INDUCTION OF OVULATION IN URETHANE-TREATED RATS
|
|
|
- Erika Lucas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 5 INDUCTION OF OVULATION IN URETHANE-TREATED RATS Ronald D. Johnson* and Barbara Shirley Faculty of Natural Sciences, University of Tulsa, Tulsa, Oklahoma Subcutaneous injection of urethane (1 g/kg body weight) on the morning of proestrus blocked spontaneous ovulation of rats. When rats injected with urethane were paired with males, however, a significant number of the treated animals ovulated regardless of whether or not they copulated. In cases in which the females did not mate, induction of ovulation was attributed to some type of physical contact with the males or to their presence. When ovulation was induced, a full complement of ova was shed. Results of urethane administration were compared to results that have been reported when barbiturates were used to block ovulation. INTRODUCTION Spontaneous ovulation of rats can be blocked by any one of several pharmacological agents, including the barbiturates (1) and urethane (2), if the drug is injected prior to release of the surge of pituitary luteinizing hormone (LH) that occurs between and h on proestrus, a period known as the critical period. The barbiturates block ovulation by inhibiting the surge of LH from the pituitary gland (1). Urethane also inhibits LH release but does so indirectly by inhibiting release of luteinizing hormone-releasing-hormone (LH-RH) from the hypothalamus, thus interfering with hypothalamic stimulation of the pituitary (2). Urethane at a dosage sufficient to block ovulation also differs in action from the barbiturates in that it causes a much longer period of anesthesia (3 ). Injection of LH can cause both barbiturate-blocked and urethane-blocked rats to ovulate. However, the dosage of exogenous LH that is required to override the ovulation-blocking effect of urethane has been reported by some investigators (3) to be lower than that required to cause ovulation in barbiturate-blocked rats, but reported by others (2) to be greater than the dosage required to override barbiturate blockade. Although barbiturates block pituitary LH release, and thereby block spontaneous ovulation, stimulation of the hypothalamus of a barbiturate-blocked rat causes pituitary LH to be released and consequently induces ovulation. Several experiments have shown that electrical stimulation of the hypothalami of pentobarbital-blocked rats causes the animals to exhibit elevated plasma LH levels and to ovulate (4, 5). In addition it has been shown that stimulation of the hypothalami of barbiturate-blocked rats by mating causes the animals to ovulate (6, 7). Since urethane inhibits function of the hypothalamus, the present study was done to determine whether mating of urethane-blocked rats could induce them to ovulate, as it does barbiturate-blocked rats, or whether the inhibitory influence of urethane on hypothalamic LH-RH release would prevent the induction of ovulation. A dosage of barbital that will block ovulation, if administered at proestrus, causes an increase in uterine weight at estrus and in addition prolongs the ballooning of the uterus that is characteristic of proestrus (7). Therefore, the effects of urethane on the uterus were examined as a part of the present investigation. MATERIALS AND METHODS Virgin, female rats (200 to 300 g) of the Sprague-Dawley strain were kept on a rigidly controlled lighting schedule with lights on from to hr. Other environmental conditions in the animal colony have been previously described (8). Purina laboratory chow and water were provided ad libitum. Vaginal smears were taken from all animals each morning to monitor their estrous cycles and rats were assigned to experimental groups only after completing a minimum of two consecutive estrous cycles of the same length. Rats with both four-day and five-day estrous cycles were included in the study. Urethane (Sigma), dissolved in physiological saline in a concentration of 0.33 g/ml, was injected subcutaneously in a dos- *Present address: Tulsa City/County Health Department, Tulsa, Oklahoma Proc. Okla. Acad. Sci. 60:5-9 (1980)
2 6 age of 1.0 g/kg body weight. (Pilot studies had revealed that this dosage provided an effective block of ovulation.) Control rats were injected with physiological saline in the same ratio of volume to body weight (3 ml/kg). All injections were given between and hr on proestrus. Some urethane-treated rats were placed in the cages of proven male breeders at a time between and hr on proestrus and left with the males until hr the following day. (Males were used as breeders no more frequently than one day in five to increase the likelihood of their mating.) Each female was checked on the day of estrus and the presence of one or more vaginal plugs or the presence of sperm in the vaginal smear or in the uterus was used as evidence that an animal had mated. One group of urethane-injected females was not placed with males. Autopsies of female rats were performed between and hr on estrus. Urethane causes prolonged anesthesia and it was, therefore, expected that rats paired with males might not mate until shortly before being removed from the cages of the males. Since ovulation has been shown to occur 9 to 11 hr after hypophyseal activation (9), autopsies were postponed until late in the afternoon on estrus to allow time for ovulation to occur even if mating should induce pituitary LH release as late as the morning of estrus. At autopsy the oviducts of each rat were excised, placed between microscope slides, and examined at a magnification of 100 for the presence of ova (oocytes). Any ova that were found were counted. The uterus from each rat was checked for accumulation of intraluminal fluid (ballooning) and removed. After any fluid that the uterus contained was expressed, the uterine tissue was weighed, then dried to a constant weight and reweighed. The chi square test, with Yates' correction for continuity, and Student's t-test were used to analyze the data. RESULTS Urethane in the dosage used provided a deep and long-lasting anesthesia. Urethane-injected female rats were completely unresponsive when they were placed in the cages of male rats. At this time, the males became sexually aroused and attempted to mount the females, but no copulations were witnessed during the short time that the rats were observed after being paired. Urethane-treated rats were in many cases
3 7 still deeply sedated at the time that they were removed from the cages of the males on the morning of estrus. This prolonged effect of urethane was expected to cause a low incidence of mating. Our expectations were confirmed as only 8 of 34 rats left overnight with males were found to have mated when examined at estrus (Table 1). Rats injected with urethane were classified in three groups: (a) those that were not placed with males; (b) those that were placed with males but did not mate; and (c) those that mated. The drug was effective in blocking ovulation in rats not placed with males (Tables 1 and 2). However, the number of rats that ovulated in each of the urethane-treated groups placed with males was significantly greater (Table 2) than the number that ovulated in the urethane-treated group not placed with males. Ovulation in rats placed with males was not dependent on the rats having mated. The numbers of rats that ovulated in the two groups given urethane and later placed with males did not differ significantly from one another or from the number that ovulated in the control group. Similarly, the two groups of urethane-treated rats that were placed with males also failed to differ significantly from one another (p > 0.05) in the numbers of ova shed (Table 1). In neither of these groups was the number of ova shed per ovulation significantly different from the number of ova shed by rats injected with saline (p > 0.05). Since only one rat ovulated in the group which was given urethane but not placed with males, the number of ova shed per ovulation following that treatment could not be compared statistically to the numbers of ova shed by rats subjected to other experimental conditions. The single rat that ovulated in that group shed only two ova; this was considered to be a partial ovulation.
