and minimum divided by the maximum. All ultrasound images were recorded on medical-grade DVD for later review Diagnostic confirmation and other outcomes measurements Primary outcome measure was diagnosis of CHF or alternate diagnosis. Final diagnosis was determined using previously published methods consisting of a standardized chart review performed independently by 2 physician investigators blinded to results of ultrasound measurements. [4]. Data were collected and recorded on preprinted data sheets (see Table 1 for listing of data points). Diagnoses were divided into 3 categories: (1) shortness of breath secondary to volume overload, (2) history of CHF but shortness of breath due to alternate pathology, and (3) shortness of breath due to alternative cause. For the purposes of statistical analysis, categories 2 and 3 were combined. In the event of a disagreement between the 2 investigators, a third investigator performed a standardized review of the patient records and categorized the patient as described above Statistical analysis The diagnostic performance of a sonographic measurement of the respiratory variation of the IVC for discriminating CHF from non-chf was assessed using a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. The optimal cutoff value of respiratory variation of the IVC to diagnose CHF was chosen by analyzing the ROC curve for maximum sensitivity and specificity. Approval for this study was obtained from University of Massachusetts Institutional Review Board, and written consent was obtained from all participants. 3. Results Forty-six patients were enrolled over a 10-month period. Patients were enrolled in a convenience sample upon the availability of one of the study authors to perform the bedside ultrasound. Patient characteristics for each group are provided in Table 2. Twenty-nine percent of patients had a diagnosis of CHF as the etiology of their shortness of breath. There was no statistical difference between patients with CHF and patients without CHF with the exception of the presence of diabetes. Ultrasound measurements of IVC respiratory variation differentiated CHF from non-chf. Respiratory variation in IVC diameter averaged 9.6% in CHF and 46% in non-chf (P b.0001). Absolute diameter of IVC (taken as the maximum diameter in expiration) was nondiagnostic (18 mm in CHF vs 15 mm in non-chf, P =.084). Receiver operating characteristic curve using respiratory variation of the IVC as diagnostic criteria for CHF produced an area under the curve of 0.96 and revealed 15% respiratory variation or less as the optimum cutoff (see Fig. 2). This cutoff value showed a sensitivity of 93% (95% confidence interval [CI], 76%-99%) and specificity of 84% (95% CI, 77%-88%) for CHF (P b.0001). A secondary analysis of the data showed that no patients in the CHF group had an absolute diameter of the IVC less than 10 mm. There were patients, however, in the non-chf group with diameters of less than 10 mm and respiratory variation below the 15% cutoff value. If a 10-mm cutoff for absolute diameter is added to the diagnostic criteria for CHF, the specificity of the test increased to 91% (95% CI, 83%-93%). Four patients were classified in category 2 (history of CHF but shortness of breath due to alternative cause). All 4 of these patients had BNP measurements greater than 100 μg/ml. Using test criteria of IVC diameter greater than 10 mm and respiratory variation of greater than 15% correctly, we identified all 4 patients as non-chf. 4. Discussion This study examined the utility of sonographic measurement of the IVC as a marker of volume overload in patients with acute shortness of breath. We found that respiratory variation of the IVC was highly sensitive and specific for the diagnosis of CHF.
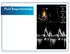
3 Identification of congestive heart failure 73 Fig. 1 Inferior vena cava diameter changes with respiratory cycle. Inferior vena cava imaged in the same patient without movement of the ultrasound probe. The top image demonstrates maximum AP diameter during expiration with measurement taken as demonstrated by the arrow. Hepatic veins are also seen in this view (arrowhead). The bottom image shows collapse of the IVC (arrow) during inspiration, which has also led to collapse of hepatic veins (arrowhead). The diameter of the IVC is dynamic and changes with changes in intrathoracic pressure. During inspiration, intrathoracic pressure decreases thereby increasing venous return and causing collapse of the IVC. During expiration, increase in intrathoracic pressure decreases venous return and leads to increase in diameter of the IVC. The changes in IVC diameter with respiration reflect the elasticity of this capacitance vessel. In cases of CHF, volume overload dilates the IVC to the limits of its elasticity such that the increase in pressure during expiration leads to minimal increase in diameter. Therefore, despite the wide variation between individual patients in absolute diameter of IVC, volume overload can be assessed by observation of decreased change with the respiratory cycle. Measurements of IVC diameter have been shown to trend with changes in volume status in patients with renal failure [7] as well as heart failure [8,9]. Absolute diameter decreases with progressive diuresis in CHF and with
4 74 D.J. Blehar et al. Table 1 History of CHF Standardized chart review data points Hospital discharge diagnosis of CHF Echocardiogram evidence of CHF BNP N100 Chest x-ray evidence of CHF Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea Jugular venous distention Rales S3 gallop Elevated central venous pressure Hepatojugular reflux Weight loss N4.5 kg in 5 d with treatment Improvement with diuresis or dialysis hemodialysis in renal failure [10]. Inferior vena cava diameter has also been shown to decrease after blood donation in healthy volunteers [11]. While helpful, the need for trending measurements makes IVC diameter a poor diagnostic technique for patients where baseline diameter is not known. The wide variation from individual to individual of IVC diameter [12,13] makes isolated measurements difficult to interpret as a true marker of volume status. Recent research in critical care has shown that respiratory variation in IVC diameter can be used to predict volume responsiveness in patients with septic shock [5,6]. Patients with wide variation in IVC diameter with respiratory cycle were found to be more responsive to fluid therapy than those with smaller variations. Use of this respiratory variation has advantages of eliminating the need for baseline or trending measurements, and offers a noninvasive means to ascertain volume status quickly and at the patient's bedside. Brennan et al [14] recently compared IVC measurements to right atrial pressure in patients undergoing right heart catheterization and correlated IVC collapsibility with right atrial pressure. Although they found decreased respiratory variation to be predictive Table 2 Patient characteristics CHF Not-CHF P Total no. of patients Average age (y) Male (%) Admitted (%) Coronary disease (%) Hypertension (%) Diabetes (%) CHF (%) COPD (%) Asthma (%) Renal insufficiency (%) COPD indicates chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Fig. 2 Receiver operating characteristic curve. Respiratory variation of IVC diameter showed good diagnostic accuracy with area under curve of of elevated right atrial pressure, their optimum cutoff was identified at 40%, markedly greater than our cutoff of 15%. There are 2 possible explanations for the differences in our cutoff values. First, patients in the Brennan study had already received treatment and were at least partially diuresed before the ultrasound. As fluid was removed the respiratory variation would increase. Secondly, patients in the Brennan study were positioned for catheterization in a recumbent position, whereas most patients in our study were imaged in a semirecumbent position due to inability to lie flat. This reflects the difference in volume status after diuresis. It