Lijekovi koji djeluju na renin-angiotenzin- -aldosteronski sustav Drugs Targeting the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System
|
|
|
- Esmond Tyler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PRINCIPI FARMAKOTERAPIJE KARDIOVASKULARNIH BOLESTI PRINCIPLES OF CARDIOVASCULAR PHARMACOTHERAPY Lijekovi koji djeluju na renin-angiotenzin- -aldosteronski sustav Drugs Targeting the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Dragan Ljutić, Ivo Jeličić Interna klinika Medicinskog fakulteta Sveučilišta u Splitu KBC Split Split, Spinčićeva 1 Sažetak Renin-angiotenzin-aldosteronski sustav ima ključnu ulogu u regulaciji arterijskog tlaka, regulaciji perfuzije tkiva i homeostazi elektrolita i tjelesnih tekućina. Njegov konačni produkt angiotenzin II odgovoran je za većinu učinaka tog sustava: vazokonstrikciju venula i arteriola, lučenje antidiuretskog hormona iz hipofize, aldosterona iz nadbubrežne žlijezde, aktivaciju simpatikusa, stimulaciju centra za žeđu, koji u konačnici imaju za posljedicu porast sistoličkog i dijastoličkog arterijskog tlaka. Blokiranje ovog sustava lijekovima danas je moguće na više razina: ACE-inhibitori, blokatori angiotenzinskih receptora, direktni inhibitori renina, blokada aldosteronskih receptora, blokada β1-receptora na stanicama makule denze. U istraživanju su i lijekovi koji stimuliraju AT2-receptor, imunizacija protiv angiotenzina te inhibitori kimaze. Summary The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system plays a key role in the regulation of blood pressure and tissue perfusion and in electrolyte and body fluids homeostasis. Its final product is angiotensin II, which is responsible for the majority of its effects: vasoconstriction of venules and arterioles, secretion of antidiuretic hormone from the hypophysis, secretion of aldosterone from the suprarenal gland, activation of the sympathicus, and stimulation of the thirst centre. These effects finally lead to a rise in systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Nowadays, this system can be blocked by drugs on different levels, namely by ACE inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, direct renin inhibitors, aldosterone receptor blockers, and by blocking β1 receptors on the macula densa. The research of new drugs such as AT2 receptor agonists, angiotensin vaccine and chymase inhibitors is underway. Ključne riječi: renin, angiotenzin, aldosteron, angiotenzinski receptor Key words: renin, angiotensin, aldosterone, angiotensin receptor Jedan od sustava koji ima bitnu ulogu u regulaciji arterijskog tlaka, regulaciji perfuzije tkiva i homeostazi elektrolita i tjelesnih tekućina jest renin-angiotenzin-aldosteronski sustav (RAAS). Karakteristika ovog sustava očituje se u nizu interakcija različitih supstancija kojima je ciljno stvaranje vazoaktivnog angiotenzina II (Ang II) s ekspresijom njegovih brojnih djelovanja. No, novija istraživanja pokazuju da se ne radi samo o Ang II, nego da aktivnost posjeduju i druge supstancije koje su dio sustava. I zaista posljednjih 30 godina ovaj sustav ne prestaje biti u središtu interesa brojnih istraživača. Štoviše, jedna od podjela esencijalne arterijske hipertenzije bazirana je na razini reninske aktivnosti plazme: hipo-, normo- i hiperreninemijska arterijska hipertenzija. Danas se, zaista, ne može zamisliti moderna kardiovaskularna terapija bez lijekova koji utječu na ovaj sustav. Od kada datiraju prva saznanja o RAAS-u? Za povijest ovog sustava bitna su tri razdoblja: kraj 19. stoljeća, te tridesete i pedesete godine 20. stoljeća. Naime, godine finski fiziolog Robert Tigerstedt i njegov student, Šveđanin Per Bergman iz zečjeg bubrega (kora, a ne srž) izolirali su tvar koja je, uštrcana u jugularnu venu zeca, povisila arterijski tlak. Tu su tvar nazvali renin te su zaključili da bi mogla biti povezana s hipertrofijom srca u bubrežnoj bolesti i visokim arterijskim tlakom (1). Ali, kako drugi laboratoriji nisu mogli ponoviti ovaj pokus, ovo je saznanje bilo zanemareno do tridesetih godina 20. stoljeća: godine Goldblatt je objavio da bubrežna ishemija uzroko- 139
2 Angiotenzin II djeluje vazokonstriktorno na venule povećavajući volumno opterećenje (preload) i udarni volumen, odnosno sistolički tlak. Istodobno djeluje vazokonstriktorno na arteriole, povećavajući tlačno opterećenje (afterload) i podižući dijastolički tlak. Uz to potiče lučenje antidiuretskog hormona iz hipofize, aldosterona iz nadbubrežne žlijezde, aktivira simpatikus (stimulira simpatičke ganglije, povećava sekreciju i smanjuje povrat adrenalina na zavrvana klamping tehnikom renalne arterije uzrokuje arterijsku hipertenziju. Nedugo nakon toga utvrđeno je da bubreg izlučuje još jednu supstanciju neovisno o reninu. Utvrđeno je da renin sam po sebi nema punu aktivnost nego da djeluje na drugu supstanciju koja je nazvana angiotenzinogen da bi se oslobodila aktivna supstancija. Ova supstancija nazvana je angiotonin od istraživača u Americi i hipertenzin od istraživača u Australiji, a kao kompromis angiotenzin. U ranim pedesetim godinama Steggs i suradnici utvrdili su da ovaj peptid egzistira u dvije forme koje su nazvane Ang I i Ang II. Poslije se utvrdilo da se dekapeptid Ang I cijepa pod utjecajem enzima angiotenzin konvertaze u aktivni oktapeptid Ang II. Potom je utvrđeno da Ang II stimulira i izlučivanje aldosterona (glavnog regulatora ravnoteže natrija i kalija) iz nadbubrežne žlijezde. Koje su komponentne RAAS-a? U ranim 1970-ima otkrivene su glavne komponente klasičnoga cirkulirajućeg RAAS-a (slika 1). U bilo kojem slučaju sniženja arterijskog tlaka (pada efektivnog arterijskog volumena plazme: npr. proljev, povraćanje, krvarenje, bijeg intravaskularne tekućine/dekompenzacija srca, ciroza jetre, nefrotski sindrom) smanjuje se perfuzija bubrega što registriraju jukstaglomerularne (JG) stanice (oblažu aferentnu, a katkad i eferentnu arteriolu) koje tada u krvotok otpuštaju renin. Renin je prehormon. Bubreg izlučuje renin, ali i prorenin. Prorenin se detektira u 70% do 90% imunoreaktivnog renina u humanoj cirkulaciji. Osim već spomenutoga baroreceptorskog mehanizma u aferentnoj arterioli bubrega aktivnu sekreciju renina reguliraju i: promjene u izlučivanju NaCl (registrira se kao promjena u Cl) prema stanicama makule denze distalnog tubula (koje su blizu JG-stanica i zajedno čine jukstaglomerularni aparat, JGA), stimulacija simpatičkih živaca putem β 1 -adrenergičkih receptora te negativna povratna sprega putem izravnog djelovanja Ang II na JG-stanice (2). Renin sintetiziraju i druga tkiva kao što su: mozak, nadbubrežna žlijezda, ovariji, visceralno masno tkivo te vjerojatno srce i vaskulatura (2). Čimbenici koji reguliraju izlučivanje renina u ovim tkivima slabo su poznati. Kontrola sekrecije renina ključ je u aktivaciji RAAS-a. Angiotenzinogen u najvećem dijelu i permanentno sintetizira jetra, ali ga sintetiziraju i bubreg, mozak, srce, vaskulatura, nadbubrežna žlijezda, ovariji, placenta i masno tkivo (2). Koncentracija u plazmi mu je stabilna; sinteza mu raste kao odgovor na glukokortikoide, estrogene i druge spolne hormone, te hormone štitnjače, citokine (npr. IL-1, TNF-α) i Ang II (2). Ova se tvar uz pomoć renina pretvara u dekapeptid Ang I, koji se zatim uz pomoć angiotenzin-konvertirajućeg enzima (ACE, najvećim se dijelom nalazi na endotelnim stanicama pluća), pretvara u oktapeptid Ang II koji je snažan vazokonstriktor i glavni aktivni produkt RAAS-a. ACE metabolizira i brojne druge peptide, uključujući i vazoaktivne bradikinin i kalidin u inaktivne metabolite (3). Koji su učinci angiotenzina II? Slika 1. Pojednostavnjen izgled RAAS-a 140
3 šecima neurona, povećava osjetljivost ciljnih organa na noradrenalin), stimulira centar za žeđu. Na staničnoj razini potiče fibrozu, hipertrofiju i proliferaciju te povećava oksidativni stres (4). Također povećava ekspresiju adhezijskih molekula na vaskularnim stanicama te potiče lučenje raznih kemokina i citokina (5). Koji su učinci aldosterona? Aldosteron koji se pod utjecajem Ang II (ali i kalija i ACTH) luči iz klupčastog sloja (zona glomerulosa) nadbubrežne žlijezde djeluje na glavne stanice sabirnih tubula povećavajući sintezu Na + /K + pumpe, Na i K kanala te na taj način povećava reapsorpciju natrija (i vode) u zamjenu za ione kalija (genomski učinci). U novije vrijeme sve se više govori o negenomskim učincima aldosterona. Signalni putovi još nisu potpuno definirani, ali ključnu ulogu ima unos natrija (soli) koji ih pojačava. Mnogi organi (srce, krvne žile, β-stanice gušterače, glomerularne mezangijske stanice) imaju mineralokortikoidne receptore koji odgovaraju na učinke aldosterona, a uključuju aktivaciju nuklearnog faktora κb (NF-κB) što dovodi do upale, oksidativnog stresa, apoptoze i fibroze (6). Koje su osobitosti tkivnog RAAS-a? Danas je poznato da ne postoji samo cirkulirajući RAAS. Uloga ovog sustava u fiziologiji nadilazi samo regulaciju arterijskog tlaka i izvanstaničnog volumena (slika 2). Pokazalo se, naime, da osim klasičnoga cirkulirajućeg RAAS- -a postoji i tkivni RAAS opisan do sada u nadbubrežnim žlijezdama i mozgu gdje funkcionira neovisno o cirkulirajućem RAAS-u, te u mozgu, srcu, bubregu i masnom tkivu gdje je u uskoj interakciji s cirkulirajućim RAAS-om (7). U novije vrijeme sve je više dokaza i o unutarstaničnom RAAS-u koji sudjeluje u promjenama tijeka Ca 2+ i aktivaciji gena (8, 9). S obzirom na ove činjenice RAAS je ne samo endokrini već parakrini i intrakrini sustav. Kojim još putem može nastati Ang II? Tkivni Ang II može nastati i alternativnim enzimatskim putem iz Ang I putem kimaze. Kimaza se normalno