BIOS222 Pathology and Clinical Science 2 & 3
|
|
|
- Junior O’Brien’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BIOS222 Pathology and Clinical Science 2 & 3 Session 17 Male Reproductive Disorders Bioscience Department
2 Session Learning Outcomes At the end of the session, you should be able to: o Review the normal structure and functioning of male genital system. o Describe and discuss the clinical presentation, in male reproductive system. o Discuss the aetiology, clinical features, investigations and management of various prostatic disorders prostatitis, BPH and prostate cancer. o Outline and discuss various penile and testicular disorders. Endeavour College of Natural Health 2
3 Session Plan o Overview of the male reproductive system o Presenting problems in male reproductive disease: Hypogonadism Gynaecomastia Klinefelter s syndrome o Prostate disorders: Prostatitis Benign prostatic hyperplasia Carcinoma Endeavour College of Natural Health 3
4 Session Plan o Penile and testicular disorders: Congenital and acquired penile disorders Penile Infections and Inflammations Penile carcinoma Erectile dysfunction Testicular swellings Inguinal Hernia Cryptorchidism Testicular tumours Endeavour College of Natural Health 4
5 Overview of the Male Reproductive System Presenting Problems in Male Reproductive Disease Endeavour College of Natural Health 5
6 Male Reproductive System ORGANS MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM FUNCTION GONADS Testes Produce sperm and the male sex hormone testosterone DUCTS ACCESSORY SEX GLANDS SUPPORTING STRUCTURES Epididymis, Ductus Deference, Ejaculatory Duct, Urethra Seminal Vesicles, Prostate, Bulbourethral Glands Scrotum, Spermatic Cord, Penis Maturation of gametes Storage of gametes Delivery of gametes Producing Semen Scrotum supports and protects the testes as well as regulates the temperature of the testes. Tortora, GJ & Derrickson, B 2014, Principles of anatomy and physiology, 14th edn, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, NJ. Endeavour College of Natural Health 6
7 Presenting Problems in Male Reproductive Disease o Hypogonadism o Gynaecomastia o Klinefelter s syndrome o Male menopause o Prostatitis o Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy o Prostate cancer o Penile disorders o Infertility Endeavour College of Natural Health 7
8 Hypogonadism o Definition: Decreased function of the gonads. o Aetiology: Hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism Structural pituitary/ hypothalamic disease Functional gonadotrophin deficiency Isolated gonadotrophin deficiency Hypergonadotrophic hypogonadism Developmental/congenital gonadal disorders Acquired gonadal damage Endeavour College of Natural Health 8
9 Hypogonadism o Clinical features: Loss of libido Lethargy with muscle weakness Decreased frequency of shaving Gynaecomastia Infertility Delayed puberty Osteoporosis Anaemia of chronic disease Endeavour College of Natural Health 9
10 o Diagnosis: Hypogonadism Serum testosterone level Random LH and FSH, GnRH Investigations for ptuitary disease Testicular examination Karyotype analysis o Management: Testosterone replacement Regular measuring and monitoring prostate-specific antigen (PSA) and haemoglobin concentration Treatment for fertility Endeavour College of Natural Health 10
11 Gynaecomastia o Definition: It is the presence of glandular breast tissue in males resulting from an imbalance between androgen and oestrogen activity, which may reflect androgen deficiency or oestrogen excess. o Aetiology: Idiopathic Physiological Drug-induced Hypogonadism Androgen resistance syndromes Oestrogen excess Endeavour College of Natural Health 11
12 o Diagnosis: Clinical history Gynaecomastia Breast and testes examination Ultrasonography or mammography Random serum Testosterone, LH, FSH, oestradiol, Prolactin and hcg o Management: Self resolving in pubertal boys Androgen replacement Anti-oestrogen therapy Surgical excision for cosmetic reasons Endeavour College of Natural Health 12
13 Klinefelter s Syndrome o Definition: It is a genetic abnormality with mainly 47XXY karyotype, characterised by dysgenesis of the seminiferous tubules and impairment of Leydig cell function resulting in hypogonadism. o Clinical features: Gynaecomastia Failure to progress normally through puberty Infertility Small, firm testes. Tall stature increased risk of breast cancer and type 2 diabetes Endeavour College of Natural Health 13
14 Klinefelter s Syndrome o Diagnosis: Clinical presentation Karyotype analysis o Management: Androgen replacement Grossman SC & Porth CM 2014, Porth s Pathophysiology- Concepts of Altered Health States, 9th edn. Wolters Kluwer Health - Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins Endeavour College of Natural Health 14
15 Male Menopause o Definition: A progressive decline in gonadal functions in male around age of 40 years but not complete cessation. o Aetiology: Decrease in testosterone Alcohol excess Malnutrition Stress Lack of sleep Certain medications o Clinical features: Erectile dysfunction, Depression, anxiety, fatigue Reduced libido Reduced cognitive functions and memory o Management: Androgen replacement Endeavour College of Natural Health 15
16 Prostate Disorders Endeavour College of Natural Health 16
17 Prostatitis o Definition: It is an infection or inflammation of the prostate gland. o Aetiology: Acute bacterial: E. coli, Gram-negative bacteria (Proteus, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas) and enterococci Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis: Gram-negative enterobacteria Chronic non-bacterial (Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome): Autoimmune. functional obstruction of the bladder neck, Prolonged tension of the pelvic floor muscles Endeavour College of Natural Health 17
18 Prostatitis o Clinical features: Frequent urination, dysuria, difficulty passing urine Painful ejaculation, perineal or groin pain Systemic disturbance (in acute disease) o Diagnosis: Digital rectal examination Microbial culture of urine or urethral discharge o Management: Antibiotics Combination of α-blockers, NSAIDs and amitriptyline Endeavour College of Natural Health 18
19 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia o Definition: It is an age-related, non-malignant enlargement of the prostate gland that occurs due to increase in cell number of both the glandular and stromal components giving rise to large nodules. o Aetiology: unknown o Risk factors: Age Family history Race, ethnicity Dietary fat and meat consumption Hormonal factors: Testosterone and dihydrotestosterone Oestrogens Endeavour College of Natural Health 19
20 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia 60 SIZE (mm) Marked enlargement 80 gram Moderate enlargement 25 gram gram 8 gram 15 gram NEWBORN AGE (years) Endeavour College of Natural Health 20
21 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia o Clinical features: Difficulty in voiding urine: Hesitancy, poor urinary flow and a sensation of incomplete emptying Urinary frequency, urgency of micturition and urge incontinence Acute urinary retention with a painful distended bladder o Complications: Bladder hypertrophy and hyperplasia Bladder calculi Bladder diverticulum Increased predisposition to UTI s and prostatitis Hydroureter Hydronephrosis Renal damage Endeavour College of Natural Health 21
22 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia o Complications: Hydronephrosis Infection Hydroureter Trabeculation Bladder wall hypertrophy and hyperplasia Diverticulum formation Calculus formation Compression of urethra, obstruction Vardaxis, N A, 2010, a Textbook of Pathology, 2nd edn, Elsevier, Australia Endeavour College of Natural Health 22
23 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia o Diagnosis: Digital rectal examination Urinalysis Test for urine flow rate Blood tests for prostate-specific antigen (PSA) o Management: Medical Prostate < 30 g: α- adrenoceptor blockers Prostate > 30 g: 5αreductase inhibitors +/- α adrenoceptor blockers Surgical Transurethral resection of prostate (TURP) Holmium laser enucleation Open prostatectomy Endeavour College of Natural Health 23
