2805/05 Mammalian Physiology and Behaviour. January Mark Scheme
|
|
|
- Christal Imogen Chapman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mammalian Physiology and Behaviour
2 7 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions. 2. Please mark all post-standardisation scripts in red ink. A tick ( ) should be used for each answer judged worthy of a mark. Ticks should be placed as close as possible to the point in the answer where the mark has been awarded. The number of ticks should be the same as the number of marks awarded. If two (or more) responses are required for one mark, use only one tick. Half marks (½) should never be used. 3. The following annotations may be used when marking. No comments should be written on scripts unless they relate directly to the mark scheme. Remember that scripts may be returned to Centres. x ^ bod ecf con sf = incorrect response (errors may also be underlined) = omission mark = benefit of the doubt (where professional judgement has been used) = error carried forward (in consequential marking) = contradiction (in cases where candidates contradict themselves in the same response) = error in the number of significant figures 4. The marks awarded for each part question should be indicated in the margin provided on the right hand side of the page. The mark total for each question should be ringed at the end of the question, on the right hand side. These totals should be added up to give the final total on the front of the paper. 5. In cases where candidates are required to give a specific number of answers, (e.g. give three reasons ), mark the first answer(s) given up to the total number required. Strike through the remainder. In specific cases where this rule cannot be applied, the exact procedure to be used is given in the mark scheme. 6. Correct answers to calculations should gain full credit even if no working is shown, unless otherwise indicated in the mark scheme. (An instruction on the paper to Show your working is to help candidates, who may then gain partial credit even if their final answer is not correct.) 7. Strike through all blank spaces and/or pages in order to give a clear indication that the whole of the script has been considered. 8. An element of professional judgement is required in the marking of any written paper, and candidates may not use the exact words that appear in the mark scheme. If the science is correct and answers the question, then the mark(s) should normally be credited. If you are in doubt about the validity of any answer, contact your Team Leader/Principal Examiner for guidance.
3 Page 3 of 10 Abbreviations, annotations and conventions used in the / = alternative and acceptable answers for the same marking point ; = separates marking points NOT = answers which are not worthy of credit ( ) = words which are not essential to gain credit = (underlining) key words which must be used to gain credit ecf = error carried forward A = accept R = reject AW = alternative wording ora = or reverse argument 1 (a) peripheral (ns); autonomic (ns); spinal cord; cerebrum; cerebellum; 5 (b) (electrically) insulated / described; R idea of mechanical protection speeds up conduction of, impulses / action potentials; R signals / messages / information / more efficient idea saltatory conduction / ref. to nodes (of Ranvier); max 2 (c) (i) idea of heat transfer / conduction / absorption; R diffusion high (specific) heat capacity of water; idea of circulation / movement (of CSF); max 2 (ii) proteins / named protein, in blood; low(er) the water potential of blood (plasma); ora osmosis / diffusion (in correct direction); down water potential gradient / from high to low water potential; AVP; e.g. ref. to meninges max 3 [Total: 12]
4 Page 4 of 10 2 (a) any two of hepatic artery hepatic vein hepatic portal vein ; 1 (b) (c) (d) drainage of / removal of excess, bile (into, bile duct / small intestine); A collection of bile for testing / AW 1 antigens (on liver cells); recognised as, foreign / non self; ref to antibodies; produced by, B lymphocytes / plasma cells; A cells ref to T lymphocytes; A cells AVP; e.g. ref to complementary / specific max 3 no bile to emulsify fats; no bile to neutralise stomach acid; ref to incorrect ph for, pancreatic / intestinal enzyme(s); less digestion of fat by lipase; less digestion of protein by protease; less absorption of, fatty acids / amino acids; use of fat stores; AVP; e.g. breakdown of muscle protein max 3
5 Page 5 of 10 (e) marking point 6 may be accepted as part of protein metabolism accept interferes, disrupts, damages, but reject affect / effect carbohydrate metabolism 1 less glucose absorbed (by liver cells); 2 (less) glycogen stored / glycogen synthesis / glycogenesis; 3 (because) cells do not respond to insulin; 4 (less) release of glucose from stored glycogen / glycogenolysis; 5 (if) cells do not respond to glucagon; 6 (less) production of glucose from, amino acids / glycerol; A gluconeogenesis max 5 protein metabolism 7 (less) breakdown of (named) protein / hormone; 8 (less) conversion of amino acids to ammonia / (less) deamination; 9 (less) urea production / disruption of ornithine cycle; 10 ref to disruption of transamination; 11 (reduced) synthesis of protein; 12 ref to named protein; max 5 allow the following general points once but in either section 13 disruption of cell surface receptors / cell membranes; 14 reduced synthesis / activity of enzymes; 15 AVP; e.g. consequences of any of the above, such as 16 AVP; blood clotting transport role of proteins antibodies / immunoglobulins water potential / solute potential/ oedema less substrate for Krebs cycle blood glucose concentration is high / inability to regulate blood glucose / diabetic like symptoms need for amino acid supplements max 8 QWC legible text with accurate spelling, punctuation and grammar; 1 [Total: 17]