nalazi u sekretornim granulama mastocita, i to u kompleksu s heparin proteoglikanom (10). Interesantno je da je u normalnom (zdravom) vaskularnom tkivu kimaza inaktivna: kimaza je aktivna samo u oštećenim i aterosklerotski izmijenjenim krvnim žilama (11). Kimaza također podiže razinu tkivnoga transformirajućeg faktora rasta (engl. transforming growth factor, TGF)-ß i matriks metaloproteinaze (MMP)-9 koji induciraju upalu i fibrozu, što rezultira oštećenjem organa (11). Slika 2. Trenutačni izgled proširenog RAAS-a Legenda: RPR - renin proreninski receptor; Mas - mas-onkogen, receptor za Ang 1 7; AT2R - angiotenzin tip 2-receptor; AT1R - angiotenzin tip 1-receptor; IRAP - aminopeptidaza regulirana inzulinom; Ang IV receptor AM- PA - aminopeptidaza A; AMPM - aminopeptidaza M; ACE - angiotenzin-konvertirajući enzim; ACE2 - angiotenzin-konvertirajući enzim 2; NEP - neutralna endopeptidaza Što su angiotenzin III i IV? Angiotenzin III nastaje uklanjanjem aminokiseline na N- terminalnom kraju Ang II aminopeptidazom A, a angiotenzin IV daljnjom degradacijom Ang III aminopeptidazom M (12). Angiotenzin II i III djeluju preko angiotenzinskih receptora AT 1 i AT 2 (4). Angiotenzin IV djeluje putem aminopeptidaznog receptora reguliranog inzulinom (IRAP, engl. insulin-regulated aminopeptidase receptor), a dovodi do bubrežne vazodilatacije, hipertrofije i aktivacije NF-κB, što izaziva povećanu ekspresiju inhibitora aktivacije trombocita (PAI-1), monocitnoga kemotaktičnog proteina 1 (MCP-1), interleukina 6 i faktora nekroze tumora-α (13, 14). Koje su osobitosti AT-receptora? AT 1 -receptori posreduju vazokonstrikciju, žeđu, otpuštanje vazopresina i aldosterona, fibrozu, stanični rast i migraciju (4). AT 2 -receptori izraženi su u prenatalnom razdoblju, a nakon rođenja njihova se razina značajno smanjuje. Ponovna reekspresija javlja se u slučaju oštećenja tkiva (infarkt miokarda, inzult, incizije kože). Posreduju vazodilataciju, otpuštanje dušičnog oksida (NO) i inhibiciju staničnog rasta (slika 3) (15). Što je poznato o angiotenzinu 1-7? Angiotenzin 1-7 nastaje iz Ang I preko nedavno otkrivenog enzima ACE2, a djeluje preko mas-receptora i ima učin- 141
4 Slika 3. Učinci peptida angiotenzina i reninprorenina preko odgovarajućih receptora 142 ke suprotne onima Ang II (vazodilatacija, natriureza, endotelna funkcija, antihipertrofični i antifibrotični učinak) (16). Što znamo o renin-proreninskim receptorima? Nedavno su opisani i renin-proreninski receptori (RPR) u srcu, mozgu i placenti te nešto manje u bubrezima i jetri. Ovi receptori povećavaju kontraktilnost, hipertrofiju i fibrozu (17). Vezanjem renina za RPR povećava se njegova katalitička aktivnost 4 do 5 puta ubrzavajući produkciju Ang I. Vezanjem za RPR renin i prorenin vrše fiziološki učinak (aktiviraju unutarstanične signalne putove p42/44, p38, induciraju sintezu DNA, potiču otpuštanje TGF-β i PAI-1) neovisno o Ang II (18). Kakva je povezanost RAAS-a i efektivnog arterijskog volumena plazme? RAAS također ima ključnu ulogu u nekoliko stanja s normalnim arterijskim tlakom, posebno u kroničnom zatajenju srca i drugim poremećajima s edemima (ciroza jetre, nefrotski sindrom). Svima im je zajednička hipoperfuzija bubrega zbog smanjenog efektivnog arterijskog volumena plazme, sekundarna hipersekrecija renina, što dovodi do sekundarnog aldosteronizma koji pridonosi progresiji edema. Povećavajući vaskularnu rezistenciju, Ang II povećava tlačno opterećenje srca (afterload) i pogoršava disfunkciju klijetke u zatajenju srca (4). Postoji li razlika u aktivnosti RAAS-a ovisno o spolu? Dosadašnje studije uočile su mnoge razlike RAAS-a u muškarca i žene. Poznato je da spolni kromosomski komple- ment i spolni hormoni utječu na povećanu reninsku aktivnost plazme, povećanu aktivnost i izražajnost ACE te povećanu izraženost AT1-receptora na bubrezima kod muškaraca. Isto tako različit je i odgovor na liječenje ACE-inhibitorima u žena tijekom vremena učinkovitost opada (19). Koji lijekovi i na koji način djeluju na RAAS? Razumijevanje fiziologije RAAS-a (što i jest tema i naznaka prethodnog prikaza) te patofizioloških zbivanja karakterističnih za pojedine bolesti kardiovaskularnog sustava temelj su razvoja lijekova koji djeluju na pojedine etape sinteze i djelovanja aktivne vazokonstrikcijske supstancije Ang II. Blokiranje RAAS-a lijekovima danas je moguće na više razina: ACE-inhibitori, blokatori angiotenzinskih receptora (BAR), direktni inhibitori renina, blokada aldosteronskih receptora. Beta-blokatori također djeluju na RAAS putem β 1 - receptora na stanicama makule denze. Istražuju se i lijekovi koji stimuliraju AT 2 -receptor, imunizacija protiv angiotenzina te inhibitori kimaze (slika 4). Što se zna o utjecaju β-blokatora na RAAS? Još od 70-ih godina poznat je učinak β-blokatora na sniženje plazmatskog renina u hipertoničara blokiranjem simpatički (β 1 ) posredovanog lučenja renina (20). Zadnjih desetak godina pokazan je i utjecaj β-blokatora na smanjenje Ang II, aldosterona te inhibiciju konverzije prorenina u renin (21, 22).
5 Slika 4. Shema inhibicije RAAS-a na određenim razinama Na koji je način povezana upotreba diuretika i RAAS-a? Diuretici snižavaju arterijski tlak povećanim lučenjem natrija urinom, ali istodobno aktiviraju cirkulirajući RAAS. Novija istraživanja upućuju na moguću aktivaciju tkivnog RAAS-a u stanjima prekomjernog uzimanja soli te inhibiciju u dijeti s niskim unosom soli (23). S obzirom na to da diuretici snižavaju koncentraciju natrija u krvi, djeluju na inhibiciju tkivnog RAAS-a, te se predlažu kao kombinacija s BAR u liječenju arterijske hipertenzije zbog sinergističkog djelovanja na blokadu RAAS-a (24). Koji su učinci ACE-inhibitora na hemodinamiku? Povijesno gledajući, prvi ACE-inhibitor otkriven je godine u otrovu brazilske zmije Bothrops jararaca. Naime, taj je otrov uzrokovao drastičan pad tlaka putem inhibicije angiotenzin-konvertirajućeg enzima. Iz otrova te zmije bio je izoliran teprotid, peptid koji je pokazivao osobine ACE- -inhibitora. Iz njega je prvo dizajniran kaptopril, a kasnije i drugi ACE-inhibitori. Sulfhidrilna skupina kaptoprila koja je bila odgovorna za većinu nuspojava, zamijenjena je karboksilnom skupinom (lizinopril, kvinalapril, perindopril, cilazapril, trandolapril, benazepril) i fosforilnom skupinom (fosinopril). Prisutnost tih skupina poboljšala je lipofilnost i vezanje za ACE. ACE-inhibitori snižavaju koncentraciju Ang II, aldosterona, sekreciju vazopresina i aktivnost simpatikusa, ali i dalje postoje kontroverze o blokiranju tkivnog RAAS-a (25). Tijekom dužeg vremena uzimanja ACE-inhibitora dolazi do porasta Ang II i aldosterona prema početnim vrijednostima tzv. fenomen bijega, vjerojatno zbog alternativnih putova sinteze (26). Kratkotrajni farmakodinamski učinci ACE-inhibitora smanjenjem Ang II uključuju smanjenje volumnog i tlačnog opterećenja (preload i afterload) sa smanjenjem sistoličkog i dijastoličkog arterijskog tlaka. Za razliku od direktnih vazodilatatora kod smanjenja perifernoga vaskularnog otpora ne dolazi do značajnih promjena u frekvenciji srca (24). Ovi lijekovi također smanjuju vaskularnu rezistenciju u bubregu, povećavaju protok krvi kroz bubreg i potiču izlučivanje Na i vode. Preveniraju progresiju mikroalbuminurije, smanjuju proteinuriju, a usporavaju i progresiju kronične bubrežne bolesti (25). ACE-inhibitori u 40-60% bolesnika s arterijskom hipertenzijom postižu zadovoljavajuće sniženje arterijskog tlaka (27). U bolesnika s kroničnim zatajenjem srca venodilatacijom smanjuju plućnu kongestiju i preload te arteriodilatacijom smanjuju afterload odnosno povećavaju udarni volumen (21). Velike studije (CONSEN- SUS (28), SOLVD (29), V-heFT-II (30)) pokazale su ne samo smanjenje simptoma nego i značajno smanjenje smrtnosti bolesnika s kroničnim zatajenjem srca liječenih ACE- -inhibitorima. U bolesnika s preboljenim infarktom miokarda liječenje ACE-inhibitorima prevenira remodelaciju klijetke i progresiju u kronično zatajenje srca te tako smanjuje mortalitet (SAVE (31), AIRE (32), TRACE (33)). Studija HO- PE je pokazala brojne pogodnosti terapije ACE-inhibitorima u visokorizičnih bolesnika, neovisno o sniženju arterijskog tlaka (34). Poznato je da Ang II izaziva supresiju adiponektina i time vjerojatno oštećuje toleranciju glukoze, da djeluje proinflamatorno, povećava rezistenciju inzulina, utječe na apoptozu β-stanica, redukciju glukoneogeneze i izlučivanje glukoze iz jetre, povisuje razinu triglicerida plazme. To su i vjerojatni mehanizmi kojima liječenje ACE-inhibitorima smanjuje incidenciju šećerne bolesti, što je dokazano u velikim kliničkim studijama (CAPP (35), HOPE (34), SOLVD (29), PEACE (36)). Nuspojave ACE-inhibitora su suhi kašalj koji je uzrokovan supstancijom P koju inače degradira ACE, angioedem (potenciran smanjenim katabolizmom kinina) i fetalne malformacije. Druge fiziološke nuspojave mogu biti hipotenzija, smanjenje bubrežne funkcije i hiperkaliemija (2). Što znamo o blokatorima angiotenzinskih receptora (BAR)? Sintezom losartana početkom 1990-ih počinje razvoj oralnih, selektivnih blokatora AT 1 -receptora (37). Od tada su sintetizirani i brojni drugi BAR valsartan, irbesartan, kandesartan, eprosartan, telmisartan i olmesartan. Za razliku od ACE-inhibitora tijekom liječenja BAR dolazi do porasta razine Ang II (38). Blokada AT 1 -receptora inhibira negativnu povratnu spregu i dovodi do povećane sekrecije renina i sinteze Ang I. Kao i ACE-inhibitori, BAR snižavaju arterijski tlak snižavanjem periferne vaskularne rezistencije. Ovi lijekovi nemaju značajnog utjecaja na frekvenciju srca. Smanjena periferna vaskularna rezistencija rezultat je inhibicije vazokonstrikcije posredovane angiotenzinom II, 143
