Warning: Avoid putting the tip of the syringe needle too deeply into the hole to avoid damage to the heart tissue.
|
|
|
- Johnathan Sullivan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Experiment AM-12: Crayfish Electrocardiogram (ECG) Exercise 1: The Crayfish ECG and Heart Rate Aim: To record the electrical trace (ECG) produced by the contraction of a resting heart, and to determine the resting heart rate. Procedure 1. Type Resting in the Mark box to the right of the Mark button. 2. Click the Record button and press the Enter key on the keyboard to attach the comment to the record. Click AutoScale to increase the size of the deflection on the Main window. 3. Record the resting ECG and heart rate for thirty seconds. 4. Click Stop to halt the recording. 5. Select Save As in the File menu, type a name for the file. Choose a destination on the computer in which to save the file, like your lab group folder). Click on the Save button to save the data file. Note: If the recording is noisy, or if it seems to be shorted out altogether, try removing the green ground and recording with just the two other electrodes. Exercise 2: Effects of Cold Temperature on the ECG and Heart Rate Aim: To record changes in the ECG and heart rate after the heart is bathed in cold Ringer s solution. Procedure 1. Type Room Temp Ringer s in the Mark box to the right of the Mark button. 2. Click the Record button. Click AutoScale to increase the size of the deflection on the Main window. 3. Record the ECG and heart rate for thirty seconds. 4. Use the syringe to inject about 0.3 ml of room temperature saline into the hole in the carapace between the red and black electrodes. Warning: Avoid putting the tip of the syringe needle too deeply into the hole to avoid damage to the heart tissue. 5. Place the beaker with chilled Ringer's solution near the preparation. 6. Type Cold Ringer's in the Mark box. AM-12-1
2 7. Twenty seconds after the addition of room temperature Ringer s to the heart, apply 0.3 ml of the cold Ringer s solution through the hole in the carapace. Repeat two more times, leaving 10 seconds between applications. 8. Press the Enter key on the keyboard after the third application of cold Ringer s solution. 9. Record until the heart has recovered from the effects of cold Ringer s solution. Note: Recovery is when the ECG amplitudes and rate of the heart contraction have returned to the resting values. 10. Click Stop to halt the recording. 11. Select Save in the File menu. 12. Use the syringe to inject about 0.3 ml of room temperature saline onto the heart. Exercise 3: Effects of Warm Temperature on the ECG and Heart Rate Aim: To record changes in the ECG and heart rate after the heart is bathed in warm Ringer s solution. Procedure 1. Type Room Temp Ringer s in the Mark box to the right of the Mark button. 2. Click the Record button. Click AutoScale to increase the size of the deflection on the Main window. 3. Record the ECG and heart rate for thirty seconds. 4. Apply 0.3 ml of Ringer's solution (at room temperature) to the heart. Press the Enter key on the keyboard when the Ringer s solution is injected onto the heart. 5. Place the beaker with warm Ringer's solution near the preparation. 6. Type Warm Ringer's in the Mark box. 7. Twenty seconds after the addition of room temperature Ringer s to the heart, apply 0.3 ml of warm Ringer's solution to the heart. Repeat two more times. leaving 10 seconds between applications. 8. Press the Enter key on the keyboard after the third application of warm Ringer s solution. 9. Record until the heart has recovered from the effects of warm Ringer s solution. Note: Recovery is when the ECG amplitudes and rate of the heart contraction have returned to the resting values. 10. Click Stop to halt the recording. 11. Select Save in the File menu. 12. Use the syringe to inject about 0.3 ml of room temperature saline onto the heart. AM-12-2
3 Exercise 4: Effects of Drugs on the Crayfish Heart Aim: To monitor the effects of serotonin and GABA on the ECG amplitudes and rate of heart contraction. Procedure - Serotonin 1. Type Resting in the Mark box to the right of the Mark button. 2. Click the Record button. Press the Enter key on the keyboard to mark the recording. Click AutoScale to increase the size of the deflection on the Main window. 3. Record the ECG and heart rate for thirty seconds. 4. Type 0.01 mm Serotonin in the Mark box to the right of the Mark button. 5. Apply 0.3 ml of 0.01 mm serotonin solution (at room temperature) to the heart. Repeat two more times. leaving 10 seconds between applications. 6. Press the Enter key on the keyboard after the third application of 0.01 mm Serotonin. 7. If you didn t see a clear response, repeat steps 4-6 with 0.1 mm serotonin. 8. After recording the effects of serotonin for sixty seconds, inject 0.3 ml of room temperature Ringer s solution onto the heart at 10 second intervals until the ECG and heart rate return to the resting state. 9. Click Stop to halt the recording. 10. Select Save in the File menu. 11. Inject 0.3 ml of room temperature Ringer s solution onto the heart. Procedure - GABA 1. Type 0.01 mm GABA in the Mark box to the right of the Mark button. 2. Click the Record button. Click AutoScale to increase the size of the deflection on the Main window. 3. Record the ECG and heart rate for thirty seconds. 4. Apply 0.3 ml of 0.01 mm GABA solution (at room temperature) to the heart. Repeat two more times. leaving 10 seconds between applications. 5. Press the Enter key on the keyboard after the third GABA application. Continue recording. Warning: If the heart goes into cardiac arrest, rinse the GABA solution off the heart with fresh, room temperature Ringer s solution. If the heart is still in cardiac arrest after 10 seconds, add 0.3 ml of 0.01 mm Serotonin solution to the heart. 6. If you don t see a clear response to the 0.01 mm GABA, repeat steps 1-5 with 0.1 mm GABA. 7. After recording the effects of GABA for sixty seconds, rinse the heart with room temperature Ringer s solution until the ECG and heart rate return to the resting rate. AM-12-3
4 8. Click Stop to halt the recording. 9. Select Save in the File menu. 10. Apply 0.3 ml of room temperature saline to the heart. Data Analysis Exercise 1: Resting Heart Rate 1. Scroll to the resting heart rate data. Click the AutoScale button to maximize the size of the ECG and heart rate channels on the window (Figure AM-12-L1). Figure AM-12-L1: Crayfish ECG and heart rate displayed on the Main Window. 2. Use the Display Time icons to adjust the Display Time of the Main window to show five complete cardiac cycles on the Main window. The cycles can be selected by: Placing a cursor before the first deflection, and a cursor before the sixth deflection; and Clicking the Zoom between Cursors button on the LabScribe toolbar to expand the five selected cardiac cycles to the width of the Main window. 3. Click on the Analysis window icon in the toolbar (Figure AM-12-L2) or select Analysis from the Windows menu to transfer the data displayed in the Main window to the Analysis window. 4. Look at the Function Table that is above the uppermost channel displayed in the Analysis window. The mathematical functions, V2-V1 and Mean should appear in this table. The values for V2-V1 and Mean for each channel are seen in the table across the channel s top margin. AM-12-4