6 Page 6 of 10 3 (a) several / different, tissues; A more than one named tissue working together to, perform a function / detect light; A functional unit R to see / to be aware of surroundings 2 (b) (i) nucleus; 1 (ii) line to one of the outer segments; 1 (c) produce ATP; for sodium potassium pump / pumping Na + out, K + in; in inner segment / resting potential / hyperpolarised when light hits rods; synthesis of, neurotransmitter / glutamate; movement of synaptic vesicles / for exocytosis; synthesis of, visual pigment / rhodopsin; A trans to cis R for pigments to function AVP; e.g. production of named protein / protein for named function max 3 (d) (dark) adaptation; R light adaptation 1 (e) 1 ref to 9 minutes; A +/- 1 minute / 2 small squares cone cells detect light of high intensity / rods detect light of low intensity; rhodopsin present in rods; (rhodopsin) bleached / broken down, by (5 minutes of white) light; detail of breakdown products; takes time to resynthesise (during dark); idea of more synthesis of pigment / lower threshold; ora max 4 (f) curve levelling off at 9 minutes; line straight across (to at least 25 minutes), no lower than 30 arbitrary units; 2 [Total: 14]
7 Page 7 of 10 4 (a) (i) for leopard, two of the following for one mark fewer pre-molars / different number of pre-molars in upper and lower jaw less premolars in its lower jaw fewer molars ; 1 (ii) no need to, immobilise prey / tear off flesh / kill prey; ref to diastema / gap between teeth / more space to mix food; allows separation of cud from (freshly cropped) grass; efficient chewing of plant food; horny pad to crop of grass; max 3 (b) (c) carnassial; sharp, edges or cusps or crowns or points, for piercing / tearing; stop bones (of prey) moving; high pressure on a small point; ref to shearing / scissors action / slicing past each other; R grinding / sawing / chewing cracking / crunching bones; R grinding or chewing cut meat in (small) pieces (for swallowing); (completely) covered in enamel, therefore hard; R refs. to roots of teeth max 3 assume statements refer to ileum unless stated otherwise villi; lack of (gastric) pits; no crypts (of Lieberkuhn); microvilli / brush border; no, oxyntic / parietal / chief / HCl-secreting cells; R mucus secreting cells / goblet cells max 2 (d) award two marks if correct answer (25) is given 55 (mm) = 0.55 (mm) ; = 25 (hours) ;
8 Page 8 of 10 (e) folded surface membrane / microvilli / brush border; R villi (gives) large surface area; (allows) high rate of; facilitated diffusion; (protein) channels / pores / carriers / pumps; for, polar molecules / glucose / amino acids; non-polar molecules / fat soluble molecules / fatty acids / monoglycerides / glycerol; diffuse / pass through, phospholipid (bilayer) of surface membrane; many mitochondria; supply ATP; active uptake; ref. to co-transport of, glucose / amino acids, with sodium ions; pinocytosis / endocytosis / described; fatty acids + glycerol to triglycerides in smooth ER; Golgi body, produces chylomicrons / coated by proteins; AVP; e.g. hydrolysis in brush border / glycocalyx AVP; max 7 QWC clear, well organised answer, using specialist terms 1 [Total: 19]
9 Page 9 of 10 5 (a) inherited / genetic / inborn; no, learning / practice needed; instinctive; (often) stereotyped / shown by all members of same species; R hard wired / pre-set / not taught max 2 (b) (c) trial and error; a chance (correct) response becomes more common / AW; rat learns to carry out a, behaviour / response; associated with a, reward / food; max 2 rats learn at faster rate if given more food; by day, 12 /13, all rats respond equally successfully (despite amount of food given); rats given one pellet learn more slowly; use of data for number of pellets; no difference between 0 and 5 second delay in receiving food; delaying food, by 30 seconds / long time, slows learning; use of data for delay in receiving pellets; max 5 (d) (e) controlled diet (outside of test runs); fasting of rats, before each trial / between trials; A hungry rats type of food (as reward); age of rats; variety of rats; gender of rats; (environmental) temperature; (environmental) light intensity; environmental noise; random allocation of each rat to one of the groups; AVP; e.g. only use rats not previously tested in T maze use of a clean maze for each trial max 2 idea of a random / chance correct response / 50% probability / chance of correct response; variation about mean; measure of significance; max 2 [Total: 13 ]
10 Page 10 of 10 6 (a) (i) two of actin tropomyosin troponin ; R myosin 1 (ii) from Z line to Z line; 1 (iii) wide H zone; wide I band; little overlap of filaments / AW; ref to length of sarcomere (may be annotated on Fig. 6.1); max 2 (b) calcium ions (normally) bind to troponin; in presence of hydrogen ions, less binding (of calcium ions); less / no, change in shape / movement, of tropomyosin; binding sites (on actin) not exposed; R active sites no binding of myosin head / fewer cross bridges / no ratchet action; effect of hydrogen ions on tertiary structure of (named) protein; effect on named bond; R peptide max 5 (c) (i) E hyaline / articular; 1 (ii) F - compact; 1 (d) calcium phosphate; A CaPO 4 1 (e) osteoclast; R osteocyte 1 (f) increased fractures / brittle bones; reduced mobility; increased pain; Dowager s hump; AVP; e.g. take named supplements AVP; advised to take, oestrogen / HRT max 2 [Total: 15]
2804 Central Concepts. June Mark Scheme
 Central Concepts June 00 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions.. Please mark all post-standardisation
Central Concepts June 00 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions.. Please mark all post-standardisation
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans
 Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Subject: Transport Code: 2803 / 01. Session: January Year: Mark Scheme
 Subject: Transport Code: 2803 / 01 : : MAXIMUM MARK 60 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions.
Subject: Transport Code: 2803 / 01 : : MAXIMUM MARK 60 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions.