6 144 smanjenja simpatičkog tonusa i inhibicije sekrecije aldosterona (34). Ovi su lijekovi učinkoviti u 40-60% bolesnika s arterijskom hipertenzijom; smanjuju i biljege upale u bolesnika s aterosklerozom (39). Velikim studijama dokazano je da BAR usporavaju progresiju dijabetičke nefropatije (IDTN (40), RENAAL (41)). U bolesnika s kroničnim zatajenjem srca smanjuju kardiovaskularnu smrtnost i hospitalizaciju (CHARM (42); Val-HeFT (43)), a u bolesnika s preboljenim infarktom miokarda smanjuju sveukupnu smrtnost, ponovni infarkt, iznenadnu srčanu smrt i hospitalizaciju (OPTIMAAL (44). Studija LIFE jasno je pokazala da zaštita ciljnih organa nije samo posljedica sniženog arterijskog tlaka: u ovoj su studiji bolesnici (s podjednako reguliranom arterijskom hipertenzijom i hipertrofijom lijeve klijetke) liječeni BAR, u usporedbi s beta-blokatorom, imali značajno nižu kardiovaskularnu smrtnost, moždani udar, infarkt miokarda i pojavnost šećerne bolesti (45). BAR se većinom dobro podnose. Kao i ACE-inhibitori BAR su kontraindicirani u trudnica jer uzrokuju povećanu fetalnu smrtnost i morbiditet, osobito u drugom i trećem tromjesečju (2). Koja je korist od lijekova koji direktno inhibiraju renin? Prvi peroralni inhibitori renina za liječenje arterijske hipertenzije sintetizirani su tek 50 godina nakon što je pretpostavljeno da bi inhibicija renina bila logičan i poželjan pristup blokadi RAAS-a (1957. godine Skeggs) (46). Prva generacija oralnih sintetskih izravnih inhibitora renina (remikiren, zankiren) nije ušla u kliničku praksu zbog loše bioraspoloživosti (velika molekularna masa i lipofilnost rezultirale su slabijom apsorpcijom iz crijeva, značajni metabolizam pri prvom prolasku kroz jetru), kratkog poluživota, visoke cijene sinteze i neučinkovitosti na arterijski tlak. Molekularnim modeliranjem stvoren je niskomolekularni nepeptidni inhibitor renina aliskiren (15). Kliničkim studijama pokazalo se da ovaj lijek ima značajan antihipertenzivni i organoprotektivni učinak (renoprotekcija studija AVOID (47), kardioprotekcija studije ALLAY (48) i ALOFT (49)), uz dobru podnošljivost (15). Što je s antagonistima aldosteronskih receptora? Antagonisti aldosteronskih receptora dijele se na neselektivne (spironolakton) i selektivne (eplerenon). Ovi lijekovi imaju svoje mjesto u liječenju stanja sekundarnog hiperaldosteronizma kao što su ciroza jetre i dekompenzacija srca s malim minutnim volumenom (karakterizirane niskim efektivnim arterijskim volumenom plazme i smanjenom perfuzijom bubrega) (50). U tim stanjima antagonisti aldosteronskih receptora dokazano smanjuju smrtnost: kao što su npr. u dekompenzaciji srca (studije RALES i EPHE- SUS) (51, 52). Antagonisti aldosteronskih receptora pokazali su se važnim i u liječenju rezistentne arterijske hipertenzije (ASCOT) (53). Dobro poznata nuspojava neselektivnih antagonista aldosteronskih receptora jest ginekomastija oko 10% (50). D. Ljutić, I. Jeličić Lijekovi koji djeluju na renin-angiotenzin-aldosteronski sustav Što je s agonistima AT2-receptora? Prvi agonisti AT2-receptora sintetizirani su godine kada su slučajno sintetizirani i ligandi za AT1-receptor (losartan tada označen kao DUP723) i AT2-receptor (CGP42112A) (54). Peptid CGP42112A se, međutim, mogao davati samo intravenski i brzo se degradirao pa nije bio povoljan za ispitivanja in vivo. Godine sintetiziran je novi peroralni agonist AT2-receptora nazvan Compound 21 (C21) i za sada je ispitivan samo na životinjama: pokazao je kardioprotektivan, neuroprotektivan, antiinflamatoran, antiapoptotski učinak i protektivni učinak na crijeva. Učinak na sniženje arterijskog tlaka ova tvar nije imala (54). Što je s imunizacijom na angiotenzin? Jedan od interesantnijih pristupa u istraživanju mogućih terapijskih postupaka jest imunizacija na angiotenzin. Cjepivo na Ang I (PMD3117) pokazalo se sigurno i imunogeno, ali bez učinka na sniženje arterijskog tlaka, vjerojatno zbog niskih razina antitijela. Međutim cjepivo na Ang II (CYT006-AngQb) pokazalo se sigurno i učinkovito u pretkliničkim i kliničkim istraživanjima. Nastalo je kovalentnim vezanjem modificiranog angiotenzina II i čestica sličnih virusima izvedenih iz ovojnice bakteriofaga Qb (55). Cjepivo je izazvalo odgovor antitijela s poluživotom od oko 4 mjeseca. Sniženje arterijskog tlaka bilo je značajno u usporedbi s placebom, te posebno učinkovito u sniženju ranojutarnjeg sistoličkog i dijastoličkog tlaka (25/13 mmhg) kada se i događa najviše koronarnih incidenata. U do sada testiranih bolesnika nisu zabilježene značajne nuspojave, a od blažih nuspojava zabilježeni su samo simptomi slični prehladi (55). Postoje li istraživanja o učinkovitosti inhibitora kimaze? Inhibitori kimaze u pokusima na životinjama pokazuju određenu aktivnost, pokusi na ljudima još nisu rađeni (56). Naime, na psećem modelu, za razliku od ACE-inhibitora, inhibitori kimaze sprječavali su vaskularnu proliferaciju nakon ozljede (dilatacije) balonskim kateterom (57). Dobro je poznato da kimaza djeluje samo u bolesnom tkivu, a ne u zdravom. Njihova je budućnost u liječenju vaskularne proliferacije, u sprječavanju fibroze miokarda nakon infarkta, u prevenciji razvoja dijabetičke retinopatije i u prevenciji nastanka aneurizme abdominalne aorte (58). Zaključak Kao što se iz ovoga kratkog pregleda može zaključiti razvijene su i razvijaju se brojne supstancije kojima je svrha djelovanje na RAAS, a time i uspješno liječenje bolesnika s bolestima u kojima ovaj sustav ima ključnu patofiziološku ulogu.
7 Literatura 1. TIGERSTEDT R, BERGMAN P. Niere und Kreislauf. Arch Physiol 1989;8: ATLAS SA. The Renin-Angiotensin Aldosterone System: Pathophysiological Role and Pharmacologic Inhibition. J Manag Care Pharm. 2007;13:S CAREY RM, SIRAGY HM. Newly recognized components of the renin-angiotensin system: potential roles in cardiovascular and renal regulation. Endocr Rev 2003;24: FYHRQUIST F, SAIJONMAA O. Renin-angiotensin system revisited. J Intern Med 2008;264: SATA M, FUKADA D. Crucial role of renin-angiotensin system in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. J Med Invest 2010;57: LEROY V, De SEIGNEUX S, AGASSIZ V i sur. Aldosterone activates NF-kappaB in the collecting duct. J Am Soc Nephrol 2009;20: FLEMING I, KOHLSTEDT K, BUSSE R. The tissue renin-angiotensin system and intracellular signalling. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 2006;15: KUMAR R, SINGH VP, BAKER KM. The intracellular reninangiotensin system: a new paradigm. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2007;18: RE RN, COOK JL. The intracrine hypothesis: an update. Regul Pept 2006;133: TAKAI S, JIN D, MURAMATSU M, MIYAZAKI M. Chymase as a novel target for the prevention of vascular diseases. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2004;25: TAKAI S, JIN D, MIYAZAKI M. New approaches to blockade of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system: chymase as an important target to prevent organ damage. J Pharmacol Sci 2010;113: REUDELHUBER TL. The renin-angiotensin system: peptides and enzymes beyond angiotensin II. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2005;14: ALBISTON AL, McDOWALL SG, MATSACOS D i sur. Evidence that the angiotensin IV (AT(4)) receptor is the enzyme insulinregulated aminopeptidase. J Biol Chem 2001;276: CHAI SY, FERNANDO R, PECK G i sur. The angiotensin IV AT4 receptor. Cell Mol Life Sci 2004;61: STECKELINGS UM, ROMPE F, KASCHINA E i sur. The past, present and future of angiotensin II type 2 receptor stimulation. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2010;11: FERRARIO CM. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and angiotensin-(1-7): an evolving story in cardiovascular regulation. Hypertension 2006;47: NGUYEN G. The (pro)renin receptor: pathophysiological roles in cardiovascular and renal pathology. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 2007;16: GRADMAN AH, KAD R. Renin inhibition in hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 2008;51: SULLIVAN JC. Sex and renin-angiotensin system: inequality between the sexes in responce to RAS stimulation and inhibition. Am J Physiol Integr Comp Physiol 2008;294: LARAGH JH, BÜHLER FR. Propranolol, renin and hypertension: a review. Postgrad Med J 1976;52: BLUMENFELD JD, SEALEY JE, MANN SJ i sur. β-adrenergic receptor blockade as a therapeutic approach for suppressing the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in normotensive and hypertensive subjects. Am J Hypertens 1999;12: AGGARWAL A, WONG J, CAMPBELL DJ. Carvedilol reduces aldosterone release in systolic heart failure. Heart Lung Circ 2006;15: TAKEDA Y, YONEDA T, DEMURA M i sur. Effects of high sodium intake on cardiovascular aldosterone synthesis in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Hypertens 2001;19: YOSHIMURA M, KAWAI M. Synergistic inhibitory effect of angiotensin II receptor blocker and thiazide diuretic on the tissue renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst 2010;11: LOPEZ-SENDON J, SWEDBERG K, McMURRAY J i sur. for the Task Force on ACE-inhibitors of the European Society of Cardiology. Expert consensus document on angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors in cardiovascular disease. Eur Heart J 2004;25: ATHYROS VG, MIKHAILIDIS DP, KAKAFIKA AI, TZIOMALOS K, KARAGIANNIS A. Angiotensin II reactivation and aldosterone escape phenomena in renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockade: is oral renin inhibition the solution? Expert Opin Pharmacother 2007;8: IBRAHIM