Acute pulmonary thromboembolism (PE) is a common,
|
|
|
- Miranda French
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
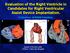
1 Role of Echocardiography in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Pulmonary Thromboembolism David Leibowitz, MD, Jerusalem, Israel The diagnosis and treatment of acute pulmonary thromboembolism (PE) remains a complex clinical challenge. Many studies have used both transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiography as a diagnostic and/or prognostic tool in this common disorder. In patients with central, hemodynamically significant PE, echocardiography can directly visualize thrombus or demonstrate the hemodynamic consequences of PE, whereas in the majority of patients, the sensitivity of echocardiography appears limited. Echocardiography may be useful in assessing the prognosis of patients with PE as well as their response to therapy. Further studies are needed in larger populations of patients to clarify the role of echocardiography in the assessment of patients with clinically suspected PE. (J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2001;14:921-6.) Acute pulmonary thromboembolism (PE) is a common, life-threatening illness that is an important cause of morbidity and mortality. Population-based studies estimate that there are approximately 170,000 new cases of PE in the United States alone, with a 1-year mortality rate of up to 25%. 1,2 The diagnosis of this common disorder remains a clinical challenge despite the extensive use of ventilationperfusion scintigraphy, pulmonary angiography, Doppler ultrasound of the lower extremities, and newer techniques such as spiral/helical computed tomography, serum D-dimer, and magnetic resonance imaging. Although many reports have investigated the potential role of transthoracic (TTE) and transesophageal (TEE) echocardiography in the diagnosis and treatment of PE, the clinical utility of these techniques in this setting remains unclear. This review will examine the role of TTE and TEE in the diagnosis and treatment of acute pulmonary thromboembolism. From the Coronary Care Unit, Hadassah University Hospital, Mount Scopus, Jerusalem, Israel. Reprint requests: David Leibowitz, MD, Coronary Care Unit, Hadassah University Hospital, p.o.b , Mount Scopus, Jerusalem, Israel ( oleibo@hadassah.org.il). Copyright 2001 by the American Society of Echocardiography /2001/$ /1/ doi: /mje TEE IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF PULMONARY EMBOLISM TEE directly images the right-sided cardiac structures, the main pulmonary artery, a significant portion of the right pulmonary artery, and the proximal portion of the left pulmonary artery. The ability of TEE to directly visualize central pulmonary emboli, initially described by Nixdorf et al 3 in 1988, has since been documented in several case reports and small series 4-7 (Figures 1 and 2). One prospective study of 32 patients referred for TEE with clinical or TTE suspicion of pulmonary embolism and documentation of right ventricular overload on TTE noted a sensitivity of 80% and a specificity of 100% for acute PE. 8 Pruszcyk et al 9 prospectively compared the value of TEE and spiral computed tomography (CT) in 49 consecutive patients with clinical suspicion of PE and right ventricular overload noted on TTE. PE was diagnosed in 40 patients by means of reference diagnostic methods (lung scan in 27, angiography in 13). Sensitivity was noted to be 90% for spiral CT and 80% for TEE (not significant), with 100% specificity for both methods.the relatively low negative predictive value (52.9%) of TEE led the authors to caution that TEE could not reliably exclude the diagnosis of PE. In another study of 30 patients with clinically suspected PE and right ventricular overload on TTE, the sensitivity of TEE was 58% when compared with helical CT or angiography. 10 The authors noted that the sensitivity of TEE was limited primarily by difficulty in imaging the left pulmonary and lobar arteries. 921
2 922 Leibowitz September 2001 T Figure 1 Thrombus seen attached to right atrial free wall demonstrated by transesophageal echocardiography. T, Thrombus. Figure 2 Thrombus seen on transesophageal echocardiography in right pulmonary artery in patient with acute shortness of breath and right heart failure. T, Thrombus. Other studies have shown TEE to be an effective diagnostic tool for major PE.In the study of Krivec et al, patients with unexplained shock and distended neck veins admitted to the medical intensive care unit were examined with TEE, and evidence of central pulmonary emboli was noted in 13.The sensitivity of TEE was 92% and specificity was 100% for PE in those patients with right ventricular dilation noted on TTE. 11 In addition,wittlich et al 12 noted a sensitivity of 97% and a specificity of 88% for TEE in detecting central PE when compared with ventilation-perfusion scan and pulmonary angiography. In conclusion, in some but not all studies, TEE appears to be a specific and relatively sensitive diagnostic tool in patients with clinically or echocardiographically suspected central PE. The role of TEE in the more common clinical scenario of peripheral pulmonary emboli is limited because of its inability to image the more distal pulmonary vessels as well as the invasive nature of the procedure. TTE IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF PULMONARY EMBOLISM Although the ability of TTE to directly image the proximal pulmonary arteries is limited, several case reports and series have documented findings of right-sided or pulmonary thrombi by TTE in patients with suspected PE. 13 Chartier et al 14 demonstrated free-floating right-heart thrombi in 38 patients with suspected PE over a 12-year period. Thirty-two patients were in New York Heart Association class IV, and mortality rate was 44.7%.Although these authors did not report the incidence of free-floating thrombi among the general population of patients with sus- pected PE, other studies have suggested that they occur in 7% to 18% of patients. 15,16 Because the number of patients with PE who have directly visualized thrombus on TTE is small, the utility of TTE as a diagnostic test in PE is mainly related to its ability to demonstrate secondary changes in cardiac size and function caused by the hemodynamic effects of PE (Table 1). Kasper et al 17 in 1986 reviewed echocardiographic studies performed in 105 patients with confirmed PE. In their study, right ventricular dilation was found in 70 (75%) patients, reduced left ventricular diameter in 38 (42%) patients, dilated right pulmonary artery in 78 (77%) patients, and abnormal motion of the septum in 41 (44%) patients (Figures 3 and 4). Of note, echocardiographic parameters were normal in 19 (18%) patients. It is also important to note that 33 of the patients in their series had recurrent or chronic pulmonary emboli and so might be expected to have a higher incidence of echocardiographic findings than patients with a single, acute PE. Several prospective studies have examined the utility of TTE as a primary diagnostic tool for PE (Table 2). Cheriex et al 18 studied 60 consecutive patients seen with clinically suspected PE including 11 with cardiovascular collapse who were referred for cardiological consultation. Corroborative investigations, which were not performed systematically, included ventilation-perfusion scanning, pulmonary angiography, surgery, and autopsies but did not confirm the diagnosis of PE in all patients. In this series, 56 (94%) patients had elevated pulmonary systolic pressures as measured by velocity of the tricuspid regurgitation jet. In 56 patients, right ventricular end-diastolic diameter was enlarged, and diastolic bulging of the septum toward the left ventricle
3 Volume 14 Number 9 Leibowitz 923 Figure 3 Short-axis transthoracic view showing dilated right ventricle and septal flattening in patient with pleuritic chest pain and tachycardia. Spiral computed tomography confirmed diagnosis of acute pulmonary thromboembolism. noted. Intracardiac or vascular thrombi were noted in 10 patients. The authors concluded that echocardiography is a sensitive technique for the identification of right ventricular overload in PE.The applicability of this study to the general population of patients with PE is limited because it incorporated a highly selected population, a high proportion of which had hemodynamic abnormalities. In addition, many patients did not undergo definitive diagnostic procedures, and the diagnosis of PE remained unconfirmed. Another prospective study was reported by Nazeyrollas et al. 19 The authors examined 132 patients admitted to the cardiac intensive care unit with suspected pulmonary embolism, excluding patients with previously known cardiac disease. Seven patients died before completion of the protocol, and 55 had other diagnoses (mainly reduced left ventricular function) established by echocardiographic study. Of the final group of 70 patients, 31 had PE documented on pulmonary angiography, and 39 had negative pulmonary angiograms. Significant differences in several echocardiographic variables were noted between the two groups including right ventricular diameter >25 mm (70% versus 14%), ratio of right ventricular diameter to left ventricular diameter >0.5 (85% versus 22%), and tricuspid velocity >2.5 m/s (93% versus 18%). When combined in an echocardiographic logistic model, these echocardiographic parameters had a sensitivity of 93%, specificity of 81%, positive predictive value of 78%, and negative predictive value of 93%.This study was limited to patients admitted to the cardiac intensive care unit, again leading to a selection bias in favor of Figure 4 Apical 4-chamber view (same patient as in Figure 3) showing dilated right ventricle and right atrium. Table 1 Echocardiographic signs used in diagnosis of acute pulmonary thromboembolism 1. Direct visualization of thrombus in the right-sided chambers or the pulmonary artery 2. Right ventricular dilation 3. Reduced right ventricular function 4. Reduced left ventricular cavity size 5. Dilated pulmonary arteries 6. Abnormal septal motion/systolic flattening of the septum 7. Significant (moderate to severe) tricuspid regurgitation 8. Increased velocity of tricuspid regurgitation jet 9. Dilation of the inferior vena cava sicker, more compromised patients who would be expected to have more significant hemodynamic and hence echocardiographic abnormalities than the general population of patients with PE. Several studies have examined the use of TTE as a diagnostic tool for patients with suspected PE who are examined in the emergency department, a more generalized population of patients. Perrier et al 20 prospectively studied 50 patients with suspected PE referred primarily from the emergency ward. The diagnostic gold standard was a sequential noninvasive strategy including lung scan, D-dimers, and lower-extremity Doppler. The prevalence of PE was 36% (18 of 50 patients).the combination of echocardiographic criteria of right ventricular dilation and tricuspid regurgitation velocity of >2.7 m/s yielded a sensitivity of 67% and specificity of 94% when compared with the gold standard. Another prospective study of patients examined in the emergency department was recently reported by Jackson et al. 21 TTE was performed on all patients with suspected PE, with a combination of noninvasive testing considered diagnostic. They reported a sensitivity of only