Session: January... Year: Mark Scheme
 Post stand /0/05 Subject: BIOCHEMISTRY Code:85/0. Session: January... Year: 005. MAXIMUM MARK 45 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You
Post stand /0/05 Subject: BIOCHEMISTRY Code:85/0. Session: January... Year: 005. MAXIMUM MARK 45 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You
Subject: Unifying Concepts in Biology Code: 2806/01. Session: January Year: Mark Scheme
 Subject: Unifying Concepts in Biology Code: : : MAXIMUM MARK 60 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft
Subject: Unifying Concepts in Biology Code: : : MAXIMUM MARK 60 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft
Syllabus / Component: 2801 Biology Foundation
 JANUARY 2003 ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE UNIT MARK SCHEME MAXIMUM MARK: 60 Syllabus / Component: 2801 Biology Foundation Paper Set Date: 15/01/03 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please
JANUARY 2003 ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE UNIT MARK SCHEME MAXIMUM MARK: 60 Syllabus / Component: 2801 Biology Foundation Paper Set Date: 15/01/03 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please
Subject: Mammalian Physiology and Behaviour Code: 2805/05. Session: January Year: Mark Scheme
 Subject: Mammalian Physiology and Behaviour Code: : : MAXIMUM MARK 90 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy
Subject: Mammalian Physiology and Behaviour Code: : : MAXIMUM MARK 90 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy
Subject: Central Concepts Code: Session: January Year: Mark Scheme
 Subject: Central Concepts Code: : : MAXIMUM MARK 90 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions.
Subject: Central Concepts Code: : : MAXIMUM MARK 90 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions.
2804 Central Concepts. January Mark Scheme
 - 2804 Central Concepts ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions. 2. Please mark all post-standardisation
- 2804 Central Concepts ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions. 2. Please mark all post-standardisation
Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement QUESTION
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement QUESTION
Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2015 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement ONE NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2015 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement ONE NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5
2806/01 Unifying Concepts in Biology. June Mark Scheme
 Unifying Concepts in Biology ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions. 2. Please mark all post-standardisation
Unifying Concepts in Biology ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions. 2. Please mark all post-standardisation
2806/01 Unifying Concepts in Biology. January Mark Scheme
 Unifying Concepts in Biology ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions. 2. Please mark all post-standardisation
Unifying Concepts in Biology ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions. 2. Please mark all post-standardisation
Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance 1 (a) 3 max
 Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance 1 (a) phospholipid bilayer containing proteins ; head / hydrophilic region, facing outwards OR tail / hydrophobic region, facing inwards ; Marks can
Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance 1 (a) phospholipid bilayer containing proteins ; head / hydrophilic region, facing outwards OR tail / hydrophobic region, facing inwards ; Marks can
2801 Biology Foundation. January Mark Scheme
 Biology Foundation ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions. 2. Please mark all post-standardisation
Biology Foundation ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions. 2. Please mark all post-standardisation
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition
 B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
ADVANCED GCE UNIT MARK SCHEME MAXIMUM MARK: 90. Syllabus / Component: 2805/05. Options in Biology: Mammalian Physiology and Behaviour
 JANUARY 00 ADVANCED GCE UNIT MARK SCHEME MAXIMUM MARK: 90 Syllabus / Component: 0/0 Options in Biology: Mammalian Physiology and Behaviour Paper Set Date: 0/01/0 Page of ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION
JANUARY 00 ADVANCED GCE UNIT MARK SCHEME MAXIMUM MARK: 90 Syllabus / Component: 0/0 Options in Biology: Mammalian Physiology and Behaviour Paper Set Date: 0/01/0 Page of ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition
 CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
1. (a) (i) Ability to distinguish points (close together); 1 (ii) Electrons have a shorter wavelength; 1
 1. (a) (i) Ability to distinguish points (close together); 1 Electrons have a shorter wavelength; 1 (b) (i) Golgi / nucleus / mitochondrion / endoplasmic reticulum / chromosome / larger ribosomes; R Membrane
1. (a) (i) Ability to distinguish points (close together); 1 Electrons have a shorter wavelength; 1 (b) (i) Golgi / nucleus / mitochondrion / endoplasmic reticulum / chromosome / larger ribosomes; R Membrane
Summary of chemical breakdown of food by hydrolytic enzymes (Protein enzymes).
 Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
No ATP formed / no energy released by respiration; [reject making energy] Link ATP to active transport (of galactose) into cells; 2 [5]
![No ATP formed / no energy released by respiration; [reject making energy] Link ATP to active transport (of galactose) into cells; 2 [5] No ATP formed / no energy released by respiration; [reject making energy] Link ATP to active transport (of galactose) into cells; 2 [5]](/thumbs/81/83055588.jpg) 1. (a) Digestion/hydrolysis/breakdown of a disaccharide into monosaccharides; OR (glucose and galactose form lactose) glucose is a monosaccharide; max 1 (i) Dipeptidase / disaccharidase / named disaccharidase;
1. (a) Digestion/hydrolysis/breakdown of a disaccharide into monosaccharides; OR (glucose and galactose form lactose) glucose is a monosaccharide; max 1 (i) Dipeptidase / disaccharidase / named disaccharidase;
Cell Membranes Valencia college
 6 Cell Membranes Valencia college 6 Cell Membranes Chapter objectives: The Structure of a Biological Membrane The Plasma Membrane Involved in Cell Adhesion and Recognition Passive Processes of Membrane
6 Cell Membranes Valencia college 6 Cell Membranes Chapter objectives: The Structure of a Biological Membrane The Plasma Membrane Involved in Cell Adhesion and Recognition Passive Processes of Membrane
Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) o Balanced diet: getting all the right nutrients in correct proportions o Diet related to: - Age - Gender - Activity - Pregnant women o Malnutrition:
Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) o Balanced diet: getting all the right nutrients in correct proportions o Diet related to: - Age - Gender - Activity - Pregnant women o Malnutrition:
Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
 The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
Physiology Unit 4 DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 4 DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Functions Motility Ingestion Mastication Deglutition Peristalsis Secretion 7 liters/day! Exocrine/endocrine Digestion Absorption Digestion of
Physiology Unit 4 DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Functions Motility Ingestion Mastication Deglutition Peristalsis Secretion 7 liters/day! Exocrine/endocrine Digestion Absorption Digestion of
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
Name: Enzymes. Class: Date: 101 minutes. Time: 100 marks. Marks: Level 1,2 and 3. Increasing demand. Comments:
 Enzymes Name: Class: Date: Time: 0 minutes Marks: 00 marks Comments: Level,2 and 3. Increasing demand Q. Catalase is an enzyme. Catalase controls the following reaction: hydrogen peroxide water + oxygen
Enzymes Name: Class: Date: Time: 0 minutes Marks: 00 marks Comments: Level,2 and 3. Increasing demand Q. Catalase is an enzyme. Catalase controls the following reaction: hydrogen peroxide water + oxygen
Tissues and organs PART 1
 Tissues and organs PART 1 Animals and plants are multicellular (made of many cells). Cells become specialised according to their function Tissues: Many cells that perform one or several functions; they
Tissues and organs PART 1 Animals and plants are multicellular (made of many cells). Cells become specialised according to their function Tissues: Many cells that perform one or several functions; they
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education. Published
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/4 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This mark scheme
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/4 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This mark scheme
Station One: Nutrition
 Station One: Nutrition Name that thing! 1. Chemical substances, found in foods, which are used in the human body. 2. Nutrient in human diet where foods are the only possible source of the nutrient. 3.