24 Prostate Carcinoma o Definition: Carcinoma of the prostate that predominately affect peripheral zones of the gland. o Aetiology: Unknown o Risk factors: Age Race Heredity A high-fat diet Male hormone o Clinical features: Asymptomatic Lower urinary tract symptoms as BPH Metastases S/S: Back pain, weight loss, anaemia and obstruction of the ureters. Endeavour College of Natural Health 24
25 Prostate Carcinoma o Diagnosis: Digital rectal examination Blood tests for prostate-specific antigen (PSA) Transrectal ultrasound-guided prostate biopsies o Management: Surgery Androgen-suppressing drugs Androgen receptor blockers Gonadotrophin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analogues Endeavour College of Natural Health 25
26 Penile and Testicular Disorders Endeavour College of Natural Health 26
27 Congenital and Acquired Penile Disorders o Micropenis: Very small penis usually due to prenatal androgen production, defective testosterone synthesis or pituitary gonadotrophin defect. o Epispadiasis: Urethra opens on dorsal aspect of penis. Urethral opening on ventral surface o Hypospadiasis: Urethra opens on ventral aspect of penis. Urethral opening on dorsal surface Grossman SC & Porth CM 2014, Porth s Pathophysiology- Concepts of Altered Health States, 9th edn. Wolters Kluwer Health - Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins Endeavour College of Natural Health 27
28 Micropenis Epispadias Hypospadias Normal testes, fertile man Urethra opens on dorsal aspect (upper surface) of penis Urethra opens on ventral aspect (under surface) of penis Image courtesy of Prof. Vardaxis. Endeavour College Endeavour College of Natural Health 28
29 Congenital and Acquired Penile Disorders o Phimosis: It refers to a tightening of the prepuce or penile foreskin that prevents its retraction over the glans (congenital or acquired) Foreskin covering the glans o Paraphimosis: The foreskin is so tight and constricted that it cannot cover the glans. A tight foreskin can constrict the blood supply to the glans and lead to ischemia and necrosis.. Retracted foreskin Endeavour College of Natural Health 29
30 Penile Infections and Inflammations o Balanitis: It is an acute or chronic inflammation of the glans penis. Men with poor hygiene, immunosuppression, or diabetes are more prone to balanitis o Balanoposthitis: It refers to inflammation of the glans and prepuce. It is usually encountered in men with phimosis or a large, redundant prepuce that interferes with cleanliness and predisposes to bacterial growth Endeavour College of Natural Health 30
31 Penile Carcinoma o Aetiology: Unknown o Risk factors: Increasing age Poor hygiene Smoking HPV types 16 and 18 infections Ultraviolet Radiation exposure Immunodeficiency states o Clinical features: Small lump or ulcer Painful swelling Purulent drainage Difficulty urinating Palpable lymph nodes in the inguinal region o Management: Surgery 5-year survival >95% Endeavour College of Natural Health 31
32 Erectile Dysfunction o Definition: It is defined as the inability to achieve and maintain an erection sufficient to permit satisfactory sexual intercourse. o Aetiology: Psychogenic: Performance anxiety, A strained relationship with a sexual partner, depression Overt psychotic disorders. Organic: Neurogenic disorders Hormonal disorders Vascular disorders drug-induced penile-related aetiologies Endeavour College of Natural Health 32
33 Erectile Dysfunction o Diagnosis: Careful history (medical, sexual, and psychosocial), Physical examination Investigations for underlying organic causes o Management: Psychosexual counseling, Androgen replacement therapy, Oral and intracavernous drug therapy, Vacuum constriction devices, and Surgical implants Endeavour College of Natural Health 33
34 Testicular Swellings o Hydrocele: A collection of excessive fluid between the layers of the tunica vaginalis. o Hematocele: It is an accumulation of blood in the tunica vaginalis, which causes the scrotal skin to become dark red or purple. o Varicocele: It is characterized by varicosities of the pampiniform plexus, a network of veins supplying the testes. o Spermatocele: It is a painless, sperm-containing cyst that forms at the end of the epididymis. Endeavour College of Natural Health 34
35 Testicular Swellings Grossman SC & Porth CM 2014, Porth s Pathophysiology- Concepts of Altered Health States, 9th edn. Wolters Kluwer Health - Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins Endeavour College of Natural Health 35
36 Testicular Swellings Hydrocele Varicocoele AF7E8D7281E3A972DC08672B11E489584CFF825E&first=391&FORM=ID FRIR Image courtesy of Prof. Vardaxis. Endeavour College Endeavour College of Natural Health
37 Inguinal Hernia o Definition: It is a protrusion of the parietal peritoneum and part of the intestine through an abnormal opening from the abdominal cavity. o Aetiology: Congenital: Patent vaginal process ( 1% of paediatric disorders) Acquired: When obliterated vaginal process opens due to excessive stress being placed upon it o Management: Immediate Surgery o Complications: Intestinal obstruction, compression of veins, infarction and gangrene due to strangulated hernia Endeavour College of Natural Health 37
38 Inguinal Hernia Vaginal process Normal Hernia Vardaxis, N A, 2010, a Textbook of Pathology, 2nd edn, Elsevier, Australia Endeavour College of Natural Health 38
39 Cryptorchidism o Definition: It occurs when one or both of the testicles fail to move down into the scrotal sac (undescended testes). The undescended testes may remain in the lower abdomen, at a point of descent in the inguinal canal, or in the upper scrotum. o Clinical features: Absence of one or both testes from the scrotum Increased risk of Infertility, Malignancy, Testicular torsion Endeavour College of Natural Health 39
40 Cryptorchidism o Management: Spontaneous descent Hormone therapy Orchiopexy Lifelong follow-up Testicular selfexamination Possible locations of undescended testes. Grossman SC & Porth CM 2014, Porth s Pathophysiology- Concepts of Altered Health States, 9th edn. Wolters Kluwer Health - Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins Endeavour College of Natural Health 40
41 Orchitis and Epididymoörchitis o Definition: It is an Infection or inflammation of the testis or of testis and epididymis. o Aetiology: Associated with other infections of the genitourinatry tract such as cystitis, prostatitis and urethritis Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Mumps (Mumps orchitis). o Clinical features: Unilateral pain and swelling, Erythema and oedema of the overlying scrotal skin Scarring, atrophy, infertility or sterility Endeavour College of Natural Health 41
42 Torsion of the Testis o Definition: It is a is a condition in which there is twisting of the testis on itself. o Aetiology: Violent movements, trauma (sportsmen) Abnormalities of situation or attachment of the epididymis, a long spermatic cord or testicular atrophy o Clinical features: Distress within hours of onset and often have nausea, vomiting, and tachycardia. Affected testis is large and tender, with pain radiating to the inguinal area o Management: Immediate Surgery Endeavour College of Natural Health 42
43 o Aetiology: Unknown Testicular Tumours o Risk factors: Genetic predisposition Disorders of testicular development: Klinefelter syndrome and testicular feminization, Cryptorchidism HIV o Clinical features: scrotal mass painless or mild dull pain o Diagnosis: Biopsy, USG, CT scan for metastasis o Managemen: Orchidectomy, Radiotherapy, chemotherapy Endeavour College of Natural Health 43
44 Testicular Self-Examination (TSE) o 12% of cancer deaths between 16 and 36 years due to testicular tumours o Monthly, three minute testicular self-examination after a shower or bath o Discovery of changes in size, consistency of the testis, presence of hard lumps, pain or tenderness should be followed by a doctor s examination Endeavour College of Natural Health 44
45 Reading and Resources o o o o o o o Crowley LV, 2012, An Introduction to Human Diseases Pathology and Pathophysiology Correlations, 9th edn, Jones and Bartlett Learning Grossman SC & Porth CM 2014, Porth s Pathophysiology- Concepts of Altered Health States, 9th edn. Wolters Kluwer Health - Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins Hinson, J, Raven, P & Chew, S 2010, The endocrine system: basic science and clinical conditions, 2nd edn, Churchill Livingstone Elsevier, Edinburgh Jamison, JR 2006, Differential diagnosis for primary care: a handbook for health care practitioners, 2nd edn, Churchill Livingstone Elsevier, Edinburgh. Jarvis, C, 2012 Physical Examination & Health Assessment, 6th ed., Elsevier Saunders, Philadelphia. Kumar, P & Clark, M 2012, Kumar and Clark s clinical medicine, 8th edn, Saunders Elsevier, Edinburgh. Kumar, V, Abbas, AK & Aster, JC 2015, Robbins & Cotran pathologic basis of disease, 9th edn, Elsevier Saunders, Philadelphia. Endeavour College of Natural Health 45
