THE incidence of cancer of the prostate gland among men who have symptoms
|
|
|
- Susan Montgomery
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PROSTATE GLAND BIOPSY EUGENE F. POUTASSE, Department of Urology M.D. THE incidence of cancer of the prostate gland among men who have symptoms of bladder neck obstruction is about one out of five. The actual incidence of cancer is higher because many men are seen with symptoms unrelated to the urinary tract, such as bone pain, or who have evidence of the tumor without symptoms. It is the third most common cancer in men, exceeded only by cancer of the skin and alimentary tract in frequency of recognition. The chief methods by which a physician discovers prostatic cancer are rectal palpation of the gland, serum acid phosphatase determination, and roentgenographic study of the urinary tract and skeleton. These are satisfactory when the tumor has spread widely beyond the prostate. In this paper methods of biopsy for establishing the diagnosis when cancer of the prostate gland is suspected or when it is desirable to corroborate the clinical diagnosis of extensive cancer will be discussed. The actual diagnosis of cancer is made by microscopic definition, preferably on a block of tumor tissue. Under study is the cytologic examination of prostatic secretion for exfoliated tumor cells, 1 which requires a great deal of time and experience. Methods of Biopsy A. Perineal. Exposure of the prostate gland through the perineum permits biopsy of any area of the gland which has been suspected of malignancy on rectal palpation. This approach is particularly useful because more than 90 per cent of all prostatic neoplasms arise in the posterior lobe accessible to rectal palpation. The reason for biopsy of such suspicious areas is to offer the patient an opportunity by total prostatectomy for complete removal of an early cancer or assurance of the benign nature of the lesion. Patients are selected for perineal biopsy chiefly on the basis of rectal findings of an area of nodularity and induration within the confines of the gland. The size of the gland means little because cancer has a development independent of benign enlargement. Evidence of metastasis on physical examination, roentgenographic study of the bones, or elevation of the serum acid or alkaline phosphatase are contraindications to operative perineal biopsy. A plain film of the pelvis will exclude prostatic calculi as the cause of induration within the gland. History of chronic prostatitis or genitourinary tuberculosis may influence the necessity for biopsy. Men who have a poor life expectancy from the age or health standpoint are not considered suitable candidates for perineal biopsy and possible radical prostatectomy. It is not suggested that every pros- 263
2 POUTASSE tate with slight irregularity should be biopsied. Many patients with prostatic irregularity not initially suggestive of cancer can be reexamined at intervals for change. With the prostate exposed perineally, a suitable block of tissue is removed from the area under suspicion and submitted to the pathologist for frozen section. Frequently, cancer can be suspected when the fragment presents both induration and yellowish surface color. With the frozen section technic utilized by Dr. John B. Hazard 2 of the Department of Pathology, accurate correlation between rapid sections and later permanent sections has been attained. Interpretation of prostatic tissue by frozen section is generally considered difficult and unreliable, but use of a method providing differential staining and uniform results is of great value. A portion of each tissue block is used for frozen section and the remainder saved for permanent section. Freezing causes distortion of tissue and use of this second and unfrozen portion permits accurate interpretation of each sample. With the presence of cancer confirmed by frozen section, the entire prostate gland is separated from the bladder and urethra and removed with adjacent portions of the bladder and genital tract, provided cancer has not spread beyond resectability into these structures. Failure to find cancer on the first frozen section necessitates additional biopsies of adjacent areas of the gland. If these are negative and there is no indication for enucleating obstructing prostatic tissue, the perineal incision is closed and the patient is usually out of the hospital within three to four days. Over a two year period, 40 men were subjected to open perineal biopsy because of suspected early cancer. Twenty-two were proved to have benign conditions causing the induration. Chronic prostatitis and acinar hyperplasia are the main lesions simulating carcinoma. There were no complications among this group. Eighteen men of this group of 40 were found to have cancer. Of these 18, four were shown to have spread of the tumor into the bladder base, urethral bulb, or laterally, and therefore had biopsy only. Fourteen men had total prostatectomy, ten of whom are believed to have a good chance of complete removal of the cancer based on the pathologic examination of the prostate. The remaining four were found to have carcinoma at the line of excision from the bladder base, discovered only after removal of the gland. The effect of estrogenic hormones prior to biopsy often leads to confusion. It has been generally accepted that prostatic cancer softens under the influence of estrogens. This is often true of suspected early lesions, making the selection of a proper area for biopsy difficult at operation. Not all malignant nodules soften, however. Figure 1 illustrates a section of a totally removed prostate from a man who was treated with estrogens for a year. The original nodular area did not change significantly in size or consistency during this time. It should be noted that estrogens did not alter the malignant appearance of the tumor microscopically. The extent of prostatic cancer is best evaluated prior to estrogenic therapy. Alteration of the hardness of tumor spread beyond the prostate with such 264
3 PROSTATE GLAND BIOPSY I /«F^^FC É'T 1 1 V ««, '. : ffc '. ; v v *. m FIG. 1. Adenocarcinoma of prostate gland. Estrogen therapy for one year prior to total prostatectomy. Note perineural lymphatic involvement. treatment may convey the impression that total prostatectomy will remove all cancer. Complete destruction of tumor cells with hormones does not occur. When a patient is fortunate enough to have a localized prostatic neoplasm diagnosed, the original plan of treatment is most important. Measures should be taken promptly for biopsy and extirpation of these potentially curable tumors. B. Needle Biopsy. A practical method of securing prostatic tissue for pathologic examination without operation is often desirable to corroborate the clinical impression of cancer. The prostate is accessible to needle biopsy by puncture of the perineum, a finger in the rectum guiding the needle into the desired part of the gland. This is done under analgesia, often in conjunction with a cystoscopy. A Silverman needle is used, although there are several other types of prostate biopsy devices available. Several pieces of tissue 0.5 to 1. cm. long can be obtained from various parts of the gland or perineum. It has been noted that the most satisfactory specimens for biopsy are obtained when carcinoma is present; the least satisfactory when the prostate is small and fibrotic. No complications have arisen and there is no morbidity connected with the procedure. Should bleeding occur, digital pressure against the prostate and perineum for a few moments will suffice to control it. During the same two-year period, 41 such needle biopsies were performed. Of 33 men who were considered clinically to have prostatic cancer, the diagnosis was confirmed by biopsy in 29. There were four false negative biopsies of men who had metastases demonstrable by x-ray or later operation. This illustrates 265
