O pêe je poznata uloga renin-angiotenzinskog sustav
|
|
|
- Patience Gallagher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2010;5(11):270. Pregledni rad Antagonisti angiotenzinskih receptora Review article Angiotensin receptor antagonists Aleksandar KneæeviÊ* OpÊa bolnica Zadar, Zadar, Hrvatska Zadar General Hospital, Zadar, Croatia SAÆETAK: Antagonisti angiotenzinskih receptora predstavljaju vaænu skupinu kardiovaskularnih lijekova s dokazanom uëinkovitoπêu u: lijeëenju arterijske hipertenzije, zatajivanja srca, primjeni u bolesnika nakon infarkta miokarda s disfunkcijom lijeve klijetke, prevenciji moædanog udara, kardiovaskularnoj protekciji u visokoriziënih bolesnika, prevenciji i lijeëenju bolesti bubrega s proteinurijim ukljuëujuêi i dijabetiëku nefropatiju. Zbog malog broja nuspojava omoguêavaju dobru ustrajnost bolesnika u lijeëenju, πto omoguêava bolju kardiovaskularnu protekciju. Nedavna studija koja je pokazala neπto veêu moguênost izazivanja malignih bolesti u odnosu na komparabilnu terapiju nije prihvaêena od veêine znanstvene zajednice i regulatornih tijela tako da se ti lijekovi i dalje mogu primjenjivati prema dosadaπnjim uputama omogu- ÊavajuÊi adekvatno lijeëenje i prevenciju kardiovaskularnih bolesti. KLJU»NE RIJE»I: antagonisti angiotenzinskih receptora, ACE inhibitori, arterijska hipertenzija. SUMMARY: Angiotensin receptor antagonists are the important group of cardiovascular drugs with proved efficiency in patients with hypertension, heart failure, after myocardial infarction with left ventricular dysfunction, stroke prevention, cardiovascular protection in high-risk patients, prevention and treatment of kidney diseases with proteinuria including diabetic nephropathy. Due to a small number of side-effects, they provide good patients persistence in treatment which enables better cardiovascular protection. The recent study that has showed somewhat greater possibility of causing malignancy compared to comparative therapy has not been accepted by the majority of the scientific community and regulatory bodies, so that such medicines may still be applied according to the recent instructions, enabling adequate treatment and prevention of cardiovascular diseases. KEYWORDS: angiotensin receptor antagonists, ACE inhibitors, hypertension CITATION: Kardio list. 2010;5(11): O pêe je poznata uloga renin-angiotenzinskog sustav (RAAS) kao regulatornog mehanizma, primarno u arterijskoj hipertenziji (AH) i ravnoteæi tekuêina u tijelu. RAAS Ëini enzimski sustav koji poëinje kad renin, hidrolizirajuêi angiotenzin, dovodi do nastajanja bioloπki inaktivnog dekapetida angiotenzin I (A I). Angiotenzin konvertirajuêi enzim (ACE) hidrolizira A I u bioloπki aktivni oktapeptid angiotenzin II (A II) koji predstavlja glavni Ëimbenik aktivnosti RAAS. Angiotenzin II je snaæan vazokonstriktor koji svojim djelovanjem na remodeliranje lijeve klijetke (LK) i vaskulature te aktiviranjem ostalih neurohormonalnih agonista (noradrenalin, aldosteron i endotelin) zna- Ëajno doprinosi razvoju ateroskleroze te nepoæeljnom uëinku na bubreg i srce u bolesnika s AH i zatajivanjem srca. Vremenom su definirani receptori za A II πto je dalo moguênost i za pronalaæenje njihovih specifiënih inhibitora. Za sada su poznata Ëetiri podtipa A II receptora: AT 1, AT 2, AT 3 i AT 4. AT 1 receptori imaju ulogu u vazokonstrikciji, potiëu otpuπtanje aldosterona, endotelina i vazopresina, potiëu aktivaciju simpatikusa, potiëu reapsorpciju natrija u tubulima, potiëu fibrozu u stijenci krvne æile i miokardu, poveêavaju kontraktilnost miokarda i moguênost nastajanja srëanih aritmija. Njihova inhibicija rezultira primarno sniæenjem arterijskog tlaka (AT), ali i suprimira neæeljene kemijske i strukturne promjene u stijenci krvnih æila i miokardu. UËinci stimulacije AT 2 receptora su slabije poznati. Njihovom stimulacijom postiæe se antiproliferativni uëinak, potiëe se diferencijacija stanica te regeneracija tkiva nakon ozljede. PoveÊava se oslobaappleanje bradikinina i prostaglandina u bubregu, a moguêe je postiêi i stanovitu vazodilataciju. UËinci AT 1 i AT 2 receptora u naëelu su R enin-angiotensin system (RAAS) as the regulation mechanism plays a pivotal role in hypertension and balance of fluids in the body. RAAS is the enzymatic system that starts when renin, hydrolyzing angiotensin causes occurrence of biologically inactive decapetide angiotensin I (A I). Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) hydrolyzes A I in biologically active octapeptide angiotensin II (A II) that represents the main factor of the RAAS activities. Angiotensin II is the strong vasoconstrictor that owing to its effects on remodeling of the left ventricle (LV) and vasculature as well as activation of other neurohormonal agonists (noradrenaline, aldesterone and endothelin) greatly contributes to the development of atherosclerosis and undesired effect on the kidney and heart in patients with AH and heart failure. With the time, the receptors for A II have been defined which made it possible to search for their specific inhibitors. At the moment there are four subtypes of A II receptors that are well-known for the time being: AT 1, AT 2, AT 3 and AT 4. AT 1 receptors play a role in vasoconstriction, stimulate the release of aldesterone, endothelin and vasopressin, they stimulate the activation of simpaticus, reabsorption of sodium in tubules, fibrosis in the wall of the blood vessel and myocardium, increase contractility of myocardium and possibility of occurrence of cardiac arrhythmia. Their inhibition results primarily in lowering blood pressure (BP) and suppresses undesired chemical and structural changes in the wall of blood vessels and myocardium. The effects of the stimulation of AT 2 receptors are less known. Their stimulation results in antiproliferative effect, stimulates differentiation of cells and regeneration of tissue after injury. It increases the release of bradykinin and prostaglandin in kidney and vasodilatation may be achieved as well. The effects of AT 1 and AT 2 receptors are principally contradic-
2 2010;5(11):271. opreëni. Blokadom AT 1 receptora i istovremenim neblokiranjem AT 2 receptora (πto je uëinak antagonista A II receptora) postiæe se u konaënici pozitivan uëinak za bolesnika, primarno sniæenjem AT te spreëavanjem strukturnih promjena stijenke krvnih æila i miokarda. Uloga AT 3 i AT 4 receptora za sada je slabo poznata 1. ACE- inhibitori su bili prva skupina lijekova kojima se djelovalo na πtetne uëinke A II. No oni su spreëavanjem nastanka A II (koje nije potpuno) istovremeno spreëavali i korisne uëinke A II koji se ostvaruju stimulacijom AT 2 podskupine receptora (premda do sada ova hipoteza nije i kliniëki dokazana). Takoappleer, ACE inhibitori (primarno poveêavajuêi nivo bradikinina) izazivaju nadraæajni kaπalj πto ograniëava njihovu primjenu. Da bi se prevladala ova ograniëenja ACE inhibitora u terapijsku uporabu ukljuëena je nova skupina lijekova antagonisti A II receptora-at 1 podskupine (ARB). Stoga se danas ARB sve viπe upotrebljavaju u lijeëenju hipertenzije, zatajivanja srca, prevenciji cerebrovaskularnog inzulta, bolesti bubrega s proteinurijim ukljuëujuêi i dijabetiëku nefropatiju. Skupina ARB predstavlja uëinkovitu i dobro podnoπljive lijekove za lijeëenje AH, πto im je osiguralo vaæno mjesto u lijeëenju ove bolesti. U kliniëkim studijama prevencije moædanog udara u bolesnika s hipertrofijom LK i dijabetiëkom nefropatijom pokazali su se boljim od usporednih lijekova. Zbog svog dobrog sigurnosnog profila omoguêavaju ustrajnost bolesnika u antihipertenzivnoj terapiji, πto dovodi do bolje prevencije kardiovaskularnih komplikacija te u konaënici manjih troπkova lijeëenja antihipertenzivima. Tako je jedna analiza lijeëenja AH pokazala da je najveêa ustrajnost bolesnika u prvoj godini lijeëenja bila u onih lijeëenih ARB u odnosu na druge skupine antihipertenziva, a zbog nuspojava je odustalo 4% bolesnika lijeëenih ARB u odnosu na 8% lijeëenih ACE inhibitorima 2. Stoga su uvrπteni u sve smjernice antihipertenzivnog lijeëenja, a u Europskim smjernicama za lijeëenje AH (a time i hrvatskim) se preporuëuju u bolesnika sa: zatajivanjem srca, nakon akutnog infarkta miokarda, atrijskom fibrilacijom, dijabetiëkom nefropatijom, metaboliëkim sindromom, mikroalbuminurijom, proteinurijom, hipertrofijom LK te kaπljem kod primjene ACE inhibitora 3. Kako se te indikacije uglavnom preklapaju s indikacijama odobrenim za ACE inhibitore, to osiguravateljska druπtva (pa tako i Hrvatski zavod za zdravstveno osiguranje) u svojim listama lijekova zbog, joπ uvijek, niæe cijene prednost daju ACE inhibitorima, dok je uloga ARB ograniëena na one bolesnike koje ne podnose ACE inhibotore, πto se primarno odnosi na kaπalj i angioedem. Pri tome moramo znati da kontraindikacije koje vrijede za ACE inhibitore, kao πto su trudnoêa i bilateralna renalna stenoza, vrijede i za ARB. U lijeëenju zatajivanja srca ARB se sve viπe nameêu kao alternativa ACE inhibitorima, primarno temeljem rezultata Val-HeFt i VALIANT studija gdje su pokazali usporedive rezultate 4,5. Stoga se sve viπe nameêu kao prvi izbor u lijeëenju tih bolesnika, a ne samo kao alternativno lije- Ëenje u onih koji imaju nuspojave na ACE inhibitore. Glavni argumenti za uporabu ARB u bolesnika sa zatajivanjem srca su: uëinkovitost uz minimalne nuspojave, glavni nepoæeljni uëinci RAAS u bolesnika sa zatajivanjem srca nastaju stimuliranjem AT 1 receptora πto ARB specifiëno blokiraju, nastanak angiotenzina II ide Ëesto mimo posre- tory. The blockade of AT 1 receptors and simultaneous non-blocking AT 2 receptors (which is an effect of antagonist A II receptor) finally results in a positive effect for a patient, primarily by lowering BP and preventing structural changes of the wall of blood vessels and myocardium. The role of AT 3 and AT 4 receptors are for the time