Ciliary Movement of Sea-urchin Embryos
|
|
|
- Nathaniel Atkinson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ciliary Movement of Sea-urchin Embryos Kogiku Shiba*, Yoshihiro Mogami** and Shoji A. Baba*** *Division of Life Sciences, Graduate School of Humanities and Sciences **Department of Biology ***Department of Advanced Biosciences, Graduate School of Humanities and Sciences Ochanomizu University Otsuka, Tokyo , Japan Abstract Living matter is constantly in motion: we human and faster than before its application. Dopamine, which is beings walk through the repeated contraction and relaxation of known to decrease the swimming speed, increased the leg muscles; migratory fish swim long way also by the muscle fluctuation and the period of E 4 antagonistically to serotonin contraction; a great number of unicellular and multicellular and, in addition, prolonged the pause between E 1 and E 2 and microorganisms swim about through the beating of miniature reduced the rate of angular change in E 3. The potassium ion at hairlike appendages called cilia. To address the unsolved higher concentrations than of standard seawater, which will question how cilia are regulated when these microorganisms depolarize the cell membrane and known to reduce the explore their environment and are successful in life, we studied swimming speed, and to induce backward swimming in larvae the ciliary movement of embryos and larvae of sea urchins by of the pluteus and later stages, modified the beating in a manner means of high-speed video micrography and by computerized similar to dopamine. Pauses between E 2 and E 3 often found in analysis of ciliary beating at a high resolution. We found the the pluteus stage were lengthened by serotonin and the four stages, E 1 through E 4, in the effective stroke with pauses potassium ion. These findings indicate that the internal motility intervening between one and the next. Serotonin, which has machinery, i.e., the axoneme, can be regulated by modifying one been demonstrated to increase the swimming speed of or more of independently controllable stages of beating sea-urchin embryos, reduced reversibly the fluctuation and the including E 1 through E 4 described in the present study. length of period of E 4, and hence made the beating more stable Introduction Living matter is constantly in motion: we human beings walk through the repeated contraction and relaxation of leg muscles; migratory fish swim long way also by the muscle contraction; a great number of unicellular and multicellular microorganisms swim about through the beating of miniature hairlike appendages called cilia. Cilia and flagella, similar hairlike appendages that are usually longer and less massive than cilia, are also found in our body; they are found in the ciliary epithelium of tracheal airway, the ventricle of the brain, the oviduct and as the tail of spermatozoon. The function of these organelles is undoubtedly important for individuals of ciliary dyskinesia often die at the early stage of development and, if lived longer, will be affected by heavy diseases and often infertile. Even in the healthy body, the activity of cilia and flagella are precisely regulated by the nervous system and under variable environmental conditions. Sea-urchin embryos or larvae swim about through the beating of cilia, which cover the almost entire surface of the body (Fig. 1). They regulate the swimming behavior by gathering various keys from their environment; they control the vertical position in the water column changing the propulsion depending on the direction of swimming in the late stages of development (Mogami et al. 1988). They might also regulate the orientation against the physical torque, which has been demonstrated to alter in the nature of mechanical origin in the curse of development, heterogeneity of form or of mass distribution (Mogami et al. 2001). They also use cilia for filter feeding and regulate their activity responding to external stimuli, size or chemicals, and depending on internal states, hungry or stuffed (Strathmann, 1971). Thus, the cilia of sea urchin perform a variety of movement and regulation; in fact, they show at least five distinct states of activity (Mogami et al
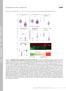
2 1991). The ciliated cells of sea urchins bear only one cilium of 9+2 and also Mogami et al. 1993). These are why we chose the cilia of axoneme per cell and are extraordinarily suitable for beating sea urchin embryos as materials for the study of ciliary movement. analysis when compared with those from other animals (see Fig. 2 Fig. 1. Multiple-exposure photographs of swimming embryos of the sea urchin, Hemicentrotus pulcherrimus. A: gastrula stage; B: pluteus stage. Exposure intervals: 1 s (A) and 2 s (B); the brightest images are made by the first flash of stroboscopic exposure. 12. Fig. 2. Massive vs. single cilia. A: the lateral cilia of the gill of the mussel Mytilus edulis. B: the sea-urchin embryo cilia of the pluteus larva of Hemicentrotus pulcherrimus. Photos are from frames of high-speed cinematographs taken at 500 fps. The cell to the right of B was isolated from the ciliated epithelium of a pluteus larva in dissociation medium and was observed in ASW (for dissociation, see Mogami et al., 1993)
3 Several authors have demonstrated that the ciliary Materials and Methods movement of sea urchins can be modified by the potassium ion Embryos of the sea urchin, Hemicentrotus pulcherrimus, (Markman, 1972), electrical stimulation (Baba, 1975; Baba and were reared to the stage of gastrula through pluteus at 17. The Mogami, 1987a), the calcium ionophore A23187 (Degawa et al. embryos in artificial seawater (ASW) were placed in the specially 1986) and pharmacological substances (Soliman, 1983; Mogami et designed chamber made of a slide glass with two depression holes al. 1992; Wada et al. 1997). Of these it intrigues us that dopamine both side the cover slips placed on the embryos as shown in Fig. 2. increases the fluctuation of beat cycle as well as the duration of the The movement of a cilium just brought in focus (inset of Fig. 2) cycle and serotonin reduces them antagonistically. It has been was recorded with a Kodak HC1000 high-speed video camera demonstrated that the cilia of early stages stop the motion short through phase-contrast optics and with xenon flashes operated on a time at the middle of the effective stroke when stimulated laboratory-designed power supply (Baba and Mogami, 1987b; electrically independently of the time of stimulation during one Miyake et al. 1998). ASW containing 10-5 M dopamine, 10-5 M beat cycle; the time of pause fluctuates and the pause itself is found 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT or serotonin), or K + at increased even before stimulation (Baba, 1975; Baba and Mogami, 1987a). concentrations (up to 160 mm as compared with 10 mm of the The same phase dependent modification of beating and the standard ASW) was perfused through the chamber; the movement fluctuation of beating have been described with the large abfrontal was recorded in this experimental solution and in ASW later again. cilia of Mytilus gill by Baba (1979). In the present study, we found The time course of the shear angle or angular direction of the that the modification of beating by dopamine, serotonin and cilium, as defined in Fig. 2, was measured by a software for increased concentrations of the potassium ion is due to the phase automatic tracking of the cilium along its length, Bohboh dependent regulation of the length and rate of four distinct stages (BohbohSoft, Tokyo) as shown in Fig. 3. The framing rate of the and the length of pauses between them. high-speed camera was 1000 fps so that the movement could be analyzed at a resolution of 1 ms, which revealed the characteristic features of distinct four stages of beating. Fig. 3. High-time resolution analysis of ciliary beating in terms of the shear angle. This diagram illustrates the experimental chamber, microscope, analysis with an auto tracking software, and the definition of the shear angle. 51
