of the tumour and its effect on the functional The patient, a 17-year-old white youth, was adholz, to the Eugene Talmadge Memorial Hospital
|
|
|
- Myron James
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 British Heart Journal, 1977, 39, Echocardiographic features of cardiac compression by a thymoma simulating cardiac tamponade and obstruction of the superior vena cava MARIO I. CANEDO, LUTHER OTKEN, AND MILTIADIS A. STEFADOUROS From the Sections of Cardiology and Pathology, Medical College of Georgia, Augusta, Georgia 30902, U.S.A. A patient with a large tumour of the superior mediastinum, detected by routine chest x-ray examination, is presented. Compression of the heart and the superior mediastinum produced the clinical picture of cardiac tamponade and obstruction of the superior vena cava and trachea. The solid nature of the tumour was established by echocardiography which, in addition, showed: (1) posterior displacement of the heart; (2) diminished dimensions of the left atrium and left ventricle; (3) prominent respiratory variation in the position of the interventricular septum, the dimensions of both ventricles, and the duration of systolic separation of the aortic valve cusps; and (4) 'pseudo-prolapse' of the mitral valve. All abnormal clinical signs and echocardiographic findings disappeared promptly after surgical resection of the tumour which was found to be a thymoma. Large 'tumours' of the anterior mediastinum occasionally produce clinical symptoms and physical anatomy of the heart were studied by echocardio- of the tumour and its effect on the functional signs suggestive of heart disease (Shaver et al., graphy. 1965; Allee et al., 1973; Peterson et al., 1975; Schloss et al., 1975). Though plain chest x-ray Case report films can easily show their presence, more sophisticated radiological (Ferrane et al., 1970), angiocardiographic (Kincaid et al., 1960), or ultrasonic (Birnmitted to the Eugene Talmadge Memorial Hospital The patient, a 17-year-old white youth, was adholz, 1973; Friday, 1973; Goldberg, 1973; Cardello on 20 May He had been in apparently good et al., 1974; Peterson et al., 1975; Schloss et al., health until one month before admission when he 1975) techniques are usually required to establish began having progressive dyspnoea at rest, followed their extracardiac origin and to define their gross by dysphagia, dysphonia, and weight loss of morphology further. B-scan ultrasonography has 6-8 kg (15 lb). He also noticed distension of his been successfully used to separate cystic from solid neck and arm veins and swelling of the neck and mediastinal masses (Friday, 1973; Peterson et al., face. On physical examination the patient was in 1975) but the very nature of this technique precludes assessment of the possible mechanical effects stridor and a respiratory rate of 28/min. There was moderate respiratory distress with inspiratory of the tumour on the function of the contracting distinct venous distension with moderate oedema heart. In two recent reports of the use of M-mode and cyanosis involving the head, neck, upper chest, echocardiography in the diagnosis of a large pericardial cyst (Peterson et al., 1975) or a cystic to the angle of the mandible in the sitting or standing and the arms. The jugular veins were distended up thymoma (Schloss et al., 1975), no echocardiographic evidence of mechanical interference of these rate was 88/min and showed sinus arrhythmia. position without any visible pulsations. The pulse 'tumours' with the function of the heart was noted. The carotid and other peripheral arterial pulses This report describes a patient with a large superior were normal on expiration but very weak on inspiration; the blood pressure on expiration was mediastinal tumour producing clinical manifestations of cardiac tamponade and obstruction of the 110/80 mmhg, with a 40 mmhg pulsus paradoxus. superior vena cava, in whom both the gross nature The apex beat was not palpable. On auscultation the 1038
2 Echocardiographic features of heart compressed by thymoma heart sounds were normal; there were no murmurs or added sounds. Examination of the remainder of the systems was noncontributory. The haemoglobin was 15 g/dl and the haematocrit 43 per cent. The electrocardiogram and other laboratory findings were normal. The chest x-ray film showed a large mass in the superior and anterior mediastinum; the heart was normal in size and configuration but displaced posteriorly (Fig. 1, upper). NONINVASIVE STUDY The M-mode echocardiogram, phonocardiogram, external carotid pulse, and respiratory tracing were simultaneously recorded on a strip chart, with the patient in a semi-reclining position. Fig. 2 shows a slow continuous M-mode sector scan obtained from the fourth intercostal space parasternally. With the transducer directed superiorly and slightly medially, the aortic root could be seen at a depth of 5-5 to 8 cm 1039 Fig. 1 Posteroanterior (left) and left lateral (right) chest film taken before (upper) and 11 days after surgical resection of the thymoma (lower). Note the remaining part of the tumour in the superior mediastinum in the right upper lung field. Also note posterior displacement of the heart by the tumour (upper right) with return of the heart in the normal anterior position after removal of the tumour (lower right). from the posterior surface of the anterior chest wall, the intervening space being occupied by a homogeneous 4 5 cm wide band of echoes originating from the tumour (T). These tumour echoes appeared as parallel lines of medium intensity with a small (1 to 2 mm) amplitude motion whose directionanterior in systole and posterior in diastole-was similar to that of the aortic root, from which they were presumably transmitted. The anterior wall of the right ventricle was about 5 cm from the anterior chest wall in close proximity to the anterior aortic wall. The anteroposterior dimensions of the right ventricular outflow tract and the left atrium were diminished (0 5 to 0*1 cm). The aortic valve echogram was normal but the duration of the ejection was abbreviated on inspiration. There was striking respiratory variation in the dimensions of the ventricles (Fig. 2, lower); thus, a prominent posterior displacement of the septum on inspiration was
3 1040 T ECG ---- U. T - AO -..r "M=te 'IN -1 NW, I_ * L _w-r WOMPONNAMONSIO ll. 7.w :.: :;:,%..::'.:,. 1- Seo c4 I,-:! :' :,,,.::.:. somma Canedo, Otken, and Stefadouros Fig. 2 Preoperative echocardiographic scan (continuous recording). The band of echoes from the tumour (T) are seen to occupy the space between the anterior wall of the right ventricle (shown by the arrow on the lower tracing) and the anterior chest wall(cw). Note the progressive decrease in tumour dimension as the scan moves from the base of the heart towards the apex. See text for discussion. ECG, electrocardiogram, AO, aortic root; LA, left atrium; S, interventricular septum. The tissue depth scale is constant throughout and shown at the ens of the lower tracing. In this and all subsequent tracings the respiratory trace (R) moves upward on inspiration. Fig. 3 Preoperative echocardiograms obtained with the transducer held stationary on the chest wall and pointed toward the respective valves. Upper: Note the effect of respiration (R) on the position of the septum (S), on the right ventricular dimension, and on the degree of 'pseudo-prolapse' of the anterior mitral valve leaflet (MV). The space between the anterior wall of the right ventricle (RVW) and the chest wall is occupied by the tumour (T). Lower: Note the posterior displacement of the aortic root and the profound effect of respiration on the duration of ejection as measured on the aorticvalve echogram. The ejection time is 240 ms on expiration, whereas on inspiration the aortic valve barely opens for 80 ms (black arrow). See text for discussion. C, external carotid pulse tracing. Other abbreviations as in Fig. 2.
