Biology 13A Lab #10: Cardiovascular System II ECG & Heart Disease
|
|
|
- Lorin Fox
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biology 13A Lab #10: Cardiovascular System II ECG & Heart Disease Lab #10 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes Introduction Activity 1: Collecting ECG Data Activity 2: Film: The Hidden Epidemic; Heart Disease in America 87 Expected Learning Outcomes At the end of this lab, you will be able to use an ECG sensor to collect data on cardiac electrical activity; interpret and explain the wave patterns of the ECG; determine heart rate based on intervals of time between peaks of the ECG trace; explain why the ECG is a useful clinical tool; and apply knowledge of heart anatomy and physiology to clinical symptoms and treatments for heart disease. Figure 10.1 Heart & ECG 83
2 Introduction Next to listening to the heart sounds with a stethoscope, the most common clinical method of evaluating heart function is the electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). The depolarization and repolarization of the atrial and ventricular myocardium generate electrical currents that are conducted through the fluid in the chest cavity. Electrodes placed on the skin detect the electrical activity and after the signals have been amplified, they can be displayed on a computer screen. Three major events are seen in the ECG: the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave. The P wave reflects depolarization of the atria. The QRS complex represents depolarization of the ventricles. It is the largest wave of the ECG because the ventricles constitute the largest muscle mass in the heart and generate the greatest electrical current. The atria repolarize during the QRS complex but the effect is largely masked by depolarization of the ventricles. The T wave represents ventricular repolarization. The electrical events slightly precede the mechanical events of the heart; there is a slight delay between the electrical stimulation and the contraction of the sheets of cardiomyocytes. For example, ventricular systole (contraction) begins shortly after the QRS complex. Ventricular systole, then, occurs in the ST segment. The electrocardiogram is useful because it provides a non-invasive, if indirect, snapshot of heart function. The horizontal axis represents time. Heart rate can be determined by measuring the time between successive R peaks. Myocardial infarctions (heart attacks) produce changes in the ECG such as an elevated ST segment. Thus, the ECG provides a valuable tool for rapid preliminary diagnosis of a variety of cardiac conditions. In this activity, you will use the ECG sensor to make a graphical recording of your heart's electrical events. From this recording, you will determine the time interval associated with each of the previously mentioned ECG waveforms. Figure 10.2 ECG 84
3 Check Your Understanding: Answer the following questions based on your reading of the introduction. 1. What is happening in the heart to produce the P, QRS, and T waves? 2. Why is the ECG a valuable clinical tool? Activity 1: Collecting ECG Data Getting Started 1. The equipment for today s experiment is listed below. Computer Biopac MP35 Acquisition unit BIOPAC electrode lead set Disposable paste-on electrodes Yoga mat 2. Use the checklist below to ensure that the basic set-up is working: Check to make sure the electrode lead set is plugged into Channel 2. Turn the computer on. For Mac laptops, press the on silver "ON" button located above the computer keyboard. The computer must finish booting up before turning on the Biopac unit (blue box). Check that the Biopac unit is plugged into the electrical outlet. Check that the Biopac unit is connected to the computer via a black USB cable. Make sure the Biopac unit is turned ON. The Power switch is on the back panel on the right. Check that the AC adapter for the unit is plugged into the back. Wait until the "Busy" light stops flashing before launching software. 3. The subject should remove all jewelry from wrists and ankles. 4. Clean and scrub the regions on the right forearm, and medial right and left ankle for electrode attachment using an alcohol pad (see Figure 10.3) for electrode placement). Let the areas dry after cleaning with the alcohol pad. Place the electrode on the anterior surface of the RIGHT forearm superior to the wrist. Place the second and third electrode on the MEDIAL surface of the lower leg, just superior to the medial malleolus (see Figure 10.3) 5. Each of the pinch connectors needs to be attached to a specific electrode. Each lead cable is a different color. Be sure that, when you attach the pinch connector to each electrode, the metal side of the pinch connector faces down. Attach the WHITE lead to the electrode on the RIGHT FOREARM. Attach the BLACK lead to the electrode on the RIGHT LEG. Attach the RED lead to the electrode on the LEFT LEG. Position the lead cables so that they are not pulling on the electrodes. 85
4 Figure 10.3 Electrode and lead placement Calibration Calibration allows the software to determine the high and low points of your subject s trace. 1. Launch the Biopac student lab program. The icon is located on the dock at the bottom of the screen (see figure 10.4). Select lesson L05-ECG-1 from the menu. Click on OK. Figure 10.4 BSL Icon 2. Type in a file name for your experiment. Use a name that distinguishes both your lab group and the exercise you are performing, like Barbara s ECG, not just ECG. Click on OK. 3. Have the subject lie down and make sure he/she is relaxed. Do not laugh, cough, sneeze, or have any other shifts in body position during calibration. 4. Make sure the electrodes are securely adhered to the subject s skin. 5. Click on the Calibrate button in the upper left corner of the screen. If an error message occurs, click Ignore. 6. Wait for the calibration procedure to stop. At the end of 8 seconds, there should be a recognizable ECG waveform with no large baseline drifts. If your data resembles Figure 10.5, proceed to the data recording section. If your data shows any large drifts or does not resemble figure 6 you must redo the calibration. Click on REDO CALIBRATION, then follow the above directions again. 86
5 Figure 10.5 ECG Calibration Data Recording Now that the computer is calibrated, you can collect your data. During all of the recordings do not talk, laugh, or have any other activity that may alter the ECG recording. 1. Have the subject sit in a relaxed position; the arms should rest palms up on the bench in front of him/her. 2. When everything is positioned properly, click RECORD. 3. Record for 20 seconds. 4. Click SUSPEND. 5. Review the data to ensure that it resembles Figure If it does, proceed to the next seciton. If it does not, click REDO and rerecord the data. Figure 10.6 ECG sitting 6. When you have obtained an acceptable recording, click DONE. A window will appear asking if you are sure you are done recording. Click YES. 7. A window will appear asking what you would like to do now. Select ANALYZE CURRENT DATA FILE. Click on OK. 87
6 Analyzing the Data 1. All of the data you collected will initially be displayed on a single screen no matter how long you recorded. The longer you record, the more squished together your pulses will appear and it can be difficult to place the cursor accurately when measuring your ECG. 2. Adjusting your image: Use the zoom tool to widen your pulses. To do this, click on the zoom tool icon in the lower right hand corner of the screen. The zoom tool looks like a magnifying lens (see Figure 10.7). Figure 10.7 Editing and Selection Tools. From left to right: the Arrow, the I-Beam, and Zoom. Click anywhere on your trace to enlarge your trace. The peaks will get higher and wider and some of the trace may be off screen. To adjust your trace so that the peaks and valleys are visible, pull down the Display menu and select Autoscale Waveforms. This automatically adjusts the Y-axis so that the highest and lowest points are on screen. If your peaks are still too squished together, click on the trace again to zoom in further. Readjust the Y-axis by selecting Autoscale Waveforms again. (Note the Autoscale Horizontal function in the Display menu. This readjusts the X- axis so all the data you collected is once again displayed on the screen.) Now enlarge a specific area of your trace. To do this, position the zoom tool at the point that you want to start your enlargement and click and drag the zoom tool to draw a box around a section that contains five successive peaks. Be sure to include the lowest point before the first peak and the lowest point after the last peak. All five peaks should be displayed together now. To undo the zoom, pull down the Display menu and select Zoom Back. There is also a Zoom Forward function to redo a zoom. 3. Set the first two measurement boxes at the top of the screen so the following are displayed: Channel Measurement Function CH2 Delta T ( T) CH2 BPM (Beats Per Minute) Figure 10.8 Channel Settings Delta T ( T) is the time measured along the X-axis by the selected region BPM (beats per minute) is heart rate calculated based on the Delta T selected and is valid only if the selected region is one complete cardiac cycle. 88
