Transanal irrigation for the management of neurogenic bowel dysfunction: evidence summary
|
|
|
- Charlene Perkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Transanal irrigation for the management of neurogenic bowel dysfunction: evidence summary A randomized, controlled trial of transanal irrigation versus conservative bowel management in spinal cord-injured patients Christensen P, et al. Gastroenterology 2006;131: Treatment of neurogenic bowel dysfunction using transanal irrigation: a multicenter Italian study Del Popolo G, et al. Spinal Cord 2008;46: Cost-effectiveness of transanal irrigation versus conservative bowel management for spinal cord injury patients Christensen P, et al. Spinal Cord 2009;47: Long-term outcome and safety of transanal colonic irrigation for neurogenic bowel dysfunction Faaborg PM, et al. Spinal Cord 2009;47: Long-term outcome and safety of transanal irrigation for constipation and fecal incontinence Christensen P, et al. Dis Colon Rectum 2009;52: Transanal irrigation for the treatment of neuropathic bowel dysfunction López Pereira P, et al. J Pediatr Urol 2009;6: Long-term follow-up of retrograde colonic irrigation for defaecation disturbances Gosselink MP, et al. Colorectal Dis 2005;7:65 69 Neurogenic bowel dysfunction score Krogh K, et al. Spinal Cord 2006;44: Review of the efficacy and safety of transanal irrigation for neurogenic bowel dysfunction Emmanuel A. Spinal Cord 2010;48: Neurogenic bowel management after spinal cord injury: a systematic review of the evidence Krassioukov A, et al. Spinal Cord 2010;48: Transanal irrigation for disordered defecation: a systematic review Christensen P, Krogh K. Scand J Gastroenterol 2010;45: Transanal irrigation for the management of neurogenic bowel dysfunction: summary of benefits
2
3 Transanal irrigation for the management of neurogenic bowel dysfunction Introduction This booklet summarises key data on the use of transanal irrigation (TAI) for the management of neurogenic bowel dysfunction (NBD), primarily in patients with spinal cord injury (SCI) and spina bifida, in terms of efficacy, safety, well-being, quality of life, and overall cost to society. Defaecation disturbances affect many individuals with neurological damage or disease The term NBD describes a range of defaecation disturbances, including constipation and faecal incontinence, caused by neurological damage or disease. NBD is common following SCI, and in patients with spina bifida, multiple sclerosis, and other neurological diseases. Moderate-to-severe NBD symptoms affect approximately half of all patients with SCI 1 Constipation is very common among children and young adults with spina bifida and approximately one third are faecally incontinent 2,3 Approximately 68% of patients with multiple sclerosis develop bowel symptoms 4 The importance of an effective bowel care routine The symptoms of NBD can cause significant physical and emotional distress, affecting self-esteem, 5 personal relationships, 5 and social life. 6 Quality of life has been observed to decrease as the severity of NBD increases 1 and patients with SCI report that bowel dysfunction impacts more on life than any other SCI-related impairment. 7 As well as being socially disabling, NBD may cause patients to experience pain, bloating and discomfort on a regular basis. Many patients with NBD spend a significant part of their day on bowel management: 14% to 63% spend more than 1 hour on each episode. 7,8 Furthermore, complete assistance from a care giver is required by 23% and some help is required by 12%. 7 3
4 Transanal irrigation putting patients in control In addition to providing relief from the symptoms of NBD, the ideal bowel management routine should support the patient s dignity and independence to help promote their self-esteem and minimise the cost of assistance from healthcare professionals and carers. TAI is a technique used to empty faeces from the bowel in a controlled manner and is an alternative to conventional bowel management strategies. Water is introduced into the rectum and colon via the anus, and subsequently evacuated into a toilet together with the content of the descending colon, sigmoid and rectum. Figure: The bowel Transverse colon Ascending colon Descending colon Sigmoid colon Rectum Anus Conducting TAI on a regular basis can be used to help prevent accidents in patients with faecal incontinence; clinical studies observe fewer urinary tract infections (UTIs) than conservative bowel management strategies. 9,10 In addition, regular evacuation of the recto-sigmoid area promotes transport through the entire colon, therefore helping to prevent blockages in patients with constipation. TAI should always be started under medical supervision. However, after an initial period of training, many individuals can successfully take control of their own bowel management by conducting TAI, without the help of a carer. 4
5 How transanal irrigation works to normalise bowel function Radiographic markers can be used to visualise the contents of the bowel (the scintigraphy method). Using this technique, the images below show how SCI can affect emptying of the bowel. 11 In a non-injured person, the rectum and most of the descending colon are empty after defaecation. In contrast, in a patient with SCI, a lot of faeces remain in the bowel after defaecation, putting the person at risk of a faecal incontinence episode. Figure: Scintigraphic images of the bowel without using TAI Before defaecation After normal defaecation Non-injured person SCI patient The following two images show the bowel contents of an SCI patient this time before and after defaecation using TAI. After TAI, the contents of the rectum, sigmoid and most of the descending colon have been efficiently emptied; the image resembles what would be seen after defaecation in a non-injured person. After TAI, new faeces take an average of two days to reach the rectum, 11 helping users of TAI to remain continent between regular irrigations. Figure: Scintigraphic images of the bowel in an SCI patient using TAI Before defaecation After defaecation 5
6 A randomized, controlled trial of transanal irrigation versus conservative bowel management in spinal cord-injured patients 9 Christensen P, et al. Gastroenterology 2006;131: Intervention: Transanal irrigation (TAI) with Peristeen vs conservative bowel management (best supportive care without irrigation) Study design: Large, prospective, multicentre, randomised controlled trial (10 weeks) 87 patients randomised Peristeen (n=42) 10 weeks Conservative bowel management (n=45) 10 weeks Assessed (n=37) Assessed (n=44) Patients: 87 spinal cord injured adults (including spina bifida, n=2) Lesion complete (n=48) or incomplete (n=39) 74% T9 or above injury Predominant symptom constipation (n=66), faecal incontinence (n=17), or other (n=4) 6
7 Key efficacy data: Significantly reduced symptoms of constipation with Peristeen vs conservative bowel management Mean Cleveland Clinic constipation scoring system score Peristeen (n=39) P= Conservative (n=41) Increasing symptoms (0 30 scale) Significantly reduced symptoms of faecal incontinence with Peristeen vs conservative bowel management Mean St Mark s Fecal Incontinence Grading System score Peristeen (n=42) P= Conservative (n=45) Increasing symptoms (0 24 scale) Significantly reduced symptoms of neurogenic bowel dysfunction with Peristeen vs conservative bowel management P= Mean neurogenic bowel dysfunction score Increasing symptoms (0 47 scale) 0 Peristeen (n=41) Conservative (n=45) 7
8 Improved symptom-related quality of life with Peristeen vs conservative bowel management Peristeen (n=42) Conservative (n=45) Modified American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons fecal incontinence score P= Lifestyle P= Coping / behaviour 2.4 P= Depression/ self-perception P= Embarrassment Better quality of life (1 4 scale) Improved bowel function, general satisfaction and quality of life with Peristeen vs conservative bowel management Peristeen (n=42) Conservative (n=45) 6 P= P=0.48 P=0.023 P= Mean numeric box scale score Improvement 0 Bowel function Influence on daily activities General satisfaction Improvement of quality of life* * n=35 Peristeen; n=44 conservative Reduced daily time spent on bowel management with Peristeen vs conservative bowel management Total time spent on bowel management (minutes) Peristeen (n=37) P= Conservative (n=43) 8
9 Key safety data: During the trial, fewer urinary tract infections (UTIs) with prescribed antibiotics were reported in the Peristeen group (5.9%) than in the conservative bowel management group (15.5%; P=0.0052) Few and only mild side effects were reported. Four patients reported adverse effects while using Peristeen; none were considered serious or related to irrigation No serious episodes of autonomic dysreflexia were reported; symptoms indicating autonomic dysreflexia (sweating, headache, flushing, or pronounced general discomfort) tended to be less frequent in the Peristeen group than in the conservative bowel management group (17.3% vs 30.0%, respectively; P=0.099) Conclusions: Peristeen reduced symptoms of constipation and faecal incontinence compared with conservative bowel management in a large (n=87), randomised controlled multicentre trial of bowel management strategies in patients with spinal cord injury (SCI) Peristeen was safe, with only mild and transient side effects Peristeen was associated with significantly fewer UTIs than conservative bowel management Peristeen significantly improved symptom-related quality of life compared with conservative bowel management Peristeen significantly reduced time spent on bowel management compared with conservative bowel management, freeing-up nearly 30 minutes a day for other activities 9
10 Treatment of neurogenic bowel dysfunction using transanal irrigation: a multicenter Italian study 12 Del Popolo G, et al. Spinal Cord 2008;46: Intervention: Transanal irrigation (TAI) with Peristeen Study design: Prospective, before after study (3-week) Patients: 33 spinal cord injured adults (spina bifida, n=12; multiple sclerosis, n=2; trauma, n=14; other, n=5); 32 completed the study Lesion complete (n=13), incomplete (n=14), or not specified (n=6) Predominant symptom constipation (n=27), faecal incontinence (n=4), or not specified (n=2) Key efficacy data: Compared with baseline, significant (P=0.001) improvement in patients opinion of: Intestinal function Quality of life Degree of satisfaction A successful outcome was reported for 68% of patients with faecal incontinence and 63% with constipation Before starting Peristeen, eight patients (24%) reported spending >1 hour on each evacuation or attempt at evacuation; after starting Peristeen, this was reduced to just one patient (3%) Reductions were reported in pharmaceutical use and dependence on caregivers 90% of patients did not report any urinary tract infections (UTIs) during the study, while 39% reported having more than two UTIs a year on entrance into the study Key safety data: No adverse events were reported 10
11 Before Peristeen After Peristeen Number of patients >120 Time necessary for each evacuation or attempt (minutes) Conclusions: Peristeen significantly improved patients opinion of intestinal functionality after 3 weeks compared with baseline Patients reported significantly improved quality of life and degree of satisfaction after 3 weeks of treatment with Peristeen compared with baseline Peristeen was equally successful in spinal cord injury patients with faecal incontinence and constipation After 3 weeks of treatment, Peristeen was associated with reduced pharmaceutical use, low incidence of UTIs, reduced time spent on evacuation, and reduced dependence on caregivers Peristeen had a good safety profile 11
12 Cost-effectiveness of transanal irrigation versus conservative bowel management for spinal cord injury patients 13 Christensen P, et al. Spinal Cord 2009;47: Intervention: Transanal irrigation (TAI) with Peristeen vs conservative bowel management (best supportive care without irrigation) Study design: Health economic analysis of data from the randomised controlled trial (see pages 6 9; Christensen P, et al. Gastroenterology 2006;131: ) Patients: 87 spinal cord injured adults (including spina bifida, n=2) Lesion complete (n=48) or incomplete (n=39) 74% T9 or above injury Predominant symptom constipation (n=66), faecal incontinence (n=17), or other (n=4) Key efficacy data: Peristeen was associated with lower total cost to society than conservative management, when considering: Urinary tract infection (UTI) cost (cost for general practitioner visit, urine test, antibiotics) Labour cost (cost of carer helping with bowel management and changes/baths because of soiling) Total product-related costs (cost of products used for changes/baths because of soiling, products for TAI, and constipation medicine) Indirect cost (patient productivity increases when less time is spent on bowel management) The cost for a 2-day period was less with Peristeen than conservative management when non-product related costs were factored in TAI with Peristeen significantly improved all outcome measures of bowel function, including symptoms of constipation, faecal incontinence and neurogenic bowel dysfunction score (see pages 7 8) 12
