Systemic Hypertension
|
|
|
- Chester Russell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BCS Theme Session Cardiovascular Block Pathology of Hypertension Department of Pathology University of Sydney Systemic Hypertension Definition of Systemic hypertension: consistent blood pressure elevation at rest >140 systolic and/or >90 diastolic mm Hg Types of Systemic hypertension: Benign - stable for years Malignant - >200/120 mm Hg year course 1
2 Cardiac output is the volume of blood being pumped by the heart in a minute. It is equal to the heart rate multiplied by the stroke volume Cardiac Output Blood Pressure Regulation Aldosterone Blood volume fluid retention Na + reabsorption Heart Rate Stroke volume contractility end-diastolic volume Chamber size Total Peripheral (arteriolar) Resistance Systemic Local Vasoconstrictors Vasodilators Pressure ph Hypoxia humoral neuronal Causes of Systemic Hypertension Idiopathic in ~95% of patients ( essential HT) Secondary to known disease in ~5% Sometimes remediable in this category 2
3 Secondary Causes of Hypertension Kidney: Chronic renal / renal-vascular disease press/flow afferent arteriole JG cells Renin Plasma angiotensinogen Angiotensin I (ACE) Angiotensin II: constriction of VSMC PR BP aldosterone secretion reabsorption of Na + blood volume CO BP Endocrine: Adrenal medullary tumour eg phaeochromocytoma Cardiovascular: Coarctation of the aorta Renal causes of Hypertension (1) a derangement in the renal handling of sodium and fluids leading to volume expansion, or (2) an alteration in renal secretion of vasoactive materials resulting in a systemic or local change in arteriolar tone. Reno-vascular hypertension (eg renal artery stenosis, renal artery fibromuscular dysplasia): Decreased perfusion of renal tissue (nearly always because of atherosclerosis) Activates the renin-angiotensin system Circulating angiotensin II elevates arterial pressure: By directly causing vasoconstriction, by stimulating aldosterone secretion with resulting Na + retention, and/or By stimulating the adrenergic nervous system. Renal Parenchymal Disease (eg acute and chronic glomerulonephritis, polycystic disease, renal vasculitis): Decreased perfusion of renal tissue due to inflammatory and fibrotic changes involving multiple small intrarenal vessels, Activates the renin-angiotensin system Renal tumours: Rare results from the excess secretion of renin by juxtaglomerular cell tumors or nephroblastomas Initial presentation is similar to that of hyperaldosteronism, with hypertension, and overproduction of aldosterone. 3
4 J9 Kidney Diabetes Renal artery atheroma x a Renal artery fibromuscular dysplasia H&E x25 4
5 Normal kidney cut surface Cortex Medulla (including renal pyramid) Pelvo-calyceal system (embedded in fat) Normal kidney 5
6 Kidneys: Chronic Glomerulo- nephritis Cortical thinning Indistinct corticomedullary junction Enlarged fat filled hilum Adrenal cortical adenoma Adrenal Adenoma Adrenal cortical adenomas are usually non-functional and an incidental finding. However, they can cause: Hyperaldosteronism (hypertension, hypokalemia) Cushing Syndrome (hypercortisolism HT, wt gain, centripetal fat etc) 6
7 Adrenal Phaeochromocytoma Adrenalin secreting tumour 10% may be malignant 70% cause chronic hypertension 50% have paroxysmal episodes of HT, palpitations etc 10% are extra-adrenal eg carotid body Heart in Benign HT Concentric left ventricular hypertrophy Heart weight exceeds 250 gm in women and g in men (these are approx normal ranges) (Build of patient is important in determining the upper level of normal) 7
8 Normal Heart (posterior view) Left Atrium Mitral valve Chordae tendineae Papillary muscles Left Ventricle Right Atrium Tricuspid valve Right Ventricle Post. IV groove Left ventricular concentric hypertrophy in hypertension 8
9 Cardiac Myocytes Normal Hypertrophy I Myocardial Hypertrophy: abnormal nuclei H&E x250 9
10 Myocardial perfusion myocytes blood vessel blood vessel NORMAL Necrotic myocyte -> Fibrosis HYPERTROPHIED I37-1 Heart hypertrophy interstitial fibrosis H&E x20 10
11 Effects of hypertension on the vascular system The Arteries Loss of elastin and smooth muscle in the media, with replacement by fibrous tissue = hypertensive arteriosclerosis (an exaggeration of age changes) High risk factor for atherosclerosis Atheromatous coronary artery 11
12 Hypertensive vascular damage to kidney Kidney is supplied by end arteries Glomeruli supplied first Medulla is supplied (in line) after glomeruli Normal kidney cut surface 12
13 Normal kidney Kidney in Benign Hypertension Loss of glomeruli and related nephrons Hyperplasia of tubules of surviving nephrons Bilateral finely granular contracted kidneys result Renal function is seldom compromised 13