is also possible that a cutoff of 40% detects all patients with increased right heart pressures but a cutoff of 15% detects patients with elevated heart pressures who are symptomatic. In our study, 15% respiratory variation or less of IVC diameter was highly sensitive and specific for the diagnosis of CHF. The test's specificity was further increased by the addition of a 10-mm cutoff for absolute diameter of IVC. Although absolute diameter of IVC in itself was nondiagnostic, patients with small IVC diameter posed a challenge for measurement of respiratory variation as it approached the limits of resolution of the imaging technique. Data published by Brennan et al [14] likewise supports the use of 10 mm as a cutoff for diagnosis of elevated right atrial pressure. As no patient diagnosed with CHF had an IVC diameter less than 10 mm in our study, we feel this cutoff is a reasonable addition to the test criteria Limitations There were several limitations in our study. More men than women were enrolled in the study, and in particular, more men were ultimately diagnosed with CHF (71%). This may be due simply to chance or reflect the higher prevalence of cardiovascular disease in men than women [15]. Differences in patient groups and sex bias may be explained by our small sample size of 48 patients. This sample size was
5 Identification of congestive heart failure chosen after interim analysis revealed good diagnostic accuracy with area under ROC curve of This remains, however, a small study, and certainly, future studies may be warranted to confirm our results in larger, more uniform populations. Another limitation of the technique that is difficult to quantify is the potential confounder of conditions such as tricuspid regurgitation. One would reason that this would lead to false positive tests in using this technique to diagnose CHF. We did not have echocardiogram data on all the patients in our study so we cannot speak to its bearing on our study population. References [1] Levy WC, Mozaffarian D, Linker DT, et al. The Seattle heart failure model: prediction of survival in heart failure. Circulation 2006;113: [2] Weir RA, McMurray JJ, Velazquez EJ. Epidemiology of heart failure and left ventricular systolic dysfunction after acute myocardial infarction: prevalence, clinical characteristics, and prognostic importance. Am J Cardiol 2006;97:13F-25F. [3] Zannad F, Mebazaa A, Juilliere Y, et al. Clinical profile, contemporary management and one-year mortality in patients with severe acute heart failure syndromes: the EFICA study. Eur J Heart Fail 2006;8(7): [4] McCullough PA, Nowak RM, McCord J, et al. B-type natriuretic peptide and clinical judgment in emergency diagnosis of heart failure: analysis from Breathing Not Properly (BNP) Multinational Study. Circulation 2002;106: [5] Feissel M, Michard F, Faller JP, et al. The respiratory variation in inferior vena cava diameter as a guide to fluid therapy. Intensive Care Med 2004;30: [6] Barbier C, Loubieres Y, Schmit C, et al. Respiratory changes in inferior vena cava diameter are helpful in predicting fluid responsiveness in ventilated septic patients. Intensive Care Med 2004;30: [7] Yanagiba S, Ando Y, Kusano E, et al. Utility of the inferior vena cava diameter as a marker of dry weight in nonoliguric hemodialyzed patients. Asaio J 2001;47: [8] Moreno FL, Hagan AD, Holmen JR, et al. Evaluation of size and dynamics of the inferior vena cava as an index of right-sided cardiac function. Am J Cardiol 1984;53: [9] Goei R, Ronnen HR, Kessels AH, et al. Right heart failure: diagnosis via ultrasonography of the inferior vena cava and hepatic veins. Rofo 1997;166:36-9. [10] Tetsuka T, Ando Y, Ono S, et al. Change in inferior vena caval diameter detected by ultrasonography during and after hemodialysis. Asaio J 1995;41: [11] Lyon M, Blaivas M, Brannam L. Sonographic measurement of the inferior vena cava as a marker of blood loss. Am J Emerg Med 2005;23: [12] Rein AJ, Lewis N, Forst L, et al. Echocardiography of the inferior vena cava in healthy subjects and in patients with cardiac disease. Isr J Med Sci 1982;18: [13] Goldhammer E, Mesnick N, Abinader EG, et al. Dilated inferior vena cava: a common echocardiographic finding in highly trained elite athletes. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 1999;12: [14] Brennan JM, Blair JE, Goonewardena S, et al. Reappraisal of the use of inferior vena cava for estimating right atrial pressure. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2007;20: [15] Ho KK, Pinsky JL, Kannel WB, et al. The epidemiology of heart failure: the Framingham Study. J Am Coll Cardiol 1993;22:6A-13A. 75
Background: Bedside ultrasound is emerging as a useful tool in the assessment of
 Abstract: Background: Bedside ultrasound is emerging as a useful tool in the assessment of intravascular volume status by examining measurements of the inferior vena cava (IVC). Many previous studies do
Abstract: Background: Bedside ultrasound is emerging as a useful tool in the assessment of intravascular volume status by examining measurements of the inferior vena cava (IVC). Many previous studies do
Point-of-Care Ultrasound Closer look at the Inferior Vena Cavae &
 Point-of-Care Ultrasound Closer look at the Inferior Vena Cavae & Brief Introduction to Gross Systolic Function Omar S. Darwish, MS, DO Certified in Point-of-Care Ultrasound Hospitalist University of California,
Point-of-Care Ultrasound Closer look at the Inferior Vena Cavae & Brief Introduction to Gross Systolic Function Omar S. Darwish, MS, DO Certified in Point-of-Care Ultrasound Hospitalist University of California,
The Effect of Weight-based Volume Loading on the Inferior Vena Cava in Fasting Subjects: A Prospective Randomized Double-blinded Trial
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH CONTRIBUTION The Effect of Weight-based Volume Loading on the Inferior Vena Cava in Fasting Subjects: A Prospective Randomized Double-blinded Trial Anthony J. Weekes, MD, Margaret R.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH CONTRIBUTION The Effect of Weight-based Volume Loading on the Inferior Vena Cava in Fasting Subjects: A Prospective Randomized Double-blinded Trial Anthony J. Weekes, MD, Margaret R.
Protocol Identifier Subject Identifier Visit Description. [Y] Yes [N] No. [Y] Yes [N] N. If Yes, admission date and time: Day Month Year
![Protocol Identifier Subject Identifier Visit Description. [Y] Yes [N] No. [Y] Yes [N] N. If Yes, admission date and time: Day Month Year Protocol Identifier Subject Identifier Visit Description. [Y] Yes [N] No. [Y] Yes [N] N. If Yes, admission date and time: Day Month Year](/thumbs/76/74263761.jpg) PAST MEDICAL HISTORY Has the subject had a prior episode of heart failure? o Does the subject have a prior history of exposure to cardiotoxins, such as anthracyclines? URGENT HEART FAILURE VISIT Did heart
PAST MEDICAL HISTORY Has the subject had a prior episode of heart failure? o Does the subject have a prior history of exposure to cardiotoxins, such as anthracyclines? URGENT HEART FAILURE VISIT Did heart
Lnformation Coverage Guidance
 Lnformation Coverage Guidance Coverage Indications, Limitations, and/or Medical Necessity Abstract: B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) is a cardiac neurohormone produced mainly in the left ventricle. It
Lnformation Coverage Guidance Coverage Indications, Limitations, and/or Medical Necessity Abstract: B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) is a cardiac neurohormone produced mainly in the left ventricle. It
Original Research Article
 ASSESSMENT AND COMPARISON OF CARDIAC FUNCTION AND VOLUME STATUS USING BEDSIDE ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IN CRITICALLY ILL PATIENTS WITH OTHER CONVENTIONAL METHODS Priyanka Dwivedi, Shahbaz Ahmad, Vivek Pushp 3,
ASSESSMENT AND COMPARISON OF CARDIAC FUNCTION AND VOLUME STATUS USING BEDSIDE ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IN CRITICALLY ILL PATIENTS WITH OTHER CONVENTIONAL METHODS Priyanka Dwivedi, Shahbaz Ahmad, Vivek Pushp 3,
