Chronic Critical Limb Ischemia: Diagnosis, Treatment and Prognosis
|
|
|
- Randolf Davidson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chronic Critical Limb Ischemia: Diagnosis, Treatment and Prognosis JAMIE D. SANTILLI, M.D., and STEVEN M. SANTILLI, M.D., PH.D. University of Minnesota School of Medicine Minneapolis, Minnesota Chronic critical limb ischemia is manifested by pain at rest, nonhealing wounds and gangrene. Ischemic rest pain is typically described as a burning pain in the arch or distal foot that occurs while the patient is recumbent but is relieved when the patient returns to a position in which the feet are dependent. Objective hemodynamic parameters that support the diagnosis of critical limb ischemia include an ankle-brachial index of 0.4 or less, an ankle systolic pressure of 50 mm Hg or less, or a toe systolic pressure of 30 mm Hg or less. Intervention may include conservative therapy, revascularization or amputation. Progressive gangrene, rapidly enlarging wounds or continuous ischemic rest pain can signify a threat to the limb and suggest the need for revascularization in patients without prohibitive operative risks. Bypass grafts are usually required because of the multilevel and distal nature of the arterial narrowing in critical limb ischemia. Patients with diabetes are more likely than other patients to have distal disease that is less amenable to bypass grafting. Compared with amputation, revascularization is more costeffective and is associated with better perioperative morbidity and mortality. Limb preservation should be the goal in most patients with critical limb ischemia. Atherosclerosis underlies most peripheral arterial disease. Narrowed vessels that cannot supply sufficient blood flow to exercising leg muscles may cause claudication, which is brought on by exercise and relieved by rest. (For a review of the diagnosis and management of claudication, see the article by Santilli, et al., in the March 1996 issue of American Family Physician. 1 ) As vessel narrowing increases, critical limb ischemia can develop when the blood flow does not meet the metabolic demands of tissue at rest. While critical limb ischemia may be due to an acute condition such as an embolus or thrombosis, most cases are the progressive result of a chronic condition, most commonly atherosclerosis. Chronic critical limb ischemia is defined not only by the clinical presentation but also by an objective measurement of impaired blood flow. Criteria for diagnosis include either one of the following (1) more than two weeks of recurrent foot pain at rest that requires regular use of analgesics and is associated with an ankle systolic pressure of 50 mm Hg or less, or a toe systolic pressure of 30 mm Hg or less, or (2) a nonhealing wound or gangrene of the foot or toes, with similar hemodynamic measurements. 2 The hemodynamic parameters may be less reliable in patients with diabetes because arterial wall calcification can impair compression by a blood pressure cuff and produce systolic pressure measurements that are greater than the actual levels. Risk Factors An ankle systolic pressure of 50 mm Hg or less or a toe systolic pressure of 30 mm Hg or less suggests the presence of critical limb ischemia.
2 Chronic critical limb ischemia is the end result of arterial occlusive disease, most commonly atherosclerosis. In addition to atherosclerosis in association with hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, cigarette smoking and diabetes, 3,4 less frequent causes of chronic critical limb ischemia include Buerger's disease, or thromboangiitis obliterans, and some forms of arteritis. 5 FIGURE 1A. Right heel ulcer in a 56-year-old patient with diabetes. The ulcer failed to heal after three months of conservative treatment. Diabetes is a particularly important risk factor because it is frequently associated with severe peripheral arterial disease. Atherosclerosis develops at a younger age in patients with diabetes and progresses rapidly. Moreover, atherosclerosis affects more distal vessels in patients with diabetes; the profunda femoris, popliteal and tibial arteries are frequently affected, while the aorta and iliac arteries are minimally narrowed. These distal lesions are less amenable to revascularization. Atherosclerosis in distal arteries in combination with diabetic neuropathy contributes to the higher rates of limb loss in diabetic patients compared with nondiabetic patients. 6,7 Clinical Presentation The development of chronic critical limb ischemia usually requires multiple sites of arterial obstruction that severely reduce blood flow to the tissues. 7,8 Critical tissue ischemia is manifested clinically as rest pain, nonhealing wounds (because of the increased metabolic requirements of wound healing) or tissue necrosis (gangrene). Ischemic rest pain is classically described as a burning pain in the ball of the foot and toes that is worse at night when the patient is in bed. The pain is exacerbated by the recumbent position because of the loss of gravity-assisted flow to the foot. Ischemic rest pain is located in the foot, where tissue is farthest from the heart and distal to the arterial occlusions. 1 Patients with ischemic rest pain often need to dangle their legs over the side of the bed or sleep in a recliner to regain gravity-augmented blood flow and relieve the pain. Patients who keep their legs in a dependent position for comfort often present with considerable edema of the feet and ankles. Nonhealing wounds are usually found in areas of foot trauma caused by improperly fitting shoes or an injury. A wound is generally considered to be nonhealing if it fails to respond to a four- to 12-week trial of conservative therapy such as regular dressing changes, avoidance of trauma, treatment of infection and debridement of necrotic tissue. Gangrene is usually found on the toes. It develops when the blood supply is so low that spontaneous necrosis occurs in the most poorly perfused tissues. Ankle-Brachial Index
3 FIGURE 1B. Segmental pressures and ankle-brachial index (ABI) in the same patient as in Figure 1a. The ABI of 0.58 on the right and the pulsatile monophasic waveform in the posterior tibial artery suggested that the ulcer could heal with conservative therapy. Diagnosis The presence of rest pain can sometimes be difficult to discern in patients with other chronic leg pain, such as that caused by peripheral neuropathy. Labeling a wound as nonhealing can also be a subjective assessment. However, a number of physical findings and objective hemodynamic parameters can be used to substantiate a diagnosis of Patients with diabetes develop atherosclerotic lesions in the more distal leg vessels, which are less amenable to revascularization. chronic critical limb ischemia. Typical physical findings include absent or diminished pedal pulses, shiny smooth skin of the feet and legs, and muscle wasting of the calves.
4 An objective measurement of blood flow is easily accomplished with the use of a handheld Doppler probe and a blood pressure cuff. 1 The cuff is inflated until the pulse distal to the cuff is no longer heard by Doppler. The cuff is then slowly deflated until the pulse is again detected. This measurement is recorded as the systolic pressure. As previously mentioned, an ankle systolic pressure of 50 mm Hg or less or a toe systolic pressure of 30 mm Hg or less suggests the presence of critical limb ischemia. FIGURE 1C. The patient underwent operative debridement and began a regimen of dressing changes (gauze dampened with normal saline) three times a day. He also began wearing a shoe that allowed ambulation without direct pressure on the ulcer. He was followed weekly in the outpatient clinic. FIGURE 1D. The ulcer shows good progress in healing after three weeks of conservative therapy. FIGURE 1E. After six weeks of outpatient treatment, the ulcer is well healed. Another widely used parameter is the ankle-brachial index, which is a ratio of the systolic pressure at the dorsalis pedis or posterior tibial artery divided by the systolic pressure at the brachial artery. Patients with claudication typically have an anklebrachial index of 0.5 to 0.8, while patients with critical limb ischemia usually have an ankle-brachial index of 0.4 or less. 9,10
5 FIGURE 2A. Left foot of a 77-year-old patient with diabetes who presented with a two-year history of progressively worsening claudication. The foot shows dependent rubor and several areas of gangrene, characteristic of severe ischemia. The patient's rest pain had worsened during the past month. Vascular laboratories also use Doppler probes to measure the pulse volume waveform at segmental locations in the leg arteries. A change in the Doppler waveform from triphasic to biphasic to monophasic and then stenotic waveforms can identify sites of arterial blockage. Differential Diagnosis Ischemic rest pain may be confused with night cramps, arthritis or diabetic neuropathy. Night cramps occur in the calf muscles; they usually awaken the patient from sleep and are relieved by massaging the muscle, by walking or by using antispasmodic agents. Patients with arthritis of the metatarsal bones may have pain in the foot. This pain is often experienced at night and may be relieved by standing. The distinguishing characteristic of arthritic pain is that it usually occurs intermittently and at sporadic intervals, whereas ischemic rest pain consistently occurs after a specific interval of recumbency. Diabetic neuropathy may also present with pain in the foot and is occasionally associated with diminished pulses and trophic skin changes. This pain, however, is not steadfastly associated with recumbency. The other features of diabetic neuropathy, such as loss of light touch (i.e., the monofilament test) and decreased vibratory sense, can also serve as distinguishing characteristics. Conservative Treatment Risk factor modification, including smoking cessation, blood pressure control, good glycemic control and reduction of lipid levels, should be instituted. Antiplatelet therapy with aspirin has been shown to substantially decrease the risk of myocardial infarction, stroke and death in patients with peripheral vascular disease and also reduces the rate of arterial reocclusion after angioplasty or bypass grafting. 11 Ischemic Rest Pain Patients with ischemic rest pain should be given pain medication as necessary, and any underlying systemic cause of inadequate blood flow, such as cardiac failure, should be corrected. If pain persists after four to eight weeks of conservative therapy with pain medication and interventions to optimize the patient's overall condition, the possibility of operative intervention should be explained to the patient, including the risks and benefits of the procedure.