Station One: Nutrition Name that thing! 1. Chemical substances, found in foods, which are used in the human body. 2. Nutrient in human diet where foods are the only possible source of the nutrient. 3.
The gallbladder. Bile secretion:
 The gallbladder is a thin walled green muscular sac on the inferior surface of the liver. The gallbladder stores bile that is not immediately needed for digestion and concentrates it. When the muscular
The gallbladder is a thin walled green muscular sac on the inferior surface of the liver. The gallbladder stores bile that is not immediately needed for digestion and concentrates it. When the muscular
Cell Membranes and Signaling
 5 Cell Membranes and Signaling Concept 5.1 Biological Membranes Have a Common Structure and Are Fluid A membrane s structure and functions are determined by its constituents: lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates.
5 Cell Membranes and Signaling Concept 5.1 Biological Membranes Have a Common Structure and Are Fluid A membrane s structure and functions are determined by its constituents: lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates.
AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST SUPPLY CHEMICAL ENERGY, ORGANIC MOLECULES, AND ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS
 1 ANIMAL NUTRITION 2 3 4 5 6 7 Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores eat mainly plants and algae Carnivores
1 ANIMAL NUTRITION 2 3 4 5 6 7 Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores eat mainly plants and algae Carnivores
GCE. Edexcel GCE Biology / Biology (Human) (6104/02) January Edexcel GCE. Mark Scheme (Results) Biology / Biology (Human) (6104/02)
 GCE Edexcel GCE Biology / Biology (Human) (6104/02) January 2006 Mark Scheme (Results) Edexcel GCE Biology / Biology (Human) (6104/02) Symbols used in the mark scheme General Principles Symbol Meaning
GCE Edexcel GCE Biology / Biology (Human) (6104/02) January 2006 Mark Scheme (Results) Edexcel GCE Biology / Biology (Human) (6104/02) Symbols used in the mark scheme General Principles Symbol Meaning
Questions on Digestion
 Name: Questions on Digestion Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topic 6.1 (Digestion). Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for the next quiz.
Name: Questions on Digestion Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topic 6.1 (Digestion). Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for the next quiz.
Name: Date: Block: Biology 12
 Name: Date: Block: Biology 12 Provincial Exam Review: Cell Processes and Applications January 2003 Use the following diagram to answer questions 1 and 2. 1. Which labelled organelle produces most of the
Name: Date: Block: Biology 12 Provincial Exam Review: Cell Processes and Applications January 2003 Use the following diagram to answer questions 1 and 2. 1. Which labelled organelle produces most of the
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System. Part 3
 Digestive System Part 3 Digestion Ingested materials must be broken down for absorption Majority of absorption in small intestine Water and alcohol in stomach mucosa Some salts and vitamins in large intestine
Digestive System Part 3 Digestion Ingested materials must be broken down for absorption Majority of absorption in small intestine Water and alcohol in stomach mucosa Some salts and vitamins in large intestine
Proteins their functions and uses revision 3
 Proteins their functions and uses revision 3 59 minutes 59 marks Page of 23 Q. The diagram gives information about some parts of the human digestive system. (a) (i) Name the organ which makes bile. Label
Proteins their functions and uses revision 3 59 minutes 59 marks Page of 23 Q. The diagram gives information about some parts of the human digestive system. (a) (i) Name the organ which makes bile. Label
ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY (AS) General Certificate of Education Biology Assessment Unit AS 1. assessing. Molecules and Cells [SBY11]
![ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY (AS) General Certificate of Education Biology Assessment Unit AS 1. assessing. Molecules and Cells [SBY11] ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY (AS) General Certificate of Education Biology Assessment Unit AS 1. assessing. Molecules and Cells [SBY11]](/thumbs/81/83055831.jpg) New Specification ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY (AS) General Certificate of Education 2017 Biology Assessment Unit AS 1 assessing Molecules and Cells [SBY11] THURSDAY 25 MAY, AFTERNOON MARK SCHEME General Marking
New Specification ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY (AS) General Certificate of Education 2017 Biology Assessment Unit AS 1 assessing Molecules and Cells [SBY11] THURSDAY 25 MAY, AFTERNOON MARK SCHEME General Marking
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer Pearson Edexcel GCSE in Biology (5BI1F) Paper 01 Unit B1: Influences on Life
 Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2015 Pearson Edexcel GCSE in Biology (5BI1F) Paper 01 Unit B1: Influences on Life Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications are awarded by Pearson, the
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2015 Pearson Edexcel GCSE in Biology (5BI1F) Paper 01 Unit B1: Influences on Life Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications are awarded by Pearson, the
GCE. Human Biology. Mark Scheme for January Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F221: Molecules, Blood and Gas Exchange
 GCE Human Biology Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F221: Molecules, Blood and Gas Exchange Mark Scheme for January 2013 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK
GCE Human Biology Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F221: Molecules, Blood and Gas Exchange Mark Scheme for January 2013 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK
MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2010 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2010 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY 0610/62
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2010 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY 0610/62
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge Ordinary Level. Published
 Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge Ordinary Level BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 Theory MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and candidates,
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge Ordinary Level BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 Theory MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and candidates,
Mark Scheme (Results)
 Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2017 Pearson Edexcel GCSE In Biology (5BI2H) Paper 01 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications are awarded by Pearson, the UK s largest awarding body.