5 Figure AM-12-L2: The LabScribe toolbar. 5. The value for Mean on the Heart Rate (Crayfish ECG) channel is the mean heart rate for the five cycle period. Note: Because the depolarization waves are of fluctuating height and direction, it may be necessary to invert the trace or reconfigure the Periodic setup in order to detect all the heart beats. To invert the trace, select Invert from the Crayfish ECG channel menu. To adjust the Periodic setup, click on P. Rate (Crayfish ECG) in the Heart Rate channel bar and choose Setup Function. Adjust the Threshold and Tolerance lines so that they pass through the Depolarization wave of each cycle. Exercise 2: Effect of Cold Temperature 1. Scroll to the data recorded from the heart fifteen seconds before cold Ringer s solution was added to the heart. Click the AutoScale button to maximize the size of the ECG and heart rate channels on the window. 2. Use the Display Time icons to adjust the Display Time of the Main window to show five complete cardiac cycles on the Main window. 3. Transfer the data displayed in the Main window to the Analysis window. 4. Values for V2-V1 and Mean are seen in the Function Table across the top margin of each channel. 5. Once the cursors are placed in the correct positions for determining the heart rate and the amplitude of each cardiac parameter, the values of the parameters in the Function Table can be recorded in the on-line notebook of LabScribe by typing their names and values directly into the Journal, or on a separate data table. 6. The functions in the channel pull-down menus of the Analysis window can also be used to enter the names and values of the parameters from the recording to the Journal. To use these functions: Place the cursors at the locations used to measure the heart rate and the amplitude of each cardiac parameter. Transfer the names of the mathematical functions used to determine the amplitude and AM-12-5
6 times to the Journal using the Add Title to Journal function in the Crayfish ECG Channel pull-down menu. Transfer the amplitude values to the Journal using the Add Ch. Data to Journal function in the Crayfish ECG Channel pull-down menu. Transfer the average rate over the selected cycles to the Journal using the Add Ch. Data to Journal function in the Heart Rate (Crayfish ECG) Channel pull-down menu. 7. On the Crayfish ECG Channel, use the mouse to click on and drag the cursors to specific points on the recording to measure the following parameters: The Depolarization wave amplitude. To measure the amplitude of the Depolarization wave, place one cursor on the positive peak and the second cursor on the negative peak of the Depolarization wave, as illustrated in Figure AM-12-L3. The value for V2-V1 on the Crayfish ECG channel is this amplitude. Measure the amplitudes of four additional depolarization waves. The Repolarization wave amplitude, To measure the amplitude of the Repolarization wave, place one cursor on the baseline before the Repolarization wave and the second cursor on the peak of the Repolarization wave. The value for V2-V1 on the Crayfish ECG channel is this amplitude. Measure the amplitudes of four additional Repolarization waves. Mean Heart Rate, is the average heart rate calculated from the Crayfish ECG Channel. To measure this parameter, place one cursor at the beginning of the first of five cardiac cycles selected and the second cursors at the end of the cycles selected. The value for Mean on the Heart Rate (Crayfish ECG) channel is this mean heart rate for that five cycle period. Figure AM-12-L3: Crayfish ECG and heart rate displayed in the Analysis window. The cursors are placed to measure the amplitude of the depolarization wave. AM-12-6
7 8. Record the values in the Journal using the one of the techniques described in Steps 6 or 7, and on Table AM-12-L1. 9. Scroll to the section of data recorded when cold Ringer s solution was added to the heart. Click AutoScale to maximize the size of the response on the window. 10. Repeat these steps to measure and record the various amplitudes and heart rate at the time the cold Ringer s solution was added to the heart and at 10 second intervals for the first minute after the addition of the cold Ringer s. 11. Measure and record the ECG amplitudes and the heart rate at the end of the recovery period from the effects of cold Ringer s. 12. Select Save in the File menu. Exercise 3: Effect of Warm Temperature 1. Scroll to the data recorded from the heart fifteen seconds before warm Ringer s solution was added to the heart. Click the AutoScale button to maximize the size of the ECG and heart rate channels on the window. 2. Use the same techniques used in Exercise 2 to measure the ECG amplitudes and heart rates during the rest, treatment, and recovery periods when warm Ringer s was applied to the heart. 3. Record your data in Table AM-12-L1. Exercise 4: Drug Effects 1. Scroll to the beginning of the data from Exercise 4 and find the normal heart contractions that occurred before the first drug treatment. 2. Use the same techniques used in Exercise 2 to measure the ECG amplitudes and heart rates during the rest, treatment, and recovery periods for the two drugs applied to the heart. 3. Record the values for the amplitudes and heart rates from this exercise in the Journal and on Table AM-12-L2 for Serotonin and Table AM-12-L3 for GABA AM-12-7
8 Table AM-12-L1: Amplitudes and Rate of Heart Contractions at Different Temperatures. Treatment Room Temp Ringer s Cold Ringer s 10 sec after Cold Ringer s 20 sec after Cold Ringer s 30 sec after Cold Ringer s 40 sec after Cold Ringer s 50 sec after Cold Ringer s 60 sec after Cold Ringer s Recovered from Cold Room Temp Ringer s Warm Ringer s 10sec after Warm Ringer s 20sec after Warm Ringer s 30sec after Warm Ringer s 40sec after Warm Ringer s 50sec after Warm Ringer s 60sec after Warm Ringer s Recovered from Heat Crayfish ECG Depolarization Wave (V) Repolarization Wave (V) Mean Heart Rate (BPM) AM-12-8
9 Table AM-12-L2: Amplitudes and Rate of Heart Contraction with Serotonin Treatment. Frog ECG Treatment Depolarization Wave (V) Repolarization Wave (V) Resting Serotonin 10 sec after Serotonin 20 sec after Serotonin 30 sec after Serotonin 40 sec after Serotonin 50 sec after Serotonin 60 sec after Serotonin Recovered Heart Rate (BPM) Table AM-12-L3: Amplitudes and Rate of Heart Contraction with GABA Treatment. Frog ECG Treatment Depolarization Wave (V) Repolarization Wave (V) Resting GABA 10 sec after GABA 20 sec after GABA 30 sec after GABA 40 sec after GABA 50 sec after GABA 60 sec after GABA Recovered Heart Rate (BPM) AM-12-9
10 Questions 1. What is the effect of cold Ringer's solution on heart rate and the amplitude of the ventricular depolarization? What mechanism is responsible for this effect? 2. How does warm Ringer s affect the heart? How do the wave amplitudes and heart rate differ from when cold Ringer s was applied to the heart? 3. What effect does Serotonin have on the heart rate and the amplitudes of the ECG waves? 4. How does Serotonin produce its effects on the heart rate and the amplitude of the ventricular contraction specifically? 5. What effect does GABA have on the heart rate and the amplitude of the ECG waves? 6. How does GABA produce its effects on the heart rate and the amplitude of the ventricular contraction specifically? 7. Do the time courses for the effect of each drug on the amplitude and the rate of ventricular contraction differ? Suggested Variations 1. Although Serotonin and GABA are more appropriate to crustaceans, what are the effects of the vertebrate cardiac transmitters, Epinephrine and Acetylcholine? 2. Use a force transducer to measure and record the heart rate and force of contraction under the same conditions using the methods in Experiment AM-7. AM-12-10
Exercise 2: Effects of Cold Temperature Aim: To record changes in heart rate after the heart is bathed in cold Ringer s solution.