4 8 Although the wet and dry weights of uteri from those urethane-treated rats that mated were somewhat lower than the weights of uteri from rats in other treatment groups (Table 1), no statistically significant differences between the uterine weights of rats in any groups were found (p > 0.05). In addition there were no significant differences between body weights (Table 1) of rats in the four groups studied, either at the time at which the rats were injected (p > 0.05) or the time at which they were autopsied (p > 0.05). Ballooning of the uterus at estrus was seen in a significantly greater number of rats in the group that was given urethane but not placed with males than in the group of urethane-treated rats that was placed with males but which failed to mate (Tables 1 and 3). No other groups differed significantly from one another (p > 0.05) in the numbers of rats exhibiting uterine ballooning at estrus (Table 3). DISCUSSION Placing of urethane-injected female rats with males induced ovulation in a significant number of cases. This result was similar to the result that is seen when barbiturate-treated rats are placed with males but differed in at least one significant way: The presence of male rats without mating does not induce ovulation in barbiturate-blocked rats (7) but the rats may be induced to ovulate by mating (6, 7). Yet, a significantly greater number of rats was found to ovulate in a group that was given urethane and placed with males, even though they did not mate, than was found to ovulate in a group given urethane and not placed with males. It has been reported that mounts by a male rat without intromission can induce a female to ovulate (10). Results of some experiments have indicated, however, that the stimulation of coitus is necessary to induce ovulation in the rat, e.g., when chlorpromazine-blocked females were placed with "spent" males (ones that had recently mated with receptive females), the blocked females failed to ovulate (11). In the chlorpromazine study (11), as in the present study, female rats were left with males overnight and evidences of ejaculation (presence of vaginal plugs or vaginal sperm) were sought the following day but females were not watched throughout the night to verify that no intromissions occurred. In our study the females that failed to mate were still so deeply sedated at the time of their removal from the males' cages on the morning of estrus that any responsiveness to the males would have been passive. Consequently, urethane-treated females that ovulated without having mated were considered to have been induced to ovulate by the presence of the males and/or physical contact with the males exclusive of copulation e.g., by the males nudging the females or sniffing the genitalia of the females. Our data, therefore, are in agreement with the report that male rats can in some instances induce females to ovulate without the stimulus of copulation (10). It has been found that urethane may only reduce and delay release of LH in the rat, rather than completely blocking LH release, and that the amount of exogenous LH necessary to elicit ovulation in a urethane-blocked rat is lower than that required to overcome barbiturate blockade (3). These findings suggest that a stimulus sufficient to induce ovulation in a urethane-blocked rat needs to stimulate only release of the remainder of the LH complement necessary for ovulation rather than release of the total requirement. It is probable, therefore, that the presence of a male rat without copulation can cause release of enough LH to meet the requirement for ovulation in a urethane-blocked rat but that the amount of LH released is less than that which would be required to overcome barbiturate blockade. It has been reported that a partial ovulation can follow urethane injection but that the effect of a barbiturate on ovulation is "all or none" (3). In the present study the single rat that ovulated in a group that was injected with urethane but not paired with males had only a partial ovulation. The number of ova shed by each of the other groups of urethane-treated rats was not significantly less (p > 0.05 ) than the number of ova shed by the group of saline-injected controls. This indicated that when ovulation was induced by mating or some other interaction with a male rat, a full complement of ova was shed. Increased uterine weight in rats given barbital as an ovulation-blocking agent has
5 9 been attributed to a concomitant increase in estrogen secretion (7), since uterine weights can be correlated with estrogen titers (12). Urethane caused no significant change in uterine weights of test animals and it was, therefore, concluded that this drug neither stimulates nor prolongs estrogen secretion to the extent that certain barbiturates do while blocking ovulation. Uterine ballooning occurs characteristically at proestrus (13) and in the normal cycle the uterus is no longer ballooned on the day of estrus. Barbiturates differ in the degree to which they cause uterine ballooning to persist; barbital causes uterine ballooning in some rats to be prolonged until estrus but pentobarbital does not (7). Administration of urethane to rats that were not subsequently placed with males caused a significantly greater number of these rats to have ballooned uteri at estrus than was seen in the group of urethane-treated rats that was placed with males but which failed to mate, a group in which many rats ovulated. Since progesterone secretion late in the afternoon of proestrus is necessary if loss of luminal fluid from the uterus is to occur by the day of estrus (14), our data indicate that the amount of progester-one secreted on proestrus by the urethane-treated rats that were not placed with males, a group in which ovulation was blocked, was less that that secreted by rats in a group in which ovulation was induced. In conclusion our experiments indicated that, although urethane will act to block spontaneous ovulation as the barbiturates will, rats that are placed with males following treatment with urethane exhibit some responses that are unlike responses seen in barbiturate-treated females placed with males. These differences suggest a need for further examination and comparison of the effects of different types of ovulation-blocking agents on pituitary LH release and on ovarian hormone activity. ACKNOWLEDGMENT This work was supported in part by a University of Tulsa Research Grant (R ). REFERENCES 1. J. W. EVERETT and C. H. SAWYER, Endocrinology 47: (1950). 2. C. A. BLAKE and C. H. SAWYER, Endocrinology 91: (1972). 3. D. W. LINCOLN and W. A. KELLY, Endocrinology 90: (1972). 4. O. M. CRAMER and C. A. BARRACLOUGH, Endocrinology 88: (1971). 5. R. G. GOSDEN, J. W. EVERETT, and L. TYREY, Endocrinology 99: (1976). 6. J. W. EVERETT, Endocrinology 80: (1967). 7. B. SHIRLEY, Proc. Okla. Acad. Sci. 55: (1975). 8. B. SHIRLEY, J. Endocr. 77: (1978). 9. J. W. EVERETT, C. H. SAWYER, and J. E. MARKEE, Endocrinology 44: (1949). 10. C. ARON, J. ROOS, and G. ASCH, Neuroendocrinology 3: (1968). 11. F. E. HARRINGTON, R. G. EGGERT, R. D. WILBUR, and W. H. LINKENHEIMER, Endocrinology 79: (1966). 12. D. T. ARMSTRONG, Am. J. Physiol. 214: (1968). 13. E. B. ASTWOOD, Am. J. Physiol. 126: (1939). 14. T. G. KENNEDY and D. T. ARMSTRONG, Endocrinology 97: (1975).