46 Reading and Resources o Lee, G & Bishop, P 2009, Microbiology and infection control for health professionals, 4th edn, Pearson Education, Frenchs Forest, NSW. o McCance, KL, Heuther, SE, & Brashers, VL 2014, Pathophysiology: the biologic basis for disease in adults and children, 7th edn, Elsevier. o Michael-Titus, A, Revest, P & Shortland, P 2010, The nervous system: basic science and clinical conditions, 2nd edn, Churchill Livingstone Elsevier, Edinburgh o Mosby s dictionary of medicine, nursing and health professions 2013, 9th edn, Elsevier, St. Louis, MO. o Tortora, GJ & Derrickson, B 2014, Principles of anatomy and physiology, 14th edn, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, NJ. o VanMeter, KC & Hubert, RJ 2014, Gould's pathophysiology for the health professions, 5th edn, Elsevier, St Louis, MO. o Vardaxis, N A, 2010, a Textbook of Pathology, 2nd edn, Elsevier, Australia o Walker, BR, Colledge, NR, Ralston, SH, & Penman, ID (eds) 2014, Davidson s principles and practice of medicine, 22nd edn, Churchill Livingstone Elsevier, Edinburgh. Endeavour College of Natural Health 46
47 COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright Regulations 1969 WARNING This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of the Endeavour College of Natural Health pursuant to Part VB of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act). The material in this communication may be subject to copyright under the Act. Any further reproduction or communication of this material by you may be the subject of copyright protection under the Act. Do not remove this notice. Endeavour College of Natural Health 47
BIOS222 Pathology and Clinical Science 2
 BIOS222 Pathology and Clinical Science 2 Session 3 Lymphatic and Haematological Disorders 1 Bioscience Department www.endeavour.edu.au Session Learning Outcomes At the end of this session, you should be
BIOS222 Pathology and Clinical Science 2 Session 3 Lymphatic and Haematological Disorders 1 Bioscience Department www.endeavour.edu.au Session Learning Outcomes At the end of this session, you should be
1/3/2008. Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown. Medical-Surgical Nursing Care, 2e Karen Burke, Priscilla LeMone, and Elaine Mohn-Brown
 Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 34 Caring for Male Clients with Reproductive System Disorders Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Testosterone
Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 34 Caring for Male Clients with Reproductive System Disorders Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Testosterone
BIOS222 Pathology and Clinical Science 2 & 3
 BIOS222 Pathology and Clinical Science 2 & 3 Session 16 Endocrine system disorders 3 Bioscience Department www.endeavour.edu.au Session Learning Outcomes At the end of the session, you should be able to:
BIOS222 Pathology and Clinical Science 2 & 3 Session 16 Endocrine system disorders 3 Bioscience Department www.endeavour.edu.au Session Learning Outcomes At the end of the session, you should be able to:
Male Reproductive System. Anatomy
 Male Reproductive System Medical Terminology Chapter Seven HIT # 141 Anatomy Testis or testicle = main male sex organs, paired, oval shaped, enclosed in a sac called the scrotum. Seminiferous tubules =
Male Reproductive System Medical Terminology Chapter Seven HIT # 141 Anatomy Testis or testicle = main male sex organs, paired, oval shaped, enclosed in a sac called the scrotum. Seminiferous tubules =
The Good News. The Comprehensive Approach. Examining the Male Patient: Sexually Transmitted Infections. April 25, 2013 Brittany Grier, M.
 Examining the Male Patient: Sexually Transmitted Infections April 25, 2013 Brittany Grier, M.S, PA-C The Good News Learning how to do a proper male exam can provide high yield information in formulating
Examining the Male Patient: Sexually Transmitted Infections April 25, 2013 Brittany Grier, M.S, PA-C The Good News Learning how to do a proper male exam can provide high yield information in formulating
Chapter 7. Male Reproductive System
 Chapter 7 Male Reproductive System 1 Sexual Reproduction Sexual reproduction two individuals produce offspring that have genetic characteristics from both parents Sexual reproduction introduces new gene
Chapter 7 Male Reproductive System 1 Sexual Reproduction Sexual reproduction two individuals produce offspring that have genetic characteristics from both parents Sexual reproduction introduces new gene
BIOS222 Pathology and Clinical Science 2 & 3
 BIOS222 Pathology and Clinical Science 2 & 3 Session 10 Disorders of Musculoskeletal System 1 Bioscience Department www.endeavour.edu.au Session Learning Outcomes At the end of the session, you should
BIOS222 Pathology and Clinical Science 2 & 3 Session 10 Disorders of Musculoskeletal System 1 Bioscience Department www.endeavour.edu.au Session Learning Outcomes At the end of the session, you should
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) You are the nurse providing care for a client reporting symptoms of bloating, irritability,
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) You are the nurse providing care for a client reporting symptoms of bloating, irritability,
What You Need to Know
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION What You Need to Know Facts about male infertility This handout explains what causes male infertility, how it is diagnosed, and possible treatments. Infertility is defined
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION What You Need to Know Facts about male infertility This handout explains what causes male infertility, how it is diagnosed, and possible treatments. Infertility is defined
DISORDERS OF MALE GENITALS
 Wit JM, Ranke MB, Kelnar CJH (eds): ESPE classification of paediatric endocrine diagnosis. 9. Testicular disorders/disorders of male genitals. Horm Res 2007;68(suppl 2):63 66 ESPE Code Diagnosis OMIM ICD10
Wit JM, Ranke MB, Kelnar CJH (eds): ESPE classification of paediatric endocrine diagnosis. 9. Testicular disorders/disorders of male genitals. Horm Res 2007;68(suppl 2):63 66 ESPE Code Diagnosis OMIM ICD10
BIOS222 Pathology and Clinical Science 2 & 3
 BIOS222 Pathology and Clinical Science 2 & 3 Session 12 Disorders of Musculoskeletal System 3 Bioscience Department www.endeavour.edu.au Session Learning Outcomes At the end of the session, student should
BIOS222 Pathology and Clinical Science 2 & 3 Session 12 Disorders of Musculoskeletal System 3 Bioscience Department www.endeavour.edu.au Session Learning Outcomes At the end of the session, student should
Vascular Related Torsion Venous compression Hemorrhagic infarct Young men At night Very painful Can be reduced Scrotal Masses Testicular Tumors (solid
 Pathology of the Male Reproductive System Testis and Epididymis Failure of Testis to Descend Testis are not always in scrotum at birth. Testes from in abdomen with kidneys Migrate to scrotum May get stuck
Pathology of the Male Reproductive System Testis and Epididymis Failure of Testis to Descend Testis are not always in scrotum at birth. Testes from in abdomen with kidneys Migrate to scrotum May get stuck
UROLOGY UROLOGY REFERRAL RECOMMENDATIONS
 UROLOGY PAGE 1 These referral recommendations are provided for core Urology Services in the public health system. They exclude social or cultural circumcision, vasectomy and vasectomy reversal, and access
UROLOGY PAGE 1 These referral recommendations are provided for core Urology Services in the public health system. They exclude social or cultural circumcision, vasectomy and vasectomy reversal, and access
Prostate Health PHARMACIST VIEW
 Prostate Health PHARMACIST VIEW Prostate Definition Prostate is a gland made of fibromuscular tissue. It is about 4 cm and surrounds the neck of the bladder and the urethra. It produces seminal fluid.