14 Kidney: hypertensive nephrosclerosis (interior) Kidney hypertensive nephrosclerosis (exterior) 14
15 Dr Hambly will now appear! Effects of HT on Vascular System Arterioles: Replacement of smooth muscle with homogeneous eosinophilic hyaline in walls of afferent arterioles.the lumen of these vessels is narrowed. Elongation of these vessels leading to tortuosity. 15
16 Nephron within the Kidney J17 Hypertensive vascular damage to kidney 16
17 J17 Kidney benign hypertension: thick walled artery H&E x50 J17 Kidney benign hypertension: hyaline afferent arteriole x100 17
18 J17 Kidney benign hypertension: tortuous benign afferent arteriole J17 Kidney benign hypertension: obsolete glomerulus and tubular atrophy H&E x50 18
19 J17 Kidney benign hypertension: subcapsular scar H&E x20 Brain in Benign Hypertension Increased risk of cerebral infarction (atherosclerosis), a common form of stroke Increased risk of intracerebral haemorrhage (degeneration of penetrating arteries) Increased risk of rupture of berry aneurysms in Circle of Willis with subarachnoid haemorrhage 19
20 Internal capsule White matter deep in the brain connecting cerebral cortex with brainstem and spinal cord Horizontal section Coronal section Cerebral striate vessel in hypertension: thick walled muscle lost 20
21 Micro cerebral striate artery microaneurysm in hypertension Brain: Intracerebral Haemorrhage 59 yo woman with long Hx HT Large hemorrhage into R basal ganglia & ventricles Flattening of gyri and midline shift 21
22 Brain: Aneurysm (unruptured) Macro - unruptured berry aneurysm of circle of willis 22
23 Micro - unruptured berry aneurysm LP Brain: Ruptured Saccular (berry) Aneurysm 23
24 Types of hypertension Benign stable Malignant unstable and accelerated with diastolic pressures > 120 mmhg 1455 Kidney - malignant hypertension: fibrinoid necrosis of arterioles, glomeruli 24
25 Retina - normal Retina - hypertensive AV nipping 25
26 Retina Malignant hypertension Papilloedema of optic cup Cotton wool exudates Flame hemorrhages Deaths due to undiagnosed or inadequately controlled hypertension Congestive cardiac failure (often biventricular) 60% Strokes 30% Aortic dissection (comparatively infrequent) However, renal failure in benign hypertension is uncommon 26
27 Macro aortic dissection Bottles and Slides (for lab) J17 Hypertensive vascular damage to kidney KIDNEYS - CHRONIC GLOMERULONEPHRITIS ADRENAL - CORTICAL ADENOMA Adrenal phaeochromocytoma HEART - HYPERTENSION Atheromatous coronary artery Atheromatous coronary artery Normal kidney Kidney hypertensive nephrosclerosis Brain Intracerebral Haemorrhage BRAIN - ANEURYSM (UNRUPTURED) BRAIN - SACCULAR (BERRY) ANEURYSM 27
Pathology of Hypertension
 2016-03-07 Pathology of Hypertension Honghe Zhang honghezhang@zju.edu.cn Tel:88208199 Department of Pathology ❶ Genetic predisposition ❷ Dietary factors ❸ Environmental factors ❹ Others Definition and
2016-03-07 Pathology of Hypertension Honghe Zhang honghezhang@zju.edu.cn Tel:88208199 Department of Pathology ❶ Genetic predisposition ❷ Dietary factors ❸ Environmental factors ❹ Others Definition and
Functional vascular disorders
 Functional vascular disorders Raynaud s phenomenon Raynaud s phenomenon Refers to Intermittent,bilateral attacks of ischemia of the fingers or toes, and sometimes ears or nose. It clinically manifests
Functional vascular disorders Raynaud s phenomenon Raynaud s phenomenon Refers to Intermittent,bilateral attacks of ischemia of the fingers or toes, and sometimes ears or nose. It clinically manifests
HYPERTENSIVE VASCULAR DISEASE
 HYPERTENSIVE VASCULAR DISEASE Cutoffs in diagnosing hypertension in clinical practice sustained diastolic pressures >90 mm Hg, or sustained systolic pressures >140 mm Hg Malignant hypertension A small
HYPERTENSIVE VASCULAR DISEASE Cutoffs in diagnosing hypertension in clinical practice sustained diastolic pressures >90 mm Hg, or sustained systolic pressures >140 mm Hg Malignant hypertension A small
Blood Vessels. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 Blood Vessels Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the structure and function of blood vessels. Discuss the different mechanisms of blood pressure regulation. Compare and contrast the following types
Blood Vessels Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the structure and function of blood vessels. Discuss the different mechanisms of blood pressure regulation. Compare and contrast the following types
Circulation. Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications. Venous Return. Arterial flow. Regulation of Cardiac Output.