Fukushima-ku, Osaka. Synopsis. and LH release by investigating the effects of exogenous estrogen on the progesteroneinduced
 Further Studies on the Causal Relationship between the Secretion of Estrogen and the Release of Luteinizing Hormone in the Rat FUMIHIKO KOBAYASHI, KATSUMI HARA AND TAMOTSU MIYAKE Shionogi Research Laboratory,
Further Studies on the Causal Relationship between the Secretion of Estrogen and the Release of Luteinizing Hormone in the Rat FUMIHIKO KOBAYASHI, KATSUMI HARA AND TAMOTSU MIYAKE Shionogi Research Laboratory,
Fertility and early embryonic development. Chris Willoughby, Huntingdon Life Sciences 11 October 2012
 Fertility and early embryonic development Chris Willoughby, Huntingdon Life Sciences 11 October 2012 Outline 2 What sort of compounds may affect fertility? What areas of reproduction are we assessing in
Fertility and early embryonic development Chris Willoughby, Huntingdon Life Sciences 11 October 2012 Outline 2 What sort of compounds may affect fertility? What areas of reproduction are we assessing in
Facilitation of Luteinizing Hormone Release by Progesterone in Proestrous Rats FUMIHIKO KOBAYASHI, KATSUMI HARA AND TAMOTSU MIYAKE
 Facilitation of Luteinizing Hormone Release by Progesterone in Proestrous Rats FUMIHIKO KOBAYASHI, KATSUMI HARA AND TAMOTSU MIYAKE Shionogi Research Laboratory, Shionogi & Co., Ltd., Fukushima-ku, Osaka
Facilitation of Luteinizing Hormone Release by Progesterone in Proestrous Rats FUMIHIKO KOBAYASHI, KATSUMI HARA AND TAMOTSU MIYAKE Shionogi Research Laboratory, Shionogi & Co., Ltd., Fukushima-ku, Osaka
different ratios of PMSG and HCG on the occurrence of follicular haemorrhage THE induction of ovulation with PMSG and HCG in the rat has been studied
 Q. Jl exp. Physiol. (1968) 53, 129-135 THE INDUCTION OF OVULATION IN IMMATURE RATS TREATED WITH PREGNANT MARE'S SERUM GONADOTROPHIN AND HUMAN CHORIONIC GONADOTROPHIN. By S. F. LUNN and E. T. BELL. From
Q. Jl exp. Physiol. (1968) 53, 129-135 THE INDUCTION OF OVULATION IN IMMATURE RATS TREATED WITH PREGNANT MARE'S SERUM GONADOTROPHIN AND HUMAN CHORIONIC GONADOTROPHIN. By S. F. LUNN and E. T. BELL. From
REPRODUCTION & GENETICS. Hormones
 REPRODUCTION & GENETICS Hormones http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=np0wfu_mgzo Objectives 2 Define what hormones are; Compare and contrast the male and female hormones; Explain what each hormone in the mail
REPRODUCTION & GENETICS Hormones http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=np0wfu_mgzo Objectives 2 Define what hormones are; Compare and contrast the male and female hormones; Explain what each hormone in the mail
CYCLIC MOUSE. and NEENA B. SCHWARTZ INTRODUCTION
 TIMING OF LH RELEASE AND OVULATION IN THE CYCLIC MOUSE AUDREY S. BINGEL and NEENA B. SCHWARTZ Department of Physiology, University of Illinois College of Medicine, Chicago, Illinois, U.S.A. (Received 1st
TIMING OF LH RELEASE AND OVULATION IN THE CYCLIC MOUSE AUDREY S. BINGEL and NEENA B. SCHWARTZ Department of Physiology, University of Illinois College of Medicine, Chicago, Illinois, U.S.A. (Received 1st
Pituitary Regulation of Preovulatory Estrogen Secretion MAKOTO IDE AND TAMOTSU MIYAKE
 Pituitary Regulation of Preovulatory Estrogen Secretion in the Rat TAKASHI HORI, MAKOTO IDE AND TAMOTSU MIYAKE Shionogi Research Laboratory, Shionogi & Co., Ltd., Fukushima-ku, Osaka Synopsis A role of
Pituitary Regulation of Preovulatory Estrogen Secretion in the Rat TAKASHI HORI, MAKOTO IDE AND TAMOTSU MIYAKE Shionogi Research Laboratory, Shionogi & Co., Ltd., Fukushima-ku, Osaka Synopsis A role of
Domestic Animal Behavior ANSC 3318 SEXUAL BEHAVIOR. Image courtesy : USDA ARS Image Library
 SEXUAL BEHAVIOR Image courtesy : USDA ARS Image Library Importance of Sexual Behavior Without reproduction, life would come to an end! In production situations, it is economically important to have good
SEXUAL BEHAVIOR Image courtesy : USDA ARS Image Library Importance of Sexual Behavior Without reproduction, life would come to an end! In production situations, it is economically important to have good
(Received 9th January 1973)
 EFFECT OF 5\m=infty\-DIHYDROPROGESTERONE, PREGN-5-ENE-3,2-DIONE, PREGNENOLONE AND RELATED PROGESTINS ON OVULATION IN PMSG-TREATED IMMATURE RATS B. N. SRIDHARAN, R. K. MEYER and H. J. KARAVOLAS Departments
EFFECT OF 5\m=infty\-DIHYDROPROGESTERONE, PREGN-5-ENE-3,2-DIONE, PREGNENOLONE AND RELATED PROGESTINS ON OVULATION IN PMSG-TREATED IMMATURE RATS B. N. SRIDHARAN, R. K. MEYER and H. J. KARAVOLAS Departments
Central Progesterone Involvement in Estrogen- Induced Prolactin and Luteinizing Hormone Secretion Surges in Female Rats
 Southern Illinois University Carbondale OpenSIUC Honors Theses University Honors Program 5-10-2014 Central Progesterone Involvement in Estrogen- Induced Prolactin and Luteinizing Hormone Secretion Surges
Southern Illinois University Carbondale OpenSIUC Honors Theses University Honors Program 5-10-2014 Central Progesterone Involvement in Estrogen- Induced Prolactin and Luteinizing Hormone Secretion Surges
4-7 July 2000 Valencia Spain
 Proceedings of the 4-7 July 2000 Valencia Spain These proceedings were printed as a special issue of WORLD RABBIT SCIENCE, the journal of the World Rabbit Science Association, Volume 8, supplement 1 ISSN
Proceedings of the 4-7 July 2000 Valencia Spain These proceedings were printed as a special issue of WORLD RABBIT SCIENCE, the journal of the World Rabbit Science Association, Volume 8, supplement 1 ISSN
Female Reproductive System. Justin D. Vidal
 Female Reproductive System Justin D. Vidal If you cannot identify the tissue, then it is probably part of the female reproductive system! Introduction The female reproductive system is constantly changing,
Female Reproductive System Justin D. Vidal If you cannot identify the tissue, then it is probably part of the female reproductive system! Introduction The female reproductive system is constantly changing,
The beginning of puberty is marked by the progressive increase in the production of sex hormones.
