Summary. Rong WangABCE, Xiang-Jiu XuADG, Gang HuangAG, Xing ZhouEF, Wen-Wen ZhangA, Ya-Qiong MaF, Xiao-na ZuoA. Background
|
|
|
- Madlyn Marsh
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: DOI: /PJR ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: Accepted: Published: Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection C Statistical Analysis D Data Interpretation E Manuscript Preparation F Literature Search G Funds Collection Comparison of Image Quality, Diagnostic Accuracy and Radiation Dose Between Flash Model and Retrospective ECG-Triggered Protocols in Dual Source Computed Tomography (DSCT) in Congenital Heart Diseases Rong WangABCE, Xiang-Jiu XuADG, Gang HuangAG, Xing ZhouEF, Wen-Wen ZhangA, Ya-Qiong MaF, Xiao-na ZuoA Department of Radiology, Gansu Provincial Hospital, Lanzhou, Gansu, P.R. China Author s address: Rong Wang, Gansu University Traditional Chinese and Department of Radiology, Gansu Provincial Hospital, Lanzhou, China, Wang R1821@126.com, and Xiang-Jiu Xu, Department of Radiology, Gansu Provincial Hospital, Lanzhou, China, xvxiangjiu@sina.com Background: Material/Methods: Results: Conclusions: MeSH Keywords: Summary Dual source computed tomography (DSCT) plays an important role in the diagnosis of congenital heart diseases (CHD). However, the issue of radiation-related side effects constitutes a wide public concern. The aim of the study was to explore the differences in diagnostic accuracy, radiation dose and image quality between a prospectively ECG triggered high pitch spiral acquisition (flash model) and a retrospective ECG-gated protocol of DSCT used for the detection of CHD. The study included 58 patients with CHD who underwent a DSCT examination, including two groups of 29 patients in each protocol. Then, both subjective and objective image quality, diagnostic accuracy and radiation dose were compared between the two protocols. The image quality and the total as well as partial diagnostic accuracy did not differ significantly between the protocols. The radiation dose in the flash model was obviously lower than that in the retrospective model (P<0.05). Compared to the retrospective protocol, the flash model can significantly reduce the dose of radiation, while maintaining both diagnostic accuracy and image quality. Image Enhancement Jervell-Lange Nielsen Syndrome Multidetector Computed Tomography Radiation Dosage PDF file: Background CT has seen a rapid technical improvement in recent years, with improved temporal and spatial resolutions and better image post-processing. Moreover, CT is a noninvasive procedure. All these advantages have made CT a useful modality for the detection of congenital heart diseases (CHD), especially in the case of complex CHD. While CT imaging of CHD has become more popualr, concerns have been raised about the overuse of ionizing radiation in vulnerable patients, especially in infants and young children. How to obtain a satisfying CT image quality with an ultralow radiation dose in infants and young children with CHD remains challenging [1]. A second generation dual source CT system has the advantage of providing a high-pitch spiral mode, which makes it possible to acquire the entire data within a single cardiac cycle. Some studies [2] have shown ultra-low radiation doses of less than 0.1 msv. The aim of the study was to explore the differences in diagnostic accuracy, radiation dose and image quality between a prospectively ECG-triggered high pitch spiral acquisition (flash model) and a retrospective ECG-triggered model in dual source computed tomography (DSCT) for the detection of congenital heart diseases. 114
2 Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: Wang R. et al. Comparison of image quality, diagnostic accuracy Table 1. Comparison of radiation dose. Material and Methods Patients From January 2015 to February 2016, we included 58 patients with CHD who underwent a DSCT examination. The patients were divided into two groups - 29 patients in the flash group (mean age: 5.89 years; range: 5 months 35years; male: 19; female: 10) and 29 patients in the retrospective protocol group (mean age: 4.96 years; range: 4 months 21years; male: 16; female: 13). In total, 40 patients underwent surgical treatment. Written consent was obtained from the patients or their parents. DSCT protocol All patients underwent flash CT (Siemens Definition). We protected vital organs of patients before scanning. The patients were trained to comply with breathing restrictions, and infants were examined under general anesthesia or chloral hydrate mg/Kg. ECG-gated modulation, pitch automatic matching technology and Sinogram Affirmed Iterative Reconstruction (SAFIRE) were used. The scan range was from the thoracic inlet to the bottom of the diaphragm. The parameters of flash were high-pitch of 3.4; starting at 55% of the R R interval; acquisition collimation: mm; slice thickness: 0.6 mm; gantry rotation time: 0.28 second; tube voltage: 80 Kv; Care Dose 4D technology was used, the reference tube current was 110 mas. The parameters of the retrospective ECG-gated protocol were pitch: 0.17; starting at BestDiast; the other parameters were similar to flash. Contrast medium used was Visipaque (270 mg/ml; GE Healthcare), flow rate: 0.17 ml/kg/s with bolus tracking, the region of interest was double the ventricle level when the density value of left ventricle reached 100 HU. The scan commenced automatically after a delay of 2 seconds. Diagnostic analysis Flash Retrospective t P CTDIvol 1.14± ± DLP 23.51± ± ED 0.45± ± CTDIvol CT dose index volume; DLP dose length product; ED effective dose. (ED) was estimated according to an equation (ED=DLPxk) where k is the conversion coefficient [1,3] varying according to age (infants up to 4 months, k=(0.039 m Sv mgy 1 cm 1, from 4 months to 1 year of age, k=0.026 m Sv mgy 1 cm 1, from1 year to 6 years of age, k=0.018 m Sv mgy 1 cm 1 and older than 6 years old, k=0.014 m Sv mgy 1 cm 1 ). Image quality analysis The subjective image quality was estimated according to a five-point scale [4], where 5 was excellent; 4 was good; 3 was applicable; 2 was poor; 1 was unable to diagnose. Sores 3-5 were satisfying. The objective image quality was estimated based on CT values, image noise, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR). CT values and image noise were measured on the ascending aorta, main pulmonary artery, left ventricular cavity and dorsal muscles. ROI were drawn as large as possible. Then, we calculated SNR and CNR according to an equation (SNR=CT/image noise, CNR=(CT CT muscle)/image noise) [5]. Statistical analysis The 17.0 SPSS software was used for statistical analysis. The Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare subjective image quality. Objective parameters and radiation dose were compared by the T test. Diagnostic accuracy was compared by the chi-square test. A P value lower than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Results There was no statistical difference in both age and weight between the two groups. All patients successfully completed the examinations. Two experienced radiologists analyzed the data. The postprocessing techniques of volume rendering (VR), maximum intensity projection (MIP) and multiplanar reformation (MPR) were used. Surgery findings were treated as the gold standard. Cardiovascular anomalies were divided into intracardiac anomalies, large vascular connecting anomalies of the heart and extra-cardiac anomalies according to the anatomical structure. We calculated the diagnostic accuracy. Radiation dose Dose length product (DLP) and CT dose index volume (CTDIvol) of the two groups were recorded. Effective dose Radiation dose in two groups The radiation dose measured by flash was obviously lower than that in the retrospective protocol, and there was a statistically significant difference. The effective radiation dose was reduced by 87.7% (Table 1). Image quality in two groups All images were of a satisfying quality. Some examples are shown in Figures