 Circulation Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications Two systems Pulmonary (low pressure) Systemic (high pressure) Aorta 120 mmhg Large arteries 110 mmhg Arterioles 40 mmhg Arteriolar capillaries
Circulation Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications Two systems Pulmonary (low pressure) Systemic (high pressure) Aorta 120 mmhg Large arteries 110 mmhg Arterioles 40 mmhg Arteriolar capillaries
BIOH122 Session 6 Vascular Regulation
 BIOH122 Session 6 Vascular Regulation To complete this worksheet, select: Module: Distribution Title: Vascular Regulation Introduction 1. a. How do Mean Arterial Blood Pressure (MABP) and Systemic Vascular
BIOH122 Session 6 Vascular Regulation To complete this worksheet, select: Module: Distribution Title: Vascular Regulation Introduction 1. a. How do Mean Arterial Blood Pressure (MABP) and Systemic Vascular
Cardiovascular System. Heart
 Cardiovascular System Heart Electrocardiogram A device that records the electrical activity of the heart. Measuring the relative electrical activity of one heart cycle. A complete contraction and relaxation.
Cardiovascular System Heart Electrocardiogram A device that records the electrical activity of the heart. Measuring the relative electrical activity of one heart cycle. A complete contraction and relaxation.
Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide
 Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide Main Idea: The function of the circulatory system is to maintain adequate blood flow to all tissues. Clinical
Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide Main Idea: The function of the circulatory system is to maintain adequate blood flow to all tissues. Clinical
(D) (E) (F) 6. The extrasystolic beat would produce (A) increased pulse pressure because contractility. is increased. increased
 Review Test 1. A 53-year-old woman is found, by arteriography, to have 5% narrowing of her left renal artery. What is the expected change in blood flow through the stenotic artery? Decrease to 1 2 Decrease
Review Test 1. A 53-year-old woman is found, by arteriography, to have 5% narrowing of her left renal artery. What is the expected change in blood flow through the stenotic artery? Decrease to 1 2 Decrease
Cardiovascular Disorders. Heart Disorders. Diagnostic Tests for CV Function. Bio 375. Pathophysiology
 Cardiovascular Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology Heart Disorders Heart disease is ranked as a major cause of death in the U.S. Common heart diseases include: Congenital heart defects Hypertensive heart
Cardiovascular Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology Heart Disorders Heart disease is ranked as a major cause of death in the U.S. Common heart diseases include: Congenital heart defects Hypertensive heart
Year 2004 Paper two: Questions supplied by Megan 1
 Year 2004 Paper two: Questions supplied by Megan 1 QUESTION 96 A 32yo woman if found to have high blood pressure (180/105mmHg) at an insurance medical examination. She is asymptomatic. Clinical examination
Year 2004 Paper two: Questions supplied by Megan 1 QUESTION 96 A 32yo woman if found to have high blood pressure (180/105mmHg) at an insurance medical examination. She is asymptomatic. Clinical examination
- Dr Alia Shatnawi. 1 P a g e
 - 1 مها أبو عجمية - - - Dr Alia Shatnawi 1 P a g e A Skippable Intr0 Blood pressure normally decreases during the night. Absence of this phenomenon is called (nondipping) Wikipedia: Circadian rhythm....
- 1 مها أبو عجمية - - - Dr Alia Shatnawi 1 P a g e A Skippable Intr0 Blood pressure normally decreases during the night. Absence of this phenomenon is called (nondipping) Wikipedia: Circadian rhythm....
Hypertension The normal radial artery blood pressures in adults are: Systolic arterial pressure: 100 to 140 mmhg. Diastolic arterial pressure: 60 to
 Hypertension The normal radial artery blood pressures in adults are: Systolic arterial pressure: 100 to 140 mmhg. Diastolic arterial pressure: 60 to 90 mmhg. These pressures are called Normal blood pressure
Hypertension The normal radial artery blood pressures in adults are: Systolic arterial pressure: 100 to 140 mmhg. Diastolic arterial pressure: 60 to 90 mmhg. These pressures are called Normal blood pressure
CASE 13. What neural and humoral pathways regulate arterial pressure? What are two effects of angiotensin II?
 CASE 13 A 57-year-old man with long-standing diabetes mellitus and newly diagnosed hypertension presents to his primary care physician for follow-up. The patient has been trying to alter his dietary habits
CASE 13 A 57-year-old man with long-standing diabetes mellitus and newly diagnosed hypertension presents to his primary care physician for follow-up. The patient has been trying to alter his dietary habits
Veins. VENOUS RETURN = PRELOAD = End Diastolic Volume= Blood returning to heart per cardiac cycle (EDV) or per minute (Venous Return)
 Veins Venous system transports blood back to heart (VENOUS RETURN) Capillaries drain into venules Venules converge to form small veins that exit organs Smaller veins merge to form larger vessels Veins
Veins Venous system transports blood back to heart (VENOUS RETURN) Capillaries drain into venules Venules converge to form small veins that exit organs Smaller veins merge to form larger vessels Veins
Blood Pressure Regulation 2. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Blood Pressure Regulation 2. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System. Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD
 Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume. Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM
 Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM Maintaining Volume Plasma water and sodium (Na + ) are regulated independently - you are already familiar
Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM Maintaining Volume Plasma water and sodium (Na + ) are regulated independently - you are already familiar
Outline the functional anatomy, and the physiological factors, that determine oxygen delivery to the renal medulla.