6 Surgical intervention includes revascularization and amputation. If the patient wants to undergo revascularization and is an acceptable operative candidate, arteriography is often performed for further evaluation and planning of revascularization. Some centers are utilizing magnetic resonance angiography as an alternative or supplement to arteriography to minimize the risk of dye exposure. 12 Patients with claudication typically have an anklebrachial ratio of 0.5 to 0.8, while patients with critical limb ischemia usually have a ratio of 0.4 or less. Nonhealing Wounds Patients with nonhealing wounds or gangrene should be evaluated for the presence of infection. Infected wounds require antibiotic therapy, surgical debridement, or both. Conservative therapy includes teaching the patient ways to avoid trauma to the wound site, including the wearing of properly fitting shoes. Dressings should be changed frequently; the patient should be seen weekly until the wound heals (Figures 1a through 1e). Further intervention may be required if conservative therapy does not lead to improvement, as indicated by increasing wound size, persistent or spreading infection or no evidence of healing after four to eight weeks. Progressive gangrene, rapidly enlarging wounds and continuous ischemic rest pain unrelieved by dependency are each unstable conditions that can rapidly lead to limb loss and require urgent intervention. However, many patients with critical limb ischemia have a stable or slowly progressive presentation. Review of the data reveals that patients with chronic critical limb ischemia have a three-year limb loss rate of about 40 percent This suggests that a substantial proportion of patients with critical ischemia are not at risk of imminent limb loss. Ankle-Brachial Index
7 FIGURE 2B. Segmental pressures and ankle-brachial index (ABI) in the same patient as in Figure 2a. The brachial pressure on the right side was 86 mm Hg because of subclavian artery stenosis. (The ABI is calculated using the highest normal brachial pressure, which in this patient was 150 mm Hg.) The ABI of 0.30 on the left side, the stenotic nonpulsatile waveform in the posterior tibial and dorsalis pedal arteries, and the rapid progression of ischemic symptoms suggested that this patient was in imminent danger of limb loss and was not a candidate for conservative therapy.
8 Ankle-Brachial Index FIGURE 2C. Arteriography in the same patient as in Figures 2a and 2b, showing diffuse but nonsignificant occlusive disease in the aorta, iliac and common femoral arteries. FIGURE 2E. A reconstituted posterior tibial artery (arrow) in the calf continued into the foot. This artery was considered an acceptable vessel for bypass. FIGURE 2D. Runoff of the left leg shows no superficial femoral or popliteal artery. There was only collateral flow (arrow) from the thigh to the calf. FIGURE 2F. Intraoperative arteriography shows the distal end of a common femoral to posterior tibial artery saphenous vein bypass (arrows). FIGURE 2G. Postoperative anklebrachial index (ABI) of this patient revealed a significant improvement in values, from 0.30 preoperatively to 0.75 postoperatively. As noted in the legend for Figure 2b, the brachial pressure on the right side was 86 mm Hg because of subclavian artery stenosis. The patient's highest normal brachial pressure (114 mm Hg) was used to calculate the ABI.
9 FIGURE 2H. Even after revascularization, however, necrotic tissue persisted in the foot. Despite wound debridement, transmetatarsal amputation was required. This photograph was taken at the follow-up visit three weeks after amputation. The surgical wound healed satisfactorily. The patient was fitted with a special shoe and has maintained an active and independent lifestyle. Operative Intervention Revascularization While carefully designed conservative therapy can benefit many patients with critical limb ischemia, the severe nature of their disease may lead to consideration of operative intervention. Surgical interventions include revascularization or amputation. If the patient wants to undergo revascularization and is an acceptable operative candidate, arteriography is often performed for further evaluation and planning of revascularization. At some centers, magnetic resonance angiography is used as an alternative or supplement to arteriography to minimize the risk of dye exposure. 12 Limb preservation by means of revascularization is cost-effective, leads to a better quality of life for most patients and is associated with lower perioperative morbidity and mortality than amputation. Limb preservation should be the goal in most patients with chronic critical limb ischemia. 13,14 The feasibility of revascularization is determined by the arteriographic findings as well as the availability of a bypass conduit (Figures 2a through 2h). Angioplasty or stent placement, or both, is most successful with short, proximal lesions, such as those in patients with claudication, but is unlikely to be the only treatment necessary in the setting of critical limb ischemia because of the multilevel nature of the arterial occlusive disease. The ideal bypass conduit is the greater saphenous vein, but other conduits include the lesser saphenous veins, the arm veins or a prosthetic conduit. In most surgical series, three-year bypass patency rates of calf arteries range from 40 percent for prosthetic bypasses to 85 percent for saphenous vein bypasses In comparison, studies of conservative therapy have demonstrated a 25 to 49 percent success rate with nonhealing wounds and a 50 to 80 percent rate of improvement in ischemic rest pain Primary Amputation Primary amputation may be indicated in certain patients, such as those with extensive tissue necrosis, life-threatening infection or lesions not amenable to revascularization. The decision to monitor the patient's condition with watchful waiting and conservative management or to perform revascularization or amputation depends on careful assessment of the attendant risks and benefits of surgery versus conservative management. More importantly, it depends on the patient's interpretation of the invasiveness or appropriateness of the available options. Even patients unable to walk because of their condition may consider amputation inappropriate, and not all patients are motivated to do the work necessary for rehabilitation after amputation. If the decision is made to
10 amputate, the level of amputation should be one that has the greatest likelihood of healing while giving the patient the maximal chance for functional rehabilitation. Follow-up Patients with chronic critical limb ischemia require lifelong follow-up for a number of reasons. After amputation or revascularization, patients require rehabilitation to hasten their return to maximal independence. Careful attention to nutritional status will assist in wound healing and recovery. In addition, bypass graft patency should be assessed frequently after revascularization. Some authorities recommend periodic surveillance with duplex Revascularization is costeffective and results in less perioperative morbidity and mortality than amputation. Limb preservation should be the goal in most patients with critical limb ischemia. ultrasonography every three months to maximize the chance that re-stenosis is identified early, when it is more amenable to repair. 12 Four-year survival rates as low as 40 percent are reported in patients with critical limb ischemia, with the vast majority of deaths caused by coronary artery disease and cerebrovascular disease. 17 Close follow-up of coronary artery disease and cerebrovascular disease may help extend life expectancy in these high-risk patients. The Authors JAMIE D. SANTILLI, M.D., is an assistant professor in the Department of Family Practice and Community Health at the University of Minnesota School of Medicine, Minneapolis. Dr. Santilli graduated from the Medical College of Ohio at Toledo and completed her postgraduate training in family practice at the University of Minnesota. STEVEN M. SANTILLI, M.D., PH.D., is an assistant professor in the Department of Surgery, Vascular Surgery Section, at the University of Minnesota School of Medicine. He also has an appointment at the Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Minneapolis. Dr. Santilli graduated from the Medical College of Ohio at Toledo. He completed his postgraduate training in general surgery at the University of Minnesota and a fellowship in vascular surgery at the University of California, San Francisco, School of Medicine. REFERENCES 1. Santilli JD, Rodnick JE, Santilli SM. Claudication: diagnosis and treatment. Am Fam Physician 1996; 53: Dormandy J, Verstraete M, Andreani D, et al. Second European consensus document on chronic critical leg ischemia. Circulation 1991;84(suppl 4): Gordon T, Kannel WB. Predisposition to atherosclerosis in the head, heart, and legs. The Framingham study. JAMA 1972;221:661-6.