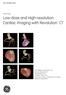
3 Original Article Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: A B Figure 1. Multiplanar reformation sagittal (A) and coronal (B) images of a 4-year-old girl with an overriding aorta (arrow B) and right ventricular outflow tract stenosis (arrow A), obtained with the use of the retrospective ECG-gated protocol. A B C Figure 2. Multiplanar reformation coronal (A), sagittal (B) and axial (C) images of a 4-year-old boy with an overriding aorta (arrow A) and right ventricular outflow tract stenosis (arrows B, C), obtained with the use of the flash model. A B C Figure 3. Multiplanar reformation sagittal (A) and volume rendering (B) images of a 3-year-old girl with a patent ductus arteriosus (arrows A, B) obtained with the use of the retrospective ECG-gated protocol. Maximum intensity projection (C) images of a 3-year-old boy with a patent ductus arteriosus (arrow C) obtained with the use of the flash model. 116
4 Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: Wang R. et al. Comparison of image quality, diagnostic accuracy Table 2. Comparison of objective image quality. Flash Retrospective t/z P CT value AA ± ± MPA ± ± LV ± ± Muscle 70.82± ± Image noise AA 29.31± ± MPA 29.17± ± LV 33.10± ± Muscle 27.10± ± SNR AA 18.11± ± MPA 15.63± ± LV 16.12± ± Muscle 3.13± ± CNR AA 15.33± ± MPA 13.00± ± LV 13.65± ± SNR signal-to-noise ratio; CNR contrast-to-noise ratio. The subjective image quality was evaluated in the range of 3 5 points, the mean score was 3.72(±0.80) in the flash group and 4.00(±0.75) in the retrospective group, with no significant difference (Z= 1.221, P=0.222). There were no statistically significant differences in any of the objective parameters between the two groups (Table 2). Diagnostic accuracy in two groups The overall diagnostic accuracy of the flash and retrospective models was 87.1(81/93) and 86.7% (65/75), respectively, with no statistically significant difference (c 2 =0.007, P=0.935), (Table 3). With respect to the intra-cardiac anomalies, the diagnostic accuracy of the flash and retrospective models was 82.9% (29/35) and 83.3% (25/30), respectively, with no statistically significant difference (c 2 =0.030, P=0.959). With respect to the large vascular connecting anomalies of the heart, the diagnostic accuracy was 91.3% (21/23) and 84.2% (16/19), respectively, with no statistically significant difference between the two groups (c 2 =0.052, P=0.820). With respect to the extra-cardiac anomalies, it was 88.6%(31/35) and 92.3% (24/26), respectively, with no statistically significant difference (c 2 =0.002, P=0.960). Discussion Congenital heart disease is common in infants and young children, and most congenital heart diseases can be cured or relieved by surgical correction. An accurate and detailed preoperative evaluation plays an important role in planning surgery, which is key to a successful repair of CHD [6]. A good image quality guarantees accurate diagnosis. Our study showed that the two scanning modes of DSCT can obtain satisfying image quality. The image quality in the retrospective group was better than that in the flash group, however, there was no statistically significant difference. In the flash model, regular heart rate is key to obtaining a satisfactory image quality, because the data are acquired within a certain time frame of a single cardiac cycle. The advantage of the retrospective ECG-gated protocol with dual-source CT is that it is not limited by heart rate, which is suitable for patients with a high heart rate [7]. In addition, the retrospective model can analyze cardiac function. Our study showed that the two scanning modes of DSCT have a high diagnostic accuracy in detecting cardiovascular anomalies. Both the total and partial diagnostic accuracy was comparable between the models. The volume data obtained from CT can better show subtle structures through powerful post-processing techniques. CT has an absolute advantage for diagnosing extra-cardiac anomalies [8,9], coronary artery anomalies [6,10] and assessing the development of pulmonary artery before surgery [11]. Studies have shown that children with CHD receive too much cumulative doses that can cause DNA damage [12]. Therefore, reducing radiation dose is currently the most important issue for infants and young children. It reminds radiologists that before each examination the principle of as low as reasonably achievable (ALARA) should be applied.. The dose reduction strategies must be well and properly used, and include reduced tube voltage, highpitch scans, prospective ECG-gated modes and technologies of automated tube current modulation [13,14]. Our study employed the above method as we aimed to reduce 117
5 Original Article Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: Table 3. Comparison of diagnostic accuracy. Cardiovascular deformities Flash Retrospective Surgery Detect Fault Surgery Detect Fault Intra-cardiac anomalies Atrial septal defect Right ventricular hypertrophy Ventricular septal defect Discrete subaortic membrane 1 1 Patent foramen ovale Heart-large vascular connecting anomalies Overriding aorta Pulmonary arterial hypertension Right ventricular outflow tract stenosis Right ventricular outflow tract broadening 1 1 Transposition of great arteries Double outlet right ventricle Extra-cardiac anomalies Pulmonary artery stenosis Coarctation of the aorta patent ductus arteriosus Coronary artery anomaly Collateral abnormal Persistent left superior vena cava Aortopulmonary window 1 1 Pulmonary artery atresia 1 1 Anomalous pulmonary venous return 1 1 Cor triatriatum 1 1 Total the radiation dose and we also protected the vital organs of patients before scans. Moreover, we used the Care Dose 4D technology, ECG-gated modulation, pitch automatic matching technology and SAFIRE. Several studies have shown the advantage of SAFIRE in image noise reduction and improved image quality [15 17], which has been used for cardiac CT and have effectively reduced the radiation dose. Our study showed that the radiation dose measured by the flash mode was lower than that in the retrospective protocol (P<0.05), and the effective dose was reduced by 87.7%. Schuhbaeck et al. [2] reported an average radiation dose of less than 0.1 msv. This is attributed to a high-pitch spiral. The reason why our study showed a slightly higher radiation dose is that we included adults. How to obtain a satisfying diagnostic CT image quality with ultra-low radiation doses in infants and young children with CHD still remains challenging. Conclusions In conclusion, the two models can achieve a satisfying image quality and have a high diagnostic accuracy. The flash model can significantly help reduce the radiation dose as compared to the retrospective ECG-triggered protocol. 118