4 POUTASSE the well known fact that a negative biopsy is meaningless and should not influence the course of treatment under such circumstances. Eight men who had clinically benign prostate glands or metastatic tumor from other sites surrounding the genital structures, had prostate biopsy specimens which showed no evidence of malignancy. For the purpose of perfecting and evaluating this method of needle biopsy, many patients with extensive metastases and abnormal serum phosphatase levels were utilized. Biopsy is not considered essential in such instances, however a satisfactory needle biopsy will provide sufficient tissue to distinguish adenocarcinoma from an undifferentiated carcinoma. This may be of some value in anticipating the result of estrogenic therapy. Biopsy corroboration of prostatic cancer has been particularly useful when metastases are present in an unusual form, as in the following case report: A 53 year old man was admitted to the hospital, having been bedridden with back pain, weight loss and nausea. The pain in the dorsal area began three months previously. Physical examination disclosed only tenderness over the spine. Roentgen study revealed compression fracture of D6 and D8 vertebrae, and osteolytic metastasis in the right scapula, ribs and iliac bones. The acid phosphatase was 1.5 B.U. Sternal marrow biopsy disclosed adenocarcinoma; following this the prostate gland was reexamined. It was small with a firm upper border joining the bladder base, from which hard cords of tissue extended laterally to the walls of the pelvis. Needle biopsy of the prostate was performed disclosing adenocarcinoma (fig. 2). Immediate weight gain and relief of pain followed institution of estrogenic therapy. Carcinoma of the prostate usually causes osteoblastic metastases and in this man the bone lesions were destructive. The serum acid phosphatase is elevated in approximately two thirds of all patients with osseous metastases of prostatic origin; 3 serum acid phosphatase value of 1.5 B.U., such as in this case, is not considered abnormal. C. Transurethral Biopsy. Since most prostatic neoplasms develop in the posterior part of the gland, transurethral resection often fails to go deep enough to secure representative tissue from this portion. Unless there is evidence of pathologic change or tumor extension around the vesical neck or into the prostatic urethra cystoscopically, biopsy by this means is usually inadequate. Its usefulness should not be overlooked under appropriate circumstances such as the following case: A 35 year old man entered the hospital with chills, fever, dyspnea, and abdominal masses of one month's duration. One episode of acute urinary retention occurred followed by frequency and urgency. There were rales in both lungs, a large spleen, and an enlarged firm right lobe of the prostate gland. Chest x-ray showed patchy infiltration of both lungs. Abdominal film showed localized inflammatory changes in the 12th vertebral body, and a large splenic shadow with displacement of the left kidney downwards. The urogram revealed normal kidneys but the bladder base was indented, consistent with a large prostate. The hemoglobin was 9.8 Gm. per hundred cubic centimeters; urine was loaded with pus cells, red blood cells, and showed albumin; it was sterile on culture. The urine, gastric washings, and sputum were all negative for acid fast bacilli. PPD. was negative on first strength but positive on second strength. Cysto- 266
5 PROSTATE GLAND BIOPSY scopy revealed elevation of the posterior commissure; several pieces of tissue were removed from this area with the resectoscope. These showed active caseating tuberculosis. The differential diagnosis in this man was between Hodgkin's disease and tuberculosis. Transurethral biopsy of his abnormal prostate gland proved a simple and efficacious means of establishing the diagnosis. Summary 1. Three methods of prostatic biopsy are described with their indications and limitations. 2. The results of 81 prostate gland biopsies are presented. There were 40 open perineal biopsies in men suspected of having localized prostatic cancer. Twenty-two of these showed no evidence of cancer on biopsy; 18 demonstrated cancer on biopsy and appropriate surgical measures were taken wherever possible. There was an accurate correlation between the frozen and permanent sections in all instances. Forty-one perineal needle biopsies were done during the same period. Of 33 men known to have metastatic prostatic cancer, 29 biopsies showed cancer and four did not (false negative). The eight remaining patients were not considered to have prostatic cancer and had negative biopsies. 3. Transurethral biopsy of the prostate is usually inadequate unless there is evidence of pathologic change along the urethra. FIG. 2. Adenocarcinoma of prostate gland. Specimen secured by needle biopsy. Note reduplication of lumina and nuclear dedifferentiation. 267
6 POUTASSE 4. Open perineal biopsy is the preferred method of accurately establishing the diagnosis of localized prostatic cancer, and is necessary for histologic confirmation prior to radical prostatectomy. Chronic prostatitis and acinar hyperplasia often simulate cancer on rectal palpation. 5. Needle biopsy is a useful means of obtaining tissue for histologic confirmation of metastatic prostatic cancer, particularly when the metastases are of an unusual nature. It is not accurate enough to use with localized lesions nor is it adaptable to frozen section technics. References 1. Peters, H. and Young, J. D.: Prostatic smear in cancer diagnosis. J.A.M.A. 145: 556 (Feb. 24) Hazard, J. B. and Stevenson, G. F.: A frozen section technic. Am. J. Clin. Path. 19: 873 (Sept.) Nesbit, R. M. and Baum, W. C.: Serum phosphatase determinations in diagnosis of prostatic cancer. J.A.M.A. 145: 1321 (April 28)
Prostate Case Scenario 1
 Prostate Case Scenario 1 H&P 5/12/16: A 57-year-old Hispanic male presents with frequency of micturition, urinary urgency, and hesitancy associated with a weak stream. Over the past several weeks, he has
Prostate Case Scenario 1 H&P 5/12/16: A 57-year-old Hispanic male presents with frequency of micturition, urinary urgency, and hesitancy associated with a weak stream. Over the past several weeks, he has
Questions and Answers About the Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Questions and Answers
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Questions and Answers
Glossary of Terms Primary Urethral Cancer
 Patient Information English Glossary of Terms Primary Urethral Cancer Advanced cancer A tumour that grows into deeper layers of tissue, adjacent organs, or surrounding muscles. Anaesthesia (general, spinal,
Patient Information English Glossary of Terms Primary Urethral Cancer Advanced cancer A tumour that grows into deeper layers of tissue, adjacent organs, or surrounding muscles. Anaesthesia (general, spinal,
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options
 AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
Some prostatic diseases
 Some prostatic diseases Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (Nodular Hyperplasia) Extremely common Present in a significant number of men by the age of 40 & its frequency rises progressively with age, reaching
Some prostatic diseases Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (Nodular Hyperplasia) Extremely common Present in a significant number of men by the age of 40 & its frequency rises progressively with age, reaching
THE UROLOGY GROUP
 THE UROLOGY GROUP www.urologygroupvirginia.com 1860 Town Center Drive Suite 150/160 Reston, VA 20190 703-480-0220 19415 Deerfield Avenue Suite 112 Leesburg, VA 20176 703-724-1195 224-D Cornwall Street,