Using Lung Ultrasound to Diagnose and Manage Acute Heart Failure
 Using Lung Ultrasound to Diagnose and Manage Acute Heart Failure Jennifer Martindale, MD Assistant Professor Department of Emergency Medicine SUNY Downstate/Kings County Hospital Brooklyn, NY What is acute
Using Lung Ultrasound to Diagnose and Manage Acute Heart Failure Jennifer Martindale, MD Assistant Professor Department of Emergency Medicine SUNY Downstate/Kings County Hospital Brooklyn, NY What is acute
Inferior vena cava diameters and collapsibility index reveal early volume depletion in a blood donor model
 DOI 10.1186/s13089-015-0034-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Inferior vena cava diameters and collapsibility index reveal early volume depletion in a blood donor model Paolo Pasquero 1*, Stefano Albani 1, Elena Sitia
DOI 10.1186/s13089-015-0034-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Inferior vena cava diameters and collapsibility index reveal early volume depletion in a blood donor model Paolo Pasquero 1*, Stefano Albani 1, Elena Sitia
ALLHAT. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. National Institutes of Health. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute
 U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Review of Heart Failure Events in the Antihypertensive and Lipid Lowering Treatment
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Review of Heart Failure Events in the Antihypertensive and Lipid Lowering Treatment
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies
 Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
Non Invasive Hemodynamic Monitoring in the ED
 Is haemodinamic monitoring useful in the ED? Non Invasive Hemodynamic Monitoring in the ED Roberta PETRINO Director Emergency Medicine Unit S. Andrea Hospital, Vercelli - Italy EuSEM Vice-president Helps
Is haemodinamic monitoring useful in the ED? Non Invasive Hemodynamic Monitoring in the ED Roberta PETRINO Director Emergency Medicine Unit S. Andrea Hospital, Vercelli - Italy EuSEM Vice-president Helps
Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea
 Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea Jahrestagung Schweizerische Gesellschaft für /Schweizerische Gesellschaft für Pneumologie B. Kaufmann 16.06.2016 Chronic dyspnea Shortness of breath lasting
Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea Jahrestagung Schweizerische Gesellschaft für /Schweizerische Gesellschaft für Pneumologie B. Kaufmann 16.06.2016 Chronic dyspnea Shortness of breath lasting
Sonographic measurement of the inferior vena cava as a marker of blood loss
 American Journal of Emergency Medicine (2005) 23, 45 50 www.elsevier.com/locate/ajem Sonographic measurement of the inferior vena cava as a marker of blood loss Matthew Lyon MD, Michael Blaivas MD, RDMS*,
American Journal of Emergency Medicine (2005) 23, 45 50 www.elsevier.com/locate/ajem Sonographic measurement of the inferior vena cava as a marker of blood loss Matthew Lyon MD, Michael Blaivas MD, RDMS*,
Department of General Medicine, Kilpauk Medical College and Hospital, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India * Corresponding author
 Original Research Article Study on clinical assessment of volume status and correlation to the respiratory variation in inferior vena cava diameter by echocardiography, a non-invasive method of measuring
Original Research Article Study on clinical assessment of volume status and correlation to the respiratory variation in inferior vena cava diameter by echocardiography, a non-invasive method of measuring
Estimation of Right Atrial Pressure from the Inspiratory Collapse of the Inferior Vena cava in Pediatric Patients
 Original Article Iran J Pediatr Jun 2010; Vol 20 (No 2), Pp:206-210 Estimation of Right Atrial Pressure from the Inspiratory Collapse of the Inferior Vena cava in Pediatric Patients Hamid Amoozgar*, MD;
Original Article Iran J Pediatr Jun 2010; Vol 20 (No 2), Pp:206-210 Estimation of Right Atrial Pressure from the Inspiratory Collapse of the Inferior Vena cava in Pediatric Patients Hamid Amoozgar*, MD;
The caval index: an adequate non-invasive ultrasound parameter to predict fluid responsiveness in the emergency department?
 de Valk et al. BMC Anesthesiology 2014, 14:114 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The caval index: an adequate non-invasive ultrasound parameter to predict fluid responsiveness in the emergency department? Silke
de Valk et al. BMC Anesthesiology 2014, 14:114 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The caval index: an adequate non-invasive ultrasound parameter to predict fluid responsiveness in the emergency department? Silke
*Christian M. Carlsen, 1 Mette Mouridsen, 1 Ahmad Sajadieh, 1 Lars Køber, 2 Olav W. Nielsen 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND
 USE OF N-TERMINAL NATRIURETIC PEPTIDE IN A REAL- WORLD SETTING OF PATIENTS ADMITTED WITH ACUTE DYSPNOEA AND THE IMPLICATION FOR TRIAGING PATIENTS IN THE EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT *Christian M. Carlsen, 1 Mette
USE OF N-TERMINAL NATRIURETIC PEPTIDE IN A REAL- WORLD SETTING OF PATIENTS ADMITTED WITH ACUTE DYSPNOEA AND THE IMPLICATION FOR TRIAGING PATIENTS IN THE EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT *Christian M. Carlsen, 1 Mette
Ultrasound in Emergency Medicine
 doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2010.11.040 The Journal of Emergency Medicine, Vol. 41, No. 3, pp. 270 275, 2011 Copyright Ó 2011 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0736-4679/$ - see front matter
doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2010.11.040 The Journal of Emergency Medicine, Vol. 41, No. 3, pp. 270 275, 2011 Copyright Ó 2011 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0736-4679/$ - see front matter
ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΟΣ EUROPEAN ACCREDITATION IN TRANSTHORACIC AND TRANSESOPHAGEAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY
 1 ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΟΣ EUROPEAN ACCREDITATION IN TRANSTHORACIC AND TRANSESOPHAGEAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY 2 Constrictive pericarditis (CP) is characterized by impaired ventricular filling due to a stiffened or noncompliant
1 ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΟΣ EUROPEAN ACCREDITATION IN TRANSTHORACIC AND TRANSESOPHAGEAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY 2 Constrictive pericarditis (CP) is characterized by impaired ventricular filling due to a stiffened or noncompliant
Diagnostic Bedside Ultrasound for the Hospitalist
 Diagnostic Bedside Ultrasound for the Hospitalist Trevor Jensen MD MS Assistant Professor, UCSF Nima Afshar MD Associate Professor, UCSF Diagnostic Bedside Ultrasound AKA Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS)
Diagnostic Bedside Ultrasound for the Hospitalist Trevor Jensen MD MS Assistant Professor, UCSF Nima Afshar MD Associate Professor, UCSF Diagnostic Bedside Ultrasound AKA Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS)
ACUTE HEART FAILURE in the ED. Pr. Samir Nouira Emergency Department Fattouma Bourguiba University Hospital Monastir Tunisia
 ACUTE HEART FAILURE in the ED Pr. Samir Nouira Emergency Department Fattouma Bourguiba University Hospital Monastir Tunisia ACUTE HEART FAILURE 80% Acute Heart Failure Syndrome Sensitivity Specificity
ACUTE HEART FAILURE in the ED Pr. Samir Nouira Emergency Department Fattouma Bourguiba University Hospital Monastir Tunisia ACUTE HEART FAILURE 80% Acute Heart Failure Syndrome Sensitivity Specificity
Disclosure Information : No conflict of interest
 Intravenous nicorandil improves symptoms and left ventricular diastolic function immediately in patients with acute heart failure : a randomized, controlled trial M. Shigekiyo, K. Harada, A. Okada, N.
Intravenous nicorandil improves symptoms and left ventricular diastolic function immediately in patients with acute heart failure : a randomized, controlled trial M. Shigekiyo, K. Harada, A. Okada, N.