being less known 1. ACE inhibitors were the first group of drugs having effect on A II adverse effects. However, preventing the occurrence of A II (not complete) they simultaneously prevented even A II good effects that are achieved by stimulation of AT 2 receptor subgroup (although this hypothesis so far has not been clinically proved). ACE inhibitors (primarily by increasing the level of bradykinin) cause irritating cough which limits its application. In order to overcome these limitations of ACE inhibitors in the therapeutic use, a new group of drugs A II receptor antagonists of the AT 1 subgroup (ARB) was included. Therefore, today ARB medicines are more used in treatment of hypertension, heart failure, stroke prevention, renal diseases with proteinuria including diabetic nephropathy as well. The ARB group represents the efficient and well tolerable antihypertensive drugs, which ensured them an important position in the treatment of this disease. In the clinical studies of prevention of the stroke in patients with LV hypertrophy and diabetic nephropathy they proved to be better than comparative drugs. Owing to their good safety profile, they enable persistence of patients in antihypertensive therapy causing better prevention of cardiovascular complications and finally reduced costs of antihypertensive treatment. So, one of the analysis of hypertension treatment showed that the greatest persistence of patients during the first year of treatment was in those treated with ARB medicines compared to the other groups of hypertensive medicines, while some 4% of patients treated with ARB medicines gave it up due to side-effects compared to 8% of those treated with ACE inhibitors 2. Therefore, they are included in all antihypertensive treatment guidelines, and the European guidelines for the treatment of hypertension (consequently the Croatian guidelines as well) recommend them for the patients with: heart failure, after acute myocardial infarction, atrial fibrillation, diabetic nephropathy, metabolic syndrome, microalbuminuria, proteinuria, LV hypertrophy and cough when applying ACE-inhibitors 3. Since such indications usually overlap with indications approved for ACE inhibitors, the insurance companies (the Croatian Health Insurance Institute as well) prioritize ACE inhibitors in their list of medicines due to their lower prices, while the role of ARB medicines is limited to those patients who do not tolerate ACE inhibitors, which primarily refers to cough and angioedema. We must know that side-effects applicable to ACE inhibitors, such as pregnancy and bilateral renal stenosis, are applicable to ARB medicines. In treatment of heart failure, ARB medicines are more and more used as alternative medicines compared to ACE inhibitors, primarily based on results of Val-HeFt and VA- LIANT studies where they showed comparative results 4,5. Therefore, they are more and more imposed as the first choice medicines in treatment of these patients, not only as alternative treatment in those who have ACE inhibitor sideeffects. The main reasons for the application of ARB medicines in patients with heart failure are: efficacy with minimum side-effects, main undesired effects of RAAS in patients with heart failure occur by stimulating AT 1 receptor
3 2010;5(11):272. dovanja ACE, ne djeluju na AT 2 receptore πto moæe imati kliniëku korist 6. ARB imaju bolje dokaze iz kliniëkih studija u prevenciji dijabetiëke nefropatije u dijabetesu tipa 2, dok ACE inhibitori to imaju u dijabetesu tip 1. U renalnoj bolesti s proteinurijom, u bolesnika s dijabetesom ili bez njega, ARB i ACE inhibitori jednako su uëinkoviti u reduciranju proteinurije. Takoappleer je u kliniëkim studijama lijeëenja hipertenzije i zatajivanja srca zapaæeno manje novonastalog dijabetesa u onih ispitanika koji su lijeëeni ARB u odnosu na komparativne lijekove (atenolol, amlodipin, hidroklorotijazid). U pet kliniëkih ispitivanja na bolesnika izravno su usporeappleivani ACE inhibitori i ARB u kardiovaskularnoj protekciji (uglavnom kaptopril 3x50 mg dnevno u usporedbi s losartanom 50 mg dnevno u tri studije, telmisartanom 80 mg dnevno u jednoj studiji i valsartanom 2x160 mg dnevno u jednoj studiji) te nije registrirana razlika meappleu njima u kardiovaskularnim ishodima i ukupnoj smrtnosti. Ipak temeljem meta-analiza u kojim je pokazana neπto ve- Êa (za 4%), ali statistiëki neznaëajna, poveêana incidencija infarkta miokarda u osoba koje su upotrebljavale ARB u odnosu na ACE inhibitore, neki autori govore o ARB paradoksu. Premda je to vjerojatno samo statistiëki fenomen i kliniëki bez znaëaja, ipak u ovom Ëasu ACE inhibitori imaju Ëvrste dokaze o kardiovaskularnoj protekciji u osoba s koronarnom bolesti i bez sistoliëke disfunkcije lijeve klijetke i zatajivanja srca, dok ARB ti Ëvrsti dokazi joπ nedostaju 7. To potvrappleuju rezultati ONTARGET studije u kojoj su usporeappleivani telmisartan 80 mg s ramiprilom 10 mg te njihova kombinacija u prevenciji kardiovaskularnih zbivanja u visokoriziënih bolesnika. Premda je telmisartan bolje sniæavao AT od ramiprila, nije bio bolji u kardiovaskularnoj protekciji. Njihova kombinacija je imala viπe nuspojava, uz isti uëinak, u odnosu na monoterapiju 8. Uporaba kombinacije ACE inhibitora i ARB za sada je dokazana korisnom u lijeëenju zatajivanja srca i kroniëne bolesti bubrega s proteinurijom. Pri tome postoji poveêana moguênost nuspojava, poglavito hiperkalijemije. U lijeëenju zatajivanja srca dodatak valsartana ili kandersartana bolesnicima kojima se bolest ne moæe kontrolirati optimalnom ACE inhibicijom dovodi do boljeg ishoda, vjerojatno spreëavanjem djelovanja preostalog angiotenzina II. Takoappleer ARB (primarno kandesartan) ima smisla dati bolesnicima kojima se simptomi ne mogu optimalno kontrolirati ACE inhibitorom i beta blokatorom 9. U kliniëkoj uporabi postoji viπe ARB, koji su gotovo svi odobreni za uporabu u Hrvatskoj. U tekstu koji slijedi navest Êemo njihove karakteristike. Losartan To je prvi ARB s kliniëkim studijama koje dokazuju njegovu uëinkovitost u lijeëenju AH, dijabetiëkoj nefropatiji i hipertrofiji LK. Doza mu je 25 do 100 mg. Kao i kod drugih ARB, poveêanje doze je manje uëinkovito u regulaciji AH, no πto je dodatak male doze diuretika. Doza od 50 mg pokazala se manje uëinkovitom u lijeëenju zatajivanja srca, dok 100 mg daje bolji uëinak. Kao i kod svih ARB, puni antihipertenzivni uëinak nastaje nakon 3 do 6 tjedana terapije. that are specifically blocked by ARB medicines, the occurrence of antiotensin II frequently occurs without ACE mediation, they have no effect on AT 2 receptors which may have clinical benefit 6. ARB have better evidence from clinical studies in prevention of diabetic nephropathy in diabetes type 2, while ACE inhibitors have it in diabetes type 1. In renal disease with proteinuria, in patients with diabetes or without it, ARB and ACE inhibitors are equally efficient in reducing proteinuria. Clinical studies of treatment of hypertension and heart failure record less newly occurred diabetes in those examinees treated with ARB compared to comparative drugs (atenolol, amlodipine, hydrochlorothiazide). In five clinical tests including 19,419 patients, ACE inhibitors and ARB were directly compared in cardiovascular protection, (mainly captopril 3x50 mg a day compared with losartan 50 mg a day in three studies, with telmisartan 80 mg a day in one study and valsartan 2x160 mg a day in one study), and no difference was recorded among them in cardiovascular outcomes and total mortality. Anyway, based on meta-analyses that showed some greater (by 4%), but statistically insignificant, increased incidence of myocardial infarction in persons that used ARB compared to ACE inhibitors, some authors speak about ARB paradox. Although it may be only a statistical phenomena and clinically unimportant, anyway at the moment, ACE inhibitors have stronger evidence for cardiovascular protection in persons with coronary heart disease and without systolic LV dysfunction and heart failure, while such strong evidence for ARB is still missing 7. It is confirmed by the results of the ONTARGET study in which telmisartan 80 mg was compared with ramipril 10 mg and their combination in prevention of cardiovascular events in high-risk patients. Although telmisartan was better to lower BP than ramipril, it was not better in cardiovascular protection. Their combination showed a greater number of side-effects with the same effect in comparison with monotherapy 8. The use of the combination of ACE and ARB has been so far proved to be beneficial in the treatment of heart failure and chronic kidney disease with proteinuria. However, there is an increased possibility of side-effects, especially of hyperkaliemia. In treatment of heart failure, an addition of valsartan or candersartan to patients whose disease may not be controlled by optimum ACE inhibition, leads to a better outcome, probably by preventing the effect of the remaining angiotensin II. ARB (primarily candesartan) are also to be given to patients whose symptoms may not be optimally controlled by ACE inhibitor and beta blocker 9. In clinical use there are several ARB medicines, whereas almost all of them are approved for the use in Croatia. In the text that follows, we shall name some of their characteristics. Losartan This is the first ARB with clinical studies that prove its efficacy in treatment of hypertension, diabetic nephropathy and LV hypertrophy. Its dose is 25 to 100 mg. The same as in other ARB, the increase in dose is less efficient in regulation of hypertension, compared to the addition of a small dose of diuretics. The dose of 50 mg has proved to be less efficient in treatment of heart failure, while 100 mg provides a better effect. The same as in all ARB, a full antihypertensive effect occurs after 3 to 6 weeks of therapy.