6 Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: Wang R. et al. Comparison of image quality, diagnostic accuracy References: 1. Zheng M, Zhao H, Xu J et al: Image quality of ultra-low-dose dualsource CT angiography using high-pitch spiral acquisition and iterative reconstruction in young children with congenital heart disease. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr, 2013; 7(6): Schuhbaeck A, Achenbach S, Layritz C et al: Image quality of ultralow radiation exposure coronary Ct angiography with an effective dose 0.1 Msv using high-pitch spiral acquisition and raw data-based iterative reconstruction. Eur Radiol, 2013; 23(3): Achenbach S, Anders K, Kalender WA: Dual-source cardiac computed tomography: image quality and dose considerations. Eur Radiol, 2008; 18(6): Nie P, Li H, Duan Y et al: Impact of Sinogram Affirmed Iterative Reconstruction (SAFIRE) algorithm on image quality with 70 kvptube-voltage dual-source CT angiography in children with congenital heart disease. PLoS One, 2014, 9(3): e Tricarico F, Hlavacek A M, Schoepf UJ et al: Cardiovascular CT angiography in neonates and children: image quality and potential for radiation dose reduction with iterative image reconstruction techniques. Eur Radiol, 2013; 23(5): Yu FF, Lu B, Gao Y et al: Congenital anomalies of coronary arteries in complex congenital heart disease: Diagnosis and analysis with dualsource CT. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr, 2013; 7(6): Nakagawa M, Ozawa Y, Nomura N et al: Utility of dual source CT with ECG triggered high pitch spiral acquisition (Flash Spiral Cardio mode) to evaluate morphological features of ventricles in children with complex congenital heart defects. Jpn J Radiol, 2016; 34(4): Pache G, Grohmann J, Bulla S et al: Prospective electrocardiographytriggered CT angiography of the great thoracic vessels in infants and toddlers with congenital heart disease: Feasibility and image quality. Eur J Radiol, 2011; 80(3): Sedaghat F, Pouraliakbar H, Motevalli M et al: Comparison of diagnostic accuracy of dual-source CT and conventional angiography in detecting congenital heart diseases. Pol J Radiol, 2014, 79: Wang XM, Wu LB, Sun C et al: Clinical application of 64-slice spiral CT in the diagnosis of the tetralogy of fallot. Eur J Radiol, 2007; 64(2): Reimann A J, Rinck D, Birinciaydogan A et al: Dual-source computed tomography: advances of improved temporal resolution in coronary plaque imaging. Invest Radiol, 2007; 42(42): Aitali L, Andreassi MG, Foffa I et al: Cumulative patient effective dose and acute radiation-induced chromosomal DNA damage in children with congenital heart disease. Heart, 2010; 96(4): Jun BR, Yong HS, Kang EY et al: 64-slice coronary computed tomography angiography using low tube voltage of 80 kv in subjects with normal body mass indices: Comparative study using 120 kv. Acta Radiol, 2012; 53(10): Liu Y, Li J, Zhao H et al: Image quality and radiation dose of dualsource CT cardiac angiography using prospective ECG-triggering technique in pediatric patients with congenital heart disease. J Cardiothorac Surg, 2016, 11: Han BK, Grant KLR, Garberich R et al: Assessment of an iterative reconstruction algorithm (SAFIRE) on image quality in pediatric cardiac CT datasets. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr, 2012; 6(6): Moscariello A, Takx R, Schoepf UJ et al: Coronary CT angiography: Image quality, diagnostic accuracy, and potential for radiation dose reduction using a novel iterative image reconstruction technique comparison with traditional filtered back projection. Eur Radiol, 2011; 21(10): Ebersberger U, Tricarico F, Schoepf UJ et al: CT evaluation of coronary artery stents with iterative image reconstruction: Improvements in image quality and potential for radiation dose reduction. Eur Radiol, 2013; 23(1):
Low-dose prospective ECG-triggering dual-source CT angiography in infants and children with complex congenital heart disease: first experience
 Low-dose prospective ECG-triggering dual-source CT angiography in infants and children with complex congenital heart disease: first experience Ximing Wang, M.D., Zhaoping Cheng, M.D., Dawei Wu, M.D., Lebin
Low-dose prospective ECG-triggering dual-source CT angiography in infants and children with complex congenital heart disease: first experience Ximing Wang, M.D., Zhaoping Cheng, M.D., Dawei Wu, M.D., Lebin
Original Article. Yohei Marukawa a,b*, Shuhei Sato b, Takashi Tanaka b, Akihiro Tada b, Yuichiro Kanie c, and Susumu Kanazawa b
 Original Article http ://escholarship.lib.okayama-u.ac.jp/amo/ Evaluating Low-kV Dual-source CT Angiography by High-pitch Spiral Acquisition and Iterative Reconstruction in Pediatric Congenital Heart Disease
Original Article http ://escholarship.lib.okayama-u.ac.jp/amo/ Evaluating Low-kV Dual-source CT Angiography by High-pitch Spiral Acquisition and Iterative Reconstruction in Pediatric Congenital Heart Disease
Introduction ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 Pediatr Radiol (2015) 45:1472 1479 DOI 10.1007/s00247-015-3372-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Image quality at low tube voltage (70 kv) and sinogram-affirmed iterative reconstruction for computed tomography in infants
Pediatr Radiol (2015) 45:1472 1479 DOI 10.1007/s00247-015-3372-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Image quality at low tube voltage (70 kv) and sinogram-affirmed iterative reconstruction for computed tomography in infants
Original Article Application of flash dual-source CT at low radiation dose and low contrast medium dose in triple-rule-out (tro) examination
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(11):21898-21905 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0015005 Original Article Application of flash dual-source CT at low radiation dose and low contrast medium dose in triple-rule-out
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(11):21898-21905 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0015005 Original Article Application of flash dual-source CT at low radiation dose and low contrast medium dose in triple-rule-out
Index. radiologic.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ALCAPA. See Anomalous left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery. Angiosarcoma computed tomographic assessment of, 809 811 Anomalous
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ALCAPA. See Anomalous left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery. Angiosarcoma computed tomographic assessment of, 809 811 Anomalous
128-slice dual-source CT coronary angiography using highpitch scan protocols in 102 patients
 128-slice dual-source CT coronary angiography using highpitch scan protocols in 102 patients Poster No.: C-0634 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Cardiac Authors: Y. H. Choe, J. W. Lee,
128-slice dual-source CT coronary angiography using highpitch scan protocols in 102 patients Poster No.: C-0634 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Cardiac Authors: Y. H. Choe, J. W. Lee,
Cardiac Computed Tomography
 Cardiac Computed Tomography Authored and approved by Koen Nieman Stephan Achenbach Francesca Pugliese Bernard Cosyns Patrizio Lancellotti Anastasia Kitsiou Contents CARDIAC COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Page 1.
Cardiac Computed Tomography Authored and approved by Koen Nieman Stephan Achenbach Francesca Pugliese Bernard Cosyns Patrizio Lancellotti Anastasia Kitsiou Contents CARDIAC COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Page 1.
A study on CT pulmonary angiography at low kv and low-concentration contrast medium using iterative reconstruction.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (17): 7683-7687 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info A study on CT pulmonary angiography at low kv and low-concentration contrast medium using iterative reconstruction. Yanhe
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (17): 7683-7687 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info A study on CT pulmonary angiography at low kv and low-concentration contrast medium using iterative reconstruction. Yanhe
Application of CARE kv and SAFIRE in Contrast-Enhanced CT Examination on Thorax
 Application of CARE kv and SAFIRE in Contrast-Enhanced CT Examination on Thorax Poster No.: C-0013 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit Z. Dejian 1, X. Zhuodong 2, J. Hui 2, L. Xiao 3 ;
Application of CARE kv and SAFIRE in Contrast-Enhanced CT Examination on Thorax Poster No.: C-0013 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit Z. Dejian 1, X. Zhuodong 2, J. Hui 2, L. Xiao 3 ;
Aortic Coarctation: Evaluation with Computed Tomography Angiography in Pediatric Patients
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 2, June: 63-70, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Aortic Coarctation: Evaluation with Computed Tomography Angiography in Pediatric Patients MOHAMED ZAKI, M.D.
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 2, June: 63-70, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Aortic Coarctation: Evaluation with Computed Tomography Angiography in Pediatric Patients MOHAMED ZAKI, M.D.