Prostate Health PHARMACIST VIEW Prostate Definition Prostate is a gland made of fibromuscular tissue. It is about 4 cm and surrounds the neck of the bladder and the urethra. It produces seminal fluid.
The Reproductive System
 16 PART A The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reproductive
16 PART A The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reproductive
Male History, Clinical Examination and Testing
 Male History, Clinical Examination and Testing Dirk Vanderschueren, MD, PhD Case Jan is 29 years old and consults for 1 year primary subfertility partner 28 years old and normal gynaecological investigation
Male History, Clinical Examination and Testing Dirk Vanderschueren, MD, PhD Case Jan is 29 years old and consults for 1 year primary subfertility partner 28 years old and normal gynaecological investigation
The Reproductive System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 16 The Reproductive System Slides 16.1 16.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Reproductive System Gonads
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 16 The Reproductive System Slides 16.1 16.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Reproductive System Gonads
Appendix D Answers to the KAP Survey
 From Trainer s Resource Book to accompany Management of Men s Reproductive Health Problems 2003 EngenderHealth Appendix D Answers to the KAP Survey In the answer key that follows: The answers appear in
From Trainer s Resource Book to accompany Management of Men s Reproductive Health Problems 2003 EngenderHealth Appendix D Answers to the KAP Survey In the answer key that follows: The answers appear in
The Reproductive System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Reproductive System 16PART A The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Reproductive System 16PART A The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males
Miss Rashmi Singh Consultant urological Surgeon. Men s Health Seminar Parkside Hospital November 2016
 Miss Rashmi Singh Consultant urological Surgeon Men s Health Seminar Parkside Hospital November 2016 Hernia Hydrocele Varicocele Infections Epididymal cyst Testicular Ca Miscellaneous Phimosis Paraphimosis
Miss Rashmi Singh Consultant urological Surgeon Men s Health Seminar Parkside Hospital November 2016 Hernia Hydrocele Varicocele Infections Epididymal cyst Testicular Ca Miscellaneous Phimosis Paraphimosis
A USER S GUIDE WHAT EVERY MAN NEEDS TO KNOW
 A USER S GUIDE WHAT EVERY MAN NEEDS TO KNOW 1. Why men need to know more Good health is vital for a happy and full life. But, with work and family responsibilities, men often overlook their own health
A USER S GUIDE WHAT EVERY MAN NEEDS TO KNOW 1. Why men need to know more Good health is vital for a happy and full life. But, with work and family responsibilities, men often overlook their own health
- production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote
 Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Information for Patients. Male infertility. English
 Information for Patients Male infertility English Table of contents What is male infertility?... 3 Diagnosis... 3 Medical history... 3 Physical examination... 3 Hormone blood tests... 3 Semen analysis...
Information for Patients Male infertility English Table of contents What is male infertility?... 3 Diagnosis... 3 Medical history... 3 Physical examination... 3 Hormone blood tests... 3 Semen analysis...
Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries. Accessory reproductive organs: ducts, glands, and external genitalia
 Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
Male Reproductive System. Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD
 Male Reproductive System Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD Learning Objectives 1. Describe the General Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System 2. Identify the structures that are related to the prostate.
Male Reproductive System Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD Learning Objectives 1. Describe the General Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System 2. Identify the structures that are related to the prostate.
Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Reproductive System Basics Primary sex organs (gonads) testes in males, ovaries in females Gonads produce sex cells called gametes (gametes means spouses) and
Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Reproductive System Basics Primary sex organs (gonads) testes in males, ovaries in females Gonads produce sex cells called gametes (gametes means spouses) and
Maldescended testis in Adults. Dr. BG GAUDJI Urologist STEVE BIKO ACADEMIC HOSPITAL
 Maldescended testis in Adults Dr. BG GAUDJI Urologist STEVE BIKO ACADEMIC HOSPITAL Definitions Cryptorchid: testis neither resides nor can be manipulated into the scrotum Ectopic: aberrant course Retractile:
Maldescended testis in Adults Dr. BG GAUDJI Urologist STEVE BIKO ACADEMIC HOSPITAL Definitions Cryptorchid: testis neither resides nor can be manipulated into the scrotum Ectopic: aberrant course Retractile:
MALE GENITAL SURGICAL PROCEDURES
 Male Genital Surgical ProceduresDecember 22, 2015 (effective March 1, 201) PENIS Slit of prepuce (complete care) S5 - newborn... 14.35 S58 - infant... 21.50 S59 - adult or child... 30.25 EXCISION Circumcision
Male Genital Surgical ProceduresDecember 22, 2015 (effective March 1, 201) PENIS Slit of prepuce (complete care) S5 - newborn... 14.35 S58 - infant... 21.50 S59 - adult or child... 30.25 EXCISION Circumcision
Neoplasia 2. Lecture 9. Pathology and Clinical Science 1 (BIOC211) Department of Bioscience. endeavour.edu.au
 Neoplasia 2 Lecture 9 Pathology and Clinical Science 1 (BIOC211) Department of Bioscience Text Reference: Grossman, S.C. & Porth, C.M. (2014). Porth s Pathophysiology: concepts of altered health states,
Neoplasia 2 Lecture 9 Pathology and Clinical Science 1 (BIOC211) Department of Bioscience Text Reference: Grossman, S.C. & Porth, C.M. (2014). Porth s Pathophysiology: concepts of altered health states,
4 th Year Urology Core Objectives Keith Rourke (Revised June 1, 2007)
 4 th Year Urology Core Objectives Keith Rourke (Revised June 1, 2007) I. Genitourinary Trauma: 1. Goal: The student will be able to demonstrate a basic clinical approach to the management & diagnosis of
4 th Year Urology Core Objectives Keith Rourke (Revised June 1, 2007) I. Genitourinary Trauma: 1. Goal: The student will be able to demonstrate a basic clinical approach to the management & diagnosis of
UROLOGY TOPICS FOR SENIOR CLERKSHIP HEMATURIA
 UROLOGY TOPICS FOR SENIOR CLERKSHIP HEMATURIA Blood in urine is an important presenting symptom for many diseases of the urinary tract as well as for systemic disorders. Degree of hematuria has poor correlation