2
 1 2 Although the term "cardiomyopathy" could theoretically apply to almost any disease affecting the heart, it is usually reserved for "severe myocardial disease leading to heart failure".cardiomyopathy
1 2 Although the term "cardiomyopathy" could theoretically apply to almost any disease affecting the heart, it is usually reserved for "severe myocardial disease leading to heart failure".cardiomyopathy
Research Article Caval Aorta Index and Central Venous Pressure Correlation in Assessing Fluid Status! Ultrasound Bridging the Gap
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Emergency Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 828626, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/828626 Research Article Caval Aorta Index and Central Venous Pressure Correlation
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Emergency Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 828626, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/828626 Research Article Caval Aorta Index and Central Venous Pressure Correlation
Dr. Md. Rajibul Alam Prof. of Medicine Dinajpur Medical college
 Dr. Md. Rajibul Alam Prof. of Medicine Dinajpur Medical college PULMONARY HYPERTENSION Difficult to diagnose early Because Not detected during routine physical examination and Even in advanced cases symptoms
Dr. Md. Rajibul Alam Prof. of Medicine Dinajpur Medical college PULMONARY HYPERTENSION Difficult to diagnose early Because Not detected during routine physical examination and Even in advanced cases symptoms
A Practical Approach to Ultrasound Assessment of Respiratory Distress
 A Practical Approach to Ultrasound Assessment of Respiratory Distress Yanick Beaulieu, MD, FRCPC Director, Bedside Ultrasound Curriculum Division of Cardiology and Critical Care Hôpital du Sacré-Coeur
A Practical Approach to Ultrasound Assessment of Respiratory Distress Yanick Beaulieu, MD, FRCPC Director, Bedside Ultrasound Curriculum Division of Cardiology and Critical Care Hôpital du Sacré-Coeur
A study of Brain Natriuretic Peptide levels in acute cardiac failure
 Original Research Article A study of Brain Natriuretic Peptide levels in acute cardiac failure Bhavik Prajapati 1*, Anirudh Kulkarni 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, SMS Multispecialty
Original Research Article A study of Brain Natriuretic Peptide levels in acute cardiac failure Bhavik Prajapati 1*, Anirudh Kulkarni 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, SMS Multispecialty
Derivation of a pediatric growth curve for inferior vena caval diameter in healthy pediatric patients: brief report of initial curve development
 Haines et al. Critical Ultrasound Journal 22, 4:2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Open Access Derivation of a pediatric growth curve for inferior vena caval diameter in healthy pediatric patients: brief report of initial
Haines et al. Critical Ultrasound Journal 22, 4:2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Open Access Derivation of a pediatric growth curve for inferior vena caval diameter in healthy pediatric patients: brief report of initial
The right heart: the Cinderella of heart failure
 The right heart: the Cinderella of heart failure Piotr Ponikowski, MD, PhD, FESC Medical University, Centre for Heart Disease Clinical Military Hospital Wroclaw, Poland none Disclosure Look into the Heart
The right heart: the Cinderella of heart failure Piotr Ponikowski, MD, PhD, FESC Medical University, Centre for Heart Disease Clinical Military Hospital Wroclaw, Poland none Disclosure Look into the Heart
Pericardial Diseases. Smonporn Boonyaratavej, MD. Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University
 Pericardial Diseases Smonporn Boonyaratavej, MD Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Cardiac Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital 21 AUGUST 2016 Pericardial
Pericardial Diseases Smonporn Boonyaratavej, MD Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Cardiac Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital 21 AUGUST 2016 Pericardial
Abstract. ª 2011 by the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine 912 PII ISSN doi: /j
 Comparison of Serial Qualitative and Quantitative Assessments of Caval Index and Left Ventricular Systolic Function During Early Fluid Resuscitation of Hypotensive Emergency Department Patients Anthony
Comparison of Serial Qualitative and Quantitative Assessments of Caval Index and Left Ventricular Systolic Function During Early Fluid Resuscitation of Hypotensive Emergency Department Patients Anthony
Cor pulmonale. Dr hamid reza javadi
 1 Cor pulmonale Dr hamid reza javadi 2 Definition Cor pulmonale ;pulmonary heart disease; is defined as dilation and hypertrophy of the right ventricle (RV) in response to diseases of the pulmonary vasculature
1 Cor pulmonale Dr hamid reza javadi 2 Definition Cor pulmonale ;pulmonary heart disease; is defined as dilation and hypertrophy of the right ventricle (RV) in response to diseases of the pulmonary vasculature
Diastolic Heart Failure. Edwin Tulloch-Reid MBBS FACC Consultant Cardiologist Heart Institute of the Caribbean December 2012
 Diastolic Heart Failure Edwin Tulloch-Reid MBBS FACC Consultant Cardiologist Heart Institute of the Caribbean December 2012 Disclosures Have spoken for Merck, Sharpe and Dohme Sat on a physician advisory
Diastolic Heart Failure Edwin Tulloch-Reid MBBS FACC Consultant Cardiologist Heart Institute of the Caribbean December 2012 Disclosures Have spoken for Merck, Sharpe and Dohme Sat on a physician advisory
Impedance Cardiography (ICG) Application of ICG in Intensive Care and Emergency
 Impedance Cardiography (ICG) Application of ICG in Intensive Care and Emergency Aim of haemodynamic monitoring in ICU and ED Detection and therapy of insufficient organ perfusion Answers to common cardiovascular
Impedance Cardiography (ICG) Application of ICG in Intensive Care and Emergency Aim of haemodynamic monitoring in ICU and ED Detection and therapy of insufficient organ perfusion Answers to common cardiovascular
Q: What is the best approach to a high systolic
 1-MINUTE CONSULT BRIEF ANSWERS TO SPECIFIC CLINICAL QUESTIONS Approaches range from no further testing to right heart catheterization to referral MOSTAFA AHMED, MD Research Fellow, Department of Pulmonary,
1-MINUTE CONSULT BRIEF ANSWERS TO SPECIFIC CLINICAL QUESTIONS Approaches range from no further testing to right heart catheterization to referral MOSTAFA AHMED, MD Research Fellow, Department of Pulmonary,
Hemodynamic Monitoring
 Perform Procedure And Interpret Results Hemodynamic Monitoring Tracheal Tube Cuff Pressure Dean R. Hess PhD RRT FAARC Hemodynamic Monitoring Cardiac Rate and Rhythm Arterial Blood Pressure Central Venous
Perform Procedure And Interpret Results Hemodynamic Monitoring Tracheal Tube Cuff Pressure Dean R. Hess PhD RRT FAARC Hemodynamic Monitoring Cardiac Rate and Rhythm Arterial Blood Pressure Central Venous
Heart Failure Dr ahmed almutairi Assistant professor internal medicin dept
 Heart Failure Dr ahmed almutairi Assistant professor internal medicin dept (MBBS)(SBMD) Introduction Epidemiology Pathophysiology diastolic/systolic Risk factors Signs and symptoms Classification of HF
Heart Failure Dr ahmed almutairi Assistant professor internal medicin dept (MBBS)(SBMD) Introduction Epidemiology Pathophysiology diastolic/systolic Risk factors Signs and symptoms Classification of HF
Right Heart Hemodynamics: Echo-Cath Discrepancies
 Department of cardiac, thoracic and vascular sciences University of Padua, School of Medicine Padua, Italy Right Heart Hemodynamics: Echo-Cath Discrepancies Luigi P. Badano, MD, PhD, FESC, FACC **Dr. Badano
Department of cardiac, thoracic and vascular sciences University of Padua, School of Medicine Padua, Italy Right Heart Hemodynamics: Echo-Cath Discrepancies Luigi P. Badano, MD, PhD, FESC, FACC **Dr. Badano
Estimation of Right Atrial Pressure on Inferior Vena Cava Ultrasound in Asian Patients
 962 LEE SL et al. Circulation Journal ORIGINAL ARTICLE Official Journal of the Japanese Circulation Society http://www.j-circ.or.jp Pulmonary Circulation Estimation of Right Atrial Pressure on Inferior
962 LEE SL et al. Circulation Journal ORIGINAL ARTICLE Official Journal of the Japanese Circulation Society http://www.j-circ.or.jp Pulmonary Circulation Estimation of Right Atrial Pressure on Inferior
CHAPTER 13. Fluid Responsiveness