7 4. Highlight the area you want to measure: Once you have your trace of five peaks adjusted so that it can be easily viewed, use the I-Beam tool to highlight areas of the trace you want to measure. The I-Beam icon is located in the bottom right corner of the screen (see Figure 10.7). You will be determining the time intervals of the following segments: R R Interval (time from the peak of one R wave to the peak of the next R wave: corresponds to one full cardiac cycle): Using the I-Beam cursor, select the area between two successive R waves (R R segment; see Fig. 10.9). To do this, click on the I-Beam icon, then position the I-Beam at the peak of the R wave where you want to begin your measurement; click and drag the I-Beam until the I-Beam is positioned at the peak of the next R wave; release the mouse. The area between the two R waves should be highlighted. Record the T and the BPM from this reading (look at the two measurement boxes at the top of the screen) for Cardiac Cycle 1 in Table Take R R measurements for two other cardiac cycles in this display and record the same data in Table 1. Calculate the mean of the these 3 values by adding them together and dividing by 3. P R Interval (time from the beginning of the P wave to the start of the QRS complex): Again using the I-Beam cursor, select the area between the the beginning of one P wave and the beginning of the subsequent QRS complex (see Figure 10.9). Record the T from this reading in Table QRS Interval (time from Q deflection to S deflection): Using the I-Beam cursor, select the area between the beginning of the Q wave and the end of the S wave (see Figure 10.9). Record the T from this reading in Table Q T Interval (time from Q deflection to the end of the T wave): Select the area between the beginning of the Q wave and the end of the T wave (see figure 10.9). Record the the T from this reading in Table R T Interval (time from the peak of the R wave to the end of the T wave: corresponds to ventricular systole): Select the area between the peak of one R wave and the end of the subsequent T wave (see Figure 10.9). Record the T from this reading in Table T R Interval (time from the end of the T wave to the subsequent R wave: corresponds to ventricular diastole): Select the area between the end of one T wave and peak of the subsequent R wave (see Figure 10.9). Record the T from this reading in Table
8 Figure ECG segments for measurements Recording the Data Table 10.1 Measurement From Channel Cardiac Cycle T (Delta Time) (R-R Interval) BPM (Beats Per Minute) CH 2 CH 2 Mean Table 10.2 Measurement CH 2 T Standard Resting ECG Interval Times P R Interval 0.12 to 0.20 s QRS Interval Q T Interval less than 0.10 s 0.30 to 0.40 s Table
9 Ventricular Readings R T Interval (corresponds to Ventricular Systole) T R Interval (corresponds to Ventricular Diastole) CH 2 T Check Your Understanding: Answer the following questions. 1. What property of heart muscle must be altered in order for an ECG to detect a problem? Explain. 2. Why can t an ECG be used to diagnose all diseases or defects of the heart? 3. Name and describe a cardiovascular problem that could be diagnosed by a cardiologist using an electrocardiogram recording. 4. What mechanical event is occurring in the heart during the Q T portion of the ECG? What is occurring during the T Q portion? Which portion is longer? Which do you suppose would be shorter or longer during exercise? Why? Portions of this lab were adopted from University of Pittsburgh s Science in Motion program for science education. < Activity 2: Film The Hidden Epidemic Heart Disease in America We will watch a NOVA video that first aired in 2007 that interviews patients, doctors, and researchers about heart disease. It explores the history of the incidence of the disease and contributing factors, including lifestyle. Be prepared to answer the following questions: What lifestyle factors contribute to heart disease? What can individuals do to lessen their risk of developing heart disease? What is the role of smoking in heart disease? Diet? What medical procedures have been developed in the past several decades to treat heart disease? Explain the procedures using precise anatomical and physiological vocabulary. What specific new information did you learn from this film? 91
Exercise 5: Muscle Physiology I - Electromyography
 Exercise 5: Muscle Physiology I - Electromyography Readings: Silverthorn, 6 th ed. pg. 410 420 Your brain communicates with your muscles through action potentials on the motor neurons, which are then transmitted
Exercise 5: Muscle Physiology I - Electromyography Readings: Silverthorn, 6 th ed. pg. 410 420 Your brain communicates with your muscles through action potentials on the motor neurons, which are then transmitted
Biopac Student Lab Lesson 5 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) I Procedure. Rev
 42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 5 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) I Procedure Rev. 07112013 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University School
42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 5 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) I Procedure Rev. 07112013 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University School
Lesson 4 ECG 2 Electrocardiography
 Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Science Lab MP40 Lesson 4 ECG 2 Electrocardiography PC running Windows XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Lesson Revision 1.20.2006 BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 42 Aero Camino,
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Science Lab MP40 Lesson 4 ECG 2 Electrocardiography PC running Windows XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Lesson Revision 1.20.2006 BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 42 Aero Camino,
Experiment HH-2: The Electrocardiogram and Heart Sounds
 Experiment HH-2: The Electrocardiogram and Heart Sounds Exercise 1: The ECG in a Resting Subject Aim: To measure the ECG in a resting individual. Procedure 1. Click on the Record button, located on the
Experiment HH-2: The Electrocardiogram and Heart Sounds Exercise 1: The ECG in a Resting Subject Aim: To measure the ECG in a resting individual. Procedure 1. Click on the Record button, located on the
LABORATORY INVESTIGATION
 LABORATORY INVESTIGATION Recording Electrocardiograms The taking of an electrocardiogram is an almost universal part of any complete physical examination. From the ECG record of the electrical activity
LABORATORY INVESTIGATION Recording Electrocardiograms The taking of an electrocardiogram is an almost universal part of any complete physical examination. From the ECG record of the electrical activity
#4 Cardiovascular I The Heart & EKG
 #4 Cardiovascular I Objectives: Identify a list of human heart structures using a virtual human dissection Dissect a sheep heart to identify external and internal structures Identify a list of human heart
#4 Cardiovascular I Objectives: Identify a list of human heart structures using a virtual human dissection Dissect a sheep heart to identify external and internal structures Identify a list of human heart
Experiment HH-3: Exercise, the Electrocardiogram, and Peripheral Circulation
 Experiment HH-3: Exercise, the Electrocardiogram, and Peripheral Circulation Background The arterial system functions as a pressure reservoir. Blood enters via the heart and exits through the capillaries.