4 Fig. 4. An auto tracking software, Bohboh.exe. A cilium of a sea-urchin embryo is ready for tracking (upper) and the tracking has been finished with some 130 points being determined along the cilium (lower). Results and Discussion The beating of a cilium was fluctuated in the length of time even in the standard seawater particularly in the late stage of the effective stroke. From the analysis of beating of the cilium in experimental solutions, we identified at least four distinct stages, E 1 through E 4 in the effective stroke in terms of phase, fluctuation, length and rate (Fig. 4). As summarized in this figure, the modification of beating is phase dependent: the pause between E 1 and E 2 is elongated by dopamine and high K + ; E 2 is little affected by all tested; the pause between E 2 and E 3 is elongated a little by serotonin and high K + ; the rate of angular change in E 3 is reduced by dopamine and high K+; E 4 often with small pauses is greatly prolonged by dopamine and high K+. These findings indicate that different components of the axonemes may work for the motility at different phases of beating and have a specificity to different conditions, respectively. The separation of these components in terms of regulatory proteins or putative phosphorylation remained to be studied. 52
5 Fig. 5. Four stages E 1 through E 4 in the effective stroke of embryo cilia of Hemicentrotus pulcherrimus and intervening pauses between them. The time course of the shear angle measured at 5 μm from the base is drawn schematically. References Baba, S. A. (1975). Developmental changes in the pattern of ciliary response and the swimming behavior in some invertebrate larvae. In Swimming and Flying in Nature (Edited by Wu, T. Y.-T., Brokaw, C. J. and Brenner, C.), Vol. 1, pp Plenum, New York. Baba, S. A. (1979). Regular steps in bending cilia during the effective stroke. Nature 282, Baba S. A. and Mogami, Y. (1987a). High time-resolution analysis of transient bending patterns during ciliary responses following electric stimulation in sea urchin embryos. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 7, Baba S. A. and Mogami, Y. (1987b). Device for controlled intensification of the light output of xenon flash tubes. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 58, Degawa, M., Mogami, Y. and Baba, S. A. (1986). Developmental changes in Ca 2+ sensitivity of sea-urchin embryo cilia. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 85A, Markman, B. (1972). Swimming activity of sea urchin embryos subject to increased concentration of potassium ions. Acta Embryol. Exp. 1972, Suppl Mogami, Y., Ishii, J. and Baba, S. A. (2001). Theoretical and experimental dissection of gravity-dependent mechanical orientation in gravitactic microorganisms. Biol. Bull. 201, Mogami, Y., Oobayashi, C., Yamaguchi, T., Ogiso, Y. and Baba, S. A. (1988). Negative geotaxis in sea urchin larvae: a possible role of mechanoreception in the late stages of development. J. Exp. Biol. 137, Mogami, Y., Sekiguchi, S. and Baba S. A. (1993). Beating of cilia of sea urchin embryos: a critical comparison of the normal and reversed beating of cilia of isolated cells. J. Exp. Biol. 175, Mogami, Y., Watanabe, K., Ooshima, C., Kawano, A. and Baba, S. A. (1992). Regulation of ciliary movement in sea urchin embryos: dopamine and 5-HT change the swimming behaviour. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 110C Miyake, M. O., Mogami, Y., Kataoka, E., Kajita, E. and Baba, S. A. (1998). Improvement in time and space resolution of stroboscopic micrography using high power xenon flash. Rev. Sci Instrum. 69, Soliman, S. (1983). Pharmacological Control of Ciliary Activity in 53
6 The Young Sea Urchin Larvae. Graphic Systems, Göteborg. Wada, Y., Mogami, Y. and Baba, S. A. (1997). Modification of Strathmann, R. R. (1971). The feeding behavior of planktotrophic ciliary beating in sea urchin larvae induced by neurotransmitters: echinoderm larvae: Mechanisms, regulation, and rates of Beat-plane rotation and control of frequency fluctuation. J. Exp. suspension feeding. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 6, Biol. 200,
MODIFICATION OF CILIARY BEATING IN SEA URCHIN LARVAE INDUCED BY NEUROTRANSMITTERS: BEAT-PLANE ROTATION AND CONTROL OF FREQUENCY FLUCTUATION
 The Journal of Experimental iology, () Printed in Great ritain The Company of iologists Limited JE4 MODIFICTION OF CILIRY ETING IN SE URCHIN LRVE INDUCED Y NEUROTRNSMITTERS: ET-PLNE ROTTION ND CONTROL
The Journal of Experimental iology, () Printed in Great ritain The Company of iologists Limited JE4 MODIFICTION OF CILIRY ETING IN SE URCHIN LRVE INDUCED Y NEUROTRNSMITTERS: ET-PLNE ROTTION ND CONTROL
RECONSTITUTION OF METACHRONAL WAVES IN CILIATED CORTICAL SHEETS OF PARAMECIUM
 J. exp. Biol. 192, 73 81 (1994) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1994 73 RECONSTITUTION OF METACHRONAL WAVES IN CILIATED CORTICAL SHEETS OF PARAMECIUM II. ASYMMETRY OF THE CILIARY
J. exp. Biol. 192, 73 81 (1994) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1994 73 RECONSTITUTION OF METACHRONAL WAVES IN CILIATED CORTICAL SHEETS OF PARAMECIUM II. ASYMMETRY OF THE CILIARY
Ciliobrevin is a specific and membrane-permeable inhibitor
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Cytoskeleton, April 2015 72:182 192 (doi: 10.1002/cm.21218) VC 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Effects of the Dynein Inhibitor Ciliobrevin on the Flagellar Motility of Sea Urchin Spermatozoa
RESEARCH ARTICLE Cytoskeleton, April 2015 72:182 192 (doi: 10.1002/cm.21218) VC 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Effects of the Dynein Inhibitor Ciliobrevin on the Flagellar Motility of Sea Urchin Spermatozoa
ON FEEDING MECHANISMS AND CLEARANCE RATES OF MOLLUSCAN VELIGERS
 ON FEEDING MECHANISMS AND CLEARANCE RATES OF MOLLUSCAN VELIGERS By: R. R. Strathmann and Esther Leise Strathmann, R.R. and Leise, E. (1979) On Feeding Mechanisms and Clearance Rates of Molluscan Veligers.
ON FEEDING MECHANISMS AND CLEARANCE RATES OF MOLLUSCAN VELIGERS By: R. R. Strathmann and Esther Leise Strathmann, R.R. and Leise, E. (1979) On Feeding Mechanisms and Clearance Rates of Molluscan Veligers.