13 Peristeen Conservative Cost for 2-day period ( ) (average interval between procedures) Labour cost Productrelated cost 1 3 Urinary tract infection cost Indirect cost Total cost to society Conclusions: Peristeen significantly reduced symptoms of neurogenic bowel dysfunction compared with conservative management In patients with spinal cord injury, self-administered TAI with Peristeen was associated with lower total cost to society than conservative bowel management Product-related costs were offset by: Lower costs for a carer to help with bowel management and changes/washing due to leakage Lower costs associated with UTIs Lower indirect costs as a result of increased productivity by patients due to spending less time on bowel management 13
14 Long-term outcome and safety of transanal colonic irrigation for neurogenic bowel dysfunction 14 Faaborg PM, et al. Spinal Cord 2009;47: Intervention: Transanal irrigation (TAI) with rectal balloon catheter (48%), cone-shaped colostomy tip (32%), other system (20%) Study design: Long-term follow-up study (mean, 1.6 years; range, years) Patients: 211 patients, predominantly spinal cord injured (n=173; including spina bifida, n=32) or with multiple sclerosis (n=25) or other central nervous system aetiology (n=13) using TAI after failure of conservative bowel management Key efficacy data: Treatment success was recorded at long-term follow-up (defined as patient still using TAI at follow-up or had continued using it until they died or symptoms resolved) Treatment discontinuations were most frequent during the first few months of treatment; however, at 3 years the success rate stabilised at 35% for the entire group Neurogenic bowel dysfunction aetiology Patients with treatment success, % a Total spinal cord injury (n=173) 49 Traumatic spinal cord injury (n=74) 53 Spina bifida (n=32) 50 Prolapsed intervertebral disc (n=29) 45 Spinal stenosis (n=17) 50 Intraspinal haemorrhagia (n=4) 50 Intraspinal tumour (n=10) 50 Intraspinal infection (n=7) 43 Multiple sclerosis (n=25) 40 Other central nervous system aetiology (n=13) 31 Stroke or cerebral palsy (n=10) 30 Parkinson s disease (n=3) 33 TOTAL (n=211) 46 a At mean follow-up of 1.6 years 14
15 Key safety data: Minor side effects were reported in 48% of patients One non-lethal bowel perforation occurred in ~50,000 irrigations No side effects Abdominal pain or discomfort Minor rectal bleeding Fatigue General discomfort Perspiration Peri-anal discomfort Nausea Shivers Massive headache Facial flushing Patients (%) Conclusions: Overall, treatment success was achieved in 46% of long-term users of TAI, in whom conservative bowel management had failed Among the subgroup of patients with spinal cord injury (SCI) using TAI long term, treatment success was achieved in 49% One in five treatment discontinuations occurred during the first few months of treatment, after which the rate of discontinuations slowed TAI had a good safety profile when used long term The risk of bowel perforation with TAI was low (estimated risk 0.002% per irrigation) 15
16 Long-term outcome and safety of transanal irrigation for constipation and fecal incontinence 15 Christensen P, et al. Dis Colon Rectum 2009;52: Intervention: Transanal irrigation (TAI) with a rectal balloon catheter (Peristeen or Mallinckrodt; 69%), Alterna cone-shaped colostomy tip (25%), other catheter (7%) Study design: Long-term follow-up study (mean, 1.8 years; range, years) Patients: 348 patients with various defaecation disturbances and using TAI after first-line treatments had failed Key efficacy data: Treatment success (defined as patient still using TAI, or had continued using it until they died or symptoms resolved) was recorded at the long-term follow-up Defaecation disturbance aetiology Patients with treatment success, % a Neurogenic bowel dysfunction (n=107) 63 Spinal cord injury (n=68) 62 Spina bifida (n=18) 67 Multiple sclerosis (n=10) 50 Parkinson s disease (n=1) 100 Cerebral thrombosis (n=10) 70 Anal insufficiency (n=241) 40 Idiopathic faecal incontinence (n=49) 51 Obstetric sphincter injury (n=21) 52 Sequelae from rectal surgery (n=15) 40 Sequelae from rectal prolapse (n=21) 24 Sequelae from anal surgery (n=12) 25 Idiopathic constipation (n=79) 34 Miscellaneous (n=44) 43 TOTAL (n=348) 47 a At mean follow-up of 1.8 years 16
17 The majority of treatment discontinuations occurred during the start of treatment; if the first 3 months of treatment was considered a test phase, the overall success rate for patients continuing treatment increased from 47% to 56% Key safety data: Mild and transient symptoms were reported by about 60% of active users of irrigation Non-lethal bowel perforation occurred in two patients in ~110,000 irrigations Any side effects Abdominal pain Anorectal pain Subsequent tiredness Nausea Anal bleeding Chills Sweating Pounding headache Facial flushing Other Patients (%) Conclusions: Treatment success was achieved in 47% of the cohort of long-term users of TAI, in whom first-line treatment had failed; TAI was often given to patients awaiting invasive surgery and therefore at high risk of treatment failure TAI was particularly effective in patients with neurogenic bowel dysfunction, with a success rate of 63% The majority of treatment discontinuations occurred during the start of treatment; the overall success rate was 56% among patients who continued to use TAI after a 3-month test phase TAI had a good safety profile when used long term The risk of bowel perforation with TAI was low (estimated risk 0.002% per irrigation) 17
18 Transanal irrigation for the treatment of neuropathic bowel dysfunction 8 López Pereira P, et al. J Pediatr Urol 2009;6: Intervention: Transanal irrigation (TAI) with Peristeen Study design: Prospective study (mean follow-up, 12 months; range, 4 18 months) Patients: 40 children and youths (mean age, 12.5 years; range, 6 25 years) with spina bifida and neurogenic bowel dysfunction (NBD) that did not respond satisfactorily to conventional bowel management Key efficacy data: In the 35 patients who completed the study, there was a significant improvement in symptoms of bowel dysfunction while using Peristeen Peristeen significantly reduced: Difficulty and/or pain during defaecation (P<0.005) Feeling of incomplete evacuation (P<0.0001) Leakage of faeces (P<0.0001) Abdominal pain or discomfort before or after defaecation (P<0.0001) Sweating or headache during or after defaecation (P<0.05) Peristeen significantly improved patients opinion of intestinal functionality (P<0.0001) Peristeen reduced the total time spent on bowel management; before Peristeen, 63% of children spent >1 hour; with Peristeen, this was reduced to 3% Independence was improved with Peristeen; before Peristeen, 28% of patients were partially or totally independent in terms of bowel evacuation; with Peristeen, 46% were partially or totally independent Key safety data: No adverse events were reported 18
19 Patients spending >1 hour on bowel management (%) Before Peristeen 3 After Peristeen Patients partially or totally independent (%) Before Peristeen 46 After Peristeen Conclusions: Peristeen is an effective therapeutic approach in children and youths with spina bifida and NBD After changing from conservative bowel management to Peristeen, patients experienced significantly reduced symptoms of bowel dysfunction, including faecal incontinence Using Peristeen led to greater partial or total independence, reducing the need for assistance with bowel evacuation in children and youths with spina bifida Peristeen significantly reduced the total time spent on bowel management, decreasing the proportion of children spending more than an hour on bowel management from 63% to 3% Peristeen had a good safety profile in children and youths with spina bifida and NBD 19
20 Long-term follow-up of retrograde colonic irrigation for defaecation disturbances 16 Gosselink MP, et al. Colorectal Dis 2005;7:65 69 Intervention: Transanal irrigation (TAI) using conventional colostomy irrigation set comprising an irrigation bag, tube and cone-tip (Biotrol Iryflex, B. Braun Medical B.V., Oss, Netherlands) Study design: Long-term, follow-up study (median follow-up, 4.7 years; range, years) in a consecutive series of 267 patients who were offered retrograde colonic irrigation Patients: 169 patients with disturbed continence or obstructed defaecation (not responding to medical treatment or biofeedback) who both started irrigation and returned a questionnaire Key efficacy data: Overall, TAI was reported to be effective in 54% of patients TAI was particularly effective in patients with defaecation disturbances due to obstruction or after low anterior resection or pouch surgery Transanal irrigation effective (percentage of patients) Soiling (n=32) Incontinence (n=71) LAR, lower anterior resection Obstructed defaecation (n=37) LAR or pouch surgery (n=29) 20
21 TAI was stopped by 78 patients in whom it was not effective and by 15 patients who encountered a benefit, giving an overall long-term success rate of 45% Key safety data: Of the patients who regularly performed TAI at the time of follow-up (n=76), 74% reported irrigation-related problems most commonly technical problems 50 Irrigation-related problems (percentage of patients)* Abdominal discomfort Technical problems Too time consuming Fluid loss Anal pain *Approximate numbers Conclusions: TAI can be used successfully in the long term to manage symptoms of defaecation disturbances TAI is an effective therapeutic approach for a variety of defaecation disturbances including soiling, faecal incontinence, obstructed defaecation, and after low anterior resection or pouch surgery After a median follow-up of 4.7 years, more than half (54%) of patients with defaecation disturbances of mixed aetiology considered TAI to be effective The most commonly reported therapy-related problems among long-term users of TAI were technical in nature 21
22 Neurogenic bowel dysfunction score 17 Krogh K, et al. Spinal Cord 2006;44: Aim: To develop and validate a symptom-based score for neurogenic bowel dysfunction (NBD) Scope: Cross-sectional analysis of a questionnaire sent to 589 Danish individuals with spinal cord injury (SCI); questions included: background parameters (n=8), faecal incontinence (n=10), constipation (n=10), obstructed defaecation (n=8) and impact on quality of life (n=3); the reproducibility and validity of each item within the questionnaire were also tested Key findings: A total of 424 individuals with SCI (72%) responded to the questionnaire Reproducibility and validity were good or very good for most questions describing severity of symptoms and bowel-emptying procedure: Only fair for average time required for each defaecation and frequency of digital stimulation/ evacuation, probably caused by a larger number of possible answers Reproducibility and validity were fair, good or very good for questions relating to quality of life Telephone interviews determined that some questions were not well defined: Few individuals knew how to define constipation Respondents did not know whether the severity of their symptoms had changed or they had learnt to live with the symptoms Median NBD score was 10 (range 0 31): 90% of respondents had scores between 0 and 18 Mean score differed significantly (P<0.001) between patients reporting different levels of impact on quality of life: 15.2 for those reporting major impact 11.4 for those reporting some impact 8.1 for those reporting minor impact 4.8 for those reporting no impact 22
23 NBD score versus impact on QoL caused by bowel dysfunction Very minor dysfunction (NBD 0 6) Minor dysfunction (NBD 7 9) Moderate dysfunction (NBD 10 13) Severe dysfunction (NBD 14) Total Major impact on quality of life Some impact on quality of life Little impact on quality of life No impact on quality of life 0% (n=0) 13% (n=7) 10% (n=10) 38% (n=40) 57 8% (n=8) 13% (n=7) 30% (n=30) 27% (n=28) 73 34% (n=34) 46% (n=24) 36% (n=36) 29% (n=30) % (n=58) 27% (n=14) 23% (n=23) 6% (n=6) 101 TOTAL 100 (28%) 52 (15%) 99 (28%) 104 (29%) 355 Conclusions: 10 of the 28 items investigated were found to have acceptable validity and reproducibility Associations between the 10 items included in the NBD score and self-reported impact on quality of life were very strong and most were highly significant The questions were designed for use in adults; only 4 respondents were aged less than 15 years and so any potential bias caused by instruction from parents is likely to be insignificant Individuals with severe symptoms should be referred to centres with special interest in the evaluation and treatment of bowel symptoms in individuals with SCI This NBD score is valid for SCI patients It is our hope that the score can be used to make future studies of bowel symptoms in SCI patients comparable and to assess changes in bowel function when treatment modalities are evaluated 23