Experiment HH-3: Exercise, the Electrocardiogram, and Peripheral Circulation Background The arterial system functions as a pressure reservoir. Blood enters via the heart and exits through the capillaries.
BIO 360: Vertebrate Physiology Performing and analyzing an EKG Lab 11: Performing and analyzing an EKG Lab report due April 17 th
 BIO 60: Vertebrate Physiology Lab : Lab report due April 7 th All muscles produce an electrical current when they contract. The heart is no exception. An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording
BIO 60: Vertebrate Physiology Lab : Lab report due April 7 th All muscles produce an electrical current when they contract. The heart is no exception. An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording
CAMOSUN COLLEGE BIOLOGY 144 (2010) LABS
 LAB 8: CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY PART 1. HEART SOUNDS AND PULSE DETERMINATIONS Introduction Two distinct sounds can be heard during each cardiac cycle. These sounds are commonly described as lub and dup
LAB 8: CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY PART 1. HEART SOUNDS AND PULSE DETERMINATIONS Introduction Two distinct sounds can be heard during each cardiac cycle. These sounds are commonly described as lub and dup
Figure 1 muscle tissue to its resting state. By looking at several beats you can also calculate the rate for each component.
 ANALYZING THE HEART WITH EKG WITH LABQUEST LAB From Human Physiology with Vernier Westminster College INTRODUCTION An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring
ANALYZING THE HEART WITH EKG WITH LABQUEST LAB From Human Physiology with Vernier Westminster College INTRODUCTION An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY NAME Detection of heart sounds. Clean the ear pieces of the stethoscope before using. The ear pieces should be pointing slightly forward when inserted into the ears because
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY NAME Detection of heart sounds. Clean the ear pieces of the stethoscope before using. The ear pieces should be pointing slightly forward when inserted into the ears because
Exercise 6: Muscle Physiology II Twitch & Summation
 Exercise 6: Muscle Physiology II Twitch & Summation Text Reading: Silverthorn, 5 th ed. 412 419, 425 427; 6 th ed. pg. 410 420 In this exercise, we will investigate the physiology of contraction in the
Exercise 6: Muscle Physiology II Twitch & Summation Text Reading: Silverthorn, 5 th ed. 412 419, 425 427; 6 th ed. pg. 410 420 In this exercise, we will investigate the physiology of contraction in the
Analyzing the Heart with EKG
 Analyzing the Heart with EKG LabQuest An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Analyzing the Heart with EKG LabQuest An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Experiment HH-3: Exercise, the Electrocardiogram, and Peripheral Circulation
 Experiment HH-3: Exercise, the Electrocardiogram, and Peripheral Circulation Exercise 1: The ECG and the Pulse in a Resting Subject Aim: To measure and correlate the ECG and the pulse in a resting individual.
Experiment HH-3: Exercise, the Electrocardiogram, and Peripheral Circulation Exercise 1: The ECG and the Pulse in a Resting Subject Aim: To measure and correlate the ECG and the pulse in a resting individual.
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HH-4: The Six-Lead Electrocardiogram
 Experiment HH-4: The Six-Lead Electrocardiogram Background The cardiac cycle involves a sequential contraction of the atria and the ventricles. These contractions are triggered by the coordinated electrical
Experiment HH-4: The Six-Lead Electrocardiogram Background The cardiac cycle involves a sequential contraction of the atria and the ventricles. These contractions are triggered by the coordinated electrical
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG)
 Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Cardiovascular Physiology
 Cardiovascular Physiology The mammalian heart is a pump that pushes blood around the body and is made of four chambers: right and left atria and right and left ventricles. The two atria act as collecting
Cardiovascular Physiology The mammalian heart is a pump that pushes blood around the body and is made of four chambers: right and left atria and right and left ventricles. The two atria act as collecting
Lesson 2 EMG 2 Electromyography: Mechanical Work
 Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Science Lab MP40 Lesson 2 EMG 2 Electromyography: Mechanical Work PC running Windows XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Lesson Revision 5.23.2006 BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 42
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Science Lab MP40 Lesson 2 EMG 2 Electromyography: Mechanical Work PC running Windows XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Lesson Revision 5.23.2006 BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 42
Cardiovascular Effects of Exercise. Background Cardiac function
 Cardiovascular Effects of Exercise In this experiment, you will record an electrocardiogram, or ECG, and finger pulse from a healthy volunteer. You will then compare the ECG and pulse recordings when the
Cardiovascular Effects of Exercise In this experiment, you will record an electrocardiogram, or ECG, and finger pulse from a healthy volunteer. You will then compare the ECG and pulse recordings when the
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG)
 Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Lab 4: Introduction to Physiological Measurements - Cardiovascular
 Lab 4: Introduction to Physiological Measurements - Cardiovascular INTRODUCTION: This lab will demonstrate cardiovascular measurements by creating an ECG with instruments used in previous labs. Students
Lab 4: Introduction to Physiological Measurements - Cardiovascular INTRODUCTION: This lab will demonstrate cardiovascular measurements by creating an ECG with instruments used in previous labs. Students
Overview. Page 1 of 9. Impedance Cardiography
 Updated 05.14.10 BSL PRO Lesson H21: Impedance Cardiography Data collected from a subject using the referenced set-up procedure. Note that dz/dt maximum is determined on a cycle by cycle basis from the
Updated 05.14.10 BSL PRO Lesson H21: Impedance Cardiography Data collected from a subject using the referenced set-up procedure. Note that dz/dt maximum is determined on a cycle by cycle basis from the
Biopac Student Lab Lesson 6 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) II Analysis Procedure. Rev
 42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 6 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) II Analysis Procedure Rev. 12292017 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University
42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 6 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) II Analysis Procedure Rev. 12292017 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University
Sample. Analyzing the Heart with EKG. Computer
 Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Lab 5: Electromyograms (EMGs)
 Lab 5: Electromyograms (EMGs) Overview A motorneuron and all the muscle fibers that it innervates is known as a motor unit. Under normal circumstances, a neuronal action potential activates all of the
Lab 5: Electromyograms (EMGs) Overview A motorneuron and all the muscle fibers that it innervates is known as a motor unit. Under normal circumstances, a neuronal action potential activates all of the
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab
 Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab Lesson 6 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY II Bipolar Leads (Leads I, II, III) Einthoven s Law Mean Electrical Axis on the Frontal Plane Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D.