4 2010;5(11):273. Kandesartan Primjenjuje se kao predlijek kandesartancileksetil koji se tijekom apsorpcije u probavnom sustavu hidrolizira u djelatnu tvar kandesartan. Indikacije su mu lijeëenje AH i zatajivanja srca, a primjenjuje se u dozama od 4 do 32 mg. U CHARM-Added studiji se pokazao uëinkovit kao dodatna terapija bolesnicima sa zatajivanjem srca koji su veê lijeëeni ACE inhibitorom i beta-blokatorom 10. Valsartan Primjenjuje se u dozama od 80 do 320 mg u indikacijama AH, zatajivanja srca kada se ne mogu primjeniti ACE inhibitori ili beta blokatori (ne u trojnoj terapiji) te nakon infarkta miokarda u bolesnika s disfunkcijom LK ili znakovima zatajivanja srca. Ovo je dokazano u dvije velike studije Val-HeFT i VALIANT. Bolesnici lijeëeni valsartanom u Val-HeFT studiji pokazali su signifikantno poboljπanje NYHA stupnja, kao i znakova i simptoma zatajivanja srca ukljuëujuêi zaduhu, umor, edeme i hropce, u usporedbi s placebom. Bolesnici na valsartanu imali su bolju kvalitetu æivota nego bolesnici na placebu, πto se pokazalo tijekom lijeëenja i promjenom rezultata ljestvice Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Quality of Life u odnosu na polazne vrijednosti. Udarni volumen u bolesnika lije- Ëenih valsartanom porastao je signifikantno, a LVIDD se znaëajno smanjio prema polaznoj vrijednosti u usporedbi s placebom 4. U VALIANT studiji je dokazano da je valsartan jednako uëinkovit kao i ACE-inhibitor kaptopril u smanjenu mortaliteta i kardiovaskularnog pobola u visokoriziënih bolesnika nakon akutnog infarkta miokarda 5. Telmisartan Ima vrlo dugo vrijeme poluæivota u plazmi od 24 sata 11. Pogodan je za lijeëenje AH πto mu je i jedina indikacija. Primjenjuje se u dozama od 40 do 80 mg. U ONTARGET studiji se pokazao jednako uëinkovit ramiprilu u kardiovaskularnoj protekciji kod visokoriziënih bolesnika 8. Irbesartan Indiciran je za lijeëenje AH i nefropatije u bolesnika s dijabetesom tipa 2. Primjenjuje se u dozama od 150 do 300 mg. Nema aktivnih metabolita, a poluæivot u plazmi mu je 11 do 15 sati. U kliniëkom ispitivanju IRMA2 u dijabetiëara je prevenirao progresiju nefropatije 12. Eprosartan Indiciran je za lijeëenje AH u dozi od 600 mg, jednom dnevno. U kliniëkom ispitivanju MOSES bio je bolji od kalcijskog antagonista nitrendipina u sekundarnoj prevenciji cerebrovaskularnog inzulta 13. ARB i kancerogenost U lipnju ove godine veliku pozornost je izazvala metaanaliza objavljena u Ëasopisu Lancet Oncology prema kojoj bolesnici lijeëeni ARB imaju veêu πansu oboljeti od kar- Candesartan Pre-drug is applied as candesartan cilexetil that is during the absorption in the digestive system hydrolyzed into active substance candesartan. The indications are the treatment of hypertension and heart failure, and it is applied in doses from 4 to 32 mg. In the CHARM-Added study it has already proved to be efficient as additional therapy to patients with heart failure that had already been treated with ACE inhibitor and beta-blocker 10. Valsartan It is applied in doses from 80 to 320 mg in indications of hypertension, heart failure when ACE inhibitors or beta blockers may not be applied (not in triple therapy) and following the myocardial infarction in patients with LV dysfunction or signs of heart failure. This has been proved in the two large studies Val-HeFT and VALIANT. The patients treated with valsartan in the Val-HeFT study showed more significant improvement of the NYHA scale and the symptoms of heart failure including dyspnoea, fatigue, edema and rattles in comparison with placebo. The patients using valsartan had better quality of life than the patients using placebo, which proved to be true during treatment and with a change to results of the scale Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Quality of Life in comparison with initial values. The impact volume in patients treated with valsartan has significantly increased, while LVIDD has greatly reduced to the initial value in comparison with placebo 4. In the VALIANT study, valsartan has proved to be equally efficient as the ACE inhibitor captopril in reducing mortality and cardiovascular diseases in high-risk patients following acute myocardial infarction 5. Telmisartan It has a very long time of half-life of 24 hours 11. It is suitable for the treatment of hypertension which is its only indication. It is applied in doses from 40 to 80 mg. In the ONTARGET study it has proved to be as efficient as ramipril in the cardiovascular protection in high-risk patients 8. Irbesartan It is indicated for the treatment of hypertension and nephropathy in patients with diabetes type 2. It is applied in doses from 150 to 300 mg. There are no active metabolites, while plasma half-life is 11 to 15 hours. In the clinical study IRMA2 in diabetic patients, it prevented progression of nephropathy 12. Eprosartan It is indicated for the treatment of hypertension in dose of 600 mg once a day. In the clinical test MOSES it was better than the calcium antagonist nitrendipine in the secondary prevention of stroke 13. ARB medicines and carcinogenicity In June this year, great attention was drawn by metaanalysis published in the journal Lancet Oncology according to which patients treated with ARB have a greater
5 2010;5(11):274. cinoma nego oni lijeëeni placebom. Prema rezultatima pet randomiziranih kliniëkih ispitivanja u kojima je sudjelovalo bolesnika naappleeno je da oni koji su uzimali ARB (85% telmisartan) imaju veêi rizik za oboljevanje od karcinoma u odnosu na kontrolnu skupinu (7,2% : 6,0%). Pri tome je samo znaëajan bio rizik od novonastalog karcinoma pluêa. Prema autorima 1 od 143 bolesnika koji Êe tijekom Ëetiri godine biti lijeëeni ARB zbog toga Êe dobiti karcinom. Autori Ëlanka su rizik nastanka karcinoma ocjenili umjerenim, a mehanizam nastanka nepoznatim. Takoappleer su naglasili da se rizik ne moæe povezati sa pojedinim ARB, veê se odnosi na skupinu 14. Ipak i pored opreznog stava autora rada, u medijima su odmah objavljeni bombastiëni naslovi npr. Lijekovi za visoki tlak mogu izazvati rak ili Lijekovi za visoki tlak izazivaju rak, sreêom s komentarima naπih uglednih struënjaka (prof. FrancetiÊ, prof. PoliÊ) koji su apelirali na stiπavanje panike te obrazloæili moguêe slabosti studije, ali i znaëenje uëinkovite terapije AH koja se postiæe primjenom ARB. Iste stavove je imala i veêina eksperata koji su se javili na tu temu u vodeêim medicinskim publikacijama, a neki su bili toliko radikalni da su Ëak izjavili da se radi o smetlarskoj znanosti ( junk science ). Takoappleer se priopêenjem oglasila i FDA (AmeriËka agencija za lijekove) koja je izjavila da temeljem njihovih podataka korist od primjene ARB daleko prelazi moguêe nuspojave 15. Stavovi koji dovode u pitanje rezultate studije navode da autori nisu raspolagali s izvornom studijskom dokumentacijom veê samo zbirnim podacima iz publikacija, da su bolesnici koji su primali ARB bili uglavnom oni koji nisu mogli uzimati ACE inhibitore zbog kaπlja, a da je to moæda bio prvi znak pluênog maligniteta (jedini tumor statistiëki znaëajniji u bolesnika koji su rabili ARB), takoappleer da nisu uzeti u obzir ostali Ëimbenici koji doprinose malignitetu, npr. puπenje, izloæenost azbestu itd. Na kraju je ve- Êina autora zakljuëila da je korist od uzimanja ARB daleko veêa od moguêe πtete te da bolesnici mogu sa sigurnoπêu nastaviti uzimati ovu terapiju. Received: 10 th Sep 2010 *Address for correspondence: OpÊa bolnica Zadar, Boæe PeriËiÊa 5 HR Zadar, Croatia; Phone: ; aleksandar.knezevic@zd.t-com.hr chance to become ill of carcinoma than those treated with placebo. According to the results of five randomized clinical tests in which 62,000 patients participated, it was found out that those taking ARB (85% telmisartan) show a greater risk of becoming ill of carcinoma in comparison to the control group (7.2% : 6.0%). Then, it was only the risk of newly occurred pulmonary carcinoma that mattered. According to the authors, 1 out of 143 patients treated with ARB will become of carcinoma. The authors of the article evaluated the risk of occurrence of carcinoma as moderate and the mechanism of occurrence as unknown. They also emphasized that the risk may not be linked with a specific ARB, but it refers to the group 14. Even though the authors carefully put forward their attitude, the media publicized some bombastic headings, such as: Hypertension medicines may cause cancer or Hypertension medicines cause cancer, luckily along with the comments of our renowned experts (Prof. FrancetiÊ, Prof. PoliÊ) who called for avoiding panic and explained potential weaknesses of the study and who also explained the importance of the efficient therapy of hypertension that is achieved by application of ARB. Most of the experts who referred to this topic in the leading international medical journals shared the same opinion, but some of them were so radical to declare that it was junk science. FDA (Federal Drug Administration) also stated its opinion by making a statement that based on the data they have available, the benefits from the application of ARB are far greater than any potential side-effects 15. The attitudes making the results of the study doubtful imply that the authors did not have the original study documentation available, but only collective data from publications, that patients who took ARB medicines were only those who could not take ACE inhibitors as a consequence of cough, and that it was the first sign of the pulmonary malignity (the only tumor statistically more significant in patients who used ARB), some other factors that contribute to malignity, such as smoking, exposure to asbestos etc. were not taken into consideration. Eventually, most of the authors concluded that the benefit of taking ARB medicine largely exceeds any potential damage, so patients may safely continue to apply this therapy. Literature 1. Burnier M. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers. Circulation. 2001;103: Catanzaro DF, Frishman MD. Angiotensin receptor blockers for management of hypertension. South Med J. 2010;103: JelakoviÊ B. Smjernice za dijagnosticiranje i lijeëenje arterijske hipertenzije Radne skupine Europskog druπtva za hipertenziju i Europskog kardioloπkog druπtva. Kardio list. 2007;2(12): Cohn JN, Tognoni G. A randomized trial of the angiotensin-receptor blocker valsartan in chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2001;345: Pfeffer MA, Mc Murray JJV, Velazquez EJ, Rouleau JL, Kober L, Maggioni AP, et al. Valsartan, captopril or both in myocardial infarction complicated by heart failure, left ventricular dysfunction or both. N Engl J Med. 2003;349: Shibata MC, Tsuyuki RT, Wiebe N. Effects of ARB on mortality and morbidity in heart failure. Int J Clin Pract. 2008; 62: Opie LH, Pfeffer MA. Inhibitors of ACE, ARB, aldosterone and renin. In: Opie LH, Gersh BJ. Drugs for the heart, Saunders, ONTARGET Investigators. Telmisartan, ramipril or both in patients at high risk for vascular events. N Engl J Med. 2008;358: The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Heart Failure. ESC Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure Eur Heart J. 2008;29: McMurray, Ostergren J, Swedberg K, Granger CG, Helad P, Michelson EL, et al. Effects of candesartan in patients with chronic heart failure and reduced left-ventricular systolic function taking angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors: the CHARM-Added trial. Lancet. 2003;362: Bergovac M, Knezevic A, Plavec D, Trkulja V. Telmisartan in daily clinical practice: Factors affecting efficacy in treatment of primary arterial hypertension. J Postgrad Med. 2009;55:27-32.