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2017 Pearson Edexcel GCSE In Biology (5BI2H) Paper 01 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications are awarded by Pearson, the UK s largest awarding body.
Membrane Structure and Membrane Transport of Small Molecules. Assist. Prof. Pinar Tulay Faculty of Medicine
 Membrane Structure and Membrane Transport of Small Molecules Assist. Prof. Pinar Tulay Faculty of Medicine Introduction Cell membranes define compartments of different compositions. Membranes are composed
Membrane Structure and Membrane Transport of Small Molecules Assist. Prof. Pinar Tulay Faculty of Medicine Introduction Cell membranes define compartments of different compositions. Membranes are composed
TRANSPORT ACROSS MEMBRANES
 Unit 2: Cells, Membranes and Signaling TRANSPORT ACROSS MEMBRANES Chapter 5 Hillis Textbook TYPES OF TRANSPORT ACROSS THE CELL (PLASMA) MEMBRANE: What do you remember? Complete the chart with what you
Unit 2: Cells, Membranes and Signaling TRANSPORT ACROSS MEMBRANES Chapter 5 Hillis Textbook TYPES OF TRANSPORT ACROSS THE CELL (PLASMA) MEMBRANE: What do you remember? Complete the chart with what you
At the end of this lesson, you should be able to:
 Digestion Learning Objectives At the end of this lesson, you should be able to: Enzymes Explain enzyme action in terms of the lock and key hypothesis Explain the effects of temperature and ph on the rate
Digestion Learning Objectives At the end of this lesson, you should be able to: Enzymes Explain enzyme action in terms of the lock and key hypothesis Explain the effects of temperature and ph on the rate
/ The following functional group is a. Aldehyde c. Carboxyl b. Ketone d. Amino
 Section A: Multiple Choice Select the answer that best answers the following questions. Please write your selected choice on the line provided, in addition to circling the answer. /25 1. The following
Section A: Multiple Choice Select the answer that best answers the following questions. Please write your selected choice on the line provided, in addition to circling the answer. /25 1. The following
HUMAN NUTRITION: ABSORPTION & ASSIMILATION 14 MAY 2014
 HUMAN NUTRITION: ABSORPTION & ASSIMILATION 14 MAY 2014 In this lesson, we: Absorption Lesson Description Examine and understand absorption Define absorption and describe where it occurs Study the structure
HUMAN NUTRITION: ABSORPTION & ASSIMILATION 14 MAY 2014 In this lesson, we: Absorption Lesson Description Examine and understand absorption Define absorption and describe where it occurs Study the structure
Candidate Number. No additional materials are required. You may use a calculator. Number
 Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education January 2004 Advanced Level Examination BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 6 Physiology and
Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education January 2004 Advanced Level Examination BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 6 Physiology and
Save My Exams! The Home of Revision For more awesome GCSE and A level resources, visit us at Cell Structure.
 Cell Structure Mark Scheme 1 Level International A Level Subject Biology Exam Board CIE Topic Cell Structure Sub Topic Booklet Cell Structure Theory Paper Type Mark Scheme 1 Time Allowed : 64 minutes Score
Cell Structure Mark Scheme 1 Level International A Level Subject Biology Exam Board CIE Topic Cell Structure Sub Topic Booklet Cell Structure Theory Paper Type Mark Scheme 1 Time Allowed : 64 minutes Score
NUTRIENT DIGESTION & ABSORPTION
 NUTRIENT DIGESTION & ABSORPTION NUTR 2050: Nutrition for Nursing Professionals Mrs. Deborah A. Hutcheon, MS, RD, LD Lesson Objectives At the end of the lesson, the student will be able to: 1. Differentiate
NUTRIENT DIGESTION & ABSORPTION NUTR 2050: Nutrition for Nursing Professionals Mrs. Deborah A. Hutcheon, MS, RD, LD Lesson Objectives At the end of the lesson, the student will be able to: 1. Differentiate
23.1 Lipid Metabolism in Animals. Chapter 23. Micelles Lipid Metabolism in. Animals. Overview of Digestion Lipid Metabolism in
 Denniston Topping Caret Copyright! The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 23 Fatty Acid Metabolism Triglycerides (Tgl) are emulsified into fat droplets
Denniston Topping Caret Copyright! The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 23 Fatty Acid Metabolism Triglycerides (Tgl) are emulsified into fat droplets
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
UNIT 2 BIODIVERSITY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF BODY SYSTEMS MARK SCHEME GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
 GCE AS and A LEVEL BIOLOGY Specimen Assessment Materials 148 UNIT 2 BIODIVERSITY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF BODY SYSTEMS MARK SCHEME GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS Recording of marks Examiners must mark in red ink. One tick
GCE AS and A LEVEL BIOLOGY Specimen Assessment Materials 148 UNIT 2 BIODIVERSITY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF BODY SYSTEMS MARK SCHEME GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS Recording of marks Examiners must mark in red ink. One tick
SPECIMEN. day June 20XX Morning/Afternoon MAXIMUM MARK 100 PMT. A Level Biology A H420/01 Biological processes SAMPLE MARK SCHEME
 day June 0XX Morning/Afternoon A Level Biology A H40/01 Biological processes SAMPLE MARK SCHEME MAXIMUM MARK 100 This document consists of 0 pages Duration: hours 15 minutes PREPARATION FOR MARKING SCORIS