 Experiment AM-3: Heart Muscle Warning: The heart preparation used in this experiment is functional for a limited period of time. If the muscle is bathed periodically in Ringer s solution, it will work
Experiment AM-3: Heart Muscle Warning: The heart preparation used in this experiment is functional for a limited period of time. If the muscle is bathed periodically in Ringer s solution, it will work
Experiment HH-2: The Electrocardiogram and Heart Sounds
 Experiment HH-2: The Electrocardiogram and Heart Sounds Exercise 1: The ECG in a Resting Subject Aim: To measure the ECG in a resting individual. Procedure 1. Click on the Record button, located on the
Experiment HH-2: The Electrocardiogram and Heart Sounds Exercise 1: The ECG in a Resting Subject Aim: To measure the ECG in a resting individual. Procedure 1. Click on the Record button, located on the
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HC-3: Pulse Wave Velocity
 Experiment HC-3: Pulse Wave Velocity Exercise 1: The Pulse Wave Velocity at Rest Aim: To measure the pulse wave velocity in a resting individual. Procedure 1. Click on the Record button, located on the
Experiment HC-3: Pulse Wave Velocity Exercise 1: The Pulse Wave Velocity at Rest Aim: To measure the pulse wave velocity in a resting individual. Procedure 1. Click on the Record button, located on the
Experiment HH-3: Exercise, the Electrocardiogram, and Peripheral Circulation
 Experiment HH-3: Exercise, the Electrocardiogram, and Peripheral Circulation Exercise 1: The ECG and the Pulse in a Resting Subject Aim: To measure and correlate the ECG and the pulse in a resting individual.
Experiment HH-3: Exercise, the Electrocardiogram, and Peripheral Circulation Exercise 1: The ECG and the Pulse in a Resting Subject Aim: To measure and correlate the ECG and the pulse in a resting individual.
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HH-4: The Six-Lead Electrocardiogram
 Experiment HH-4: The Six-Lead Electrocardiogram Exercise 1: Six Lead ECG from Resting Subject Aim: To record a Six Lead ECG from a resting subject and determine the QRS axis of the subject s heart. Procedure
Experiment HH-4: The Six-Lead Electrocardiogram Exercise 1: Six Lead ECG from Resting Subject Aim: To record a Six Lead ECG from a resting subject and determine the QRS axis of the subject s heart. Procedure
iworx Sample Lab Experiment AN-5: Cockroach Leg Mechanoreceptors
 Experiment AN-5: Cockroach Leg Mechanoreceptors Exercise 1: Chordotonal Organs Aim: To explore the basic characteristics of the chordotonal organs, their response to direction and intensity of leg movement,
Experiment AN-5: Cockroach Leg Mechanoreceptors Exercise 1: Chordotonal Organs Aim: To explore the basic characteristics of the chordotonal organs, their response to direction and intensity of leg movement,
Figure HN-5-L1: The Sequence menu containing the preprogramming light sequences used in this experiment.
 HN-5: Visual Reflexes and Color Stimulation Exercise 1: Reaction Time and Single Color Visual Cues Aim: To measure the reaction time of a subject to a visual cue. Procedure 1. Instruct the subject to:
HN-5: Visual Reflexes and Color Stimulation Exercise 1: Reaction Time and Single Color Visual Cues Aim: To measure the reaction time of a subject to a visual cue. Procedure 1. Instruct the subject to:
Exercise 1: Eye-Hand Reaction Times Aim: To measure the reaction time of a subject to a visual cue when responding with the hand.
 Experiment HN-4: Hand vs. Foot Reactions Exercise 1: Eye-Hand Reaction Times Aim: To measure the reaction time of a subject to a visual cue when responding with the hand. Procedure 1. Instruct the subject
Experiment HN-4: Hand vs. Foot Reactions Exercise 1: Eye-Hand Reaction Times Aim: To measure the reaction time of a subject to a visual cue when responding with the hand. Procedure 1. Instruct the subject
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HC-5: Body Position, Exercise, and Cardiac Output
 Experiment HC-5: Body Position, Exercise, and Cardiac Output Exercise 1: Cardiac Output While Reclining Aim: To determine the cardiac output of a subject through the measurement of blood pressures and
Experiment HC-5: Body Position, Exercise, and Cardiac Output Exercise 1: Cardiac Output While Reclining Aim: To determine the cardiac output of a subject through the measurement of blood pressures and
Experiment HH-3: Exercise, the Electrocardiogram, and Peripheral Circulation
 Experiment HH-3: Exercise, the Electrocardiogram, and Peripheral Circulation Background The arterial system functions as a pressure reservoir. Blood enters via the heart and exits through the capillaries.
Experiment HH-3: Exercise, the Electrocardiogram, and Peripheral Circulation Background The arterial system functions as a pressure reservoir. Blood enters via the heart and exits through the capillaries.
iworx Sample Lab Experiment AN-1: Membrane Potentials
 Experiment AN-1: Membrane Potentials Exercise 1: Impaling Muscle Fibers Aim: To measure the membrane potentials in different muscle fibers. Procedure 1. Look through the microscope; you should see the
Experiment AN-1: Membrane Potentials Exercise 1: Impaling Muscle Fibers Aim: To measure the membrane potentials in different muscle fibers. Procedure 1. Look through the microscope; you should see the
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HH-4: The Six-Lead Electrocardiogram
 Experiment HH-4: The Six-Lead Electrocardiogram Background The cardiac cycle involves a sequential contraction of the atria and the ventricles. These contractions are triggered by the coordinated electrical
Experiment HH-4: The Six-Lead Electrocardiogram Background The cardiac cycle involves a sequential contraction of the atria and the ventricles. These contractions are triggered by the coordinated electrical
Lab 5: Electromyograms (EMGs)
 Lab 5: Electromyograms (EMGs) Overview A motorneuron and all the muscle fibers that it innervates is known as a motor unit. Under normal circumstances, a neuronal action potential activates all of the
Lab 5: Electromyograms (EMGs) Overview A motorneuron and all the muscle fibers that it innervates is known as a motor unit. Under normal circumstances, a neuronal action potential activates all of the
Experiment HC-1: Blood Pressure, Peripheral Circulation, and Body Position
 Experiment HC-1: Blood Pressure, Peripheral Circulation, and Body Position Exercise 1: Blood Pressures from the Left Arm Aim: To determine the systolic and diastolic blood pressures in a reclining subject,
Experiment HC-1: Blood Pressure, Peripheral Circulation, and Body Position Exercise 1: Blood Pressures from the Left Arm Aim: To determine the systolic and diastolic blood pressures in a reclining subject,
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HP-6: Cynicism/Hostility and the Hot Reactor
 Experiment HP-6: Cynicism/Hostility and the Hot Reactor Exercise 1: Baseline Heart Rate and Blood Pressure Aim: To determine the resting heart rate and blood pressure of the subject. Procedure 1. Select
Experiment HP-6: Cynicism/Hostility and the Hot Reactor Exercise 1: Baseline Heart Rate and Blood Pressure Aim: To determine the resting heart rate and blood pressure of the subject. Procedure 1. Select
Experiment HM-11: Electromyograms (EMG) for Paired Arm Wrestling
 Experiment HM-11: Electromyograms (EMG) for Paired Arm Wrestling Background The movement of parts of the body is accomplished through a system of levers composed of skeletal muscles and bones. In a lever,
Experiment HM-11: Electromyograms (EMG) for Paired Arm Wrestling Background The movement of parts of the body is accomplished through a system of levers composed of skeletal muscles and bones. In a lever,
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HP-7: Hypothesis-driven Biofeedback Lab/Research Study
 Experiment HP-7: Hypothesis-driven Biofeedback Lab/Research Study What is Biofeedback? Biofeedback is a technique that people can use to learn to control their body's physiological functions. The definition
Experiment HP-7: Hypothesis-driven Biofeedback Lab/Research Study What is Biofeedback? Biofeedback is a technique that people can use to learn to control their body's physiological functions. The definition
Experiment HM-7: Electromyogram (EMG) Activity in Antagonistic Muscles and Range of Motion
 Experiment HM-7: Electromyogram (EMG) Activity in Antagonistic Muscles and Range of Motion Exercise 1: Antagonistic Muscles in Forearm Aim: To study the EMG activity in muscles that work in opposition