MM. RAS inhibition in hypertension. J Hum Hypertens 2006;20: LJUNGMAN S, KJEKSHUS J, SWEDBERG K. Renal function in severe congestive heart failure during treatment with enalapril (the Cooperative North Scandinavian Enalapril Survival Study [CONSENSUS] Trial). Am J Cardiol 1992;70: VERMES E, DUCHARME A, BOURASSA MG, LESSARD M, WHITE M, TARDIF J-C. Enalapril reduces the incidence of diabetes in patients with chronic heart failure: insight from the Studies Of Left Ventricular Dysfunction (SOLVD). Circulation 2003;107: The V-HeFT VA Cooperative Studies Group. Francis GS, Cohn JN, Johnson G, Rector TS, Goldman S, Simon A. Plasma norepinephrine, plasma renin activity, and congestive heart failure. Relations to survival and the effects of therapy in V-HeFT II. Circulation 1993;87:VI PFEFFER MA, BRAUNWALD E, MOYE LA i sur. Effect of captopril on mortality and morbidity in patients with left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction. Results of the survival and ventricular enlargement trial. The SAVE Investigators. N Engl J Med 1992;327: The Acute Infarction Ramipril Efficacy (AIRE) Study Investigators. Effect of ramipril on mortality and morbidity of survivors of acute myocardial infarction with clinical evidence of heart failure. Lancet 1993;342: TORP-PEDERSEN C, KØBER L. Effect of ACE inhibitor trandolapril on life expectancy of patients with reduced leftventricular function after acute myocardial infarction. TRACE Study Group. Trandolapril Cardiac Evaluation. Lancet 1999 Jul 3;354(9172): YUSUF S, SLEIGHT P, POGUE J i sur. for The Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation Study Investigators. Effects of an angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor, ramipril, on cardiovascular events in high-risk patients. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:
8 35. HANSSON L, LINDHOLM LH, NISKANEN L i sur. Effect of angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibition compared with conventional therapy on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in hypertension: the Captopril Prevention Project (CAPPP) randomised trial. Lancet 1999;353: The PEACE Trial Investigators. Angiotensin-convertingenzyme inhibition in stable coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med 2004;351: FERRARIO CM. Role of angiotensin II in cardiovascular disease - therapeutic implications of more than a century of research. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst 2006;7: HERNANDEZ-HERNANDEZ R, SOSA-CANACHE B, VELAS- CO M, ARMAS-HERNANDEZ MJ, ARMAS-PADILLA MC, CAMMARATA R. Angiotensin II receptor antagonists role in arterial hypertension. J Hum Hypertens 2002;16:S KOH KK, AHN JY, HAN SH i sur. Pleiotropic effects of angiotensin II receptor blocker in hypertensive patients. J Am Coll Cardiol 2003;42: LEWIS EJ, HUNSICKER LG, CLARKE WR i sur. Renoprotective effect of the angiotensin-receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2001;345: BRENNER BM, COOPER ME, De ZEEUW D i sur. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med 2001;345: PFEFFER MA, SWEDBERG K, GRANGER CB i sur. Effects of candesartan on mortality and morbidity in patients with chronic heart failure: the CHARM-Overall programme. Lancet 2003;362: MAGGIONI AP, ANAND I, GOTTLIEB SO i sur. Effects of valsartan on morbidity and mortality in patients with heart failure not receiving angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. J Am Coll Cardiol 2002;40: DICKSTEIN K, KJEKSHUS J. Effects of losartan and captopril on mortality and morbidity in high-risk patients after acute myocardial infarction: the OPTIMAAL randomised trial. Optimal Trial in Myocardial Infarction with Angiotensin II Antagonist Losartan. Lancet 2002;360: DAHLOF B, DEVEREUX RB, KJELDSEN SE i sur. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in the Losartan Intervention For Endpoint reduction in hypertension study (LIFE): a randomised trial against atenolol. Lancet 2002;359: SKEGGS LT, KAHN JR, LENTZ K, SHUMWAY NP. Preparation, purification and aminoacid sequence of a polypeptide renin substrate. J Exp Med 1957;106: PARVING HH, PERSSON F, LEWIS JB, LEWIS EJ, HOLLE- NBERG NK. AVOID Study Investigators. Aliskiren combined with losartan in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med 2008;358: SOLOMON SD, APPELBAUM E, MANNING WJ i sur. Aliskiren in Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (ALLAY) Trial Investigators. Effect of the direct Renin inhibitor aliskiren, the Angiotensin receptor blocker losartan, or both on left ventricular mass in patients with hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy. Circulation 2009;119: McMURRAY JJ, PITT B, LATINI R i sur. Aliskiren Observation of Heart Failure Treatment (ALOFT) Investigators. Effects of the oral direct renin inhibitor aliskiren in patients with symptomatic heart failure. Circ Heart Fail 2008;1: SCHRIER RW, MASOUMI A, ELHASSAN E. Aldosterone: Role in Edematous Disorders, Hypertension, Chronic Renal Failure, and Metabolic Syndrome. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2010;5: PITT B, ZANNAD F, REMME WJ i sur. The effect of spironolactone on morbidity and mortality in patients with severe heart failure. Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study Investigators. N Engl J Med 1999;341: PITT B, BAKRIS G, RUILOPE LM, DiCARLO L, MUKHERJEE R. EPHESUS Investigators. Serum potassium and clinical outcomes in the Eplerenone Post-Acute Myocardial Infarction Heart Failure Efficacy and Survival Study (EPHE- SUS). Circulation 2008;118: CHAPMAN N, DOBSON J, WILSON S i sur. Anglo-Scandinavian Cardiac Outcomes Trial Investigators. Effect of spironolactone on blood pressure in subjects with resistant hypertension. Hypertension 2007;49: STECKELINGS UM, ROMPE F, KASCHINA E i sur. The past, present and future of angiotensin II type 2 receptor stimulation. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst 2010;11: MAURER P, BACHMANN MF. Immunization against angiotensins for the treatment of hypertension. Clin Immunol 2010;134: MIYAZAKI M, TAKAI S, JIN D, MURAMATSU M. Pathological roles of angiotensin II produced by mast cell chymase and the effects of chymase inhibition in animal models. Pharmacol Ther 2006;112: TAKAI S, SAKONJO H, FUKUDA K i sur. A novel chymase inhibitor, 2-(5-formylamino-6-oxo-2-phenyl-1,6-dihydropyrimidine-1-yl)-N-[[,4-dioxo-1-phenyl-7-(2- pyridyloxy)] 2-heptyl] acetamide (NK3201), suppressed intimal hyperplasia after balloon injury. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2003;304: TAKAI S, JIN D, MIYAZAKI M. New approaches to blockade of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system: chymase as an important target to prevent organ damage. J Pharmacol Sci. 2010;113: Adresa za dopisivanje: Prof. dr. sc. Dragan Ljutić. dr. med. Interna klinika Medicinskog fakulteta Sveučilišta u Splitu KBC Split Split, Spinčićeva 1 dragan.ljutic@yahoo.com Primljeno / Received December 7, 2010 Prihvaćeno / Accepted December 11,
Preventing the cardiovascular complications of hypertension
 European Heart Journal Supplements (2004) 6 (Supplement H), H37 H42 Preventing the cardiovascular complications of hypertension Peter Trenkwalder* Department of Internal Medicine, Starnberg Hospital, Ludwig
European Heart Journal Supplements (2004) 6 (Supplement H), H37 H42 Preventing the cardiovascular complications of hypertension Peter Trenkwalder* Department of Internal Medicine, Starnberg Hospital, Ludwig
Since the initial description of angiotensin II mediated
 CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY: PHYSICIAN UPDATE Manipulation of the Renin-Angiotensin System Michael M. Givertz, MD Since the initial description of angiotensin II mediated hypertension 40 years ago, basic and clinical
CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY: PHYSICIAN UPDATE Manipulation of the Renin-Angiotensin System Michael M. Givertz, MD Since the initial description of angiotensin II mediated hypertension 40 years ago, basic and clinical
Drugs acting on the reninangiotensin-aldosterone
 Drugs acting on the reninangiotensin-aldosterone system John McMurray Eugene Braunwald Scholar in Cardiovascular Diseases, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Boston & Visiting Professor, Harvard Medical School
Drugs acting on the reninangiotensin-aldosterone system John McMurray Eugene Braunwald Scholar in Cardiovascular Diseases, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Boston & Visiting Professor, Harvard Medical School
Understanding and Development of New Therapies for Heart Failure - Lessons from Recent Clinical Trials -
 Understanding and Development of New Therapies for Heart Failure - Lessons from Recent Clinical Trials - Clinical trials Evidence-based medicine, clinical practice Impact upon Understanding pathophysiology
Understanding and Development of New Therapies for Heart Failure - Lessons from Recent Clinical Trials - Clinical trials Evidence-based medicine, clinical practice Impact upon Understanding pathophysiology
Optimal blockade of the Renin- Angiotensin-Aldosterone. in chronic heart failure
 Optimal blockade of the Renin- Angiotensin-Aldosterone Aldosterone- (RAA)-System in chronic heart failure Jan Östergren Department of Medicine Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm, Sweden Key Issues
Optimal blockade of the Renin- Angiotensin-Aldosterone Aldosterone- (RAA)-System in chronic heart failure Jan Östergren Department of Medicine Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm, Sweden Key Issues
heart failure John McMurray University of Glasgow.