4 924 Leibowitz September 2001 Table 2 Prospective studies of transthoracic echocardiography as a diagnostic tool in acute peripheral pulmonary thromboembolism Positive Negative No. of Source of Diagnostic predictive predictive Author patients patients gold standard Sensitivity Specificity value value Nazeyrollas et al 70 CCU Pulmonary angiography 93% 81% 78% 93% Perrier et al 50 ED Noninvasive testing 67% 94% 86% 83% Jackson et al 124 ED Pulmonary angiography or noninvasive testing 41% 91% NS NS Grifoni et al 117 ED Pulmonary angiography or noninvasive testing 51% 87% 82% 60% Steiner et al 35 NS Helical CT 59% 77% 81% 37% NS, Not stated; CT, computed tomography; CCU, coronary care unit; ED, emergency department. 41% and concluded accordingly that TTE was not a sensitive test for the diagnosis of acute PE. Grifoni et al 22 studied 117 consecutive patients with suspected PE in the emergency department. Sixty-three of these patients had a diagnosis of PE confirmed by either lung scan or angiography. Echocardiography had a sensitivity of 51%, with a relatively high specificity of 87%. 22 A study by Steiner et al 23 prospectively examined 35 consecutive patients with clinically suspected PE with TTE, TEE, and helical CT. Twenty-two (63%) of this patient sample had PE documented on helical CT that was defined as the diagnostic gold standard. The sensitivity and specificity of the combination of both echocardiographic studies (relying on both direct and indirect signs of PE) were relatively low,at 59% and 77%,respectively.When including only patients with central PE (50% of the total sample), the sensitivity and specificity rose to 82% and 92%,respectively.The relatively low sensitivity in these studies indicates that echocardiography cannot reliably exclude the diagnosis of PE. Limitations of these studies include the small sample sizes and use of noninvasive testing as the gold standard instead of pulmonary angiography. McConnell et al 24 described a regional pattern of right ventricular dysfunction in patients with PE with akinesia of the right ventricular free wall but normal motion at the right ventricular apex. This finding was in contrast to patients with right ventricular dysfunction secondary to other causes in which wall motion was abnormal in all segments. In their validation cohort that included 13 patients with PE and 72 patients with right ventricular dysfunction from any cause, this finding had a sensitivity of 77% and 94% specificity, with a positive predictive value of 71% and negative predictive value of 96%. The authors postulated several potential mechanisms for this finding including tethering of the right ventricular apex to a hyperdynamic left ventricle or localized ischemia of the free wall caused by increased wall stress. ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IN THE ASSESSMENT OF PROGNOSIS OF PATIENTS WITH PE Several studies have examined the prognostic role of TTE in patients with PE. In a short-term study, Grifoni et al 25 studied 209 consecutive patients with acute PE diagnosed by lung scan, CT, or pulmonary angiography by TTE within 1 hour of admission. Patients who were normotensive were divided into 2 groups, based on the presence or absence of right ventricular dysfunction.the group of patients with right ventricular dysfunction (31% of the total cohort) had a 10% rate of PE-related shock, with a 5% mortality rate in the hospital. PE-related death was 0 in the normal right ventricular function group.the negative predictive value of echocardiography for PE-related death was 100%; however, the positive predictive value was low (5%), leading to the authors conclusion that echocardiography was most effective as a screening test for the identification of low-risk patients. 25 Ribeiro et al 26 studied 126 patients with PE by TTE on the day of diagnosis. The study noted a significantly higher mortality rate in the group with moderately or severely reduced right ventricular function (7% versus 21%,P =.04).Seventy-eight members of this study population underwent repeated follow-up TTE during the first year after diagnosis. 27 More than 90% of patients had stabilization of pulmonary pressures and right ventricular function within 30 days after diagnosis. Multiple logistic regression analysis of variables associated with persistent pulmonary hypertension/right ventricular dysfunction showed an odds ratio of 3.3 for patients with pulmonary artery systolic pressure >50 mm Hg at the time of diagnosis. The authors concluded that early echocardiography may predict long-term outcome in patients with PE. Kasper et al 28 prospectively studied 317 patients with clinically suspected PE with TTE, of whom 87 (27%) had evidence of right ventricular afterload stress. One-year mortality rate from PE was 13% in this group versus 1.3% in the group without right
5 Volume 14 Number 9 Leibowitz 925 ventricular afterload stress. A major limitation of this study was the absence of confirmation of the diagnosis of PE in a significant number of patients. Wolfe et al 29 examined the relation between right ventricular hypokinesis assessed by echocardiography and the degree of perfusion scan defects in 90 patients with PE. The degree of perfusion defect was greater in the patients with right ventricular dysfunction (54% versus 30%, P <.001). Interestingly, all of the patients with recurrent PE were in the group with right ventricular dysfunction at baseline (13% versus 0%, P <.01), suggesting a strong association between echocardiographic demonstration of right ventricular dysfunction and the risk of recurrent PE. Ribeiro et al 30 demonstrated a correlation between echocardiographically determined right ventricular dysfunction and perfusion defects but noted wide variability in both groups, with large confidence intervals. Miller et al 31 failed to show a correlation between right ventricular dysfunction and perfusion defects in a group of 64 patients with acute PE.The mixed results of these studies suggest that the extent of perfusion defects cannot accurately predict the presence of RV dysfunction. The prevalence of a patent foramen ovale (PFO) detected by contrast echocardiography is increased in patients with PE.In a study of 40 patients with PE diagnosed primarily with high-probability nuclear scans, Miller et al 32 noted an association between the presence of a PFO and extent of perfusion abnormalities. The study was not powered to assess the effect of PFO on prognosis. Konstantinides et al 33 prospectively examined 139 patients with a diagnosis of PE based on defined clinical criteria and findings on echocardiography of right-sided pressure overload and/or pulmonary hypertension. All patients underwent contrast echocardiography, and PFO was diagnosed in 35%. Patients with a PFO had a 33% mortality rate as opposed to a 14% mortality rate in patients with a negative contrast study.a PFO was an independent predictor of death on logistic regression analysis. Because the diagnosis of PE required evidence of pulmonary hypertension, this was a high-risk population, as evidenced by the overall mortality rate of 21%, and as such may not reflect the general population of patients with PE. ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY AND THROMBOLYTIC THERAPY FOR PE Thrombolytic therapy has emerged as a therapeutic option not only in patients with shock but in hemodynamically stable PE as well. Several small studies have studied the effect of thrombolytic therapy on right ventricular function as assessed by TTE. Come et al 34 serially examined 7 patients by TTE before and after (mean 9 hours) therapy with tissue-type plasminogen activator for pulmonary embolism and noted significant decreases in pulmonary artery systolic pressure, right ventricular diameter, and systolic septal flattening after lytic therapy. Metz et al 35 used an automated boundary detection system to examine changes in right ventricular function within 1 hour after thrombolysis in patients with PE.In accordance with the findings of Come et al, decreases in right ventricular diastolic diameter and area and increased right ventricular fractional area change was noted post thrombolysis. Nass et al, 36 in a retrospective study of 18 patients with acute PE and right ventricular dysfunction who received thrombolytic therapy, noted normalization of right ventricular function in most patients after therapy. Follow-up studies were performed at varying intervals, but normalization was reported as early as 3 days after therapy in this series.these small studies support the concept that thrombolytic therapy in acute PE results in prompt improvement in right ventricular function and reduction of pulmonary pressures and that TTE can be used to assess the response to thrombolytic therapy in patients with acute PE. CONCLUSION In summary, in patients with central or massive pulmonary emboli, echocardiography may directly visualize the embolus or, more commonly, provide evidence of its hemodynamic sequelae with reasonable sensitivity. In the majority of patients with clinically suspected PE, the limited sensitivity of echocardiography restricts its role as a primary diagnostic tool. Limitations of the published studies include selected populations, varying diagnostic gold standards, and small numbers of patients. Echocardiography appears to be useful in the assessment of prognosis of patients with PE, particularly in the identification of a low-risk population, and in the hemodynamic response to thrombolytic therapy if used. Further studies incorporating echocardiography as part of a diagnostic algorithm in large, unselected populations of patients with suspected PE are necessary to further delineate the role of echocardiography in this common, frustrating diagnostic dilemma. REFERENCES 1. Hansson PO, Welin L, Tibblin G, Eriksson H. Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in the general population: the Study of Men Born in Arch Intern Med 1997; 157:
6 926 Leibowitz September Carson JL, Kelley MA, Duff A, et al. The clinical course of pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med 1992;326: Nixdorf U, Erbel R, Drexler M, et al. Detection of thromboembolus of the right pulmonary artery by transesophageal two-dimensional echocardiography. Am J Cardiol 1988;61: Rittoo D, Sutherland GR, Samuel L, Flapan AD, Shaw TRD. Role of transesophageal echocardiography in diagnosis and management of central pulmonary artery thromboembolism. Am J Cardiol 1993;71: Cerel A, Burger AJ. The diagnosis of a pulmonary artery thrombus by transesophageal echocardiography. Chest 1993; 103: Richaud M, Drobinsky G, Montalscot G, Salloum J, Bizec JL, Isnard R. Diagnosis of pulmonary embolism by transesophageal echocardiography. Eur Heart J 1992;13: Ritchie ME, Srivastava BK. Use of transesophageal echocardiography to detect unsuspected massive pulmonary emboli. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 1998;11: Pruszczyk P, Torbicki A, Kuch-Wocial A, Chlebus M, Miskiwicz ZC, Jedrusik P. Transesophageal echocardiography for definitive diagnosis of hemodynamically significant pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J 1995;16: Pruszczyk P, Torbicki A, Pacho R, et al. Noninvasive diagnosis of suspected severe pulmonary embolism: transesophageal echocardiography vs spiral CT. Chest 1997;112: Vieillard-Baron A, Qanadli SD, Antakly Y, et al. Transesophageal echocardiography for the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism with acute cor pulmonale: a comparison with radiological procedures. Intensive Care Med 1998;24: Krivec B, Voga G, Zuran I, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of shock due to massive pulmonary embolism. Chest 1997;112: Wittlich N, Erbel R, Eichler A, et al. Detection of central pulmonary artery thrombi by transesophageal echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 1992;5: Mancuso L, Marchi S, Mizio G, Iacona MA, Celona G. Echocardiographic detection of right-sided cardiac thrombi in pulmonary embolism. Chest 1987;92: Chartier L, Bera J, Delomez M, et al. Free-floating thrombi in the right heart: diagnosis, management and prognostic indexes in 38 consecutive patients. Circulation 1999;99: Chapoutot L, Nazeyrollas P, Metz D, et al. Floating right heart thrombi and pulmonary embolism: diagnosis, outcome, and therapeutic management. Cardiology 1996;87: Casazza F, Bongarzoni A, Centonze F, Morpugo M. Prevalence and prognostic significance of right-sided cardiac mobile thrombi in acute massive pulmonary embolism. Am J Cardiol 1997;79: Kasper W, Meinertz T, Henkel B, et al. Echocardiographic findings in patients with proved pulmonary embolism. Am Heart J 1986;112: Cheriex EC, Sreeram N, Eussen YF, Pieters FA, Wellens HJ. Cross sectional Doppler echocardiography as the initial technique for the diagnosis of acute pulmonary embolism. Br Heart J 1994;72: Nazeyrollas P, Metz D, Jolly D, et al. Use of transthoracic Doppler echocardiography combined with clinical and electrocardiographic data to predict acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J 1996;17: Perrier A, Tamm C, Unger PF, Lerch R, Sztajzel J. Diagnostic accuracy of Doppler echocardiography in unselected patients with suspected pulmonary embolism. Int J Cardiol 1998;65: Jackson RE, Rudoni RR, Hauser AM, Pascual RG, Hussey ME. Prospective evaluation of two-dimensional transthoracic echocardiography in emergency department patients with suspected pulmonary embolism. Acad Emerg Med 2000;7: Grifoni S, Olivotto I, Cecchini P, et al. Utility of an integrated clinical, echocardiographic and venous ultrasonographic approach for triage of patients with suspected pulmonary embolism. Am J Cardiol 1998;135: Steiner P, Lund GK, Debatin JF, et al. Acute pulmonary embolism: value of transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiography in comparison with helical CT. Am J Roentgenol 1996;167: McConnell MV, Solomon SD, Rayan ME, Come PC, Goldhaber SZ, Lee RT. Regional right ventricular dysfunction detected by echocardiography in acute pulmonary embolism. Am J Cardiol 1996;78: Grifoni S, Olivotto I, Cecchini P, et al. Short-term clinical outcome of patients with acute pulmonary embolism, normal blood pressure, and echocardiographic right ventricular dysfunction. Circulation 2000;101: Ribeiro A, Lindmarker P, Juhlin-Dannfelt A, Johnsson H, Jorfedt L. Echocardiography Doppler in pulmonary embolism: right ventricular dysfunction as a predictor of mortality rate. Am Heart J 1997;134: Ribeiro A, Lindmarker P, Johnsson H, Juhlin-Dannfelt A, Jorfedt L. Pulmonary embolism: one-year follow-up with echocardiography Doppler and five-year survival analysis. Circulation 1999;99: Kasper W, Konstantinides S, Geibel A, Tiede N, Krause T, Just H. Prognostic significance of right ventricular afterload stress detected by echocardiography in patients with clinically suspected pulmonary embolism. Heart 1997;77: Wolfe MW, Lee RT, Feldstein ML, Parker JA, Come PC, Goldhaber SZ. Prognostic significance of right ventricular hypokinesis and perfusion lung scan defects in pulmonary embolism. Am Heart J 1994;127: Ribiero A, Juhlin-Dannfelt A, Brodin L, Holmgren A, Jorfeldt L. Pulmonary embolism: relation between the degree of right ventricle overload and the extent of perfusion defects. Am Heart J 1998;135: Miller RL, Das S, Anandarangam T, et al. Association between right ventricular function and perfusion abnormalities in hemodynamically stable patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Chest 1998;113: Miller RL, Das S, Anandarangam T, et al. Relation between patent foramen ovale and perfusion abnormalities in acute pulmonary embolism. Am J Cardiol 1997;80: Konstantinides S, Geibel A, Kasper W, Olschewski M, Blumel L, Just H. Patent foramen ovale is an important predictor of adverse outcome in patients with major pulmonary embolism. Circulation 1998;97: Come PC, Kim D, Parker JA, Goldhaber SZ, Braunwald E, Markis JE. Early reversal of right ventricular dysfunction in patients with acute pulmonary embolism after treatment with intravenous tissue plasminogen activator. J Am Coll Cardiol 1987;10: Metz D, Nazeyrollas P, Mailier B, et al. Regression of right ventricular hypokinesis after thrombolysis in acute pulmonary embolism. Am J Cardiol 1996;77: Nass N, McConnell MV, Goldhaber SZ, Chyu S, Solomon SD. Recovery of regional right ventricular function after thrombolysis for pulmonary embolism. Am J Cardiol 1999; 83:804-6.
DIAGNOSTIC evaluation for acute pulmonary
 994 2-D ECHO Jackson et al. ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY FOR PULMONARY EMBOLISM Prospective Evaluation of Two-dimensional Transthoracic Echocardiography in Emergency Department Patients with Suspected Pulmonary Embolism
994 2-D ECHO Jackson et al. ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY FOR PULMONARY EMBOLISM Prospective Evaluation of Two-dimensional Transthoracic Echocardiography in Emergency Department Patients with Suspected Pulmonary Embolism
Early Transoesophageal Echocardiography (TOE) in Cardiac Arrest: A Case Study
 Case reports Early Transoesophageal Echocardiography (TOE) in Cardiac Arrest: A Case Study N. SIMPSON, N. ORFORD Intensive Care Unit, The Geelong Hospital, Geelong, VICTORIA ABSTRACT We describe a case
Case reports Early Transoesophageal Echocardiography (TOE) in Cardiac Arrest: A Case Study N. SIMPSON, N. ORFORD Intensive Care Unit, The Geelong Hospital, Geelong, VICTORIA ABSTRACT We describe a case
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION
 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Prognostic Role of Echocardiography Among Patients With Acute Pulmonary Embolism and a Systolic Arterial Pressure of 90 mm Hg or Higher Nils Kucher, MD; Elisa Rossi, BS; Marisa De
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Prognostic Role of Echocardiography Among Patients With Acute Pulmonary Embolism and a Systolic Arterial Pressure of 90 mm Hg or Higher Nils Kucher, MD; Elisa Rossi, BS; Marisa De
Emergency department bedside echocardiography diagnosis of massive pulmonary embolism with direct visualization of thrombus in the pulmonary artery
 Crit Ultrasound J (2011) 3:155 160 DOI 10.1007/s13089-011-0081-4 CASE REPORT Emergency department bedside echocardiography diagnosis of massive pulmonary embolism with direct visualization of thrombus
Crit Ultrasound J (2011) 3:155 160 DOI 10.1007/s13089-011-0081-4 CASE REPORT Emergency department bedside echocardiography diagnosis of massive pulmonary embolism with direct visualization of thrombus
Cardiovascular Images
 Cardiovascular Images Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosed From Right Heart Changes Seen After Exercise Stress Echocardiography Brian C. Case, MD; Micheas Zemedkun, MD; Amarin Sangkharat, MD; Allen J. Taylor,
Cardiovascular Images Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosed From Right Heart Changes Seen After Exercise Stress Echocardiography Brian C. Case, MD; Micheas Zemedkun, MD; Amarin Sangkharat, MD; Allen J. Taylor,
Diagnostic value of transoesophageal echocardiography in suspected haemodynamically significant pulmonary embolism
 628 Heart 2001;85:628 634 Department of Internal Medicine and Hypertension, The Medical University of Warsaw, Banacha 1a, 02-097 Warsaw, Poland P Pruszczyk A Kuch-Wocial M Szulc Institute of Lung Diseases
628 Heart 2001;85:628 634 Department of Internal Medicine and Hypertension, The Medical University of Warsaw, Banacha 1a, 02-097 Warsaw, Poland P Pruszczyk A Kuch-Wocial M Szulc Institute of Lung Diseases
Chapter 1. Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction Introduction 9 Even though the first reports on venous thromboembolism date back to the 13 th century and the mechanism of acute pulmonary embolism (PE) was unraveled almost 150
Chapter 1 Introduction Introduction 9 Even though the first reports on venous thromboembolism date back to the 13 th century and the mechanism of acute pulmonary embolism (PE) was unraveled almost 150
Prognostic value of the ECG on admission in patients with acute major pulmonary embolism
 Eur Respir J 2005; 25: 843 848 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.05.00119704 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2005 Prognostic value of the ECG on admission in patients with acute major pulmonary embolism A. Geibel*, M.