Experiment HM-7: Electromyogram (EMG) Activity in Antagonistic Muscles and Range of Motion Exercise 1: Antagonistic Muscles in Forearm Aim: To study the EMG activity in muscles that work in opposition
1724 Lab: Frog Skeletal Muscle Physiology (Marieb Exercise 16A) Marieb/iWorx / Ziser, 2002
 1724 Lab: Frog Skeletal Muscle Physiology (Marieb Exercise 16A) Marieb/iWorx / Ziser, 2002 I. Introduction. Read the introductory material in your lab manual Marieb Ex 16A: Skeletal Muscle Physiology Frog
1724 Lab: Frog Skeletal Muscle Physiology (Marieb Exercise 16A) Marieb/iWorx / Ziser, 2002 I. Introduction. Read the introductory material in your lab manual Marieb Ex 16A: Skeletal Muscle Physiology Frog
Experiment HP-13: The Gaze Cue Paradigm
 Experiment HP-13: The Gaze Cue Paradigm Background During almost all social interactions, people s eyes convey information about their direction of attention as well as their emotional and mental status.
Experiment HP-13: The Gaze Cue Paradigm Background During almost all social interactions, people s eyes convey information about their direction of attention as well as their emotional and mental status.
Biopac Student Lab Lesson 6 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) II Analysis Procedure. Rev
 42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 6 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) II Analysis Procedure Rev. 12292017 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University
42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 6 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) II Analysis Procedure Rev. 12292017 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University
Metabolic and Thermal Response to Exercise
 iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HE-1 Metabolic and Thermal Response to Exercise Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should refer to the User Area
iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HE-1 Metabolic and Thermal Response to Exercise Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should refer to the User Area
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG)
 Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Lab 7. Physiology of Electrocardiography
 7.1 Lab 7. Physiology of Electrocardiography The heart is a muscular pump that circulates blood throughout the body. To efficiently pump the blood, cardiac contractions must be coordinated and are regulated
7.1 Lab 7. Physiology of Electrocardiography The heart is a muscular pump that circulates blood throughout the body. To efficiently pump the blood, cardiac contractions must be coordinated and are regulated
Biology 13A Lab #10: Cardiovascular System II ECG & Heart Disease
 Biology 13A Lab #10: Cardiovascular System II ECG & Heart Disease Lab #10 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes...... 83 Introduction....... 84 Activity 1: Collecting ECG Data..... 85 Activity
Biology 13A Lab #10: Cardiovascular System II ECG & Heart Disease Lab #10 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes...... 83 Introduction....... 84 Activity 1: Collecting ECG Data..... 85 Activity
LABORATORY INVESTIGATION
 LABORATORY INVESTIGATION Recording Electrocardiograms The taking of an electrocardiogram is an almost universal part of any complete physical examination. From the ECG record of the electrical activity
LABORATORY INVESTIGATION Recording Electrocardiograms The taking of an electrocardiogram is an almost universal part of any complete physical examination. From the ECG record of the electrical activity
FT-302 Force Transducer
 Technical Note FT-302 LabScribe is a trademark of 2015 Overview The FT-302 is a high-sensitivity dual-range research grade force transducer designed to measure forces in the 0.005 to 10 gram and 0 to 100
Technical Note FT-302 LabScribe is a trademark of 2015 Overview The FT-302 is a high-sensitivity dual-range research grade force transducer designed to measure forces in the 0.005 to 10 gram and 0 to 100
Biopac Student Lab Lesson 8 RESPIRATORY CYCLE I Analysis Procedure. Rev
 42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 8 RESPIRATORY CYCLE I Analysis Procedure Rev. 12292017 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University
42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 8 RESPIRATORY CYCLE I Analysis Procedure Rev. 12292017 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG)
 Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Cardiovascular Effects of Exercise. Background Cardiac function
 Cardiovascular Effects of Exercise In this experiment, you will record an electrocardiogram, or ECG, and finger pulse from a healthy volunteer. You will then compare the ECG and pulse recordings when the
Cardiovascular Effects of Exercise In this experiment, you will record an electrocardiogram, or ECG, and finger pulse from a healthy volunteer. You will then compare the ECG and pulse recordings when the
Cardiovascular Physiology
 Cardiovascular Physiology The mammalian heart is a pump that pushes blood around the body and is made of four chambers: right and left atria and right and left ventricles. The two atria act as collecting
Cardiovascular Physiology The mammalian heart is a pump that pushes blood around the body and is made of four chambers: right and left atria and right and left ventricles. The two atria act as collecting
Lesson 2 EMG 2 Electromyography: Mechanical Work
 Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Science Lab MP40 Lesson 2 EMG 2 Electromyography: Mechanical Work PC running Windows XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Lesson Revision 5.23.2006 BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 42
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Science Lab MP40 Lesson 2 EMG 2 Electromyography: Mechanical Work PC running Windows XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Lesson Revision 5.23.2006 BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 42
The Gaze Cueing Paradigm with Eye Tracking Background Set-up Lab
 iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HP-17 The Gaze Cueing Paradigm with Eye Tracking Background Set-up Lab Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should
iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HP-17 The Gaze Cueing Paradigm with Eye Tracking Background Set-up Lab Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should
BP-600 Noninvasive Blood Pressure Sensor
 Technical Note BP-600 Overview A person's cardiac output, peripheral vascular resistance, blood pressure, and other cardiovascular parameters change in response to the activities and events taking place
Technical Note BP-600 Overview A person's cardiac output, peripheral vascular resistance, blood pressure, and other cardiovascular parameters change in response to the activities and events taking place
Lesson 4 ECG 2 Electrocardiography
 Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Science Lab MP40 Lesson 4 ECG 2 Electrocardiography PC running Windows XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Lesson Revision 1.20.2006 BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 42 Aero Camino,
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Science Lab MP40 Lesson 4 ECG 2 Electrocardiography PC running Windows XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Lesson Revision 1.20.2006 BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 42 Aero Camino,
Red Light - Green Light
 iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HN-9 Red Light - Green Light Background Setup Lab Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should refer to the User
iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HN-9 Red Light - Green Light Background Setup Lab Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should refer to the User
Lab #4: Physiology of the in situ Amphibian Heart
 Lab #4: Physiology of the in situ Amphibian Heart This experiment explores the basic principles of cardiac muscle physiology, including contraction force, ECG, the effect of temperature, and the effect
Lab #4: Physiology of the in situ Amphibian Heart This experiment explores the basic principles of cardiac muscle physiology, including contraction force, ECG, the effect of temperature, and the effect
Each student should record the ECG of one of the members of the lab group and have their own ECG recorded.