THE FORM OF BEAT IN CILIA OF STENTOR AND OPALINA
 VOLUME 37, No. 1 MARCH i960 THE FORM OF BEAT IN CILIA OF STENTOR AND OPALINA BY M. A. SLEIGH Department of Zoology, University of Exeter {Received 26 May 1959) (With Plate 1) INTRODUCTION Descriptions
VOLUME 37, No. 1 MARCH i960 THE FORM OF BEAT IN CILIA OF STENTOR AND OPALINA BY M. A. SLEIGH Department of Zoology, University of Exeter {Received 26 May 1959) (With Plate 1) INTRODUCTION Descriptions
FORM OF DEVELOPING BENDS IN REACTIVATED SPERM FLAGELLA
 J. exp. Biol. (1976). 64. i73-'84 173 P
J. exp. Biol. (1976). 64. i73-'84 173 P
Effects of pco 2 on the fertilization and development of the sea urchin Stronglyocentrotus nudus
 Effects of pco 2 on the fertilization and development of the sea urchin Stronglyocentrotus nudus Young-Gyu Park, Sang-wha Choi, Seong-Gil Kang Korea Ocean R & D Inst., Korea Jung-Suk Lee, Chan-Gyung Sung,
Effects of pco 2 on the fertilization and development of the sea urchin Stronglyocentrotus nudus Young-Gyu Park, Sang-wha Choi, Seong-Gil Kang Korea Ocean R & D Inst., Korea Jung-Suk Lee, Chan-Gyung Sung,
Correlation between Membrane Potential Responses and Tentacle Movement in the Dinoflagellate Noctiluca miliaris
 ZOOLOGICAL SCIENCE 21: 131 138 (2004) 2004 Zoological Society of Japan Correlation between Membrane Potential Responses and Tentacle Movement in the Dinoflagellate Noctiluca miliaris Kazunori Oami* Institute
ZOOLOGICAL SCIENCE 21: 131 138 (2004) 2004 Zoological Society of Japan Correlation between Membrane Potential Responses and Tentacle Movement in the Dinoflagellate Noctiluca miliaris Kazunori Oami* Institute
Mechanism regulating Ca 2+ -dependent mechanosensory behaviour in sea urchin spermatozoa
 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Received on: 2010/11/01 Accepted on: 2011/01/07 Released online on: 2011/02/25 Advance Publication by J-STAGE doi:10.1247/csf.10020 Mechanism regulating Ca 2+ -dependent mechanosensory
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Received on: 2010/11/01 Accepted on: 2011/01/07 Released online on: 2011/02/25 Advance Publication by J-STAGE doi:10.1247/csf.10020 Mechanism regulating Ca 2+ -dependent mechanosensory
A QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS OF CILIARY MOVEMENT BY MEANS OF HIGH-SPEED MICROCINEMATOGRAPHY
 J. Exp. Biol. (1970). S3. 675-690 With I plate and 8 text-figures Printed in Great Britain A QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS OF CILIARY MOVEMENT BY MEANS OF HIGH-SPEED MICROCINEMATOGRAPHY BY SHOJI A. BABA AND YUKIO
J. Exp. Biol. (1970). S3. 675-690 With I plate and 8 text-figures Printed in Great Britain A QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS OF CILIARY MOVEMENT BY MEANS OF HIGH-SPEED MICROCINEMATOGRAPHY BY SHOJI A. BABA AND YUKIO
ASSET Student Laboratory
 ASSET Student Laboratory The Effect of Cigarette Smoke and Alcohol on Tetrahymena Background Information While the general effects of smoking and alcohol use on humans are well documented, it is useful
ASSET Student Laboratory The Effect of Cigarette Smoke and Alcohol on Tetrahymena Background Information While the general effects of smoking and alcohol use on humans are well documented, it is useful
ENERGETICS OF CILIARY MOVEMENT IN SABELLARIA AND MYTILUS
 J. Exp. Biol. (1969), 50, 733-743 733 With 3 text-figures Printed m Great Britain ENERGETICS OF CILIARY MOVEMENT IN SABELLARIA AND MYTILUS BY M. A. SLEIGH Department of Zoology, The University, Bristol
J. Exp. Biol. (1969), 50, 733-743 733 With 3 text-figures Printed m Great Britain ENERGETICS OF CILIARY MOVEMENT IN SABELLARIA AND MYTILUS BY M. A. SLEIGH Department of Zoology, The University, Bristol
EFFECT OF BEAT FREQUENCY ON THE VELOCITY OF MICROTUBULE SLIDING IN REACTIVATED SEA URCHIN SPERM FLAGELLA UNDER IMPOSED HEAD VIBRATION
 The Journal of Experimental Biology 98, 645 65 (995) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 995 645 EFFECT OF BEAT FREQUENCY ON THE VELOCITY OF MICROTUBULE SLIDING IN REACTIVATED SEA
The Journal of Experimental Biology 98, 645 65 (995) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 995 645 EFFECT OF BEAT FREQUENCY ON THE VELOCITY OF MICROTUBULE SLIDING IN REACTIVATED SEA
MAINTENANCE OF CONSTANT WAVE PARAMETERS BY SPERM FLAGELLA AT REDUCED FREQUENCIES OF BEAT
 J. Exp. Biol. (1973). 59. 617-628 61 7 With 1 plate and 3 text-figures Printed in Great Britain MAINTENANCE OF CONSTANT WAVE PARAMETERS BY SPERM FLAGELLA AT REDUCED FREQUENCIES OF BEAT BY C. J. BROKAW
J. Exp. Biol. (1973). 59. 617-628 61 7 With 1 plate and 3 text-figures Printed in Great Britain MAINTENANCE OF CONSTANT WAVE PARAMETERS BY SPERM FLAGELLA AT REDUCED FREQUENCIES OF BEAT BY C. J. BROKAW
Philip S. Oshida and Jean LWright EFFECTS OF HEXAVALENT CHROMIUM ON SEA URCHIN EMBRYOS AND BRITTLE STARS
 Philip S. Oshida and Jean LWright EFFECTS OF HEXAVALENT CHROMIUM ON SEA URCHIN EMBRYOS AND BRITTLE STARS A goal of the Project's investigations into the chronic effects of exposure to chromium on marine
Philip S. Oshida and Jean LWright EFFECTS OF HEXAVALENT CHROMIUM ON SEA URCHIN EMBRYOS AND BRITTLE STARS A goal of the Project's investigations into the chronic effects of exposure to chromium on marine
A study of cilia density in sea urchin embryos during gastrulation
 A study of cilia density in sea urchin embryos during gastrulation Steve Das Independent Research Project Report Bio 254 Developmental Biology May 3, 2012 Introduction Embryo growth and development is
A study of cilia density in sea urchin embryos during gastrulation Steve Das Independent Research Project Report Bio 254 Developmental Biology May 3, 2012 Introduction Embryo growth and development is
INFRARED LASER DAMAGE TO CILIARY MOTION IN PHRAGMATOPOMA
 J. Cell Sci. M, 361-37 1 (i977) 361 Printed in Great Britain INFRARED LASER DAMAGE TO CILIARY MOTION IN PHRAGMATOPOMA ROBERT RIKMENSPOEL, SANDRA E. ORRIS AND PETER O'DAY Department of Biological Sciences,
J. Cell Sci. M, 361-37 1 (i977) 361 Printed in Great Britain INFRARED LASER DAMAGE TO CILIARY MOTION IN PHRAGMATOPOMA ROBERT RIKMENSPOEL, SANDRA E. ORRIS AND PETER O'DAY Department of Biological Sciences,
TOWARDS PERFECT TURNOUT
 TOWARDS PERFECT TURNOUT BY NOA SPECTOR FLOCK 1 Section I Imagery & Integration Create ease, inner-space, awareness, re patterning and readiness, 1. Contract / Relax 2. Sea Weed 3. Leg out of the Pelvis
TOWARDS PERFECT TURNOUT BY NOA SPECTOR FLOCK 1 Section I Imagery & Integration Create ease, inner-space, awareness, re patterning and readiness, 1. Contract / Relax 2. Sea Weed 3. Leg out of the Pelvis
LIGHT AND HIGH POTASSIUM CAUSE SIMILAR PHASE SHIFTS OF THE APLYSIA EYE CIRCADIAN RHYTHM.
 J. exp. Biol. (1981), 94. 345~349 345 With 3 figures ferina nted in Great Britain LIGHT AND HIGH POTASSIUM CAUSE SIMILAR PHASE SHIFTS OF THE APLYSIA EYE CIRCADIAN RHYTHM. BY JON W. JACKLET AND DAVID P.
J. exp. Biol. (1981), 94. 345~349 345 With 3 figures ferina nted in Great Britain LIGHT AND HIGH POTASSIUM CAUSE SIMILAR PHASE SHIFTS OF THE APLYSIA EYE CIRCADIAN RHYTHM. BY JON W. JACKLET AND DAVID P.