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab Lesson 6 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY II Bipolar Leads (Leads I, II, III) Einthoven s Law Mean Electrical Axis on the Frontal Plane Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D.
Lesson 5 BIOPAC Systems, Inc. Manual Revision PL3.7.5
 Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab Lesson 5 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY I Components of the ECG Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University School of Medicine Purdue
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab Lesson 5 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY I Components of the ECG Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University School of Medicine Purdue
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab. Lesson 1 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY I Standard and Integrated EMG
 Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab Lesson 1 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY I Standard and Integrated EMG Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University School of Medicine
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab Lesson 1 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY I Standard and Integrated EMG Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University School of Medicine
Lesson 1 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY I Standard and Integrated EMG
 Physiology Lessons for use with the PC running Windows 98SE, Me, 2000 Pro, XP Pro/Home/Media Lesson 1 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY I Standard and Integrated EMG Manual Revision PL3.7.0 080706 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D.
Physiology Lessons for use with the PC running Windows 98SE, Me, 2000 Pro, XP Pro/Home/Media Lesson 1 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY I Standard and Integrated EMG Manual Revision PL3.7.0 080706 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D.
Lab 7. Physiology of Electrocardiography
 7.1 Lab 7. Physiology of Electrocardiography The heart is a muscular pump that circulates blood throughout the body. To efficiently pump the blood, cardiac contractions must be coordinated and are regulated
7.1 Lab 7. Physiology of Electrocardiography The heart is a muscular pump that circulates blood throughout the body. To efficiently pump the blood, cardiac contractions must be coordinated and are regulated
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HC-3: Pulse Wave Velocity
 Experiment HC-3: Pulse Wave Velocity Exercise 1: The Pulse Wave Velocity at Rest Aim: To measure the pulse wave velocity in a resting individual. Procedure 1. Click on the Record button, located on the
Experiment HC-3: Pulse Wave Velocity Exercise 1: The Pulse Wave Velocity at Rest Aim: To measure the pulse wave velocity in a resting individual. Procedure 1. Click on the Record button, located on the
Warning: Avoid putting the tip of the syringe needle too deeply into the hole to avoid damage to the heart tissue.
 Experiment AM-12: Crayfish Electrocardiogram (ECG) Exercise 1: The Crayfish ECG and Heart Rate Aim: To record the electrical trace (ECG) produced by the contraction of a resting heart, and to determine
Experiment AM-12: Crayfish Electrocardiogram (ECG) Exercise 1: The Crayfish ECG and Heart Rate Aim: To record the electrical trace (ECG) produced by the contraction of a resting heart, and to determine
Exercise 2: Effects of Cold Temperature Aim: To record changes in heart rate after the heart is bathed in cold Ringer s solution.
 Experiment AM-3: Heart Muscle Warning: The heart preparation used in this experiment is functional for a limited period of time. If the muscle is bathed periodically in Ringer s solution, it will work
Experiment AM-3: Heart Muscle Warning: The heart preparation used in this experiment is functional for a limited period of time. If the muscle is bathed periodically in Ringer s solution, it will work
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HH-4: The Six-Lead Electrocardiogram
 Experiment HH-4: The Six-Lead Electrocardiogram Exercise 1: Six Lead ECG from Resting Subject Aim: To record a Six Lead ECG from a resting subject and determine the QRS axis of the subject s heart. Procedure
Experiment HH-4: The Six-Lead Electrocardiogram Exercise 1: Six Lead ECG from Resting Subject Aim: To record a Six Lead ECG from a resting subject and determine the QRS axis of the subject s heart. Procedure
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HP-7: Hypothesis-driven Biofeedback Lab/Research Study
 Experiment HP-7: Hypothesis-driven Biofeedback Lab/Research Study What is Biofeedback? Biofeedback is a technique that people can use to learn to control their body's physiological functions. The definition
Experiment HP-7: Hypothesis-driven Biofeedback Lab/Research Study What is Biofeedback? Biofeedback is a technique that people can use to learn to control their body's physiological functions. The definition
ECE ECE PRINCIPLES OF BIOMEDICAL SYSTEMS & DEVICES LAB 1 - ELECTROCARDIOGRAM
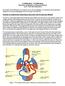 ECE0909.404.01 ECE 0909.504.03 PRINCIPLES OF BIOMEDICAL SYSTEMS & DEVICES LAB 1 - ELECTROCARDIOGRAM The purpose of this laboratory is to introduce you to electrocardiogram, its acquisition and interpretation.
ECE0909.404.01 ECE 0909.504.03 PRINCIPLES OF BIOMEDICAL SYSTEMS & DEVICES LAB 1 - ELECTROCARDIOGRAM The purpose of this laboratory is to introduce you to electrocardiogram, its acquisition and interpretation.
Lab 16. The Cardiovascular System Heart and Blood Vessels. Laboratory Objectives
 Lab 16 The Cardiovascular System Heart and Blood Vessels Laboratory Objectives Describe the anatomical structures of the heart to include the pericardium, chambers, valves, and major vessels. Describe
Lab 16 The Cardiovascular System Heart and Blood Vessels Laboratory Objectives Describe the anatomical structures of the heart to include the pericardium, chambers, valves, and major vessels. Describe
2The Concept of Periodic Functions
 The Concept of Periodic Functions EKG INTRODUCTION The heart is a fist-sized muscle that acts as an electrical generator lying in a conducting medium made of body tissue and fluids. The heart pumps oxygen-rich
The Concept of Periodic Functions EKG INTRODUCTION The heart is a fist-sized muscle that acts as an electrical generator lying in a conducting medium made of body tissue and fluids. The heart pumps oxygen-rich
Experiment HM-7: Electromyogram (EMG) Activity in Antagonistic Muscles and Range of Motion
 Experiment HM-7: Electromyogram (EMG) Activity in Antagonistic Muscles and Range of Motion Exercise 1: Antagonistic Muscles in Forearm Aim: To study the EMG activity in muscles that work in opposition
Experiment HM-7: Electromyogram (EMG) Activity in Antagonistic Muscles and Range of Motion Exercise 1: Antagonistic Muscles in Forearm Aim: To study the EMG activity in muscles that work in opposition
Science in Sport. 204a ECG demonstration (Graph) Read. The Electrocardiogram. ECG Any 12 bit EASYSENSE. Sensors: Loggers: Logging time: 10 seconds
 Sensors: Loggers: ECG Any 12 bit EASYSENSE Science in Sport Logging time: 10 seconds 204a ECG demonstration (Graph) Read Regular medical check ups are essential part of the life of a professional sports
Sensors: Loggers: ECG Any 12 bit EASYSENSE Science in Sport Logging time: 10 seconds 204a ECG demonstration (Graph) Read Regular medical check ups are essential part of the life of a professional sports
BP-600 Noninvasive Blood Pressure Sensor
 Technical Note BP-600 Overview A person's cardiac output, peripheral vascular resistance, blood pressure, and other cardiovascular parameters change in response to the activities and events taking place
Technical Note BP-600 Overview A person's cardiac output, peripheral vascular resistance, blood pressure, and other cardiovascular parameters change in response to the activities and events taking place
Lesson 2 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY II Motor unit recruitment Fatigue
 Physiology Lessons for use with the PC running Windows 98SE, Me, 2000 Pro, XP Pro/Home/Media Lesson 2 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY II Motor unit recruitment Fatigue Manual Revision PL3.7.0 M3.0.6 080706 Richard Pflanzer,
Physiology Lessons for use with the PC running Windows 98SE, Me, 2000 Pro, XP Pro/Home/Media Lesson 2 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY II Motor unit recruitment Fatigue Manual Revision PL3.7.0 M3.0.6 080706 Richard Pflanzer,
Each student should record the ECG of one of the members of the lab group and have their own ECG recorded.