11 4. Brown AL, Juergens JL. Arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis. In: Allen EV, et al. Peripheral vascular disease. Philadelphia: Saunders, 1972; DeBakey ME, Crawford ES, Garrett E, et al. Occlusive disease of the lower extremities in patients 16 to 37 years of age. Ann Surg 1964;159: Haid SP, Conn J Jr, Bergan JJ. Cystic adventitial disease of the popliteal artery. Arch Surg 1970;101: Haimovici H. Patterns of arteriosclerotic lesions of the lower extremity. Arch Surg 1967;95: Mavor GE. The pattern of occlusion in atheroma of the lower limb arteries. The correlation of clinical and arteriographic findings. Br J Surg 1956;43: Cutajar CL, Marston A, Newcombe JF. Value of cuff occlusion pressures in assessment of peripheral vascular disease. Br Med J 1973;2(863): Ouriel K, McDonnell AE, Metz CE, Zarins CK. Critical evaluation of stress testing in the diagnosis of peripheral vascular disease. Surgery 1982;91: Golledge J. Lower-limb arterial disease. Lancet 1997;350: Welch HJ. Chronic lower extremity ischemia. Compr Ther 1997;23: Cheshire NJ, Wolfe JH, Noone MA, Davies L, Drummond M. The economics of femorocrural reconstruction for critical leg ischemia with and without autologous vein. J Vasc Surg 1992;15: Albers M, Fratezi AC, De Luccia N. Assessment of quality of life of patients with severe ischemia as a result of infrainguinal arterial occlusive disease. J Vasc Surg 1992;16: Eklund AE, Eriksson G, Olsson AG. A controlled study showing significant short term effect of prostaglandin E1 in healing of ischaemic ulcers of the lower limb in man. Prostaglandins Leukot Med 1982;8: Schuler JJ, Flanigan DP, Holcroft JW, Ursprung JJ, Mohrland JS, Pyke J. Efficacy of prostaglandin E1 in the treatment of lower extremity ischemic ulcers secondary to peripheral vascular occlusive disease: results of a prospective randomized, double-blind, multicenter clinical trial. J Vasc Surg 1984;1: Taylor LM Jr, Porter JM. Current status of the reversed saphenous vein graft. In: Bergan JJ, Yao J, eds. Arterial surgery. New York: Grune and Stratton, 1987: Taylor LM Jr, Edwards JM, Porter JM. Present status of reversed vein bypass grafting: five-year results of a modern series. J Vasc Surg 1990;11: Donaldson MC, Mannick JA, Whittemore AD. Femoral-distal bypass with in situ greater saphenous vein. Long-term results using the Mills valvulotome. Ann Surg 1991;213: Bergamini TM, Towne JB, Bandyk DF, Seabrook GR, Schmitt DD. Experience with in situ saphenous vein bypasses during 1981 to 1989: determinant factors of long-term patency. J Vasc Surg 1991; 13: Quinones-Baldrich WJ, Prego AA, Ucelay-Gomez R, Freischlag JA, Ahn SS, Baker JD. Longterm results of infrainguinal revascularization with polytetrafluoroethylene: a ten-year experience. J Vasc Surg 1992;16:
Peripheral Arterial Disease Extremity
 Peripheral Arterial Disease Lower Extremity 05 Contributor Dr Steven Chong Advisors Dr Ashish Anil Dr Tay Jam Chin Introduction Risk Factors Clinical Presentation Classification History PHYSICAL examination
Peripheral Arterial Disease Lower Extremity 05 Contributor Dr Steven Chong Advisors Dr Ashish Anil Dr Tay Jam Chin Introduction Risk Factors Clinical Presentation Classification History PHYSICAL examination
Practical Point in Diabetic Foot Care 3-4 July 2017
 Diabetic Foot Ulcer : Role of Vascular Surgeon Practical Point in Diabetic Foot Care 3-4 July 2017 Supapong Arworn, MD Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Department of Surgery, Chiang Mai University
Diabetic Foot Ulcer : Role of Vascular Surgeon Practical Point in Diabetic Foot Care 3-4 July 2017 Supapong Arworn, MD Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Department of Surgery, Chiang Mai University
Introduction. Risk factors of PVD 5/8/2017
 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND CLINICAL FEATURES OF PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE Dr. Muhamad Zabidi Ahmad Radiologist and Section Chief, Radiology, Oncology and Nuclear Medicine Section, Advanced Medical and Dental
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND CLINICAL FEATURES OF PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE Dr. Muhamad Zabidi Ahmad Radiologist and Section Chief, Radiology, Oncology and Nuclear Medicine Section, Advanced Medical and Dental
Role of ABI in Detecting and Quantifying Peripheral Arterial Disease
 Role of ABI in Detecting and Quantifying Peripheral Arterial Disease Difference in AAA size between US and Surgeon 2 1 0-1 -2-3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Mean AAA size between US and Surgeon Kathleen G. Raman MD,
Role of ABI in Detecting and Quantifying Peripheral Arterial Disease Difference in AAA size between US and Surgeon 2 1 0-1 -2-3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Mean AAA size between US and Surgeon Kathleen G. Raman MD,
Practical Point in Holistic Diabetic Foot Care 3 March 2016
 Diabetic Foot Ulcer : Vascular Management Practical Point in Holistic Diabetic Foot Care 3 March 2016 Supapong Arworn, MD Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Department of Surgery, Chiang Mai
Diabetic Foot Ulcer : Vascular Management Practical Point in Holistic Diabetic Foot Care 3 March 2016 Supapong Arworn, MD Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Department of Surgery, Chiang Mai
Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease
 Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease James G. Jollis, MD Director, Rex Hospital Cardiovascular Imaging Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease 54 year old male with exertional calf pain in his right
Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease James G. Jollis, MD Director, Rex Hospital Cardiovascular Imaging Imaging for Peripheral Vascular Disease 54 year old male with exertional calf pain in his right
Stratifying Management Options for Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia: When Should Open Surgery Be the Initial Option for CLI?
 Stratifying Management Options for Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia: When Should Open Surgery Be the Initial Option for CLI? Peter F. Lawrence, M.D. Gonda Vascular Center Division of Vascular Surgery
Stratifying Management Options for Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia: When Should Open Surgery Be the Initial Option for CLI? Peter F. Lawrence, M.D. Gonda Vascular Center Division of Vascular Surgery
Non-invasive examination
 Non-invasive examination Segmental pressure and Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) The segmental blood pressure (SBP) examination is a simple, noninvasive method for diagnosing and localizing arterial disease.
Non-invasive examination Segmental pressure and Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) The segmental blood pressure (SBP) examination is a simple, noninvasive method for diagnosing and localizing arterial disease.