 Puberty is characterized by the changes that prepare the human body for the ability to reproduce. This stage generally occurs between the ages of 10 and 14 years old. The beginning of puberty is marked
Puberty is characterized by the changes that prepare the human body for the ability to reproduce. This stage generally occurs between the ages of 10 and 14 years old. The beginning of puberty is marked
Changes in FSH, LH and Prolactin Secretion During Estrous Cycle in Rats
 Changes in FSH, LH and Prolactin Secretion During Estrous Cycle in Rats KAZUYOSHI TAYA AND MASAO IGARASHI Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology, School of Medicine, Gunma University, Maebashi Synopsis
Changes in FSH, LH and Prolactin Secretion During Estrous Cycle in Rats KAZUYOSHI TAYA AND MASAO IGARASHI Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology, School of Medicine, Gunma University, Maebashi Synopsis
Female Reproductive System. Lesson 10
 Female Reproductive System Lesson 10 Learning Goals 1. What are the five hormones involved in the female reproductive system? 2. Understand the four phases of the menstrual cycle. Human Reproductive System
Female Reproductive System Lesson 10 Learning Goals 1. What are the five hormones involved in the female reproductive system? 2. Understand the four phases of the menstrual cycle. Human Reproductive System
Breeding Management in the Bitch: Timing Really is Everything! Erin E. Runcan, DVM, DACT Fairfield Pet Hospital, Lancaster, OH
 Breeding Management in the Bitch: Timing Really is Everything! Erin E. Runcan, DVM, DACT Fairfield Pet Hospital, Lancaster, OH It is often surprising how many well-seasoned breeders will have little knowledge
Breeding Management in the Bitch: Timing Really is Everything! Erin E. Runcan, DVM, DACT Fairfield Pet Hospital, Lancaster, OH It is often surprising how many well-seasoned breeders will have little knowledge
Course: Animal Production. Instructor: Ms. Hutchinson. Objectives: After completing this unit of instruction, students will be able to:
 Course: Animal Production Unit Title: Hormones TEKS: 130.3 (C)(6)(A) Instructor: Ms. Hutchinson Objectives: After completing this unit of instruction, students will be able to: A. Define what hormones
Course: Animal Production Unit Title: Hormones TEKS: 130.3 (C)(6)(A) Instructor: Ms. Hutchinson Objectives: After completing this unit of instruction, students will be able to: A. Define what hormones
Reproductive Endocrinology. Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007
 Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
Overripeness and the Mammalian Ova
 Overripeness and the Mammalian Ova II. Delayed Ovulation and Chromosome Anomalies ROY L. BUTCHER, PH.D., and N. W. FUGO, PH.D., M.D. THE CAUSES of abortion and birth defects are undoubtedly multiple and
Overripeness and the Mammalian Ova II. Delayed Ovulation and Chromosome Anomalies ROY L. BUTCHER, PH.D., and N. W. FUGO, PH.D., M.D. THE CAUSES of abortion and birth defects are undoubtedly multiple and
9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System
 9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System The Reproductive System to unite a single reproductive cell from a female with a single reproductive cell from a male Both male and female reproductive systems include
9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System The Reproductive System to unite a single reproductive cell from a female with a single reproductive cell from a male Both male and female reproductive systems include
Small Ruminant Reproductive Management Workshop
 Small Ruminant Reproductive Management Workshop Animal Nutrition and Physiology Center, North Dakota State University Sponsors: American Sheep and Goat Center, North Dakota State University, University
Small Ruminant Reproductive Management Workshop Animal Nutrition and Physiology Center, North Dakota State University Sponsors: American Sheep and Goat Center, North Dakota State University, University
Male Stimulation of Luteinizing Hormone Surge, Progesterone SeCretion and Ovulation in Spontaneously Persistent- Estrous, Aging Rats
 BIOLOGY OF REPRODUCTION 38, 1019-1026 (1988) Male Stimulation of Luteinizing Hormone Surge, Progesterone SeCretion and Ovulation in Spontaneously Persistent- Estrous, Aging Rats JONATHAN R. DAY, TONY H.
BIOLOGY OF REPRODUCTION 38, 1019-1026 (1988) Male Stimulation of Luteinizing Hormone Surge, Progesterone SeCretion and Ovulation in Spontaneously Persistent- Estrous, Aging Rats JONATHAN R. DAY, TONY H.
CHANGES IN LEVELS OF FOLLICLE STIMULATING HORMONE AND LUTEINIZING HORMONE IN THE BOVINE PITUITARY GLAND AT OVULATION
 CHANGES IN LEVELS OF FOLLICLE STIMULATING HORMONE AND LUTEINIZING HORMONE IN THE BOVINE PITUITARY GLAND AT OVULATION A. M. RAKHA and H. A. ROBERTSON The Division of Agricultural Biochemistry, Department
CHANGES IN LEVELS OF FOLLICLE STIMULATING HORMONE AND LUTEINIZING HORMONE IN THE BOVINE PITUITARY GLAND AT OVULATION A. M. RAKHA and H. A. ROBERTSON The Division of Agricultural Biochemistry, Department
Ovarian Follicular Development in the Untreated and
 Ovarian Follicular Development in the Untreated and PMSG-treated Cyclic Rat Hajime MIYAMOTO, Goro KATSUURA and Takehiko ISHIBASHI Department of Animal Science, College of Agriculture, Kyoto University,
Ovarian Follicular Development in the Untreated and PMSG-treated Cyclic Rat Hajime MIYAMOTO, Goro KATSUURA and Takehiko ISHIBASHI Department of Animal Science, College of Agriculture, Kyoto University,
10.7 The Reproductive Hormones
 10.7 The Reproductive Hormones December 10, 2013. Website survey?? QUESTION: Who is more complicated: men or women? The Female Reproductive System ovaries: produce gametes (eggs) produce estrogen (steroid
10.7 The Reproductive Hormones December 10, 2013. Website survey?? QUESTION: Who is more complicated: men or women? The Female Reproductive System ovaries: produce gametes (eggs) produce estrogen (steroid
Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction
 Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction Overview Asexual (one parent) fission (parent separation) budding (corals) fragmentation & regeneration (inverts) parthenogenesis Sexual (fusion of haploid gametes) gametes
Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction Overview Asexual (one parent) fission (parent separation) budding (corals) fragmentation & regeneration (inverts) parthenogenesis Sexual (fusion of haploid gametes) gametes
Reproductive Hormones
 Reproductive Hormones Male gonads: testes produce male sex cells! sperm Female gonads: ovaries produce female sex cells! ovum The union of male and female sex cells during fertilization produces a zygote
Reproductive Hormones Male gonads: testes produce male sex cells! sperm Female gonads: ovaries produce female sex cells! ovum The union of male and female sex cells during fertilization produces a zygote
Basic Reproduction & Genetics. Steve Pritchard UNL Extension Educator Boone-Nance Counties
 Basic Reproduction & Genetics Steve Pritchard UNL Extension Educator Boone-Nance Counties Hormonal Regulation of the Estrous Cycle Several hormones regulate the estrous cycle Changes in the concentrations
Basic Reproduction & Genetics Steve Pritchard UNL Extension Educator Boone-Nance Counties Hormonal Regulation of the Estrous Cycle Several hormones regulate the estrous cycle Changes in the concentrations
OVARIAN SENSITIVITY TO EXOGENOUS GONADOTROPHINS IN PHENOBARBITAL TREATED UNILATERALLY OVARIECTOMIZED ALBINO RATS
 Indian J Physiol Phannacol 1994; 38(2) : 108-112 OVARIAN SENSITIVITY TO EXOGENOUS GONADOTROPHINS IN PHENOBARBITAL TREATED UNILATERALLY OVARIECTOMIZED ALBINO RATS PRABHAKARA RAO ADURI AND SARASWATI BASVARAJ
Indian J Physiol Phannacol 1994; 38(2) : 108-112 OVARIAN SENSITIVITY TO EXOGENOUS GONADOTROPHINS IN PHENOBARBITAL TREATED UNILATERALLY OVARIECTOMIZED ALBINO RATS PRABHAKARA RAO ADURI AND SARASWATI BASVARAJ
Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment
 Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
AnS 214 SI Multiple Choice Set 4 Weeks 10/14-10/23