 EXPERIMENT 1 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY The purpose of this experiment is to introduce you to the techniques of electrocardiography and the interpretation of electrocardiograms. In Part A of the experiment, you
EXPERIMENT 1 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY The purpose of this experiment is to introduce you to the techniques of electrocardiography and the interpretation of electrocardiograms. In Part A of the experiment, you
Experiment HM-11: Electromyograms (EMG) for Paired Arm Wrestling
 Experiment HM-11: Electromyograms (EMG) for Paired Arm Wrestling Background The movement of parts of the body is accomplished through a system of levers composed of skeletal muscles and bones. In a lever,
Experiment HM-11: Electromyograms (EMG) for Paired Arm Wrestling Background The movement of parts of the body is accomplished through a system of levers composed of skeletal muscles and bones. In a lever,
Lesson 9. Measuring Emotional Responses to the Acoustic Startle Reflex: Stimulus Habituation & Sensitization
 Measuring Emotional Responses to the Acoustic Startle Reflex: Stimulus Habituation & Sensitization Revised 10 / 29 / 2012 Lesson 9 METHOD: GALVANIC SKIN RESPONSE & THE POLYGRAPH David W. Pittman, Ph.D.
Measuring Emotional Responses to the Acoustic Startle Reflex: Stimulus Habituation & Sensitization Revised 10 / 29 / 2012 Lesson 9 METHOD: GALVANIC SKIN RESPONSE & THE POLYGRAPH David W. Pittman, Ph.D.
Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. J.C. Uyehara, Ph.D. William McMullen David Pittman, Ph.D. Manual Revision PL3.7.0 M3.0.6 Modified by David Pittman
 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY (EMG) Laboratory Motor unit recruitment & Fatigue Comparison of dominant versus non-dominant arm using a within subject repeated measures statistical analysis Written by: Richard Pflanzer,
ELECTROMYOGRAPHY (EMG) Laboratory Motor unit recruitment & Fatigue Comparison of dominant versus non-dominant arm using a within subject repeated measures statistical analysis Written by: Richard Pflanzer,
EKG Sensor Product Number: ENEKG189
 imagine explore learn EKG Sensor Product Number: ENEKG189 Overview An electrocardiogram abbreviated as EKG or ECG is a test that measures the electrical activity of the heartbeat. With each beat, an electrical
imagine explore learn EKG Sensor Product Number: ENEKG189 Overview An electrocardiogram abbreviated as EKG or ECG is a test that measures the electrical activity of the heartbeat. With each beat, an electrical
Lesson 10 Aerobic Exercise Physiology
 Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Science Lab MP40 Lesson 10 Aerobic Exercise Physiology PC running Windows XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Lesson Revision 12.19.2005 BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 42 Aero Camino,
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Science Lab MP40 Lesson 10 Aerobic Exercise Physiology PC running Windows XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Lesson Revision 12.19.2005 BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 42 Aero Camino,
Cardiovascular Physiology Laboratory Clive M. Baumgarten, Ph.D.
 Cardiovascular Physiology Laboratory Clive M. Baumgarten, Ph.D. To pump blood, the heart has a rhythmical sequence of both electrical and mechanical events, the cardiac cycle. The electrical activity,
Cardiovascular Physiology Laboratory Clive M. Baumgarten, Ph.D. To pump blood, the heart has a rhythmical sequence of both electrical and mechanical events, the cardiac cycle. The electrical activity,
How Do We Sense, Think, and Move? -- Lab #11 Bioelectronics Measuring Electrical Properties of the Body
 How Do We Sense, Think, and Move? -- Lab #11 Bioelectronics Measuring Electrical Properties of the Body Experiment #1 Your Body's Resistance Equipment: Digital multimeter, Banana leads Important Equipment
How Do We Sense, Think, and Move? -- Lab #11 Bioelectronics Measuring Electrical Properties of the Body Experiment #1 Your Body's Resistance Equipment: Digital multimeter, Banana leads Important Equipment
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II. Lab #5: Physiology of the Cardiovascular System For Labs Associated With Dr. Thompson s Lectures
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Lab #5: Physiology of the Cardiovascular System For Labs Associated With Dr. Thompson s Lectures References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Lab #5: Physiology of the Cardiovascular System For Labs Associated With Dr. Thompson s Lectures References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form
1724 Lab: Frog Skeletal Muscle Physiology (Marieb Exercise 16A) Marieb/iWorx / Ziser, 2002
 1724 Lab: Frog Skeletal Muscle Physiology (Marieb Exercise 16A) Marieb/iWorx / Ziser, 2002 I. Introduction. Read the introductory material in your lab manual Marieb Ex 16A: Skeletal Muscle Physiology Frog
1724 Lab: Frog Skeletal Muscle Physiology (Marieb Exercise 16A) Marieb/iWorx / Ziser, 2002 I. Introduction. Read the introductory material in your lab manual Marieb Ex 16A: Skeletal Muscle Physiology Frog
Figure 1 The respiratory cycle
 RESPIRATORY CYCLE Introduction Three primary functions of the respiratory system are to provide oxygen for the body's energy needs, provide an outlet for C0 2 and help maintain the ph of the blood plasma.
RESPIRATORY CYCLE Introduction Three primary functions of the respiratory system are to provide oxygen for the body's energy needs, provide an outlet for C0 2 and help maintain the ph of the blood plasma.