24 Review of the efficacy and safety of transanal irrigation for neurogenic bowel dysfunction 18 Emmanuel A. Spinal Cord 2010;48: Aim: To summarise current evidence for the efficacy and safety of transanal irrigation (TAI) in patients with neurogenic bowel dysfunction (NBD) Scope: Online literature search via PubMed for articles describing the use of TAI in NBD Key findings: 23 relevant articles were identified 1 large randomised controlled trial in adults with spinal cord injury (SCI) 9 22 mostly retrospective or observational studies TAI was more effective than conservative bowel management in individuals with SCI with respect to long-term improvements in symptoms and quality of life In children and youths with NBD associated with spina bifida, symptoms of constipation and faecal incontinence can be reduced with TAI TAI can also be an effective therapy for bowel dysfunction caused by a range of other neurological disorders, including multiple sclerosis (MS), Parkinson s disease, stroke, cerebral palsy or cerebral thrombosis Conclusions: TAI is superior to conservative management for treating individuals with NBD There is a need for larger and longer-term trials of TAI in specific NBD populations, especially adults with spina bifida or MS Taken together, these data show that for patients with SCI, TAI is more effective than conservative bowel management, resulting in an improvement in symptoms and quality of life, and that success is maintained in the long term 24
25 Key publications on TAI in paediatric populations with NBD TAI intervention Enema continence catheter (saline enema) Study design Patients Key efficacy and safety results Publication Prospective, before after study (follow-up at 18 and 30 months) 31 children and youths with spinal cord disease (spina bifida, n=30) or injury (n=1) Mean age 9 years (range, 3 19 years) Significantly increased proportion of continent stools, from 28% to 94% (P<0.01) Significantly decreased proportion of constipated stools, from 55% to 15% (P<0.01) Increased satisfaction with bowel programme No adverse events reported Liptak, Revell Enema continence catheter (saline enema) Descriptive study (follow-up duration not reported) 112 children and youths with spina bifida and faecal incontinence Age range 4 20 years Continence achieved in 100% of patients Allergic phenomena reported in 3 patients (possibly due to manufacturing inconsistency in catheter components) Shandling, Gilmour Enema continence catheter (saline enema) Descriptive study (up to 30 months follow-up) 33 children and youths with spina bifida and neurogenic faecal incontinence Mean age 12 years (range, 5 22 years) Continence achieved in 32 of 33 patients Eire et al Irrigation cone Retrospective, descriptive study 24 children with spina bifida who had failed manual evacuation or who had a non-functioning sphincter Continence achieved in 21 of 24 patients Vande Velde et al Cone-tipped catheter (hand-warm tap water) Questionnaire follow-up and chart review (mean follow-up, 33 months; range, 6 55 months) 41 children and youths with spina bifida and bowel dysfunction Constipation and faecal incontinence in 27% of patients each Mean age 8 years (range, 7 months to 22 years) Complete faecal continence achieved in 66% of patients Constipation remained in 39% of patients; no cases of faecal retention or impaction All patients reported either high (63%) or good (37%) levels of satisfaction with therapy Schöller- Gyüre et al Stoma Cone Irrigation Set or Colotip (luke-warm tap water) Questionnaire follow-up study (median follow-up, 1.5 years; range, 4 months to 8 years) 40 children with spina bifida and neurogenic bladder and bowel Median age 2 years 8 months (range, 10 months to 11 years) 85% of patients/parents were satisfied with the procedure All 40 patients were constipation-free 35 of 40 patients were faecally continent 35 of 40 patients remained on TAI at follow-up Mattsson et al Peristeen Prospective study (mean follow-up, 12 months; range, 4 18 months) 40 children and youths with spina bifida and neurogenic bowel dysfunction that did not respond to conventional bowel management Significant reduction in symptoms of bowel dysfunction Reduced proportion of patients spending >1 hour on bowel management from 63% to 3% Increased proportion of patients partially or totally independent in terms of bowel management from 28% to 46% López Pereira et al * Peristeen Prospective before after study (follow-up at 3 months) 60 young patients with myelomeningocele and chronic constipation or unsatisfactory bowel management Mean age 12.5 years (range, 8 17 years) Relief from constipation in 60% and from faecal incontinence in 75% of patients Improved quality of life, including degree of general satisfaction (P<0.001) Fewer urinary tract infections (14 before vs 6 after; P<0.01) Ausili et al
26 Neurogenic bowel management after spinal cord injury: a systematic review of the evidence 25 Krassioukov A, et al. Spinal Cord 2010;48: Aim: To summarise the evidence for the management of neurogenic bowel dysfunction (NBD) in individuals with spinal cord injury (SCI) Scope: Online database search followed by manual search of retrieved articles published from 1950 to July 2009 Key findings: 57 relevant articles were identified The level of evidence offered by each study was rated on a scale from 1 to 5: 25 describe non-pharmacological conservative management strategies 10 describe pharmacological treatment strategies 22 describe surgical interventions 4 studies describe the use of transanal irrigation (TAI) to improve bowel management in SCI patients Conclusions: More than one treatment strategy is often necessary to develop an effective bowel routine Multi-faceted bowel management strategies are usually the first approach and are supported by lower-level evidence Some pharmacological interventions are supported by strong evidence, although some require further investigation into their safety Surgical interventions are not routinely used and are supported by lower-level evidence The use of TAI in individuals with SCI is supported by Level 5 (one observational study), Level 4 (two pre post studies) and Level 1 (one large, good-quality, multicentre, randomised controlled trial) evidence The use of common, validated scoring systems such as the NBD score and the International Bowel Function Data Sets should be implemented to allow comparisons of results and meta-analyses 26
27 Key publications on TAI in adult populations with NBD Publication; country; score; research design; total sample size Christensen et al 2006; 9 Denmark; PEDro score = 7; randomised controlled trial; N=87 Christensen et al 2008; 26 USA; Downs and Black score = 20; pre post; N=55 Christensen et al 2000; 27 Denmark; Downs and Black score = 17; retrospective interviews and case series; N=29; 19 SCI patients Methods Population: TAI group: mean age: 47.5 years; level of injury: T10 S1, 23 complete and 12 incomplete Conservative management group: mean age: 50.6 years; T10 S1, 23 complete and 23 incomplete Treament: TAI (Peristeen) or conservative management (PVA clinical guidelines) for 10 weeks OM: CCCSS, FIGS, a faecal incontinence score Population: mean age 47.5 ± 15.5 years; level of injury: 61 supraconal, 37 complete, 25 incomplete Treament: TAI (Peristeen) for 10 weeks OM: CCCSS, FIGS, and NBD Population: ECC group: mean age: 39.9 years, range: 7 72 years; level of injury: T2 T11, conal or cauda equina injuries (n=15). MACE group: mean age: 32.8 years, range:15 66 years; level of injury: C5 T2 (n=4) Treatment: ECC verus MACE OM: colorectal function, practical procedure, impact on daily living and QoL, general satisfaction Outcome 1. TAI group scored better on symptom-related QoL, CCCSS, FIGS, and NBD 2. Improvement found in the TAI group was not confined to the more physically able patients 3. The frequency of urinary tract infection was lower in the TAI group 1. CCCSS, FIGS, and NBD scores improved 2. TAI significantly reduced constipation, improved anal continence, and improved symptom-related QoL 1. The ECC was successful in 53% of participants (8 subjects) 2. The MACE procedure was successful in 75% of participants (3 subjects) 3. Successful treatment with the ECC or the MACE led to significant improvements in QoL Del Popolo et al 2008; 12 Italy; Downs and Black score = 14; pre post; N=32 Faaborg et al 2009; 14 Denmark; Downs and Black score = 13; observational; N=211 Puet et al 1997; 28 USA; Downs and Black score = 12; case series; N=31 Population: median age: 31.6 years, 13 complete, 14 incomplete Treatment: TAI (Peristeen) for 3 weeks OM: QoL; use of pharmaceutical, incidence of incontinence and constipation, abdominal pain or discomfort Population: median age 49 years, range: 7 81 years; aetiology: 74 traumatic, 32 spinal bifida, 29 prolapsed intervertebral disk, 38 other, 38 non-sci Treatment: TAI OM: rate of success (treatment was successful if (1) currently using TAI, (2) the patient used TAI until death, or (3) symptoms resolved while using TAI) Population: age: NA; level of injury: 8 tetraplegic, 4 complete; 23 paraplegic, 9 complete Treatment: pulsed irrigation OM: efficacy of technique, outpatient use 1. Significant increase in QoL scores and improvements of constipation 2. Significant decrease in abdominal pain and incidence of incontinence 3. Nine patients reduced or eliminated pharmaceutical use patients stopped TAI in the first 3 months 2. Success in 98 patients after 19 months; and 73 patients after 3 years of follow-up 3. Abdominal pain, minor rectal bleeding, and general discomfort were observed in 101 patients 1. Success in removing stool in all but three patients patients had multiple procedures Abbreviations: CCCSS, Cleveland Clinic Constipation Scoring System; ECC, enema continence catheter; FIGS, St Mark s Fecal Incontinence Grading System; MACE, Malone antegrade continence enema; NBD, neurogenic bowel dysfunction; OM, outcome measures; PEDro, Physiotherapy Evidence Database; PVA, Paralyzed Veterans of America; QoL, Quality of life; TAI, transanal irrigation. Transanal irrigation is a promising technique to reduce constipation and faecal incontinence 27
28 Transanal irrigation for disordered defecation: a systematic review 29 Christensen P, Krogh K. Scand J Gastroenterol 2010;45: Aim: To summarise the accumulated evidence and experience of transanal irrigation (TAI) in the treatment of disordered defaecation Scope: Online database search for TAI articles published up to and including September 2009; reference lists of relevant articles were also searched Key findings: 27 relevant articles were identified, describing treatment in 1,901 individuals aged between 7 months and 90 years One study was conducted as a multicentre, randomised controlled trial of TAI versus conservative bowel management in individuals with spinal cord injury Indications covered the full spectrum of conditions resulting in disordered defaecation TAI was used in a variety of strategies: from front-line treatment to salvage therapy 12 studies evaluated treatment in a total of 672 children: Successful in 81% of constipation cases Successful in 90% of faecal incontinence cases Successful in 66% of mixed symptom cases 17 studies evaluated treatment in a total of 1,229 adults: Successful in 45% of constipation cases Successful in 47% of faecal incontinence cases Successful in 59% of mixed symptom cases Inconsistent measurement of quality of life improvement confounds comparison and assessment; overall, the trend is stable and predictable: a treatment-associated reduction in symptoms raises quality of life scores Conclusions: Very few controlled trials have been performed; current practice is based mainly on clinical experience or short-term follow-up in a small group of individuals Given the especially encouraging results in children with spina bifida or severe constipation, TAI should be considered for bowel dysfunction in these patient groups TAI represents a simple, reversible treatment option if conservative bowel management is unsuccessful, and should be considered before irreversible surgical procedures are considered The authors propose a scheme by which a series of flexible interventions could be considered sequentially in order to optimise TAI for each individual and increase the likelihood of treatment success 28