 AnS 214 SI Multiple Choice Set 4 Weeks 10/14-10/23 The following multiple choice questions pertain to material covered in the last two weeks' lecture sets. Answering the following questions will aid your
AnS 214 SI Multiple Choice Set 4 Weeks 10/14-10/23 The following multiple choice questions pertain to material covered in the last two weeks' lecture sets. Answering the following questions will aid your
Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction
 Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction 11. Functions Testosterone Makes the male sex organs function normally, and also inhibits hypothalamus s release of GnRH and thus LH & FSH and thus testosterone
Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction 11. Functions Testosterone Makes the male sex organs function normally, and also inhibits hypothalamus s release of GnRH and thus LH & FSH and thus testosterone
(Received 10 September 1965)
 402 r J. Phy8iol. (1966), 184, pp. 402-417 L I B R A R Y ) Printed in Great Britain 4MASS THE IP BETWEEN OVULATION AND THE CHA THYROID GLAND ACTIVITY THAT OCCUR DURING THE OESTROUS CYCLE IN RATS, MICE
402 r J. Phy8iol. (1966), 184, pp. 402-417 L I B R A R Y ) Printed in Great Britain 4MASS THE IP BETWEEN OVULATION AND THE CHA THYROID GLAND ACTIVITY THAT OCCUR DURING THE OESTROUS CYCLE IN RATS, MICE
Animal Reproduction Chapter 46. Fission. Budding. Parthenogenesis. Fragmentation 11/27/2017
 Animal Reproduction Chapter 46 Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Sexual reproduction is the creation of an offspring by fusion of a male gamete (sperm) and female gamete
Animal Reproduction Chapter 46 Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Sexual reproduction is the creation of an offspring by fusion of a male gamete (sperm) and female gamete
I nfluence of Semen on the Motility of the Uterus in the Guinea Pig
 I nfluence of Semen on the Motility of the Uterus in the Guinea Pig In-Vitro Studies M. FREUND, PH.D., AND ALBERT M. LEFKOVITS, A.B. AN UNANSWERED QUESTION lo on the physiology of reproduction is: "Are
I nfluence of Semen on the Motility of the Uterus in the Guinea Pig In-Vitro Studies M. FREUND, PH.D., AND ALBERT M. LEFKOVITS, A.B. AN UNANSWERED QUESTION lo on the physiology of reproduction is: "Are
Reproduction and Development. Female Reproductive System
 Reproduction and Development Female Reproductive System Outcomes 5. Identify the structures in the human female reproductive system and describe their functions. Ovaries, Fallopian tubes, Uterus, Endometrium,
Reproduction and Development Female Reproductive System Outcomes 5. Identify the structures in the human female reproductive system and describe their functions. Ovaries, Fallopian tubes, Uterus, Endometrium,
GARY S. KLEDZIK LIONEL CUSAN CLAUDE AUCLAIR, PH.D. PAUL A. KELLY, PH.D. FERNAND LABRIE, M.D., PH.D.*
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright 1978 The American Fertility Society Vol. 3, No.3, September 1978 Printed in U S.A. INHIBITION OF OVARIAN LUTEINIZING HORMONE (LH) AND FOLLICLE-STIMULATING HORMONE RECEPTOR
FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright 1978 The American Fertility Society Vol. 3, No.3, September 1978 Printed in U S.A. INHIBITION OF OVARIAN LUTEINIZING HORMONE (LH) AND FOLLICLE-STIMULATING HORMONE RECEPTOR
Hormonal Control of Human Reproduction
 Hormonal Control of Human Reproduction Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The human male and female reproductive cycles are controlled by the interaction of hormones from the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary with
Hormonal Control of Human Reproduction Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The human male and female reproductive cycles are controlled by the interaction of hormones from the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary with
INFLUENCE OF NEONATAL CASTRATION OR NEONATAL ANTI-GONADOTROPIN TREATMENT ON FERTILITY, PHALLUS DEVELOPMENT, AND MALE SEXUAL BEHAVIOR IN THE MOUSE*
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright 1975 The American Fertility Society Vol. 26, No.9. September 1975 Printed in U.SA. INFLUENCE OF NEONATAL CASTRATION OR NEONATAL ANTI-GONADOTROPIN TREATMENT ON FERTILITY,
FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright 1975 The American Fertility Society Vol. 26, No.9. September 1975 Printed in U.SA. INFLUENCE OF NEONATAL CASTRATION OR NEONATAL ANTI-GONADOTROPIN TREATMENT ON FERTILITY,
CASE 41. What is the pathophysiologic cause of her amenorrhea? Which cells in the ovary secrete estrogen?
 CASE 41 A 19-year-old woman presents to her gynecologist with complaints of not having had a period for 6 months. She reports having normal periods since menarche at age 12. She denies sexual activity,
CASE 41 A 19-year-old woman presents to her gynecologist with complaints of not having had a period for 6 months. She reports having normal periods since menarche at age 12. She denies sexual activity,
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 26 For this lab you
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 26 For this lab you
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Induced Ovulation in the Mouse and the Measurement of Its Inhibition
 Induced Ovulation in the Mouse and the Measurement of Its Inhibition t' NATESAIER PURSHOTTAM, ~ MARCUS M. MASON, AND GREGORY PINCUS RUNNER has shown that the immature mouse ovary responds by superovulation
Induced Ovulation in the Mouse and the Measurement of Its Inhibition t' NATESAIER PURSHOTTAM, ~ MARCUS M. MASON, AND GREGORY PINCUS RUNNER has shown that the immature mouse ovary responds by superovulation
lr IS WELL KNOWN that diabetes often is accompanied by a disturbance in
 Altered O,vul,ation Pattern in Experimental Diabetes RAM6N A. CHIERI, M.D., OMAR H. PIVETT A, M.D., and VIRGILIO G. FOGLIA, M.D. lr IS WELL KNOWN that diabetes often is accompanied by a disturbance in
Altered O,vul,ation Pattern in Experimental Diabetes RAM6N A. CHIERI, M.D., OMAR H. PIVETT A, M.D., and VIRGILIO G. FOGLIA, M.D. lr IS WELL KNOWN that diabetes often is accompanied by a disturbance in
Phases of the Ovarian Cycle
 OVARIAN CYCLE An ovary contains many follicles, and each one contains an immature egg called an oocyte. A female is born with as many as 2 million follicles, but the number is reduced to 300,000 to 400,000
OVARIAN CYCLE An ovary contains many follicles, and each one contains an immature egg called an oocyte. A female is born with as many as 2 million follicles, but the number is reduced to 300,000 to 400,000
Chapter 27 The Reproductive System. MDufilho
 Chapter 27 The Reproductive System 1 Figure 27.19 Events of oogenesis. Before birth Meiotic events 2n Oogonium (stem cell) Mitosis Follicle development in ovary Follicle cells Oocyte 2n Primary oocyte
Chapter 27 The Reproductive System 1 Figure 27.19 Events of oogenesis. Before birth Meiotic events 2n Oogonium (stem cell) Mitosis Follicle development in ovary Follicle cells Oocyte 2n Primary oocyte
(Received 8th October 1973)
 THE INFLUENCE OF A CANNULA IN THE RABBIT OVIDUCT II. EFFECT ON EMBRYO SURVIVAL M. H. SLOAN, S. L. COLEY and A. D. JOHNSON Animal Science Department, Livestock-Poultry Building, University of Georgia, Athens,
THE INFLUENCE OF A CANNULA IN THE RABBIT OVIDUCT II. EFFECT ON EMBRYO SURVIVAL M. H. SLOAN, S. L. COLEY and A. D. JOHNSON Animal Science Department, Livestock-Poultry Building, University of Georgia, Athens,
Ovarian Remnant Syndrome
 Ovarian Remnant Syndrome Dawna L. Voelkl, DVM, Dipl ACT University of Missouri College of Veterinary Medicine Ovarian Remnant Syndrome Definition Incidence Clinically applicable anatomy and etiology Clinical
Ovarian Remnant Syndrome Dawna L. Voelkl, DVM, Dipl ACT University of Missouri College of Veterinary Medicine Ovarian Remnant Syndrome Definition Incidence Clinically applicable anatomy and etiology Clinical
REPRODUCCIÓN. La idea fija. Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development Section 1 1. Distinguish between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. 2. Which form of reproduction: a.