 2011-2-21 Outline the functional anatomy, and the physiological factors, that determine oxygen delivery to the renal medulla. Oxygen delivery = Blood flow CaO 2 Where Blood flow determined by (arterial
2011-2-21 Outline the functional anatomy, and the physiological factors, that determine oxygen delivery to the renal medulla. Oxygen delivery = Blood flow CaO 2 Where Blood flow determined by (arterial
Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction There are two basic mechanisms for regulating
Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction There are two basic mechanisms for regulating
Cardiac Pathophysiology
 Cardiac Pathophysiology Evaluation Components Medical history Physical examination Routine laboratory tests Optional tests Medical History Duration and classification of hypertension. Patient history of
Cardiac Pathophysiology Evaluation Components Medical history Physical examination Routine laboratory tests Optional tests Medical History Duration and classification of hypertension. Patient history of
Histopathology: Hypertension and diabetes in the kidney These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features.
 Histopathology: Hypertension and diabetes in the kidney These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need
Histopathology: Hypertension and diabetes in the kidney These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need
Special Lecture 11/08/2013. Hypertension Dr. HN Mayrovitz
 Special Lecture 11/08/2013 Hypertension Dr. HN Mayrovitz Arterial Blood Pressure (ABP) Major Factors Summarized Sympathetic Hormones Arteriole MAP ~ Q x TPR + f (V / C) SV x HR Renal SBP Hypertension =
Special Lecture 11/08/2013 Hypertension Dr. HN Mayrovitz Arterial Blood Pressure (ABP) Major Factors Summarized Sympathetic Hormones Arteriole MAP ~ Q x TPR + f (V / C) SV x HR Renal SBP Hypertension =
Diseases of cardiavascular system
 Diseases of cardiavascular system Ph.D Wei Zhang ( 张伟 ) Associate Professor Institute of Pathology & Forensic Medicine, Zhejiang University, School of Medicine zwei72@zju.edu.cn Hypertension Introduction
Diseases of cardiavascular system Ph.D Wei Zhang ( 张伟 ) Associate Professor Institute of Pathology & Forensic Medicine, Zhejiang University, School of Medicine zwei72@zju.edu.cn Hypertension Introduction
10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Kidney Structure. Renal Lobe = renal pyramid & overlying cortex. Renal Lobule = medullary ray & surrounding cortical labryinth.
 Kidney Structure Capsule Hilum ureter renal pelvis major and minor calyxes renal and vein segmental arteries interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries Medulla renal pyramids cortical/renal
Kidney Structure Capsule Hilum ureter renal pelvis major and minor calyxes renal and vein segmental arteries interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries Medulla renal pyramids cortical/renal
Therefore MAP=CO x TPR = HR x SV x TPR
 Regulation of MAP Flow = pressure gradient resistance CO = MAP TPR Therefore MAP=CO x TPR = HR x SV x TPR TPR is the total peripheral resistance: this is the combined resistance of all blood vessels (remember
Regulation of MAP Flow = pressure gradient resistance CO = MAP TPR Therefore MAP=CO x TPR = HR x SV x TPR TPR is the total peripheral resistance: this is the combined resistance of all blood vessels (remember
Structure and organization of blood vessels
 The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1 Terms you should understand: hemorrhage, intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms, anoxia, myocardial contractility, residual
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1 Terms you should understand: hemorrhage, intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms, anoxia, myocardial contractility, residual
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
Questions? Homework due in lab 6. PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!)
 Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Cardiovascular System B L O O D V E S S E L S 2
 Cardiovascular System B L O O D V E S S E L S 2 Blood Pressure Main factors influencing blood pressure: Cardiac output (CO) Peripheral resistance (PR) Blood volume Peripheral resistance is a major factor
Cardiovascular System B L O O D V E S S E L S 2 Blood Pressure Main factors influencing blood pressure: Cardiac output (CO) Peripheral resistance (PR) Blood volume Peripheral resistance is a major factor
Heart. Large lymphatic vessels Lymph node. Lymphatic. system Arteriovenous anastomosis. (exchange vessels)
 Venous system Large veins (capacitance vessels) Small veins (capacitance vessels) Postcapillary venule Thoroughfare channel Heart Large lymphatic vessels Lymph node Lymphatic system Arteriovenous anastomosis
Venous system Large veins (capacitance vessels) Small veins (capacitance vessels) Postcapillary venule Thoroughfare channel Heart Large lymphatic vessels Lymph node Lymphatic system Arteriovenous anastomosis
Common Codes for ICD-10
 Common Codes for ICD-10 Specialty: Cardiology *Always utilize more specific codes first. ABNORMALITIES OF HEART RHYTHM ICD-9-CM Codes: 427.81, 427.89, 785.0, 785.1, 785.3 R00.0 Tachycardia, unspecified
Common Codes for ICD-10 Specialty: Cardiology *Always utilize more specific codes first. ABNORMALITIES OF HEART RHYTHM ICD-9-CM Codes: 427.81, 427.89, 785.0, 785.1, 785.3 R00.0 Tachycardia, unspecified
Chapter 20 Diseases of the kidney:
 Chapter 20 Diseases of the kidney: 1. Which of the following is seen in Nephrotic syndrome (2000, 2004) (a) Albumin is lost in the urine, while other globulins are unaffected (b) Early hypertension (c)
Chapter 20 Diseases of the kidney: 1. Which of the following is seen in Nephrotic syndrome (2000, 2004) (a) Albumin is lost in the urine, while other globulins are unaffected (b) Early hypertension (c)
Systemic Hypertension Dr ahmed almutairi Assistant professor Internal medicine dept
 Systemic Hypertension Dr ahmed almutairi Assistant professor Internal medicine dept Continents 1- introduction 2- classification/definition 3- classification/etiology 4-etiology in both categories 5- complications
Systemic Hypertension Dr ahmed almutairi Assistant professor Internal medicine dept Continents 1- introduction 2- classification/definition 3- classification/etiology 4-etiology in both categories 5- complications
HYPERTENSION: Sustained elevation of arterial blood pressure above normal o Systolic 140 mm Hg and/or o Diastolic 90 mm Hg
 Lecture 39 Anti-Hypertensives B-Rod BLOOD PRESSURE: Systolic / Diastolic NORMAL: 120/80 Systolic = measure of pressure as heart is beating Diastolic = measure of pressure while heart is at rest between
Lecture 39 Anti-Hypertensives B-Rod BLOOD PRESSURE: Systolic / Diastolic NORMAL: 120/80 Systolic = measure of pressure as heart is beating Diastolic = measure of pressure while heart is at rest between
Hypertension Coronary artery disease
 Hypertension Coronary artery disease 1 Problem Magnitude Hypertension( HTN) is the most common primary diagnosis. Worldwide prevalence estimates for HTN may be as much as 1 billion. Arterial hypertension
Hypertension Coronary artery disease 1 Problem Magnitude Hypertension( HTN) is the most common primary diagnosis. Worldwide prevalence estimates for HTN may be as much as 1 billion. Arterial hypertension
Presenter: Tom Mulvey
 Slides are from Level 3 Biology Course Content Day, 7 th November 2012 Presenter: Tom Mulvey Teachers are free to use these for teaching purposes with appropriate acknowledgement Blood Pressure Ways of
Slides are from Level 3 Biology Course Content Day, 7 th November 2012 Presenter: Tom Mulvey Teachers are free to use these for teaching purposes with appropriate acknowledgement Blood Pressure Ways of
Blood pressure. Formation of the blood pressure: Blood pressure. Formation of the blood pressure 5/1/12
 Blood pressure Blood pressure Dr Badri Paudel www.badripaudel.com Ø Blood pressure means the force exerted by the blood against the vessel wall Ø ( or the force exerted by the blood against any unit area
Blood pressure Blood pressure Dr Badri Paudel www.badripaudel.com Ø Blood pressure means the force exerted by the blood against the vessel wall Ø ( or the force exerted by the blood against any unit area
Chapter 25 The Urinary System
 Chapter 25 The Urinary System 10/30/2013 MDufilho 1 Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph Gluconeogenesis
Chapter 25 The Urinary System 10/30/2013 MDufilho 1 Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph Gluconeogenesis
Blood Pressure Regulation. Slides 9-12 Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) = 1/3 systolic pressure + 2/3 diastolic pressure
 Sheet physiology(18) Sunday 24-November Blood Pressure Regulation Slides 9-12 Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) = 1/3 systolic pressure + 2/3 diastolic pressure MAP= Diastolic Pressure+1/3 Pulse Pressure CO=MAP/TPR
Sheet physiology(18) Sunday 24-November Blood Pressure Regulation Slides 9-12 Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) = 1/3 systolic pressure + 2/3 diastolic pressure MAP= Diastolic Pressure+1/3 Pulse Pressure CO=MAP/TPR
Means failure of heart to pump enough blood to satisfy the need of the body.
