Cutler, Power & Wilder, 1938; Hall & Langley, 1940), in the dog (Winkler &
|
|
|
- Brendan Barnett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 8 J. Physiol. (I948) I07, 8-I3 6I2.46I.6 RENAL EXCRETION OF SODIUM AND POTASSIUM IN RATS BY S. E. DICKER (Beit Memorial Fellow) From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Bristol (Received 30 December 1946) Renal excretion of potassium has been investigated in man (Griffon, 1936; Cutler, Power & Wilder, 1938; Hall & Langley, 1940), in the dog (Winkler & Smith, 1942) and in the cat (Wirz, 1945), but opinions as to its mechanism are divergent. It is not clear from these papers whether the amount of potassium excreted is related to the rate of glomerular filtration. It was, therefore, decided to investigato the mechanism of potassium excretion in rats and to compare it with that of chloride and of sodium. METHODS Experimental animals. Male adult albino rats were used. The animals, before being used, were on a standard diet for several weeks. Experimenta procedures. Inulin was injected subcutaneously and 5% of the body weight of tap water was given by stomach tube. The routine procedure for determining the clearances conformed with that described previously (Dicker & Heller, 1945). Analytical methods. Inulin in plasma and in urine was determined by the method of Smith, Goldring & Chasis (1938). Chloride in plasma was determined by Whitehorn's (1921) method, and in urine by that of Volhard (1878). Sodium in plasma and in urine was determined by the method of McCance & Shipp (1931), and potassium in plasma and in urine by Kramer & Tisdall's method as modified by McCance & Shipp (1933); the empirical factor used in the calculation being that proposed by McCance & Shipp, i.e The inulin preparation used was Inulin (Kerfoot & Co.). Method of calculation. The following formula was used to calculate the tubular reabsorption rate of electrolytes (TE): CIn x E - U x EU =T, where C,, =inulin clearance/min./100 g. =glomerular filtration rate (GoF.R.), EP=concentration of the ion E per 100 c.c. plasma, U =urinary volume/min./100 g. body weight and Eu =concentra. tion of the ion E per 100 c.c. urine. To allow for possible variations of the glomerular filtration rate, T was expressed as percentage of the amount of ion E filtered thus: T C E * Statistical treatment of result. A 'small sample' method was used throughout for the estimation of the significance of means (Fisher, 1944). As the population of the samples was small, the standard deviation was multiplied by /(n/n -1) (Bradford Hill, 1942). Correlation coefficients (r) were calculated according to Mainland (1938). The values for the probability (P) of r and of t were obtained from the Fisher & Yates (1943) tables.
2 RENAL EXCRETION OF Na AND K 9 RESULTS Renal excretion of chloride, sodium and potassium during a water diuresis. It has been shown (Dicker & Heller, 1945) that the G.F.R. of rats does not change significantly during a water diuresis. The mean value for G.F.R. in the present series amounted to *024 c.c./100 g. rat/min. (S.E. of mean of twelve observations). The mean values for the concentration of chloride, sodium and potassium in the plasma were: 274* (9), 283* (9) and (12) mg./100 c.c., respectively. The mean amount of the three ions filtered through the glomeruli was therefore: 1*08 mg./100 g./min. for chloride, 1H12 mg./100 g./min. for sodium and 0 09 mg./100 g./min. for potassium. It will be seen from Fig. 1 that the reabsorption of chloride and that of sodium, expiessed as percentages of the amount of chloride and of sodium filtered, remained unchanged with variations of urine flow ranging from to c.c./100 g./min.; in other words the rates of chloride and of sodium reabsorption (Tca and TNa) remained practically constant at the very low and at the very high rates of urine formation encountered in the experiments. They were independent of the amount of chloride and sodium filtered and of the rate of water reabsorption. The reabsqrption of chloride, expressed as percentage of chloride filtered (TC1) amounted to % (9) and that of sodium (TN.) to / (9) (Table 1). It will be noted that the rate of tubular reabsorption of chloride was significantly different from that of sodium (t = 3 070, P < 0.02). The rate of potassium reabsorption was quite different from that of sodium and of chloride. It was high at low rates of urine flow and low at high rates of urine formation (Fig. 1, A, I). The mean rate of potassium reabsorption, expressed as percentage of the amount df potassium filtered (TK), was %; it was found to be related (a) to the amount of potassium filtered, r =-0940, P <0 001 (coefficient of regression, b =-531); (b) to the rate of water reabsorption (Tw), r = , P < 0-01; and (c) to the urine flow, r = -0887, P < (Table,l). It is thus clear that in rats during a normal water diuresis, the rates of chloride and of sodium reabsorption are independent of the rate of water reabsorption and the rate of urine flow, bat that the rate of potassium reabsorption varies with the rate of water reabsorption and, therefore, with the urinary output. Renal excretion of chloride, sodium and potassium after injection of potassium chloride. To determine how an increase of plasma potassium affects potassium excretion, rats were injected subcutaneously with 041 c.c./100 g. body weight of a 3-0 % KCl solution. Inulin, chloride, sodium and potassium clearances were estimated in the usual way.
3 (quiwfrooifra)h ia a.. i~~~~~~~~~~~. t.4 ( I -2O llad ~ ~ ~~ I. o0 o.-: 6.1 o _~ 6 1A o : 4~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~0 B' 3 a8 o o e 0 I 8 x04 XO4 0 I Ie II..8' ;t * ' 9o,o, o9 4.~~~~~~~~~~4..;o X 0 4 XO 44 I X 0 xo I I-I I < 4 I 4~~~~~4 IWOl 14<, o _4, ; a, 7 6 o 0.0 Ull 9 a * 0 6 4~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~4 4 ~~~~6 0 o 04 C 4 '. D 4. x 0 4 _ x 4 _ x0 44 I 4) y o 8 co Q I' b e~~404 I x ff -P4) 0 4. I No t, co
4 RENAL EXCRETION OF Na AND K 11 TABLE 1 Cl Na K G.F.R. ifitered filtered filtered (c.c./100 g./ (mg./loo g./ (mg./100 g./ (mg./100 g./ min.) mm.) min.) min.) Water diuresis 0* ±0-024 (12) (9) +0*047 (9) ±0*006 (12) After injection of 0 1 c.c./100 g of a 3.0% KCI solution ±0*042 (12) (12) (12) ±0-007 (12), After administration of 5.0 c.c./ g. of 85 mm solution of +0*049 (11) (11) ±04134 (11) (11) NaCl r r between r between rate of between TK and urine To TNa TK TK and K flow (%) (%) (%) Tw filtered and Tr Water diuresis 96* '995 i0 96 (9) (9) (12) After injection of0 1 c.c./ 100 g '660-0O of a 3*0% KCIsolution ±0.57 (12) t028 (12) (12) Afteradministration of5-0c.c./ 97*8 98X O g. of 85 mm solution of (11) ±0-14 (11) ±2-5I (11) NaCl The figures are mean results with standard errors; r = correlation coefficient between the values indicated. Number of experiments in brackets. Such an injection resulted in an increase of potassium and of chloride in the plasma, and had a pronounced diuretic effect. The mean value for the G.F.R. was (12) c.c./100 g./min., a value which is comparable to that observed during a normal water diuresis. The mean plasma chloride amounted to (12) mg./100 g., and the plasma potassium was (12) mg./100 c.c., compared with in normal rats. However, the plasma sodium remained normal ( (12) mg./100 c.c.). The increase in the plasma concentration of chloride and of potassium resulted necessarily in an increase in the amount of these ions filtered. After injection of the KC1 solution the mean amount of chloride filtered per 100 g. body weight per nun. was 1-39 mg., that of potassium 0 11 mg. and that of sodium 1-21 mg. (Table 1). The mean value for the rate of chloride reabsorption, expressed as percentage of the amount of chloride filtered was Tc = 97.4 ± 0-57 % (12), a figure which is significantly different from that obtained during a normal water diuresis (t = 2-258, P <0.05). The mean value for the rate of sodium ' reabsorption was TNa = (12). The difference between the rate of chloride and of sodium reabsorption remained significant, t = 2.806, P <0-02. It is thus clear that both chloride and sodium were reabsorbed at higher rates. than during a normal water diuresis, but that, just as in control rats, the two rates were not the same. The rates of chloride and of sodium reabsorption,