Low Dose Era in Cardiac CT
 Low Dose Era in Cardiac CT DIANA E. LITMANOVICH, MD Department of Radiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Disclosures Neither I nor my immediate family members have a financial
Low Dose Era in Cardiac CT DIANA E. LITMANOVICH, MD Department of Radiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Disclosures Neither I nor my immediate family members have a financial
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
Cardiac CT Techniques in Neonates (and infants)
 Cardiac CT Techniques in Neonates (and infants) Siddharth P. Jadhav, MD Director, Body CT and MRI Edward B. Singleton Department of Pediatric Radiology Texas Children s Hospital Disclosures None Objectives
Cardiac CT Techniques in Neonates (and infants) Siddharth P. Jadhav, MD Director, Body CT and MRI Edward B. Singleton Department of Pediatric Radiology Texas Children s Hospital Disclosures None Objectives
Fundamentals, Techniques, Pitfalls, and Limitations of MDCT Interpretation and Measurement
 Fundamentals, Techniques, Pitfalls, and Limitations of MDCT Interpretation and Measurement 3 rd Annual Imaging & Physiology Summit November 20-21, 21, 2009 Seoul, Korea Wm. Guy Weigold, MD, FACC Cardiovascular
Fundamentals, Techniques, Pitfalls, and Limitations of MDCT Interpretation and Measurement 3 rd Annual Imaging & Physiology Summit November 20-21, 21, 2009 Seoul, Korea Wm. Guy Weigold, MD, FACC Cardiovascular
Cardiac CT Lowering the Dose Dramatically
 Cardiac CT Lowering the Dose Dramatically U. Joseph Schoepf, MD, FAHA, FSCBT MR, FSCCT Professor of Radiology, Medicine, and Pediatrics Director of Cardiovascular Imaging Disclosures Consultant for / research
Cardiac CT Lowering the Dose Dramatically U. Joseph Schoepf, MD, FAHA, FSCBT MR, FSCCT Professor of Radiology, Medicine, and Pediatrics Director of Cardiovascular Imaging Disclosures Consultant for / research
Triple Rule-out using 320-row-detector volume MDCT: A comparison of the wide volume and helical modes
 Triple Rule-out using 320-row-detector volume MDCT: A comparison of the wide volume and helical modes Poster No.: C-0488 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit E.-J. Kang,
Triple Rule-out using 320-row-detector volume MDCT: A comparison of the wide volume and helical modes Poster No.: C-0488 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit E.-J. Kang,
Exploration the Method of Low Dose Coronary Artery Imaging with Dual-Source CT
 Journal of Biosciences and Medicines, 2013, 1, 6-10 doi:10.4236/jbm.2013.11002 Published Online February 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jbm/) Exploration the Method of Low Dose Coronary Artery Imaging
Journal of Biosciences and Medicines, 2013, 1, 6-10 doi:10.4236/jbm.2013.11002 Published Online February 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jbm/) Exploration the Method of Low Dose Coronary Artery Imaging
Pushing the limits of cardiac CT. Steven Dymarkowski Radiology / Medical Imaging Research Centre
 Pushing the limits of cardiac CT Steven Dymarkowski Radiology / Medical Imaging Research Centre 5 X 2013 Introduction Rapid technological advances and new clinical applications in cardiovascular imaging
Pushing the limits of cardiac CT Steven Dymarkowski Radiology / Medical Imaging Research Centre 5 X 2013 Introduction Rapid technological advances and new clinical applications in cardiovascular imaging
Improvement of Image Quality with ß-Blocker Premedication on ECG-Gated 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography
 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Shim et al. 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Sung Shine Shim 1 Yookyung Kim Soo Mee Lim Received December 1, 2003; accepted after revision June 1, 2004. 1 All authors: Department
16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Shim et al. 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Sung Shine Shim 1 Yookyung Kim Soo Mee Lim Received December 1, 2003; accepted after revision June 1, 2004. 1 All authors: Department
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Scientific Exhibit Authors:
 Preoperative evaluation of infants and children with congenital heart disease with ECG triggered 128 Dual Source CT Angiography- Portugal- Angola collaboration Poster No.: C-0942 Congress: ECR 2013 Type:
Preoperative evaluation of infants and children with congenital heart disease with ECG triggered 128 Dual Source CT Angiography- Portugal- Angola collaboration Poster No.: C-0942 Congress: ECR 2013 Type:
Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Costa, A. Proença Ramos, J. C. A. Costa, V. Silva, C.
 Preoperative evaluation of infants and children with congenital heart disease with ECG triggered 128 Dual Source CT Angiography- Portugal- Angola collaboration Poster No.: C-0942 Congress: ECR 2013 Type:
Preoperative evaluation of infants and children with congenital heart disease with ECG triggered 128 Dual Source CT Angiography- Portugal- Angola collaboration Poster No.: C-0942 Congress: ECR 2013 Type:
Scientific Exhibit. Authors: D. Takenaka, Y. Ohno, Y. Onishi, K. Matsumoto, T.
 The feasibility of biphasic contrast-media-injection-protocol for chest imaging on 320-slice volume MDCT: Direct comparison of biphasic and bolus contrast-media injection protocols on 320-slice volume
The feasibility of biphasic contrast-media-injection-protocol for chest imaging on 320-slice volume MDCT: Direct comparison of biphasic and bolus contrast-media injection protocols on 320-slice volume
Computed Tomography of the Coronary Arteries
 Cardiology Update DAVOS 2011 Computed Tomography of the Coronary Arteries Anders Persson M.D., Ph.D Director, Assoc. Professor Center for Medical Image Science and Visualization Linköping University SWEDEN
Cardiology Update DAVOS 2011 Computed Tomography of the Coronary Arteries Anders Persson M.D., Ph.D Director, Assoc. Professor Center for Medical Image Science and Visualization Linköping University SWEDEN
Dual Energy CT of the Heart: Perfusion and Beyond
 Dual Energy CT of the Heart: Perfusion and Beyond U. Joseph Schoepf, MD, FAHA, FSCBT MR, FSCCT Professor of Radiology, Medicine, and Pediatrics Director of Cardiovascular Imaging Disclosures Consultant
Dual Energy CT of the Heart: Perfusion and Beyond U. Joseph Schoepf, MD, FAHA, FSCBT MR, FSCCT Professor of Radiology, Medicine, and Pediatrics Director of Cardiovascular Imaging Disclosures Consultant
Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We. ACHD Patients
 Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We Have Learned to Apply to ACHD Patients Faris Al Mousily, MBChB, FAAC, FACC Consultant, Pediatric Cardiology, KFSH&RC/Jeddah Adjunct Faculty, Division of Pediatric Cardiology
Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We Have Learned to Apply to ACHD Patients Faris Al Mousily, MBChB, FAAC, FACC Consultant, Pediatric Cardiology, KFSH&RC/Jeddah Adjunct Faculty, Division of Pediatric Cardiology
Low-dose CT coronary angiography: Role of adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction (ASIR)
 Low-dose CT coronary angiography: Role of adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction (ASIR) Poster No.: 456 Congress: ESCR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit M. A. Glazkova, I. Arkhipova,
Low-dose CT coronary angiography: Role of adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction (ASIR) Poster No.: 456 Congress: ESCR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit M. A. Glazkova, I. Arkhipova,
Case 47 Clinical Presentation
 93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
Common Defects With Expected Adult Survival:
 Common Defects With Expected Adult Survival: Bicuspid aortic valve :Acyanotic Mitral valve prolapse Coarctation of aorta Pulmonary valve stenosis Atrial septal defect Patent ductus arteriosus (V.S.D.)
Common Defects With Expected Adult Survival: Bicuspid aortic valve :Acyanotic Mitral valve prolapse Coarctation of aorta Pulmonary valve stenosis Atrial septal defect Patent ductus arteriosus (V.S.D.)
9/8/2009 < 1 1,2 3,4 5,6 7,8 9,10 11,12 13,14 15,16 17,18 > 18. Tetralogy of Fallot. Complex Congenital Heart Disease.
 Current Indications for Pediatric CTA S Bruce Greenberg Professor of Radiology Arkansas Children s Hospital University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences greenbergsbruce@uams.edu 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10
Current Indications for Pediatric CTA S Bruce Greenberg Professor of Radiology Arkansas Children s Hospital University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences greenbergsbruce@uams.edu 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10
CT Perfusion. U. Joseph Schoepf, MD, FAHA, FSCBT MR, FSCCT Professor of Radiology, Medicine, and Pediatrics Director of Cardiovascular Imaging
 CT Perfusion U. Joseph Schoepf, MD, FAHA, FSCBT MR, FSCCT Professor of Radiology, Medicine, and Pediatrics Director of Cardiovascular Imaging Disclosures Consultant for / research support from Bayer Bracco
CT Perfusion U. Joseph Schoepf, MD, FAHA, FSCBT MR, FSCCT Professor of Radiology, Medicine, and Pediatrics Director of Cardiovascular Imaging Disclosures Consultant for / research support from Bayer Bracco
Medical Physics and Informatics Original Research
 Medical Physics and Informatics Original Research Jadhav et al. CT Angiography of Neonates and Infants Medical Physics and Informatics Original Research Siddharth P. Jadhav 1 Farahnaz Golriz 1 Lamya A.
Medical Physics and Informatics Original Research Jadhav et al. CT Angiography of Neonates and Infants Medical Physics and Informatics Original Research Siddharth P. Jadhav 1 Farahnaz Golriz 1 Lamya A.