 CHAPTER 13 Fluid Responsiveness SECTION 1 Introduction Administration of an intravenous fluid challenge is a common medical intervention in the hypotensive or hypovolemic patient. Ideally, a fluid challenge
CHAPTER 13 Fluid Responsiveness SECTION 1 Introduction Administration of an intravenous fluid challenge is a common medical intervention in the hypotensive or hypovolemic patient. Ideally, a fluid challenge
Impact of Nicorandil on Renal Function in Patients With Acute Heart Failure and Pre-Existing Renal Dysfunction
 Impact of Nicorandil on Renal Function in Patients With Acute Heart Failure and Pre-Existing Renal Dysfunction Masahito Shigekiyo, Kenji Harada, Ayumi Okada, Naho Terada, Hiroyoshi Yoshikawa, Akira Hirono,
Impact of Nicorandil on Renal Function in Patients With Acute Heart Failure and Pre-Existing Renal Dysfunction Masahito Shigekiyo, Kenji Harada, Ayumi Okada, Naho Terada, Hiroyoshi Yoshikawa, Akira Hirono,
Strategies to assess and manage hypervolemia The invisible threat in dialysis
 Strategies to assess and manage hypervolemia The invisible threat in dialysis Rajiv Agarwal MD Professor of Medicine, Indiana University School of Medicine Volume excess is common and costly. Admission
Strategies to assess and manage hypervolemia The invisible threat in dialysis Rajiv Agarwal MD Professor of Medicine, Indiana University School of Medicine Volume excess is common and costly. Admission
JACC: CARDIOVASCULAR IMAGING VOL. 1, NO. 5, PUBLISHED BY ELSEVIER INC. DOI: /j.jcmg
 JACC: CARDIOVASCULAR IMAGING VOL. 1, NO. 5, 2008 2008 BY THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY FOUNDATION ISSN 1936-878X/08/$34.00 PUBLISHED BY ELSEVIER INC. DOI:10.1016/j.jcmg.2008.06.005 Comparison of Hand-Carried
JACC: CARDIOVASCULAR IMAGING VOL. 1, NO. 5, 2008 2008 BY THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY FOUNDATION ISSN 1936-878X/08/$34.00 PUBLISHED BY ELSEVIER INC. DOI:10.1016/j.jcmg.2008.06.005 Comparison of Hand-Carried
COPD as a comorbidity of heart failure in elderly patients
 COPD as a comorbidity of heart failure in elderly patients Professor Mitja Lainscak, MD, PhD, FESC, FHFA Departments of Cardiology and Research&Education, General Hospital Celje Faculty of Medicine, University
COPD as a comorbidity of heart failure in elderly patients Professor Mitja Lainscak, MD, PhD, FESC, FHFA Departments of Cardiology and Research&Education, General Hospital Celje Faculty of Medicine, University
The role of bedside ultrasound in the diagnosis of pericardial effusion and cardiac tamponade
 Symposium The role of bedside ultrasound in the diagnosis of pericardial effusion and cardiac tamponade Adam Goodman, Phillips Perera, Thomas Mailhot, Diku Mandavia Department of Emergency Medicine, Los
Symposium The role of bedside ultrasound in the diagnosis of pericardial effusion and cardiac tamponade Adam Goodman, Phillips Perera, Thomas Mailhot, Diku Mandavia Department of Emergency Medicine, Los
Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension
 ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
DIASTOLOGY DON T BE SUCH A STIFF
 DIASTOLOGY DON T BE SUCH A STIFF Michael Mallin, MD University of Utah Director Emergency Ultrasound www.ultrasoundpodcast.com Warning: The education found within this presentation is not approved by anyone
DIASTOLOGY DON T BE SUCH A STIFF Michael Mallin, MD University of Utah Director Emergency Ultrasound www.ultrasoundpodcast.com Warning: The education found within this presentation is not approved by anyone
AAENP US WORKSHOP 2/25/17
 Know the components of the Rapid Ultrasound for Shock & Hypotension & Extended Focused Assessment Sonography in Trauma & how they can help quickly determine diagnosis. Be comfortable obtaining and interpreting
Know the components of the Rapid Ultrasound for Shock & Hypotension & Extended Focused Assessment Sonography in Trauma & how they can help quickly determine diagnosis. Be comfortable obtaining and interpreting
EHMRG SCORE STUDY version 6.2; date: 11Jul11 PI: Dr. Douglas Lee. Study Background
 EHMRG SCORE STUDY version 6.2; date: 11Jul11 PI: Dr. Douglas Lee Study Background Heart failure (HF) is a leading cause of morbidity and cardiovascular mortality. The burden of HF has increased over time
EHMRG SCORE STUDY version 6.2; date: 11Jul11 PI: Dr. Douglas Lee Study Background Heart failure (HF) is a leading cause of morbidity and cardiovascular mortality. The burden of HF has increased over time
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
THE FRAMINGHAM STUDY Protocol for data set vr_soe_2009_m_0522 CRITERIA FOR EVENTS. 1. Cardiovascular Disease
 THE FRAMINGHAM STUDY Protocol for data set vr_soe_2009_m_0522 CRITERIA FOR EVENTS 1. Cardiovascular Disease Cardiovascular disease is considered to have developed if there was a definite manifestation
THE FRAMINGHAM STUDY Protocol for data set vr_soe_2009_m_0522 CRITERIA FOR EVENTS 1. Cardiovascular Disease Cardiovascular disease is considered to have developed if there was a definite manifestation
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute coronary syndrome(s), anticoagulant therapy in, 706, 707 antiplatelet therapy in, 702 ß-blockers in, 703 cardiac biomarkers in,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute coronary syndrome(s), anticoagulant therapy in, 706, 707 antiplatelet therapy in, 702 ß-blockers in, 703 cardiac biomarkers in,
Outline. Echocardiographic Assessment of Pericardial Effusion/Tamponade: The Essentials
 Echocardiographic Assessment of Pericardial Effusion/Tamponade: The Essentials John R Schairer DO FACC Henry Ford Heart and Vascular Institute No Disclosures Outline Normal Anatomy and Physiology Pathophysiology
Echocardiographic Assessment of Pericardial Effusion/Tamponade: The Essentials John R Schairer DO FACC Henry Ford Heart and Vascular Institute No Disclosures Outline Normal Anatomy and Physiology Pathophysiology
Topic Page: congestive heart failure
 Topic Page: congestive heart failure Definition: congestive heart f ailure from Merriam-Webster's Collegiate(R) Dictionary (1930) : heart failure in which the heart is unable to maintain an adequate circulation
Topic Page: congestive heart failure Definition: congestive heart f ailure from Merriam-Webster's Collegiate(R) Dictionary (1930) : heart failure in which the heart is unable to maintain an adequate circulation
ARIC HEART FAILURE HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM
 ARIC HEART FAILURE HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM ID NUMBER: FORM NAME: H F A DATE: 10/01/2015 VERSION: D CONTACT YEAR NUMBER: FORM SEQUENCE NUMBER: General Instructions: The Heart Failure Hospital Record
ARIC HEART FAILURE HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM ID NUMBER: FORM NAME: H F A DATE: 10/01/2015 VERSION: D CONTACT YEAR NUMBER: FORM SEQUENCE NUMBER: General Instructions: The Heart Failure Hospital Record
LCD L B-type Natriuretic Peptide (BNP) Assays
 LCD L30559 - B-type Natriuretic Peptide (BNP) Assays Contractor Information Contractor Name: Novitas Solutions, Inc. Contractor Number(s): 12501, 12502, 12101, 12102, 12201, 12202, 12301, 12302, 12401,
LCD L30559 - B-type Natriuretic Peptide (BNP) Assays Contractor Information Contractor Name: Novitas Solutions, Inc. Contractor Number(s): 12501, 12502, 12101, 12102, 12201, 12202, 12301, 12302, 12401,
Diagnosis & Management of Heart Failure. Abena A. Osei-Wusu, M.D. Medical Fiesta
 Diagnosis & Management of Heart Failure Abena A. Osei-Wusu, M.D. Medical Fiesta Learning Objectives: 1) Become familiar with pathogenesis of congestive heart failure. 2) Discuss clinical manifestations
Diagnosis & Management of Heart Failure Abena A. Osei-Wusu, M.D. Medical Fiesta Learning Objectives: 1) Become familiar with pathogenesis of congestive heart failure. 2) Discuss clinical manifestations
Prevention of Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure in the Hypertensive Patient
 Prevention of Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure in the Hypertensive Patient The Issue of Primary Prevention of A.Fib. (and Heart Failure) and not the Prevention of Recurrent A.Fib. after Electroconversion
Prevention of Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure in the Hypertensive Patient The Issue of Primary Prevention of A.Fib. (and Heart Failure) and not the Prevention of Recurrent A.Fib. after Electroconversion
New CHF Patient in my Office: What Should I Do?