UROLOGY TOPICS FOR SENIOR CLERKSHIP HEMATURIA Blood in urine is an important presenting symptom for many diseases of the urinary tract as well as for systemic disorders. Degree of hematuria has poor correlation
BIOS222 Pathology and Clinical Science 2 & 3
 BIOS222 Pathology and Clinical Science 2 & 3 Session 15 Endocrine system disorders 2 Bioscience Department www.endeavour.edu.au Session Learning Outcomes At the end of the session, you should be able to:
BIOS222 Pathology and Clinical Science 2 & 3 Session 15 Endocrine system disorders 2 Bioscience Department www.endeavour.edu.au Session Learning Outcomes At the end of the session, you should be able to:
MANAGING BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERTROPHY IN PRIMARY CARE DR GEORGE G MATHEW CONSULTANT FAMILY PHYSICIAN FELLOW IN SEXUAL & REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH
 MANAGING BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERTROPHY IN PRIMARY CARE DR GEORGE G MATHEW CONSULTANT FAMILY PHYSICIAN FELLOW IN SEXUAL & REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH INTRODUCTION (1) Part of male sexual reproductive organ Size
MANAGING BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERTROPHY IN PRIMARY CARE DR GEORGE G MATHEW CONSULTANT FAMILY PHYSICIAN FELLOW IN SEXUAL & REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH INTRODUCTION (1) Part of male sexual reproductive organ Size
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 9 Urinary Tract and Perineum Key Points 2 9.1 Urinary Bladder & Urinary Retention Acute retention of urine is an indication for emergency drainage of the bladder
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 9 Urinary Tract and Perineum Key Points 2 9.1 Urinary Bladder & Urinary Retention Acute retention of urine is an indication for emergency drainage of the bladder
M. Al-Mohtaseb. Tala Saleh. Faisal Nimri
 4 5 M. Al-Mohtaseb Tala Saleh Faisal Nimri Inguinal Hernia - An abdominal hernia is the protrusion of part of the abdominal content beyond the normal confines of the abdominal wall through weak points
4 5 M. Al-Mohtaseb Tala Saleh Faisal Nimri Inguinal Hernia - An abdominal hernia is the protrusion of part of the abdominal content beyond the normal confines of the abdominal wall through weak points
HMM 4401 Genito-urinary tract diseases
 HMM 4401 Genito-urinary tract diseases Urine production Core elements: Glomerulus, proximal and distal convoluted tube, loop of Henle, collecting tubules, ureters, bladder, sphincter, uretra, and out
HMM 4401 Genito-urinary tract diseases Urine production Core elements: Glomerulus, proximal and distal convoluted tube, loop of Henle, collecting tubules, ureters, bladder, sphincter, uretra, and out
GUIDELINES ON MALE HYPOGONADISM
 GUIDELINES ON MALE HYPOGONADISM (Text update March 2015) G.R. Dohle (Chair), S. Arver, C. Bettocchi, T.H. Jones, S. Kliesch, M. Punab Introduction Male hypogonadism is a clinical syndrome caused by androgen
GUIDELINES ON MALE HYPOGONADISM (Text update March 2015) G.R. Dohle (Chair), S. Arver, C. Bettocchi, T.H. Jones, S. Kliesch, M. Punab Introduction Male hypogonadism is a clinical syndrome caused by androgen
Scrotal pain and Swelling
 Scrotal pain and Swelling Color index : Important Further explanation Done By: Nada Alamri Editing link Acute Scrotal Pain DDx: 1) Testicular torsion : Twisting and strangulation of the testicle on the
Scrotal pain and Swelling Color index : Important Further explanation Done By: Nada Alamri Editing link Acute Scrotal Pain DDx: 1) Testicular torsion : Twisting and strangulation of the testicle on the
Female Reproduction. Ova- Female reproduction cells stored in the ovaries
 Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE
 Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
GUIDELINES ON. Introduction. G.R. Dohle, S. Arver, C. Bettocchi, S. Kliesch, M. Punab, W. de Ronde
 GUIDELINES ON Male Hypogonadism G.R. Dohle, S. Arver,. Bettocchi, S. Kliesch, M. Punab, W. de Ronde Introduction Male hypogonadism is a clinical syndrome caused by androgen deficiency. It may adversely
GUIDELINES ON Male Hypogonadism G.R. Dohle, S. Arver,. Bettocchi, S. Kliesch, M. Punab, W. de Ronde Introduction Male hypogonadism is a clinical syndrome caused by androgen deficiency. It may adversely
BENIGN & MALIGNANT TESTIS DISEASES. Gary J. Faerber, M.D. Associate Professor, Dept of Urology March 2009 OBJECTIVES
 BENIGN & MALIGNANT TESTIS DISEASES Gary J. Faerber, M.D. Associate Professor, Dept of Urology March 2009 OBJECTIVES 1. Become familiar with the scrotal contents and their anatomical relationship with each
BENIGN & MALIGNANT TESTIS DISEASES Gary J. Faerber, M.D. Associate Professor, Dept of Urology March 2009 OBJECTIVES 1. Become familiar with the scrotal contents and their anatomical relationship with each
Science and Health THE HUMAN REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 5 Module 1 Science and Health THE HUMAN REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Male Female A DepEd-BEAM Distance Learning Program supported by the Australian Agency for International Development NOTICE Section 9 of the Presidential
5 Module 1 Science and Health THE HUMAN REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Male Female A DepEd-BEAM Distance Learning Program supported by the Australian Agency for International Development NOTICE Section 9 of the Presidential
Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems
 CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
Chapter 7. Male Reproductive System. Copyright 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 7 Male Reproductive System Chapter 7 Objective 1: Pronounce organs and anatomic structures of the male reproductive system. Organs (1 of 2) The organs of the male reproductive system include the
Chapter 7 Male Reproductive System Chapter 7 Objective 1: Pronounce organs and anatomic structures of the male reproductive system. Organs (1 of 2) The organs of the male reproductive system include the
An Undergraduate Syllabus for Urology. Produced on behalf of the British Association of Urological Surgeons. March 2012
 An Undergraduate Syllabus for Urology Produced on behalf of the British Association of Urological Surgeons March 2012 Authors H Hashim, P Jones, KJ O Flynn, I Pearce, J Royle, M Shaw, AM Sinclair Correspondence
An Undergraduate Syllabus for Urology Produced on behalf of the British Association of Urological Surgeons March 2012 Authors H Hashim, P Jones, KJ O Flynn, I Pearce, J Royle, M Shaw, AM Sinclair Correspondence
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock)
 Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Male Reproductive System
 Male Hormone Issues The Ideal Male What describes a healthy male? Happy guy, well-muscled, good sex drive, focused brain This is what a guy can expect with the right level of testosterone Low testosterone?