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 6/30/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 79 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 6/30/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 79 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
VASCULAR DISEASE: THREE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW JAMES A.M. SMITH, D.O. KANSAS VASCULAR MEDICINE, P.A. WICHITA, KANSAS
 VASCULAR DISEASE: THREE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW JAMES A.M. SMITH, D.O. KANSAS VASCULAR MEDICINE, P.A. WICHITA, KANSAS KANSAS ASSOCIATION OF OSTEOPATHIC MEDICINE ANNUAL CME CONVENTION APRIL 13, 2018 THREE
VASCULAR DISEASE: THREE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW JAMES A.M. SMITH, D.O. KANSAS VASCULAR MEDICINE, P.A. WICHITA, KANSAS KANSAS ASSOCIATION OF OSTEOPATHIC MEDICINE ANNUAL CME CONVENTION APRIL 13, 2018 THREE
Perfusion Assessment in Chronic Wounds
 Perfusion Assessment in Chronic Wounds American Society of Podiatric Surgeons Surgical Conference September 22, 2018 Michael Maier, DPM, FACCWS Cardiovascular Medicine Cleveland Clinic Disclosures Speaker,
Perfusion Assessment in Chronic Wounds American Society of Podiatric Surgeons Surgical Conference September 22, 2018 Michael Maier, DPM, FACCWS Cardiovascular Medicine Cleveland Clinic Disclosures Speaker,
Garland Green, MD Interventional Cardiologist. Impact of PAD: Prevalence, Risk Factors, Testing, and Medical Management
 Garland Green, MD Interventional Cardiologist Impact of PAD: Prevalence, Risk Factors, Testing, and Medical Management Peripheral Arterial Disease Affects over 8 million Americans Affects 12% of the general
Garland Green, MD Interventional Cardiologist Impact of PAD: Prevalence, Risk Factors, Testing, and Medical Management Peripheral Arterial Disease Affects over 8 million Americans Affects 12% of the general
Endovascular Should Be Considered First Line Therapy
 Revascularization of Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia Endovascular Should Be Considered First Line Therapy Michael Conte David Dawson David L. Dawson, MD Revised Presentation Title A Selective Approach
Revascularization of Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia Endovascular Should Be Considered First Line Therapy Michael Conte David Dawson David L. Dawson, MD Revised Presentation Title A Selective Approach
USWR 23: Outcome Measure: Non Invasive Arterial Assessment of patients with lower extremity wounds or ulcers for determination of healing potential
 USWR 23: Outcome Measure: Non Invasive Arterial Assessment of patients with lower extremity wounds or ulcers for determination of healing potential MEASURE STEWARD: The US Wound Registry [Note: This measure
USWR 23: Outcome Measure: Non Invasive Arterial Assessment of patients with lower extremity wounds or ulcers for determination of healing potential MEASURE STEWARD: The US Wound Registry [Note: This measure
Imaging Strategy For Claudication
 Who are the Debators? Imaging Strategy For Claudication Duplex Ultrasound Alone is Adequate to Select Patients for Endovascular Intervention - Pro: Dennis Bandyk MD No Disclosures PRO - Vascular Surgeon
Who are the Debators? Imaging Strategy For Claudication Duplex Ultrasound Alone is Adequate to Select Patients for Endovascular Intervention - Pro: Dennis Bandyk MD No Disclosures PRO - Vascular Surgeon
GLOBAL VASCULAR GUIDELINES: A NEW PATHWAY FOR LIMB SALVAGE
 GLOBAL VASCULAR GUIDELINES: A NEW PATHWAY FOR LIMB SALVAGE Michael S. Conte MD Professor and Chief, Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Co-Director, Center for Limb Preservation Co-Director, Heart and Vascular
GLOBAL VASCULAR GUIDELINES: A NEW PATHWAY FOR LIMB SALVAGE Michael S. Conte MD Professor and Chief, Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Co-Director, Center for Limb Preservation Co-Director, Heart and Vascular
Surgery is and Remains the Gold Standard for Limb-Threatening Ischemia
 Surgery is and Remains the Gold Standard for Limb-Threatening Ischemia Albeir Mousa, MD., FACS.,MPH., MBA Professor of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery West Virginia University Disclosure None What you
Surgery is and Remains the Gold Standard for Limb-Threatening Ischemia Albeir Mousa, MD., FACS.,MPH., MBA Professor of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery West Virginia University Disclosure None What you
John E. Campbell, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery and Medicine Department of Vascular Surgery West Virginia University, Charleston Division
 John E. Campbell, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery and Medicine Department of Vascular Surgery West Virginia University, Charleston Division John Campbell, MD For the 12 months preceding this CME activity,
John E. Campbell, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery and Medicine Department of Vascular Surgery West Virginia University, Charleston Division John Campbell, MD For the 12 months preceding this CME activity,
Surgical Options for revascularisation P E T E R S U B R A M A N I A M
 Surgical Options for revascularisation P E T E R S U B R A M A N I A M The goal Treat pain Heal ulcer Preserve limb Preserve life The options Conservative Endovascular Surgical bypass Primary amputation
Surgical Options for revascularisation P E T E R S U B R A M A N I A M The goal Treat pain Heal ulcer Preserve limb Preserve life The options Conservative Endovascular Surgical bypass Primary amputation
National Vascular Registry
 National Vascular Registry Bypass Patient Details Patient Consent* 2 Not Required If patient not consented: Date consent recorded / / (DD/MM/YYYY) Do not record NHS number, NHS number* name(s) or postcode.
National Vascular Registry Bypass Patient Details Patient Consent* 2 Not Required If patient not consented: Date consent recorded / / (DD/MM/YYYY) Do not record NHS number, NHS number* name(s) or postcode.
Intercepting PAD. Playbook for Cardiovascular Care 2018 February 24, Jonathan D Woody, MD, FACS. University Surgical Vascular
 Intercepting PAD Playbook for Cardiovascular Care 2018 February 24, 2018 Jonathan D Woody, MD, FACS University Surgical Vascular Attending Vascular Surgeon - Piedmont Athens Regional Adjunct Clinical Associate
Intercepting PAD Playbook for Cardiovascular Care 2018 February 24, 2018 Jonathan D Woody, MD, FACS University Surgical Vascular Attending Vascular Surgeon - Piedmont Athens Regional Adjunct Clinical Associate
EVALUATION OF THE VASCULAR STATUS OF DIABETIC WOUNDS Travis Littman, MD NorthWest Surgical Specialists
 EVALUATION OF THE VASCULAR STATUS OF DIABETIC WOUNDS Travis Littman, MD NorthWest Surgical Specialists Nothing To Disclosure DISCLOSURES I have no outside conflicts of interest, financial incentives, or
EVALUATION OF THE VASCULAR STATUS OF DIABETIC WOUNDS Travis Littman, MD NorthWest Surgical Specialists Nothing To Disclosure DISCLOSURES I have no outside conflicts of interest, financial incentives, or
Limb Salvage in Diabetic Ischemic Foot. Kritaya Kritayakirana, MD, FACS Assistant Professor Chulalongkorn University April 30, 2017
 Limb Salvage in Diabetic Ischemic Foot Kritaya Kritayakirana, MD, FACS Assistant Professor Chulalongkorn University April 30, 2017 Case Male 67 years old Underlying DM, HTN, TVD Present with gangrene
Limb Salvage in Diabetic Ischemic Foot Kritaya Kritayakirana, MD, FACS Assistant Professor Chulalongkorn University April 30, 2017 Case Male 67 years old Underlying DM, HTN, TVD Present with gangrene
Due to Perimed s commitment to continuous improvement of our products, all specifications are subject to change without notice.
 A summary Disclaimer The information contained in this document is intended to provide general information only. It is not intended to be, nor does it constitute, medical advice. Under no circumstances
A summary Disclaimer The information contained in this document is intended to provide general information only. It is not intended to be, nor does it constitute, medical advice. Under no circumstances
National Vascular Registry
 National Vascular Registry Angioplasty Patient Details Patient Consent* 2 Not Required If patient not consented: Date consent recorded / / (DD/MM/YYYY) Do not record NHS number, NHS number* name(s) or
National Vascular Registry Angioplasty Patient Details Patient Consent* 2 Not Required If patient not consented: Date consent recorded / / (DD/MM/YYYY) Do not record NHS number, NHS number* name(s) or
Long-term results of infragenicular bypasses with autogenous vein originating from the distal superficial femoral and popliteal arteries
 Long-term results of infragenicular bypasses with autogenous vein originating from the distal superficial femoral and popliteal arteries Mark S. Rosenbloom, M.D., James J. Walsh, M.D., James J. Schuler,
Long-term results of infragenicular bypasses with autogenous vein originating from the distal superficial femoral and popliteal arteries Mark S. Rosenbloom, M.D., James J. Walsh, M.D., James J. Schuler,
Disclosures. Talking Points. An initial strategy of open bypass is better for some CLI patients, and we can define who they are
 An initial strategy of open bypass is better for some CLI patients, and we can define who they are Fadi Saab, MD, FASE, FACC, FSCAI Metro Heart & Vascular Metro Health Hospital, Wyoming, MI Assistant Clinical
An initial strategy of open bypass is better for some CLI patients, and we can define who they are Fadi Saab, MD, FASE, FACC, FSCAI Metro Heart & Vascular Metro Health Hospital, Wyoming, MI Assistant Clinical
National Clinical Conference 2018 Baltimore, MD
 National Clinical Conference 2018 Baltimore, MD No relevant financial relationships to disclose Wound Care Referral The patient has been maximized from a vascular standpoint. She has no other options.
National Clinical Conference 2018 Baltimore, MD No relevant financial relationships to disclose Wound Care Referral The patient has been maximized from a vascular standpoint. She has no other options.