4 Echocardiographic features of heart compressed by thymoma primarily responsible for an increase in right ventricular dimension at the expense of the left ventricle whose end-diastolic dimension varied from about 35 mm on expiration to 25 mm on inspiration. The mitral valve showed a prominent systolic posterior movement that became maximal on expiration (Fig. 3, upper). In the lower strip of Fig. 3, the profound effect of respiration on the volume and output of the left ventricle can be appreciated; thus, the ejection time, as measured on both the carotid pulse tracing and the aortic valve echogram (Stefadouros and Witham, 1975), varied from a maximal value of 240 ms on expiration (5th beat, lower strip, Fig. 3) to a minimal value of 80 ms on inspiration, during which the aortic valve barely opened and the carotid pulse tracing collapsed (3rd beat, lower strip, Fig. 3). Intermediate values for the ejection time were observed in other beats. Because of increasing respiratory distress, an emergency thoractomy was carried out on the day after admission, and the greater part of the tumour was excised. It was impossible to resect it entirely because of its extension into the superior portion of the anterior mediastinum laterally and posteriorly around the great vessels, trachea, and oesophagus. The excised mass, a poorly differentiated thymocytic thymoma, was a solid tumour of 988 g, containing a few areas of cystic degeneration. After operation the patient was initially supported by a mechanical respirator, and received a course of irradiation to the mediastinum (total dose 4800 rads), with considerable symptomatic improvement. The postoperative chest x-ray film (Fig. 1, lower) showed the remaining part of the tumour in the superior mediastinum; the heart size, configuration, and position were normal. An echogram carried out on the 10th postoperative day showed the remainder of the tumour as a 1 cm band immediately behind the anterior wall of the chest, normal dimensions of the cardiac cavities without respiratory variation, disappearance of the mitral valve 'pseudo-prolapse' seen before operation, and a small effusion behind the posterior wall of the left atrium. The ejection time was normal and unaffected by respiration. Discussion The clinical syndrome of cardiac tamponade, superior vena caval obstruction, dysphagia, and respiratory distress in this patient can be completely accounted for by the mechanical compression the tumour exerted on the heart, superior vena cava, oesophagus, and trachea, respectively. Though the tumour-being obvious on the chest film-was not actually 'discovered' by M-mode echocardiography, this technique was very useful in two respects: 1041 it demonstrated the extracardiac situation and solid nature of the tumour, and it excluded possibly coexisting cardiac lesions whose presence might have been obscured by the dramatic clinical picture produced by the tumour. Large anterior or superior mediastinal masses are easily detectable on routine chest x-ray films but their differentiation from cardiomegaly or vascular tumours, and the determination of their gross anatomy usually necessitate additional radiographic, angiocardiographic, or ultrasonic studies. Ultrasound B-scan examination has been often, though not invariably (Cardello et al., 1974), successful in making the clinically important discrimination between solid and cystic mediastinal masses (Friday, 1973; Peterson et al., 1975), and similar results have been obtained with A-mode ultrasonography (Birnbolz, 1973; Goldberg, 1973). In at least two cases, M-mode echocardiography has been successful in defining the cystic nature of a large pericardial cyst (Friday, 1973) and a large cystic thymoma (Schloss et al., 1975) and excluding any associated heart abnormality, other than a prolapsed mitral valve found in the former case (Friday, 1973). The echocardiographic appearance of the tumour in our patient was indicative of a solid mass. Thus, at a gain level low enough to permit visualisation of the heart cavities as echo-free spaces, discrete linear echoes of medium intensity were present at any depth within the tumour (Fig. 3). Furthermore, these echoes showed a small but distinct systolic anterior motion which was concordant and synchronous with that of the aortic root from which it was presumably transmitted. This echocardiographic pattern bears no resemblance to the echofree space observed by M-mode echocardiography in cases of cystic masses (Schloss et al., 1975; Peterson et al., 1975). The echogram of the heart itself was helpful in excluding such conditions as constrictive pericarditis or pericardial effusion as a cause of the cardiac tamponade. Mechanical external compression of the heart by the tumour significantly affected the echocardiographic functional anatomy of the heart. Thus, the normal phenomenon of decreased left ventricular (and increased right ventricular) filling on inspiration was much exaggerated in this patient, resulting in a drastic inspiratory curtailment of left ventricular stroke volume and ejection time, and a prominent pulsus paradoxus. Similar, pronounced reciprocal respiratory variations in the echocardiographic dimension and hence volume of the two ventricles is a frequent finding in patients with significant pericardial effusion (unpublished observations), in whom a posterior 'pseudo-prolapse' of
5 1042 the mitral valve is also occasionally seen (Levisman and Abbasi, 1976; Vignola et al., 1976). The functional nature of this 'pseudo-prolapse' and its indirect association with the compression of the heart in these cases is established by its prompt disappearance after aspiration of the pericardial effusion (Levisman and Abbasi, 1976; Vignola et al., 1976) or, in this patient, resection of the compressing mediastinal tumour. Our experience from this patient together with that of other investigators indicates that M-mode echocardiography is as useful as other noninvasive radiographic or ultrasonic techniques in the evaluation of mediastinal tumours and their mechanical effect upon the function of the heart. References Allee G., Logue, B., and Mansour, K. (1973). Thymic cys I simulating multiple cardiovascular abnormalities and presenting with pericarditis and pericardial tamponade. American Journal of Cardiology, 31, Birnholz, J. C. (1973). Sonic differentiation of cysts and homogeneous solid masses. Radiology, 108, Cardello, F. P.,McQuown, D. S., and Dollinger, M. (1974). Ultrasound in diagnosis of parapericardial masses. (Letter to the Editor.) J'ournal of the American Medical Association, 227, Ferran6, J., Guermonprez, J. L., Vasile, N., and Maurice, P. (1970). Silhouette cardiaque anormale