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development Section 1 1. Distinguish between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. 2. Which form of reproduction: a.
Male Reproduction Organs. 1. Testes 2. Epididymis 3. Vas deferens 4. Urethra 5. Penis 6. Prostate 7. Seminal vesicles 8. Bulbourethral glands
 Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Web Activity: Simulation Structures of the Female Reproductive System
 differentiate. The epididymis is a coiled tube found along the outer edge of the testis where the sperm mature. 3. Testosterone is a male sex hormone produced in the interstitial cells of the testes. It
differentiate. The epididymis is a coiled tube found along the outer edge of the testis where the sperm mature. 3. Testosterone is a male sex hormone produced in the interstitial cells of the testes. It
MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure.
 Chapter 27 Exam Due NLT Thursday, July 31, 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure. Figure 27.1 Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
Chapter 27 Exam Due NLT Thursday, July 31, 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure. Figure 27.1 Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
Reproductive System. Testes. Accessory reproductive organs. gametogenesis hormones. Reproductive tract & Glands
 Reproductive System Testes gametogenesis hormones Accessory reproductive organs Reproductive tract & Glands transport gametes provide nourishment for gametes Hormonal regulation in men Hypothalamus - puberty
Reproductive System Testes gametogenesis hormones Accessory reproductive organs Reproductive tract & Glands transport gametes provide nourishment for gametes Hormonal regulation in men Hypothalamus - puberty
1. During the follicular phase of the ovarian cycle, the hypothalamus releases GnRH.
 1. During the follicular phase of the ovarian cycle, the hypothalamus releases GnRH. 2. This causes the anterior pituitary to secrete small quantities of FSH and LH. 3. At this time, the follicles in the
1. During the follicular phase of the ovarian cycle, the hypothalamus releases GnRH. 2. This causes the anterior pituitary to secrete small quantities of FSH and LH. 3. At this time, the follicles in the
Investigation: The Human Menstrual Cycle Research Question: How do hormones control the menstrual cycle?
 Investigation: The Human Menstrual Cycle Research Question: How do hormones control the menstrual cycle? Introduction: The menstrual cycle (changes within the uterus) is an approximately 28-day cycle that
Investigation: The Human Menstrual Cycle Research Question: How do hormones control the menstrual cycle? Introduction: The menstrual cycle (changes within the uterus) is an approximately 28-day cycle that
The Why s, What s, and How s of Timed Artificial Insemination Programs
 Kansas Agricultural Experiment Station Research Reports Volume 1 Issue 8 Dairy Research Article 5 January 2015 The Why s, What s, and How s of Timed Artificial Insemination Programs J. Stevenson Kansas
Kansas Agricultural Experiment Station Research Reports Volume 1 Issue 8 Dairy Research Article 5 January 2015 The Why s, What s, and How s of Timed Artificial Insemination Programs J. Stevenson Kansas
Animal Reproductive Systems. Chapter 42
 Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
Semen-induced ovulation in the bactrian camel (Camelus bactrianus)
 Semen-induced ovulation in the bactrian camel (Camelus bactrianus) B. X. Chen, Z. X. Yuen and G. W. Pan Department of Veterinary Medicine, Gansu Agricultural University, Wuwei, Gansu and *Haixi Institute
Semen-induced ovulation in the bactrian camel (Camelus bactrianus) B. X. Chen, Z. X. Yuen and G. W. Pan Department of Veterinary Medicine, Gansu Agricultural University, Wuwei, Gansu and *Haixi Institute
Information Booklet. Exploring the causes of infertility and treatment options.
 Information Booklet Exploring the causes of infertility and treatment options www.ptafertility.co.za info@ptafertility.co.za +27 12 998 8854 Faith is taking the first step even if you don t see the whole
Information Booklet Exploring the causes of infertility and treatment options www.ptafertility.co.za info@ptafertility.co.za +27 12 998 8854 Faith is taking the first step even if you don t see the whole
female dogs for mating tests with males by injecting them with estradiol benzoate.1
 COITAL BEHAVIOR IN DOGS, IV. EFFECTS OF PROGESTERONE IN THE BITCH* BY FRANK A. BEACH AND ARIEL MERARI UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY Communicated August 15, 1968 For a number of years it has been the
COITAL BEHAVIOR IN DOGS, IV. EFFECTS OF PROGESTERONE IN THE BITCH* BY FRANK A. BEACH AND ARIEL MERARI UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY Communicated August 15, 1968 For a number of years it has been the
6.7 IN. Continuity through Reproduction. What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes.
 6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
HORMONES & REPRODUCTION OUTLINE
 1 HORMONES & REPRODUCTION Dr. Steinmetz OUTLINE 2 The Endocrine System Sexual Reproduction Hormonal Role in Sexual Differentiation Gender Differences and Gender Identity Characterizing Complex Behaviors
1 HORMONES & REPRODUCTION Dr. Steinmetz OUTLINE 2 The Endocrine System Sexual Reproduction Hormonal Role in Sexual Differentiation Gender Differences and Gender Identity Characterizing Complex Behaviors
to ensure the. Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion of.