Interpreting Electrocardiograms (ECG) Physiology Name: Per:
 Interpreting Electrocardiograms (ECG) Physiology Name: Per: Introduction The heart has its own system in place to create nerve impulses and does not actually require the brain to make it beat. This electrical
Interpreting Electrocardiograms (ECG) Physiology Name: Per: Introduction The heart has its own system in place to create nerve impulses and does not actually require the brain to make it beat. This electrical
INTRODUCTION TO ECG. Dr. Tamara Alqudah
 INTRODUCTION TO ECG Dr. Tamara Alqudah Excitatory & conductive system of the heart + - The ECG The electrocardiogram, or ECG, is a simple & noninvasive diagnostic test which records the electrical
INTRODUCTION TO ECG Dr. Tamara Alqudah Excitatory & conductive system of the heart + - The ECG The electrocardiogram, or ECG, is a simple & noninvasive diagnostic test which records the electrical
Chapter 08. Health Screening and Risk Classification
 Chapter 08 Health Screening and Risk Classification Preliminary Health Screening and Risk Classification Protocol: 1) Conduct a Preliminary Health Evaluation 2) Determine Health /Disease Risks 3) Determine
Chapter 08 Health Screening and Risk Classification Preliminary Health Screening and Risk Classification Protocol: 1) Conduct a Preliminary Health Evaluation 2) Determine Health /Disease Risks 3) Determine
Experiment HC-1: Blood Pressure, Peripheral Circulation, and Body Position
 Experiment HC-1: Blood Pressure, Peripheral Circulation, and Body Position Exercise 1: Blood Pressures from the Left Arm Aim: To determine the systolic and diastolic blood pressures in a reclining subject,
Experiment HC-1: Blood Pressure, Peripheral Circulation, and Body Position Exercise 1: Blood Pressures from the Left Arm Aim: To determine the systolic and diastolic blood pressures in a reclining subject,
Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory Cardiovascular Physiology
 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory Cardiovascular Physiology 1 This lab involves two exercises: 1) Conduction System of the Heart and Electrocardiography and 2) Human Cardiovascular Physiology:
Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory Cardiovascular Physiology 1 This lab involves two exercises: 1) Conduction System of the Heart and Electrocardiography and 2) Human Cardiovascular Physiology:
12 Lead EKG. Brigham and Women's Hospital
 12 Lead EKG What is the heart? The heart is the organ that is responsible for pumping blood rich in oxygen to all parts of the body It is located in the center of the chest and is approximately the size
12 Lead EKG What is the heart? The heart is the organ that is responsible for pumping blood rich in oxygen to all parts of the body It is located in the center of the chest and is approximately the size
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG)
 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) The heart is a muscular organ, which pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. Blood provides the body with oxygen and nutrients, as well as assists in
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) The heart is a muscular organ, which pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. Blood provides the body with oxygen and nutrients, as well as assists in
L63 - Bioelectronics Measuring Electrical Properties of the Body
 L63 - Bioelectronics Measuring Electrical Properties of the Body Experiment #1 Your Body's Resistance Equipment: Digital multimeter, Banana leads Important Equipment Warnings for Today's Lesson In general
L63 - Bioelectronics Measuring Electrical Properties of the Body Experiment #1 Your Body's Resistance Equipment: Digital multimeter, Banana leads Important Equipment Warnings for Today's Lesson In general
Physicians and research nurses trained in the method are responsible for recording electrocardiograms from all subjects.
 Electrocardiogram (ECG) No: 004D 1. Introduction The electrocardiogram provides a baseline reading which shows the electrical alterations within the intracellular potential of myocardial cells. This facilitates
Electrocardiogram (ECG) No: 004D 1. Introduction The electrocardiogram provides a baseline reading which shows the electrical alterations within the intracellular potential of myocardial cells. This facilitates
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HC-5: Body Position, Exercise, and Cardiac Output
 Experiment HC-5: Body Position, Exercise, and Cardiac Output Exercise 1: Cardiac Output While Reclining Aim: To determine the cardiac output of a subject through the measurement of blood pressures and
Experiment HC-5: Body Position, Exercise, and Cardiac Output Exercise 1: Cardiac Output While Reclining Aim: To determine the cardiac output of a subject through the measurement of blood pressures and
CRITICAL THINKING QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS AND CYCLE 2 LAB EXAM TEMPLATE. There are two main mechanisms that work in conjunction to return the blood
 CRITICAL THINKING QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS AND CYCLE 2 LAB EXAM TEMPLATE There are two main mechanisms that work in conjunction to return the blood THE CARDIAC PUMP 1) The forward pull(vis a fronte) This
CRITICAL THINKING QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS AND CYCLE 2 LAB EXAM TEMPLATE There are two main mechanisms that work in conjunction to return the blood THE CARDIAC PUMP 1) The forward pull(vis a fronte) This
Electrocardiogram sensor (ECG/EKG sensor)
 [KDS-1040] Electrocardiogram sensor (ECG/EKG sensor) User's Manual Note This product is designed for educational use only. Not recommended for industrial, medical, commercial use. What is Electrocardiogram?
[KDS-1040] Electrocardiogram sensor (ECG/EKG sensor) User's Manual Note This product is designed for educational use only. Not recommended for industrial, medical, commercial use. What is Electrocardiogram?
Lesson 5 EEG 1 Electroencephalography: Brain Rhythms
 Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Science Lab MP40 PC running Windows XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Lesson 5 EEG 1 Electroencephalography: Brain Rhythms Lesson Revision 2.23.2006 BIOPAC Systems, Inc.
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Science Lab MP40 PC running Windows XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Lesson 5 EEG 1 Electroencephalography: Brain Rhythms Lesson Revision 2.23.2006 BIOPAC Systems, Inc.
3/26/15 HTEC 91. EKG Sign-in Book. The Cardiac Cycle. Parts of the ECG. Waves. Waves. Review of protocol Review of placement of chest leads (V1, V2)
 EKG Sign-in Book HTEC 91 Review of protocol Review of placement of chest leads (V1, V2) Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 2 http://www.cvphysiology.com/arrhythmias/a013c.htm The Cardiac Cycle Represents
EKG Sign-in Book HTEC 91 Review of protocol Review of placement of chest leads (V1, V2) Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 2 http://www.cvphysiology.com/arrhythmias/a013c.htm The Cardiac Cycle Represents
Biopac Student Lab Lesson 3 ELECTROENCEPHALOGRAPHY (EEG) I Analysis Procedure. Rev
 42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 3 ELECTROENCEPHALOGRAPHY (EEG) I Analysis Procedure Rev. 12112014 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana
42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 3 ELECTROENCEPHALOGRAPHY (EEG) I Analysis Procedure Rev. 12112014 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana
Lesson 1: Types of ECG s
 Electrocardiography Lesson 1: Types of ECG s Objectives: Distinguish between a single-channel ECG machine and a multi-channel machine. Distinguish between a manual ECG machine and an automatic ECG machine.
Electrocardiography Lesson 1: Types of ECG s Objectives: Distinguish between a single-channel ECG machine and a multi-channel machine. Distinguish between a manual ECG machine and an automatic ECG machine.