Congenital Heart Defects
 Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
Assessing Cardiac Anatomy With Digital Subtraction Angiography
 485 JACC Vol. 5, No. I Assessing Cardiac Anatomy With Digital Subtraction Angiography DOUGLAS S., MD, FACC Cleveland, Ohio The use of intravenous digital subtraction angiography in the assessment of patients
485 JACC Vol. 5, No. I Assessing Cardiac Anatomy With Digital Subtraction Angiography DOUGLAS S., MD, FACC Cleveland, Ohio The use of intravenous digital subtraction angiography in the assessment of patients
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 9: , 2015
 2384 Dose study of electrocardiogram automatic tube current modulation technology in prospective coronary computed tomography angiography scans of overweight patients GUIRU HE, XIAOPEI LIU, YAN LIU, WEI
2384 Dose study of electrocardiogram automatic tube current modulation technology in prospective coronary computed tomography angiography scans of overweight patients GUIRU HE, XIAOPEI LIU, YAN LIU, WEI
Chapter 3.14 Aortic arch interruption
 Chapter 3.14 Aortic arch interruption z Definition The aortic arch is described as three segments: proximal, distal and isthmus. The proximal component extends from the takeoff of the innominate artery
Chapter 3.14 Aortic arch interruption z Definition The aortic arch is described as three segments: proximal, distal and isthmus. The proximal component extends from the takeoff of the innominate artery
Simon Nepveu 1, Irina Boldeanu 1, Yves Provost 1, Jean Chalaoui 1, Louis-Mathieu Stevens 2,3, Nicolas Noiseux 2,3, Carl Chartrand-Lefebvre 1,3
 Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Imaging with CT Angiography and Iterative Reconstruction: Quantitave Evaluation of Radiation Dose Reduction and Image Quality Simon Nepveu 1, Irina Boldeanu 1, Yves Provost
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Imaging with CT Angiography and Iterative Reconstruction: Quantitave Evaluation of Radiation Dose Reduction and Image Quality Simon Nepveu 1, Irina Boldeanu 1, Yves Provost
Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research
 Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Apfaltrer et al. High-Pitch Versus Standard-Pitch CTA of the Aorta Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Paul Apfaltrer 1,2 E.
Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Apfaltrer et al. High-Pitch Versus Standard-Pitch CTA of the Aorta Vascular and Interventional Radiology Original Research Paul Apfaltrer 1,2 E.
Justification of the use of CT for individual health assessment of asymptomatic people: the Chinese experience
 Justification of the use of CT for individual health assessment of asymptomatic people: the Chinese experience Liang Wang, MD, PhD Professor, attending radiologist wang6@tjh.tjmu.edu.cn Dept. of Radiology
Justification of the use of CT for individual health assessment of asymptomatic people: the Chinese experience Liang Wang, MD, PhD Professor, attending radiologist wang6@tjh.tjmu.edu.cn Dept. of Radiology
CT Myocardial Perfusion: Is there Added Value to Coronary CT?
 CT Myocardial Perfusion: Is there Added Value to Coronary CT? U. Joseph Schoepf, MD, FAHA, FSCBT MR, FSCCT Professor of Radiology, Medicine, and Pediatrics Director of Cardiovascular Imaging Disclosures
CT Myocardial Perfusion: Is there Added Value to Coronary CT? U. Joseph Schoepf, MD, FAHA, FSCBT MR, FSCCT Professor of Radiology, Medicine, and Pediatrics Director of Cardiovascular Imaging Disclosures
CT angiography techniques. Boot camp
 CT angiography techniques Boot camp Overview Basic concepts Contrast administration arterial opacification Time scan acquisition during the arterial phase Protocol examples Helical non-gated CTA Pulmonary
CT angiography techniques Boot camp Overview Basic concepts Contrast administration arterial opacification Time scan acquisition during the arterial phase Protocol examples Helical non-gated CTA Pulmonary
Managing Radiation Risk in Pediatric CT Imaging
 Managing Radiation Risk in Pediatric CT Imaging Mahadevappa Mahesh, MS, PhD, FAAPM, FACR, FACMP, FSCCT. Professor of Radiology and Cardiology Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Chief Physicist
Managing Radiation Risk in Pediatric CT Imaging Mahadevappa Mahesh, MS, PhD, FAAPM, FACR, FACMP, FSCCT. Professor of Radiology and Cardiology Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Chief Physicist
Combined Anatomical and Functional Imaging with Revolution * CT
 GE Healthcare Case studies Combined Anatomical and Functional Imaging with Revolution * CT Jean-Louis Sablayrolles, M.D. Centre Cardiologique du Nord, Saint-Denis, France Case 1 Whole Brain Perfusion and
GE Healthcare Case studies Combined Anatomical and Functional Imaging with Revolution * CT Jean-Louis Sablayrolles, M.D. Centre Cardiologique du Nord, Saint-Denis, France Case 1 Whole Brain Perfusion and
Heart and Lungs. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship of pulmonary parenchyma to heart and chest wall.
 Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Multimodality Imaging of Septal Defects
 Multimodality Imaging of Septal Defects Ohio-ACC 2018 Annual Meeting October 27, 2018 Kan N. Hor, MD Director, Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging Associate Professor of Pediatrics The Heart Center, Nationwide
Multimodality Imaging of Septal Defects Ohio-ACC 2018 Annual Meeting October 27, 2018 Kan N. Hor, MD Director, Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging Associate Professor of Pediatrics The Heart Center, Nationwide
A new method for radiation dose reduction at cardiac CT with multi-phase data-averaging and non-rigid image registration: preliminary clinical trial
 A new method for radiation dose reduction at cardiac CT with multi-phase data-averaging and non-rigid image registration: preliminary clinical trial Poster No.: C-0595 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors:
A new method for radiation dose reduction at cardiac CT with multi-phase data-averaging and non-rigid image registration: preliminary clinical trial Poster No.: C-0595 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors:
The diagnostic evaluation of dual-source CT (DSCT) in the diagnosis of coronary artery stenoses
 Original Article Open Access The diagnostic evaluation of dual-source CT (DSCT) in the diagnosis of coronary artery stenoses Ziqiao Lei 1, Jin Gu 2, Qing Fu 3, Heshui Shi 4, Haibo Xu 5, Ping Han 6, Jianming
Original Article Open Access The diagnostic evaluation of dual-source CT (DSCT) in the diagnosis of coronary artery stenoses Ziqiao Lei 1, Jin Gu 2, Qing Fu 3, Heshui Shi 4, Haibo Xu 5, Ping Han 6, Jianming
ROLE OF 64 MULTI-DETECTOR COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN CONGENITAL HEART DISEASES
 ROLE OF 64 MULTI-DETECTOR COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN CONGENITAL HEART DISEASES Duong Phi Son MD Nguyen Tuan Vu PhD Phan Thanh Hai MD Department of Cardiology Medic Medical Center, Vietnam I. INTRODUCTION -
ROLE OF 64 MULTI-DETECTOR COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN CONGENITAL HEART DISEASES Duong Phi Son MD Nguyen Tuan Vu PhD Phan Thanh Hai MD Department of Cardiology Medic Medical Center, Vietnam I. INTRODUCTION -
Non Contrast MRA. Mayil Krishnam. Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine
 Non Contrast MRA Mayil Krishnam Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine No disclosures Non contrast MRA-Why? Limitations of CTA Radiation exposure Iodinated contrast
Non Contrast MRA Mayil Krishnam Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine No disclosures Non contrast MRA-Why? Limitations of CTA Radiation exposure Iodinated contrast
Cardiac Catheterization Cases Primary Cardiac Diagnoses Facility 12 month period from to PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient)
 PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient) Septal Defects ASD (Atrial Septal Defect) PFO (Patent Foramen Ovale) ASD, Secundum ASD, Sinus venosus ASD, Coronary sinus ASD, Common atrium (single atrium) VSD (Ventricular
PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient) Septal Defects ASD (Atrial Septal Defect) PFO (Patent Foramen Ovale) ASD, Secundum ASD, Sinus venosus ASD, Coronary sinus ASD, Common atrium (single atrium) VSD (Ventricular
Customizing Contrast Injection for Body MDCT: Algorithmic Approach
 Customizing Contrast Injection for Body MDCT: Algorithmic Approach Lincoln L. Berland, M.D., F.A.C.R. University of Alabama at Birmingham Before Contrast Prep and Hydration Hydration single most important
Customizing Contrast Injection for Body MDCT: Algorithmic Approach Lincoln L. Berland, M.D., F.A.C.R. University of Alabama at Birmingham Before Contrast Prep and Hydration Hydration single most important
Egyptian Society of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine. The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine
 The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine (2011) 42, 297 303 Egyptian Society of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrnm
The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine (2011) 42, 297 303 Egyptian Society of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrnm
Go With The Flow: Role of 4D Flow Imaging
 4D Flow Go With The Flow: Role of 4D Flow Imaging Niti R. Aggarwal, MD Associate Director of Cardiac MRI Assistant Professor of Medicine & Radiology University of Wisconsin Madison Disclosures GE Healthcare
4D Flow Go With The Flow: Role of 4D Flow Imaging Niti R. Aggarwal, MD Associate Director of Cardiac MRI Assistant Professor of Medicine & Radiology University of Wisconsin Madison Disclosures GE Healthcare
"Lecture Index. 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development.