 The Reproductive System Fill-In Notes Purpose of life: to ensure the. Stages of Human Development Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion
The Reproductive System Fill-In Notes Purpose of life: to ensure the. Stages of Human Development Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion
CATEGORY Endocrine System Review. Provide labels for the following diagram CHAPTER 13 BLM
 CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
MASAZUMI KAWAKAMI, FUKUKO KIMURA AND TAKASHI HIGUCHI 2nd Department of Physiology, Yokohama City University School of Medicine, Yokohama
 Effects of Electrical Stimulation of the Brain on Gonadotropin Secretion in Male Rats MASAZUMI KAWAKAMI, FUKUKO KIMURA AND TAKASHI HIGUCHI 2nd Department of Physiology, Yokohama City University School
Effects of Electrical Stimulation of the Brain on Gonadotropin Secretion in Male Rats MASAZUMI KAWAKAMI, FUKUKO KIMURA AND TAKASHI HIGUCHI 2nd Department of Physiology, Yokohama City University School
Reproductive ability of pubertal male and female rats
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2003) 36: 871-877 Reproduction in pubertal rats ISSN 0100-879X 871 Reproductive ability of pubertal male and female rats T. Zemunik 1, M. Peruzoviƒ
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2003) 36: 871-877 Reproduction in pubertal rats ISSN 0100-879X 871 Reproductive ability of pubertal male and female rats T. Zemunik 1, M. Peruzoviƒ
FOLLICLE-STIMULATING HORMONE CONTENT OF THE PITUITARY GLAND BEFORE IMPLANTATION IN THE MOUSE AND RAT
 FOLLICLE-STIMULATING HORMONE CONTENT OF THE PITUITARY GLAND BEFORE IMPLANTATION IN THE MOUSE AND RAT B. M. BINDON Department of Veterinary Physiology, University of Sydney, Sydney 2006, Australia (Received
FOLLICLE-STIMULATING HORMONE CONTENT OF THE PITUITARY GLAND BEFORE IMPLANTATION IN THE MOUSE AND RAT B. M. BINDON Department of Veterinary Physiology, University of Sydney, Sydney 2006, Australia (Received
Plasma LH and Progesterone Levels before and after Ovulation and Observation of Ovarian Follicles by Ultrasonographic Diagnosis System in Dogs
 FULL PAPER Theriogenology Plasma LH and Progesterone Levels before and after Ovulation and Observation of Ovarian Follicles by Ultrasonographic Diagnosis System in Dogs Masayoshi HASE, Tatsuya HORI, Eiichi
FULL PAPER Theriogenology Plasma LH and Progesterone Levels before and after Ovulation and Observation of Ovarian Follicles by Ultrasonographic Diagnosis System in Dogs Masayoshi HASE, Tatsuya HORI, Eiichi
Human Reproductive Anatomy The female anatomy first just the reproductive parts:
 Human Reproduction: Structures, Functions, and Hormones Human reproduction differs from the mechanisms in lower vertebrates and many invertebrates. We depend on internal fertilization sperm are deposited
Human Reproduction: Structures, Functions, and Hormones Human reproduction differs from the mechanisms in lower vertebrates and many invertebrates. We depend on internal fertilization sperm are deposited
Interval between PMSG Priming and hcg Injection in Superovulation of the Mongolian Gerbil
 J. Mamm. Ova Res. Vol. 21, 105 109, 2004 105 Original Interval between PMSG Priming and hcg Injection in Superovulation of the Mongolian Gerbil Yuichi Kameyama 1 *, Kaori Arai 1 and Yoshiro Ishijima 1
J. Mamm. Ova Res. Vol. 21, 105 109, 2004 105 Original Interval between PMSG Priming and hcg Injection in Superovulation of the Mongolian Gerbil Yuichi Kameyama 1 *, Kaori Arai 1 and Yoshiro Ishijima 1
Studies on Induced Ovulation in the Intact Immature Hamster. Charles W. Bodemer, Ph.D., Ruth E. Rumery, Ph.D., and Richard J. Blandau, Ph.D., M.D.
 Studies on Induced Ovulation in the Intact Immature Hamster Charles W. Bodemer, Ph.D., Ruth E. Rumery, Ph.D., and Richard J. Blandau, Ph.D., M.D. IT IS WELL KNOWN that gonadotropins are incapable of inducing
Studies on Induced Ovulation in the Intact Immature Hamster Charles W. Bodemer, Ph.D., Ruth E. Rumery, Ph.D., and Richard J. Blandau, Ph.D., M.D. IT IS WELL KNOWN that gonadotropins are incapable of inducing
Induction of Infertility in Male Rats by Treatment with Gonadotropin Antiserum During Neonatal Life1 2
 BIOLOGY OF REPRODUTION 2, 444-45 1 (1970) Induction of Infertility in Male Rats by Treatment with Gonadotropin Antiserum During Neonatal Life1 2 BRUE D. GOLDMAN1 AND VIRENDRA B. MAHESH Department of Endocrinology,
BIOLOGY OF REPRODUTION 2, 444-45 1 (1970) Induction of Infertility in Male Rats by Treatment with Gonadotropin Antiserum During Neonatal Life1 2 BRUE D. GOLDMAN1 AND VIRENDRA B. MAHESH Department of Endocrinology,
C ONSIDERABLE ATTENTION has been given to the antifertility effects of
 Effects of Clomiphene at Different Stages of Pregnancy in the Rat Implications Regarding Possible Action Mechanisms 0. W. DAVIDSON, M.D.,"' K. WADA, M.D.,t and S. J. SEGAL, Ph.D. C ONSIDERABLE ATTENTION
Effects of Clomiphene at Different Stages of Pregnancy in the Rat Implications Regarding Possible Action Mechanisms 0. W. DAVIDSON, M.D.,"' K. WADA, M.D.,t and S. J. SEGAL, Ph.D. C ONSIDERABLE ATTENTION
INDICATIONS OF IVF/ICSI
 PROCESS OF IVF/ICSI INDICATIONS OF IVF/ICSI IVF is most clearly indicated when infertility results from one or more causes having no other effective treatment; Tubal disease. In women with blocked fallopian
PROCESS OF IVF/ICSI INDICATIONS OF IVF/ICSI IVF is most clearly indicated when infertility results from one or more causes having no other effective treatment; Tubal disease. In women with blocked fallopian
hormone was demonstrated to stimulate RNA and protein synthesis in the blastocyst Holland, Richard Brooks and Erich Weidenbener
 Plasma Progesterone, Blastocyst Steriodogenesis and Blastocyst Survival in Rats with Altered Thyroid Status James P. Holland, Richard Brooks and Erich Weidenbener Department of Biology Indiana University
Plasma Progesterone, Blastocyst Steriodogenesis and Blastocyst Survival in Rats with Altered Thyroid Status James P. Holland, Richard Brooks and Erich Weidenbener Department of Biology Indiana University
The Science of your Cycle
 The Science of your Cycle Day 3: Get to know your cycle (Part I) with Jennifer Aldoretta Cofounder & CEO of Groove Today s goals Learn how your hormones work together to create the changes that happen
The Science of your Cycle Day 3: Get to know your cycle (Part I) with Jennifer Aldoretta Cofounder & CEO of Groove Today s goals Learn how your hormones work together to create the changes that happen
THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE DIURNAL LIGHT CYCLE AND THE TIME OF OVULATION IN MICE
 THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE DIURNAL LIGHT CYCLE AND THE TIME OF OVULATION IN MICE A. W. H. BRADEN* Institute of Animal Genetics, West Mains Road, Edinburgh {Received November 56) INTRODUCTION It is now
THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE DIURNAL LIGHT CYCLE AND THE TIME OF OVULATION IN MICE A. W. H. BRADEN* Institute of Animal Genetics, West Mains Road, Edinburgh {Received November 56) INTRODUCTION It is now
LH and FSH. Women. Men. Increased LH. Decreased LH. By Ronald Steriti, ND, PhD 2011
 LH and FSH By Ronald Steriti, ND, PhD 2011 Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) are gonadotropins that stimulate the gonads - the testes in males, and the ovaries in females.