THE UROLOGY GROUP www.urologygroupvirginia.com 1860 Town Center Drive Suite 150/160 Reston, VA 20190 703-480-0220 19415 Deerfield Avenue Suite 112 Leesburg, VA 20176 703-724-1195 224-D Cornwall Street,
THE UROLOGY GROUP
 THE UROLOGY GROUP www.urologygroupvirginia.com 1860 Town Center Drive Suite 150/160 Reston, VA 20190 703-480-0220 19415 Deerfield Avenue Suite 112 Leesburg, VA 20176 703-724-1195 224-D Cornwall Street,
THE UROLOGY GROUP www.urologygroupvirginia.com 1860 Town Center Drive Suite 150/160 Reston, VA 20190 703-480-0220 19415 Deerfield Avenue Suite 112 Leesburg, VA 20176 703-724-1195 224-D Cornwall Street,
Prostate Overview Quiz
 Prostate Overview Quiz 1. The path report reads: Gleason 3 + 4 = 7. The Gleason s score is a. 3 b. 4 c. 7 d. None of the above 2. The path report reads: Moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma of the
Prostate Overview Quiz 1. The path report reads: Gleason 3 + 4 = 7. The Gleason s score is a. 3 b. 4 c. 7 d. None of the above 2. The path report reads: Moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma of the
Clinical Studies with Speman in Cases of Benign Enlargement of Prostate
 [The Indian Practitioner (1971): 6, 281] Clinical Studies with Speman in Cases of Benign Enlargement of Prostate Agarwal, V.K., M.S., F.I.C.S., Professor of Surgery, and Gupta, R.K., M.B.,B.S., Research
[The Indian Practitioner (1971): 6, 281] Clinical Studies with Speman in Cases of Benign Enlargement of Prostate Agarwal, V.K., M.S., F.I.C.S., Professor of Surgery, and Gupta, R.K., M.B.,B.S., Research
P rare and, therefore, their histopathologic
 PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA OF DUCTAL ORIGIN VOLKER E. DUBE, MD,+ GEORGE M. FARROW, AND LAURENCE F. GREENE, MD+ MD+ Clinical and histopathologic features of prostatic ductal adenocarcinomas have been incompletely
PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA OF DUCTAL ORIGIN VOLKER E. DUBE, MD,+ GEORGE M. FARROW, AND LAURENCE F. GREENE, MD+ MD+ Clinical and histopathologic features of prostatic ductal adenocarcinomas have been incompletely
Melanoma Case Scenario 1
 Melanoma Case Scenario 1 History and physical 11/5/16 Patient is a single, 48-year-old male in good health who presented to his primary physician for a yearly physical exam during which a 3.4 x 2.8 x 1.5
Melanoma Case Scenario 1 History and physical 11/5/16 Patient is a single, 48-year-old male in good health who presented to his primary physician for a yearly physical exam during which a 3.4 x 2.8 x 1.5
4 th Year Urology Core Objectives Keith Rourke (Revised June 1, 2007)
 4 th Year Urology Core Objectives Keith Rourke (Revised June 1, 2007) I. Genitourinary Trauma: 1. Goal: The student will be able to demonstrate a basic clinical approach to the management & diagnosis of
4 th Year Urology Core Objectives Keith Rourke (Revised June 1, 2007) I. Genitourinary Trauma: 1. Goal: The student will be able to demonstrate a basic clinical approach to the management & diagnosis of
Bladder Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging
 Bladder Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
Bladder Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
came from a carcinoma and in 12 from a sarcoma. Ninety lesions were intrapulmonary and the as the chest wall and pleura. Details of the primary
 Thorax 1982;37:366-370 Thoracic metastases MARY P SHEPHERD From the Thoracic Surgical Unit, Harefield Hospital, Harefield ABSTRACI One hundred and four patients are reviewed who were found to have thoracic
Thorax 1982;37:366-370 Thoracic metastases MARY P SHEPHERD From the Thoracic Surgical Unit, Harefield Hospital, Harefield ABSTRACI One hundred and four patients are reviewed who were found to have thoracic
Melanoma Case Scenario 1
 Melanoma Case Scenario 1 History and physical 11/5/16 Patient is a single, 48-year-old male in good health who presented to his primary physician for a yearly physical exam during which a 3.4 x 2.8 x 1.5
Melanoma Case Scenario 1 History and physical 11/5/16 Patient is a single, 48-year-old male in good health who presented to his primary physician for a yearly physical exam during which a 3.4 x 2.8 x 1.5
ADENOCARCINOMA OF THE PROSTATE
 Ref : ADENOCARCINOMA OF THE PROSTATE Div. of Urology, Dept. Surgery Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Clinical Manual of Urology, (Philip M. Hanno et al eds), McGraw-Hill Int ed, 3 rd ed, 2001
Ref : ADENOCARCINOMA OF THE PROSTATE Div. of Urology, Dept. Surgery Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Clinical Manual of Urology, (Philip M. Hanno et al eds), McGraw-Hill Int ed, 3 rd ed, 2001
Prostate Gland Disorders
 Prostate Gland Disorders THE PROSTATE GLAND A male s prostate gland is located in the floor of the pelvis surrounding the urethra between the bladder and the penis. The prostate is positioned immediately
Prostate Gland Disorders THE PROSTATE GLAND A male s prostate gland is located in the floor of the pelvis surrounding the urethra between the bladder and the penis. The prostate is positioned immediately
6 UROLOGICAL CANCERS. 6.1 Key Points
 6 UROLOGICAL CANCERS 6.1 Key Points Prostate Cancer Commonest cancer in males in Scotland Approximately 99% of cases occur in men aged > 50 years About 40% of cases present in men aged < 70 years when
6 UROLOGICAL CANCERS 6.1 Key Points Prostate Cancer Commonest cancer in males in Scotland Approximately 99% of cases occur in men aged > 50 years About 40% of cases present in men aged < 70 years when
The Role of Lymphography in 11 Apparently Localized" Prostatic Carcinoma
 16 Lymphology 8 (1975) 16-20 Georg Thieme Verlag Stuttgart The Role of Lymphography in 11 Apparently Localized" Prostatic Carcinoma R. A. Castellino - Department of Radiology, Stanford-University School
16 Lymphology 8 (1975) 16-20 Georg Thieme Verlag Stuttgart The Role of Lymphography in 11 Apparently Localized" Prostatic Carcinoma R. A. Castellino - Department of Radiology, Stanford-University School
Patient Information. Prostate Tissue Ablation. High Intensity Focused Ultrasound for
 High Intensity Focused Ultrasound for Prostate Tissue Ablation Patient Information CAUTION: Federal law restricts this device to sell by or on the order of a physician CONTENT Introduction... 3 The prostate...
High Intensity Focused Ultrasound for Prostate Tissue Ablation Patient Information CAUTION: Federal law restricts this device to sell by or on the order of a physician CONTENT Introduction... 3 The prostate...
2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a Pseudocapsule
 GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D. Renal Cell Carcinoma 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow Necrotic Mass Grossly is a Bright
GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D. Renal Cell Carcinoma 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow Necrotic Mass Grossly is a Bright
Procedures Needle Biopsy Transurethral Prostatic Resection Suprapubic or Retropubic Enucleation (Subtotal Prostatectomy) Radical Prostatectomy
 Prostate Gland Protocol applies to invasive carcinomas of the prostate gland. Protocol web posting date: July 2006 Protocol effective date: April 2007 Based on AJCC/UICC TNM, 6 th edition Procedures Needle
Prostate Gland Protocol applies to invasive carcinomas of the prostate gland. Protocol web posting date: July 2006 Protocol effective date: April 2007 Based on AJCC/UICC TNM, 6 th edition Procedures Needle
BLADDER CANCER: PATIENT INFORMATION
 BLADDER CANCER: PATIENT INFORMATION The bladder is the balloon like organ located in the pelvis that stores and empties urine. Urine is produced by the kidneys, is conducted to the bladder by the ureters,
BLADDER CANCER: PATIENT INFORMATION The bladder is the balloon like organ located in the pelvis that stores and empties urine. Urine is produced by the kidneys, is conducted to the bladder by the ureters,
Case Scenario 1. 4/19/13 Bone Scan: No scintigraphic findings to suggest skeletal metastases.