Male Hormone Issues The Ideal Male What describes a healthy male? Happy guy, well-muscled, good sex drive, focused brain This is what a guy can expect with the right level of testosterone Low testosterone?
Reproductive System Purpose General Structures Male Structures Functions Female Anatomy Structures Functions Clinical Applications
 The Reproductive System: Male, Ch 23 Outline of class lecture After studying the male reproductive system you should be able to: 1. Define the purpose of reproduction and identify the general organs of
The Reproductive System: Male, Ch 23 Outline of class lecture After studying the male reproductive system you should be able to: 1. Define the purpose of reproduction and identify the general organs of
Hths 2231 Laboratory 14 Alterations in the Reproductive System and STDs
 Complete activities 1-3. Activity #1: Click on the STD fact-sheet link under activity 1 to complete the information on the STD tables. Write the information on the lab worksheet. Activity #2: Complete
Complete activities 1-3. Activity #1: Click on the STD fact-sheet link under activity 1 to complete the information on the STD tables. Write the information on the lab worksheet. Activity #2: Complete
Surgical Presentations in Children
 From Gums to Bums: Surgical Presentations in Children Sebastian King Paediatric Colorectal Surgeon From Gums to Bums (and the rest): Surgical Presentations in Children Sebastian King Paediatric Colorectal
From Gums to Bums: Surgical Presentations in Children Sebastian King Paediatric Colorectal Surgeon From Gums to Bums (and the rest): Surgical Presentations in Children Sebastian King Paediatric Colorectal
DEFINITION HX & PH/EX
 DEFINITION HX & PH/EX Because of the success of the assisted reproductive techniques (ART), the evaluation of the man is often ignored. The physician should not forget the fact that many causes of male
DEFINITION HX & PH/EX Because of the success of the assisted reproductive techniques (ART), the evaluation of the man is often ignored. The physician should not forget the fact that many causes of male
حسام أبو عوض. -Dr. Mohammad Muhtasib. 1 P a g e
 5 حسام أبو عوض - -Dr. Mohammad Muhtasib 1 P a g e There are two types of inguinal hernia: direct and indirect. Hernia: protrusion of the small intestine or the greater omentum of the intra-abdominal organs
5 حسام أبو عوض - -Dr. Mohammad Muhtasib 1 P a g e There are two types of inguinal hernia: direct and indirect. Hernia: protrusion of the small intestine or the greater omentum of the intra-abdominal organs
Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings
 Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings Unit 10 Reproductive Systems 1 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Objectives Define, understand and correctly pronounce medical terms related to
Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings Unit 10 Reproductive Systems 1 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Objectives Define, understand and correctly pronounce medical terms related to
Some prostatic diseases
 Some prostatic diseases Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (Nodular Hyperplasia) Extremely common Present in a significant number of men by the age of 40 & its frequency rises progressively with age, reaching
Some prostatic diseases Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (Nodular Hyperplasia) Extremely common Present in a significant number of men by the age of 40 & its frequency rises progressively with age, reaching
We are gong to focus on: Unit 9. Before we begin: Chronic Renal Failure/Uremia ESRD/Dialysis Prostate Cancer Testicular Cancer Renal Cancer
 Unit 9 Problems with excretion Before we begin: You are to understand on your own: A & P of Renal System Common terms of renal system How to perform a focused health history How to perform a Physical Exam
Unit 9 Problems with excretion Before we begin: You are to understand on your own: A & P of Renal System Common terms of renal system How to perform a focused health history How to perform a Physical Exam
Structure and Function
 Section 2 Objectives ~ Describe three functions of the male reproductive system. ~ Identify five ways to keep the male reproductive system healthy. Vocabulary sperm fertilization testes testosterone scrotum
Section 2 Objectives ~ Describe three functions of the male reproductive system. ~ Identify five ways to keep the male reproductive system healthy. Vocabulary sperm fertilization testes testosterone scrotum
Laboratory Investigation of Male Gonadal Function. Dr N Oosthuizen Dept of Chemical Pathology UP 2010
 Laboratory Investigation of Male Gonadal Function Dr N Oosthuizen Dept of Chemical Pathology UP 2010 1 Figure 1. Hypothalamic-pituitary pituitary-testicular testicular axis 2 Testosterone (T) measurement
Laboratory Investigation of Male Gonadal Function Dr N Oosthuizen Dept of Chemical Pathology UP 2010 1 Figure 1. Hypothalamic-pituitary pituitary-testicular testicular axis 2 Testosterone (T) measurement
EAU GUIDELINES ON MALE HYPOGONADISM
 EAU GUIDELINES ON MALE HYPOGONADISM (Text update March 2015) G.R. Dohle (Chair), S. Arver, C. Bettocchi, T.H. Jones, S. Kliesch, M. Punab Introduction Male hypogonadism is a clinical syndrome caused by
EAU GUIDELINES ON MALE HYPOGONADISM (Text update March 2015) G.R. Dohle (Chair), S. Arver, C. Bettocchi, T.H. Jones, S. Kliesch, M. Punab Introduction Male hypogonadism is a clinical syndrome caused by
Male Reproductive System
 21-1 21-2 Reproductive System Male Reproductive System Genital Tract In males the testes, held outside the body in the scrotum (optimum temp of about 35 0 C), produce sperm. Sperm mature in coiled tubes
21-1 21-2 Reproductive System Male Reproductive System Genital Tract In males the testes, held outside the body in the scrotum (optimum temp of about 35 0 C), produce sperm. Sperm mature in coiled tubes
Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems
 CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems Review of Male Reproductive Anatomy Fig 15.9 Vas deferens
CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems Review of Male Reproductive Anatomy Fig 15.9 Vas deferens
RATIONALE: The organs making up the urinary system consist of the kidneys, bladder, urethra, and ureters.
 Chapter 12 Section Review 12.1 1. A. Kidneys RATIONALE: The renal pelvis receives urine from the kidney, travels through the ureters on the way to the bladder, but urine is formed in the kidney. 2. C.
Chapter 12 Section Review 12.1 1. A. Kidneys RATIONALE: The renal pelvis receives urine from the kidney, travels through the ureters on the way to the bladder, but urine is formed in the kidney. 2. C.
