Asian Journal of Pharmacy and Life Science ISSN Vol.3 (2), April-June, 2013
|
|
|
- Donna Warner
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AN INVESTIGATION OF THE NEPHROPROTECTIVE EFFECTS OF TRIPHALA-AN AYURVEDIC FORMULATION IN EXPERIMENTAL MODELS OF NEPHROTOXICITY. Monojit Mitra, Shivalinge Gowda KP* Department of Pharmacology, PES College of Pharmacy, Bangalore *Corresponding author s - shivalinge65@gmail.com ABSTRACT The objective of this study was to evaluate the nephroprotective activity of triphala on gentamicin induced nephrotoxicity in albino wistar rats. Twenty- four albino wistar rats were divided into four groups (n=6). Rats in group I (normal) received normal saline (p.o.) per day for 11 days. The group II rats were treated with gentamicin (80mg/kg,i.p.) for 8 days, in order to induce nephrotoxicity. The rats in group III and IV were pre treated with triphala (500mg/kg, p.o. and 1000 mg/kg, p.o.) for first three days followed by gentamicin (80mg/kg, i.p.) treatment till eleventh day. Body weight, urinary glucose, sodium, potassium and creatinine levels, serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels, kidney weight and lipid peroxidation were evaluated along with histopathological investigation in various experimental groups of rats. It was observed that the gentamicin treated rats (group II) had significantly reduced (*** P <0.001) body weight, urinary sodium, potassium and creatinine while significantly elevated values (*** P <0.001) of urinary glucose, serum urea (BUN) and creatinine, kidney weight and lipid peroxidation when compared to group I (normal) rats. Histological observations of rat kidney tissues further correlated the nephroprotective effect of triphala. The result of this study provides the experimental evidence for claiming the nephroprotective effect of triphala. Keywords: Blood urea nitrogen, gentamicin, lipid peroxidation, nephrotoxicity INTRODUCTION Nephrotoxic injury is damage to one or both of the kidneys that results from exposure to a toxic material, usually through ingestion. Nephrotoxic injury can lead to acute renal failure, in which the kidneys suddenly lose their ability to function, or chronic renal failure, in which kidney function slowly deteriorates. If unchecked, renal failure can result in death. Chronic exposure to drugs, occupational hazards, or environmental toxins can lead to chronic interstitial renal diseases. 1 Aminoglycoside gentamicin sulphate (GS) is commonly used for the treatment of Gramnegative bacterial infection, but nearly 13-30% patients suffer from nephrotoxicity thus limiting its use. Gentamicin Sulfate has been used clinically due to its wide spectrum of activities against Gram-negative bacterial infection caused by pseudomonas, proteus and serratia. Gentamicin induced nephrotoxicity is characterized by an increase in generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) such as superoxide anions, hydroxyl radicals, hydrogen peroxide and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) in kidneys and lead to renal injuries. GS induced renal damage is linked with lipid and protein oxidation in renal cortex.gs induces poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase in proximal tubules. GS is not metabolized in the body but is essentially eliminated by glomerular filtration and partially reabsorbed by proximal tubular cells. The specificity of gentamicin induced nephrotoxicity is apparently related to its accumulation in the renal proximal convoluted tubules causing a number of morphologic, metabolic and functional alterations. 2,3 66 P a g e Available online on Original Research Article
2 Triphala (in Sanskrit tri = three and phala = fruits) is composed of the three myrobalans, Terminalia chebula (Haritaki), Terminalia belerica (Bibhitaki), and Emblica officinalis (Amalaki) and is one of the most commonly used Ayurvedic preparations. The formulation generally consists of equal proportions of pericarps of these myrobalans. Triphala has been described in the ancient Ayurvedic text as a Tridoshic rasayana, a therapeutic agent with balancing and rejuvenating effects on the three humours or constitutional elements in Ayurveda vata, pitta and kapha. T. chebula and T.belerica have a warm energy, while E. officinalis is cool in nature. Triphala, being a combination of all three, is therefore balanced, making it useful as an internal cleansing, detoxifying formula. Triphala is regarded as an important rasayana and good purgative in Ayurvedic medicine. Recipe for this traditional herbal supplement is described in the traditional Indian texts, the Charak Samhita and Susruta Samhita which date back to 1500 B.C. 4,5 MATERIALS AND METHODS Animals: Healthy albino wistar rats, weighing g, were purchased from authentic animal supplier in Bangalore, which were maintained in the animal house of PES college of Pharmacy, Bangalore for experimental purpose. All these animals were housed in temperature controlled room 25±1 C, relative humidity 45-55% and a 12 h light/ 12h dark cycle. They were acclimatized for 7 days and fed with standard rat chow (Amruth Animal Feeds Pvt Ltd, Bangalore, India) and water ad libitum. Animals were habituated to laboratory conditions for 48h prior to experiment, to minimize stress. All animal studies including protocols and experiments were performed in accordance to the guidelines and ethical principles as per the Committee for the purpose of Control and Supervision of Experiments on Animals (CPCSEA), 6 Govt. of India, New Delhi. Prior approval was taken from the Institutional Animal Ethical Committee (IAEC approval No- PESCP/IAEC/ 10 /11) of P.E.S College of Pharmacy, Bangalore, Karnataka for conducting animal studies. Chemicals: Triphala churna maunufactured by Shree Baidyanath Ayurved bhawan PVT. LTD, Nagpur was purchased from local Baidyanath Pharmacy, Bangalore with batch no Each 10gram contains haritaki, bibhitaka and amalaki (weight-3.333g each) in ratio of 1:1:1 as per product literature The aqueous suspension of triphala was prepared by taking triphala powder in required quantity and to it distilled water was added (5g in 100ml) and homogenized to form uniform suspension of the extract. The extract was freshly prepared every day before dosing the animals. Dosages: The dose of aqueous suspension of Baidyanath triphala powder for the pharmacological studies was selected on the basis of previous research work performed on triphala. The acute toxicity study was done as per the organization of economic co-operation and development (OECD) guidelines and it was found to be safe up to 2000 mg/kg. The dose of triphala was taken as 500mg/kg, b.w as low dose and 1000mg/kg, b.w. as high dose, based upon literature survey and previous work done. 7 Grouping and dosage regimen: Twenty four albino wistar rats were divided into four groups with six animals each. (n=6) Group I: Control which receives vehicle p.o. throughout the course. Group II: Gentamicin (80 mg/kg/ i.p.) for 8 days. 67 P a g e Available online on Original Research Article