 New CHF Patient in my Office: What Should I Do? Joseph Mishkin MD FACC Advanced Heart Failure, Transplantation and Mechanical Circulatory Support No disclosures Disclosures Clinical Presentation 38 year
New CHF Patient in my Office: What Should I Do? Joseph Mishkin MD FACC Advanced Heart Failure, Transplantation and Mechanical Circulatory Support No disclosures Disclosures Clinical Presentation 38 year
Correlation between Central Venous Pressure and Inferior Vena Cava Sonographic Diameter; Determining the Best Anatomic Location
 83 Emergency (2016); 4 (2): 83-87 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Correlation between Central Venous Pressure and Inferior Vena Cava Sonographic Diameter; Determining the Best Anatomic Location Bahman Naghipour 1, Gholamreza
83 Emergency (2016); 4 (2): 83-87 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Correlation between Central Venous Pressure and Inferior Vena Cava Sonographic Diameter; Determining the Best Anatomic Location Bahman Naghipour 1, Gholamreza
Natriuretic Peptides The Cardiologists View. Christopher defilippi, MD University of Maryland Baltimore, MD, USA
 Natriuretic Peptides The Cardiologists View Christopher defilippi, MD University of Maryland Baltimore, MD, USA Disclosures Research support: Alere, BG Medicine, Critical Diagnostics, Roche Diagnostics,
Natriuretic Peptides The Cardiologists View Christopher defilippi, MD University of Maryland Baltimore, MD, USA Disclosures Research support: Alere, BG Medicine, Critical Diagnostics, Roche Diagnostics,
Echocardiographic Cardiovascular Risk Stratification: Beyond Ejection Fraction
 Echocardiographic Cardiovascular Risk Stratification: Beyond Ejection Fraction October 4, 2014 James S. Lee, M.D., F.A.C.C. Associates in Cardiology, P.A. Silver Spring, M.D. Disclosures Financial none
Echocardiographic Cardiovascular Risk Stratification: Beyond Ejection Fraction October 4, 2014 James S. Lee, M.D., F.A.C.C. Associates in Cardiology, P.A. Silver Spring, M.D. Disclosures Financial none
Heart failure (HF) is a complex clinical syndrome that results in the. impairment of the heart s ability to fill or to pump out blood.
 Introduction: Heart failure (HF) is a complex clinical syndrome that results in the impairment of the heart s ability to fill or to pump out blood. As of 2013, an estimated 5.8 million people in the United
Introduction: Heart failure (HF) is a complex clinical syndrome that results in the impairment of the heart s ability to fill or to pump out blood. As of 2013, an estimated 5.8 million people in the United
Case Report Respirophasic Variations in the QRS Complex and Echocardiographic Equivalent in Pulmonary Embolism
 www.ipej.org 313 Case Report Respirophasic Variations in the QRS Complex and Echocardiographic Equivalent in Pulmonary Embolism Eftychios Siniorakis, MD, Spyridon Arvanitakis, BM, Dimitris Barlagiannis,
www.ipej.org 313 Case Report Respirophasic Variations in the QRS Complex and Echocardiographic Equivalent in Pulmonary Embolism Eftychios Siniorakis, MD, Spyridon Arvanitakis, BM, Dimitris Barlagiannis,
B-type Natriuretic Peptide for Diagnosis of Heart Failure in Emergency Department Patients: A Critical Appraisal
 686 Schwam d BNP FOR DIAGNOSIS OF HF B-type Natriuretic Peptide for Diagnosis of Heart Failure in Emergency Department Patients: A Critical Appraisal Abstract The diagnosis of heart failure in the outpatient
686 Schwam d BNP FOR DIAGNOSIS OF HF B-type Natriuretic Peptide for Diagnosis of Heart Failure in Emergency Department Patients: A Critical Appraisal Abstract The diagnosis of heart failure in the outpatient
Hemodynamic Comparison Between Right Heart Catheterization and Transthoracic Echocardiography in the Critically Ill Patients: A Prospective Study
 The Open Critical Care Medicine Journal, 2012, 5, 1-8 1 Open Access Hemodynamic Comparison Between Right Heart Catheterization and Transthoracic Echocardiography in the Critically Ill Patients: A Prospective
The Open Critical Care Medicine Journal, 2012, 5, 1-8 1 Open Access Hemodynamic Comparison Between Right Heart Catheterization and Transthoracic Echocardiography in the Critically Ill Patients: A Prospective
DUKECATHR Dataset Dictionary
 DUKECATHR Dataset Dictionary Version of DUKECATH dataset for educational use that has been modified to be unsuitable for clinical research or publication (Created Date and Time: 28OCT16 14:35) Table of
DUKECATHR Dataset Dictionary Version of DUKECATH dataset for educational use that has been modified to be unsuitable for clinical research or publication (Created Date and Time: 28OCT16 14:35) Table of
Prof. Dr. Iman Riad Mohamed Abdel Aal
 The Use of New Ultrasound Indices to Evaluate Volume Status and Fluid Responsiveness in Septic Shock Patients Thesis Submitted for partial fulfillment of MD degree in Anesthesiology, Surgical Intensive
The Use of New Ultrasound Indices to Evaluate Volume Status and Fluid Responsiveness in Septic Shock Patients Thesis Submitted for partial fulfillment of MD degree in Anesthesiology, Surgical Intensive
Cardiovascular Images
 Cardiovascular Images Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosed From Right Heart Changes Seen After Exercise Stress Echocardiography Brian C. Case, MD; Micheas Zemedkun, MD; Amarin Sangkharat, MD; Allen J. Taylor,
Cardiovascular Images Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosed From Right Heart Changes Seen After Exercise Stress Echocardiography Brian C. Case, MD; Micheas Zemedkun, MD; Amarin Sangkharat, MD; Allen J. Taylor,
Lung Ultrasound in COPD and Bronchial Asthma-Measurements. of Lung Deformation with our Novel. Imaging Approach.