Eur Respir J 2005; 25: 843 848 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.05.00119704 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2005 Prognostic value of the ECG on admission in patients with acute major pulmonary embolism A. Geibel*, M.
Case Report Free Floating Right Heart Thrombus Associated with Acute Pulmonary Embolism: An Unsettled Therapeutic Difficulty
 Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2015, Article ID 364780, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/364780 Case Report Free Floating Right Heart Thrombus Associated with Acute Pulmonary Embolism: An Unsettled
Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2015, Article ID 364780, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/364780 Case Report Free Floating Right Heart Thrombus Associated with Acute Pulmonary Embolism: An Unsettled
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/21764 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Mos, Inge Christina Maria Title: A more granular view on pulmonary embolism Issue
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/21764 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Mos, Inge Christina Maria Title: A more granular view on pulmonary embolism Issue
A 50-year-old woman with syncope
 Hira Shahzad 1, Ali Bin Sarwar Zubairi 2 1 Medical College, Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi 2 Department of Medicine, Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi, Pakistan Ali Bin Sarwar Zubairi Associate
Hira Shahzad 1, Ali Bin Sarwar Zubairi 2 1 Medical College, Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi 2 Department of Medicine, Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi, Pakistan Ali Bin Sarwar Zubairi Associate
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies
 Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION. Thrombolysis vs Heparin in the Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism
 Thrombolysis vs Heparin in the Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism A Clinical Outcome Based Meta-analysis ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Giancarlo Agnelli, MD; Cecilia Becattini, MD; Timo Kirschstein, MD Background:
Thrombolysis vs Heparin in the Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism A Clinical Outcome Based Meta-analysis ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Giancarlo Agnelli, MD; Cecilia Becattini, MD; Timo Kirschstein, MD Background:
Case Report Sinus Venosus Atrial Septal Defect as a Cause of Palpitations and Dyspnea in an Adult: A Diagnostic Imaging Challenge
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 128462, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/128462 Case Report Sinus Venosus Atrial Septal Defect as a Cause of Palpitations and Dyspnea in an Adult:
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 128462, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/128462 Case Report Sinus Venosus Atrial Septal Defect as a Cause of Palpitations and Dyspnea in an Adult:
Echocardiography Conference
 Echocardiography Conference David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY-6 September 20, 2005 Atrial Septal Aneurysm Bulging of Fossa Ovalis Associated commonly with Atrial septal defect or small perforations
Echocardiography Conference David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY-6 September 20, 2005 Atrial Septal Aneurysm Bulging of Fossa Ovalis Associated commonly with Atrial septal defect or small perforations
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) and right ventricular (RV)
 Pulmonary Embolism One-Year Follow-Up With Echocardiography Doppler and Five-Year Survival Analysis Ary Ribeiro, MD; Per Lindmarker, MD; Hans Johnsson, MD, PhD; Anders Juhlin-Dannfelt, MD, PhD; Lennart
Pulmonary Embolism One-Year Follow-Up With Echocardiography Doppler and Five-Year Survival Analysis Ary Ribeiro, MD; Per Lindmarker, MD; Hans Johnsson, MD, PhD; Anders Juhlin-Dannfelt, MD, PhD; Lennart
ΠΝΔΤΜΟΝΙΚΗ ΔΜΒΟΛΗ Ο ΡΟΛΟ ΣΗ ΓΔΞΙΑ ΚΟΙΛΙΑ
 ΠΝΔΤΜΟΝΙΚΗ ΔΜΒΟΛΗ Ο ΡΟΛΟ ΣΗ ΓΔΞΙΑ ΚΟΙΛΙΑ Γ. Καρατασάκης ΔΚΔ 02/11/12 FACTS ON PE Related to DVT High morbidity Mortality is (still) high Low detection rate before death Frequent overdiagnosis and overtreatment
ΠΝΔΤΜΟΝΙΚΗ ΔΜΒΟΛΗ Ο ΡΟΛΟ ΣΗ ΓΔΞΙΑ ΚΟΙΛΙΑ Γ. Καρατασάκης ΔΚΔ 02/11/12 FACTS ON PE Related to DVT High morbidity Mortality is (still) high Low detection rate before death Frequent overdiagnosis and overtreatment
CARDIAC PROBLEMS IN PREGNANCY
 CARDIAC PROBLEMS IN PREGNANCY LAS VEGAS, NEVADA, USA 27 February 1 March 2016 SUCCESSFUL TREATMENT WITH RECOMBINANT TISSUE PLASMINOGEN ACTIVATOR OF MASSIVE PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN THE 16 TH WEEK OF PREGNANCY
CARDIAC PROBLEMS IN PREGNANCY LAS VEGAS, NEVADA, USA 27 February 1 March 2016 SUCCESSFUL TREATMENT WITH RECOMBINANT TISSUE PLASMINOGEN ACTIVATOR OF MASSIVE PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN THE 16 TH WEEK OF PREGNANCY
Left atrial function. Aliakbar Arvandi MD
 In the clinic Left atrial function Abstract The left atrium (LA) is a left posterior cardiac chamber which is located adjacent to the esophagus. It is separated from the right atrium by the inter-atrial
In the clinic Left atrial function Abstract The left atrium (LA) is a left posterior cardiac chamber which is located adjacent to the esophagus. It is separated from the right atrium by the inter-atrial
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Department of Internal Medicine and Cardiology, The Medical University of Warsaw, Poland
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cardiology Journal 2010, Vol. 17, No. 1, pp. 1 XXX Copyright 2009 Via Medica ISSN 1897 5593 Signs of myocardial ischemia on electrocardiogram correlate with elevated plasma cardiac troponin
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cardiology Journal 2010, Vol. 17, No. 1, pp. 1 XXX Copyright 2009 Via Medica ISSN 1897 5593 Signs of myocardial ischemia on electrocardiogram correlate with elevated plasma cardiac troponin
ECHO HAWAII. My home. Pulmonary Hypertension and Pulmonary Embolism: Role of Echo U.S.A. Japan. Hawaii Island 1/9/2018
 Pulmonary Hypertension and Pulmonary Embolism: Role of Echo ECHO HAWAII January 15 19, 2018 Kenya Kusunose, MD, PhD, FASE Tokushima University Hospital Japan My home Japan U.S.A Hawaii Island 1 Economy
Pulmonary Hypertension and Pulmonary Embolism: Role of Echo ECHO HAWAII January 15 19, 2018 Kenya Kusunose, MD, PhD, FASE Tokushima University Hospital Japan My home Japan U.S.A Hawaii Island 1 Economy
ACUTE PULMONARY EMBOLISM MIMICS ACUTE CORONARY SYNDROME IN OLDER PATIENT
 CASE REPORT ACUTE PULMONARY EMBOLISM MIMICS ACUTE CORONARY SYNDROME IN OLDER PATIENT Chun-Chieh Liu 1,2 *, Ta-Chuan Hung 1,2, Charles Jia-Yin Hou 1,2, Cheng-Ho Tsai 1,2,3 1 Cardiovascular Medicine, Department
CASE REPORT ACUTE PULMONARY EMBOLISM MIMICS ACUTE CORONARY SYNDROME IN OLDER PATIENT Chun-Chieh Liu 1,2 *, Ta-Chuan Hung 1,2, Charles Jia-Yin Hou 1,2, Cheng-Ho Tsai 1,2,3 1 Cardiovascular Medicine, Department
Despite important advances in diagnosis and treatment,
 Importance of Cardiac Troponins I and T in Risk Stratification of Patients With Acute Pulmonary Embolism Stavros Konstantinides, MD; Annette Geibel, MD; Manfred Olschewski, PhD; Wolfgang Kasper, MD; Nadine
Importance of Cardiac Troponins I and T in Risk Stratification of Patients With Acute Pulmonary Embolism Stavros Konstantinides, MD; Annette Geibel, MD; Manfred Olschewski, PhD; Wolfgang Kasper, MD; Nadine
Diversion of the inferior vena cava following repair of atrial septal defect causing hypoxemia
 Marshall University Marshall Digital Scholar Internal Medicine Faculty Research Spring 5-2004 Diversion of the inferior vena cava following repair of atrial septal defect causing hypoxemia Ellen A. Thompson
Marshall University Marshall Digital Scholar Internal Medicine Faculty Research Spring 5-2004 Diversion of the inferior vena cava following repair of atrial septal defect causing hypoxemia Ellen A. Thompson
Prognostic Value of Emergency Physician Performed Echocardiography in Patients With Acute Pulmonary Thromboembolism
 Abstract and Introduction Abstract www.medscape.com Prognostic Value of Emergency Physician Performed Echocardiography in Patients With Acute Pulmonary Thromboembolism Maurizio Zanobetti, MD, Cristiano
Abstract and Introduction Abstract www.medscape.com Prognostic Value of Emergency Physician Performed Echocardiography in Patients With Acute Pulmonary Thromboembolism Maurizio Zanobetti, MD, Cristiano
Is Thrombolysis Only for a Crisis?