3 Group III: Gentamicin (80mg/kg i.p) for eight days + aqueous solution of triphala (500mg/kg, p.o.) which is started 3 days prior to gentamicin treatment continued by 8 days gentamicin treatment Group IV: Gentamicin (80mg/kg i.p) for eight days + aqueous solution of triphala (1000mg/kg, p.o.) which is started 3 days prior to gentamicin treatment continued by 8 days gentamicin treatment. 8 Sample collection and biochemical assays: After the eleventh day treatment, all the rats were hydrated with the administration of additional vehicle (0.5ml/kg b.w) and were kept in individual metabolic cages for 24-hour urine collection. The collected urine was transferred to clean eppendorf tubes and centrifuged at 2000 r.p.m for 10 min. The supernatant was transferred to cleaned eppendorf tubes and used for estimation of sodium, potassium, glucose and creatinine.24h after the 11 th day treatment blood was collected from retro orbital sinus under ether anaesthesia in eppendorf tubes and serum was separated by cold centrifugation at 3000 r.p.m for 10 min. The supernatant serum was transferred to clean epindroff tubes and used for the estimation of urea and creatinine. The serum and urinary estimations were carried out by using ERBA diagnostic kits. Then, the rats were sacrificed by cervical dislocation method as per CPCSEA guidelines. Kidneys were isolated and weighed. They were thoroughly washed with ice- cold PBS solution. 10% homogenate was prepared in phosphate buffer saline (PBS) 0.05 M, ph 7) using a remi homogenizer at 25 C at 5000rpm for 15 min. The homogenate was centrifuged to remove unwanted cell debris, nuclei and mitochondria. It was used for estimation of kidney tissue anti oxidant levels. Determination of lipid peroxidation (MDA) levels: Malondialdehyde (MDA) levels were determined by the method of Ohkawa.et.al.,. In this process, 0.2ml of kidney tissue homogenate, 0.2ml of 8.1% sodium dodecyl sulfate, 1.5ml of 20% acetic acid and 1.5ml of 0.8% TBA were added. The volume of the mixture was made up to 4ml with distilled water and then heated at 95 C in a water bath for 60min. After incubation the tubes were cooled to room temperature and the final volume was made upto 5ml with distilled water in each tube. Then, 5ml of n-butanol: pyridine mixture (15:1, v/v) was added and shaken vigorously for 2 min. After centrifugation at 4000rpm for 10 min, the upper organic layer was taken and its optical density (OD) was read at 532nm against blank. The levels of lipid peroxides were expressed as millimoles of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS)/100g of cardiac tissue using an extinction co-efficient of M -1 cm HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES One kidney from each sacrificed rat was taken and fixed in 10% v/v neutral formalin and processed to paraffin wax. Sections (5 microns) were stained with haematoxyllin and eosin and were examined under light microscope at 40 X and 100 X magnifications. STATISTICAL ANALYSIS Statistical analysis was performed by one way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) followed by Dunnet s test for post comparison using software Graph pad prism version 5.0. Results were expressed as mean ± SEM. P values <0.05 were considered to be statistically significant. 68 P a g e Available online on Original Research Article
4 RESULTS There is a significant decrease in urinary sodium, potassium and creatinine levels while a significant increase is seen in urinary glucose levels in group II rats while compared to group I. The rats treated with triphala 500mg/kg, p.o. and 1000mg/kg, p.o. + gentamicin 80mg/kg,i.p. have showed significant nephroprotection by increasing urinary sodium, potassium and creatinine and by decreasing urinary glucose levels as showed in the table 1. TABLE - 1 Showing the effect of vehicle, gentamicin and triphala on urinary sodium, urinary potassium, urinary glucose and urinary creatinine levels in rats Group (n=6) Treatment Dose and Route Duration Days Urinary sodium (meq/day) Urinary potassiu m (meq/da y) Urinary glucose (mg/dl) Urinary Creatinine (mg/dl) I Vehicle, p.o ± ± ± ± II GEN (80mg/kg,), i.p ± *** 5.05± 1.126** 278.4± 35.03** * 1.360± 0.188*** III Triphala (500mg/kg, p.o), GEN (80mg/kg,), i.p ± ± *** 1.177** ± * 4.923± 0.486*** IV Triphala (1000mg/kg, p.o.), GEN (80mg/kg,), i.p ± ± ** ** ± 4.478± ** 0.414*** Values are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. n = 6. Significant values were compared with* P <0.05, ** P <0.01 and *** P <0.001 Control Vs treated groups using one way ANOVA followed by Dunnett s test. 69 P a g e Available online on Original Research Article
5 TABLE 2 Showing effect of vehicle, gentamicin and triphala on serum urea, serum creatinine, kidney weight and lipid peroxidation in rats. Group (n=6) Treatment Dose and Route Duration Serum urea (mg/dl) Serum creatinine (mg/dl) Kidney weight (g) Lipid peroxidation I Vehicle, P.O 11 days 21.35± ± ± ± II GEN (80mg/kg,), i.p. 7 days 26.25± ± 1.327*** 1.138± * 648.9± 29.00*** III Triphala (500mg/kg, p.o), GEN i.p (80mg/kg,), 11days 7 days 11days 19.41± ± 1.065*** 1.017± ± 27.88** IV Triphala 17.52± 7.36± ± 371.9± (1000mg/kg, p.o.), *** *** *** 7 days GEN (80mg/kg,), i.p Values are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. n = 6. Significant values were compared with* P <0.05, ** P <0.01 and *** P <0.001 Control Vs treated groups using one way ANOVA followed by Dunnett s test. There is a significant increase in serum urea, serum creatinine, kidney weight and lipid peroxidation levels in group II rats while compared to group I. The rats treated with triphala (500mg/kg, p.o. and 1000mg/kg, p.o. + GEN 80mg/kg, i.p) have showed significant nephroprotection by decreased serum urea, creatinine and lipid peroxidation levels while compared to group II whereas the decrease in kidney weight in group III and IV was not found to be significant. Histopathology of rat kidney Fig I Effect of vehicle on rat kidney (X400) Fig II Effect of GM on rat kidney (X400) 70 P a g e Available online on Original Research Article