Global Vascular Guideline on the Management of Chronic Limb Threatening Ischemia -a new foundation for evidence-based care
 Global Vascular Guideline on the Management of Chronic Limb Threatening Ischemia -a new foundation for evidence-based care Michael S. Conte MD Professor and Chief, Division of Vascular and Endovascular
Global Vascular Guideline on the Management of Chronic Limb Threatening Ischemia -a new foundation for evidence-based care Michael S. Conte MD Professor and Chief, Division of Vascular and Endovascular
EDUCATION. Peripheral Artery Disease
 EDUCATION Peripheral Artery Disease Peripheral Artery Disease You may have circulation problems that have to do with your blood vessels. You may feel aches, pains, cramps, numbness or muscle fatigue when
EDUCATION Peripheral Artery Disease Peripheral Artery Disease You may have circulation problems that have to do with your blood vessels. You may feel aches, pains, cramps, numbness or muscle fatigue when
Objectives. Abdominal Aortic Aneuryms 11/16/2017. The Vascular Patient: Diagnosis and Conservative Treatment
 The Vascular Patient: Diagnosis and Conservative Treatment Ferrell-Duncan Clinic Zachary C. Schmittling, M.D., F.A.C.S. Vascular and General Surgery Ferrell-Duncan Clinic Cox Health Systems Objectives
The Vascular Patient: Diagnosis and Conservative Treatment Ferrell-Duncan Clinic Zachary C. Schmittling, M.D., F.A.C.S. Vascular and General Surgery Ferrell-Duncan Clinic Cox Health Systems Objectives
Clinical and social consequences of Buerger disease
 Clinical and social consequences of Buerger disease Takashi Ohta, MD, Hiroyuki Ishioashi, MD, Minoru Hosaka, MD, and Ikuo Sugimoto, MD, Aichi, Japan Purpose: This study was undertaken to assess the clinical
Clinical and social consequences of Buerger disease Takashi Ohta, MD, Hiroyuki Ishioashi, MD, Minoru Hosaka, MD, and Ikuo Sugimoto, MD, Aichi, Japan Purpose: This study was undertaken to assess the clinical
Will it heal? How to assess the probability of wound healing
 Will it heal? How to assess the probability of wound healing Richard F. Neville, M.D. Professor of Surgery Chief, Division of Vascular Surgery George Washington University Limb center case 69 yr old male
Will it heal? How to assess the probability of wound healing Richard F. Neville, M.D. Professor of Surgery Chief, Division of Vascular Surgery George Washington University Limb center case 69 yr old male
FOR THE 18 MILLION INDIVIDUALS with diabetes mellitus in
 11 Evaluation and Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease Joseph L. Mills, Sr., MD FOR THE 18 MILLION INDIVIDUALS with diabetes mellitus in the United States, foot problems ulceration, infection, and
11 Evaluation and Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease Joseph L. Mills, Sr., MD FOR THE 18 MILLION INDIVIDUALS with diabetes mellitus in the United States, foot problems ulceration, infection, and
Pedal Bypass With Deep Venous Arterialization:
 Pedal Bypass With Deep Venous Arterialization: Long Term Result For Critical Limb Ischemia With Unreconstructable Distal Arteries Pramook Mutirangura Professor of Vascular Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj
Pedal Bypass With Deep Venous Arterialization: Long Term Result For Critical Limb Ischemia With Unreconstructable Distal Arteries Pramook Mutirangura Professor of Vascular Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj
Current Vascular and Endovascular Management in Diabetic Vasculopathy
 Current Vascular and Endovascular Management in Diabetic Vasculopathy Yang-Jin Park Associate professor Vascular Surgery, Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Peripheral artery
Current Vascular and Endovascular Management in Diabetic Vasculopathy Yang-Jin Park Associate professor Vascular Surgery, Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Peripheral artery
Vascular claudication: How to individualize treatment
 REVIEW BRUCE H. GRAY, DO Codirector, Peripheral Interventional Laboratory, Cleveland Clinic. TIMOTHY M. SULLIVAN, MD Codirector, Peripheral Interventional Laboratory, Cleveland Clinic. Vascular claudication:
REVIEW BRUCE H. GRAY, DO Codirector, Peripheral Interventional Laboratory, Cleveland Clinic. TIMOTHY M. SULLIVAN, MD Codirector, Peripheral Interventional Laboratory, Cleveland Clinic. Vascular claudication:
Diagnosis and Endovascular Treatment of Critical Limb Ischemia: What You Need to Know S. Jay Mathews, MD, MS, FACC
 Diagnosis and Endovascular Treatment of Critical Limb Ischemia: What You Need to Know S. Jay Mathews, MD, MS, FACC Interventional Cardiologist/Endovascular Specialist Bradenton Cardiology Center Bradenton,
Diagnosis and Endovascular Treatment of Critical Limb Ischemia: What You Need to Know S. Jay Mathews, MD, MS, FACC Interventional Cardiologist/Endovascular Specialist Bradenton Cardiology Center Bradenton,
Lower Extremity Arterial Disease
 Lower Extremity Arterial Disease Circulating the Facts About Peripheral Disease Brought to you by the Education Committee of the Society for 1 www.svnnet.org Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) Many people
Lower Extremity Arterial Disease Circulating the Facts About Peripheral Disease Brought to you by the Education Committee of the Society for 1 www.svnnet.org Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) Many people
PUT YOUR BEST FOOT FORWARD
 PUT YOUR BEST FOOT FORWARD Bala Ramanan, MBBS 1 st year vascular surgery fellow Introduction The epidemic of diabetes and ageing of our population ensures critical limb ischemia will continue to grow.
PUT YOUR BEST FOOT FORWARD Bala Ramanan, MBBS 1 st year vascular surgery fellow Introduction The epidemic of diabetes and ageing of our population ensures critical limb ischemia will continue to grow.
Fluorescent Angiography: Practical uses in the Clinical Setting
 Fluorescent Angiography: Practical uses in the Clinical Setting Charles Andersen MD, FACS, MAPWCA Chief Vascular/Endovascular/ Limb Preservation Surgery Service (Emeritus) Chief of Wound Care Service Madigan
Fluorescent Angiography: Practical uses in the Clinical Setting Charles Andersen MD, FACS, MAPWCA Chief Vascular/Endovascular/ Limb Preservation Surgery Service (Emeritus) Chief of Wound Care Service Madigan
Peripheral Arterial Occlusive Disease- The Challenge in patients with diabetes
 Peripheral Arterial Occlusive Disease- The Challenge in patients with diabetes Ashok Handa Reader in Surgery and Consultant Surgeon Nuffield Department of Surgery University of Oxford Introduction Vascular
Peripheral Arterial Occlusive Disease- The Challenge in patients with diabetes Ashok Handa Reader in Surgery and Consultant Surgeon Nuffield Department of Surgery University of Oxford Introduction Vascular
The Struggle to Manage Stroke, Aneurysm and PAD
 The Struggle to Manage Stroke, Aneurysm and PAD In this article, Dr. Salvian examines the management of peripheral arterial disease, aortic aneurysmal disease and cerebrovascular disease from symptomatology
The Struggle to Manage Stroke, Aneurysm and PAD In this article, Dr. Salvian examines the management of peripheral arterial disease, aortic aneurysmal disease and cerebrovascular disease from symptomatology
Subclavian artery Stenting
 Subclavian artery Stenting Etiology Atherosclerosis Takayasu s arteritis Fibromuscular dysplasia Giant Cell Arteritis Radiation-induced Vascular Injury Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Neurofibromatosis Incidence
Subclavian artery Stenting Etiology Atherosclerosis Takayasu s arteritis Fibromuscular dysplasia Giant Cell Arteritis Radiation-induced Vascular Injury Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Neurofibromatosis Incidence
Detection of peripheral vascular disease in patients with type-2 DM using Ankle Brachial Index (ABI)
 Original article: Detection of peripheral vascular disease in patients with type-2 DM using Ankle Brachial Index (ABI) 1DR Anu N Gaikwad, 2 Dr Vikrant V Rasal, 3 Dr S A Kanitkar, 4 Dr Meenakshi Kalyan
Original article: Detection of peripheral vascular disease in patients with type-2 DM using Ankle Brachial Index (ABI) 1DR Anu N Gaikwad, 2 Dr Vikrant V Rasal, 3 Dr S A Kanitkar, 4 Dr Meenakshi Kalyan
Introduction to Peripheral Arterial Disease. Stacey Clegg, MD Interventional Cardiology August
 Introduction to Peripheral Arterial Disease Stacey Clegg, MD Interventional Cardiology August 20 2014 Outline (and for the ABIM board exam * ** ***) Prevalence* Definitions Lower Extremity: Aorta*** Claudication***
Introduction to Peripheral Arterial Disease Stacey Clegg, MD Interventional Cardiology August 20 2014 Outline (and for the ABIM board exam * ** ***) Prevalence* Definitions Lower Extremity: Aorta*** Claudication***
Peripheral Arterial Disease Management A Practical Guide for Internists. EFIM Vascular Working Group
 2 Peripheral Arterial Disease Management A Practical Guide for Internists EFIM Vascular Working Group 1 Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) is a growing concern among our aging population. More than 27 million
2 Peripheral Arterial Disease Management A Practical Guide for Internists EFIM Vascular Working Group 1 Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) is a growing concern among our aging population. More than 27 million
Peripheral Arterial Disease: Who has it and what to do about it?
 Peripheral Arterial Disease: Who has it and what to do about it? Seth Krauss, M.D. Alaska Annual Nurse Practitioner Conference September 16, 2011 Scope of the Problem Incidence: 20%
Peripheral Arterial Disease: Who has it and what to do about it? Seth Krauss, M.D. Alaska Annual Nurse Practitioner Conference September 16, 2011 Scope of the Problem Incidence: 20%
Introduction What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease? How Do Doctors Treat Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 9
 Patient Information Table of Contents Introduction... 3 What is Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 5 What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 7 What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease?...
Patient Information Table of Contents Introduction... 3 What is Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 5 What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 7 What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease?...