 Editorial imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Insights in Allergy, Asthma & Bronchitis DOI: 10.21767/2471-304X.100006 Abstract Lung Ultrasound in COPD and Bronchial Asthma-Measurements of Lung Deformation
Editorial imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Insights in Allergy, Asthma & Bronchitis DOI: 10.21767/2471-304X.100006 Abstract Lung Ultrasound in COPD and Bronchial Asthma-Measurements of Lung Deformation
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1
 Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 PERICARDIAL DISEASE The pericardial effusion ends anteriorly to the descending aorta and is best visualised in the PLAX. PSAX is actually very useful sometimes for looking at posterior
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 PERICARDIAL DISEASE The pericardial effusion ends anteriorly to the descending aorta and is best visualised in the PLAX. PSAX is actually very useful sometimes for looking at posterior
ARIC HEART FAILURE HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM. General Instructions: ID NUMBER: FORM NAME: H F A DATE: 10/13/2017 VERSION: CONTACT YEAR NUMBER:
 ARIC HEART FAILURE HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM General Instructions: The Heart Failure Hospital Record Abstraction Form is completed for all heart failure-eligible cohort hospitalizations. Refer to
ARIC HEART FAILURE HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM General Instructions: The Heart Failure Hospital Record Abstraction Form is completed for all heart failure-eligible cohort hospitalizations. Refer to
Krediet slide di 18
 1 di 18 Assessment of fluid status in PD patients Raymond T. Krediet, Amsterdam, Netherlands Chairs:Walther H. Boer, Utrecht, The Netherlands F. Fevzi Ersoy, Antalya, Turkey Prof. Raymond T. Krediet DDivision
1 di 18 Assessment of fluid status in PD patients Raymond T. Krediet, Amsterdam, Netherlands Chairs:Walther H. Boer, Utrecht, The Netherlands F. Fevzi Ersoy, Antalya, Turkey Prof. Raymond T. Krediet DDivision
Echocardiography Volume assessment. Justin Mandeville 2014
 Echocardiography Volume assessment Justin Mandeville 2014 Volume assessment and the intensivist Hypovolaemic shock Fluid tolerance Optimising cardiac output Avoiding overloading Guided fluid removal Add
Echocardiography Volume assessment Justin Mandeville 2014 Volume assessment and the intensivist Hypovolaemic shock Fluid tolerance Optimising cardiac output Avoiding overloading Guided fluid removal Add
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Role of Ultrasound in Evaluation of Undifferentiated Shock in ICU Settings
 Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 66 August 2018 13 Role of Ultrasound in Evaluation of Undifferentiated Shock in ICU Settings Tanvi Vaidya 1*, Pradeep D costa 2, Satish Pande 3 ORIGINAL
Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 66 August 2018 13 Role of Ultrasound in Evaluation of Undifferentiated Shock in ICU Settings Tanvi Vaidya 1*, Pradeep D costa 2, Satish Pande 3 ORIGINAL
County of Santa Clara Emergency Medical Services System
 County of Santa Clara Emergency Medical Services System Policy #700-M12: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE Effective: February 8, 2013TBD Replaces: NewFebruary 8,
County of Santa Clara Emergency Medical Services System Policy #700-M12: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE Effective: February 8, 2013TBD Replaces: NewFebruary 8,
Heart Failure. Subjective SOB (shortness of breath) Peripheral edema. Orthopnea (2-3 pillows) PND (paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea)
 Pharmacology I. Definitions A. Heart Failure (HF) Heart Failure Ezra Levy, Pharm.D. HF Results when one or both ventricles are unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the body s needs There are 2 types
Pharmacology I. Definitions A. Heart Failure (HF) Heart Failure Ezra Levy, Pharm.D. HF Results when one or both ventricles are unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the body s needs There are 2 types
February 25, WHI Heart Failure Data Summary. A. Original WHI outcome (referred to as CHF)
 February 25, 2014 WHI Heart Failure Data Summary A. Original WHI outcome (referred to as CHF) Process: Sample: Collected and centrally adjudicated for HT participants and locally adjudicated on all non-ht
February 25, 2014 WHI Heart Failure Data Summary A. Original WHI outcome (referred to as CHF) Process: Sample: Collected and centrally adjudicated for HT participants and locally adjudicated on all non-ht
Type of intervention Diagnosis. Economic study type Cost-effectiveness analysis.
 The use of B-type natriuretic peptide in the management of patients with diabetes and acute dyspnoea Mueller C, Laule-Kilian K, Christ A, Perruchoud A P Record Status This is a critical abstract of an
The use of B-type natriuretic peptide in the management of patients with diabetes and acute dyspnoea Mueller C, Laule-Kilian K, Christ A, Perruchoud A P Record Status This is a critical abstract of an
Bedside Ultrasound. US Guided Fluid Resuscitation. Michiel J. van Veelen, Emergency Physician, DTM&H
 Bedside Ultrasound US Guided Fluid Resuscitation Michiel J. van Veelen, Emergency Physician, DTM&H Outline Shock and Fluid Resuscitation in ICU Ultrasound in Shock Ultrasound Guided Fluid Resuscitation
Bedside Ultrasound US Guided Fluid Resuscitation Michiel J. van Veelen, Emergency Physician, DTM&H Outline Shock and Fluid Resuscitation in ICU Ultrasound in Shock Ultrasound Guided Fluid Resuscitation
Dr Dinna Soon. Consultant Cardiologist, Department of Cardiology. GP symposium 2 April 2016
 Dr Dinna Soon Consultant Cardiologist, Department of Cardiology GP symposium 2 April 2016 Case presentation 76 years old male, chronic smoker, hypertension, previous MI 3/7 SOB and chest tightness BP
Dr Dinna Soon Consultant Cardiologist, Department of Cardiology GP symposium 2 April 2016 Case presentation 76 years old male, chronic smoker, hypertension, previous MI 3/7 SOB and chest tightness BP
Evaluating dyspnea: A practical approach -- When to consider cardiopulmonary exercise testing.