6 Fig III Effect of TRI 500 mg/kg + GEN on rat kidney(x400) Fig IV Effect of TRI 1000 mg/kg + GEN on rat kidney (X400) Histopathological studies clearly indicate kidney damage in gentamicin only treated animals. In the present study, kidneys of group I (normal) rats show renal parenchyma of normal architecture. In group II (gentamicin treated) rats various degrees of focal lesions in many sections including tubular congestion, tubular desquamation and hyaline casts have been seen. The groups that received both triphala along with gentamicin respectively have shown mild glomerular necrosis, few intraluminal casts, moderate mononuclear inflammatory infiltration within the interstitium and blood vessels appearing unremarkable indicating the protective effect of triphala. DISCUSSION In the present study, the rats administered with gentamicin have shown significant decrease in the urinary sodium and potassium levels when compared to normal rats. As it is evident that the aminoglycosides also can induce renal potassium and magnesium wasting, with resulting hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia. Aminoglycosides produce tubular cell necrosis, which is largely confined to the proximal convoluted tubule and pars recta. Several tubular cell membrane functional changes occur with aminoglycoside exposure. The rats treated with triphala and gentamicin have shown significant increase in sodium and potassium levels when compared to gentamicin induced nephrotoxic rats suggesting the nephroprotection. 10 There is significant decrease in the urine creatinine levels in gentamicin induced nephrotoxic rats when compared to normal rats. This is due to structural damage of the podocytes, pedicels of the visceral layer of the Bowman s capsule and the endothelium of the glomerular capillaries of the nephron. This disturbs the glomerular filteration of the creatinine. Hence creatinine excretion gets decreased and it remains in the blood.the rats treated with gentamicin and triphala have shown significant increase in the urinary creatinine level while compared to gentamicin induced nephrotoxic rats. This protective effect of triphala may be due the prevention of the damage of the glomerular filteration apparatus and the normal filteration of creatinine across the glomerulus. A significant increase in urinary glucose in gentamicin induced nephrotoxic rats is seen when compared to normal rats. This is due to the damage of Na + / Glucose symporter expressed on the apical surface of PCT cells by the aminoglycosides. This decreases the re- absorption of glucose by the Na + / Glucose symporter. Hence, there is increase in urinary glucose in the gentamicin induced nephrotoxic rats. There is significant decrease in the urinary glucose level in rats treated with triphala and gentamicin when compared to nephrotoxic rats. This may be due to the protective effect of triphala on Na + / Glucose symporter. The protected symporter allows the reabsorption of glucose along with sodium ions. Further, the rats treated with gentamicin have shown significant increase in the serum urea concentration when compared to normal rats. This is due to structural damage of the glomerular filter and leads to the accumulation of urea in serum. Hence, the serum urea concentration is more in gentamicin induced nephrotoxic rats. 71 P a g e Available online on Original Research Article
7 The rats treated with triphala and gentamicins have shown significantly decreased serum urea concentration when compared to nephro toxic rats. 11 Also, increased malondialdehyde levels have been seen. Increased lipid peroxidation appears to be the initial stage to the tissue making it more susceptible to oxidative damage. The apical and basolateral membrane damage of the tubular cell is due to elevated levels of lipid peroxidation. This expressed in terms of TBARS. The TBARS level in rats treated with triphala and gentamicin is significantly reduced when compared to gentamicin induced nephrotoxic rats. This may be due to lipid peroxide free radical scavenging 12, 13 activity of the triphala. Hence this leads to the protection of apical and basolateral membranes of the tubular cells. As various symporters and anti porters are expressed on these membranes, the normal function of the nephron gets resumed. These protective effects on the various transporters by triphala suggesting its nephroprotective effect. 14 Further, histopathological examination shows restored renal parenchyma in triphala treated rats which may further strengthen this fact. REFERENCES 1. Nuyts GD, Van VE, Thys J, De Leersnijder D, D'Haese PC, Elseviers MM, et al. New occupational risk factors for chronic renal failure. Lancet. 1995;346 (8966): Salgado CM, Hernández FJL, Novoa JML. Glomerular nephrotoxicity of aminoglycosides. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2007;223: Balakumara, P., A. Rohillab, et al. "Gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity: Do we have a promising therapeutic approach to blunt it?" Pharmacological Research. 2010; 62: Kokate CK, Purohit AP, Gokhale SB. Pharmacognosy. 34 ed: Nirali Prakashan; Ponnusankar, S., S. Pandit, et al. "Cytochrome P450 inhibitory potential of Triphala a rasayana from Ayurveda." Journal of Ethnopharmacology.2011; 133: "CPCSEA guidelines for laboratory animal facility." Indian Journal of Pharmacology.2003; 35: Sabina, E. P. and M. Rasool. "An in vivo and in vitro potential of Indian ayurvedic herbal formulation Triphala on experimental gouty arthritis in mice." Vascular Pharmacology.2008; 48: Vijay KK, Naidu MUR, Anwar A, Ratnakar KS. Probucol protects against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Indian J Pharmacol. 2000; 32: Ohkawa, H., N. Ohishi, et al. "Assay for Lipid Peroxides in Animal Tissues by Thiobarbituric Acid Reaction." Analytical biochemistry. 1979; 95: Martinez-Salgado, C., N. Eleno, et al. "Gentamicin treatment induces simultaneous mesangial proliferation and apoptosis in rats." Kidney International. 2004; 65: Laurent, G., M.B. Carlier, et al. "Mechanism of aminoglycoside-induced lysosomal phospholipidosis: In vitro and in vivo studies with gentamicin and amikacin" Biochemical pharmacology. 1982; 31(23): Devasagayam, T., J. Tilak, et al. "Free Radicals and Antioxidants in Human Health: Current Status and Future Prospects." JAPI. 2004; P a g e Available online on Original Research Article