A Study of Ciliary Beating in Chlamydomonas
 Syracuse University SURFACE Syracuse University Honors Program Capstone Projects Syracuse University Honors Program Capstone Projects Spring 5-1-2014 A Study of Ciliary Beating in Chlamydomonas Xin Li
Syracuse University SURFACE Syracuse University Honors Program Capstone Projects Syracuse University Honors Program Capstone Projects Spring 5-1-2014 A Study of Ciliary Beating in Chlamydomonas Xin Li
Cyclical bending movements induced locally by successive iontophoretic application of ATP to an elastase-treated flagellar axoneme
 Journal of Cell Science 108, 1359-1369 (1995) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1995 1359 Cyclical bending movements induced locally by successive iontophoretic application of
Journal of Cell Science 108, 1359-1369 (1995) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1995 1359 Cyclical bending movements induced locally by successive iontophoretic application of
Rotating the plane of imposed vibration can rotate the plane of flagellar beating in sea-urchin sperm without twisting the axoneme
 Rotating the plane of imposed vibration can rotate the plane of flagellar beating in sea-urchin sperm without twisting the axoneme CHIKAKO SHINGY0J1*, JUN KATADA, KEHCHI TAKAHASHI Zoological Institute,
Rotating the plane of imposed vibration can rotate the plane of flagellar beating in sea-urchin sperm without twisting the axoneme CHIKAKO SHINGY0J1*, JUN KATADA, KEHCHI TAKAHASHI Zoological Institute,
MICROMANIPULATION OF THE FLAGELLUM OF CRITHIDIA ONCOPELTI
 Jf. Exp. Biol. (1974), 60, 437-444 437 With 2 text-figures Printed in Great Britain MICROMANIPULATION OF THE FLAGELLUM OF CRITHIDIA ONCOPELTI I. MECHANICAL EFFECTS* BY M. E. J. HOLWILL AND J. L. MCGREGOR
Jf. Exp. Biol. (1974), 60, 437-444 437 With 2 text-figures Printed in Great Britain MICROMANIPULATION OF THE FLAGELLUM OF CRITHIDIA ONCOPELTI I. MECHANICAL EFFECTS* BY M. E. J. HOLWILL AND J. L. MCGREGOR
Anatomy & Homeostasis. Unit 5
 Anatomy & Homeostasis Unit 5 Main Ideas discuss with a buddy 2 What is Homeostasis? How is homeostasis different in single-celled organisms vs. multicellular organisms? What unique challenges to maintaining
Anatomy & Homeostasis Unit 5 Main Ideas discuss with a buddy 2 What is Homeostasis? How is homeostasis different in single-celled organisms vs. multicellular organisms? What unique challenges to maintaining
Spermatozoa motility in reverse gear? An observation of backward-moving human spermatozoa.
 Spermatozoa motility in reverse gear? An observation of backward-moving human spermatozoa. Correspondence sranjanivenkadesan@gmail.com Disciplines Medical Sciences Keywords Spermatozoa, Motility Humans
Spermatozoa motility in reverse gear? An observation of backward-moving human spermatozoa. Correspondence sranjanivenkadesan@gmail.com Disciplines Medical Sciences Keywords Spermatozoa, Motility Humans
Animal Locomotion. Lots of ways to get around. What are the advantages of locomotion? Why Do We Need All That ATP?
 Animal Locomotion What are the advantages of locomotion? Motor Mechanisms sessile (Muscles & Motor Locomotion) motile Why Do We Need All That ATP? 2006-2007 mollusk mammal bird reptile We saw how some
Animal Locomotion What are the advantages of locomotion? Motor Mechanisms sessile (Muscles & Motor Locomotion) motile Why Do We Need All That ATP? 2006-2007 mollusk mammal bird reptile We saw how some
Ciliary Reversal without Rotation of Axonemal Structures in Ctenophore Comb Plates
 Published Online: 1 June, 1981 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.89.3.495 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on July 15, 2018 Ciliary Reversal without Rotation of Axonemal Structures in Ctenophore Comb
Published Online: 1 June, 1981 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.89.3.495 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on July 15, 2018 Ciliary Reversal without Rotation of Axonemal Structures in Ctenophore Comb
Locomotion: The act or power of moving from place to place
 Locomotion Locomotion: The act or power of moving from place to place Vocabulary 1. Motile = The ability to move from place to place 2. Sessile = 3. Muscle contraction = 4. Exoskeleton = 5. Endoskeleton
Locomotion Locomotion: The act or power of moving from place to place Vocabulary 1. Motile = The ability to move from place to place 2. Sessile = 3. Muscle contraction = 4. Exoskeleton = 5. Endoskeleton
sphere A diameter / cm 1 3 (i) The student calculated the surface area: volume ratio of sphere B as 2:1.
 1. A student investigated how the surface area of a single-celled organism is related to its volume. The student used two spheres, A and B, as models of two organisms. The surface area and volume of each
1. A student investigated how the surface area of a single-celled organism is related to its volume. The student used two spheres, A and B, as models of two organisms. The surface area and volume of each
Laboratory 10 Factors Controlling Phagocytosis in Tetrahymena,
 BIO354: Cell Biology Laboratory 1 Laboratory 1 Factors Controlling Phagocytosis in Tetrahymena, I. Introduction A characteristic feature of all eukaryotic cells is the ability to pinch off portions of
BIO354: Cell Biology Laboratory 1 Laboratory 1 Factors Controlling Phagocytosis in Tetrahymena, I. Introduction A characteristic feature of all eukaryotic cells is the ability to pinch off portions of
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Brooks and Wallingford, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201204072/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Quantification of ciliary compartments in control
Supplemental material Brooks and Wallingford, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201204072/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Quantification of ciliary compartments in control
VESTIBULAR SYSTEM ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. Professor.Dr. M.K.Rajasekar MS., DLO.,
 VESTIBULAR SYSTEM ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Professor.Dr. M.K.Rajasekar MS., DLO., Life is hard for those who don t have a VOR During a walk I found too much motion in my visual picture of the surroundings
VESTIBULAR SYSTEM ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Professor.Dr. M.K.Rajasekar MS., DLO., Life is hard for those who don t have a VOR During a walk I found too much motion in my visual picture of the surroundings
Chapter 42: Circulation / Gas Exchange. d = t 2
 Chapter 42: Circulation / Gas Exchange Transport systems connect organs of exchange with body cells Diffusion Lung Blood 100 m 1 s 1 mm 100 s 1 cm 10000 s d = t 2 Bulk Flow (Pressure) Blood Cells Methods
Chapter 42: Circulation / Gas Exchange Transport systems connect organs of exchange with body cells Diffusion Lung Blood 100 m 1 s 1 mm 100 s 1 cm 10000 s d = t 2 Bulk Flow (Pressure) Blood Cells Methods
NEUROPHYSIOLOGICAL CORRELATES OF THE DOPAMINERGIC CILIO-INHIBITORY MECHANISM OF MYTILUS EDULIS
 J. exp. Biol. (1979), 83, 315-323 315 Wkth 5 figures tinted in Great Britain NEUROPHYSIOLOGICAL CORRELATES OF THE DOPAMINERGIC CILIO-INHIBITORY MECHANISM OF MYTILUS EDULIS BY EDWARD J. CATAPANE, Department
J. exp. Biol. (1979), 83, 315-323 315 Wkth 5 figures tinted in Great Britain NEUROPHYSIOLOGICAL CORRELATES OF THE DOPAMINERGIC CILIO-INHIBITORY MECHANISM OF MYTILUS EDULIS BY EDWARD J. CATAPANE, Department
Microanatomy of Muscles. Anatomy & Physiology Class
 Microanatomy of Muscles Anatomy & Physiology Class Three Main Muscle Types Objectives: By the end of this presentation you will have the information to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Describe the 3 main types of muscles.
Microanatomy of Muscles Anatomy & Physiology Class Three Main Muscle Types Objectives: By the end of this presentation you will have the information to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Describe the 3 main types of muscles.