 "Lecture Index 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development. 5) Septation and Maturation. 6) Changes in Blood Flow during Development.
"Lecture Index 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development. 5) Septation and Maturation. 6) Changes in Blood Flow during Development.
Ultralow Dose Chest CT with MBIR
 Ultralow Dose Chest CT with MBIR Ella A. Kazerooni, M.D. Professor & Director Cardiothoracic Radiology Associate Chair for Clinical Affairs University of Michigan Disclosures Consultant: GE Healthcare
Ultralow Dose Chest CT with MBIR Ella A. Kazerooni, M.D. Professor & Director Cardiothoracic Radiology Associate Chair for Clinical Affairs University of Michigan Disclosures Consultant: GE Healthcare
Pulmonary Embolism. Thoracic radiologist Helena Lauri
 Pulmonary Embolism Thoracic radiologist Helena Lauri 8.5.2017 Statistics 1-2 out of 1000 adults annually are diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and/or pulmonary embolism (PE) About half of patients
Pulmonary Embolism Thoracic radiologist Helena Lauri 8.5.2017 Statistics 1-2 out of 1000 adults annually are diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and/or pulmonary embolism (PE) About half of patients
PULMONARY EMBOLISM ANGIOCT (CTA) ASSESSMENT OF VASCULAR OCCLUSION EXTENT AND LOCALIZATION OF EMBOLI 1. BACKGROUND
 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL INFORMATICS & TECHNOLOGIES Vol. 11/2007, ISSN 1642-6037 Damian PTAK * pulmonary embolism, AngioCT, postprocessing techniques, Mastora score PULMONARY EMBOLISM ANGIOCT (CTA) ASSESSMENT
JOURNAL OF MEDICAL INFORMATICS & TECHNOLOGIES Vol. 11/2007, ISSN 1642-6037 Damian PTAK * pulmonary embolism, AngioCT, postprocessing techniques, Mastora score PULMONARY EMBOLISM ANGIOCT (CTA) ASSESSMENT
Acknowledgments. A Specific Diagnostic Task: Lung Nodule Detection. A Specific Diagnostic Task: Chest CT Protocols. Chest CT Protocols
 Personalization of Pediatric Imaging in Terms of Needed Indication-Based Quality Per Dose Acknowledgments Duke University Medical Center Ehsan Samei, PhD Donald Frush, MD Xiang Li PhD DABR Cleveland Clinic
Personalization of Pediatric Imaging in Terms of Needed Indication-Based Quality Per Dose Acknowledgments Duke University Medical Center Ehsan Samei, PhD Donald Frush, MD Xiang Li PhD DABR Cleveland Clinic
Fulfilling the Promise
 Fulfilling the Promise of Cardiac MR Non-contrast, free-breathing technique generates comprehensive evaluation of the coronary arteries By Maggie Fung, MR Cardiovascular Clinical Development Manager; Wei
Fulfilling the Promise of Cardiac MR Non-contrast, free-breathing technique generates comprehensive evaluation of the coronary arteries By Maggie Fung, MR Cardiovascular Clinical Development Manager; Wei
Purpose. Methods and Materials
 Comparison of iterative and filtered back-projection image reconstruction techniques: evaluation of heavily calcified vessels with coronary CT angiography Poster No.: C-1644 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific
Comparison of iterative and filtered back-projection image reconstruction techniques: evaluation of heavily calcified vessels with coronary CT angiography Poster No.: C-1644 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific
Anatomy & Physiology
 1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
Devendra V. Kulkarni, Rahul G. Hegde, Ankit Balani, and Anagha R. Joshi. 2. Case Report. 1. Introduction
 Case Reports in Radiology, Article ID 614647, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/614647 Case Report A Rare Case of Pulmonary Atresia with Ventricular Septal Defect with a Right Sided Aortic Arch and
Case Reports in Radiology, Article ID 614647, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/614647 Case Report A Rare Case of Pulmonary Atresia with Ventricular Septal Defect with a Right Sided Aortic Arch and
Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart
 Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Ivana M. Vettraino, M.D., M.B.A. Clinical Associate Professor, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine Objectives Review the embryology of the formation
Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Ivana M. Vettraino, M.D., M.B.A. Clinical Associate Professor, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine Objectives Review the embryology of the formation
Update on Acute Aortic Syndrome
 SUNDAY Update on Acute Aortic Syndrome Diana Litmanovich, MD Learning objectives To be familiar with the definition, natural history, and imaging findings of acute aortic syndrome, including: I. Aortic
SUNDAY Update on Acute Aortic Syndrome Diana Litmanovich, MD Learning objectives To be familiar with the definition, natural history, and imaging findings of acute aortic syndrome, including: I. Aortic
Correlation of Cardiac CTA to Conventional Cardiac Angiography in Diagnosing Coronary Artery Stenosis in a Community Based Center
 Correlation of Cardiac CTA to Conventional Cardiac Angiography in Diagnosing Coronary Artery Stenosis in a Community Based Center Mathieu Sabbagh, R3 Michigan State University Radiology Garden City Hospital
Correlation of Cardiac CTA to Conventional Cardiac Angiography in Diagnosing Coronary Artery Stenosis in a Community Based Center Mathieu Sabbagh, R3 Michigan State University Radiology Garden City Hospital
Impact of SSF on diagnostic performance of coronary CT angiography within one heart beat in patients with high heart rate using a 256-row detector CT
 Impact of SSF on diagnostic performance of coronary CT angiography within one heart beat in patients with high heart rate using a 256-row detector CT Junfu Liang 1,2, Hui Wang 1, Lei Xu 1, Li Dong 1, Zhanming
Impact of SSF on diagnostic performance of coronary CT angiography within one heart beat in patients with high heart rate using a 256-row detector CT Junfu Liang 1,2, Hui Wang 1, Lei Xu 1, Li Dong 1, Zhanming
3/14/2011 MANAGEMENT OF NEWBORNS CARDIAC INTENSIVE CARE CONFERENCE FOR HEALTH PROFESSIONALS IRVINE, CA. MARCH 7, 2011 WITH HEART DEFECTS
 CONFERENCE FOR HEALTH PROFESSIONALS IRVINE, CA. MARCH 7, 2011 MANAGEMENT OF NEWBORNS WITH HEART DEFECTS A NTHONY C. CHANG, MD, MBA, MPH M E D I C AL D I RE C T OR, HEART I N S T I T U T E C H I LDRE N
CONFERENCE FOR HEALTH PROFESSIONALS IRVINE, CA. MARCH 7, 2011 MANAGEMENT OF NEWBORNS WITH HEART DEFECTS A NTHONY C. CHANG, MD, MBA, MPH M E D I C AL D I RE C T OR, HEART I N S T I T U T E C H I LDRE N
Aims and objectives. Page 2 of 13
 Evaluation of right heart function with use of retrospectively ECG- gated 64-slice low dose computed tomography in subjects with and without pulmonary hypertension Poster No.: C-2562 Congress: ECR 2015
Evaluation of right heart function with use of retrospectively ECG- gated 64-slice low dose computed tomography in subjects with and without pulmonary hypertension Poster No.: C-2562 Congress: ECR 2015
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
SPECIFIC PRINCIPLES FOR DOSE REDUCTION IN HEAD CT IMAGING. Rajiv Gupta, MD, PhD Neuroradiology, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School