8 13. Kunwar, A. and K. I. Priyadarsini. "Free radicals, oxidative stress and importance of antioxidants in human health." J Me d A l l i e d S c i. 2011; 1(2): Kaloyanides,G.J. and E. Pastoriza -Munoz. "Aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity." Kidney International : P a g e Available online on Original Research Article
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
EFFECT OF VEDIYUPPU CHEYANEER IN ETHYLENE GLYCOL INDUCED HYPEROXALURIA MODEL IN RATS ABSTRACT
 EFFECT OF VEDIYUPPU CHEYANEER IN ETHYLENE GLYCOL INDUCED HYPEROXALURIA MODEL IN RATS V.VELPANDIAN 1, S. S.RAJAPREHIDHA 1 *, V.BANUMATHI 1, J. ANBU *2 AND ASHWINI ANJANA 2 1 Department of, Govt. Siddha
EFFECT OF VEDIYUPPU CHEYANEER IN ETHYLENE GLYCOL INDUCED HYPEROXALURIA MODEL IN RATS V.VELPANDIAN 1, S. S.RAJAPREHIDHA 1 *, V.BANUMATHI 1, J. ANBU *2 AND ASHWINI ANJANA 2 1 Department of, Govt. Siddha
Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine
 Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Urinary system. Urinary system
 INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
Use the following diagram to answer the next question. 1. In the diagram above, pressure filtration occurs in a. W b. X c. Y d. Z
 Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT
 AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015
 RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
Nephron Function and Urine Formation. Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S
 Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1
 Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The separation and ejection of metabolic wastes, usually in aqueous solution, is: a. reabsorption b. secretion c. filtration d. excretion e. endocrinology 2. Besides
Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The separation and ejection of metabolic wastes, usually in aqueous solution, is: a. reabsorption b. secretion c. filtration d. excretion e. endocrinology 2. Besides
YR10. IGCSE Biology. Homeostasis
 YR10 IGCSE Biology Homeostasis Name: Prepared by William Green DBGS 2010 Homeostasis Body cells work best if they have the correct conditions e.g. 1. 2. 3. Write the definition of Homeostasis in the box
YR10 IGCSE Biology Homeostasis Name: Prepared by William Green DBGS 2010 Homeostasis Body cells work best if they have the correct conditions e.g. 1. 2. 3. Write the definition of Homeostasis in the box
THE PHARMA INNOVATION - JOURNAL Chemoprotective effect of ethanolic extract of Morinda citrifolia against Cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity
 Received: 29-12-2013 Accepted: 27-02-2014 ISSN: 2277-7695 CODEN Code: PIHNBQ ZDB-Number: 2663038-2 IC Journal No: 7725 Vol. 3 No. 1. 2014 Online Available at www.thepharmajournal.com THE PHARMA INNOVATION
Received: 29-12-2013 Accepted: 27-02-2014 ISSN: 2277-7695 CODEN Code: PIHNBQ ZDB-Number: 2663038-2 IC Journal No: 7725 Vol. 3 No. 1. 2014 Online Available at www.thepharmajournal.com THE PHARMA INNOVATION
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology
 Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Urinary System. consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra
 Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
7. NOOTROPIC AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY. 7.1 Introduction
 268 7. NOOTROPIC AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY 7.1 Introduction Alzheimer s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder, which according to World Health Organization (WHO) affects 22 million people world wide,
268 7. NOOTROPIC AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY 7.1 Introduction Alzheimer s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder, which according to World Health Organization (WHO) affects 22 million people world wide,
Ch 19: The Kidneys. Functional unit of kidneys:?? Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM
 Ch 19: The Kidneys Homeostatic regulation of ECF volume and BP Osmolarity 290 mosm Ion balance Na+ and K+, etc. ph (acid-base balance Excretion of wastes & foreign substances Hormone production EPO Renin
Ch 19: The Kidneys Homeostatic regulation of ECF volume and BP Osmolarity 290 mosm Ion balance Na+ and K+, etc. ph (acid-base balance Excretion of wastes & foreign substances Hormone production EPO Renin
1. remove: waste products: urea, creatinine, and uric acid foreign chemicals: drugs, water soluble vitamins, and food additives, etc.
 Making Water! OR is it really Just Water Just Ask the Nephron!! Author: Patricia L. Ostlund ostlundp@faytechcc.edu (910) 678-9892 Fayetteville Technical Community College Fayetteville, NC 28303 Its just
Making Water! OR is it really Just Water Just Ask the Nephron!! Author: Patricia L. Ostlund ostlundp@faytechcc.edu (910) 678-9892 Fayetteville Technical Community College Fayetteville, NC 28303 Its just
Original article: EXTRACT OF FERULA FOETIDA REGEL REVERSES GENTAMICIN- INDUCED NEPHROTOXICITY IN RATS
 Original article: EXTRACT OF FERULA FOETIDA REGEL REVERSES GENTAMICIN- INDUCED NEPHROTOXICITY IN RATS Rasikh Javaid 1 *, Mohd Aslam 1, Raheela Javaid 2, Qudsia Nizami 1, Kalim Javed 3, M.U. Azhar 4 1 Department
Original article: EXTRACT OF FERULA FOETIDA REGEL REVERSES GENTAMICIN- INDUCED NEPHROTOXICITY IN RATS Rasikh Javaid 1 *, Mohd Aslam 1, Raheela Javaid 2, Qudsia Nizami 1, Kalim Javed 3, M.U. Azhar 4 1 Department
The Urinary System 15PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
The principal functions of the kidneys
 Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal Pharmacology. Diuretics: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Thiazides Loop Diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics BIMM118
 Diuretics: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Thiazides Loop Diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive ~25% of the total arterial blood
Diuretics: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Thiazides Loop Diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive ~25% of the total arterial blood
Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System
 Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHYTOTHERAPY RESEARCH ISSN Research article
 Research article EVALUATION OF SAFETY OF VETTUMARAN GUTIKA THROUGH SUB ACUTE TOXICITY STUDY IN WISTAR RATS Sanjaya Kumar Y.R*, Sushant S Parekar, Thamizh Selvam N, Sanal Gopi C.G and Sudarsanan Nair PK
Research article EVALUATION OF SAFETY OF VETTUMARAN GUTIKA THROUGH SUB ACUTE TOXICITY STUDY IN WISTAR RATS Sanjaya Kumar Y.R*, Sushant S Parekar, Thamizh Selvam N, Sanal Gopi C.G and Sudarsanan Nair PK
EXCRETION QUESTIONS. Use the following information to answer the next two questions.
 EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
Renal System Physiology
 M58_MARI0000_00_SE_EX09.qxd 7/18/11 2:37 PM Page 399 E X E R C I S E 9 Renal System Physiology Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Prior to the lab, suggest to the students that they become familiar with the
M58_MARI0000_00_SE_EX09.qxd 7/18/11 2:37 PM Page 399 E X E R C I S E 9 Renal System Physiology Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Prior to the lab, suggest to the students that they become familiar with the
Chapter 23. The Nephron. (functional unit of the kidney
 Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body.
 Excretion What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body. Excretion in Plants Plants produce very little waste products. Plants lose oxygen and water vapour through the stomata.
Excretion What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body. Excretion in Plants Plants produce very little waste products. Plants lose oxygen and water vapour through the stomata.
Research Article GALLIC ACID AND FLAVONOID ACTIVITIES OF AMARANTHUS GANGETICUS
 ISSN 2395-3411 Available online at www.ijpacr.com 238 Research Article GALLIC ACID AND FLAVONOID ACTIVITIES OF AMARANTHUS GANGETICUS G. Jyoti Jain 1* and S. Ramachandra Setty 2 1 Department of Pharmacology,
ISSN 2395-3411 Available online at www.ijpacr.com 238 Research Article GALLIC ACID AND FLAVONOID ACTIVITIES OF AMARANTHUS GANGETICUS G. Jyoti Jain 1* and S. Ramachandra Setty 2 1 Department of Pharmacology,
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013
 EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
4. Determination of fat content (AOAC, 2000) Reagents
 94 ANALYTICAL METHODS 1. Determination of moisture content (AOAC, 2000) 1. Dry the empty dish and lid in the oven at 105 C for 3 h and transfer to desiccator to cool. Weigh the empty dish and lid. 2. Weigh
94 ANALYTICAL METHODS 1. Determination of moisture content (AOAC, 2000) 1. Dry the empty dish and lid in the oven at 105 C for 3 h and transfer to desiccator to cool. Weigh the empty dish and lid. 2. Weigh
Antiurolithiatic activity of Triphala Karpa Chooranam
 Research Article Antiurolithiatic activity of Triphala Karpa Chooranam A.Tamil Selvan *1, B. Jayalaxmi, R. PAshvini, R.Suthakaran, Vishwanath 2 1 Department of Pharmacology, Teegala Ram Reddy College of
Research Article Antiurolithiatic activity of Triphala Karpa Chooranam A.Tamil Selvan *1, B. Jayalaxmi, R. PAshvini, R.Suthakaran, Vishwanath 2 1 Department of Pharmacology, Teegala Ram Reddy College of
The Urinary System PART A
 15 The Urinary System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Functions of the Urinary
15 The Urinary System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Functions of the Urinary
Nephron Structure inside Kidney:
 In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
Data sheet. TBARS Assay kit. (Colorimetric/Fluorometric) Kit Contents. MDA-TBA Adduct. 2-Thiobarbituric Acid. Cat. No: CA995.
 Data sheet Cat. No: CA995 TBARS Assay kit (Colorimetric/Fluorometric) Introduction Oxidative stress in the cellular environment results in the formation of highly reactive and unstable lipid hydroperoxides.
Data sheet Cat. No: CA995 TBARS Assay kit (Colorimetric/Fluorometric) Introduction Oxidative stress in the cellular environment results in the formation of highly reactive and unstable lipid hydroperoxides.
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Kidneys and Homeostasis
 16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
Functions of the Urinary System
 The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
PARTS OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST
 014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
Chapter 10: Urinary System & Excretion
 Chapter 10: Urinary System & Excretion Organs of Urinary System Kidneys (2) form urine Ureters (2) Carry urine from kidneys to bladder Bladder Stores urine Urethra Carries urine from bladder to outside
Chapter 10: Urinary System & Excretion Organs of Urinary System Kidneys (2) form urine Ureters (2) Carry urine from kidneys to bladder Bladder Stores urine Urethra Carries urine from bladder to outside
The Urinary System. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 16 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 16 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