Laboratory Exercise 1 Laboratory Examination of a Basal Deuterostome: Sea Urchin Embryos
 S. S. SUMIDA BIOLOGY 340 Comparative Embryology Introduction Laboratory Exercise 1 Laboratory Examination of a Basal Deuterostome: Sea Urchin Embryos Many laboratories that examine sea urchin embryos do
S. S. SUMIDA BIOLOGY 340 Comparative Embryology Introduction Laboratory Exercise 1 Laboratory Examination of a Basal Deuterostome: Sea Urchin Embryos Many laboratories that examine sea urchin embryos do
Phylum Echinodermata
 Phylum Echinodermata Spiny Skin Echinodermata Radially symmetrical in five ways (pentamerous) Echinodermata No head, right or left side, or top or bottom, so we refer to the oral surface (mouth side) and
Phylum Echinodermata Spiny Skin Echinodermata Radially symmetrical in five ways (pentamerous) Echinodermata No head, right or left side, or top or bottom, so we refer to the oral surface (mouth side) and
How we study the brain: a survey of methods used in neuroscience
 How we study the brain: a survey of methods used in neuroscience Preparing living neurons for recording Large identifiable neurons in a leech Rohon-Beard neurons in a frog spinal cord Living slice of a
How we study the brain: a survey of methods used in neuroscience Preparing living neurons for recording Large identifiable neurons in a leech Rohon-Beard neurons in a frog spinal cord Living slice of a
The Role of Zinc in the Regulation of Ultradian Rhythms in Paramecium Tetraurelia
 Indiana University of Pennsylvania Knowledge Repository @ IUP Theses and Dissertations (All) 8-2015 The Role of Zinc in the Regulation of Ultradian Rhythms in Paramecium Tetraurelia Brianne J. Seitz Indiana
Indiana University of Pennsylvania Knowledge Repository @ IUP Theses and Dissertations (All) 8-2015 The Role of Zinc in the Regulation of Ultradian Rhythms in Paramecium Tetraurelia Brianne J. Seitz Indiana
ON A MECHATRONIC SYSTEM TO DETERMINE DYNAMIC PARAMETERS OF THE HUMAN LIMB DURING LOCOMOTION USED FOR ARTIFICIAL MUSCLES AND IMPLANT DESIGN
 6th International DAAAM Baltic Conference INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING 24-26 April 2008, Tallinn, Estonia ON A MECHATRONIC SYSTEM TO DETERMINE DYNAMIC PARAMETERS OF THE HUMAN LIMB DURING LOCOMOTION USED FOR
6th International DAAAM Baltic Conference INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING 24-26 April 2008, Tallinn, Estonia ON A MECHATRONIC SYSTEM TO DETERMINE DYNAMIC PARAMETERS OF THE HUMAN LIMB DURING LOCOMOTION USED FOR
In Vitro Speeds of Bovine Spermatozoa
 In Vitro Speeds of Bovine Spermatozoa A. N. Moeller, M.S., and N. l. VanDemark, Ph.D. THE RATE OF progressive movement of the spermatozoa has been used as one criterion in physiologic studies for evaluation
In Vitro Speeds of Bovine Spermatozoa A. N. Moeller, M.S., and N. l. VanDemark, Ph.D. THE RATE OF progressive movement of the spermatozoa has been used as one criterion in physiologic studies for evaluation
Organismic Biology Bio 207. Lecture 6. Muscle and movement; sliding filaments; E-C coupling; length-tension relationships; biomechanics. Prof.
 Organismic Biology Bio 207 Lecture 6 Muscle and movement; sliding filaments; E-C coupling; length-tension relationships; biomechanics Prof. Simchon Today s Agenda Skeletal muscle Neuro Muscular Junction
Organismic Biology Bio 207 Lecture 6 Muscle and movement; sliding filaments; E-C coupling; length-tension relationships; biomechanics Prof. Simchon Today s Agenda Skeletal muscle Neuro Muscular Junction
Phosphoinositides Regulate Ciliary Protein Trafficking to Modulate Hedgehog Signaling
 Developmental Cell Supplemental Information Phosphoinositides Regulate Ciliary Protein Trafficking to Modulate Hedgehog Signaling Francesc R. Garcia-Gonzalo, Siew Cheng Phua, Elle C. Roberson, Galo Garcia
Developmental Cell Supplemental Information Phosphoinositides Regulate Ciliary Protein Trafficking to Modulate Hedgehog Signaling Francesc R. Garcia-Gonzalo, Siew Cheng Phua, Elle C. Roberson, Galo Garcia
Axon Nerve impulse. Axoplasm Receptor. Axomembrane Stimuli. Schwann cell Effector. Myelin Cell body
 Nervous System Review 1. Explain a reflex arc. 2. Know the structure, function and location of a sensory neuron, interneuron, and motor neuron 3. What is (a) Neuron Axon Nerve impulse Axoplasm Receptor
Nervous System Review 1. Explain a reflex arc. 2. Know the structure, function and location of a sensory neuron, interneuron, and motor neuron 3. What is (a) Neuron Axon Nerve impulse Axoplasm Receptor
Morphological Aspects of Ciliary Motility
 Morphological Aspects of Ciliary Motility PETER SATIR From the Department of Zoology, University of Chicago A B S T R A C T In Elliptio complanatus lateral cilia, two distinct patterns of filament termination
Morphological Aspects of Ciliary Motility PETER SATIR From the Department of Zoology, University of Chicago A B S T R A C T In Elliptio complanatus lateral cilia, two distinct patterns of filament termination
33.2. Muscular System. Humans have three types of muscle.
 33.2 Muscular System VOCABULARY muscular system muscle fiber skeletal muscle tendon smooth muscle cardiac muscle myofibril sarcomere 10A, 10C, 11A Key Concept Muscles are tissues that can contract, enabling
33.2 Muscular System VOCABULARY muscular system muscle fiber skeletal muscle tendon smooth muscle cardiac muscle myofibril sarcomere 10A, 10C, 11A Key Concept Muscles are tissues that can contract, enabling
AnS SI 214 Practice Exam 2 Nervous, Muscle, Cardiovascular
 AnS SI 214 Practice Exam 2 Nervous, Muscle, Cardiovascular Select the best answer choice in the questions below. 1) On the electrocardiogram, repolarization of the atria is represented by the: A) P wave
AnS SI 214 Practice Exam 2 Nervous, Muscle, Cardiovascular Select the best answer choice in the questions below. 1) On the electrocardiogram, repolarization of the atria is represented by the: A) P wave
Minimal Effects When Acute Nicotine Exposure Introduced to 3 Day Old Chick Embryos
 Minimal Effects When Acute Nicotine Exposure Introduced to 3 Day Old Chick Embryos Amy Langevin Independent Research Project Bio254- Developmental Biology November 28, 2007 Introduction Thousands of mothers
Minimal Effects When Acute Nicotine Exposure Introduced to 3 Day Old Chick Embryos Amy Langevin Independent Research Project Bio254- Developmental Biology November 28, 2007 Introduction Thousands of mothers
BioMEDIA ASSOCIATES LLC HIDDEN BIODIVERSITY Series
 BioMEDIA ASSOCIATES LLC HIDDEN BIODIVERSITY Series Locomotion of Microorganisms Study Guide Written and Photographed by Rubén Duro Pérez Supplement to Video Program All Text and Images 2015 BioMEDIA ASSOCIATES
BioMEDIA ASSOCIATES LLC HIDDEN BIODIVERSITY Series Locomotion of Microorganisms Study Guide Written and Photographed by Rubén Duro Pérez Supplement to Video Program All Text and Images 2015 BioMEDIA ASSOCIATES
Underwater noise: behavioural responses of fishes and invertebrates
 Underwater noise: behavioural responses of fishes and invertebrates Louise Roberts 1, Rafael Pérez-Domínguez, Michael Elliott 1 1 Institute of Estuarine and Coastal Studies (IECS), University of Hull,
Underwater noise: behavioural responses of fishes and invertebrates Louise Roberts 1, Rafael Pérez-Domínguez, Michael Elliott 1 1 Institute of Estuarine and Coastal Studies (IECS), University of Hull,
METACHRONISM AND FREQUENCY OF BEAT IN THE PERISTOMIAL CILIA OF STENTOR
 METACHRONISM AND FREQUENCY OF BEAT IN THE PERISTOMIAL CILIA OF STENTOR BY M. A. SLEIGH Department of Zoology, University of Bristol {Received lojvne 1955) INTRODUCTION Co-ordination between cilia has attracted
METACHRONISM AND FREQUENCY OF BEAT IN THE PERISTOMIAL CILIA OF STENTOR BY M. A. SLEIGH Department of Zoology, University of Bristol {Received lojvne 1955) INTRODUCTION Co-ordination between cilia has attracted
Functional Anatomy, Biomechanics and Exercise Physiology