Critical Limb Ischemia A Collaborative Approach to Patient Care. Christopher LeSar, MD Vascular Institute of Chattanooga July 28, 2017
 Critical Limb Ischemia A Collaborative Approach to Patient Care Christopher LeSar, MD Vascular Institute of Chattanooga July 28, 2017 Surgeons idea Surgeons idea represents the final stage of peripheral
Critical Limb Ischemia A Collaborative Approach to Patient Care Christopher LeSar, MD Vascular Institute of Chattanooga July 28, 2017 Surgeons idea Surgeons idea represents the final stage of peripheral
Revascularization for Peripheral Arterial Disease among Older Adults: Referral, Management, and Prognosis
 Cardiovascular Disease Revascularization for Peripheral Arterial Disease among Older Adults: Referral, Management, and Prognosis Marc Schermerhorn, MD, Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, Beth
Cardiovascular Disease Revascularization for Peripheral Arterial Disease among Older Adults: Referral, Management, and Prognosis Marc Schermerhorn, MD, Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, Beth
PAD and CRITICAL LIMB ISCHEMIA: EVALUATION AND TREATMENT 2014
 PAD and CRITICAL LIMB ISCHEMIA: EVALUATION AND TREATMENT 2014 Van Crisco, MD, FACC, FSCAI First Coast Heart and Vascular Center, PLLC Jacksonville, FL 678-313-6695 Conflict of Interest Bayer Healthcare
PAD and CRITICAL LIMB ISCHEMIA: EVALUATION AND TREATMENT 2014 Van Crisco, MD, FACC, FSCAI First Coast Heart and Vascular Center, PLLC Jacksonville, FL 678-313-6695 Conflict of Interest Bayer Healthcare
Lower-Extremity Revascularization
 Lower-Extremity Revascularization The open approach to treating limb-threatening lower-extremity ischemia has proven to be an effective means of achieving revascularization. BY RICHARD F. NEVILLE, MD,
Lower-Extremity Revascularization The open approach to treating limb-threatening lower-extremity ischemia has proven to be an effective means of achieving revascularization. BY RICHARD F. NEVILLE, MD,
Patient Brochure. Clearstream Technologies, Ltd. Moyne Upper Enniscorthy Co. Wexford, Ireland. PK Rev. 0 05/17
 Patient Brochure Clearstream Technologies, Ltd. Moyne Upper Enniscorthy Co. Wexford, Ireland PK1411100 Rev. 0 05/17 LIFESTREAM Patient Brochure If you or a member of your family has been diagnosed with
Patient Brochure Clearstream Technologies, Ltd. Moyne Upper Enniscorthy Co. Wexford, Ireland PK1411100 Rev. 0 05/17 LIFESTREAM Patient Brochure If you or a member of your family has been diagnosed with
Recommendations for Follow-up After Vascular Surgery Arterial Procedures SVS Practice Guidelines
 Recommendations for Follow-up After Vascular Surgery Arterial Procedures 2018 SVS Practice Guidelines vsweb.org/svsguidelines About the guidelines Published in the July 2018 issue of Journal of Vascular
Recommendations for Follow-up After Vascular Surgery Arterial Procedures 2018 SVS Practice Guidelines vsweb.org/svsguidelines About the guidelines Published in the July 2018 issue of Journal of Vascular
The Accuracy of a Volume Plethysmography System as Assessed by Contrast Angiography
 Research imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/ DOI: 10.21767/2572-5483.100036 Journal of Preventive Medicine The Accuracy of a Volume Plethysmography System as Assessed by Contrast Angiography Andrew
Research imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/ DOI: 10.21767/2572-5483.100036 Journal of Preventive Medicine The Accuracy of a Volume Plethysmography System as Assessed by Contrast Angiography Andrew
Disclosures. Critical Limb Ischemia. Vascular Testing in the CLI Patient. Vascular Testing in Critical Limb Ischemia UCSF Vascular Symposium
 Disclosures Vascular Testing in the CLI Patient None 2015 UCSF Vascular Symposium Warren Gasper, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery UCSF Division of Vascular Surgery Critical Limb Ischemia Chronic Limb
Disclosures Vascular Testing in the CLI Patient None 2015 UCSF Vascular Symposium Warren Gasper, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery UCSF Division of Vascular Surgery Critical Limb Ischemia Chronic Limb
High Risk Podiatry in a Vascular Setting; A new paradigm in Diabetic Foot Disease? Ereena Torpey Senior Podiatrist - FMC
 High Risk Podiatry in a Vascular Setting; A new paradigm in Diabetic Foot Disease? Ereena Torpey Senior Podiatrist - FMC A new paradigm? Foot ulceration 101 Assessing Perfusion a new challenge Pressure
High Risk Podiatry in a Vascular Setting; A new paradigm in Diabetic Foot Disease? Ereena Torpey Senior Podiatrist - FMC A new paradigm? Foot ulceration 101 Assessing Perfusion a new challenge Pressure
Steven Hadesman, MD Chief Medical Officer, MeridianRx Internal Medicine Physician, St. John Hospital
 Steven Hadesman, MD Chief Medical Officer, MeridianRx Internal Medicine Physician, St. John Hospital Deep Venous Thrombosis Varicose Veins Venous insufficiency Phlebitis Lymphedema Elephantiasis nostras
Steven Hadesman, MD Chief Medical Officer, MeridianRx Internal Medicine Physician, St. John Hospital Deep Venous Thrombosis Varicose Veins Venous insufficiency Phlebitis Lymphedema Elephantiasis nostras
What s New in the Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease
 What s New in the Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease Sibu P. Saha, MD, MBA Professor of Surgery Chairman, Directors Council Gill Heart Institute University of Kentucky Lexington, KY Disclosure My
What s New in the Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease Sibu P. Saha, MD, MBA Professor of Surgery Chairman, Directors Council Gill Heart Institute University of Kentucky Lexington, KY Disclosure My
Peripheral Vascular Disease
 Peripheral artery disease (PAD) results from the buildup of plaque (atherosclerosis) in the arteries of the legs. For people with PAD, symptoms may be mild, requiring no treatment except modification of
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) results from the buildup of plaque (atherosclerosis) in the arteries of the legs. For people with PAD, symptoms may be mild, requiring no treatment except modification of
DON T LET LEG PAIN BECOME A REAL THREAT.
 DON T LET LEG PAIN BECOME A REAL THREAT. These three words have the power to change lives. Between 8 to 10 million Americans are estimated to suffer from poor blood flow to the legs and feet potentially
DON T LET LEG PAIN BECOME A REAL THREAT. These three words have the power to change lives. Between 8 to 10 million Americans are estimated to suffer from poor blood flow to the legs and feet potentially
The long-term value of composite limb salvage
 The long-term value of composite limb salvage grafts for John B. Chang, MD, and Theodore A. Stein, PhD, Roslyn, N.Y. Purpose: We determined the long-term efficacy of composite grafts for limb salvage when
The long-term value of composite limb salvage grafts for John B. Chang, MD, and Theodore A. Stein, PhD, Roslyn, N.Y. Purpose: We determined the long-term efficacy of composite grafts for limb salvage when
Guidelines for Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease
 Guidelines for Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease Subhash Banerjee, MD, FACC, FSCAI Professor of Medicine, Univ. of Texas Southwestern Medical Center Chief, Division of Cardiology, VA North Texas
Guidelines for Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease Subhash Banerjee, MD, FACC, FSCAI Professor of Medicine, Univ. of Texas Southwestern Medical Center Chief, Division of Cardiology, VA North Texas
Popliteal-to-distal bypass for limb-threatening ischemia
 Popliteal-to-distal bypass for limb-threatening ischemia Jeffrey Marks, MD, Terry A, King, MD, Henry Baele, MD, Jeffrey Rubin, MD, and Cynthia Marmen, RN, Cleveland, Ohio In a subset of patients requiring
Popliteal-to-distal bypass for limb-threatening ischemia Jeffrey Marks, MD, Terry A, King, MD, Henry Baele, MD, Jeffrey Rubin, MD, and Cynthia Marmen, RN, Cleveland, Ohio In a subset of patients requiring
Lower Extremity Arterial Duplex Evaluation
 VASCULAR TECHNOLOGY PROFESSIONAL PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES Lower Extremity Arterial Duplex Evaluation This Guideline was prepared by the Professional Guidelines Subcommittee of the Society for Vascular Ultrasound
VASCULAR TECHNOLOGY PROFESSIONAL PERFORMANCE GUIDELINES Lower Extremity Arterial Duplex Evaluation This Guideline was prepared by the Professional Guidelines Subcommittee of the Society for Vascular Ultrasound
Lower Extremity Artery: Physiologic Testing
 Master Title Ultrasound for Initial Evaluation of Lower Extremity Arterial Occlusive Disease: WHY? Gregory L. Moneta MD Professor and Chief Knight Cardiovascular Institute Division of Vascular Surgery
Master Title Ultrasound for Initial Evaluation of Lower Extremity Arterial Occlusive Disease: WHY? Gregory L. Moneta MD Professor and Chief Knight Cardiovascular Institute Division of Vascular Surgery
V.A. is a 62-year-old male who presents in referral
 , LLC an HMP Communications Holdings Company Clinical Case Update Latest Trends in Critical Limb Ischemia Imaging Amit Srivastava, MD, FACC, FABVM Interventional Cardiologist Bay Area Heart Center St.