 EXPERIMENT 1 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY The purpose of this experiment is to introduce you to the techniques of electrocardiography and the interpretation of electrocardiograms. In Part A of the experiment, you
EXPERIMENT 1 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY The purpose of this experiment is to introduce you to the techniques of electrocardiography and the interpretation of electrocardiograms. In Part A of the experiment, you
Biopac Student Lab Lesson 3 ELECTROENCEPHALOGRAPHY (EEG) I Analysis Procedure. Rev
 42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 3 ELECTROENCEPHALOGRAPHY (EEG) I Analysis Procedure Rev. 12112014 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana
42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 3 ELECTROENCEPHALOGRAPHY (EEG) I Analysis Procedure Rev. 12112014 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana
BIO 360: Vertebrate Physiology Performing and analyzing an EKG Lab 11: Performing and analyzing an EKG Lab report due April 17 th
 BIO 60: Vertebrate Physiology Lab : Lab report due April 7 th All muscles produce an electrical current when they contract. The heart is no exception. An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording
BIO 60: Vertebrate Physiology Lab : Lab report due April 7 th All muscles produce an electrical current when they contract. The heart is no exception. An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording
Interpreting Electrocardiograms (ECG) Physiology Name: Per:
 Interpreting Electrocardiograms (ECG) Physiology Name: Per: Introduction The heart has its own system in place to create nerve impulses and does not actually require the brain to make it beat. This electrical
Interpreting Electrocardiograms (ECG) Physiology Name: Per: Introduction The heart has its own system in place to create nerve impulses and does not actually require the brain to make it beat. This electrical
ECE ECE PRINCIPLES OF BIOMEDICAL SYSTEMS & DEVICES LAB 1 - ELECTROCARDIOGRAM
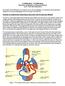 ECE0909.404.01 ECE 0909.504.03 PRINCIPLES OF BIOMEDICAL SYSTEMS & DEVICES LAB 1 - ELECTROCARDIOGRAM The purpose of this laboratory is to introduce you to electrocardiogram, its acquisition and interpretation.
ECE0909.404.01 ECE 0909.504.03 PRINCIPLES OF BIOMEDICAL SYSTEMS & DEVICES LAB 1 - ELECTROCARDIOGRAM The purpose of this laboratory is to introduce you to electrocardiogram, its acquisition and interpretation.
Kidney Dialysis and Conductivity Background Set-up Lab Appendix
 iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HK-2 Kidney Dialysis and Conductivity Background Set-up Lab Appendix Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should
iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HK-2 Kidney Dialysis and Conductivity Background Set-up Lab Appendix Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should
Cardiac muscle is different from other types of muscle in that cardiac muscle
 6 E X E R C I S E Cardiovascular Physiology O B J E C T I V E S 1. To define autorhythmicity, sinoatrial node, pacemaker cells, and vagus nerves 2. To understand the effects of the sympathetic and parasympathetic
6 E X E R C I S E Cardiovascular Physiology O B J E C T I V E S 1. To define autorhythmicity, sinoatrial node, pacemaker cells, and vagus nerves 2. To understand the effects of the sympathetic and parasympathetic
Biopac Student Lab Lesson 5 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) I Procedure. Rev
 42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 5 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) I Procedure Rev. 07112013 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University School
42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 5 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) I Procedure Rev. 07112013 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University School
Biology 325 Fall 2003 Human anatomy and physiology
 SKELETAL MUSCLE PROPERTIES Background : In this experiment, you will investigate the physiological properties of skeletal muscle from the isolated amphibian gastrocnemius. You will examine skeletal muscle
SKELETAL MUSCLE PROPERTIES Background : In this experiment, you will investigate the physiological properties of skeletal muscle from the isolated amphibian gastrocnemius. You will examine skeletal muscle
Effects of Temperature, Stretch, and Various Drug Treatments on the
 Nicole Rodi Bio 235: Animal Physiology Heart Muscle Lab Report 10/24/2014 Effects of Temperature, Stretch, and Various Drug Treatments on the Cardiac Muscle Activity of Rana pipiens Abstract Mechanical
Nicole Rodi Bio 235: Animal Physiology Heart Muscle Lab Report 10/24/2014 Effects of Temperature, Stretch, and Various Drug Treatments on the Cardiac Muscle Activity of Rana pipiens Abstract Mechanical
Lesson 2 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY II Motor unit recruitment Fatigue
 Physiology Lessons for use with the PC running Windows 98SE, Me, 2000 Pro, XP Pro/Home/Media Lesson 2 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY II Motor unit recruitment Fatigue Manual Revision PL3.7.0 M3.0.6 080706 Richard Pflanzer,
Physiology Lessons for use with the PC running Windows 98SE, Me, 2000 Pro, XP Pro/Home/Media Lesson 2 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY II Motor unit recruitment Fatigue Manual Revision PL3.7.0 M3.0.6 080706 Richard Pflanzer,
Investigation of human cardiovascular physiology is very interesting, but many
 6 E X E R C I S E Frog Cardiovascular Physiology O B J E C T I V E S 1. To list the properties of cardiac muscle as automaticity and rhythmicity, and to define each. 2. To explain the statement, Cardiac
6 E X E R C I S E Frog Cardiovascular Physiology O B J E C T I V E S 1. To list the properties of cardiac muscle as automaticity and rhythmicity, and to define each. 2. To explain the statement, Cardiac
Experiment HE-12: Targeted Exercise with Wireless Electrocardiogram (ECG)
 Experiment HE-12: Targeted Exercise with Wireless Electrocardiogram (ECG) Get Your Cardio On Preparations for this experiment need to be reviewed with the students in advance. There will be exercise routines
Experiment HE-12: Targeted Exercise with Wireless Electrocardiogram (ECG) Get Your Cardio On Preparations for this experiment need to be reviewed with the students in advance. There will be exercise routines
Exercise 6: Muscle Physiology II Twitch & Summation
 Exercise 6: Muscle Physiology II Twitch & Summation Text Reading: Silverthorn, 5 th ed. 412 419, 425 427; 6 th ed. pg. 410 420 In this exercise, we will investigate the physiology of contraction in the
Exercise 6: Muscle Physiology II Twitch & Summation Text Reading: Silverthorn, 5 th ed. 412 419, 425 427; 6 th ed. pg. 410 420 In this exercise, we will investigate the physiology of contraction in the
iworx Sample Lab Experiment AN-10: Crustacean Stretch Receptor
 Experiment AN-10: Crustacean Stretch Receptor Background Animals use their senses to gather information about their environment. Most senses use specialized sensory organs (eyes, ears, nares) to receive
Experiment AN-10: Crustacean Stretch Receptor Background Animals use their senses to gather information about their environment. Most senses use specialized sensory organs (eyes, ears, nares) to receive
Experiment HP-28: Control of EEG and Biofeedback Lab/Research Study
 Experiment HP-28: Control of EEG and Biofeedback Lab/Research Study Equipment Required PC or Mac Computer IXTA, USB cable and power supply iwire-b3g cable and EEG leads Reusable Gold-Cup EEG Electrodes
Experiment HP-28: Control of EEG and Biofeedback Lab/Research Study Equipment Required PC or Mac Computer IXTA, USB cable and power supply iwire-b3g cable and EEG leads Reusable Gold-Cup EEG Electrodes
Biopac Student Lab Lesson 20 SPINAL CORD REFLEXES Analysis Procedure. Rev
 42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 20 SPINAL CORD REFLEXES Analysis Procedure Rev. 12292017 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University
42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 20 SPINAL CORD REFLEXES Analysis Procedure Rev. 12292017 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University
Figure 1 muscle tissue to its resting state. By looking at several beats you can also calculate the rate for each component.