 W.I.T.S. Personal Trainer Certification Lecture Test Title Two: Functional Anatomy, Biomechanics and Exercise Physiology Achieving Stability Stability: ability to maintain a stable, balanced position after
W.I.T.S. Personal Trainer Certification Lecture Test Title Two: Functional Anatomy, Biomechanics and Exercise Physiology Achieving Stability Stability: ability to maintain a stable, balanced position after
NON-SINUSOIDAL BENDING WAVES OF SPERM FLAGELLA*
 J. Exp. Biol. (1965), 43, 155-169 155 With 2 plates and 2 text-figures Printed in Great Britain NON-SINUSOIDAL BENDING WAVES OF SPERM FLAGELLA* BY C. J. BROKAW Division of Biology, California Institute
J. Exp. Biol. (1965), 43, 155-169 155 With 2 plates and 2 text-figures Printed in Great Britain NON-SINUSOIDAL BENDING WAVES OF SPERM FLAGELLA* BY C. J. BROKAW Division of Biology, California Institute
-Detect heat or cold and help maintain body temperature
 Sensory Receptors -Transduce stimulus energy and transmit signals to the central nervous system -Reception occurs when a receptor detectd a stimulus -Perception occurs in the brain as this information
Sensory Receptors -Transduce stimulus energy and transmit signals to the central nervous system -Reception occurs when a receptor detectd a stimulus -Perception occurs in the brain as this information
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF MAMMALIAN SPERM MOTILITY
 Published Online: 1 May, 1972 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.53.2.561 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on June 6, 2018 COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF MAMMALIAN SPERM MOTILITY DAVID M. PHILLIPS From the
Published Online: 1 May, 1972 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.53.2.561 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on June 6, 2018 COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF MAMMALIAN SPERM MOTILITY DAVID M. PHILLIPS From the
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 10 - Balance
 The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 10 - Balance www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 1 The sense of balance originates from the labyrinth... 2 The auditory and vestibular systems have a common
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 10 - Balance www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 1 The sense of balance originates from the labyrinth... 2 The auditory and vestibular systems have a common
WAVE DYNAMYCS OF HUMAN SPERM MOTILITY
 Page 1 of 14 WAVE PARAMETERS OF THE SPERM FLAGELLUM AS PREDICTORS OF HUMAN SPERMATOZOA MOTILITY Andrologia 30: 153-157, 1998 O. Vera 1, M.G. Muñoz 2 and K. Jaffe 2 1 Facultad de Ciencias Veterinarias,
Page 1 of 14 WAVE PARAMETERS OF THE SPERM FLAGELLUM AS PREDICTORS OF HUMAN SPERMATOZOA MOTILITY Andrologia 30: 153-157, 1998 O. Vera 1, M.G. Muñoz 2 and K. Jaffe 2 1 Facultad de Ciencias Veterinarias,
Review from Biology A
 Chapter 4 Review from Biology A The Cell Theory All organisms are made of cells Cells come from pre-existing cells The cell is the simplest collection of matter that can live Scientists whose work you
Chapter 4 Review from Biology A The Cell Theory All organisms are made of cells Cells come from pre-existing cells The cell is the simplest collection of matter that can live Scientists whose work you
3.E.2 Continued. This is the essential knowledge statement from the curriculum framework. Detect---process--- response
 Nervous System: Part III What Happens at a Synapse? 3.E. Continued Animals have nervous systems that detect external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information, and produce responses. This
Nervous System: Part III What Happens at a Synapse? 3.E. Continued Animals have nervous systems that detect external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information, and produce responses. This
Golfers Stretch. for Success by Performing Exercises using the Body Bar Flex
 Golfers Stretch for Success by Performing Exercises using the Body Bar Flex Stretching before hitting your first golf ball can improve your game! Stretching before beginning in any sport can enhance your
Golfers Stretch for Success by Performing Exercises using the Body Bar Flex Stretching before hitting your first golf ball can improve your game! Stretching before beginning in any sport can enhance your
Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition
 Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Two principles about neurons were defined by Ramón y Cajal. The principle of connectional specificity states that, whereas the principle
Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Two principles about neurons were defined by Ramón y Cajal. The principle of connectional specificity states that, whereas the principle
Lecture Series Outline
 Impact of vitamins & nutrients on neurological function Lecture Series Outline Week 1: Introduction to the brain Week 2: B-vitamins and development (Guest Lecture: Usha Shan) Week 3: B-vitamins and aging
Impact of vitamins & nutrients on neurological function Lecture Series Outline Week 1: Introduction to the brain Week 2: B-vitamins and development (Guest Lecture: Usha Shan) Week 3: B-vitamins and aging
Asymmetry of the central apparatus defines the location of active microtubule sliding in Chlamydomonas flagella
 Asymmetry of the central apparatus defines the location of active microtubule sliding in Chlamydomonas flagella Matthew J. Wargo and Elizabeth F. Smith* Department of Biological Sciences, Dartmouth College,
Asymmetry of the central apparatus defines the location of active microtubule sliding in Chlamydomonas flagella Matthew J. Wargo and Elizabeth F. Smith* Department of Biological Sciences, Dartmouth College,
Zoology. Lab Guide. Exercise 16A Class Asteroidea Sea Stars
 Zoology Exercise #16: Echinoderms Lab Guide STARFISH ONLY!!! Echinoderms contain the sea stars, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars, and sea cucumbers. The name echinoderm is derived from this group
Zoology Exercise #16: Echinoderms Lab Guide STARFISH ONLY!!! Echinoderms contain the sea stars, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars, and sea cucumbers. The name echinoderm is derived from this group
Biomechanical Analysis of the Deadlift (aka Spinal Mechanics for Lifters) Tony Leyland
 Biomechanical Analysis of the Deadlift (aka Spinal Mechanics for Lifters) Tony Leyland Mechanical Terminology The three directions in which forces are applied to human tissues are compression, tension,
Biomechanical Analysis of the Deadlift (aka Spinal Mechanics for Lifters) Tony Leyland Mechanical Terminology The three directions in which forces are applied to human tissues are compression, tension,
Illustrative exercises for the lectures
 Biomechanics Illustrative exercises for the lectures Ingrid Svensson 2015 1 1. To practise the use of free-body diagram, consider the problem of analyzing the stress in man s back muscles when performing
Biomechanics Illustrative exercises for the lectures Ingrid Svensson 2015 1 1. To practise the use of free-body diagram, consider the problem of analyzing the stress in man s back muscles when performing
The Muscular System. Muscles are. There are more than 600 muscles in the Human Body!!! Needed for all types of movement. Needed to pump blood
 The Muscular System There are more than 600 muscles in the Human Body!!! Muscles are Needed for all types of movement. Needed to pump blood Needed to breathe (diaphragm muscle). Needed to produce body
The Muscular System There are more than 600 muscles in the Human Body!!! Muscles are Needed for all types of movement. Needed to pump blood Needed to breathe (diaphragm muscle). Needed to produce body
MATERIALS AND METHODS
 Develop. Growth and Differ. Vol. 21 No. 5 1979 pp. 423-430. CRYOPRESERVATION OF SEA URCHIN EMBRYOS AND SPERM EIZO ASAHINA AND TSUNEO TAKAHASHI Minami 5. Nishi 24 Sapporo 060 Japan and The American National