 Case Scenario 1 3/8/13 H&P 68 YR W/M presents w/elevated PSA. Patient is a non-smoker, current alcohol use. Physical Exam: On digital rectal exam the sphincter tone is normal and there is a 1 cm nodule
Case Scenario 1 3/8/13 H&P 68 YR W/M presents w/elevated PSA. Patient is a non-smoker, current alcohol use. Physical Exam: On digital rectal exam the sphincter tone is normal and there is a 1 cm nodule
Cleveland Clinic Quarterly
 Cleveland Clinic Quarterly Volume 31 JULY 1964 No. 3 A MEDICAL SILASTIC PROSTHESIS FOR THE CONTROL OF URINARY INCONTINENCE IN THE MALE A Preliminary Report J A M E S K. W A T K I N S, M. D., * R A L P
Cleveland Clinic Quarterly Volume 31 JULY 1964 No. 3 A MEDICAL SILASTIC PROSTHESIS FOR THE CONTROL OF URINARY INCONTINENCE IN THE MALE A Preliminary Report J A M E S K. W A T K I N S, M. D., * R A L P
Bladder Cancer Canada November 21st, Bladder Cancer 2018: A brighter light at the end of the cystoscope
 Bladder Cancer Canada November 21st, 2018 Bladder Cancer 2018: A brighter light at the end of the cystoscope Chris Morash MD FRCSC Associate Professor, University of Ottawa Head, Urological Oncology Bladder
Bladder Cancer Canada November 21st, 2018 Bladder Cancer 2018: A brighter light at the end of the cystoscope Chris Morash MD FRCSC Associate Professor, University of Ottawa Head, Urological Oncology Bladder
About the authors Dr S. Larry Goldenberg Dr Tom Pickles Dr Kim N. Chi
 Authors S. Larry Goldenberg, CM, OBC, MD, FRCSC, FCAHS Professor and Head, University of British Columbia Department of Urologic Sciences, Stephen A. Jarislowski Chair in Urologic Sciences at Vancouver
Authors S. Larry Goldenberg, CM, OBC, MD, FRCSC, FCAHS Professor and Head, University of British Columbia Department of Urologic Sciences, Stephen A. Jarislowski Chair in Urologic Sciences at Vancouver
MUSCLE - INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER
 10 MUSCLE - INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER Recommendations from the EAU Working Party on Muscle Invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer G. Jakse (chairman), F. Algaba, S. Fossa, A. Stenzl, C. Sternberg
10 MUSCLE - INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER Recommendations from the EAU Working Party on Muscle Invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer G. Jakse (chairman), F. Algaba, S. Fossa, A. Stenzl, C. Sternberg
Abdomen and Genitalia Injuries. Chapter 28
 Abdomen and Genitalia Injuries Chapter 28 Hollow Organs in the Abdominal Cavity Signs of Peritonitis Abdominal pain Tenderness Muscle spasm Diminished bowel sounds Nausea/vomiting Distention Solid Organs
Abdomen and Genitalia Injuries Chapter 28 Hollow Organs in the Abdominal Cavity Signs of Peritonitis Abdominal pain Tenderness Muscle spasm Diminished bowel sounds Nausea/vomiting Distention Solid Organs
Bladder Case # 1. Principal Diagnosis: Bladder Tumor, Suspect Transitional Cell Carcinoma. Secondary Diagnoses: 1. Hypertension. 2. Hyperlipidemia.
 DISCHARGE SUMMARY Bladder Case # 1 Date: 04/22/2010 Principal Diagnosis: Bladder Tumor, Suspect Transitional Cell Carcinoma. Secondary Diagnoses: 1. Hypertension. 2. Hyperlipidemia. Hospital Course: Mr.
DISCHARGE SUMMARY Bladder Case # 1 Date: 04/22/2010 Principal Diagnosis: Bladder Tumor, Suspect Transitional Cell Carcinoma. Secondary Diagnoses: 1. Hypertension. 2. Hyperlipidemia. Hospital Course: Mr.
Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test
 Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test What is the PSA test? Prostate-specific antigen, or PSA, is a protein produced by normal, as well as malignant, cells of the prostate gland. The PSA test measures the
Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test What is the PSA test? Prostate-specific antigen, or PSA, is a protein produced by normal, as well as malignant, cells of the prostate gland. The PSA test measures the
performed to help sway the clinician in what the appropriate diagnosis is, which can substantially alter the treatment of management.
 Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
Case #1: 75 y/o Male (treated and followed by prostate cancer oncology specialist ).
 SOLID TUMORS WORKSHOP Cases for review Prostate Cancer Case #1: 75 y/o Male (treated and followed by prostate cancer oncology specialist ). January 2009 PSA 4.4, 20% free; August 2009 PSA 5.2; Sept 2009
SOLID TUMORS WORKSHOP Cases for review Prostate Cancer Case #1: 75 y/o Male (treated and followed by prostate cancer oncology specialist ). January 2009 PSA 4.4, 20% free; August 2009 PSA 5.2; Sept 2009
Prostate Cancer Case Study 1. Medical Student Case-Based Learning
 Prostate Cancer Case Study 1 Medical Student Case-Based Learning The Case of Mr. Powers Prostatic Nodule The effervescent Mr. Powers is found by his primary care provider to have a prostatic nodule. You
Prostate Cancer Case Study 1 Medical Student Case-Based Learning The Case of Mr. Powers Prostatic Nodule The effervescent Mr. Powers is found by his primary care provider to have a prostatic nodule. You
Prostate Cancer Screening. A Decision Guide
 Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
Boot Camp Case Scenarios
 Boot Camp Case Scenarios Case Scenario 1 Patient is a 69-year-old white female. She presents with dyspnea on exertion, cough, and right rib pain. Patient is a smoker. 9/21/12 CT Chest FINDINGS: There is
Boot Camp Case Scenarios Case Scenario 1 Patient is a 69-year-old white female. She presents with dyspnea on exertion, cough, and right rib pain. Patient is a smoker. 9/21/12 CT Chest FINDINGS: There is
Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1981), 27(11):
 Title METASTATIC URETHRAL TUMOR FROM CARC OF THE BREAST: A CASE REPORT Author(s) Tanaka, Yoichi; Okabe, Tatsushiro; Kiyiyama, Tadao; Yoshida, Osamu Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1981), 27(11): 1393-1397 Issue Date
Title METASTATIC URETHRAL TUMOR FROM CARC OF THE BREAST: A CASE REPORT Author(s) Tanaka, Yoichi; Okabe, Tatsushiro; Kiyiyama, Tadao; Yoshida, Osamu Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1981), 27(11): 1393-1397 Issue Date
What Is Prostate Cancer? Prostate cancer is the development of cancer cells in the prostate gland (a gland that produces fluid for semen).