5 12 S. E. DICKER expressed as percentages of the amounts filtered (Tll and TN.) were unaffected by the rate of water reabsorption and that of urine flow, i.e. they remained practically constant at all rates of urine flow encountered. In contrast to the rate of chloride and of sodium reabsorption, the rate of potassium reabsorption, expressed in percentage of the amount of potassium filtered (TK) was found to be significantly correlated with the amount of potassium filtered r = , P <0001 (coefficient of regression, b = 5.27) and with the rate of water reabsorption, r = , P < 002, (Table 1). A comparison with the data obtained during a normal water diuresis shows that the relationship between TK and Tw was no longer the same (r= instead of r = ), but that the degree of relation between the amount of potassium filtered and the rate of potassium reabsorbed remained unaltered (r -0*950 and r ). Renal excretion of chloride, sodium and potassium after the administration of 85 mm solution of NaCl. Inulin, chloride, sodium and potassium clearances were estimated as usual. The weight of 85 mmasolution of NaCl given by stomach tube was 5 % of the rat's body weight. This caused a rise in the rate of water reabsorption and ultimately a decrease in the rate of urine flow (Dicker, 1946). The plasma chloride and sodium levels increased without affecting that of potassium. The mean G.F.R. amounted to (11) c.c./100 g./min. The plasma chloride concentration was (11) mg./100 c.c., a figure which is comparable with that found in rats injected with KCI (t = 1*124, P> 0.2) and the plasma sodium level rose to (11) mg./100 c.c. The plasma potassium concentration was almost the same as that in rats during a water diuresis 234 mg./100 c.c. (t = 0745, P>0.4). The mean amount of chloride filtered per min. per 100 g. rat was 3-01 mg., that of sodium was 3 04 mg. and that of potassium 0-22 mg. (Table 1). The rates of chloride and of sodium reabsorption expressed as percentages of the amount of chloride and of sodium filtered (Tci and TNa) did not change with changes of urine flow and were independent of the rate of water reabsorption (Tw). The mean value for Tci was % (11) and that for TNa % (11). These values do not differ significantly from those for TcI and TNa in rats given KCO solution (t = 0-560, P > 0-6 and t = 1-869, P > 0 05, respectively) though the amounts of chloride and of sodium filtered were significantly higher (Table 1). The rate of potassium reabsorption (TK) was no longer significantly correlated with the rate of water reabsorption r = , P >0 1. The amounts of potassium reabsorbed were much higher than in the other two series but remained closely correlated with the amount of potassium filtered r =-0955, P <0001 (coefficient of regression, b =-489) (Table 1).
6 RENAL EXCRElTION OF Na AND K DISCUSSION The mechanism of renal excretion of potassium in rats has been found to be the same as that observed in aogs by Winkler & Smith (1942). During a normal water diuresis the amount of potassium reabsorbed proved to be closely correlated with the amount of potassium filtered. This correlation persisted when the amount of potassium filtered was raised either by increasing the level of potassium in the plasma or by increasinxg the glomerular filtration rate -as after administration of a 85 mm solution of NaCl. The mechanism of renal potassium excretion in rats stands thus in complete contraist to the mechanism of renal excretion of other ions like chloride and sodium. SUMMARY 1. The renal excretion of chloride, sodium and potassium in rats was investigated with the aid of inulin clearances: (a) during a water diuresis, (b) after injection of 0.1 c.c./100 g. body weight of a 3 0% KCl solution, and (c) after administration of 5*0 c.c./100 g. body weight of a 85 mm solution of NaCl. 2. The rates of chloride and of sodium reabsorption were significantly different, and independent of the urine flow and of the rate of water reabsorption. No correlation could be found between the rate of chloride and of sodium reabsorption by the tubules and the amount of chloride and of sodium filtered. 3. During a water diuresis the rate of potassium reabsorption was correlated with the amount of potassium filtered per unit time. This correlation persisted when the amount of potassium filtered was raised either ty increasing the level of potassium in the plasma or by increasing the glomerular filtration rate. 4. The reabsorption of potassium does not passively follow that of water. The expenses ofthis investigation were defrayed by agrant from the Colston Research Committee. This help is gratefillly acknowledged. REFERENCES Bradford Hill, A. (1942). Principles of Medical Statistics, 3rd ed., p London: The Lancet. Cutler, H. H., Power, M. H. & Wilder, R. M. (1938). J. Amer. med. Ass. 111, 117. Dicker, S. E. (1946). Brit. J. Pharmacol. Chemother. 1, 194. Dicker, S. E. & Heller, H. (1945). J. Physiol. 103, 449. Fisher, R. A. (1944). Statistical Method for Research Workers, 9th ed. London: Oliver and Boyd. aisher, R. A. & Yates, F. (1943). Statistical Tables for Biological, Agricultural and Medical Research, 2nd ed. London: Oliver and Boyd. Griffon, H. (1936). C.R. Soc. Biol., Paris, 121, 47. Hall, V. E. & Langley, L. L. (1940). Proc. Soc. exp. Biol., N.Y., 44, 425. Mainland, D. (1938). The Treatment of Clinical and Laboratory Data, 1st ed. London: Oliver and Boyd. McCance, R. A. & Shipp, H. L. (1931). Biochem. J. 25, 449. McCance, R. A. & Shipp, H. L. (1933). Spec. Rep. Ser. med. Res. Coun., Lond., 187, 35. Smith, H. W., Goldring, W. & Chasis, H. (1938). J. din. Invest. 17, 263. Volhard, J. (1878). Z. anal. Chem. 17, 482. Whitehorn, J. C. (1921). J. biol. Chem. 45, 449. Winkler, A. W. & Smith, P. K. (1942). Amer. J. Physiol. 138, 94. Wirz, H. (1945). Helv. physiol. pharmacol. Acta, 3,
THEOPHYLLINE SODIUM ACETATE ON
 Brit. J. Pharmacol., 1946, 1, 194. THE ACTION OF MERSALYL, CALOMEL AND THEOPHYLLINE SODIUM ACETATE ON THE KIDNEY OF THE RAT BY S. E. DICKER From the Department of Pharnmacology, University of Bristol (Received
Brit. J. Pharmacol., 1946, 1, 194. THE ACTION OF MERSALYL, CALOMEL AND THEOPHYLLINE SODIUM ACETATE ON THE KIDNEY OF THE RAT BY S. E. DICKER From the Department of Pharnmacology, University of Bristol (Received
From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Bristol (Received 5 April 1948)
 197 J. Physiol. (I949) io8, I97-202 6I2.398.I45:6I2.46 EFFECT OF THE PROTEIN CONTENT OF THE DIET ON THE GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE OF YOUNG AND ADULT RATS BY S. E. DICKER From the Department of Pharmacology,
197 J. Physiol. (I949) io8, I97-202 6I2.398.I45:6I2.46 EFFECT OF THE PROTEIN CONTENT OF THE DIET ON THE GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE OF YOUNG AND ADULT RATS BY S. E. DICKER From the Department of Pharmacology,
CONCERNING THE EFFECTS OF MAGNESIUM SULFATE ON RENAL FUNCTION, ELECTROLYTE EXCRETION, AND CLEARANCE OF MAGNESIUM
 CONCERNING THE EFFECTS OF MAGNESIUM SULFATE ON RENAL FUNCTION, ELECTROLYTE EXCRETION, AND CLEARANCE OF MAGNESIUM B. I. Heller,, J. F. Hammarsten, F. L. Stutzman J Clin Invest. 1953;32(9):858-861. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci102803.
CONCERNING THE EFFECTS OF MAGNESIUM SULFATE ON RENAL FUNCTION, ELECTROLYTE EXCRETION, AND CLEARANCE OF MAGNESIUM B. I. Heller,, J. F. Hammarsten, F. L. Stutzman J Clin Invest. 1953;32(9):858-861. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci102803.