GUIDELINES FOR THE INVESTIGATION AND TREATMENT OF MALE INFERTILITY
 GUIDELINES FOR THE INVESTIGATION AND TREATMENT OF MALE INFERTILITY G.R. Dohle, Z. Kopa, A. Jungwirth, T.B. Hargreave. Eur Urol 2002;42(4):313-322 Eur Urol 2004;46(5):555-558 Definition Infertility is the
GUIDELINES FOR THE INVESTIGATION AND TREATMENT OF MALE INFERTILITY G.R. Dohle, Z. Kopa, A. Jungwirth, T.B. Hargreave. Eur Urol 2002;42(4):313-322 Eur Urol 2004;46(5):555-558 Definition Infertility is the
9/13/2017. Highgate Private Hospital & Whittington Health NHS Trust. London Cancer Urology Guidelines for Target Referrals. Urological Cancer Groups
 London Cancer Urology Guidelines for Target Referrals Mr Paul Erotocritou MBBS BSc MSc, MRCS, FRCS (Urol)Eng Highgate Private Hospital & Whittington Health NHS Trust Urological Cancer Groups 5 groups:
London Cancer Urology Guidelines for Target Referrals Mr Paul Erotocritou MBBS BSc MSc, MRCS, FRCS (Urol)Eng Highgate Private Hospital & Whittington Health NHS Trust Urological Cancer Groups 5 groups:
Scrotum Kacey Morrison Amanda Baxter Sabrina Tucker July 18, 2006 SCROTUM
 Scrotum Kacey Morrison Amanda Baxter Sabrina Tucker July 18, 2006 SCROTUM 1) Other Names: Scrotum None Testicles Testes (Curry Tempkin, p. 236, 2/3/2) Ductus deferens spermatic cord (Tempkin, p. 279, Anatomy
Scrotum Kacey Morrison Amanda Baxter Sabrina Tucker July 18, 2006 SCROTUM 1) Other Names: Scrotum None Testicles Testes (Curry Tempkin, p. 236, 2/3/2) Ductus deferens spermatic cord (Tempkin, p. 279, Anatomy
GUIDELINES ON THE INVESTIGATION AND TREATMENT OF MALE INFERTILITY
 GUIDELINES ON THE INVESTIGATION AND TREATMENT OF MALE INFERTILITY G. Dohle (chairman), A. Jungwirth and W. Weidner. Eur Urol 2002;42(4):313-322 Eur Urol 2004;46(5):555-558 1. Introduction Infertility is
GUIDELINES ON THE INVESTIGATION AND TREATMENT OF MALE INFERTILITY G. Dohle (chairman), A. Jungwirth and W. Weidner. Eur Urol 2002;42(4):313-322 Eur Urol 2004;46(5):555-558 1. Introduction Infertility is
ESUR SCROTAL AND PENILE IMAGING WORKING GROUP MULTIMODALITY IMAGING APPROACH TO SCROTAL AND PENILE PATHOLOGIES 2ND ESUR TEACHING COURSE
 ESUR SCROTAL AND PENILE IMAGING WORKING GROUP MULTIMODALITY IMAGING APPROACH TO SCROTAL AND PENILE PATHOLOGIES 2ND ESUR TEACHING COURSE NORMAL ANATOMY OF THE SCROTUM MICHAEL NOMIKOS M.D. F.E.B.U. UROLOGICAL
ESUR SCROTAL AND PENILE IMAGING WORKING GROUP MULTIMODALITY IMAGING APPROACH TO SCROTAL AND PENILE PATHOLOGIES 2ND ESUR TEACHING COURSE NORMAL ANATOMY OF THE SCROTUM MICHAEL NOMIKOS M.D. F.E.B.U. UROLOGICAL
Urinary tract pathology Renal syndromes Acute nephritic syndrome syndrome includes oliguria hematuria proteinuria edema hypertension typically occurs
 Urinary tract Structure [Figs. 13-1, 13-2] Kidneys (left and right) cortex (glomeruli and tubules) medulla (tubules, loops of Henle, and collecting ducts) calices and pelvis forming the collecting system
Urinary tract Structure [Figs. 13-1, 13-2] Kidneys (left and right) cortex (glomeruli and tubules) medulla (tubules, loops of Henle, and collecting ducts) calices and pelvis forming the collecting system
Chris Davies & Greg Handley
 Chris Davies & Greg Handley Contents Definition Epidemiology Aetiology Conditions for pregnancy Female Infertility Male Infertility Shared infertility Treatment Definition Failure of a couple to conceive
Chris Davies & Greg Handley Contents Definition Epidemiology Aetiology Conditions for pregnancy Female Infertility Male Infertility Shared infertility Treatment Definition Failure of a couple to conceive
EAU GUIDELINES ON MALE HYPOGONADISM
 EAU GUIDELINES ON MALE HYPOGONADISM (Limited text update March 2017) G.R. Dohle (Chair), S. Arver, C. Bettocchi, T.H. Jones, S. Kliesch Introduction Male hypogonadism is a clinical syndrome caused by androgen
EAU GUIDELINES ON MALE HYPOGONADISM (Limited text update March 2017) G.R. Dohle (Chair), S. Arver, C. Bettocchi, T.H. Jones, S. Kliesch Introduction Male hypogonadism is a clinical syndrome caused by androgen
Index. urologic.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acquired hypogonadism, prevalence of, 165 167 primary, 165 secondary, 167 Adipose tissue, as an organ, 240 241 Adrenal hyperplasia, congenital,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acquired hypogonadism, prevalence of, 165 167 primary, 165 secondary, 167 Adipose tissue, as an organ, 240 241 Adrenal hyperplasia, congenital,
Clinical evaluation of infertility
 Clinical evaluation of infertility DR. FARIBA KHANIPOUYANI OBSTETRICIAN & GYNECOLOGIST PRENATOLOGIST Definition: inability to achieve conception despite one year of frequent unprotected intercourse. Male
Clinical evaluation of infertility DR. FARIBA KHANIPOUYANI OBSTETRICIAN & GYNECOLOGIST PRENATOLOGIST Definition: inability to achieve conception despite one year of frequent unprotected intercourse. Male
Testicular Cancer: Questions and Answers. Testicular cancer is a disease in which cells become malignant (cancerous) in one or both testicles.
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Testicular Cancer: Questions
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Testicular Cancer: Questions
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
What are Varicoceles?
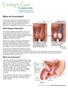 What are Varicoceles? A varicocele is when veins become enlarged inside your scrotum (the pouch of skin that holds your testicles). These veins are called the pampiniform plexus. Ten to 15 of every 100
What are Varicoceles? A varicocele is when veins become enlarged inside your scrotum (the pouch of skin that holds your testicles). These veins are called the pampiniform plexus. Ten to 15 of every 100
Reproductive System: Male
 Reproductive System Reproductive System: Male Produces new life Same types of organs for males and females Gonads, or sex glands Male organs located mainly outside of body Testes The male gonads Located
Reproductive System Reproductive System: Male Produces new life Same types of organs for males and females Gonads, or sex glands Male organs located mainly outside of body Testes The male gonads Located
Prostate Cancer Case Study 1. Medical Student Case-Based Learning
 Prostate Cancer Case Study 1 Medical Student Case-Based Learning The Case of Mr. Powers Prostatic Nodule The effervescent Mr. Powers is found by his primary care provider to have a prostatic nodule. You
Prostate Cancer Case Study 1 Medical Student Case-Based Learning The Case of Mr. Powers Prostatic Nodule The effervescent Mr. Powers is found by his primary care provider to have a prostatic nodule. You
Dr. Syah Mirsya Warli, SpU Dr. Bungaran Sihombing,SpU Div. of Urology, Surgery Dept. Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara
 Emergency Room Urology Dr. Syah Mirsya Warli, SpU Dr. Bungaran Sihombing,SpU Div. of Urology, Surgery Dept. Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Ref : Clinical Manual of Urology, (Philip M. Hanno
Emergency Room Urology Dr. Syah Mirsya Warli, SpU Dr. Bungaran Sihombing,SpU Div. of Urology, Surgery Dept. Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Ref : Clinical Manual of Urology, (Philip M. Hanno
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization
 Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
All about the Prostate
 MEN S HEALTH Dr Nick Pendleton January 16 th 2018 All about the Prostate 1 What does it do? Functions of the Prostate 1. Secretes Prostatic Fluid slightly alkaline fluid, 30% of volume of seminal fluid,
MEN S HEALTH Dr Nick Pendleton January 16 th 2018 All about the Prostate 1 What does it do? Functions of the Prostate 1. Secretes Prostatic Fluid slightly alkaline fluid, 30% of volume of seminal fluid,
Urology Teaching. Affects ~15% of females and 5% of males, with prevalence increasing with age. Cost to NHS of billion annually.