et tumeurs thymiques. Journal de Radiologie et d'electrologie et de Medecine Nucleaire, 51, Notice Canedo, Otken, and Stefadouros Friday, R. 0. (1973). Paracardiac cyst: diagnosis by ultrasound and puncture. (Letter to the Editor.) Journal of the American Medical Association, 226, 82. Goldberg, B. B. (1973). Mediastinal ultrasonography. journal of Clinical Ultrasound, 1, Kincaid, 0. W., Brandenburg, R. O., and Bernatz, P. E. (1960). Experiences with angiography as a guide to mediastinal exploration. J'ournal of the American Medical Association, 173, Levisman, J. A., and Abbasi, A. S. (1976). Abnormal motion of the mitral valve with pericardial effusion: pseudoprolapse of the mitral valve. American Heart J7ournal, 91, Peterson, D. T., Zatz, L. M., and Popp, R. L. (1975). Pericardial cyst ten years after acute pericarditis. Chest, 67, Schloss, M., Kronzon, I., Gelber, P. M., Reed, G. E., and Berger, A. (1975). Cystic thymoma simulating constrictive pericarditis. The role of echocardiography in the differential diagnosis. Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, 70, Shaver, V. C., Bailey, W. R., and Marrangoni, A. G. (1965). Acquired pulmonic stenosis due to external cardiac compression. American Journal of Cardiology, 16, Stefadouros, M. A., and Witham, A. C. (1975). Systolic time intervals by echocardiography. Circulation, 51, Vignola, P. A., Pohost, G. M., Curfman, G. D., and Myers, G. S. (1976). Correlation of echocardiographic and clinical findings in patients with pericardial effusion. American Journal of Cardiology, 37, Requests for reprints to Dr. Miltiadis A. Stefadouros, Section of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, Medical College of Georgia, Augusta, Georgia 30902, U.S.A. Clinical application of intra-aortic balloon pump A course will be held on November 1977 at the Konover Hotel, Miami Beach, Florida. It will cover indications for use of the intra-aortic balloon pump and other circulatory assist devices for patients in cardiogenic shock. Information can be obtained by writing to Division of Continuing Medical Education, University of Miami School of Medicine, PO Box , Miami, Florida 33152, U.S.A. (Tel. A/C ).
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1
 Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 PERICARDIAL DISEASE The pericardial effusion ends anteriorly to the descending aorta and is best visualised in the PLAX. PSAX is actually very useful sometimes for looking at posterior
Adel Hasanin Ahmed 1 PERICARDIAL DISEASE The pericardial effusion ends anteriorly to the descending aorta and is best visualised in the PLAX. PSAX is actually very useful sometimes for looking at posterior
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy.
 HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus. Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE)
 Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE) Purpose: Rapid Cardiac Echocardiography (RCE) This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE) Purpose: Rapid Cardiac Echocardiography (RCE) This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by the fact that a murmur was heard at birth?
 HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
Aortic root and left atrial wall motion
 British Heart Journal, 1977, 39, 1082-1087 Aortic root and left atrial wall motion An echocardiographic study GONES AKGtYN AND CLIVE LAYTON1 From the Cardiac Department, The London Hospital, London The
British Heart Journal, 1977, 39, 1082-1087 Aortic root and left atrial wall motion An echocardiographic study GONES AKGtYN AND CLIVE LAYTON1 From the Cardiac Department, The London Hospital, London The
Heart and Lungs. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship of pulmonary parenchyma to heart and chest wall.
 Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
PRACTICAL GUIDE TO FETAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IC Huggon and LD Allan
 PRACTICAL GUIDE TO FETAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IC Huggon and LD Allan Fetal Cardiology Unit, Harris Birthright Research Centre for Fetal Medicine, King's College Hospital, London, UK IMPORTANCE OF PRENATAL
PRACTICAL GUIDE TO FETAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IC Huggon and LD Allan Fetal Cardiology Unit, Harris Birthright Research Centre for Fetal Medicine, King's College Hospital, London, UK IMPORTANCE OF PRENATAL
PERICARDIAL DIAESE. Kaijun Cui Associated professor Sichuan University
 PERICARDIAL DIAESE Kaijun Cui Associated professor Sichuan University CLASSIFICATION acute pericarditis pericardial effusion cardiac tamponade constrictive pericarditis congenitally absent pericardium
PERICARDIAL DIAESE Kaijun Cui Associated professor Sichuan University CLASSIFICATION acute pericarditis pericardial effusion cardiac tamponade constrictive pericarditis congenitally absent pericardium
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies
 Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
2. The heart sounds are produced by a summed series of mechanical events, as follows:
 Heart Sounds. Phonocardiography 1 Objectives 1. Phonocardiography - Definition 2. What produces the heart sounds 3. Where to listen for the heart sounds 4. How to record a phonocardiogram 5. Normal heart
Heart Sounds. Phonocardiography 1 Objectives 1. Phonocardiography - Definition 2. What produces the heart sounds 3. Where to listen for the heart sounds 4. How to record a phonocardiogram 5. Normal heart
Echocardiographic Patterns of Pulmonic Valve Motion with Pulmonary Hypertension
 Echocardiographic Patterns of Pulmonic Valve Motion with Pulmonary Hypertension By ARTHUR E. WEYMAN, M.D., JAMES C. DILLON, M.D., HARVEY FEIGENBAUM, M.D., AND SONIA CHANG, B.A. SUMMARY Echocardiographic
Echocardiographic Patterns of Pulmonic Valve Motion with Pulmonary Hypertension By ARTHUR E. WEYMAN, M.D., JAMES C. DILLON, M.D., HARVEY FEIGENBAUM, M.D., AND SONIA CHANG, B.A. SUMMARY Echocardiographic
Pseudo Heart Disease: 1/5 Norman Bethune Faculty of Medicine, Jilin University, China
 http://www.medicine-on-line.com Pseudo Heart Disease: 1/5 Case 060: Pseudo Heart Disease Author: Affiliation: Zhang Shu Norman Bethune Faculty of Medicine, Jilin University, China A 17 year-old girl presented
http://www.medicine-on-line.com Pseudo Heart Disease: 1/5 Case 060: Pseudo Heart Disease Author: Affiliation: Zhang Shu Norman Bethune Faculty of Medicine, Jilin University, China A 17 year-old girl presented
HISTORY. Question: How do you interpret the patient s history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: 45-year-old man.
 HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
The Cardiac Cycle Clive M. Baumgarten, Ph.D.