 A to Z of RAAS blockade in heart failure John McMurray BHF Cardiovascular Research Centre University of Glasgow. RAAS inhibition in CHF ACE inhibition in patients with low LVEF CHF CONSENSUS Enalapril
A to Z of RAAS blockade in heart failure John McMurray BHF Cardiovascular Research Centre University of Glasgow. RAAS inhibition in CHF ACE inhibition in patients with low LVEF CHF CONSENSUS Enalapril
THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM
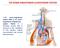 THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM The renin angiotensin system (RAS) or the renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) is a hormone system that is involved in the regulation of the plasma sodium
THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM The renin angiotensin system (RAS) or the renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) is a hormone system that is involved in the regulation of the plasma sodium
Scientific conclusions and detailed explanation of the scientific grounds for the differences from the PRAC recommendation
 Annex I Scientific conclusions, grounds for variation to the terms of the marketing authorisations and detailed explanation of the scientific grounds for the differences from the PRAC recommendation 1
Annex I Scientific conclusions, grounds for variation to the terms of the marketing authorisations and detailed explanation of the scientific grounds for the differences from the PRAC recommendation 1
The role of angiotensin II receptor blockers in the management of heart failure
 European Heart Journal Supplements (2005) 7 (Supplement J), J10 J14 doi:10.1093/eurheartj/sui057 The role of angiotensin II receptor blockers in the management of heart failure John J.V. McMurray* Department
European Heart Journal Supplements (2005) 7 (Supplement J), J10 J14 doi:10.1093/eurheartj/sui057 The role of angiotensin II receptor blockers in the management of heart failure John J.V. McMurray* Department
Analysis of Factors Causing Hyperkalemia
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Analysis of Factors Causing Hyperkalemia Kenmei Takaichi 1, Fumi Takemoto 1, Yoshifumi Ubara 1 and Yasumichi Mori 2 Abstract Objective Patients with impaired renal function or diabetes
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Analysis of Factors Causing Hyperkalemia Kenmei Takaichi 1, Fumi Takemoto 1, Yoshifumi Ubara 1 and Yasumichi Mori 2 Abstract Objective Patients with impaired renal function or diabetes
Entresto Development of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction
 Cardio-Metabolic Franchise Entresto Development of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction Randy L Webb, PhD Rutgers Workshop October 21, 2016 Heart
Cardio-Metabolic Franchise Entresto Development of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction Randy L Webb, PhD Rutgers Workshop October 21, 2016 Heart
The value of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
 New Drugs and Technologies Which Inhibitor of the Renin Angiotensin System Should Be Used in Chronic Heart Failure and Acute Myocardial Infarction? John J.V. McMurray, MD; Marc A. Pfeffer, MD, PhD; Karl
New Drugs and Technologies Which Inhibitor of the Renin Angiotensin System Should Be Used in Chronic Heart Failure and Acute Myocardial Infarction? John J.V. McMurray, MD; Marc A. Pfeffer, MD, PhD; Karl
The Road to Renin System Optimization: Renin Inhibitor
 The Road to Renin System Optimization: Renin Inhibitor A New Perspective on the Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS) Yong-Jin Kim, MD Seoul National University Hospital Human and Economic Costs of Hypertension
The Road to Renin System Optimization: Renin Inhibitor A New Perspective on the Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS) Yong-Jin Kim, MD Seoul National University Hospital Human and Economic Costs of Hypertension
RAS Blockade Across the CV Continuum
 A Summary of Recent International Meetings RAS Blockade Across the CV Continuum Copyright New Evidence Presented at the 2009 Congress of the European Society of Cardiology (August 29-September 2, Barcelona)
A Summary of Recent International Meetings RAS Blockade Across the CV Continuum Copyright New Evidence Presented at the 2009 Congress of the European Society of Cardiology (August 29-September 2, Barcelona)
Mayo Clin Proc, March 2003, Vol 78 Role of ARBs in Treatment of Heart Failure 335 system, tissue-based RAS has long-term effects that can modify cardi
 334 Concise Review for Clinicians Therapeutic Role of Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers in the Treatment of Heart Failure Concise Review for Clinicians PRERANA MANOHAR, MD, AND ILEANA L. PIÑA, MD Angiotensin
334 Concise Review for Clinicians Therapeutic Role of Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers in the Treatment of Heart Failure Concise Review for Clinicians PRERANA MANOHAR, MD, AND ILEANA L. PIÑA, MD Angiotensin
Hypertension Management Focus on new RAAS blocker. Disclosure
 Hypertension Management Focus on new RAAS blocker Rameshkumar Raman M.D Endocrine Associates of The Quad Cities Disclosure Speaker bureau Abbott, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, Takeda, Merck, Solvay
Hypertension Management Focus on new RAAS blocker Rameshkumar Raman M.D Endocrine Associates of The Quad Cities Disclosure Speaker bureau Abbott, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, Takeda, Merck, Solvay
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
 Cardiology 59 Using ARBs in the elderly patient Effective management of hypertension can substantially reduce the risk of complications. The angiotensin receptor blockers are one of the latest anti-hypertensive
Cardiology 59 Using ARBs in the elderly patient Effective management of hypertension can substantially reduce the risk of complications. The angiotensin receptor blockers are one of the latest anti-hypertensive
Metabolic Consequences of Anti Hypertensives: Is It Clinically Important?
 Metabolic Consequences of Anti Hypertensives: Is It Clinically Important?,FACA,FICA,MASH,FVBWG,MISCP CONSULTANT OF CARDIOLOGY DIRECTOR OF PORT-FOUAD HOSPITAL CCU Consideration of antihypertensive agents
Metabolic Consequences of Anti Hypertensives: Is It Clinically Important?,FACA,FICA,MASH,FVBWG,MISCP CONSULTANT OF CARDIOLOGY DIRECTOR OF PORT-FOUAD HOSPITAL CCU Consideration of antihypertensive agents
Pharmacy Medical Policy Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonists
 Pharmacy Medical Policy Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonists Table of Contents Policy: Commercial Information Pertaining to All Policies Endnotes Policy: Medicare References Forms Policy History Policy
Pharmacy Medical Policy Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonists Table of Contents Policy: Commercial Information Pertaining to All Policies Endnotes Policy: Medicare References Forms Policy History Policy
I know the trials in heart failure but how do I manage my patient? Dosing of neurohormones antagonists
 I know the trials in heart failure but how do I manage my patient? Dosing of neurohormones antagonists Alessandro Fucili (Ferrara, IT) Massimo F Piepoli (Piacenza, IT) Clinical Case: 82 year old woman
I know the trials in heart failure but how do I manage my patient? Dosing of neurohormones antagonists Alessandro Fucili (Ferrara, IT) Massimo F Piepoli (Piacenza, IT) Clinical Case: 82 year old woman
Position Statement on ALDOSTERONE ANTAGONIST THERAPY IN CHRONIC HEART FAILURE
 Position Statement on ALDOSTERONE ANTAGONIST THERAPY IN CHRONIC HEART FAILURE Over 8,000 patients have been studied in two well-designed placebo-controlled outcome-driven clinical trials to evaluate the
Position Statement on ALDOSTERONE ANTAGONIST THERAPY IN CHRONIC HEART FAILURE Over 8,000 patients have been studied in two well-designed placebo-controlled outcome-driven clinical trials to evaluate the
Renin Angiotensin System Current and Potential Targets
 Renin Angiotensin System Current and Potential Targets Dae Suk Han, MD. Seung Hyeok Han, MD. Department of Internal Medicine Division of Nephrology Yonsei University College of Medicine Renin The First
Renin Angiotensin System Current and Potential Targets Dae Suk Han, MD. Seung Hyeok Han, MD. Department of Internal Medicine Division of Nephrology Yonsei University College of Medicine Renin The First
Prevention of Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure in the Hypertensive Patient
 Prevention of Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure in the Hypertensive Patient The Issue of Primary Prevention of A.Fib. (and Heart Failure) and not the Prevention of Recurrent A.Fib. after Electroconversion
Prevention of Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure in the Hypertensive Patient The Issue of Primary Prevention of A.Fib. (and Heart Failure) and not the Prevention of Recurrent A.Fib. after Electroconversion
ACE inhibitors: still the gold standard?
 ACE inhibitors: still the gold standard? Session: Twenty-five years after CONSENSUS What have we learnt about the RAAS in heart failure? Lars Køber, MD, D.Sci Department of Cardiology Rigshospitalet University
ACE inhibitors: still the gold standard? Session: Twenty-five years after CONSENSUS What have we learnt about the RAAS in heart failure? Lars Køber, MD, D.Sci Department of Cardiology Rigshospitalet University
ACE inhibitors vs ARBs: Is one class better for heart failure?
 HEART FAILURE UPDATE MARK E. DUNLAP, MD * Associate Professor of Medicine, Physiology, and Biophysics, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, and Louis B. Stokes Cleveland VA Medical Center,
HEART FAILURE UPDATE MARK E. DUNLAP, MD * Associate Professor of Medicine, Physiology, and Biophysics, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, and Louis B. Stokes Cleveland VA Medical Center,
Two landmark clinical trials, CONSEN-
 Heart 2001;86:97 103 HEART FAILURE Angiotensin receptor blockers for chronic heart failure and acute myocardial infarction John J V McMurray Clinical Research Initiative in Heart Failure, Wolfson Building,
Heart 2001;86:97 103 HEART FAILURE Angiotensin receptor blockers for chronic heart failure and acute myocardial infarction John J V McMurray Clinical Research Initiative in Heart Failure, Wolfson Building,
Data Alert #2... Bi o l o g y Work i n g Gro u p. Subject: HOPE: New validation for the importance of tissue ACE inhibition
 Vascular Bi o l o g y Work i n g Gro u p c/o Medical Education Consultants, In c. 25 Sy l van Road South, We s t p o rt, CT 06880 Chairman: Carl J. Pepine, MD Professor and Chief Division of Cardiovascular
Vascular Bi o l o g y Work i n g Gro u p c/o Medical Education Consultants, In c. 25 Sy l van Road South, We s t p o rt, CT 06880 Chairman: Carl J. Pepine, MD Professor and Chief Division of Cardiovascular
ACEIs / ARBs NDHP dihydropyridine ( DHP ) ACEIs ARBs ACEIs ARBs NDHP. ( GFR ) 60 ml/min/1.73m ( chronic kidney disease, CKD )
 005 16 175-180 1 1 ( chronic kidney disease, CKD ) 003 ( end-stage renal disease, ESRD ) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors ( ) angiotensin receptor blockers ( ) nondihydropyridine ( NDHP ) / NDHP
005 16 175-180 1 1 ( chronic kidney disease, CKD ) 003 ( end-stage renal disease, ESRD ) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors ( ) angiotensin receptor blockers ( ) nondihydropyridine ( NDHP ) / NDHP
Review. Renin Inhibitors in Chronic Heart Failure: The Aliskiren Observation of Heart Failure Treatment Study in Context
 Review Renin Inhibitors in Chronic Heart Failure: The Aliskiren Observation of Heart Failure Treatment Study in Context Address for correspondence: HenryKrum,MBBS,PhD,FRACP Centre of Cardiovascular Research
Review Renin Inhibitors in Chronic Heart Failure: The Aliskiren Observation of Heart Failure Treatment Study in Context Address for correspondence: HenryKrum,MBBS,PhD,FRACP Centre of Cardiovascular Research
State of the art treatment of hypertension: established and new drugs. Prof. M. Burnier Service of Nephrology and Hypertension Lausanne, Switzerland
 State of the art treatment of hypertension: established and new drugs Prof. M. Burnier Service of Nephrology and Hypertension Lausanne, Switzerland First line therapies in hypertension ACE inhibitors AT
State of the art treatment of hypertension: established and new drugs Prof. M. Burnier Service of Nephrology and Hypertension Lausanne, Switzerland First line therapies in hypertension ACE inhibitors AT
What is the Role of Direct Renin Inhibitors in the Treatment of the Hypertensive Diabetic Patient?