Develop. Growth and Differ. Vol. 21 No. 5 1979 pp. 423-430. CRYOPRESERVATION OF SEA URCHIN EMBRYOS AND SPERM EIZO ASAHINA AND TSUNEO TAKAHASHI Minami 5. Nishi 24 Sapporo 060 Japan and The American National
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS
 CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
CONTROL OF THE ORIENTATION OF CILIA BY ATP AND DIVALENT CATIONS IN TRITON-GLYCEROL-EXTRACTED PARAMECIUM CAUDATUM
 J. exp. Biol. 120, 105-117 (1986) 105 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1986 CONTROL OF THE ORIENTATION OF CILIA BY ATP AND DIVALENT CATIONS IN TRITON-GLYCEROL-EXTRACTED PARAMECIUM
J. exp. Biol. 120, 105-117 (1986) 105 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1986 CONTROL OF THE ORIENTATION OF CILIA BY ATP AND DIVALENT CATIONS IN TRITON-GLYCEROL-EXTRACTED PARAMECIUM
Cardiac muscle is different from other types of muscle in that cardiac muscle
 6 E X E R C I S E Cardiovascular Physiology O B J E C T I V E S 1. To define autorhythmicity, sinoatrial node, pacemaker cells, and vagus nerves 2. To understand the effects of the sympathetic and parasympathetic
6 E X E R C I S E Cardiovascular Physiology O B J E C T I V E S 1. To define autorhythmicity, sinoatrial node, pacemaker cells, and vagus nerves 2. To understand the effects of the sympathetic and parasympathetic
EVALUATION OF THE ANKLE ROLL GUARD S EFFECTIVENESS TO IMPROVE ITS CLINICAL BENEFIT PROGRESS REPORT. Prepared By:
 EVALUATION OF THE ANKLE ROLL GUARD S EFFECTIVENESS TO IMPROVE ITS CLINICAL BENEFIT PROGRESS REPORT Prepared By: Dr. Tyler Brown, Principal Investigator Wyatt Ihmels, Graduate Research Assistant Research
EVALUATION OF THE ANKLE ROLL GUARD S EFFECTIVENESS TO IMPROVE ITS CLINICAL BENEFIT PROGRESS REPORT Prepared By: Dr. Tyler Brown, Principal Investigator Wyatt Ihmels, Graduate Research Assistant Research
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM BLOOD VESSELS
 Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
CONTROL OF CILIARY ACTIVITIES BY ADENOSINETRIPHOSPHATE AND DIVALENT CATIONS IN TRITON-EXTRACTED MODELS OF PARAMECIUM CAUDATUM
 y. Exp. Bio/. (1973). 58,657-676 657 *.With 1 plate and 13 text-figures ''Printed in Great Britain CONTROL OF CILIARY ACTIVITIES BY ADENOSINETRIPHOSPHATE AND DIVALENT CATIONS IN TRITON-EXTRACTED MODELS
y. Exp. Bio/. (1973). 58,657-676 657 *.With 1 plate and 13 text-figures ''Printed in Great Britain CONTROL OF CILIARY ACTIVITIES BY ADENOSINETRIPHOSPHATE AND DIVALENT CATIONS IN TRITON-EXTRACTED MODELS
2.1 Biological Inspiration
 26 Chapter 2 2.6 Concluding Remarks / References / 41 2.1 Biological Inspiration Human-made mobility platforms excel on paved roads, but off road they often get stuck in the dirt. It has been argued that
26 Chapter 2 2.6 Concluding Remarks / References / 41 2.1 Biological Inspiration Human-made mobility platforms excel on paved roads, but off road they often get stuck in the dirt. It has been argued that
Microtubule Teardrop Patterns
 Supporting Information Microtubule Teardrop Patterns Kosuke Okeyoshi 1, Ryuzo Kawamura 1, Ryo Yoshida 2, and Yoshihito Osada 1 * 1 RIKEN Advanced Science Institute, 2-1 Hirosawa, Wako-shi, Saitama 351-0198,
Supporting Information Microtubule Teardrop Patterns Kosuke Okeyoshi 1, Ryuzo Kawamura 1, Ryo Yoshida 2, and Yoshihito Osada 1 * 1 RIKEN Advanced Science Institute, 2-1 Hirosawa, Wako-shi, Saitama 351-0198,
Lesson 8: Effect of temperature on an oyster s heart rate
 Lesson 8: Effect of temperature on an oyster s heart rate Focus Question: How does temperature affect the heart rate of an oyster? Purpose: In this lab based activity, students investigate the effect of
Lesson 8: Effect of temperature on an oyster s heart rate Focus Question: How does temperature affect the heart rate of an oyster? Purpose: In this lab based activity, students investigate the effect of
CETR Adhesion Testing on Glass/Al Surface for Corning Inc.
 CETR Adhesion Testing on Glass/Al Surface for Corning Inc. I. Introduction 1.1 Objective The goal of the study was to differentiate stiction from various glass composites and surface treatments using the
CETR Adhesion Testing on Glass/Al Surface for Corning Inc. I. Introduction 1.1 Objective The goal of the study was to differentiate stiction from various glass composites and surface treatments using the
Physiology and pharmacology of smooth muscle contractions a brief introduction
 SimVessel: Physiology and pharmacology of smooth muscle contractions a brief introduction The virtual SimVessel Laboratory is for recordings of smooth muscle contractions of small muscle stripes of different
SimVessel: Physiology and pharmacology of smooth muscle contractions a brief introduction The virtual SimVessel Laboratory is for recordings of smooth muscle contractions of small muscle stripes of different
Evaluation of The Effect of Paraben Exposure on Sea Urchin (Strongylocentrotus Purpuratus) Fertility. Hannah Schalyo AP Research
 Evaluation of The Effect of Paraben Exposure on Sea Urchin (Strongylocentrotus Purpuratus) Fertility Hannah Schalyo AP Research Background Current Problems, Previous Studies and Purpose Parabens Preservatives
Evaluation of The Effect of Paraben Exposure on Sea Urchin (Strongylocentrotus Purpuratus) Fertility Hannah Schalyo AP Research Background Current Problems, Previous Studies and Purpose Parabens Preservatives
Nervous and chemical regulation heart
 Nervous and chemical regulation heart Myogenic heart when separated out from the body keep on beating on their own but when in the body the rate of heart beat is modified through various stimuli such as
Nervous and chemical regulation heart Myogenic heart when separated out from the body keep on beating on their own but when in the body the rate of heart beat is modified through various stimuli such as
Computerized semen analysis. Product features. Basic system
 AndroVision - more than CASA AndroVision CASA system with Zeiss AxioScope optics and automated ScanStage Computerized semen analysis AndroVision is a highly precise CASA* system for standardised, interactive
AndroVision - more than CASA AndroVision CASA system with Zeiss AxioScope optics and automated ScanStage Computerized semen analysis AndroVision is a highly precise CASA* system for standardised, interactive
System for Evaluation of the Static Posturography Based on Wii Balance Board
 System for Evaluation of the Static Posturography Based on Wii Balance Board PIVNICKOVA L., DOLINAY V., VASEK V. Faculty of Applied Informatics Tomas Bata University in Zlin nam. T.G.Masaryka 5555, 760
System for Evaluation of the Static Posturography Based on Wii Balance Board PIVNICKOVA L., DOLINAY V., VASEK V. Faculty of Applied Informatics Tomas Bata University in Zlin nam. T.G.Masaryka 5555, 760
Q: What is the relationship between muscle forces and EMG data that we have collected?
 FAQs ABOUT OPENSIM Q: What is the relationship between muscle forces and EMG data that we have collected? A: Muscle models in OpenSim generate force based on three parameters: activation, muscle fiber
FAQs ABOUT OPENSIM Q: What is the relationship between muscle forces and EMG data that we have collected? A: Muscle models in OpenSim generate force based on three parameters: activation, muscle fiber
LOCALIZED ACTIVATION OF BENDING IN PROXIMAL, MEDIAL AND DISTAL REGIONS OF SEA-URCHIN SPERM FLAGELLA
 J. Cell Sci. 13, 1-10 (1973) Printed in Great Britain LOCALIZED ACTIVATION OF BENDING IN PROXIMAL, MEDIAL AND DISTAL REGIONS OF SEA-URCHIN SPERM FLAGELLA C. J. BROKAW* AND I. R. GIBBONS Pacific Biomedical
J. Cell Sci. 13, 1-10 (1973) Printed in Great Britain LOCALIZED ACTIVATION OF BENDING IN PROXIMAL, MEDIAL AND DISTAL REGIONS OF SEA-URCHIN SPERM FLAGELLA C. J. BROKAW* AND I. R. GIBBONS Pacific Biomedical
In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question.