 Means failure of heart to pump enough blood to satisfy the need of the body. Due to an impaired ability of the heart to adequately to fill or eject blood. HEART FAILURE Heart failure (HF) means decreased
Means failure of heart to pump enough blood to satisfy the need of the body. Due to an impaired ability of the heart to adequately to fill or eject blood. HEART FAILURE Heart failure (HF) means decreased
Regulation of Body Fluids: Na + and Water Linda Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Regulation of Body Fluids: Na + and Water Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. Why body sodium content determines ECF volume and the relationships
Regulation of Body Fluids: Na + and Water Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. Why body sodium content determines ECF volume and the relationships
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Blood Pressure Regulation 2. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
1. Urinary System, General
 S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, Name Student Number
 Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, 2015 Name Student Number For Questions 1 2 refer to the following table. 1 Ventricular pressure is greater than aortic 6 AV valve is open 2
Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, 2015 Name Student Number For Questions 1 2 refer to the following table. 1 Ventricular pressure is greater than aortic 6 AV valve is open 2
Cardiovascular Physiology
 Cardiovascular Physiology Lecture 1 objectives Explain the basic anatomy of the heart and its arrangement into 4 chambers. Appreciate that blood flows in series through the systemic and pulmonary circulations.
Cardiovascular Physiology Lecture 1 objectives Explain the basic anatomy of the heart and its arrangement into 4 chambers. Appreciate that blood flows in series through the systemic and pulmonary circulations.
Some renal vascular disorders
 Some renal vascular disorders Introduction Nearly all diseases of the kidney involve the renal blood vessels secondarily We will discuss: -Hypertension (arterionephrosclerosis in benign HTN & hyperplastic
Some renal vascular disorders Introduction Nearly all diseases of the kidney involve the renal blood vessels secondarily We will discuss: -Hypertension (arterionephrosclerosis in benign HTN & hyperplastic
SPECIAL PATHOPHYSIOLOGY HYPERTENSION
 SPECIAL PATHOPHYSIOLOGY HYPERTENSION 1. Systolic blood pressure is elevated when it is over: 1. 120mmHg. 2. 130mmHg. 3. 160mmHg. 4. 140mmHg. 5. 150mmHg. 2. Diastolic blood pressure is elevated when it
SPECIAL PATHOPHYSIOLOGY HYPERTENSION 1. Systolic blood pressure is elevated when it is over: 1. 120mmHg. 2. 130mmHg. 3. 160mmHg. 4. 140mmHg. 5. 150mmHg. 2. Diastolic blood pressure is elevated when it
Vascular pathology. dr. Budiana Tanurahardja.,SpPA
 Vascular pathology dr. Budiana Tanurahardja.,SpPA DEPARTMENT of ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY FACULTY of MEDICINE UNIVERSITY of INDONESIA Center of Anatomic Pathology Studies Vascular Pathology Normal blood vessels.
Vascular pathology dr. Budiana Tanurahardja.,SpPA DEPARTMENT of ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY FACULTY of MEDICINE UNIVERSITY of INDONESIA Center of Anatomic Pathology Studies Vascular Pathology Normal blood vessels.
Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph
 The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
describe the location of the kidneys relative to the vertebral column:
 Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1 Terms you should understand by the end of this section: diuresis, antidiuresis, osmoreceptors, atrial stretch
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1 Terms you should understand by the end of this section: diuresis, antidiuresis, osmoreceptors, atrial stretch
Blood Pressure. a change in any of these could cause a corresponding change in blood pressure
 Blood Pressure measured as mmhg Main factors affecting blood pressure: 1. cardiac output 2. peripheral resistance 3. blood volume a change in any of these could cause a corresponding change in blood pressure
Blood Pressure measured as mmhg Main factors affecting blood pressure: 1. cardiac output 2. peripheral resistance 3. blood volume a change in any of these could cause a corresponding change in blood pressure
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1. Resting membrane potential of the ventricular myocardium is: A. -55 to-65mv B. --65 to-75mv C. -75 to-85mv D. -85 to-95 mv E. -95 to-105mv 2. Regarding myocardial contraction:
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1. Resting membrane potential of the ventricular myocardium is: A. -55 to-65mv B. --65 to-75mv C. -75 to-85mv D. -85 to-95 mv E. -95 to-105mv 2. Regarding myocardial contraction:
Lab Activity 31. Anatomy of the Urinary System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure
 Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline. University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology
 Arterial Diseases Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Disease Spectrum Arteriosclerosis Atherosclerosis
Arterial Diseases Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Disease Spectrum Arteriosclerosis Atherosclerosis
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY ROLE OF THE URINARY SYSTEM THE URINARY SYSTEM. Components and function. V BS 122 Physiology II 151 Class of 2011
 19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
Copyright 2011, 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Normal Cardiac Anatomy
 Mosby,, an affiliate of Elsevier Normal Cardiac Anatomy Impaired cardiac pumping Results in vasoconstriction & fluid retention Characterized by ventricular dysfunction, reduced exercise tolerance, diminished
Mosby,, an affiliate of Elsevier Normal Cardiac Anatomy Impaired cardiac pumping Results in vasoconstriction & fluid retention Characterized by ventricular dysfunction, reduced exercise tolerance, diminished
Do Now. Get out work from last class to be checked
 Do Now Get out work from last class to be checked Heart Actions Cardiac Cycle: One complete heartbeat. The contraction of a heart chamber is called systole and the relaxation of a chamber is called diastole.