 ANALYZING THE HEART WITH EKG WITH LABQUEST LAB From Human Physiology with Vernier Westminster College INTRODUCTION An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring
ANALYZING THE HEART WITH EKG WITH LABQUEST LAB From Human Physiology with Vernier Westminster College INTRODUCTION An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HP-1: The Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) and Emotion
 Experiment HP-1: The Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) and Emotion What is a GSR? The Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) is one of several electrodermal responses (EDRs). EDRs are changes in the electrical properties
Experiment HP-1: The Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) and Emotion What is a GSR? The Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) is one of several electrodermal responses (EDRs). EDRs are changes in the electrical properties
Figure 1 The respiratory cycle
 RESPIRATORY CYCLE Introduction Three primary functions of the respiratory system are to provide oxygen for the body's energy needs, provide an outlet for C0 2 and help maintain the ph of the blood plasma.
RESPIRATORY CYCLE Introduction Three primary functions of the respiratory system are to provide oxygen for the body's energy needs, provide an outlet for C0 2 and help maintain the ph of the blood plasma.
BSL PRO Lesson H03: Nerve Conduction Velocity: Along the Ulnar Nerve of a Human Subject
 Updated 12-22-03 BSL PRO Lesson H03: Nerve Conduction Velocity: Along the Ulnar Nerve of a Human Subject This PRO lesson describes hardware and software setup of the BSL PRO System to record and measure
Updated 12-22-03 BSL PRO Lesson H03: Nerve Conduction Velocity: Along the Ulnar Nerve of a Human Subject This PRO lesson describes hardware and software setup of the BSL PRO System to record and measure
Sample. Analyzing the Heart with EKG. Computer
 Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Analyzing the Heart with EKG
 Analyzing the Heart with EKG LabQuest An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Analyzing the Heart with EKG LabQuest An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Lesson 5 BIOPAC Systems, Inc. Manual Revision PL3.7.5
 Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab Lesson 5 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY I Components of the ECG Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University School of Medicine Purdue
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab Lesson 5 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY I Components of the ECG Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University School of Medicine Purdue
Chapter 1: Introduction to iworx and LabScribe
 Chapter 1: Introduction to iworx and LabScribe Overview The iworx/204 data acquisition unit is a four-channel recording instrument (Figure 1-1 on page 1). Channels 1 and 2 receive electrical inputs through
Chapter 1: Introduction to iworx and LabScribe Overview The iworx/204 data acquisition unit is a four-channel recording instrument (Figure 1-1 on page 1). Channels 1 and 2 receive electrical inputs through
Labs #7 and #8: Vertebrate Skeletal Muscle
 Labs #7 and #8: Vertebrate Skeletal Muscle In this experiment, you will investigate the physiological properties of skeletal muscle from the isolated toad gastrocnemius. Concepts to understand include
Labs #7 and #8: Vertebrate Skeletal Muscle In this experiment, you will investigate the physiological properties of skeletal muscle from the isolated toad gastrocnemius. Concepts to understand include
ELECTROMYOGRAM ANALYSIS OF MUSCLE FUNCTION INTRODUCTION
 ELECTROMYOGRAM ANALYSIS OF MUSCLE FUNCTION STANDARDS: 3.3.10.B - Explain cell functions and processes in terms of chemical reactions and energy changes. 3.3.12.B - Evaluate relationships between structure
ELECTROMYOGRAM ANALYSIS OF MUSCLE FUNCTION STANDARDS: 3.3.10.B - Explain cell functions and processes in terms of chemical reactions and energy changes. 3.3.12.B - Evaluate relationships between structure
Lab 4: Introduction to Physiological Measurements - Cardiovascular
 Lab 4: Introduction to Physiological Measurements - Cardiovascular INTRODUCTION: This lab will demonstrate cardiovascular measurements by creating an ECG with instruments used in previous labs. Students
Lab 4: Introduction to Physiological Measurements - Cardiovascular INTRODUCTION: This lab will demonstrate cardiovascular measurements by creating an ECG with instruments used in previous labs. Students
Science in Sport. 204a ECG demonstration (Graph) Read. The Electrocardiogram. ECG Any 12 bit EASYSENSE. Sensors: Loggers: Logging time: 10 seconds
 Sensors: Loggers: ECG Any 12 bit EASYSENSE Science in Sport Logging time: 10 seconds 204a ECG demonstration (Graph) Read Regular medical check ups are essential part of the life of a professional sports
Sensors: Loggers: ECG Any 12 bit EASYSENSE Science in Sport Logging time: 10 seconds 204a ECG demonstration (Graph) Read Regular medical check ups are essential part of the life of a professional sports
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab. Lesson 1 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY I Standard and Integrated EMG
 Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab Lesson 1 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY I Standard and Integrated EMG Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University School of Medicine
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab Lesson 1 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY I Standard and Integrated EMG Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University School of Medicine
Lesson 10 Aerobic Exercise Physiology
 Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Science Lab MP40 Lesson 10 Aerobic Exercise Physiology PC running Windows XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Lesson Revision 12.19.2005 BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 42 Aero Camino,
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Science Lab MP40 Lesson 10 Aerobic Exercise Physiology PC running Windows XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Lesson Revision 12.19.2005 BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 42 Aero Camino,
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY NAME Detection of heart sounds. Clean the ear pieces of the stethoscope before using. The ear pieces should be pointing slightly forward when inserted into the ears because
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY NAME Detection of heart sounds. Clean the ear pieces of the stethoscope before using. The ear pieces should be pointing slightly forward when inserted into the ears because
Exercise 5: Muscle Physiology I - Electromyography
 Exercise 5: Muscle Physiology I - Electromyography Readings: Silverthorn, 6 th ed. pg. 410 420 Your brain communicates with your muscles through action potentials on the motor neurons, which are then transmitted
Exercise 5: Muscle Physiology I - Electromyography Readings: Silverthorn, 6 th ed. pg. 410 420 Your brain communicates with your muscles through action potentials on the motor neurons, which are then transmitted
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab
 Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab Lesson 6 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY II Bipolar Leads (Leads I, II, III) Einthoven s Law Mean Electrical Axis on the Frontal Plane Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D.