 CHAPTER 3 TEST Cell Structure Circle T if the statement is true or F if it is false. T F 1. Small cells can transport materials and information more quickly than larger cells can. T F 2. Newly made proteins
CHAPTER 3 TEST Cell Structure Circle T if the statement is true or F if it is false. T F 1. Small cells can transport materials and information more quickly than larger cells can. T F 2. Newly made proteins
Fig. 1. The reverse change is shown in Fig. 3. fluid, and then when activity was re-established the fluid replaced by a
 CARDIAC TETANUS. By W. BURRID GE, M.B. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Oxford.) WALTHER(13) gives complete references to the experiments on cardiac tetanus and in his discussion concludes that superposition
CARDIAC TETANUS. By W. BURRID GE, M.B. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Oxford.) WALTHER(13) gives complete references to the experiments on cardiac tetanus and in his discussion concludes that superposition
Visit for Videos, Questions and Revision Notes.
 Q1.A biologist investigated the behaviour of a species of worm that lives in soil. He cultured three samples of worms in three separate trays of soil for many days. Each culture: contained a food supply
Q1.A biologist investigated the behaviour of a species of worm that lives in soil. He cultured three samples of worms in three separate trays of soil for many days. Each culture: contained a food supply
Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Nervous system development Part of the ectoderm
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Nervous system development Part of the ectoderm
IMPROVEMENT OF PNEUMATIC FOOTBALL KICKING DEVICE BASED ON IMITATION OF HUMAN DYNAMICS
 11th International DAAAM Baltic Conference "INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING" 20th 22nd April 2016, Tallinn, Estonia IMPROVEMENT OF PNEUMATIC FOOTBALL KICKING DEVICE BASED ON IMITATION OF HUMAN DYNAMICS Paukkunen,
11th International DAAAM Baltic Conference "INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING" 20th 22nd April 2016, Tallinn, Estonia IMPROVEMENT OF PNEUMATIC FOOTBALL KICKING DEVICE BASED ON IMITATION OF HUMAN DYNAMICS Paukkunen,
UV Exposure to Sea Urchin Gametes and Success of Fertilization Envelope Liftoff
 Bio254 Home UV Exposure to Sea Urchin Gametes and Success of Fertilization Envelope Liftoff Amanda Crouch-Smith Web Posted on 12/02/04 Introduction Materials & Methods Results Conclusion & Discussion Bibliography
Bio254 Home UV Exposure to Sea Urchin Gametes and Success of Fertilization Envelope Liftoff Amanda Crouch-Smith Web Posted on 12/02/04 Introduction Materials & Methods Results Conclusion & Discussion Bibliography
Clockwise Translocation of Microtubules by Flagellar Inner-Arm Dyneins In Vitro
 4014 Biophysical Journal Volume 94 May 2008 4014 4019 Clockwise Translocation of Microtubules by Flagellar Inner-Arm Dyneins In Vitro Kenji Kikushima* and Ritsu Kamiya* y *Department of Biological Sciences,
4014 Biophysical Journal Volume 94 May 2008 4014 4019 Clockwise Translocation of Microtubules by Flagellar Inner-Arm Dyneins In Vitro Kenji Kikushima* and Ritsu Kamiya* y *Department of Biological Sciences,
II. E.ffects of viscosity and thiourea
 Mechanochemical Coupling in Flagella II. E.ffects of viscosity and thiourea on metabolism and motility of Ciona spermatozoa C.]. BROKAW and B. BENEDICT From the Division of Biology, California Institute
Mechanochemical Coupling in Flagella II. E.ffects of viscosity and thiourea on metabolism and motility of Ciona spermatozoa C.]. BROKAW and B. BENEDICT From the Division of Biology, California Institute
Circulation: Chapter 25. Cardiac Output. The Mammalian Heart Fig Right side of the heart
 Circulation: Chapter 25 1. Limits of Diffusion A. Small organisms use diffusion B. rapid over small distances 2. Most animals have circulatory systems A. Blood B. Pump (Heart) or propulsive structures
Circulation: Chapter 25 1. Limits of Diffusion A. Small organisms use diffusion B. rapid over small distances 2. Most animals have circulatory systems A. Blood B. Pump (Heart) or propulsive structures
Fluid Dynamic Models of Flagellar and Ciliary Beating
 Fluid Dynamic Models of Flagellar and Ciliary Beating ROBERT H. DILLON, a LISA J. FAUCI, b CHARLOTTE OMOTO, c AND XINGZHOU YANG d a Department of Mathematics, Washington State University, Pullman, Washington,
Fluid Dynamic Models of Flagellar and Ciliary Beating ROBERT H. DILLON, a LISA J. FAUCI, b CHARLOTTE OMOTO, c AND XINGZHOU YANG d a Department of Mathematics, Washington State University, Pullman, Washington,
[775 ] THE MOVEMENT OF SEA-URCHIN SPERMATOZOA
![[775 ] THE MOVEMENT OF SEA-URCHIN SPERMATOZOA [775 ] THE MOVEMENT OF SEA-URCHIN SPERMATOZOA](/thumbs/86/94161581.jpg) [775 ] THE MOVEMENT OF SEA-URCHIN SPERMATOZOA BY J. GRAY Department of Zoology, University of Cambridge (.Received 2 May 955) (With Plates and ) Although the mechanical activity of spermatozoa plays an
[775 ] THE MOVEMENT OF SEA-URCHIN SPERMATOZOA BY J. GRAY Department of Zoology, University of Cambridge (.Received 2 May 955) (With Plates and ) Although the mechanical activity of spermatozoa plays an
Circulation and Gas Exchange
 Circulation and Gas Exchange Sponges (porifera) Flat worms (platyhelminthes) Round worms (nematoda) Segmented worms (annelida) Stinging celled (cnidaria) Squishy (mollusca) Hard shelled (arthropods) Spiny
Circulation and Gas Exchange Sponges (porifera) Flat worms (platyhelminthes) Round worms (nematoda) Segmented worms (annelida) Stinging celled (cnidaria) Squishy (mollusca) Hard shelled (arthropods) Spiny
Heavy Metals Effect on the Fertilization and Development of Sea Urchin Embryos
 Heavy Metals Effect on the Fertilization and Development of Sea Urchin Embryos Kristin Parish, Jessica Brown, Renee Cook and Megan Kapp January 2012 Abstract Heavy metal pollution is a prevalent threat
Heavy Metals Effect on the Fertilization and Development of Sea Urchin Embryos Kristin Parish, Jessica Brown, Renee Cook and Megan Kapp January 2012 Abstract Heavy metal pollution is a prevalent threat
PHONOCARDIOGRAPHY (PCG)
 PHONOCARDIOGRAPHY (PCG) The technique of listening to sounds produced by the organs and vessels of the body is called auscultation. The areas at which the heart sounds are heard better are called auscultation
PHONOCARDIOGRAPHY (PCG) The technique of listening to sounds produced by the organs and vessels of the body is called auscultation. The areas at which the heart sounds are heard better are called auscultation
Neurons: Structure and communication
 Neurons: Structure and communication http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/gall1.html Common Components of a Neuron Dendrites Input, receives neurotransmitters Soma Processing, decision Axon Transmits
Neurons: Structure and communication http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/gall1.html Common Components of a Neuron Dendrites Input, receives neurotransmitters Soma Processing, decision Axon Transmits