29 Algorithm for adjustment of transanal irrigation Malfunction of transanal irrigation Pain Consider Constipation Consider Faecal incontinence Reduce volume Increase volume or frequency (or both) Reduce volume Add sodium chloride Hard stools: lactulose ml or magnesium oxide 1 2 g Obstructed defaecation: bisacodyl 5 15 mg Re-empty rectum after 1 2 h Add bisacodyl 5 15 mg Add lactulose or magnesium oxide Add bulking agent Add phosphoral klysma to the irrigation fluid Add loperamide Re-start the bowel with Movicol up to 8 doses per day until defaecation Consider other treatment modalities (Movicol, sacral nerve stimulation, antegrade colonic irrigation, or colostomy) Moreover, transanal irrigation outperformed conservative bowel management, and transanal irrigation is thus both cheaper and more effective than conservative bowel management 29
30 Transanal irrigation for the management of neurogenic bowel dysfunction: summary of benefits Benefit Reference SCI Reduces symptoms of constipation compared with conservative bowel management Reduces symptoms of faecal incontinence compared with conservative bowel management 9, 13 9, 13 Reduces incidence of urinary tract infections 9 Improves patients opinion of intestinal functionality compared with baseline 12 Improves symptom-related quality of life compared with conservative bowel management 9 Improves quality of life compared with baseline 12 Reduces time spent on bowel management compared with conservative bowel management 9, 12, 13 Is well tolerated and has a good safety profile in the short and long term 9, 14, 15 Is associated with lower total cost to society than conservative bowel management 13 Spina bifida Shows promise as an effective and well-tolerated therapeutic approach in children and youths with spina bifida and neurogenic bowel dysfunction Reduces symptoms of constipation and faecal incontinence in children and youths with spina bifida and neurogenic bowel dysfunction* 8, 10, 14, 15, , 10, 14, 15, Reduces incidence of urinary tract infections 10 Other Shows promise as an effective and well-tolerated therapeutic approach for a variety of defaecation disturbances due to neurogenic bowel dysfunction and other causes *References must be used together to support the statement 30
31 References 1. Liu CW, Huang CC, Yang YH, et al. Relationship between neurogenic bowel dysfunction and healthrelated quality of life in persons with spinal cord injury. J Rehabil Med 2009;41: Verhoef M, Lurvink M, Barf HA, et al. High prevalence of incontinence among young adults with spina bifida: description, prediction and problem perception. Spinal Cord 2005;43: Yuan Z, Cheng W, Hou A, et al. Constipation is associated with spina bifida occulta in children. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2008;6: Hinds JP, Eidelman BH, Wald A. Prevalence of bowel dysfunction in multiple sclerosis. A population survey. Gastroenterology 1990;98: Roach MJ, Frost FS, Creasey G. Social and personal consequences of acquired bowel dysfunction for persons with spinal cord injury. J Spinal Cord Med 2000;23: Naicker AS, Roohi SA, Naicker MS, Zaleha O. Bowel dysfunction in spinal cord injury. Med J Malaysia 2008;63: Coggrave M, Norton C, Wilson-Barnett J. Management of neurogenic bowel dysfunction in the community after spinal cord injury: a postal survey in the United Kingdom. Spinal Cord 2009;47: López Pereira P, Salvador OP, Arcas JA, et al. Transanal irrigation for the treatment of neuropathic bowel dysfunction. J Pediatr Urol 2009;6: Christensen P, Bazzocchi G, Coggrave M, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of transanal irrigation versus conservative bowel management in spinal cord-injured patients. Gastroenterology 2006;131: Ausili E, Focarelli B, Tabacco F, et al. Transanal irrigation in myelomeningocele children: an alternative, safe and valid approach for neurogenic constipation. Spinal Cord 2010;48: Christensen P, Olsen N, Krogh K, Bacher T, Laurberg S. Scintigraphic assessment of retrograde colonic washout in fecal incontinence and constipation. Dis Colon Rectum 2003;46: Del Popolo G, Mosiello G, Pilati C, et al. Treatment of neurogenic bowel dysfunction using transanal irrigation: a multicenter Italian study. Spinal Cord 2008;46: Christensen P, Andreasen J, Ehlers L. Cost-effectiveness of transanal irrigation versus conservative bowel management for spinal cord injury patients. Spinal Cord 2009;47: Faaborg PM, Christensen P, Kvitsau B, et al. Long-term outcome and safety of transanal colonic irrigation for neurogenic bowel dysfunction. Spinal Cord 2009;47: Christensen P, Krogh K, Buntzen S, Payandeh F, Laurberg S. Long-term outcome and safety of transanal irrigation for constipation and fecal incontinence. Dis Colon Rectum 2009;52: Gosselink MP, Darby M, Zimmerman DD, et al. Long-term follow-up of retrograde colonic irrigation for defaecation disturbances. Colorectal Dis 2005;7: Krogh K, Christensen P, Sabroe S, Laurberg S. Neurogenic bowel dysfunction score. Spinal Cord 2006;44: Emmanuel A. Review of the efficacy and safety of transanal irrigation for neurogenic bowel dysfunction. Spinal Cord 2010;48:
32 Liptak GS, Revell GM. Management of bowel dysfunction in children with spinal cord disease or injury by means of the enema continence catheter. J Pediatr 1992;120: Shandling B, Gilmour RF. The enema continence catheter in spina bifida: successful bowel management. J Pediatr Surg 1987;22: Eire PF, Cives RV, Gago MC. Faecal incontinence in children with spina bifida: the best conservative treatment. Spinal Cord 1998;36: Vande Velde S, Van Biervilet S, Van Renterghem K, et al. Achieving fecal continence in patients with spina bifida: a descriptive cohort study. J Urol 2007;178: Schöller-Gyüre M, Nesselaar C, van Wieringen H, van Gool JD. Treatment of defecation disorders by colonic enemas in children with spina bifida. Eur J Pediatr Surg 1996;6(Suppl 1): Mattsson S, Gladh G. Tap-water enema for children with myelomeningocele and neurogenic bowel dysfunction. Acta Paediatr 2006;95: Krassioukov A, Eng JJ, Claxton G, et al. Neurogenic bowel management after spinal cord injury: a systematic review of the evidence. Spinal Cord 2010;48: Christensen P, Bazzocchi G, Coggrave M, et al. Outcome of transanal irrigation for bowel dysfunction in patients with spinal cord injury. J Spinal Cord Med 2008;31: Christensen P, Kvitzau B, Krogh K, Buntzen S, Laurberg S. Neurogenic colorectal dysfunction use of new antegrade and retrograde colonic wash-out methods. Spinal Cord 2000;38: Puet TA, Jackson H, Amy S. Use of pulsed irrigation evacuation in the management of the neuropathic bowel. Spinal Cord 1997;35: Christensen P, Krogh K. Transanal irrigation for disordered defacation: a systematic review. Scand J Gastroenterol 2010;45:
33 Notes 33
34 34
35
36 Coloplast develops products and services that make life easier for people with very personal and private medical conditions. Working closely with the people who use our products, we create solutions that are sensitive to their special needs. We call this intimate healthcare. Our business includes ostomy care, urology and continence care and wound and skin care. We operate globally and employ more than 7,000 people. The Coloplast logo is a registered trademark of Coloplast A/S All rights reserved Coloplast A/S, 3050 Humlebæk, Denmark. CV610N Coloplast Ltd Nene Hall Peterborough Business Park Peterborough PE2 6FX
Transanal irrigation for the management of neurogenic bowel dysfunction: Evidence summary
 Transanal irrigation for the management of neurogenic bowel dysfunction: Evidence summary Transanal irrigation for the management of neurogenic bowel dysfunction: evidence summary A randomized, controlled
Transanal irrigation for the management of neurogenic bowel dysfunction: Evidence summary Transanal irrigation for the management of neurogenic bowel dysfunction: evidence summary A randomized, controlled
Efficacy of Peristeen transanal irrigation system for neurogenic bowel in the pediatric population: Preliminary findings
 Efficacy of Peristeen transanal irrigation system for neurogenic bowel in the pediatric population: Preliminary findings Tiffany Gordon, MSN, RN, CRRN, CPN David Vandersteen, MD John Belew RN, PhD Gillette
Efficacy of Peristeen transanal irrigation system for neurogenic bowel in the pediatric population: Preliminary findings Tiffany Gordon, MSN, RN, CRRN, CPN David Vandersteen, MD John Belew RN, PhD Gillette
Transanal colonic irrigation has recently become an
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Long-Term Outcome and Safety of Transanal Irrigation for Constipation and Fecal Incontinence Peter Christensen, Ph.D. 1,2 & Klaus Krogh, D.M.Sci. 2 & Steen Buntzen, D.M.Sci. 1 Fariborz
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Long-Term Outcome and Safety of Transanal Irrigation for Constipation and Fecal Incontinence Peter Christensen, Ph.D. 1,2 & Klaus Krogh, D.M.Sci. 2 & Steen Buntzen, D.M.Sci. 1 Fariborz
Peristeen and the Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Score (NBD) for pediatric patients with spina bifida
 Peristeen and the Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Score (NBD) for pediatric patients with spina bifida Coloplast develops products and services that make life easier for people with very personal and private
Peristeen and the Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Score (NBD) for pediatric patients with spina bifida Coloplast develops products and services that make life easier for people with very personal and private
When the bowel works, life works
 When the bowel works, life works Feeling better by taking control It can be difficult to establish a regular bowel routine for people living with chronic constipation, incontinence or time-consuming bowel
When the bowel works, life works Feeling better by taking control It can be difficult to establish a regular bowel routine for people living with chronic constipation, incontinence or time-consuming bowel
Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction. Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders DEFECATION Delivery of colon contents to the rectum Rectal compliance
Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders DEFECATION Delivery of colon contents to the rectum Rectal compliance
Treatment of neurogenic bowel dysfunction using transanal irrigation: a multicenter Italian study
 (), & International Society All rights reserved -/ $. www.nature.com/sc ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment of neurogenic bowel dysfunction using transanal irrigation: a multicenter Italian study G Del Popolo,
(), & International Society All rights reserved -/ $. www.nature.com/sc ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment of neurogenic bowel dysfunction using transanal irrigation: a multicenter Italian study G Del Popolo,
Bowel Dysfunction in Neurological Disease Best Practice in an Evolving Disorder
 Bowel Dysfunction in Neurological Disease Best Practice in an Evolving Disorder Anton Emmanuel October 2016 National Hospital for Neurology & Neurosurgery Regulation of colonic function Brain gut axis
Bowel Dysfunction in Neurological Disease Best Practice in an Evolving Disorder Anton Emmanuel October 2016 National Hospital for Neurology & Neurosurgery Regulation of colonic function Brain gut axis
Transanal irrigation systems for neurogenic bowel dysfunction, chronic constipation, and chronic faecal incontinence
 Transanal irrigation systems for neurogenic bowel dysfunction, chronic constipation, and chronic faecal incontinence Lead author: Hayley Johnson Regional Drug & Therapeutics Centre (Newcastle) March 2016
Transanal irrigation systems for neurogenic bowel dysfunction, chronic constipation, and chronic faecal incontinence Lead author: Hayley Johnson Regional Drug & Therapeutics Centre (Newcastle) March 2016
HELPING YOU HELP OTHERS RECTAL IRRIGATION WITH AQUAFLUSH CONE BASED RECTAL IRRIGATION SYSTEMS FOR HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS
 HELPING YOU HELP OTHERS RECTAL IRRIGATION WITH AQUAFLUSH CONE BASED RECTAL IRRIGATION SYSTEMS FOR HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS Effective bowel emptying is the norm for most people. However, for your patients,
HELPING YOU HELP OTHERS RECTAL IRRIGATION WITH AQUAFLUSH CONE BASED RECTAL IRRIGATION SYSTEMS FOR HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS Effective bowel emptying is the norm for most people. However, for your patients,
1. What evidence exists that prevention of constipation in the first year of life improves outcome of bowel management in later childhood?