 Adv Ther (2011) 28(9):716-727. DOI 10.1007/s12325-011-0049-6 REVIEW What is the Role of Direct Renin Inhibitors in the Treatment of the Hypertensive Diabetic Patient? Alejandro de la Sierra Jorge Salazar
Adv Ther (2011) 28(9):716-727. DOI 10.1007/s12325-011-0049-6 REVIEW What is the Role of Direct Renin Inhibitors in the Treatment of the Hypertensive Diabetic Patient? Alejandro de la Sierra Jorge Salazar
The Therapeutic Potential of Novel Approaches to RAAS. Professor of Medicine University of California, San Diego
 The Therapeutic Potential of Novel Approaches to RAAS Inhibition in Heart Failure Barry Greenberg, M.D. Professor of Medicine University of California, San Diego Chain of Events Leading to End-Stage Heart
The Therapeutic Potential of Novel Approaches to RAAS Inhibition in Heart Failure Barry Greenberg, M.D. Professor of Medicine University of California, San Diego Chain of Events Leading to End-Stage Heart
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
Clinical Issues Research Implemented April 2010
 Hypertension General Management Principals (from the JNC7) In persons older than 50 years, systolic blood pressure greater than 140 mmhg is a much more important cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factor
Hypertension General Management Principals (from the JNC7) In persons older than 50 years, systolic blood pressure greater than 140 mmhg is a much more important cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factor
Combination of renin-angiotensinaldosterone. how to choose?
 Combination of renin-angiotensinaldosterone system inhibitors how to choose? Karl Swedberg Professor of Medicine Sahlgrenska Academy University of Gothenburg karl.swedberg@gu.se Disclosures Research grants
Combination of renin-angiotensinaldosterone system inhibitors how to choose? Karl Swedberg Professor of Medicine Sahlgrenska Academy University of Gothenburg karl.swedberg@gu.se Disclosures Research grants
Cardiac Protection across the cardiac continuum. Dong-Ju Choi, MD, PhD College of Medicine Seoul National University
 Cardiac Protection across the cardiac continuum Dong-Ju Choi, MD, PhD College of Medicine Seoul National University Renin Angiotensin Cascade Nitric oxide (NO) Bradykinin Degradation products ACE ACEI
Cardiac Protection across the cardiac continuum Dong-Ju Choi, MD, PhD College of Medicine Seoul National University Renin Angiotensin Cascade Nitric oxide (NO) Bradykinin Degradation products ACE ACEI
Combination Therapy with Aldosterone Blockade and Renin-Angiotensin Inhibitors Confers Organ Protection
 211 Review Hypertens Res Vol.29 (2006) No.4 p.211-216 Combination Therapy with Aldosterone Blockade and Renin-Angiotensin Inhibitors Confers Organ Protection Atsuhisa SATO 1), Takao SARUTA 2), and John
211 Review Hypertens Res Vol.29 (2006) No.4 p.211-216 Combination Therapy with Aldosterone Blockade and Renin-Angiotensin Inhibitors Confers Organ Protection Atsuhisa SATO 1), Takao SARUTA 2), and John
(renoprotective (end-stage renal disease, ESRD) therapies) (JAMA)
 [1], 1., 2. 3. (renoprotective (end-stage renal disease, ESRD) therapies) (JAMA) (multiple risk (renal replacement therapy, RRT) factors intervention treatment MRFIT) [2] ( 1) % (ESRD) ( ) ( 1) 2001 (120
[1], 1., 2. 3. (renoprotective (end-stage renal disease, ESRD) therapies) (JAMA) (multiple risk (renal replacement therapy, RRT) factors intervention treatment MRFIT) [2] ( 1) % (ESRD) ( ) ( 1) 2001 (120
The Role of Angiotensin Receptor Blockers in Heart Failure
 ARBS IN HF CHF MARCH/APRIL 2000 103 The Role of Angiotensin Receptor Blockers in Heart Failure The effectiveness of ACE inhibitors in reducing morbidity and mortality in patients with heart failure is
ARBS IN HF CHF MARCH/APRIL 2000 103 The Role of Angiotensin Receptor Blockers in Heart Failure The effectiveness of ACE inhibitors in reducing morbidity and mortality in patients with heart failure is
Hypertension and diabetic nephropathy
 Hypertension and diabetic nephropathy Elisabeth R. Mathiesen Professor, Chief Physician, Dr sci Dep. Of Endocrinology Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen Denmark Hypertension Brain Eye Heart Kidney
Hypertension and diabetic nephropathy Elisabeth R. Mathiesen Professor, Chief Physician, Dr sci Dep. Of Endocrinology Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen Denmark Hypertension Brain Eye Heart Kidney
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs
 Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs Blood Pressure Normal = sys
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs Blood Pressure Normal = sys
Angiotensin receptor blockers in the treatment of heart failure
 Heart Failure: Pharmacologic Management Edited by Arthur M. Feldman Copyright 2006 by Blackwell Publishing 4 CHAPTER 4 Angiotensin receptor blockers in the treatment of heart failure Anita Deswal, MD,
Heart Failure: Pharmacologic Management Edited by Arthur M. Feldman Copyright 2006 by Blackwell Publishing 4 CHAPTER 4 Angiotensin receptor blockers in the treatment of heart failure Anita Deswal, MD,
ACE inhibitors as cardioprotective agents James B. Young, MD From the Kaufman Center for Heart Failure, The Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Ohio
 Cardiovascular Risk Protection ACE inhibitors as cardioprotective agents James B. Young, MD From the Kaufman Center for Heart Failure, The Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Ohio James B. Young, MD The beneficial
Cardiovascular Risk Protection ACE inhibitors as cardioprotective agents James B. Young, MD From the Kaufman Center for Heart Failure, The Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Ohio James B. Young, MD The beneficial
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is
 Hellenic J Cardiol 2010; 51: 195-199 Editorial Effect of Antihypertensive Drug-Associated Diabetes on Cardiovascular Risk As t e r i o s Ka r a g i a n n i s 1, Ko n s t a n t i n o s Tz i o m a l o s
Hellenic J Cardiol 2010; 51: 195-199 Editorial Effect of Antihypertensive Drug-Associated Diabetes on Cardiovascular Risk As t e r i o s Ka r a g i a n n i s 1, Ko n s t a n t i n o s Tz i o m a l o s
NQF-ENDORSED VOLUNTARY CONSENSUS STANDARDS FOR HOSPITAL CARE. Measure Information Form
 Last Updated: Version 3.2 NQF-ENDORSED VOLUNTARY CONSENSUS STANDARDS FOR HOSPITAL CARE Measure Information Form Measure Set: Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) Set Measure ID#: Performance Measure Name:
Last Updated: Version 3.2 NQF-ENDORSED VOLUNTARY CONSENSUS STANDARDS FOR HOSPITAL CARE Measure Information Form Measure Set: Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) Set Measure ID#: Performance Measure Name:
Checklist for Treating Heart Failure. Alan M. Kaneshige MD, FACC, FASE Oklahoma Heart Institute
 Checklist for Treating Heart Failure Alan M. Kaneshige MD, FACC, FASE Oklahoma Heart Institute Novartis Disclosure Heart Failure (HF) a complex clinical syndrome that arises secondary to abnormalities
Checklist for Treating Heart Failure Alan M. Kaneshige MD, FACC, FASE Oklahoma Heart Institute Novartis Disclosure Heart Failure (HF) a complex clinical syndrome that arises secondary to abnormalities
Scientific conclusions and detailed explanation of the scientific grounds for the differences from the PRAC recommendation
 Annex I Scientific conclusions, grounds for variation to the terms of the marketing authorisations and detailed explanation of the scientific grounds for the differences from the PRAC recommendation 1
Annex I Scientific conclusions, grounds for variation to the terms of the marketing authorisations and detailed explanation of the scientific grounds for the differences from the PRAC recommendation 1
Selecting an ACE inhibitor:
 Selecting an ACE inhibitor: A Question of Class Effect? All members of a drug class are not therapeutically equivalent. In recent years, the concept of class effect has been under considerable debate,
Selecting an ACE inhibitor: A Question of Class Effect? All members of a drug class are not therapeutically equivalent. In recent years, the concept of class effect has been under considerable debate,
KDIGO Controversies Conference on Management of Patients with Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease
 KDIGO Controversies Conference on Management of Patients with Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease February 5-8, 2015 Vancouver, Canada Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) is an international
KDIGO Controversies Conference on Management of Patients with Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease February 5-8, 2015 Vancouver, Canada Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) is an international
9/17/2015. Reference: Ruschitzka F. J Hypertens 2011;29(Suppl 1):S9-14.
 0 1 2 Reference: Ruschitzka F. J Hypertens 2011;29(Suppl 1):S9-14. 3 Slide notes: Large trials such as ALLHAT, LIFE and ASCOT show that the majority of patients with hypertension will require multiple
0 1 2 Reference: Ruschitzka F. J Hypertens 2011;29(Suppl 1):S9-14. 3 Slide notes: Large trials such as ALLHAT, LIFE and ASCOT show that the majority of patients with hypertension will require multiple
ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS: MORE THAN THE ALTERNATIVE PRESENTATION BY: PATRICK HO, USC PHARM D. CANDIDATE OF 2017 MENTOR: DR.
 ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS: MORE THAN THE ALTERNATIVE PRESENTATION BY: PATRICK HO, USC PHARM D. CANDIDATE OF 2017 MENTOR: DR. CRAIG STERN, PHARMD, MBA, RPH, FASCP, FASHP, FICA, FLMI, FAMCP RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN
ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS: MORE THAN THE ALTERNATIVE PRESENTATION BY: PATRICK HO, USC PHARM D. CANDIDATE OF 2017 MENTOR: DR. CRAIG STERN, PHARMD, MBA, RPH, FASCP, FASHP, FICA, FLMI, FAMCP RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN
LXIV: DRUGS: 4. RAS BLOCKADE
 LXIV: DRUGS: 4. RAS BLOCKADE ACE Inhibitors Components of RAS Actions of Angiotensin i II Indications for ACEIs Contraindications RAS blockade in hypertension RAS blockade in CAD RAS blockade in HF Limitations
LXIV: DRUGS: 4. RAS BLOCKADE ACE Inhibitors Components of RAS Actions of Angiotensin i II Indications for ACEIs Contraindications RAS blockade in hypertension RAS blockade in CAD RAS blockade in HF Limitations
ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure
 ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure - 2005 Karl Swedberg Professor of Medicine Department of Medicine Sahlgrenska University Hospital/Östra Göteborg University Göteborg
ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure - 2005 Karl Swedberg Professor of Medicine Department of Medicine Sahlgrenska University Hospital/Östra Göteborg University Göteborg
ACEI or ARB for LVSD (HF-3, AMI-3): ACE-inhibitor and ARB Contraindication/Intolerance May 2, 2005
 ACEI or ARB for LVSD (HF-3, AMI-3): ACE-inhibitor and ARB Contraindication/Intolerance May 2, 2005 Blockade of the renin angiotensin system with angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors has been
ACEI or ARB for LVSD (HF-3, AMI-3): ACE-inhibitor and ARB Contraindication/Intolerance May 2, 2005 Blockade of the renin angiotensin system with angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors has been
Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular outcomes in elderly hypertensive patients treated with either ARB or ACEI
 Journal of Geriatric Cardiology (2012) 9: 252 257 2012 JGC All rights reserved; www.jgc301.com Research Articles Open Access Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular outcomes in elderly hypertensive patients
Journal of Geriatric Cardiology (2012) 9: 252 257 2012 JGC All rights reserved; www.jgc301.com Research Articles Open Access Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular outcomes in elderly hypertensive patients
Update on pharmacological treatment of heart failure. Aldo Pietro Maggioni, MD, FESC ANMCO Research Center Firenze, Italy
 Update on pharmacological treatment of heart failure Aldo Pietro Maggioni, MD, FESC ANMCO Research Center Firenze, Italy Presenter Disclosures Dr. Maggioni : Serving in Committees of studies sponsored
Update on pharmacological treatment of heart failure Aldo Pietro Maggioni, MD, FESC ANMCO Research Center Firenze, Italy Presenter Disclosures Dr. Maggioni : Serving in Committees of studies sponsored
ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING
 BRIEF REPORT Impact of on Nonfatal Myocardial Infarction and Cardiovascular Death in Patients With Heart Failure Catherine Demers, MD, MSc John J. V. McMurray, MD Karl Swedberg, MD, PhD Marc A. Pfeffer,
BRIEF REPORT Impact of on Nonfatal Myocardial Infarction and Cardiovascular Death in Patients With Heart Failure Catherine Demers, MD, MSc John J. V. McMurray, MD Karl Swedberg, MD, PhD Marc A. Pfeffer,
KDIGO Controversies Conference on Management of Patients with Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease
 KDIGO Controversies Conference on Management of Patients with Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease February 5-8, 2015 Vancouver, Canada Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) is an international
KDIGO Controversies Conference on Management of Patients with Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease February 5-8, 2015 Vancouver, Canada Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) is an international
Management of Hypertension
 Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
Uloga obiteljskog liječnika u prepoznavanju bolesnika s neuroendokrinim tumorom
 Uloga obiteljskog liječnika u prepoznavanju bolesnika s neuroendokrinim tumorom Dr.sc. Davorin Pezerović OB Vinkovci 11.05.2017. For Za uporabu use by Novartisovim speakers predavačima and SAMO appropriate
Uloga obiteljskog liječnika u prepoznavanju bolesnika s neuroendokrinim tumorom Dr.sc. Davorin Pezerović OB Vinkovci 11.05.2017. For Za uporabu use by Novartisovim speakers predavačima and SAMO appropriate
ACE inhibitors vs ARBs Myths and Facts
 ACE inhibitors vs ARBs Myths and Facts Prof. Dr. med. Frank Ruschitzka, FRCP (Edinburgh) Director Heart Failure/Transplantation Clinic University Clinic Zurich Switzerland Conflict of interest: Bayer,
ACE inhibitors vs ARBs Myths and Facts Prof. Dr. med. Frank Ruschitzka, FRCP (Edinburgh) Director Heart Failure/Transplantation Clinic University Clinic Zurich Switzerland Conflict of interest: Bayer,
Valsartan Amlodipine HCT Combination: Control To Goal. Dr. Sameh Shaheen M.B.B.Ch, MSc, MD, FESC, FSCAI. Prof of cardiology Ain Shams University
 Valsartan Amlodipine HCT Combination: Control To Goal Dr. Sameh Shaheen M.B.B.Ch, MSc, MD, FESC, FSCAI Prof of cardiology Ain Shams University Sonesta Hotel Cairo Egypt December 4 th 5 th ; 213 Hypertension
Valsartan Amlodipine HCT Combination: Control To Goal Dr. Sameh Shaheen M.B.B.Ch, MSc, MD, FESC, FSCAI Prof of cardiology Ain Shams University Sonesta Hotel Cairo Egypt December 4 th 5 th ; 213 Hypertension
Therapeutic Targets and Interventions
 Therapeutic Targets and Interventions Ali Valika, MD, FACC Advanced Heart Failure and Pulmonary Hypertension Advocate Medical Group Midwest Heart Foundation Disclosures: 1. Novartis: Speaker Honorarium
Therapeutic Targets and Interventions Ali Valika, MD, FACC Advanced Heart Failure and Pulmonary Hypertension Advocate Medical Group Midwest Heart Foundation Disclosures: 1. Novartis: Speaker Honorarium
Antialdosterone treatment in heart failure
 Update on the Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure 2012 Antialdosterone treatment in heart failure 전남의대윤현주 Chronic Heart Failure Prognosis of Heart failure Cecil, Text book of Internal Medicine, 22 th edition
Update on the Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure 2012 Antialdosterone treatment in heart failure 전남의대윤현주 Chronic Heart Failure Prognosis of Heart failure Cecil, Text book of Internal Medicine, 22 th edition
Otkazivanje rada bubrega
 Kidney Failure Kidney failure is also called renal failure. With kidney failure, the kidneys cannot get rid of the body s extra fluid and waste. This can happen because of disease or damage from an injury.
Kidney Failure Kidney failure is also called renal failure. With kidney failure, the kidneys cannot get rid of the body s extra fluid and waste. This can happen because of disease or damage from an injury.
VALUE OF ACEI IN THE MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSION
 VALUE OF ACEI IN THE MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSION Dr Catherine BESEME Paris 6 th December 2005 6 th International Congress of Bangladesh Society of Medicine Hypertension is a risk factor at the source, with
VALUE OF ACEI IN THE MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSION Dr Catherine BESEME Paris 6 th December 2005 6 th International Congress of Bangladesh Society of Medicine Hypertension is a risk factor at the source, with
Blood pressure control. Rok Humar, PhD Department of Research
 Blood pressure control Rok Humar, PhD Department of Research Mean arterial blood pressure is determined by Blood volume Cardiac output Peripheral resistance Blood capacitance Resistance of the system to
Blood pressure control Rok Humar, PhD Department of Research Mean arterial blood pressure is determined by Blood volume Cardiac output Peripheral resistance Blood capacitance Resistance of the system to
Aldosterone Antagonism in Heart Failure: Now for all Patients?
 Aldosterone Antagonism in Heart Failure: Now for all Patients? Inder Anand, MD, FRCP, D Phil (Oxon.) Professor of Medicine, University of Minnesota, Director Heart Failure Program, VA Medical Center 111C
Aldosterone Antagonism in Heart Failure: Now for all Patients? Inder Anand, MD, FRCP, D Phil (Oxon.) Professor of Medicine, University of Minnesota, Director Heart Failure Program, VA Medical Center 111C
Where are we with RAS blockade? New Targets.
 Where are we with RAS blockade? New Targets. Pr. M. Burnier Service of Nephrology and Hypertension Consultation Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois Lausanne, Switzerland Introduction of new antihypertensive
Where are we with RAS blockade? New Targets. Pr. M. Burnier Service of Nephrology and Hypertension Consultation Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois Lausanne, Switzerland Introduction of new antihypertensive
The Beneficial Role of Angiotensin- Converting Enzyme Inhibitor in Acute Myocardial Infarction
 The Beneficial Role of Angiotensin- Converting Enzyme Inhibitor in Acute Myocardial Infarction Cardiovascular Center, Korea University Guro Hospital 2007. 4. 20 Seung-Woon Rha, MD, PhD Introduction 1.
The Beneficial Role of Angiotensin- Converting Enzyme Inhibitor in Acute Myocardial Infarction Cardiovascular Center, Korea University Guro Hospital 2007. 4. 20 Seung-Woon Rha, MD, PhD Introduction 1.
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Heart Failure Clin 2 (2006) 101 105 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACE inhibitors, in diabetic hypertension, 30 31 Adipokines, cardiovascular events related to, 6 Advanced
Heart Failure Clin 2 (2006) 101 105 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACE inhibitors, in diabetic hypertension, 30 31 Adipokines, cardiovascular events related to, 6 Advanced
Treating HF Patients with ARNI s Why, When and How?
 Treating HF Patients with ARNI s Why, When and How? 19 th Annual San Diego Heart Failure Symposium for Primary Care Physicians January 11-12, 2019 La Jolla, CA Barry Greenberg M.D. Distinguished Professor
Treating HF Patients with ARNI s Why, When and How? 19 th Annual San Diego Heart Failure Symposium for Primary Care Physicians January 11-12, 2019 La Jolla, CA Barry Greenberg M.D. Distinguished Professor
Combination Therapy for Hypertension
 Combination Therapy for Hypertension Se-Joong Rim, MD Cardiology Division, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Goals of Therapy Reduce CVD and renal morbidity and mortality. Treat to BP
Combination Therapy for Hypertension Se-Joong Rim, MD Cardiology Division, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Goals of Therapy Reduce CVD and renal morbidity and mortality. Treat to BP
INDEX. Index 517. A AASK, see African-American Study of Kidney Disease ACE inhibitors, see Angiotensinconverting
 Index 517 INDEX A AASK, see African-American Study of Kidney Disease ACE inhibitors, see Angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitors ACS, see Acute coronary syndrome Acute coronary syndrome (ACS), classification
Index 517 INDEX A AASK, see African-American Study of Kidney Disease ACE inhibitors, see Angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitors ACS, see Acute coronary syndrome Acute coronary syndrome (ACS), classification
Conversion of losartan to lisinopril
 Cari untuk: Cari Cari Conversion of losartan to lisinopril Dania Alsammarae, Strategy Director and co-founder of Anglo Arabian Healthcare speaks with Neil Halligan of Arabian Business on what it takes
Cari untuk: Cari Cari Conversion of losartan to lisinopril Dania Alsammarae, Strategy Director and co-founder of Anglo Arabian Healthcare speaks with Neil Halligan of Arabian Business on what it takes
Kidney Failure. Kidney. Kidney. Ureters. Bladder. Ureters. Vagina. Urethra. Bladder. Urethra. Penis
 Kidney Failure Kidney failure is also called renal failure. With kidney failure, the kidneys cannot get rid of the body s extra fluid and waste. This can happen because of disease or damage from an injury.
Kidney Failure Kidney failure is also called renal failure. With kidney failure, the kidneys cannot get rid of the body s extra fluid and waste. This can happen because of disease or damage from an injury.
A Fresh Look at ARBs : Focus on HF survival data
 A Fresh Look at ARBs : Focus on HF survival data Seok-Min Kang, MD, Ph D. Division of Cardiology, Severance Cardiovascular Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea HF specialists ARBs,
A Fresh Look at ARBs : Focus on HF survival data Seok-Min Kang, MD, Ph D. Division of Cardiology, Severance Cardiovascular Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea HF specialists ARBs,
Should All Patients Be Treated with Ace-inh /ARB after STEMI with Preserved LV Function?
 Should All Patients Be Treated with Ace-inh /ARB after STEMI with Preserved LV Function? Avi Shimony, MD, FESC Cardiology Division Soroka University Medical Center Ben-Gurion University, Beer-Sheva Disclosure
Should All Patients Be Treated with Ace-inh /ARB after STEMI with Preserved LV Function? Avi Shimony, MD, FESC Cardiology Division Soroka University Medical Center Ben-Gurion University, Beer-Sheva Disclosure
COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF RISK FACTORS, TREATMENT PROFILE AND CLINICAL OUTCOMES OF HEART FAILURE PATIENTS
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF RISK FACTORS, TREATMENT PROFILE AND CLINICAL OUTCOMES OF HEART FAILURE
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF RISK FACTORS, TREATMENT PROFILE AND CLINICAL OUTCOMES OF HEART FAILURE
VIEWPOINT. Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 37, No. 5, by the American College of Cardiology ISSN /01/$20.