 The Cardiac Cycle Clive M. Baumgarten, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe periods comprising cardiac cycle and events within each period 2. Describe the temporal relationships between pressure, blood flow,
The Cardiac Cycle Clive M. Baumgarten, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe periods comprising cardiac cycle and events within each period 2. Describe the temporal relationships between pressure, blood flow,
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Manila Times College of Subic Prepared by: Stevens B. Badar, RN, MANc THE HEART Anatomy of the Heart Location and Size approx. the size of a person s fist, hollow and cone-shaped,
The Cardiovascular System The Manila Times College of Subic Prepared by: Stevens B. Badar, RN, MANc THE HEART Anatomy of the Heart Location and Size approx. the size of a person s fist, hollow and cone-shaped,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II
 Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of this session, the student should be able to: Identify and discuss clinical anatomy of mediastinum such as its deflection,
Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of this session, the student should be able to: Identify and discuss clinical anatomy of mediastinum such as its deflection,
HEALTH ASSESSMENT. Afnan Tunsi BSN, RN, MSc.
 HEALTH ASSESSMENT Afnan Tunsi BSN, RN, MSc. Learning Outcomes 2 After completion of this lecture, the student will be able to: Describe suggested sequencing to conduct a thorax and lungs physical health
HEALTH ASSESSMENT Afnan Tunsi BSN, RN, MSc. Learning Outcomes 2 After completion of this lecture, the student will be able to: Describe suggested sequencing to conduct a thorax and lungs physical health
Hemodynamic Monitoring
 Perform Procedure And Interpret Results Hemodynamic Monitoring Tracheal Tube Cuff Pressure Dean R. Hess PhD RRT FAARC Hemodynamic Monitoring Cardiac Rate and Rhythm Arterial Blood Pressure Central Venous
Perform Procedure And Interpret Results Hemodynamic Monitoring Tracheal Tube Cuff Pressure Dean R. Hess PhD RRT FAARC Hemodynamic Monitoring Cardiac Rate and Rhythm Arterial Blood Pressure Central Venous
Pericardial Diseases. Smonporn Boonyaratavej, MD. Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University
 Pericardial Diseases Smonporn Boonyaratavej, MD Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Cardiac Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital 21 AUGUST 2016 Pericardial
Pericardial Diseases Smonporn Boonyaratavej, MD Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Cardiac Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital 21 AUGUST 2016 Pericardial
CARDIAC EXAMINATION MINI-QUIZ
 CARDIAC EXAMINATION MINI-QUIZ 1. Sitting bolt upright, your dyspneic (short of breath) patient has visible jugular venous pulsations to the angle of his jaw, which is 12 cm above his sternal angle. What
CARDIAC EXAMINATION MINI-QUIZ 1. Sitting bolt upright, your dyspneic (short of breath) patient has visible jugular venous pulsations to the angle of his jaw, which is 12 cm above his sternal angle. What
1. how a careful cardiovascular evaluation can accurately assess pathology and physiology at the bedside, and
 This program will demonstrate: 1. how a careful cardiovascular evaluation can accurately assess pathology and physiology at the bedside, and 2. the importance of integrating this information with selected
This program will demonstrate: 1. how a careful cardiovascular evaluation can accurately assess pathology and physiology at the bedside, and 2. the importance of integrating this information with selected
Pulmonary valve echo motion in pulmonary
 British HeartJournal, I975, 37, ii84-ii90. Pulmonary valve echo motion in pulmonary regurgitation' Arthur E. Weyman, James C. Dillon, Harvey Feigenbaum, and Sonia Chang From the Department of Medicine,
British HeartJournal, I975, 37, ii84-ii90. Pulmonary valve echo motion in pulmonary regurgitation' Arthur E. Weyman, James C. Dillon, Harvey Feigenbaum, and Sonia Chang From the Department of Medicine,
THE HEART OBJECTIVES: LOCATION OF THE HEART IN THE THORACIC CAVITY CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
Clinical significance of cardiac murmurs: Get the sound and rhythm!
 Clinical significance of cardiac murmurs: Get the sound and rhythm! Prof. dr. Gunther van Loon, DVM, PhD, Ass Member ECVDI, Dip ECEIM Dept. of Large Animal Internal Medicine Ghent University, Belgium Murmurs
Clinical significance of cardiac murmurs: Get the sound and rhythm! Prof. dr. Gunther van Loon, DVM, PhD, Ass Member ECVDI, Dip ECEIM Dept. of Large Animal Internal Medicine Ghent University, Belgium Murmurs
Case 47 Clinical Presentation
 93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY
 CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY LECTURE 4 Cardiac cycle Polygram - analysis of cardiac activity Ana-Maria Zagrean MD, PhD The Cardiac Cycle - definitions: the sequence of electrical and mechanical events that
CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY LECTURE 4 Cardiac cycle Polygram - analysis of cardiac activity Ana-Maria Zagrean MD, PhD The Cardiac Cycle - definitions: the sequence of electrical and mechanical events that
Echocardiographic findings in persistent truncus
 British HeartJournal, I974, 36, 732-736. Echocardiographic findings in persistent truncus arteriosus in a young adult Premindra A. N. Chandraratna, Udayan Bhaduri, Benjamin B. Littman, and Frank J. Hildner
British HeartJournal, I974, 36, 732-736. Echocardiographic findings in persistent truncus arteriosus in a young adult Premindra A. N. Chandraratna, Udayan Bhaduri, Benjamin B. Littman, and Frank J. Hildner
Disclosures. Cardiac Ultrasound. Introductory Case. 80 y/o male Syncope at home Emesis x 3 in ambulance Looks sick. No pain.