 BOWEL FUNCTION AND CARE Overall Outcomes Primary Outcomes o Maintenance of social continence as appropriate for age level Secondary Outcomes o Maximization of independence with managing bowel program o
BOWEL FUNCTION AND CARE Overall Outcomes Primary Outcomes o Maintenance of social continence as appropriate for age level Secondary Outcomes o Maximization of independence with managing bowel program o
Rectal irrigation: a useful tool in the armamentarium for functional bowel disorders
 Original article doi:10.1111/j.1463-1318.2011.02797.x Rectal irrigation: a useful tool in the armamentarium for functional bowel disorders D. S. Y. Chan*, A. Saklani, P. R. Shah, M. Lewis and P. N. Haray
Original article doi:10.1111/j.1463-1318.2011.02797.x Rectal irrigation: a useful tool in the armamentarium for functional bowel disorders D. S. Y. Chan*, A. Saklani, P. R. Shah, M. Lewis and P. N. Haray
Rectal irrigation (DROP-List)
 B171 February 2017 2.0 Community Interest Company Rectal irrigation (DROP-List) This is one of a number of bulletins providing further information on medicines and medical devices contained in the PrescQIPP
B171 February 2017 2.0 Community Interest Company Rectal irrigation (DROP-List) This is one of a number of bulletins providing further information on medicines and medical devices contained in the PrescQIPP
Transanal irrigation for bowel dysfunction in chronic stage of spinal cord-injured patients
 9 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2019) Original Article Transanal irrigation for bowel dysfunction in chronic stage of spinal cord-injured patients Megumi Ozeki, MD, DMSc, 1
9 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2019) Original Article Transanal irrigation for bowel dysfunction in chronic stage of spinal cord-injured patients Megumi Ozeki, MD, DMSc, 1
Latest developments in transanal irrigation therapy CHRONIC CONSTIPATION
 CONTINENCE Latest developments in transanal irrigation therapy Sharon Holroyd Transanal irrigation has been acknowledged as a minimally invasive in patients with neurogenic bowel disorders. The severity
CONTINENCE Latest developments in transanal irrigation therapy Sharon Holroyd Transanal irrigation has been acknowledged as a minimally invasive in patients with neurogenic bowel disorders. The severity
Bowel Function and Care. Pat Beierwaltes, Chair Paige Church Lusine Ambartsumyan Sharon Braille Julie Dicker Tiffany Gordon Sue Liebold
 Bowel Function and Care Pat Beierwaltes, Chair Paige Church Lusine Ambartsumyan Sharon Braille Julie Dicker Tiffany Gordon Sue Liebold Outcomes Primary Outcomes Maintenance of social continence as appropriate
Bowel Function and Care Pat Beierwaltes, Chair Paige Church Lusine Ambartsumyan Sharon Braille Julie Dicker Tiffany Gordon Sue Liebold Outcomes Primary Outcomes Maintenance of social continence as appropriate
encathopedia Volume 8 NEUROGENIC BOWEL DYSFUNCTION AND TAI
 encathopedia Volume 8 NEUROGENIC BOWEL DYSFUNCTION AND TAI Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction (NBD) is when the bowel does not work properly due to loss of normal sensory or motor
encathopedia Volume 8 NEUROGENIC BOWEL DYSFUNCTION AND TAI Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction (NBD) is when the bowel does not work properly due to loss of normal sensory or motor
PROCEDURE FOR THE USE OF PERISTEEN ANAL IRRIGATION SYSTEM FOR ADULTS (FOR THE PURPOSE OF RECTAL IRRIGATION)
 PROCEDURE FOR THE USE OF PERISTEEN ANAL IRRIGATION SYSTEM FOR ADULTS (FOR THE PURPOSE OF RECTAL IRRIGATION) Issue History Issue Version Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date One To
PROCEDURE FOR THE USE OF PERISTEEN ANAL IRRIGATION SYSTEM FOR ADULTS (FOR THE PURPOSE OF RECTAL IRRIGATION) Issue History Issue Version Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date One To
Bowel Function and Care
 Bowel Function and Care Workgroup Members: Patricia Beierwaltes, DNP, CPNP (Chair); Lusine Ambartsumyan, MD; Sharon Baillie, RN, CNC, MN; Paige Church, MD; Julie Dicker, RN; Tiffany Gordon, MSN, RN, CPN;
Bowel Function and Care Workgroup Members: Patricia Beierwaltes, DNP, CPNP (Chair); Lusine Ambartsumyan, MD; Sharon Baillie, RN, CNC, MN; Paige Church, MD; Julie Dicker, RN; Tiffany Gordon, MSN, RN, CPN;
Neurogenic bowel management after spinal cord injury: a systematic review of the evidence
 (2010) 48, 718 733 & 2010 International Society All rights reserved 1362-4393/10 $32.00 www.nature.com/sc REVIEW Neurogenic bowel management after spinal cord injury: a systematic review of the evidence
(2010) 48, 718 733 & 2010 International Society All rights reserved 1362-4393/10 $32.00 www.nature.com/sc REVIEW Neurogenic bowel management after spinal cord injury: a systematic review of the evidence
SACRAL NERVE STIMULATION FOR EXPERIENCE IN CHILDREN
 SACRAL NERVE STIMULATION FOR COLORECTAL DISEASES: EXPERIENCE IN CHILDREN C. LOUIS-BORRIONE - JM. GUYS TIMONE-ENFANTS MARSEILLE SACRAL NEUROMODULATION IN CHILDREN 26 : Humphreys et al - 23 children with
SACRAL NERVE STIMULATION FOR COLORECTAL DISEASES: EXPERIENCE IN CHILDREN C. LOUIS-BORRIONE - JM. GUYS TIMONE-ENFANTS MARSEILLE SACRAL NEUROMODULATION IN CHILDREN 26 : Humphreys et al - 23 children with
Childhood constipation, a real problem..? Marc Benninga, Emma Children s Hospital, AMC, Amsterdam, the Netherlands
 Childhood constipation, a real problem..? Marc Benninga, Emma Children s Hospital, AMC, Amsterdam, the Netherlands Constipation 0-10% >10-20% >20-30% >30-40% Mugie SM, et al. Best Pract & Res Clin Gastroenterol
Childhood constipation, a real problem..? Marc Benninga, Emma Children s Hospital, AMC, Amsterdam, the Netherlands Constipation 0-10% >10-20% >20-30% >30-40% Mugie SM, et al. Best Pract & Res Clin Gastroenterol
Peristeen Anal Irrigation
 Peristeen Anal Irrigation Advice & Instructions Anal Irrigation Advice and Instructions for patients.indd 1 04/05/2011 11:29:28 Contents Introduction 3 History 3 The bowel system 4 Constipation 6 Faecal
Peristeen Anal Irrigation Advice & Instructions Anal Irrigation Advice and Instructions for patients.indd 1 04/05/2011 11:29:28 Contents Introduction 3 History 3 The bowel system 4 Constipation 6 Faecal
Transanal irrigation. Toolbox for neurogenic bowel management. Information for patients Spinal Injuries
 Transanal irrigation Toolbox for neurogenic bowel management Information for patients Spinal Injuries Neurogenic bowel dysfunction A number of people with a spinal injury experience faecal incontinence
Transanal irrigation Toolbox for neurogenic bowel management Information for patients Spinal Injuries Neurogenic bowel dysfunction A number of people with a spinal injury experience faecal incontinence
Prior Authorization Review Panel MCO Policy Submission
 Prior Authorization Review Panel MCO Policy Submission A separate copy of this form must accompany each policy submitted for review. Policies submitted without this form will not be considered for review.
Prior Authorization Review Panel MCO Policy Submission A separate copy of this form must accompany each policy submitted for review. Policies submitted without this form will not be considered for review.