, LLC an HMP Communications Holdings Company Clinical Case Update Latest Trends in Critical Limb Ischemia Imaging Amit Srivastava, MD, FACC, FABVM Interventional Cardiologist Bay Area Heart Center St.
The Peripheral Vascular System
 The Peripheral Vascular System Anatomy and Physiology Arteries Arteries contain 3 concentric layers of tissue: - the intima - the media - the adventitia The intima The endothelium of the intima has metabolic
The Peripheral Vascular System Anatomy and Physiology Arteries Arteries contain 3 concentric layers of tissue: - the intima - the media - the adventitia The intima The endothelium of the intima has metabolic
Radiologic Evaluation of Peripheral Arterial Disease
 January 2003 Radiologic Evaluation of Peripheral Arterial Disease Grace Tye, Harvard Medical School Year III Patient D.M. CC: 44 y/o male with pain in his buttocks Occurs after walking 2 blocks. Pain is
January 2003 Radiologic Evaluation of Peripheral Arterial Disease Grace Tye, Harvard Medical School Year III Patient D.M. CC: 44 y/o male with pain in his buttocks Occurs after walking 2 blocks. Pain is
Introduction 3. What is Peripheral Vascular Disease? 5. What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease? 6
 Patient Information Table of Contents Introduction 3 What is Peripheral Vascular Disease? 5 What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease? 6 What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease? 7 How
Patient Information Table of Contents Introduction 3 What is Peripheral Vascular Disease? 5 What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease? 6 What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease? 7 How
How to manage leg ulcers in the elderly
 How to manage leg ulcers in the elderly David Riding Clinical Research Fellow / Specialty Registrar in Vascular Surgery University of Manchester / MFT British Geriatric Society Trainees Meeting 2018 Objectives
How to manage leg ulcers in the elderly David Riding Clinical Research Fellow / Specialty Registrar in Vascular Surgery University of Manchester / MFT British Geriatric Society Trainees Meeting 2018 Objectives
Peripheral Arterial. Disease
 Peripheral Arterial Disease Peripheral Arterial Disease People take better care of their health when they know what s going on in their bodies. For those with peripheral arterial occlusive disease, this
Peripheral Arterial Disease Peripheral Arterial Disease People take better care of their health when they know what s going on in their bodies. For those with peripheral arterial occlusive disease, this
Maximally Invasive Vascular Surgery for the Treatment of Critical Limb Ischemia
 Maximally Invasive Vascular Surgery for the Treatment of Critical Limb Ischemia Traci A. Kimball, MD Department of Surgery Grand Rounds Septemember 13, 2010 Overview Defining Critical Limb Ischemia Epidemiology
Maximally Invasive Vascular Surgery for the Treatment of Critical Limb Ischemia Traci A. Kimball, MD Department of Surgery Grand Rounds Septemember 13, 2010 Overview Defining Critical Limb Ischemia Epidemiology
Peripheral Vascular Examination. Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment
 Peripheral Vascular Examination Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment Competencies 1. Inspection of upper extremity for: size symmetry swelling venous pattern color Texture nail beds Competencies
Peripheral Vascular Examination Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment Competencies 1. Inspection of upper extremity for: size symmetry swelling venous pattern color Texture nail beds Competencies
SOURCE EMBOLI (mural thrombi ) FROM THE HEART : -LEFT ATRIUM -LEFT VENTRICLE -AORTIC VALVE -MITRAL VALVE
 ARTERIAL PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASES ACUTE ARTERIAL OCCLUSION : SUDDEN INTERRUPTION OF THE BLOOD SUPPPLY RESULT IN A SPECTRUM OF SYMPTOMS AND SIGNS WHICH ARE DEPENDENT UPON THE LOCATION AND EXTENT OF
ARTERIAL PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASES ACUTE ARTERIAL OCCLUSION : SUDDEN INTERRUPTION OF THE BLOOD SUPPPLY RESULT IN A SPECTRUM OF SYMPTOMS AND SIGNS WHICH ARE DEPENDENT UPON THE LOCATION AND EXTENT OF
Influence of vein size (diameter) on infrapopliteal reversed vein graft patency
 Influence of vein size (diameter) on infrapopliteal reversed vein graft patency Kurt R. Wengerter, MD, Frank J. Veith, MD, Sushil K. Gupta, MD, Enrico Ascer, MD, and Steven P. Rivers, MD, New York, N.Y.
Influence of vein size (diameter) on infrapopliteal reversed vein graft patency Kurt R. Wengerter, MD, Frank J. Veith, MD, Sushil K. Gupta, MD, Enrico Ascer, MD, and Steven P. Rivers, MD, New York, N.Y.
Case Discussion. Disclosures. Critical Limb Ischemia: A Selective Approach to Revascularization Works Best 4/28/2012. None. 58 yo M, DM, CAD, HTN
 Critical Limb Ischemia: A Selective Approach to Revascularization Works Best None Disclosures Michael S. Conte MD, FACS Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Co-Director, Heart and Vascular Center
Critical Limb Ischemia: A Selective Approach to Revascularization Works Best None Disclosures Michael S. Conte MD, FACS Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Co-Director, Heart and Vascular Center
Intended Learning Outcomes
 2011 Acute Limb Ischemia Definition, Etiology & Pathophysiology Clinical Evaluation Management Ali SABBOUR Prof. of Vascular Surgery, Ain Shams University Acute Limb Ischemia Intended Learning Outcomes
2011 Acute Limb Ischemia Definition, Etiology & Pathophysiology Clinical Evaluation Management Ali SABBOUR Prof. of Vascular Surgery, Ain Shams University Acute Limb Ischemia Intended Learning Outcomes
Lower Extremity Peripheral Arterial Disease: Less is Sometimes More. Spence M Taylor, M.D.