LH and FSH By Ronald Steriti, ND, PhD 2011 Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) are gonadotropins that stimulate the gonads - the testes in males, and the ovaries in females.
Peripubertal, leptin-deficient ob/ob female mice were used in an investigation of
 ESSICK-BROOKSHIRE, ELIZABETH ANN, M.S. The Effects of Peripherally Administered 17-β Estradiol and BIBP3226, a NPY Y1 Receptor Antagonist, on Food Intake, Body Mass, Reproductive Development and Behavior
ESSICK-BROOKSHIRE, ELIZABETH ANN, M.S. The Effects of Peripherally Administered 17-β Estradiol and BIBP3226, a NPY Y1 Receptor Antagonist, on Food Intake, Body Mass, Reproductive Development and Behavior
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I)
 Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Understanding Natural Animal Reproduction
 Lesson B4 2 Understanding Natural Animal Reproduction Unit B. Animal Science and the Industry Problem Area 4. Understanding Animal Reproduction and Biotechnology Lesson 2. Understanding Natural Animal
Lesson B4 2 Understanding Natural Animal Reproduction Unit B. Animal Science and the Industry Problem Area 4. Understanding Animal Reproduction and Biotechnology Lesson 2. Understanding Natural Animal
In domestic animals, we have limited period of estrus (sexual receptivity) and the term estrous
 REPRODUCTIVE CYCLES 1. Estrous cycle 2. Menstrual cycle In domestic animals, we have limited period of estrus (sexual receptivity) and the term estrous cycle is used. The onset of proestrus defines the
REPRODUCTIVE CYCLES 1. Estrous cycle 2. Menstrual cycle In domestic animals, we have limited period of estrus (sexual receptivity) and the term estrous cycle is used. The onset of proestrus defines the
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems. Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems 1 Terms Alimentary canal Bladder Cervix Clitoris Cloaca Copulation Cowper s gland Epididymis Fallopian
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems 1 Terms Alimentary canal Bladder Cervix Clitoris Cloaca Copulation Cowper s gland Epididymis Fallopian
Chapter 14 The Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Tongkat Ali.
 Tongkat Ali www.powertongkatali.com Tongkat Ali Tongkat Ali is a very potent herbal product in South East Asia. It has been used by the locals for centuries to improve male s vitality and virility. Page
Tongkat Ali www.powertongkatali.com Tongkat Ali Tongkat Ali is a very potent herbal product in South East Asia. It has been used by the locals for centuries to improve male s vitality and virility. Page
The Reproductive System
 C h a p t e r 27 The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
C h a p t e r 27 The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
(17fl-hydroxyandrost-4-en-3-one) to produce this syndrome experimentally
 J. Physiol. (1964), 176, pp. 91-14 91 Printed in Great Britain THE EFFECT OF TESTOSTERONE DURING THE NEONATAL PERIOD ON THE THYROID GLAND OF MALE AND FEMALE RATS BY K. BROWVN-GRANT* From the Department
J. Physiol. (1964), 176, pp. 91-14 91 Printed in Great Britain THE EFFECT OF TESTOSTERONE DURING THE NEONATAL PERIOD ON THE THYROID GLAND OF MALE AND FEMALE RATS BY K. BROWVN-GRANT* From the Department
Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
I. ART PROCEDURES. A. In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
 DFW Fertility Associates ASSISTED REPRODUCTIVE TECHNOLOGY (ART) Welcome to DFW Fertility Associates/ Presbyterian-Harris Methodist Hospital ARTS program. This document provides an overview of treatment
DFW Fertility Associates ASSISTED REPRODUCTIVE TECHNOLOGY (ART) Welcome to DFW Fertility Associates/ Presbyterian-Harris Methodist Hospital ARTS program. This document provides an overview of treatment
Animal and Veterinary Science Department University of Idaho. REGULATION OF REPRODUCTION AVS 222 (Instructor: Dr. Amin Ahmadzadeh) Chapter 5
 Animal and Veterinary Science Department University of Idaho REGULATION OF REPRODUCTION AVS 222 (Instructor: Dr. Amin Ahmadzadeh) Chapter 5 I. DEFINITIONS A. Endocrine Gland B. Hormone Chemical messenger
Animal and Veterinary Science Department University of Idaho REGULATION OF REPRODUCTION AVS 222 (Instructor: Dr. Amin Ahmadzadeh) Chapter 5 I. DEFINITIONS A. Endocrine Gland B. Hormone Chemical messenger
(Szent'agothai, Flerko, Mess & Hal6asz, 1962). This feed-back promotes
 J. Phy8iol. (1964), 172, pp. 383-392 383 With 4 text-figure Printed in Great Britain HYPOTHALAMIC CONTROL OF THE ENDOCRINE AND BEHAVIOURAL CHANGES ASSOCIATED WITH OESTRUS IN THE RAT BY G. C. KENNEDY From
J. Phy8iol. (1964), 172, pp. 383-392 383 With 4 text-figure Printed in Great Britain HYPOTHALAMIC CONTROL OF THE ENDOCRINE AND BEHAVIOURAL CHANGES ASSOCIATED WITH OESTRUS IN THE RAT BY G. C. KENNEDY From
breeders really don t want to miss!!!
 Oestrus induction in the canine species: dream or reality? The bitch: a mono-oestrian species Most mammals In the bitch in seasons twice a year Restricted breeding Breed variations: periods breeders really
Oestrus induction in the canine species: dream or reality? The bitch: a mono-oestrian species Most mammals In the bitch in seasons twice a year Restricted breeding Breed variations: periods breeders really
6.6 Hormones, homeostasis and reproduction
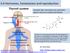 6.6 Hormones, homeostasis and reproduction Essential idea: Hormones are used when signals need to be widely distributed. Thyroxin is a hormone produced by the thyroid gland. It's key role is in controlling
6.6 Hormones, homeostasis and reproduction Essential idea: Hormones are used when signals need to be widely distributed. Thyroxin is a hormone produced by the thyroid gland. It's key role is in controlling
The reproductive lifespan
 The reproductive lifespan Reproductive potential Ovarian cycles Pregnancy Lactation Male Female Puberty Menopause Age Menstruation is an external indicator of ovarian events controlled by the hypothalamicpituitary
The reproductive lifespan Reproductive potential Ovarian cycles Pregnancy Lactation Male Female Puberty Menopause Age Menstruation is an external indicator of ovarian events controlled by the hypothalamicpituitary
Medical Endocrinology / Introduction 4 Medical Endocrinology
 Medical Endocrinology / Introduction 4 Medical Endocrinology 1 2 : Positive feedback control of labor contractions during birth of a baby. The solid return arrow symbolizes positive feedback. If the response
Medical Endocrinology / Introduction 4 Medical Endocrinology 1 2 : Positive feedback control of labor contractions during birth of a baby. The solid return arrow symbolizes positive feedback. If the response
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System
 I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE
 Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