 What Is Prostate Cancer? Prostate cancer is the development of cancer cells in the prostate gland (a gland that produces fluid for semen). It is a very common cancer in men; some cancers grow very slowly,
What Is Prostate Cancer? Prostate cancer is the development of cancer cells in the prostate gland (a gland that produces fluid for semen). It is a very common cancer in men; some cancers grow very slowly,
SUPRAPUBIC PUNCTURE IN THE TREATMENT OF NEUROGENIC BLADDER
 SUPRAPUBIC PUNCTURE IN THE TREATMENT OF NEUROGENIC BLADDER CHARLES C. HIGGINS, M.D. W. JAMES GARDNER, M.D. WM. A. NOSIK, M.D. The treatment of "cord bladder", a disturbance of bladder function from disease
SUPRAPUBIC PUNCTURE IN THE TREATMENT OF NEUROGENIC BLADDER CHARLES C. HIGGINS, M.D. W. JAMES GARDNER, M.D. WM. A. NOSIK, M.D. The treatment of "cord bladder", a disturbance of bladder function from disease
Kidney Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT
 Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Elevated PSA. Dr.Nesaretnam Barr Kumarakulasinghe Associate Consultant Medical Oncology National University Cancer Institute, Singapore 9 th July 2017
 Elevated PSA Dr.Nesaretnam Barr Kumarakulasinghe Associate Consultant Medical Oncology National University Cancer Institute, Singapore 9 th July 2017 Issues we will cover today.. The measurement of PSA,
Elevated PSA Dr.Nesaretnam Barr Kumarakulasinghe Associate Consultant Medical Oncology National University Cancer Institute, Singapore 9 th July 2017 Issues we will cover today.. The measurement of PSA,
Multi-Organ Distant Metastases in Follicular Thyroid Cancer- Rare Case Report
 Multi-Organ Distant Metastases in Follicular Thyroid Cancer- Rare Case Report Dr. Mohammed Raza 1, Dr. Sindhuri K 2, Dr. Dinesh Reddy Y 3 1 Professor, Department of Surgery, JSS University, Mysore, India
Multi-Organ Distant Metastases in Follicular Thyroid Cancer- Rare Case Report Dr. Mohammed Raza 1, Dr. Sindhuri K 2, Dr. Dinesh Reddy Y 3 1 Professor, Department of Surgery, JSS University, Mysore, India
Proposed All Wales Vulval Cancer Guidelines. Dr Amanda Tristram
 Proposed All Wales Vulval Cancer Guidelines Dr Amanda Tristram Previous FIGO staging FIGO Stage Features TNM Ia Lesion confined to vulva with
Proposed All Wales Vulval Cancer Guidelines Dr Amanda Tristram Previous FIGO staging FIGO Stage Features TNM Ia Lesion confined to vulva with
General information about prostate cancer
 Prostate Cancer General information about prostate cancer Key points Prostate cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the prostate. Signs of prostate cancer include
Prostate Cancer General information about prostate cancer Key points Prostate cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the prostate. Signs of prostate cancer include
GUIDELINES ON NON-MUSCLE- INVASIVE BLADDER CANCER
 GUIDELINES ON NON-MUSCLE- INVASIVE BLADDER CANCER (Limited text update December 21) M. Babjuk, W. Oosterlinck, R. Sylvester, E. Kaasinen, A. Böhle, J. Palou, M. Rouprêt Eur Urol 211 Apr;59(4):584-94 Introduction
GUIDELINES ON NON-MUSCLE- INVASIVE BLADDER CANCER (Limited text update December 21) M. Babjuk, W. Oosterlinck, R. Sylvester, E. Kaasinen, A. Böhle, J. Palou, M. Rouprêt Eur Urol 211 Apr;59(4):584-94 Introduction
A 64 y.o. man presents to the hospital with persistent cough and hemoptysis. Fernando Mut Montevideo - Uruguay
 A 64 y.o. man presents to the hospital with persistent cough and hemoptysis Fernando Mut Montevideo - Uruguay Teaching case Bone # 1 A 64 y.o. man presents to the hospital with persistent cough and hemoptysis.
A 64 y.o. man presents to the hospital with persistent cough and hemoptysis Fernando Mut Montevideo - Uruguay Teaching case Bone # 1 A 64 y.o. man presents to the hospital with persistent cough and hemoptysis.
!! 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers.!! Peak Incidence is 6th Decade!! M:F = 2:1
 !! Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D.!! 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers!! Peak Incidence is 6th Decade!! M:F = 2:1!! Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a Pseudocapsule 1 !!Conventional RCC! Clear
!! Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D.!! 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers!! Peak Incidence is 6th Decade!! M:F = 2:1!! Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a Pseudocapsule 1 !!Conventional RCC! Clear
THE PROSTATE. SMALL GLAND BIG PROBLEM By John Crow. Chapter 4
 THE PROSTATE SMALL GLAND BIG PROBLEM By John Crow Chapter 4 In this chapter I want to address the big issue CANCER. What is CANCER? As you will already know, our body tissue is made up of literally Billions
THE PROSTATE SMALL GLAND BIG PROBLEM By John Crow Chapter 4 In this chapter I want to address the big issue CANCER. What is CANCER? As you will already know, our body tissue is made up of literally Billions
Kidney, Bladder and Prostate Neoplasia. David Bingham MD
 Kidney, Bladder and Prostate Neoplasia David Bingham MD typical malignant cytology of bladder washings 1 benign 2 malignant typical malignant cytology of bladder washings b Bladder tumor Non invasive papillary
Kidney, Bladder and Prostate Neoplasia David Bingham MD typical malignant cytology of bladder washings 1 benign 2 malignant typical malignant cytology of bladder washings b Bladder tumor Non invasive papillary
Neoplasia part I. Dr. Mohsen Dashti. Clinical Medicine & Pathology nd Lecture
 Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
A Study of Prostatic Lesions With Reference To FNAC Evaluation and Histopathology
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 2 Ver. II (Feb. 2015), PP 42-46 www.iosrjournals.org A Study of Prostatic Lesions With Reference
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 2 Ver. II (Feb. 2015), PP 42-46 www.iosrjournals.org A Study of Prostatic Lesions With Reference
Prostate Cancer Awareness - Prevention, Symptoms and. Treatment
 Quality Assurance Lunch and Learn Sessions: Prostate Cancer Awareness - Prevention, Symptoms and What s wrong with my prostate? Treatment??? Sponsored by the Chief Engineer s Team and Quality Assurance
Quality Assurance Lunch and Learn Sessions: Prostate Cancer Awareness - Prevention, Symptoms and What s wrong with my prostate? Treatment??? Sponsored by the Chief Engineer s Team and Quality Assurance
Lung. 10/24/13 Chest X-ray: 2.9 cm mass like density in the inferior lingular segment worrisome for neoplasm. Malignancy cannot be excluded.