 Evaluating dyspnea: A practical approach -- When to consider cardiopulmonary exercise testing. ABSTRACT: Shortness of breath is a common complaint associated with a number of conditions. Although the results
Evaluating dyspnea: A practical approach -- When to consider cardiopulmonary exercise testing. ABSTRACT: Shortness of breath is a common complaint associated with a number of conditions. Although the results
Navigating the identification, diagnosis and management of pulmonary hypertension using the updated ESC/ERS guidelines
 Navigating the identification, diagnosis and management of pulmonary hypertension using the updated ESC/ERS guidelines Host: Marc Humbert Speaker: Simon Gibbs Marc HUMBERT, MD, PhD Professor of Respiratory
Navigating the identification, diagnosis and management of pulmonary hypertension using the updated ESC/ERS guidelines Host: Marc Humbert Speaker: Simon Gibbs Marc HUMBERT, MD, PhD Professor of Respiratory
63-year old female with dyspnea
 Indiana University Pulmonary and Critical Care Fellowship Fellows Case Archive Case #1 63-year old female with dyspnea Gabriel Bosslet, MD; Chadi Hage MD A 63-year-old female presented to pulmonary clinic
Indiana University Pulmonary and Critical Care Fellowship Fellows Case Archive Case #1 63-year old female with dyspnea Gabriel Bosslet, MD; Chadi Hage MD A 63-year-old female presented to pulmonary clinic
The ACC 50 th Annual Scientific Session
 Special Report The ACC 50 th Annual Scientific Session Part One From March 18 to 21, 2001, physicians from around the world gathered to learn, to teach and to discuss at the American College of Cardiology
Special Report The ACC 50 th Annual Scientific Session Part One From March 18 to 21, 2001, physicians from around the world gathered to learn, to teach and to discuss at the American College of Cardiology
Intensivist Use of Hand-Carried Ultrasonography to Measure IVC Collapsibility in Estimating Intravascular Volume Status: Correlations with CVP
 Intensivist Use of Hand-Carried Ultrasonography to Measure IVC Collapsibility in Estimating Intravascular Volume Status: Correlations with CVP S Peter Stawicki, MD, Benjamin M Braslow, MD, FACS, Nova L
Intensivist Use of Hand-Carried Ultrasonography to Measure IVC Collapsibility in Estimating Intravascular Volume Status: Correlations with CVP S Peter Stawicki, MD, Benjamin M Braslow, MD, FACS, Nova L
QUESTION-BY-QUESTION INSTRUCTIONS FOR MMCC HEART FAILURE FINAL DIAGNOSIS FORM (HDX)
 QUESTION-BY-QUESTION INSTRUCTIONS FOR MMCC HEART FAILURE FINAL DIAGNOSIS FORM (HDX) HDX, Version A, 09-10-2009 HDX QxQ An MMCC Heart Failure Diagnosis Form (HDX) is completed for each ARIC Heart Failure
QUESTION-BY-QUESTION INSTRUCTIONS FOR MMCC HEART FAILURE FINAL DIAGNOSIS FORM (HDX) HDX, Version A, 09-10-2009 HDX QxQ An MMCC Heart Failure Diagnosis Form (HDX) is completed for each ARIC Heart Failure
Introduction. Summary. Karim Gariani a, Alain Delabays b, Thomas V. Perneger c, Thomas Agoritsas a,c
 Published 9 November 2011, doi:10.4414/smw.2011.13298 Cite this as: Use of brain natriuretic peptide to detect previously unknown left ventricular dysfunction in patients with acute exacerbation of chronic
Published 9 November 2011, doi:10.4414/smw.2011.13298 Cite this as: Use of brain natriuretic peptide to detect previously unknown left ventricular dysfunction in patients with acute exacerbation of chronic
THE PERICARDIUM: LOOKING OUTSIDE THE HEART
 THE PERICARDIUM: LOOKING OUTSIDE THE HEART DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate
THE PERICARDIUM: LOOKING OUTSIDE THE HEART DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate
The NEW Heart Failure Guidelines
 The NEW Heart Failure Guidelines Daily Practice HF scenario of the Case Presentations HF as a complex and heterogeneous syndrome Several proposed pathophysiological mechanisms involving the heart and the
The NEW Heart Failure Guidelines Daily Practice HF scenario of the Case Presentations HF as a complex and heterogeneous syndrome Several proposed pathophysiological mechanisms involving the heart and the
A Study Conducted At A Tertiary Care Teaching Institute in Chennai, on The Clinical And Etiological Profile Of Patients With Acute Heart Failure.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 12 Ver. VIII (Dec. 2017), PP 27-33 www.iosrjournals.org A Study Conducted At A Tertiary Care
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 12 Ver. VIII (Dec. 2017), PP 27-33 www.iosrjournals.org A Study Conducted At A Tertiary Care
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy.
 HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
Objectives. Hepatobiliary Ultrasound: Anatomy, Technique, Pathology. RUQ: Normal Anatomy. Emergency Ultrasound: Gallbladder Location
 Hepatobiliary Ultrasound: Anatomy, Technique, Pathology Laleh Gharahbaghian, MD FAAEM Associate Director, EM Ultrasound Co-Director, EM Ultrasound Fellowship Stanford University Medical Center Seric Cusick,
Hepatobiliary Ultrasound: Anatomy, Technique, Pathology Laleh Gharahbaghian, MD FAAEM Associate Director, EM Ultrasound Co-Director, EM Ultrasound Fellowship Stanford University Medical Center Seric Cusick,
My Patient Needs a Stress Test
 My Patient Needs a Stress Test Amy S. Burhanna,, MD, FACC Coastal Cardiology Cape May Court House, New Jersey Absolute and relative contraindications to exercise testing Absolute Acute myocardial infarction
My Patient Needs a Stress Test Amy S. Burhanna,, MD, FACC Coastal Cardiology Cape May Court House, New Jersey Absolute and relative contraindications to exercise testing Absolute Acute myocardial infarction
B-Type Natriuretic Peptide Predicts Future Cardiac Events in Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department With Dyspnea
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION B-Type Natriuretic Peptide Predicts Future Cardiac Events in Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department With Dyspnea From the Division of Cardiology and General Internal Medicine
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION B-Type Natriuretic Peptide Predicts Future Cardiac Events in Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department With Dyspnea From the Division of Cardiology and General Internal Medicine
Pulmonary Embolism. Thoracic radiologist Helena Lauri
 Pulmonary Embolism Thoracic radiologist Helena Lauri 8.5.2017 Statistics 1-2 out of 1000 adults annually are diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and/or pulmonary embolism (PE) About half of patients
Pulmonary Embolism Thoracic radiologist Helena Lauri 8.5.2017 Statistics 1-2 out of 1000 adults annually are diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and/or pulmonary embolism (PE) About half of patients
ΒΙΟΔΕΙΚΤΕΣ ΣΤΗΝ ΚΑΡΔΙΑΚΗ ΑΝΕΠΑΡΚΕΙΑ. ΔΗΜΗΤΡΙΟΣ ΤΟΥΣΟΥΛΗΣ Καθηγητής Καρδιολογίας
 ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΚΑΙ ΚΑΠΟΔΙΣΤΡΙΑΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΑΘΗΝΩΝ ΙΑΤΡΙΚΗ ΣΧΟΛΗ Ά ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΙΚΗ ΚΛΙΝΙΚΗ Διευθυντής: Καθηγητής Δημήτριος Τούσουλης ΒΙΟΔΕΙΚΤΕΣ ΣΤΗΝ ΚΑΡΔΙΑΚΗ ΑΝΕΠΑΡΚΕΙΑ ΔΗΜΗΤΡΙΟΣ ΤΟΥΣΟΥΛΗΣ Καθηγητής Καρδιολογίας
ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΚΑΙ ΚΑΠΟΔΙΣΤΡΙΑΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΑΘΗΝΩΝ ΙΑΤΡΙΚΗ ΣΧΟΛΗ Ά ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΙΚΗ ΚΛΙΝΙΚΗ Διευθυντής: Καθηγητής Δημήτριος Τούσουλης ΒΙΟΔΕΙΚΤΕΣ ΣΤΗΝ ΚΑΡΔΙΑΚΗ ΑΝΕΠΑΡΚΕΙΑ ΔΗΜΗΤΡΙΟΣ ΤΟΥΣΟΥΛΗΣ Καθηγητής Καρδιολογίας
Catheter-based mitral valve repair MitraClip System
 Percutaneous Mitral Valve Repair: Results of the EVEREST II Trial William A. Gray MD Director of Endovascular Services Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine Columbia University Medical Center The Cardiovascular
Percutaneous Mitral Valve Repair: Results of the EVEREST II Trial William A. Gray MD Director of Endovascular Services Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine Columbia University Medical Center The Cardiovascular
HEART AND SOUL STUDY OUTCOME EVENT - MORBIDITY REVIEW FORM
 REVIEW DATE REVIEWER'S ID HEART AND SOUL STUDY OUTCOME EVENT - MORBIDITY REVIEW FORM : DISCHARGE DATE: RECORDS FROM: Hospitalization ER Please check all that may apply: Myocardial Infarction Pages 2, 3,
REVIEW DATE REVIEWER'S ID HEART AND SOUL STUDY OUTCOME EVENT - MORBIDITY REVIEW FORM : DISCHARGE DATE: RECORDS FROM: Hospitalization ER Please check all that may apply: Myocardial Infarction Pages 2, 3,
Mitral Regurgitation
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Mitral Regurgitation Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes mitral regurgitation, a disease of the mitral valve. It explains how this disease is
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Mitral Regurgitation Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes mitral regurgitation, a disease of the mitral valve. It explains how this disease is