day June 0XX Morning/Afternoon A Level Biology A H40/01 Biological processes SAMPLE MARK SCHEME MAXIMUM MARK 100 This document consists of 0 pages Duration: hours 15 minutes PREPARATION FOR MARKING SCORIS
Chapter 1 Plasma membranes
 1 of 5 TEXTBOOK ANSWERS Chapter 1 Plasma membranes Recap 1.1 1 The plasma membrane: keeps internal contents of the cell confined to one area keeps out foreign molecules that damage or destroy the cell
1 of 5 TEXTBOOK ANSWERS Chapter 1 Plasma membranes Recap 1.1 1 The plasma membrane: keeps internal contents of the cell confined to one area keeps out foreign molecules that damage or destroy the cell
Objective 4- Digestion
 Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
a. parotid b. sublingual c. submandibular
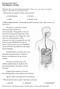 Bozeman Science/ Nature The Digestive System Watch the videos, and answer the questions below. Please write your answers in complete sentences, and explain all concepts thoroughly. 1. What are the four
Bozeman Science/ Nature The Digestive System Watch the videos, and answer the questions below. Please write your answers in complete sentences, and explain all concepts thoroughly. 1. What are the four
Chapter 8: Digestion. Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes
 Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Chapter 4: Cell Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 4: Cell Membrane Structure and Function Plasma Membrane: Thin barrier separating inside of cell (cytoplasm) from outside environment Function: 1) Isolate cell s contents from outside environment
Chapter 4: Cell Membrane Structure and Function Plasma Membrane: Thin barrier separating inside of cell (cytoplasm) from outside environment Function: 1) Isolate cell s contents from outside environment
thebiotutor.com F214 Module 2 Excretion Answers
 thebiotut.com F24 Module 2 Excretion Answers thebiotut.com . excretion secretion one difference (metabolic) waste toxin / harmful substance is to be removed from body does not use vesicles useful product
thebiotut.com F24 Module 2 Excretion Answers thebiotut.com . excretion secretion one difference (metabolic) waste toxin / harmful substance is to be removed from body does not use vesicles useful product
Digestion & The Alimentary Canal
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
2003 Assessment Report Biology GA 1: Written examination 1. SPECIFIC INFORMATION Section A Multiple choice
 2003 Assessment Report 2003 Biology GA 1: Written examination 1 SPECIFIC INFORMATION Section A Multiple choice This table indicates the approximate percentage of students choosing each distractor. The
2003 Assessment Report 2003 Biology GA 1: Written examination 1 SPECIFIC INFORMATION Section A Multiple choice This table indicates the approximate percentage of students choosing each distractor. The
(i) N ; 1 IGNORE nitrogen
 (a) (i) N ; IGNORE nitrogen (a) (iii) (a) (iiii) polypeptide / protein ; name peptide (bond / link) ; DO NOT CREDIT n or N 2 Mark the first answer. If the answer is correct and an additional answer is
(a) (i) N ; IGNORE nitrogen (a) (iii) (a) (iiii) polypeptide / protein ; name peptide (bond / link) ; DO NOT CREDIT n or N 2 Mark the first answer. If the answer is correct and an additional answer is
Chapter 3 Review Assignment
 Class: Date: Chapter 3 Review Assignment Multiple Choice 40 MC = 40 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following organelles produces transport
Class: Date: Chapter 3 Review Assignment Multiple Choice 40 MC = 40 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following organelles produces transport
Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 35
 Biology Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 35 Digestion The breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino acids
Biology Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 35 Digestion The breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino acids
Transport: Cell Membrane Structure and Function. Biology 12 Chapter 4
 Transport: Cell Membrane Structure and Function Biology 12 Chapter 4 FLUID-MOSAIC MODEL OF MEMBRANE STRUCTURE The cell membrane (plasma membrane) is made of two layers of phospholipid molecules (bilayer)
Transport: Cell Membrane Structure and Function Biology 12 Chapter 4 FLUID-MOSAIC MODEL OF MEMBRANE STRUCTURE The cell membrane (plasma membrane) is made of two layers of phospholipid molecules (bilayer)
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion
 Chapter 15 Food and Digestion Activity: Use Qualitative Observations (5 senses) to describe: What happens when you see candy? How does it smell? How do you chomp it into smaller pieces or swallow candy
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion Activity: Use Qualitative Observations (5 senses) to describe: What happens when you see candy? How does it smell? How do you chomp it into smaller pieces or swallow candy
Thebiotutor.com. A2 Biology OCR. Unit F214: Communication, Homeostasis and Energy. Module Communication, Nerves & Hormones.
 Thebiotut.com A2 Biology OCR Unit F214: Communication, Homeostasis and Energy Module 1.1 1.3 Communication, Nerves & Hmones Answers Andy Todd 1 1. (a) 1 myelin / myelinated / lipid / fatty (sheath); DO
Thebiotut.com A2 Biology OCR Unit F214: Communication, Homeostasis and Energy Module 1.1 1.3 Communication, Nerves & Hmones Answers Andy Todd 1 1. (a) 1 myelin / myelinated / lipid / fatty (sheath); DO
BY4. Question Answer Mark. D = Synaptic knob/motor end plate/ axon ending/ axon. NOT synpase/ dendrite/ nerve ending/ neuromuscular.
 BY4 1. (a) (i) A = Dendrite(s), accept dendron; B = Axon/ axoplasm; C = Node(s) of Ranvier; D = Synaptic knob/motor end plate/ axon ending/ axon 4 terminal/ synaptic bulb; NOT synpase/ dendrite/ nerve
BY4 1. (a) (i) A = Dendrite(s), accept dendron; B = Axon/ axoplasm; C = Node(s) of Ranvier; D = Synaptic knob/motor end plate/ axon ending/ axon 4 terminal/ synaptic bulb; NOT synpase/ dendrite/ nerve
The Small Intestine. The pyloric sphincter at the bottom of the stomach opens, squirting small amounts of food into your small intestine.
 The Small Intestine The pyloric sphincter at the bottom of the stomach opens, squirting small amounts of food into your small intestine. approximately six metres (the longest section of your digestive
The Small Intestine The pyloric sphincter at the bottom of the stomach opens, squirting small amounts of food into your small intestine. approximately six metres (the longest section of your digestive
Answer Marks Guidance ( 1 idea of maintaining (relatively) stable internal, environment / state ;
 Question Answer Marks Guidance 1 (a) ( 1 idea of maintaining (relatively) stable internal, environment / state ; 1 Need the idea of constant or steady and regulation or keeping and in the body within (narrow)
Question Answer Marks Guidance 1 (a) ( 1 idea of maintaining (relatively) stable internal, environment / state ; 1 Need the idea of constant or steady and regulation or keeping and in the body within (narrow)
3. From non-carbohydrates / amino acids / fatty acids. Accept: gluconeogenesis / references to glycogen as source of glucose 3
 M1.(a) 1. Release of glucagon;. Leads to formation of glucose in liver (cells); Reject: glucagon breaks down glycogen, or any other biological molecule 3. From non-carbohydrates / amino acids / fatty acids.
M1.(a) 1. Release of glucagon;. Leads to formation of glucose in liver (cells); Reject: glucagon breaks down glycogen, or any other biological molecule 3. From non-carbohydrates / amino acids / fatty acids.
Save My Exams! The Home of Revision For more awesome GCSE and A level resources, visit us at Lipids.
 Lipids Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Topic Sub-Topic Booklet International A Level Biology Edexcel Molecules, Transport and Health Lipids Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 63 minutes Score: /52 Percentage:
Lipids Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Topic Sub-Topic Booklet International A Level Biology Edexcel Molecules, Transport and Health Lipids Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 63 minutes Score: /52 Percentage:
Ingestion Digestion- Absorption- Elimination
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
ANIMAL NUTRITION 24 APRIL 2013
 ANIMAL NUTRITION 24 APRIL 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Look at nutrition in various animals o Herbivores, Carnivores and Omnivores Study the structure of the human digestive system Look
ANIMAL NUTRITION 24 APRIL 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Look at nutrition in various animals o Herbivores, Carnivores and Omnivores Study the structure of the human digestive system Look
GCE BIOLOGY BY4. Cells increase in size / storage of nutrients; (iii) Population grows at an increasing rate / doubles in unit time /
 GCE BIOLOGY BY4 1. (a) (i) 8.0-13.8/13.8 OR 14./13.8; 10.9 / 103%; ( marks for correct answer) (1 mark for calculation if answer incorrect) (ii) Any from: Genes switched on; Synthesis of enzymes / protein
GCE BIOLOGY BY4 1. (a) (i) 8.0-13.8/13.8 OR 14./13.8; 10.9 / 103%; ( marks for correct answer) (1 mark for calculation if answer incorrect) (ii) Any from: Genes switched on; Synthesis of enzymes / protein
Human Biology. Digestive System
 Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Figure Nutrition: omnivore, herbivore, carnivore
 Figure 41.1 Nutrition: omnivore, herbivore, carnivore Essential Nutrients: Amino acids Fatty acids Vitamins Minerals Figure 41.2 Complete vs incomplete Omnivore vs herbivore (vegetarian) Table 41.1 Table
Figure 41.1 Nutrition: omnivore, herbivore, carnivore Essential Nutrients: Amino acids Fatty acids Vitamins Minerals Figure 41.2 Complete vs incomplete Omnivore vs herbivore (vegetarian) Table 41.1 Table
Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root. Tooth type and job. Why do humans have more than one type of tooth?
 Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ORGANS MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE SALIVARY GLANDS PANCREAS LIVER
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ORGANS MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE SALIVARY GLANDS PANCREAS LIVER
Version 1.0. General Certificate of Education (A-level) June Biology BIOL1. (Specification 2410) Unit 1: Biology and Disease. Final.
 Version 1.0 General Certificate of Education (A-level) Biology BIOL1 (Specification 2410) Unit 1: Biology and Disease Final Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner and considered,
Version 1.0 General Certificate of Education (A-level) Biology BIOL1 (Specification 2410) Unit 1: Biology and Disease Final Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Examiner and considered,
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 5090 BIOLOGY. 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is published as
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is published as
Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look
 Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Bởi: OpenStaxCollege As you have learned, the process of mechanical digestion is relatively simple. It involves the physical breakdown of food but does
Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Bởi: OpenStaxCollege As you have learned, the process of mechanical digestion is relatively simple. It involves the physical breakdown of food but does
Cell Membrane and Transport
 Cell Membrane and Transport 29/06/2015 11:08 AM Describe the Characteristics of the phospholipid Bilayer. The Phospholipid bilayer is made up of a double layer of membrane lipids that have a hydrophobic
Cell Membrane and Transport 29/06/2015 11:08 AM Describe the Characteristics of the phospholipid Bilayer. The Phospholipid bilayer is made up of a double layer of membrane lipids that have a hydrophobic
Biol 219 Lec 7 Fall 2016
 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Energy to form ATP Cellular Respiration and Metabolism Glucose ATP Pyruvate Lactate Acetyl CoA NAD + Introducing The Players primary substrate for cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Energy to form ATP Cellular Respiration and Metabolism Glucose ATP Pyruvate Lactate Acetyl CoA NAD + Introducing The Players primary substrate for cellular respiration
(a) (i) Describe how the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein.