6 2010;5(11): Lewis EJ, Hinsicker LG, Clarke WR, Berl T, Pohl MA, Lewis JB, et al. Renoprotective effect of the angiotensin-receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2001;345: Schrader J, Luder S, Kulschewski A, Hammersen F, Plate K, Berger J, et al. Morbidity and mortality after stroke, eprosartan compared with nitrendipine for secondary prevention: principal results of a prospective randomized controlled study (MOSES). Stroke. 2005;36: Sipahi I, Debanne SM, Rowland DY, Simon DI, Fang JC. Angiotensin-receptor blockade and risk of canncer: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11: Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs): Ongoing Safety Review for Cancer Risk. AlertsforHumanMedicalProducts/ucm htm ( )
Optimal blockade of the Renin- Angiotensin-Aldosterone. in chronic heart failure
 Optimal blockade of the Renin- Angiotensin-Aldosterone Aldosterone- (RAA)-System in chronic heart failure Jan Östergren Department of Medicine Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm, Sweden Key Issues
Optimal blockade of the Renin- Angiotensin-Aldosterone Aldosterone- (RAA)-System in chronic heart failure Jan Östergren Department of Medicine Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm, Sweden Key Issues
ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS: MORE THAN THE ALTERNATIVE PRESENTATION BY: PATRICK HO, USC PHARM D. CANDIDATE OF 2017 MENTOR: DR.
 ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS: MORE THAN THE ALTERNATIVE PRESENTATION BY: PATRICK HO, USC PHARM D. CANDIDATE OF 2017 MENTOR: DR. CRAIG STERN, PHARMD, MBA, RPH, FASCP, FASHP, FICA, FLMI, FAMCP RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN
ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS: MORE THAN THE ALTERNATIVE PRESENTATION BY: PATRICK HO, USC PHARM D. CANDIDATE OF 2017 MENTOR: DR. CRAIG STERN, PHARMD, MBA, RPH, FASCP, FASHP, FICA, FLMI, FAMCP RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN
Mayo Clin Proc, March 2003, Vol 78 Role of ARBs in Treatment of Heart Failure 335 system, tissue-based RAS has long-term effects that can modify cardi
 334 Concise Review for Clinicians Therapeutic Role of Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers in the Treatment of Heart Failure Concise Review for Clinicians PRERANA MANOHAR, MD, AND ILEANA L. PIÑA, MD Angiotensin
334 Concise Review for Clinicians Therapeutic Role of Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers in the Treatment of Heart Failure Concise Review for Clinicians PRERANA MANOHAR, MD, AND ILEANA L. PIÑA, MD Angiotensin
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
The role of angiotensin II receptor blockers in the management of heart failure
 European Heart Journal Supplements (2005) 7 (Supplement J), J10 J14 doi:10.1093/eurheartj/sui057 The role of angiotensin II receptor blockers in the management of heart failure John J.V. McMurray* Department
European Heart Journal Supplements (2005) 7 (Supplement J), J10 J14 doi:10.1093/eurheartj/sui057 The role of angiotensin II receptor blockers in the management of heart failure John J.V. McMurray* Department
Scientific conclusions and detailed explanation of the scientific grounds for the differences from the PRAC recommendation
 Annex I Scientific conclusions, grounds for variation to the terms of the marketing authorisations and detailed explanation of the scientific grounds for the differences from the PRAC recommendation 1
Annex I Scientific conclusions, grounds for variation to the terms of the marketing authorisations and detailed explanation of the scientific grounds for the differences from the PRAC recommendation 1
ACE inhibitors: still the gold standard?
 ACE inhibitors: still the gold standard? Session: Twenty-five years after CONSENSUS What have we learnt about the RAAS in heart failure? Lars Køber, MD, D.Sci Department of Cardiology Rigshospitalet University
ACE inhibitors: still the gold standard? Session: Twenty-five years after CONSENSUS What have we learnt about the RAAS in heart failure? Lars Køber, MD, D.Sci Department of Cardiology Rigshospitalet University
Understanding and Development of New Therapies for Heart Failure - Lessons from Recent Clinical Trials -
 Understanding and Development of New Therapies for Heart Failure - Lessons from Recent Clinical Trials - Clinical trials Evidence-based medicine, clinical practice Impact upon Understanding pathophysiology
Understanding and Development of New Therapies for Heart Failure - Lessons from Recent Clinical Trials - Clinical trials Evidence-based medicine, clinical practice Impact upon Understanding pathophysiology
Preventing the cardiovascular complications of hypertension
 European Heart Journal Supplements (2004) 6 (Supplement H), H37 H42 Preventing the cardiovascular complications of hypertension Peter Trenkwalder* Department of Internal Medicine, Starnberg Hospital, Ludwig
European Heart Journal Supplements (2004) 6 (Supplement H), H37 H42 Preventing the cardiovascular complications of hypertension Peter Trenkwalder* Department of Internal Medicine, Starnberg Hospital, Ludwig
Since the initial description of angiotensin II mediated
 CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY: PHYSICIAN UPDATE Manipulation of the Renin-Angiotensin System Michael M. Givertz, MD Since the initial description of angiotensin II mediated hypertension 40 years ago, basic and clinical
CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY: PHYSICIAN UPDATE Manipulation of the Renin-Angiotensin System Michael M. Givertz, MD Since the initial description of angiotensin II mediated hypertension 40 years ago, basic and clinical
State of the art treatment of hypertension: established and new drugs. Prof. M. Burnier Service of Nephrology and Hypertension Lausanne, Switzerland
 State of the art treatment of hypertension: established and new drugs Prof. M. Burnier Service of Nephrology and Hypertension Lausanne, Switzerland First line therapies in hypertension ACE inhibitors AT
State of the art treatment of hypertension: established and new drugs Prof. M. Burnier Service of Nephrology and Hypertension Lausanne, Switzerland First line therapies in hypertension ACE inhibitors AT
RAS Blockade Across the CV Continuum
 A Summary of Recent International Meetings RAS Blockade Across the CV Continuum Copyright New Evidence Presented at the 2009 Congress of the European Society of Cardiology (August 29-September 2, Barcelona)
A Summary of Recent International Meetings RAS Blockade Across the CV Continuum Copyright New Evidence Presented at the 2009 Congress of the European Society of Cardiology (August 29-September 2, Barcelona)
HYPERTENSION IN CKD. LEENA ONGAJYOOTH, M.D., Dr.med RENAL UNIT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL
 HYPERTENSION IN CKD LEENA ONGAJYOOTH, M.D., Dr.med RENAL UNIT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL Stages in Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease and Therapeutic Strategies Complications Normal Increased risk Damage GFR
HYPERTENSION IN CKD LEENA ONGAJYOOTH, M.D., Dr.med RENAL UNIT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL Stages in Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease and Therapeutic Strategies Complications Normal Increased risk Damage GFR
Cardiac Protection across the cardiac continuum. Dong-Ju Choi, MD, PhD College of Medicine Seoul National University
 Cardiac Protection across the cardiac continuum Dong-Ju Choi, MD, PhD College of Medicine Seoul National University Renin Angiotensin Cascade Nitric oxide (NO) Bradykinin Degradation products ACE ACEI
Cardiac Protection across the cardiac continuum Dong-Ju Choi, MD, PhD College of Medicine Seoul National University Renin Angiotensin Cascade Nitric oxide (NO) Bradykinin Degradation products ACE ACEI
heart failure John McMurray University of Glasgow.