 Is Thrombolysis Only for a Crisis? December 19, 2017 Is Thrombolysis Only for a Crisis? Indications for Thrombolytic Therapy in Patients with Acute Pulmonary Embolism Case Scenario A 28 year old woman
Is Thrombolysis Only for a Crisis? December 19, 2017 Is Thrombolysis Only for a Crisis? Indications for Thrombolytic Therapy in Patients with Acute Pulmonary Embolism Case Scenario A 28 year old woman
Cardiac troponin I for predicting right ventricular dysfunction and intermediate risk in patients with normotensive pulmonary embolism
 Neth Heart J (2015) 23:55 61 DOI 10.1007/s12471-014-0628-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE: SHORT COMMUNICATION Cardiac troponin I for predicting right ventricular dysfunction and intermediate risk in patients with normotensive
Neth Heart J (2015) 23:55 61 DOI 10.1007/s12471-014-0628-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE: SHORT COMMUNICATION Cardiac troponin I for predicting right ventricular dysfunction and intermediate risk in patients with normotensive
Pulmonary Embolism. Thoracic radiologist Helena Lauri
 Pulmonary Embolism Thoracic radiologist Helena Lauri 8.5.2017 Statistics 1-2 out of 1000 adults annually are diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and/or pulmonary embolism (PE) About half of patients
Pulmonary Embolism Thoracic radiologist Helena Lauri 8.5.2017 Statistics 1-2 out of 1000 adults annually are diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and/or pulmonary embolism (PE) About half of patients
Should thrombolysis have a greater role in the management of pulmonary embolism?
 ORIGINAL PAPERS Clinical Medicine 2009, Vol 9, No 5: 431 5 Should thrombolysis have a greater role in the management of pulmonary embolism? Peter O Jenkins, Javed Sultanzadeh, Manasi Bhagwat and Paul F
ORIGINAL PAPERS Clinical Medicine 2009, Vol 9, No 5: 431 5 Should thrombolysis have a greater role in the management of pulmonary embolism? Peter O Jenkins, Javed Sultanzadeh, Manasi Bhagwat and Paul F
Das recht Ventrikel ist auch noch da! RV function The RV operates as. Physiology Not very sensitive to preload Good compliance of the free wall
 Das recht Ventrikel ist auch noch da! I.Michaux Intensive Care Medicine University Hospital CHU UCL Namur Mont-Godinne Belgium RV function The RV operates as a low pressure, volume pump, moving the blood
Das recht Ventrikel ist auch noch da! I.Michaux Intensive Care Medicine University Hospital CHU UCL Namur Mont-Godinne Belgium RV function The RV operates as a low pressure, volume pump, moving the blood
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Systematic Review of Treatment for Trapped Thrombus in Patent Foramen Ovale
 Korean Circ J. 2017 Sep;47(5):776-785 pissn 1738-5520 eissn 1738-5555 Original Article Systematic Review of Treatment for Trapped Thrombus in Patent Foramen Ovale Won-Woo Seo, MD, Sung Eun Kim, MD, Myung-Soo
Korean Circ J. 2017 Sep;47(5):776-785 pissn 1738-5520 eissn 1738-5555 Original Article Systematic Review of Treatment for Trapped Thrombus in Patent Foramen Ovale Won-Woo Seo, MD, Sung Eun Kim, MD, Myung-Soo
L'échocardiographie en réanimation - Echocardiography in intensive care - Acute Co...
 Page 1 sur 9 Acute Cor Pulmonale Sunday, 02 January 2005 Click on each figure to increase it - If the enlarging does not function, check in your browser's option that 'javascript' is well activated. Definition
Page 1 sur 9 Acute Cor Pulmonale Sunday, 02 January 2005 Click on each figure to increase it - If the enlarging does not function, check in your browser's option that 'javascript' is well activated. Definition
PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE): DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
 PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE): DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide a diagnostic algorithm and treatment options for patients with acute pulmonary embolism (PE). BACKGROUND: Venous thromboembolism (VTE)
PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE): DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide a diagnostic algorithm and treatment options for patients with acute pulmonary embolism (PE). BACKGROUND: Venous thromboembolism (VTE)
Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We. ACHD Patients
 Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We Have Learned to Apply to ACHD Patients Faris Al Mousily, MBChB, FAAC, FACC Consultant, Pediatric Cardiology, KFSH&RC/Jeddah Adjunct Faculty, Division of Pediatric Cardiology
Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We Have Learned to Apply to ACHD Patients Faris Al Mousily, MBChB, FAAC, FACC Consultant, Pediatric Cardiology, KFSH&RC/Jeddah Adjunct Faculty, Division of Pediatric Cardiology
High density thrombi of pulmonary embolism on precontrast CT scan: Is it dangerous?
 High density thrombi of pulmonary embolism on precontrast CT scan: Is it dangerous? Poster No.: C-1753 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit B. Y. Lee, H. R. KIM, J. I. Jung,
High density thrombi of pulmonary embolism on precontrast CT scan: Is it dangerous? Poster No.: C-1753 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit B. Y. Lee, H. R. KIM, J. I. Jung,
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute coronary syndrome(s), anticoagulant therapy in, 706, 707 antiplatelet therapy in, 702 ß-blockers in, 703 cardiac biomarkers in,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute coronary syndrome(s), anticoagulant therapy in, 706, 707 antiplatelet therapy in, 702 ß-blockers in, 703 cardiac biomarkers in,
Thrombolysis in PE. Outline. Disclosure. Overview on Pulmonary Embolism. Hot Topics in Emergency Medicine 2012 Midyear Clinical Meeting
 Disclosure Thrombolysis in PE Daniel P. Hays, PharmD, BCPS, FASHP reports no relevant financial relationships. Daniel P. Hays, PharmD, BCPS, FASHP Outline 55 YOF presents to ED with SOB PMH of DVT + noncompliance
Disclosure Thrombolysis in PE Daniel P. Hays, PharmD, BCPS, FASHP reports no relevant financial relationships. Daniel P. Hays, PharmD, BCPS, FASHP Outline 55 YOF presents to ED with SOB PMH of DVT + noncompliance
PE is a difficult diagnosis that may be missed because of non-specific clinical presentation.
 Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a relatively common cardiovascular emergency. By occluding the pulmonary arterial bed it may lead to acute life-threatening (3% early mortality rate), but potentially reversible
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a relatively common cardiovascular emergency. By occluding the pulmonary arterial bed it may lead to acute life-threatening (3% early mortality rate), but potentially reversible
Heart Health ESC Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism
 Heart Health Open Access Received: Oct 22, 2014 Accepted: Dec 01, 2014 Published: Dec 05, 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.14437/hhoa-1-105 Review Jiri Widimsky, Heart Health Open Access 2014, 1:1 2014 ESC Guidelines
Heart Health Open Access Received: Oct 22, 2014 Accepted: Dec 01, 2014 Published: Dec 05, 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.14437/hhoa-1-105 Review Jiri Widimsky, Heart Health Open Access 2014, 1:1 2014 ESC Guidelines
PULMONARY EMBOLISM ANGIOCT (CTA) ASSESSMENT OF VASCULAR OCCLUSION EXTENT AND LOCALIZATION OF EMBOLI 1. BACKGROUND
 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL INFORMATICS & TECHNOLOGIES Vol. 11/2007, ISSN 1642-6037 Damian PTAK * pulmonary embolism, AngioCT, postprocessing techniques, Mastora score PULMONARY EMBOLISM ANGIOCT (CTA) ASSESSMENT
JOURNAL OF MEDICAL INFORMATICS & TECHNOLOGIES Vol. 11/2007, ISSN 1642-6037 Damian PTAK * pulmonary embolism, AngioCT, postprocessing techniques, Mastora score PULMONARY EMBOLISM ANGIOCT (CTA) ASSESSMENT
Epidemiology. Update on Pulmonary Embolism. Keys to PE Management 5/5/2014. Diagnosis. Risk stratification. Treatment
 Update on Pulmonary Embolism Steven M. Dean, DO, FACP, RPVI Program Director- Vascular Medicine Associate Professor of Internal Medicine Division of Cardiovascular Medicine The Ohio State University Keys
Update on Pulmonary Embolism Steven M. Dean, DO, FACP, RPVI Program Director- Vascular Medicine Associate Professor of Internal Medicine Division of Cardiovascular Medicine The Ohio State University Keys
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY. Patient Care. Goals and Objectives PF EF MF LF Aspirational
 Patient Care Be able to: Perform and interpret basic TTE and X cardiac Doppler examinations Perform and interpret a comprehensive X TTE and cardiac Doppler examination Perform and interpret a comprehensive
Patient Care Be able to: Perform and interpret basic TTE and X cardiac Doppler examinations Perform and interpret a comprehensive X TTE and cardiac Doppler examination Perform and interpret a comprehensive
Diagnosis and Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism
 Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Evidence Report/Technology Assessment Diagnosis and Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Summary Number 68 Overview Venous thromboembolism
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Evidence Report/Technology Assessment Diagnosis and Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Summary Number 68 Overview Venous thromboembolism
The use of transthoracic echocardiography for diagnosis of pulmonary embolism: a case report and review literature
 2026 The use of transthoracic echocardiography for diagnosis of pulmonary embolism: a case report and review literature Mohammad Javad Alemzadeh-Ansari 1, Mohammad Hasan Alemzadeh-Ansari 2* 1 Department
2026 The use of transthoracic echocardiography for diagnosis of pulmonary embolism: a case report and review literature Mohammad Javad Alemzadeh-Ansari 1, Mohammad Hasan Alemzadeh-Ansari 2* 1 Department
Pulmonary Embolism. Pulmonary Embolism. Pulmonary Embolism. PE - Clinical
 Pulmonary embolus - a practical approach to investigation and treatment Sam Janes Wellcome Senior Fellow and Respiratory Physician, University College London Background Diagnosis Treatment Common: 50 cases
Pulmonary embolus - a practical approach to investigation and treatment Sam Janes Wellcome Senior Fellow and Respiratory Physician, University College London Background Diagnosis Treatment Common: 50 cases
Index. K Knobology, TTE artifact, image resolution, ultrasound, 14
 A Acute aortic regurgitation (AR), 124 128 Acute aortic syndrome (AAS) classic aortic dissection diagnosis, 251 263 evolutive patterns, 253 255 pathology, 250 251 classifications, 247 248 incomplete aortic
A Acute aortic regurgitation (AR), 124 128 Acute aortic syndrome (AAS) classic aortic dissection diagnosis, 251 263 evolutive patterns, 253 255 pathology, 250 251 classifications, 247 248 incomplete aortic
Screening for CETPH after acute pulmonary embolism: is it needed? Menno V. Huisman Department of Vascular Medicine LUMC Leiden
 Screening for CETPH after acute pulmonary embolism: is it needed? Menno V. Huisman Department of Vascular Medicine LUMC Leiden m.v.huisman@lumc.nl Background CETPH Chronic Thrombo Embolic Pulmonary Hypertension
Screening for CETPH after acute pulmonary embolism: is it needed? Menno V. Huisman Department of Vascular Medicine LUMC Leiden m.v.huisman@lumc.nl Background CETPH Chronic Thrombo Embolic Pulmonary Hypertension
Clinical Guide - Suspected PE (Reviewed 2006)
 Clinical Guide - Suspected (Reviewed 2006) Principal Developer: B. Geerts Secondary Developers: C. Demers, C. Kearon Background Investigation of patients with suspected pulmonary emboli () remains problematic
Clinical Guide - Suspected (Reviewed 2006) Principal Developer: B. Geerts Secondary Developers: C. Demers, C. Kearon Background Investigation of patients with suspected pulmonary emboli () remains problematic
QCVC Committees Scientific Activities Central Hall General Information FAC. SPECT tomography has the advantage of quantifying biventricular volumes.
 QCVC Committees Scientific Activities Central Hall General Information FAC Thematic Units Arrhythmias and Electrophysiology Basic Research Bioengineering and Medical Informatics Cardiac Surgical Intensive
QCVC Committees Scientific Activities Central Hall General Information FAC Thematic Units Arrhythmias and Electrophysiology Basic Research Bioengineering and Medical Informatics Cardiac Surgical Intensive
Questions on Chamber Quantitation
 Questions on Chamber Quantitation @RobertoMLang Which of the following statements is true? 1. The aortic annulus should be measured in midsystole. 2. The aortic annulus should be measured in enddiastole.
Questions on Chamber Quantitation @RobertoMLang Which of the following statements is true? 1. The aortic annulus should be measured in midsystole. 2. The aortic annulus should be measured in enddiastole.
Management of Pulmonary Embolism. Michael Hooper, M.D., MSc Associate Professor, Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Eastern Virginia Medical School
 Management of Pulmonary Embolism Michael Hooper, M.D., MSc Associate Professor, Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Eastern Virginia Medical School I have no conflicts of interest to report. VTE Overview
Management of Pulmonary Embolism Michael Hooper, M.D., MSc Associate Professor, Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Eastern Virginia Medical School I have no conflicts of interest to report. VTE Overview
Little is known about the degree and time course of
 Differential Changes in Regional Right Ventricular Function Before and After a Bilateral Lung Transplantation: An Ultrasonic Strain and Strain Rate Study Virginija Dambrauskaite, MD, Lieven Herbots, MD,
Differential Changes in Regional Right Ventricular Function Before and After a Bilateral Lung Transplantation: An Ultrasonic Strain and Strain Rate Study Virginija Dambrauskaite, MD, Lieven Herbots, MD,
Cor pulmonale. Dr hamid reza javadi
 1 Cor pulmonale Dr hamid reza javadi 2 Definition Cor pulmonale ;pulmonary heart disease; is defined as dilation and hypertrophy of the right ventricle (RV) in response to diseases of the pulmonary vasculature
1 Cor pulmonale Dr hamid reza javadi 2 Definition Cor pulmonale ;pulmonary heart disease; is defined as dilation and hypertrophy of the right ventricle (RV) in response to diseases of the pulmonary vasculature
Innovative Endovascular Approach to Pulmonary Embolism by Ultrasound Enhanced Thrombolysis. Prof. Ralf R.Kolvenbach MD,PhD,FEBVS
 Innovative Endovascular Approach to Pulmonary Embolism by Ultrasound Enhanced Thrombolysis Prof. Ralf R.Kolvenbach MD,PhD,FEBVS Conflict of Interest BTG Standard PE therapy ANTICOAGULATION (AC) HEPARIN
Innovative Endovascular Approach to Pulmonary Embolism by Ultrasound Enhanced Thrombolysis Prof. Ralf R.Kolvenbach MD,PhD,FEBVS Conflict of Interest BTG Standard PE therapy ANTICOAGULATION (AC) HEPARIN
Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension
 ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
Pulmonary Hypertension. Echocardiography: Pearls & Pitfalls
 Pulmonary Hypertension Echocardiography: Pearls & Pitfalls Αθανάσιος Γ. Κουτσάκης Ειδικευόμενος Καρδιολογίας Α Καρδιολογική Κλινική ΑΠΘ Σεμινάρια Ομάδων Εργασίας Ελληνικής Καρδιολογικής Εταιρείας Ιωάννινα,
Pulmonary Hypertension Echocardiography: Pearls & Pitfalls Αθανάσιος Γ. Κουτσάκης Ειδικευόμενος Καρδιολογίας Α Καρδιολογική Κλινική ΑΠΘ Σεμινάρια Ομάδων Εργασίας Ελληνικής Καρδιολογικής Εταιρείας Ιωάννινα,
Fig.1 Normal appearance of RV in SAX:
 Tutorial 7 - Assessment of the right heart Assessment of the Right heart The right heart assessment clinically and echocardiographically is not a very important part of mainstream cardiology. In the ICU,
Tutorial 7 - Assessment of the right heart Assessment of the Right heart The right heart assessment clinically and echocardiographically is not a very important part of mainstream cardiology. In the ICU,