 Disclosures Cardiac Ultrasound Justin A Davis, MD MPH RDMS Subchief for Emergency Ultrasound Kaiser Permanente East Bay Medical Center I have nothing to disclose. Introductory Case HR 118 BP 65/43 RR 27
Disclosures Cardiac Ultrasound Justin A Davis, MD MPH RDMS Subchief for Emergency Ultrasound Kaiser Permanente East Bay Medical Center I have nothing to disclose. Introductory Case HR 118 BP 65/43 RR 27
Cardiac Ausculation in the Elderly
 Cardiac Ausculation in the Elderly 박성하 신촌세브란스병원심장혈관병원심장내과 Anatomy Surface projection of the Heart and Great Vessels Evaluating pulsation Superior vena cava Rt. pulmonary artery Right atrium Right ventricle
Cardiac Ausculation in the Elderly 박성하 신촌세브란스병원심장혈관병원심장내과 Anatomy Surface projection of the Heart and Great Vessels Evaluating pulsation Superior vena cava Rt. pulmonary artery Right atrium Right ventricle
Large Arteries of Heart
 Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
SMALL GROUP SESSION 19 January 30 th or February 1st. Groups 1-12: Cardiac Case and Cardiac Exam Workshop
 SMALL GROUP SESSION 19 January 30 th or February 1st Groups 1-12: Cardiac Case and Cardiac Exam Workshop Readings: Complete the cardiac examination tutorial on the POM1 web site. Optional: http://medicine.ucsd.edu/clinicalmed/heart.htm
SMALL GROUP SESSION 19 January 30 th or February 1st Groups 1-12: Cardiac Case and Cardiac Exam Workshop Readings: Complete the cardiac examination tutorial on the POM1 web site. Optional: http://medicine.ucsd.edu/clinicalmed/heart.htm
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart -
 Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Anomalous muscle bundle of the right ventricle
 British Heart Journal, 1978, 40, 1040-1045 Anomalous muscle bundle of the right ventricle Its recognition and surgical treatment M. D. LI, J. C. COLES, AND A. C. McDONALD From the Department of Paediatrics,
British Heart Journal, 1978, 40, 1040-1045 Anomalous muscle bundle of the right ventricle Its recognition and surgical treatment M. D. LI, J. C. COLES, AND A. C. McDONALD From the Department of Paediatrics,
suggested by Katz and Gauchat (3) for the ex- diaphragm during inspiration, traction is applied Dornhorst, Howard, and Leathart (2), using an
 Journal of Clinical Investigation Vol. 42, No. 2, 1963 THE MECHANISM OF PULSUS PARADOXUS DURING ACUTE PERICARDIAL TAMPONADE * By RICHARD J. GOLINKO,t NEVILLE KAPLAN, AND ABRAHAM M. RUDOLPH t (From the
Journal of Clinical Investigation Vol. 42, No. 2, 1963 THE MECHANISM OF PULSUS PARADOXUS DURING ACUTE PERICARDIAL TAMPONADE * By RICHARD J. GOLINKO,t NEVILLE KAPLAN, AND ABRAHAM M. RUDOLPH t (From the
Surface anatomy of Cardiovascular system
 Surface anatomy of Cardiovascular system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The lines cover the front, side, and back of the thorax Midsternal
Surface anatomy of Cardiovascular system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The lines cover the front, side, and back of the thorax Midsternal
Potential pitfalls in quantification of pericardial effusions by echocardiography'
 Potential pitfalls in quantification of pericardial effusions by echocardiography' British Heart J7ournal, 1977, 39, 529-535 IVAN D'CRUZ, RAVINDRA PRABHU, HOWARD C. COHEN, AND GERALD GLICK From the Cardiovascular
Potential pitfalls in quantification of pericardial effusions by echocardiography' British Heart J7ournal, 1977, 39, 529-535 IVAN D'CRUZ, RAVINDRA PRABHU, HOWARD C. COHEN, AND GERALD GLICK From the Cardiovascular
ERDHEIM-CHESTER DISEASE LUNG & HEART ISSUES
 ERDHEIM-CHESTER DISEASE LUNG & HEART ISSUES GIULIO CAVALLI, M.D. INTERNAL MEDICINE AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY IRCCS SAN RAFFAELE HOSPITAL VITA-SALUTE SAN RAFFAELE UNIVERSITY MILAN, ITALY cavalli.giulio@hsr.it
ERDHEIM-CHESTER DISEASE LUNG & HEART ISSUES GIULIO CAVALLI, M.D. INTERNAL MEDICINE AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY IRCCS SAN RAFFAELE HOSPITAL VITA-SALUTE SAN RAFFAELE UNIVERSITY MILAN, ITALY cavalli.giulio@hsr.it
TAMPONADE CARDIAQUE. Dr Cédrick Zaouter TUSAR 15 décembre 2015
 TAMPONADE CARDIAQUE Dr Cédrick Zaouter TUSAR 15 décembre 2015 OUTLINE History Incidence Definition Pathophysiology Aetiologies Investigations - Echocardiography Treatment of cardiac tamponade Pericardial
TAMPONADE CARDIAQUE Dr Cédrick Zaouter TUSAR 15 décembre 2015 OUTLINE History Incidence Definition Pathophysiology Aetiologies Investigations - Echocardiography Treatment of cardiac tamponade Pericardial
M-Mode Echocardiography Is it still Alive? Itzhak Kronzon, MD,FASE. Sampling Rate M-Mode: 1800 / sec 2D: 30 / sec
 M-Mode Echocardiography Is it still Alive? Itzhak Kronzon, MD,FASE Honoraria: Philips Classical M-mode Echocardiography M-Mode offers better time and image resolution. Sampling Rate M-Mode: 1800 / sec
M-Mode Echocardiography Is it still Alive? Itzhak Kronzon, MD,FASE Honoraria: Philips Classical M-mode Echocardiography M-Mode offers better time and image resolution. Sampling Rate M-Mode: 1800 / sec
HISTORY. Question: What type of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance.
 HISTORY 15-year-old male. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance. PRESENT ILLNESS: A heart murmur was noted in childhood, but subsequent medical care was sporadic. Easy fatigability and slight
HISTORY 15-year-old male. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance. PRESENT ILLNESS: A heart murmur was noted in childhood, but subsequent medical care was sporadic. Easy fatigability and slight
left atrial myxoma causes paradoxical motion of the catheter; posterior
 Am JRoentgenolla6:II55-II58, 1976 ABNORMAL LEFT VENTRICULAR CATHETER MOTION: AN ANCILLARY ANGIOGRAPHIC SIGN OF LEFT ATRIAL MYXOMA ABsTRACT: J. M. RAU5CH, R. T. REINKE, K. L. PETERSON,2 AND C. B. HIGGINs
Am JRoentgenolla6:II55-II58, 1976 ABNORMAL LEFT VENTRICULAR CATHETER MOTION: AN ANCILLARY ANGIOGRAPHIC SIGN OF LEFT ATRIAL MYXOMA ABsTRACT: J. M. RAU5CH, R. T. REINKE, K. L. PETERSON,2 AND C. B. HIGGINs
The Mammalian Circulatory System
 The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
THE HEART. A. The Pericardium - a double sac of serous membrane surrounding the heart
 THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
PRACTICAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IN THE ADULT with Doppler and color-doppler flow imaging
 PRACTICAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IN THE ADULT with Doppler and color-doppler flow imaging PRACTICAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IN THE ADULT with Doppler and color-doppler flow imaging by J.P.M. HAMER Thoraxcentre, Department
PRACTICAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IN THE ADULT with Doppler and color-doppler flow imaging PRACTICAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IN THE ADULT with Doppler and color-doppler flow imaging by J.P.M. HAMER Thoraxcentre, Department
The Cardiovascular System. Chapter 15. Cardiovascular System FYI. Cardiology Closed systemof the heart & blood vessels. Functions
 Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Echocardiography of Cardiac Valves in
 Echocardiography of Cardiac Valves in Pericardial Effusion NAVN C. NANDA, M.D., RAYMOND GRAMAK, M.D., AND CHARLES M. GROSS, M.D. SUMMARY Nine adult patients with large pericardial effusions (PE) demonstrated
Echocardiography of Cardiac Valves in Pericardial Effusion NAVN C. NANDA, M.D., RAYMOND GRAMAK, M.D., AND CHARLES M. GROSS, M.D. SUMMARY Nine adult patients with large pericardial effusions (PE) demonstrated
10/14/2018 Dr. Shatarat
 2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to:
 The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
DIAGNOSING HEART FAILURE IN DOGS
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk DIAGNOSING HEART FAILURE IN DOGS Author : Mike Martin Categories : Vets Date : November 7, 2011 Mike Martin offers advice
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk DIAGNOSING HEART FAILURE IN DOGS Author : Mike Martin Categories : Vets Date : November 7, 2011 Mike Martin offers advice
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING
 PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
Outline. Echocardiographic Assessment of Pericardial Effusion/Tamponade: The Essentials
 Echocardiographic Assessment of Pericardial Effusion/Tamponade: The Essentials John R Schairer DO FACC Henry Ford Heart and Vascular Institute No Disclosures Outline Normal Anatomy and Physiology Pathophysiology
Echocardiographic Assessment of Pericardial Effusion/Tamponade: The Essentials John R Schairer DO FACC Henry Ford Heart and Vascular Institute No Disclosures Outline Normal Anatomy and Physiology Pathophysiology
Atrioventricular Valve Dysplasia
 Atrioventricular Valve Dysplasia How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job
Atrioventricular Valve Dysplasia How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW
 PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13}
 Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13} E. Skeleton of the Heart 1. The skeleton of the heart is composed of rings of dense connective tissue and other masses of connective tissue in the interventricular
Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13} E. Skeleton of the Heart 1. The skeleton of the heart is composed of rings of dense connective tissue and other masses of connective tissue in the interventricular
The role of bedside ultrasound in the diagnosis of pericardial effusion and cardiac tamponade
 Symposium The role of bedside ultrasound in the diagnosis of pericardial effusion and cardiac tamponade Adam Goodman, Phillips Perera, Thomas Mailhot, Diku Mandavia Department of Emergency Medicine, Los
Symposium The role of bedside ultrasound in the diagnosis of pericardial effusion and cardiac tamponade Adam Goodman, Phillips Perera, Thomas Mailhot, Diku Mandavia Department of Emergency Medicine, Los
Cardiovascular System. Heart Anatomy
 Cardiovascular System Heart Anatomy 1 The Heart Location & general description: Atria vs. ventricles Pulmonary vs. systemic circulation Coverings Walls The heart is found in the mediastinum, the medial
Cardiovascular System Heart Anatomy 1 The Heart Location & general description: Atria vs. ventricles Pulmonary vs. systemic circulation Coverings Walls The heart is found in the mediastinum, the medial
MR Advance Techniques. Cardiac Imaging. Class IV
 MR Advance Techniques Cardiac Imaging Class IV Heart The heart is a muscular organ responsible for pumping blood through the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions. Layers of the heart Endocardium
MR Advance Techniques Cardiac Imaging Class IV Heart The heart is a muscular organ responsible for pumping blood through the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions. Layers of the heart Endocardium
Outcomes of Mitral Valve Repair for Mitral Regurgitation Due to Degenerative Disease
 Outcomes of Mitral Valve Repair for Mitral Regurgitation Due to Degenerative Disease TIRONE E. DAVID, MD ; SEMIN THORAC CARDIOVASC SURG 19:116-120c 2007 ELSEVIER INC. PRESENTED BY INTERN 許士盟 Mitral valve
Outcomes of Mitral Valve Repair for Mitral Regurgitation Due to Degenerative Disease TIRONE E. DAVID, MD ; SEMIN THORAC CARDIOVASC SURG 19:116-120c 2007 ELSEVIER INC. PRESENTED BY INTERN 許士盟 Mitral valve
Non-invasive diagnosis of pseudoaneurysm of left
 British Heart Journal, 1978, 40, 812-816 Non-invasive diagnosis of pseudoaneurysm of left ventricle R. VAN MECHELEN, N. M. VAN HEMEL, AND P. P. VAN RIJK From the Departments of Cardiology and Cardiovascular
British Heart Journal, 1978, 40, 812-816 Non-invasive diagnosis of pseudoaneurysm of left ventricle R. VAN MECHELEN, N. M. VAN HEMEL, AND P. P. VAN RIJK From the Departments of Cardiology and Cardiovascular
Chapter 14. Circulatory System Images. VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II
 Chapter 14 Circulatory System Images VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II The mediastinum Dog heart Dog heart Cat heart Dog heart ultrasound Can see pericardium as distinct bright line Pericardial effusion Fluid
Chapter 14 Circulatory System Images VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II The mediastinum Dog heart Dog heart Cat heart Dog heart ultrasound Can see pericardium as distinct bright line Pericardial effusion Fluid
Introduction. Cardiac Imaging Modalities MRI. Overview. MRI (Continued) MRI (Continued) Arnaud Bistoquet 12/19/03
 Introduction Cardiac Imaging Modalities Arnaud Bistoquet 12/19/03 Coronary heart disease: the vessels that supply oxygen-carrying blood to the heart, become narrowed and unable to carry a normal amount
Introduction Cardiac Imaging Modalities Arnaud Bistoquet 12/19/03 Coronary heart disease: the vessels that supply oxygen-carrying blood to the heart, become narrowed and unable to carry a normal amount
Looking Outside the Box: Incidental Extracardiac Finding in Echo
 Looking Outside the Box: Incidental Extracardiac Finding in Echo Dr. Aijaz Shah Head of Division, Adult Echocardiography Laboratory Prince Sultan Cardiac Centre Riyadh Case 1 17 year old boy presented
Looking Outside the Box: Incidental Extracardiac Finding in Echo Dr. Aijaz Shah Head of Division, Adult Echocardiography Laboratory Prince Sultan Cardiac Centre Riyadh Case 1 17 year old boy presented
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Lab Activity 23. Cardiac Anatomy. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 23 Cardiac Anatomy Portland Community College BI 232 Cardiac Muscle Histology Branching cells Intercalated disc: contains many gap junctions connecting the adjacent cell cytoplasm, creates
Lab Activity 23 Cardiac Anatomy Portland Community College BI 232 Cardiac Muscle Histology Branching cells Intercalated disc: contains many gap junctions connecting the adjacent cell cytoplasm, creates
The Jugular Venous Pressure and Pulse Contour
 19 The Jugular Venous Pressure and Pulse Contour MARK M. APPLEFELD Definition Information that can be derived from an assessment of the jugular venous pulse includes determination of the mean venous pressure,
19 The Jugular Venous Pressure and Pulse Contour MARK M. APPLEFELD Definition Information that can be derived from an assessment of the jugular venous pulse includes determination of the mean venous pressure,
Cardiac Mass in a 15-Year-Old Boy
 Cardiac Mass in a 15-Year-Old Boy Echocardiographic Case Report Hortensia Vuçini Department of Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery UHC Mother Theresa Tirana, Albania October 20, 2007 Case Presentation 15 year-old
Cardiac Mass in a 15-Year-Old Boy Echocardiographic Case Report Hortensia Vuçini Department of Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery UHC Mother Theresa Tirana, Albania October 20, 2007 Case Presentation 15 year-old
Heart sounds and murmurs. Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 15. Oct
 Heart sounds and murmurs Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 15. Oct. 2013. Conditions for auscultation of the heart Quiet room Patient comfortable Chest fully exposed
Heart sounds and murmurs Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 15. Oct. 2013. Conditions for auscultation of the heart Quiet room Patient comfortable Chest fully exposed
CV Anatomy Quiz. Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green
 CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
Rotational excursion of heart in massive pericardial effusion studied by phased-array echocardiography
 British Heart journal, 1979, 41, 513-521 Rotational excursion of heart in massive pericardial effusion studied by phased-array echocardiography HIROHIDE MATSUO, MASAYUKI MATSUMOTO, YASUHIKO HAMANAKA, TATSUHIKO
British Heart journal, 1979, 41, 513-521 Rotational excursion of heart in massive pericardial effusion studied by phased-array echocardiography HIROHIDE MATSUO, MASAYUKI MATSUMOTO, YASUHIKO HAMANAKA, TATSUHIKO
Intro to Bedside Ultrasound. Cardiac Ultrasound
 Intro to Bedside Ultrasound Cardiac Ultrasound TEACHERS University of California-Irvine School of Medicine Nathan Molina nathan.d.molina@gmail.com Trevor Plescia taplescia90@gmail.com Jack Silva jpsilva42@gmail.com
Intro to Bedside Ultrasound Cardiac Ultrasound TEACHERS University of California-Irvine School of Medicine Nathan Molina nathan.d.molina@gmail.com Trevor Plescia taplescia90@gmail.com Jack Silva jpsilva42@gmail.com
Ultrasound 10/1/2014. Basic Echocardiography for the Internist. Mechanical (sector) transducer Piezoelectric crystal moved through a sector sweep
 Ultrasound Basic Echocardiography for the Internist Carol Gruver, MD, FACC UT Erlanger Cardiology Mechanical wave of compression and rarefaction Requires a medium for transmission Ultrasound frequency
Ultrasound Basic Echocardiography for the Internist Carol Gruver, MD, FACC UT Erlanger Cardiology Mechanical wave of compression and rarefaction Requires a medium for transmission Ultrasound frequency
COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD
 COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD Disclosure No Relevant Financial Relationships with Commercial Interests Fetal Echo: How to do it? Timing of Study -optimally between 22-24 weeks
COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD Disclosure No Relevant Financial Relationships with Commercial Interests Fetal Echo: How to do it? Timing of Study -optimally between 22-24 weeks
Congenital heart disease. By Dr Saima Ali Professor of pediatrics
 Congenital heart disease By Dr Saima Ali Professor of pediatrics What is the most striking clinical finding in this child? Learning objectives By the end of this lecture, final year student should be able
Congenital heart disease By Dr Saima Ali Professor of pediatrics What is the most striking clinical finding in this child? Learning objectives By the end of this lecture, final year student should be able
Anatomy of the Heart. Figure 20 2c
 Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY
 (YEARS 1 3) CURRICULUM FOR RADIOLOGY 13 B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY KNOWLEDGE To describe the normal anatomy of the heart and vessels including the lymphatic system as demonstrated by radiographs,
(YEARS 1 3) CURRICULUM FOR RADIOLOGY 13 B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY KNOWLEDGE To describe the normal anatomy of the heart and vessels including the lymphatic system as demonstrated by radiographs,
Cardiac ultrasound protocols
 Cardiac ultrasound protocols IDEXX Telemedicine Consultants Two-dimensional and M-mode imaging planes Right parasternal long axis four chamber Obtained from the right side Displays the relative proportions
Cardiac ultrasound protocols IDEXX Telemedicine Consultants Two-dimensional and M-mode imaging planes Right parasternal long axis four chamber Obtained from the right side Displays the relative proportions
The Vigileo monitor by Edwards Lifesciences supports both the FloTrac Sensor for continuous cardiac output and the Edwards PreSep oximetry catheter
 1 2 The Vigileo monitor by Edwards Lifesciences supports both the FloTrac Sensor for continuous cardiac output and the Edwards PreSep oximetry catheter for continuous central venous oximetry (ScvO2) 3
1 2 The Vigileo monitor by Edwards Lifesciences supports both the FloTrac Sensor for continuous cardiac output and the Edwards PreSep oximetry catheter for continuous central venous oximetry (ScvO2) 3
Pericardial Effusion
 Pericardial Effusion How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right
Pericardial Effusion How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right
Clinical Anatomy Series Cardiac Anatomy
 2012 Scottish Universities Medical Journal, Dundee Published online: Feb 2012 Vol 1 Issue 1: page 76-80 Kennedy J Clinical Anatomy Cardiac Anatomy Clinical Anatomy Series Cardiac Anatomy John Kennedy (5
2012 Scottish Universities Medical Journal, Dundee Published online: Feb 2012 Vol 1 Issue 1: page 76-80 Kennedy J Clinical Anatomy Cardiac Anatomy Clinical Anatomy Series Cardiac Anatomy John Kennedy (5
The Heart. Size, Form, and Location of the Heart. 1. Blunt, rounded point; most inferior part of the heart.