 Lung Case Scenario 1 A 54 year white male presents with a recent abnormal CT of the chest. The patient has a history of melanoma, kidney, and prostate cancers. 10/24/13 Chest X-ray: 2.9 cm mass like density
Lung Case Scenario 1 A 54 year white male presents with a recent abnormal CT of the chest. The patient has a history of melanoma, kidney, and prostate cancers. 10/24/13 Chest X-ray: 2.9 cm mass like density
X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary
 X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Pancreatic cancer is the 4th leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S. About 37,000 new cases of pancreatic cancer are diagnosed each year in the
X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Pancreatic cancer is the 4th leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S. About 37,000 new cases of pancreatic cancer are diagnosed each year in the
ANATOMICAL PATHOLOGY TARIFF
 ANATOMICAL PATHOLOGY TARIFF A GUIDE TO UTILISATION. The following guidelines have been agreed by consensus of Anatomical Pathologists who are members of the Anatomical Pathologist s Group, or the National
ANATOMICAL PATHOLOGY TARIFF A GUIDE TO UTILISATION. The following guidelines have been agreed by consensus of Anatomical Pathologists who are members of the Anatomical Pathologist s Group, or the National
Muscle spasm Diminished bowel sounds Nausea/vomiting
 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Chapter 8: Abdomen and Genitalia Injuries Abdominal Injuries Abdomen is major body cavity extending from to pelvis. Contains organs that make up digestive, urinary, and genitourinary systems.
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Chapter 8: Abdomen and Genitalia Injuries Abdominal Injuries Abdomen is major body cavity extending from to pelvis. Contains organs that make up digestive, urinary, and genitourinary systems.
A re-audit of Prostate biopsies from January to December 2010 and 2013.
 A re-audit of Prostate biopsies from January to December 2010 and 2013. Dr. M S Siddiqui Consultant Histopathologist University Hospital of North Tees Stockton on Tees. Objectives To assess and compare
A re-audit of Prostate biopsies from January to December 2010 and 2013. Dr. M S Siddiqui Consultant Histopathologist University Hospital of North Tees Stockton on Tees. Objectives To assess and compare
Vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia
 Vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia The terminology and pathology of VAIN are analogous to those of CIN (VAIN I-III). The main difference is that vaginal epithelium does not normally have crypts, so the
Vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia The terminology and pathology of VAIN are analogous to those of CIN (VAIN I-III). The main difference is that vaginal epithelium does not normally have crypts, so the
Continuing Professional Development
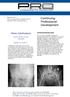 Volume 15.4.1 This Lecture Serties qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Continuing Professional Development Pelvic Calcifications By Dr Kristin Grace (DACBR) WHAT IS THAT??? Calcifications in
Volume 15.4.1 This Lecture Serties qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Continuing Professional Development Pelvic Calcifications By Dr Kristin Grace (DACBR) WHAT IS THAT??? Calcifications in
Louisa Fleure. Advanced Prostate Cancer Clinical Nurse Specialist. Guys and St Thomas NHS Trust
 Louisa Fleure Advanced Prostate Cancer Clinical Nurse Specialist Guys and St Thomas NHS Trust The classification of advanced prostate cancer The incidence of patients presenting with, or developing advanced
Louisa Fleure Advanced Prostate Cancer Clinical Nurse Specialist Guys and St Thomas NHS Trust The classification of advanced prostate cancer The incidence of patients presenting with, or developing advanced
An Anteriorly Positioned Midline Prostatic Cyst Resulting in Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms
 Case Report INJ 2010;14:125-129 An Anteriorly Positioned Midline Prostatic Cyst Resulting in Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Joo-Yong Lee, Dong-Hyuk Kang, Hee-Young Park, Jung-Soo Park, Young-Woo Son, Hong-Sang
Case Report INJ 2010;14:125-129 An Anteriorly Positioned Midline Prostatic Cyst Resulting in Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Joo-Yong Lee, Dong-Hyuk Kang, Hee-Young Park, Jung-Soo Park, Young-Woo Son, Hong-Sang
THE UROLOGY GROUP
 THE UROLOGY GROUP www.urologygroupvirginia.com 1860 Town Center Drive Suite 150/160 Reston, VA 20190 703-480-0220 19415 Deerfield Avenue Suite 112 Leesburg, VA 20176 703-724-1195 224-D Cornwall Street,
THE UROLOGY GROUP www.urologygroupvirginia.com 1860 Town Center Drive Suite 150/160 Reston, VA 20190 703-480-0220 19415 Deerfield Avenue Suite 112 Leesburg, VA 20176 703-724-1195 224-D Cornwall Street,
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER VULVAR
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER VULVAR Last Revision Date July 2015 1 Site Group: Gynecologic Cancer Vulvar Author: Dr. Stephane Laframboise 1. INTRODUCTION
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER VULVAR Last Revision Date July 2015 1 Site Group: Gynecologic Cancer Vulvar Author: Dr. Stephane Laframboise 1. INTRODUCTION
DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OB' LESIONS
 DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OB' LESIONS OF THE BREAST' STUART W. RARRINGTON, M.D. Division of Surgemj, The Mayo Clinic, Rorhrslcr, Minaesola The educational program which the American Medical Associiltion
DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OB' LESIONS OF THE BREAST' STUART W. RARRINGTON, M.D. Division of Surgemj, The Mayo Clinic, Rorhrslcr, Minaesola The educational program which the American Medical Associiltion
Information for Patients. Primary urethral cancer. English
 Information for Patients Primary urethral cancer English Table of contents What is primary urethral cancer?... 3 Risk factors... 3 Symptoms... 4 Diagnosis... 4 Clinical examination... 4 Urinary cytology...
Information for Patients Primary urethral cancer English Table of contents What is primary urethral cancer?... 3 Risk factors... 3 Symptoms... 4 Diagnosis... 4 Clinical examination... 4 Urinary cytology...
Bladder Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT. Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT)
 Bladder Case 1 February 17, 2007 Specimen (s) received: Bladder Tumor Pre-operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Post operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of
Bladder Case 1 February 17, 2007 Specimen (s) received: Bladder Tumor Pre-operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Post operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of
Providence Medford Medical Center Pathology Department
 Providence Medford Medical Center Pathology Department Anatomic pathology services including histology, cytology and autopsies are offered through Providence Medford Medical Center Pathology Department.
Providence Medford Medical Center Pathology Department Anatomic pathology services including histology, cytology and autopsies are offered through Providence Medford Medical Center Pathology Department.
BLADDER PROSTATE PENIS TESTICLES BE YO ND YO UR CA NC ER
 BLADDER PROSTATE PENIS TESTICLES THE PROSTATE IS A SMALL, WALNUT-SIZED GLAND THAT IS PART OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM. IT RESTS BELOW THE BLADDER, IN FRONT OF THE RECTUM AND SURROUNDS PART OF THE URETHRA.
BLADDER PROSTATE PENIS TESTICLES THE PROSTATE IS A SMALL, WALNUT-SIZED GLAND THAT IS PART OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM. IT RESTS BELOW THE BLADDER, IN FRONT OF THE RECTUM AND SURROUNDS PART OF THE URETHRA.