 A to Z of RAAS blockade in heart failure John McMurray BHF Cardiovascular Research Centre University of Glasgow. RAAS inhibition in CHF ACE inhibition in patients with low LVEF CHF CONSENSUS Enalapril
A to Z of RAAS blockade in heart failure John McMurray BHF Cardiovascular Research Centre University of Glasgow. RAAS inhibition in CHF ACE inhibition in patients with low LVEF CHF CONSENSUS Enalapril
ACP Brief Fall 2006 prioritization. Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs) for Proteinuria, Hypertension (HTN) and Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
 ACP Brief Fall 2006 prioritization Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs) for Proteinuria, Hypertension (HTN) and Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) Background This topic was submitted by BC PharmaCare during
ACP Brief Fall 2006 prioritization Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs) for Proteinuria, Hypertension (HTN) and Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) Background This topic was submitted by BC PharmaCare during
Hypertension and diabetic nephropathy
 Hypertension and diabetic nephropathy Elisabeth R. Mathiesen Professor, Chief Physician, Dr sci Dep. Of Endocrinology Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen Denmark Hypertension Brain Eye Heart Kidney
Hypertension and diabetic nephropathy Elisabeth R. Mathiesen Professor, Chief Physician, Dr sci Dep. Of Endocrinology Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen Denmark Hypertension Brain Eye Heart Kidney
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs
 Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs Blood Pressure Normal = sys
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs Blood Pressure Normal = sys
ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure
 ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure - 2005 Karl Swedberg Professor of Medicine Department of Medicine Sahlgrenska University Hospital/Östra Göteborg University Göteborg
ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure - 2005 Karl Swedberg Professor of Medicine Department of Medicine Sahlgrenska University Hospital/Östra Göteborg University Göteborg
Angiotensin Receptor Blockers: Novel Role in High-Risk Patients
 Angiotensin Receptor Blockers: Novel Role in High-Risk Patients UsmanJaved, MD a, Prakash C. Deedwania, MD, FACC, FACP, FCCP, FAHA a,b, * KEYWORDS Angiotensin receptor blockers RAAS blockade Cardioprotection
Angiotensin Receptor Blockers: Novel Role in High-Risk Patients UsmanJaved, MD a, Prakash C. Deedwania, MD, FACC, FACP, FCCP, FAHA a,b, * KEYWORDS Angiotensin receptor blockers RAAS blockade Cardioprotection
The Therapeutic Potential of Novel Approaches to RAAS. Professor of Medicine University of California, San Diego
 The Therapeutic Potential of Novel Approaches to RAAS Inhibition in Heart Failure Barry Greenberg, M.D. Professor of Medicine University of California, San Diego Chain of Events Leading to End-Stage Heart
The Therapeutic Potential of Novel Approaches to RAAS Inhibition in Heart Failure Barry Greenberg, M.D. Professor of Medicine University of California, San Diego Chain of Events Leading to End-Stage Heart
1. Antihypertensive agents 2. Vasodilators & treatment of angina 3. Drugs used in heart failure 4. Drugs used in arrhythmias
 1. Antihypertensive agents 2. Vasodilators & treatment of angina 3. Drugs used in heart failure 4. Drugs used in arrhythmias Only need to know drugs discussed in class At the end of this section you should
1. Antihypertensive agents 2. Vasodilators & treatment of angina 3. Drugs used in heart failure 4. Drugs used in arrhythmias Only need to know drugs discussed in class At the end of this section you should
VALUE OF ACEI IN THE MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSION
 VALUE OF ACEI IN THE MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSION Dr Catherine BESEME Paris 6 th December 2005 6 th International Congress of Bangladesh Society of Medicine Hypertension is a risk factor at the source, with
VALUE OF ACEI IN THE MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSION Dr Catherine BESEME Paris 6 th December 2005 6 th International Congress of Bangladesh Society of Medicine Hypertension is a risk factor at the source, with
Therapeutic Targets and Interventions
 Therapeutic Targets and Interventions Ali Valika, MD, FACC Advanced Heart Failure and Pulmonary Hypertension Advocate Medical Group Midwest Heart Foundation Disclosures: 1. Novartis: Speaker Honorarium
Therapeutic Targets and Interventions Ali Valika, MD, FACC Advanced Heart Failure and Pulmonary Hypertension Advocate Medical Group Midwest Heart Foundation Disclosures: 1. Novartis: Speaker Honorarium
Management of Hypertension
 Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
Two landmark clinical trials, CONSEN-
 Heart 2001;86:97 103 HEART FAILURE Angiotensin receptor blockers for chronic heart failure and acute myocardial infarction John J V McMurray Clinical Research Initiative in Heart Failure, Wolfson Building,
Heart 2001;86:97 103 HEART FAILURE Angiotensin receptor blockers for chronic heart failure and acute myocardial infarction John J V McMurray Clinical Research Initiative in Heart Failure, Wolfson Building,
M2 TEACHING UNDERSTANDING PHARMACOLOGY
 M2 TEACHING UNDERSTANDING PHARMACOLOGY USING CVS SYSTEM AS AN EXAMPLE NIGEL FONG 2 JAN 2014 TODAY S OBJECTIVE Pharmacology often seems like an endless list of mechanisms and side effects to memorize. To
M2 TEACHING UNDERSTANDING PHARMACOLOGY USING CVS SYSTEM AS AN EXAMPLE NIGEL FONG 2 JAN 2014 TODAY S OBJECTIVE Pharmacology often seems like an endless list of mechanisms and side effects to memorize. To
ACE inhibitors vs ARBs Myths and Facts
 ACE inhibitors vs ARBs Myths and Facts Prof. Dr. med. Frank Ruschitzka, FRCP (Edinburgh) Director Heart Failure/Transplantation Clinic University Clinic Zurich Switzerland Conflict of interest: Bayer,
ACE inhibitors vs ARBs Myths and Facts Prof. Dr. med. Frank Ruschitzka, FRCP (Edinburgh) Director Heart Failure/Transplantation Clinic University Clinic Zurich Switzerland Conflict of interest: Bayer,
By Prof. Khaled El-Rabat
 What is The Optimum? By Prof. Khaled El-Rabat Professor of Cardiology - Benha Faculty of Medicine HT. Introduction Despite major worldwide efforts over recent decades directed at diagnosing and treating
What is The Optimum? By Prof. Khaled El-Rabat Professor of Cardiology - Benha Faculty of Medicine HT. Introduction Despite major worldwide efforts over recent decades directed at diagnosing and treating
Angiotensin-receptor blockade and risk of cancer: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials
 Angiotensin-receptor blockade and risk of cancer: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials Ilke Sipahi, Sara M Debanne, Douglas Y Rowland, Daniel I Simon, James C Fang Summary Background Angiotensin-receptor
Angiotensin-receptor blockade and risk of cancer: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials Ilke Sipahi, Sara M Debanne, Douglas Y Rowland, Daniel I Simon, James C Fang Summary Background Angiotensin-receptor
Ferrari R, Fox K, Bertrand M, Mourad J.J, Akkerhuis KM, Van Vark L, Boersma E.
 Effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers on cardiovascular mortality in hypertension: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials Ferrari R, Fox K, Bertrand
Effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers on cardiovascular mortality in hypertension: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials Ferrari R, Fox K, Bertrand
Executive Summary. Different antihypertensive drugs as first line therapy in patients with essential hypertension 1
 IQWiG Reports Commission No. A05-09 Different antihypertensive drugs as first line therapy in patients with essential hypertension 1 Executive Summary 1 Translation of the executive summary of the final
IQWiG Reports Commission No. A05-09 Different antihypertensive drugs as first line therapy in patients with essential hypertension 1 Executive Summary 1 Translation of the executive summary of the final
A Fresh Look at ARBs : Focus on HF survival data
 A Fresh Look at ARBs : Focus on HF survival data Seok-Min Kang, MD, Ph D. Division of Cardiology, Severance Cardiovascular Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea HF specialists ARBs,
A Fresh Look at ARBs : Focus on HF survival data Seok-Min Kang, MD, Ph D. Division of Cardiology, Severance Cardiovascular Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea HF specialists ARBs,
THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM
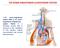 THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM The renin angiotensin system (RAS) or the renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) is a hormone system that is involved in the regulation of the plasma sodium
THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM The renin angiotensin system (RAS) or the renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) is a hormone system that is involved in the regulation of the plasma sodium
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
 Cardiology 59 Using ARBs in the elderly patient Effective management of hypertension can substantially reduce the risk of complications. The angiotensin receptor blockers are one of the latest anti-hypertensive
Cardiology 59 Using ARBs in the elderly patient Effective management of hypertension can substantially reduce the risk of complications. The angiotensin receptor blockers are one of the latest anti-hypertensive
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat
 Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
DIASTOLIC HEART FAILURE
 DIASTOLIC HEART FAILURE M Mohsen Ibrahim, MD Alexandria, Proposed Criteria for Diastolic Heart Failure ESC Working Group (EHJ 1998) CHF signs/symptoms EF 45% Hemodynamic or echo evidence of diastolic dysfunction
DIASTOLIC HEART FAILURE M Mohsen Ibrahim, MD Alexandria, Proposed Criteria for Diastolic Heart Failure ESC Working Group (EHJ 1998) CHF signs/symptoms EF 45% Hemodynamic or echo evidence of diastolic dysfunction
The Road to Renin System Optimization: Renin Inhibitor
 The Road to Renin System Optimization: Renin Inhibitor A New Perspective on the Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS) Yong-Jin Kim, MD Seoul National University Hospital Human and Economic Costs of Hypertension
The Road to Renin System Optimization: Renin Inhibitor A New Perspective on the Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS) Yong-Jin Kim, MD Seoul National University Hospital Human and Economic Costs of Hypertension
I nicijativa za smanjenje ostatnog rizika (R3i) je akademska, T he initiative for reduction of residual risk (R3i) is the
 2010;5(12):294. StruËni rad Rezidualni rizik danas, sutra...; joπ jedan pogled na rezultate ACCORD studije i podstudija Professional article Residual risk today, tomorrow...; Another look at the results
2010;5(12):294. StruËni rad Rezidualni rizik danas, sutra...; joπ jedan pogled na rezultate ACCORD studije i podstudija Professional article Residual risk today, tomorrow...; Another look at the results
The value of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
 New Drugs and Technologies Which Inhibitor of the Renin Angiotensin System Should Be Used in Chronic Heart Failure and Acute Myocardial Infarction? John J.V. McMurray, MD; Marc A. Pfeffer, MD, PhD; Karl
New Drugs and Technologies Which Inhibitor of the Renin Angiotensin System Should Be Used in Chronic Heart Failure and Acute Myocardial Infarction? John J.V. McMurray, MD; Marc A. Pfeffer, MD, PhD; Karl
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Heart Failure Clin 2 (2006) 101 105 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACE inhibitors, in diabetic hypertension, 30 31 Adipokines, cardiovascular events related to, 6 Advanced
Heart Failure Clin 2 (2006) 101 105 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACE inhibitors, in diabetic hypertension, 30 31 Adipokines, cardiovascular events related to, 6 Advanced
Hypertension (JNC-8)
 Hypertension (JNC-8) Southern California University of Health Sciences Physician Assistant Program Management and Treatment of Hypertension April 17, 2018, presented by Ezra Levy, Pharm.D.! The 8 th Joint
Hypertension (JNC-8) Southern California University of Health Sciences Physician Assistant Program Management and Treatment of Hypertension April 17, 2018, presented by Ezra Levy, Pharm.D.! The 8 th Joint
Angiotensin receptor blockers in the treatment of heart failure
 Heart Failure: Pharmacologic Management Edited by Arthur M. Feldman Copyright 2006 by Blackwell Publishing 4 CHAPTER 4 Angiotensin receptor blockers in the treatment of heart failure Anita Deswal, MD,
Heart Failure: Pharmacologic Management Edited by Arthur M. Feldman Copyright 2006 by Blackwell Publishing 4 CHAPTER 4 Angiotensin receptor blockers in the treatment of heart failure Anita Deswal, MD,
Drugs acting on the reninangiotensin-aldosterone
 Drugs acting on the reninangiotensin-aldosterone system John McMurray Eugene Braunwald Scholar in Cardiovascular Diseases, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Boston & Visiting Professor, Harvard Medical School
Drugs acting on the reninangiotensin-aldosterone system John McMurray Eugene Braunwald Scholar in Cardiovascular Diseases, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Boston & Visiting Professor, Harvard Medical School
Combination of renin-angiotensinaldosterone. how to choose?
 Combination of renin-angiotensinaldosterone system inhibitors how to choose? Karl Swedberg Professor of Medicine Sahlgrenska Academy University of Gothenburg karl.swedberg@gu.se Disclosures Research grants
Combination of renin-angiotensinaldosterone system inhibitors how to choose? Karl Swedberg Professor of Medicine Sahlgrenska Academy University of Gothenburg karl.swedberg@gu.se Disclosures Research grants
DRUGS USED TO TREAT HYPERTENSION BY ALI ALALAWI
 DRUGS USED TO TREAT HYPERTENSION BY ALI ALALAWI 3. Vasodilators Drugs which dilate blood vessels ( decrease peripheral vascular resistance) by acting on smooth muscle cells through non-autonomic mechanisms:
DRUGS USED TO TREAT HYPERTENSION BY ALI ALALAWI 3. Vasodilators Drugs which dilate blood vessels ( decrease peripheral vascular resistance) by acting on smooth muscle cells through non-autonomic mechanisms:
Scientific conclusions and detailed explanation of the scientific grounds for the differences from the PRAC recommendation
 Annex I Scientific conclusions, grounds for variation to the terms of the marketing authorisations and detailed explanation of the scientific grounds for the differences from the PRAC recommendation 1
Annex I Scientific conclusions, grounds for variation to the terms of the marketing authorisations and detailed explanation of the scientific grounds for the differences from the PRAC recommendation 1
Entresto Development of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction
 Cardio-Metabolic Franchise Entresto Development of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction Randy L Webb, PhD Rutgers Workshop October 21, 2016 Heart
Cardio-Metabolic Franchise Entresto Development of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction Randy L Webb, PhD Rutgers Workshop October 21, 2016 Heart
Section 3, Lecture 2
 59-291 Section 3, Lecture 2 Diuretics: -increase in Na + excretion (naturesis) Thiazide and Related diuretics -decreased PVR due to decreases muscle contraction -an economical and effective treatment -protect
59-291 Section 3, Lecture 2 Diuretics: -increase in Na + excretion (naturesis) Thiazide and Related diuretics -decreased PVR due to decreases muscle contraction -an economical and effective treatment -protect
Rationale for the use of Single Pill Combination (SPC) and Asian data of ARB/CCB SPC
 Rationale for the use of Single Pill Combination (SPC) and Asian data of ARB/CCB SPC Seung Woo Park, MD Samsung Medical Center BP Control Rates in Asia BP controlled BP uncontrolled 24.3% 36.6% 19% Turkey
Rationale for the use of Single Pill Combination (SPC) and Asian data of ARB/CCB SPC Seung Woo Park, MD Samsung Medical Center BP Control Rates in Asia BP controlled BP uncontrolled 24.3% 36.6% 19% Turkey
7/7/ CHD/MI LVH and LV dysfunction Dysrrhythmias Stroke PVD Renal insufficiency and failure Retinopathy. Normal <120 Prehypertension
 Prevalence of Hypertension Hypertension: Diagnosis and Management T. Villela, M.D. Program Director University of California, San Francisco-San Francisco General Hospital Family and Community Medicine
Prevalence of Hypertension Hypertension: Diagnosis and Management T. Villela, M.D. Program Director University of California, San Francisco-San Francisco General Hospital Family and Community Medicine
Phase 3 investigation of aprocitentan for resistant hypertension management. Investor Webcast June 2018
 Phase 3 investigation of aprocitentan for resistant hypertension management Investor Webcast June 2018 The following information contains certain forward-looking statements, relating to the company s business,
Phase 3 investigation of aprocitentan for resistant hypertension management Investor Webcast June 2018 The following information contains certain forward-looking statements, relating to the company s business,
Analysis of Factors Causing Hyperkalemia
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Analysis of Factors Causing Hyperkalemia Kenmei Takaichi 1, Fumi Takemoto 1, Yoshifumi Ubara 1 and Yasumichi Mori 2 Abstract Objective Patients with impaired renal function or diabetes
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Analysis of Factors Causing Hyperkalemia Kenmei Takaichi 1, Fumi Takemoto 1, Yoshifumi Ubara 1 and Yasumichi Mori 2 Abstract Objective Patients with impaired renal function or diabetes
National Horizon Scanning Centre. Irbesartan (Aprovel) for heart failure with preserved systolic function. August 2008
 Irbesartan (Aprovel) for heart failure with preserved systolic function August 2008 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It
Irbesartan (Aprovel) for heart failure with preserved systolic function August 2008 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It
Clinical cases with Coversyl 10 mg
 Clinical cases Coversyl 10 mg For upgraded benefits in hypertension A Editorial This brochure, Clinical cases Coversyl 10 mg for upgraded benefits in hypertension, illustrates a variety of hypertensive
Clinical cases Coversyl 10 mg For upgraded benefits in hypertension A Editorial This brochure, Clinical cases Coversyl 10 mg for upgraded benefits in hypertension, illustrates a variety of hypertensive
RENAAL, IRMA-2 and IDNT. Three featured trials linking a disease spectrum IDNT RENAAL. Death IRMA 2
 Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy and Proteinuria Background End stage renal disease is a major cause of death and disability among diabetics BP reduction is important to slow the progression of diabetic
Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy and Proteinuria Background End stage renal disease is a major cause of death and disability among diabetics BP reduction is important to slow the progression of diabetic
Nurse-sensitive factors in hypertension management
 Nurse-sensitive factors in hypertension management Hypertension treatment State of the Art Copper Hall 14:45-15:04 02/04/2011 Philippe van de Borne, MD, PhD Department of cardiology ULB-Erasme Hospital
Nurse-sensitive factors in hypertension management Hypertension treatment State of the Art Copper Hall 14:45-15:04 02/04/2011 Philippe van de Borne, MD, PhD Department of cardiology ULB-Erasme Hospital
I know the trials in heart failure but how do I manage my patient? Dosing of neurohormones antagonists
 I know the trials in heart failure but how do I manage my patient? Dosing of neurohormones antagonists Alessandro Fucili (Ferrara, IT) Massimo F Piepoli (Piacenza, IT) Clinical Case: 82 year old woman
I know the trials in heart failure but how do I manage my patient? Dosing of neurohormones antagonists Alessandro Fucili (Ferrara, IT) Massimo F Piepoli (Piacenza, IT) Clinical Case: 82 year old woman
Since 1898, when renin was isolated from
 NARRATIVE REVIEW Dual Blockade of the Renin-Angiotensin System for Cardiorenal Protection: An Update Mustafa Arıcı, MD, and Yunus Erdem, MD The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) has an important role in hypertension
NARRATIVE REVIEW Dual Blockade of the Renin-Angiotensin System for Cardiorenal Protection: An Update Mustafa Arıcı, MD, and Yunus Erdem, MD The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) has an important role in hypertension
LCZ696: LA NUOVA RIVOLUZIONE NELLA TERAPIA DELLO SCOMPENSO CARDIACO. Dario Leosco Università di Napoli Federico II
 LCZ696: LA NUOVA RIVOLUZIONE NELLA TERAPIA DELLO SCOMPENSO CARDIACO Dario Leosco Università di Napoli Federico II Projected changes in cardiovascular diseases CVD Deaths Increase 33% CVD DALYS 22% CAD
LCZ696: LA NUOVA RIVOLUZIONE NELLA TERAPIA DELLO SCOMPENSO CARDIACO Dario Leosco Università di Napoli Federico II Projected changes in cardiovascular diseases CVD Deaths Increase 33% CVD DALYS 22% CAD
ACE inhibitors vs ARBs: Is one class better for heart failure?