Patient Information Leaflet
 Patient Information Leaflet Background Faecal incontinence is a common health problem, affecting over 1% of community-dwelling adults (1;2). Chronic constipation may affect 3-5% of the population depending
Patient Information Leaflet Background Faecal incontinence is a common health problem, affecting over 1% of community-dwelling adults (1;2). Chronic constipation may affect 3-5% of the population depending
15. Prevention of UTI and lifestyle modifications
 15. Prevention of UTI and lifestyle modifications Key questions: Does improving poor voiding habits help prevent UTI recurrence? Does improving constipation help prevent UTI recurrence? Does increasing
15. Prevention of UTI and lifestyle modifications Key questions: Does improving poor voiding habits help prevent UTI recurrence? Does improving constipation help prevent UTI recurrence? Does increasing
Pelvic Floor Disorders. Amir Darakhshan MD FRCS (Gen Surg) Consultant Colorectal and General Surgeon
 Pelvic Floor Disorders Amir Darakhshan MD FRCS (Gen Surg) Consultant Colorectal and General Surgeon What is Pelvic Floor Disorder Surgical perspective symptoms of RED, FI or prolapse on the background
Pelvic Floor Disorders Amir Darakhshan MD FRCS (Gen Surg) Consultant Colorectal and General Surgeon What is Pelvic Floor Disorder Surgical perspective symptoms of RED, FI or prolapse on the background
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. A New Standard of Care for Persons with Disability: Bowel Management
 Slide 1 A New Standard of Care for Persons with Disability: Bowel Management CYNTHIA HERNANDEZ, MSN/ED.,RN,CRRN Slide 2 Objectives Describe standards for bowel management based on disability Discuss the
Slide 1 A New Standard of Care for Persons with Disability: Bowel Management CYNTHIA HERNANDEZ, MSN/ED.,RN,CRRN Slide 2 Objectives Describe standards for bowel management based on disability Discuss the
External Assessment Centre report
 External Assessment Centre report Title: Peristeen anal irrigation system to manage bowel dysfunction Produced by: Authors: Cedar Megan Dale (Cedar, Cardiff & Vale University Health Board) Grace Carolan-Rees
External Assessment Centre report Title: Peristeen anal irrigation system to manage bowel dysfunction Produced by: Authors: Cedar Megan Dale (Cedar, Cardiff & Vale University Health Board) Grace Carolan-Rees
Bowel Function After Spinal Cord Injury
 Bowel Function After Spinal Cord Injury A resource for individuals with SCI and their supporters This presentation is based on SCI Model Systems research and was developed with support from the National
Bowel Function After Spinal Cord Injury A resource for individuals with SCI and their supporters This presentation is based on SCI Model Systems research and was developed with support from the National
Duc M. Vo, MD, FACS Northwest Surgical Specialists
 Duc M. Vo, MD, FACS Northwest Surgical Specialists Disclosures none Outline Definition Etiologies Exam findings Additional testing Medical management Surgical options What is fecal incontinence? Recurrent
Duc M. Vo, MD, FACS Northwest Surgical Specialists Disclosures none Outline Definition Etiologies Exam findings Additional testing Medical management Surgical options What is fecal incontinence? Recurrent
ORIGINAL ARTICLE International spinal cord injury bowel function basic data set (Version 2.0)
 (2017) 55, 692 698 & 2017 International Society All rights reserved 1362-4393/17 www.nature.com/sc ORIGINAL ARTICLE International spinal cord injury bowel function basic data set (Version 2.0) K Krogh
(2017) 55, 692 698 & 2017 International Society All rights reserved 1362-4393/17 www.nature.com/sc ORIGINAL ARTICLE International spinal cord injury bowel function basic data set (Version 2.0) K Krogh
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sacral anterior root stimulation improves bowel function in subjects with spinal cord injury
 (2015) 53, 297 301 & 2015 International Society All rights reserved 1362-4393/15 www.nature.com/sc ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sacral anterior root stimulation improves bowel function in subjects with spinal cord
(2015) 53, 297 301 & 2015 International Society All rights reserved 1362-4393/15 www.nature.com/sc ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sacral anterior root stimulation improves bowel function in subjects with spinal cord
REVIEW Consensus review of best practice of transanal irrigation in adults
 (2013) 51, 732 738 & 2013 International Society All rights reserved 1362-4393/13 www.nature.com/sc OPEN REVIEW Consensus review of best practice of transanal irrigation in adults AV Emmanuel 1, K Krogh
(2013) 51, 732 738 & 2013 International Society All rights reserved 1362-4393/13 www.nature.com/sc OPEN REVIEW Consensus review of best practice of transanal irrigation in adults AV Emmanuel 1, K Krogh
B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e. For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries
 B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries 1 Bladder Specific Care Intermittent Catheterization (IC) is used to empty the bladder with a catheter. A catheter is a tube that
B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries 1 Bladder Specific Care Intermittent Catheterization (IC) is used to empty the bladder with a catheter. A catheter is a tube that
Stapled transanal rectal resection for obstructed defaecation syndrome
 Stapled transanal rectal resection for obstructed Issued: June 2010 www.nice.org.uk/ipg351 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce interventional
Stapled transanal rectal resection for obstructed Issued: June 2010 www.nice.org.uk/ipg351 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce interventional
Fecal Incontinence. What is fecal incontinence?
 Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
PARTICULARS, SCHEDULE 2- THE SERVICES, A- SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS. A08/S/d Colorectal: Faecal Incontinence (Adult)
 A08/S/d 2013/14 NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR COLORECTAL: FAECAL INCONTINENCE (ADULT) PARTICULARS, SCHEDULE 2- THE SERVICES, A- SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS Service Specification No. Service Commissioner Lead Provider
A08/S/d 2013/14 NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR COLORECTAL: FAECAL INCONTINENCE (ADULT) PARTICULARS, SCHEDULE 2- THE SERVICES, A- SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS Service Specification No. Service Commissioner Lead Provider
Incontinence in neurological disease
 nice bulletin Incontinence in neurological disease NICE provided the content for this booklet which is independent of any company or product advertised NICE Bulletin - Incontinence in neurological disease.indd
nice bulletin Incontinence in neurological disease NICE provided the content for this booklet which is independent of any company or product advertised NICE Bulletin - Incontinence in neurological disease.indd
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE The management of faecal incontinence in adults 1.1 Short title Faecal incontinence 2 Background (a) (b) (c) The National Institute
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE The management of faecal incontinence in adults 1.1 Short title Faecal incontinence 2 Background (a) (b) (c) The National Institute
Medicines and Technologies Programme Adoption Scoping Report MTG315 Peristeen
 Medicines and Technologies Programme Adoption Scoping Report MTG315 Peristeen SUMMARY for MTAC1 meeting Contributors questioned why NICE are writing guidance on this system alone when it is viewed and
Medicines and Technologies Programme Adoption Scoping Report MTG315 Peristeen SUMMARY for MTAC1 meeting Contributors questioned why NICE are writing guidance on this system alone when it is viewed and
Viscous Fluid Retention: A New Method for Evaluating Anorectal Function
 Viscous Fluid Retention: A New Method for Evaluating Anorectal Function Michael Srensen, M.D., Tine Tetzschner, M.D., le 0. Rasmussen, M.D., John Christiansen, M.D. From the Department of Surgery D, Glostrup
Viscous Fluid Retention: A New Method for Evaluating Anorectal Function Michael Srensen, M.D., Tine Tetzschner, M.D., le 0. Rasmussen, M.D., John Christiansen, M.D. From the Department of Surgery D, Glostrup
A Nursing Assessment Tool for Adults With Fecal Incontinence
 Journal of Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nursing 2000, 279- A Nursing Assessment Tool for Adults With Fecal Incontinence Christine Norton, MA, RN, and Sonya Chelvanayagam, MSc, RN Abstract Fecal incontinence
Journal of Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nursing 2000, 279- A Nursing Assessment Tool for Adults With Fecal Incontinence Christine Norton, MA, RN, and Sonya Chelvanayagam, MSc, RN Abstract Fecal incontinence
Incidence of Colorectal Cancers- Australia. Anterior Resection 5/23/2018. What spurs us to investigate?
 Incidence of Colorectal Cancers- Australia 17,000 Colorectal cancers in 2018 20% of Colorectal cancers are in the Rectum 12.3% of all new cancers Anterior Resection Syndrome (ARS) Lisa Wilson. Colorectal
Incidence of Colorectal Cancers- Australia 17,000 Colorectal cancers in 2018 20% of Colorectal cancers are in the Rectum 12.3% of all new cancers Anterior Resection Syndrome (ARS) Lisa Wilson. Colorectal
Active ingredients per ml: Docusate sodium 1 mg/sorbitol solution (70%) (crystallising) 357 mg Structural formula: Docusate.