 12 The Heart FOCUS: The heart is composed of cardiac muscle cells, which are elongated, branching cells that appear striated. Cardiac muscle cells behave as a single electrical unit, and the highly coordinated
12 The Heart FOCUS: The heart is composed of cardiac muscle cells, which are elongated, branching cells that appear striated. Cardiac muscle cells behave as a single electrical unit, and the highly coordinated
See below for descriptions of the waveform
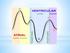 The internal jugular vein (IJV) connects to the right atrium without any intervening valves. The pulsation of the right atrium therefore causes the column of blood in the IJV to rise and fall this is called
The internal jugular vein (IJV) connects to the right atrium without any intervening valves. The pulsation of the right atrium therefore causes the column of blood in the IJV to rise and fall this is called
the Cardiovascular System I
 the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
SAMPLE HLTEN610A. TAFE NSW Training and Education Support Industry Skills Unit, Meadowbank. Practise in the cardiovascular nursing environment
 TAFE NSW Training and Education Support Industry Skills Unit, Meadowbank HLTEN610A Practise in the cardiovascular nursing environment Version 1.0 Flexible Learner Resource Product Code: ISO 9001 HLTEN610A
TAFE NSW Training and Education Support Industry Skills Unit, Meadowbank HLTEN610A Practise in the cardiovascular nursing environment Version 1.0 Flexible Learner Resource Product Code: ISO 9001 HLTEN610A
Signs of pericardial constriction in rupture of ventricular septum complicating myocardial
 British Heart Journal, I972, 34, I176-iI80. Signs of pericardial constriction in rupture of ventricular septum complicating myocardial infarction T. G. Feest,' G. C. Sutton,2 R. J. Vecht, and R. V. Gibson
British Heart Journal, I972, 34, I176-iI80. Signs of pericardial constriction in rupture of ventricular septum complicating myocardial infarction T. G. Feest,' G. C. Sutton,2 R. J. Vecht, and R. V. Gibson
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY. Guidelines. Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta.
 BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY Guidelines Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta. Course 1 The number of hours 3 1. The
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY Guidelines Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta. Course 1 The number of hours 3 1. The
Anatomy of the Heart
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Heart References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapter
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Heart References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapter
Syncope Due to Intracavitary Left Ventricular Obstruction Secondary to Giant Esophageal Hiatus Hernia
 American Journal of Medical Case Reports, 2017, Vol. 5, No. 4, 89-93 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajmcr/5/4/4 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajmcr-5-4-4 Syncope Due to Intracavitary
American Journal of Medical Case Reports, 2017, Vol. 5, No. 4, 89-93 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajmcr/5/4/4 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajmcr-5-4-4 Syncope Due to Intracavitary
cardiac imaging planes planning basic cardiac & aortic views for MR
 cardiac imaging planes planning basic cardiac & aortic views for MR Dianna M. E. Bardo, M. D. Assistant Professor of Radiology & Cardiovascular Medicine Director of Cardiac Imaging cardiac imaging planes
cardiac imaging planes planning basic cardiac & aortic views for MR Dianna M. E. Bardo, M. D. Assistant Professor of Radiology & Cardiovascular Medicine Director of Cardiac Imaging cardiac imaging planes
Pulmonic Stenosis. How does the heart work?
 Pulmonic Stenosis How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right
Pulmonic Stenosis How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART
 ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
Index of subjects. effect on ventricular tachycardia 30 treatment with 101, 116 boosterpump 80 Brockenbrough phenomenon 55, 125
 145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
Case # 1. Page: 8. DUKE: Adams
 Case # 1 Page: 8 1. The cardiac output in this patient is reduced because of: O a) tamponade physiology O b) restrictive physiology O c) coronary artery disease O d) left bundle branch block Page: 8 1.
Case # 1 Page: 8 1. The cardiac output in this patient is reduced because of: O a) tamponade physiology O b) restrictive physiology O c) coronary artery disease O d) left bundle branch block Page: 8 1.
Diversion of the inferior vena cava following repair of atrial septal defect causing hypoxemia
 Marshall University Marshall Digital Scholar Internal Medicine Faculty Research Spring 5-2004 Diversion of the inferior vena cava following repair of atrial septal defect causing hypoxemia Ellen A. Thompson
Marshall University Marshall Digital Scholar Internal Medicine Faculty Research Spring 5-2004 Diversion of the inferior vena cava following repair of atrial septal defect causing hypoxemia Ellen A. Thompson
Cardiovascular Structure & Function
 Cardiovascular Structure & Function Cardiovascular system: The heart Arteries Veins Capillaries Lymphatic vessels Weighting of the heart ceremony: Ancient Egyptians William Harvey and Blood Flow April
Cardiovascular Structure & Function Cardiovascular system: The heart Arteries Veins Capillaries Lymphatic vessels Weighting of the heart ceremony: Ancient Egyptians William Harvey and Blood Flow April
Tricuspid and Pulmonic Valve Disease
 Chapter 31 Tricuspid and Pulmonic Valve Disease David A. Tate Acquired disease of the right-sided cardiac valves is much less common than disease of the leftsided counterparts, possibly because of the
Chapter 31 Tricuspid and Pulmonic Valve Disease David A. Tate Acquired disease of the right-sided cardiac valves is much less common than disease of the leftsided counterparts, possibly because of the
UNILATERAL ELEVATION OF THE INTERNAL JUGULAR PULSE
 BY PETER SLEIGHT From St. George's Hospital Received September 8, 1961 This paper describes a group of patients in whom the venous pressure, as shown by a distended and pulsating internal jugular vein,
BY PETER SLEIGHT From St. George's Hospital Received September 8, 1961 This paper describes a group of patients in whom the venous pressure, as shown by a distended and pulsating internal jugular vein,
The Heart and Cardiovascular System
 The Heart and Cardiovascular System What you will learn The location of the heart 3 layers and covering of the heart Explain the function of the heart as 2 separate pumps Identify the 4 chambers of the
The Heart and Cardiovascular System What you will learn The location of the heart 3 layers and covering of the heart Explain the function of the heart as 2 separate pumps Identify the 4 chambers of the
Atrial Septal Defects
 Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