MIGUEL CHIAPPORI 4. Renal function. Twelve healthy Peruvian males between the ages of 20 and 28 years were studied. None
 ORAL SODIUM LOADING IN NORMAL INDIVIDUALS By KEHL MARKLEY,1 MANUEL BOCANEGRA,2 GUILLERMO MORALES,3 AND MIGUEL CHIAPPORI 4 (From the U. S. Public Health Service, U. S. Department of Health, Education, and
ORAL SODIUM LOADING IN NORMAL INDIVIDUALS By KEHL MARKLEY,1 MANUEL BOCANEGRA,2 GUILLERMO MORALES,3 AND MIGUEL CHIAPPORI 4 (From the U. S. Public Health Service, U. S. Department of Health, Education, and
(ethanol) suggests that it is similar to the diuresis following ingestion of water.
 435 J. Physiol. (I946) I04, 435-442 6I2.464.I THE EFFECT OF ETHYL ALCOHOL AND SOME OTHER DIURETICS ON CHLORIDE EXCRETION IN MAN BY M. GRACE EGGLETON AND ISABEL G. SMITH, From the Physiology Department,
435 J. Physiol. (I946) I04, 435-442 6I2.464.I THE EFFECT OF ETHYL ALCOHOL AND SOME OTHER DIURETICS ON CHLORIDE EXCRETION IN MAN BY M. GRACE EGGLETON AND ISABEL G. SMITH, From the Physiology Department,
Medicine, Cambridge, England, and Wuppertal, B.A.O.R.
 182 J. Physiol. (I948) I07, i82-i86 6I2.46I.62 PHOSPHATE CLEARANCES IN INFANTS AND ADULTS BY R. F. A. DEAN AND R. A. McCANCE From the Medical Research Council, Department. of Experimental Medicine, Cambridge,
182 J. Physiol. (I948) I07, i82-i86 6I2.46I.62 PHOSPHATE CLEARANCES IN INFANTS AND ADULTS BY R. F. A. DEAN AND R. A. McCANCE From the Medical Research Council, Department. of Experimental Medicine, Cambridge,
(Received 23 January 1961) Crawford & Kennedy (1959) found the prolonged saluretic and diuretic
 454 J. Phyeiol. (1961), 157, pp. 454-461 With 3 text-figure Printed in Great Britain THE ACTION OF CHLOROTHIAZIDE IN THE PERFUSED CAT KIDNEY BY T. DE LIMA AND MARY F. LOCKETT From the Department of Physiology
454 J. Phyeiol. (1961), 157, pp. 454-461 With 3 text-figure Printed in Great Britain THE ACTION OF CHLOROTHIAZIDE IN THE PERFUSED CAT KIDNEY BY T. DE LIMA AND MARY F. LOCKETT From the Department of Physiology
Chapter 23. Composition and Properties of Urine
 Chapter 23 Composition and Properties of Urine Composition and Properties of Urine (1 of 2) urinalysis the examination of the physical and chemical properties of urine appearance - clear, almost colorless
Chapter 23 Composition and Properties of Urine Composition and Properties of Urine (1 of 2) urinalysis the examination of the physical and chemical properties of urine appearance - clear, almost colorless
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology
 Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Functional morphology of kidneys Clearance
 Functional morphology of kidneys Clearance Assoc. Prof. MUDr. Markéta Bébarová, Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University This presentation includes only the most important
Functional morphology of kidneys Clearance Assoc. Prof. MUDr. Markéta Bébarová, Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University This presentation includes only the most important
(Received 10 June 1948)
 33 J. Physiol. (I949) Io8, 33-3I4 6I2.391:612.14.46I.3 EFFECTS OF DEHYDRATION ON ADULT AND NEWBORN RATS BY H. HELLER From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Bristol (Received 1 June 1948) There
33 J. Physiol. (I949) Io8, 33-3I4 6I2.391:612.14.46I.3 EFFECTS OF DEHYDRATION ON ADULT AND NEWBORN RATS BY H. HELLER From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Bristol (Received 1 June 1948) There
clamped. At 30- or 60-minute intervals urine specimens were collected and the bladder washed out with saline
 Downloaded from http://www.jci.org on January 11, 218. https://doi.org/1.1172/jci11171 THE MECHANISM OF THE EXCRETION OF VITAMIN C BY THE HUMAN KIDNEY AT LOW AND NORMAL PLASMA LEVELS OF ASCORBIC ACID 1
Downloaded from http://www.jci.org on January 11, 218. https://doi.org/1.1172/jci11171 THE MECHANISM OF THE EXCRETION OF VITAMIN C BY THE HUMAN KIDNEY AT LOW AND NORMAL PLASMA LEVELS OF ASCORBIC ACID 1
simultaneously excreted. They also brought forward some evidence to
 THE EXCRETION OF CHLORIDES AND BICARBON- ATES BY THE HUMAN KIDNEY. BY H. W. DAVIES, M.B., B.S., J. B. S. HALDANE, M.A. AND G. L. PESKETT, B.A. (From the Laboratory, Cherwell, Oxford.) AM BARD and PAPI
THE EXCRETION OF CHLORIDES AND BICARBON- ATES BY THE HUMAN KIDNEY. BY H. W. DAVIES, M.B., B.S., J. B. S. HALDANE, M.A. AND G. L. PESKETT, B.A. (From the Laboratory, Cherwell, Oxford.) AM BARD and PAPI
The kidney. (Pseudo) Practical questions. The kidneys are all about keeping the body s homeostasis. for questions Ella
 The kidney (Pseudo) Practical questions for questions Ella (striemit@gmail.com) The kidneys are all about keeping the body s homeostasis Ingestion Product of metabolism H 2 O Ca ++ Cl - K + Na + H 2 O
The kidney (Pseudo) Practical questions for questions Ella (striemit@gmail.com) The kidneys are all about keeping the body s homeostasis Ingestion Product of metabolism H 2 O Ca ++ Cl - K + Na + H 2 O
THE WATER-BALANCE PRINCIPLE OF CRUSTACEAN EYE-STALK EXTRACTS
 [388] THE WATER-BALANCE PRINCIPLE OF CRUSTACEAN EYE-STALK EXTRACTS BY H. HELLER AND B. SMITH From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Bristol (Received 15 August 1948) (With Four Text-figurea)
[388] THE WATER-BALANCE PRINCIPLE OF CRUSTACEAN EYE-STALK EXTRACTS BY H. HELLER AND B. SMITH From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Bristol (Received 15 August 1948) (With Four Text-figurea)
Lund, 1948), the effect of which was to produce glomerular lesions without. relationship between increased protein loads and the tubular reabsorption
 544 J. Phy8iol. (1961), 156, pp. 544-554 With 5 text-ftgure8 Printed in Great Britain TUBULAR REABSORPTION OF PROTEIN IN RATS WITH EXPERIMENTAL PROTEINURIA BY D. MENDEL* From the Department of Physiology,
544 J. Phy8iol. (1961), 156, pp. 544-554 With 5 text-ftgure8 Printed in Great Britain TUBULAR REABSORPTION OF PROTEIN IN RATS WITH EXPERIMENTAL PROTEINURIA BY D. MENDEL* From the Department of Physiology,
kenal EFFECTS OF PROTEIN-DEFICIENT VEGETABLE DIETS: A FUNCTIONAL AND HISTOLOGICAL STIIDY.