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab Lesson 6 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY II Bipolar Leads (Leads I, II, III) Einthoven s Law Mean Electrical Axis on the Frontal Plane Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D.
Experiment B-18 Heart Rate and Coughing
 1 Experiment B-18 Heart Rate and Coughing Objectives To study the changes in heart rate at rest and after coughing. Modules and Sensors PC + NeuLog application USB-200 module NUL-208 Heart rate & pulse
1 Experiment B-18 Heart Rate and Coughing Objectives To study the changes in heart rate at rest and after coughing. Modules and Sensors PC + NeuLog application USB-200 module NUL-208 Heart rate & pulse
Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. J.C. Uyehara, Ph.D. William McMullen David Pittman, Ph.D. Manual Revision PL3.7.0 M3.0.6 Modified by David Pittman
 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY (EMG) Laboratory Motor unit recruitment & Fatigue Comparison of dominant versus non-dominant arm using a within subject repeated measures statistical analysis Written by: Richard Pflanzer,
ELECTROMYOGRAPHY (EMG) Laboratory Motor unit recruitment & Fatigue Comparison of dominant versus non-dominant arm using a within subject repeated measures statistical analysis Written by: Richard Pflanzer,
Lesson 1 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY I Standard and Integrated EMG
 Physiology Lessons for use with the PC running Windows 98SE, Me, 2000 Pro, XP Pro/Home/Media Lesson 1 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY I Standard and Integrated EMG Manual Revision PL3.7.0 080706 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D.
Physiology Lessons for use with the PC running Windows 98SE, Me, 2000 Pro, XP Pro/Home/Media Lesson 1 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY I Standard and Integrated EMG Manual Revision PL3.7.0 080706 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D.
INTRODUCTION TO ECG. Dr. Tamara Alqudah
 INTRODUCTION TO ECG Dr. Tamara Alqudah Excitatory & conductive system of the heart + - The ECG The electrocardiogram, or ECG, is a simple & noninvasive diagnostic test which records the electrical
INTRODUCTION TO ECG Dr. Tamara Alqudah Excitatory & conductive system of the heart + - The ECG The electrocardiogram, or ECG, is a simple & noninvasive diagnostic test which records the electrical
Lab #9: Muscle Physiology
 Background Overview of Skeletal Muscle Contraction Sarcomere Thick Filaments Skeletal muscle fibers are very large, elongated cells (Fig 9.1). Roughly 80% of the content of each muscle fiber consists of
Background Overview of Skeletal Muscle Contraction Sarcomere Thick Filaments Skeletal muscle fibers are very large, elongated cells (Fig 9.1). Roughly 80% of the content of each muscle fiber consists of
Experiment HM-5: Kinesiology and Electromyogram (EMG) Activity in Targeted Muscles
 Experiment HM-5: Kinesiology and Electromyogram (EMG) Activity in Targeted Muscles Lab written in conjunction with: Kelly Helm PhD, Director Exercise Science, Department of Kinesiology; Amanda Ulin & Kelsey
Experiment HM-5: Kinesiology and Electromyogram (EMG) Activity in Targeted Muscles Lab written in conjunction with: Kelly Helm PhD, Director Exercise Science, Department of Kinesiology; Amanda Ulin & Kelsey
#4 Cardiovascular I The Heart & EKG
 #4 Cardiovascular I Objectives: Identify a list of human heart structures using a virtual human dissection Dissect a sheep heart to identify external and internal structures Identify a list of human heart
#4 Cardiovascular I Objectives: Identify a list of human heart structures using a virtual human dissection Dissect a sheep heart to identify external and internal structures Identify a list of human heart
Posner s Attention Test
 iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HP-18 Posner s Attention Test Background Setup Lab Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should refer to the User
iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HP-18 Posner s Attention Test Background Setup Lab Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should refer to the User
CAMOSUN COLLEGE BIOLOGY 144 (2010) LABS
 LAB 8: CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY PART 1. HEART SOUNDS AND PULSE DETERMINATIONS Introduction Two distinct sounds can be heard during each cardiac cycle. These sounds are commonly described as lub and dup
LAB 8: CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY PART 1. HEART SOUNDS AND PULSE DETERMINATIONS Introduction Two distinct sounds can be heard during each cardiac cycle. These sounds are commonly described as lub and dup
Experiment HP-3: The Galvanic Skin Response, Deception, Cognitive Complexity, and Vigilance
 Experiment HP-3: The Galvanic Skin Response, Deception, Cognitive Complexity, and Vigilance Exercise 4: GSR and Deliberate Deception Aim: To test an experimental hypothesis about deliberate deception and
Experiment HP-3: The Galvanic Skin Response, Deception, Cognitive Complexity, and Vigilance Exercise 4: GSR and Deliberate Deception Aim: To test an experimental hypothesis about deliberate deception and
Actiwatch. Clinician Guide
 Actiwatch Clinician Guide 2013 Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. and its affiliates. All rights reserved. Overview of Actiwatch The Actiwatch is designed for documenting physical movements associated
Actiwatch Clinician Guide 2013 Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. and its affiliates. All rights reserved. Overview of Actiwatch The Actiwatch is designed for documenting physical movements associated
ECG-PS ECG SIGNAL MEASUREMENT MODULE. Operation Manual. March 2005
 ECG-PS ECG SIGNAL MEASUREMENT MODULE Operation Manual March 2005 2555 Collins Avenue, Suite C-5 - Miami Beach FL - 33140 - U.S.A. Phone #: (305) 534-5905 Fax: (305) 534-8222 e-mail: info@galix-gbi.com
ECG-PS ECG SIGNAL MEASUREMENT MODULE Operation Manual March 2005 2555 Collins Avenue, Suite C-5 - Miami Beach FL - 33140 - U.S.A. Phone #: (305) 534-5905 Fax: (305) 534-8222 e-mail: info@galix-gbi.com
SANAKO Lab 100 STS USER GUIDE
 SANAKO Lab 100 STS USER GUIDE Copyright 2008 SANAKO Corporation. All rights reserved. Microsoft is a registered trademark. Microsoft Windows 2000 and Windows XP are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
SANAKO Lab 100 STS USER GUIDE Copyright 2008 SANAKO Corporation. All rights reserved. Microsoft is a registered trademark. Microsoft Windows 2000 and Windows XP are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Experiment HP-4: The Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) and Investigation into Cheating
 Experiment HP-4: The Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) and Investigation into Cheating This iworx lab experiment was graciously provided by Dr. Paul Wagner and Dr. Tracy Wagner, Asst. Professors, Washburn University,
Experiment HP-4: The Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) and Investigation into Cheating This iworx lab experiment was graciously provided by Dr. Paul Wagner and Dr. Tracy Wagner, Asst. Professors, Washburn University,