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HP-6: Cynicism/Hostility and the Hot Reactor
 Experiment HP-6: Cynicism/Hostility and the Hot Reactor Exercise 1: Baseline Heart Rate and Blood Pressure Aim: To determine the resting heart rate and blood pressure of the subject. Procedure 1. Select
Experiment HP-6: Cynicism/Hostility and the Hot Reactor Exercise 1: Baseline Heart Rate and Blood Pressure Aim: To determine the resting heart rate and blood pressure of the subject. Procedure 1. Select
Biopac Student Lab Lesson 8 RESPIRATORY CYCLE I Analysis Procedure. Rev
 42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 8 RESPIRATORY CYCLE I Analysis Procedure Rev. 12292017 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University
42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 8 RESPIRATORY CYCLE I Analysis Procedure Rev. 12292017 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University
Blood Pressure Laboratory
 Introduction The blood that circulates throughout the body maintains a flow and pressure. The nervous system can change the flow and pressure based on the particular needs at a given time. For example,
Introduction The blood that circulates throughout the body maintains a flow and pressure. The nervous system can change the flow and pressure based on the particular needs at a given time. For example,
Experiment HP-13: The Gaze Cue Paradigm
 Experiment HP-13: The Gaze Cue Paradigm Background During almost all social interactions, people s eyes convey information about their direction of attention as well as their emotional and mental status.
Experiment HP-13: The Gaze Cue Paradigm Background During almost all social interactions, people s eyes convey information about their direction of attention as well as their emotional and mental status.
ELECTROMYOGRAM ANALYSIS OF MUSCLE FUNCTION INTRODUCTION
 ELECTROMYOGRAM ANALYSIS OF MUSCLE FUNCTION STANDARDS: 3.3.10.B - Explain cell functions and processes in terms of chemical reactions and energy changes. 3.3.12.B - Evaluate relationships between structure
ELECTROMYOGRAM ANALYSIS OF MUSCLE FUNCTION STANDARDS: 3.3.10.B - Explain cell functions and processes in terms of chemical reactions and energy changes. 3.3.12.B - Evaluate relationships between structure
MR Advance Techniques. Cardiac Imaging. Class IV
 MR Advance Techniques Cardiac Imaging Class IV Heart The heart is a muscular organ responsible for pumping blood through the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions. Layers of the heart Endocardium
MR Advance Techniques Cardiac Imaging Class IV Heart The heart is a muscular organ responsible for pumping blood through the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions. Layers of the heart Endocardium
11/18/13 ECG SIGNAL ACQUISITION HARDWARE DESIGN. Origin of Bioelectric Signals
 ECG SIGNAL ACQUISITION HARDWARE DESIGN Origin of Bioelectric Signals 1 Cell membrane, channel proteins Electrical and chemical gradients at the semi-permeable cell membrane As a result, we get a membrane
ECG SIGNAL ACQUISITION HARDWARE DESIGN Origin of Bioelectric Signals 1 Cell membrane, channel proteins Electrical and chemical gradients at the semi-permeable cell membrane As a result, we get a membrane
Exercise 1: Eye-Hand Reaction Times Aim: To measure the reaction time of a subject to a visual cue when responding with the hand.
 Experiment HN-4: Hand vs. Foot Reactions Exercise 1: Eye-Hand Reaction Times Aim: To measure the reaction time of a subject to a visual cue when responding with the hand. Procedure 1. Instruct the subject
Experiment HN-4: Hand vs. Foot Reactions Exercise 1: Eye-Hand Reaction Times Aim: To measure the reaction time of a subject to a visual cue when responding with the hand. Procedure 1. Instruct the subject
By the end of this lecture, you will be able to: Understand the 12 lead ECG in relation to the coronary circulation and myocardium Perform an ECG
 By the end of this lecture, you will be able to: Understand the 12 lead ECG in relation to the coronary circulation and myocardium Perform an ECG recording Identify the ECG changes that occur in the presence
By the end of this lecture, you will be able to: Understand the 12 lead ECG in relation to the coronary circulation and myocardium Perform an ECG recording Identify the ECG changes that occur in the presence
PHYS 1112L - Introductory Physics Laboratory II
 PHYS 1112L - Introductory Physics Laboratory II Laboratory Advanced Sheet EKG Lab (IBEAM) 1. Objectives. The objectives of this laboratory are a. to study the electrical activity of human heart b. to observe
PHYS 1112L - Introductory Physics Laboratory II Laboratory Advanced Sheet EKG Lab (IBEAM) 1. Objectives. The objectives of this laboratory are a. to study the electrical activity of human heart b. to observe
12.2 Monitoring the Human Circulatory System
 12.2 Monitoring the Human Circulatory System Video 1: 3D Animation of Heart Pumping Blood blood flow through the heart... Video 2: Hank Reviews Everything on the Heart https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x9zz6tcxari
12.2 Monitoring the Human Circulatory System Video 1: 3D Animation of Heart Pumping Blood blood flow through the heart... Video 2: Hank Reviews Everything on the Heart https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x9zz6tcxari
BSL PRO Lesson H03: Nerve Conduction Velocity: Along the Ulnar Nerve of a Human Subject
 Updated 12-22-03 BSL PRO Lesson H03: Nerve Conduction Velocity: Along the Ulnar Nerve of a Human Subject This PRO lesson describes hardware and software setup of the BSL PRO System to record and measure
Updated 12-22-03 BSL PRO Lesson H03: Nerve Conduction Velocity: Along the Ulnar Nerve of a Human Subject This PRO lesson describes hardware and software setup of the BSL PRO System to record and measure
Biopac Student Lab Lesson 20 SPINAL CORD REFLEXES Analysis Procedure. Rev
 42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 20 SPINAL CORD REFLEXES Analysis Procedure Rev. 12292017 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University
42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 20 SPINAL CORD REFLEXES Analysis Procedure Rev. 12292017 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University
This presentation will deal with the basics of ECG description as well as the physiological basics of
 Snímka 1 Electrocardiography basics This presentation will deal with the basics of ECG description as well as the physiological basics of Snímka 2 Lecture overview 1. Cardiac conduction system functional
Snímka 1 Electrocardiography basics This presentation will deal with the basics of ECG description as well as the physiological basics of Snímka 2 Lecture overview 1. Cardiac conduction system functional
Experiment HE-12: Targeted Exercise with Wireless Electrocardiogram (ECG)
 Experiment HE-12: Targeted Exercise with Wireless Electrocardiogram (ECG) Get Your Cardio On Preparations for this experiment need to be reviewed with the students in advance. There will be exercise routines
Experiment HE-12: Targeted Exercise with Wireless Electrocardiogram (ECG) Get Your Cardio On Preparations for this experiment need to be reviewed with the students in advance. There will be exercise routines
The Function of an ECG in Diagnosing Heart Conditions. A useful guide to the function of the heart s electrical system for patients receiving an ECG
 The Function of an ECG in Diagnosing Heart Conditions A useful guide to the function of the heart s electrical system for patients receiving an ECG Written by Erhan Selvi July 28, 2014 Audience and Scope
The Function of an ECG in Diagnosing Heart Conditions A useful guide to the function of the heart s electrical system for patients receiving an ECG Written by Erhan Selvi July 28, 2014 Audience and Scope
Cardiac Telemetry Self Study: Part One Cardiovascular Review 2017 THINGS TO REMEMBER
 Please review the above anatomy of the heart. THINGS TO REMEMBER There are 3 electrolytes that affect cardiac function o Sodium, Potassium, and Calcium When any of these electrolytes are out of the normal
Please review the above anatomy of the heart. THINGS TO REMEMBER There are 3 electrolytes that affect cardiac function o Sodium, Potassium, and Calcium When any of these electrolytes are out of the normal
ECG SENSOR ML84M USER S GUIDE. CENTRE FOR MICROCOMPUTER APPLICATIONS
 ECG SENSOR ML84M USER S GUIDE CENTRE FOR MICROCOMPUTER APPLICATIONS http://www.cma-science.nl Short description The ECG sensor measures electrical potentials produced by the heart (Electro- cardiogram).
ECG SENSOR ML84M USER S GUIDE CENTRE FOR MICROCOMPUTER APPLICATIONS http://www.cma-science.nl Short description The ECG sensor measures electrical potentials produced by the heart (Electro- cardiogram).
Sheet 5 physiology Electrocardiography-
 *questions asked by some students Sheet 5 physiology Electrocardiography- -why the ventricles lacking parasympathetic supply? if you cut both sympathetic and parasympathetic supply of the heart the heart
*questions asked by some students Sheet 5 physiology Electrocardiography- -why the ventricles lacking parasympathetic supply? if you cut both sympathetic and parasympathetic supply of the heart the heart
Objectives of the Heart
 Objectives of the Heart Electrical activity of the heart Action potential EKG Cardiac cycle Heart sounds Heart Rate The heart s beat separated into 2 phases Relaxed phase diastole (filling of the chambers)
Objectives of the Heart Electrical activity of the heart Action potential EKG Cardiac cycle Heart sounds Heart Rate The heart s beat separated into 2 phases Relaxed phase diastole (filling of the chambers)
Heart Rate, Blood Pressure, and Exercise. Evaluation copy
 Heart Rate, Blood Pressure, and Exercise Computer 11 The adaptability of the heart can be observed during exercise, when the metabolic activity of skeletal muscles increases. The cardiovascular system,
Heart Rate, Blood Pressure, and Exercise Computer 11 The adaptability of the heart can be observed during exercise, when the metabolic activity of skeletal muscles increases. The cardiovascular system,
iworx Sample Lab Experiment AN-5: Cockroach Leg Mechanoreceptors
 Experiment AN-5: Cockroach Leg Mechanoreceptors Exercise 1: Chordotonal Organs Aim: To explore the basic characteristics of the chordotonal organs, their response to direction and intensity of leg movement,
Experiment AN-5: Cockroach Leg Mechanoreceptors Exercise 1: Chordotonal Organs Aim: To explore the basic characteristics of the chordotonal organs, their response to direction and intensity of leg movement,
The cardiovascular system is composed of the heart and blood vessels that carry blood to and from the body s organs. There are 2 major circuits:
 1 The cardiovascular system is composed of the heart and blood vessels that carry blood to and from the body s organs. There are 2 major circuits: pulmonary and systemic. The pulmonary goes out to the
1 The cardiovascular system is composed of the heart and blood vessels that carry blood to and from the body s organs. There are 2 major circuits: pulmonary and systemic. The pulmonary goes out to the
Electrocardiography Normal 5. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD
 Electrocardiography Normal 5 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Objectives 2 1. Describe the different waves in a normal electrocardiogram. 2. Recall the normal P-R and Q-T interval time of the QRS wave. 3.
Electrocardiography Normal 5 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Objectives 2 1. Describe the different waves in a normal electrocardiogram. 2. Recall the normal P-R and Q-T interval time of the QRS wave. 3.
FT-302 Force Transducer
 Technical Note FT-302 LabScribe is a trademark of 2015 Overview The FT-302 is a high-sensitivity dual-range research grade force transducer designed to measure forces in the 0.005 to 10 gram and 0 to 100
Technical Note FT-302 LabScribe is a trademark of 2015 Overview The FT-302 is a high-sensitivity dual-range research grade force transducer designed to measure forces in the 0.005 to 10 gram and 0 to 100
Matters of the Heart: Comprehensive Cardiology SARAH BEANLANDS RN BSCN MSC
 Matters of the Heart: Comprehensive Cardiology SARAH BEANLANDS RN BSCN MSC Who am I? Class Outline Gross anatomy of the heart Trip around the heart Micro anatomy: cellular and tissue level Introduction
Matters of the Heart: Comprehensive Cardiology SARAH BEANLANDS RN BSCN MSC Who am I? Class Outline Gross anatomy of the heart Trip around the heart Micro anatomy: cellular and tissue level Introduction
CASE 10. What would the ST segment of this ECG look like? On which leads would you see this ST segment change? What does the T wave represent?
 CASE 10 A 57-year-old man presents to the emergency center with complaints of chest pain with radiation to the left arm and jaw. He reports feeling anxious, diaphoretic, and short of breath. His past history
CASE 10 A 57-year-old man presents to the emergency center with complaints of chest pain with radiation to the left arm and jaw. He reports feeling anxious, diaphoretic, and short of breath. His past history
Birmingham Regional Emergency Medical Services System
 Birmingham Regional Emergency Medical Services System 2018 ALCTE Summer Conference EKG Basics Brian Gober, MAT, ATC, NRP, CSCS Education Services Manager ECC Training Center Coordinator Birmingham Regional
Birmingham Regional Emergency Medical Services System 2018 ALCTE Summer Conference EKG Basics Brian Gober, MAT, ATC, NRP, CSCS Education Services Manager ECC Training Center Coordinator Birmingham Regional
1 Non-invasive measurement of arterial pressure
 Non-invasive measurement of arterial pressure I. Background A. Circulatory systems Human circulation takes place in a closed system that consists of two subsystems, pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation,
Non-invasive measurement of arterial pressure I. Background A. Circulatory systems Human circulation takes place in a closed system that consists of two subsystems, pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation,
ECG and Cardiac Electrophysiology
 ECG and Cardiac Electrophysiology Simon Some very basic electrophysiology Intracellular fluid: 10 mm Na, 140 mm K, etc. K Na-K ATPase Extracellular fluid: 140mM Na, 4mM K, etc. Na Ion gradient plus selective
ECG and Cardiac Electrophysiology Simon Some very basic electrophysiology Intracellular fluid: 10 mm Na, 140 mm K, etc. K Na-K ATPase Extracellular fluid: 140mM Na, 4mM K, etc. Na Ion gradient plus selective