 SPECIFIC PRINCIPLES FOR DOSE REDUCTION IN HEAD CT IMAGING Rajiv Gupta, MD, PhD Neuroradiology, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School OUTLINE 1 st Presentation: Dose optimization strategies
SPECIFIC PRINCIPLES FOR DOSE REDUCTION IN HEAD CT IMAGING Rajiv Gupta, MD, PhD Neuroradiology, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School OUTLINE 1 st Presentation: Dose optimization strategies
Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016
 1 Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016 DISCLOSURES I have no disclosures relevant to today s talk 2 Why should all echocardiographers
1 Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016 DISCLOSURES I have no disclosures relevant to today s talk 2 Why should all echocardiographers
ECG Gated CT Aorta in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation
 ECG Gated CT Aorta in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Poster No.: C-2014 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. A. Ottesen; Oslo/NO Keywords: Cardiac, Arteries / Aorta, CT, CT-Angiography,
ECG Gated CT Aorta in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Poster No.: C-2014 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. A. Ottesen; Oslo/NO Keywords: Cardiac, Arteries / Aorta, CT, CT-Angiography,
An Unreported Type of Coronary Artery Anomaly in Congenitally Corrected Transposition of Great Arteries 선천성수정대혈관전위환자에서새롭게보고된관상동맥변이
 Case Report pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 J Korean Soc Radiol 2016;75(1):62-67 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2016.75.1.62 An Unreported Type of Coronary Artery Anomaly in Congenitally Corrected Transposition
Case Report pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 J Korean Soc Radiol 2016;75(1):62-67 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2016.75.1.62 An Unreported Type of Coronary Artery Anomaly in Congenitally Corrected Transposition
B-Flow, Power Doppler and Color Doppler Ultrasound in the Assessment of Carotid Stenosis: Comparison with 64-MD-CT Angiography
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 2, March: 805-809, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net B-Flow, Power Doppler and Color Doppler Ultrasound in the Assessment of Carotid Stenosis: Comparison with
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 2, March: 805-809, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net B-Flow, Power Doppler and Color Doppler Ultrasound in the Assessment of Carotid Stenosis: Comparison with
Additional Value of 3DRA in the Diagnostic Evaluation and Percutaneous Treatment of Children With Univentricular Hearts
 Additional Value of 3DRA in the Diagnostic Evaluation and Percutaneous Treatment of Children With Univentricular Hearts 3DI3 symposium 2016 October 15th Mirella Molenschot, Femke vd Stelt, Hans Breur,
Additional Value of 3DRA in the Diagnostic Evaluation and Percutaneous Treatment of Children With Univentricular Hearts 3DI3 symposium 2016 October 15th Mirella Molenschot, Femke vd Stelt, Hans Breur,
Keywords Coronary CT angiography Low dose Iterative reconstruction
 European Heart Journal Cardiovascular Imaging (2014) 15, 1238 1245 doi:10.1093/ehjci/jeu113 Accuracy of prospectively ECG-triggered very low-dose coronary dual-source CT angiography using iterative reconstruction
European Heart Journal Cardiovascular Imaging (2014) 15, 1238 1245 doi:10.1093/ehjci/jeu113 Accuracy of prospectively ECG-triggered very low-dose coronary dual-source CT angiography using iterative reconstruction
Radiation dose of cardiac CT what is the evidence?
 Eur Radiol (2009) 19: 1311 1315 DOI 10.1007/s00330-009-1312-y CARDIAC Hatem Alkadhi Radiation dose of cardiac CT what is the evidence? Received: 10 December 2008 Revised: 2 January 2009 Accepted: 12 January
Eur Radiol (2009) 19: 1311 1315 DOI 10.1007/s00330-009-1312-y CARDIAC Hatem Alkadhi Radiation dose of cardiac CT what is the evidence? Received: 10 December 2008 Revised: 2 January 2009 Accepted: 12 January
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray
 Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
Image quality and radiation dose of lower extremity CTangiography at 70 kvp on an integrated circuit detector dual-source computed tomography
 Acta Radiol OnlineFirst, published on June 11, 2014 as doi:10.1177/0284185114535391 Original Article Image quality and radiation dose of lower extremity CTangiography at 70 kvp on an integrated circuit
Acta Radiol OnlineFirst, published on June 11, 2014 as doi:10.1177/0284185114535391 Original Article Image quality and radiation dose of lower extremity CTangiography at 70 kvp on an integrated circuit
Radiation Dose Optimization in Cardiac CT: A Technical Review. CHENG Wai Kwong. 17 May Contents
 Radiation Dose Optimization in Cardiac CT: A Technical Review CHENG Wai Kwong 17 May 2014 Contents 1. Introduction and background 2. Cardiac CT synchronization techniques 3. 4. Conclusion 1 Introduction
Radiation Dose Optimization in Cardiac CT: A Technical Review CHENG Wai Kwong 17 May 2014 Contents 1. Introduction and background 2. Cardiac CT synchronization techniques 3. 4. Conclusion 1 Introduction
September 26, 2012 Philip Stockwell, MD Lifespan CVI Assistant Professor of Medicine (Clinical)
 September 26, 2012 Philip Stockwell, MD Lifespan CVI Assistant Professor of Medicine (Clinical) Advances in cardiac surgery have created a new population of adult patients with repaired congenital heart
September 26, 2012 Philip Stockwell, MD Lifespan CVI Assistant Professor of Medicine (Clinical) Advances in cardiac surgery have created a new population of adult patients with repaired congenital heart
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease
 Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease Caroline K. Lee, MD Pediatric Cardiology Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships or conflicts of interest 1 Most Common Birth Defect Most
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease Caroline K. Lee, MD Pediatric Cardiology Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships or conflicts of interest 1 Most Common Birth Defect Most
Multidetector Computed Tomography (CT) in Evaluation of Congenital Cyanotic Heart Diseases
 Signature: DOI: 10.12659/PJR.903222 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Received: 2017.01.07 Accepted: 2017.02.03 Published: 2017.11.17 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection C Statistical Analysis
Signature: DOI: 10.12659/PJR.903222 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Received: 2017.01.07 Accepted: 2017.02.03 Published: 2017.11.17 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection C Statistical Analysis
Survey of patients CT radiation dose in Jiangsu Province
 Original Article Page 1 of 6 Survey of patients CT radiation dose in Jiangsu Province Yuanyuan Zhou 1, Chunyong Yang 1, Xingjiang Cao 1, Xiang Du 1, Ningle Yu 1, Xianfeng Zhou 2, Baoli Zhu 1, Jin Wang
Original Article Page 1 of 6 Survey of patients CT radiation dose in Jiangsu Province Yuanyuan Zhou 1, Chunyong Yang 1, Xingjiang Cao 1, Xiang Du 1, Ningle Yu 1, Xianfeng Zhou 2, Baoli Zhu 1, Jin Wang