Chapter 47 1/8/2018. Urinary System Disorders. Urinary Tract Infections. Treatment
 Chapter 47 Urinary System Disorders Urinary Tract Infections Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common Infection in one area can involve the entire system Microbes enter through the urethra. Catheterization,
Chapter 47 Urinary System Disorders Urinary Tract Infections Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common Infection in one area can involve the entire system Microbes enter through the urethra. Catheterization,
Sex: 女 Age: 51 Occupation: 無 Admission date:92/07/22
 Sex: 女 Age: 51 Occupation: 無 Admission date:92/07/22 Chief complaint Unknown fever for one month Hand tremor and left huge renal tumor was noted Present illness Suffered from fever for one month, hand
Sex: 女 Age: 51 Occupation: 無 Admission date:92/07/22 Chief complaint Unknown fever for one month Hand tremor and left huge renal tumor was noted Present illness Suffered from fever for one month, hand
Collaborative Staging
 Slide 1 Collaborative Staging Site-Specific Instructions Prostate 1 In this presentation, we are going to take a closer look at the collaborative staging data items for the prostate primary site. Because
Slide 1 Collaborative Staging Site-Specific Instructions Prostate 1 In this presentation, we are going to take a closer look at the collaborative staging data items for the prostate primary site. Because
Case Scenario 1. Pathology report Specimen from mediastinoscopy Final Diagnosis : Metastatic small cell carcinoma with residual lymphatic tissue
 Case Scenario 1 Oncology Consult: Patient is a 51-year-old male with history of T4N3 squamous cell carcinoma of tonsil status post concurrent chemoradiation finished in October two years ago. He was hospitalized
Case Scenario 1 Oncology Consult: Patient is a 51-year-old male with history of T4N3 squamous cell carcinoma of tonsil status post concurrent chemoradiation finished in October two years ago. He was hospitalized
Please complete prior to the webinar. HOSPITAL REGISTRY WEBINAR FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM EXERCISES CASE 1: FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE
 Please complete prior to the webinar. HOSPITAL REGISTRY WEBINAR FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM EXERCISES PHYSICAL EXAMINATION CASE 1: FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE 3/5 Patient presents through the emergency room with
Please complete prior to the webinar. HOSPITAL REGISTRY WEBINAR FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM EXERCISES PHYSICAL EXAMINATION CASE 1: FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE 3/5 Patient presents through the emergency room with
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid
 Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
MUSCLE-INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER
 MUSCLE-INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER (Text update March 2008) A. Stenzl (chairman), N.C. Cowan, M. De Santis, G. Jakse, M. Kuczyk, A.S. Merseburger, M.J. Ribal, A. Sherif, J.A. Witjes Introduction
MUSCLE-INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER (Text update March 2008) A. Stenzl (chairman), N.C. Cowan, M. De Santis, G. Jakse, M. Kuczyk, A.S. Merseburger, M.J. Ribal, A. Sherif, J.A. Witjes Introduction
Prostate Pathology: Prostate Carcinoma, variants and Gleason Grading (Part 1)
 Prostate Pathology: Prostate Carcinoma, variants and Gleason Grading (Part 1) Jae Y. Ro, MD, PhD June 7, 2012 Ten Leading Cancer Types for the Estimated New Cancer Cases and Deaths By Sex, United States,
Prostate Pathology: Prostate Carcinoma, variants and Gleason Grading (Part 1) Jae Y. Ro, MD, PhD June 7, 2012 Ten Leading Cancer Types for the Estimated New Cancer Cases and Deaths By Sex, United States,
Louisa Fleure. Advanced Prostate Cancer Clinical Nurse Specialist. Guys and St Thomas NHS Trust
 Louisa Fleure Advanced Prostate Cancer Clinical Nurse Specialist Guys and St Thomas NHS Trust The classification of advanced prostate cancer The incidence of patients presenting with, or developing advanced
Louisa Fleure Advanced Prostate Cancer Clinical Nurse Specialist Guys and St Thomas NHS Trust The classification of advanced prostate cancer The incidence of patients presenting with, or developing advanced
GONOCOCCAL AND NON-GONOCOC-
 VI THE DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS BETWEEN GONOCOCCAL AND NON-GONOCOC- CAL EPIDIDYMITIS By KENNETH M. WALKER, F.R.C.S., Surgeon-in-Charge of Genito- Urinary Departments, Royal Northern Hospital and Miller General
VI THE DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS BETWEEN GONOCOCCAL AND NON-GONOCOC- CAL EPIDIDYMITIS By KENNETH M. WALKER, F.R.C.S., Surgeon-in-Charge of Genito- Urinary Departments, Royal Northern Hospital and Miller General
Advanced Pathophysiology Unit 7: Renal-Urologic Page 1 of 6
 Advanced Pathophysiology Unit 7: Renal-Urologic Page 1 of 6 Learning Objectives for this File: 1. Understand how clinical presentation drives the diagnostic workup 2. Recognize how patient education is
Advanced Pathophysiology Unit 7: Renal-Urologic Page 1 of 6 Learning Objectives for this File: 1. Understand how clinical presentation drives the diagnostic workup 2. Recognize how patient education is
Definition Prostate cancer
 Prostate cancer 61 Definition Prostate cancer is a malignant neoplasm that arises from the prostate gland and the most common form of cancer in men. localized prostate cancer is curable by surgery or radiation
Prostate cancer 61 Definition Prostate cancer is a malignant neoplasm that arises from the prostate gland and the most common form of cancer in men. localized prostate cancer is curable by surgery or radiation
Diagnosis and classification
 Patient Information English 2 Diagnosis and classification The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. Signs and symptoms Blood in the urine is the most common symptom when a bladder tumour is present.
Patient Information English 2 Diagnosis and classification The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. Signs and symptoms Blood in the urine is the most common symptom when a bladder tumour is present.
MANAGING BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERTROPHY IN PRIMARY CARE DR GEORGE G MATHEW CONSULTANT FAMILY PHYSICIAN FELLOW IN SEXUAL & REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH
 MANAGING BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERTROPHY IN PRIMARY CARE DR GEORGE G MATHEW CONSULTANT FAMILY PHYSICIAN FELLOW IN SEXUAL & REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH INTRODUCTION (1) Part of male sexual reproductive organ Size
MANAGING BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERTROPHY IN PRIMARY CARE DR GEORGE G MATHEW CONSULTANT FAMILY PHYSICIAN FELLOW IN SEXUAL & REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH INTRODUCTION (1) Part of male sexual reproductive organ Size
RENAL CELL CARCINOMA 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a Pseud
 GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole Toole, M.D. RENAL CELL CARCINOMA 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a
GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole Toole, M.D. RENAL CELL CARCINOMA 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a
Bladder Cancer Guidelines
 Bladder Cancer Guidelines Agreed by Urology CSG: October 2011 Review Date: September 2013 Bladder Cancer 1. Referral Guidelines The following patients should be considered as potentially having bladder
Bladder Cancer Guidelines Agreed by Urology CSG: October 2011 Review Date: September 2013 Bladder Cancer 1. Referral Guidelines The following patients should be considered as potentially having bladder
BIOPSY GUN. Delivered in sterile peel-open package. Device is made of Stainless Steel and PP material.