 HEART FAILURE UPDATE MARK E. DUNLAP, MD * Associate Professor of Medicine, Physiology, and Biophysics, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, and Louis B. Stokes Cleveland VA Medical Center,
HEART FAILURE UPDATE MARK E. DUNLAP, MD * Associate Professor of Medicine, Physiology, and Biophysics, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, and Louis B. Stokes Cleveland VA Medical Center,
Hypertension Update Clinical Controversies Regarding Age and Race
 Hypertension Update Clinical Controversies Regarding Age and Race Allison Helmer, PharmD, BCACP Assistant Clinical Professor Auburn University Harrison School of Pharmacy July 22, 2017 DISCLOSURE/CONFLICT
Hypertension Update Clinical Controversies Regarding Age and Race Allison Helmer, PharmD, BCACP Assistant Clinical Professor Auburn University Harrison School of Pharmacy July 22, 2017 DISCLOSURE/CONFLICT
Metabolic Consequences of Anti Hypertensives: Is It Clinically Important?
 Metabolic Consequences of Anti Hypertensives: Is It Clinically Important?,FACA,FICA,MASH,FVBWG,MISCP CONSULTANT OF CARDIOLOGY DIRECTOR OF PORT-FOUAD HOSPITAL CCU Consideration of antihypertensive agents
Metabolic Consequences of Anti Hypertensives: Is It Clinically Important?,FACA,FICA,MASH,FVBWG,MISCP CONSULTANT OF CARDIOLOGY DIRECTOR OF PORT-FOUAD HOSPITAL CCU Consideration of antihypertensive agents
Treating HF Patients with ARNI s Why, When and How?
 Treating HF Patients with ARNI s Why, When and How? 19 th Annual San Diego Heart Failure Symposium for Primary Care Physicians January 11-12, 2019 La Jolla, CA Barry Greenberg M.D. Distinguished Professor
Treating HF Patients with ARNI s Why, When and How? 19 th Annual San Diego Heart Failure Symposium for Primary Care Physicians January 11-12, 2019 La Jolla, CA Barry Greenberg M.D. Distinguished Professor
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 7 January 2009
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 7 January 2009 LERCAPRESS 10 mg/10 mg, film-coated tablets Pack of 30 (CIP code: 385 953-3) Pack of 90 (CIP code:
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 7 January 2009 LERCAPRESS 10 mg/10 mg, film-coated tablets Pack of 30 (CIP code: 385 953-3) Pack of 90 (CIP code:
Hypertension Management Focus on new RAAS blocker. Disclosure
 Hypertension Management Focus on new RAAS blocker Rameshkumar Raman M.D Endocrine Associates of The Quad Cities Disclosure Speaker bureau Abbott, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, Takeda, Merck, Solvay
Hypertension Management Focus on new RAAS blocker Rameshkumar Raman M.D Endocrine Associates of The Quad Cities Disclosure Speaker bureau Abbott, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, Takeda, Merck, Solvay
Healthcare Implications of Achieving JNC 7 Blood Pressure Goals in Clinical Practice
 CONTINUING EDUCATION Healthcare Implications of Achieving JNC 7 Blood Pressure Goals in Clinical Practice GOAL To provide participants with current information about current blood pressure goals and effective
CONTINUING EDUCATION Healthcare Implications of Achieving JNC 7 Blood Pressure Goals in Clinical Practice GOAL To provide participants with current information about current blood pressure goals and effective
Definition of Congestive Heart Failure
 Heart Failure Definition of Congestive Heart Failure A clinical syndrome of signs & symptoms resulting from the heart s inability to supply adequate tissue perfusion. CHF Epidemiology Affects 4.7 million
Heart Failure Definition of Congestive Heart Failure A clinical syndrome of signs & symptoms resulting from the heart s inability to supply adequate tissue perfusion. CHF Epidemiology Affects 4.7 million
Disclosure of Relationships
 Disclosure of Relationships Over the past 12 months Dr Ruilope has served as Consultant and Speakers Bureau member of Astra-Zeneca, Bayer, Daiichi-Sankyo, Menarini, Novartis, Otsuka, Pfizer, Relypsa, Servier
Disclosure of Relationships Over the past 12 months Dr Ruilope has served as Consultant and Speakers Bureau member of Astra-Zeneca, Bayer, Daiichi-Sankyo, Menarini, Novartis, Otsuka, Pfizer, Relypsa, Servier
Heart Failure. Subjective SOB (shortness of breath) Peripheral edema. Orthopnea (2-3 pillows) PND (paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea)
 Pharmacology I. Definitions A. Heart Failure (HF) Heart Failure Ezra Levy, Pharm.D. HF Results when one or both ventricles are unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the body s needs There are 2 types
Pharmacology I. Definitions A. Heart Failure (HF) Heart Failure Ezra Levy, Pharm.D. HF Results when one or both ventricles are unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the body s needs There are 2 types
Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers PROTEINURIA
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers PROTEINURIA
Elements for a public summary
 VI.2 Elements for a public summary VI.2.1Overview of disease epidemiology 1 Losartan is indicated for: Treatment of essential hypertension in adults and in children and adolescent 6 18 years of age. Treatment
VI.2 Elements for a public summary VI.2.1Overview of disease epidemiology 1 Losartan is indicated for: Treatment of essential hypertension in adults and in children and adolescent 6 18 years of age. Treatment
Pharmacy Medical Policy Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonists
 Pharmacy Medical Policy Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonists Table of Contents Policy: Commercial Information Pertaining to All Policies Endnotes Policy: Medicare References Forms Policy History Policy
Pharmacy Medical Policy Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonists Table of Contents Policy: Commercial Information Pertaining to All Policies Endnotes Policy: Medicare References Forms Policy History Policy
Individual management of arterial hypertension. Doumas Michael, Internist Lecturer, Aristotle University, Thessaloniki
 Individual management of arterial hypertension Doumas Michael, Internist Lecturer, Aristotle University, Thessaloniki From Population to Individual Management of Arterial Hypertension Epidemiologic impact
Individual management of arterial hypertension Doumas Michael, Internist Lecturer, Aristotle University, Thessaloniki From Population to Individual Management of Arterial Hypertension Epidemiologic impact
Φαρμακευτική θεραπεία της μετεμφραγματικής καρδιακής ανεπάρκειας. Α. Καραβίδας Υπεύθυνος ιατρείου καρδιακής ανεπάρκειας Γ.Ν.Α Γ.
 Φαρμακευτική θεραπεία της μετεμφραγματικής καρδιακής ανεπάρκειας Α. Καραβίδας Υπεύθυνος ιατρείου καρδιακής ανεπάρκειας Γ.Ν.Α Γ.Γεννηματάς Clinical Trials on Fibrinolysis N = 61.41 AMI pts, ( GUSTO I, GUSTOIIb,
Φαρμακευτική θεραπεία της μετεμφραγματικής καρδιακής ανεπάρκειας Α. Καραβίδας Υπεύθυνος ιατρείου καρδιακής ανεπάρκειας Γ.Ν.Α Γ.Γεννηματάς Clinical Trials on Fibrinolysis N = 61.41 AMI pts, ( GUSTO I, GUSTOIIb,
Aldosterone Antagonism in Heart Failure: Now for all Patients?
 Aldosterone Antagonism in Heart Failure: Now for all Patients? Inder Anand, MD, FRCP, D Phil (Oxon.) Professor of Medicine, University of Minnesota, Director Heart Failure Program, VA Medical Center 111C
Aldosterone Antagonism in Heart Failure: Now for all Patients? Inder Anand, MD, FRCP, D Phil (Oxon.) Professor of Medicine, University of Minnesota, Director Heart Failure Program, VA Medical Center 111C
LXIV: DRUGS: 4. RAS BLOCKADE
 LXIV: DRUGS: 4. RAS BLOCKADE ACE Inhibitors Components of RAS Actions of Angiotensin i II Indications for ACEIs Contraindications RAS blockade in hypertension RAS blockade in CAD RAS blockade in HF Limitations
LXIV: DRUGS: 4. RAS BLOCKADE ACE Inhibitors Components of RAS Actions of Angiotensin i II Indications for ACEIs Contraindications RAS blockade in hypertension RAS blockade in CAD RAS blockade in HF Limitations
LCZ696 A First-in-Class Angiotensin Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitor
 The Angiotensin Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitor LCZ696 in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction The Prospective comparison of ARNI with ARB on Management Of heart failure with preserved ejection
The Angiotensin Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitor LCZ696 in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction The Prospective comparison of ARNI with ARB on Management Of heart failure with preserved ejection
Prevention of Cardiovascular Events in Hypertension and CAD & Management of Hypertension in HF of Ischemic origin
 "Insight Heart" is also available at www.squarepharma.com.bd Vol: 911 No: 4; 4; 2012 2015 Prevention of Cardiovascular Events in Hypertension and CAD Drug-eluting & Management of Hypertension in HF of
"Insight Heart" is also available at www.squarepharma.com.bd Vol: 911 No: 4; 4; 2012 2015 Prevention of Cardiovascular Events in Hypertension and CAD Drug-eluting & Management of Hypertension in HF of
U Republici Hrvatskoj, kao i diljem suvremenog svijeta, I n the Republic of Croatia and a part of the contemporary
 2011;6(1-2):10. Pregledni Ëlanak Ranolazin: nova moguênost i novi mehanizam u lijeëenju kroniëne angine pektoris Review article Ranolazine: a new possibility and a new mechanism in the treatment of chronic
2011;6(1-2):10. Pregledni Ëlanak Ranolazin: nova moguênost i novi mehanizam u lijeëenju kroniëne angine pektoris Review article Ranolazine: a new possibility and a new mechanism in the treatment of chronic
Satish K Surabhi, MD.FACC,FSCAI,RPVI Medical Director, Cardiac Cath Labs AnMed Health Heart & Vascular Care
 Satish K Surabhi, MD.FACC,FSCAI,RPVI Medical Director, Cardiac Cath Labs AnMed Health Heart & Vascular Care None Fig. 1. Progression of Heart Failure.With each hospitalization for acute heart failure,
Satish K Surabhi, MD.FACC,FSCAI,RPVI Medical Director, Cardiac Cath Labs AnMed Health Heart & Vascular Care None Fig. 1. Progression of Heart Failure.With each hospitalization for acute heart failure,
Clinical Measurement of Drug Action
 1 Clinical Measurement of Drug Action Nick Holford Dept Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology University of Auckland 2 The $1,000,000 Questions Is this drug effective? - is it better than a competitor/alternative?