 158 kenal EFFECTS OF PROTEIN-DEFICIENT VEGETABLE DIETS: A FUNCTIONAL AND HISTOLOGICAL STIIDY. S. E. DICKER, H. HELLER AND T. F. HEWER. From the Departments of Pharmacology and Pathology, University of
158 kenal EFFECTS OF PROTEIN-DEFICIENT VEGETABLE DIETS: A FUNCTIONAL AND HISTOLOGICAL STIIDY. S. E. DICKER, H. HELLER AND T. F. HEWER. From the Departments of Pharmacology and Pathology, University of
(Received 27 September 1937)
 222 J. Physiol. (I937) 9I, 222-23I 6I2.46I:6I2.392.6 THE SECRETION OF URINE IN MAN DURING EXPERIMENTAL SALT DEFICIENCY BY R. A. McCANCE AND E. M. WIDDOWSON From the Biochemical Laboratory, King's College
222 J. Physiol. (I937) 9I, 222-23I 6I2.46I:6I2.392.6 THE SECRETION OF URINE IN MAN DURING EXPERIMENTAL SALT DEFICIENCY BY R. A. McCANCE AND E. M. WIDDOWSON From the Biochemical Laboratory, King's College
dynamic action of ingested amino acids effected
 THE.EFFECT OF GLYCINE ON THE PRODUCTION AND EXCRETION OF URIC ACID1 BY MEYER FRIEDMAN (Fromn the Harold Brunn Institute for Cardiovascular Research, San Francisco, California) Mt. Zion Hospital, (Received
THE.EFFECT OF GLYCINE ON THE PRODUCTION AND EXCRETION OF URIC ACID1 BY MEYER FRIEDMAN (Fromn the Harold Brunn Institute for Cardiovascular Research, San Francisco, California) Mt. Zion Hospital, (Received
hold for the human kidney.2 Shannon and Smith (4) have rightfully stressed
 THE RENAL EXCRETION OF INULIN AT LOW PLASMA CONCEN- TRATIONS OF THIS COMPOUND, AND ITS RELATIONSHIP TO THE GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE IN NORMAL, NEPHRITIC AND HYPERTENSIVE INDIVIDUALS' By BENJAMIN F. MILLER,
THE RENAL EXCRETION OF INULIN AT LOW PLASMA CONCEN- TRATIONS OF THIS COMPOUND, AND ITS RELATIONSHIP TO THE GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE IN NORMAL, NEPHRITIC AND HYPERTENSIVE INDIVIDUALS' By BENJAMIN F. MILLER,
Pressure Diuresis 9 Sample Student Essays
 Pressure Diuresis 9 Sample Student Essays Below please find assembled consecutively in one document the brief analyses submitted by nine students in Mammalian Physiology 08 to the Teach Yourself Pressure
Pressure Diuresis 9 Sample Student Essays Below please find assembled consecutively in one document the brief analyses submitted by nine students in Mammalian Physiology 08 to the Teach Yourself Pressure
ance of the sugar, until at plasma levels of 140 mgm. per cent the creatinine/sugar clearance ratio
 THE RENAL EXCRETION OF CREATININE IN MAN BY JAMES A. SHANNON 1 (From The Department of Physiology, New York University College of Medicine, New York City) In a previous paper the evidence on the excretion
THE RENAL EXCRETION OF CREATININE IN MAN BY JAMES A. SHANNON 1 (From The Department of Physiology, New York University College of Medicine, New York City) In a previous paper the evidence on the excretion
Renal Function. 1. Glomerular filtration 2. Active tubular secretion 3. Passive tubular reabsorption 4. Excretion
 59-291 Section 1, Lecture 5 Drug Excretion -most drugs are excreted in urine either as unchanged or drug metabolites Renal Function 1. Glomerular filtration 2. Active tubular secretion 3. Passive tubular
59-291 Section 1, Lecture 5 Drug Excretion -most drugs are excreted in urine either as unchanged or drug metabolites Renal Function 1. Glomerular filtration 2. Active tubular secretion 3. Passive tubular
A. Correct! Flushing acids from the system will assist in re-establishing the acid-base equilibrium in the blood.
 OAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following would solve a drop in blood ph? Question #01 (A) Decreased retention of acids. (B) Increased excretion
OAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following would solve a drop in blood ph? Question #01 (A) Decreased retention of acids. (B) Increased excretion
MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION AND PREPONDERANCE OF A VENTRICLE
 POTASSIUM EFFECTS ON T WAVE INVERSION IN MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION AND PREPONDERANCE OF A VENTRICLE BY E. P. SHARPEY-SCHAFER From the Department of Medicine, British Postgraduate Medical School, London Received
POTASSIUM EFFECTS ON T WAVE INVERSION IN MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION AND PREPONDERANCE OF A VENTRICLE BY E. P. SHARPEY-SCHAFER From the Department of Medicine, British Postgraduate Medical School, London Received
Urinary freezing-point depressions (A) were estimated with a Beckmann
 J. Physiol. (I944) I02, 429-440 6I2.648.046 THE RENAL FUNCTION OF NEWBORN INFANTS 429 BY H. HELLER, From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Bristol (Received 31 July 1943) In a recent paper
J. Physiol. (I944) I02, 429-440 6I2.648.046 THE RENAL FUNCTION OF NEWBORN INFANTS 429 BY H. HELLER, From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Bristol (Received 31 July 1943) In a recent paper
NATURAL HISTORY AND SURVIVAL OF PATIENTS WITH ASCITES. PATIENTS WHO DO NOT DEVELOP COMPLICATIONS HAVE MARKEDLY BETTER SURVIVAL THAN THOSE WHO DEVELOP
 PROGNOSIS Mortality rates as high as 18-30% are reported for hyponatremic patients. High mortality rates reflect the severity of underlying conditions and are not influenced by treatment of hyponatremia
PROGNOSIS Mortality rates as high as 18-30% are reported for hyponatremic patients. High mortality rates reflect the severity of underlying conditions and are not influenced by treatment of hyponatremia
EFFECTS OF PROBENECID, SODIUM SALICYLATE, 2,4-DINITROPHENOL AND PYRAZINAMIDE ON RENAL SECRETION OF URIC ACID IN CHICKENS
 8189 EFFECTS OF PROBENECID, SODIUM SALICYLATE, 2,4-DINITROPHENOL AND PYRAZINAMIDE ON RENAL SECRETION OF URIC ACID IN CHICKENS BOHDAN R. NECHAY AND LARYSSA NECHAY Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics,
8189 EFFECTS OF PROBENECID, SODIUM SALICYLATE, 2,4-DINITROPHENOL AND PYRAZINAMIDE ON RENAL SECRETION OF URIC ACID IN CHICKENS BOHDAN R. NECHAY AND LARYSSA NECHAY Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics,
Urinary System. consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra
 Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
14). Heparin (1 per cent) was used as an anticoagulant;
 THE MECHANISM OF THE EXCRETION OF VITAMIN C BY THE HUMAN KIDNEY 1 BY ELAINE P. RALLI, GERALD J. FRIEDMAN AND SAUL H. RUBIN (From the Department of Medicine, New York University College of Medicine, and
THE MECHANISM OF THE EXCRETION OF VITAMIN C BY THE HUMAN KIDNEY 1 BY ELAINE P. RALLI, GERALD J. FRIEDMAN AND SAUL H. RUBIN (From the Department of Medicine, New York University College of Medicine, and
Estimation of Serum Creatinine, Urine Creatinine and Creatinine Clearance. BCH472 [Practical] 1
![Estimation of Serum Creatinine, Urine Creatinine and Creatinine Clearance. BCH472 [Practical] 1 Estimation of Serum Creatinine, Urine Creatinine and Creatinine Clearance. BCH472 [Practical] 1](/thumbs/73/68933269.jpg) Estimation of Serum Creatinine, Urine Creatinine and Creatinine Clearance BCH472 [Practical] 1 -Kidney functions: - The kidneys serve three essential functions: 1. They function as filters, removing metabolic
Estimation of Serum Creatinine, Urine Creatinine and Creatinine Clearance BCH472 [Practical] 1 -Kidney functions: - The kidneys serve three essential functions: 1. They function as filters, removing metabolic
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D.
 RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
Using a technique by which it is possible to study gastro-intestinal absorption
 531 J. Physiol. (I956) I34, 53I-537 THE ABSORPTION OF GLUCOSE BY THE INTACT RAT BY P. C. REYNELL AND G. H. SPRAY From the Nuffield Department of Clinical Medicine, University of Oxford (Received 30 May
531 J. Physiol. (I956) I34, 53I-537 THE ABSORPTION OF GLUCOSE BY THE INTACT RAT BY P. C. REYNELL AND G. H. SPRAY From the Nuffield Department of Clinical Medicine, University of Oxford (Received 30 May
Introduction to the kidney: regulation of sodium & glucose. Dr Nick Ashton Senior Lecturer in Renal Physiology Faculty of Biology, Medicine & Health
 Introduction to the kidney: regulation of sodium & glucose Dr Nick Ashton Senior Lecturer in Renal Physiology Faculty of Biology, Medicine & Health Objectives Overview of kidney structure & function Glomerular
Introduction to the kidney: regulation of sodium & glucose Dr Nick Ashton Senior Lecturer in Renal Physiology Faculty of Biology, Medicine & Health Objectives Overview of kidney structure & function Glomerular
Glomerular Filtration Rate. Hui Li, PhD, FCACB, DABCC
 Glomerular Filtration Rate Hui Li, PhD, FCACB, DABCC Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR): Amount of blood that is filtered per unit time through glomeruli. It is a measure of the function of kidneys. The
Glomerular Filtration Rate Hui Li, PhD, FCACB, DABCC Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR): Amount of blood that is filtered per unit time through glomeruli. It is a measure of the function of kidneys. The
The technique of multiple clearance was chosen. because it supplied us with the filtration rate, the
 RENAL REABSORPTION OF CHLORIDE AND PHOSPHATE IN NORMAL SUBJECTS AND IN PATIENTS WITH ESSENTIAL ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION' By EDITH B. FARNSWORTH (From the Department of Medicine, Northwestern University Medical
RENAL REABSORPTION OF CHLORIDE AND PHOSPHATE IN NORMAL SUBJECTS AND IN PATIENTS WITH ESSENTIAL ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION' By EDITH B. FARNSWORTH (From the Department of Medicine, Northwestern University Medical
J. Physiol. (I944) I02; :6I2.0I4.46I.2
 415 J. Physiol. (I944) I02; 45-428 612.463:6I2.0I4.46I.2 THE SECRETION OF URINE DURING DEHYDRATION AND REHYDRATION BY R. A. McCANCE AND W. F. YOUNG WITH THE ASSISTANCE OF D. A. K. BLACK From the Department
415 J. Physiol. (I944) I02; 45-428 612.463:6I2.0I4.46I.2 THE SECRETION OF URINE DURING DEHYDRATION AND REHYDRATION BY R. A. McCANCE AND W. F. YOUNG WITH THE ASSISTANCE OF D. A. K. BLACK From the Department
You should know the T max for any substance that you use and for PAH ; T max = mg / min
 Tubular function - What is clearance? o clearance referred to the theoretical volume of plasma from which a substance is cleared ( cleaned ) over a period of time and so its unit would be ((ml/min)) -
Tubular function - What is clearance? o clearance referred to the theoretical volume of plasma from which a substance is cleared ( cleaned ) over a period of time and so its unit would be ((ml/min)) -
Excretion Chapter 29. The Mammalian Excretory System consists of. The Kidney. The Nephron: the basic unit of the kidney.
 Excretion Chapter 29 The Mammalian Excretory System consists of The Kidney 1. Vertebrate kidneys perform A. Ion balance B. Osmotic balance C. Blood pressure D. ph balance E. Excretion F. Hormone production
Excretion Chapter 29 The Mammalian Excretory System consists of The Kidney 1. Vertebrate kidneys perform A. Ion balance B. Osmotic balance C. Blood pressure D. ph balance E. Excretion F. Hormone production
Renal Reabsorption & Secretion
 Renal Reabsorption & Secretion Topics for today: Nephron processing of filtrate Control of glomerular filtration Reabsorption and secretion Examples of solute clearance rates Hormones affecting kidney
Renal Reabsorption & Secretion Topics for today: Nephron processing of filtrate Control of glomerular filtration Reabsorption and secretion Examples of solute clearance rates Hormones affecting kidney
Mannitol-induced Metabolic Alkalosis
 Electrolyte & Blood Pressure :, 00 ) Mannitolinduced Metabolic Alkalosis Kyung Pyo Kang, M.D., Sik Lee, M.D., Kyung Hoon Lee, M.D., and Sung Kyew Kang, M.D. Department of Internal Medicine, Research Institute
Electrolyte & Blood Pressure :, 00 ) Mannitolinduced Metabolic Alkalosis Kyung Pyo Kang, M.D., Sik Lee, M.D., Kyung Hoon Lee, M.D., and Sung Kyew Kang, M.D. Department of Internal Medicine, Research Institute
College of Medicine, Newcastle-upon-Tyne.)
 GLUCOSE ABSORPTION IN THE RENAL TUBULES OF THE FROG. BY G. A. CLARK. (From the Physiological Laboratory of the University of Durham College of Medicine, Newcastle-upon-Tyne.) OPINION is divided on the
GLUCOSE ABSORPTION IN THE RENAL TUBULES OF THE FROG. BY G. A. CLARK. (From the Physiological Laboratory of the University of Durham College of Medicine, Newcastle-upon-Tyne.) OPINION is divided on the
Renal Physiology - Lectures
 Renal Physiology - Lectures Physiology of Body Fluids PROBLEM SET, RESEARCH ARTICLE Structure & Function of the Kidneys Renal Clearance & Glomerular Filtration PROBLEM SET Regulation of Renal Blood Flow
Renal Physiology - Lectures Physiology of Body Fluids PROBLEM SET, RESEARCH ARTICLE Structure & Function of the Kidneys Renal Clearance & Glomerular Filtration PROBLEM SET Regulation of Renal Blood Flow
hydrocortisone (cortisol) appeared to increase potassium excretion without
 J. Phy8iol. (1961), 156, pp. 415-423 415 With 1 text-figure Printed in Great Britain THE EFFECTS OF INTRAVENOUS ALDOSTERONE AND HYDRORTISONE ON THE URINARY ELECTROLYTES OF THE RECUMBENT HUMAN SUBJECT BY
J. Phy8iol. (1961), 156, pp. 415-423 415 With 1 text-figure Printed in Great Britain THE EFFECTS OF INTRAVENOUS ALDOSTERONE AND HYDRORTISONE ON THE URINARY ELECTROLYTES OF THE RECUMBENT HUMAN SUBJECT BY
The principal functions of the kidneys
 Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Chapter 21. Diuretic Agents. Mosby items and derived items 2008, 2002 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 21 Diuretic Agents Renal Structure and Function Kidneys at level of umbilicus Each weighs 160 to 175 g and is 10 to 12 cm long Most blood flow per gram of weight in body 22% of cardiac output (CO)
Chapter 21 Diuretic Agents Renal Structure and Function Kidneys at level of umbilicus Each weighs 160 to 175 g and is 10 to 12 cm long Most blood flow per gram of weight in body 22% of cardiac output (CO)
Medicine, Kyoto City, Japan
 23 J. Physiol. (I959) I49, 23-33 SEASONAL VARIATIONS IN SERUM INORGANIC PHOSPHATE AND CALCIUM WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO PARATHYROID ACTIVITY BY M. IWANAMI, S. OSIBA, T. YAMADA AND H. YOSHIMURA From the
23 J. Physiol. (I959) I49, 23-33 SEASONAL VARIATIONS IN SERUM INORGANIC PHOSPHATE AND CALCIUM WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO PARATHYROID ACTIVITY BY M. IWANAMI, S. OSIBA, T. YAMADA AND H. YOSHIMURA From the
Physio 12 -Summer 02 - Renal Physiology - Page 1
 Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
Renal System Physiology
 M58_MARI0000_00_SE_EX09.qxd 7/18/11 2:37 PM Page 399 E X E R C I S E 9 Renal System Physiology Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Prior to the lab, suggest to the students that they become familiar with the
M58_MARI0000_00_SE_EX09.qxd 7/18/11 2:37 PM Page 399 E X E R C I S E 9 Renal System Physiology Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Prior to the lab, suggest to the students that they become familiar with the
BIOL 2402 Renal Function
 BIOL 2402 Renal Function Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College 1 Renal Clearance and GFR Refers to the volume of blood plasma from which a component is completely removed in one minute by all
BIOL 2402 Renal Function Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College 1 Renal Clearance and GFR Refers to the volume of blood plasma from which a component is completely removed in one minute by all
Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization,
 J. Phy8iol. (1966), 184, pp. 65-617 65 With 5 text-ftgures Printed in Great Britain THE EFFECT OF AN INTRAVENOUS INFUSION OF HYPER- TONIC SALINE ON RENAL MECHANISMS AND ON ELECTROLYTE CHANGES IN SHEEP
J. Phy8iol. (1966), 184, pp. 65-617 65 With 5 text-ftgures Printed in Great Britain THE EFFECT OF AN INTRAVENOUS INFUSION OF HYPER- TONIC SALINE ON RENAL MECHANISMS AND ON ELECTROLYTE CHANGES IN SHEEP
test. Urine was collected every 10 to 30 minutes over a period of approximately 3 hours. Typhoid vaccine (75,-
 THE URINARY EXCRETION OF SODIUM AND POTASSIUM DURING THE PYROGENIC REACTION IN MAN 1, 2 By WILLOUGHBY LATHEM 8 (From the Veterans Administration Hospital, West Haven, Connecticut, and The Department of
THE URINARY EXCRETION OF SODIUM AND POTASSIUM DURING THE PYROGENIC REACTION IN MAN 1, 2 By WILLOUGHBY LATHEM 8 (From the Veterans Administration Hospital, West Haven, Connecticut, and The Department of
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
Excretion of Drugs. Prof. Hanan Hagar Pharmacology Unit Medical College
 Excretion of Drugs Prof. Hanan Hagar Pharmacology Unit Medical College Excretion of Drugs By the end of this lecture, students should be able to! Identify main and minor routes of excretion including renal
Excretion of Drugs Prof. Hanan Hagar Pharmacology Unit Medical College Excretion of Drugs By the end of this lecture, students should be able to! Identify main and minor routes of excretion including renal
Hypoparathyroid Patients *
 Journal of Clinical Investigation Vol. 44, No. 6, 1965 Effects of Serum Calcium Level and Parathyroid Extracts on Phosphate and Calcium Excretion in Hypoparathyroid Patients * EUGENE EISENBERG t (From
Journal of Clinical Investigation Vol. 44, No. 6, 1965 Effects of Serum Calcium Level and Parathyroid Extracts on Phosphate and Calcium Excretion in Hypoparathyroid Patients * EUGENE EISENBERG t (From
Renal Pharmacology. Diuretics: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Thiazides Loop Diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics BIMM118
 Diuretics: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Thiazides Loop Diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive ~25% of the total arterial blood
Diuretics: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Thiazides Loop Diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive ~25% of the total arterial blood
Filtration and Reabsorption Amount Filter/d
 Renal Physiology 2011 Lisa M. Harrison-Bernard, PhD Contact me at lharris@lsuhsc.edu Renal Physiology Lecture 3 Renal Clearance and Glomerular Filtration Filtration and Reabsorption Amount Filter/d Amount
Renal Physiology 2011 Lisa M. Harrison-Bernard, PhD Contact me at lharris@lsuhsc.edu Renal Physiology Lecture 3 Renal Clearance and Glomerular Filtration Filtration and Reabsorption Amount Filter/d Amount
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST
 014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
BCH472 [Practical] 1
![BCH472 [Practical] 1 BCH472 [Practical] 1](/thumbs/90/103504023.jpg) BCH472 [Practical] 1 1. They function as filters, removing metabolic products and toxins from the blood and excreting them through the urine. 2. They regulate the body s fluid status, electrolyte balance,
BCH472 [Practical] 1 1. They function as filters, removing metabolic products and toxins from the blood and excreting them through the urine. 2. They regulate the body s fluid status, electrolyte balance,
Renal Physiology II Tubular functions
 Renal Physiology II Tubular functions LO. 42, 43 Dr. Kékesi Gabriella Basic points of renal physiology 1. Glomerular filtration (GF) a) Ultrafiltration 2. Tubular functions active and passive a) Reabsorption
Renal Physiology II Tubular functions LO. 42, 43 Dr. Kékesi Gabriella Basic points of renal physiology 1. Glomerular filtration (GF) a) Ultrafiltration 2. Tubular functions active and passive a) Reabsorption
ADRENALECTOMIZED rats drink less than normal rats when 2 per cent saline. daily by stomach tube and water to drink freely, died quickly but such
 THE EFFECT OF PROLONGED INTRAGASTRIC INFUSIONS OF ISOTONIC AND HYPERTONIC SALINE ON WATER AND SODIUM EXCRETION AND ON EXCHANGEABLE BODY SODIUM IN NORMAL AND ADRENALECTOMIZED RATS. By C. J. EDMONDS. From
THE EFFECT OF PROLONGED INTRAGASTRIC INFUSIONS OF ISOTONIC AND HYPERTONIC SALINE ON WATER AND SODIUM EXCRETION AND ON EXCHANGEABLE BODY SODIUM IN NORMAL AND ADRENALECTOMIZED RATS. By C. J. EDMONDS. From
KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin
![KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin](/thumbs/87/96174332.jpg) Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
Renal Clearance. Dr. Eman El Eter
 Renal Clearance Dr. Eman El Eter Concept of clearance Clearance is the volume of plasma that is completely cleared of a substance each minute. Example: Renal clearance of Substance X is defined as the
Renal Clearance Dr. Eman El Eter Concept of clearance Clearance is the volume of plasma that is completely cleared of a substance each minute. Example: Renal clearance of Substance X is defined as the
Renal Excretion of Drugs
 Renal Excretion of Drugs 3 1 Objectives : 1 Identify main and minor routes of Excretion including renal elimination and biliary excretion 2 Describe its consequences on duration of drugs. For better understanding:
Renal Excretion of Drugs 3 1 Objectives : 1 Identify main and minor routes of Excretion including renal elimination and biliary excretion 2 Describe its consequences on duration of drugs. For better understanding:
Ch 19: The Kidneys. Functional unit of kidneys:?? Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM
 Ch 19: The Kidneys Homeostatic regulation of ECF volume and BP Osmolarity 290 mosm Ion balance Na+ and K+, etc. ph (acid-base balance Excretion of wastes & foreign substances Hormone production EPO Renin
Ch 19: The Kidneys Homeostatic regulation of ECF volume and BP Osmolarity 290 mosm Ion balance Na+ and K+, etc. ph (acid-base balance Excretion of wastes & foreign substances Hormone production EPO Renin
Effect of an Intravenous Sodium Chloride Load on Renal Hemodynamics and Electrolyte Excretion in Essential Hypertension
 Effect of an Intravenous Sodium Chloride Load on Renal Hemodynamics and Electrolyte Excretion in Essential Hypertension BY PAUL T. COTTIER, M.D., JOHN M. WELLER, M.D., AND SIBLEY W. HOOBLER, M.D. Excretion
Effect of an Intravenous Sodium Chloride Load on Renal Hemodynamics and Electrolyte Excretion in Essential Hypertension BY PAUL T. COTTIER, M.D., JOHN M. WELLER, M.D., AND SIBLEY W. HOOBLER, M.D. Excretion
THE ACTION OF ANTISYMPATHOMIMETIC DRUGS ON THE URINARY EXCRETION OF ADRENALINE AND NORADRENALINE
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1959), 14, 380. THE ACTION OF ANTISYMPATHOMIMETIC DRUGS ON THE URINARY EXCRETION OF ADRENALINE AND NORADRENALINE BY B. G. BENFEY, G. LEDOUX, AND M. SEGAL From the Department ofpharmacology,
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1959), 14, 380. THE ACTION OF ANTISYMPATHOMIMETIC DRUGS ON THE URINARY EXCRETION OF ADRENALINE AND NORADRENALINE BY B. G. BENFEY, G. LEDOUX, AND M. SEGAL From the Department ofpharmacology,
Patients studied and experimental procedures followed The patients studied in our experiments were 3 nephrotic
 THE RELATION OF HIGH AND LOW UREA CLEARANCES TO THE INULIN AND CREATININE CLEARANCES IN CHIL- DREN WITH THE NEPHROTIC SYNDROME BY KENDALL EMERSON, JR., PALMER H. FUTCHER, AND LEE E. FARR (From the Hospital
THE RELATION OF HIGH AND LOW UREA CLEARANCES TO THE INULIN AND CREATININE CLEARANCES IN CHIL- DREN WITH THE NEPHROTIC SYNDROME BY KENDALL EMERSON, JR., PALMER H. FUTCHER, AND LEE E. FARR (From the Hospital
Nephron Structure inside Kidney:
 In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
originally devised in collaboration with Drs C. E. Dent and B. Senior who threshold are excreted according to a curve OB. At low concentrations in the
 268 J. Physiol. (I955) I30, 268-277 A METHOD FOR ESTIMATING Tm FOR PHOSPHATE IN MAN BY J. ANDERSON* From the Medical Unit, University College Hospital, London (Received 15 March 1955) The methods used
268 J. Physiol. (I955) I30, 268-277 A METHOD FOR ESTIMATING Tm FOR PHOSPHATE IN MAN BY J. ANDERSON* From the Medical Unit, University College Hospital, London (Received 15 March 1955) The methods used
Clearance and Reabsorption. Use the following data to answer these questions. a. plasma flow rate in the afferent arterioles:
 Bio390 thanks to Dr. J.F. Anderson, Dept Zoology Univ. of Florida, Gainesville Clearance and Reabsorption Use the following data to answer these questions. renal inulin clearance: [inulin] arterial plasma
Bio390 thanks to Dr. J.F. Anderson, Dept Zoology Univ. of Florida, Gainesville Clearance and Reabsorption Use the following data to answer these questions. renal inulin clearance: [inulin] arterial plasma
Collin College. BIOL Anatomy & Physiology. Urinary System. Summary of Glomerular Filtrate
 Collin College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology Urinary System 1 Summary of Glomerular Filtrate Glomerular filtration produces fluid similar to plasma without proteins GFR ~ 125 ml per min If nothing else
Collin College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology Urinary System 1 Summary of Glomerular Filtrate Glomerular filtration produces fluid similar to plasma without proteins GFR ~ 125 ml per min If nothing else
Regulation of fluid and electrolytes balance
 Regulation of fluid and electrolytes balance Three Compartment Fluid Compartments Intracellular = Cytoplasmic (inside cells) Extracellular compartment is subdivided into Interstitial = Intercellular +
Regulation of fluid and electrolytes balance Three Compartment Fluid Compartments Intracellular = Cytoplasmic (inside cells) Extracellular compartment is subdivided into Interstitial = Intercellular +
principles. laboratory [Stehle & Fraser, 1935] and contains 200 pressor units and (Received 20 November 1940)
![principles. laboratory [Stehle & Fraser, 1935] and contains 200 pressor units and (Received 20 November 1940) principles. laboratory [Stehle & Fraser, 1935] and contains 200 pressor units and (Received 20 November 1940)](/thumbs/92/110006249.jpg) .#Lil-RAFY 4 233 J. Physiol. (I94I) IOO, 233-238 4 V>6x2.492.8:577.I52 I THE RATIO BETWEEN ANTIDIURETIC AND PRESSOR ACTIVITIES OF POSTERIOR PITUITARY EXTRACT SUBJECTED TO MILD HYDROLYSIS BY A. M. FRASER
.#Lil-RAFY 4 233 J. Physiol. (I94I) IOO, 233-238 4 V>6x2.492.8:577.I52 I THE RATIO BETWEEN ANTIDIURETIC AND PRESSOR ACTIVITIES OF POSTERIOR PITUITARY EXTRACT SUBJECTED TO MILD HYDROLYSIS BY A. M. FRASER
After studying this lecture, you should be able to...
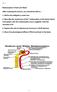 Reabsorption of Salt and Water After studying this lecture, you should be able to... 1. Define the obligatory water loss. 2. Describe the mechanism of Na ++ reabsorption in the distal tubule and explain
Reabsorption of Salt and Water After studying this lecture, you should be able to... 1. Define the obligatory water loss. 2. Describe the mechanism of Na ++ reabsorption in the distal tubule and explain
RENAL FUNCTION IN LEAD POISONING
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1952), 7, 349. RENAL FUNCTION IN LEAD POISONING BY From the Department of Pharmacology, London Hospital Medical College (Received January 23, 1952) Structural changes in the kidneys
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1952), 7, 349. RENAL FUNCTION IN LEAD POISONING BY From the Department of Pharmacology, London Hospital Medical College (Received January 23, 1952) Structural changes in the kidneys
glands are reported to have no antidiuretic action) produce a principle gland of some lower vertebrates (teleost fishes, amphibians, reptiles), has
 246 J. Physiol. (I94I) 99, 246-256 577.I74.92:596 THE DISTRIBUTION OF THE PITUITARY ANTIDIURETIC HORMONE THROUGHOUT THE VERTEBRATE SERIES BY H. HELLER1 From the Department of Ph4rmacology, Oxford (Received
246 J. Physiol. (I94I) 99, 246-256 577.I74.92:596 THE DISTRIBUTION OF THE PITUITARY ANTIDIURETIC HORMONE THROUGHOUT THE VERTEBRATE SERIES BY H. HELLER1 From the Department of Ph4rmacology, Oxford (Received
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
 LECTURE NO (2) Renal Physiology Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) Faculty Of Medicine Dept.Of Physiology The glomerulus Is a tuft of capillaries enclosed within a Bowman capsule. It is supplied by an afferent
LECTURE NO (2) Renal Physiology Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) Faculty Of Medicine Dept.Of Physiology The glomerulus Is a tuft of capillaries enclosed within a Bowman capsule. It is supplied by an afferent
EXCRETION QUESTIONS. Use the following information to answer the next two questions.
 EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
man of the effects of diabetes and of insulin on the maximum ability of the tubules to reabsorb glucose.
 EFFECT OF DIABETES AND INSULIN ON THE MAXIMUM CA- PACITY OF THE RENAL TUBULES TO REABSORB GLUCOSE t By SAUL J. FARBER, EUGENE Y. BERGER, AND DAVID P. EARLE (From the Department of Medicine, New York University
EFFECT OF DIABETES AND INSULIN ON THE MAXIMUM CA- PACITY OF THE RENAL TUBULES TO REABSORB GLUCOSE t By SAUL J. FARBER, EUGENE Y. BERGER, AND DAVID P. EARLE (From the Department of Medicine, New York University
Physiology of Excretory Systems
 Physiology of Excretory Systems Fig 12-2 (a) Urea is formed by the ornithine-urea cycle in most vertebrates. Because ATP is required for the first step, nitrogen excretion in ureotelic animals is more
Physiology of Excretory Systems Fig 12-2 (a) Urea is formed by the ornithine-urea cycle in most vertebrates. Because ATP is required for the first step, nitrogen excretion in ureotelic animals is more
Kidney Physiology. Mechanisms of Urine Formation TUBULAR SECRETION Eunise A. Foster Shalonda Reed
 Kidney Physiology Mechanisms of Urine Formation TUBULAR SECRETION Eunise A. Foster Shalonda Reed The purpose of tubular secrection To dispose of certain substances that are bound to plasma proteins. To
Kidney Physiology Mechanisms of Urine Formation TUBULAR SECRETION Eunise A. Foster Shalonda Reed The purpose of tubular secrection To dispose of certain substances that are bound to plasma proteins. To
necessity for an investigation into possible different types of urine acidity. In
 456 J. Physiol. (I947) io6, 456-465 6I2.46i SOME FACTORS AFFECTING THE ACIDITY OF URINE IN MAN BY M. GRACE EGGLETON From the Department of Physiology, University College, London (Received 22 February 1947)
456 J. Physiol. (I947) io6, 456-465 6I2.46i SOME FACTORS AFFECTING THE ACIDITY OF URINE IN MAN BY M. GRACE EGGLETON From the Department of Physiology, University College, London (Received 22 February 1947)
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
** TMP mean page 340 in 12 th edition. Questions 1 and 2 Use the following clinical laboratory test results for questions 1 and 2:
 QUESTION Questions 1 and 2 Use the following clinical laboratory test results for questions 1 and 2: Urine flow rate = 1 ml/min Urine inulin concentration = 100 mg/ml Plasma inulin concentration = 2 mg/ml
QUESTION Questions 1 and 2 Use the following clinical laboratory test results for questions 1 and 2: Urine flow rate = 1 ml/min Urine inulin concentration = 100 mg/ml Plasma inulin concentration = 2 mg/ml
v. reitschlagerova Renal Amino Acid Excretion and Aging H. NADVORNlKOVA, O. SCHUCK, V. TEPLAN, D. TOMKOVA,
 Physiol. Res. 40:87-94, 1991 Renal Amino Acid Excretion and Aging H. NADVORNlKOVA, O. SCHUCK, V. TEPLAN, D. TOMKOVA, v. reitschlagerova Institute for Clinical and Experimental Medicine, Prague Received
Physiol. Res. 40:87-94, 1991 Renal Amino Acid Excretion and Aging H. NADVORNlKOVA, O. SCHUCK, V. TEPLAN, D. TOMKOVA, v. reitschlagerova Institute for Clinical and Experimental Medicine, Prague Received
1. remove: waste products: urea, creatinine, and uric acid foreign chemicals: drugs, water soluble vitamins, and food additives, etc.