TMWSuite. DAT Interactive interface
 TMWSuite DAT Interactive interface DAT Interactive interface Using the DAT Interactive interface Using the DAT Interactive interface... 1 Setting up the system to use the DAT Interactive interface... 1
TMWSuite DAT Interactive interface DAT Interactive interface Using the DAT Interactive interface Using the DAT Interactive interface... 1 Setting up the system to use the DAT Interactive interface... 1
Kinesiology and Electromyogram (EMG) Activity in Targeted Muscles
 iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HM-9 Kinesiology and Electromyogram (EMG) Activity in Targeted Muscles Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should
iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HM-9 Kinesiology and Electromyogram (EMG) Activity in Targeted Muscles Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should
2The Concept of Periodic Functions
 The Concept of Periodic Functions EKG INTRODUCTION The heart is a fist-sized muscle that acts as an electrical generator lying in a conducting medium made of body tissue and fluids. The heart pumps oxygen-rich
The Concept of Periodic Functions EKG INTRODUCTION The heart is a fist-sized muscle that acts as an electrical generator lying in a conducting medium made of body tissue and fluids. The heart pumps oxygen-rich
How Do We Sense, Think, and Move? -- Lab #11 Bioelectronics Measuring Electrical Properties of the Body
 How Do We Sense, Think, and Move? -- Lab #11 Bioelectronics Measuring Electrical Properties of the Body Experiment #1 Your Body's Resistance Equipment: Digital multimeter, Banana leads Important Equipment
How Do We Sense, Think, and Move? -- Lab #11 Bioelectronics Measuring Electrical Properties of the Body Experiment #1 Your Body's Resistance Equipment: Digital multimeter, Banana leads Important Equipment
Comparing the Functional Performance of BIOPAC Respiratory Belt-Transducers With and Without Repair Tape
 Comparing the Functional Performance of BIOPAC Respiratory Belt-Transducers With and Without Repair Tape Ames A., Berning M., Chreptowicz N., Hackney R., Kelly E., Noffke A., Lokuta AJ.* *Corresponding
Comparing the Functional Performance of BIOPAC Respiratory Belt-Transducers With and Without Repair Tape Ames A., Berning M., Chreptowicz N., Hackney R., Kelly E., Noffke A., Lokuta AJ.* *Corresponding
Epicardio Simulation. Introductory Guide
 Epicardio Simulation Introductory Guide Introduction Epicardio Simulation is a fully validated advanced cloud-based 3D interactive real-time simulation of the heart that shortens the Cardiology learning
Epicardio Simulation Introductory Guide Introduction Epicardio Simulation is a fully validated advanced cloud-based 3D interactive real-time simulation of the heart that shortens the Cardiology learning
#20 Separation of Alcohols Using Gas Chromatography
 #20 Separation of Alcohols Using Gas Chromatography Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to determine the composition of an unknown alcohol mixture by using gas chromatography. Introduction: A gas
#20 Separation of Alcohols Using Gas Chromatography Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to determine the composition of an unknown alcohol mixture by using gas chromatography. Introduction: A gas
Overview. Page 1 of 9. Impedance Cardiography
 Updated 05.14.10 BSL PRO Lesson H21: Impedance Cardiography Data collected from a subject using the referenced set-up procedure. Note that dz/dt maximum is determined on a cycle by cycle basis from the
Updated 05.14.10 BSL PRO Lesson H21: Impedance Cardiography Data collected from a subject using the referenced set-up procedure. Note that dz/dt maximum is determined on a cycle by cycle basis from the
Allergy Basics. This handout describes the process for adding and removing allergies from a patient s chart.
 Allergy Basics This handout describes the process for adding and removing allergies from a patient s chart. Accessing Allergy Information Page 1 Recording No Known Medication Allergies Page 2 Recording
Allergy Basics This handout describes the process for adding and removing allergies from a patient s chart. Accessing Allergy Information Page 1 Recording No Known Medication Allergies Page 2 Recording
Lab 2. The Intrinsic Cardiac Conduction System. 1/23/2016 MDufilho 1
 Lab 2 he Intrinsic Cardiac Conduction System 1/23/2016 MDufilho 1 Figure 18.13 Intrinsic cardiac conduction system and action potential succession during one heartbeat. Superior vena cava ight atrium 1
Lab 2 he Intrinsic Cardiac Conduction System 1/23/2016 MDufilho 1 Figure 18.13 Intrinsic cardiac conduction system and action potential succession during one heartbeat. Superior vena cava ight atrium 1
Sanako Lab 100 STS USER GUIDE
 Sanako Lab 100 STS USER GUIDE Copyright 2002-2015 SANAKO Corporation. All rights reserved. Microsoft is a registered trademark. Microsoft Windows XP, Windows Vista and Windows 7 are trademarks of Microsoft
Sanako Lab 100 STS USER GUIDE Copyright 2002-2015 SANAKO Corporation. All rights reserved. Microsoft is a registered trademark. Microsoft Windows XP, Windows Vista and Windows 7 are trademarks of Microsoft
Lesson 5 EEG 1 Electroencephalography: Brain Rhythms
 Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Science Lab MP40 PC running Windows XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Lesson 5 EEG 1 Electroencephalography: Brain Rhythms Lesson Revision 2.23.2006 BIOPAC Systems, Inc.
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Science Lab MP40 PC running Windows XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Lesson 5 EEG 1 Electroencephalography: Brain Rhythms Lesson Revision 2.23.2006 BIOPAC Systems, Inc.
Practical Guidelines For the Enraf-Nonius Commercial Training Myomed 632
 Practical Guidelines For the Enraf-Nonius Commercial Training Myomed 632 Copyright: & Exclusive Sales and Service: Enraf-Nonius B.V. P.O. Box 12080 3004 GB ROTTERDAM The Netherlands Tel: +31 (0)10 20 30
Practical Guidelines For the Enraf-Nonius Commercial Training Myomed 632 Copyright: & Exclusive Sales and Service: Enraf-Nonius B.V. P.O. Box 12080 3004 GB ROTTERDAM The Netherlands Tel: +31 (0)10 20 30
A. User s Guide. CareCenter MD Stress and Resting ECG
 70-00533-02 A User s Guide CareCenter MD Stress and Resting ECG CARECENTER MD STRESS AND RESTING USER S GUIDE 70-00533-02 A Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Names and data
70-00533-02 A User s Guide CareCenter MD Stress and Resting ECG CARECENTER MD STRESS AND RESTING USER S GUIDE 70-00533-02 A Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Names and data
HST-582J/6.555J/16.456J-Biomedical Signal and Image Processing-Spring Laboratory Project 1 The Electrocardiogram
 HST-582J/6.555J/16.456J-Biomedical Signal and Image Processing-Spring 2007 DUE: 3/8/07 Laboratory Project 1 The Electrocardiogram 1 Introduction The electrocardiogram (ECG) is a recording of body surface
HST-582J/6.555J/16.456J-Biomedical Signal and Image Processing-Spring 2007 DUE: 3/8/07 Laboratory Project 1 The Electrocardiogram 1 Introduction The electrocardiogram (ECG) is a recording of body surface