Do Now Get out work from last class to be checked Heart Actions Cardiac Cycle: One complete heartbeat. The contraction of a heart chamber is called systole and the relaxation of a chamber is called diastole.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST
 014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY
 MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY REGULATION OF BODY FLUID VOLUME REGULATION OF OSMOTIC BALANCE REGULATION OF ELECTROLYTE COMPOSITION REGULATION OF ACID-BASE BALANCE REGULATION OF BLOOD PRESSURE ERYTHROPOIESIS
MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY REGULATION OF BODY FLUID VOLUME REGULATION OF OSMOTIC BALANCE REGULATION OF ELECTROLYTE COMPOSITION REGULATION OF ACID-BASE BALANCE REGULATION OF BLOOD PRESSURE ERYTHROPOIESIS
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
Hypertension Part 1. Overview of Hypertension.
 Hypertension Part 1 Overview of Hypertension http://silverchealth.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/01/hypertension1.gif Hypertension is sustained elevation of resting systolic BP ( 140 mm Hg), diastolic BP
Hypertension Part 1 Overview of Hypertension http://silverchealth.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/01/hypertension1.gif Hypertension is sustained elevation of resting systolic BP ( 140 mm Hg), diastolic BP
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6
 BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
Urinary system. Urinary system
 INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
Regulation of Arterial Blood Pressure 2 George D. Ford, Ph.D.
 Regulation of Arterial Blood Pressure 2 George D. Ford, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the Central Nervous System Ischemic Response. 2. Describe chemical sensitivities of arterial and cardiopulmonary chemoreceptors,
Regulation of Arterial Blood Pressure 2 George D. Ford, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the Central Nervous System Ischemic Response. 2. Describe chemical sensitivities of arterial and cardiopulmonary chemoreceptors,
Major Function of the Cardiovascular System. Transportation. Structures of the Cardiovascular System. Heart - muscular pump
 Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Blood Pressure Regulation -1
 CVS Physiology Lecture 18 Blood Pressure Regulation -1 Please study the previous sheet before studying this one, even if the first part in this sheet is revision. In the previous lecture we were talking
CVS Physiology Lecture 18 Blood Pressure Regulation -1 Please study the previous sheet before studying this one, even if the first part in this sheet is revision. In the previous lecture we were talking
Presentation of hypertensive emergency
 Presentation of hypertensive emergency Definitions surrounding hypertensive emergency Hypertension: elevated blood pressure (BP), usually defined as BP >140/90; pathological both in isolation and in association
Presentation of hypertensive emergency Definitions surrounding hypertensive emergency Hypertension: elevated blood pressure (BP), usually defined as BP >140/90; pathological both in isolation and in association
THE BLOOD VESSELS. Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department.
 THE BLOOD VESSELS Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department. Vascular pathology: 1- Narrowing or complete obstruction of vessel lumina, either progressively (e.g.,
THE BLOOD VESSELS Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department. Vascular pathology: 1- Narrowing or complete obstruction of vessel lumina, either progressively (e.g.,
Blood pressure is probably one of the most variable but
 CHAPTER 16 Alterations in Blood Pressure Control of Blood Pressure Determinants of Blood Pressure Systolic Blood Pressure Diastolic Blood Pressure Pulse Pressure Mean Arterial Pressure Mechanisms of Blood
CHAPTER 16 Alterations in Blood Pressure Control of Blood Pressure Determinants of Blood Pressure Systolic Blood Pressure Diastolic Blood Pressure Pulse Pressure Mean Arterial Pressure Mechanisms of Blood
Ischemic heart disease
 Ischemic heart disease Introduction In > 90% of cases: the cause is: reduced coronary blood flow secondary to: obstructive atherosclerotic vascular disease so most of the time it is called: coronary artery
Ischemic heart disease Introduction In > 90% of cases: the cause is: reduced coronary blood flow secondary to: obstructive atherosclerotic vascular disease so most of the time it is called: coronary artery
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 19-1c. Efferent arteriole. Juxtaglomerular apparatus
 /6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
/6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
BUSINESS. Articles? Grades Midterm Review session
 BUSINESS Articles? Grades Midterm Review session REVIEW Cardiac cells Myogenic cells Properties of contractile cells CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART Conduction pathway SA node (pacemaker) atrial depolarization
BUSINESS Articles? Grades Midterm Review session REVIEW Cardiac cells Myogenic cells Properties of contractile cells CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART Conduction pathway SA node (pacemaker) atrial depolarization
Cardiovascular System. Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12
 Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Weeks 1-3:Cardiovascular
 Weeks 1-3:Cardiovascular Cardiac Output The total volume of blood ejected from the ventricles in one minute is known as the cardiac output. Heart Rate (HR) X Stroke Volume (SV) = Cardiac Output Normal
Weeks 1-3:Cardiovascular Cardiac Output The total volume of blood ejected from the ventricles in one minute is known as the cardiac output. Heart Rate (HR) X Stroke Volume (SV) = Cardiac Output Normal
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001
 Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
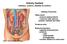 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
The Urinary System. Medical Assisting Third Edition. Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
 The Urinary System PowerPoint presentation to accompany: Medical Assisting Third Edition Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson 30-2 Learning Outcomes 30.1 Describe the structure, location, and functions
The Urinary System PowerPoint presentation to accompany: Medical Assisting Third Edition Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson 30-2 Learning Outcomes 30.1 Describe the structure, location, and functions
Duplex Ultrasound of the Renal Arteries. Duplex Ultrasound. In the Beginning
 Duplex Ultrasound of the Renal Arteries DIMENSIONS IN HEART AND VASCULAR CARE 2013 PENN STATE HEART AND VASCULAR INSTITUTE ROBERT G. ATNIP MD PROFESSOR OF SURGERY AND RADIOLOGY Duplex Ultrasound Developed
Duplex Ultrasound of the Renal Arteries DIMENSIONS IN HEART AND VASCULAR CARE 2013 PENN STATE HEART AND VASCULAR INSTITUTE ROBERT G. ATNIP MD PROFESSOR OF SURGERY AND RADIOLOGY Duplex Ultrasound Developed
Special circulations, Coronary, Pulmonary. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Special circulations, Coronary, Pulmonary Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Describe the control of blood flow to different circulations (Skeletal muscles, pulmonary and coronary) Point out special
Special circulations, Coronary, Pulmonary Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Describe the control of blood flow to different circulations (Skeletal muscles, pulmonary and coronary) Point out special
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Arteries Arteries Arteries
 CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
A CASE OF HYPERTENSION AND ACUTE RENAL FAILURE OBJECTIVES
 A CASE OF HYPERTENSION AND ACUTE RENAL FAILURE Maricel Pilapil-Pureza WLA Nephrology OBJECTIVES After the presentation, the attendee will be able to: 1. Discuss when to suspect for secondary causes of
A CASE OF HYPERTENSION AND ACUTE RENAL FAILURE Maricel Pilapil-Pureza WLA Nephrology OBJECTIVES After the presentation, the attendee will be able to: 1. Discuss when to suspect for secondary causes of
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015
 RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
CEREBROVASCULAR DISEASES. By: Shifaa AlQa qa
 CEREBROVASCULAR DISEASES By: Shifaa AlQa qa Cerebrovascular diseases Brain disorders caused by pathologic processes involving blood vessels 3 pathogenic mechanisms (1) thrombotic occlusion, (2) embolic
CEREBROVASCULAR DISEASES By: Shifaa AlQa qa Cerebrovascular diseases Brain disorders caused by pathologic processes involving blood vessels 3 pathogenic mechanisms (1) thrombotic occlusion, (2) embolic
End of chapter exercises
 End of chapter exercises Problem 1: The following diagrams show the heart during the cardiac cycle. The arrows represent the flow of blood. Study the diagrams and answer the questions that follow: Figure
End of chapter exercises Problem 1: The following diagrams show the heart during the cardiac cycle. The arrows represent the flow of blood. Study the diagrams and answer the questions that follow: Figure
Cardiovascular system: Blood vessels, blood flow. Latha Rajendra Kumar, MD
 Cardiovascular system: Blood vessels, blood flow Latha Rajendra Kumar, MD Outline 1- Physical laws governing blood flow and blood pressure 2- Overview of vasculature 3- Arteries 4. Capillaries and venules
Cardiovascular system: Blood vessels, blood flow Latha Rajendra Kumar, MD Outline 1- Physical laws governing blood flow and blood pressure 2- Overview of vasculature 3- Arteries 4. Capillaries and venules
A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12
 A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 3/20 - B 3/21 - A 3/22 - B 3/23 - A 3/24 - B 3/27 - A Dissection Ethics Debate 3/28 - B 3/29 - A Intro to Cardiovascular
A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 3/20 - B 3/21 - A 3/22 - B 3/23 - A 3/24 - B 3/27 - A Dissection Ethics Debate 3/28 - B 3/29 - A Intro to Cardiovascular
Histology Urinary system
 Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Blood Pressure Regulation. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Blood Pressure Regulation Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the short term and long term regulators of BP Know how baroreceptors and chemoreceptors work Know function of the atrial reflex.
Blood Pressure Regulation Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the short term and long term regulators of BP Know how baroreceptors and chemoreceptors work Know function of the atrial reflex.
Histopathology: Vascular pathology
 Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