Urinary System and Fluid Balance. Urine Production
 Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
3 Doddamani M.S. 4 Shankar Ravi 1 PG scholar, Dept of Pg studies in Rasashastra and Bhaishajya Kalpana, TGAMC, Ballari.
 International Journal of Applied Ayurved Research ISSN: 2347-6362 ASSESSMENT OF NEPHROPROTECTIVE ACTIVITY OF TRAIKANTAKA GHRITA ON WISTAR ALBINO RATS 1 M Pallavi. 2 Gowda Shankar 3 Doddamani M.S. 4 Shankar
International Journal of Applied Ayurved Research ISSN: 2347-6362 ASSESSMENT OF NEPHROPROTECTIVE ACTIVITY OF TRAIKANTAKA GHRITA ON WISTAR ALBINO RATS 1 M Pallavi. 2 Gowda Shankar 3 Doddamani M.S. 4 Shankar
Urinary System BIO 250. Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat. Routes of Waste Elimination
 Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
11/05/1431. Urine Formation by the Kidneys Tubular Processing of the Glomerular Filtrate
 Urine Formation by the Kidneys Tubular Processing of the Glomerular Filtrate Chapter 27 pages 327 347 1 OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture you should be able to describe: Absorptive Characteristics
Urine Formation by the Kidneys Tubular Processing of the Glomerular Filtrate Chapter 27 pages 327 347 1 OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture you should be able to describe: Absorptive Characteristics
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note
![Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note Running head: NEPHRON 1. The nephron the functional unit of the kidney. [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note](/thumbs/77/75431210.jpg) Running head: NEPHRON 1 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note NEPHRON 2 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney The kidney is an important excretory
Running head: NEPHRON 1 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney [Student Name] [Name of Institute] Author Note NEPHRON 2 The nephron the functional unit of the kidney The kidney is an important excretory
Pharmacologyonline 3: (2009)
 QUALITY ASSESSMENT OF GINKGO BILOBA IN DIABETIC NEPHROTOXICITY Moreshwar P. Patil a*, Mohan K. Kale b, Kishore P. Bhusari b, Vijay R. Patil a a T. V. E. S. Hon ble Loksevak Mahukarrao Chaudhari College
QUALITY ASSESSMENT OF GINKGO BILOBA IN DIABETIC NEPHROTOXICITY Moreshwar P. Patil a*, Mohan K. Kale b, Kishore P. Bhusari b, Vijay R. Patil a a T. V. E. S. Hon ble Loksevak Mahukarrao Chaudhari College
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE
 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE - OBJECTIVES: 1- The simple examination of urine. 2- To detect some of the normal organic constituents of urine. 3- To detect some of the
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE - OBJECTIVES: 1- The simple examination of urine. 2- To detect some of the normal organic constituents of urine. 3- To detect some of the
Hypoglycemic Activity of Seerankottai Thiravam (Semicarpus Anacardium. Linn) in Alloxan Induced Diabetic Rats
 Research Article Hypoglycemic Activity of Seerankottai Thiravam (Semicarpus Anacardium. Linn) in Alloxan Induced Diabetic Rats P. Parthiban 1, K. Kanagavalli 1, P. Sathiya Rajeswaran 2, J. Anbu 3, A. Chinnasamy
Research Article Hypoglycemic Activity of Seerankottai Thiravam (Semicarpus Anacardium. Linn) in Alloxan Induced Diabetic Rats P. Parthiban 1, K. Kanagavalli 1, P. Sathiya Rajeswaran 2, J. Anbu 3, A. Chinnasamy
2) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure.
 Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
ANTIOXIDANT POTENTIAL OF Sida retusa, Urena lobata AND Triumfetta rhomboidea
 Ancient Science Vol : XXV(3&4) January, February, March, April, May, June 2006 ANTIOXIDANT POTENTIAL OF Sida retusa, Urena lobata AND Triumfetta rhomboidea K.P.Lissy*, Thara K. Simon a and M.S. Latha b
Ancient Science Vol : XXV(3&4) January, February, March, April, May, June 2006 ANTIOXIDANT POTENTIAL OF Sida retusa, Urena lobata AND Triumfetta rhomboidea K.P.Lissy*, Thara K. Simon a and M.S. Latha b
Fifth Year Biology. Excretion. Miss Rochford
 Fifth Year Biology Excretion Miss Rochford In this Topic Excretion in plants Excretion and homeostasis Skin Organs of excretion Urinary system Kidneys Nephron Control of urine volume Characteristics of
Fifth Year Biology Excretion Miss Rochford In this Topic Excretion in plants Excretion and homeostasis Skin Organs of excretion Urinary system Kidneys Nephron Control of urine volume Characteristics of
Osmoregulation and the Excretory System
 Honors Biology Study Guide Chapter 25.4 25.10 Name Osmoregulation and the Excretory System FUNCTIONS OF THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM OSMOREGULATION Freshwater: Marine: Land Animals: Sources of Nitrogenous Wastes?
Honors Biology Study Guide Chapter 25.4 25.10 Name Osmoregulation and the Excretory System FUNCTIONS OF THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM OSMOREGULATION Freshwater: Marine: Land Animals: Sources of Nitrogenous Wastes?
Homeostatic Regulation
 Homeostatic Regulation A hormone is :a Water-soluble hormones: Composed of amino acids and bind a receptor protein on the of the target cell. This starts a signal cascade inside the cell and the signal
Homeostatic Regulation A hormone is :a Water-soluble hormones: Composed of amino acids and bind a receptor protein on the of the target cell. This starts a signal cascade inside the cell and the signal
INVESTIGATION OF NEPFROPROTECTIVE EFFECT OF SILYMARIN AGAINST METHOTREXATE AND IFOSFAMIDE INDUCED TOXICITY IN RATS.
 INVESTIGATION OF NEPFROPROTECTIVE EFFECT OF SILYMARIN AGAINST METHOTREXATE AND IFOSFAMIDE INDUCED TOXICITY IN RATS. MANOHAR NAIK K*, MANODEEP CHAKRABORTY, RIYAZ AHMED, SHAHZAD HAMZA, MOHAMMED AFSAL A R.
INVESTIGATION OF NEPFROPROTECTIVE EFFECT OF SILYMARIN AGAINST METHOTREXATE AND IFOSFAMIDE INDUCED TOXICITY IN RATS. MANOHAR NAIK K*, MANODEEP CHAKRABORTY, RIYAZ AHMED, SHAHZAD HAMZA, MOHAMMED AFSAL A R.
Chapter 32 Excretion
 Chapter 32 Excretion 3.4 Learning Objectives 3.4.6 The Excretory System in Humans 1. Role of the excretory system in homeostasis. 2. Importance of temperature regulation within the body. 3. Outline the
Chapter 32 Excretion 3.4 Learning Objectives 3.4.6 The Excretory System in Humans 1. Role of the excretory system in homeostasis. 2. Importance of temperature regulation within the body. 3. Outline the
ANTI-DIABETIC ACTIVITY OF HELICTERES ISORA ROOT
 ANTI-DIABETIC ACTIVITY OF HELICTERES ISORA ROOT Sama Venkatesh *1, G.Dayananda Reddy 1, B.Madhava Reddy 1, M.Lakshman 2. 1 Department of Pharmacognosy, G.Pulla Reddy College of Pharmacy, Mehdipatnam, Hyderabad
ANTI-DIABETIC ACTIVITY OF HELICTERES ISORA ROOT Sama Venkatesh *1, G.Dayananda Reddy 1, B.Madhava Reddy 1, M.Lakshman 2. 1 Department of Pharmacognosy, G.Pulla Reddy College of Pharmacy, Mehdipatnam, Hyderabad
April 08, biology 2201 ch 11.3 excretion.notebook. Biology The Excretory System. Apr 13 9:14 PM EXCRETORY SYSTEM.
 Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
Nephrology - the study of the kidney. Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system
 Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Collin College. BIOL Anatomy & Physiology. Urinary System. Summary of Glomerular Filtrate
 Collin College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology Urinary System 1 Summary of Glomerular Filtrate Glomerular filtration produces fluid similar to plasma without proteins GFR ~ 125 ml per min If nothing else
Collin College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology Urinary System 1 Summary of Glomerular Filtrate Glomerular filtration produces fluid similar to plasma without proteins GFR ~ 125 ml per min If nothing else
Lecture 16: The Nephron
 Lecture 16: The Nephron Reading: OpenStax A&P Text Chapter 25 Primary functions of the kidneys 1. Regulating osmolarity (blood concentration!) A. Regulating blood pressure B. Maintaining ion balance C.
Lecture 16: The Nephron Reading: OpenStax A&P Text Chapter 25 Primary functions of the kidneys 1. Regulating osmolarity (blood concentration!) A. Regulating blood pressure B. Maintaining ion balance C.
The Excretory System. Biology 20
 The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 19-1c. Efferent arteriole. Juxtaglomerular apparatus
 /6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
/6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
AAYUSHANTI GENERIC RANGE
 AAYUSHANTI GENERIC RANGE Ayurvedic medicines have been tried and tested over centuries and still hold fort even today. A product like Triphala Churna which since centuries is considered one of the best
AAYUSHANTI GENERIC RANGE Ayurvedic medicines have been tried and tested over centuries and still hold fort even today. A product like Triphala Churna which since centuries is considered one of the best
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6
 BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
Renal Physiology - Lectures
 Renal Physiology - Lectures Physiology of Body Fluids PROBLEM SET, RESEARCH ARTICLE Structure & Function of the Kidneys Renal Clearance & Glomerular Filtration PROBLEM SET Regulation of Renal Blood Flow
Renal Physiology - Lectures Physiology of Body Fluids PROBLEM SET, RESEARCH ARTICLE Structure & Function of the Kidneys Renal Clearance & Glomerular Filtration PROBLEM SET Regulation of Renal Blood Flow
Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN)
 Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN) A simple, inexpensive screening test a routine urinalysis is often the first test conducted if kidney problems are suspected. A small, randomly collected urine
Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN) A simple, inexpensive screening test a routine urinalysis is often the first test conducted if kidney problems are suspected. A small, randomly collected urine
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion. The Kidneys
 Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
5.Which part of the nephron removes water, ions and nutrients from the blood?
 Uro question 1.While reading a blood test I notice a high level of creatinine, I could assume from this that A) There is a possibility of a UTI B) There is a possibility of diabetes C) There is a possibility
Uro question 1.While reading a blood test I notice a high level of creatinine, I could assume from this that A) There is a possibility of a UTI B) There is a possibility of diabetes C) There is a possibility
Urine Formation. Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages Urine Formation. Glomerular Filtration 4/24/2016
 Urine Formation Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages 9-17 Filtrate Blood plasma minus most proteins Urine
Urine Formation Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages 9-17 Filtrate Blood plasma minus most proteins Urine
PHGY210 Renal Physiology
 PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
BCH 447. Estimation of Serum Urea
 BCH 447 Estimation of Serum Urea 1 Objective: Estimation of Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) in serum sample. 2 -Urea: Urea is the highest non-protein nitrogen compound in the blood. Urea is the major excretory
BCH 447 Estimation of Serum Urea 1 Objective: Estimation of Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) in serum sample. 2 -Urea: Urea is the highest non-protein nitrogen compound in the blood. Urea is the major excretory
Urea Nitrogen (BUN) detection Kit
 K-ASSAY KAMIYA BIOMEDICAL COMPANY KAMIYA BIOMEDICAL COMPANY Urea Nitrogen (BUN) detection Kit For the quantitative determination of urea nitrogen in saliva and TCM Cat. No. KT-747 For Research Use Only.
K-ASSAY KAMIYA BIOMEDICAL COMPANY KAMIYA BIOMEDICAL COMPANY Urea Nitrogen (BUN) detection Kit For the quantitative determination of urea nitrogen in saliva and TCM Cat. No. KT-747 For Research Use Only.
KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin
![KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin](/thumbs/87/96174332.jpg) Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
Urinary System and Excretion. Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Class XI Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination Biology
 Class XI Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination Biology Question 1: Define Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) Glomerular filtration rate is the amount of glomerular filtrate formed in all the
Class XI Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination Biology Question 1: Define Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) Glomerular filtration rate is the amount of glomerular filtrate formed in all the
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Collin County Community College RENAL PHYSIOLOGY
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Glomerular Filtration Filtration process that occurs in Bowman s Capsule Blood is filtered and
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Glomerular Filtration Filtration process that occurs in Bowman s Capsule Blood is filtered and
Outline Urinary System. Urinary System and Excretion. Urine. Urinary System. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
organs of the urinary system
 organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
Renal Physiology - Lectures
 Renal Physiology 2011 Lisa M. Harrison-Bernard, PhD lharris@lsuhsc.edu Renal Physiology - Lectures Physiology of Body Fluids 2. Structure & Function of the Kidneys 3. Renal Clearance & Glomerular Filtration
Renal Physiology 2011 Lisa M. Harrison-Bernard, PhD lharris@lsuhsc.edu Renal Physiology - Lectures Physiology of Body Fluids 2. Structure & Function of the Kidneys 3. Renal Clearance & Glomerular Filtration
A-LEVEL BIOLOGY MODULE 5: Communication, Homeostasis & Energy
 A-LEVEL BIOLOGY MODULE 5: Communication, Homeostasis & Energy TOPIC 1 Communication & Homeostasis Need for communication Organisms must maintain certain conditions Optimal conditions for cells and enzymes
A-LEVEL BIOLOGY MODULE 5: Communication, Homeostasis & Energy TOPIC 1 Communication & Homeostasis Need for communication Organisms must maintain certain conditions Optimal conditions for cells and enzymes
Renal physiology D.HAMMOUDI.MD
 Renal physiology D.HAMMOUDI.MD Functions Regulating blood ionic composition Regulating blood ph Regulating blood volume Regulating blood pressure Produce calcitrol and erythropoietin Regulating blood glucose
Renal physiology D.HAMMOUDI.MD Functions Regulating blood ionic composition Regulating blood ph Regulating blood volume Regulating blood pressure Produce calcitrol and erythropoietin Regulating blood glucose
WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure These wastes include: Carbon dioxide Mostly through breathing
EXCRETORY SYSTEM WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure These wastes include: Carbon dioxide Mostly through breathing
Excretory System Workbook
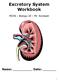 Excretory System Workbook MCHS Biology 20 Mr. Korotash Name: Date: 1 Study the diagram above. Name the structures and indicate their functions by completing the following table: Structure 1. Function 2.
Excretory System Workbook MCHS Biology 20 Mr. Korotash Name: Date: 1 Study the diagram above. Name the structures and indicate their functions by completing the following table: Structure 1. Function 2.
Renal Reabsorption & Secretion
 Renal Reabsorption & Secretion Topics for today: Nephron processing of filtrate Control of glomerular filtration Reabsorption and secretion Examples of solute clearance rates Hormones affecting kidney
Renal Reabsorption & Secretion Topics for today: Nephron processing of filtrate Control of glomerular filtration Reabsorption and secretion Examples of solute clearance rates Hormones affecting kidney
The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion. What are the functions of the urinary system? Maintenance of water-salt and acidbase
 10.1 Urinary system The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion 10.1 Urinary system What are the functions of the urinary system? 1. Excretion of metabolic wastes (urea, uric acid & creatinine) 1. Maintenance
10.1 Urinary system The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion 10.1 Urinary system What are the functions of the urinary system? 1. Excretion of metabolic wastes (urea, uric acid & creatinine) 1. Maintenance
URINARY SYSTEM. Urinary System
 URINARY SYSTEM Urinary System Kidney Functions Excretion Regulation of blood volume and pressure Regulation of electrolyte and ph levels Kidney Structure Gross Anatomy Fibrous Capsule Renal Cortex Renal
URINARY SYSTEM Urinary System Kidney Functions Excretion Regulation of blood volume and pressure Regulation of electrolyte and ph levels Kidney Structure Gross Anatomy Fibrous Capsule Renal Cortex Renal
ab Lipid Peroxidation (MDA) Assay kit (Colorimetric/ Fluorometric)
 Version 10b Last updated 19 December 2018 ab118970 Lipid Peroxidation (MDA) Assay kit (Colorimetric/ Fluorometric) For the measurement of Lipid Peroxidation in plasma, cell culture and tissue extracts.
Version 10b Last updated 19 December 2018 ab118970 Lipid Peroxidation (MDA) Assay kit (Colorimetric/ Fluorometric) For the measurement of Lipid Peroxidation in plasma, cell culture and tissue extracts.
Date... Name... Group... Urine sample (Tube No 2)
 Date... Name... Group... Instructions for the practical lesson on biochemistry Topic: Non-protein nitrogen compounds Task 1: Estimation of creatinine in serum and urine 1. Trichloroacetic acid 1.22 mol/l
Date... Name... Group... Instructions for the practical lesson on biochemistry Topic: Non-protein nitrogen compounds Task 1: Estimation of creatinine in serum and urine 1. Trichloroacetic acid 1.22 mol/l
Pharmacologyonline 1: (2010)
 THERAPEUTIC ROLE OF ANTI-OXIDANT PROPERTIES OF EMBLICA OFFICINALIS (AMLA) IN STREPTOZOTOCIN INDUCED TYPE I DIABETIC RATS P. R. Tirgar* 1, P. D. Jadav 2, D. B. Sheth 3, T. R. Desai 4 Authors addresses Pravin
THERAPEUTIC ROLE OF ANTI-OXIDANT PROPERTIES OF EMBLICA OFFICINALIS (AMLA) IN STREPTOZOTOCIN INDUCED TYPE I DIABETIC RATS P. R. Tirgar* 1, P. D. Jadav 2, D. B. Sheth 3, T. R. Desai 4 Authors addresses Pravin
Complete the table below to compare the processes of excretion and secretion.
 1. Excretion and secretion are two processes that take place in the body of a mammal. Complete the table below to compare the processes of excretion and secretion. excretion secretion one difference one
1. Excretion and secretion are two processes that take place in the body of a mammal. Complete the table below to compare the processes of excretion and secretion. excretion secretion one difference one
CHAPTER 25 URINARY. Urinary system. Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1. functions
 CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
Question 1: Solution 1: Question 2: Question 3: Question 4: Class X The Excretory System Biology
 A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (select the most appropriate option in each case) Book Name: Selina Concise Question 1: Excretion primarily involves (a) removal of all byproducts during catabolism (b) removal
A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (select the most appropriate option in each case) Book Name: Selina Concise Question 1: Excretion primarily involves (a) removal of all byproducts during catabolism (b) removal
Kidney Structure. Renal Lobe = renal pyramid & overlying cortex. Renal Lobule = medullary ray & surrounding cortical labryinth.
 Kidney Structure Capsule Hilum ureter renal pelvis major and minor calyxes renal and vein segmental arteries interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries Medulla renal pyramids cortical/renal
Kidney Structure Capsule Hilum ureter renal pelvis major and minor calyxes renal and vein segmental arteries interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries Medulla renal pyramids cortical/renal