Case Report Respirophasic Variations in the QRS Complex and Echocardiographic Equivalent in Pulmonary Embolism
 www.ipej.org 313 Case Report Respirophasic Variations in the QRS Complex and Echocardiographic Equivalent in Pulmonary Embolism Eftychios Siniorakis, MD, Spyridon Arvanitakis, BM, Dimitris Barlagiannis,
www.ipej.org 313 Case Report Respirophasic Variations in the QRS Complex and Echocardiographic Equivalent in Pulmonary Embolism Eftychios Siniorakis, MD, Spyridon Arvanitakis, BM, Dimitris Barlagiannis,
Diagnosis and initial treatment of patients with suspected pulmonary thromboembolism
 Diagnosis and initial treatment of patients with suspected pulmonary thromboembolism Pulmonary thromboembolism (PTE) remains a frequently occurring diagnostic problem, with an incidence of approximately
Diagnosis and initial treatment of patients with suspected pulmonary thromboembolism Pulmonary thromboembolism (PTE) remains a frequently occurring diagnostic problem, with an incidence of approximately
Troponin I and risk stratification of patients with acute nonmassive pulmonary embolism
 Eur Respir J 2008; 31: 847 853 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00113307 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2008 Troponin I and risk stratification of patients with acute nonmassive pulmonary embolism D. Jiménez*, G. Díaz*,
Eur Respir J 2008; 31: 847 853 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00113307 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2008 Troponin I and risk stratification of patients with acute nonmassive pulmonary embolism D. Jiménez*, G. Díaz*,
EAE RECOMMENDATIONS FOR TRANSESOPHAGEAL ECHO. Cardiac Sources of Embolism. Luigi P. Badano, MD, FESC
 EAE RECOMMENDATIONS FOR TRANSESOPHAGEAL ECHO. Cardiac Sources of Embolism Luigi P. Badano, MD, FESC Background Stroke is the 3 cause of death in several industrial countries; Embolism accounts for 15-30%
EAE RECOMMENDATIONS FOR TRANSESOPHAGEAL ECHO. Cardiac Sources of Embolism Luigi P. Badano, MD, FESC Background Stroke is the 3 cause of death in several industrial countries; Embolism accounts for 15-30%
Echocardiographic Guidance During Placement of the Buttoned Double-Disk Device for Atrial Septa1 Defect Closure
 Echocardiographic Guidance During Placement of the Buttoned Double-Disk Device for Atrial Septa1 Defect Closure L. LUANN MINICH, M.D., and A. REBECCA SNIDER, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, C.S. Mott Children
Echocardiographic Guidance During Placement of the Buttoned Double-Disk Device for Atrial Septa1 Defect Closure L. LUANN MINICH, M.D., and A. REBECCA SNIDER, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, C.S. Mott Children
Single-Center, Retrospective, Observational Analysis of Patients with Submassive Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Receiving Catheter- Directed Thrombolysis
 Single-Center, Retrospective, Observational Analysis of Patients with Submassive Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Receiving Catheter- Directed Thrombolysis John A. Phillips, M.D. OhioHealth Heart and Vascular Physicians
Single-Center, Retrospective, Observational Analysis of Patients with Submassive Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Receiving Catheter- Directed Thrombolysis John A. Phillips, M.D. OhioHealth Heart and Vascular Physicians
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (April 2018) Vol. 71 (3), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (April 2018) Vol. 71 (3), Page 2681-2688 Assessment of Pulmonary Embolism Severity and Scoring Using Multi Slice CT in Correlation with Clinical Presentation and
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (April 2018) Vol. 71 (3), Page 2681-2688 Assessment of Pulmonary Embolism Severity and Scoring Using Multi Slice CT in Correlation with Clinical Presentation and
Echocardiography can noninvasively
 Bedside echocardiography in the assessment of the critically ill Yanick Beaulieu, MD, FRCPC Advances in ultrasound technology continue to enhance its diagnostic applications in daily medical practice.
Bedside echocardiography in the assessment of the critically ill Yanick Beaulieu, MD, FRCPC Advances in ultrasound technology continue to enhance its diagnostic applications in daily medical practice.
Postoperative Acute Pulmonary Embolism: A Case Report. S Mishra, P Kundra, B Hemavathi, A Badhe, M Ravishankar
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 13 Number 2 S Mishra, P Kundra, B Hemavathi, A Badhe, M Ravishankar Citation S Mishra, P Kundra, B Hemavathi, A Badhe, M Ravishankar.. The Internet
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 13 Number 2 S Mishra, P Kundra, B Hemavathi, A Badhe, M Ravishankar Citation S Mishra, P Kundra, B Hemavathi, A Badhe, M Ravishankar.. The Internet
Evaluation of the Right Ventricle in Candidates for Right Ventricular Assist Device Implantation.
 Evaluation of the Right Ventricle in Candidates for Right Ventricular Assist Device Implantation. Evaluation of RVAD Function. Ioannis A Paraskevaidis Attikon University Hospital Historical Perspective
Evaluation of the Right Ventricle in Candidates for Right Ventricular Assist Device Implantation. Evaluation of RVAD Function. Ioannis A Paraskevaidis Attikon University Hospital Historical Perspective
Copyright 2017 American College of Emergency Physicians. All rights reserved.
 POLICY Approved April 2017 Guidelines for the Use of Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE) in the ED for Cardiac Arrest Approved by the ACEP Board of Directors April 2017 1. Introduction The American
POLICY Approved April 2017 Guidelines for the Use of Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE) in the ED for Cardiac Arrest Approved by the ACEP Board of Directors April 2017 1. Introduction The American
Case Report Mobile Intracardiac Mass after Inguinal Hernia Repair: An Unresolved Treatment Dilemma
 Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2015, Article ID 375089, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/375089 Case Report Mobile Intracardiac Mass after Inguinal Hernia Repair: An Unresolved Treatment Dilemma
Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2015, Article ID 375089, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/375089 Case Report Mobile Intracardiac Mass after Inguinal Hernia Repair: An Unresolved Treatment Dilemma
A cute pulmonary embolism (APE) is a common disease
 956 PULMONARY VASCULATURE Computed tomographic pulmonary angiography and prognostic significance in patients with acute pulmonary embolism A Ghuysen, B Ghaye, V Willems, B Lambermont, P Gerard, R F Dondelinger,
956 PULMONARY VASCULATURE Computed tomographic pulmonary angiography and prognostic significance in patients with acute pulmonary embolism A Ghuysen, B Ghaye, V Willems, B Lambermont, P Gerard, R F Dondelinger,
You Won t Believe What I Saw on. Disclosures. Goals. Dimensions 2013 October 18 th Michael Pfeiffer, MD. No Financial Disclosures
 You Won t Believe What I Saw on that ECHO! Dimensions 2013 October 18 th Michael Pfeiffer, MD Disclosures No Financial Disclosures Goals Review unusual and unique echocardiographic images. Briefly present
You Won t Believe What I Saw on that ECHO! Dimensions 2013 October 18 th Michael Pfeiffer, MD Disclosures No Financial Disclosures Goals Review unusual and unique echocardiographic images. Briefly present
Epidermiology Early pulmonary embolism
 Epidermiology Early pulmonary embolism Sitang Nirattisaikul Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 3 rd most common cause of cardiovascular death in the United States, following ischemic heart
Epidermiology Early pulmonary embolism Sitang Nirattisaikul Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 3 rd most common cause of cardiovascular death in the United States, following ischemic heart
Echocardiographic Cardiovascular Risk Stratification: Beyond Ejection Fraction
 Echocardiographic Cardiovascular Risk Stratification: Beyond Ejection Fraction October 4, 2014 James S. Lee, M.D., F.A.C.C. Associates in Cardiology, P.A. Silver Spring, M.D. Disclosures Financial none
Echocardiographic Cardiovascular Risk Stratification: Beyond Ejection Fraction October 4, 2014 James S. Lee, M.D., F.A.C.C. Associates in Cardiology, P.A. Silver Spring, M.D. Disclosures Financial none
The Right Ventricle in Critical Illness
 38 The Open Critical Care Medicine Journal, 2010, 3, 38-42 The Right Ventricle in Critical Illness Artur Alaverdian and Rubin I. Cohen * Open Access The Division of Pulmonary, Sleep and Critical Care Medicine,
38 The Open Critical Care Medicine Journal, 2010, 3, 38-42 The Right Ventricle in Critical Illness Artur Alaverdian and Rubin I. Cohen * Open Access The Division of Pulmonary, Sleep and Critical Care Medicine,
Dr. Rami M. Adil Al-Hayali Assistant Professor in Medicine
 Dr. Rami M. Adil Al-Hayali Assistant Professor in Medicine Venous thromboembolism: pulmonary embolism (PE) deep vein thrombosis (DVT) 1% of all patients admitted to hospital 5% of in-hospital mortality
Dr. Rami M. Adil Al-Hayali Assistant Professor in Medicine Venous thromboembolism: pulmonary embolism (PE) deep vein thrombosis (DVT) 1% of all patients admitted to hospital 5% of in-hospital mortality
Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) and the essential role of imaging specialists PP-ADE-ALL
 Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) and the essential role of imaging specialists PP-ADE-ALL-0086-2 CTEPH and the essential role of imaging specialists 1 Introduction, and signs, symptoms
Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) and the essential role of imaging specialists PP-ADE-ALL-0086-2 CTEPH and the essential role of imaging specialists 1 Introduction, and signs, symptoms
Left ventricle pseudoaneurysm as late postoperative complication of a large apical aneurysm
 CASE REPORT Left ventricle pseudoaneurysm as late postoperative complication of a large apical aneurysm Mariana M. Floria 1, 4, Carmen Elena Pleșoianu 2, 4, Michel Buche 3, Baudouin Marchandise 4, Erwin
CASE REPORT Left ventricle pseudoaneurysm as late postoperative complication of a large apical aneurysm Mariana M. Floria 1, 4, Carmen Elena Pleșoianu 2, 4, Michel Buche 3, Baudouin Marchandise 4, Erwin
N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide in patients with acute pulmonary embolism
 Eur Respir J 23; 22: 649 653 DOI: 1.1183/931936.3.2333 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 23 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide
Eur Respir J 23; 22: 649 653 DOI: 1.1183/931936.3.2333 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 23 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide
RISK STRATIFICATION OF PATIENTS WITH ACUTE SYMPTOMATIC PULMONARY EMBOLISM. David Jiménez, MD, PhD, FCCP Ramón y Cajal Hospital, IRYCIS Madrid, Spain
 RISK STRATIFICATION OF PATIENTS WITH ACUTE SYMPTOMATIC PULMONARY EMBOLISM David Jiménez, MD, PhD, FCCP Ramón y Cajal Hospital, IRYCIS Madrid, Spain Potential Conflicts of Interest Financial conflicts of
RISK STRATIFICATION OF PATIENTS WITH ACUTE SYMPTOMATIC PULMONARY EMBOLISM David Jiménez, MD, PhD, FCCP Ramón y Cajal Hospital, IRYCIS Madrid, Spain Potential Conflicts of Interest Financial conflicts of
Epidemiology of Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
 Why Treat Submassive PE Abstract: Massive Pulmonary Embolism (PE) requires immediate lifesaving intervention for the patient. For the submassive PE patient, characterized by presence of right ventricular
Why Treat Submassive PE Abstract: Massive Pulmonary Embolism (PE) requires immediate lifesaving intervention for the patient. For the submassive PE patient, characterized by presence of right ventricular
25 different brand names >44 different models Sizes mm
 Types of Prosthetic Valves BIOLOGIC STENTED Porcine xenograft Pericardial xenograft STENTLESS Porcine xenograft Pericardial xenograft Homograft (allograft) Autograft PERCUTANEOUS MECHANICAL Bileaflet Single
Types of Prosthetic Valves BIOLOGIC STENTED Porcine xenograft Pericardial xenograft STENTLESS Porcine xenograft Pericardial xenograft Homograft (allograft) Autograft PERCUTANEOUS MECHANICAL Bileaflet Single
Pericardial Diseases. Smonporn Boonyaratavej, MD. Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University
 Pericardial Diseases Smonporn Boonyaratavej, MD Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Cardiac Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital 21 AUGUST 2016 Pericardial
Pericardial Diseases Smonporn Boonyaratavej, MD Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Cardiac Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital 21 AUGUST 2016 Pericardial
Role of echocardiography in a patient with suspected acute pulmonary embolism: a case report
 Miranda-Bacallado et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports (2019) 13:37 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-019-1994-y CASE REPORT Open Access Role of echocardiography in a patient with suspected acute pulmonary
Miranda-Bacallado et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports (2019) 13:37 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-019-1994-y CASE REPORT Open Access Role of echocardiography in a patient with suspected acute pulmonary
Rotation: Echocardiography: Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE)
 Rotation: Echocardiography: Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE) Rotation Format and Responsibilities: Fellows rotate in the echocardiography laboratory in each clinical year. Rotations during the first
Rotation: Echocardiography: Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE) Rotation Format and Responsibilities: Fellows rotate in the echocardiography laboratory in each clinical year. Rotations during the first
Atrial Septal Defect Closure. Stephen Brecker Director, Cardiac Catheterisation Labs
 Stephen Brecker Director, Cardiac Catheterisation Labs ADVANCED ANGIOPLASTY Incorporating The Left Main 5 Plus Course Conflicts of Interest The following companies have supported educational courses held
Stephen Brecker Director, Cardiac Catheterisation Labs ADVANCED ANGIOPLASTY Incorporating The Left Main 5 Plus Course Conflicts of Interest The following companies have supported educational courses held
Case 47 Clinical Presentation
 93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
Pulmonary arteriovenous fistula
 International Journal of Medical Imaging 2014; 2(2): 34-38 Published online April 10, 2014 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmi) doi: 10.11648/j.ijmi.20140202.16 Pulmonary arteriovenous fistula
International Journal of Medical Imaging 2014; 2(2): 34-38 Published online April 10, 2014 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmi) doi: 10.11648/j.ijmi.20140202.16 Pulmonary arteriovenous fistula
Assessing the Impact on the Right Ventricle
 Advances in Tricuspid Regurgitation Congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Munich, August 25-29, 2012 Assessing the Impact on the Right Ventricle Stephan Rosenkranz, MD Clinic III for Internal
Advances in Tricuspid Regurgitation Congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Munich, August 25-29, 2012 Assessing the Impact on the Right Ventricle Stephan Rosenkranz, MD Clinic III for Internal
Atrial Septal Defects
 Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
PULMONARY EMBOLISM -CASE REPORT-
 University Goce Delcev, Faculty of Medical sciences, Stip University Clinic of Cardiology, Skopje R. Of Macedonia PULMONARY EMBOLISM -CASE REPORT- Gordana Kamceva MD mr.sci Acknowledgment Marija Vavlukis
University Goce Delcev, Faculty of Medical sciences, Stip University Clinic of Cardiology, Skopje R. Of Macedonia PULMONARY EMBOLISM -CASE REPORT- Gordana Kamceva MD mr.sci Acknowledgment Marija Vavlukis
DIAGNOSIS. Profiles in Pulmonary Embolism
 31 Profiles in Pulmonary Embolism Samuel Z. Goldhaber Harvard Medical School, Division of Cardiovascular, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts 02115 As fewer pulmonary angiograms are required
31 Profiles in Pulmonary Embolism Samuel Z. Goldhaber Harvard Medical School, Division of Cardiovascular, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts 02115 As fewer pulmonary angiograms are required
New Criteria for Ventilation-Perfusion Lung Scan Interpretation: A Basis for Optimal Interaction with Helical CT Angiography 1
 1206 July-August 2000 RG Volume 20 Number 4 New Criteria for Ventilation-Perfusion Lung Scan Interpretation: A Basis for Optimal Interaction with Helical CT Angiography 1 Alexander Gottschalk, MD Introduction
1206 July-August 2000 RG Volume 20 Number 4 New Criteria for Ventilation-Perfusion Lung Scan Interpretation: A Basis for Optimal Interaction with Helical CT Angiography 1 Alexander Gottschalk, MD Introduction
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING
 PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
The role of multi-organ ultrasonography for diagnosing non-massive pulmonary thromboembolism.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 8044-8049 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info The role of multi-organ ultrasonography for diagnosing non-massive pulmonary thromboembolism. Ülkü Aka Aktürk *, Nagihan Durmuş
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 8044-8049 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info The role of multi-organ ultrasonography for diagnosing non-massive pulmonary thromboembolism. Ülkü Aka Aktürk *, Nagihan Durmuş
Pulmonary Embolism Newer Concepts and Role of Thrombolysis
 CHAPTER 69 Pulmonary Embolism Newer Concepts and Role of Thrombolysis J. P. S. Sawhney, A. Bakhshi, B. Kandpal Introduction Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a common cardiovascular and cardiopulmonary illness
CHAPTER 69 Pulmonary Embolism Newer Concepts and Role of Thrombolysis J. P. S. Sawhney, A. Bakhshi, B. Kandpal Introduction Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a common cardiovascular and cardiopulmonary illness
pulmonary thrombosis in Eisenmenger ASD: A case report
 In situ RV thrombus with diffuse pulmonary thrombosis in Eisenmenger ASD: A case report You-Chun Huang,MD; Wei- Hsien Yin, MD,PHD. Cheng-Hsin general hospital,taiwan. 1 Present illness A 38-year-old female
In situ RV thrombus with diffuse pulmonary thrombosis in Eisenmenger ASD: A case report You-Chun Huang,MD; Wei- Hsien Yin, MD,PHD. Cheng-Hsin general hospital,taiwan. 1 Present illness A 38-year-old female
Floating right heart thrombi (FRHTS) are uncommon but
 Free-Floating Thrombi in the Right Heart Diagnosis, Management, and Prognostic Indexes in 38 Consecutive Patients Ludovic Chartier, MD; Jérôme Béra, MD; Maxence Delomez, MD; Philippe Asseman, MD; Jean-Paul
Free-Floating Thrombi in the Right Heart Diagnosis, Management, and Prognostic Indexes in 38 Consecutive Patients Ludovic Chartier, MD; Jérôme Béra, MD; Maxence Delomez, MD; Philippe Asseman, MD; Jean-Paul
Real life management of CTEPH: patient case
 2 nd International Congress on cardiovascular imaging in clinical practice k Real life management of CTEPH: patient case Anastasia Anthi Pulmonary Hypertension Clinic, Attikon University Hospital, Athens
2 nd International Congress on cardiovascular imaging in clinical practice k Real life management of CTEPH: patient case Anastasia Anthi Pulmonary Hypertension Clinic, Attikon University Hospital, Athens