 Urology Teaching Continence Types Urge o Urine loss accompanied by urgency resulting from abnormal bladder contractions Stress o Urine loss resulting from sudden increased intra-abdominal pressure Mixed
Urology Teaching Continence Types Urge o Urine loss accompanied by urgency resulting from abnormal bladder contractions Stress o Urine loss resulting from sudden increased intra-abdominal pressure Mixed
Donor Eggs Australia Summary of Male Patient Information Introduction
 Introduction 1. The following information has been requested by the respective overseas donor egg/sperm/embryo clinics for your preparation for their programmes and will be transmitted to them. 2. Please
Introduction 1. The following information has been requested by the respective overseas donor egg/sperm/embryo clinics for your preparation for their programmes and will be transmitted to them. 2. Please
PROSTATIC ARTERY EMBOLISATION (PAE) FOR BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA. A Minimally Invasive Innovative Treatment
 PROSTATIC ARTERY EMBOLISATION (PAE) FOR BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA A Minimally Invasive Innovative Treatment What is the prostate? The prostate is an accessory organ of the male reproductive system.
PROSTATIC ARTERY EMBOLISATION (PAE) FOR BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA A Minimally Invasive Innovative Treatment What is the prostate? The prostate is an accessory organ of the male reproductive system.
BIOCHEMICAL TESTS FOR THE INVESTIGATION OF COMMON ENDOCRINE PROBLEMS IN THE MALE
 Authoriser: Moya O Doherty Page 1 of 7 BIOCHEMICAL TESTS FOR THE INVESTIGATION OF COMMON ENDOCRINE PROBLEMS IN THE MALE The purpose of this protocol is to describe common tests used for the investigation
Authoriser: Moya O Doherty Page 1 of 7 BIOCHEMICAL TESTS FOR THE INVESTIGATION OF COMMON ENDOCRINE PROBLEMS IN THE MALE The purpose of this protocol is to describe common tests used for the investigation
1: : Lifetime risk for prostate cancer 1:27. Lifetime risk for. testicular cancer. Lifetime risk for. penile cancer
 *Based on the National Cancer Registry of 2010 Lifetime risk for prostate cancer 1:27 Lifetime risk for testicular cancer Lifetime risk for penile cancer 1:2 040 1:1 114 Prostate cancer 1 in 27 South African
*Based on the National Cancer Registry of 2010 Lifetime risk for prostate cancer 1:27 Lifetime risk for testicular cancer Lifetime risk for penile cancer 1:2 040 1:1 114 Prostate cancer 1 in 27 South African
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive system
 Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems. Male Reproductive Organs. Male Reproductive Organs. Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm)
 Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Male reproductive organs 1 Male Reproductive Organs posterior view 2 Male Reproductive Organs Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm) Transport these
Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Male reproductive organs 1 Male Reproductive Organs posterior view 2 Male Reproductive Organs Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm) Transport these
6.7 IN. Continuity through Reproduction. What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes.
 6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
Chapter 18: Glossary
 Chapter 18: Glossary Sutter Health Cancer Service Line: Prostate Committee Advanced cancer: When the cancer has spread to other parts of the body (including lymph nodes, bones, or other organs) and is
Chapter 18: Glossary Sutter Health Cancer Service Line: Prostate Committee Advanced cancer: When the cancer has spread to other parts of the body (including lymph nodes, bones, or other organs) and is
Genital and Uro Genital Surgical conditions
 Genital and Uro Genital Surgical conditions The Genital Tract Female The reproductive system is composed of: Ovaries Oviducts Uterus cervix vagina. The ovaries are the site of production of the unfertilized
Genital and Uro Genital Surgical conditions The Genital Tract Female The reproductive system is composed of: Ovaries Oviducts Uterus cervix vagina. The ovaries are the site of production of the unfertilized
Chapter 47 1/8/2018. Urinary System Disorders. Urinary Tract Infections. Treatment
 Chapter 47 Urinary System Disorders Urinary Tract Infections Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common Infection in one area can involve the entire system Microbes enter through the urethra. Catheterization,
Chapter 47 Urinary System Disorders Urinary Tract Infections Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common Infection in one area can involve the entire system Microbes enter through the urethra. Catheterization,
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Unit 7A STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the male reproductive system. 2. Learn the functions of the male reproductive system. 3. Learn
Unit 7A STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the male reproductive system. 2. Learn the functions of the male reproductive system. 3. Learn
What Is Prostate Cancer? Prostate cancer is the development of cancer cells in the prostate gland (a gland that produces fluid for semen).
 What Is Prostate Cancer? Prostate cancer is the development of cancer cells in the prostate gland (a gland that produces fluid for semen). It is a very common cancer in men; some cancers grow very slowly,
What Is Prostate Cancer? Prostate cancer is the development of cancer cells in the prostate gland (a gland that produces fluid for semen). It is a very common cancer in men; some cancers grow very slowly,
WJ UROGENITAL SYSTEM. UROLOGY
 WJ UROGENITAL SYSTEM. UROLOGY 1 Societies 11 History Include all aspects 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect where possible 15 Classification.
WJ UROGENITAL SYSTEM. UROLOGY 1 Societies 11 History Include all aspects 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect where possible 15 Classification.
Sexual Health Information for Gay & Bisexual Men
 Sexual Health Information for Gay & Bisexual Men When we talk about sexual health, we often focus on HIV and other STIs, but there are a number of other illness and issues that can affect men s sexual
Sexual Health Information for Gay & Bisexual Men When we talk about sexual health, we often focus on HIV and other STIs, but there are a number of other illness and issues that can affect men s sexual
General Surgery Curriculum Royal Australasian College of Surgeons, General Surgeons Australia & New Zealand Association of General Surgeons
 General Surgery Curriculum Royal Australasian College of Surgeons, General Surgeons Australia & New Zealand Association of General Surgeons MODULE TITLE: ABDOMINAL WALL, RETROPERITONEUM, UROGENITAL 5-May-2013
General Surgery Curriculum Royal Australasian College of Surgeons, General Surgeons Australia & New Zealand Association of General Surgeons MODULE TITLE: ABDOMINAL WALL, RETROPERITONEUM, UROGENITAL 5-May-2013
Prostate Gland Disorders
 Prostate Gland Disorders THE PROSTATE GLAND A male s prostate gland is located in the floor of the pelvis surrounding the urethra between the bladder and the penis. The prostate is positioned immediately
Prostate Gland Disorders THE PROSTATE GLAND A male s prostate gland is located in the floor of the pelvis surrounding the urethra between the bladder and the penis. The prostate is positioned immediately
Female and Male Reproductive Systems
 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System: Produces the female sex hormones Provides female reproductive
Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System: Produces the female sex hormones Provides female reproductive
Find Medical Solutions to Your Problems HYDRONEPHROSIS. (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis)
 HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