 Lower Extremity Peripheral Arterial Disease: Less is Sometimes More Spence M Taylor, M.D. President, Greenville Health System Clinical University Senior Associate Dean for Academic Affairs and Diversity
Lower Extremity Peripheral Arterial Disease: Less is Sometimes More Spence M Taylor, M.D. President, Greenville Health System Clinical University Senior Associate Dean for Academic Affairs and Diversity
C L I N I C A L S E Q U E L A E O F A T H E R O T H R O M B O S I S : P E R I P H E R A L A R T E R Y D I S E A S E
 T H E M E : A T H E R O T H R O M B O S I S UNIT NO. 6 C L I N I C A L S E Q U E L A E O F A T H E R O T H R O M B O S I S : P E R I P H E R A L A R T E R Y D I S E A S E Dr John Tan Choon Heng ABSTRACT
T H E M E : A T H E R O T H R O M B O S I S UNIT NO. 6 C L I N I C A L S E Q U E L A E O F A T H E R O T H R O M B O S I S : P E R I P H E R A L A R T E R Y D I S E A S E Dr John Tan Choon Heng ABSTRACT
Intermittent Claudication
 Intermittent Claudication Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ask 3 Questions Preparation for your Appointments We want you to be active in your healthcare. By telling us what is important to
Intermittent Claudication Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ask 3 Questions Preparation for your Appointments We want you to be active in your healthcare. By telling us what is important to
Peripheral arterial disease for primary care Ed Aboian, MD
 Peripheral arterial disease for primary care Ed Aboian, MD Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Palo Alto Medical Foundation, Burlingame Ca Disclosures Nothing to disclose Clinical presentation
Peripheral arterial disease for primary care Ed Aboian, MD Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Palo Alto Medical Foundation, Burlingame Ca Disclosures Nothing to disclose Clinical presentation
Learning Objectives for Rotations in Vascular Surgery Year 3 Basic Clerkship
 Learning Objectives for Rotations in Vascular Surgery Year 3 Basic Clerkship CLINICAL PROBLEMS IN VASCULAR SURGERY 1. ABDOMINAL AORTIC ANEURYSM A 70 year old man presents in the emergency department with
Learning Objectives for Rotations in Vascular Surgery Year 3 Basic Clerkship CLINICAL PROBLEMS IN VASCULAR SURGERY 1. ABDOMINAL AORTIC ANEURYSM A 70 year old man presents in the emergency department with
Larry Diaz, MD, FSCAI Mehdi H. Shishehbor, DO, FSCAI
 PAD Diagnosis Larry Diaz, MD, FSCAI Metro Health / University of Michigan Health, Wyoming, MI Mehdi H. Shishehbor, DO, FSCAI University Hospitals Harrington Heart & Vascular Institute, Cleveland, OH PAD:
PAD Diagnosis Larry Diaz, MD, FSCAI Metro Health / University of Michigan Health, Wyoming, MI Mehdi H. Shishehbor, DO, FSCAI University Hospitals Harrington Heart & Vascular Institute, Cleveland, OH PAD:
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD): Presentation, Diagnosis, and Treatment
 Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD): Presentation, Diagnosis, and Treatment Prepared and Presented by Jon Manocchio, Pharm D Blanchard Valley Hospital October 2011 Introduction PAD is a condition that is
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD): Presentation, Diagnosis, and Treatment Prepared and Presented by Jon Manocchio, Pharm D Blanchard Valley Hospital October 2011 Introduction PAD is a condition that is
Peripheral Arterial Disease: A Practical Approach
 Peripheral Arterial Disease: A Practical Approach Sanjoy Kundu BSc, MD, FRCPC, DABR, FASA, FCIRSE, FSIR The Scarborough Hospital Toronto Endovascular Centre The Vein Institute of Toronto Scarborough Vascular
Peripheral Arterial Disease: A Practical Approach Sanjoy Kundu BSc, MD, FRCPC, DABR, FASA, FCIRSE, FSIR The Scarborough Hospital Toronto Endovascular Centre The Vein Institute of Toronto Scarborough Vascular
Combat Extremity Vascular Trauma
 Combat Extremity Vascular Trauma Training teams to be a TEAM Chatt A. Johnson LTC, MC, USA 08 March 2010 US Army Trauma Training Center Core Discussion Series Outline: Combat Vascular Injury Physiologic
Combat Extremity Vascular Trauma Training teams to be a TEAM Chatt A. Johnson LTC, MC, USA 08 March 2010 US Army Trauma Training Center Core Discussion Series Outline: Combat Vascular Injury Physiologic
Arterial Studies And The Diabetic Foot Patient
 Arterial Studies And The Patient George L. Berdejo, BA, RVT, FSVU gberdejo@wphospital.org Disclosures I have nothing to disclose! Diabetes mellitus continues to grow in global prevalence and to consume
Arterial Studies And The Patient George L. Berdejo, BA, RVT, FSVU gberdejo@wphospital.org Disclosures I have nothing to disclose! Diabetes mellitus continues to grow in global prevalence and to consume
Disclosures. Tips and Tricks for Tibial Intervention. Tibial intervention overview
 Tips and Tricks for Tibial Intervention Donald L. Jacobs, MD C Rollins Hanlon Endowed Professor and Chair Chair of Surgery Saint Louis University SSM-STL Saint Louis University Hospital Disclosures Abbott
Tips and Tricks for Tibial Intervention Donald L. Jacobs, MD C Rollins Hanlon Endowed Professor and Chair Chair of Surgery Saint Louis University SSM-STL Saint Louis University Hospital Disclosures Abbott
Resident Teaching Conference 3/12/2010
 Resident Teaching Conference 3/12/2010 Goals Definition and Classification of Acute Limb Ischemia Clinical Assessment of the Vascular Patient History and Physical Diagnostic Modalities Management of Acute
Resident Teaching Conference 3/12/2010 Goals Definition and Classification of Acute Limb Ischemia Clinical Assessment of the Vascular Patient History and Physical Diagnostic Modalities Management of Acute
Arthroplasty after previous surgery: previous vascular problems
 Arthroplasty after previous surgery: previous vascular problems Jacques Menetrey & Victoria B. Duthon Centre de médecine de l appareil locomoteur et du sport Swiss Olympic medical Center Unité d Orthopédie
Arthroplasty after previous surgery: previous vascular problems Jacques Menetrey & Victoria B. Duthon Centre de médecine de l appareil locomoteur et du sport Swiss Olympic medical Center Unité d Orthopédie
Case 37 Clinical Presentation
 Case 37 73 Clinical Presentation The patient is a 62-year-old woman with gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. 74 RadCases Interventional Radiology Imaging Findings () Image from a selective digital subtraction
Case 37 73 Clinical Presentation The patient is a 62-year-old woman with gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. 74 RadCases Interventional Radiology Imaging Findings () Image from a selective digital subtraction
Vascular Surgery Cases: Detours. Brian F. Stull, RDMS, RVT UNC REX Healthcare Vascular Specialists
 Vascular Surgery Cases: Detours Brian F. Stull, RDMS, RVT UNC REX Healthcare Vascular Specialists Brian.Stull@Unchealth.unc.edu Objectives Anatomy of a bypass graft Where does it connect, where does it
Vascular Surgery Cases: Detours Brian F. Stull, RDMS, RVT UNC REX Healthcare Vascular Specialists Brian.Stull@Unchealth.unc.edu Objectives Anatomy of a bypass graft Where does it connect, where does it
Managing Conditions Resulting from Untreated Cardiometabolic Syndrome
 Managing Conditions Resulting from Untreated Cardiometabolic Syndrome Matthew P. Namanny DO, FACOS Vascular/Endovascular Surgery Saguaro Surgical/AZ Vascular Specialist Tucson Medical Center Critical Limb
Managing Conditions Resulting from Untreated Cardiometabolic Syndrome Matthew P. Namanny DO, FACOS Vascular/Endovascular Surgery Saguaro Surgical/AZ Vascular Specialist Tucson Medical Center Critical Limb
UC SF. Disclosures. Vascular Assessment of the Diabetic Foot. What are the best predictors of wound healing? None. Non-Invasive Vascular Studies
 Disclosures Vascular Assessment of the Diabetic Foot What are the best predictors of wound healing? None Shant Vartanian MD Assistant Professor of Vascular Surgery UCSF Vascular Symposium April 20, 2013
Disclosures Vascular Assessment of the Diabetic Foot What are the best predictors of wound healing? None Shant Vartanian MD Assistant Professor of Vascular Surgery UCSF Vascular Symposium April 20, 2013
Axillobrachial artery bypass grafting with in situ cephalic vein for axillary artery occlusion: A case report
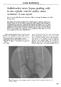 CASE REPORTS Axillobrachial artery bypass grafting with in situ cephalic vein for axillary artery occlusion: A case report Evan S. Cohen,/VII), Robert B. Holtzman, MD, and George W. Johnson, Jr., MD, Houston,
CASE REPORTS Axillobrachial artery bypass grafting with in situ cephalic vein for axillary artery occlusion: A case report Evan S. Cohen,/VII), Robert B. Holtzman, MD, and George W. Johnson, Jr., MD, Houston,
Peripheral Artery Disease Interventions Utilizing the Angiosomal Approach to the Complex Wound
 Peripheral Artery Disease Interventions Utilizing the Angiosomal Approach to the Complex Wound Craig M. Walker, MD, FACC, FACP Chairman, New Cardiovascular Horizons Clinical Professor of Medicine Tulane
Peripheral Artery Disease Interventions Utilizing the Angiosomal Approach to the Complex Wound Craig M. Walker, MD, FACC, FACP Chairman, New Cardiovascular Horizons Clinical Professor of Medicine Tulane
LIMB SALVAGE IN THE DIABETIC PATIENT
 LIMB SALVAGE IN THE DIABETIC PATIENT WHO? HOW? BEST? DISCLOSURES Educational grant from Cook Inc OBJECTIVES Review risk stratification and staging schemes for the threatened limb Discuss current concepts
LIMB SALVAGE IN THE DIABETIC PATIENT WHO? HOW? BEST? DISCLOSURES Educational grant from Cook Inc OBJECTIVES Review risk stratification and staging schemes for the threatened limb Discuss current concepts
Case Study: Chris Arden. Peripheral Arterial Disease
 Case Study: Chris Arden Peripheral Arterial Disease Patient Presentation Diane is a 65-year-old retired school teacher She complains of left calf pain when walking 50 metres; the pain goes away after she
Case Study: Chris Arden Peripheral Arterial Disease Patient Presentation Diane is a 65-year-old retired school teacher She complains of left calf pain when walking 50 metres; the pain goes away after she