 Making Water! OR is it really Just Water Just Ask the Nephron!! Author: Patricia L. Ostlund ostlundp@faytechcc.edu (910) 678-9892 Fayetteville Technical Community College Fayetteville, NC 28303 Its just
Making Water! OR is it really Just Water Just Ask the Nephron!! Author: Patricia L. Ostlund ostlundp@faytechcc.edu (910) 678-9892 Fayetteville Technical Community College Fayetteville, NC 28303 Its just
Functional Renal Physiology and Urine Production
 Functional Renal Physiology and Urine Production Urinalysis can provide insight into hydration status, renal function or dysfunction, systemic disease, and toxic insults. Accurate interpretation of urinalysis
Functional Renal Physiology and Urine Production Urinalysis can provide insight into hydration status, renal function or dysfunction, systemic disease, and toxic insults. Accurate interpretation of urinalysis
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
already been published [O'Connor, 1958 b]. emphasized that the most prominent action of adrenaline on the kidney is to
![already been published [O'Connor, 1958 b]. emphasized that the most prominent action of adrenaline on the kidney is to already been published [O'Connor, 1958 b]. emphasized that the most prominent action of adrenaline on the kidney is to](/thumbs/88/116101114.jpg) THE EFFECT ON THE VOLUME AND COMPOSITION OF THE URINE OF THE INFUSION OF ADRENALINE AND NORADRENALINE. By W. J. O'CoNNoR. From the Department of Physiology, School of Medicine, University of Leeds. (Received
THE EFFECT ON THE VOLUME AND COMPOSITION OF THE URINE OF THE INFUSION OF ADRENALINE AND NORADRENALINE. By W. J. O'CoNNoR. From the Department of Physiology, School of Medicine, University of Leeds. (Received
RENAL REGULATION OF PHOSPHATE EXCRETION IN THE PIG.
 Quarterly Journal of Experimental Phy8iology (1975) 6, 299-35 RENAL REGULATION OF PHOSPHATE EXCRETION IN THE PIG. By G. H. MCINTosH* and D. SCOTT. From the Department of Physiology, Rowett Research Institute,
Quarterly Journal of Experimental Phy8iology (1975) 6, 299-35 RENAL REGULATION OF PHOSPHATE EXCRETION IN THE PIG. By G. H. MCINTosH* and D. SCOTT. From the Department of Physiology, Rowett Research Institute,
MODULE 8: URINALYSIS AND ACID BASE BALANCE
 MODULE 8: URINALYSIS AND ACID BASE BALANCE This lab involves a tutorial that teaches you how to analyze a urine reagent strip. If you are taking the lab on campus, you will be given the opportunity to
MODULE 8: URINALYSIS AND ACID BASE BALANCE This lab involves a tutorial that teaches you how to analyze a urine reagent strip. If you are taking the lab on campus, you will be given the opportunity to
McCANCE, From The Department of Medicine, Cambridge
 196 J. Physiol. (I945) I04, I96-209 6I2.4632.2 THE EXCRETION OF UREA, SALTS AND WATER DURING PERIODS OF HYDROPAENIA IN MAN BY R. A. McCANCE, From The Department of Medicine, Cambridge (Received 20 February
196 J. Physiol. (I945) I04, I96-209 6I2.4632.2 THE EXCRETION OF UREA, SALTS AND WATER DURING PERIODS OF HYDROPAENIA IN MAN BY R. A. McCANCE, From The Department of Medicine, Cambridge (Received 20 February
Nephron Anatomy Nephron Anatomy
 Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
1.7) (21, 22, 23); (2) this ratio is depressed towards
 DEPRESSION OF THE EXOGENOUS CREATININE/INULIN OR THIOSULFATE CLEARANCE RATIOS IN MAN BY DIODRAST AND p-aminohippuric ACID1 By BETTY CRAWFORD (From the Department of Physiology, New York University College
DEPRESSION OF THE EXOGENOUS CREATININE/INULIN OR THIOSULFATE CLEARANCE RATIOS IN MAN BY DIODRAST AND p-aminohippuric ACID1 By BETTY CRAWFORD (From the Department of Physiology, New York University College
= (6000 ml air / min * 0.04 ml CO 2 / ml air) / 54 ml CO 2 / dl plasma
 Bio390 thanks to Dr. J.F. Anderson, Dept Zoology Univ. of Florida, Gainesville RENAL PROBLEMS Calculate the rate of pulmonary clearance of CO 2 given the following information. Cardiac Output: 4.8 L 6
Bio390 thanks to Dr. J.F. Anderson, Dept Zoology Univ. of Florida, Gainesville RENAL PROBLEMS Calculate the rate of pulmonary clearance of CO 2 given the following information. Cardiac Output: 4.8 L 6
GLUCOSE is the most important diffusible substance in the blood which
 ON THE ACTION OF PHLORHIZIN ON THE KIDNEY. By E. B. MAYRS. (From the Department of Pharmacology, Edinburgh.) GLUCOSE is the most important diffusible substance in the blood which is completely held back
ON THE ACTION OF PHLORHIZIN ON THE KIDNEY. By E. B. MAYRS. (From the Department of Pharmacology, Edinburgh.) GLUCOSE is the most important diffusible substance in the blood which is completely held back
All patients were well hydrated in order to obtain a. good urine flow.2 They were given a liter of water to
 URIC ACID CLEARANCE IN NORMAL PREGNANCY AND PRE-ECLAMPSIA1 By N. K SCHAFFER, L. V. DILL, AND J. F. CADDEN (From the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Cornell University Medical College, and the
URIC ACID CLEARANCE IN NORMAL PREGNANCY AND PRE-ECLAMPSIA1 By N. K SCHAFFER, L. V. DILL, AND J. F. CADDEN (From the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Cornell University Medical College, and the
Water Reabsorption and the Effect of Diuretics on Urine Formation Patricia J. Clark, Ph.D. Department of Biology, IUPUI
 Water Reabsorption and the Effect of Diuretics on Urine Formation Patricia J. Clark, Ph.D. Department of Biology, IUPUI This activity may be done in conjunction with a more traditional urinalysis lab.
Water Reabsorption and the Effect of Diuretics on Urine Formation Patricia J. Clark, Ph.D. Department of Biology, IUPUI This activity may be done in conjunction with a more traditional urinalysis lab.
capillaries, and a consequent increased transudation, without necessarily altering to any marked extent the total circulation of blood
 612.463.4 THE CONTROL OF THE GLOMERULAR PRESSURE BY VASCULAR CHANGES WITHIN THE ISOLATED MAMMALIAN KIDNEY, DEMONSTRATED BY THE ACTIONS OF ADRENALINE. BY F. R. WINT0N (Beit Memorial Research Fellow). (Depaortment
612.463.4 THE CONTROL OF THE GLOMERULAR PRESSURE BY VASCULAR CHANGES WITHIN THE ISOLATED MAMMALIAN KIDNEY, DEMONSTRATED BY THE ACTIONS OF ADRENALINE. BY F. R. WINT0N (Beit Memorial Research Fellow). (Depaortment