 NAME OF THE MEDICINE KLYX Enema Active ingredients per ml: Docusate sodium 1 mg/sorbitol solution (70%) (crystallising) 357 mg Structural formula: Docusate Sorbitol C20H37NaO7S MW: 444.56 CAS no: 577-11-7
NAME OF THE MEDICINE KLYX Enema Active ingredients per ml: Docusate sodium 1 mg/sorbitol solution (70%) (crystallising) 357 mg Structural formula: Docusate Sorbitol C20H37NaO7S MW: 444.56 CAS no: 577-11-7
CONTINENCE MODULE 3 MIMIMUM STANDARDS FOR SPECIALIST ASSESSMENT & CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF CONSTIPATION AND FAECAL INCONTINENCE
 CONTINENCE MODULE 3 MIMIMUM STANDARDS FOR SPECIALIST ASSESSMENT & CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF CONSTIPATION AND FAECAL INCONTINENCE The minimum standards required to initiate specialised conservative treatment
CONTINENCE MODULE 3 MIMIMUM STANDARDS FOR SPECIALIST ASSESSMENT & CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF CONSTIPATION AND FAECAL INCONTINENCE The minimum standards required to initiate specialised conservative treatment
Long-Term Results of Antegrade Colonic Enema in Adult Patients: Assessment of Functional Results
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Long-Term Results of Antegrade Colonic Enema in Adult Patients: Assessment of Functional Results J. Worsøe, M.D. 1 P. Christensen, M.D., Ph.D. 1,2 K. Krogh, M.D., D.M.Sc. 2 S. Buntzen,
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Long-Term Results of Antegrade Colonic Enema in Adult Patients: Assessment of Functional Results J. Worsøe, M.D. 1 P. Christensen, M.D., Ph.D. 1,2 K. Krogh, M.D., D.M.Sc. 2 S. Buntzen,
Management of the Neurogenic Bowel. June st National SBAA Conference Bloomington, Minnesota
 Management of the Neurogenic Bowel June 2016 41st National SBAA Conference Bloomington, Minnesota DEPARTMENT OF NURSING Rhonda Bolin, BSN, RN, CPN Spina Bifida Nurse Texas Children s Hospital Spina Bifida
Management of the Neurogenic Bowel June 2016 41st National SBAA Conference Bloomington, Minnesota DEPARTMENT OF NURSING Rhonda Bolin, BSN, RN, CPN Spina Bifida Nurse Texas Children s Hospital Spina Bifida
Implementing Clean Intermittent Catheterisation (CIC)
 Implementing Clean Intermittent Catheterisation (CIC) Julie Dicker (Spina Bifida CNC) Kids Rehab The Children s Hospital at Westmead Reasons for CIC: Neurogenic Bladder CIC is the gold standard for this
Implementing Clean Intermittent Catheterisation (CIC) Julie Dicker (Spina Bifida CNC) Kids Rehab The Children s Hospital at Westmead Reasons for CIC: Neurogenic Bladder CIC is the gold standard for this
Reliability of the International Spinal Cord Injury Bowel Function Basic and Extended Data Sets
 (2011) 49, 886 892 & 2011 International Society All rights reserved 1362-4393/11 $32.00 www.nature.com/sc ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reliability of the International Injury Bowel Function Basic and Extended Data
(2011) 49, 886 892 & 2011 International Society All rights reserved 1362-4393/11 $32.00 www.nature.com/sc ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reliability of the International Injury Bowel Function Basic and Extended Data
Biofeedback Therapy A nurse led management service for functional bowel disorders
 Biofeedback Therapy A nurse led management service for functional bowel disorders Brigitte Collins Lead Nurse BSc, MSc GI Nursing, Dip/Hypnotherapy St Marks Hospital Is biofeedback necessary? Conservative
Biofeedback Therapy A nurse led management service for functional bowel disorders Brigitte Collins Lead Nurse BSc, MSc GI Nursing, Dip/Hypnotherapy St Marks Hospital Is biofeedback necessary? Conservative
GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction. Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield
 GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield Aims o o o To give an overview of lower GI investigations To demonstrate
GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield Aims o o o To give an overview of lower GI investigations To demonstrate
IryPump S Rectal User Guide SWITCH ON TO IRRIGATION RECTAL IRRIGATION
 IryPump S Rectal User Guide SWITCH ON TO IRRIGATION RECTAL IRRIGATION CONTENTS INTRODUCTION TO RECTAL IRRIGATION Introduction to Rectal Irrigation page 3 What does irrigation do and where does the water
IryPump S Rectal User Guide SWITCH ON TO IRRIGATION RECTAL IRRIGATION CONTENTS INTRODUCTION TO RECTAL IRRIGATION Introduction to Rectal Irrigation page 3 What does irrigation do and where does the water
Constipation Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. gutscharity.org.uk
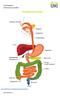 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
Fecal Incontinence. Inability to retain feces or bowel movements, resulting in involuntary passage of feces or bowel movements
 Fecal Incontinence (Involuntary Passage of Feces or Bowel Movements) Basics OVERVIEW Inability to retain feces or bowel movements, resulting in involuntary passage of feces or bowel movements GENETICS
Fecal Incontinence (Involuntary Passage of Feces or Bowel Movements) Basics OVERVIEW Inability to retain feces or bowel movements, resulting in involuntary passage of feces or bowel movements GENETICS
UCSF UROLOGY TRANSITIONAL UROLOGY CLINIC
 UCSF UROLOGY TRANSITIONAL UROLOGY CLINIC Thank you for choosing the UCSF Transitional Urology Clinic. This clinic was created to serve patients with urologic conditions diagnosed in childhood as they become
UCSF UROLOGY TRANSITIONAL UROLOGY CLINIC Thank you for choosing the UCSF Transitional Urology Clinic. This clinic was created to serve patients with urologic conditions diagnosed in childhood as they become
Voiding and bowel problems. Lise Kay, M.D. Urologist and Surgeon The Danish Society of Polio and Accident Victims
 Voiding and bowel problems Lise Kay, M.D. Urologist and Surgeon The Danish Society of Polio and Accident Victims Topics: Nervous control of voiding and bowel function Other factors with influence on voiding
Voiding and bowel problems Lise Kay, M.D. Urologist and Surgeon The Danish Society of Polio and Accident Victims Topics: Nervous control of voiding and bowel function Other factors with influence on voiding
Authors and Disclosures
 Role of Carbon Dioxide-Releasing Suppositories in the Treatment of Chronic Functional Constipation A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial M. Lazzaroni; V. Casini; G. Bianchi Porro Authors
Role of Carbon Dioxide-Releasing Suppositories in the Treatment of Chronic Functional Constipation A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial M. Lazzaroni; V. Casini; G. Bianchi Porro Authors
A70.4 Insertion of neurostimulator electrodes into peripheral nerve Z12.2 Posterior tibial nerve R15.X Faecal incontinence
 The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) has issued full guidance to the NHS in England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland on Percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation (PTNS) for
The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) has issued full guidance to the NHS in England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland on Percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation (PTNS) for
Peristeen Transanal Irrigation System to Manage Bowel Dysfunction: A NICE Medical Technology Guidance
 Applied Health Economics and Health Policy (2019) 17:25 34 https://doi.org/10.1007/s40258-018-0447-x REVIEW ARTICLE Peristeen Transanal Irrigation System to Manage Bowel Dysfunction: A NICE Medical Technology
Applied Health Economics and Health Policy (2019) 17:25 34 https://doi.org/10.1007/s40258-018-0447-x REVIEW ARTICLE Peristeen Transanal Irrigation System to Manage Bowel Dysfunction: A NICE Medical Technology
Prescribing Guidance for the Treatment of Constipation in Children
 Prescribing Guidance for the Treatment of Constipation in Children Effective Date: July 2007 Reviewed: September 2009 & December 2011 Review Date: December 2013 Gateshead Medicines Management Approved
Prescribing Guidance for the Treatment of Constipation in Children Effective Date: July 2007 Reviewed: September 2009 & December 2011 Review Date: December 2013 Gateshead Medicines Management Approved
PREPARING FOR ANORECTOAL MANOMETRY. ManoScan Anorectal Manometry System
 PREPARING FOR ANORECTOAL MANOMETRY ManoScan Anorectal Manometry System WHAT IS ANORECTAL MANOMETRY? Anorectal manometry is a test used to evaluate the function and coordination of the sphincter and pelvic
PREPARING FOR ANORECTOAL MANOMETRY ManoScan Anorectal Manometry System WHAT IS ANORECTAL MANOMETRY? Anorectal manometry is a test used to evaluate the function and coordination of the sphincter and pelvic
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: the diagnosis and management of idiopathic childhood constipation in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: the diagnosis and management of idiopathic childhood constipation in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title
Nursing Principles & Skills II. Bowel Sounds Constipation Fecal Impaction
 Nursing Principles & Skills II Bowel Sounds Constipation Fecal Impaction Bowel Sounds Definitionthe noise or sounds made by the peristaltic waves of the intestinal muscle contracting and relaxing Bowel
Nursing Principles & Skills II Bowel Sounds Constipation Fecal Impaction Bowel Sounds Definitionthe noise or sounds made by the peristaltic waves of the intestinal muscle contracting and relaxing Bowel
WHAT IS LARS? LOW ANTERIOR RESECTIONSYNDROME. Sophie Pilkington. Colorectal Surgeon University Hospital Southampton
 WHAT IS LARS? LOW ANTERIOR RESECTIONSYNDROME Sophie Pilkington Colorectal Surgeon University Hospital Southampton INTRODUCTION UK Bowel cancer 2013 41,100 new cases INTRODUCTION UK Bowel cancer 2013 41,100
WHAT IS LARS? LOW ANTERIOR RESECTIONSYNDROME Sophie Pilkington Colorectal Surgeon University Hospital Southampton INTRODUCTION UK Bowel cancer 2013 41,100 new cases INTRODUCTION UK Bowel cancer 2013 41,100
Guidelines for the Manual Evacuation of Faeces
 Rationale Guidelines for the Manual Evacuation of Faeces These guidelines are to provide the required information for designated registered nurses, health care assistants and bank support workers to perform
Rationale Guidelines for the Manual Evacuation of Faeces These guidelines are to provide the required information for designated registered nurses, health care assistants and bank support workers to perform
Treatments for Fecal Incontinence A Review of the Research for Adults
 Treatments for Fecal Incontinence A Review of the Research for Adults e Is This Information Right for Me? This information is right for you if: Your health care professional* said you or your loved one
Treatments for Fecal Incontinence A Review of the Research for Adults e Is This Information Right for Me? This information is right for you if: Your health care professional* said you or your loved one
Stimulation of the Sacral Anterior Root Combined with Posterior Sacral Rhizotomy in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury. Original Policy Date
 MP 7.01.58 Stimulation of the Sacral Anterior Root Combined with Posterior Sacral Rhizotomy in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury Medical Policy Section Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review
MP 7.01.58 Stimulation of the Sacral Anterior Root Combined with Posterior Sacral Rhizotomy in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury Medical Policy Section Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review
Developing spinal cord compression care guidelines at WPH
 Developing spinal cord compression care guidelines at WPH Spinal cord compression team: Sue Banks, Jean Buchanan, Bernie Foran, Suzanne Hodson, Jane Mason, Rebecca Mills, Jan Siddall, Rebecca Walsh, Clare
Developing spinal cord compression care guidelines at WPH Spinal cord compression team: Sue Banks, Jean Buchanan, Bernie Foran, Suzanne Hodson, Jane Mason, Rebecca Mills, Jan Siddall, Rebecca Walsh, Clare
BOWEL WASHOUTS USING AN ANTEGRADE COLONIC ENEMA (ACE)
 BOWEL WASHOUTS USING AN ANTEGRADE COLONIC ENEMA (ACE) This leaflet gives information for parents/carers whose child is having an ACE procedure and explains about giving bowel washouts. Why does my child
BOWEL WASHOUTS USING AN ANTEGRADE COLONIC ENEMA (ACE) This leaflet gives information for parents/carers whose child is having an ACE procedure and explains about giving bowel washouts. Why does my child
When the bowel works, life works. Your guide: Life with transanal irrigation
 When the bowel works, life works Your guide: Life with transanal irrigation Dear reader This guide has been made to support you who have been prescribed Navina Systems and the therapy transanal irrigation
When the bowel works, life works Your guide: Life with transanal irrigation Dear reader This guide has been made to support you who have been prescribed Navina Systems and the therapy transanal irrigation
Developing spinal cord compression care guidelines at WPH
 Developing spinal cord compression care guidelines at WPH Spinal cord compression team: Sue Banks, Jean Buchanan, Dr Bernie Foran, Suzanne Hodson, Liz Kirkham, Rebecca Mills, Jan Siddall, Rebecca Walsh,
Developing spinal cord compression care guidelines at WPH Spinal cord compression team: Sue Banks, Jean Buchanan, Dr Bernie Foran, Suzanne Hodson, Liz Kirkham, Rebecca Mills, Jan Siddall, Rebecca Walsh,
LONG TERM OUTCOME OF ELECTIVE SURGERY
 LONG TERM OUTCOME OF ELECTIVE SURGERY Roberto Persiani Associate Professor Mini-invasive Oncological Surgery Unit Institute of Surgical Pathology (Dir. prof. D. D Ugo) Dis Colon Rectum, March 2000 Dis
LONG TERM OUTCOME OF ELECTIVE SURGERY Roberto Persiani Associate Professor Mini-invasive Oncological Surgery Unit Institute of Surgical Pathology (Dir. prof. D. D Ugo) Dis Colon Rectum, March 2000 Dis
Constipation. What is constipation? What is the criteria for having constipation? What are the different types of constipation?