 BIOPSY GUN Biopsy Gun is a reusable system for histological core biopsies. It has a throw (advancement) of 25mm and is used in conjunction with a single use needle. This device is used to obtain tissue
BIOPSY GUN Biopsy Gun is a reusable system for histological core biopsies. It has a throw (advancement) of 25mm and is used in conjunction with a single use needle. This device is used to obtain tissue
Chapter 18: Glossary
 Chapter 18: Glossary Sutter Health Cancer Service Line: Prostate Committee Advanced cancer: When the cancer has spread to other parts of the body (including lymph nodes, bones, or other organs) and is
Chapter 18: Glossary Sutter Health Cancer Service Line: Prostate Committee Advanced cancer: When the cancer has spread to other parts of the body (including lymph nodes, bones, or other organs) and is
INTRADUCTAL LESIONS OF THE PROSTATE. Jonathan I. Epstein
 INTRADUCTAL LESIONS OF THE PROSTATE Jonathan I. Epstein Topics Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) Intraductal adenocarcinoma (IDC-P) Intraductal urothelial carcinoma Ductal adenocarcinoma High Prostatic
INTRADUCTAL LESIONS OF THE PROSTATE Jonathan I. Epstein Topics Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) Intraductal adenocarcinoma (IDC-P) Intraductal urothelial carcinoma Ductal adenocarcinoma High Prostatic
Suspecting Tumors, or Could it be cancer?
 Suspecting Tumors, or Could it be cancer? Donna E. Reece, M.D. Princess Margaret Cancer Centre University Health Network Toronto, ON CANADA 07 February 2018 Background Low back pain is common However,
Suspecting Tumors, or Could it be cancer? Donna E. Reece, M.D. Princess Margaret Cancer Centre University Health Network Toronto, ON CANADA 07 February 2018 Background Low back pain is common However,
Synonyms. Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma
 Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Efficacy of FNAC in early diagnosis of prostatic carcinoma
 Original Research Article Efficacy of FNAC in early diagnosis of prostatic carcinoma S. Dhanraj Reddy 1*, M. Sandhya Rani 1 1 Associate Professor, Department of Pathology, MNR Medical College and Hospital,
Original Research Article Efficacy of FNAC in early diagnosis of prostatic carcinoma S. Dhanraj Reddy 1*, M. Sandhya Rani 1 1 Associate Professor, Department of Pathology, MNR Medical College and Hospital,
Chapter 2. Understanding My Diagnosis
 Chapter 2. Understanding My Diagnosis With contributions from Nancy L. Brown, Ph.D.,Palo Alto Medical Foundation Research Institute; and Patrick Swift, M.D., Alta Bates Comprehensive Cancer Program o Facts
Chapter 2. Understanding My Diagnosis With contributions from Nancy L. Brown, Ph.D.,Palo Alto Medical Foundation Research Institute; and Patrick Swift, M.D., Alta Bates Comprehensive Cancer Program o Facts
Chapter 3. Neoplasms. Copyright 2015 Cengage Learning.
 Chapter 3 Neoplasms Terminology Related to Neoplasms and Tumors Neoplasm New growth Tumor Swelling or neoplasm Leukemia Malignant disease of bone marrow Hematoma Bruise or contusion Classification of Neoplasms
Chapter 3 Neoplasms Terminology Related to Neoplasms and Tumors Neoplasm New growth Tumor Swelling or neoplasm Leukemia Malignant disease of bone marrow Hematoma Bruise or contusion Classification of Neoplasms
Azad Mohammed Kamal Elden. Evaluation of Acid and Alkaline Phosphates in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and. Patients.
 Evaluation of Acid and Alkaline Phosphates in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and Prostatic Cancer Azad Mohammed Kamal Elden Abstract Tumors of prostate are common diseases that afflict the aging male population
Evaluation of Acid and Alkaline Phosphates in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and Prostatic Cancer Azad Mohammed Kamal Elden Abstract Tumors of prostate are common diseases that afflict the aging male population
HMM 4401 Genito-urinary tract diseases
 HMM 4401 Genito-urinary tract diseases Urine production Core elements: Glomerulus, proximal and distal convoluted tube, loop of Henle, collecting tubules, ureters, bladder, sphincter, uretra, and out
HMM 4401 Genito-urinary tract diseases Urine production Core elements: Glomerulus, proximal and distal convoluted tube, loop of Henle, collecting tubules, ureters, bladder, sphincter, uretra, and out
ACOS Inquiry and Response Selected Inquires CS Tumor Size/Extension Evaluation, CS Lymph Nodes Evaluation, CS Metastasis at Diagnosis Evaluation *
 ACOS Inquiry and Response Selected Inquires CS Tumor Size/Extension Evaluation, CS Lymph Nodes Evaluation, CS Metastasis at Diagnosis Evaluation * CS Tumor Size/Extension Evaluation 24842 12/11/2007: Q:
ACOS Inquiry and Response Selected Inquires CS Tumor Size/Extension Evaluation, CS Lymph Nodes Evaluation, CS Metastasis at Diagnosis Evaluation * CS Tumor Size/Extension Evaluation 24842 12/11/2007: Q:
I have no financial relationships to disclose. I WILL NOT include discussion of investigational or off-label use of a product in my presentation.
 Prostate t Cancer MR Report Disclosure Information Vikas Kundra, M.D, Ph.D. I have no financial relationships to disclose. I WILL NOT include discussion of investigational or off-label use of a g product
Prostate t Cancer MR Report Disclosure Information Vikas Kundra, M.D, Ph.D. I have no financial relationships to disclose. I WILL NOT include discussion of investigational or off-label use of a g product
Introduction. Growths in the prostate can be benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer).
 This information was taken from urologyhealth.org. Feel free to explore their website to learn more. Another trusted website with good information is the national comprehensive cancer network (nccn.org).
This information was taken from urologyhealth.org. Feel free to explore their website to learn more. Another trusted website with good information is the national comprehensive cancer network (nccn.org).
Controversy Surrounds Question of Who Needs to be Treated for Prostate Cancer No One Size Fits All Diagnosis or Treatment
 For Immediate Release Media Contact: Nancy Sergeant, Sergeant Marketing, 973-334-6666, nsergeant@sergeantmarketing.com Mary Appelmann, Sergeant Marketing, 973-263-6392, mappelmann@sergeantmarketing.com
For Immediate Release Media Contact: Nancy Sergeant, Sergeant Marketing, 973-334-6666, nsergeant@sergeantmarketing.com Mary Appelmann, Sergeant Marketing, 973-263-6392, mappelmann@sergeantmarketing.com
SEER Summary Stage Still Here!
 SEER Summary Stage Still Here! CCRA NORTHERN REGION STAGING SYMPOSIUM SEPTEMBER 20, 2017 SEER Summary Stage Timeframe: includes all information available through completion of surgery(ies) in the first
SEER Summary Stage Still Here! CCRA NORTHERN REGION STAGING SYMPOSIUM SEPTEMBER 20, 2017 SEER Summary Stage Timeframe: includes all information available through completion of surgery(ies) in the first