 The circulatory system contains arteries and veins. (a) (i) Describe how the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein. (2) A comparison is made between blood taken from an artery
The circulatory system contains arteries and veins. (a) (i) Describe how the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein. (2) A comparison is made between blood taken from an artery
c.uma sankar.kanchipuram.
 NAME: GLOBAL COACHING CENTRE XII STANDARD BIO ZOOLOGY DIGESTION ONE MARK PRACTICE PAPER 1. serves to transfer organic molecules, salts and water from the external environment to the body s internal environment.
NAME: GLOBAL COACHING CENTRE XII STANDARD BIO ZOOLOGY DIGESTION ONE MARK PRACTICE PAPER 1. serves to transfer organic molecules, salts and water from the external environment to the body s internal environment.
Topic 10: Nutrition & Digestion Ch. 41. Nutritional Requirements pp Essential Amino Acids p.939. Essential Fatty Acids p.
 Topic 10: Nutrition & Digestion Ch. 41 Nutritional Requirements pp.939-941 Diets for animals must satisfy three needs : 1. Metabolic fuel Energy needed to do cellular work. E.g. glucose 2. Materials for
Topic 10: Nutrition & Digestion Ch. 41 Nutritional Requirements pp.939-941 Diets for animals must satisfy three needs : 1. Metabolic fuel Energy needed to do cellular work. E.g. glucose 2. Materials for
1b. Credit: State the chemical elements present in carbohydrates, proteins and fats. See table below
 1a. General: Explain in simple terms why food is required by animals. The main types of food are carbohydrates, fats and proteins. Carbohydrates and fats are required as sources of energy. Proteins are
1a. General: Explain in simple terms why food is required by animals. The main types of food are carbohydrates, fats and proteins. Carbohydrates and fats are required as sources of energy. Proteins are
Biology 12 November 2001 Provincial Examination
 Biology 12 November 2001 Provincial Examination ANSWER KEY / SCORING GUIDE CURRICULUM: Organizers 1. Cell Biology 2. Cell Processes and Applications 3. Human Biology Sub-Organizers A, B, C, D E, F, G,
Biology 12 November 2001 Provincial Examination ANSWER KEY / SCORING GUIDE CURRICULUM: Organizers 1. Cell Biology 2. Cell Processes and Applications 3. Human Biology Sub-Organizers A, B, C, D E, F, G,
Digestion and Nutrition. Chapter 40
 Digestion and Nutrition Chapter 40 Impacts, Issues Hormones and Hunger Fat cells secrete leptin, which reduces appetite; an empty stomach secretes ghrelin, which makes you hungry the goal is healthy nutrition
Digestion and Nutrition Chapter 40 Impacts, Issues Hormones and Hunger Fat cells secrete leptin, which reduces appetite; an empty stomach secretes ghrelin, which makes you hungry the goal is healthy nutrition
BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES REVIEW-UNIT 1 1. The factor being tested in an experiment is the A. data. B. variable. C. conclusion. D. observation. 2.
 BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES REVIEW-UNIT 1 1. The factor being tested in an experiment is the A. data. B. variable. C. conclusion. D. observation. 2. A possible explanation for an event that occurs in nature is
BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES REVIEW-UNIT 1 1. The factor being tested in an experiment is the A. data. B. variable. C. conclusion. D. observation. 2. A possible explanation for an event that occurs in nature is
Chapter 14: The Digestive System
 Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
REVIEW: Section 1: Human Organization and the chemistry of life A) Chemistry of life I. Elements II. Atoms III. Matter Matter
 REVIEW: Section 1: Human Organization and the chemistry of life A) Chemistry of life I. Elements Cannot be broken down by chemical means and still retain the same chemical and physical characteristics
REVIEW: Section 1: Human Organization and the chemistry of life A) Chemistry of life I. Elements Cannot be broken down by chemical means and still retain the same chemical and physical characteristics
Nutrients. Chapter 25 Nutrition, Metabolism, Temperature Regulation
 Chapter 25 Nutrition, Metabolism, Temperature Regulation 25-1 Nutrients Chemicals used by body to produce energy, provide building blocks or function in other chemical reactions Classes Carbohydrates,
Chapter 25 Nutrition, Metabolism, Temperature Regulation 25-1 Nutrients Chemicals used by body to produce energy, provide building blocks or function in other chemical reactions Classes Carbohydrates,
Digestion. Generalized Digestive System. Salivary glands (mucin) to lubricate. 2 (incl. stomach) Tongue for chemoreception.
 Digestion 24 Generalized Digestive System Salivary glands (mucin) to lubricate 1 2 1 2 (incl. stomach) Tongue for chemoreception 3 3 4 4 (Eckert 25 15-13) 1 Foregut -Conducting, Storage, Digestion -Esophagus
Digestion 24 Generalized Digestive System Salivary glands (mucin) to lubricate 1 2 1 2 (incl. stomach) Tongue for chemoreception 3 3 4 4 (Eckert 25 15-13) 1 Foregut -Conducting, Storage, Digestion -Esophagus
Sphincters heartburn diaphragm The Stomach gastric glands pepsin, chyme The Small Intestine 1-Digestion Is Completed in the Small Intestine duodenum
 Sphincters are muscles that encircle tubes and act as valves. The tubes close when the sphincters contract and they open when the sphincters relax. When food or saliva is swallowed, the sphincter relaxes
Sphincters are muscles that encircle tubes and act as valves. The tubes close when the sphincters contract and they open when the sphincters relax. When food or saliva is swallowed, the sphincter relaxes