 What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
Danish Cancer Society Centre for Research on Survivorship and Late Adverse Effects After Cancer in the Pelvic Organs
 Danish Cancer Society Centre for Research on Survivorship and Late Adverse Effects After Cancer in the Pelvic Organs DANSK KRÆFTFORUM, marts 2018 On behalf of the steering group Peter Christensen, professor,
Danish Cancer Society Centre for Research on Survivorship and Late Adverse Effects After Cancer in the Pelvic Organs DANSK KRÆFTFORUM, marts 2018 On behalf of the steering group Peter Christensen, professor,
Colon Cancer Surgery
 Colon Cancer Surgery Introduction Colon cancer is a life-threatening condition that affects thousands of people. Doctors usually recommend surgery for the removal of colon cancer. If your doctor recommends
Colon Cancer Surgery Introduction Colon cancer is a life-threatening condition that affects thousands of people. Doctors usually recommend surgery for the removal of colon cancer. If your doctor recommends
Neurogenic bowel and continence programs for the individual with spina bifida
 Journal of Pediatric Rehabilitation Medicine: An Interdisciplinary Approach 1 (2008) 325 336 325 IOS Press Neurogenic bowel and continence programs for the individual with spina bifida Susan Leibold Clinical
Journal of Pediatric Rehabilitation Medicine: An Interdisciplinary Approach 1 (2008) 325 336 325 IOS Press Neurogenic bowel and continence programs for the individual with spina bifida Susan Leibold Clinical
Bowel Washouts Using an Antegrade Colonic Enema (ACE)
 This leaflet gives information for parents/carers whose child is having an ACE procedure and explains about giving bowel washouts. Why does my child need bowel washouts? Bowel washouts are a method of
This leaflet gives information for parents/carers whose child is having an ACE procedure and explains about giving bowel washouts. Why does my child need bowel washouts? Bowel washouts are a method of
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: management of idiopathic constipation in children in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title Constipation
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: management of idiopathic constipation in children in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title Constipation
CONSTIPATION. Atan Baas Sinuhaji
 CONSTIPATION Atan Baas Sinuhaji Sub Division of Pediatrics Gastroentero-Hepatolgy Department of ChildHealth,School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara MEDAN DEFECATION REGULAR PATTERN CONSTIPATION
CONSTIPATION Atan Baas Sinuhaji Sub Division of Pediatrics Gastroentero-Hepatolgy Department of ChildHealth,School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara MEDAN DEFECATION REGULAR PATTERN CONSTIPATION
Constipation An Overview. Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment
 CONSTIPATION Constipation An Overview Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment Definition Constipation = the infrequent passage of hard feces Definition of Infrequent The meaning
CONSTIPATION Constipation An Overview Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment Definition Constipation = the infrequent passage of hard feces Definition of Infrequent The meaning
Chapter 22. Bowel Needs. Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 22 Bowel Needs Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 22.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Describe normal defecation and the observations to report.
Chapter 22 Bowel Needs Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 22.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Describe normal defecation and the observations to report.
Chapter 19. Assisting With Bowel Elimination. Elsevier items and derived items 2014, 2010 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 19 Assisting With Bowel Elimination Normal Bowel Elimination Time and frequency of bowel movements (BMs) vary. To assist with bowel elimination, you need to know these terms: Defecation is the
Chapter 19 Assisting With Bowel Elimination Normal Bowel Elimination Time and frequency of bowel movements (BMs) vary. To assist with bowel elimination, you need to know these terms: Defecation is the
Tertiary, regional and local pelvic floor service providers: the future. model? Andrew Williams
 Tertiary, regional and local pelvic floor service providers: the future Andrew Williams model? Pelvic Floor Unit Guy s and St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust Background 23% women suffer at least one pelvic
Tertiary, regional and local pelvic floor service providers: the future Andrew Williams model? Pelvic Floor Unit Guy s and St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust Background 23% women suffer at least one pelvic
Scottish Health Technologies Group
 Scottish Health Technologies Group Advice Statement Portable bladder ultrasound scanners 8 March 2011 Advice Statement 002/11 Question: Can the use of a portable 3D ultrasound bladder scanner to measure
Scottish Health Technologies Group Advice Statement Portable bladder ultrasound scanners 8 March 2011 Advice Statement 002/11 Question: Can the use of a portable 3D ultrasound bladder scanner to measure
Summary. Neuro-urodynamics. The bladder cycle. and voiding. 14/12/2015. Neural control of the LUT Initial assessment Urodynamics
 Neuro-urodynamics Summary Neural control of the LUT Initial assessment Urodynamics Marcus Drake, Bristol Urological Institute SAFETY FIRST; renal failure, dysreflexia, latex allergy SYMPTOMS SECOND; storage,
Neuro-urodynamics Summary Neural control of the LUT Initial assessment Urodynamics Marcus Drake, Bristol Urological Institute SAFETY FIRST; renal failure, dysreflexia, latex allergy SYMPTOMS SECOND; storage,
A Case of Fecal Incontinence: Medical and Interventional Treatment Options
 A Case of Fecal Incontinence: Medical and Interventional Treatment Options HPI JP is a 69 year-old F with a 12-month history of FI. Her symptoms began after a colonoscopy She has been experiencing passive
A Case of Fecal Incontinence: Medical and Interventional Treatment Options HPI JP is a 69 year-old F with a 12-month history of FI. Her symptoms began after a colonoscopy She has been experiencing passive
Continence Promotion in
 Everybody s Business- Continence Promotion in Aged Care Melissa O Grady Clinical Nurse Consultant Continence Warning Some graphic images are contained in this presentation Objectives What is Old Age? What
Everybody s Business- Continence Promotion in Aged Care Melissa O Grady Clinical Nurse Consultant Continence Warning Some graphic images are contained in this presentation Objectives What is Old Age? What
Injectable Bulking Agents for the Treatment of Fecal Incontinence. Policy Specific Section: September 27, 2013 January 1, 2015
 Medical Policy Injectable Bulking Agents for the Treatment of Fecal Incontinence Type: Investigational / Experimental Policy Specific Section: Surgery Original Policy Date: Effective Date: September 27,
Medical Policy Injectable Bulking Agents for the Treatment of Fecal Incontinence Type: Investigational / Experimental Policy Specific Section: Surgery Original Policy Date: Effective Date: September 27,
Ein Leben nach tiefer Rektumresektion: Was erwartet unsere Patienten im Langzeitverlauf?
 Ein Leben nach tiefer Rektumresektion: Was erwartet unsere Patienten im Langzeitverlauf? Dieter Hahnloser Klinik für Viszeral- und Transplantationschirurgie UniverstätsSpital Zürich Low Rectal Resection
Ein Leben nach tiefer Rektumresektion: Was erwartet unsere Patienten im Langzeitverlauf? Dieter Hahnloser Klinik für Viszeral- und Transplantationschirurgie UniverstätsSpital Zürich Low Rectal Resection
The Malone Antegrade Continence Enema (MACE) Principle In Children: Is It Important If the Conduit Is Implanted In the Left or the Right Colon?
 Pediatric Urology Malone Antegrade Continence Enema (MACE) International Braz J Urol Vol. 34 (2): 206-213, March - April, 2008 The Malone Antegrade Continence Enema (MACE) Principle In Children: Is It
Pediatric Urology Malone Antegrade Continence Enema (MACE) International Braz J Urol Vol. 34 (2): 206-213, March - April, 2008 The Malone Antegrade Continence Enema (MACE) Principle In Children: Is It
information Sacral Anterior Root Stimulator (SARS) and Dorsal Rhizotomy (1 of 5) What is a sacral anterior root stimulator? How does the implant work?
 information Sacral Anterior Root Stimulator (SARS) and Dorsal Rhizotomy (1 of 5) What is a sacral anterior root stimulator? If you need this information in another language or medium (audio, large print,
information Sacral Anterior Root Stimulator (SARS) and Dorsal Rhizotomy (1 of 5) What is a sacral anterior root stimulator? If you need this information in another language or medium (audio, large print,
Bowel Dysfunction in Spinal Cord Injury
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bowel Dysfunction in Spinal Cord Injury A S Naicker, MMed (Rehab), S A Roohi, FRCS, M S Naicker, (M Path), O Zaleha, FRCP Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Faculty of Medicine,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bowel Dysfunction in Spinal Cord Injury A S Naicker, MMed (Rehab), S A Roohi, FRCS, M S Naicker, (M Path), O Zaleha, FRCP Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Faculty of Medicine,
Colectomy. Surgical treatment for Ulcerative Colitis (UC) and Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP) Patient and Family Education
 Patient and Family Education Colectomy Surgical treatment for Ulcerative Colitis (UC) and Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP) A colectomy is a surgery that removes the colon, or large intestine. The colectomy
Patient and Family Education Colectomy Surgical treatment for Ulcerative Colitis (UC) and Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP) A colectomy is a surgery that removes the colon, or large intestine. The colectomy
Robotic Ventral Rectopexy
 Robotic Ventral Rectopexy What is a robotic ventral rectopexy? The term rectopexy refers to an operation in which the rectum (the part of the bowel nearest the anus) is put back into its normal position
Robotic Ventral Rectopexy What is a robotic ventral rectopexy? The term rectopexy refers to an operation in which the rectum (the part of the bowel nearest the anus) is put back into its normal position
ACG Clinical Guideline: Management of Benign Anorectal Disorders
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Management of Benign Anorectal Disorders Arnold Wald, MD, MACG 1, Adil E. Bharucha, MBBS, MD 2, Bard C. Cosman, MD, MPH, FASCRS 3 and William E. Whitehead, PhD, MACG 4 1 Division
ACG Clinical Guideline: Management of Benign Anorectal Disorders Arnold Wald, MD, MACG 1, Adil E. Bharucha, MBBS, MD 2, Bard C. Cosman, MD, MPH, FASCRS 3 and William E. Whitehead, PhD, MACG 4 1 Division
Neurogenic Bowel: What You Should Know. A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury
 Neurogenic Bowel: What You Should Know A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury Why Is This Information Important? Before SCI, you didn t have to think about bowel movements After SCI, you may need more
Neurogenic Bowel: What You Should Know A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury Why Is This Information Important? Before SCI, you didn t have to think about bowel movements After SCI, you may need more
Lets talk about Faecal incontinence (FI) in Scleroderma
 Lets talk about Faecal incontinence (FI) in Scleroderma Dr. Shamaila Butt Gastroenterology Research Registrar GI Physiology unit University College Hospital London GI manifestations in Scleroderma Oesophagus
Lets talk about Faecal incontinence (FI) in Scleroderma Dr. Shamaila Butt Gastroenterology Research Registrar GI Physiology unit University College Hospital London GI manifestations in Scleroderma Oesophagus