1 Clinical Measurement of Drug Action Nick Holford Dept Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology University of Auckland 2 The $1,000,000 Questions Is this drug effective? - is it better than a competitor/alternative?
ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING
 BRIEF REPORT Impact of on Nonfatal Myocardial Infarction and Cardiovascular Death in Patients With Heart Failure Catherine Demers, MD, MSc John J. V. McMurray, MD Karl Swedberg, MD, PhD Marc A. Pfeffer,
BRIEF REPORT Impact of on Nonfatal Myocardial Infarction and Cardiovascular Death in Patients With Heart Failure Catherine Demers, MD, MSc John J. V. McMurray, MD Karl Swedberg, MD, PhD Marc A. Pfeffer,
ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure
 Patients t with acute heart failure frequently develop chronic heart failure Patients with chronic heart failure frequently decompensate acutely ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and A clinical response
Patients t with acute heart failure frequently develop chronic heart failure Patients with chronic heart failure frequently decompensate acutely ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and A clinical response
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australasians with Renal Impairment. Blood Pressure Control role of specific antihypertensives
 Blood Pressure Control role of specific antihypertensives Date written: May 2005 Final submission: October 2005 Author: Adrian Gillian GUIDELINES a. Regimens that include angiotensin-converting enzyme
Blood Pressure Control role of specific antihypertensives Date written: May 2005 Final submission: October 2005 Author: Adrian Gillian GUIDELINES a. Regimens that include angiotensin-converting enzyme
This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data.
 abcd Clinical Study Synopsis for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis which is part of the
abcd Clinical Study Synopsis for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis which is part of the
Antihypertensive drugs: I. Thiazide and other diuretics:
 Clinical assessment of hypertensive patient: You have to take history regarding the presence of other risk factors for CAb like diabetes mellitus, smoking, etc. Take history whether the patient takes medications
Clinical assessment of hypertensive patient: You have to take history regarding the presence of other risk factors for CAb like diabetes mellitus, smoking, etc. Take history whether the patient takes medications
HEART FAILURE SUMMARY. and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. the cornerstone of heart failure treatment.
 HEART FAILURE SUMMARY + Heart Failure is a condition affecting a large number of Irish people and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. + ACE inhibitors, in combination with diuretics,
HEART FAILURE SUMMARY + Heart Failure is a condition affecting a large number of Irish people and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. + ACE inhibitors, in combination with diuretics,
HeFSSA Prac++oners Program 2016 What is NEW in Heart Failure treatment?
 HeFSSA Prac++oners Program 2016 What is NEW in Heart Failure treatment? 08:00 Registra-on 08:25 Welcome and Thank You to Sponsors 08:30 09:15 10:00 10:30 The new kid on the block ARNI How do I effec-vely
HeFSSA Prac++oners Program 2016 What is NEW in Heart Failure treatment? 08:00 Registra-on 08:25 Welcome and Thank You to Sponsors 08:30 09:15 10:00 10:30 The new kid on the block ARNI How do I effec-vely
Kako optimalno lijeëiti arterijsku hipertenziju? How to Optimally Treat Arterial Hypertension?
 KARDIOLOGIJA U PRAKSI ODABRANA POGLAVLJA CARDIOLOGY IN PRACTICE SELECTED CHAPTERS Kako optimalno lijeëiti arterijsku hipertenziju? How to Optimally Treat Arterial Hypertension? Duπko KuzmaniÊ, Mario LaganoviÊ
KARDIOLOGIJA U PRAKSI ODABRANA POGLAVLJA CARDIOLOGY IN PRACTICE SELECTED CHAPTERS Kako optimalno lijeëiti arterijsku hipertenziju? How to Optimally Treat Arterial Hypertension? Duπko KuzmaniÊ, Mario LaganoviÊ
Disclosures for Presenter
 A Comparison of Angiotensin Receptor- Neprilysin Inhibition (ARNI) With ACE Inhibition in the Long-Term Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure With a Reduced Ejection Fraction Milton Packer, John J.V. McMurray,
A Comparison of Angiotensin Receptor- Neprilysin Inhibition (ARNI) With ACE Inhibition in the Long-Term Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure With a Reduced Ejection Fraction Milton Packer, John J.V. McMurray,
Hypertension. Penny Mosley MRPharmS
 Hypertension Penny Mosley MRPharmS Outline of presentation Introduction to hypertension Physiological control of arterial blood pressure What determines our bp? What determines the heart rate? What determines
Hypertension Penny Mosley MRPharmS Outline of presentation Introduction to hypertension Physiological control of arterial blood pressure What determines our bp? What determines the heart rate? What determines
Heart Failure: Combination Treatment Strategies
 Heart Failure: Combination Treatment Strategies M. McDonald MD, FRCP State of the Heart Symposium May 28, 2011 None Disclosures Case 69 F, prior MIs (LV ejection fraction 25%), HTN No demonstrable ischemia
Heart Failure: Combination Treatment Strategies M. McDonald MD, FRCP State of the Heart Symposium May 28, 2011 None Disclosures Case 69 F, prior MIs (LV ejection fraction 25%), HTN No demonstrable ischemia
Clinical Updates in the Treatment of Hypertension JNC 7 vs. JNC 8. Lauren Thomas, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Resident South Pointe Hospital
 Clinical Updates in the Treatment of Hypertension JNC 7 vs. JNC 8 Lauren Thomas, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Resident South Pointe Hospital Objectives Review the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC
Clinical Updates in the Treatment of Hypertension JNC 7 vs. JNC 8 Lauren Thomas, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Resident South Pointe Hospital Objectives Review the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC
Cardiac Drugs: Chapter 9 Worksheet Cardiac Agents. 1. drugs affect the rate of the heart and can either increase its rate or decrease its rate.
 Complete the following. 1. drugs affect the rate of the heart and can either increase its rate or decrease its rate. 2. drugs affect the force of contraction and can be either positive or negative. 3.
Complete the following. 1. drugs affect the rate of the heart and can either increase its rate or decrease its rate. 2. drugs affect the force of contraction and can be either positive or negative. 3.
Managing Hypertension in Diabetes Sean Stewart, PharmD, BCPS, BCACP, CLS Internal Medicine Park Nicollet Clinic St Louis Park.
 Managing Hypertension in Diabetes 2015 Sean Stewart, PharmD, BCPS, BCACP, CLS Internal Medicine Park Nicollet Clinic St Louis Park Case Scenario Mike M is a 59 year old man with type 2 diabetes managed
Managing Hypertension in Diabetes 2015 Sean Stewart, PharmD, BCPS, BCACP, CLS Internal Medicine Park Nicollet Clinic St Louis Park Case Scenario Mike M is a 59 year old man with type 2 diabetes managed
RAAS blocker + B Blocker Troubleshooting
 RAAS blocker + B Blocker Troubleshooting Heart Failure ECHO Clinic Virtual Heart Failure Consultation and Education Prof Ken McDonald & Dr. Patricia Campbell 13 th March 2017 HF activates 3 neurohormonal
RAAS blocker + B Blocker Troubleshooting Heart Failure ECHO Clinic Virtual Heart Failure Consultation and Education Prof Ken McDonald & Dr. Patricia Campbell 13 th March 2017 HF activates 3 neurohormonal
Renin Angiotensin System Current and Potential Targets
 Renin Angiotensin System Current and Potential Targets Dae Suk Han, MD. Seung Hyeok Han, MD. Department of Internal Medicine Division of Nephrology Yonsei University College of Medicine Renin The First
Renin Angiotensin System Current and Potential Targets Dae Suk Han, MD. Seung Hyeok Han, MD. Department of Internal Medicine Division of Nephrology Yonsei University College of Medicine Renin The First
Treating Hypertension in Individuals with Diabetes
 Treating Hypertension in Individuals with Diabetes Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted in any form or by any
Treating Hypertension in Individuals with Diabetes Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted in any form or by any
Reducing proteinuria
 Date written: May 2005 Final submission: October 2005 Author: Adrian Gillin Reducing proteinuria GUIDELINES a. The beneficial effect of treatment regimens that include angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitors
Date written: May 2005 Final submission: October 2005 Author: Adrian Gillin Reducing proteinuria GUIDELINES a. The beneficial effect of treatment regimens that include angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitors