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 37, No. 5, 2001 2001 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/01/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(01)01161-5 VIEWPOINT
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 37, No. 5, 2001 2001 by the American College of Cardiology ISSN 0735-1097/01/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0735-1097(01)01161-5 VIEWPOINT
Rationale for the use of Single Pill Combination (SPC) and Asian data of ARB/CCB SPC
 Rationale for the use of Single Pill Combination (SPC) and Asian data of ARB/CCB SPC Seung Woo Park, MD Samsung Medical Center BP Control Rates in Asia BP controlled BP uncontrolled 24.3% 36.6% 19% Turkey
Rationale for the use of Single Pill Combination (SPC) and Asian data of ARB/CCB SPC Seung Woo Park, MD Samsung Medical Center BP Control Rates in Asia BP controlled BP uncontrolled 24.3% 36.6% 19% Turkey
The control of hypertension in the. Reaching for Aggressive Blood Pressure Goals: Role of Angiotensin Receptor Blockade in Combination Therapy REPORTS
 REPORTS Reaching for Aggressive Blood Pressure Goals: Role of Angiotensin Receptor Blockade in Combination Therapy By Richard V. Milani, MD Abstract Elevated blood pressure, particularly systolic blood
REPORTS Reaching for Aggressive Blood Pressure Goals: Role of Angiotensin Receptor Blockade in Combination Therapy By Richard V. Milani, MD Abstract Elevated blood pressure, particularly systolic blood
Section 3, Lecture 2
 59-291 Section 3, Lecture 2 Diuretics: -increase in Na + excretion (naturesis) Thiazide and Related diuretics -decreased PVR due to decreases muscle contraction -an economical and effective treatment -protect
59-291 Section 3, Lecture 2 Diuretics: -increase in Na + excretion (naturesis) Thiazide and Related diuretics -decreased PVR due to decreases muscle contraction -an economical and effective treatment -protect
Should beta blockers remain first-line drugs for hypertension?
 1 de 6 03/11/2008 13:23 Should beta blockers remain first-line drugs for hypertension? Maros Elsik, Cardiologist, Department of Epidemiology and Preventive Medicine, Monash University and The Alfred Hospital,
1 de 6 03/11/2008 13:23 Should beta blockers remain first-line drugs for hypertension? Maros Elsik, Cardiologist, Department of Epidemiology and Preventive Medicine, Monash University and The Alfred Hospital,
HEART FAILURE SUMMARY. and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. the cornerstone of heart failure treatment.
 HEART FAILURE SUMMARY + Heart Failure is a condition affecting a large number of Irish people and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. + ACE inhibitors, in combination with diuretics,
HEART FAILURE SUMMARY + Heart Failure is a condition affecting a large number of Irish people and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. + ACE inhibitors, in combination with diuretics,
Benefits of angiotensin-ii receptor blockers. Are we going beyond blood pressure control?
 14 CONTRIBUIÇÃO INTERNACIONAL Benefits of angiotensin-ii receptor blockers. Are we going beyond Massimo Volpe 1,2, Giuliano Tocci 1 ABSTRACT Despite the well-known relationship between high blood pressure
14 CONTRIBUIÇÃO INTERNACIONAL Benefits of angiotensin-ii receptor blockers. Are we going beyond Massimo Volpe 1,2, Giuliano Tocci 1 ABSTRACT Despite the well-known relationship between high blood pressure
RAAS Inhibitors in the Cardiovascular Continuum: What is Still Missing?
 Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy 18 311 320 2004 C 2004 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The United States REVIEW RAAS Inhibitors in the Cardiovascular Continuum: What is Still Missing? Aldo
Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy 18 311 320 2004 C 2004 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The United States REVIEW RAAS Inhibitors in the Cardiovascular Continuum: What is Still Missing? Aldo
Journal of Hypertension 2007, 25: Received 27 November 2006 Revised 11 January 2007 Accepted 22 January 2007
 Original article 951 Blood pressure-dependent and independent effects of agents that inhibit the renin angiotensin system Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists Collaboration M Objectives To evaluate
Original article 951 Blood pressure-dependent and independent effects of agents that inhibit the renin angiotensin system Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists Collaboration M Objectives To evaluate
Hypertension is a major risk factor for
 OPTIMAL RISK MANAGEMENT OF THE HYPERTENSIVE PATIENT WITH MULTIPLE RISK FACTORS * Keith C. Ferdinand, MD, FACC ABSTRACT To determine the risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with hypertension, it
OPTIMAL RISK MANAGEMENT OF THE HYPERTENSIVE PATIENT WITH MULTIPLE RISK FACTORS * Keith C. Ferdinand, MD, FACC ABSTRACT To determine the risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with hypertension, it
Renal protection by inhibition of the renin-angiotensinaldosterone
 Renal protection by inhibition of the renin-angiotensinaldosterone system Tomas Berl Key words: angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitor, angiotensin receptor blocker, combination therapy, direct renin inhibitor,
Renal protection by inhibition of the renin-angiotensinaldosterone system Tomas Berl Key words: angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitor, angiotensin receptor blocker, combination therapy, direct renin inhibitor,
Don t let the pressure get to you:
 Balanced information for better care Don t let the pressure get to you: An update on the changing recommendations for treating hypertension New trial data and guidelines have made hypertension care more
Balanced information for better care Don t let the pressure get to you: An update on the changing recommendations for treating hypertension New trial data and guidelines have made hypertension care more
Advanced Care for Decompensated Heart Failure
 Advanced Care for Decompensated Heart Failure Sara Kalantari MD Assistant Professor of Medicine, University of Chicago Advanced Heart Failure, Mechanical Circulatory Support and Cardiac Transplantation
Advanced Care for Decompensated Heart Failure Sara Kalantari MD Assistant Professor of Medicine, University of Chicago Advanced Heart Failure, Mechanical Circulatory Support and Cardiac Transplantation
Heart Failure Update. Michael Fu. Professor, Överläkare
 Heart Failure Update Michael Fu Professor, Överläkare Update in Diagnosis Update in Pharmacological Treatment Update in Device Therapy Heart Failure in the Elderly Put Guidelines into Clinical Practice
Heart Failure Update Michael Fu Professor, Överläkare Update in Diagnosis Update in Pharmacological Treatment Update in Device Therapy Heart Failure in the Elderly Put Guidelines into Clinical Practice
Φαρμακευτική θεραπεία της μετεμφραγματικής καρδιακής ανεπάρκειας. Α. Καραβίδας Υπεύθυνος ιατρείου καρδιακής ανεπάρκειας Γ.Ν.Α Γ.
 Φαρμακευτική θεραπεία της μετεμφραγματικής καρδιακής ανεπάρκειας Α. Καραβίδας Υπεύθυνος ιατρείου καρδιακής ανεπάρκειας Γ.Ν.Α Γ.Γεννηματάς Clinical Trials on Fibrinolysis N = 61.41 AMI pts, ( GUSTO I, GUSTOIIb,
Φαρμακευτική θεραπεία της μετεμφραγματικής καρδιακής ανεπάρκειας Α. Καραβίδας Υπεύθυνος ιατρείου καρδιακής ανεπάρκειας Γ.Ν.Α Γ.Γεννηματάς Clinical Trials on Fibrinolysis N = 61.41 AMI pts, ( GUSTO I, GUSTOIIb,
Review Article. Pharmacotherapy of Heart Failure with Reduced LVEF. Sachin Mukhedkar, Ajit Bhagwat
 Review Article Vidarbha Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 22 January 2017 Pharmacotherapy of Heart Failure with Reduced LVEF 1 2 Sachin Mukhedkar, Ajit Bhagwat ABSTRACT Heart failure with reduced ejection
Review Article Vidarbha Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 22 January 2017 Pharmacotherapy of Heart Failure with Reduced LVEF 1 2 Sachin Mukhedkar, Ajit Bhagwat ABSTRACT Heart failure with reduced ejection
CT Academy of Family Physicians Scientific Symposium October 2012 Amit Pursnani, MD
 CT Academy of Family Physicians Scientific Symposium October 2012 Amit Pursnani, MD Clinical syndrome resulting from a structural or functional cardiac disorder that impairs the ability of the heart to
CT Academy of Family Physicians Scientific Symposium October 2012 Amit Pursnani, MD Clinical syndrome resulting from a structural or functional cardiac disorder that impairs the ability of the heart to
Amlodipine/Valsartan (Exforge ) Changing the Landscape of BP Management
 Amlodipine/Valsartan (Exforge ) Changing the Landscape of BP Management Bum-Kee Hong Yongdong Severance Hospital Yonsei University College of Medicine Rationale for Multiple-Mechanism Therapy Inadequacy
Amlodipine/Valsartan (Exforge ) Changing the Landscape of BP Management Bum-Kee Hong Yongdong Severance Hospital Yonsei University College of Medicine Rationale for Multiple-Mechanism Therapy Inadequacy
Klinika za bolesti srca i krvnih žila, Klinički bolnički centar Split, Split, Hrvatska
 Kardiologija danas odabrane teme / Cardiology Today Selected Topics 127 ACE-inhibitori: liječenje hipertenzije, organoprotekcija i mjere opreza ACE Inhibitors: Hypertension Treatment, Organoprotection
Kardiologija danas odabrane teme / Cardiology Today Selected Topics 127 ACE-inhibitori: liječenje hipertenzije, organoprotekcija i mjere opreza ACE Inhibitors: Hypertension Treatment, Organoprotection
New Treatment Options for Diabetic Nephropathy patients. Prof. M. Burnier, Service of Nephrology and Hypertension CHUV, Lausanne, Switzerland
 New Treatment Options for Diabetic Nephropathy patients Prof. M. Burnier, Service of Nephrology and Hypertension CHUV, Lausanne, Switzerland Diabetes and nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is the most common
New Treatment Options for Diabetic Nephropathy patients Prof. M. Burnier, Service of Nephrology and Hypertension CHUV, Lausanne, Switzerland Diabetes and nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is the most common
In the Literature 1001 BP of 1.1 mm Hg). The trial was stopped early based on prespecified stopping rules because of a significant difference in cardi
 Is Choice of Antihypertensive Agent Important in Improving Cardiovascular Outcomes in High-Risk Hypertensive Patients? Commentary on Jamerson K, Weber MA, Bakris GL, et al; ACCOMPLISH Trial Investigators.
Is Choice of Antihypertensive Agent Important in Improving Cardiovascular Outcomes in High-Risk Hypertensive Patients? Commentary on Jamerson K, Weber MA, Bakris GL, et al; ACCOMPLISH Trial Investigators.