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD)
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
Gender differences in CT calcium scoring: A phantom study
 Gender differences in CT calcium scoring: A phantom study Nicholas Petrick, Qin Li, Benjamin Berman, Marios A Gavrielides, Rongping Zeng, Berkman Sahiner CDRH/OSEL/DIDSR U.S. Food and Drug Administration
Gender differences in CT calcium scoring: A phantom study Nicholas Petrick, Qin Li, Benjamin Berman, Marios A Gavrielides, Rongping Zeng, Berkman Sahiner CDRH/OSEL/DIDSR U.S. Food and Drug Administration
Review Article Cardiovascular Imaging
 Review Article Cardiovascular Imaging eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2019;20(2):190-204 User-Friendly Vendor-Specific Guideline for Pediatric Cardiothoracic Computed Tomography Provided by the Asian Society
Review Article Cardiovascular Imaging eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2019;20(2):190-204 User-Friendly Vendor-Specific Guideline for Pediatric Cardiothoracic Computed Tomography Provided by the Asian Society
Low-dose and High-resolution Cardiac Imaging with Revolution CT
 GE Healthcare Case study Low-dose and High-resolution Cardiac Imaging with Revolution CT Prof. Philipp A. Kaufmann, M.D. Ronny R. Buechel, M.D. Fran Mikulicic, M.D. Dominik C. Benz, M.D. University of
GE Healthcare Case study Low-dose and High-resolution Cardiac Imaging with Revolution CT Prof. Philipp A. Kaufmann, M.D. Ronny R. Buechel, M.D. Fran Mikulicic, M.D. Dominik C. Benz, M.D. University of
Ultrasound. Computed tomography. Case studies. Utility of IQon Spectral CT in. cardiac imaging
 Ultrasound Computed tomography Case studies Utility of IQon Spectral CT in cardiac imaging Cardiac imaging is a challenging procedure where it is necessary to image a motion-free heart. This requires a
Ultrasound Computed tomography Case studies Utility of IQon Spectral CT in cardiac imaging Cardiac imaging is a challenging procedure where it is necessary to image a motion-free heart. This requires a
Doses from Cervical Spine Computed Tomography (CT) examinations in the UK. John Holroyd and Sue Edyvean
 Doses from Cervical Spine Computed Tomography (CT) examinations in the UK John Holroyd and Sue Edyvean Why a new dose survey? Number of enquires received concerning the current NDRL Concern that could
Doses from Cervical Spine Computed Tomography (CT) examinations in the UK John Holroyd and Sue Edyvean Why a new dose survey? Number of enquires received concerning the current NDRL Concern that could
Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot
 36 Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot E.D. Bespalova, R.M. Gasanova, O.A.Pitirimova National Scientific and Practical Center of Cardiovascular Surgery, Moscow Elena D. Bespalova, MD Professor, Director Rena M,
36 Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot E.D. Bespalova, R.M. Gasanova, O.A.Pitirimova National Scientific and Practical Center of Cardiovascular Surgery, Moscow Elena D. Bespalova, MD Professor, Director Rena M,
What every radiologist should know about cardiac CT: A case-based pictorial review
 What every radiologist should know about cardiac CT: A case-based pictorial review Poster No.: C-0555 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Cardiac Authors: C. M. Capuñay, P. Carrascosa,
What every radiologist should know about cardiac CT: A case-based pictorial review Poster No.: C-0555 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Cardiac Authors: C. M. Capuñay, P. Carrascosa,
THE ROLE OF HIGH END MULTI DETECTOR CT IN CORONARY IMAGING ESSAY
 THE ROLE OF HIGH END MULTI DETECTOR CT IN CORONARY IMAGING ESSAY Submitted for partial fulfillment of Master degree in Radiodiagnosis By Ahmed Yehia Ahmed (M.B.B.Ch., Cairo University) Supervisors Prof.
THE ROLE OF HIGH END MULTI DETECTOR CT IN CORONARY IMAGING ESSAY Submitted for partial fulfillment of Master degree in Radiodiagnosis By Ahmed Yehia Ahmed (M.B.B.Ch., Cairo University) Supervisors Prof.
Cardiac CTA Prospective Gating Broad Beam
 Cardiac CTA Prospective Gating Broad Beam ACQUISITION- Broad Beam Gating: Prospective Non Contrast Scan-Calcium Score Patient Position Supine Feet First into Gantry Heart Isocenter Scanogram AP and Lateral
Cardiac CTA Prospective Gating Broad Beam ACQUISITION- Broad Beam Gating: Prospective Non Contrast Scan-Calcium Score Patient Position Supine Feet First into Gantry Heart Isocenter Scanogram AP and Lateral
SYMPOSIA. Coronary CTA. Indications, Patient Selection, and Clinical Implications
 SYMPOSIA Indications, Patient Selection, and Clinical Implications Christian Thilo, MD,* Mark Auler, MD,* Peter Zwerner, MD,w Philip Costello, MD,* and U. Joseph Schoepf, MD* Abstract: Recent technical
SYMPOSIA Indications, Patient Selection, and Clinical Implications Christian Thilo, MD,* Mark Auler, MD,* Peter Zwerner, MD,w Philip Costello, MD,* and U. Joseph Schoepf, MD* Abstract: Recent technical
ADVANCED CARDIOVASCULAR IMAGING. Medical Knowledge. Goals and Objectives PF EF MF LF Aspirational
 Medical Knowledge Goals and Objectives PF EF MF LF Aspirational Know the basic principles of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) including the role of the magnetic fields and gradient coil systems, generation
Medical Knowledge Goals and Objectives PF EF MF LF Aspirational Know the basic principles of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) including the role of the magnetic fields and gradient coil systems, generation
ESTABLISHING DRLs in PEDIATRIC CT. Keith Strauss, MSc, FAAPM, FACR Cincinnati Children s Hospital University of Cincinnati College of Medicine
 ESTABLISHING DRLs in PEDIATRIC CT Keith Strauss, MSc, FAAPM, FACR Cincinnati Children s Hospital University of Cincinnati College of Medicine CT Dose Indices CTDI INTRODUCTION CTDI 100, CTDI w, CTDI vol
ESTABLISHING DRLs in PEDIATRIC CT Keith Strauss, MSc, FAAPM, FACR Cincinnati Children s Hospital University of Cincinnati College of Medicine CT Dose Indices CTDI INTRODUCTION CTDI 100, CTDI w, CTDI vol
CARDIAC MRI. Cardiovascular Disease. Cardiovascular Disease. Cardiovascular Disease. Overview
 CARDIAC MRI Dr Yang Faridah A. Aziz Department of Biomedical Imaging University of Malaya Medical Centre Cardiovascular Disease Diseases of the circulatory system, also called cardiovascular disease (CVD),
CARDIAC MRI Dr Yang Faridah A. Aziz Department of Biomedical Imaging University of Malaya Medical Centre Cardiovascular Disease Diseases of the circulatory system, also called cardiovascular disease (CVD),
ROLE OF CONTRAST ENHANCED MR ANGIOGRAPHY IN AORTIC COARCTATION
 ROLE OF CONTRAST ENHANCED MR ANGIOGRAPHY IN AORTIC COARCTATION By Adel El Badrawy, Ahmed Abdel Razek, Nermin Soliman, Hala El Marsafawy *, Sameh Amer** From Radiodiagnosis, Pediatric Cardiology* & Cardiothoracic
ROLE OF CONTRAST ENHANCED MR ANGIOGRAPHY IN AORTIC COARCTATION By Adel El Badrawy, Ahmed Abdel Razek, Nermin Soliman, Hala El Marsafawy *, Sameh Amer** From Radiodiagnosis, Pediatric Cardiology* & Cardiothoracic
